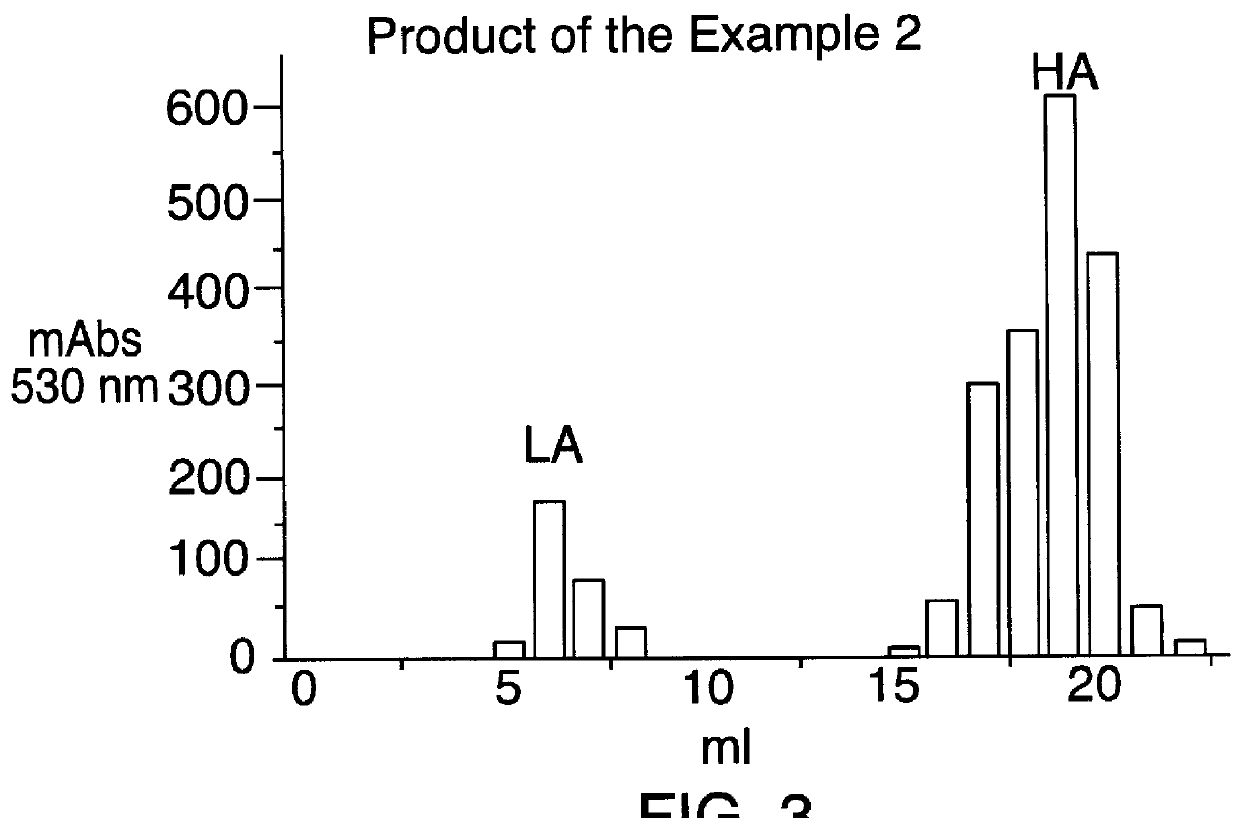
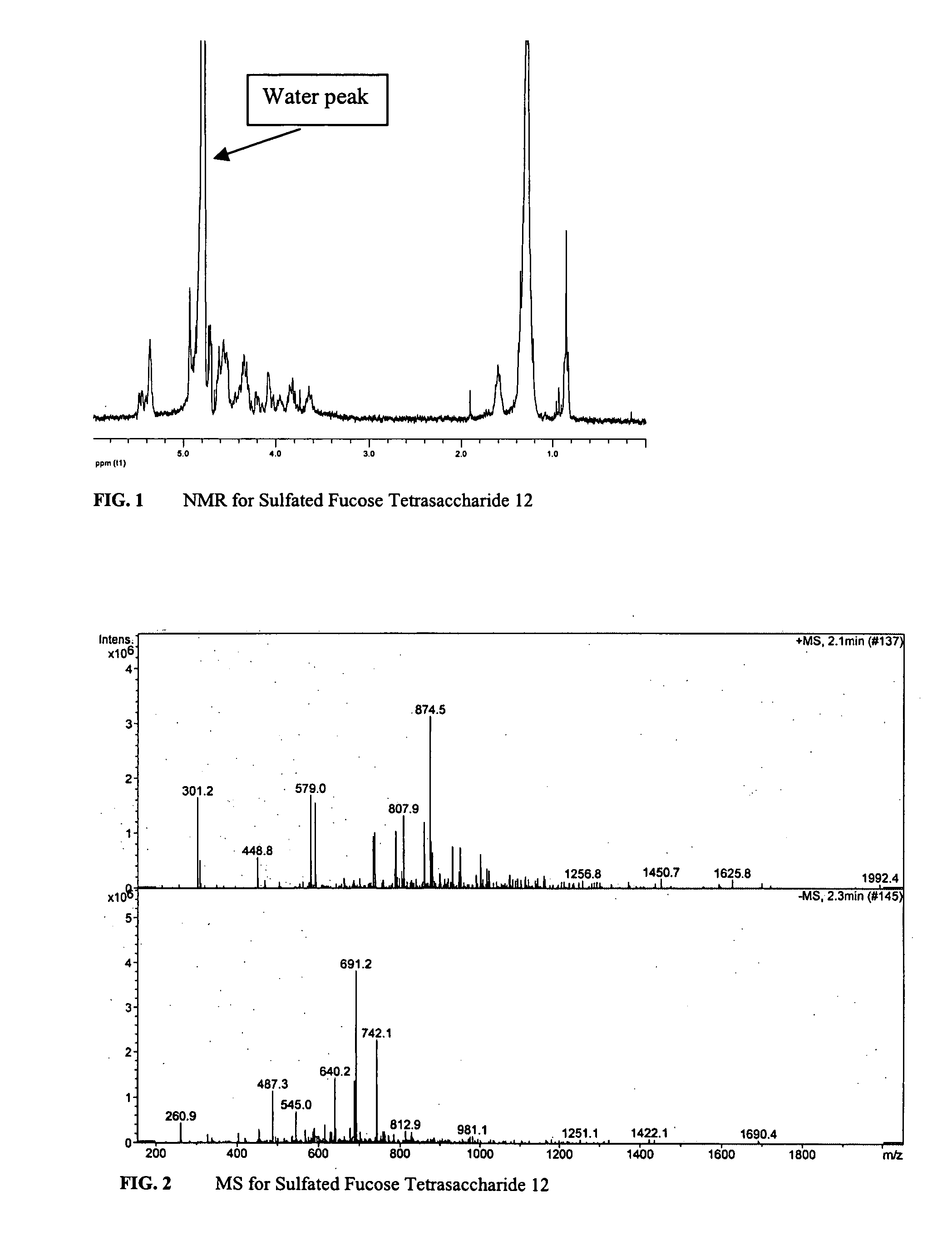
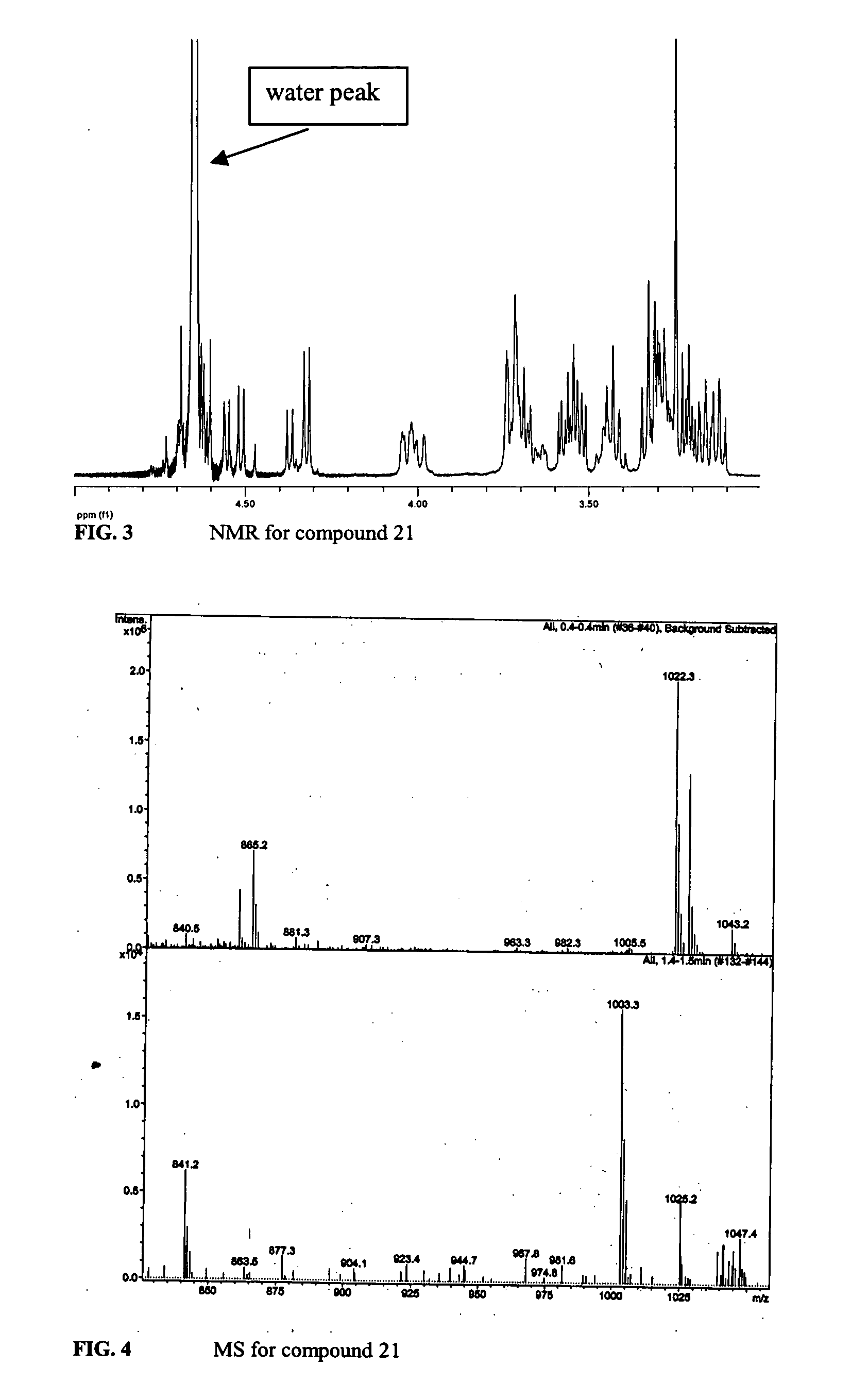
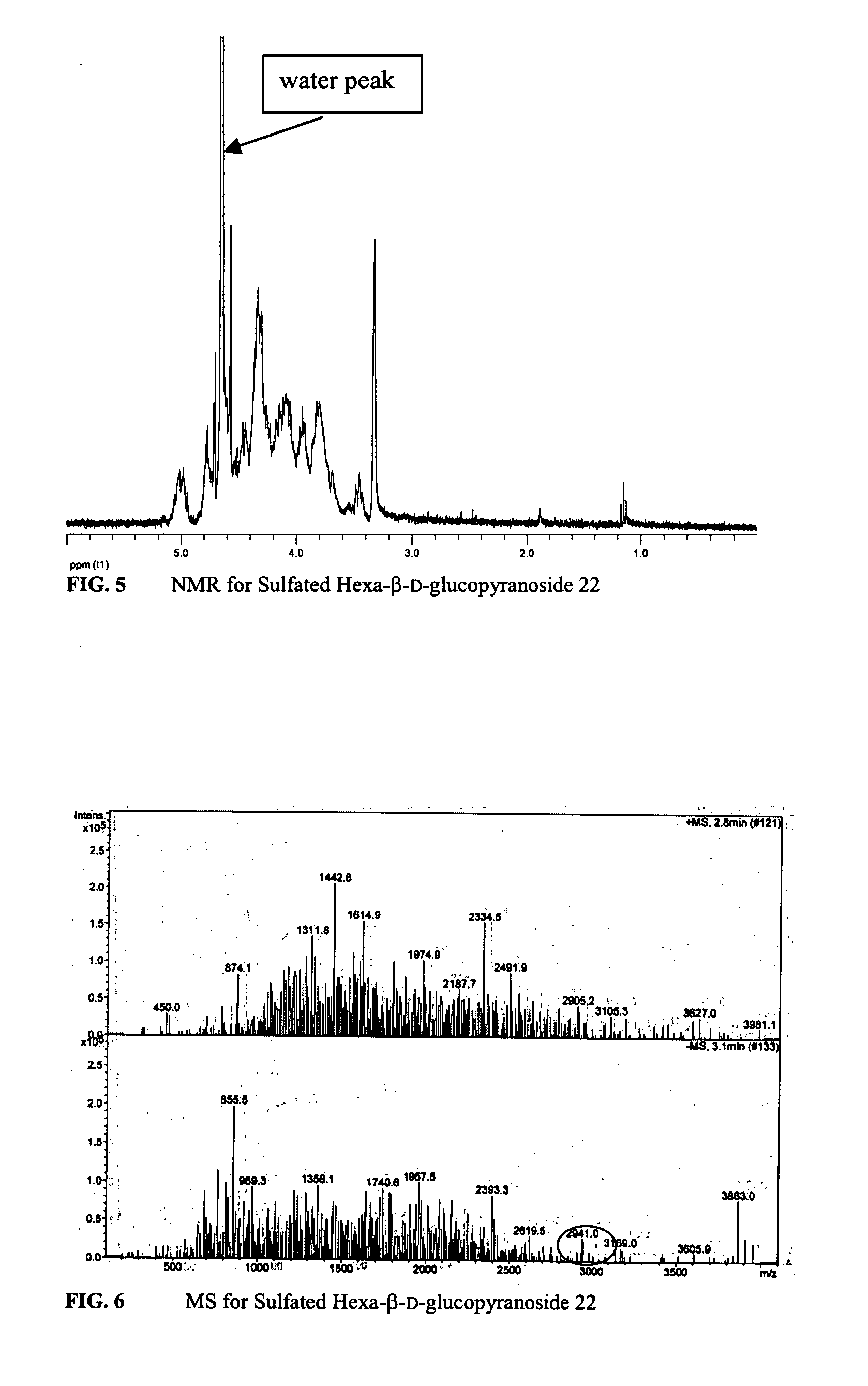
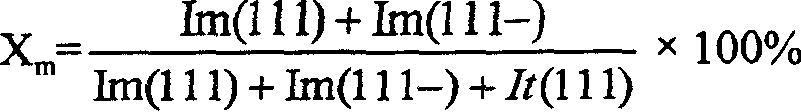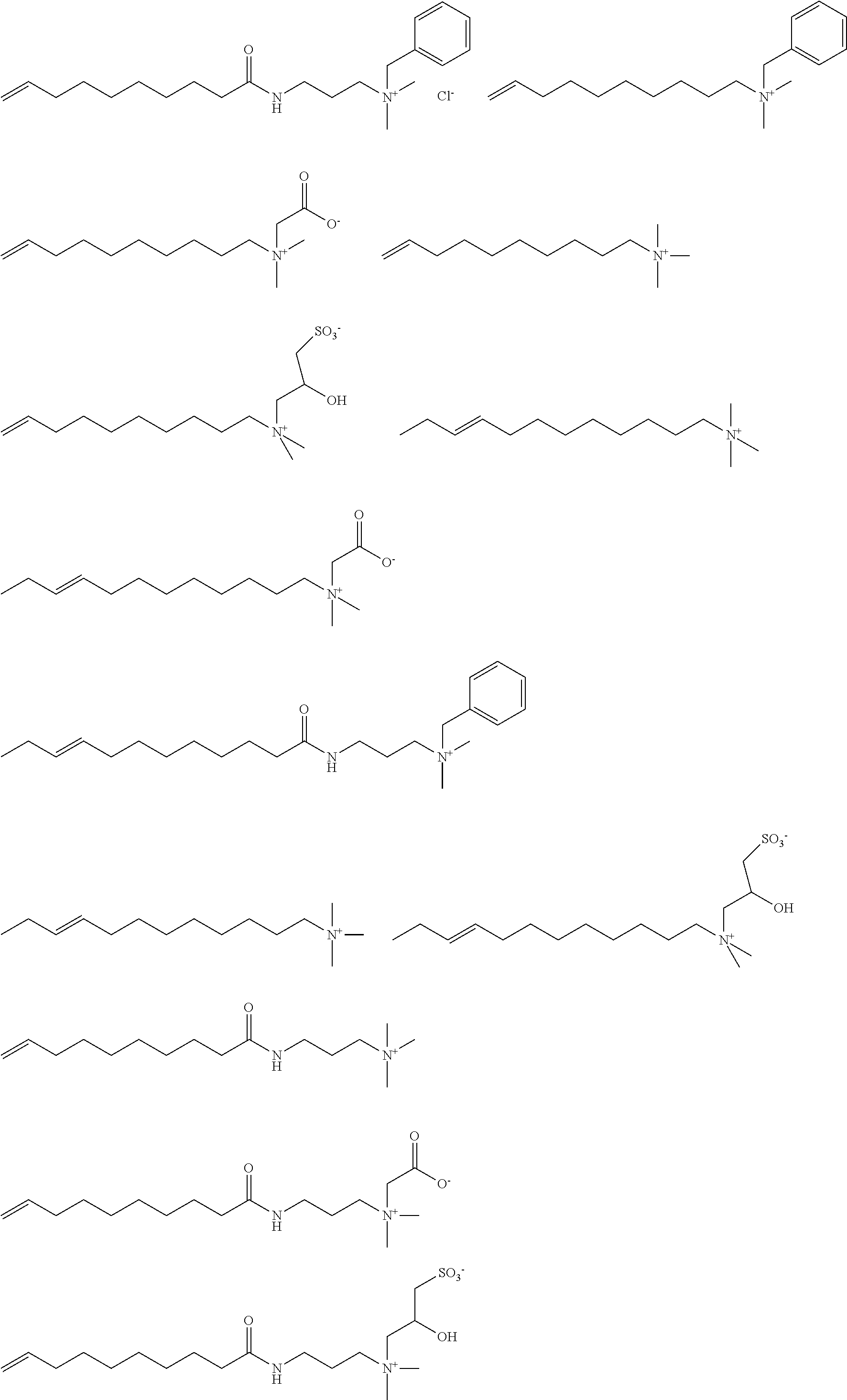Patents
Literature
588 results about "Sulfation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
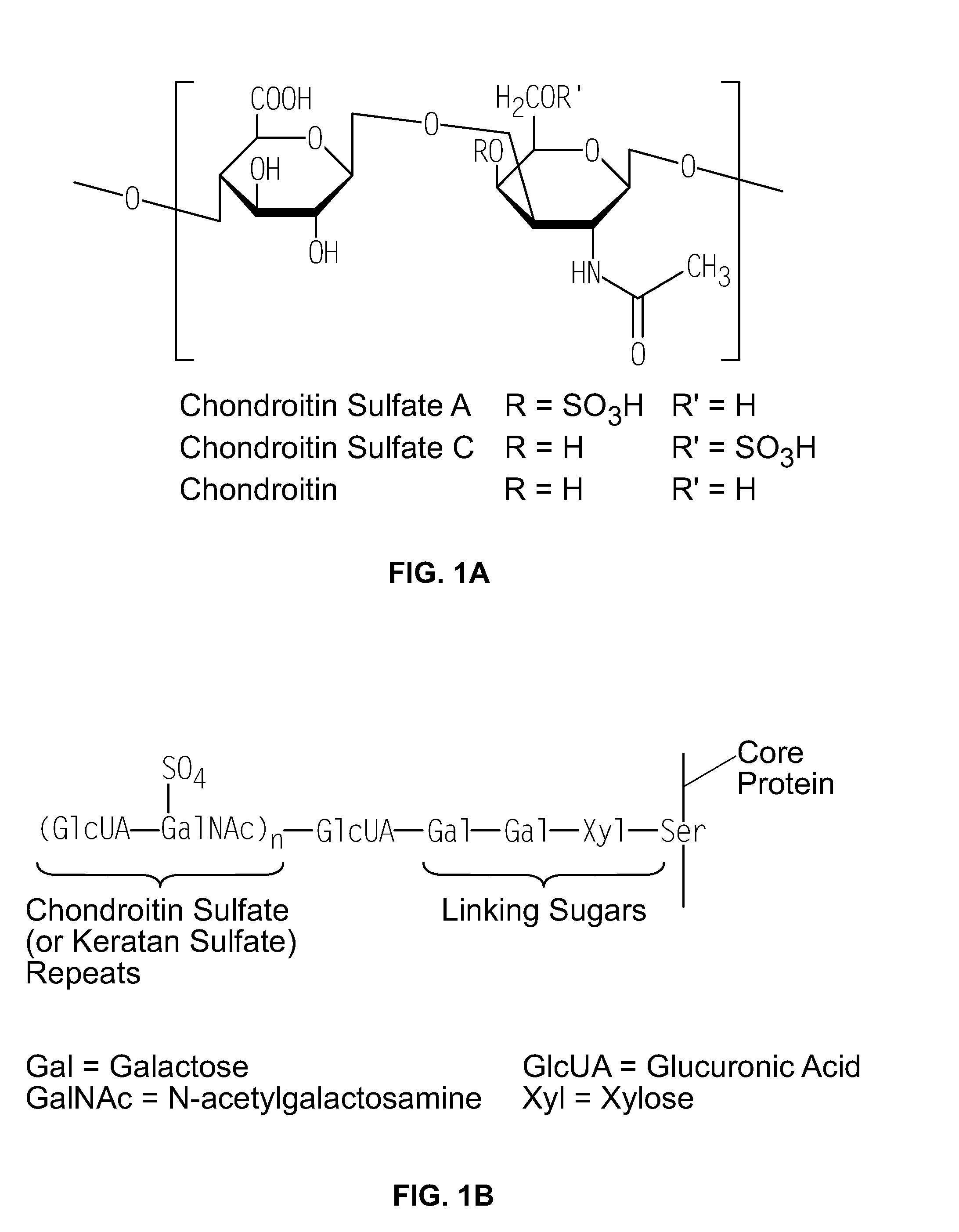
Sulfation or sulfurylation (not to be confused with sulfonation) in biochemistry is the enzyme-catalyzed conjugation of a sulfo group (not a sulfate or sulfuryl group) to another molecule. This biotransformation involves a sulfotransferase enzyme catalyzing the transfer of a sulfo group from a donor cosubstrate, usually 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS), to a substrate molecule's hydroxyl or amine. Sulfation is involved in a variety of biological processes, including detoxification, hormone regulation, molecular recognition, cell signaling, and viral entry into cells. It is among the reactions in phase II drug metabolism, frequently effective in rendering a xenobiotic less active from a pharmacological and toxicological standpoint, but sometimes playing a role in the activation of xenobiotics (e.g. aromatic amines, methyl-substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons). Another example of biological sulfation is in the synthesis of sulfonated glycosaminoglycans, such as heparin, heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and dermatan sulfate. Sulfation is also a possible posttranslational modification of proteins.
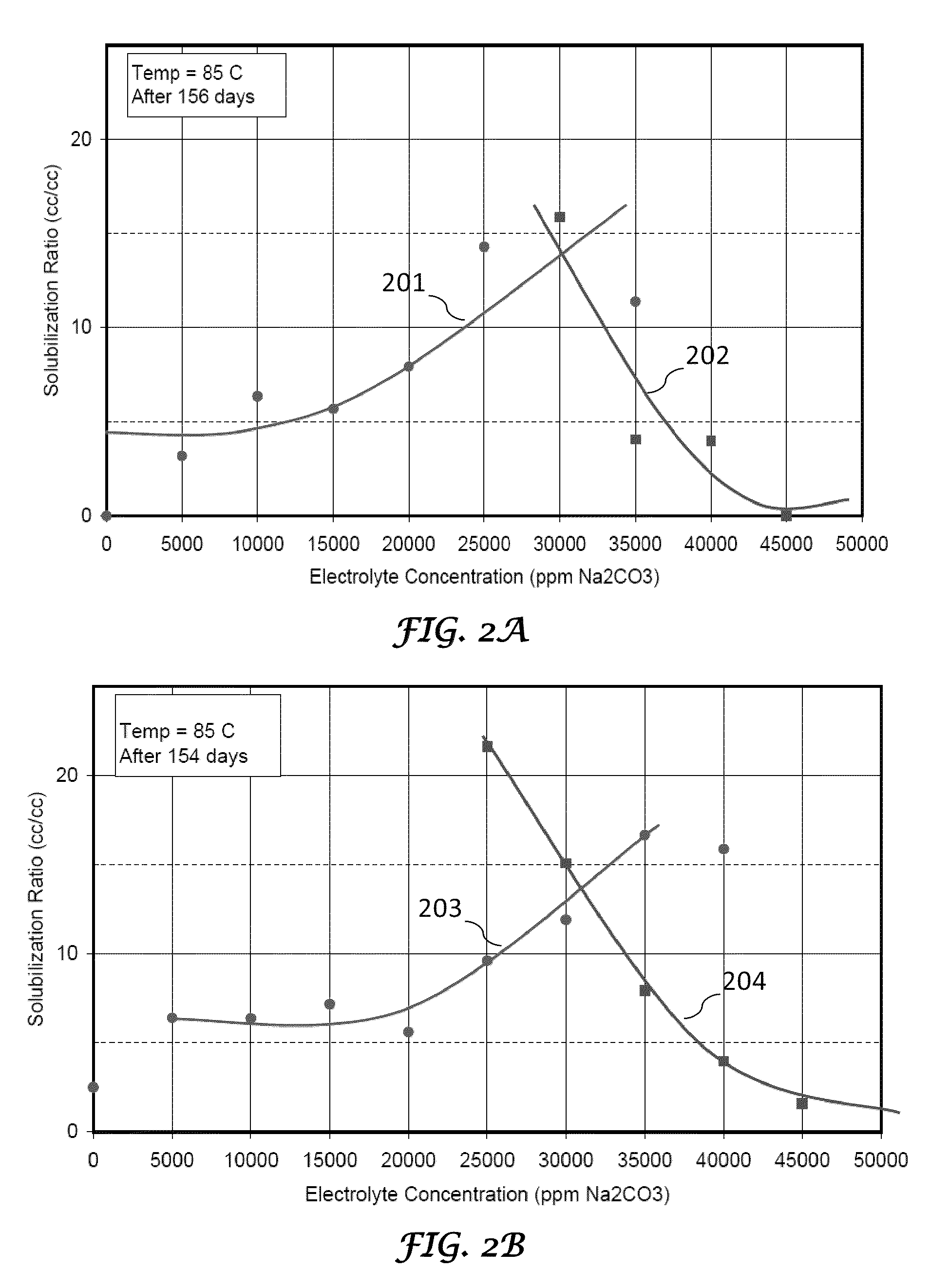
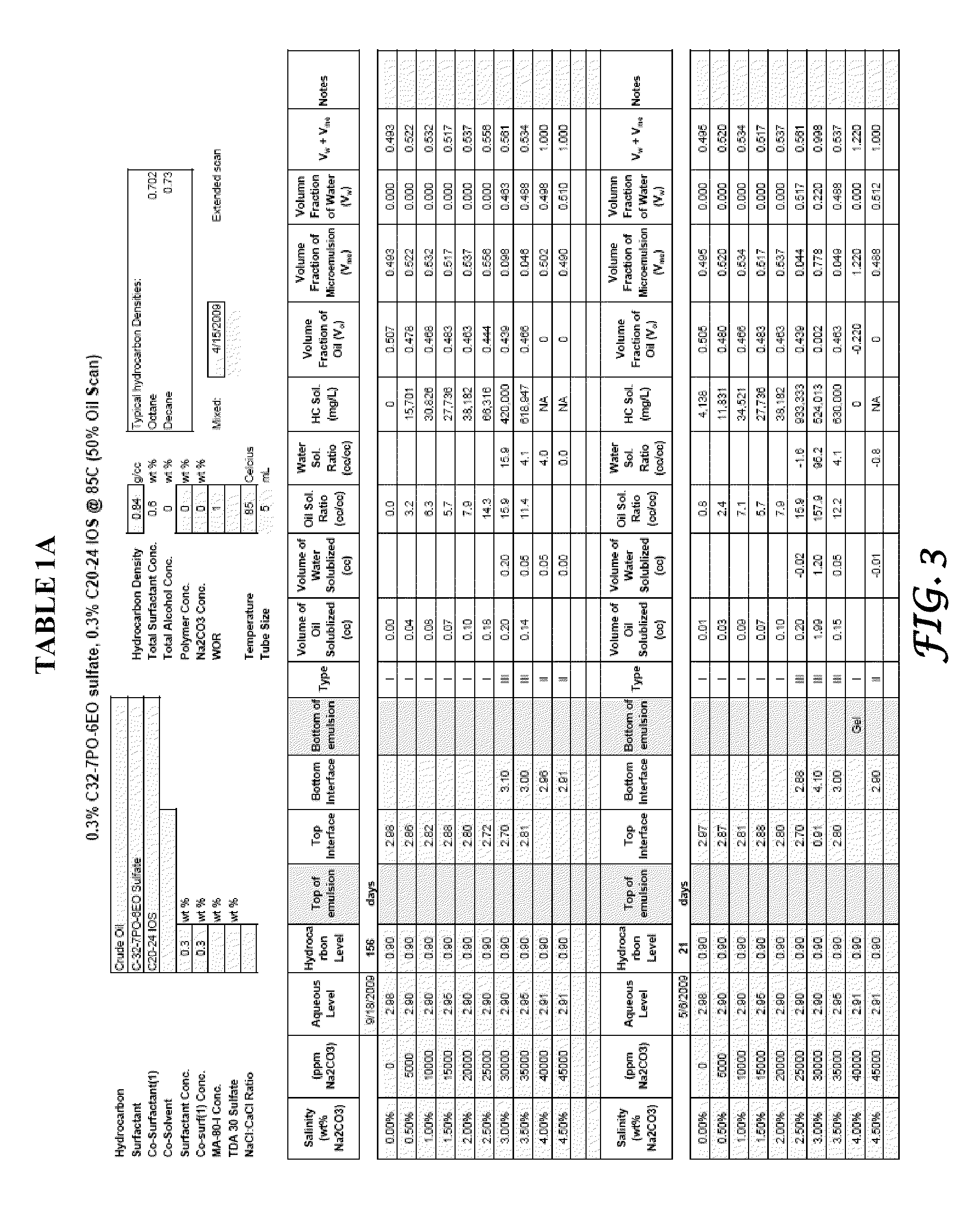
Method of manufacture and use of large hydrophobe ether sulfate surfactants in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) applications
ActiveUS8211837B2Improve usabilityLow costOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSulfationAlcohol
The present invention describes the method of making anionic ether sulfate surfactants by alkoxylation of a GA using PO and / or EO followed by a sulfation reaction. The GA of the present invention is made by a facile and inexpensive method that involves high temperature base catalyzed dimerization of a linear alcohol. The ether sulfate surfactants of the present invention find uses in EOR applications where it is used for solubilization and mobilization of oil and for environmental cleanup.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
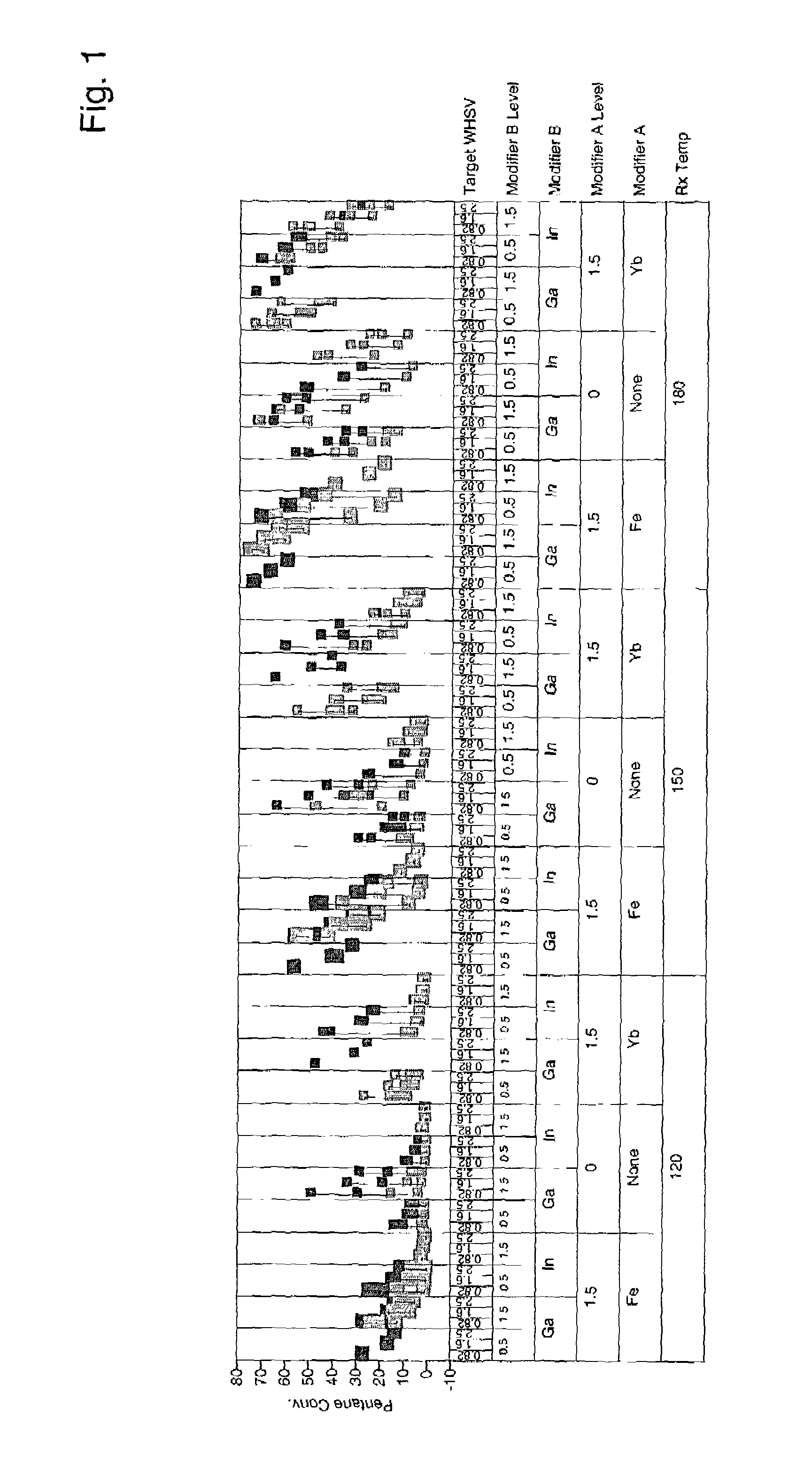
Solid-acid isomerization catalyst and process
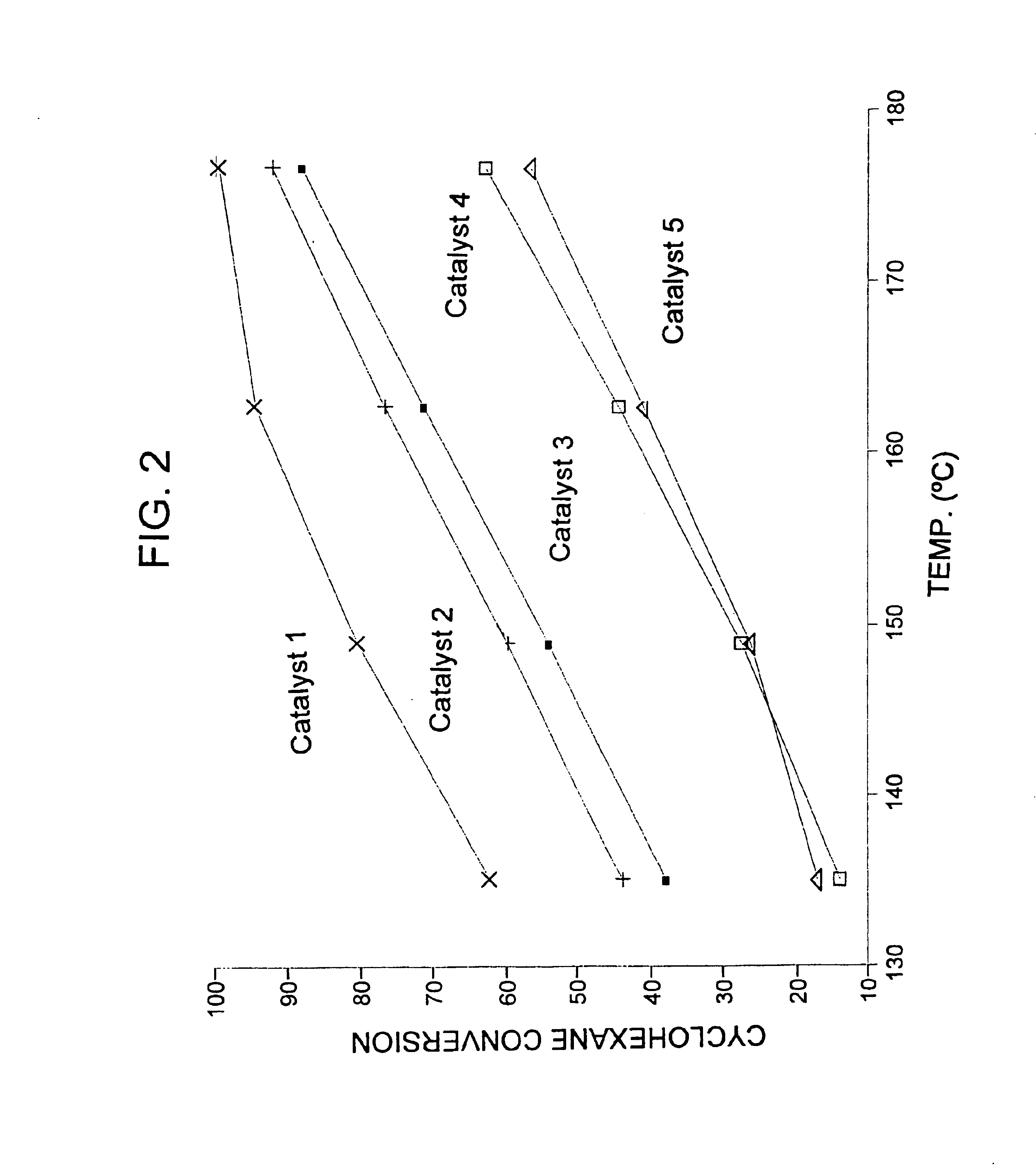
ActiveUS7041866B1Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneSulfation
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component comprising at least one Group III A (IUPAC 13) component, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Sulfated hyaluronic acid and esters thereof
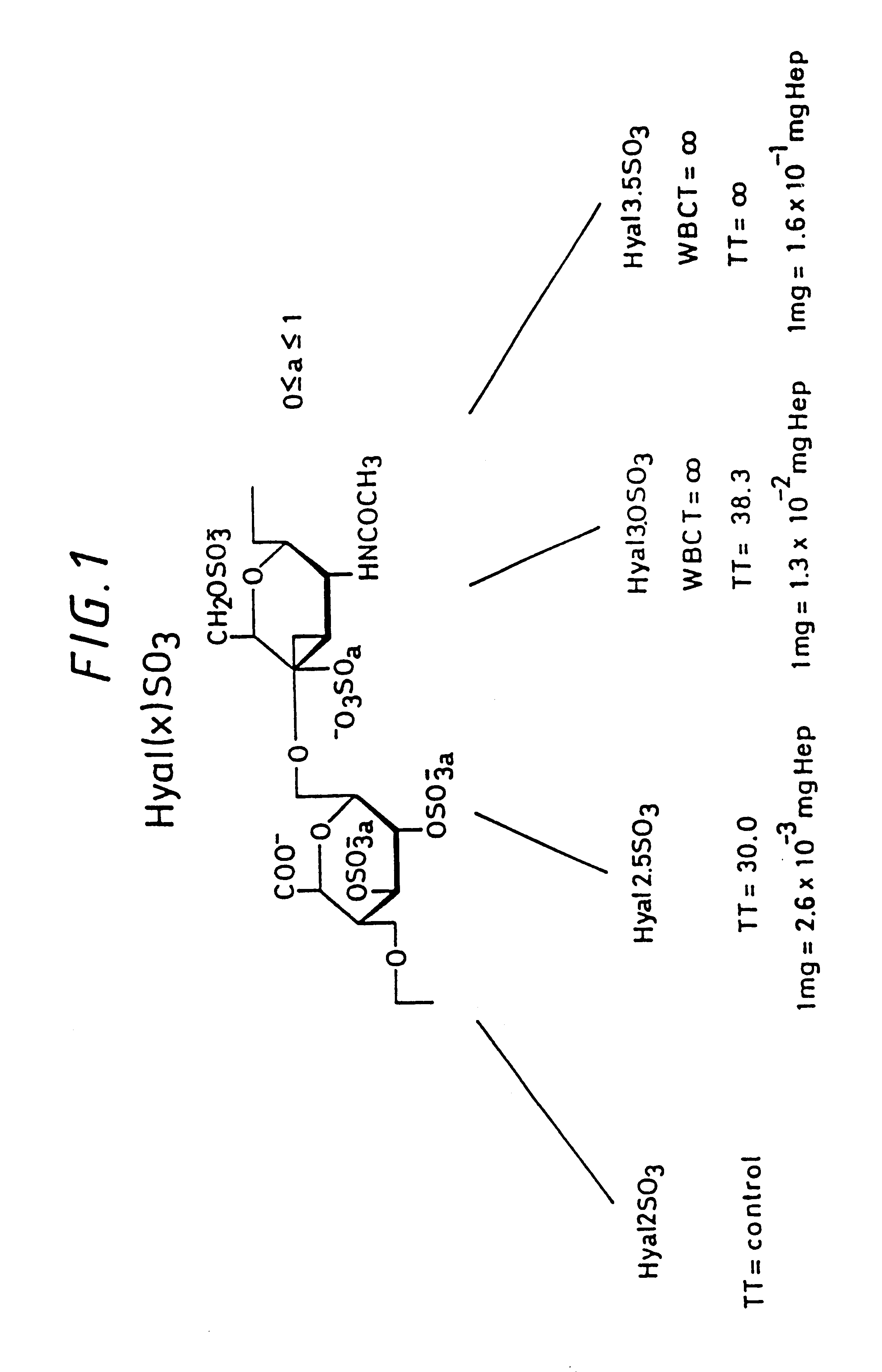
Hyaluronic acid, hyaluronate esters and salts thereof are sulfated such that the number of sulfate groups per monomeric unit is in the range of from 0.5 to 3.5. The sulfated derivatives exhibit anticoagulant and cell adhesion reduction properties, and may be used to prepare biomaterials.
Owner:FIDIA ADVANCED BIOPOLYMERS SRL
High-activity isomerization catalyst and process
InactiveUS6881873B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon by isomerisationAlkaneSulfation
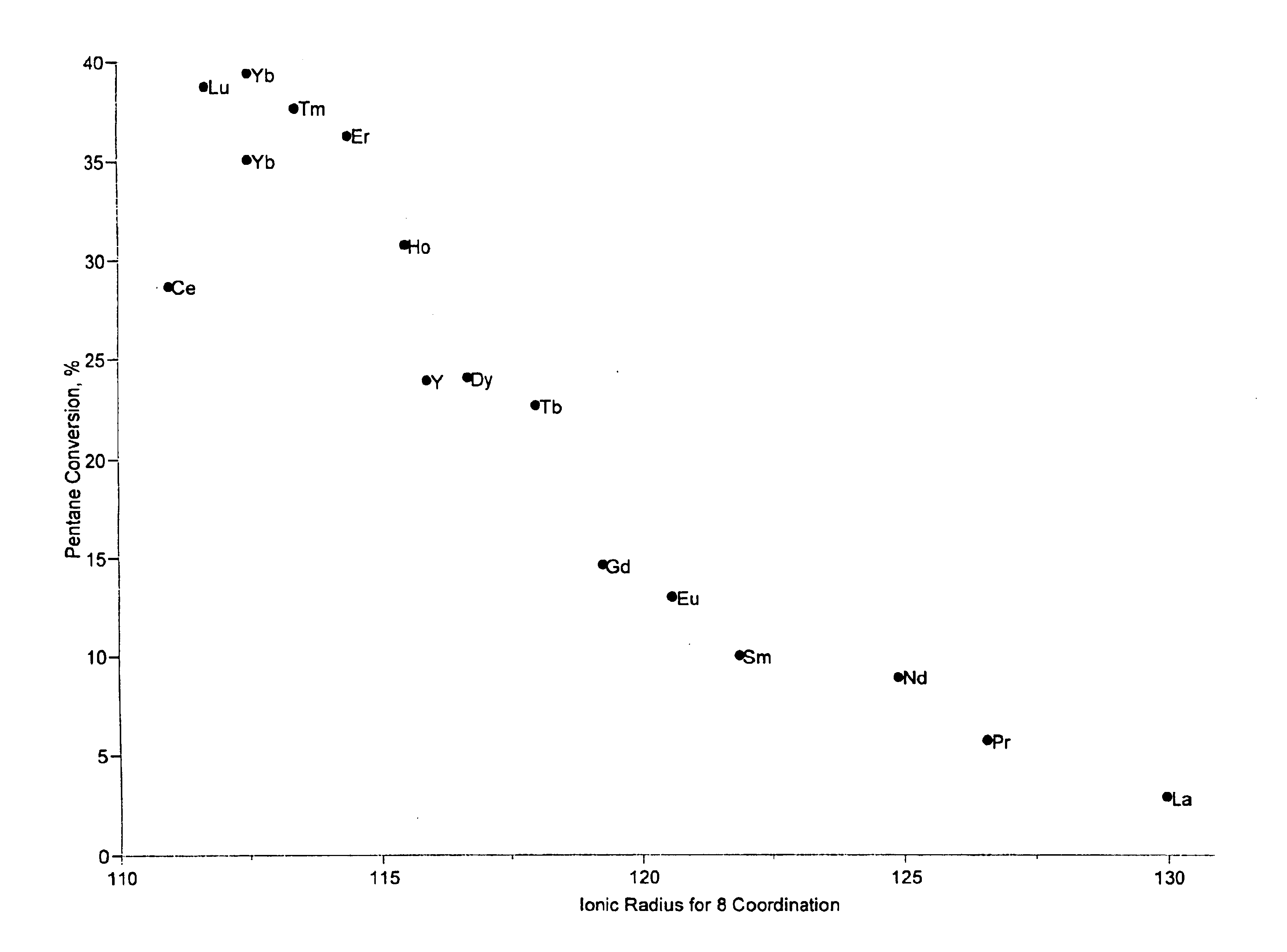
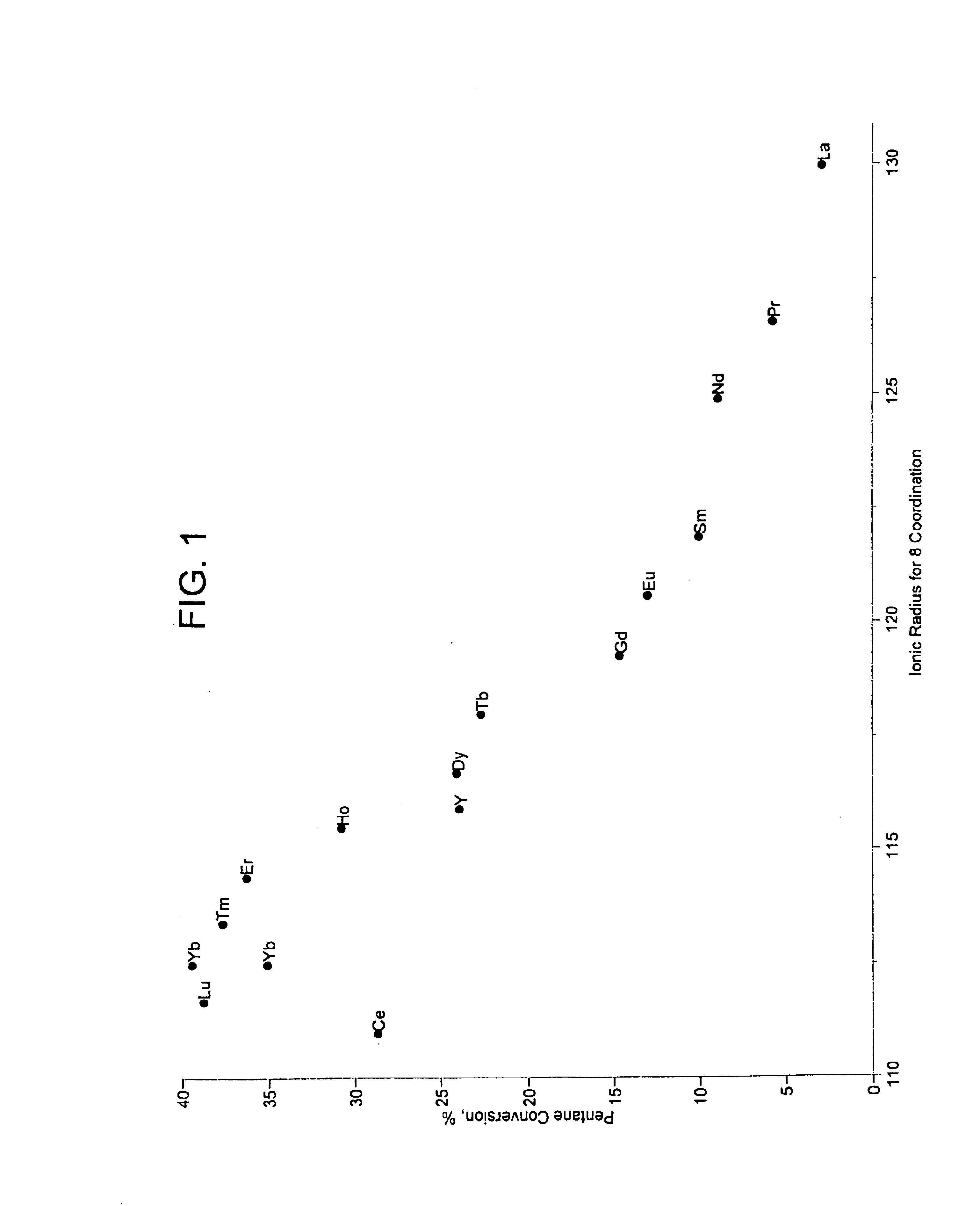
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component of at least one lanthanide element or yttrium component, which is preferably ytterbium, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Bi-modal Guerbet alkoxy sulfate surfactants
InactiveUS7119125B1Delayed reaction timeIncrease productionOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesSulfationAlcohol
The present invention relates to specific compositions made by the sulfation of alkoxylated crude guerbet alcohol mixtures that contain between 15% and 50% lower molecular weight alkoxylated alcohols. The lower molecular weight alcohols are the raw material alcohols used to make the guerbet. Sulfated compositions made from this specific bi-modal distribution have unique emulsification properties and experience minimal chromatographic separation when used in downhole applications.
Owner:OLENICK JR ANTHONY J +2
Branched, substantially unsaturated fatty alcohol sulfates
Branched, substantially unsaturated fatty alcohol sulfates are produced by a process which comprises the steps of: (a) dimerizing unsaturated C16-22 fatty acid to form a dimer fraction and a monomer fraction comprised of branched, substantially unsaturated fatty acids and straight chain saturated fatty acids, (b) removing the monomer fraction from the dimerization step, (c) converting the branched, substantially unsaturated fatty acids from step (b) into the corresponding fatty acid methyl esters, (d) hydrogenating the branched, substantially unsaturated fatty acid methyl esters with the double bonds intact to form the corresponding branched, substantially unsaturated fatty alcohols and (e) sulfating and neutralizing the branched, substantially unsaturated fatty alcohols. The fatty alcohol sulfates thus produced exhibit improved performance properties and greater oxidative stability than standard unsaturated fatty alcohol sulfates.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
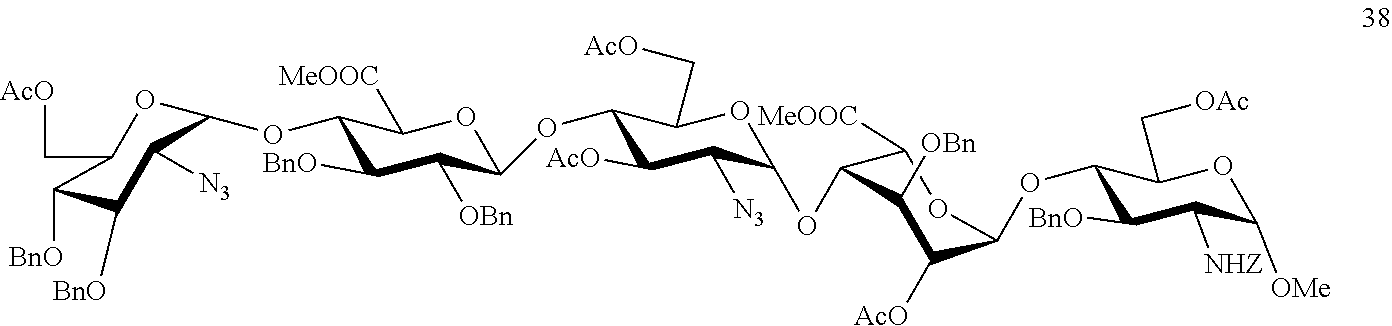
Derivatives of K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant activity
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 02379 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 6, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 6, 1998 PCT Filed May 9, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 43317 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 20, 1997Derivatives of the K5 polysaccharide having anticoagulant activity higher than heparin, obtained by a process including the steps of reacting: with an organic base a solution of K5 polysaccharide N-deacetylated, N-sulfated and epimerized at least to an iduronic acid content of 50% treating with a sulfating agent to obtain the N-resulfation of the possible N-desulfated groups.
Owner:INALCO SPA
Composition and method for treating occlusive vascular diseases, nerve regeneration, and wound healing
A composition and a method of treating a subject with respect to a pathological condition comprised by the subject. The composition comprises a sulfated saccharide conjugated to a polymer. The method comprises administering to the subject a composition comprising a sulfated saccharide conjugated to a polymer or a sulfated saccharide. The sulfated saccharide has a molecular weight less than 5000 Dalton.
Owner:MOUSA SHAKER +1
Lead-carbon battery negative pole preparation method based on ZIF-8 zeoliteimidazate framework porous carbon nanomaterial
ActiveCN106229492AImprove cycle performanceInhibition of irreversible sulfationLead-acid accumulator electrodesHigh ratePorous carbon
The invention provides a lead-carbon battery negative pole preparation method based on a ZIF-8 zeoliteimidazate framework porous carbon nanomaterial and belongs to the technical field of lead-carbon battery negative polematerials. The ZIF-8 zeoliteimidazate framework porous carbon nanomaterial is a porous carbon material prepared by conducting annealing on a metal organic framework material synthesized by using zinc as metal ions and using 2-methyl imidazole as an organic ligand under protective atmosphere. Lead and the ZIF-8 zeoliteimidazate framework porous carbon nanomaterial are grinded and mixed in a ball mill. A lead-carbon battery can effectively inhibit irreversible sulfation occurred on a negative pole plate during charging and discharging and has superior high rate capability and excellent cycle performance. A negative pole can be used for large commercial energy storage lead-carbon batteries.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Anti-inflammatory compositions for treating multiple sclerosis
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cells and followed by secretion of inflammatory biochemicals from the activated mast cells, the compositions containg one or more of a flavone or flavonoid glycoside a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan, an unrefined olive kernel extract that increases absorption of these compositions in various routes of administration, a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, S-adenosylmethionine, a histamine-1 receptor antagonist, a histamine-3 receptor agonist, an antagonist of the actions of CRH, a long-chain unsaturated fatty acid, a phospholipid, Krill oil, a polyamine, glutiramer acetate and interferon. Certain of the present compositions are useful in protecting against the neuropathological components of multiple sclerosis and similar inflammatory neurological diseases.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
Compositions and methods for regulation of active TNF- alpha
InactiveUS6020323AReduced activityReduced availabilityEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideSulfationMedicine
Substances comprising disaccharides and substances comprising carboxylated and / or sulfated oligosaccharides in substantially purified form, and methods of using same, are disclosed for the regulation of cytokine activity in a host. For instance, the secretion of active Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF- alpha ) can be either inhibited or augmented selectively by administration to the host of an effective amount of a substance of the invention. Thus, the present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and their use for the prevention and / or treatment of pathological processes involving the induction of active cytokine secretion, such as TNF- alpha . The invention also relates to the initiation of a desirable immune system-related response by the host to the presence of activators, including pathogens. The substances and pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention may be administered daily, at very low effective doses, typically below 0.1 mg / kg human, or at intervals of up to about 5-8 days, preferably once a week.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Composition for protection against superficial vasodilator flush syndrome
InactiveUS20050220909A1Promote absorptionBiocideCosmetic preparationsChondroitin Sulfate CVascular dilatation
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cells and followed by secretion of inflammatory biomolecules from the activated mast cells, composed of a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan such as shark cartilage chondroitin sulfate C, an unrefined olive kernel oil / extract that increases absorption of these compositions in various routes of administration, and one or more of a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, a flavone such as quercetin, S-adenosylmethionine, a histamine-1 receptor antagonist, a histamine-3 receptor agonist, an antagonist of the actions of CRH, caffeine, and a polyamine.
Owner:THEOHARIDES THEOHARIS C
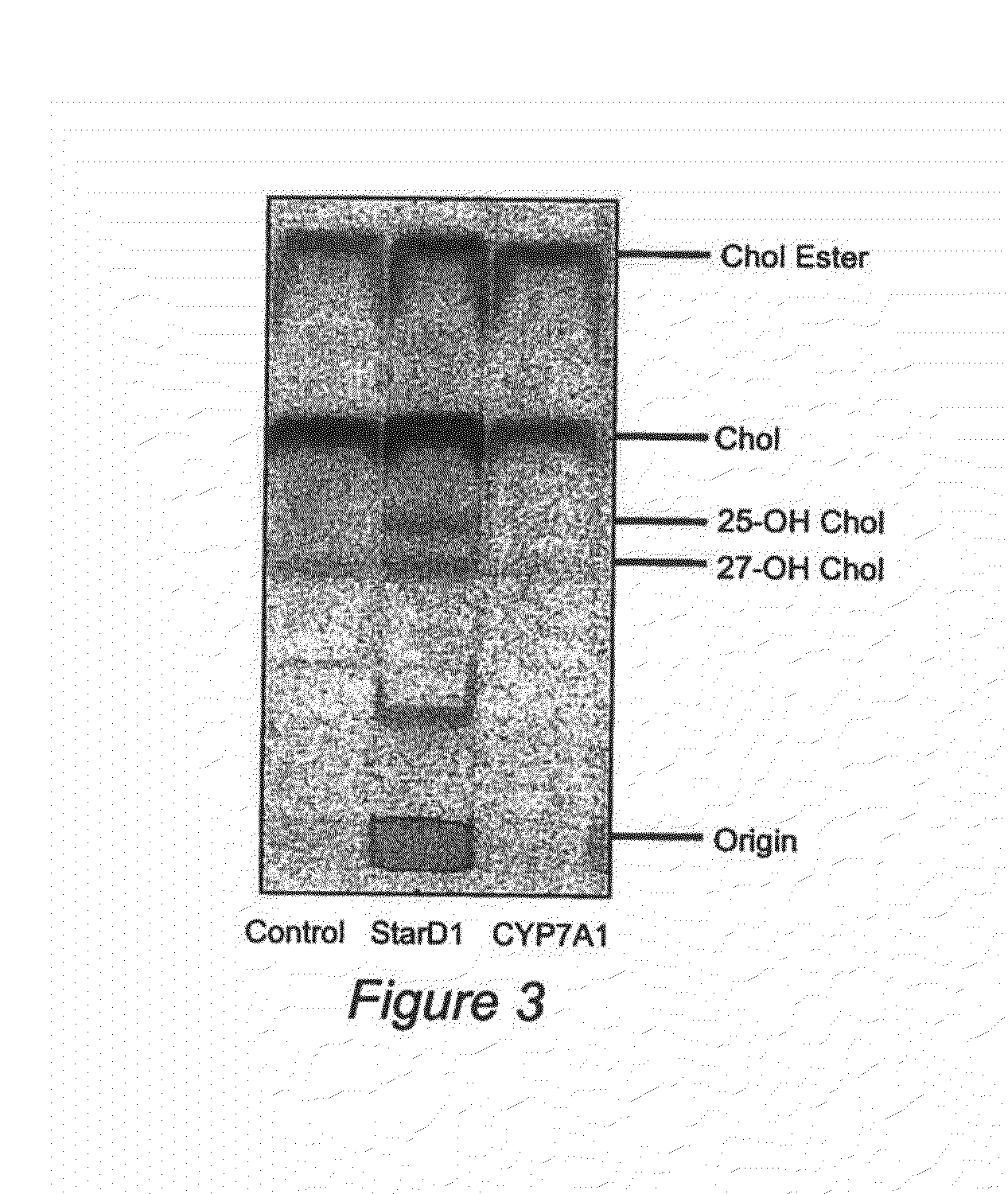
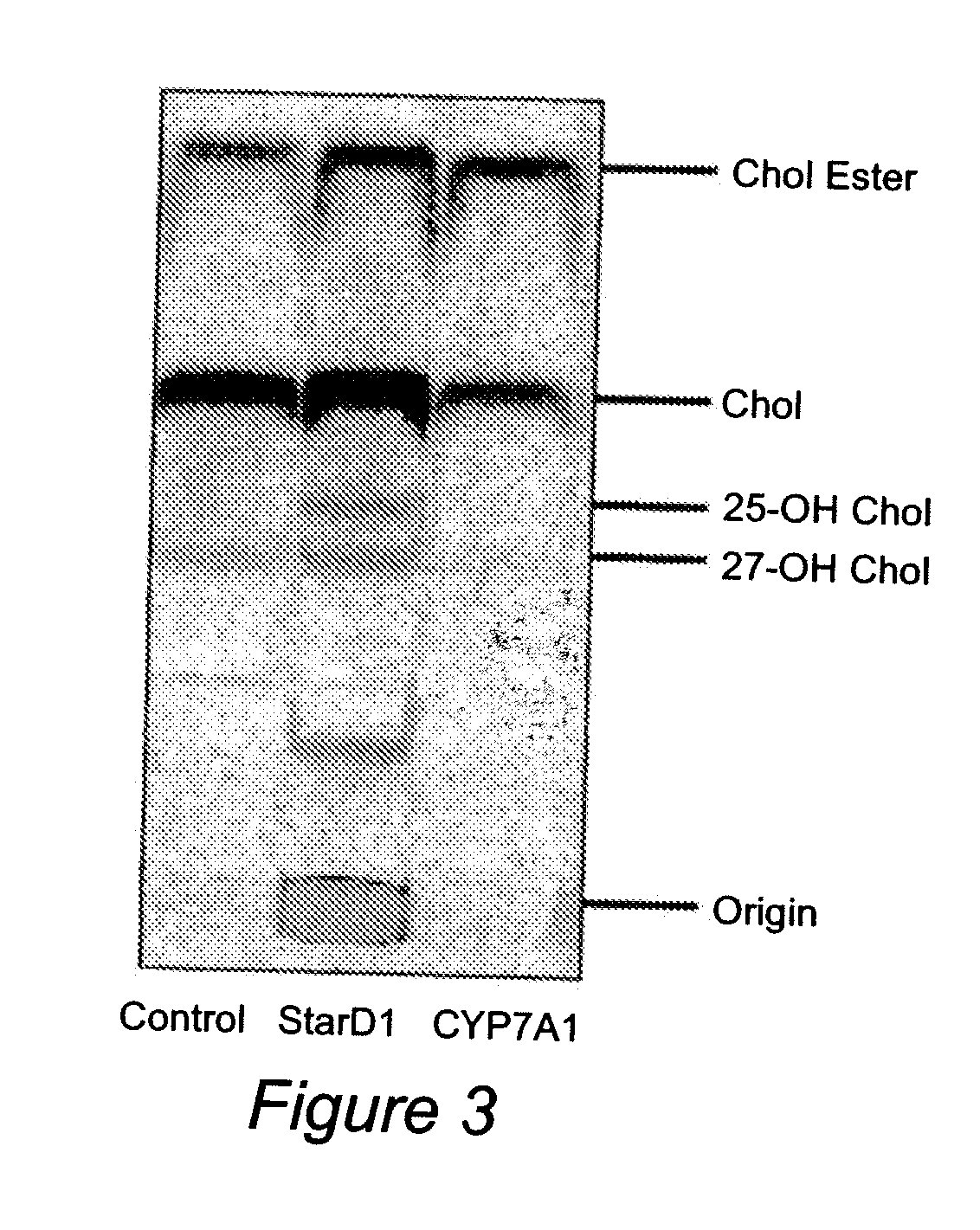
Nuclear sulfated oxysterol, potent regulator of lipid homeostasis, for therapy of hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglycerides, fatty liver diseases, and atherosclerosis
ActiveUS8399441B2Lower Level RequirementsImprove suppression propertiesOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderLipid formationMetabolite
The sulfated oxysterol 5-cholesten-3β, 25-diol 3-sulphate, a nuclear cholesterol metabolite that decreases lipid biosynthesis and increases cholesterol secretion and degradation, is provided as an agent to lower intracellular and serum cholesterol and / or triglycerides, and to prevent or treat lipid accumulation-associated inflammation and conditions associated with such inflammation. Methods which involve the use of this sulfated oxysterol to treat conditions associated with high cholesterol and / or high triglycerides and / or inflammation (e.g. hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, atherosclerosis, etc.) are also provided.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
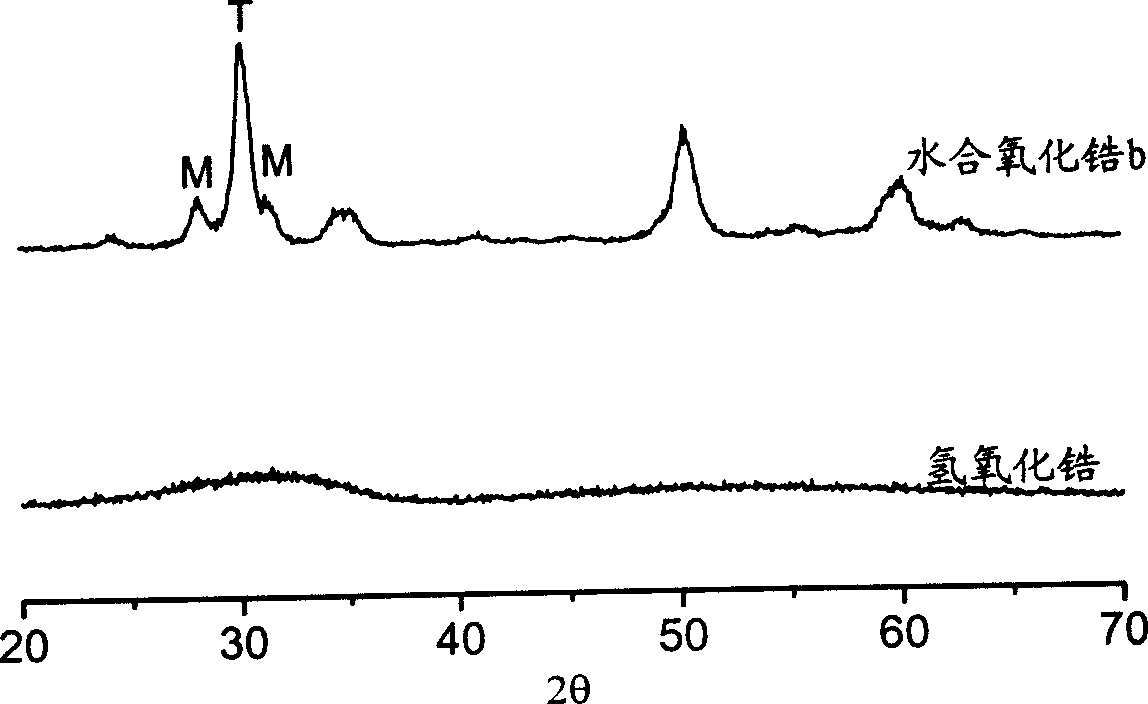
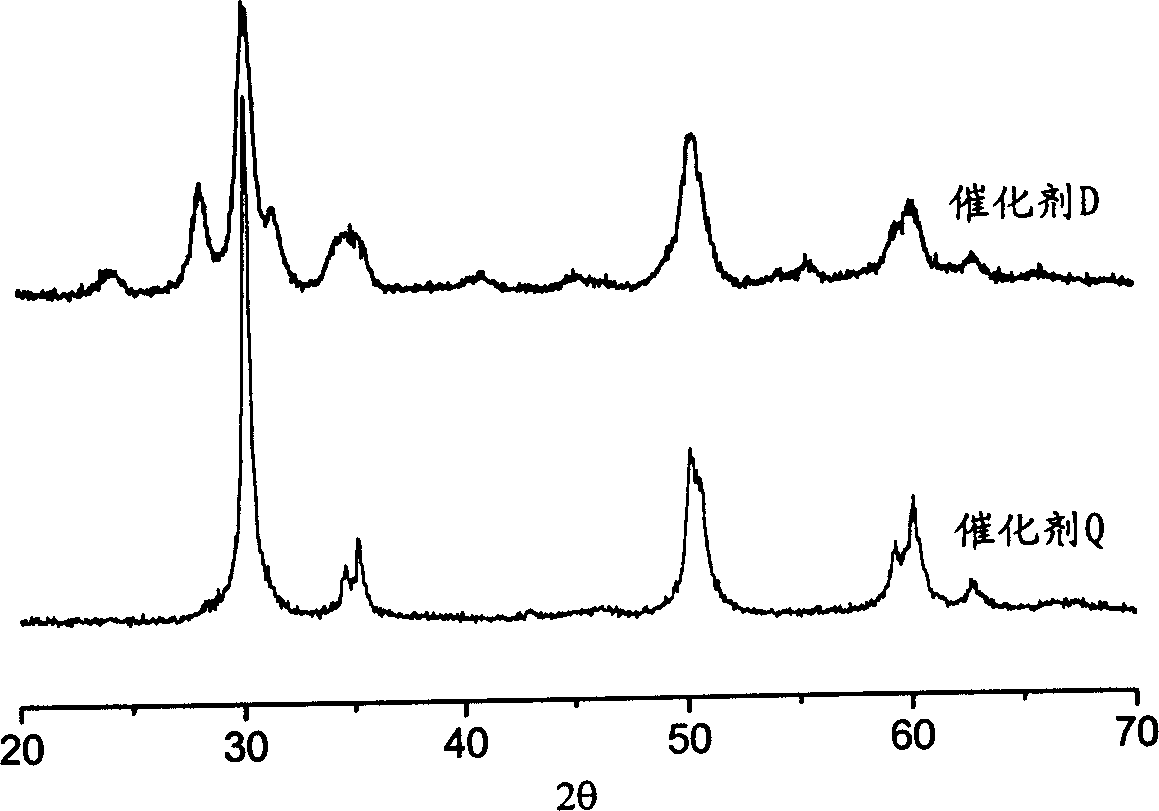
Solid strong acid catalyst and its preparing method
InactiveCN1524616ALarge specific surface areaReduce acid center distribution densityPhysical/chemical process catalystsAlkaneSulfation
The invention is a solid strong-acid catalyst, containing a mixed oxide sulfated by sulfocompound, its sulfur content 1.0-2.5 m%, where the mixed oxide is composed of zirconia, silicon oxide and alumina in the dry-based mass ratio of 30-90 to 1-30 to 9-40, and the monoclinic crystal phase proportion of zirconia is 10-70 m% and the rest square crystal phases. It is applied to isomerization reaciton of C4-C7 alkanes and has higher isomerization activity and selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Super lead carbon battery with active carbon negative electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101764263AAlleviate salinizationImprove low temperature performanceFinal product manufactureLead-acid accumulator electrodesSulfationActivated carbon
The invention discloses a super lead carbon battery with an active carbon negative electrode and a preparation method thereof. The negative electrode of the supper lead carbon battery comprises the active carbon negative electrode and a lead negative electrode which are internally parallel. A positive electrode of the battery adopts PbO2 as an active substance. A separator adopts an AGM diaphragm. Electrolyte adopts 1.0-1.4g / cm<3> sulfuric acid. By introducing the active carbon negative electrode into the lead negative electrode in parallel internally to act as the active substance, the invention can greatly promote the charge acceptance ability of the negative electrode, effectively improve the low temperature property of the super lead carbon battery, and greatly mitigate sulfation phenomenon in the negative electrode, so that the deep-cycle life can reach more than 1,800 times. Compared with cost of an inorganic system carbon-carbon symmetric mode and a nickel electrode-carbon mixed alkali system, the invention can greatly reduce the material cost of products. Compared with a traditional lead-acid battery, the invention can greatly prolong recycling lifetime of products and have obvious performance price ratio advantage.
Owner:NANJING SHUANGDENG SCI TECH DEV RES INST
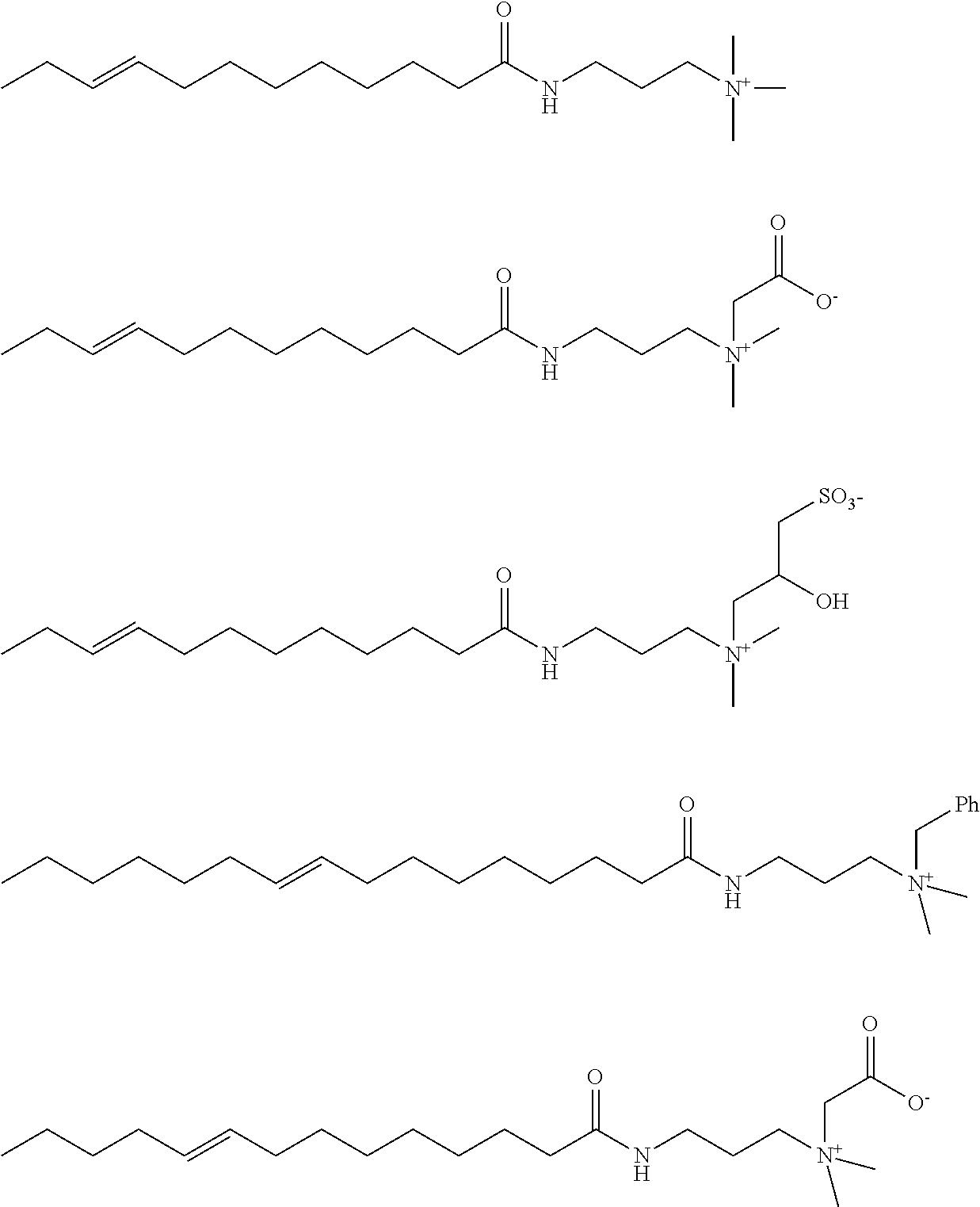
Quaternized fatty amines, amidoamines and their derivatives from natural oil metathesis
Quaternary ammonium, betaine, or sulfobetaine compositions derived from fatty amines, wherein the fatty amine is made by reducing the amide reaction product of a metathesis-derived C10-C17 monounsaturated acid, octadecene-1,18-dioic acid, or their ester derivatives and a secondary amine, are disclosed. Quaternary ammonium, betaine, or sulfobetaine compositions derived from fatty amidoamines, wherein the amidoamine is made by reacting of a metathesis-derived C10-C17 monounsaturated acid, octadecene-1,18-dioic acid, or their ester derivatives and an aminoalkyl-substituted tertiary amine, are also disclosed. The quaternized compositions are advantageously sulfonated or sulfated. In one aspect, the ester derivative of the C10-C17 monoun-saturated acid or octadecene-1,18-dioic acid is a lower alkyl ester. In other aspects, the ester derivative is a modified triglyceride made by self-metathesis of a natural oil or an unsaturated triglyceride made by cross-metathesis of a natural oil with an olefin. The quaternary ammonium, betaine, and sulfobetaine compositions and their sulfonated or sulfated derivatives are valuable for a wide variety of end uses, including cleaners, fabric treatment, hair conditioning, personal care (liquid cleansing products, conditioning bars, oral care products), antimicrobial compositions, agricultural uses, and oil field applications.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
Management of thermal fluctuations in lean NOx adsorber aftertreatment systems
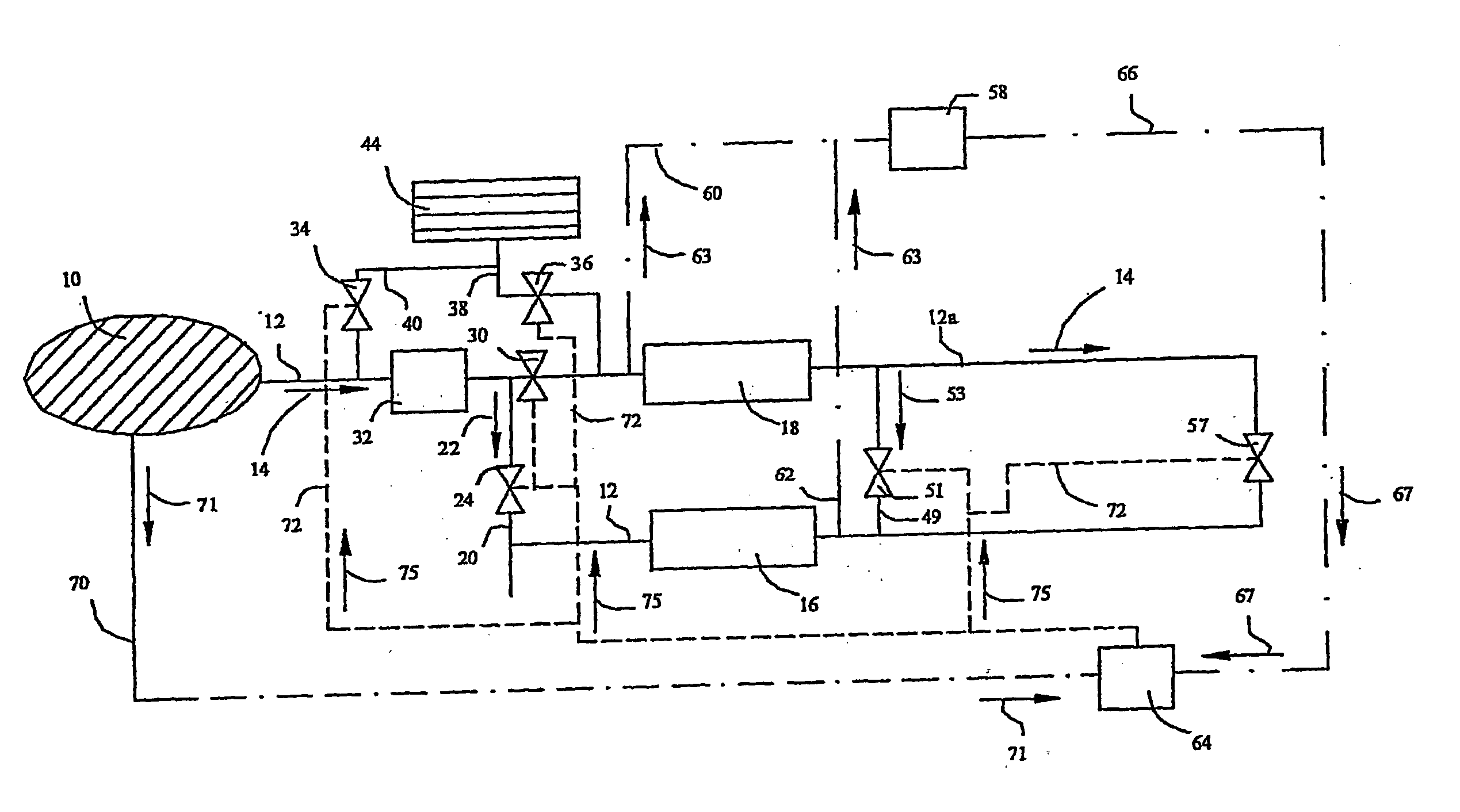
InactiveUS20060053776A1Nitrous oxide captureNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSulfationCompound (substance)
A method and apparatus manage heat in exhaust gas in an aftertreatment system that employs a lean NOx adsorber. A de-sulfation hot line and cooling line are employed to control exhaust gas temperatures for adsorption, regeneration and de-sulfation cycles of the aftertreatment system where each cycle can require different chemical and exhaust gas temperatures independent of the engine operation. The method and apparatus include a SOx adsorber to provide greater system durability.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Process for the synthesis of unprotected pentasaccharides from a protected pentasaccharide precursor
InactiveUS20110306757A1Short processing timeGood reproducibilitySugar derivativesEsterified saccharide compoundsSulfationCombinatorial chemistry
Procedure for the synthesis of deprotected pentasaccharides from a protected precursor pentasaccharide through a reaction procedure having five stages whereamong is included an N-sulphation of amino groups and a hydrogenolysis of benzyl groups. Through this procedure a drastic reduction is achieved in the total synthesis time in comparison with the process traditionally employed, together with increased reproducibility thereof, permitting the standardisation thereof.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
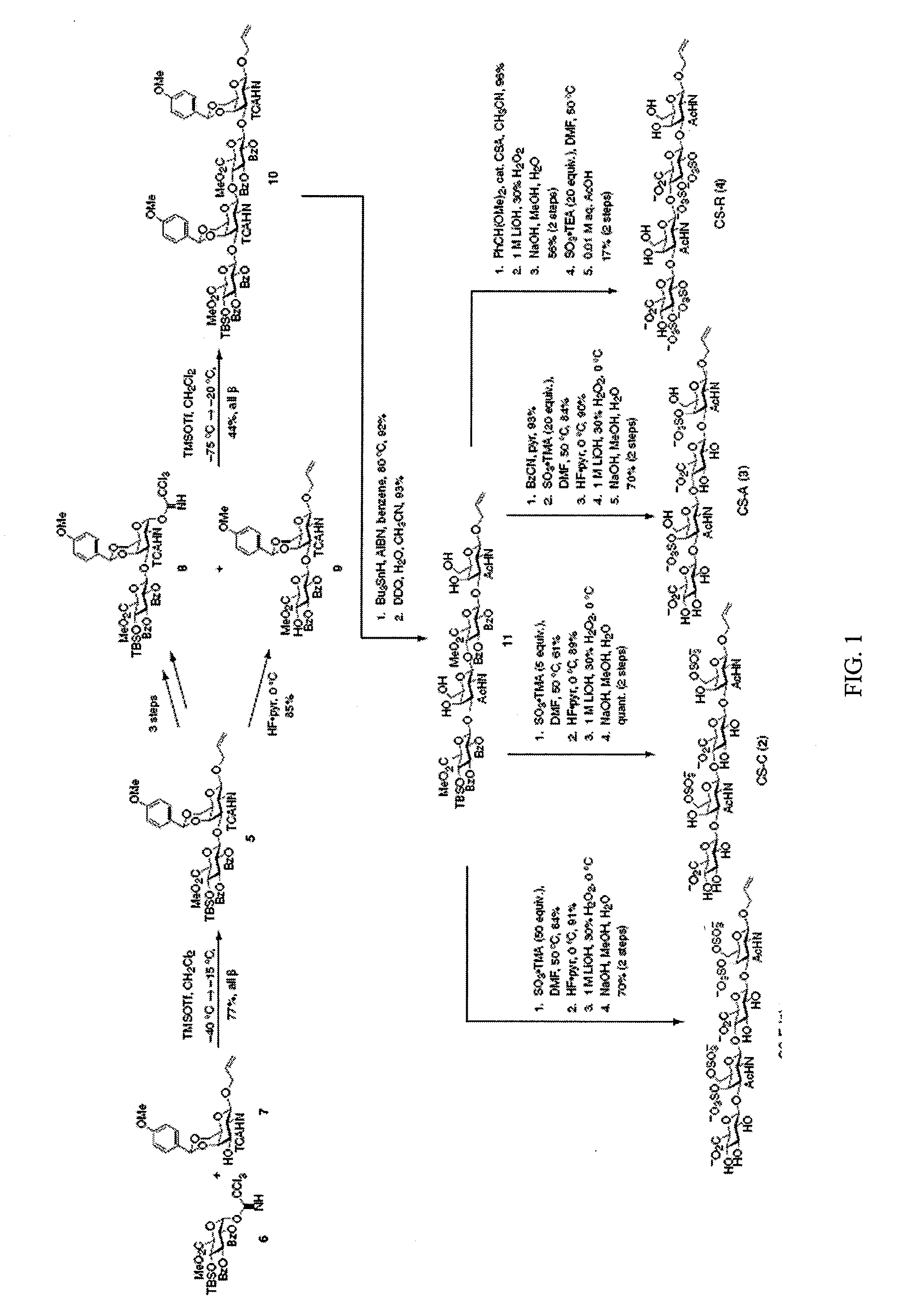
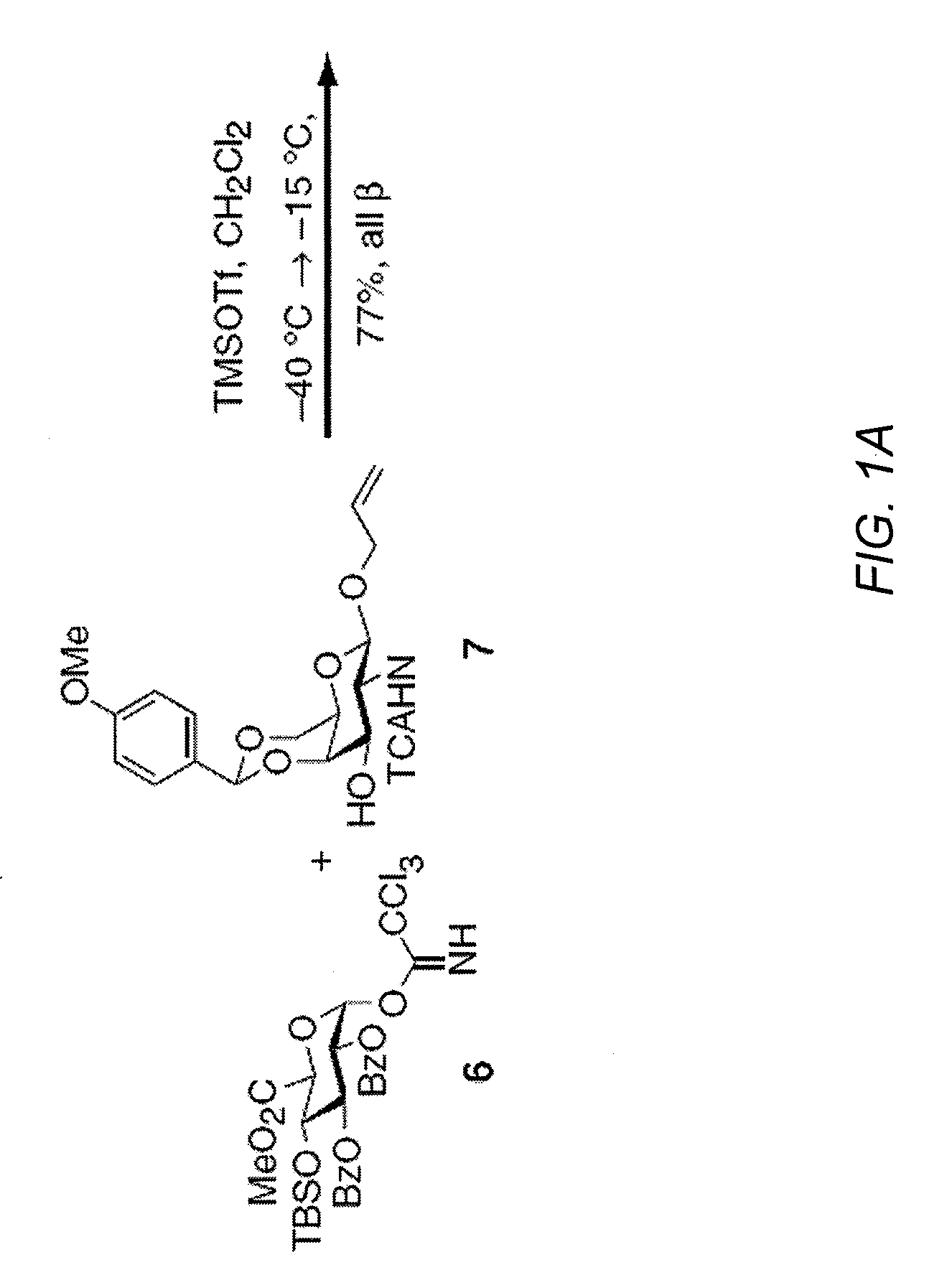
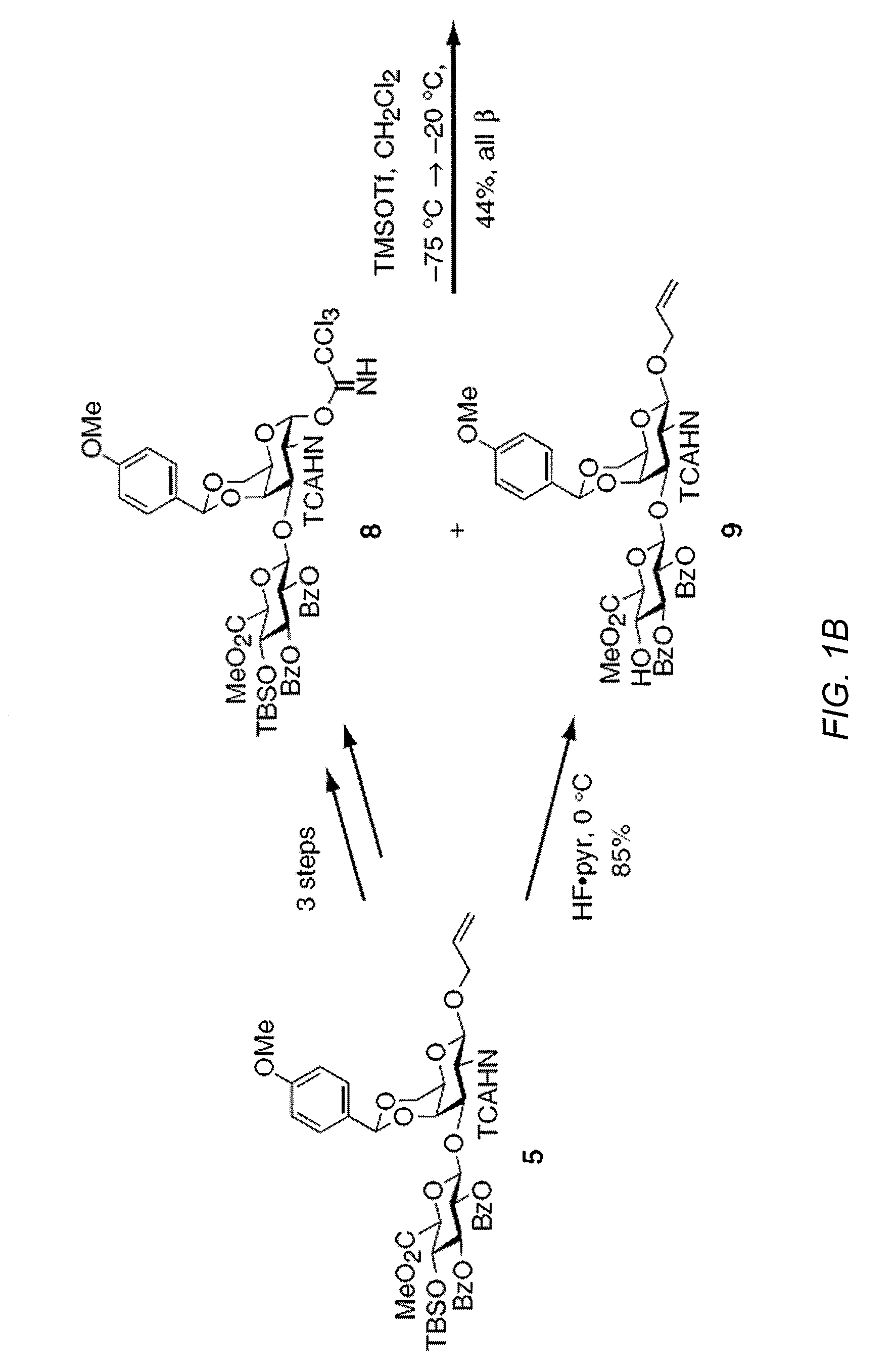
Chondroitin sulfate binding proteins and modulators thereof
Chondroitin sulfate polysaccharides with defined sulfation patterns can be synthesized. These chondroitin polysaccharides can be used to identify chondroitin sulfate binding proteins. Further, compounds that modulate the activity of chondroitin sulfate binding proteins can be identified. For example, TNF-α was found to bind specifically to CS-E and CS-E can be used to modulate the interaction of TNF-α with the TNF receptor.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Specific human antibodies
The present invention provides antibodies that bind an epitope of PSGL-1 comprising the motif D-X-Y-D, wherein X represents any amino acid or the covalent linkage between D and Y, and Y is sulfated, which antibody can be complexed with one or more copies of an agent. The antibodies of the invention can be used in a method of inducing antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity and / or stimulating natural killer (NK) cells or T cells. In addition, by administering these antibodies to a patient in need thereof, a method of inducing cell death is provided. A method of preventing infection by a virus (e.g., HIV) by administering to a patient in need thereof an antibody of the present invention is also provided. The, present invention also provides a method of introducing an agent into a cell that expresses sulfated PSGL-1 by coupling or complexing an agent to an antibody of the present invention and administering the complex to the cell. Finally, the present invention provides methods of diagnosis, prognosis and staging using the present antibodies.
Owner:BIO TECH GENERAL ISRAEL
Negative plate of lead-carbon battery
ActiveCN102856533AExtended service lifeIncrease profitLead-acid accumulator electrodesFiberHigh rate
The invention discloses a negative plate of a lead-carbon battery and a preparation method thereof. The negative plate consists of lead powder, active carbon, carbon black, barium sulfate, sodium lignosulfonate, humic acid, short fiber and sulfuric acid. The battery prepared by the negative plate has the advantages that the charging acceptance can be effectively improved, the sulfation phenomenon of the negative electrode under high-rate partial state of charge (HRPSoC) is effectively relieved, the times of 2C charge-discharge rate circulation (3%DOD) under 50% state of charge can reach 18442, and compared with the traditional lead-acid storage battery, the cycle life can be prolonged by more than two times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NARADA POWER SOURCE CO LTD +1
Anti-inflammatory composition for treating pelvic endometriosis
InactiveUS20050220912A1Promote absorptionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseChondroitin Sulfate C
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cells and followed by secretion of inflammatory biomolecules from the activated mast cells, composed of a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan such as shark cartilage chondroitin sulfate C, an unrefined olive kernel oil / extract that increases absorption of these compositions in various routes of administration, and one or more of a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, a flavone such as quercetin, S-adenosylmethionine, a histamine-1 receptor antagonist, a histamine-3 receptor agonist, an antagonist of the actions of CRH, caffeine, and a polyamine.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
Methods for synthesis of sulfated saccharides
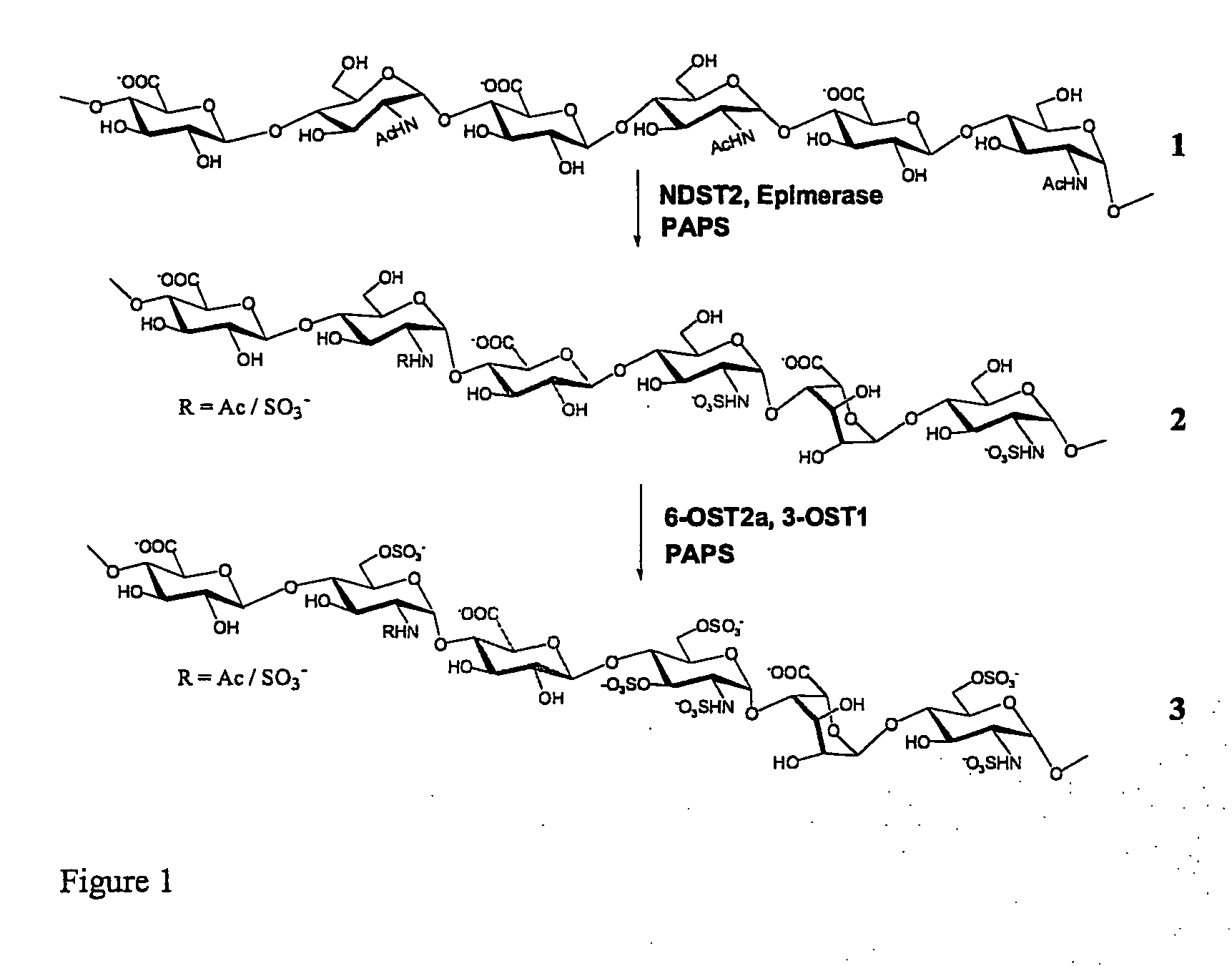
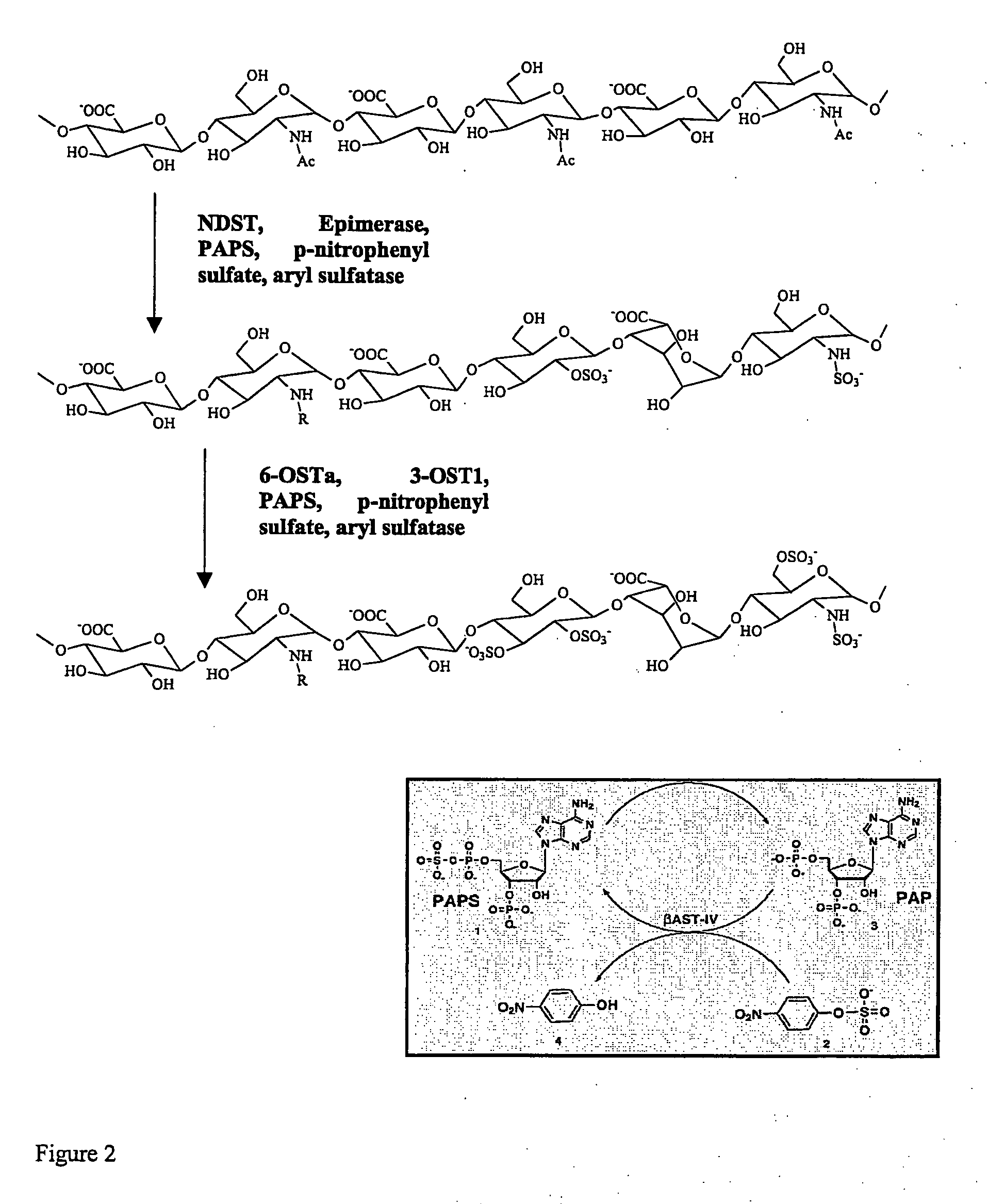
The present invention provides methods, processes and reaction mixtures, which produce sulfated heparosan polysaccharides. This invention also provides methods and reaction mixtures for the synthesis of N-deacetylate N-sulfate derivatives of non-sulfated N-acetyl heparosan (HS) polysaccharides.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Genetically programmed expression of selectively sulfated proteins in eubacteria
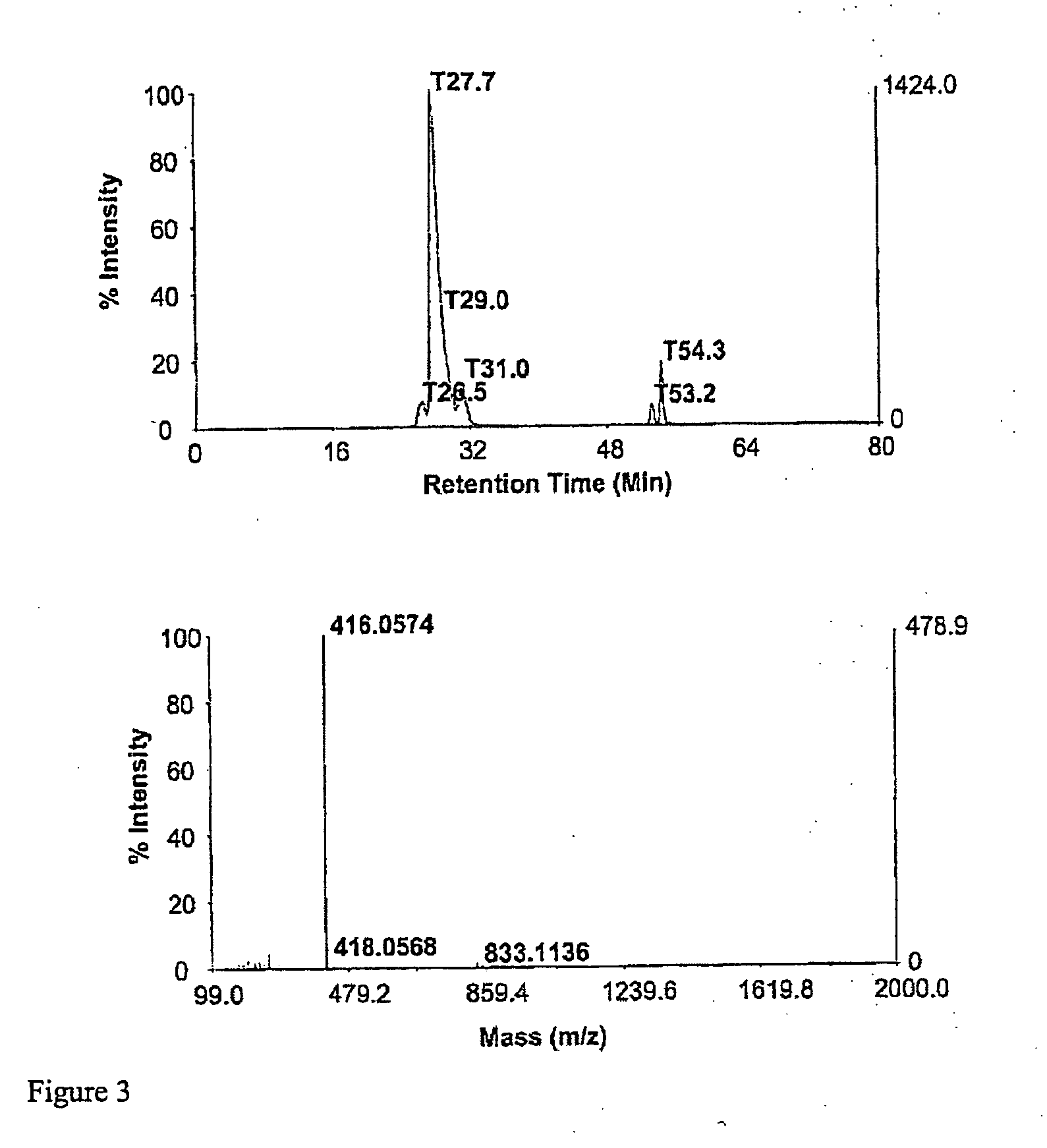
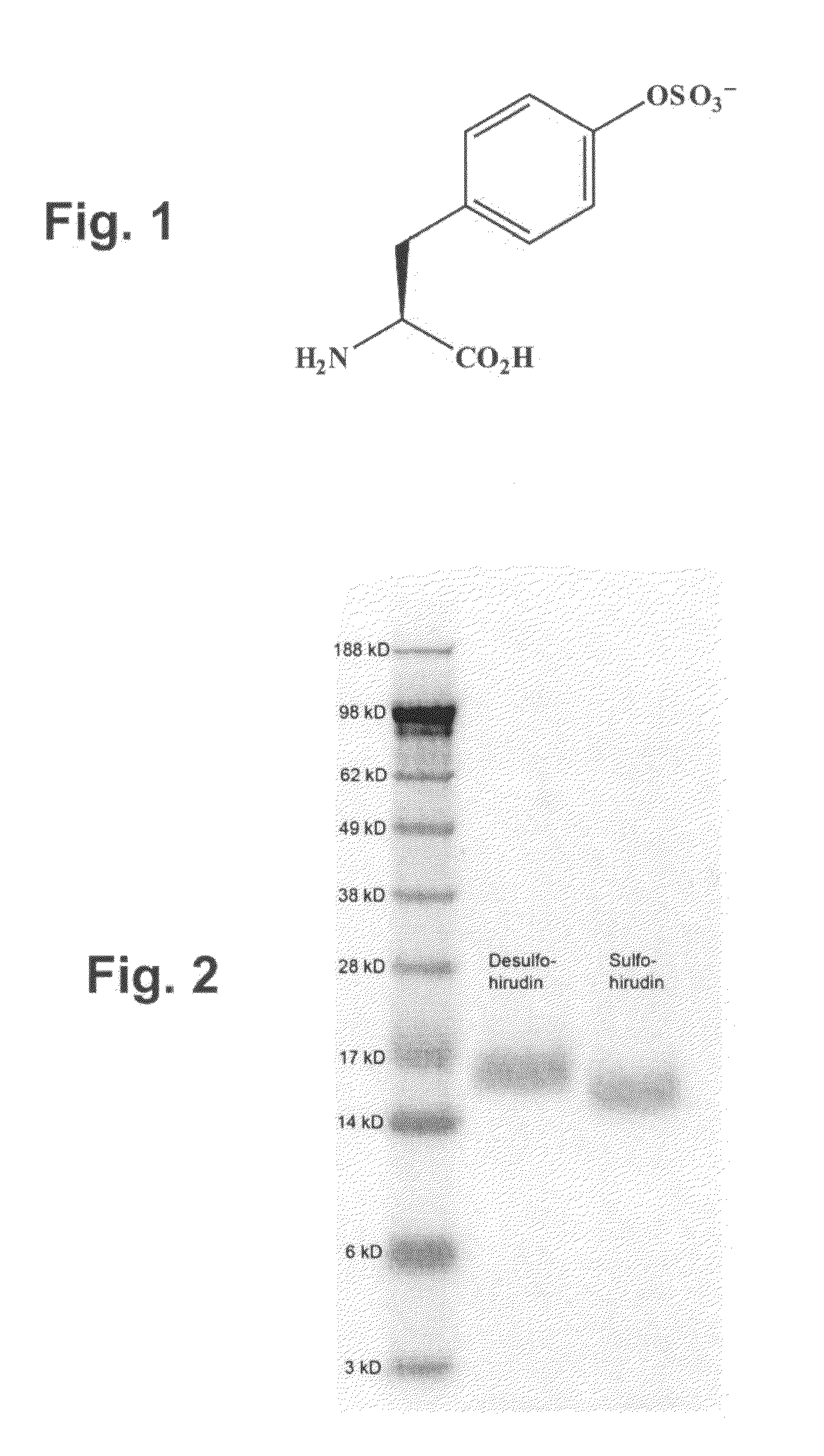
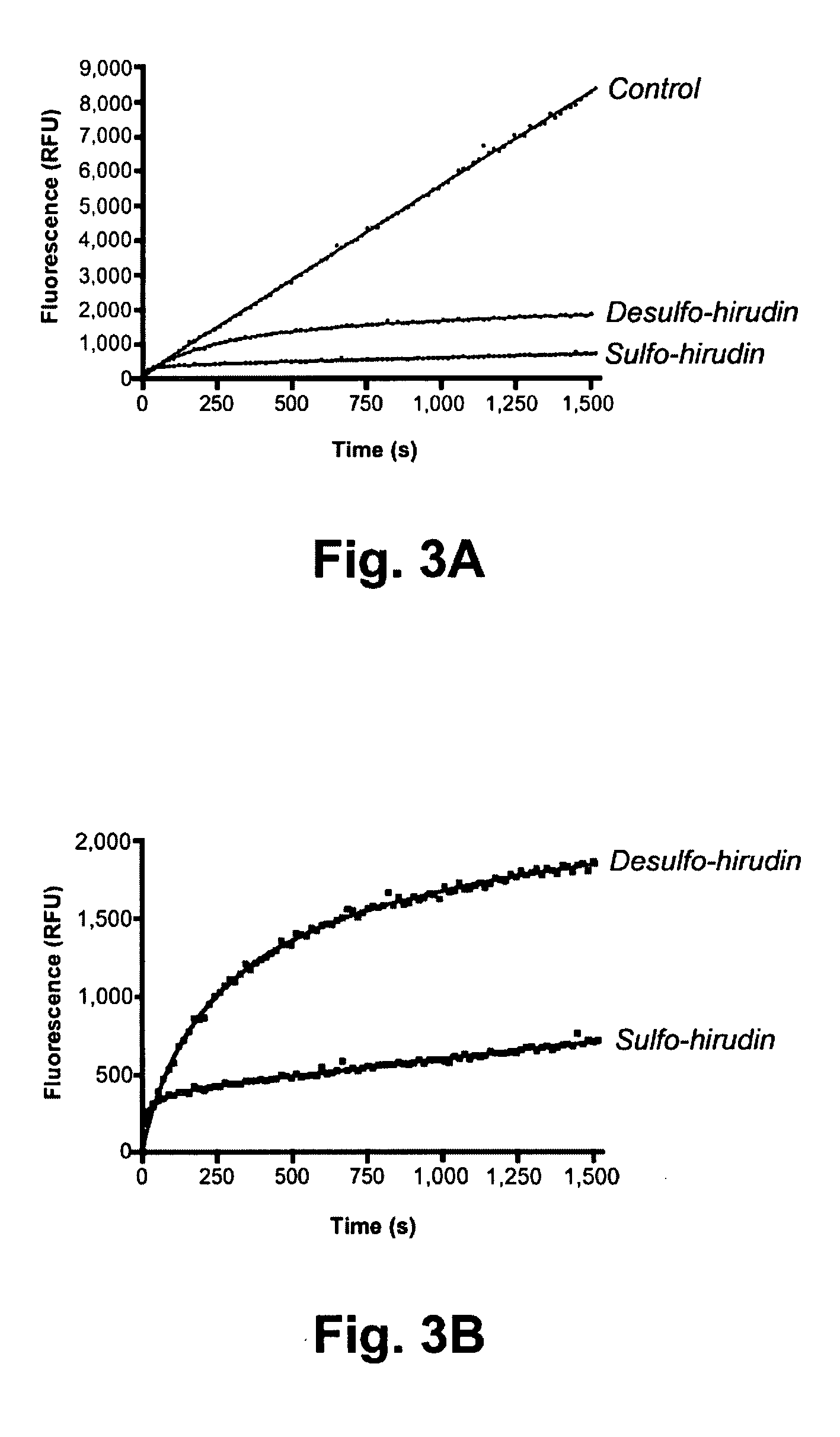
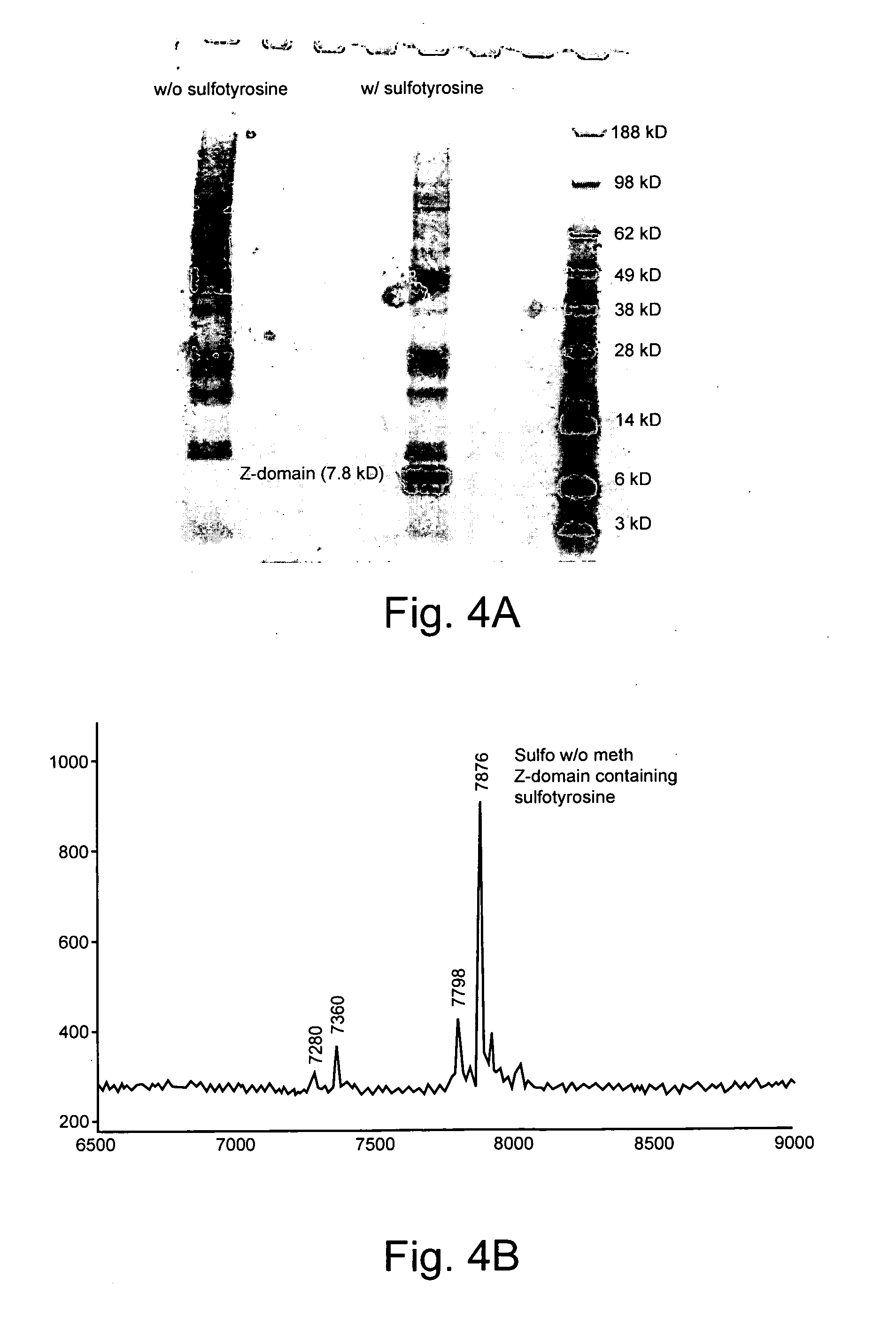
The invention relates to orthogonal pairs of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that can incorporate the unnatural amino acid sulfotyrosine into proteins produced in eubacterial host cells such as E. coli. The invention provides, for example but not limited to, novel orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, polynucleotides encoding the novel synthetase molecules, methods for identifying and making the novel synthetases, methods for producing proteins containing the unnatural amino acid sulfotyrosine and translation systems.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
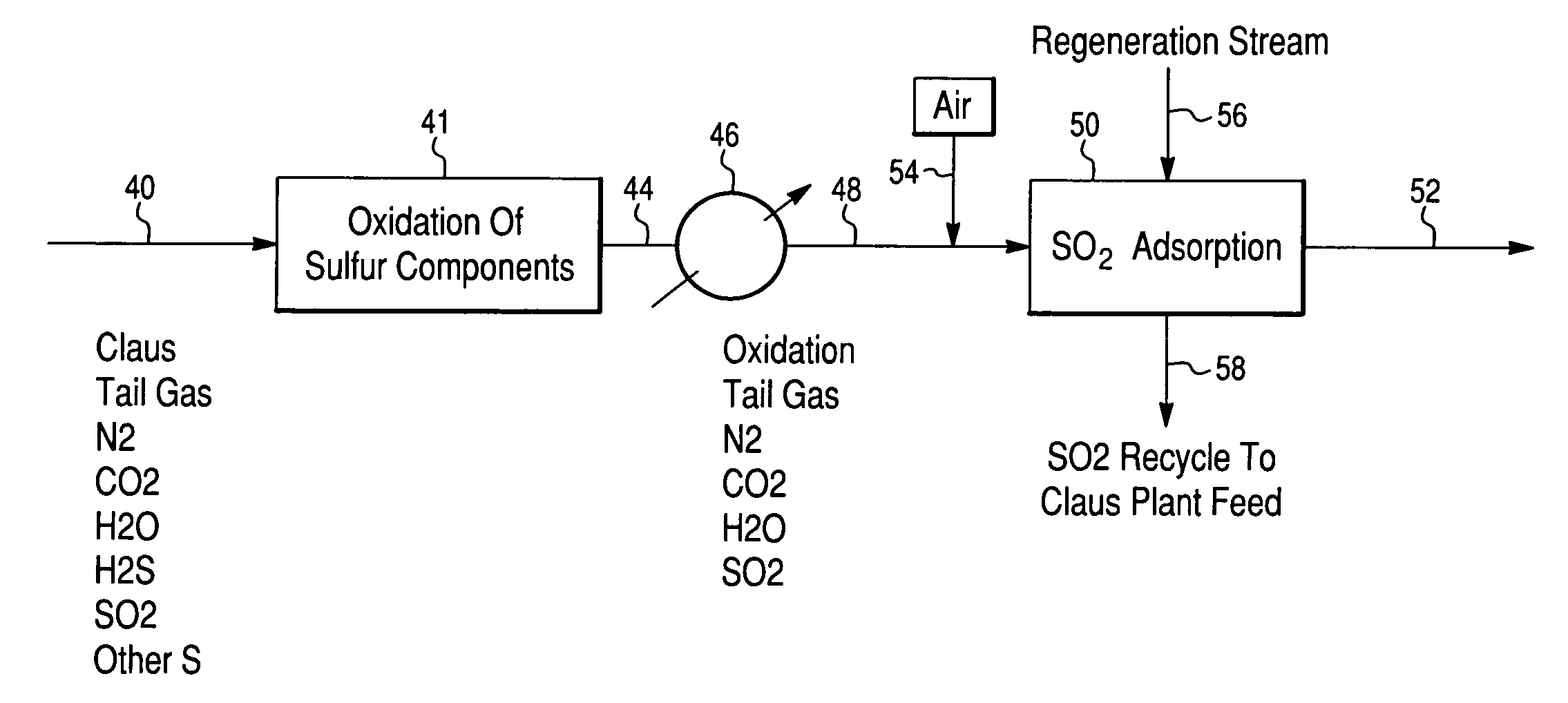
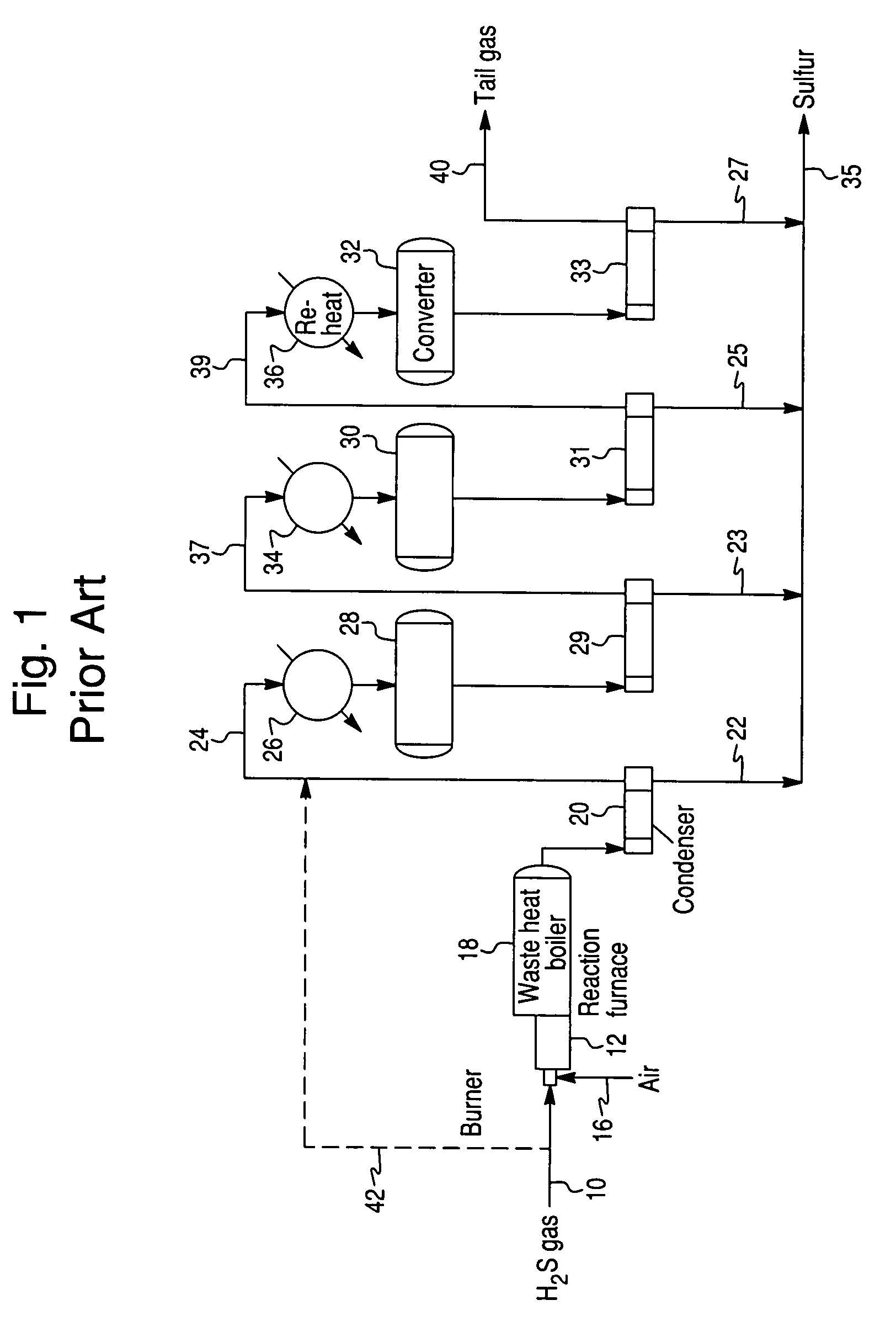
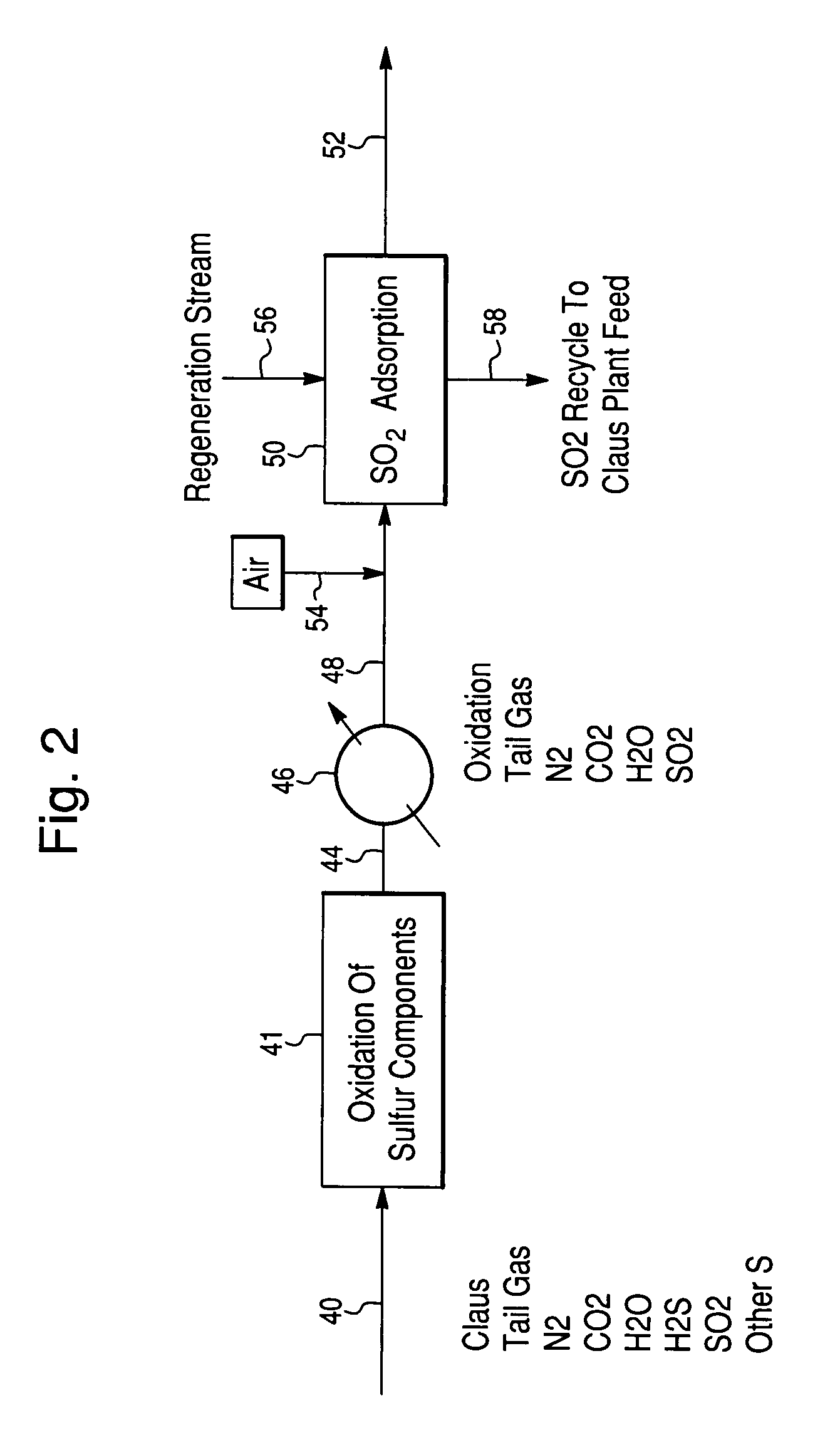
Process for the recovery of sulfur from Claus tail gas streams
Recovering sulfur from a gas stream containing hydrogen sulfide by oxidizing the gas stream to convert the hydrogen sulfide in the gas stream to sulfur oxide, and thus form a sulfur oxide enriched gas stream. The sulfur oxide enriched gas stream is contacted with a solid, sulfation resistant adsorbent bed at relatively low temperatures to extract the sulfur oxides and retain them as sulfur compounds, thus forming a sulfur oxide depleted gas stream. The adsorbent bed is then contacted with an inert or reducing gas stream to reduce the retained sulfur compounds to sulfur and / or sulfur dioxide and thereby form an enriched sulfur and / or sulfur dioxide bearing stream. The elemental sulfur is recovered and / or the sulfur dioxide bearing stream may be recycled to the Claus unit for further conversion.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
A novel graphene anode active compound used for lead-acid storage batteries and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104900876ADoes not affect capacitySlowing the trend towards sulphationCell electrodesFiberPolyvinyl alcohol
A novel graphene anode active compound used for lead-acid storage batteries is disclosed. The graphene anode active compound comprises following components by weight: 0.5-1.2% of colloidal graphite, 0.5-0.8% of humic acid, 0.3-0.8% of lignin, 0.5-1.2% of barium sulfate, 0.07-0.2% of staple fiber, 0.05-0.15% of polytetrafluoroethylene, 0.03-0.2% of poly(vinyl alcohol), 0.1-0.2% of 1,2-propanediol, 0.1-0.3% of graphene, 0.8-1.5% of acetylene black, 75-85% of lead powder and 7-10% of a diluted sulfuric acid solution, with the balance being deionized water. The graphene anode active compound enhances conductivity and low-temperature charge-discharge properties of anode plates and delays sulfation tendency of anode active compounds. Under the premise of not influencing the initial stage capacity of batteries, cyclic service lifetime of batteries is prolonged, high-current charge-discharge capability of batteries is improved, and using performance under extreme conditions is improved to a certain degree.
Owner:江苏海宝电池科技有限公司
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities and process for their preparation
InactiveUS8227449B2High activityReduce bleeding riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAntithrombotic AgentSulfation
Glycosaminoglycans derived from K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant and antithrombotic activity and useful for the control of coagulation and as antithrombotic agents are obtained starting from an optionally purified K5 polysaccharide by a process comprising the steps of N-deacetylation / N-sulfation, C5 epimerization, O-oversulfation, selective O-desulfation, 6-O-sulfation, N-sulfation, and optional depolymerization, in which said epimerization is performed with the use of the enzyme glucoronosyl C5 epimerase in solution or in immobilized form in the presence of divalent cations. New, particularly interesting antithrombin compounds are obtained by controlling the reaction time in the selective O-desulfation step and submitting the product obtained at the end of the final N-sulfation step to depolymerization.
Owner:GLYCORES 2000 SRL
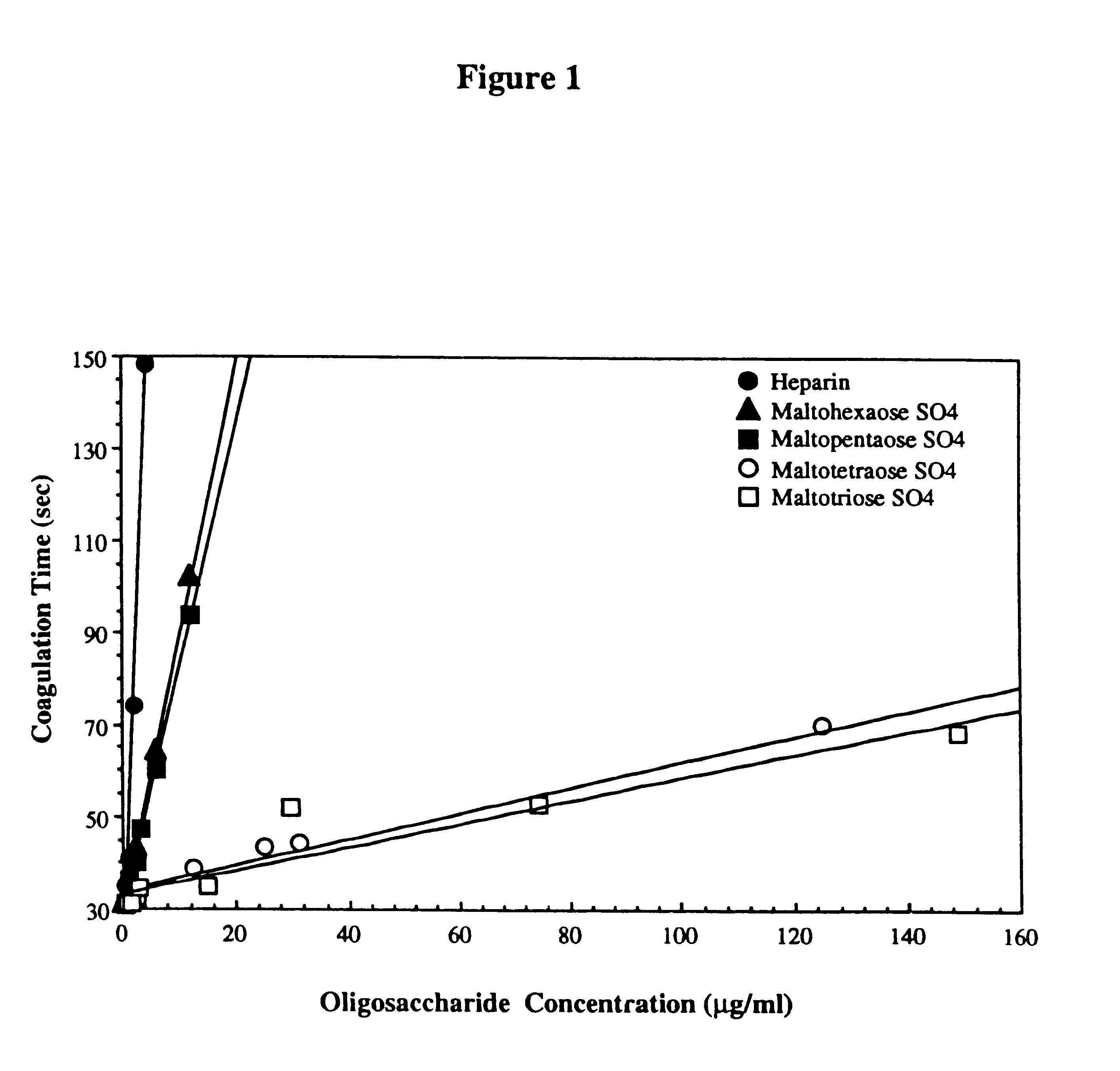
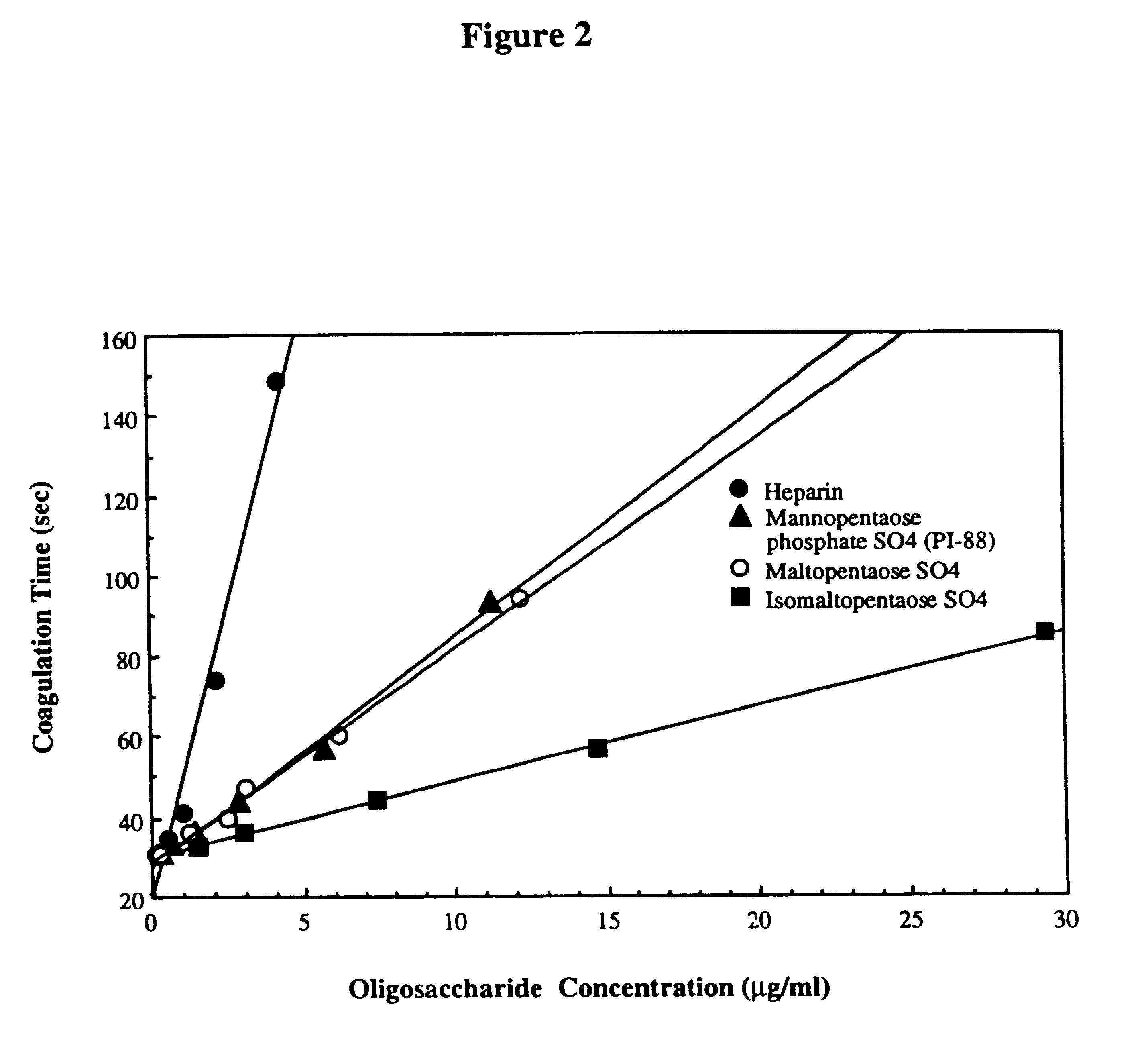
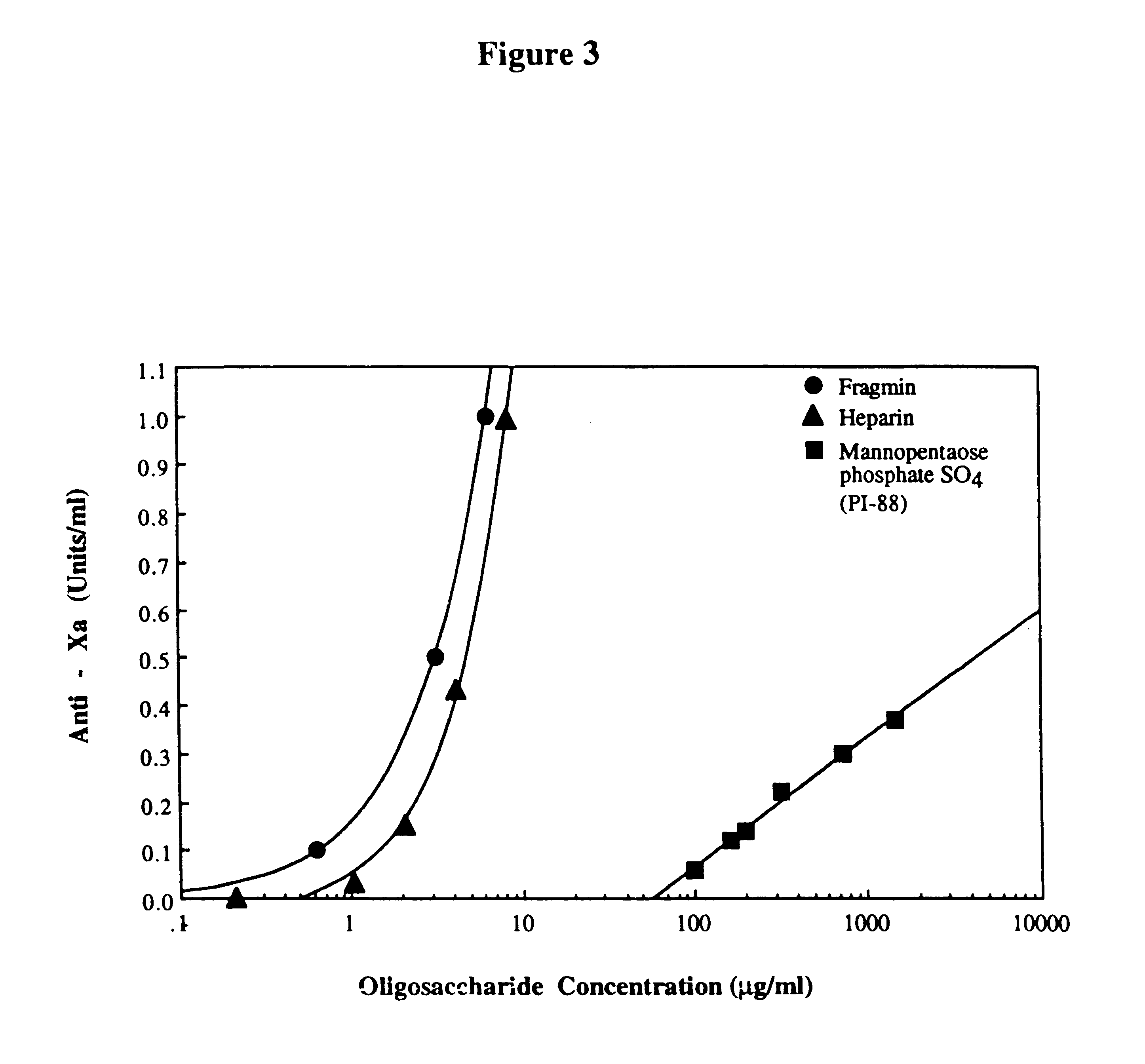
Sulfated oligosaccharides having anticoagulant/antithrombotic activity
A method for the anticoagulant and / or antithrombotic treatment of a human or other warm-blooded animal patient in need of such treatment, comprises administration to the patient of an effective amount of at least one sulfated oligosaccharide, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds andn is an integer of from 1 to 6.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Nuclear sulfated oxysterol, potent regulator of cholesterol homeostasis, for therapy of hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20070275939A1Potent cholesterol lowering propertyPromote degradationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMetaboliteOxysterol
The sulfated oxysterol 5-cholesten-3β, 25-diol 3-sulphate, a nuclear steroid metabolite that increases cholesterol secretion and degradation, is provided as an agent to lower intracellular and serum cholesterol and / or triglycerides. Methods which involve the use of this sulfated oxysterol to treat conditions associated with high cholesterol and / or high triglycerides (e.g. hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis) are also provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Compositions and Methods for Bacterial Production of Chondroitin
The invention relates to the field of recombinant DNA technology for the production of chondroitin, including the production of chondroitin sulfate via a combination of recombinant bacterial fermentation and post-fermentation sulfation.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com