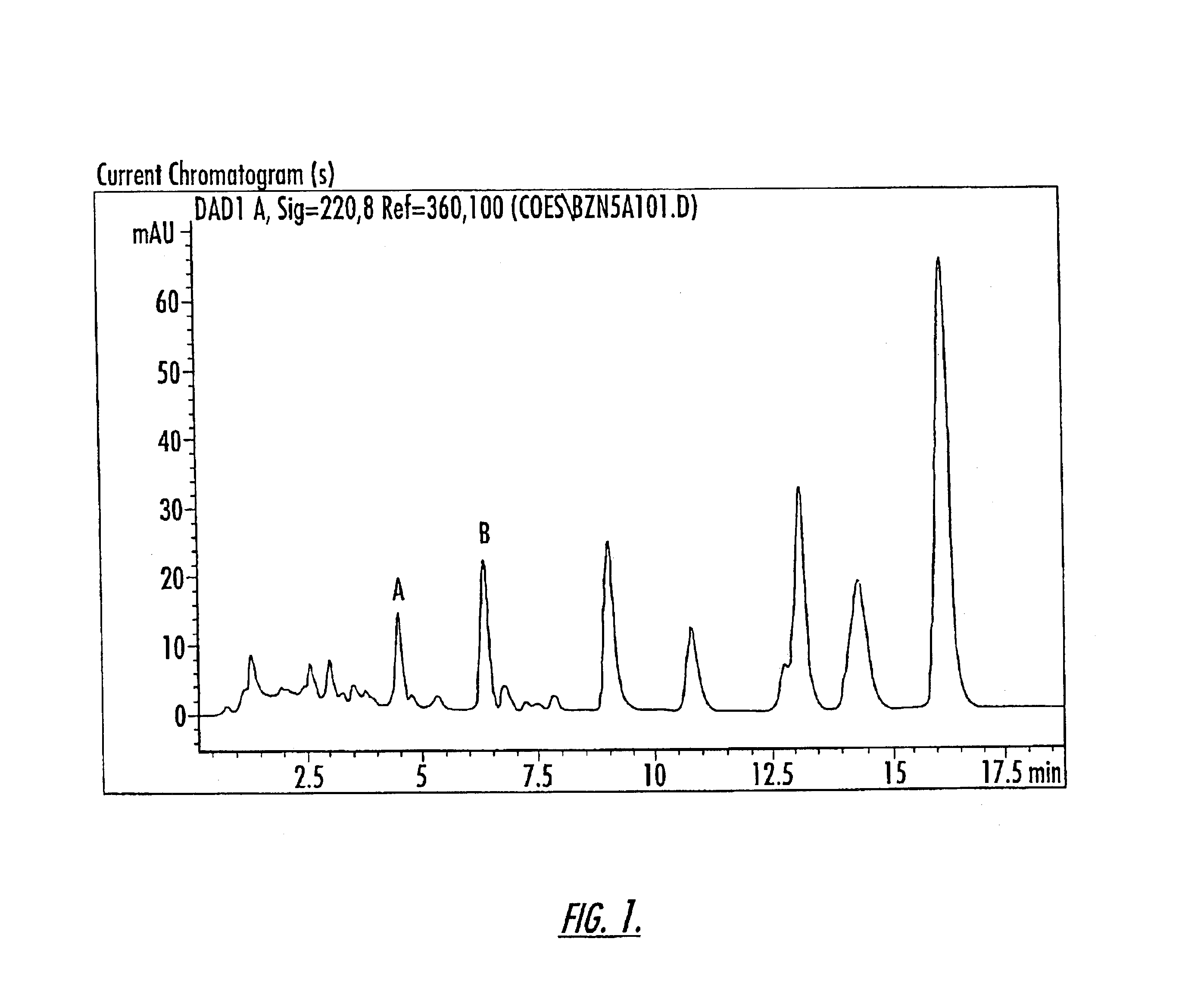
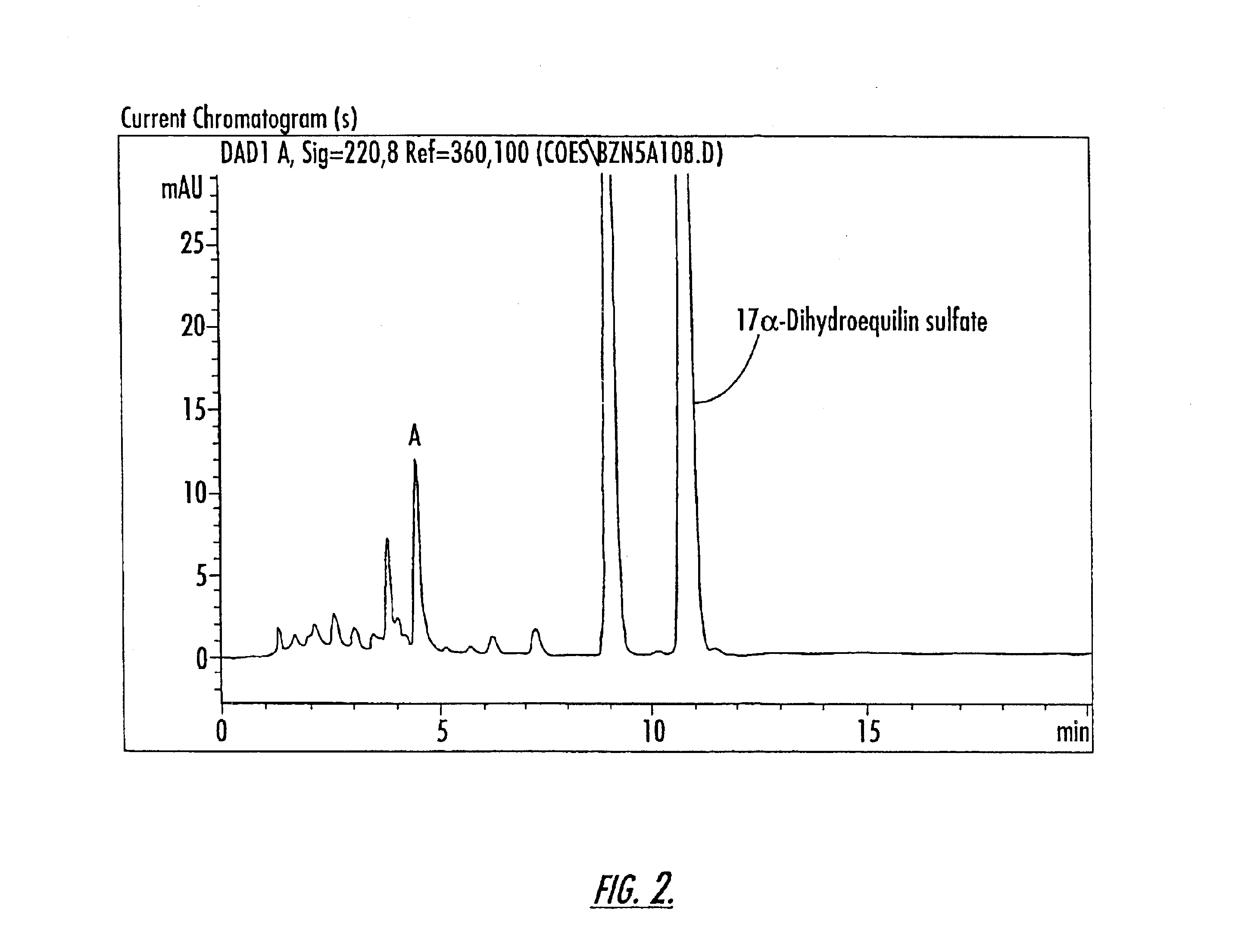
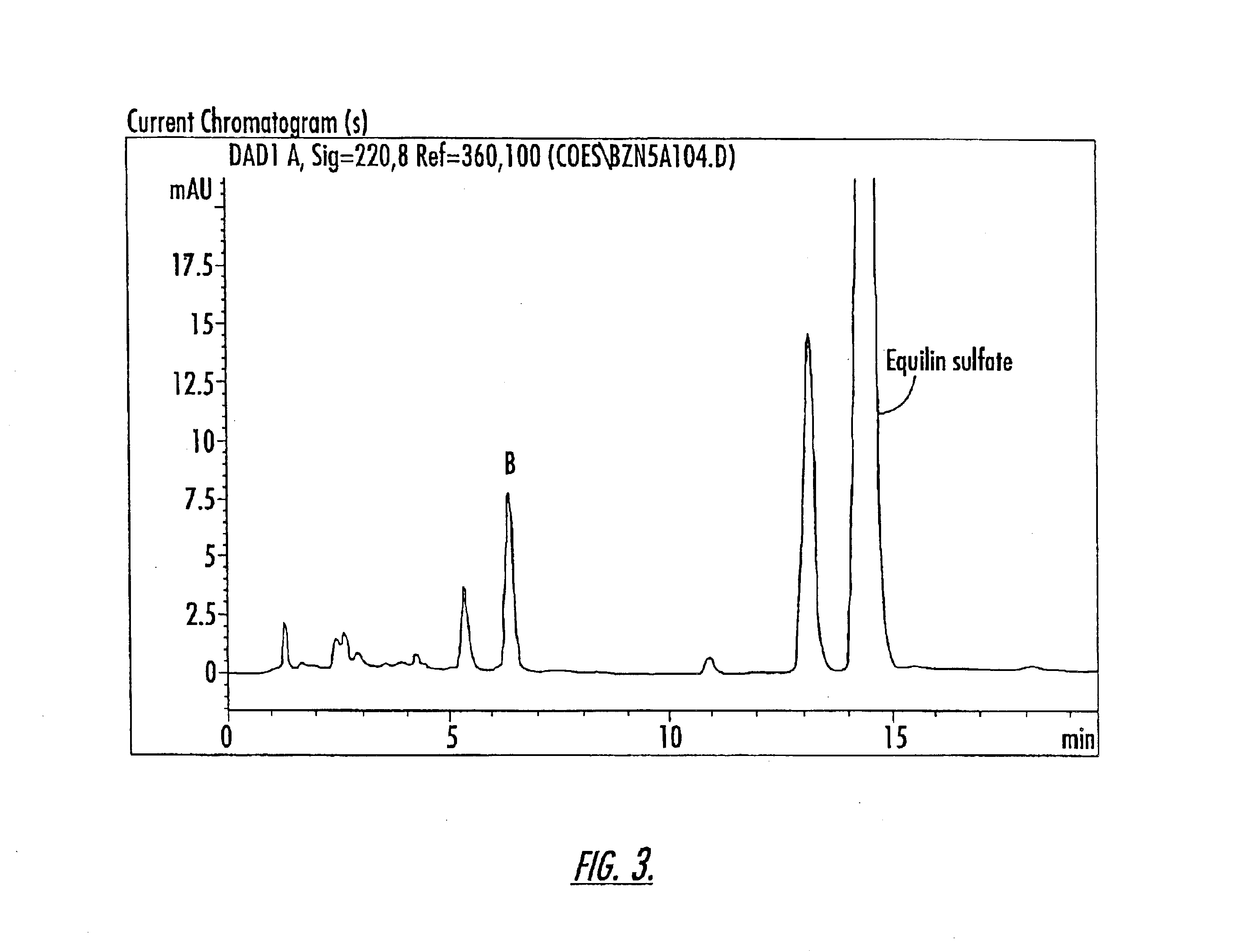
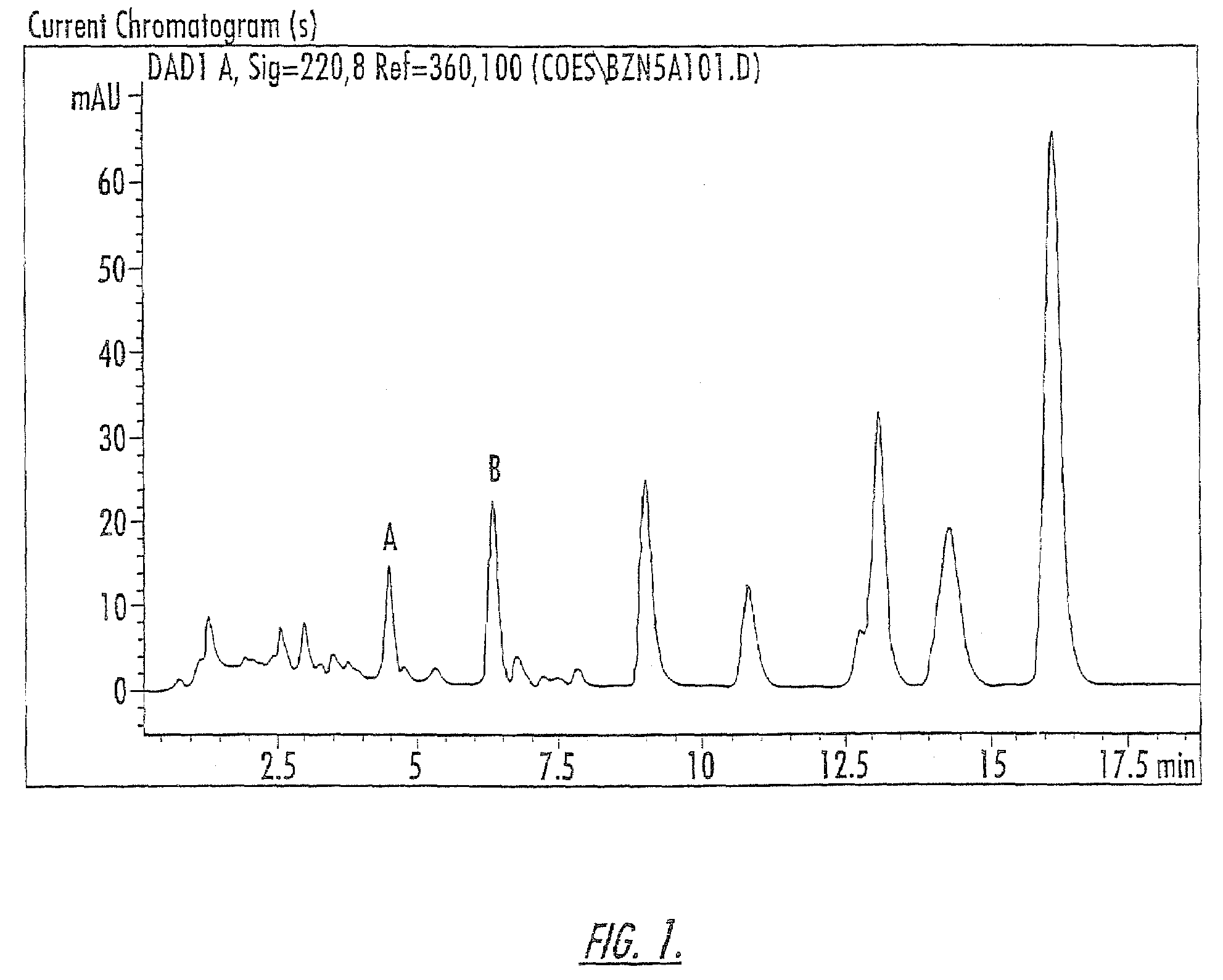
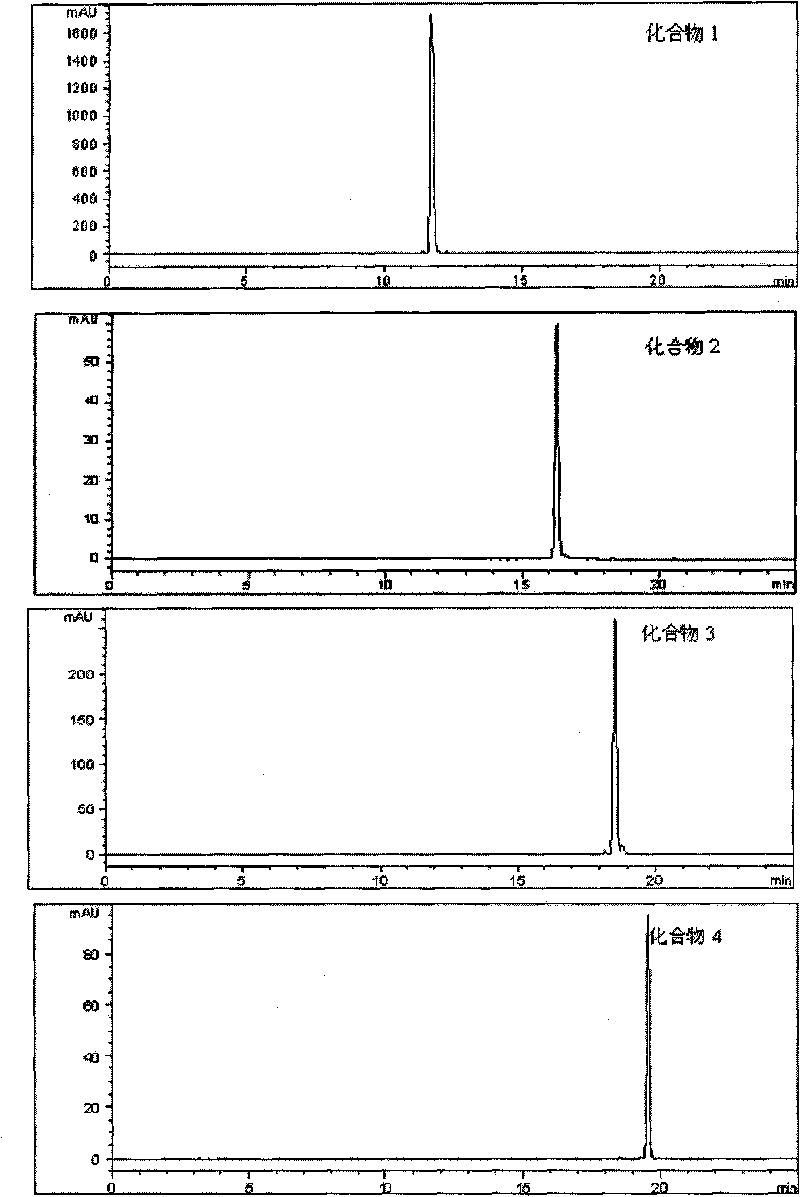
Patents
Literature
247 results about "Glucuronide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A glucuronide, also known as glucuronoside, is any substance produced by linking glucuronic acid to another substance via a glycosidic bond. The glucuronides belong to the glycosides. Glucuronidation, the conversion of chemical compounds to glucuronides, is a method that animals use to assist in the excretion of toxic substances, drugs or other substances that cannot be used as an energy source. Glucuronic acid is attached via a glycosidic bond to the substance, and the resulting glucuronide, which has a much higher water solubility than the original substance, is eventually excreted by the kidneys.
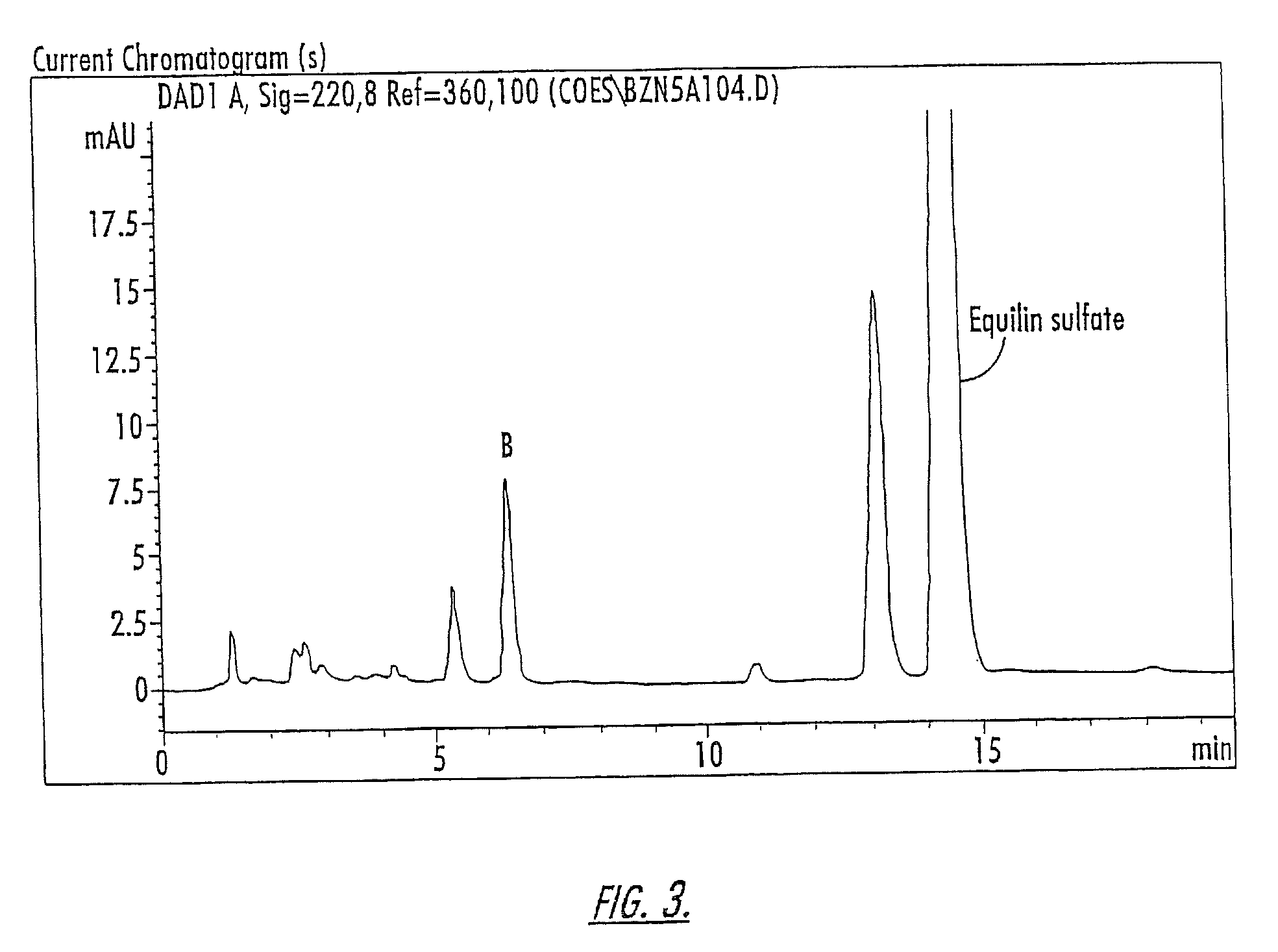
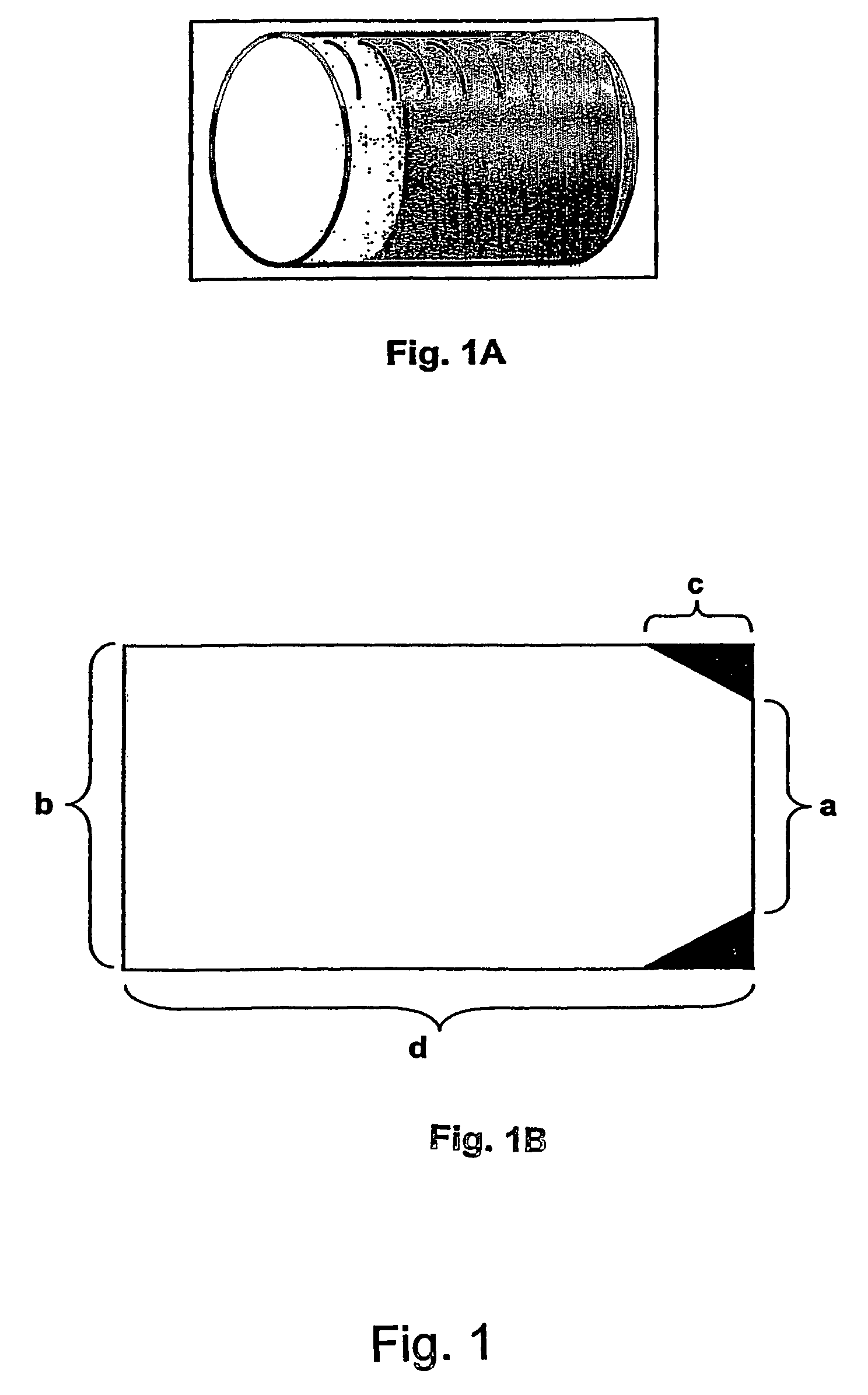
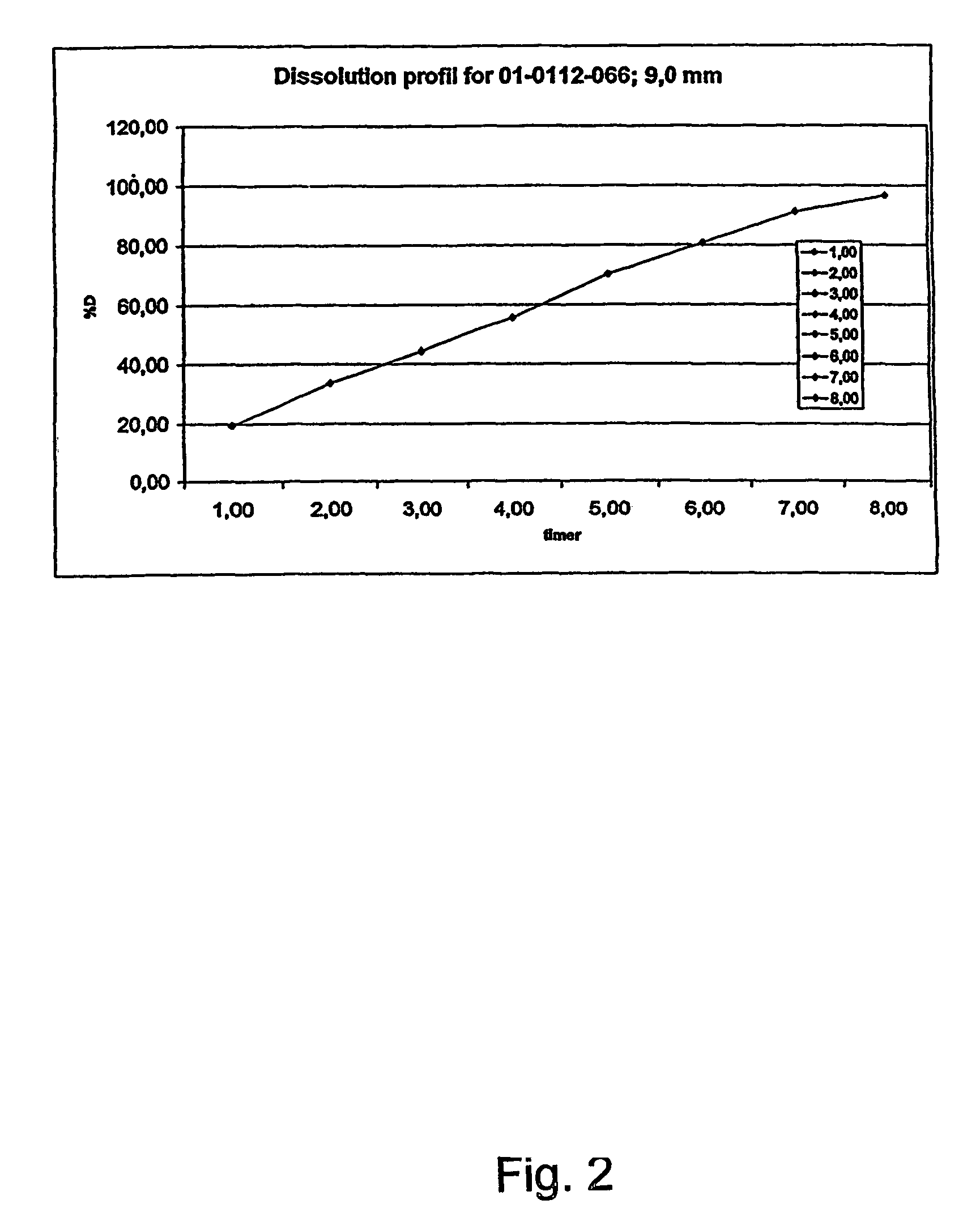
Morphine controlled release system
InactiveUS20070003617A1Low administration frequencyAffecting extent of drug bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderMorphineDissolution
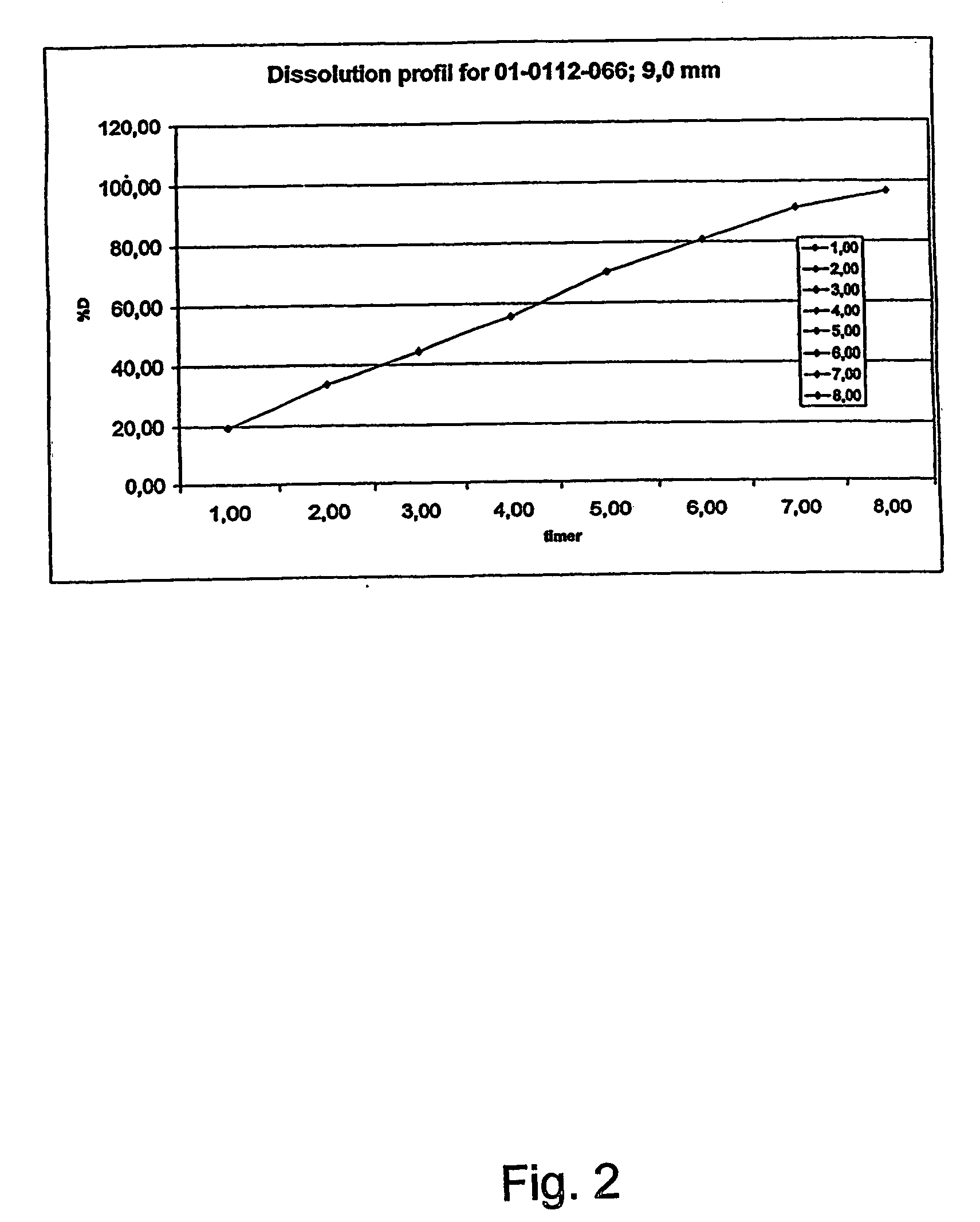
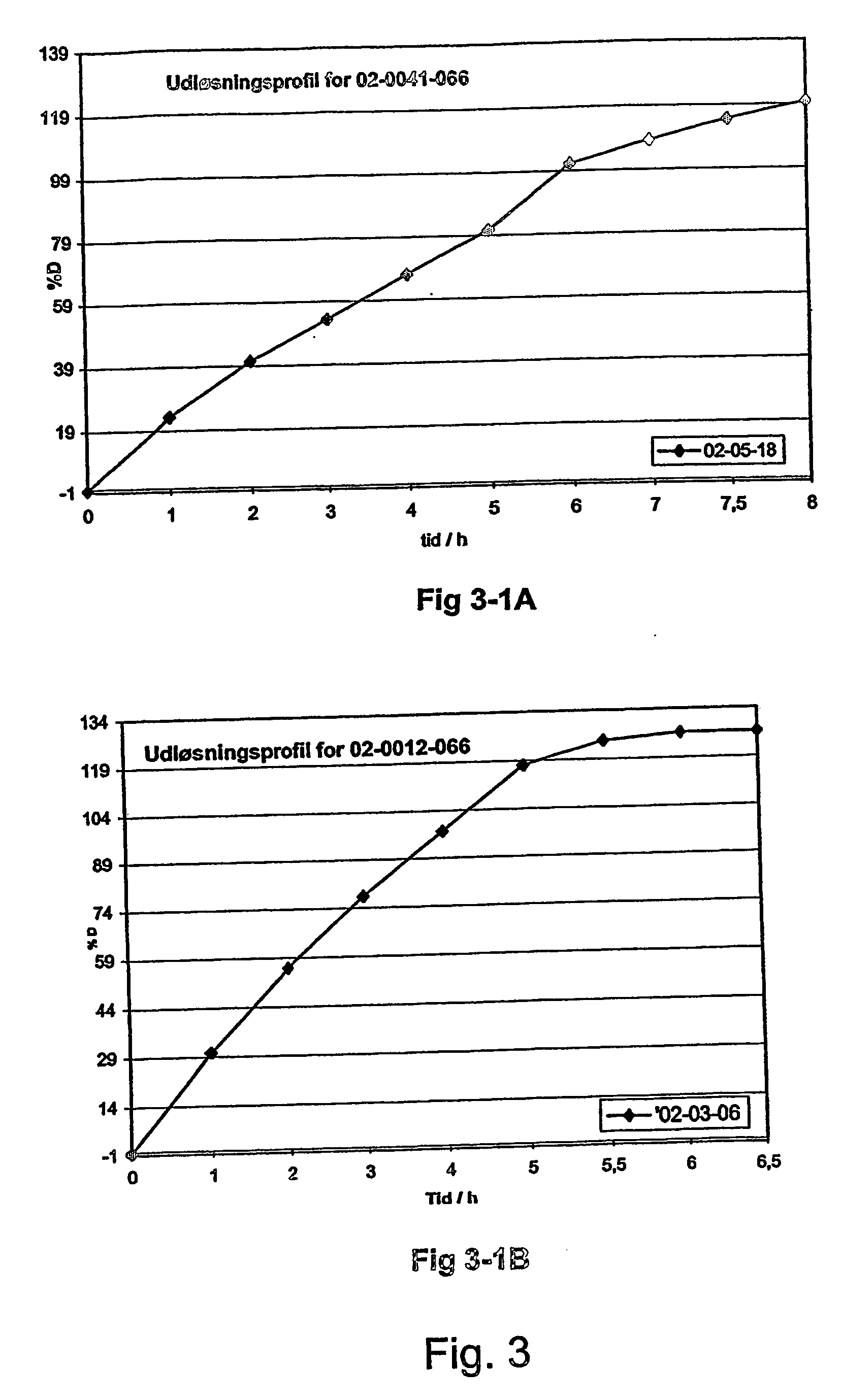
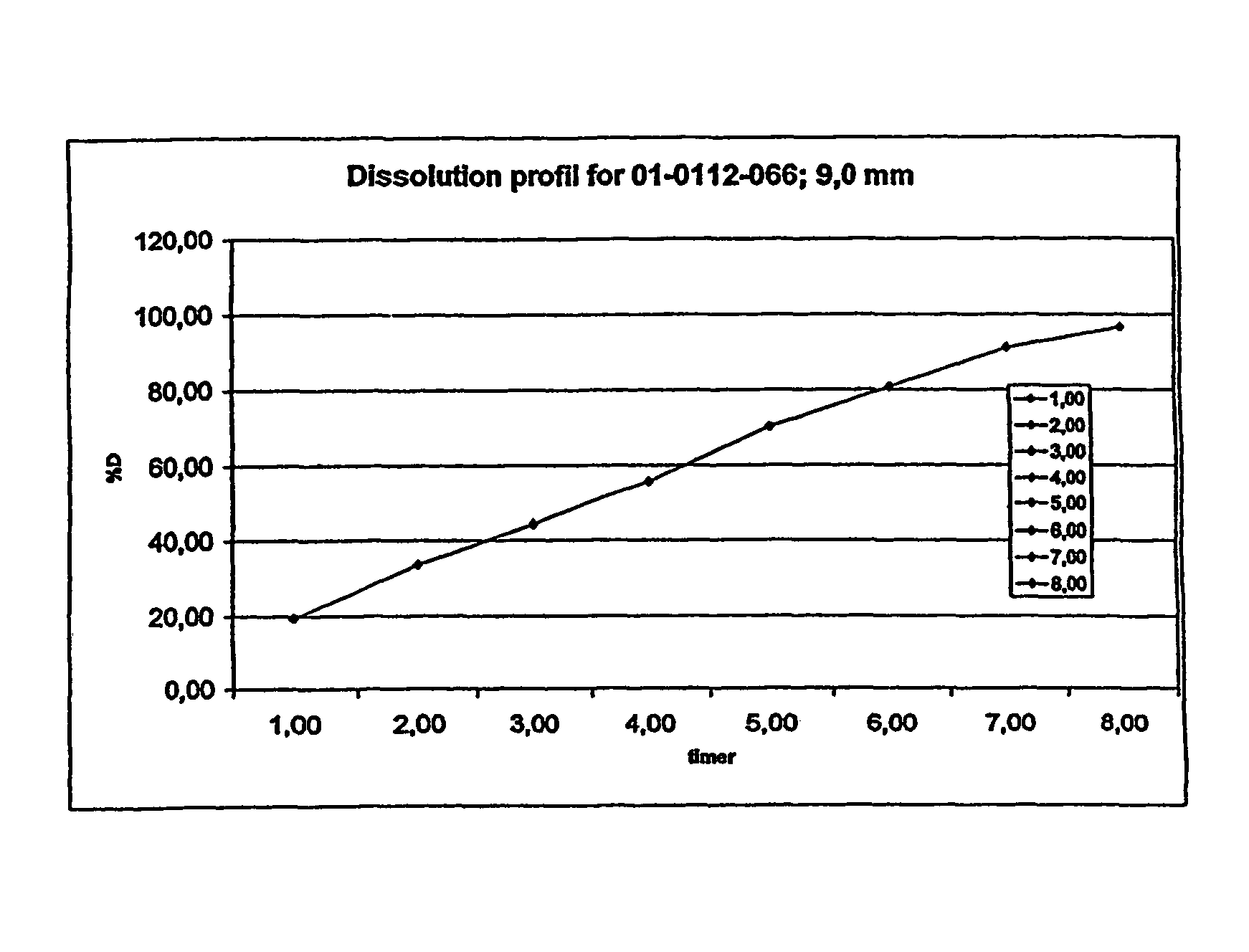
A composition for controlled release of an opioid from a pharmaceutical composition, the method comprises controlling the release of at least one opioid into an aqueous medium by erosion of at least one surface of a pharmaceutical composition comprising I) a matrix composition comprising a) polymer or a mixture of polymers, b) an opioid and, optionally, c) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, and (i) a coating. The matrix composition has a conus-like shape so the surface area exposed to the aqueous medium increases at least during initial erosion of the matrix composition, and the dissolution of the opioid-when tested in a Dissolution Test as described herein with or without application of sinkers-results in a zero order release of at least 80% of the opioid contained in the composition. Such compositions are especially suitable for controlled release of an opioid to obtain a delayed pead concentration and a prolonged therapeutically effective plasma concentration upon oral administration. Once or twice daily administration is possible. The matrix typically comprises PEO and the active substance is typically an opioid such as morphine or a glucuronide thereof.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Topical macqui berry formulation
InactiveUS20070065396A1High ORACImprove antioxidant capacityBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineOxygen radical absorbance capacity
The present invention provides a topical formulation and method of use where the formulation comprises macqui berry or a macqui berry extract containing anthocyanins having a very high oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC). The formulation provides the macqui berry in a stabilized form which includes a glucuronide or glycuronide, a photostabilizing agent, encapsulation, or light -and / or air-blocking packaging.
Owner:TRACIE MARTYN INT
Β-glucuronide-linker drug conjugates
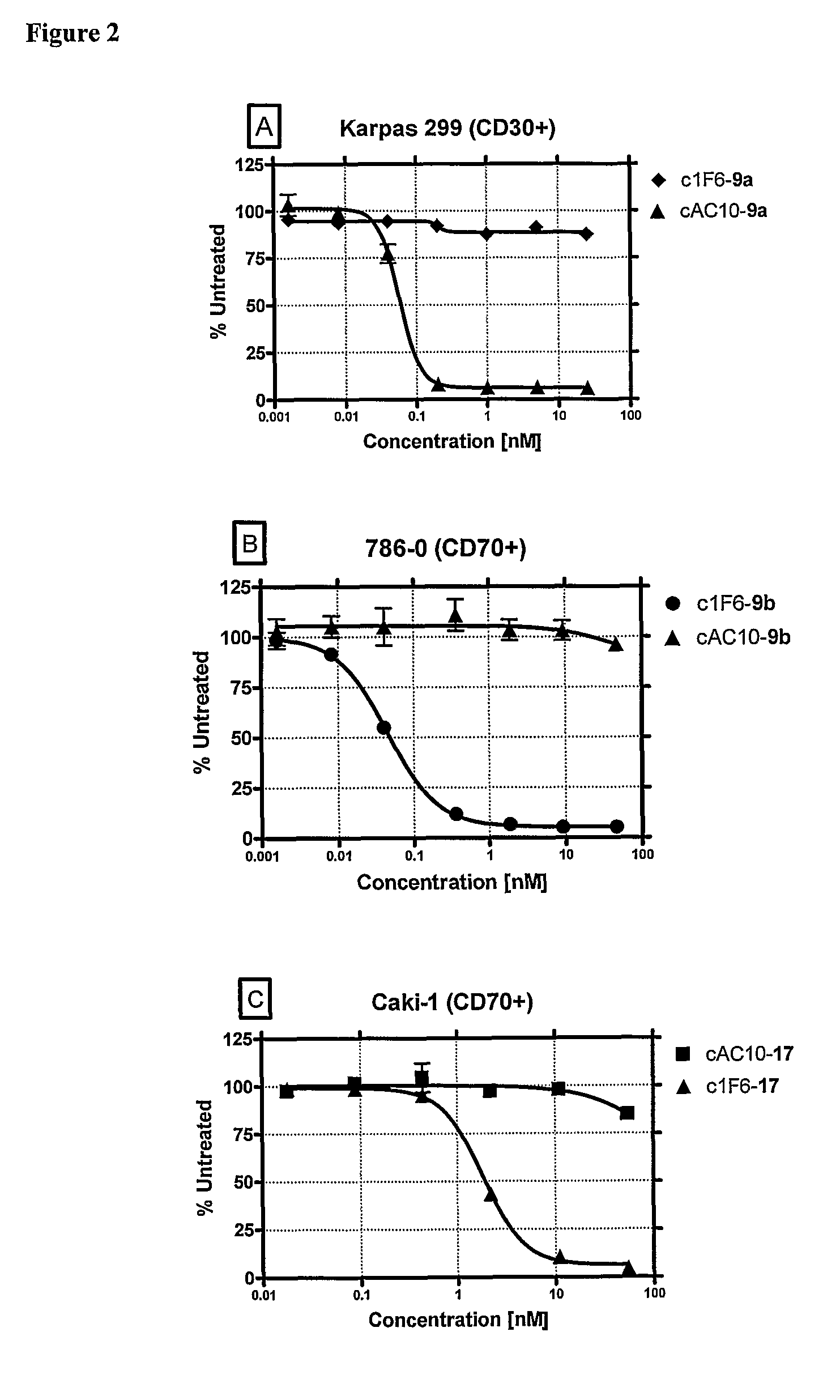
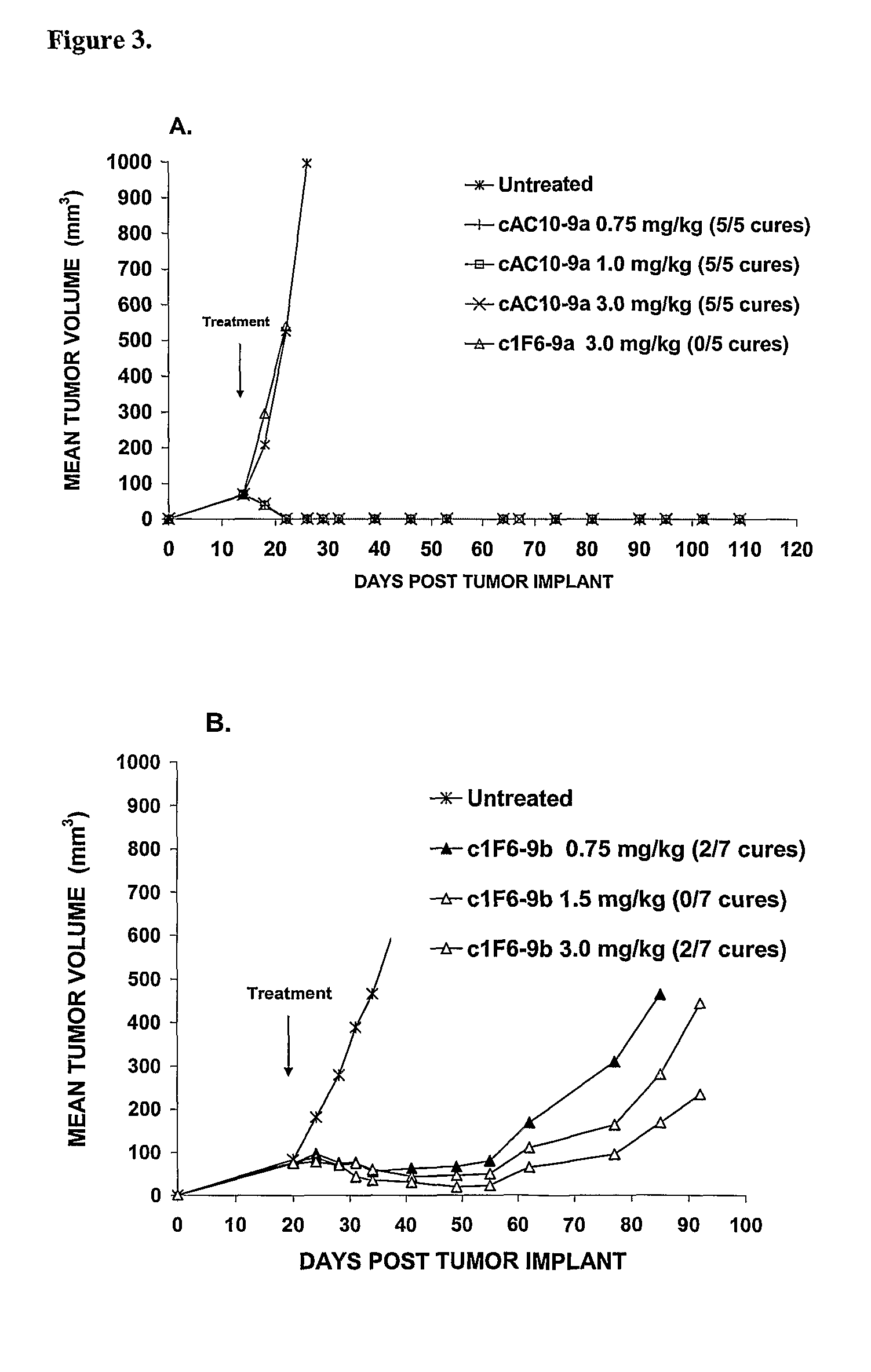
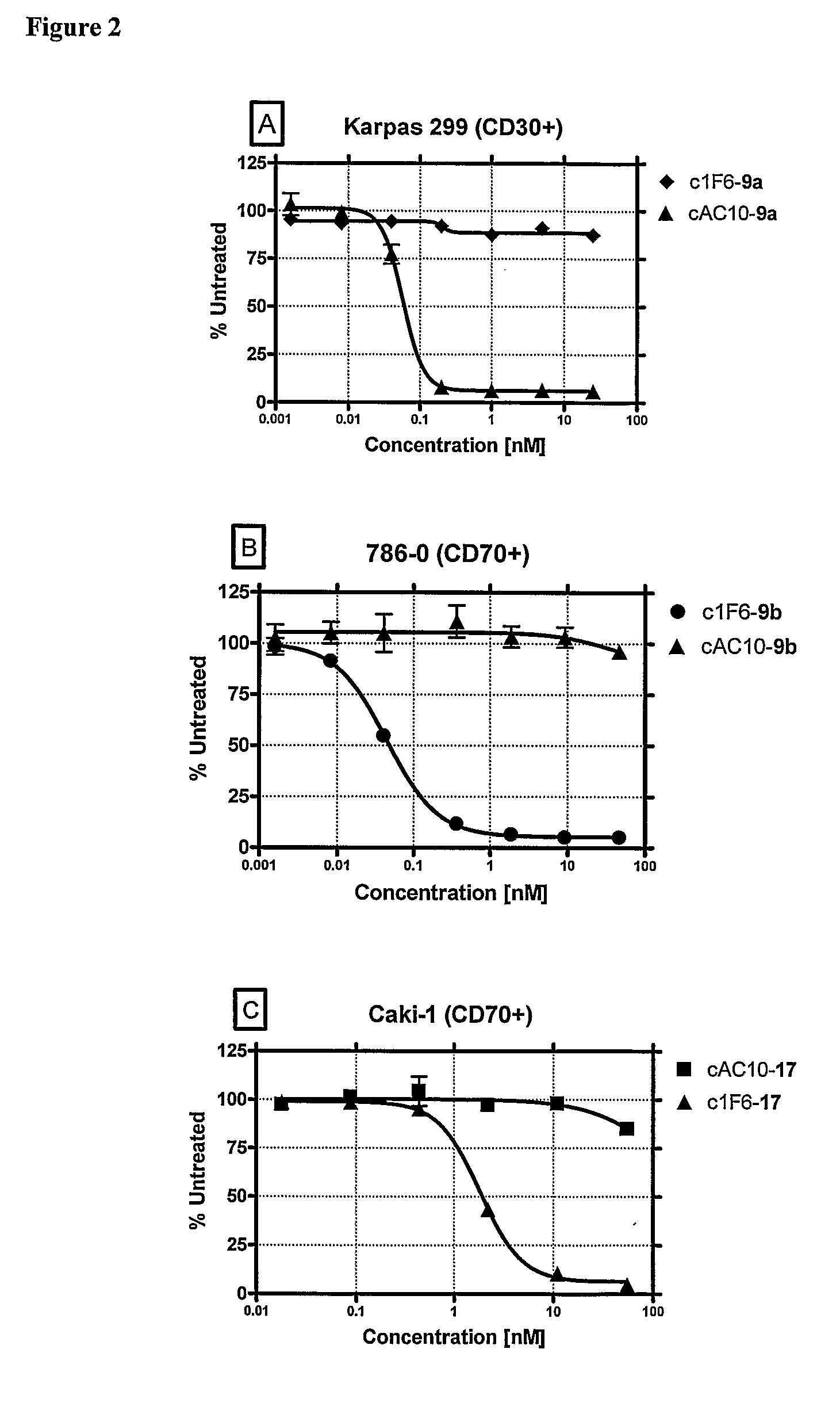
ActiveUS8039273B2Kill or inhibit the proliferation of the tumor cellsTetrapeptide ingredientsImmunoglobulinsOrganic chemistryGlucuronide
Ligand Drug conjugate compounds comprising a β-glucuronide-based linker and methods of using such compounds are provided.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
Monitoring methods and devices for use therein
InactiveUS6451619B1Reduce unreliabilityLimited usefulnessAnimal reproductionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBacteriuriaAnalyte
Methods, devices and test kits for monitoring the ovulation cycle, involve testing the body fluid, e.g. urinary, concentration of one or more analytes. Preferably estrone-3-glucuronide and luteinizing hormone are both measured, and a reference concentration for E3G is established at about day 6 of the current cycle. Preferably, disposable testing devices are used, in conjunction with a relatively permanent electronic reader / monitor. The number of "daily" tests required per month can be minimized.
Owner:INVERNESS MEDICAL SWITZERLAND GMBH
Sugar derivatives of hydromorphone, dihydromorphine and dihydroisomorphine,compositions thereof and uses for treating or preventing pain
Glucoside and glucuronide derivatives of hydromorphone, dihydromorphine, and dihydroisomorphine and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; pharmaceutical compositions comprising a glucoside or glucuronide derivative of hydromorphone, dihydromorphine, or dihydroisomorphine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; and methods for treating or preventing pain in a patient comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a glucoside or glucuronide derivative of hydromorphone, dihydromorphine, or dihydroisomorphine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are disclosed.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
Multi-Portion Intra-Oral Dosage Form With Organoleptic Properties
InactiveUS20100247586A1Efficient and effectiveCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderActive agentUrine cotinine level
A multi portion intra-oral dosage form has at least one pharmaceutically active agent or health promoting agent with at least one portion comprises a component for creating a noticeable organoleptic sensation. The sensory markers or signals are conceptual aids for a subject using the dosage form where the organoleptic sensation is such that it facilitates the subject to identify a portion and differentiate between different portions. Also contemplated are a dosage form, a method and a system for delivering active agents, such as nicotine and / or metabolites thereof, such as cotinine, nicotine N′-oxide, nomicotine, (S)-nicotine-N-β-glucuronide and mixtures, isomers, salts and complexes thereof as well as use and production of said dosage forms.
Owner:MCNEIL AB
(3) and (6) substitued estrogenic compounds
Novel estrogenic compounds of Formula I are provided. wherein the bond represented by the wavy line may be a single or double bond such that when the wavy line is a single bond, R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronate or other esters, and when the wavy line is a double bond, R1 does not exist; R2 is lower alkyl; R3 may be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate, or glucuronide or other esters; and R4 through R13 may independently be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, ketone, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, halogen, and carbonyl groups and R14 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronide and other esters. When R1 is hydroxy, the hydroxy or ester substituent may have either an α or a β orientation. Compositions of matter including compounds of the present invention are also provided as are methods of treating mammals in need of treatment using compounds of the present invention.
Owner:DURAMED PHARMA
Estrogenic compounds and topical pharmaceutical formulations of the same
Novel estrogenic compounds of Formula I are provided.wherein the bond represented by the wavy line may be a single or double bond such that when the wavy line is a single bond, R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronate or other esters, and when the wavy line is a double bond, R1 does not exist; R2 is lower alkyl; R3 may be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate, or glucuronide or other esters; and R4 through R13 may independently be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, ketone, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, halogen, and carbonyl groups and R14 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronide and other esters. When R1 is hydroxy, the hydroxy or ester substituent may have either an α or a β orientation. Compositions of matter including compounds of the present invention are also provided as are methods of treating mammals in need of treatment using compounds of the present invention.
Owner:DURAMED PHARMA
Beta-Glucuronide-Linker Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20080241128A1Effective treatmentKill or inhibit the proliferation of the tumor cellsTetrapeptide ingredientsTissue cultureGreek letter betaDrug conjugation
Ligand Drug conjugate compounds comprising a β-glucuronide-based linker and methods of using such compounds are provided.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
Tissue degeneration protection
InactiveUS20100099640A1Improve solubilityHigh dissolution rateBiocideSugar derivativesPharmaceutical medicinePharmacology
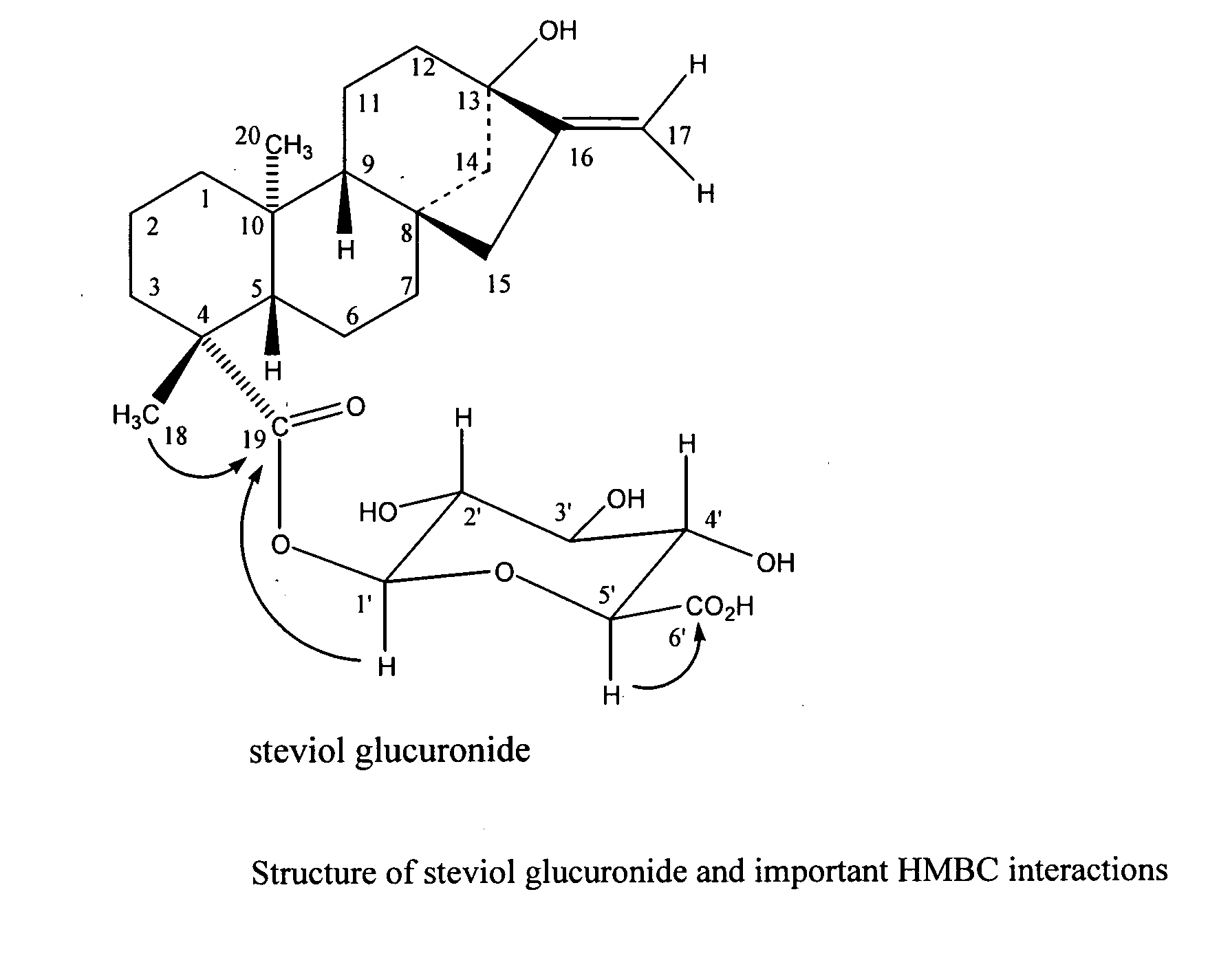
The present invention provides isolated or essentially pure diterpenoic tetrahydropyran, such as steviol-19-glucuronide, steviol, stevioside and rebaudioside processes for obtaining the same and methods for obtaining stable pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the same for use of such compounds or compositions in a treatment of cardiovascular disorders or vascular disease or for the manufacture of medicaments to treat a condition of a cardiovascular disorder or vascular disease.
Owner:GEUNS JOANNES +1
(3) and (6) substituted estrogenic compounds
Novel estrogenic compounds of Formula I are provided.wherein the bond represented by the wavy line may be a single or double bond such that when the wavy line is a single bond, R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronate or other esters, and when the wavy line is a double bond, R1 does not exist; R2 is lower alkyl; R3 may be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate, or glucuronide or other esters; and R4 through R13 may independently be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, ketone, lower allyl, lower alkoxy, halogen, and carbonyl groups and R14 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronide and other esters. When R1 is hydroxy, the hydroxy or ester substituent may have either an α or a β orientation. Compositions of matter including compounds of the present invention are also provided as are methods of treating mammals in need of treatment using compounds of the present invention.
Owner:DURAMED PHARMA
Estrogenic compounds and pharmaceutical formulations comprising the same
Novel estrogenic compounds of Formula I are provided.wherein the bond represented by the wavy line may be a single or double bond such that when the wavy line is a single bond, R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronate or other esters, and when the wavy line is a double bond, R1 does not exist; R2 is lower alkyl; R3 may be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate, or glucuronide or other esters; and R4 through R13 may independently be selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, ketone, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, halogen, and carbonyl groups and R14 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, sulfate and glucoronide and other esters. When R1 is hydroxy, the hydroxy or ester substituent may have either an α or a β orientation. Compositions of matter including compounds of the present invention are also provided as are methods of treating mammals in need of treatment using compounds of the present invention.
Owner:DURAMED PHARMA
Multi portion intra-oral dosage form and use thereof
InactiveUS20100124560A1Efficient and effectiveReduce impulseBiocideCosmetic preparationsNornicotineActive agent
The present invention relates to a multi portion intra-oral dosage form where at least one portion is rapidly disintegrating and at least one portion is slowly disintegrating, whereby the disintegration time for the slowest disintegrating portion is at least two times longer than for the most rapidly disintegrating portion. Of certain interest is use of sensory markers / signals as conceptual aids for the subject.Also contemplated are a method and a system for delivering active agents, such as nicotine and / or metabolites thereof, such as cotinine, nicotine N′-oxide, nornicotine, (S)-nicotine-N-β-glucuronide and mixtures, isomers, salts and complexes thereof as well as use and production of said formulations.
Owner:MCNEIL AB
Fucosan sulphate, preparation method thereof, and application of fucosan sulphate in preparing anti-influenza virus medicine
The invention belongs to the field of marine medicines, and relates to a fucosan sulphate, a preparation method thereof and application of the fucosan sulphate in preparing an anti-influenza virus medicine. Polysaccharide with a main chain taking alpha-1,2-D-mannose and beta-1,4-D-glucuronic acid as repetitive units, and with a branched chain of alpha-1,3-L-fucosan sulphate is obtained by virtue of hot-water extraction, calcium chloride precipitation and DEAE-Cellulose chromatographic column purification. The fucosan sulphate prepared by the invention is high in inhibition effect on the influenza virus neuraminidase activities of A H1N1, H5N1 and H3N2, and obvious in protection effect on the dog kidney epithelial cells infected by A H1N1. The fucosan sulphate provided by the invention has the advantages of being rich in raw material source, simple in preparation process, easy to industrialize, high in product water solubility, high in stability, free from toxic and side effects, and the like, and has the prospect of being developed to the anti-influenza virus medicine.
Owner:威海人生药业有限公司
6-substituted estradiol derivatives and methods of use
InactiveUS20100130463A1Improved prognosisImprove complianceOrganic active ingredientsEstrane derivativesEnantiomerPhosphate
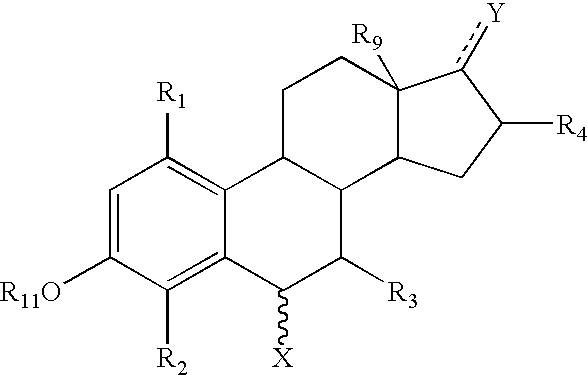
Disclosed are compounds of the formula:wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are independently hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, halo, a sulfate, a glucuronide, —OH, a bulky group, aryl, cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, heterocycloalkyl, —N(CH2)n; a phosphate group, and a phosphinate group; R9 is hydrogen, halogen or alkyl; R11 is selected from the group consisting of H, C1-C6 alkyl, halogen, a sulfate, a glucoronide, —SO2NH2, —COOH, —CN, —CH2CN—, —NHCN—, —CHO, ═CHOCH3, —COO salt, —OSO2alkyl, —NH2, and —NHCO(CH2)n; R12 is selected from the group consisting of H, a C1-C6 alkyl, a sulfate, a glucoronide, a bulky group, aryl, cycloalkyl, heteroaryl and heterocycloalkyl; X is selected from the group consisting of C1-C12 alkyl, C2-C12 alkenyl, C2-C12 alkynyl, halogen, a glucoronide, —NH2, —SO2NH2, —COOH, —CN, —CH2CN, —NHCN, —CHO, —COOsalt, —OSO2alkyl, —SH, —SCH3, —CH[(CH2)nCH2]COOCH2, —(CH2)mCOOCH3, —(CH2)m—O—CH3, —(CH2)m—O—(CH2)nCH3, (CH2)m—S—CH3, —(CH2)m—S—(CH2)nCH3, —(CH2)m—NH—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkenyl-O—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkenyl-S—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkenyl-N—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkynyl-O—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkynyl-S—(CH2)nCH3, —C2-C8 alkynyl-N—(CH2)nCH3, —(CH2)m—OH, —(CH2)m—O—NH2, —(CH2)m—S—NH2, —NH(CH2)mCH3, —NH(CH2)mOCH3, —NH(CH2)mCHOH—COOH, —N(CH3)2, —(CH2)m(NH)CH2OH, —NHCOOH, —(CH2)mNHCOOH, —NO2, —SCN, —SO2alkyl, —B(OH)2, —(CH2)m N(CH3)—SO2—NH3, —(CH2)m—NH—SO2—NH2, —NHC(═S)CH3, and —NHNH2; and Y is selected from hydrogen, ═O, —OCO(R6) and —OH; wherein m is an integer between 0-20, n is an integer between 0-8, the symbol represents either a single or a double bond capable of forming a keto group at position 3 or 17; and the symbol represents any type of bond regardless of the stereochemistry; and the respective enantiomers, other stereochemical isomers, hydrates, solvates, tautomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of said compounds. The compounds are useful in the treatment of various types of cancer.
Owner:ENDECE LLC
Morphine controlled release system
InactiveUS8877241B2Affecting extent of drug bioavailabilityReduce frequencyBiocideNervous disorderMorphineDissolution
A composition for controlled release of an opioid from a pharmaceutical composition, the method comprises controlling the release of at least one opioid into an aqueous medium by erosion of at least one surface of a pharmaceutical composition comprising I) a matrix composition comprising a) polymer or a mixture of polymers, b) an opioid and, optionally, c) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, and (i) a coating. The matrix composition has a conus-like shape so the surface area exposed to the aqueous medium increases at least during initial erosion of the matrix composition, and the dissolution of the opioid—when tested in a Dissolution Test as described herein with or without application of sinkers-results in a zero order release of at least 80% of the opioid contained in the composition. Such compositions are especially suitable for controlled release of an opioid to obtain a delayed peak concentration and a prolonged therapeutically effective plasma concentration upon oral administration. Once or twice daily administration is possible. The matrix typically comprises PEO and the active substance is typically an opioid such as morphine or a glucuronide thereof.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Multi portion intra-oral dosage form and use thereof
The present invention relates to a multi portion intra-oral dosage form where at least one portion is rapidly disintegrating and at least one portion is slowly disintegrating, whereby the disintegration time for the slowest disintegrating portion is at least two times longer than for the most rapidly disintegrating portion. Of certain interest is use of sensory markers / signals as conceptual aids for the subject.,Also contemplated are a method and a system for delivering active agents, such as,nicotine and / or metabolites thereof, such as cotinine, nicotine N'-oxide, nornicotine, (S)-nicotine-N-ss-glucuronide and mixtures, isomers, salts and complexes thereof as well as use and production of said formulations.
Owner:MCNEIL AB
Pharmaceutical compounds
InactiveUS20100152184A1Reduce and even eliminate painNarrow downBiocideNervous disorderHydrogenDrug compound
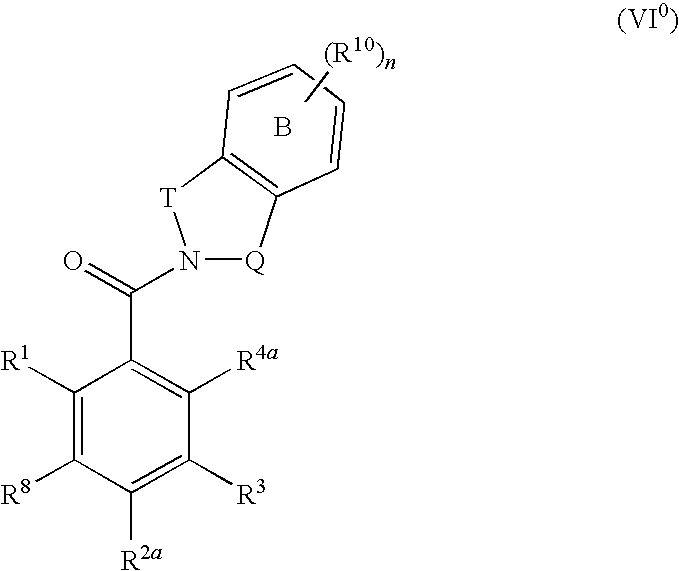
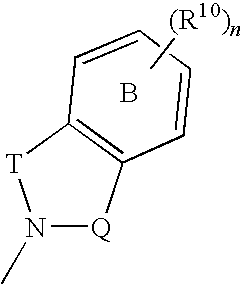
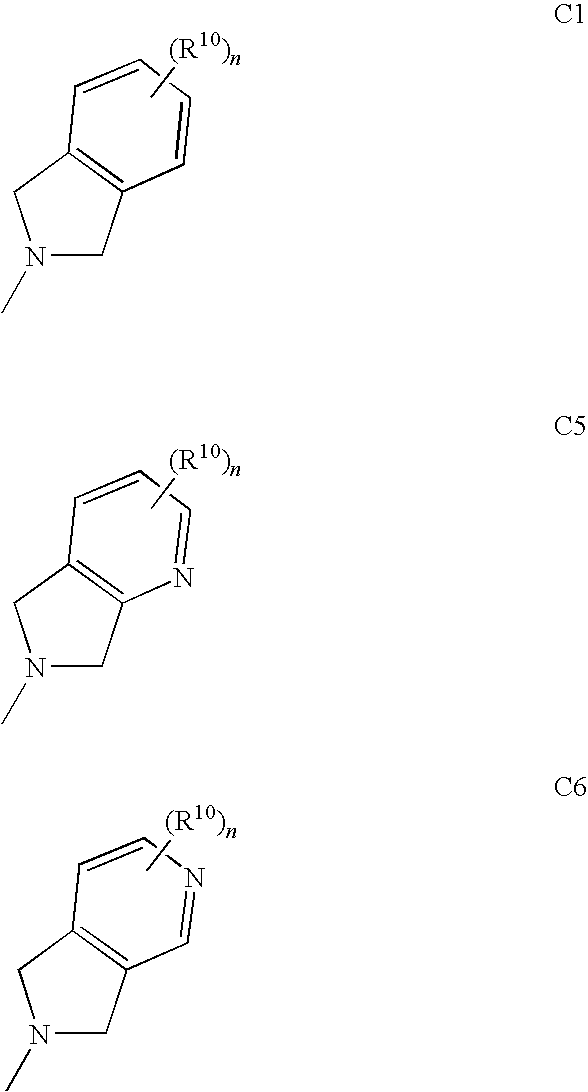
The invention provides a compound for use in medicine, the compound being a compound of the formula (VI0) or a salt, solvate, tautomer or N-oxide thereof:wherein the bicyclic group:is selected from the structures C1, C5 and C6:wherein n is 0, 1, 2 or 3; R1 is hydrogen, hydroxy, or O—Rz; R2a is hydroxy, methoxy or O—Rz; provided that at least one of R1 and R2a is O—Rz; Rz is Lp-Rp1; SO3H; a glucuronide residue; a mono-, di- or tripeptide residue; orLp is a bond, C═O, (C═O)O, (C═O)NRp1 or S(O)xNRp1; x is 1 or 2; Rp1 is hydrogen or a an optionally substituted C1-25 hydrocarbyl group containing 0, 1 or 2 carbocyclic rings and 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 carbon-carbon multiple bonds, provided that Rp1 is not hydrogen when Lp is a bond, C═O or (C═O)O; and provided also that O—Rz does not contain an O—O moiety; and excluding compounds wherein R1 is hydroxy and R2a is methoxy; Rp2 and Rp3 are the same or different and each is a group Rp1; and R3, R4a, R8 and R10 are defined in the claims.The compounds of formula (VI0) are pro-drugs of parent compounds wherein R1 and / or R2a are hydroxy, wherein the parent compounds have Hsp90 inhibiting activity.
Owner:ASTEX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Preparation method of flavonoid glycosides in scutellaria baicalensis
InactiveCN101723998AHigh purityGuaranteed puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChromatographic separationFlavonoid glycosides
The invention provides a preparation method of flavonoid glycosides in scutellaria baicalensis. The method is suitable for quickly preparing four flavonoid glycosides comprising baicalin, wogonoside, chrysin-6-C-alpha-L-Arabic glucoside-8-C-beta-D-glucoside and oroxylinA-7-O-glucuronide. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: pulverizing scutellaria baicalensis and then adding water to extract; sequentially carrying out alcohol precipitation and high-speed centrifugation; after membrane separation, loading nonpolar macroporous absorption resin and eluting by alcohol / water; collecting eluent and concentrating and drying to obtain a scutellaria baicalensis macroporous resin component; and obtaining a scutellaria baicalensis effective component through parallel preparing liquid-phase chromatographic separation by using acetonitrile water as a flow phase. The preparation method has good selectivity and high purity of the obtained compound and greatly improves the separation and purification efficiency. The preparation process has high repeatability and good maneuverability, is easy to realize standardization and industrialization and has certain guidance effects on quickly obtaining flavones active constituents in the scutellaria baicalensis.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
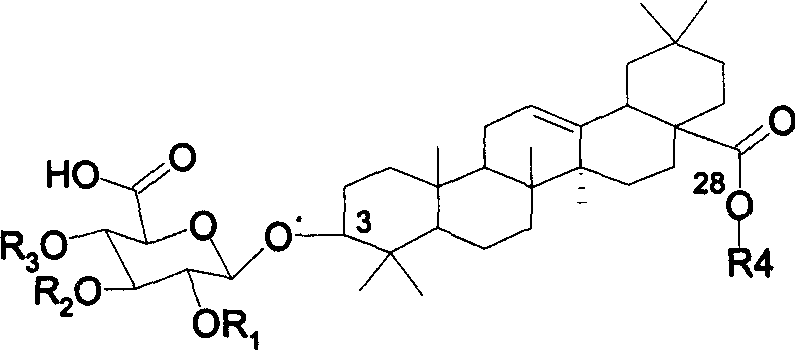
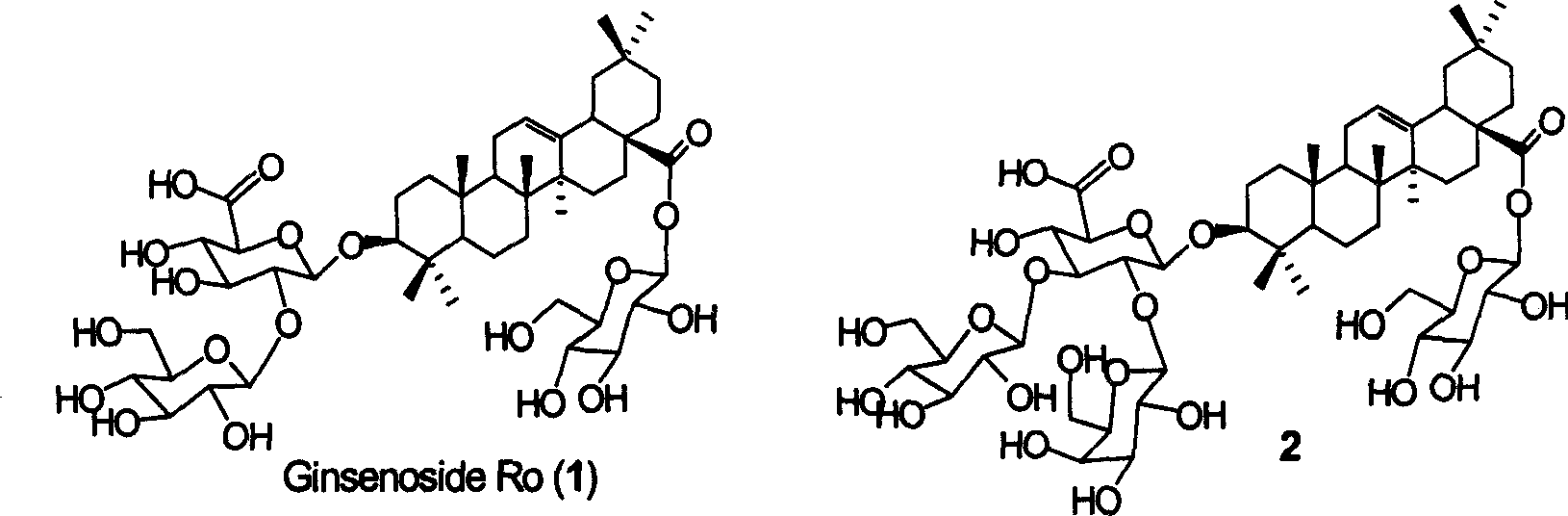
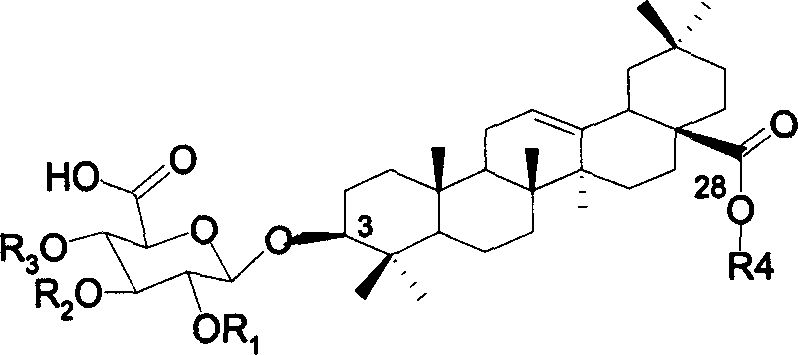
Chemosynthesis of glucuronide oleanane type double sugar chains triterpenoid saponin
The present invention provides practical GOTCAB saponin synthesis process. The synthesis process includes the following steps: connecting site-28 glucose chain; connecting site-3 glycosyl; connecting rest site-3 glycosyl after protecting radical operation; making site-6' hydroxy group empty via protecting radical operation; selectively oxidizing site-6' primer hydroxy group into carboxylic acid; and finally eliminating all the protecting radicals under alkali condition.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
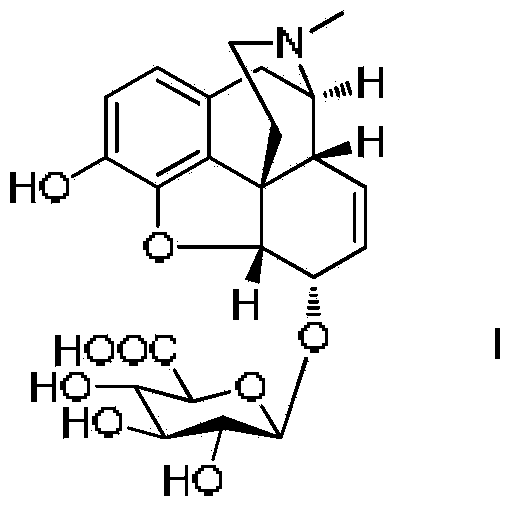
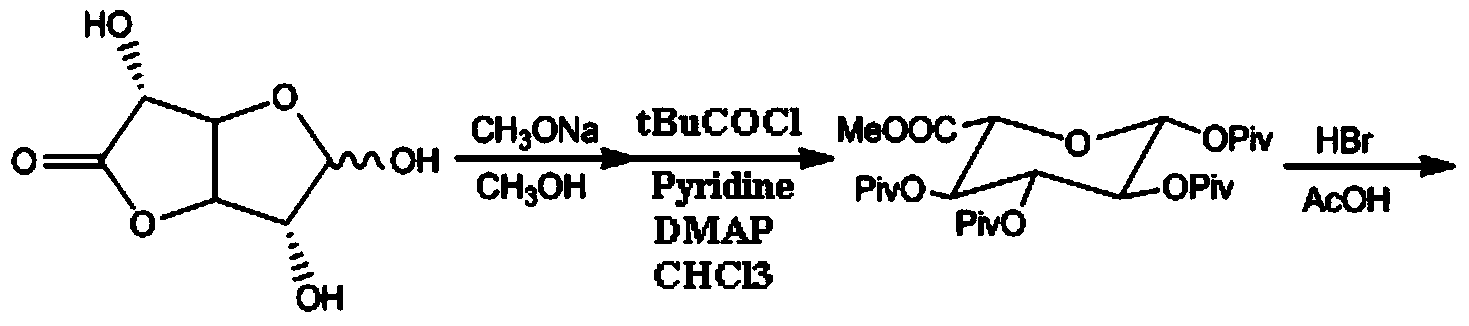
Synthesis method and intermediate compound of morphine-6-Beta-D-glucuronide
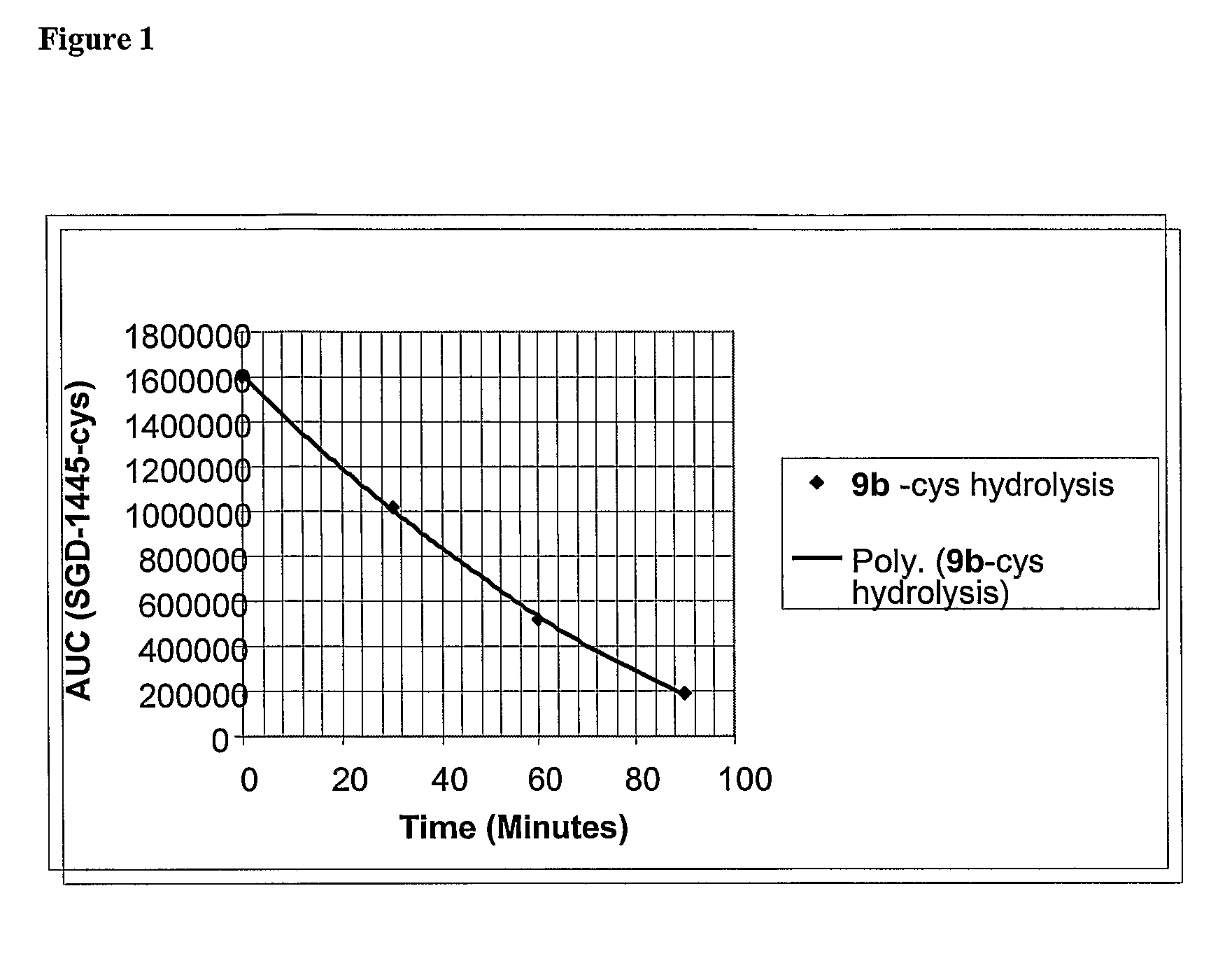
ActiveCN103864866AMedication safetyShort reaction pathEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesOrganic solventLithium hydroxide
The invention discloses a synthesis method and an intermediate compound of morphine-6-Beta-D-glucuronide. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out a reaction on 3-acetyl morphine and acyl-protected glucuronate in an organic solvent 1 under the catalysis of lewis acid so as to obtain an intermediate shown as a formula (IV); (2) hydrolyzing the intermediate shown as the formula (IV) with lithium hydroxide and neutralizing the intermediate shown as the formula (IV) with hydrobromic acid in a mixture solvent of C1-C4 alkanol and water; and washing the intermediate with the C1-C4 alkanol and drying, thereby obtaining the intermediate compound of the morphine-6-Beta-D-glucuronide, wherein the definitions of substituent groups in the formula (III) and the formula (IV) are shown in the specification. The synthesis method has the advantages of moderate condition and high yield, and is simple to operate and easy to industrialize.
Owner:YICHANG HUMANWELL PHARMA
Preparation, quality control method and application of composition of active ingredients of bitter herb
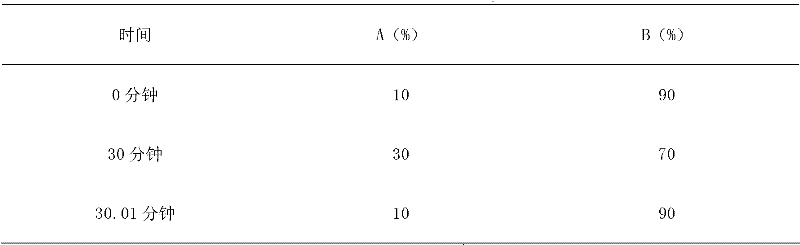
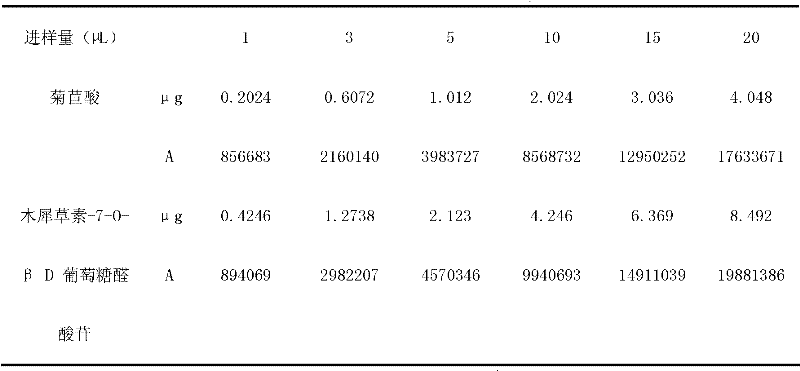
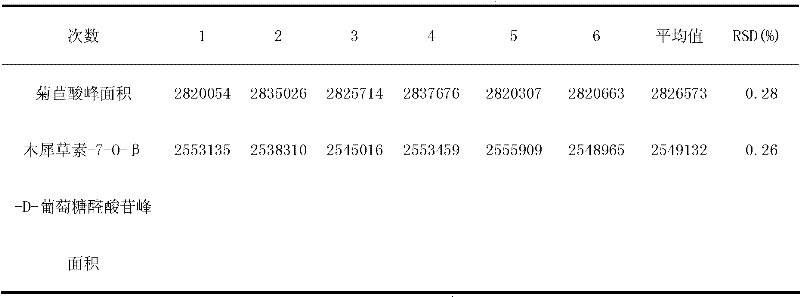
ActiveCN102362883AHigh yieldLow cost of water extractionComponent separationCardiovascular disorderMedicinal herbsPolyamide
The invention discloses a preparation method, a quality control method and an application of composition of active ingredients ob bitter herb. The composition of the active ingredients of the bitter herb disclosed by the invention mainly comprises cichoric acid and luteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide, and content of the cichoric acid and the luteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide is not less than 80%. An extraction method of the composition comprises that pretreatment is carried out by adopting an enzymatic method, then a supercritical fluid extraction method is adopted, and the obtained extract is respectively subjected to separating, purifying, concentrating and drying by virtue of an AB-8 resin column and a polyamide resin column so as to obtain the composition. Besides, the invention also relates to an application of the composition in preparation of modern bitter herb injection and treatment on coronary heart disease, angor pectoris, myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction and an application of the composition in content determination of the composition of the active ingredients of the bitter herb and quality control of bitter herb medicinal material.
Owner:沈阳双鼎制药有限公司
Nutritional supplement compositions
Dietary supplement compositions containing one or more compounds such as arginine, selenium, calcium, calcium sources, morphine precursors (e.g., reticuline), morphine, and morphine-6β-glucuronide are provided.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Topical Macqui Berry Formulation
ActiveUS20120114719A1Improve skinCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineOxygen radical absorbance capacity
The present invention provides a topical formulation and method of use where the formulation comprises macqui berry or a macqui berry extract containing anthocyanins having a very high oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC). The formulation provides the macqui berry in a stabilized form which includes a glucuronide or glycuronide, a photostabilizing agent, encapsulation, or light- and / or air-blocking packaging.
Owner:TRACIE MARTYN INT
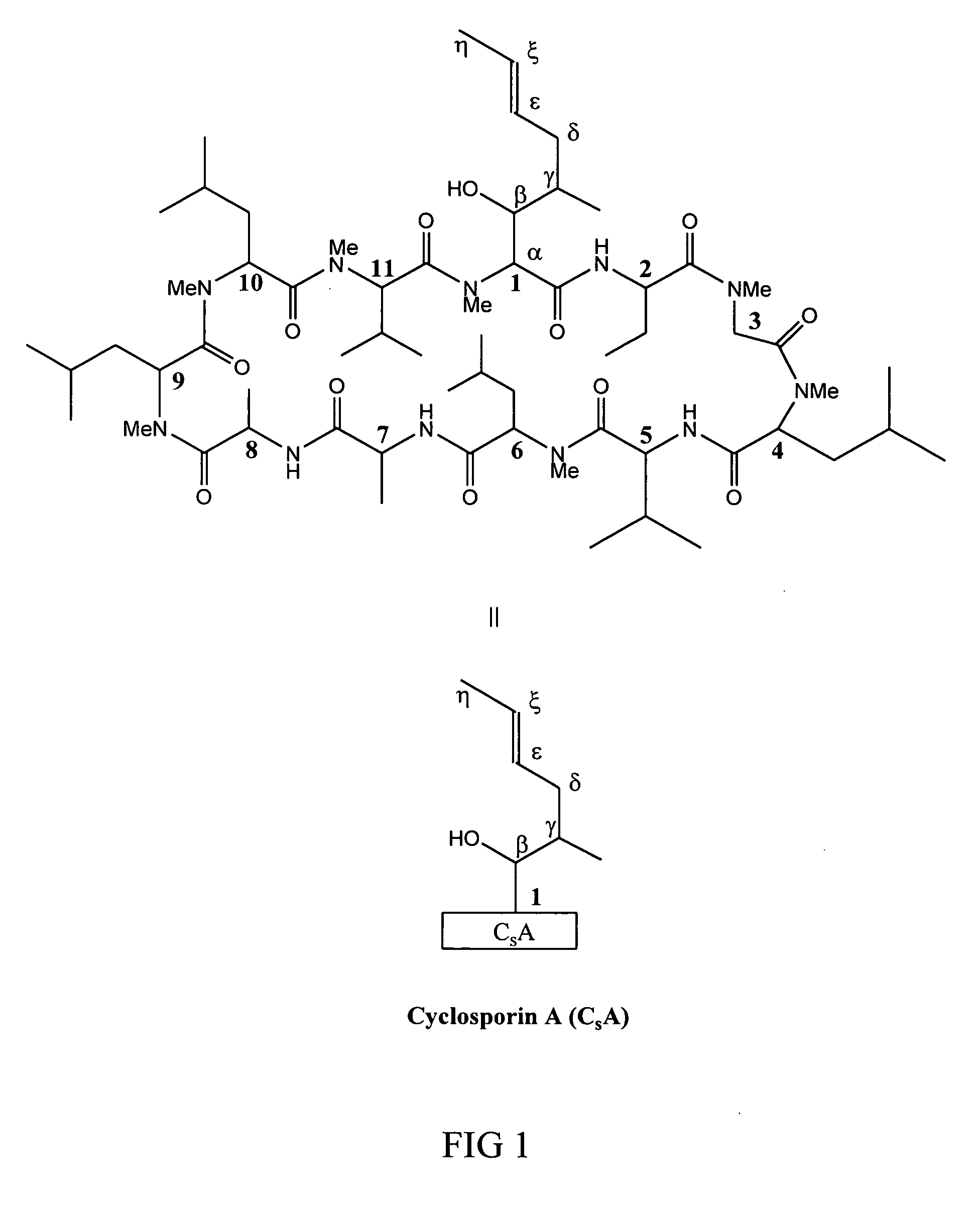
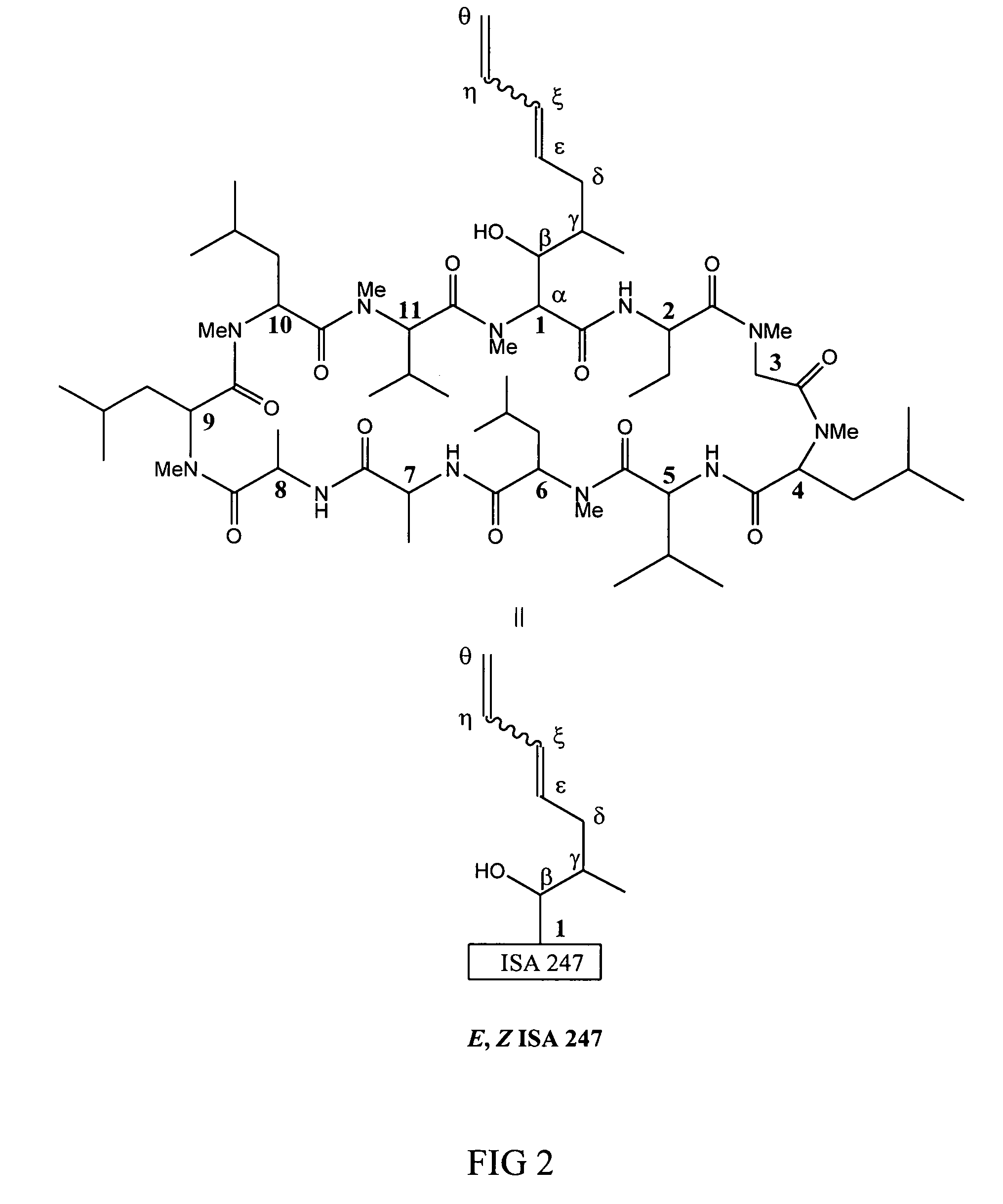
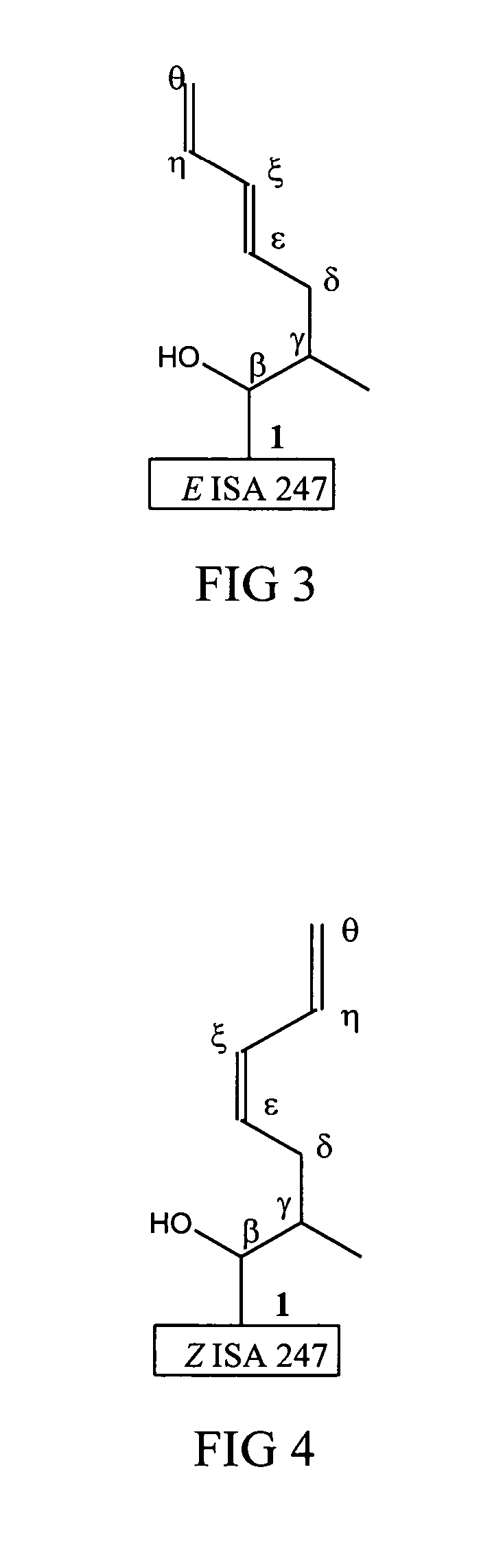
Metabolites of cyclosporin analogs
InactiveUS20060223743A1Useful immunosuppressive activityUseful for developmentCyclic peptide ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPhosphorylationCyclosporins
Isolated metabolites of the cyclosporine analog ISA247 are disclosed, including in vitro methods for their preparation. The metabolites comprise a chemical modification of ISA247, wherein the modification is at least one reaction selected from the group consisting of hydroxylation, N-demethylation, diol formation, epoxide formation, and intramolecular cyclization phosphorylation, sulfation, glucuronide formation and glycosylation. Methods of preparation include semi-synthetic methods, wherein metabolites of ISA247 are produced from the microsomal extracts of animal liver cells, or from cultures using microorganisms, and completely synthetic methods, such as chemically modifying the parent compound or isolated metabolites using organic synthetic methods.
Owner:ISOTECHNIKA INC
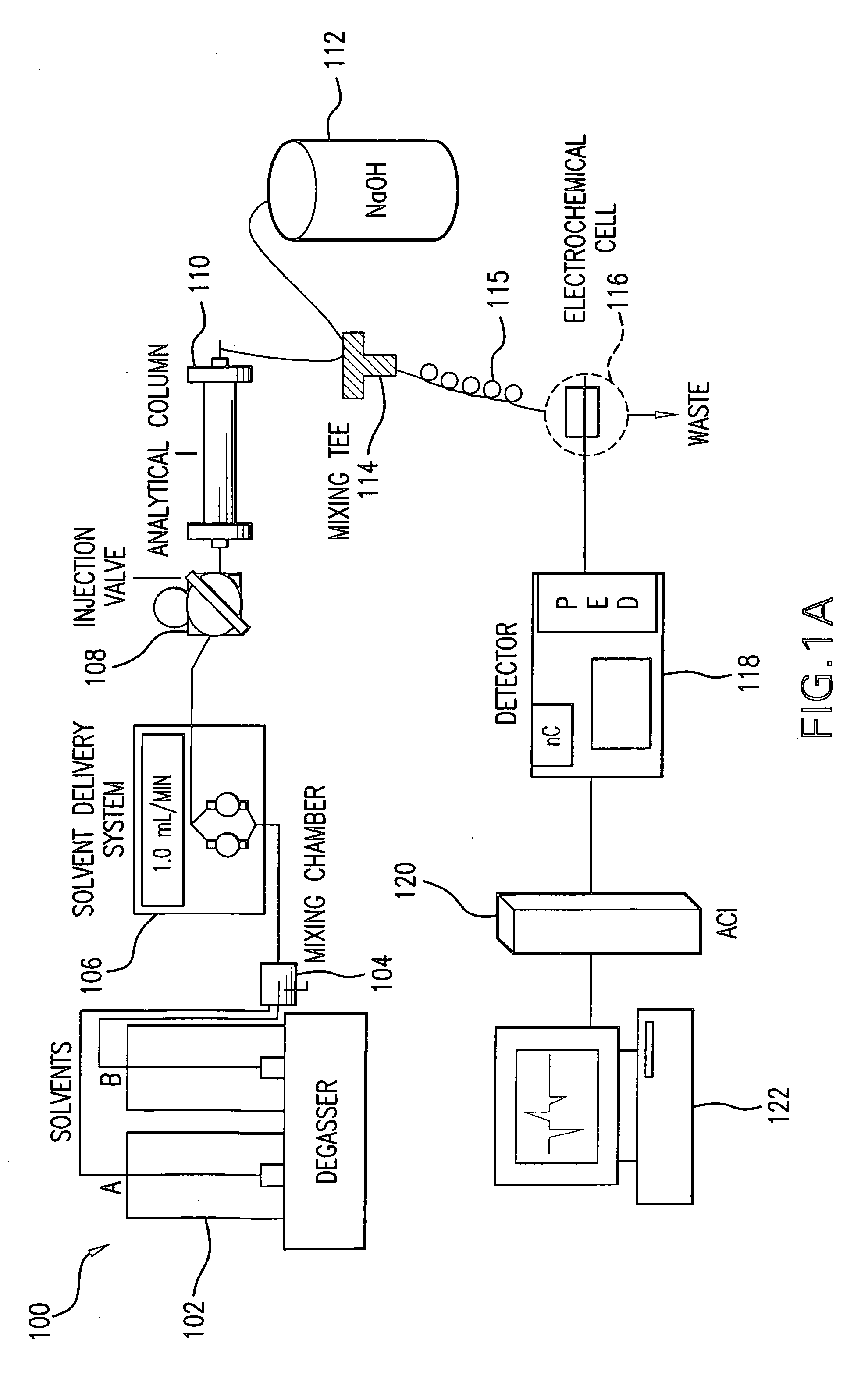
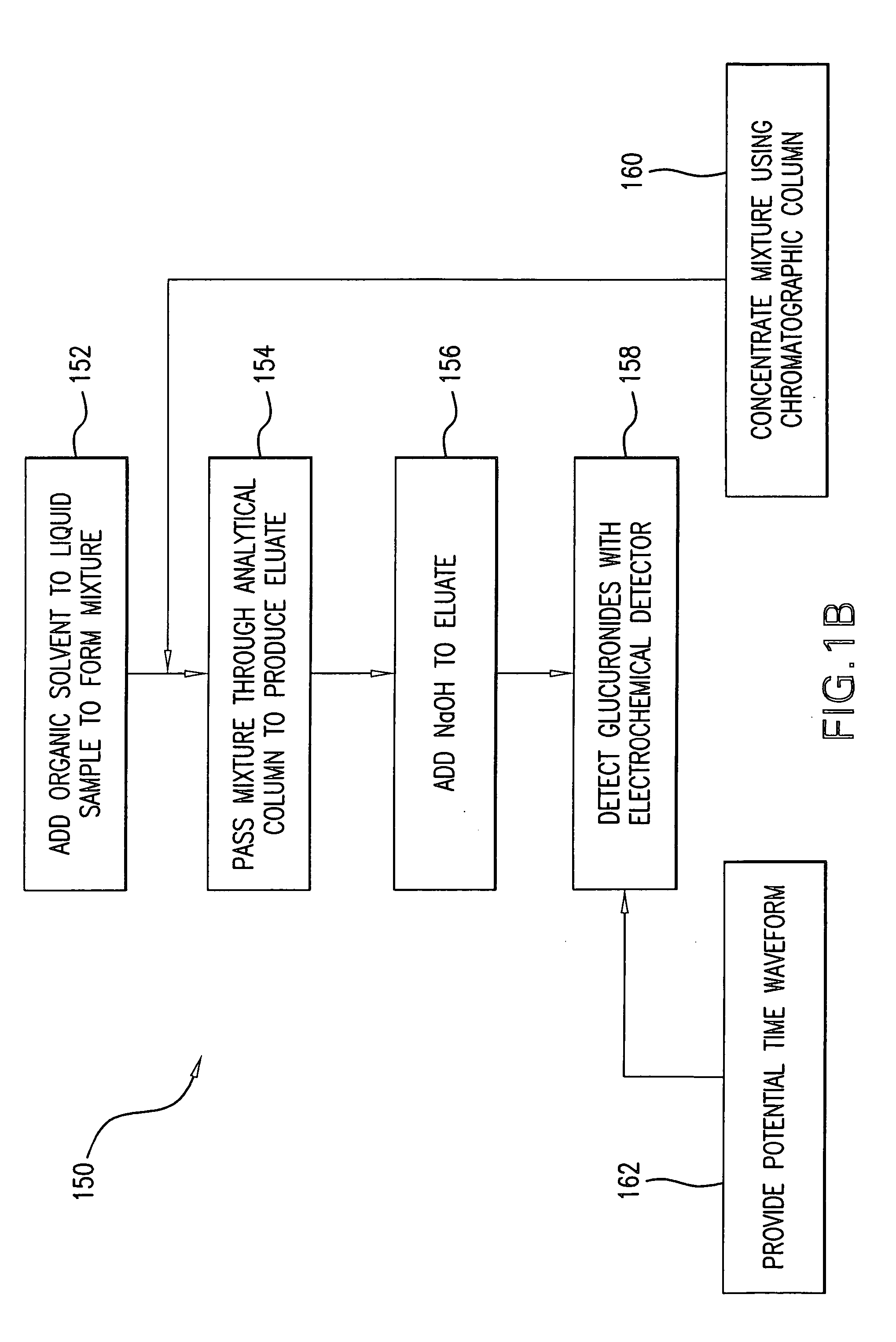
Method for the determination of glucuronides in physiological samples
The present invention provides methods and kits for the detection of glucuronide metabolites of various drugs, alcohols and other compounds using a combination of High Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled with Pulsed Electrochemical Detection. Detection of a drug and its glucuronide metabolite(s) has applications in interpretive forensic and clinical toxicology. The ability to estimate metabolite / drug ratios enables the assessment of route, dose and time of exposure. In instances where the parent drug is biotransformed quickly and can only found in low levels in biological fluids, the detection of metabolites allows for the identification of parent drugs. Furthermore, metabolite determination enables the differentiation between recent and chronic drug use.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
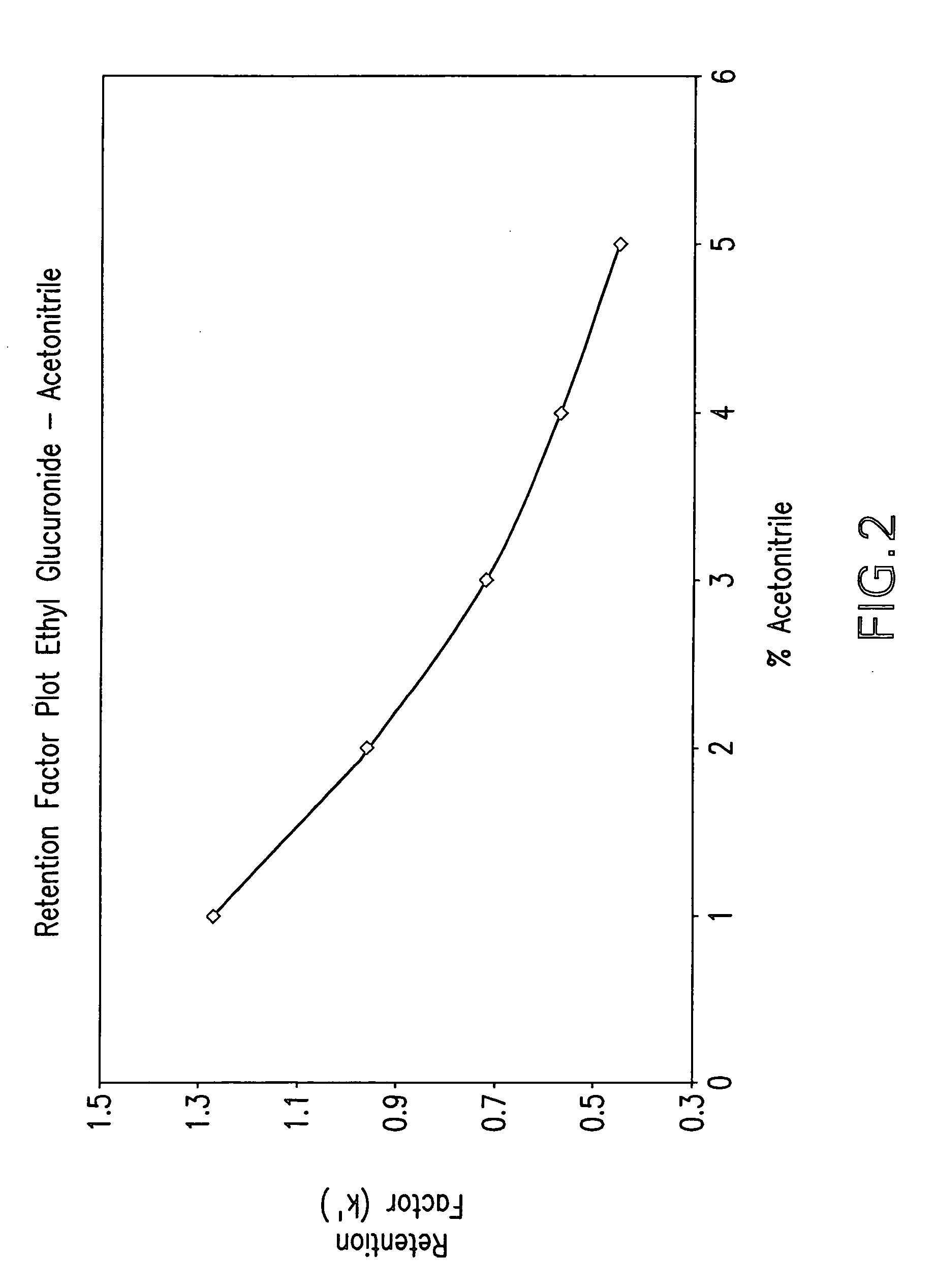
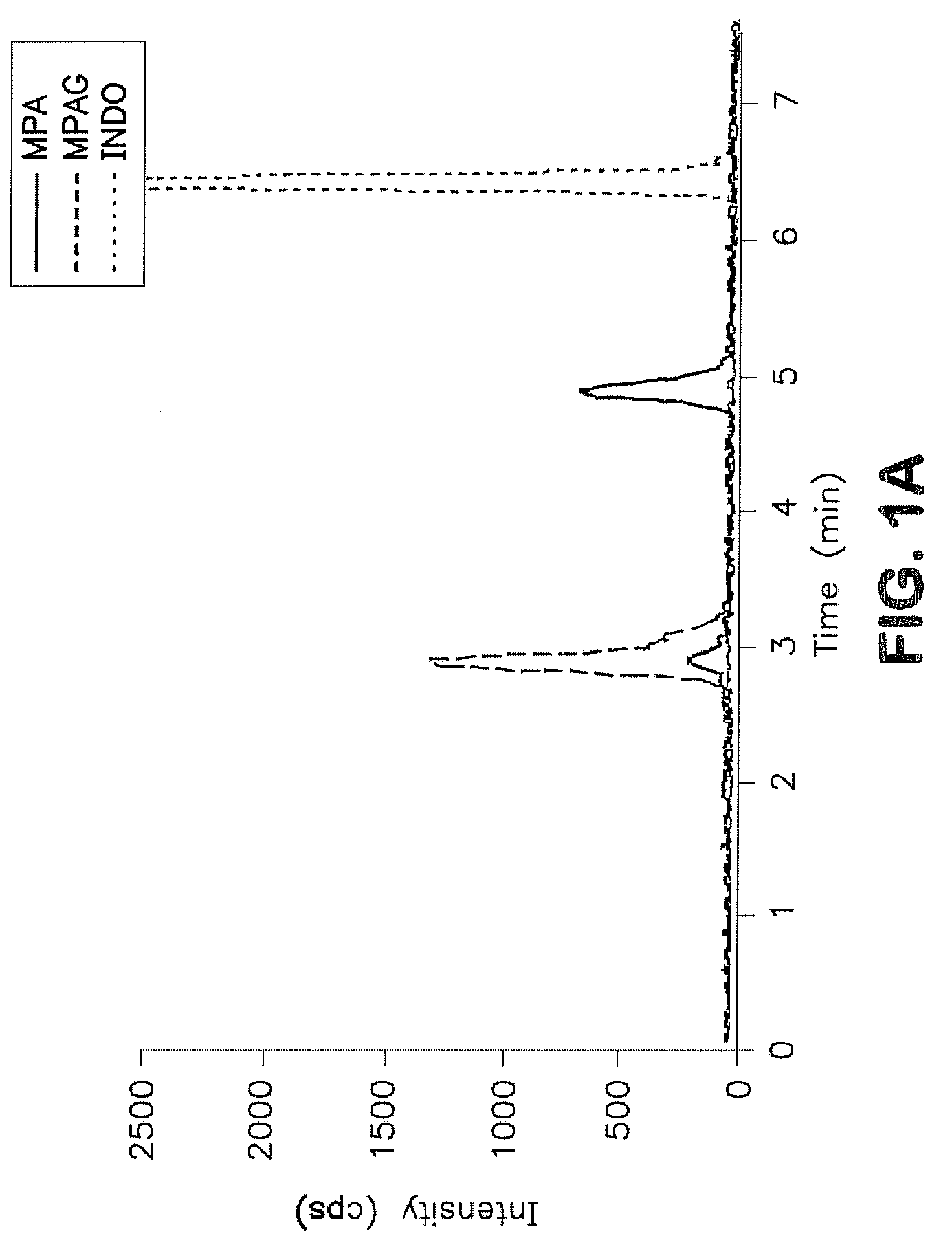
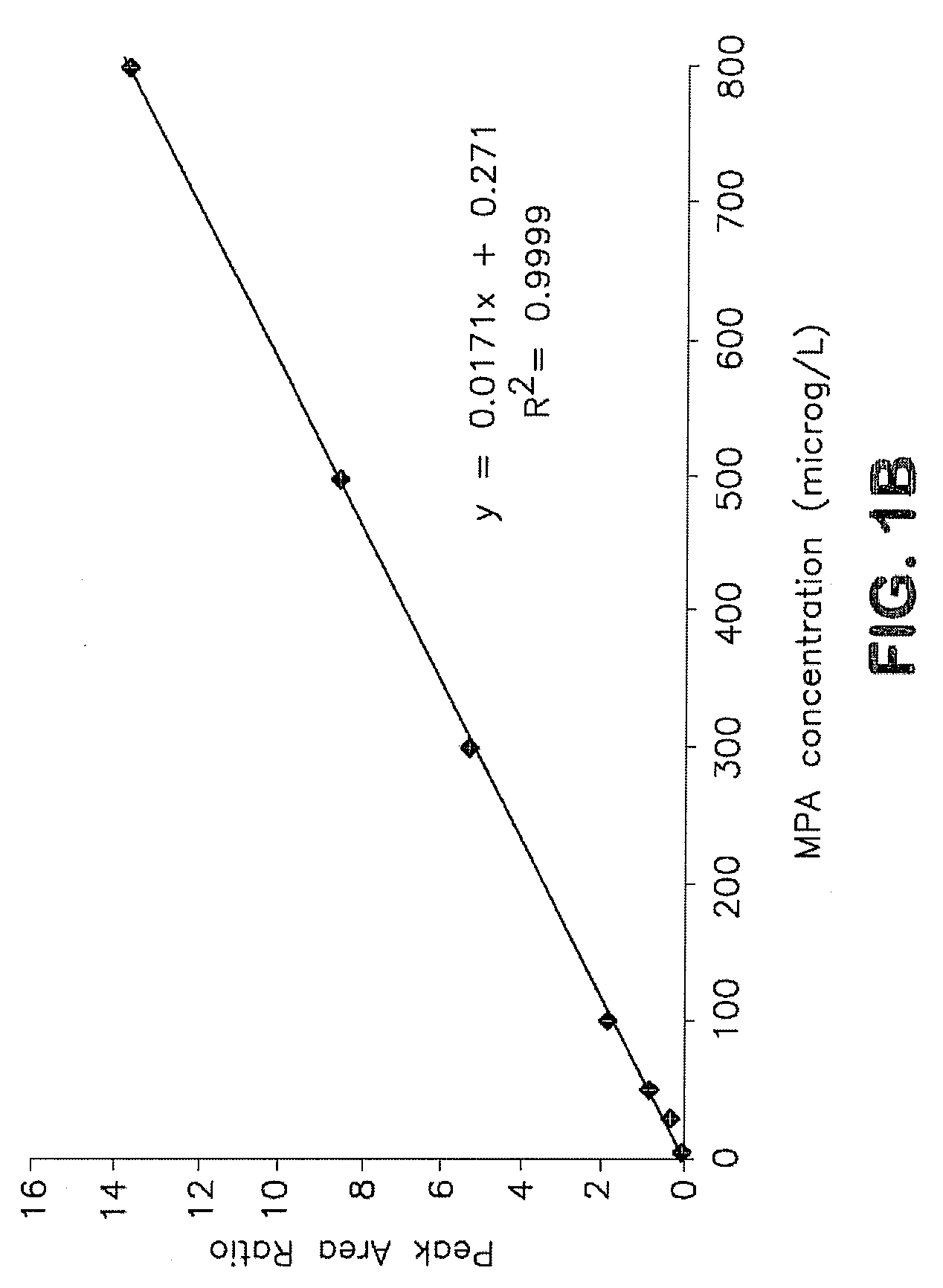
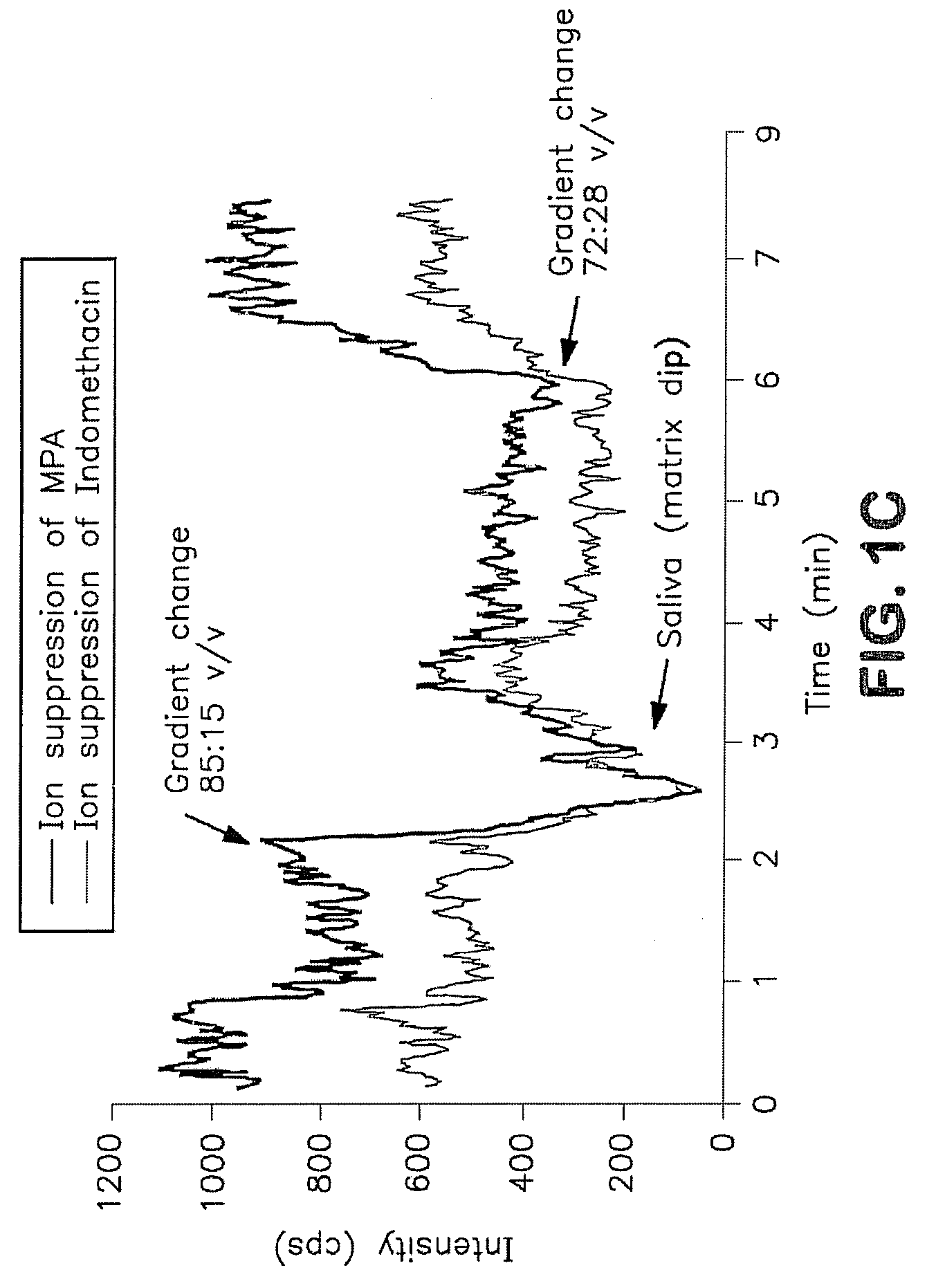
Analysis of mycophenolic acid in saliva using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080318322A1Component separationBiological testingSaliva sampleGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
A method for mass spectrometric analysis of a saliva sample possibly containing mycophenolic acid or its metabolites mycophenolic acid phenyl glucuronide (MPAG) or mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide (Acyl-MPAG), including the steps: (a) providing a saliva sample containing one or more drug or metabolites; (b) deproteinating the sample; (c) separating the one or more drug or metabolites from the saliva sample; and (d) analyzing the one or more drug or metabolites using a mass spectrometer. The sample containing one or more MPA or metabolites is obtained from in an oral fluid based biological samples i.e. whole saliva or saliva obtained by chemical or mechanical stimulation or from specific salivary glands. The size of the sample contains one or more MPA or metabolites is at least about 100 microL. A kit for use in mass spectrometric analysis of a sample may contain one or more MPA or metabolites from saliva samples, comprising: (a) reagents for deproteinating of the saliva sample, including internal standards; (b) reagents for separating the one or more MPA or metabolites from the saliva sample; (c) reagents for analyzing the one or MPA or metabolites using a mass spectrometer; (d) a solution of one or more MPA or metabolites in saliva samples; and (e) instructions for analyzing the one or more MPA or saliva using a mass spectrometer. The kit includes (a) mobile phase solutions; (b) a chromatography column; and (c) a quality control specimen.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS
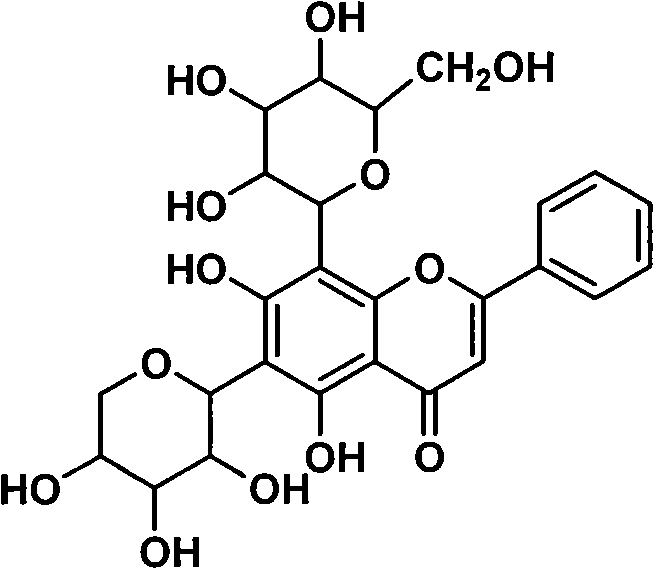
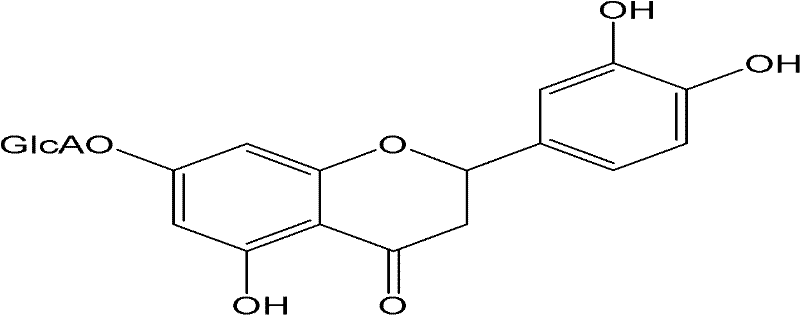
Application of digitoflavone-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide in fundus disease treatment
The invention relates to application of digitoflavone-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide in fundus disease treatment, which is characterized in that digitoflavone-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide can be used as a main active component for preparing a medicine treating the pathological change of the fundus. One kind of or a plurality of kinds of natural or synthetic active components with a synergic or auxiliary action with the digitoflavone-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide can be added for preparing a medicine treating fundus diseases. The digitoflavone-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide is used for treating the diabetic pathological change of the retina, the senile pathological change of yellow spots, retinal vein obstruction, and the like, and has an obvious curative effect.
Owner:沈阳双鼎制药有限公司
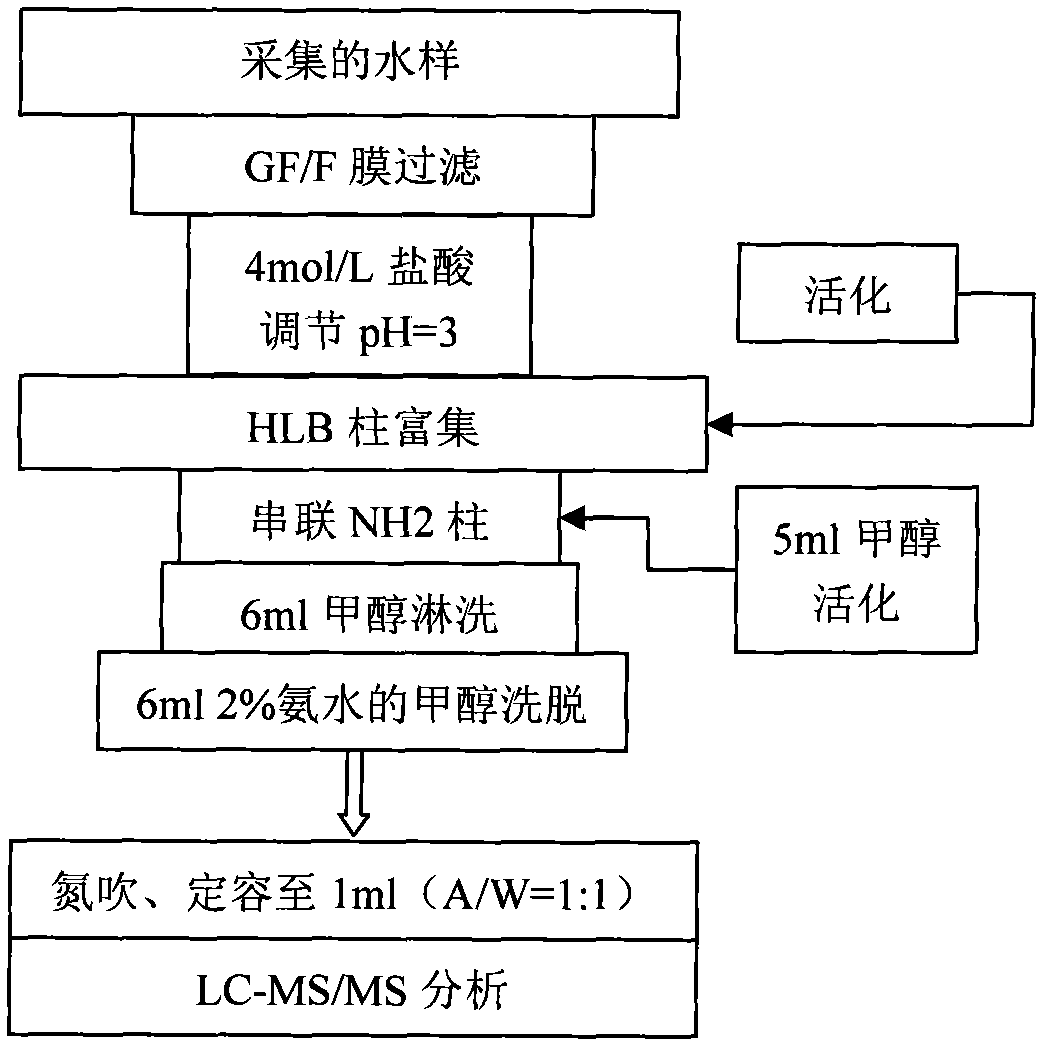
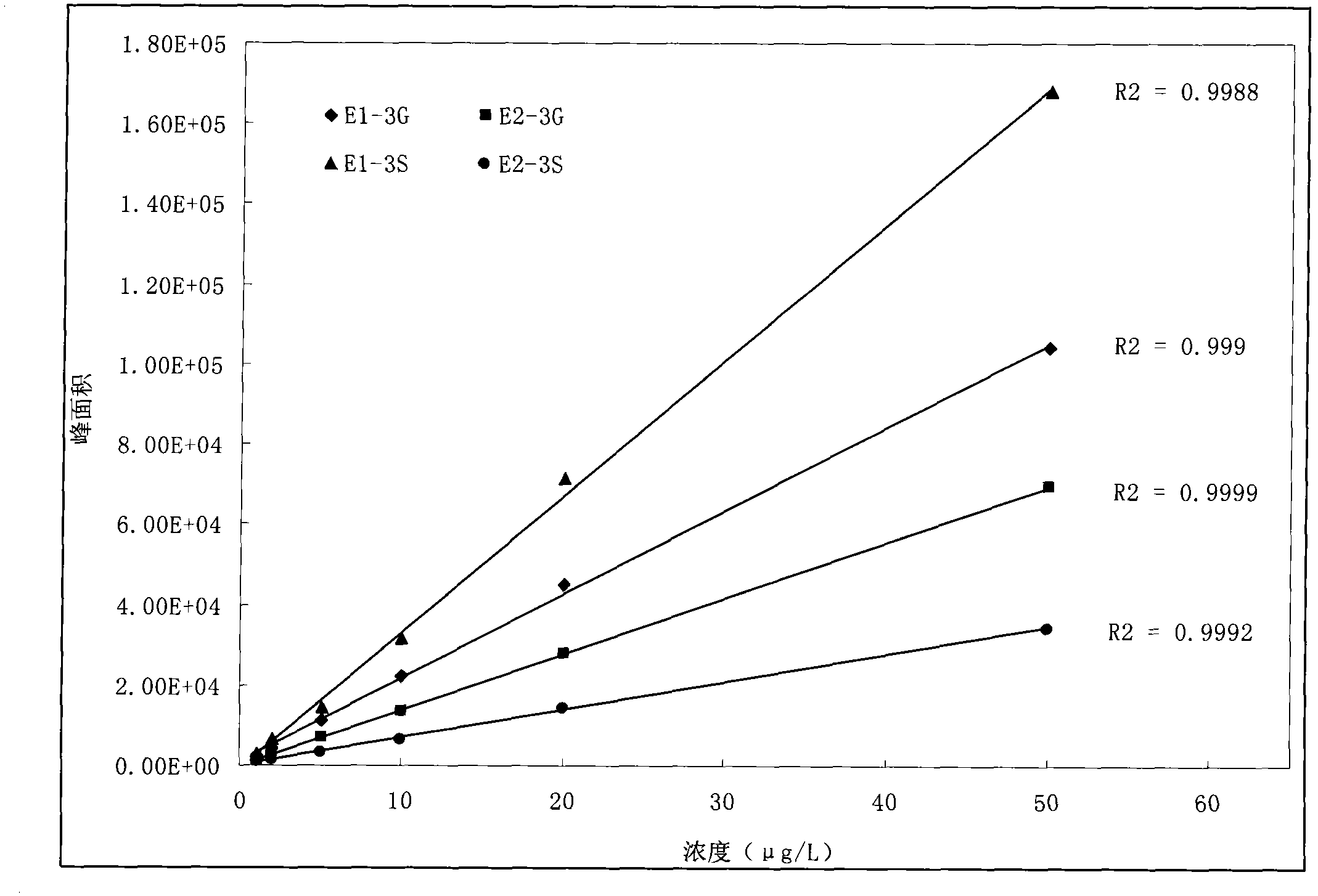
Co-detection method for estrogen coalition in water environment
InactiveCN102636610AQuick analysisFast contentComponent separationPerturbateurs endocriniensSolid phase extraction
The invention relates to a detecting technique for an endocrine disrupter in a water environment and especially relates to a co-detection method for an estrogen coalition, Estrone-3-sulfate, E1-3S, Estradiol-3-sulfate, E2-3S, Estradiol-3-glucuronide, E1-3G and17beta-Estradiol-3-glucuronide, E2-3G in a water sample by adopting a liquid chromatogram-tandem mass spectrum technique. The method comprises the steps of: enriching the E1-3S, E2-3S, E1-3G and E2-3G in a collected water sample by using a HLB (Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance) solid-phase extraction column; connecting an activated NH2 column under the HLB column and washing with carbinol; and lastly, eluting with 2% of ammonia water carbinol solution and analyzing by adopting the liquid chromatogram-tandem mass spectrum technique. The method has the advantages of environmental protection, easiness in operation, high recovery rate and quick analysis for the trace amount of estrogen coalition E1-3S, E2-3S, E1-3G and E2-3G in the watersample.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing scutellarin by using Aspergillus niger AS 3.795 for hydrolyzing scutellarin-7-O-glucuronide
ActiveCN102618593AOvercome the conditionsOvercoming conversion rateOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesScutellareinUronic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing scutellarin by using Aspergillus niger AS 3.795 for hydrolyzing scutellarin-7-O-glucuronide. Aspergillus niger AS 3.795 is used for hydrolyzing scutellarin-7-O-glucuronide glucuronyl to prepare the scutellarin. The method comprises the following steps of: using Aspergillus niger AS 3.795 to biologically transform a substrate scutellarin-7-O-glucuronide, using ethyl acetate to extract transformation products from fermentation liquor and using D101 macroporous adsorption resin column chromatography and recrystallization to purify the transformation products. The purity of the prepared transformation products can reach more than 99 percent according to high performance liquid chromatography. The method has the advantages that the defect that glucuronide is difficult to hydrolyze is overcome, the scutellarin can be prepared in a large scale under moderate conditions such as normal temperature and normal pressure, the environmental protection is facilitated, the production cost is reduced and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com