Spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and extraction method thereof
A technology of spirulina polysaccharide and extraction method, which is applied in the field of deep processing of natural products, can solve the problems of extraction and purification technology staying in the laboratory research stage, cumbersome operation steps, toxicity, etc., and achieve good anti-oxidation and scavenging free radical effect, extraction process Simple, low-cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
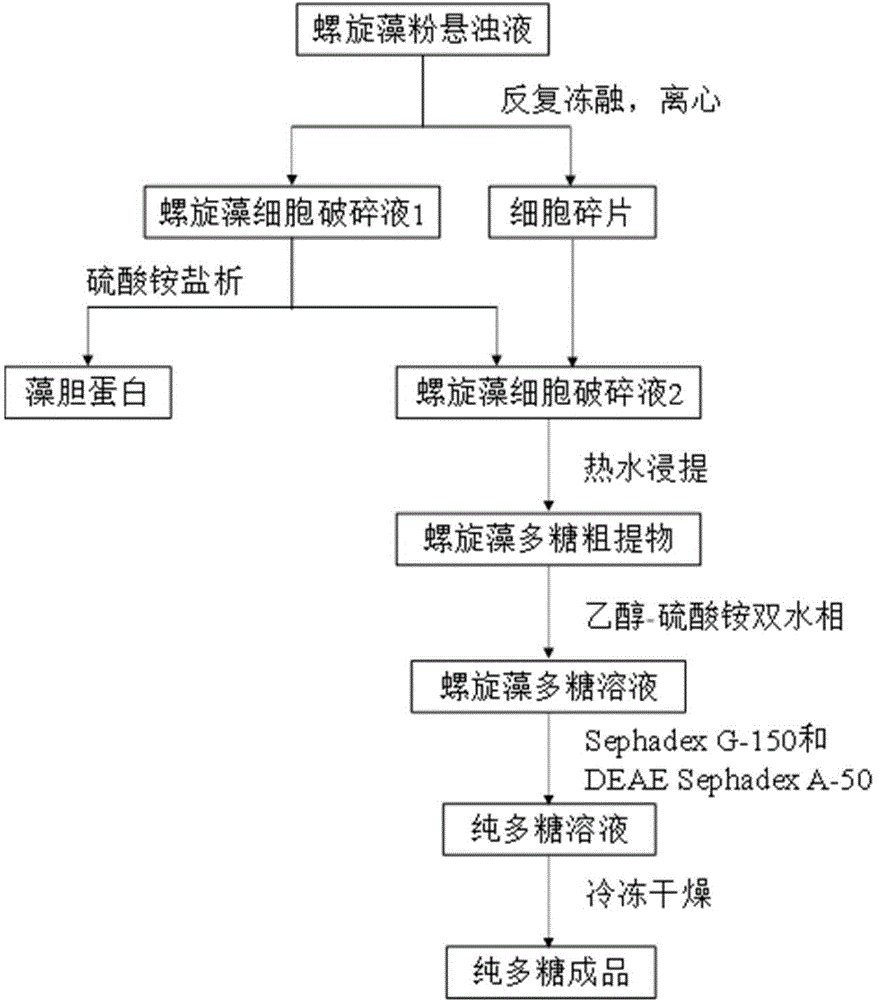
[0035] Preparation of Spirulina Polysaccharide Extract
[0036] The concrete process of preparing Spirulina polysaccharide extract in the present embodiment is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0037] (1) Preparation of spirulina powder suspension: 8 g of Spirulina platensis powder was weighed and dissolved in 400 mL of phosphate buffer (0.01 mol / L, pH=7) to prepare a spirulina powder suspension.
[0038] (2) Preparation of spirulina cell disruption solution 1: put the spirulina powder suspension at 4°C for 4 hours, then freeze it at -20°C for 3 hours, crush the ice cubes, and put it at 4°C for 4 hours. Freeze at -20°C for 3 hours, crush the ice cubes, repeat this three times, and centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 20 minutes to obtain Spirulina cell disruption solution 1 and cell fragments;
[0039] (3) Preparation of spirulina cell disruption solution 2: add ammonium sulfate solid to spirulina cell disruption solution 1 until its saturation is 50%, stir it with a magnetic stirrer to c...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity Determination Index
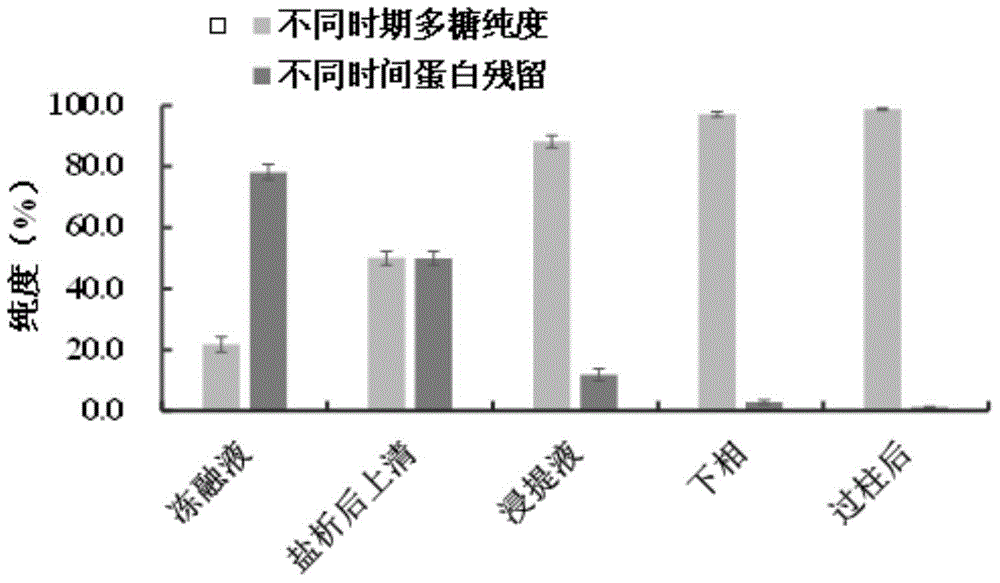
[0051] The sample solution in this embodiment is the polysaccharide extract in different extraction steps.
[0052] DPPH system: refer to the methods of Capek.P and others, and use ascorbic acid (Vc) as a positive control to measure the scavenging rate of DPPH free radicals. The samples or Vc were dissolved in water to prepare 6 gradient samples or Vc solutions (20, 40, 80, 160, 320, 640 μg / mL). According to Table 1, add 2mL of the above solution (not added to the blank tube) and 2mL DPPH solution (not added to the background tube) into the test tube in turn, make up to 4mL in each tube with distilled water, mix with a shaker, let it stand at room temperature for 30min, and measure at 517nm with Distilled water was adjusted to zero to determine the absorbance, and the calculation formula was:
[0053]
[0054] Where: V DPPH is the absorbance of the DPPH solution without adding sample or Vc; A 实验 Absorbance ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Determination of structure by infrared spectroscopy
[0071] Determination of infrared spectrogram: dialyze the obtained lower phase spirulina polysaccharide and the spirulina polysaccharide solution after passing through the column to desalinate and then freeze-dry to obtain spirulina polysaccharide powder. Press with KBr, use infrared spectrometer at 400-4000cm-1 range scan.
[0072] Spirulina polysaccharide solution through Sephadex G-150 gel column chromatography steps:
[0073] (1) Pretreatment: Weigh about 5 g of Sephadex G-150, add 100 ml of distilled water, and let it swell at room temperature for 3 hours.
[0074] (2) Column packing: the diameter and column length of the gel chromatography column are 1.6×40cm. The bottom of the column was plugged tightly with a rubber stopper equipped with a thin glass tube, and the bottom was covered with a clean nylon cloth. Then install the column vertically, first add 1 / 3 column volume of distilled water, then continuous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com