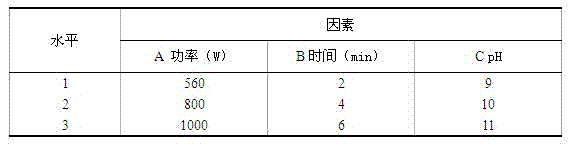
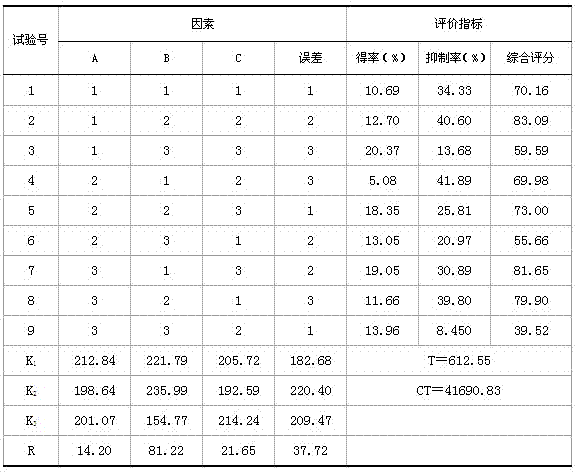
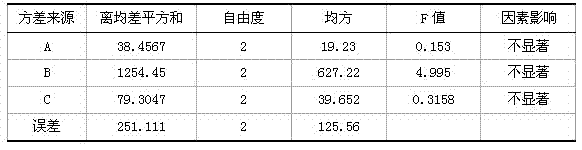
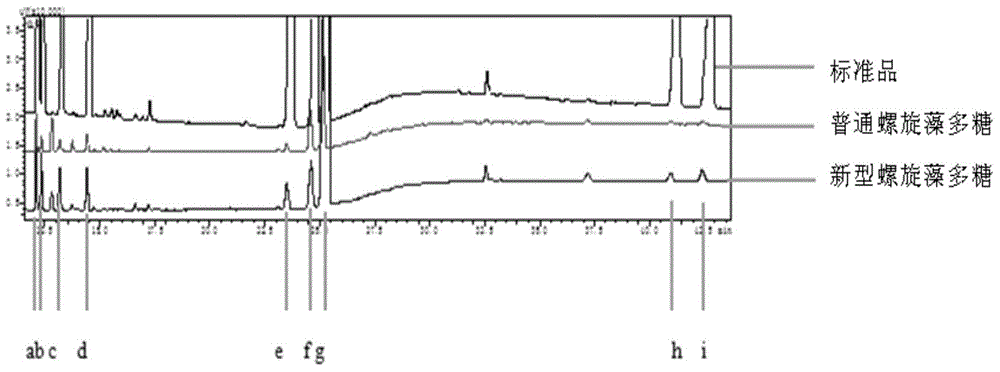
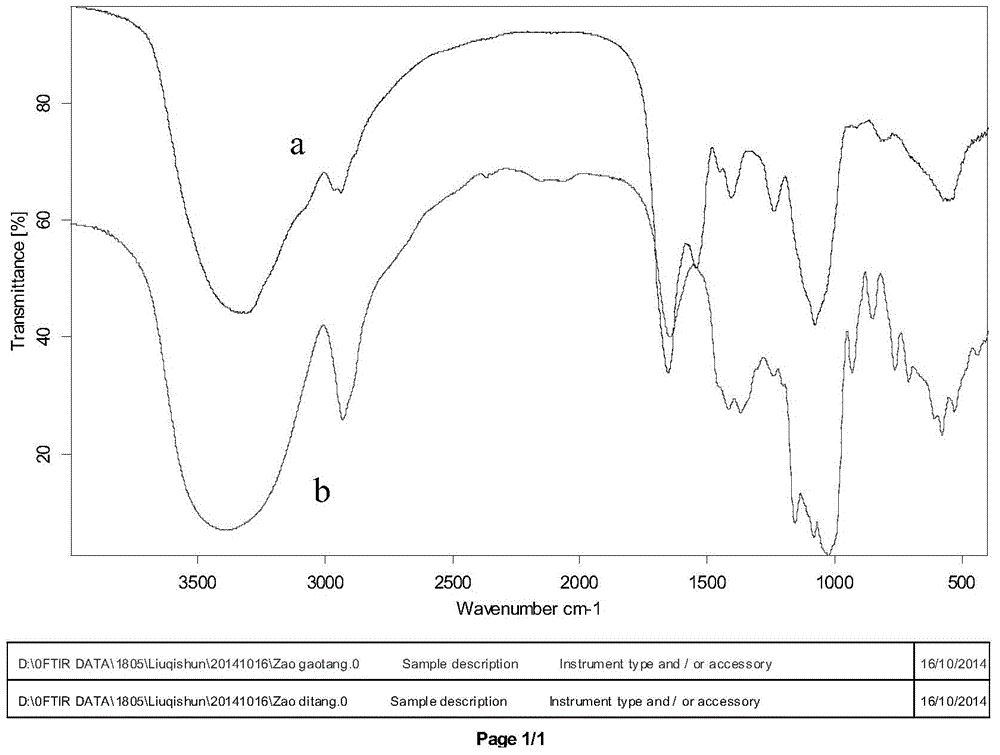
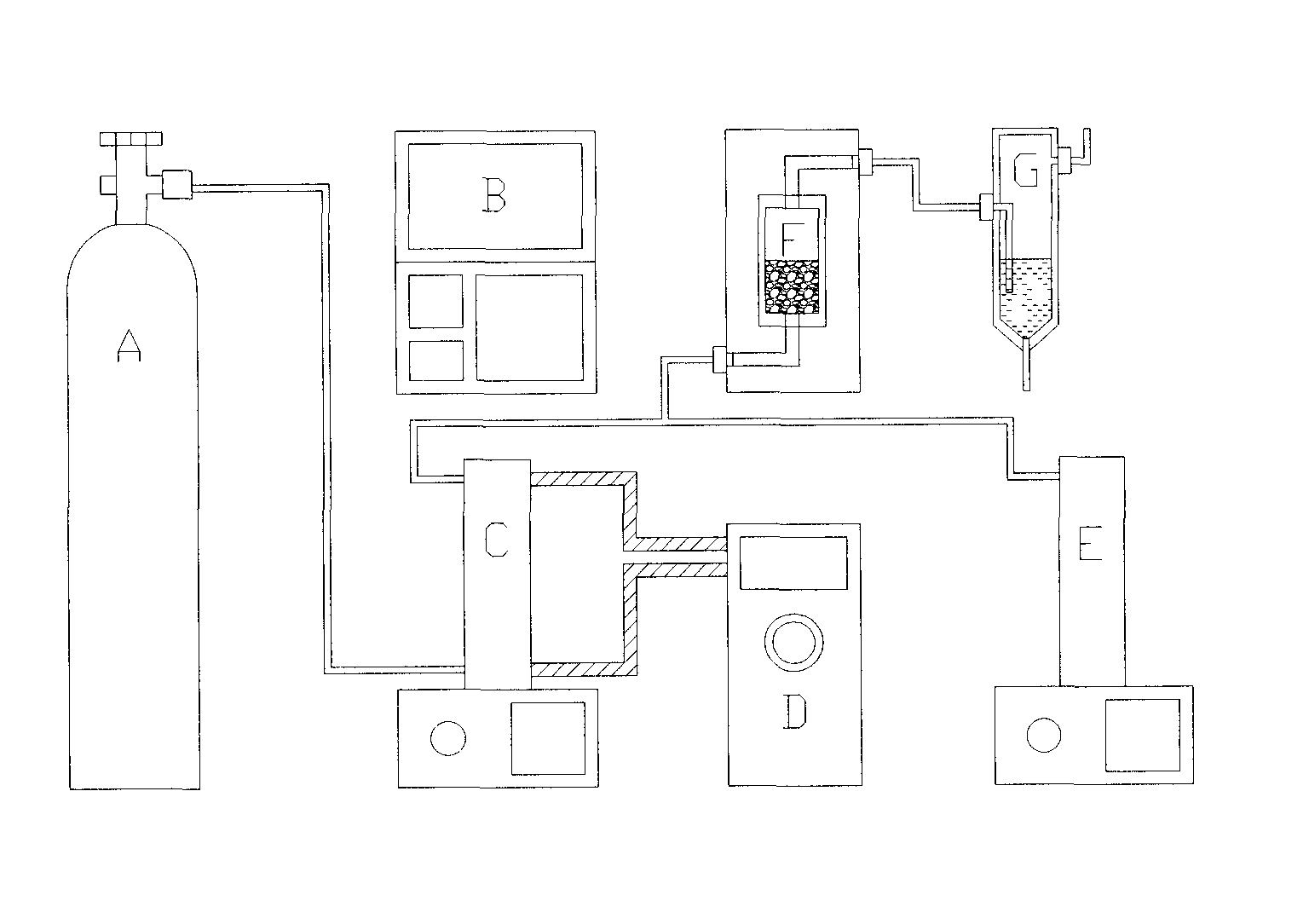
Patents
Literature
387 results about "Spirodela" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spirodela is a genus of aquatic plants, one of several genera containing plants commonly called duckweed. Spirodela species are members of the Araceae under the APG II system. They were formerly members of the Lemnaceae.
Technique for extracting phycocyanin, chlorophyll and spirulina polysaccharide in spirulina
InactiveCN101607988AEfficient use ofAvoid wastingPeptide preparation methodsAlgae/lichens peptidesFreeze and thawPhycocyanin
Owner:威海格瑞安生物工程有限公司
Five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105559064APromote absorptionEnhance immune functionFood ingredient functionsImmunologic functionCancer cell proliferation
The invention provides five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets and a preparation method thereof. The five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets are prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 10-20 parts of chlorella vulgaris, 1-10 parts of dunaliella salina, 1-10 parts of euglena, 1-10 parts of red algae, 10-20 parts of spirulina and 10-20 parts of probiotic powder. The five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets provided by the invention adopt the chlorella, dunaliella salina, red algae, spirulina and euglena for complementation in nutrition, and obtain trace elements easier to absorb by a human body through probiotic fermentation, thereby helping to reinforce the immunologic function of the human body, resist virus infection and proliferation, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, repair the damage of an organism quickly, remove vivotoxin, suppress blood pressure and blood sugar rise, reduce the serum cholesterol content, and thus improve the comprehensive conditioning of the human body.
Owner:于蜀豪 +1
Soil amendment
A disclosed soil amendment is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of water, 5-10 parts of spirulina, 30-50 parts of an organic fertilizer, 20-30 parts of peat soil, 10-18 parts of zinc sulfate , 10-15 parts of acrylamide, 8-16 parts of gypsum, 10-15 parts of sodium acrylate, 25-35 parts of montmorillonite, 11-21 parts of , 20-28 parts of furnace ash, 12-18 parts of blast-furnace slag, 7-14 parts of calcium magnesium phosphate, 4-8 parts of borax and 15-20 parts of pig manure. The provided soil amendment is capable of promoting growth of crops, enhancing resistance of crops, improving the soil structure of sand, increasing basic nutrients, stimulating growth of crops, and improving capability of resisting diseases, resisting drought and resisting cold.
Owner:QINGDAO CHENQING INFORMATION TECH
Method for extracting polysaccharide of spirulina platensis
ActiveCN103073652AHigh extraction rateDoes not affect the structureMicrofiltration membraneFilter material
The invention discloses a method for extracting polysaccharide of spirulina platensis. The method comprises the steps that spirulina platensis is subjected to an extraction process to form an extracting solution, the extracting solution is filtered through a microfiltration membrane and is subjected to ultrafilteration, concentration and drying, then more than one type of crude polysaccharide of aqueous extract spirulina platensis is obtained, the content of total sugar is larger than or equal to 10%, and the molecular weight is more than 5,000; or the extracting solution is concentrated and decontaminated, a processed solution is centrifuged under the rotating speed lower than or equal to 15,000 r / min, filtered through the microfiltration membrane and subjected to ultrafilteration by a filter material with the molecular weight in a range from 5,000 to 200,000, when no effluent flows out from an outlet of an ultrafilter, the effluent of the ultrafilter and a concentration solution in the ultrafilter are collected to be dried, then more than one type of polysaccharide of aqueous extract spirulina platensis is fromed, the content of total sugar is larger than or equal to 40%, and the molecular weight is in a range from 5,000 to 200,000. According to the method for extracting polysaccharide of spirulina platensis, reasonable processing measures are selected at different stages of a proces route according to different requirements for product purity, and then high purity olysaccharide with the scheduled molecular weight specification can be formed without detection; and moreover, polysaccharide of spirulina platensis with a pluraity of specifications can be formed simultaneosuly. Accordingly, the method has the advanatags which are impossible to be obtained by other traditional methods.
Owner:YUNNAN PHYTOPHARML
A kind of spirulina active polysaccharide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102286109AGood anti-lipid peroxidation activityAvoid destructionOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPretreatment methodAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to an active spirulina polysaccharide and a preparation method thereof. By introducing an activity evaluation index, discussing the influence of a raw material pretreatment method and different extraction processing technologies on spirulina polysaccharide yield, polysaccharide preservation rate, protein removal rate and polysaccharide lipid peroxidation resistance and evaluating and screening an extraction processing technology capable of well keeping the bioactivity of the spirulina polysaccharide and with relatively high spirulina polysaccharide yield, the active spirulina polysaccharide is prepared by preferable process conditions; the main active ingredients of the active spirulina polysaccharide are binding protein polysaccharides, the molecular weights of which are 100,000 and 95,000 respectively; the active spirulina polysaccharide has remarkable hepatic tissue lipid peroxidation activity resistance; and the two binding protein polysaccharides are qualitycontrol index ingredients of a spirulina lipid peroxidation activity resistant polysaccharide product. Compared with a method discussed in the conventional technology, the protection of the extraction, separation and purification processes on the activity of the spirulina polysaccharide is stressed; and by comprehensively evaluating and optimizing the preparation process conditions, blindness of the process discuss and destroy and loss of the active ingredients in the extraction and purification processes can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Spirulina polysaccharide and application thereof
ActiveCN105707072AInduced plant disease resistanceNatural sourceBiocideAlgae medical ingredientsMonosaccharide compositionFreeze-drying
The invention relates to glucose-rich spirulina polysaccharide and an application thereof in a plant green pesticide and an anti-tumor drug. High-sugar spirulina obtained through nutritional regulation is used as a raw material and is subjected to hot water extraction, protein removal with a flocculant, concentration, precipitation and freeze drying to obtain the water-soluble high-sugar spirulina polysaccharide having the molecular weight of 10-200 kDa; the spirulina polysaccharide comprises the monosaccharides mainly comprising rhamnose, fucose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose, glucose, glucuronic acid and galacturonic acid, and is characterized in that the glucose content is more than 50% in the monosaccharide composition. The spirulina polysaccharide can obviously induce plant disease resistance, has obvious anti-tumor effect on tumor, and can be used as the biological pesticide and the anti-tumor drug.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina by using supercritical fluid
The invention relates to a method for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina by using supercritical fluid, which comprises the following steps: placing 0.5-3g of spirulina powder into an extraction kettle, introducing carbon dioxide, boosting the pressure to 20-40MPa through a high pressure pump, setting the temperature to be 30-60 DEG C and the flow of the carbon dioxide to be 50-120g / h, extracting for 1-5h, obtaining the chlorophyll in a separator connected with the extraction kettle, or adding absolute ethyl alcohol into an extractor to be used as an entrainer, wherein the use amount of theentrainer is as follows: 0.05-0.15L of absolute ethyl alcohol is adopted in 1g of the spirulina powder. The method greatly avoids reactions of de-magging, esterification and the like occurring in theprocess of common extraction, farthest keeps the original characteristics of the chlorophyll, has simple procedure, less steps, short production period, high efficiency, complete extraction and no anynew three-wastes, and is beneficial to protecting the environment.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and extraction method thereof
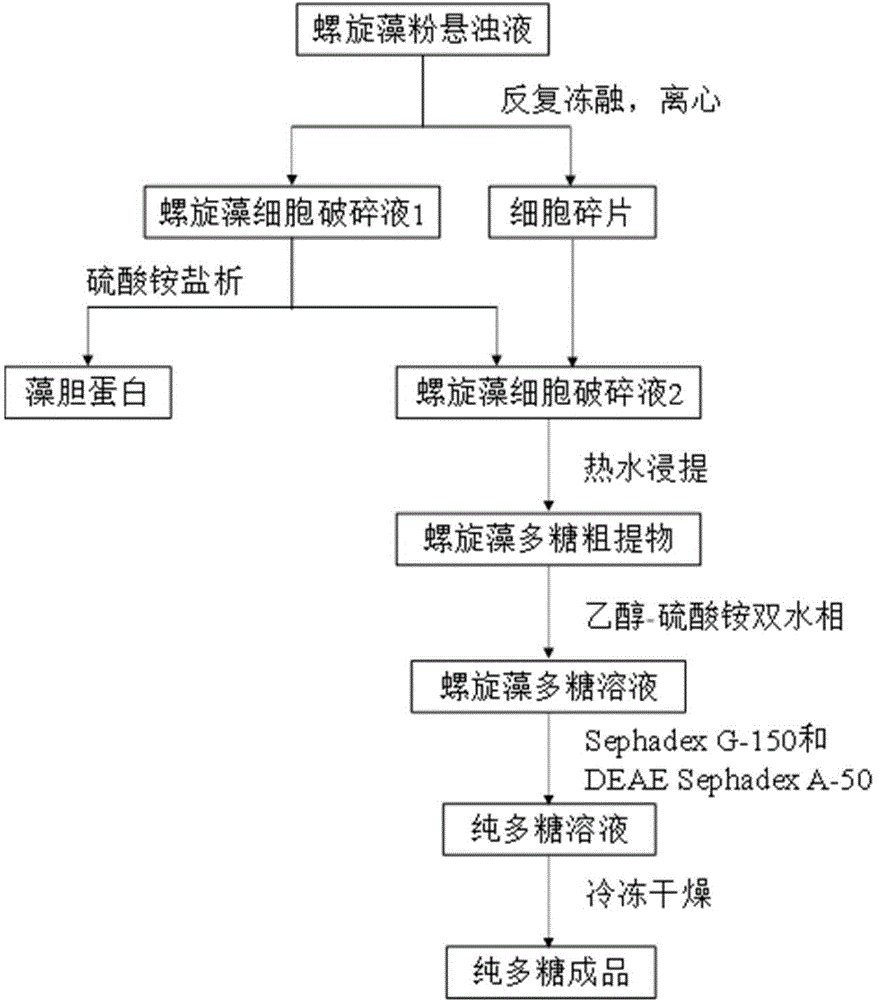
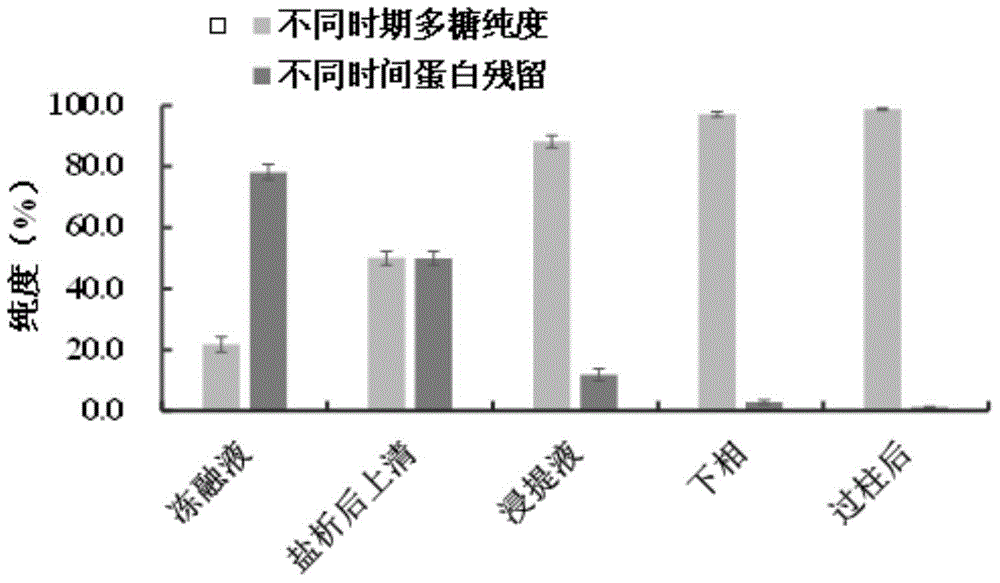
The invention relates to a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and an extraction method thereof. The extraction method comprises the following steps: after multigelation and wall breaking of a spirulina phatensis powder suspension, centrifuging to obtain a cell lysate 1 and cell debris; adding ammonium sulfate in the cell lysate 1 until the saturation is 50%, after salting-out precipitation, centrifuging to remove phycobiliprotein to obtain a supernatant, and evenly mixing the supernatant and the cell debris to obtain a cell lysate 2; obtaining a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide crude extract by using a hot water extraction method; adding the crude extract to an ethanol / ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system, and extracting to obtain a bottom-phase solution of spirulina phatensis polysaccharide with higher purity; after the bottom-phase solution is desalted by dialysis, eluting by using a Sephadex G-150 chromatographic column and a DEAE Sephadex A-50 anion exchange column to obtain a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide solution; and freeze-drying, thereby obtaining a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide finished product. The extraction method can be used for avoiding the traditional complicated protein removal operation steps, has low cost, high yield, and high purity and activity of polysaccharide, and is suitable for intermittent and large-scale production and processing.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Method for extracting phycobiliprotein from spirulina
InactiveCN104292327AIncrease contentHigh purityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCosmetic industryPhycocyanin
The invention provides a method for extracting phycobiliprotein from spirulina. The method comprises the following steps: adding water into spirulina mud to obtain a spirulina cell suspension, performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain spirulina lysate, centrifuging the lysate and taking the lysate, sequentially filtering through filter membranes which are respectively 0.8mu m and 0.45mu m, to obtain phycocyanin crude extracting liquid, then sequentially ultrafiltrating the crude extracting liquid through an ultrafiltration membranes with molecular weight cut-off of 300KD and 100KD, collecting a filtrate of the molecular section, and performing freezing and drying to the filtrate to obtain phycobiliprotein powder. According to the method, the defect of using chemical reagent to extract phycobiliprotein in the prior art is overcome, no residuals exist in the preparation, and the environment pollution does not exist. The extraction rate of the phycobiliprotein is greater than 80%, the content of phycobiliprotein is more than 60%, and the purity of the phycobiliprotein is more than 1.5. The overall technological process is safe and reliable, fast and efficient. Compared with the traditional method, by using the method, the content of the phycobiliprotein is high before using of chromatography, the phycobiliprotein with the purity not only can meet the requirement of food and cosmetic industries, but also can be applied to aspects of medical and health products, and the like.
Owner:何忠志
Germ feed for fancy carps
InactiveCN102599391AHigh in proteinIncrease cholesterolAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceAdditive ingredient
Owner:包卫空
Method for preparing phycocyanin of sea water
The invention refers to a making method of algae blue protein by using seawater spirulina as raw material. The current making method has long technical course, long cycle of extraction, high cost, low efficiency, low application value and mostly is made at low temperature. The invention can largely and at low cost extract higher-purity algae glue protein, is applied to research and development of natural pigment, health food and new sea medicament.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aquarium fish feed
InactiveCN103494016AImprove immunityReduce mortalityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an aquarium fish feed comprising the following raw materials: by weight, 20-23 parts of fishmeal, 12-15 parts of housefly larvae powder, 30-35 parts of corn starch, 10-12 parts of flour, 40-45 parts of soybean meal, 3-4 parts of beer yeast powder, 3-4 parts of spirulina, 4-5 parts of hawthorn, 1-2 parts of citric acid, 1-2 parts of fumaric acid, 4-5 parts of diatomite powder, 2-3 parts of phtheirospermum tenuisectum Bur. et Franch, 1-2 parts of catalpa flower and 4-5 parts of a feeding promoting agent; the aquarium fish feed is prepared from a plurality of materials, is rich in proteins and multiple vitamins, is reasonable in the ratio of every nutrition ingredient, can provide comprehensive nutrition for aquarium fishes, at the same time, enhances the immune power of the aquarium fishes by adding of a plurality of Chinese herbal medicines, and reduces mortality.
Owner:HEFEI QIANXI MOUNTAIN VILLA AGRI ECOLOGICAL PARK
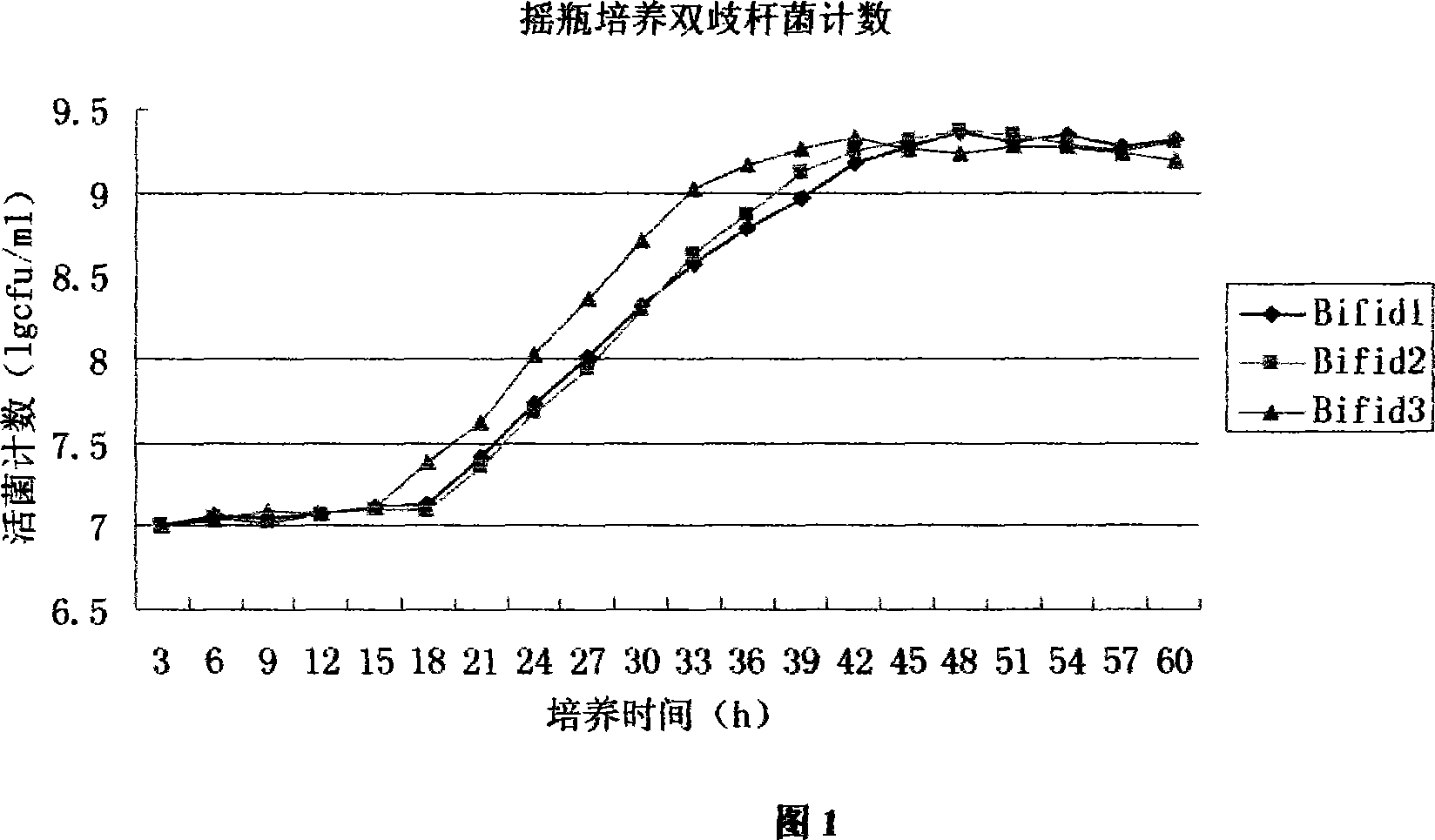
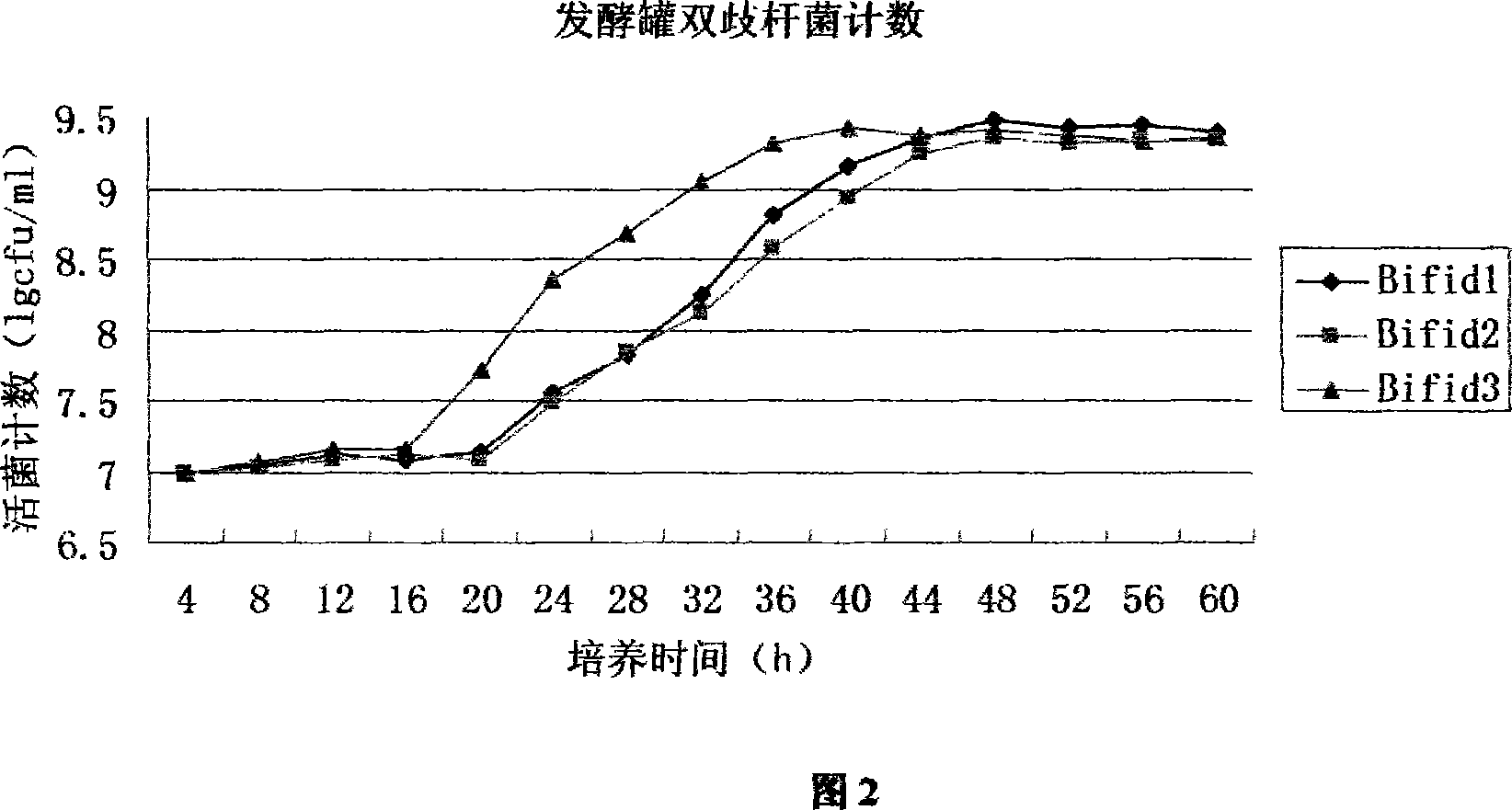
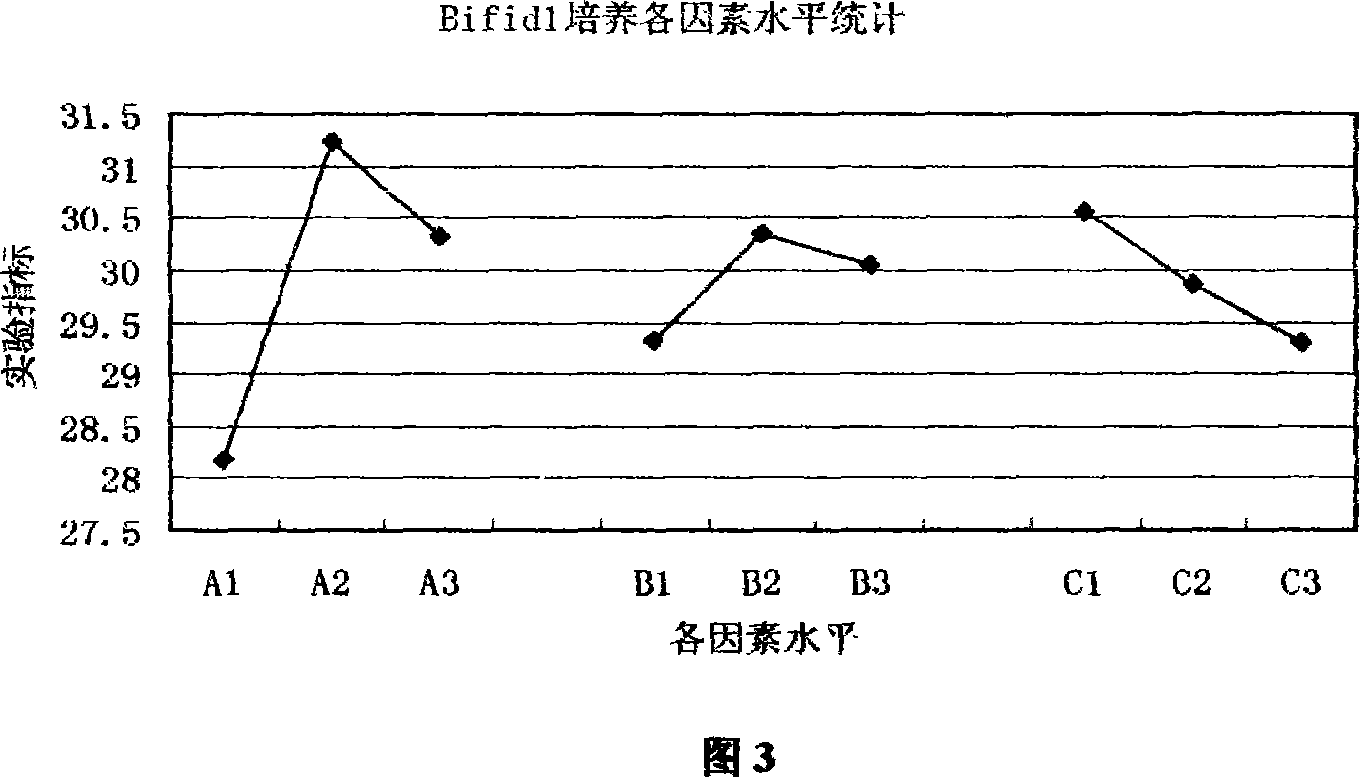
Composite culture medium for bifidobacterium fermentation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101058796AImprove applicabilitySuitable for industrial large-scale cultivationBacteriaPork LiverDistilled water
The invention discloses a composite culture medium for fermentation of bifidobacteria and the manufacturing method, which comprises the following parts: 50-150g spirulina powder, 40-80g stachyose, 30-100ml 5% pork liver infusion, 1000ml distilled water. The effect of the invention is that: the infant bifidobacteria, adolescent bifidobacteria and long bifidobacteria grow well in the culture medium; the maximum increment reaches 1010cfu / ml in the best fermentation condition; the submerged culture effect is the best of the classic bifidobacteria selective culture medium, TPY culture medium and improved TPY culture medium. The composite culture medium provides a simple formulation, a low cost, a simple manufacturing process, which can be used to the research, exploitation, production of bifidobacteria, provides the important meanings of utilizing and developing spirulina and stachyose resource.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Separation, extraction and purification process for spirulina polysaccharides and phycocyanin
InactiveCN109021096AIncrease profitImprove efficiencyDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingPhycocyanin
The invention discloses a separation, extraction and purification process for spirulina polysaccharides and phycocyanin. The separation, extraction and purification process comprises the following steps: (1) selection of raw materials; (2) wall breaking; (3) separating and filtering; (4) extraction of phycocyanin; and (5) extraction of spirulina polysaccharides: treating a pure spirulina polysaccharide solution through freeze-drying or spray-drying so as to obtain the fine extract of pure spirulina polysaccharides. According to the separation, extraction and purification process for spirulinapolysaccharides and phycocyanin, components rich in spirulina polysaccharides and phycocyanin are separated, and the extraction and purification of the spiral polysaccharides and phycocyanin are carried out respectively; so the utilization rate of spirulina is improved, the production cost of enterprises is lowered, and the benefits of enterprises are improved.
Owner:桐乡市博奥生物科技有限公司
Breeding method of Spirulina alga species
The invention discloses a breeding method of Spirulina alga species, which comprises the following steps: 1. selecting 5L of alga culture solution, filtering with a silk fabric to remove smaller algae; 2. carrying out mutagenesis with a phosphate buffer solution; 3. selecting single Spirulina with larger body and more spiral rings; culturing in a test tube, and calculating the growth rate; 4. culturing the Spirulina elements subjected to amplification culture in a 40001*12 DEG C lighting incubator; and 5. selecting the Spirulina element with the highest growth rate to obtain the mutant line subjected to mutagenesis screening, purification and cloning. The method changes the coarse breeding method of screening the alga species by the filter screen into capillary selected breeding; and the unicell screening is utilized to remove bad Spirulina individuals to obtain high purification, and the mutagenesis passivation is performed to obtain the high-quality high-growth-rate Spirulina alga species. The alga species purification and culture conditions are continuously optimized, so that the Spirulina yield is enhanced to 30-50%, and the product quality is further improved.
Owner:JIANGXI ZHONGZAO BIOTECH
Method for harvesting cultured spirulina
ActiveCN102181367AFast automatic filtrationImprove efficiencyUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesFiltrationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for harvesting cultured spirulina. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of centralized harvesting, bypass flow filtering and separating and washing and rinsing combining; a pipe network device is used for transporting spirulina liquid cultured in each culture pond to a bypass flow adjusting device in a centralized manner by way of flowing automatically; the bypass flow adjusting device is used for injecting the spirulina liquid at certain flow rate and with certain quantity of flow to a filtration and separation device and a washing device and controlling and adjusting the quantity of spirulina liquid entering into the filtration and separation device; the filtration and separation device is used for separating the spirulina oozes from the liquid nutrient media by utilizing a filter screen; and the washing system is used for washing or rinsing the spirulina oozes with salinity and high pH value with tap water to remove salt and impurities.
Owner:LIJIANG CHENGHAI BAOER BIOLOGICAL DEV
Clam worm culturing metod
A method for raising clam worm includes such steps as choosing health parents, artificial fertilization, putting the fertilized ova in the seawater contained in drum, supplying seaweed (such as spirulina) as feed to culture larvae until the larva has 5-6 pairs of legs, culturing in spool in water flowing mode for 10 days while supplying seaweed and fish powder as feed, culturing in water exchanging mode while supplying fish powder as feed, and culturing in water bath while supplying seaweed and fish powder as feed.
Owner:广东海兴农集团有限公司
Soft-shelled turtle feed containing egg yolk and fish oil
InactiveCN104026377APromote healthy growthFood processingClimate change adaptationRed mulletFish oil
A soft-shelled turtle feed containing egg yolk and fish oil comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: ginger oil 0.1-0.2, spirulina 1-2, oat flour 30-40, soy bean protein powder 10-20, egg yolk powder 6-8, chestnut 5-8, orange peel 2-4, Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort 1-2, flos sophorae immaturus 1-2, brown rice 5-15, kalimeris indica 8-10, amaranth leaves 4-6, salicornia europaea 4-6, clover 3-5, lecithin 1-2 and fish oil 1-2. The soft-shelled turtle feed contains health raw materials such as kalimeris indica, salicornia europaea and clover, and moreover the salicornia europaea has the oxidation resistance, anti-inflammation and immune regulation effect, and the health growth of soft-shelled turtle can be promoted.
Owner:ANHUI LANBOWANG MODERN AGRI SCI & TECH
Method for culturing spirulina by using livestock and poultry excrement wastewater
ActiveCN103484370ATake advantage ofSave water for cultivationBio-organic fraction processingUnicellular algaeHuman wasteNutrients substances
The invention provides a method for culturing spirulina by using livestock and poultry excrement wastewater, belonging to the fields of sewage treatment and algal culture. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment of livestock and poultry excrement wastewater: filtering, and sterilizing the filtrate to obtain a culture solution; (2) domestication of spirulina: inoculating an alga strain into fresh water or sea water, and performing domestication culture; (3) culture of spirulina: inoculating the spirulina in a logarithmic growth phase of the step (2) into the culture solution of the step (1), and culturing; (4) collection of spirulina: filtering the spirulina cultured in the step (3), cleaning, collecting the spirulina, and then drying the spirulina; and (5) filtrate recovery. The method provided by the invention solves the problems that the livestock and poultry excrement pollutes the environment and the spirulina culture cost is high. The method can realize the triple effects of protecting the environment, lowering the spirulina culture cost and producing nutrient substances required by human beings.
Owner:深圳市华胜隆科技有限公司 +1
Seawater spirulina selenium-rich culture method
InactiveCN102925359AHigh Selenite Absorption EfficiencyImprove conversion abilityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesKeshan diseaseSpirulina maxima
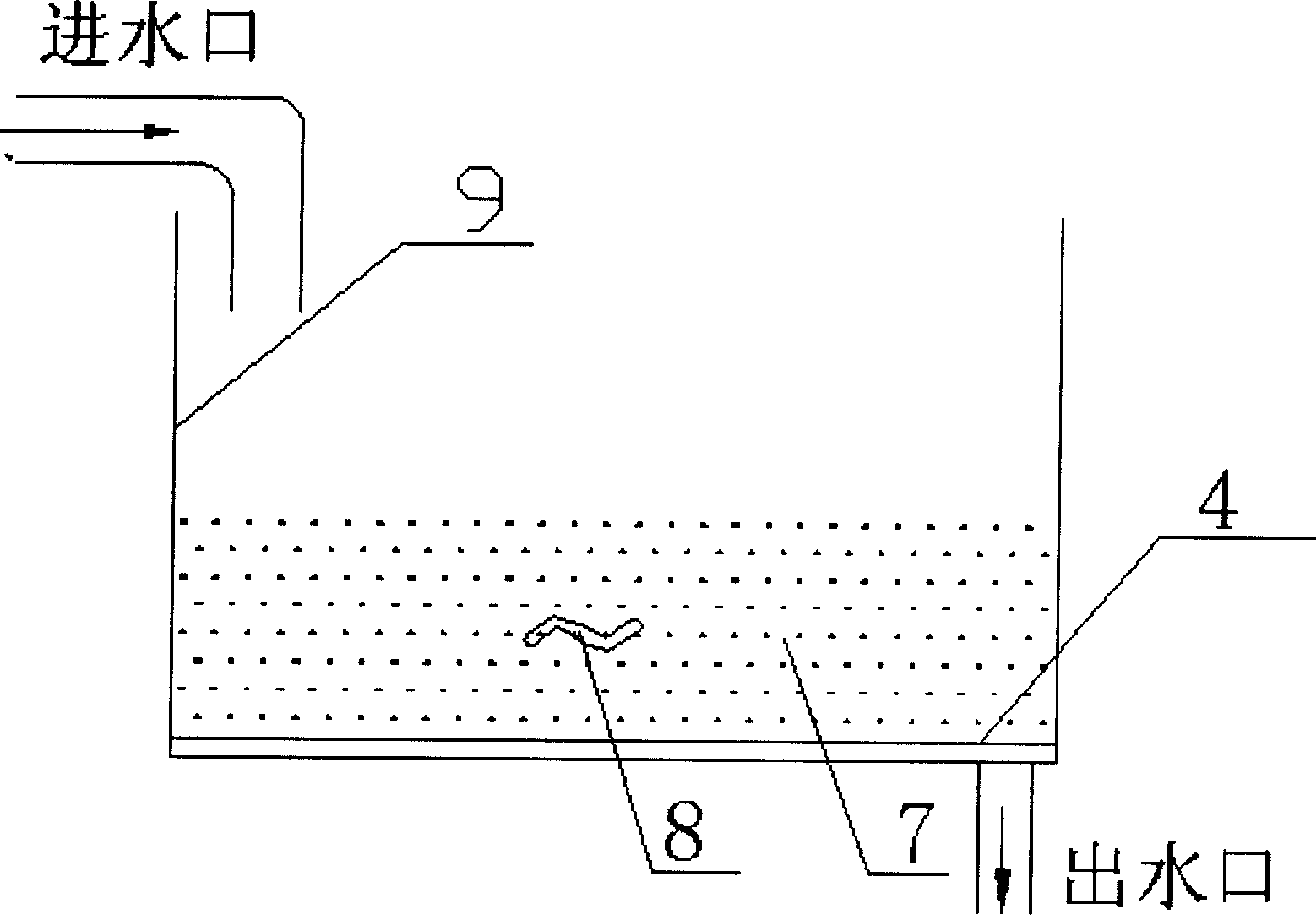
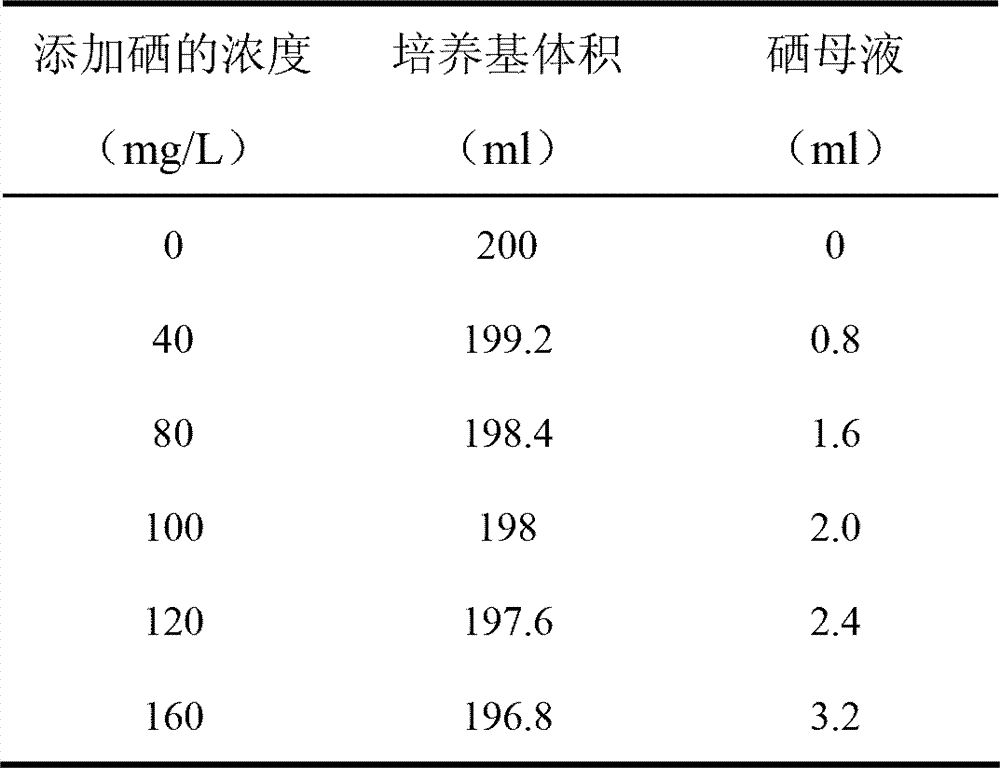
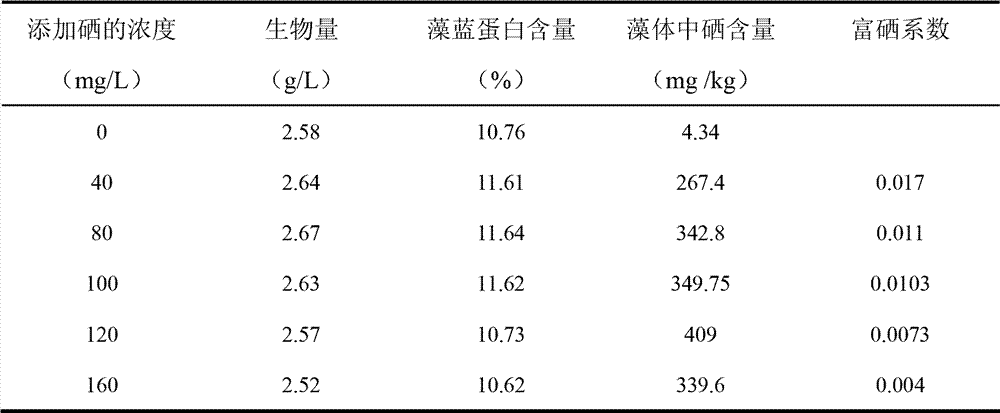
The invention discloses a seawater spirulina selenium-rich culture method. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting one or combination of more of the seawater-naturalized spirulina platensis, spirulina maxima and microcystis aeruginos as the algae seed; based on the natural seawater, artificial seawater or the mixture of the two at any ratio, adding a selenium element with concentration of 1-160mg / L to serve as a culture medium; inoculating the algae seed into a photobioreactor containing the culture medium for culture; and then collecting the cultured spirulina body to obtain the seawater spirulina which is the selenium-rich seawater spirulina. Through the invention, the method is simple, the selenium addition concentration is low, the culture medium can be recycled for a long time, the operation is simple and convenient, the selenium enrichment ability is strong, the cost is low, the method is green and safe, etc. The bioactive substance of the seawater spirulina generates a synergistic effect with organic selenium in the algae body to realize the function, and can be applied to various diseases caused by selenium lack and oxidative damage of oxygen free radical for the selenium supplement additive, oxidation resistance, aging resistance, tumor resistance, Keshan disease prevention and treatment and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Feeding method of reducing disease and insect pest occurrence of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN103563803ARegulate balanceRegulate physiological functionClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseHydrolysate
The invention discloses a feeding method of reducing the disease and insect pest occurrence of stichopus japonicus. The method comprises the steps of building a stichopus japonicus feeding pond and a substratum; building the pond suitable for the growth of the stichopus japonicus and throwing stichopus japonicus seedlings into the pond by combining with the actual conditions according to the biological habit requirements of the stichopus japonicus; under the general condition, the state that big seedlings of over 600 heads / kg are thrown in the pond in a specification of 10 heads / m<2> to 20 heads / m<2> is proper, and if the specification is larger, the throwing amount in unit area can be smaller; the feeding feed formula comprises 20-25 parts of animal protein hydrolysate dry powder, 15-20 parts of meat and bone meal, 20-22 parts of soybean meal, 4-6 parts of honeysuckle, 2-3 parts of medicated leaven, 3-5 parts of angelica sinensis, 2-3 parts of soya bean lecithin, 1-2 parts of alginate-derived oligosaccharide, 1-2 parts of vitamin C, 1-2 parts of spirulina, 2-3 parts of lupulus, 3-5 parts of tea saponin, 2-3 parts of fructus cnidii, 3-4 parts of fructus ulmi, 1-2 parts of golden larch bark. The management of the stichopus japonicus seedlings is that when winter comes, the water depth of the pond is properly increased, and the change of dissolved oxygen and substrate and the prevention and control of seaweeds must be paid attention to; when the water temperature of the pond rises at spring, the transparency of the water is reduced by fertilizing the water, and the breeding of the seaweeds is controlled.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENG LAKE FISHERIES TECH CENTCO
Mutation-preventing almond tea oil
InactiveCN104222325AEasy to removeFit for consumptionFatty-oils/fats productionEdible oils/fatsGrape seedTribulus terrestris
The invention relates to mutation-preventing almond tea oil which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 230-250 parts of camellia seeds, 50-60 parts of almond, 45-55 parts of mung beans, 40-50 parts of grape seeds, 8-10 parts of spiral seaweed, 5-7 parts of gynostemma pentaphylla, 5-6 parts of tribulus terrestris, 3-5 parts of dandelion, 6-8 parts of Chinese caterpillar fungus and the like, wherein the almond contains vitamin B17, thus the mutation-preventing almond tea oil has a mutation-preventing effect; meanwhile, in a preparation process, essences of the grape seeds and the spiral seaweed are added, thus the mutation-preventing almond tea oil has good functions of scavenging free radicals and enhancing the immunity; meanwhile, the gynostemma pentaphylla and setose thistle are added, thus the mutation-preventing almond tea oil has good functions of resisting ageing and relieving the internal heat or fever, and is suitable for being eaten by various crowds.
Owner:YUEXI GUANGSHENG TEA OIL CO LTD
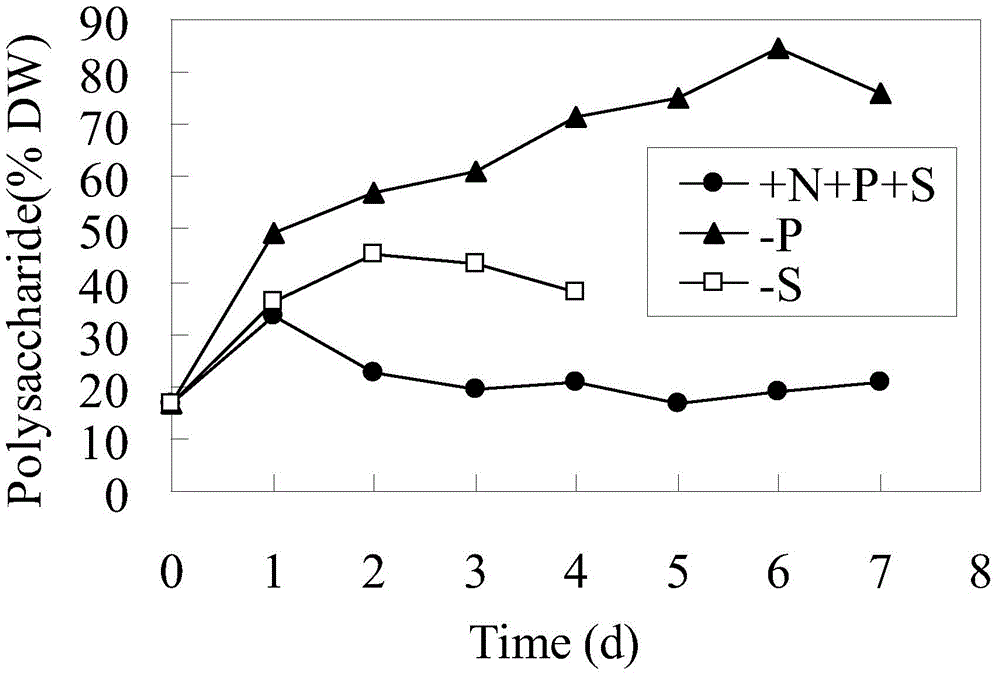
Method for concurrently improving spirulina biomass and polysaccharide yield
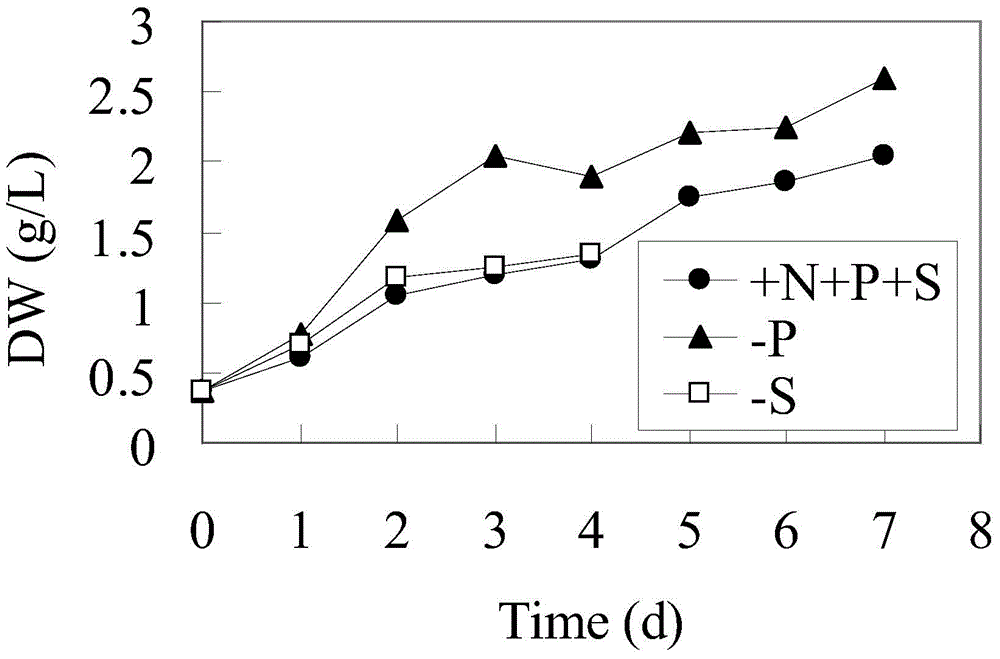
InactiveCN105647825AHigh polysaccharide yieldPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDownstream processingDry weight
The present invention relates to biomass and polysaccharide accumulation through spirulina culture, specifically to spirulina culture using the control of the addition of a nutritional salt so as to concurrently accumulate biomass and polysaccharides. According to the present invention, spirulina cells cultured to achieve a exponential growth phase are transferred into a nutrition limiting culture medium, natural illumination or artificial illumination is performed, culture is performed to achieve a stable phase, and the spirulina cells are harvested, wherein the biomass yield is 1-4 times the biomass yield of the culture under the rich nutrition condition, the polysaccharides yield is increased by 0.8-20 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition, and the polysaccharide content achieves 45-80% of the spirulina dry weight, and is increased by 2-6 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition; and the contradiction that the spirulina biomass and the polysaccharide cannot be concurrently accumulated is solved, the rapid and efficient spirulina polysaccharide production is achieved, the advantages of low nutrition salt consumption, low production cost, high polysaccharide content and the like are provided, the downstream processing operations are easily simplified, and the industrial production of the spirulina polysaccharide can be promoted.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction and determination method of crude polysaccharide in ganoderma spirulina
ActiveCN101839863ASimple extraction processSimplify the measurement stepsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationWater bathsDextrin
The invention discloses an extraction and determination method of crude polysaccharide in ganoderma spirulina, which comprises the following steps: weighing ganoderma spirulina samples accurately and putting the samples into a great capacity centrifuge tube, adding ethanol aqueous solution and mixing evenly, carrying out ultrasonic extraction and centrifugation, and discarding solution; adding the ethanol aqueous solution to the obtained sediment, vibrating and mixing evenly, carrying out ultrasonic extraction and centrifugation, precipitating, then moving to a round bottomed flask after adding water, after extraction in boiling water bath, filtering, bringing filtrate to volume, and determining the content of the crude polysaccharide by phenol-sulphuric acid method by taking glucose or dextran standardized products solution as a reference material. The method has simple steps, is accurate, has high sensitivity and is especially appropriate for the extraction and determination of the crude polysaccharide in the ganoderma spirulina which is health food and does not contain disruptors, dextrin, starch and the like.
Owner:NINGBO YUFANGTANG BIOTECH
Extraction method of water-soluble spirulina phycobiliprotein
InactiveCN101575359APromote digestionEasily absorbableCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFood additiveWater soluble
The invention relates to an extraction method of water-soluble spirulina phycobiliprotein. The extraction method of the water-soluble spirulina phycobiliprotein comprises the following steps: soaking a spirulina raw material into water, stirring and freezing the solution at a temperature of 20 DEG C below zero for 48 hours, taking out and rapidly melting the frozen matter, centrifugating and filtering the solution, extracting the phycobiliprotein from the centrifugal liquid and remaining the spirulina dreg for extracting spirulina polysaccharide; and purifying, concentrating, spraying and drying the obtained centrifugal liquid into the spirulina phycobiliprotein. The extraction method of the water-soluble spirulina phycobiliprotein is simple to operate; the extracted spirulina phycobiliprotein is water-soluble powder so as to be easy for human bodies to desist and absorb, and the water-soluble powder can be further processed to be used as a raw material of food additives, functional foods and medicaments, a natural blue pigment of foods and cosmetics, and the like, thereby having wide serviceable range; and the pretreated spirulina dreg in the extraction process can be remained for extracting the spirulina polysaccharide so as to improve the utilization rate of the spirulina raw material.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIZHIJIAO BIOTECH
Method for homologous recombining by using spirulina and expressing human gene
InactiveCN1528902AImprove conversion rateEasy to detectOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHuman bodyRecombinant expression
The invention refers to a method for reconstructing the cloned and constructed human body tumor death factor TRAIL gene expression carrier into spirulina gene group to be expressed stably with gene gun. The special components of the reconstructed TRAIL expression carrier include resistant mark gene expression box CAT, chlorophyll body photosynthetic gene promotor and ender, spirulina homologous segment, TRAIL gene segment without coding film combining part, the expression system also includes characters of primary nucleus and eukarya. The invention sets suitable striking parameter, uses gene gun to guide the reconstructed expression carrier into spirulina silk body, and through several times of sifting of chloramphenicol with incremental density and molecular biology testing, the invention gets spirulina converter of TRAIL gene. The invention applies to spirulina reconstruction and human body gene expression, it also applies to reconstruct and express other primary nucleolus and eukarya.
Owner:广东梅雁蓝藻有限公司
Process for treating spirulina
ActiveUS20060210545A1Little of odorDecrease in levelBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The treatment of spirulina by a process which includes placing spirulina that has not been previously heat-sterilized, lactic acid bacteria and sugar in water, then culturing the lactic acid bacteria provides treated spirulina in which the distinctive taste and odor of spirulina are minimized, in which active ingredients such as phycocyanin remain intact, and which contains a reduced level of bacteria other than lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Full-nutrients wheat flour
InactiveCN1350792AImprove bioavailabilityHigh nutritional valueDough treatmentPotato starchTrace element
A full-nutritive wheat flour contains wheat flour (83-93 wt portions), soybean powder (4-8), millet flour (3-5), sweet potato starch (0.5-1.5), lotus root starch (0.1-0.3), walnut powder (0.3-0.7) and spirulina (0.25-0.35). Its advantages include rich nutrients and trace elements, good enjoyment to eat it, good appearance and balanced nutrition to improve resistance to diseases.
Owner:陈大东
Maca dunaliella salina compound preparation
InactiveCN104095897ABi-directional regulation of metabolismImprove digestive systemNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseBlood sugar
The invention discloses a maca dunaliella salina compound preparation. The maca dunaliella salina compound preparation comprises dunaliella salina and spirulina and is prepared from the following materials: 3-10 percent of dunaliella salina, 40-45 percent of spirulina and 45-55 percent of maca. The maca dunaliella salina compound preparation has the effects of building body and tonifying Yang, curing organs, maintaining beauty and keeping young and improving the digestive system, achieves a two-way blood-pressure regulating function, as well as a two-way blood sugar regulating and balancing function, can regulate body metabolism and resist aging, tumor and fatigue and enhance the immunity, and has remarkable effects on cardio-cerebrovascular diseases, chronic diseases, senile dementia, climacteric syndrome and the like. When drunk frequently, the maca dunaliella salina compound preparation increases sexual intercourse, keep youth for a long time and prolongs the lifetime, has the advantages of relaxing tendons and activating collaterals, activating blood circulation to dissipate blood stasis, dispelling wind to eliminate dampness and strengthening bones and tendons and can remarkably improve memory.
Owner:伏思思
Spirulina grape wine and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101250468AShould be absorbedIntegrate nutrition and health functionsWine preparationGrape wineFood flavor
The invention relates to the production of healthcare port wine in the process of food processing, which particularly relates to a spirulina port wine and the preparing technique, wherein the spirulina port wine is mixed by spirulina primary liquid and port wine stock solution, wherein the adding amount of spirulina primary liquid is 0.05-2% of the volume of port wine stock solution. The preparing technique comprises the following steps: utilizing spirulina and grapes to be raw material, removing fishy smell of the spirulina, breaking wall, and decolourizing, enriching effective component, and getting spirulina primary liquid, fermenting grapes to brew grape brut, blending and allocating spirulina primary liquid and grape brut according to a certain propostion, and preparing spirulina port wine through storing, clarifying and sterilizing. The wine integrates the health care functions of spirulina and port wine on the basis of keeping the original flavor of port wine, which can enhance body immune in long term drinking with a certain amount, and the wine is health, which prolongs life, and has the health-care and therapeutic functions of adjusting blood sugar, adjusting blood fat, resisting apolexis, resisting tumour and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com