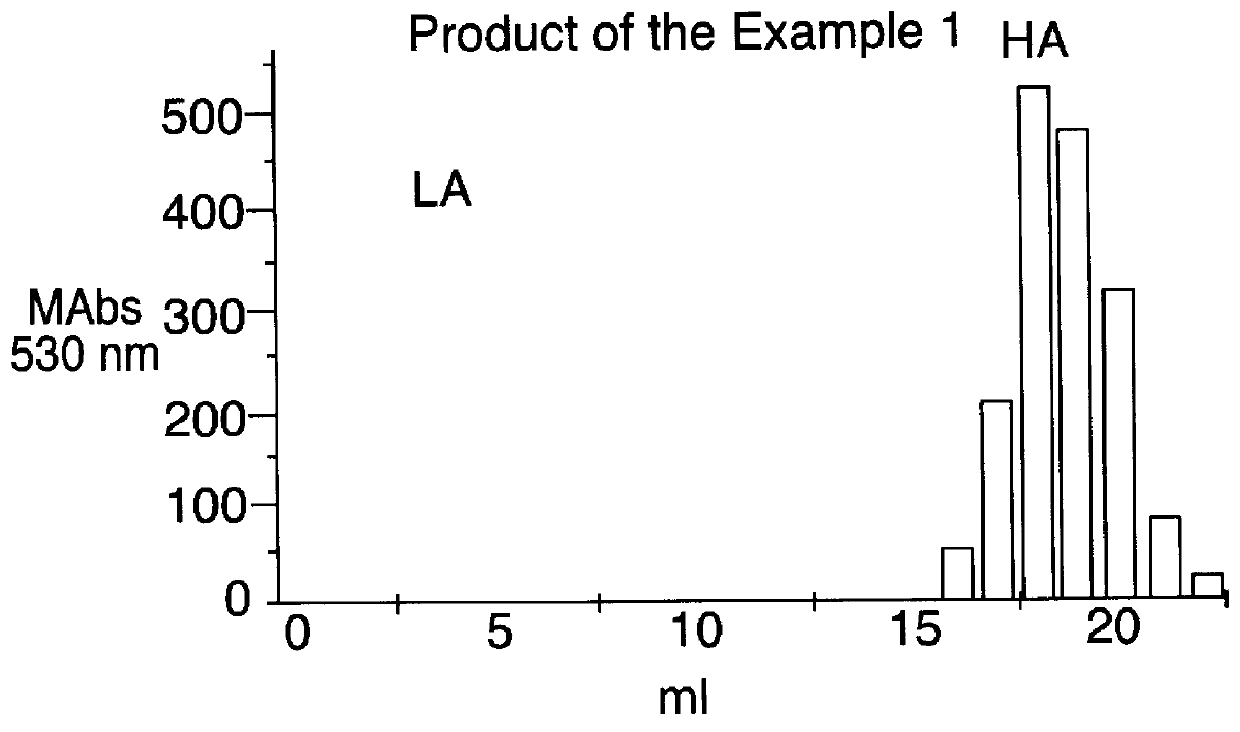
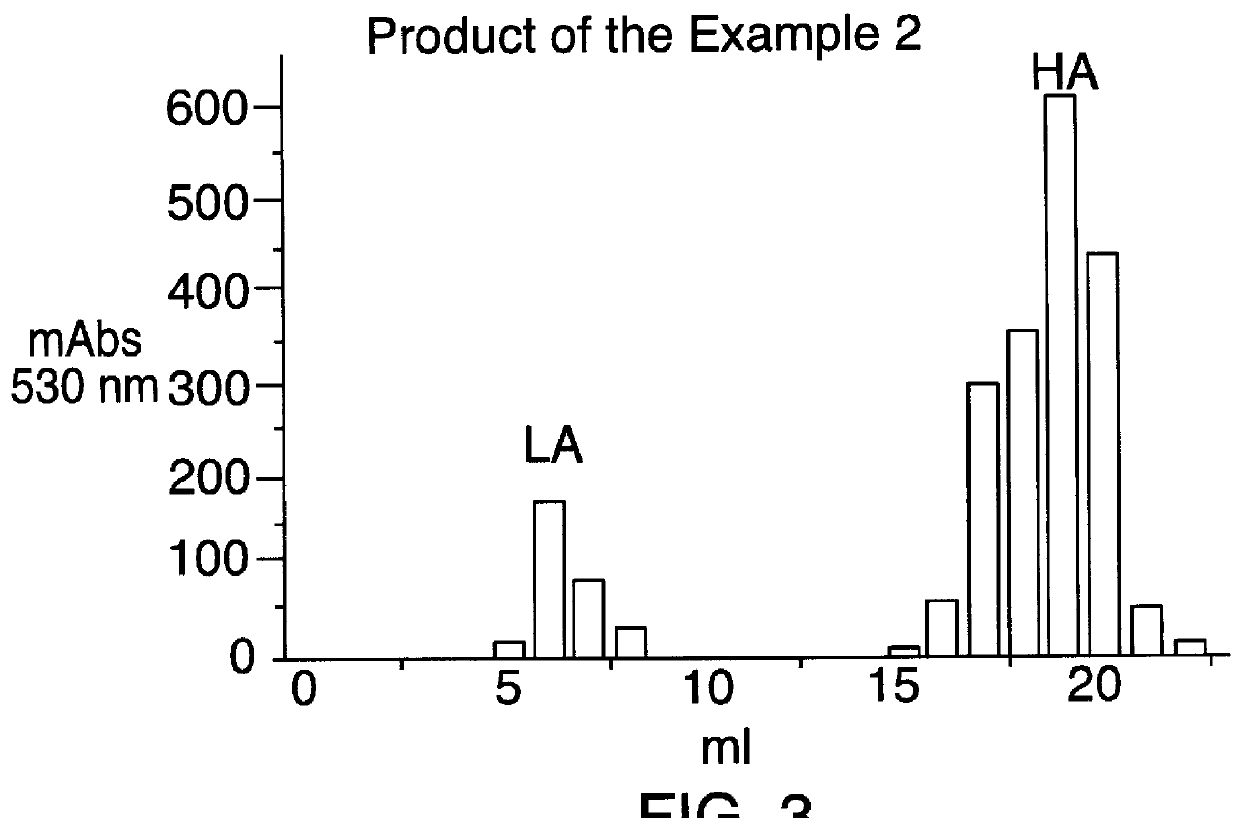
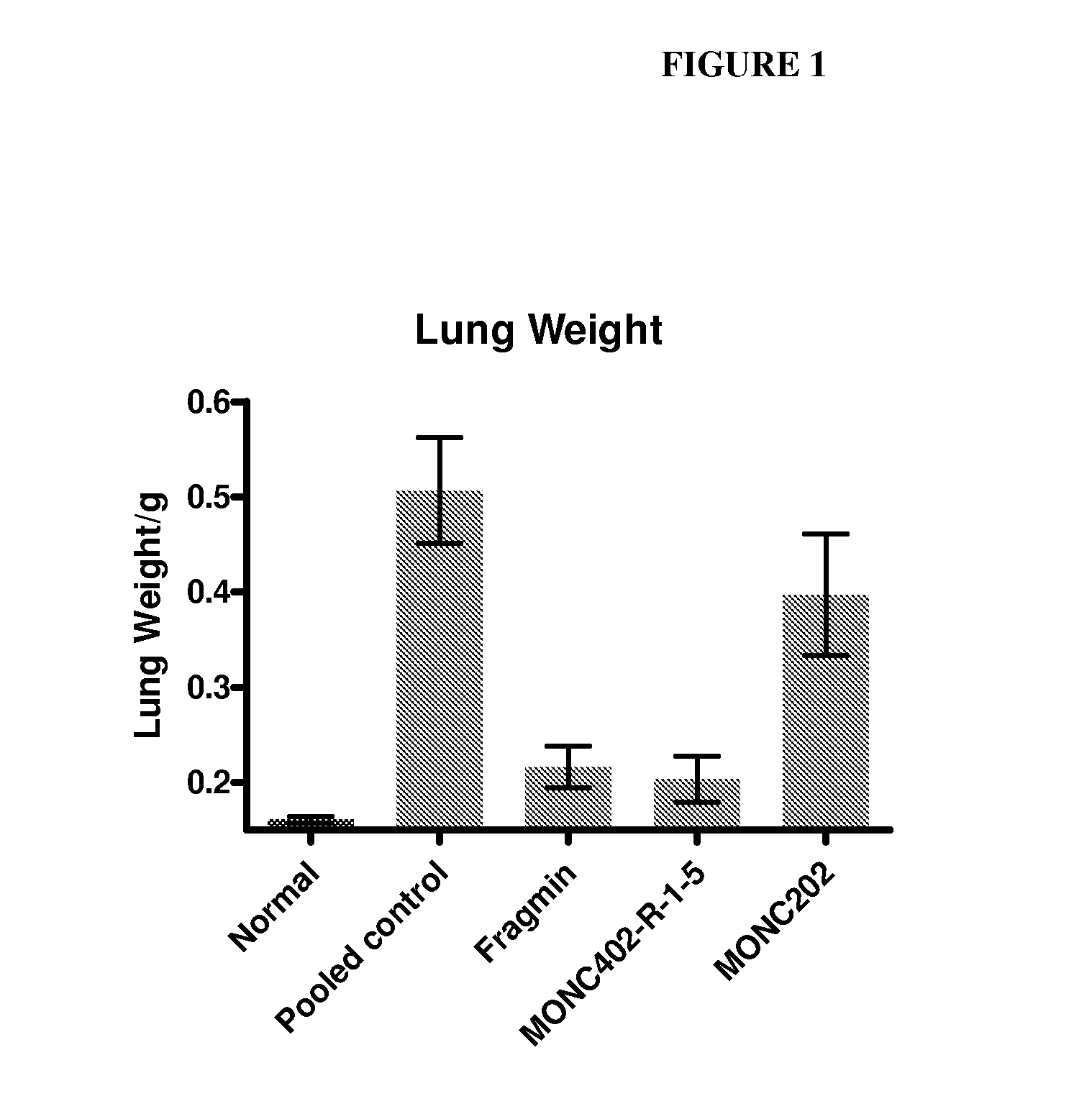
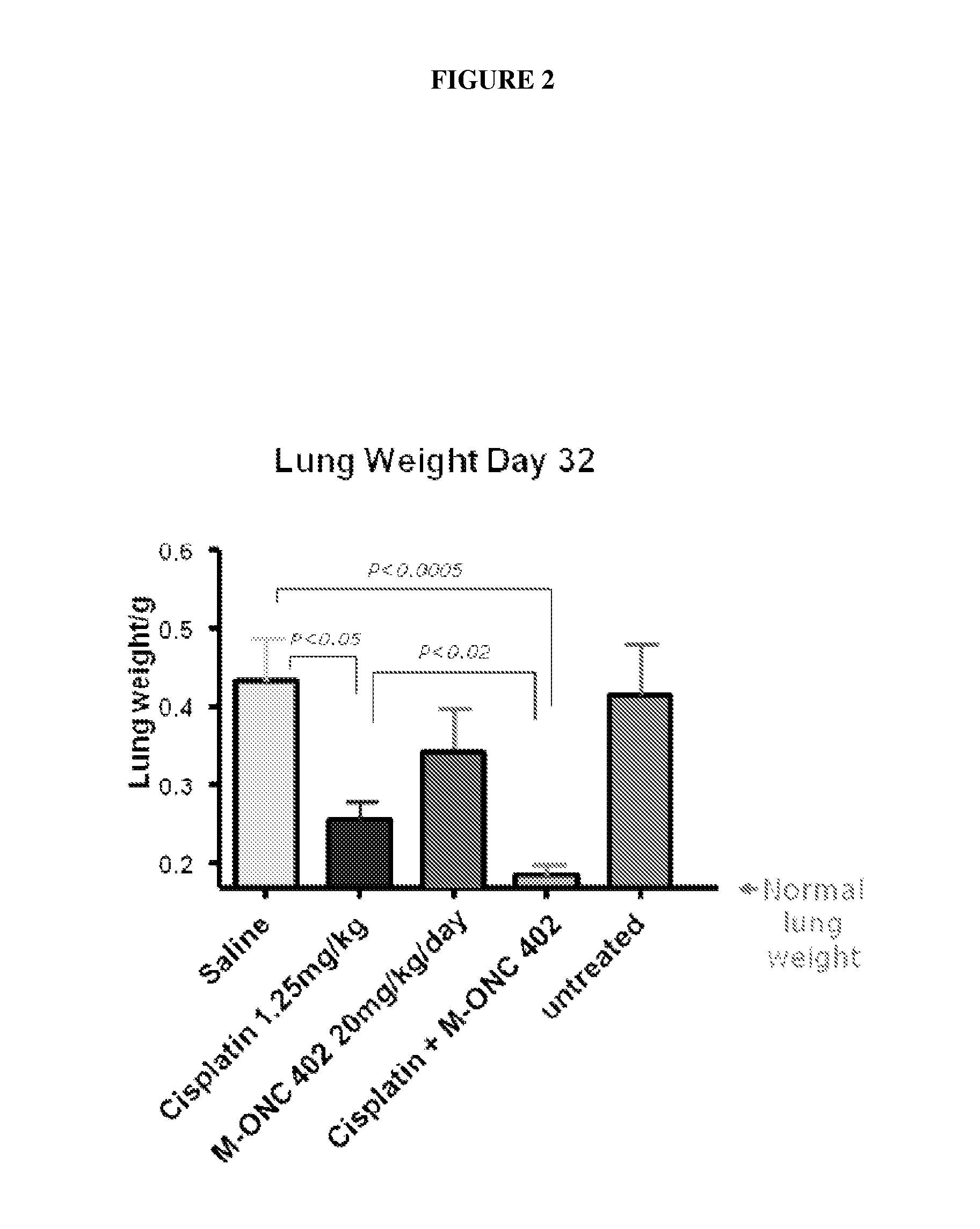
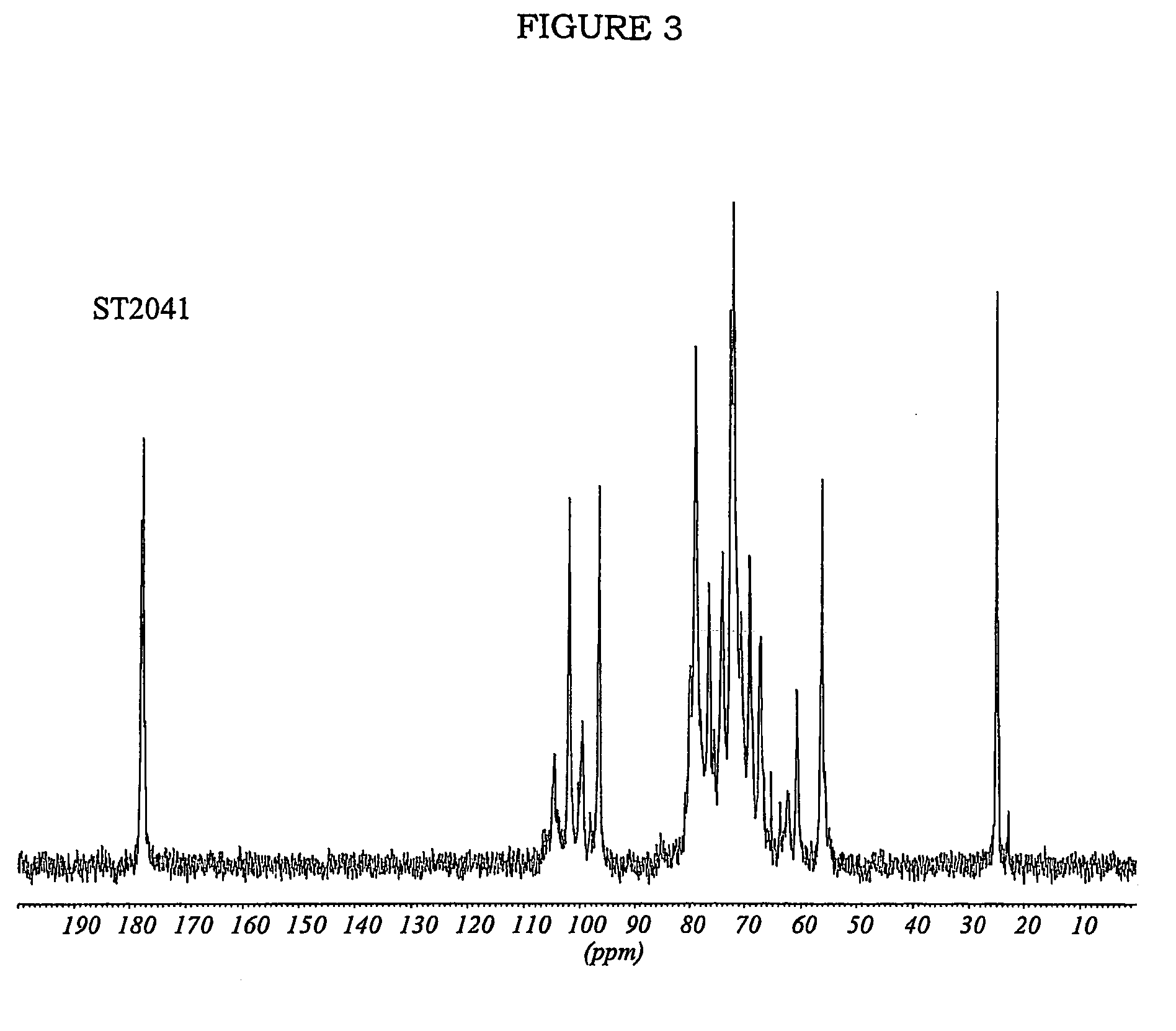
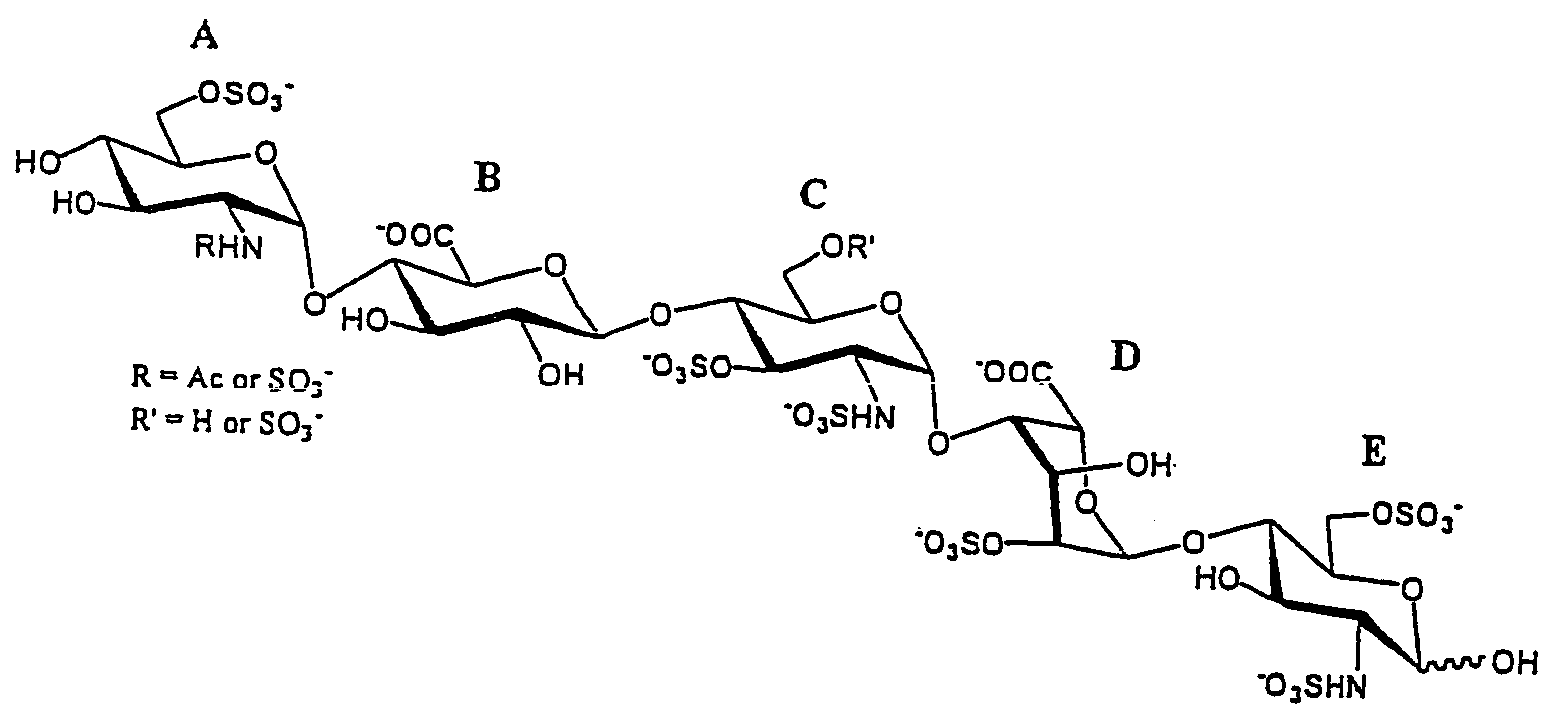
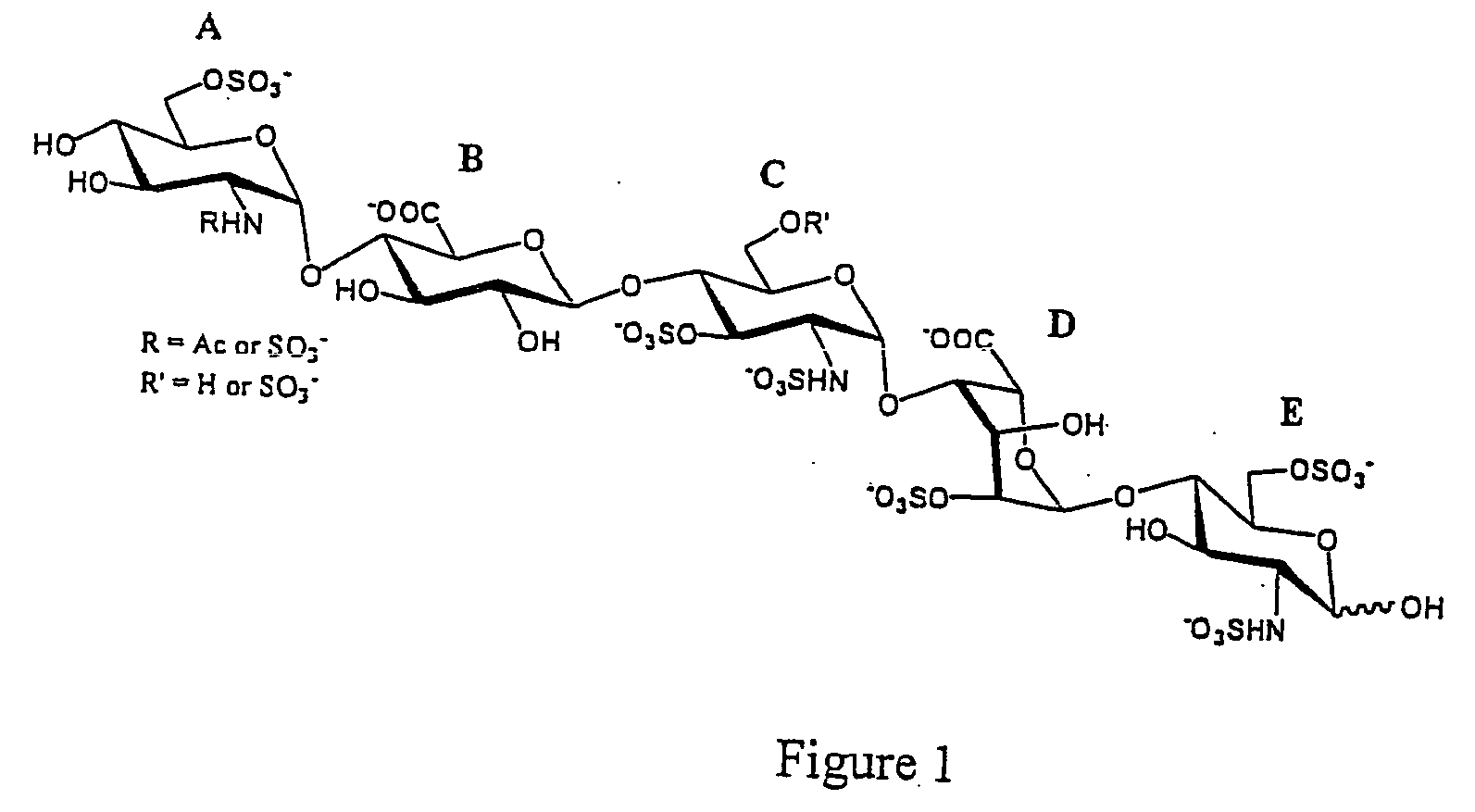
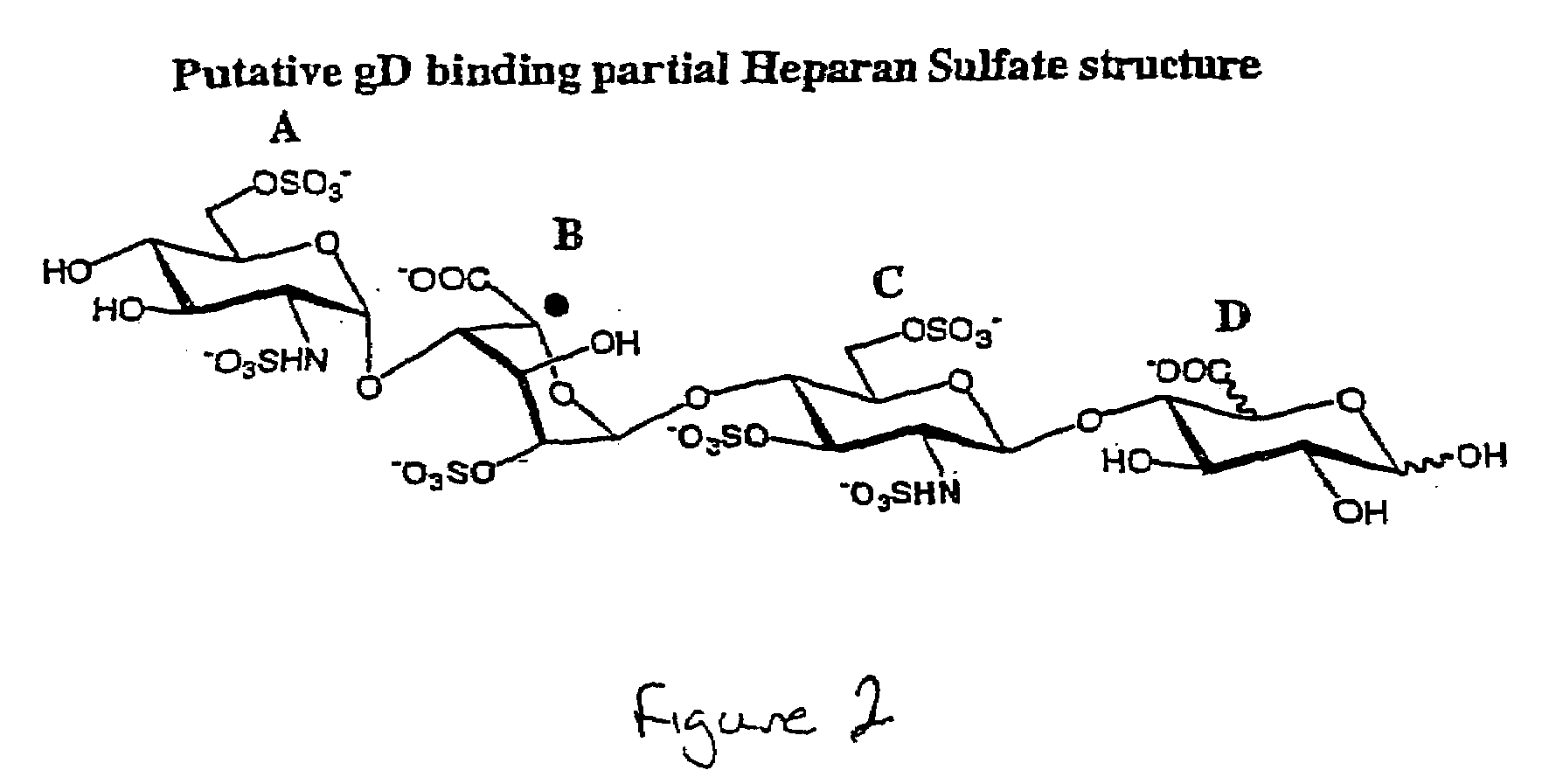
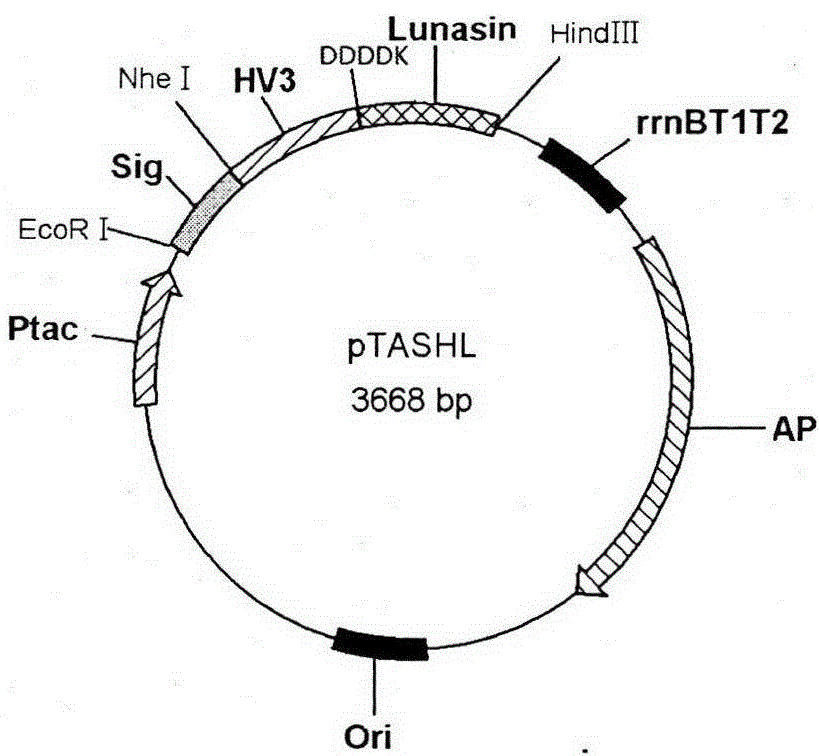
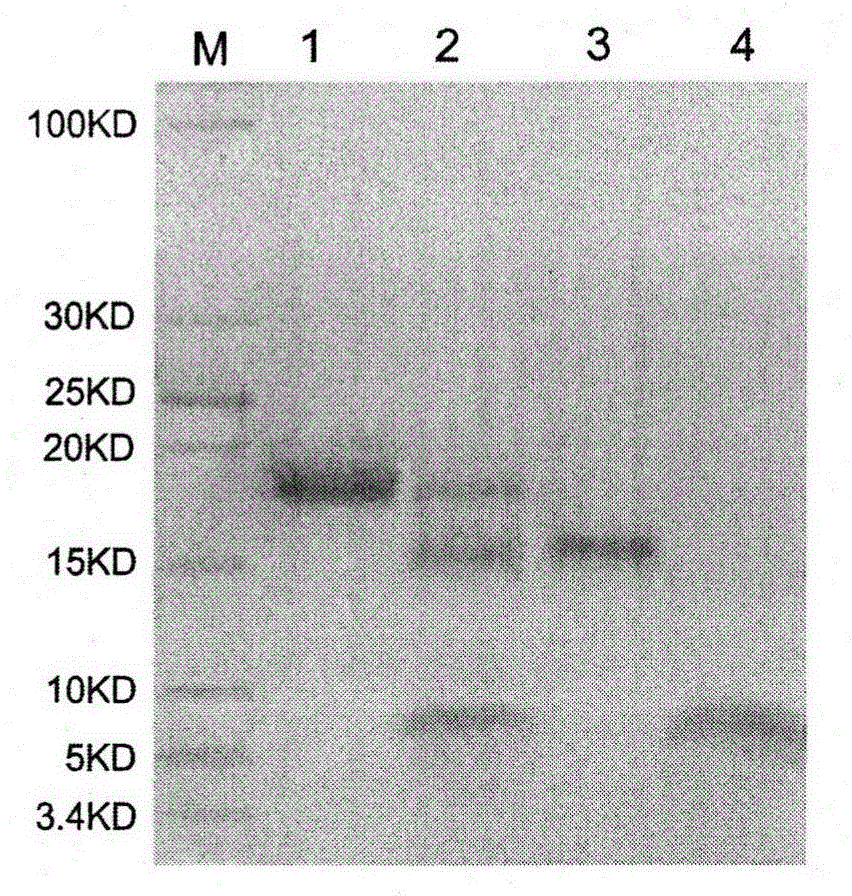
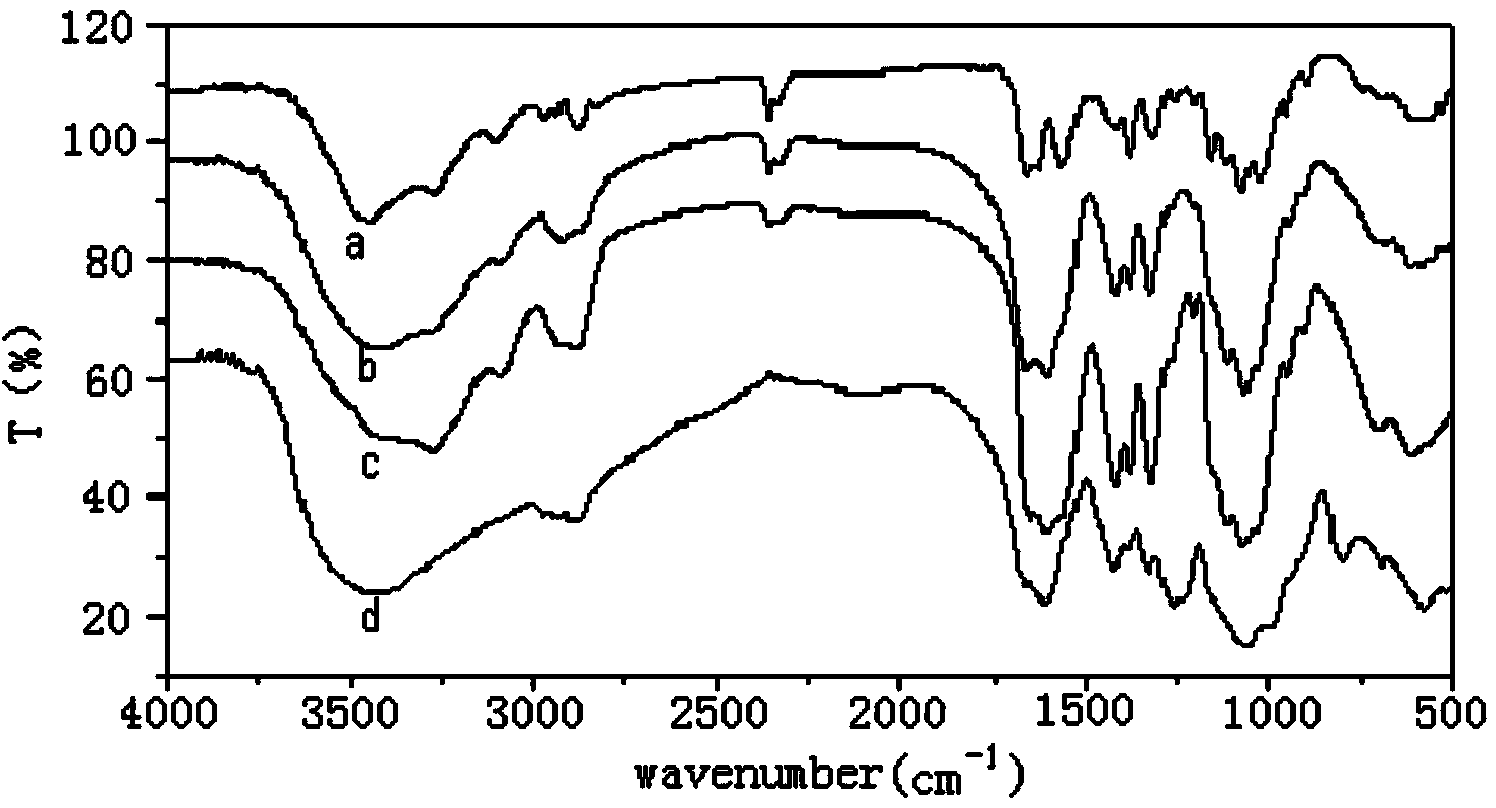
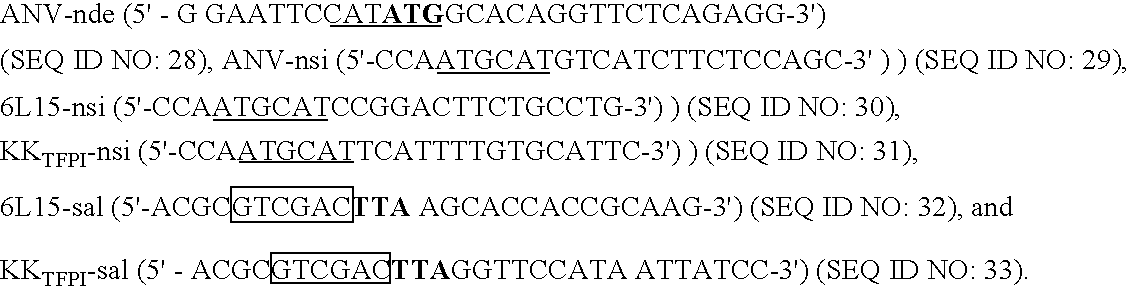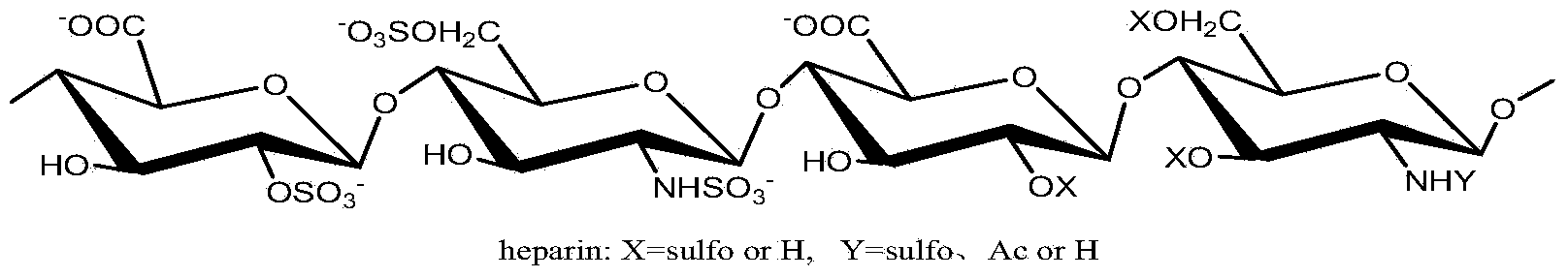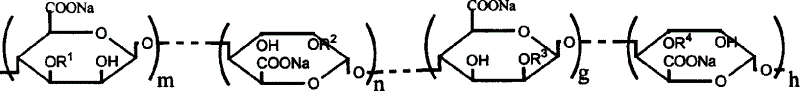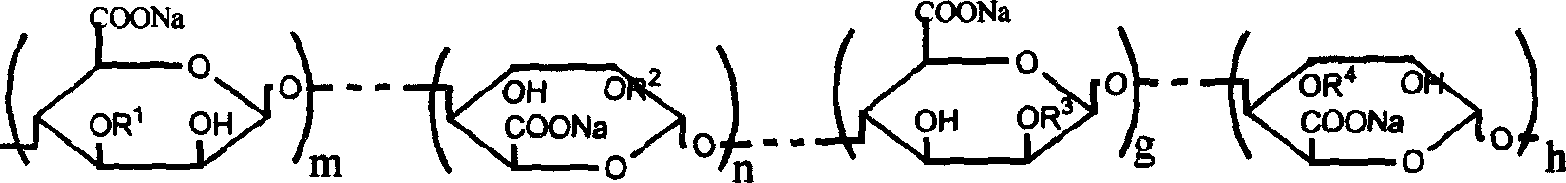Patents
Literature
239 results about "Anticoagulant activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
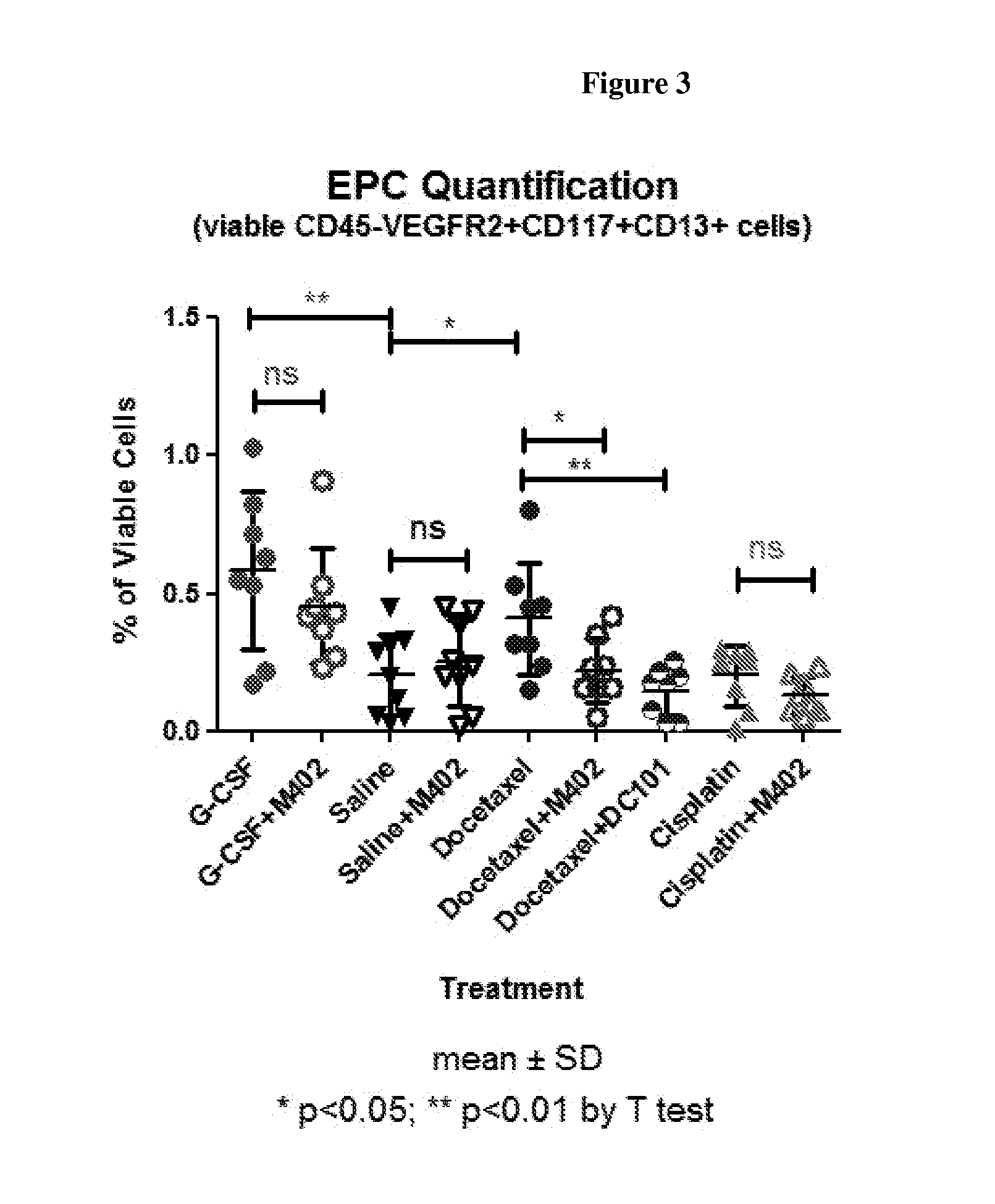
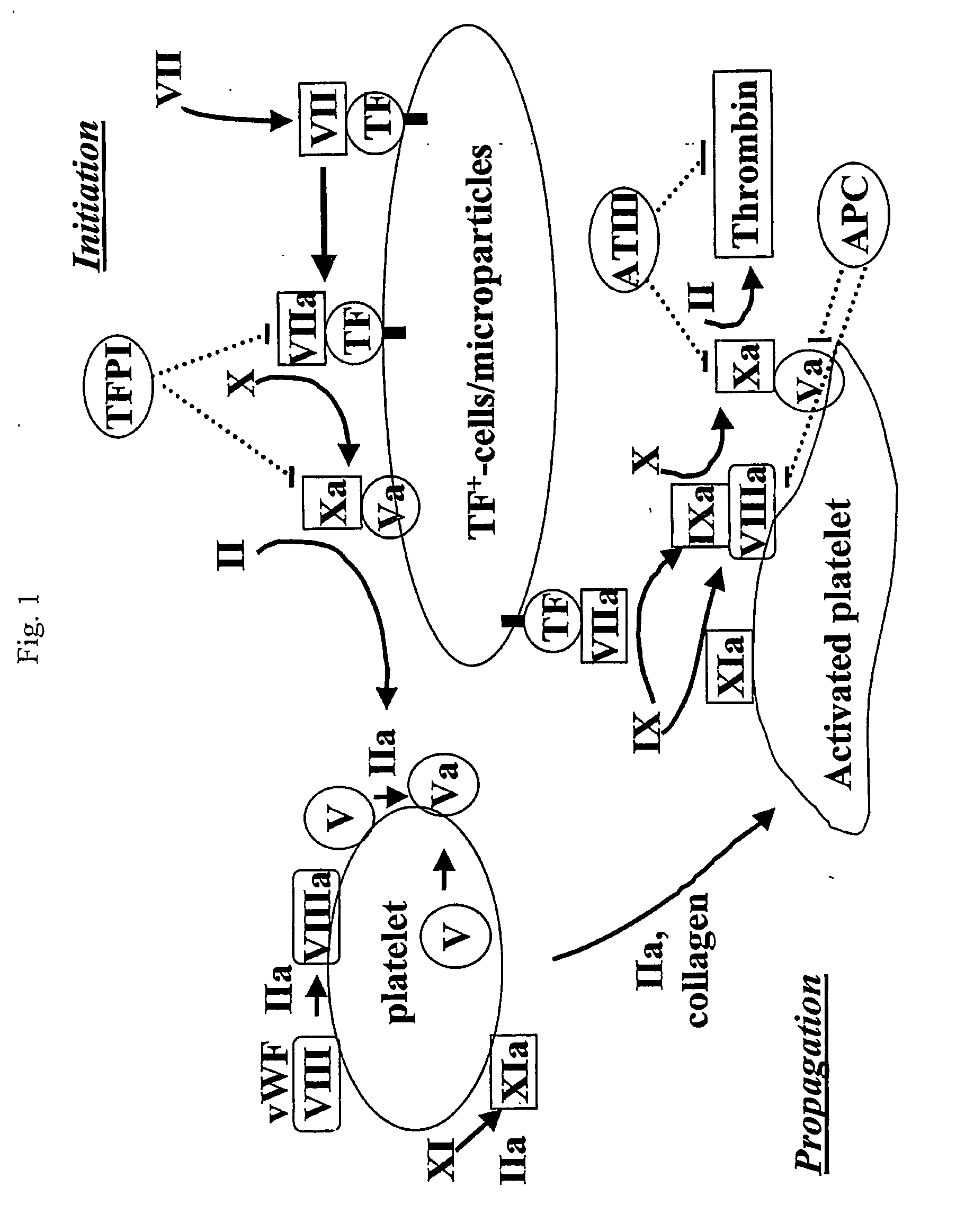
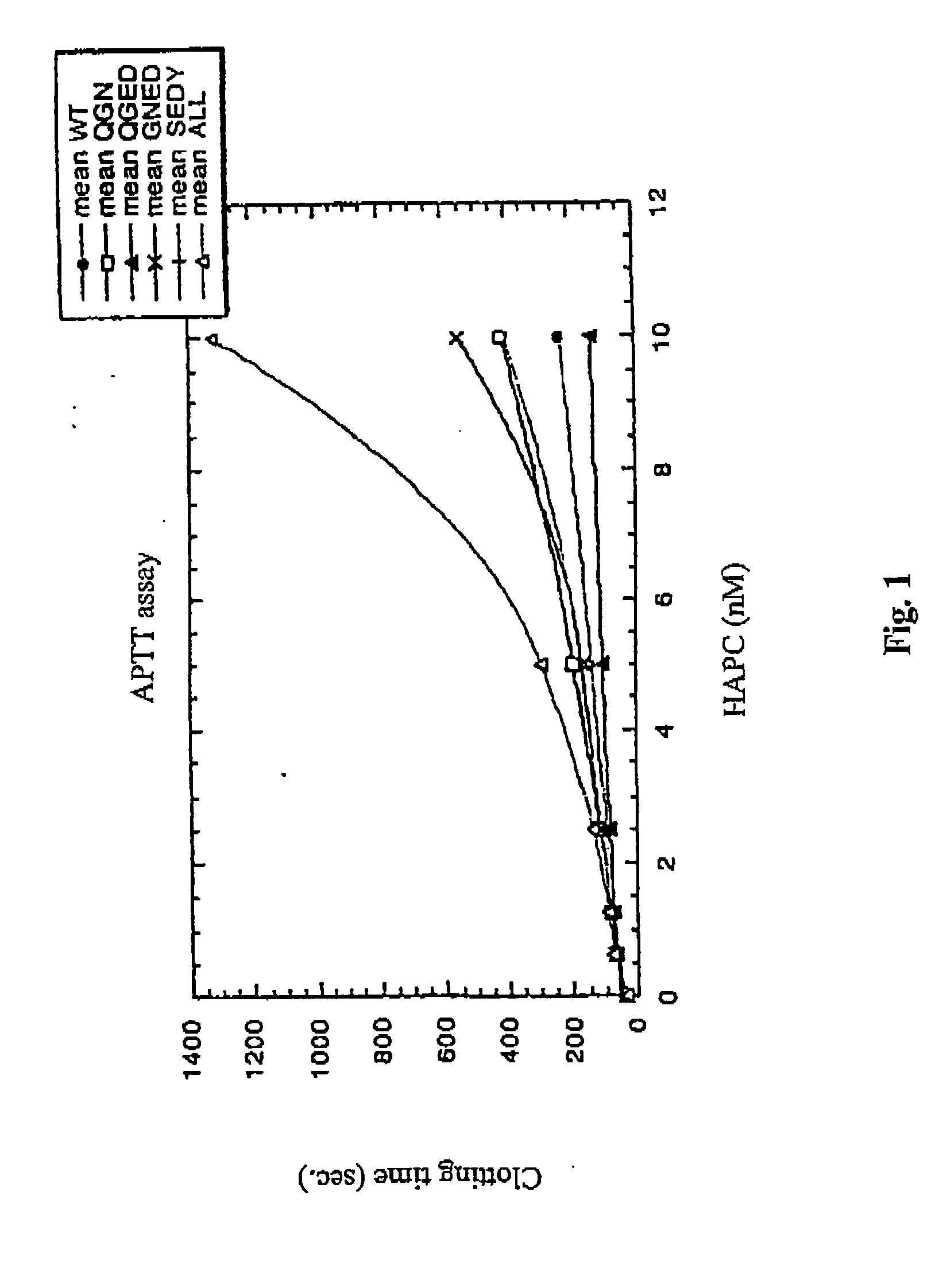
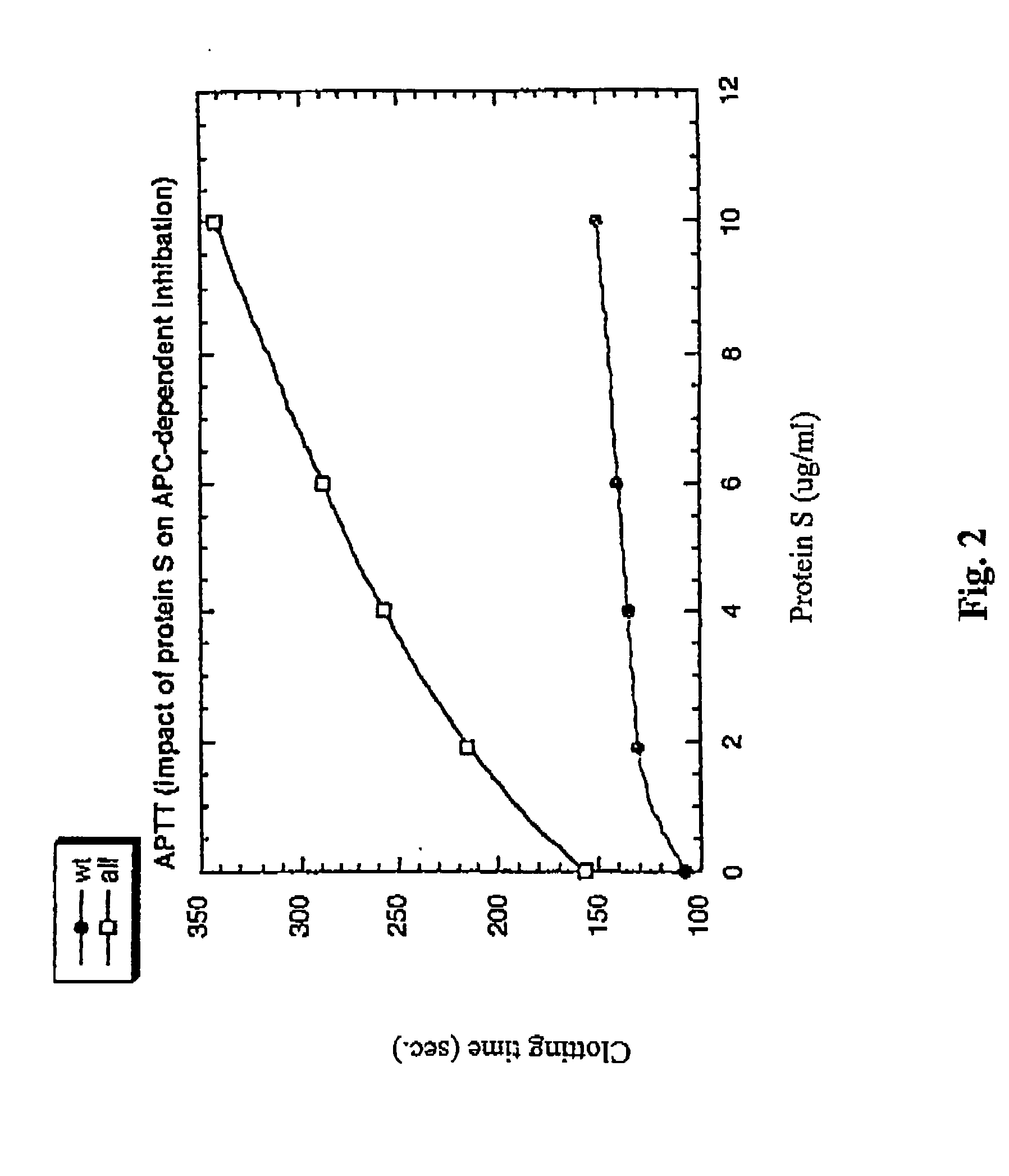
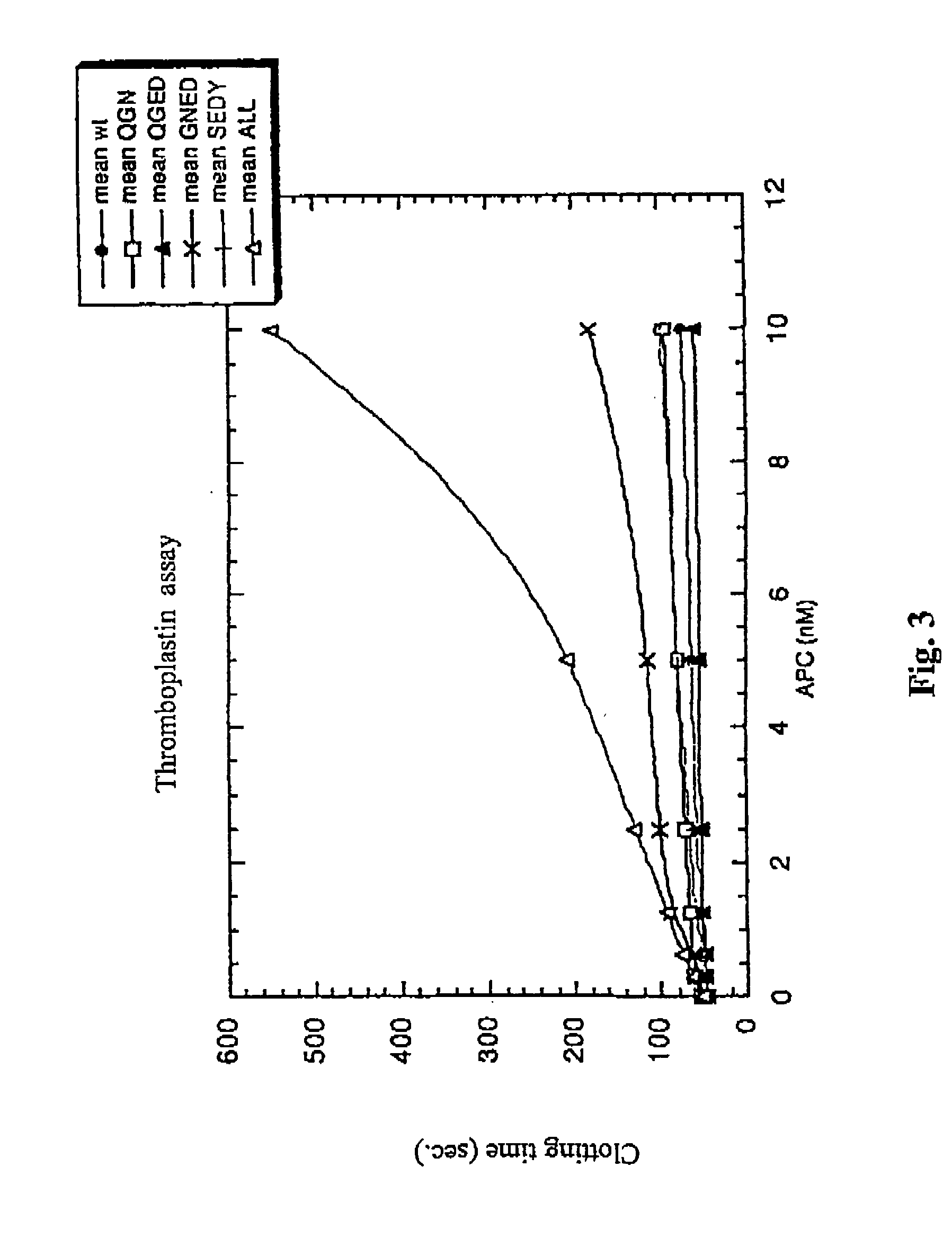
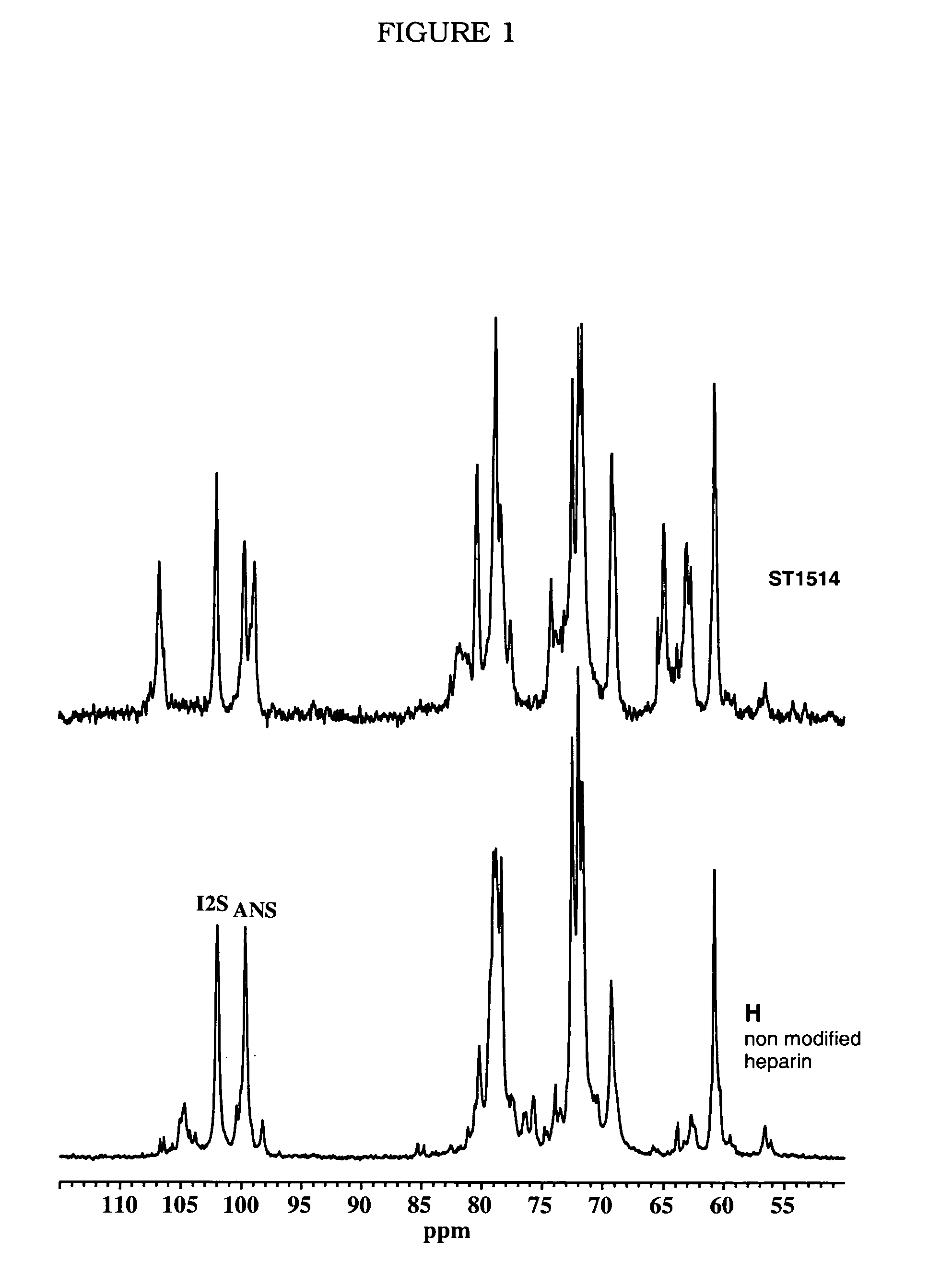
The contribution of serpins to the anticoagulant activity of FucCS and SG was determined in a plasmatic system using an aPTT test. Basically, aPTT tests are used to evaluate the anticoagulant effect of the SPs. In this assay, the anticoagulant effect of the MSPs was evaluated by the measurement of the time necessary to plasma clotting.
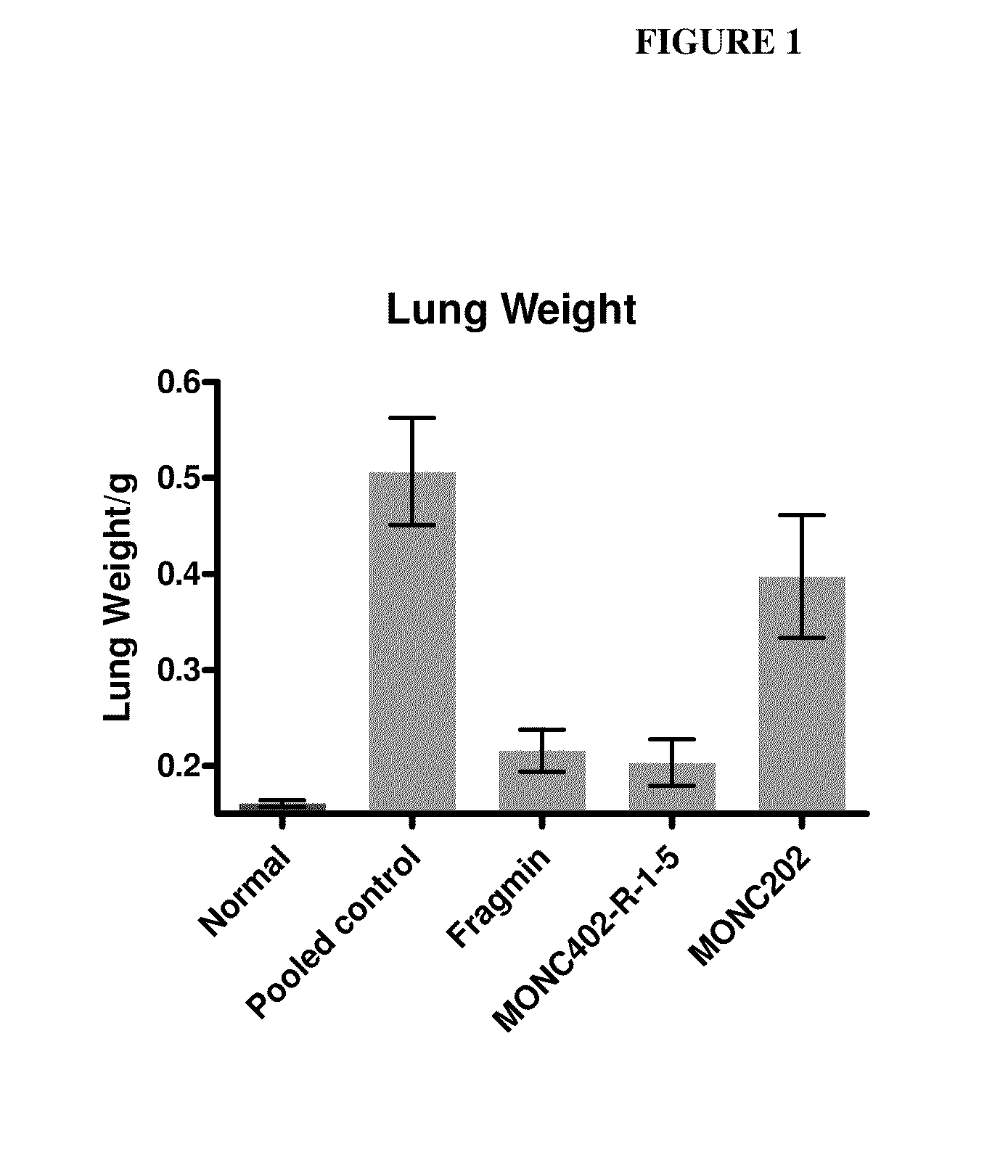
Method and medicament for anticoagulation using a sulfated polysaccharide with enhanced anti-inflammatory activity
InactiveUS20060040896A1Sufficient degreeGood anti-inflammatory activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderSulfated polysaccharidesMedicine
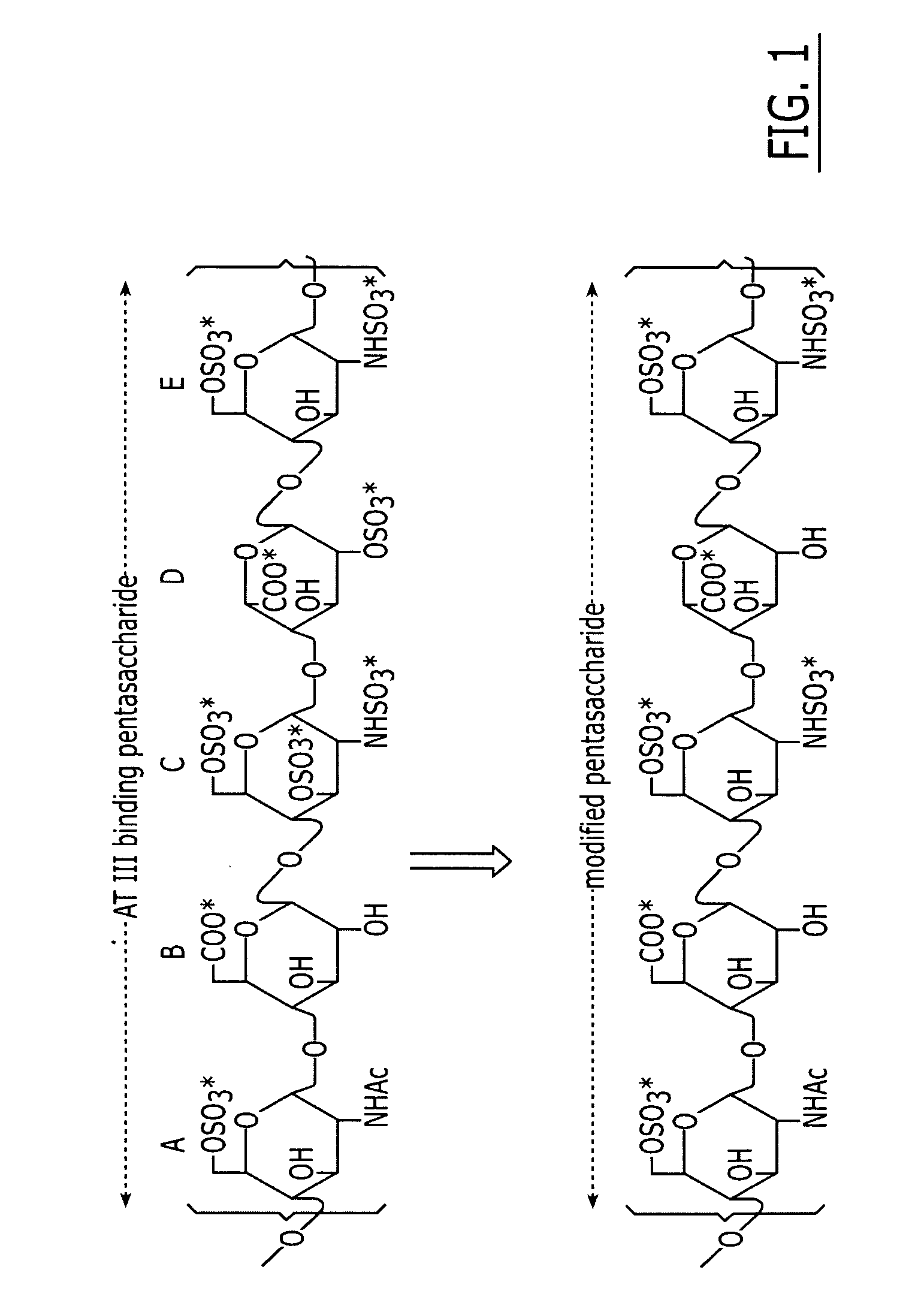
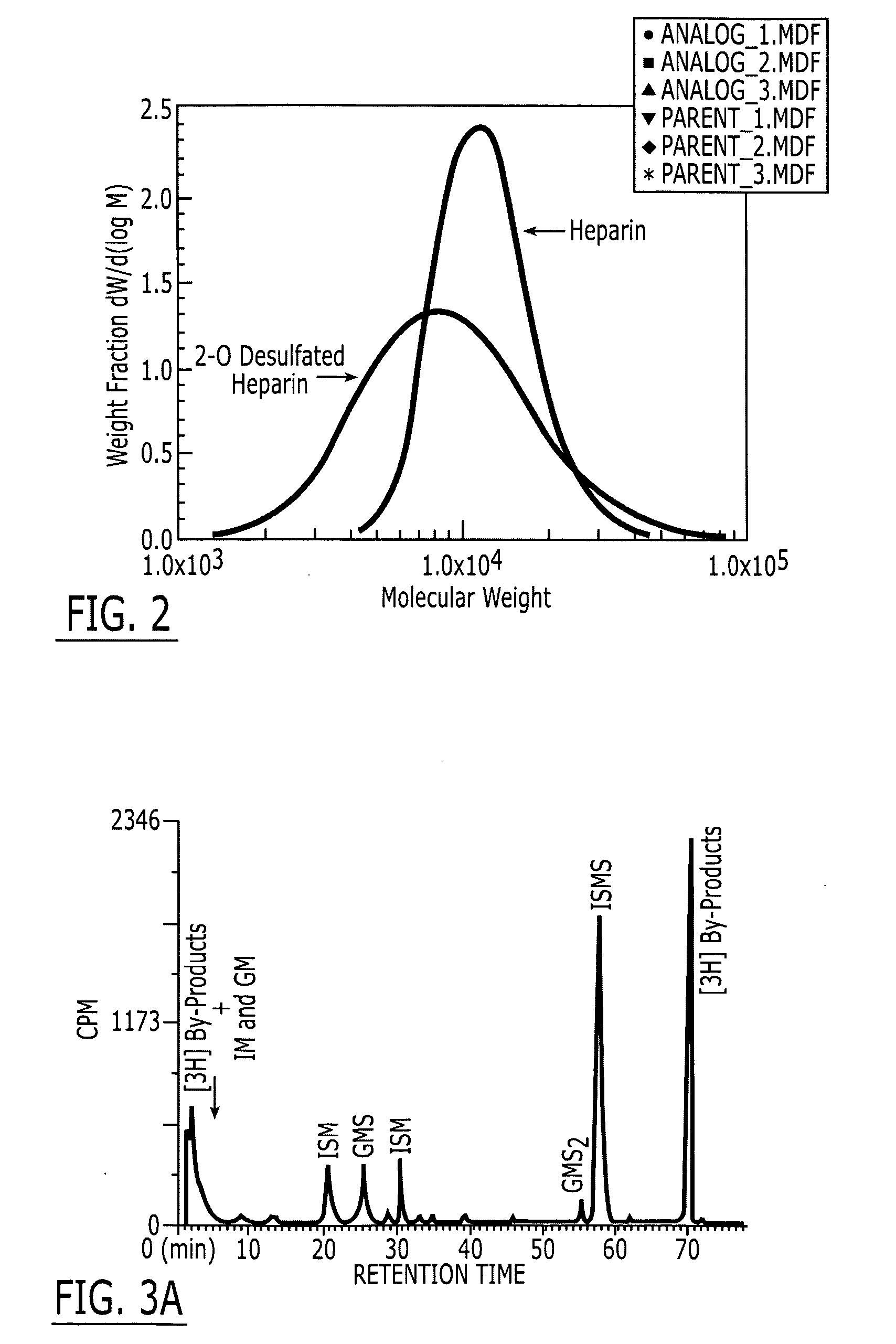
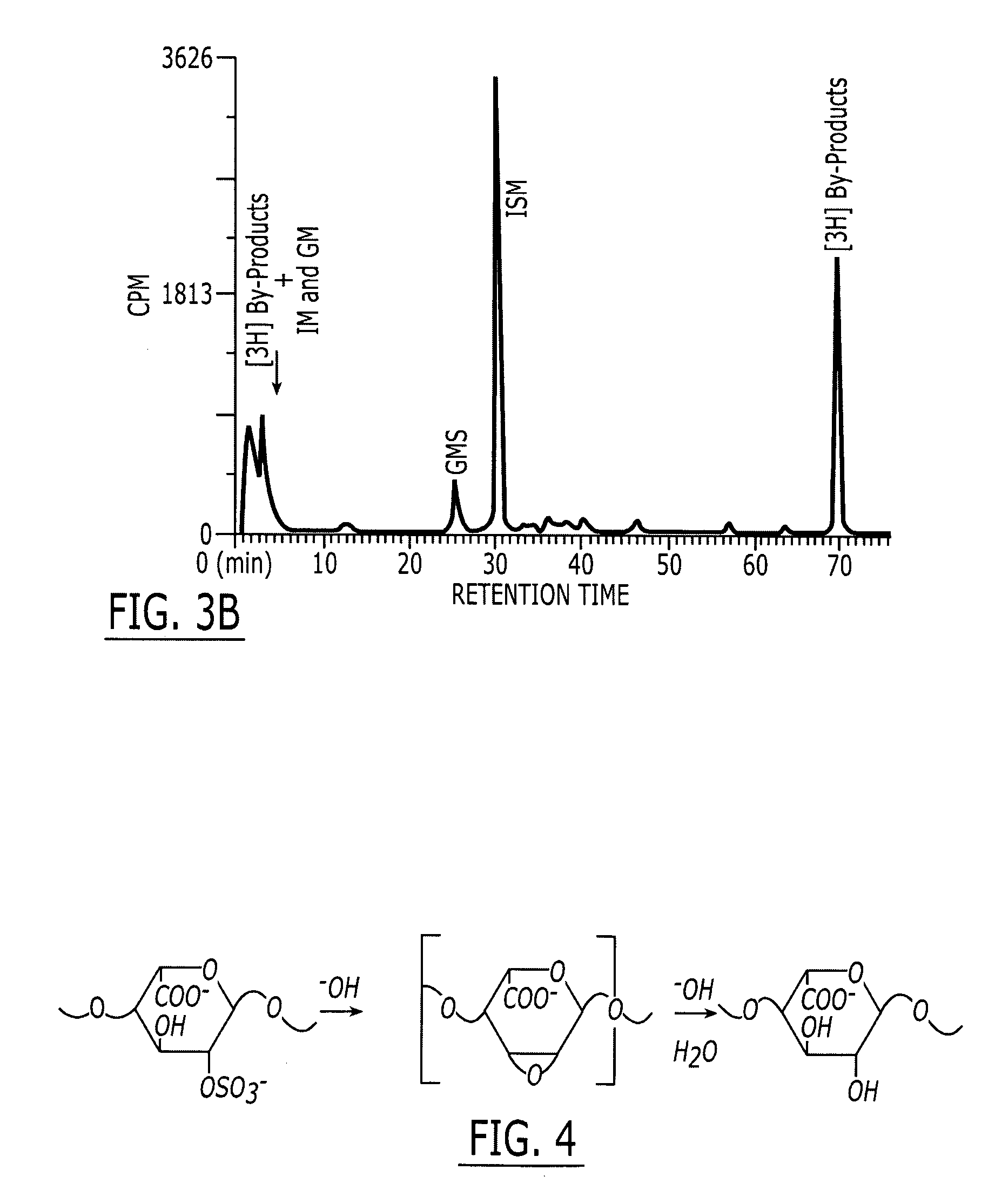
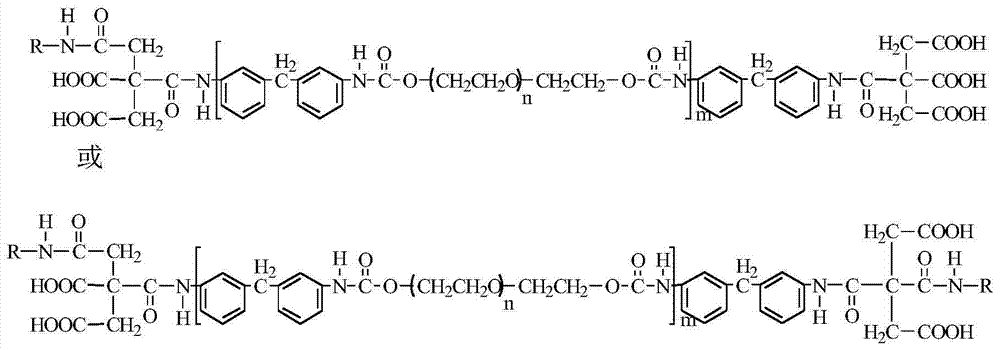
A method and medicament for anticoagulating a patient with a sulfated polysaccharide mixture that demonstrates enhanced anti-inflammatory activity compared to anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin comprising various combinations of fully anticoagulant unfractionated heparin with 2-O desulfated heparin demonstrating reduced anticoagulant activity but enhanced anti-inflammatory actions. The medicament preferably is administered intravenously, by aerosolization or orally. Preferably, the 2-O desulfated heparin medicament includes a physiologically acceptable carrier which may be selected from the group consisting of physiologically buffered saline, normal saline and distilled water. Additionally provided is a method of synthesizing 2-O desulfated heparin in commercially practical quantities for the formulation of an anticoagulant 2-O desulfated heparin and heparin mixture.
Owner:CANTEX PHARMA
Derivatives of K5 polysaccharide having high anticoagulant activity
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 02379 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 6, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 6, 1998 PCT Filed May 9, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 43317 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 20, 1997Derivatives of the K5 polysaccharide having anticoagulant activity higher than heparin, obtained by a process including the steps of reacting: with an organic base a solution of K5 polysaccharide N-deacetylated, N-sulfated and epimerized at least to an iduronic acid content of 50% treating with a sulfating agent to obtain the N-resulfation of the possible N-desulfated groups.
Owner:INALCO SPA
Polysaccharide compositions and methods of use for the treatment and prevention of disorders associated with progenitor cell mobilization
ActiveUS20100316640A1Inhibit tumor growthReduce the total massHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAnticoagulant activityPolysaccharide
Polysaccharide preparations lacking substantial anticoagulant activity are provided herein. Methods of making and using such preparations are provided.
Owner:DILAFOR
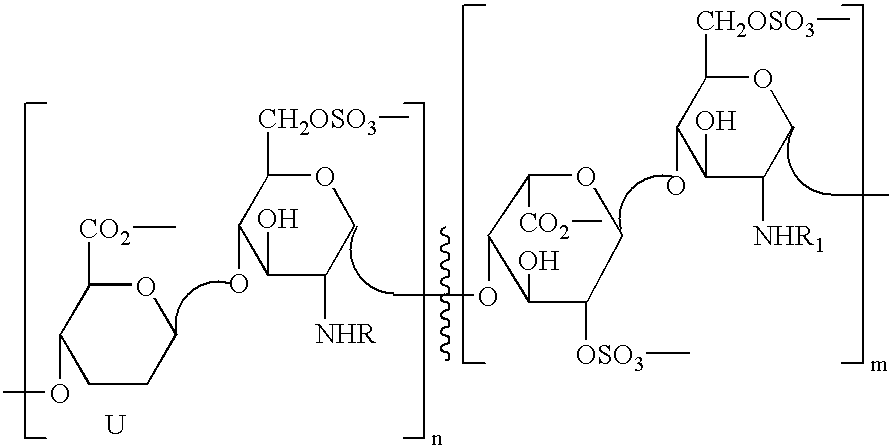
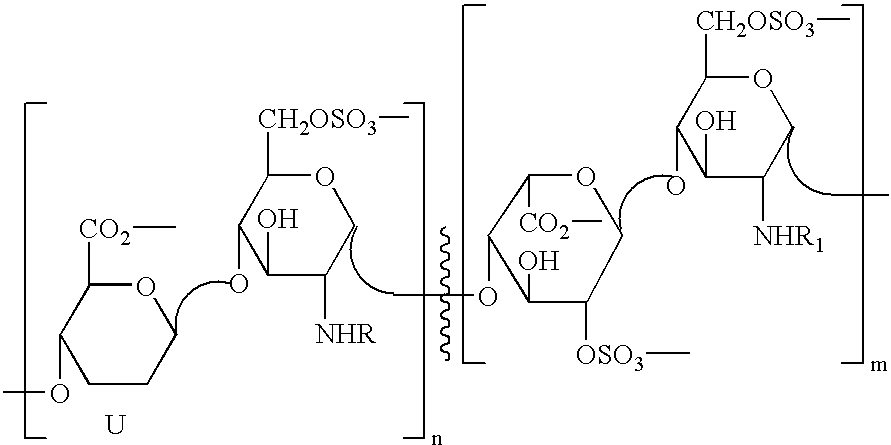
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20080051567A1Loss of anticoagulant activityImprove propertiesOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPerylene derivativesGlycosaminoglycan
Owner:LEADIANT BIOSCI SA
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20060172968A1Avoiding and reducing side effectLoss of anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicinal chemistryAnticoagulant activity
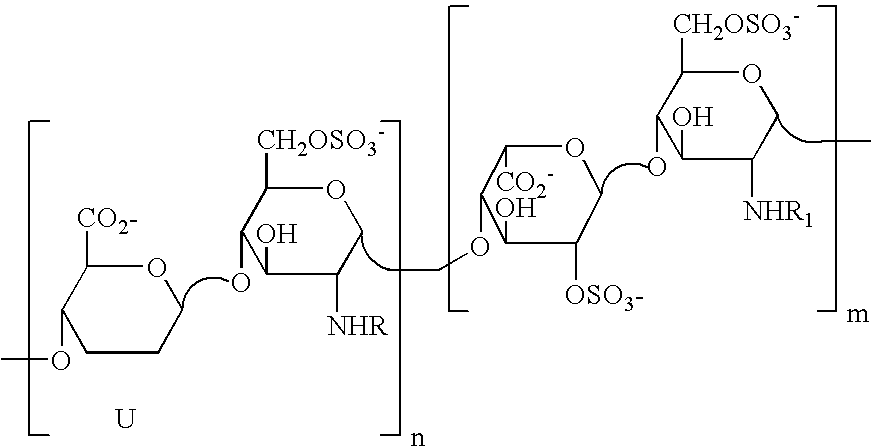
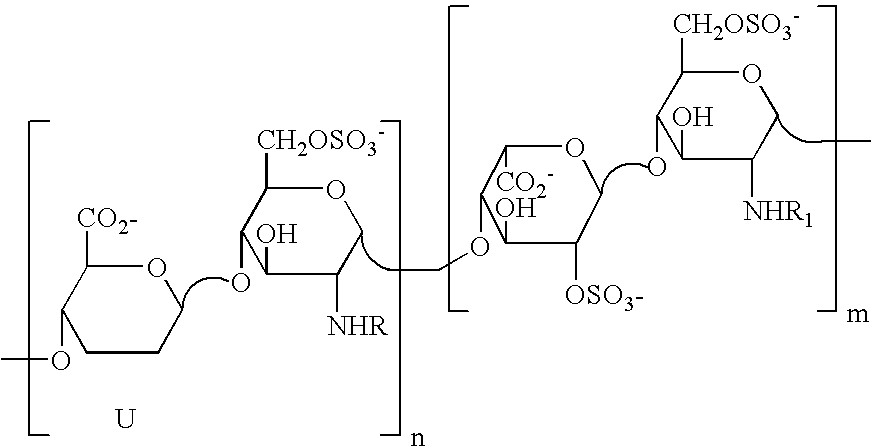
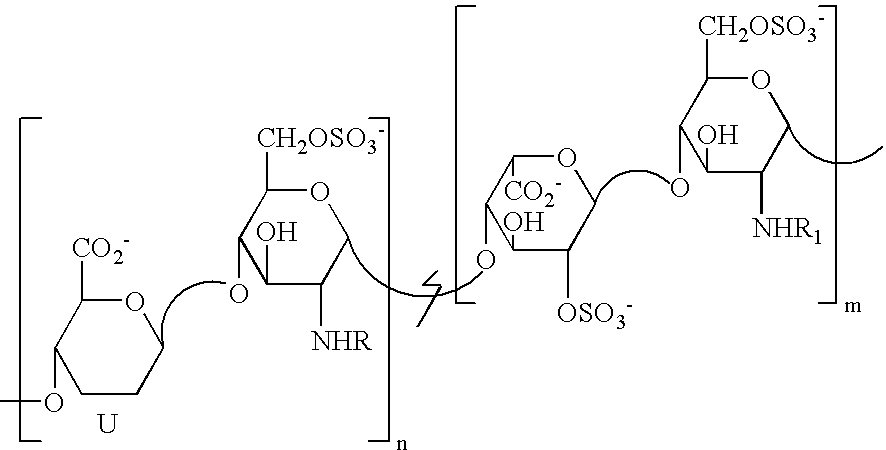
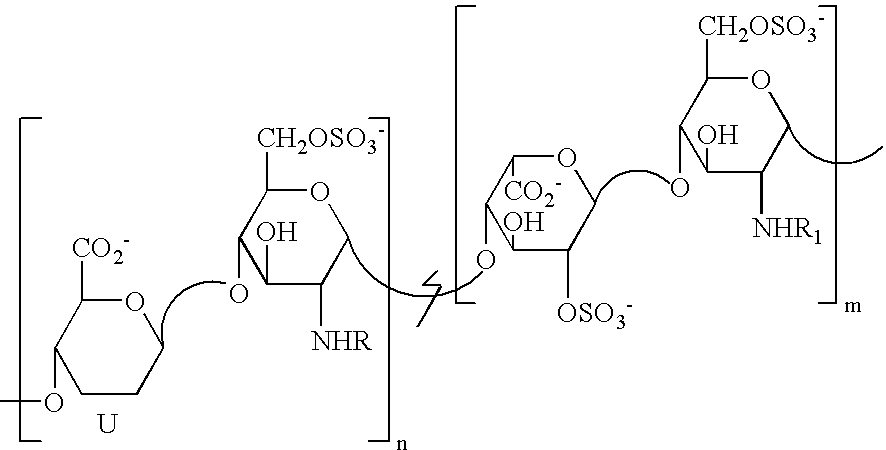
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly a compound of formula (I) where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. These glycosaminoglycan derivatives have antiangiogenic and heparanase-inhibiting activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:LEADIANT BIOSCI SA
Method of producing heparin oligosaccharide using heparinase
A process for preparing heparin oligose from heparinase includes such steps as culturing sphingobacterium (CGMCC No.0660), preparing non-cell coarse enzyme liquid, extracting and purifying heparinase, degradating heparin by the heparinase at 20-30 deg.C to obtain heparin oligose mixture, ultrafilter, gel filter for fractionation and evaporation concentration. The product has the activity of resisting smooth muscle hyperplasia.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
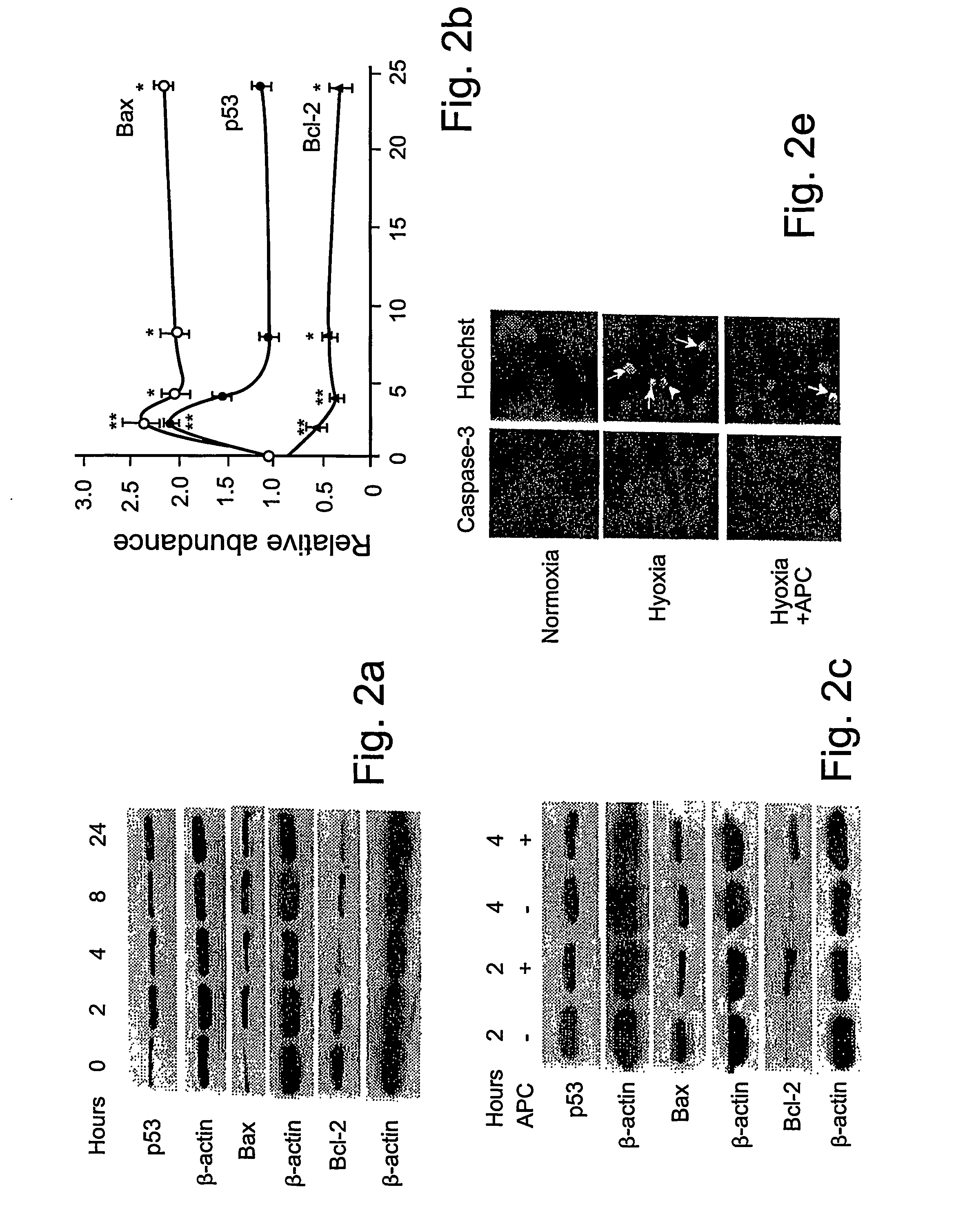
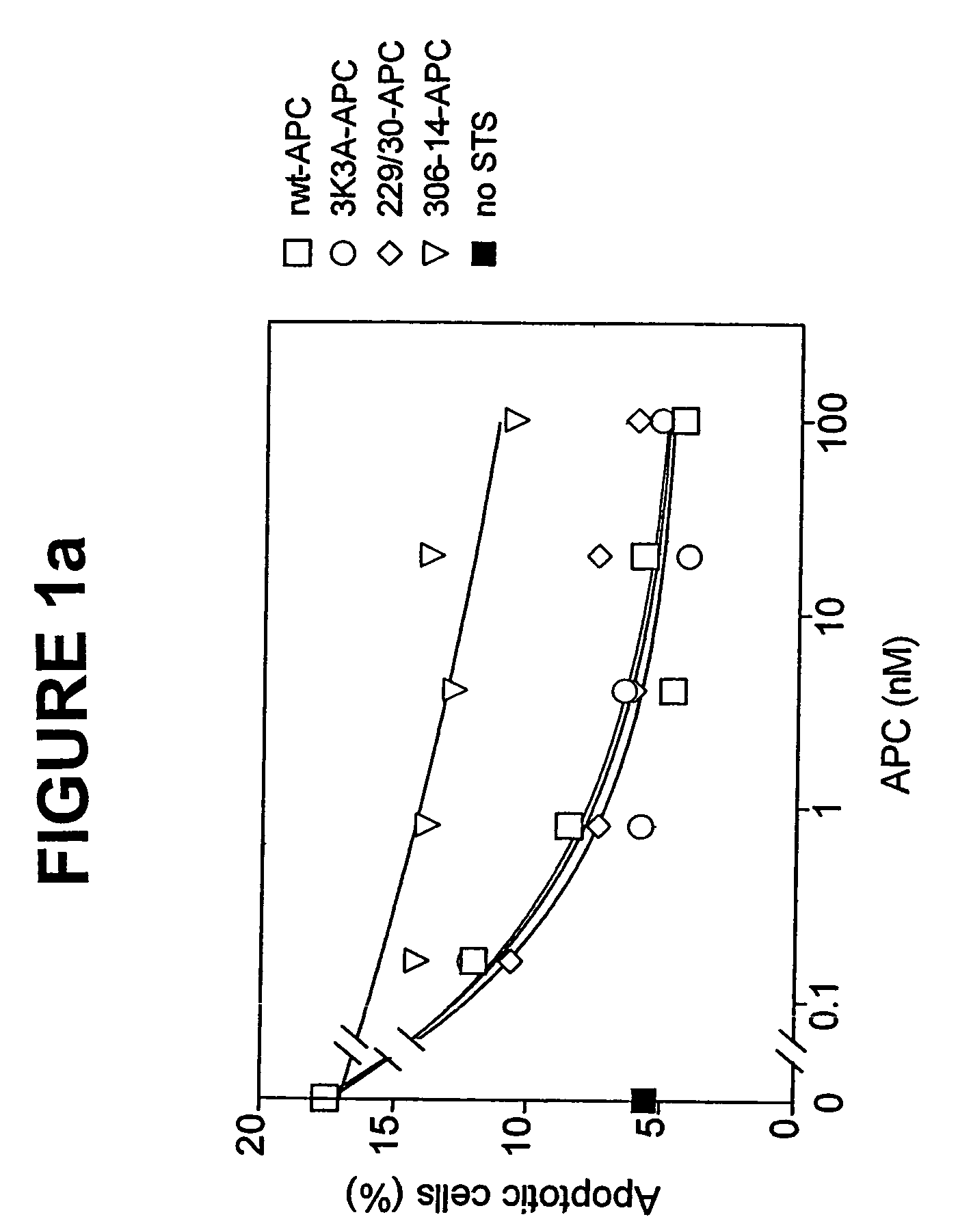
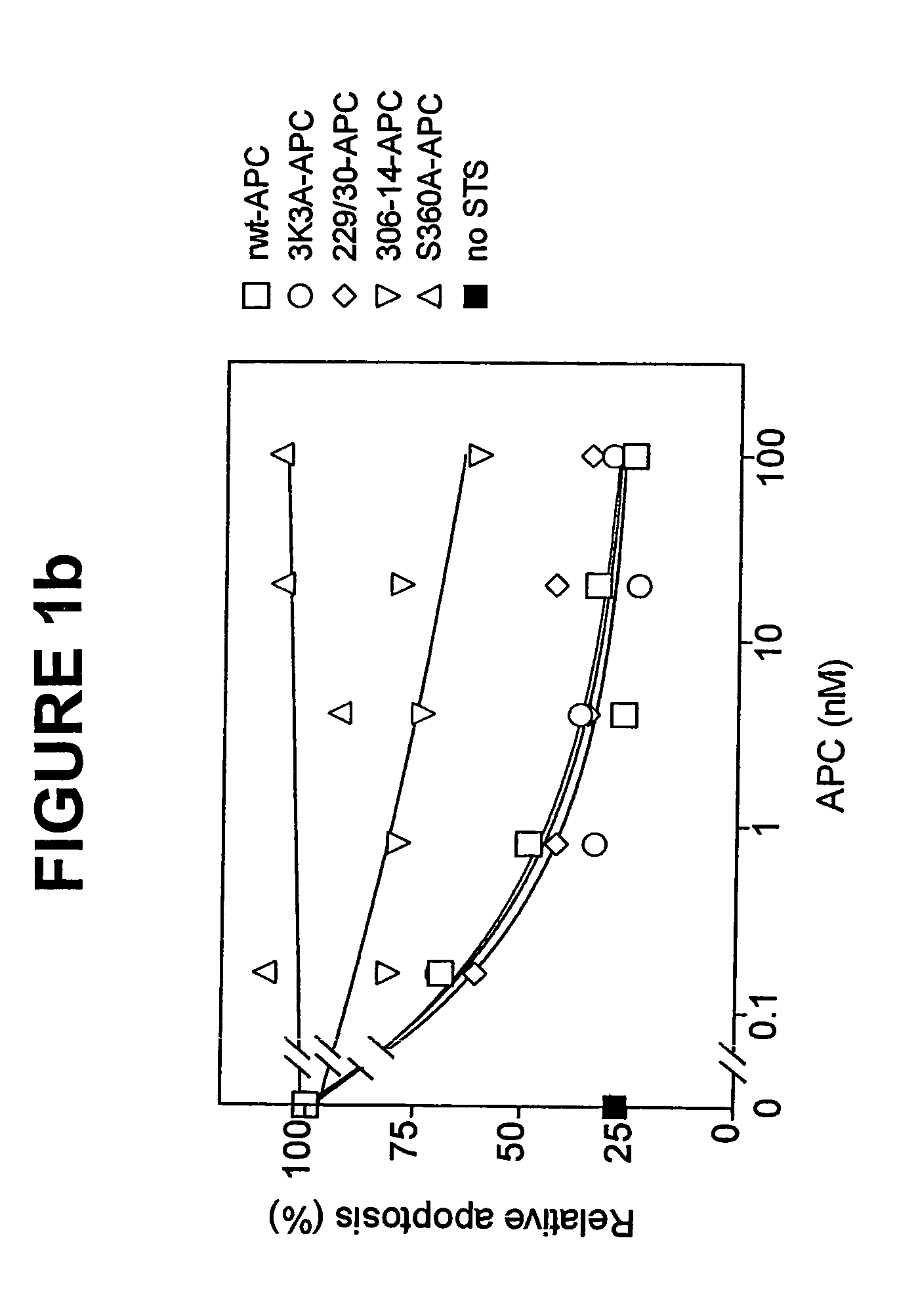
Neuroprotective activity of activated protein c independent of its anticoagulant activity
InactiveUS20070142272A1Enhancing neuroprotectionPromote cell survivalCompound screeningNervous disorderNervous systemInhibitor of apoptosis
Activated protein C (APC), prodrug, and / or a variant thereof may be used as an inhibitor of apoptosis or cell death and / or a cell survival factor, especially for stressed or injured cells or tissues of the nervous system including subjects with neurode-generative disorders. Novel biological functions (e.g., neuroprotection) can be independent or separated from inhibition of clotting or inflammation, and other biological properties of APC (e.g., antithrombotic activity, ability to reduce NFκB-regulated gene expression). It can be used in the treatment of disease or other pathological conditions by at least inhibiting the p53-dependent and / or caspase-3-dependent pro-apoptotic signaling pathways in stressed or injured cells. Thus, APC, prodrugs, and variants thereof (e.g., APC protease domain mutants with reduced anti-coagulant activity) are prototypes of a class of agents for preventing apoptosis or cell death and / or promoting cell survival by direct action on brain cells. New protein C and / or APC variants with reduced anticoagulant activity may be selected thereby.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +2
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminologycans endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticogulating effect
InactiveUS20030013682A1Increased systemic levelShorten the lengthEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsChemical compoundAnticoagulant effect
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly formula (I) compounds, where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. Said glycosaminoglycan derivatives are endowed with antiangiogenic activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS7781416B2Loss of anticoagulant activityImprove propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlycosaminoglycanAnticoagulant activity
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly a compound of formula (I)where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. These glycosaminoglycan derivatives have antiangiogenic and heparanase-inhibiting activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:LEADIANT BIOSCI SA
Novel recombinant anticoagulant proteins
Novel recombinant anticoagulation proteins, methods of their use and methods of their production are described. In particular, recombinant fusions of annexin V (ANV) and Kunitz protease inhibitors (KPI) that possess potent anticoagulant activity are provided. The fusions, abbreviated ANV:KPI, utilize ANV having high affinity for phosphatidyl-L-serine with various KPI's to target serine proteases in membrane-associated coagulation complexes in the blood coagulation cascade. ANV:KPIs are potentially useful antithrombotic drugs permitting localized passivation of thrombogenic vessel walls and associated thrombi.
Owner:WUN TZE CHEIN
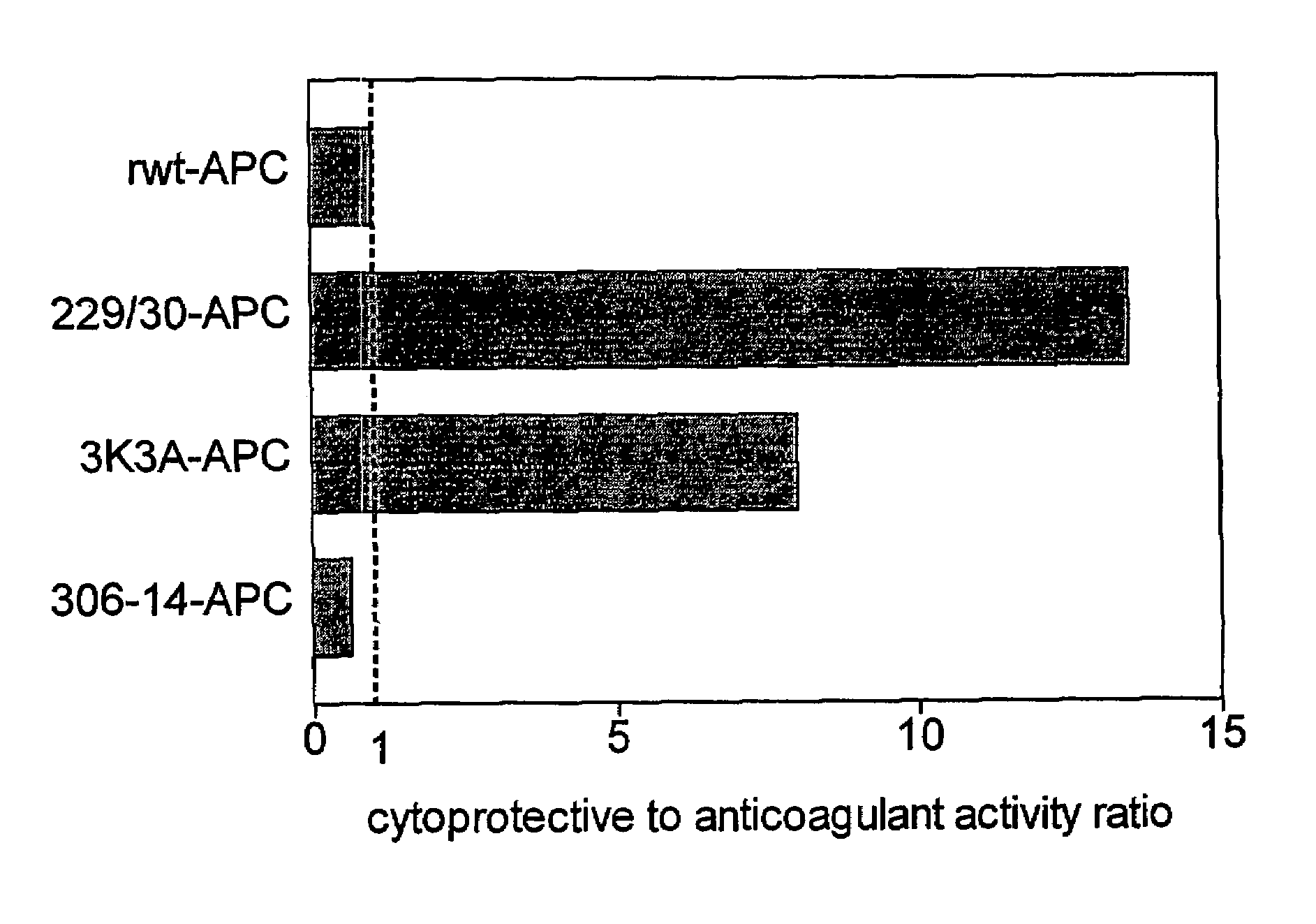
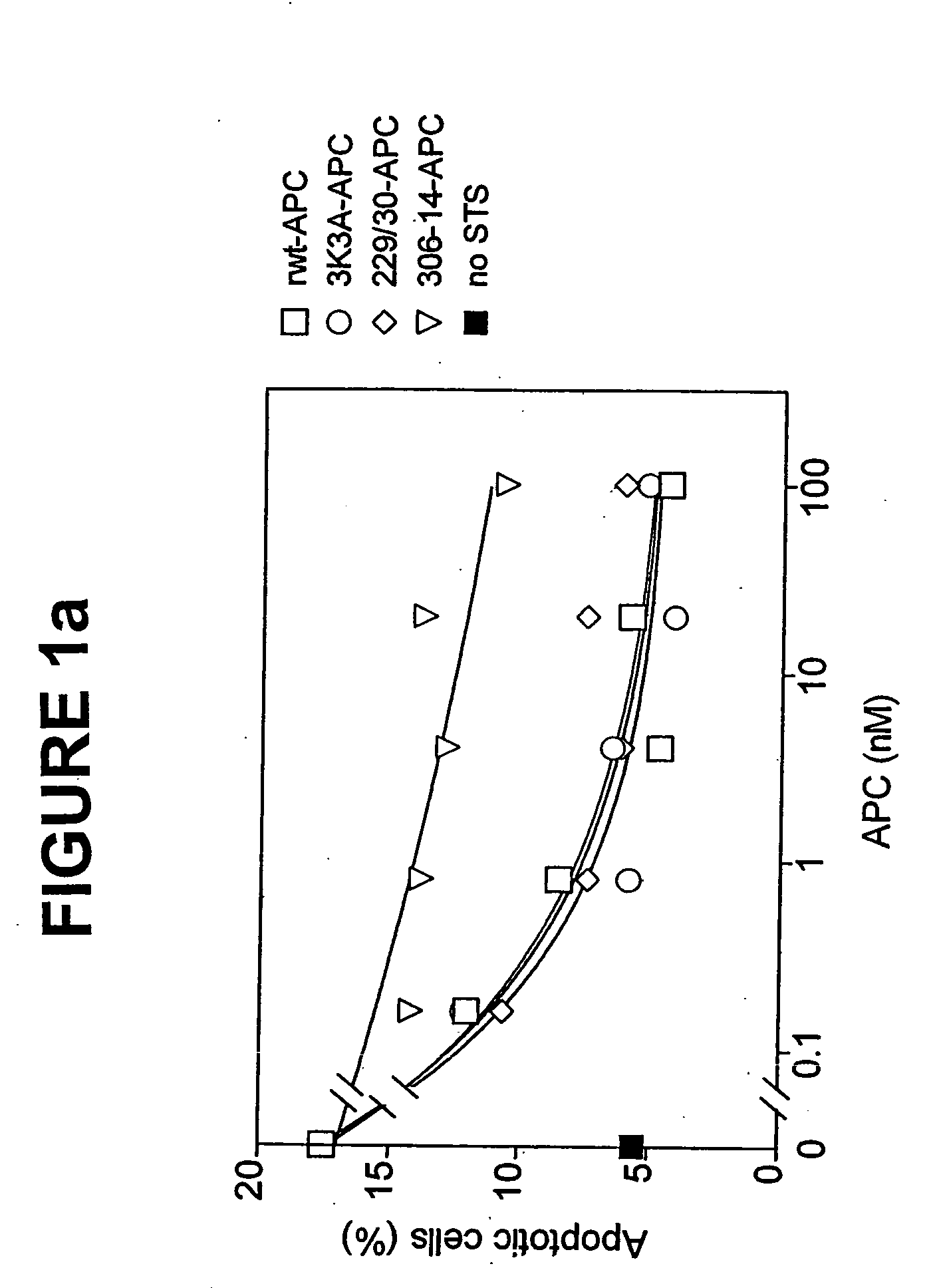
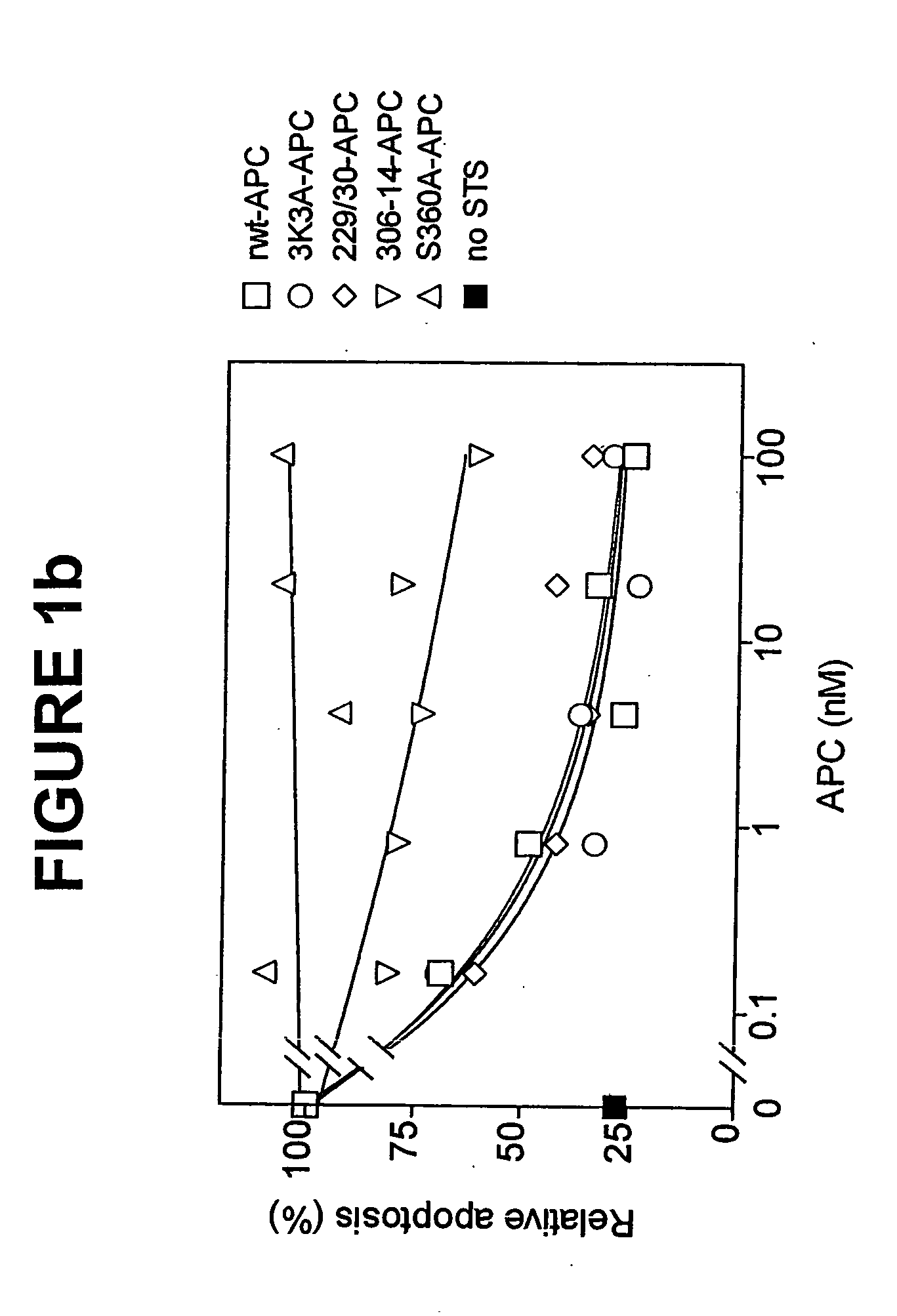
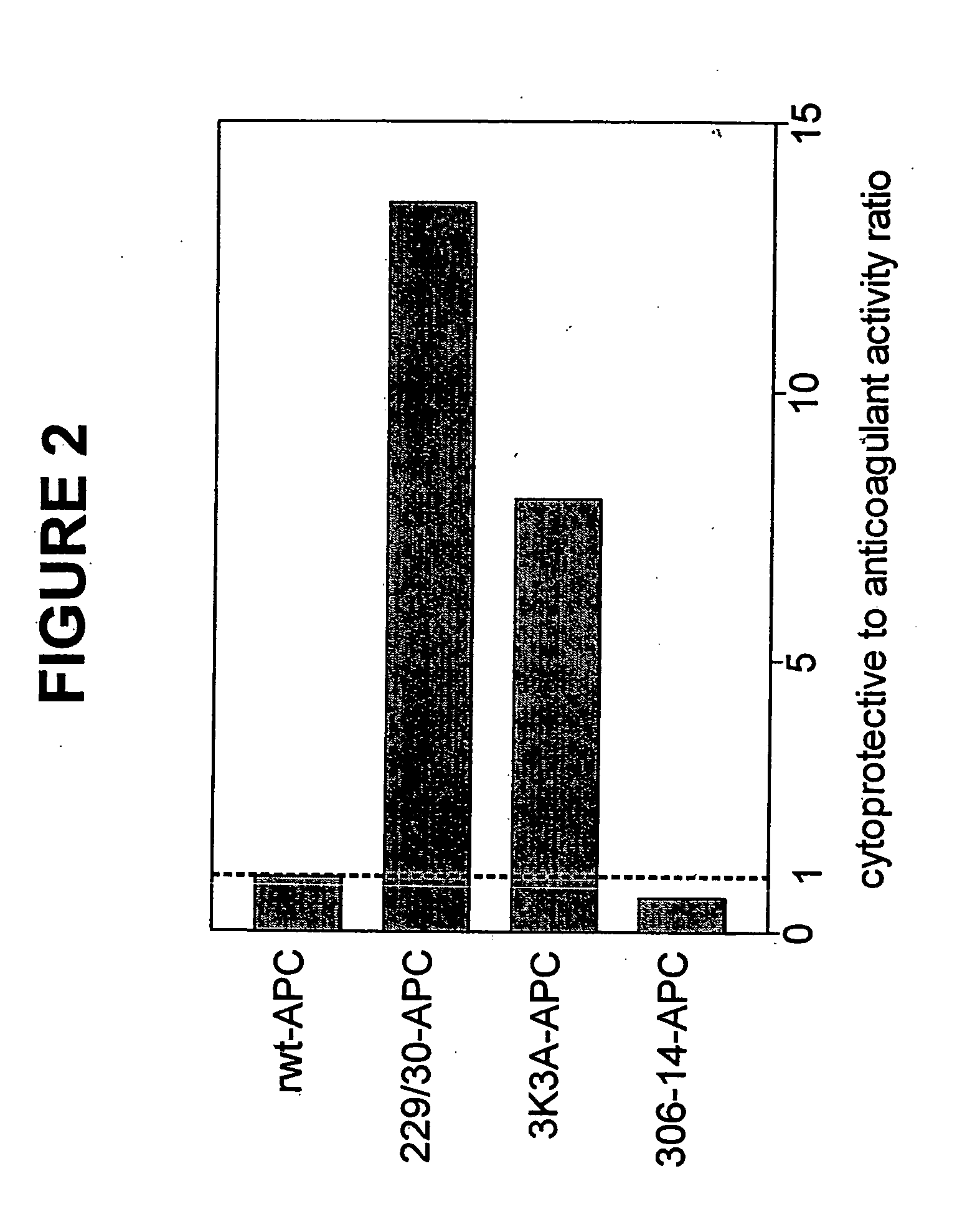
Activated protein C variants with normal cytoprotective activity but reduced anticoagulant activity
ActiveUS7498305B2Reduced activityReduce bleeding riskAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderReperfusion injuryApoptosis
Variants (mutants) of recombinant activated protein C (APC) or recombinant protein C (prodrug, capable of being converted to APC) that have substantial reductions in anticoagulant activity but that retain normal levels of anti-apoptotic activity are provided. Two examples of such recombinant APC mutants are KKK191-193AAA-APC and RR229 / 230M-APC. APC variants and prodrugs of the invention have the desirable property of being cytoprotective (anti-apoptotic effects), while having significantly reduced risk of bleeding. The invention also provides a method of using the APC variants or prodrugs of the invention to treat subjects who will benefit from APC's cytoprotective activities that are independent of APC's anticoagulant activity. These subjects include patients at risk of damage to blood vessels or tissue in various organs caused, at least in part, by apoptosis. At risk patients include, for example, those suffering (severe) sepsis, ischemia / reperfusion injury, ischemic stroke, acute myocardial infarction, acute or chronic neurodegenerative diseases, or those undergoing organ transplantation or chemotherapy, among other conditions. Methods of screening for variants of recombinant protein C or APC that are useful in accordance with the invention are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Citric acid-chitosan-modified anticoagulation polyurethane blood dialysis membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104841285AGood blood compatibilityImprove antibacterial propertiesSemi-permeable membranesPeritoneal dialysisESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENDialysis membranes
The invention discloses a citric acid-chitosan-modified anticoagulation polyurethane blood dialysis membrane and a preparation method thereof. The membrane is of a hollow fibrous structure, and the inner surface and outer surface are dense cortical layers, and the middle is a porous supporting layer, so that the blood dialysis membrane is high in permeability and separating property and antibacterial property; the inner diameter is 160 to 250mu m; the membrane thickness is 30 to 50 mu m, and the ultrafiltration coefficient is 7.0 to 60 ml / m<2>.h.mmHg; citric acid-chitosan-modified anticoagulation polyurethane is taken as membrane materials, and in membrane solution, the percentage mass content of the modified anticoagulation polyurethane is 15 to 30%, and the percentage mass content of a solvent is 70 to 85%, and the blood dialysis membrane is prepared by using a nonsolvent induced phase separation method. The preparation process of the dialysis membrane is simple and easy to control, and the prepared membrane has good anticoagulant activity, biocompatibility and antibacterial property, and the clearance rates of urea, beta2-microglobulin and albumin are respectively 55 to 80%, 48 to 60%, and 2.5 to 9%, and the rate of resisting pathogenic escherichia coli is 99%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Polysaccharide compositions and methods of use for the treatment and prevention of disorders associated with progenitor cell mobilization
ActiveUS20100324276A1Inhibit tumor growthReduce the total massAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseasePolysaccharide
Polysaccharide preparations lacking substantial anticoagulant activity are provided herein. Methods of making and using such preparations are provided.
Owner:DILAFOR
Method for preparing small-diameter artificial blood vessels on basis of nanotechnologies
InactiveCN105079874AGood tissue compatibilityHigh porosityFilament/thread formingProsthesisFiberPorosity
The invention belongs to the field of medicine and high-polymer materials, and discloses a method for preparing small-diameter artificial blood vessels on the basis of nanotechnologies. The method includes steps of dissolving, by weight, 8% of fibroin and 5% of polycaprolactone in hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain spinning liquor; manufacturing the nano-fiber blood vessels with the wall thicknesses of 130-170 micrometers on cylindrical rod-shaped receiving screens with the diameters of 1-1.2mm by means of electrospinning by the aid of electrospinning technologies. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that requirements of tissue engineering on high tissue compatibility, high porosity, plasticity and degradability can be met owing to the electrospinning technologies, vascular stents can be modified by cell activity factors (mechanical growth factors) and medicine (heparin) with anticoagulant activity, and accordingly shortcomings of technological complexity and poor tissue compatibility of existing cell-modified vascular stents can be overcome by the aid of the method.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Protein C variants
InactiveUS20050059132A1Improve propertiesHigh anticoagulant activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsProtein activationWild type
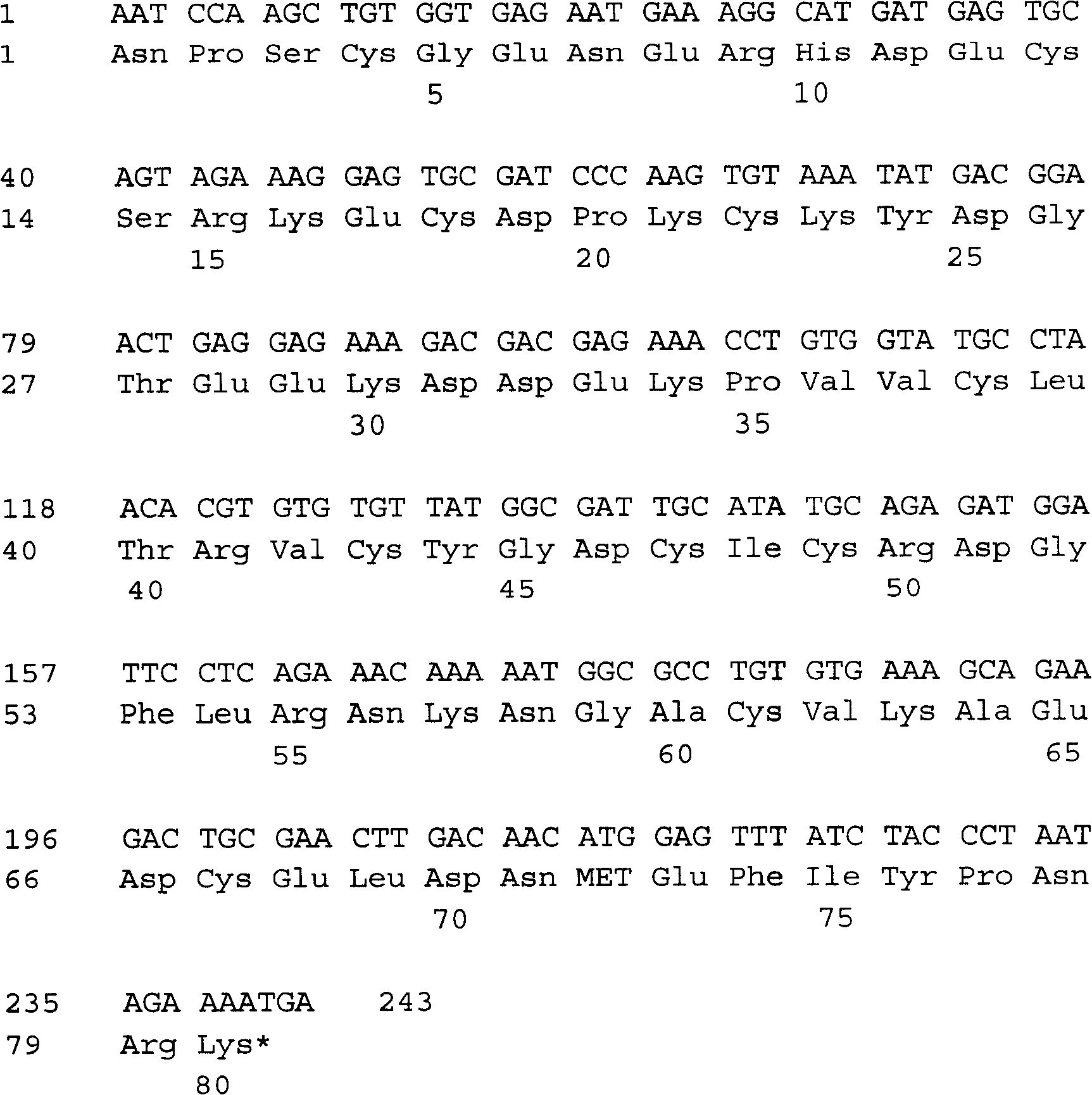
The present invention is concerned with a variant blood coagulation component, which is substantially homologous in amino acid sequences to a wild-type blood coagulation component capable of exhibiting anticoagulant activity in the protein C-anticoagulant system of blood and selected from protein C (PC) and activated protein C (APC), said variant component being capable of exhibiting an anticoagulant activity, that is enhanced in comparison with anticoagulant activity expressed by the corresponding wild-type blood coagulation component, said variant component differing from the respective wild-type component, in that it contains in comparison with said wild-type component at least one amino acid residue modification in it N-terminal amino acid residue sequence that constitutes the Gla-domain of protein C. The present invention is also concerned with methods to produce such variants based on DNA technology, with DNA segments intended for use in the said methods, and with use of said variants for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
Owner:DAHLBACK BJORN +1
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20050137167A1Avoiding and reducing side effectImprove propertiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAnticoagulant effectGlycosaminoglycan
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly formula (I) compounds where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. Said glycosaminoglycan derivatives are endowed with antiangiogenic and heparanase-inhibiting activity ans are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Methods for synthesizing polysaccharides
InactiveUS20080207895A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCombinatorial chemistryOligosaccharide
This invention provides methods for the synthesis of HS polysaccharides or oligosaccharides. This invention provides HS polysaccharides and oligosaccharides thus obtained, and polysaccharides and oligosaccharides with anticoagulant activity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20050222084A1Shorten the lengthAvoiding and reducing side effectEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsAnticoagulant effectPerylene derivatives
Partially desulfated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly formula (I) compounds where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. These glycosaminoglycan derivatives exhibit antiangiogenic activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Preparation method of polysaccharide molecule fragment composite coating
InactiveCN102600515AGood biocompatibilityGood bioadhesionSurgeryPharmaceutical containersBiocompatibility TestingAmination
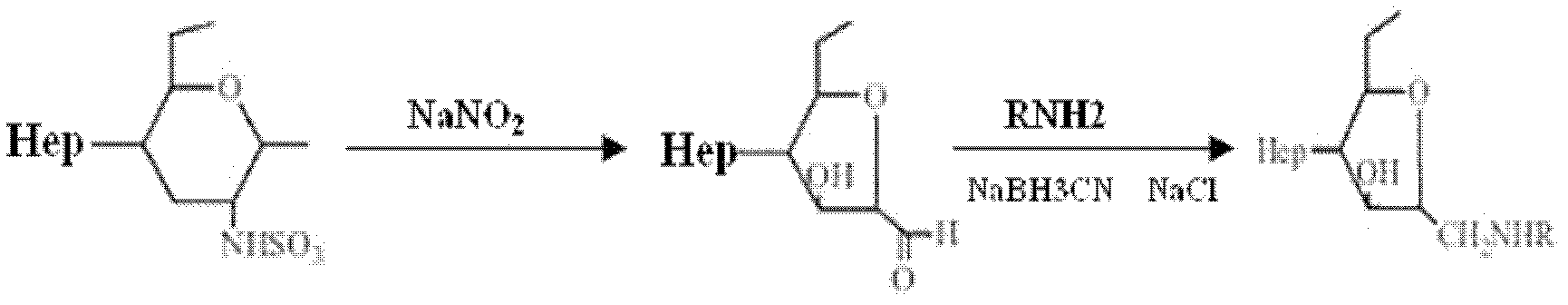
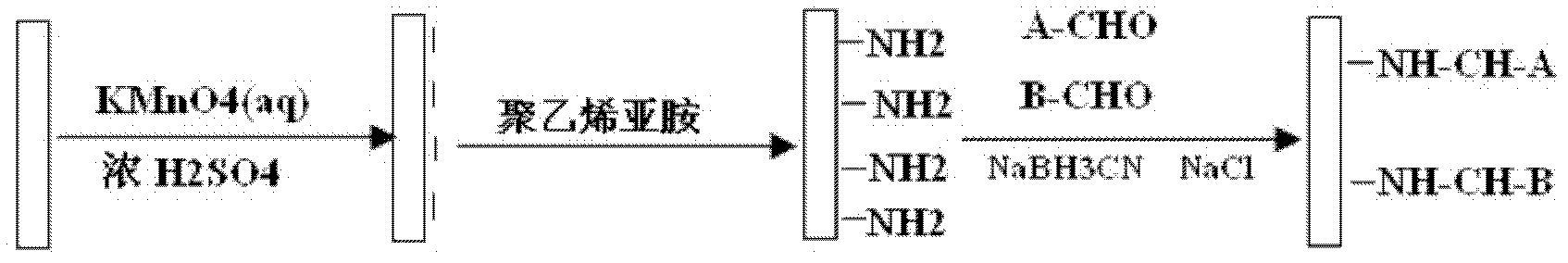
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polysaccharide molecule fragment composite coating. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking a high polymer material in a sulfuric acid solution of potassium permanganate for acidizing; placing the material in a polyethyleneimine solution to obtain an amination-modified surface; dissolving heparin sodium in deionized water, adding nitrous acid and carrying out low-temperature diazotization treatment on the heparin sodium to obtain a polysaccharide fragment A; oxidizing sodium alginate so that the aldehyde group at the tail end of the alginic acid fragment is exposed to obtain polyaldehyde sodium alginate, i.e. a polysaccharide fragment B; and preparing the reaction solution of the polysaccharide fragment A and the polysaccharide fragment B, and placing the material with the amination-modified surface in the reaction solution so as to obtain the composite coating by an endpoint fixing method. In the coating, sodium alginate and heparin group are fixed on the surface of the material, so that the contact area of the sodium alginate and heparin group with blood is enlarged to effectively exert the properties of the sodium alginate and heparin group; and the endpoint fixing method is convenient to implement and the advantages of firm bonding and good space conformation are achieved, and biocompatibility and anticoagulant activity can be effectively improved.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY THIRD CENT HOSPITAL
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20050107331A1Esterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineAnticoagulant activity
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Degradable zwitterionic polymer with biological associativity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103467728AExcellent bioassociationExcellent anticoagulant propertiesPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingBiocompatibility TestingAnticoagulant activity
The invention discloses a degradable zwitterionic polymer with biological associativity. The degradable zwitterionic polymer is prepared by copolymerizing the following materials in parts by weight by taking the total mass of monomers as 100 parts: 50-90 parts of a cyclo-ketene acetal monomer, 1-15 parts of an active ester monomer and 5-40 parts of a zwitterionic monomer. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the degradable zwitterionic polymer with biological associativity, wherein the prepared copolymer has ester groups which ensure that the copolymer can be completely degraded, amphoteric ions which ensure that the copolymer has excellent anticoagulant activity and biocompatibility, and active ester which endows the copolymer with the biological associativity. The copolymer integrates the characteristics of the three monomers, is adjustable and controllable in composition ratio, has multiple functions, and can be used for preparation and surface modification of biological medical materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide and purification method and application thereof
ActiveCN104945531ARealize separation and purificationGood anticoagulant effectBlood disorderFood preparationD-GlucoseLactose
The invention discloses a gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide and a purification method and application thereof and belongs to the field of gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide purification. The gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide comprises the following components monosaccharide including, by mole percentage content, 1-1.5% of fucose, 11-12% of rhamnose, 22-23% of arabinose, 17-18% of galactose, 3-3.5% of glucose, 3-3.5% of xylose, 0.5-1% of mannose and 39-40% of galacturonic acid. According to the gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide and the purification method and the application thereof, further separation and purification of the gentian polysaccharide are achieved, the gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide with the weight-average molecular weight of 5.8*104 Da is obtained, the anticoagulant activity of the gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide is high, the preparation method is simple, the hidden danger existing in the residual chemical reagent is avoided, and the gentian acidity uniform polysaccharide has good development application prospect.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Ancylostoma caninum anticoagulant peptide and its preparation and application
InactiveCN101260150APeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationAntithrombotic AgentAnticoagulation Activity
The invention discloses a novel ancylostoma caninum anticoagulation peptide and an encoded sequence thereof and a preparation method for the anticoagulation peptide. The anticoagulation peptide acquired by the method possesses of anticoagulation activity, can markedly prolong the plasma prothrombin time (PT) and the activation part thrombozyme time(aPTT) of people and has obvious anti thrombosis effects. The invention also relates to applications of the anticoagulation peptide on aspects of anticoagulation drugs, antithrombotic drugs or anticoagulation preparations.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Activated protein C variants with normal cytoprotective activity but reduced anticoagulant activity
ActiveUS20050037964A1Reduced anticoagulant activityReduce bleeding riskAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderReperfusion injuryApoptosis
Variants (mutants) of recombinant activated protein C (APC) or recombinant protein C (prodrug, capable of being converted to APC) that have substantial reductions in anticoagulant activity but that retain normal levels of anti-apoptotic activity are provided. Two examples of such recombinant APC mutants are KKK191-193AAA-APC and RR229 / 230M-APC. APC variants and prodrugs of the invention have the desirable property of being cytoprotective (anti-apoptotic effects), while having significantly reduced risk of bleeding. The invention also provides a method of using the APC variants or prodrugs of the invention to treat subjects who will benefit from APC's cytoprotective activities that are independent of APC's anticoagulant activity. These subjects include patients at risk of damage to blood vessels or tissue in various organs caused, at least in part, by apoptosis. At risk patients include, for example, those suffering (severe) sepsis, ischemia / reperfusion injury, ischemic stroke, acute myocardial infarction, acute or chronic neurodegenerative diseases, or those undergoing organ transplantation or chemotherapy, among other conditions. Methods of screening for variants of recombinant protein C or APC that are useful in accordance with the invention are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method of preparing recombinant small molecular protein or polypeptide with hirudin as fusion partner
InactiveCN103819546APlant peptidesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingFusion Protein ExpressionProtein target
The invention provides a new method of fusion expressing a small molecular protein (polypeptide). The new method is characterized by comprising the following steps: using hirudin as a fusion partner (label), splicing the protein (polypeptide) with a small molecular mesh to the downstream of the hirudin as the fusion partner to carry out fusion expression, designing a connecting peptide (which contains protease or a chemical cutting site or intein as a self-cuttable protein intron) between the fusion partner and a target protein (polypeptide), and releasing the target protein (polypeptide) by restriction enzyme digestion or chemical cutting or induced self cutting after fusion protein expression. The new method has the advantages that (1) as the hirudin as the fusion partner (label) is smaller (with the molecular weight of 7Kd), the rate of the protein (polypeptide) with the small molecular mesh accounting for a fusion protein can be effectively increased, and the yield of the target small molecular protein (polypeptide) is finally increased; (2) the hirudin still has the anticoagulant activity after being fused as the fusion partner (label), and the expression and the purification of the fusion protein can be conveniently detected and traced in real time.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
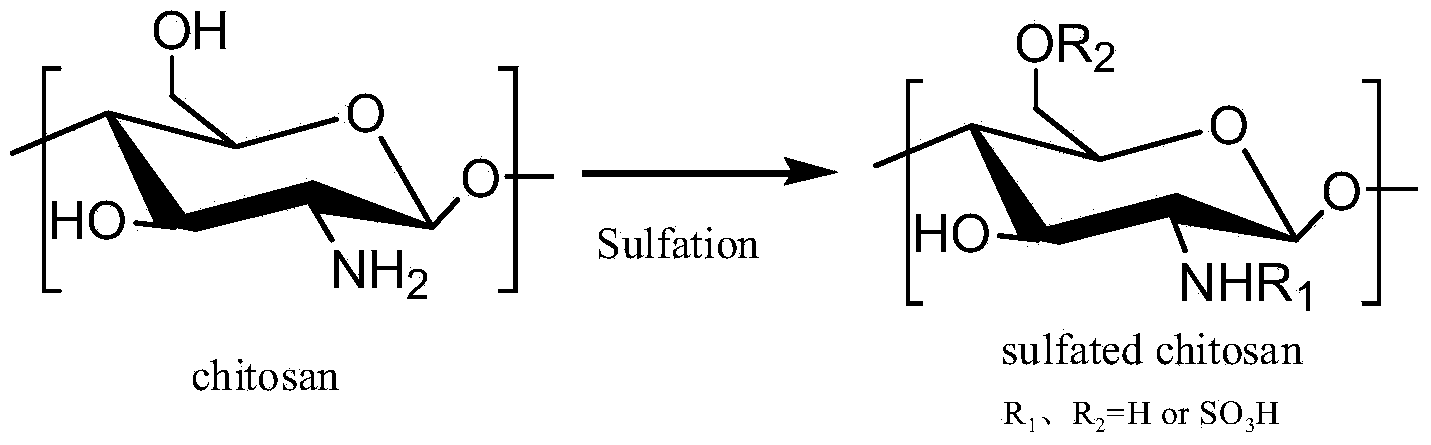
Synthesis method of 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan sulfuric sulfation product
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan sulfation product. The method comprises the following steps: (1) chitin alkaline treatment of chitin; (2) carboxymethylation of C6-O site of chitin; (3) deacetylation reaction of 6-O-carboxymethyl chitin; and (4) sulfation of 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention is a bran-new method for selectively replacing and controlling the replacement rate by using chitin. The synthesis product of the method provides N-site -SO3H with main anticoagulant activity and introduces -COOH, so that a lot of -COOH and SO3H which have negative electricity in the molecular structure are regularly distributed, and an anticoagulant effect of heparinoid is generated by the synergistic effect. High molecular polysaccharide is a heparinoid drug which is selectively modified by chitin via a safe reagent, so that reagent pollution of bulk drugs is reduced, the virus contamination risk of heparin biological extraction is avoided, the safety performance of the drug in the clinical experiment is more excellent in theory as compared with heparin sodium, so the 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan sulfation product provided by the invention is expected to serve as a cheap direct thrombin inhibitor to replace heparin sodium anti coagulation drugs.
Owner:SHENZHEN BRIGHT WAY NOVEL BIO MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
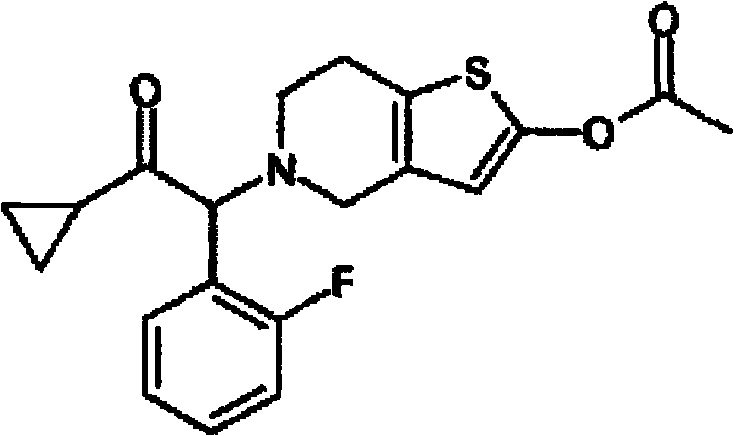
Pharmaceutical composition containing prasugrel
ActiveCN101554378ADid not affect anticoagulant activityHigh anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderThrombusCvd risk
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition containing active procyanidins and prasugrel or the pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof. The procyanidins and the prasugrel are used in a combined manner, a more effective method for curing thrombotic diseases is found, after trail for many times, the prasugrel and the procyanidins (an extract of traditional Chinese medicine) are creatively and effectively combined together, the effect of applying the procyanidins to inhibit the thrombosis in a combined manner is discovered unexpected in the process of applying the prasugrel to cure the thrombotic diseases, and not only the anticoagulant effect of the prasugrel is free from the influence of the procyanidins, but also a good effect is achieved in the aspect of reducing the adverse reaction of bleeding after the use of the prasugrel and the procyanidins in a combined manner, therefore, the risk of bleeding is greatly reduced when the advantages of good anticoagulant activity and fast effect of the prasugrel during the antiplatelet aggregation are fully exerted, the risk of bleeding of the prasugrel during the antiplatelet aggregation is effectively reduced and the adverse reaction of the prasugrel is greatly reduced.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
End-point fixing preparation method for multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating
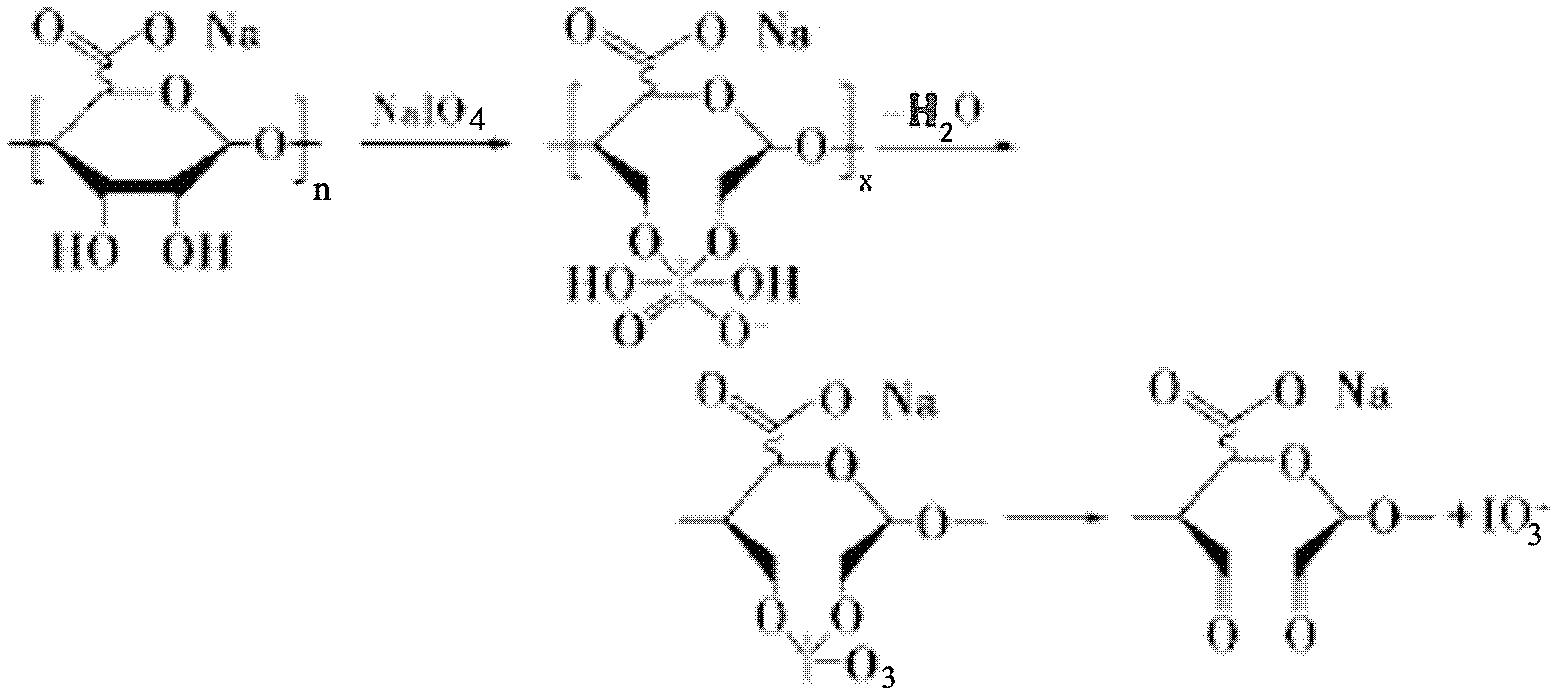
InactiveCN102617880AImprove bindingGood spatial conformationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPotential toxicityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an end-point fixing preparation method for a multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, polymer material is soaked into sulfuric acid solution of potassium permanganate for acidizing treatment; then the material subjected to acidizing treatment is placed into polyethylene imine solution so as to obtain an amination decorated surface after reaction; periodic acid or sodium periodate is used for oxidation treatment to sodium alginate, aldehyde group is exposed at the tail end of the segment of alginic acid, and multi-aldehyde sodium alginate is obtained; the liquid reactant of the multi-aldehyde sodium alginate is prepared, the material on the amination decorated surface is placed into the liquid reactant, and the multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating is obtained through an end-point fixing method. The preparation method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of bad biocompatibility, poor anticoagulant activity,potential toxicity and the like in common polymer material.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY THIRD CENT HOSPITAL
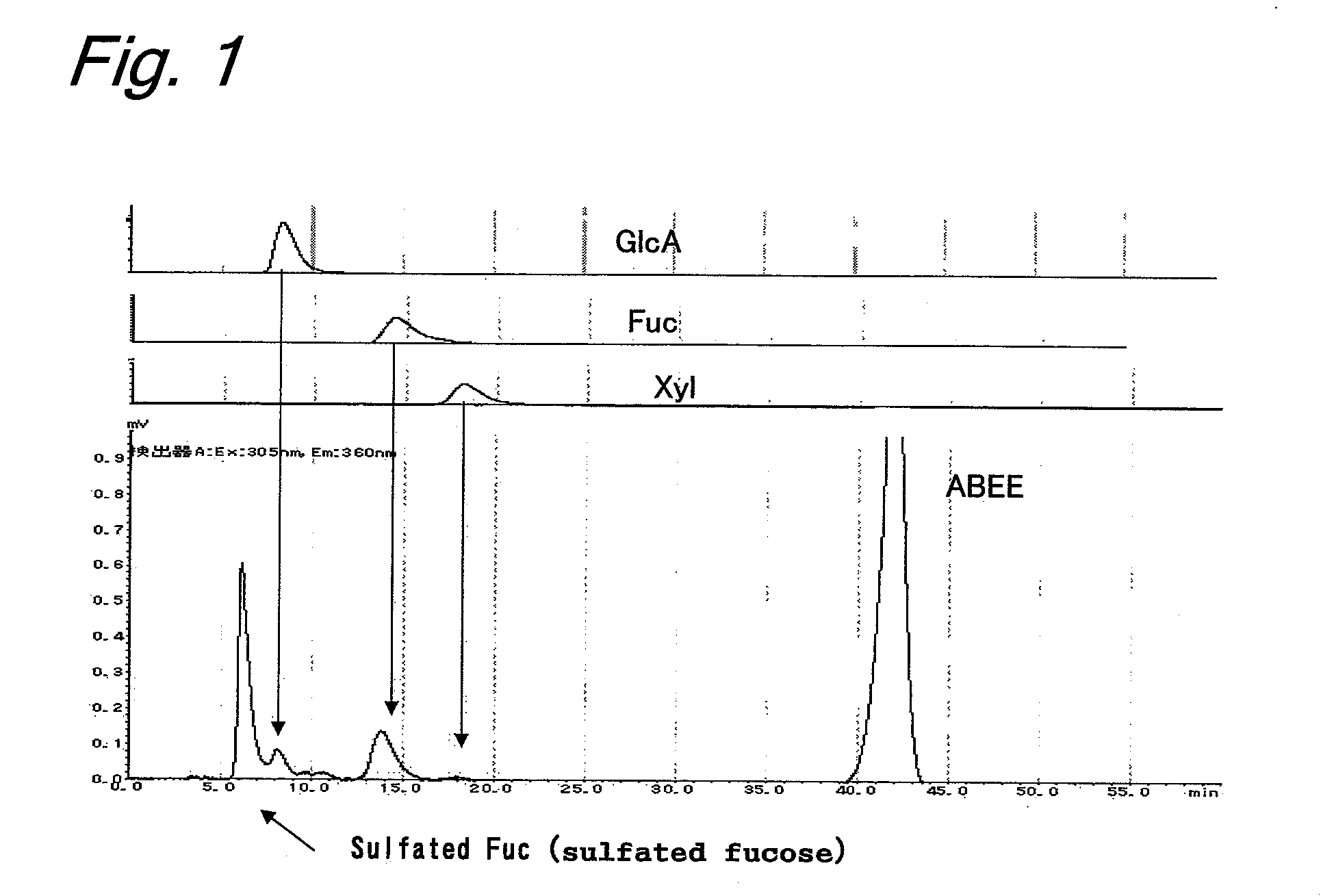
Oligosaccharides derived from fucoidan
The present invention provides a fucoidan-derived low molecular weight compound with a good quality of taste, which has a specified structure and function and is free from problems in absorption, antigenicity, uniformity, an anticoagulant activity and so on, which problems arise when developing fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide having an extremely large molecular weight, as drugs or health foods. As a result of analyzing low molecular weight compounds obtained by acid hydrolysis of fucoidan, the inventors have identified fucoidan oligosaccharides (I) to (XI). Further, these oligosaccharides have been found to have anti-obesity and / or blood glucose elevation suppressing effects through inhibition of carbohydrate and / or lipid absorption as a result of α-glucosidase inhibition and / or lipase inhibition.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD +1
Sodium alginate sulfuric ester and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN1542021AHigh anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderSulfateUronic acid
The present invention discloses one kind of new compound sodium alginate sulfate and its preparation. The preparation process includes adding ad alginate into sulfatizing reagent, reaction at 40-70 deg.c to obtain reddish brown solution, dialysis and concentration to obtain sodium alginate sulfate. The in vitro blood coagulation with the obtained sodium alginate sulfate shows that it has very high anticoagulant activity and has APTT value reaching the level of haparin in the said concentration, so that sodium alginate sulfate may be used as anticoagulant in preparing blood coagulation resisting medicine.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com