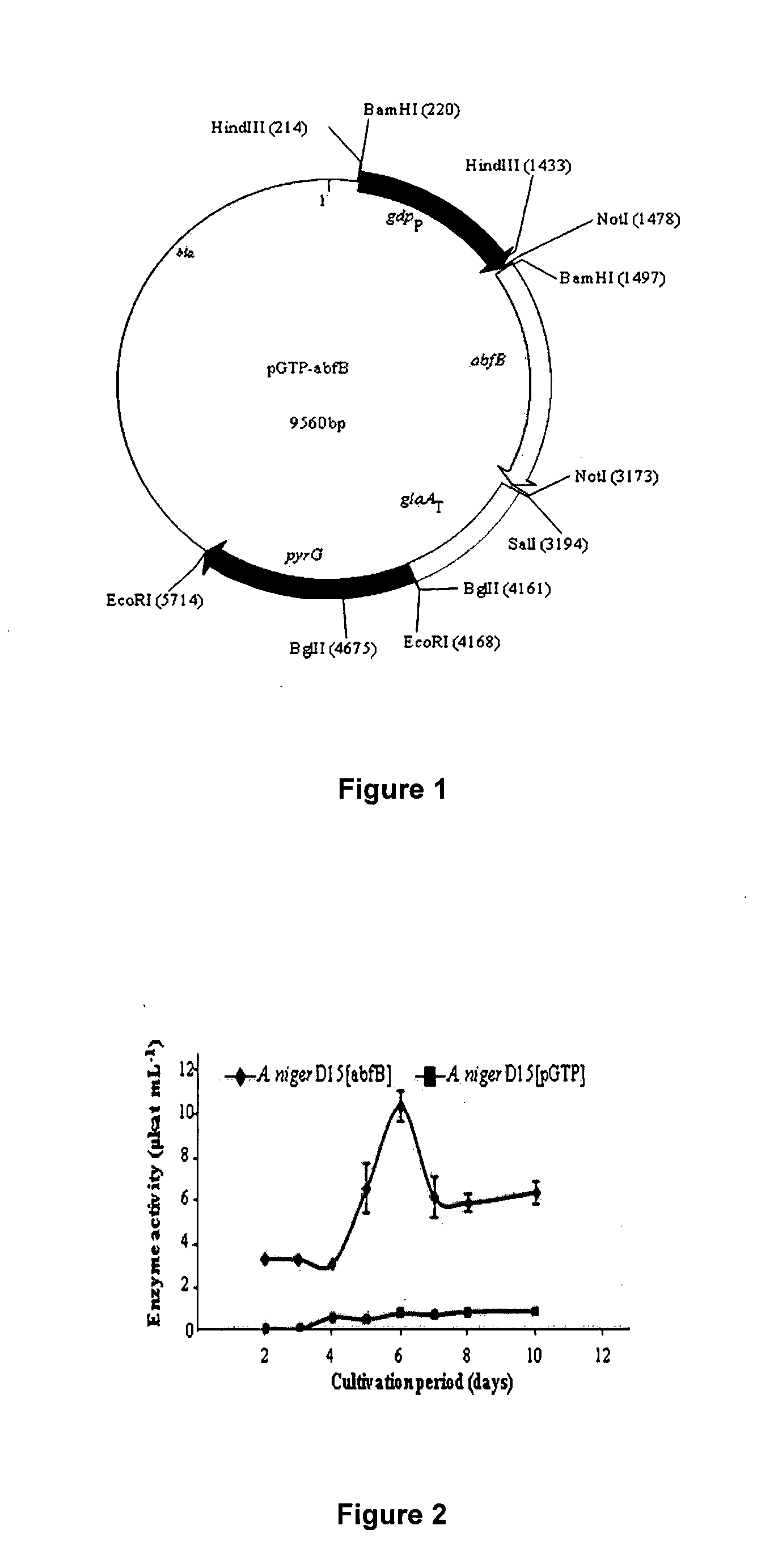
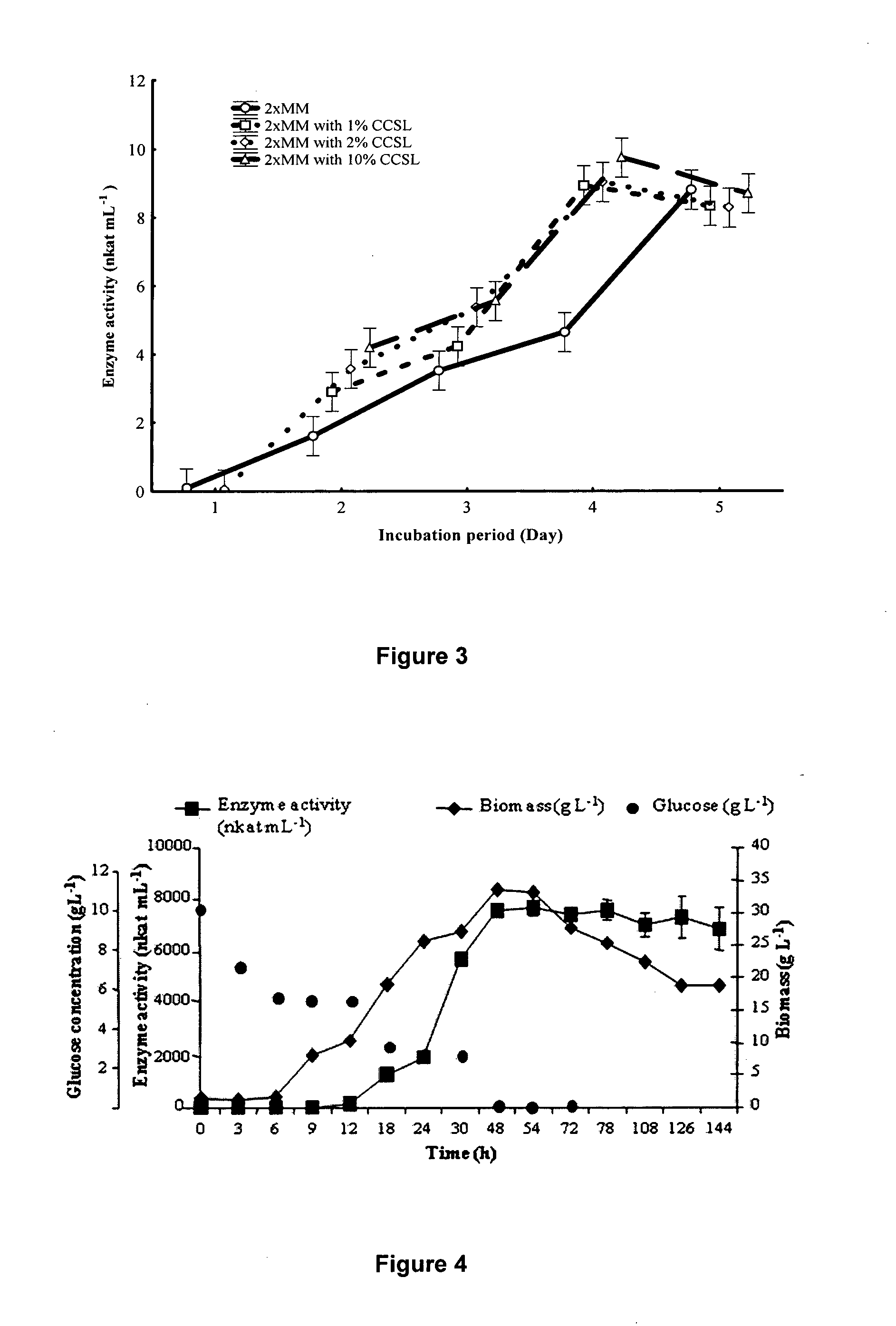
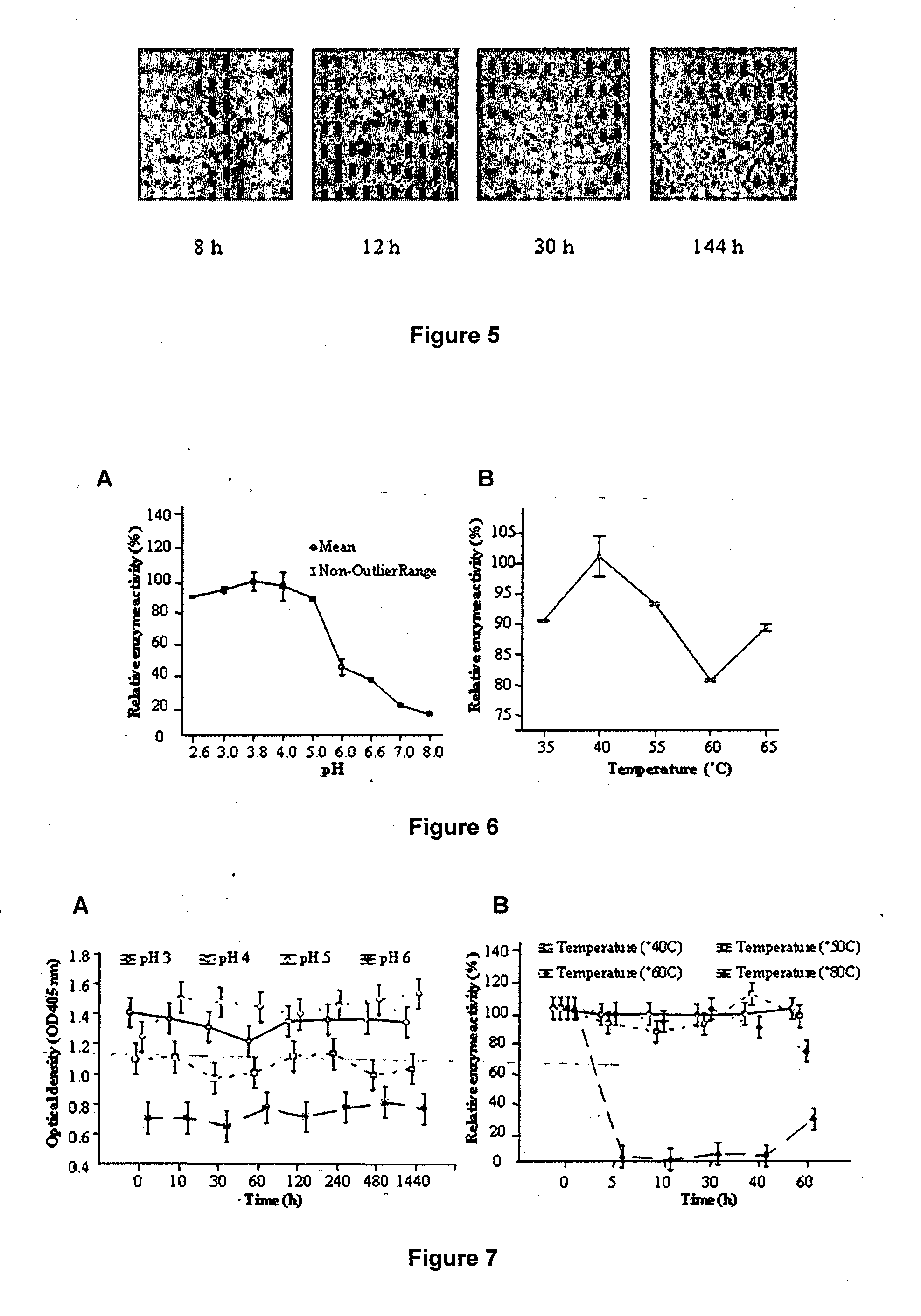
Modification of xylan
a technology of xylan and xylan, which is applied in the field of enzymatically modifying xylan, can solve the problems of reduced pulp yield, environmental hazard, and reduced fibre strength, and achieve the effect of reducing the water solubility of the modified xylan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077]The invention will now be described in more detail by way of the following non-limiting examples. Although only cotton lint is used as a substrate onto which the modified xylan can be adsorbed, it will be apparent to a person skilled in the art that the modified xylan could also be adsorbed onto other substrates.
Material and Methods
Materials
[0078]Mild alkali extracted xylan from Saccharum officinarum L (sugarcane) bagasse (BH), Bambusidae balcooa [giant bamboo (BM)], Eucalyptus grandis, [Eucalyptus (EH)], Pinus patula [Pine (PP)] (extracted using a mild alkali method described by Höije et al. [2005 Carbohydr. Polym. 61: 266-275]), commercial oatspelt xylan (Sigma), birch xylan (Roth), mild alkali H2O2 bleached xylan from bagasse (BB) (donated by Prof. A. M. F. Milagres, University of Sáo Paulo, Brazil) and xylan gel from E. grandis (ES) (donated by SAPPI—Pretoria, South Africa) were used in the experiments.
[0079]Xylan solutions (1% w / v) were prepared according to de Wet et al....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com