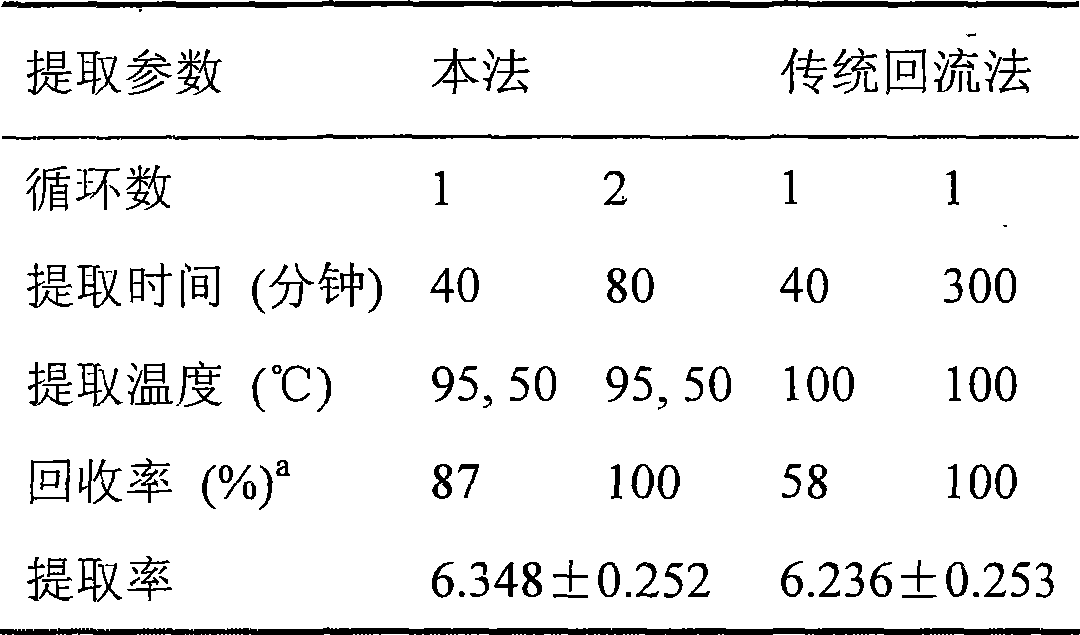
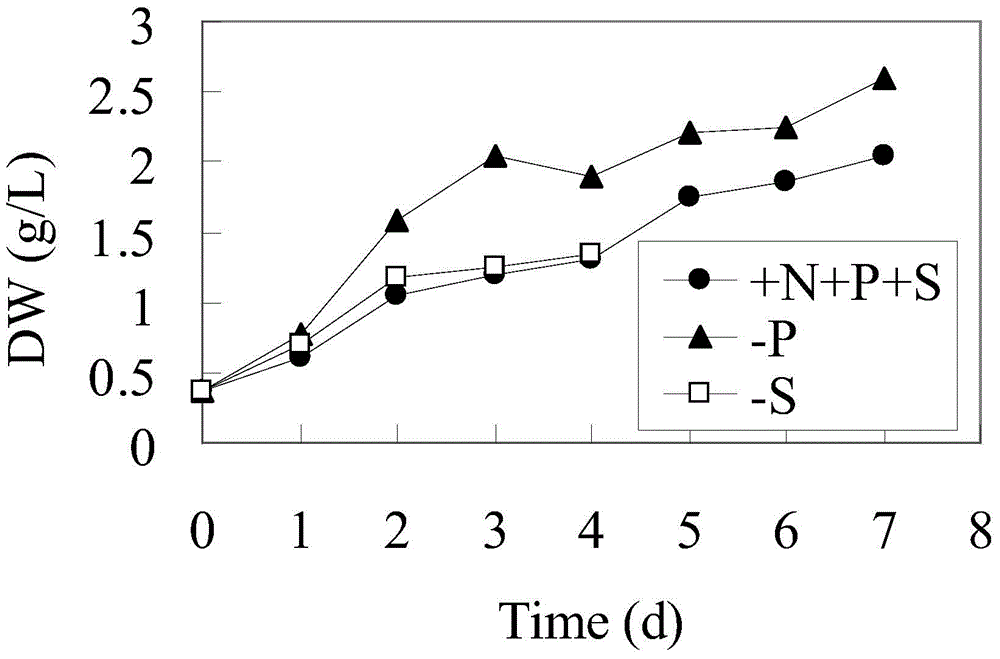
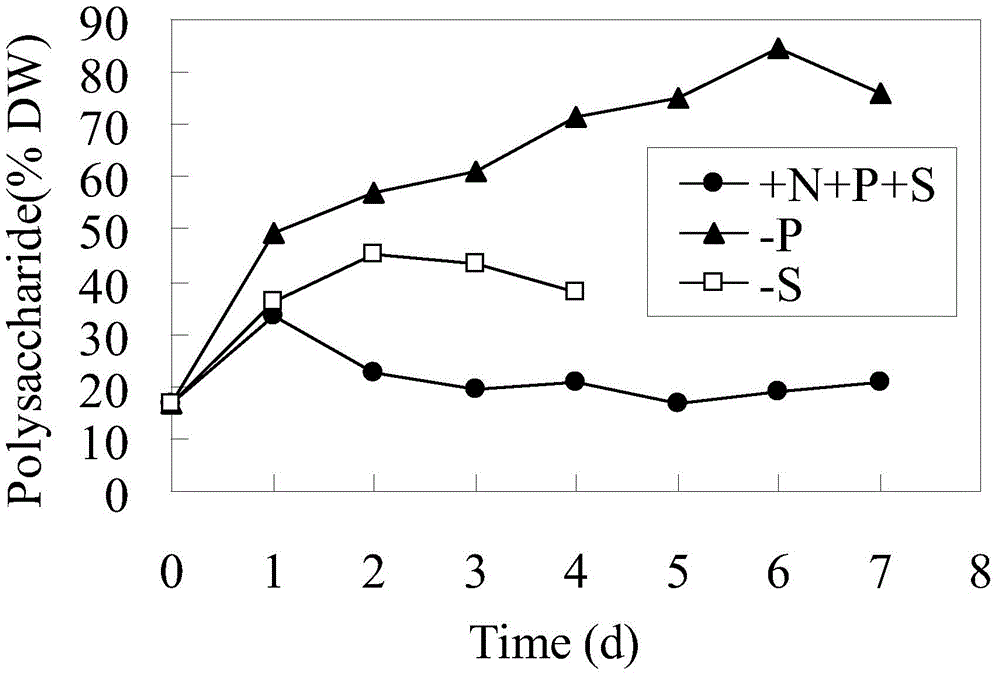
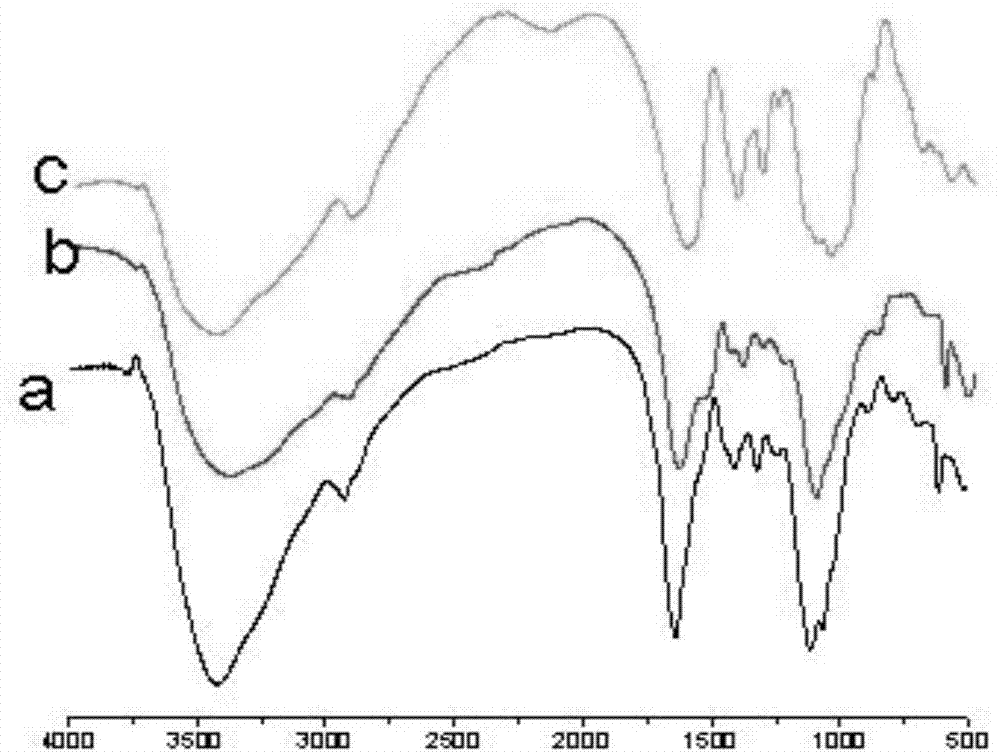
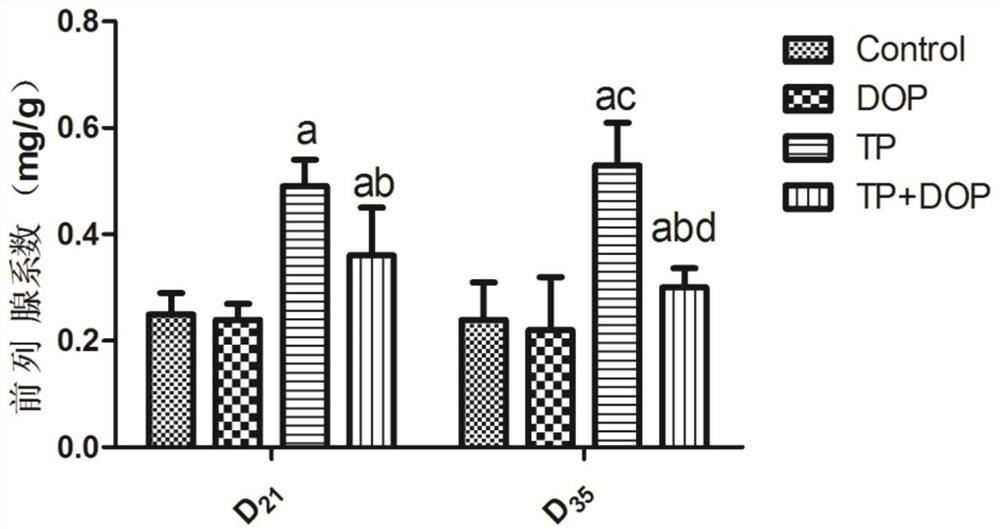
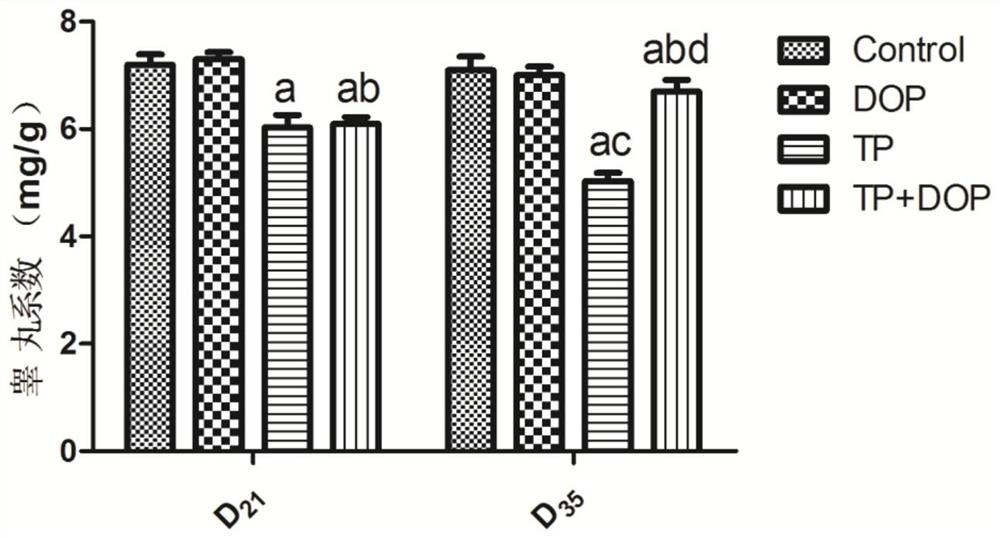
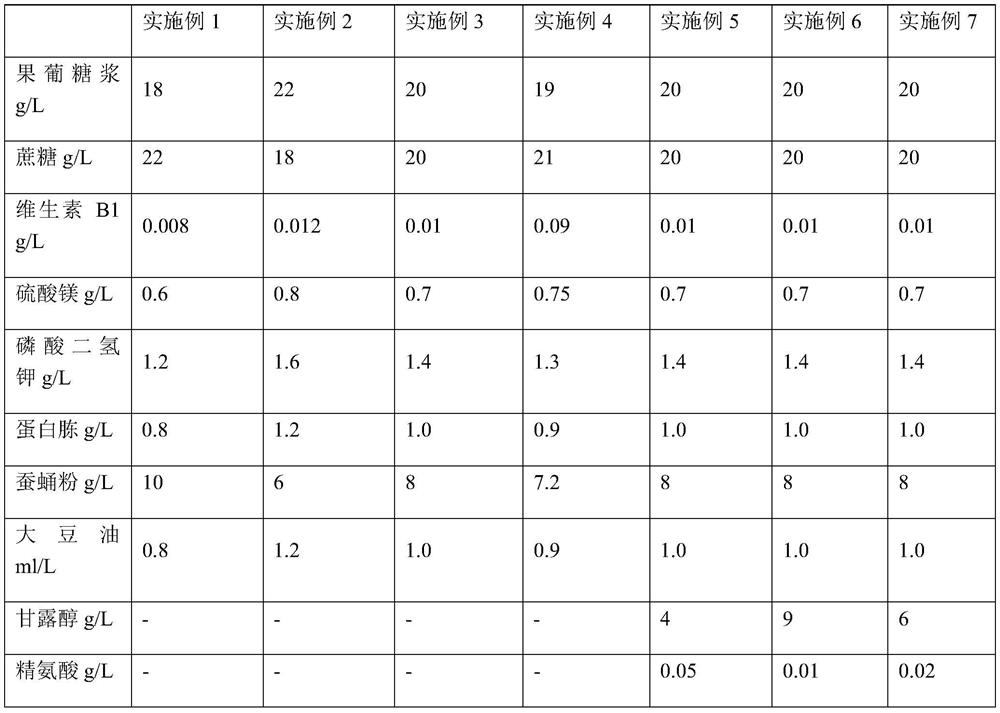
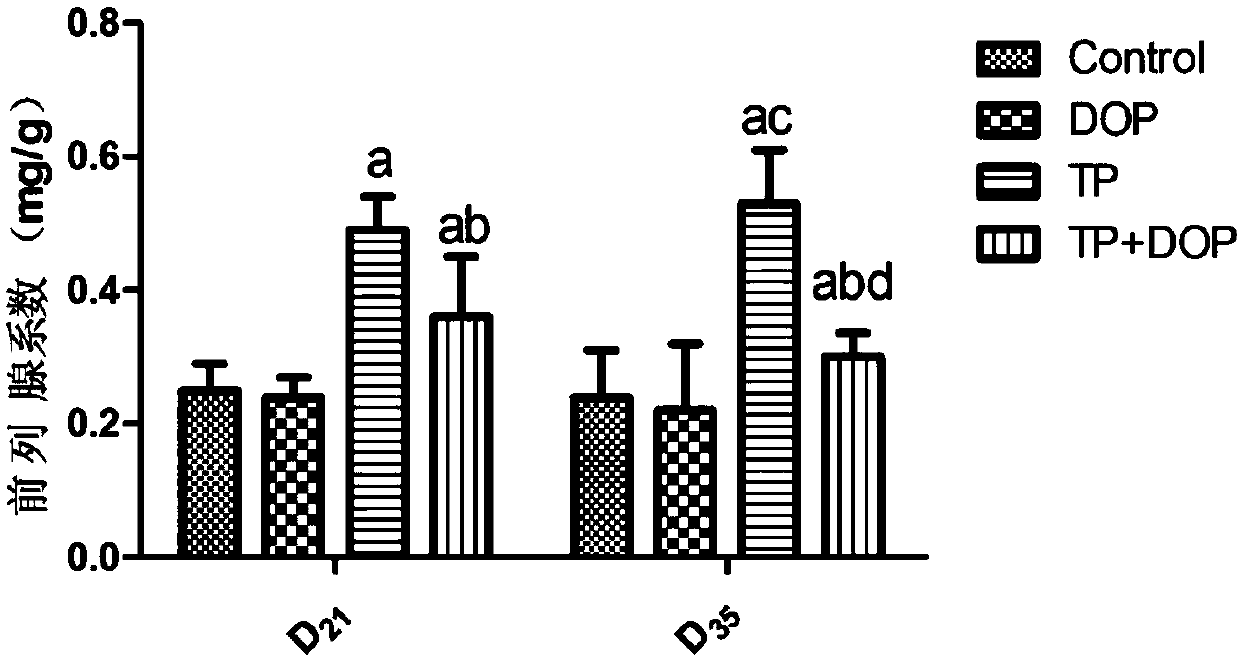
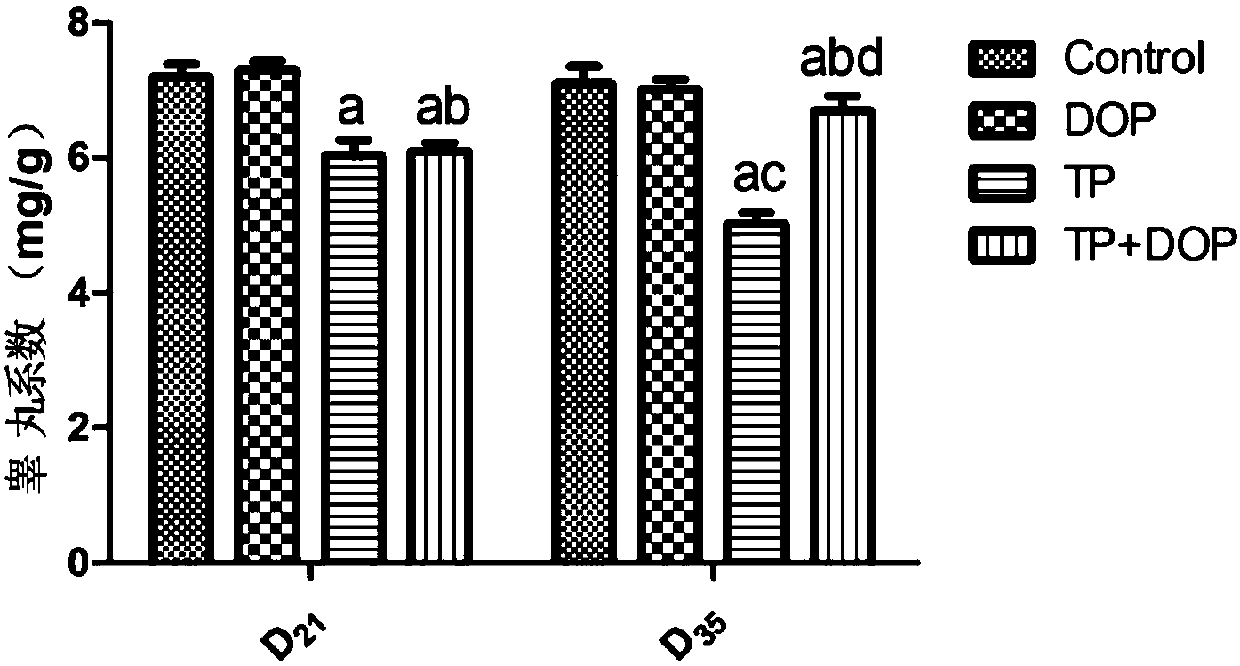
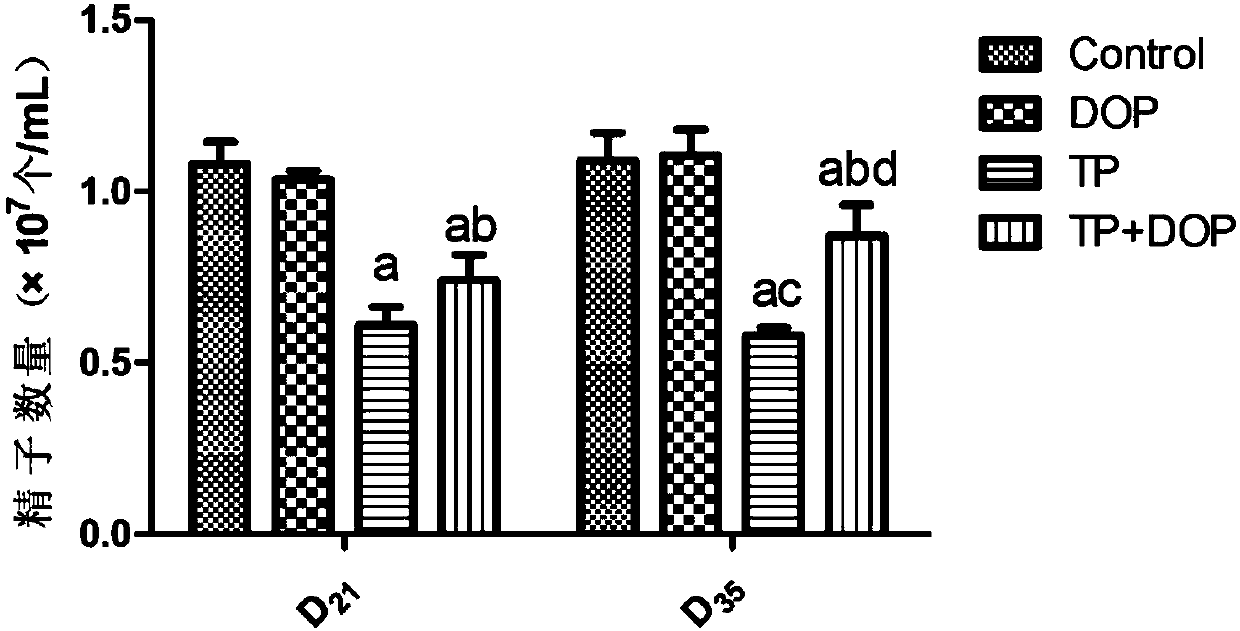
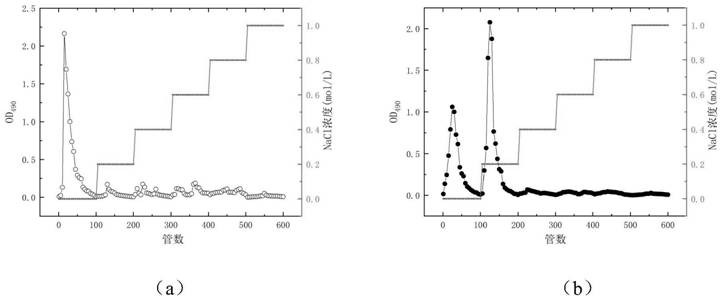
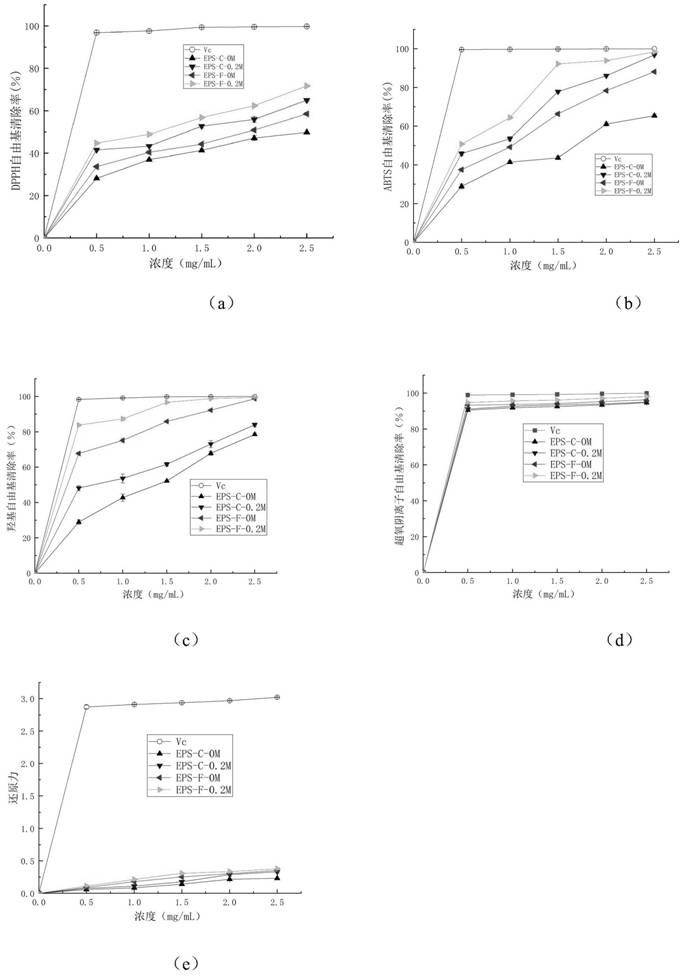
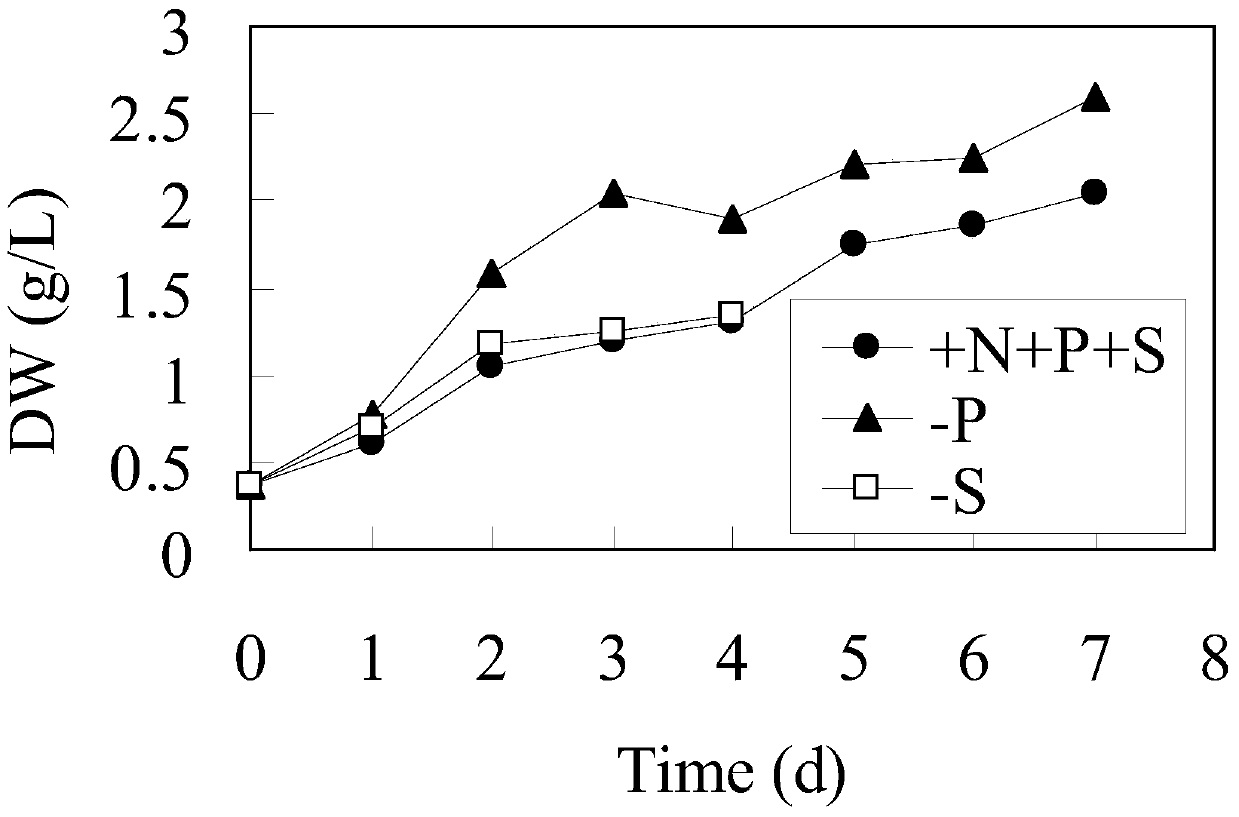
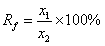Patents
Literature
34results about How to "High polysaccharide yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran
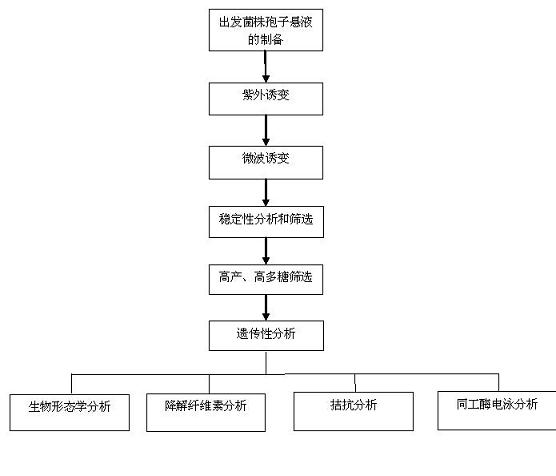
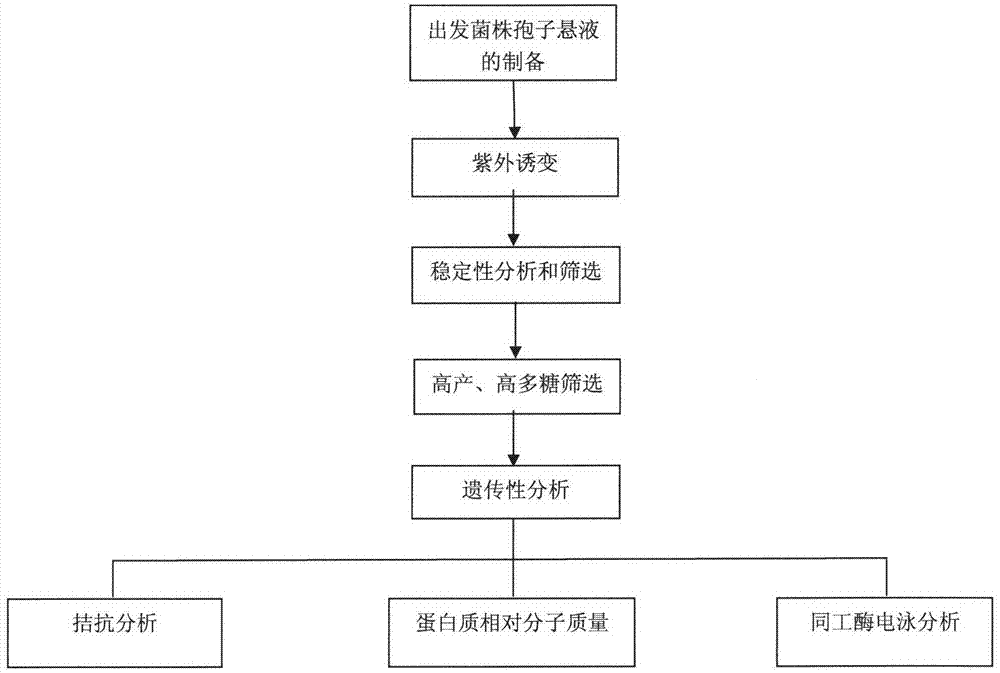
The invention discloses a Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with a composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran, which belongs to the technical field of microbial application technology and food biology. The Grifola frondosa strain JSU10 is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) in October 8th, 2010 with the CGMCC No. 4179 and is identified to be Grifolasp. The invention improves the positive mutation rate of the Grifola frondosa strain for rapidly growing and producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on a composite culture medium of rice bran and wheat bran by composite mutagenesis of ultraviolet rays and microwave to obtain a high-yield strain; the strain and the original strain are respectively a liquid fermentation rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium; and hypha dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutated strain are respectively improved by 39.24 percent and 42.58 percent compared with the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan
InactiveCN102816701AReduce use costHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumMicrobiology
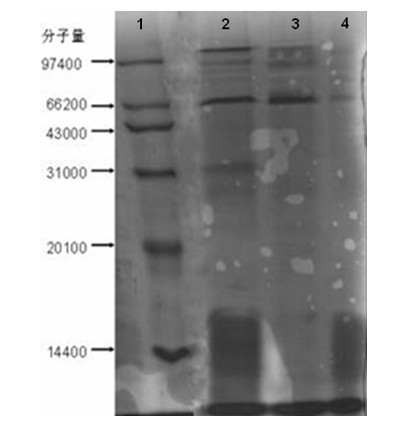
The invention belongs to the fields of microbe application technologies and food biotechnologies, and discloses a strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan. The grifola frondosa strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in Wuhan, China on Aprial 7th, 2011, and has a strain collection number of CCTCC No: M2011113. The name of the strain is Grifolasp. JSU10-2. According to the invention, through protoplast laser mutation, the strain with high yield of mycelium polysaccharide produced from cheap raw materials is obtained. When the strain and an original strain are respectively used in liquid fermentation of a rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium, the dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutant strain are respectively increased by 31.7% and 32.6% compared with those of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Grifola frondosa strain produced through rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid fermentation
InactiveCN103416313AChange the disadvantages of low utilizationFast growthFungi productsLichen productsMutagenic ProcessFood biotechnology
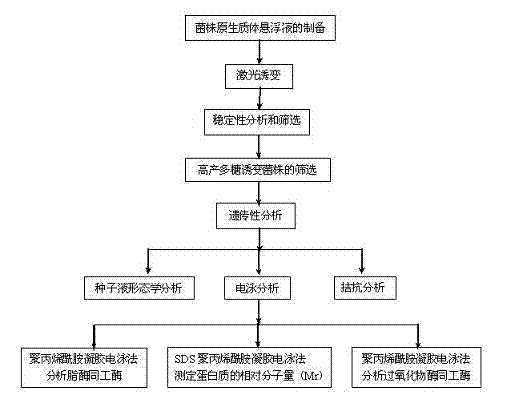
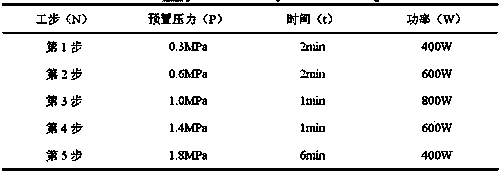
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe application and good bioscience and discloses a polysaccharide grifola strain produced through a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium. grifola Grifola sp.JSU1301 is preserved in the China Typical Model Cultivation Center (CCTCC) in June 25th, 2013, and is numbered CCTCC NO: M 2013286 and named a grifola Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2013286. According to the invention, a ultraviolet mutagenesis method is described with figures; a new strain capable of highly producing polysaccharide by starting with Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2011113; the new strain quickly ferments and highly produces polysaccharide in the rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium; the mycelial dry weight and the mycelial polysaccharide productivity of a shake flask are increased by 16.8% and 8.57% compared with those of a starting strain, and those of fermentation in a tank are improved by 30.9% and 29.7%, which reach the highest level at present.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Production method of grifolan selenium compound
ActiveCN102816806AIncrease productionIncrease valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhosphate
The invention relates to a production method of a grifolan selenium compound, and relates to the food microbiological application technology field. The method comprises the steps that: rice bran and wheat bran are leached in water with a temperature of 90 DEG C to 98 DEG C for 2.5-3h under normal pressure; residuals are removed, and a juice is obtained; the obtained process liquid is used as a culture media for fermentation, wherein the rice bran application amount is 30-120g / L culture media, the wheat bran application amount is 30-120g / L culture media, an addition amount of selenium is 5-10mg / L culture media, an addition amount of potassium dihydrogen phosphate is 1.0-1.5g / L, an addition amount of magnesium sulfate is 0.5-0.80g / L, and a pH value is natural; mycelium obtained by liquid culturing is subjected to centrifugal separation, and is washed by using distilled water; the mycelium is dried to constant weight, such that the mycelium is obtained; the mycelium is subjected to conventional water extraction, deproteinization, ethanol precipitation, and lyophilization, such that a intracellular polysaccharide selenium compound can be obtained. With the method provided by the invention, the production of grifolan selenium compound by using cheap raw materials is better realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYUAN ZHONGTIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105664862AGrow fastStrong stress resistanceOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPorphyridiumElution
The invention relates to a porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide separation purification treatment, porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide sulfonation treatment and porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide immobilization treatment. The adsorbent prepared with the method can selectively adsorb heavy metal ions and precious metal ions in water body. The porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent has the advantages of fast reaction, high adsorbent capacity, high removal rate, and easy elution. The adsorbent can be repeatedly used, such that secondary pollution to the environment can be reduced. Therefore, the adsorbent is environment-friendly. With the adsorbent, ecological risks caused by pollution residue and species introduction are reduced. The adsorbent and the method are suitable for industrialized productions.
Owner:TIANJIN SANSHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for extracting medlar polysaccharide
The invention discloses an extraction method of wolfberry polysaccharide, comprising the following steps: A picking wolfberry; B grinding the fresh wolfberry into homogeneous pulp using a pulp grinder; C pouring the homogeneous pulp into a container; D microwave processing the homogeneous pulp to 50-100 centigrade and boiling the homogeneous pulp for 10-60 minute; E stopping the microwave processing and adding the purified water into the boiled pulp and continuously stirring up the pulp until the temperature is reduced to 50-80 centigrade; F inserting an ultrasonic rod to perform ultrasonic treatment for 20-90 minute; G processing the pulp being subjected to ultrasonic treatment using an industry centrifuges at 3000-5000 r and spilling out the supernatant and decompression concentrating H at 60-90 degree and adding alcohol until the final alcohol concentration is 80-90% and separating and precipitating the mixture using the industry centrifuges at 3000-5000 r to obtain the polysaccharide raw powder or coarse paste. The extraction method has features of high efficiency, energy saving and quick extraction speed. The extraction method solves the problem that the work for drying the wolfberry is heavy and the energy source is waste in Northwest China in harvest season and the extraction technology of the wolfberry polysaccharide is increased and the wolfberry polysaccharide yield is increased.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for concurrently improving spirulina biomass and polysaccharide yield
InactiveCN105647825AHigh polysaccharide yieldPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDownstream processingDry weight
The present invention relates to biomass and polysaccharide accumulation through spirulina culture, specifically to spirulina culture using the control of the addition of a nutritional salt so as to concurrently accumulate biomass and polysaccharides. According to the present invention, spirulina cells cultured to achieve a exponential growth phase are transferred into a nutrition limiting culture medium, natural illumination or artificial illumination is performed, culture is performed to achieve a stable phase, and the spirulina cells are harvested, wherein the biomass yield is 1-4 times the biomass yield of the culture under the rich nutrition condition, the polysaccharides yield is increased by 0.8-20 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition, and the polysaccharide content achieves 45-80% of the spirulina dry weight, and is increased by 2-6 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition; and the contradiction that the spirulina biomass and the polysaccharide cannot be concurrently accumulated is solved, the rapid and efficient spirulina polysaccharide production is achieved, the advantages of low nutrition salt consumption, low production cost, high polysaccharide content and the like are provided, the downstream processing operations are easily simplified, and the industrial production of the spirulina polysaccharide can be promoted.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of carboxymethyl pachyman
InactiveCN103484510ASolve residual problemsPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeast extractCulture mediums
The invention discloses a preparation method of carboxymethyl pachyman, and particularly provides a method for fermentation preparation of carboxymethyl pachyman by regulating the variety and proportion of a carbon source and a nitrogen source in a Tuckahoe culture medium. Consisting of the processes of Tuckahoe strain activation, seed solution preparation, fermentation cultivation and carboxymethyl pachyman extraction, the preparation method is characterized in that in the process of fermentation cultivation, the fermentation culture medium comprises the following components by weight percentage: the carbon source (2.0%-4.5% of glucose, 0.1%-4.5% of carboxymethyl cellulose), the nitrogen source (0.45%-0.65% of yeast extract and 0.35%-0.55% of peptone), 0.1% of K2HPO4, 0.046% of KH2PO4, 0.05% of MgSO4.7H2O, and the balance water. The method provided in the invention can directly obtain carboxymethyl pachyman with certain degree of substitution and no chemical residue, and the carboxymethyl pachyman can be widely used in medicine, food and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
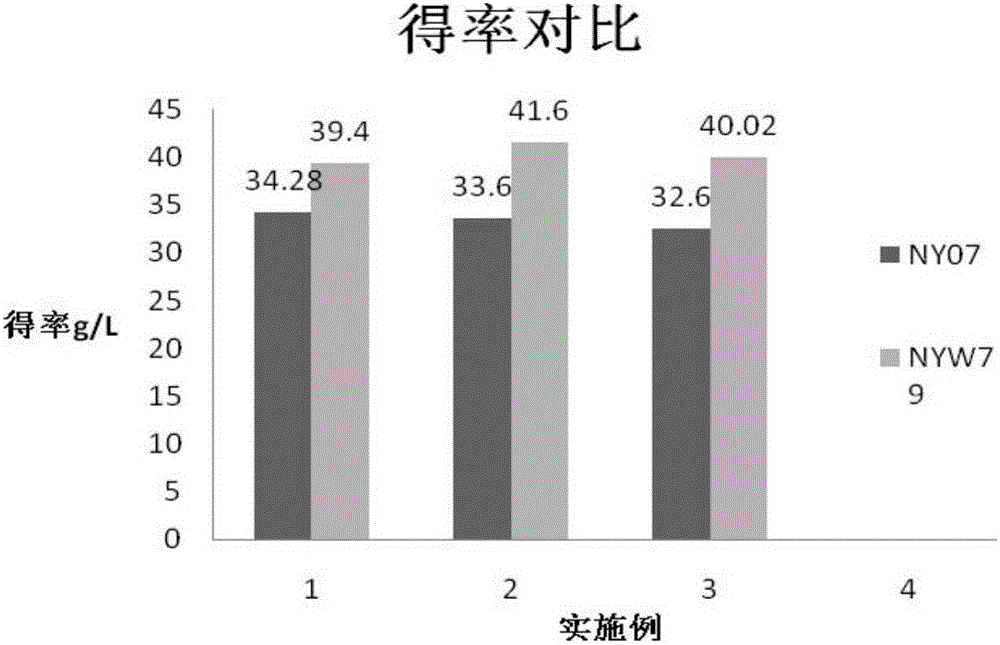
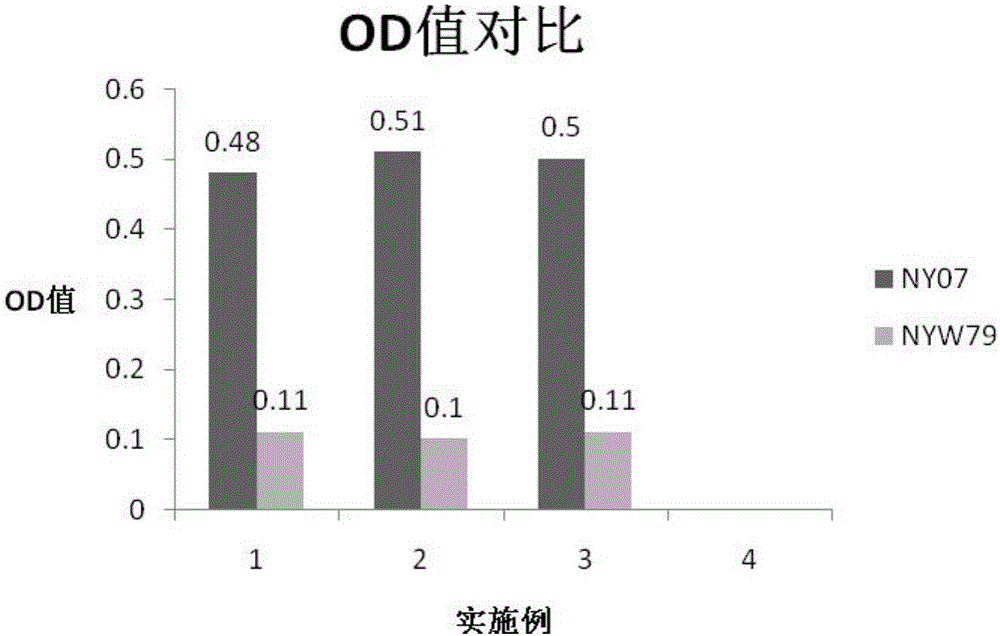
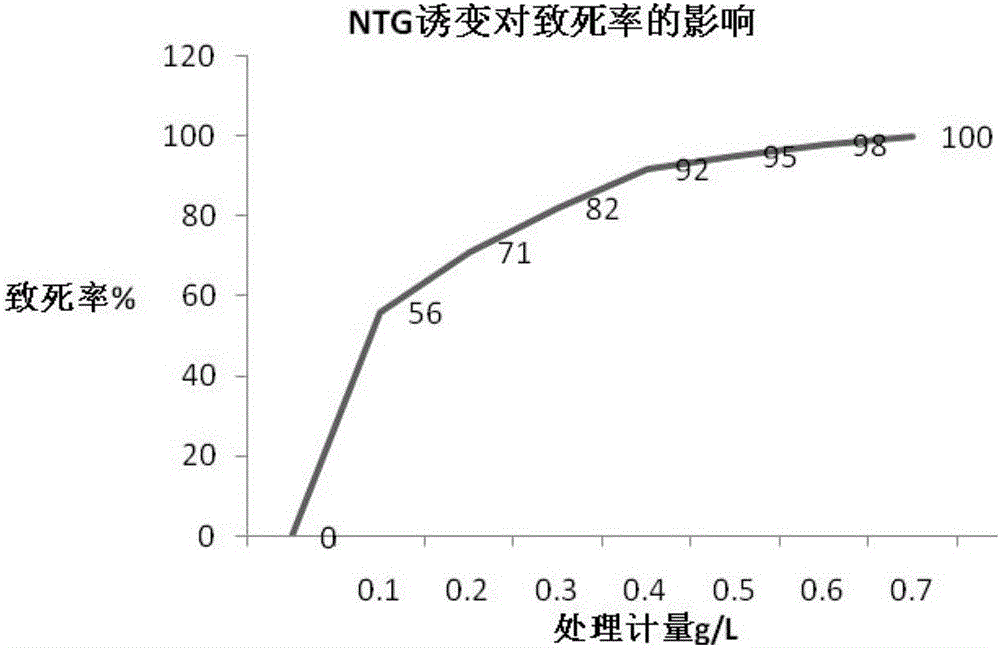
Xanthomonas sp. NYW79 and use thereof
ActiveCN105861401AIncrease productionHigh polysaccharide yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological activationXanthan gum
The invention relates to Xanthomonas sp. NYW79 and use thereof. NYW79 strain is used to produce non-pigmented xanthan gum via the following steps such as activation culturing, liquid seed culturing, fermentation culturing and xanthan gum precipitating. The yield of xanthan gum production using the NYW79 strain is higher than 14.9% as high as that by induction of starting NY07 strain; OD value of fermentation broth is decreased by higher than 77.1%, the production of xanthan gum with NYW79 strain can substantially solve the fading problem of xanthan gum products, and xanthan gum polysaccharide yield is significantly increased.
Owner:ORDOS ZHONGXUAN BIOCHEM
Method for producing exopolysaccharides by promoting fermentation of lucid ganoderma liquid
ActiveCN106755182AHigh polysaccharide yieldShort fermentation cycleMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismThallus
The invention discloses a method for producing exopolysaccharides by promoting fermentation of lucid ganoderma liquid, and belongs to the field of microorganism fermentation. According to the method, liquid shallow fermentation of lucid ganoderma is adopted, the liquid level height of a fermentation culture medium is controlled to be 0.1-5cm, and the yield of ganoderan can be increased. The method has a relatively short fermentation cycle in comparison with solid-state fermentation, does not strictly need stirring, ventilating and other devices in comparison with liquid-state fermentation, the equipment and production cost can be reduced, the polysaccharide yield of unit thallus can be remarkably increased, and 0.086g / g thallus is increased to 0.243g / g thallus, which is increased by 1.83 times, so that industrial production is benefited.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
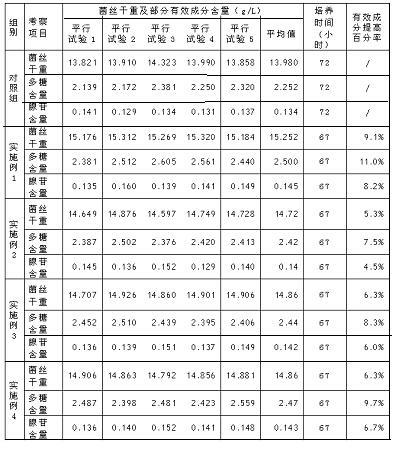
Additive for liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation
InactiveCN102690147ADry weight increaseHigh in polysaccharidesFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
The invention provides an additive for a liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation, relating to formula optimization of a liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation. Calcium lignosulphonate and natural borneol are added into the broad liquid nutrient medium to enhance the transport efficiency of Irpex lacteus cells, and promote the absorption and utilization of the Irpex lacteus for nutrient substances, thereby enhancing the yield of the cellular metabolism products adenosin and polysaccharide and the dry weight of hypha. The total adenosin content is up to 0.135-0.149 g / L, which is enhanced by 8.2% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive; the total polysaccharide content is up to 2...381-2.605 g / L, which is enhanced by 11.0% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive; and the dry weight of hypha is up to 15.176-15.320 g / L, which is enhanced by 9.1% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive. The additive can be used as a liquid nutrient medium additive for industrially fermenting Irpex lacteus.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Culture medium for screening strain capable of highly yielding Hib vaccine as well as preparation method and screening method of strain
InactiveCN104293704AImprove securityEasy to manufactureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium lactateHemin
The invention discloses a culture medium for screening a strain capable of highly yielding a Hib vaccine. The formula of the culture medium comprises the following components: a yeast extract, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, a 60% sodium lactate solution, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride dihydrate, ammonium sulfate, glucose, chlorhematin, a coenzyme I and / or agar. A preparation method of the culture medium for screening the strain capable of highly yielding the Hib vaccine comprises the steps of weighting, preparing a solution A, preparing a solution B and mixing. The high-yielding strain with a capsule is screened by virtue of carrying out passage growth on solid and liquid culture media for many times. Since the culture medium disclosed by the invention is free of animal blood and protein components derived from animals, the potential risk is avoided and the safety of the vaccine is improved; the preparation method of the culture medium has the advantages of simple operation, convenience in preparation and low cost; due to the screening method, the problem of strain screening in the scale production of the Hib vaccine is solved, the yield of the Hib capsular polysaccharide is greatly increased, the working efficiency is improved and the production cost is decreased.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM
A kind of preparation method of carboxymethyl pachyrhin
InactiveCN103484510BPromote growthHigh polysaccharide yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeast extractCulture mediums
The invention discloses a preparation method of carboxymethyl pachyman, and particularly provides a method for fermentation preparation of carboxymethyl pachyman by regulating the variety and proportion of a carbon source and a nitrogen source in a Tuckahoe culture medium. Consisting of the processes of Tuckahoe strain activation, seed solution preparation, fermentation cultivation and carboxymethyl pachyman extraction, the preparation method is characterized in that in the process of fermentation cultivation, the fermentation culture medium comprises the following components by weight percentage: the carbon source (2.0%-4.5% of glucose, 0.1%-4.5% of carboxymethyl cellulose), the nitrogen source (0.45%-0.65% of yeast extract and 0.35%-0.55% of peptone), 0.1% of K2HPO4, 0.046% of KH2PO4, 0.05% of MgSO4.7H2O, and the balance water. The method provided in the invention can directly obtain carboxymethyl pachyman with certain degree of substitution and no chemical residue, and the carboxymethyl pachyman can be widely used in medicine, food and other fields.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for extracting polysaccharide from root of pungent litse fruit
The invention discloses a method for extracting polysaccharide from the root of pungent litse fruit and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: wetting the root of the pungent litse fruit with water; performing extraction twice or three time by using a super high-pressure method under the conditions that particle diameter is 60 meshes, the solid-liquid volume ratio is 1:10-1:18 and the pressure is 400MPa, and the pressure is kept for 3 to 5 minutes; performing enzymolysis on an extracting solution by using protease; performing ultrafiltration on an enzymatic filtering solution by using an ultrafiltration membrane; collecting a permeating solution and concentrating by using the ultrafiltration membrane; collecting a concentrate and precipitating with alcohol; and performing vacuum drying, thereby obtaining the polysaccharide from the root of the pungent litse fruit. The method is simple to operate, high in extracting ratio, low in energy consumption, free of pollution and easy for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG MEDICAL TECH
Method used for recycling microalgae residue and producing spirulina rich in polysaccharides
InactiveCN106701587AIncrease profitImprove utilization efficiencyUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesDownstream processingMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method used for recycling microalgae residue and producing spirulina rich in polysaccharides. According to the method, hydrothermal carbonization is adopted to recycle nutrients in microalgae residue as nitrogen sources, carbon sources, and other nutrient elements in culturing of spirulina, conventional nutritive salt (such as sodium nitrate and urea) supplying method is replaced to produce spirulina rich in polysaccharides, the content of polysaccharide in biomass is 65% or higher, and is increased by 15 to 56% compared with that of common culture medium; polysaccharide yield is increased by 23% to 3.5 times of that of common culture medium. The method is capable of realizing resource utilization of wastes, reducing consumption of nutrient salts, increasing spirulina polysaccharide yield and quality, and reducing production cost, and is beneficial for simplifying of downstream processing operation, and promoting of industrialized production of spirulina.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
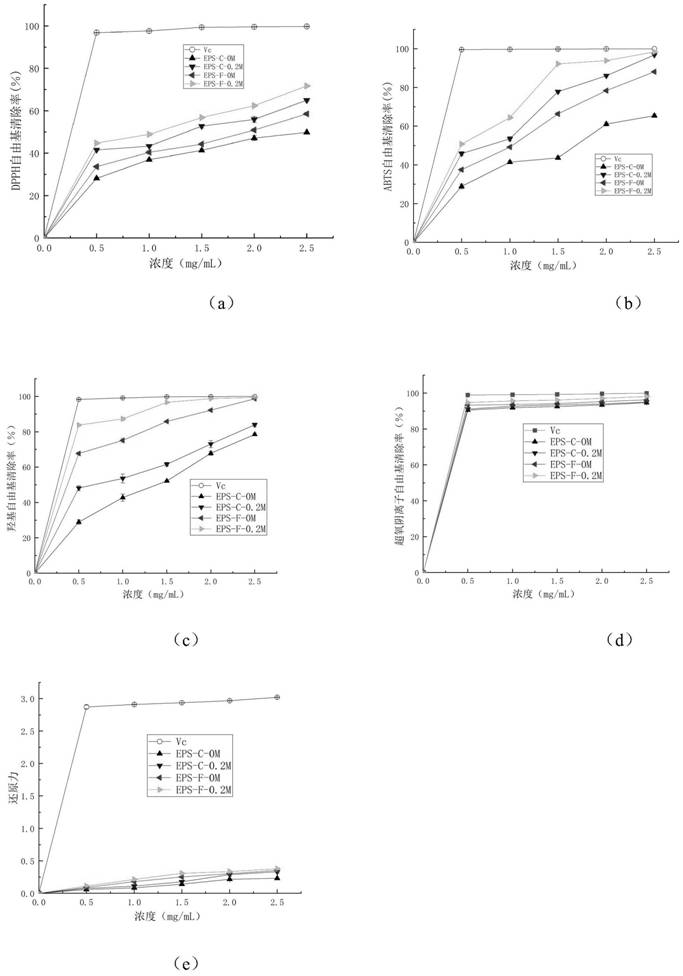
Method for preparing and purifying grifola frondosa polysaccharide with high antioxidant activity
ActiveCN113215206AGood in vitro antioxidant activityHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMolecular biologyFermentation broth
The invention discloses a method for preparing and purifying grifola frondosa polysaccharide with high in-vitro antioxidant activity. According to the method, farnesol is added at beginning of or in a process of liquid fermentation of grifola frondosa. According to the method, farnesol is added in the liquid fermentation process of grifola frondosa mycelia, so that polysaccharide yield of grifola frondosa fermentation liquor is promoted to be changed, yield of acidic polysaccharide components generated by grifola frondosa fermentation is remarkably increased, the polysaccharide yield of the grifola frondosa fermentation liquor is remarkably increased on the basis of not increasing an original fermentation period, the maximum increase amplitude reaches 149%, content of the separated and purified acidic polysaccharide is increased from 7.4% to 58.2%, the in-vitro antioxidant activity of the separated and purified acidic polysaccharide is remarkably improved compared with that of a control group, and the exogenous additive farnesol is safe, non-toxic and high in stability, so that a foundation is laid for industrial production of polysaccharide in the grifola frondosa fermentation liquor.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for extracting low-molecular-weight kelp fucoidin
The invention discloses a method for extracting low-molecular-weight kelp fucoidin, and belongs to the technical field of extraction of polysaccharide. The method for extracting the kelp fucoidin comprises the following steps: cell wall cracking, polysaccharide rough extraction, and polysaccharide extraction, separation and purification. The step of cell wall cracking is as follows: taking 10-16 parts by weight of fucus powder, soaking the fucus powder with anhydrous ethanol for degreasing, extracting solid residues with water under the condition that the solid-liquid ratio is 1: 10-15 m / V, stirring for 20-35 min, standing for 4-6 h in a sealed manner, adding active peptide, stirring for 5-8 min, carrying out steam blasting treatment, and maintaining pressure at 2-2.8 MPa for 30-40 S to obtain cell breakage liquid. The breakage rate of the kelp fucoidin is increased by the active peptide, the yield and purity of the fucoidin are improved, the extracted fucoidin is low in molecular weight, easy to absorb and good in anti-tumor and health-care effect, and the preparation cost of the fucoidin is low.
Owner:兰溪市沉默生物科技有限公司
Strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan
InactiveCN102816701BReduce use costHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMycelium
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism application technology and food biotechnology, and discloses a bacterial strain for fermenting rice bran and bran extract to produce grifola frondosa polysaccharide. The grifola frondosa strain has been preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China on April 7, 2011. The preserved strain number is CCTCC No: M2011113, and the name is Grifolasp.JSU10-2. The present invention obtains a bacterial strain that utilizes cheap raw materials to produce high-yield mycelia polysaccharides through protoplast laser mutagenesis. The bacterial strain and the original strain respectively liquid-ferment rice bran and bran compound medium, and the mycelium dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutagenic strain are respectively higher than those of the original The strains improved by 31.7% and 32.6%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Application of dendrobium polysaccharide in preparation of drugs for preventing and/or treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
ActiveCN109985061BReduced activityImprove antioxidant capacityOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderSide effectTesticular Interstitial Cells
The invention discloses the application of dendrobium polysaccharides in the preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating hyperplasia of the prostate gland. The dendrobium polysaccharide has obvious therapeutic effects, no toxicity and side effects, can improve the antioxidant capacity of the prostate and testis, restore the normal expression of key genes for steroid synthesis in Leydig cells of benign prostatic hyperplasia, and inhibit 5α-reductase in benign prostatic hyperplasia tissue Gene expression, thereby effectively treating benign prostatic hyperplasia; especially benign prostatic hyperplasia caused by exogenous androgen. The Dendrobium polysaccharide of the present invention has wide sources of raw materials, simple extraction and purification method, high sugar content of the obtained Dendrobium polysaccharide, is suitable for large-scale production and popularization, and has good performance in the preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating prostatic hyperplasia and clinical application. prospect.
Owner:中科众康(广东)生物科技研究院
A kind of Naoxinshu oral liquid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111374991BPromote growthShort fermentation cycleNervous disorderDispersion deliveryBiotechnologySodium benzoate
Owner:GUANGDONG YILI LUODING PHARMA
Application of dendrobium polysaccharide in preparation of drugs for prevention and/or treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
ActiveCN109985061AImprove antioxidant capacityGood application prospectOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderDendrobiumSide effect
The invention discloses an application of dendrobium polysaccharide in the preparation of drugs for prevention and / or treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The dendrobium polysaccharide has obvious therapeutic effect and no toxic and side effects, which can improve the antioxidant capacity of prostate and testes, restore normal expression of key genes of steroid synthesis in leydig cells of benign prostatic hyperplasis, inhibit the expression of 5 alpha-reductase gene in the benign prostatic hyperplasia tissue and effectively treats benign prostatic hyperplasia, especially benign prostatic hyperplasia induced by exogenous androgen. The dendrobium polysaccharide with wide source of raw materials is simple in extraction and purification method, high in sugar content and suitable for large-scale production and popularization and has a good prospect in the preparation and / or treatment of prostate hyperplasia.
Owner:中科众康(广东)生物科技研究院
A method for promoting the production of extracellular polysaccharides by liquid fermentation of Ganoderma lucidum
ActiveCN106755182BHigh polysaccharide yieldShort fermentation cycleMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of preparation and purification method of high antioxidant activity Grifola frondosa polysaccharide
ActiveCN113215206BGood in vitro antioxidant activityHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumFermentation broth
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for increasing the yield of Spirulina biomass and polysaccharides simultaneously
InactiveCN105647825BHigh polysaccharide yieldPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDry weightDownstream processing
The invention relates to the cultivation and accumulation of biomass and polysaccharides of spirulina, in particular to the cultivation of spirulina by controlling the addition of nutrient salts so that the biomass and polysaccharides can be accumulated simultaneously. The spirulina cells cultivated to the exponential growth phase are transferred to the nutrient-limited medium, with natural light or artificial light, and the algae cells are harvested after being cultivated to the stable phase. The yield is 0.8-20 times higher than that under the condition of rich nutrition, and the polysaccharide content reaches 45%-80% of the dry weight of algae, which is 2-6 times higher than that under the condition of rich nutrition. The invention solves the contradiction that spirulina biomass and polysaccharides cannot be accumulated at the same time, realizes the rapid and efficient production of spirulina polysaccharides, has the advantages of less nutrient salt consumption, low production cost, high polysaccharide content, etc., and is conducive to simplifying downstream processing operations and promoting spirulina Industrial production of algal polysaccharides.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
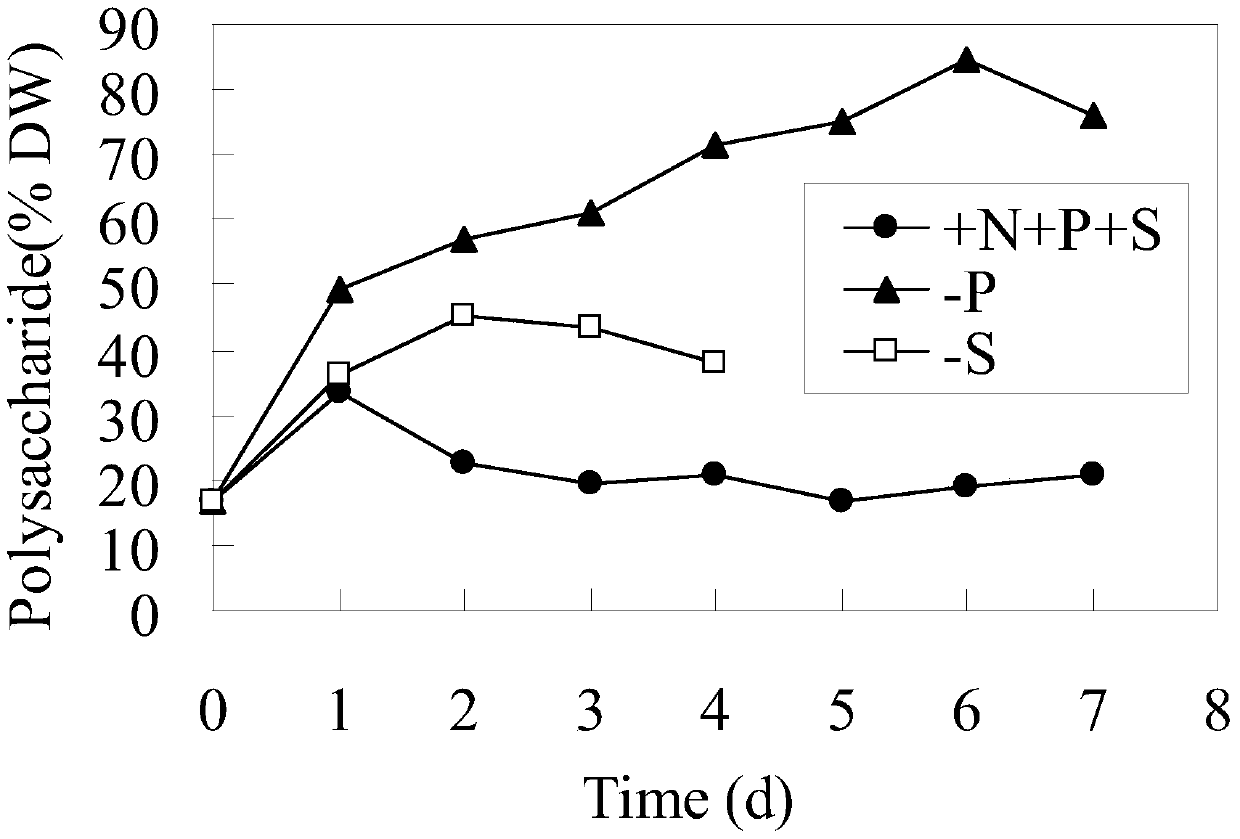
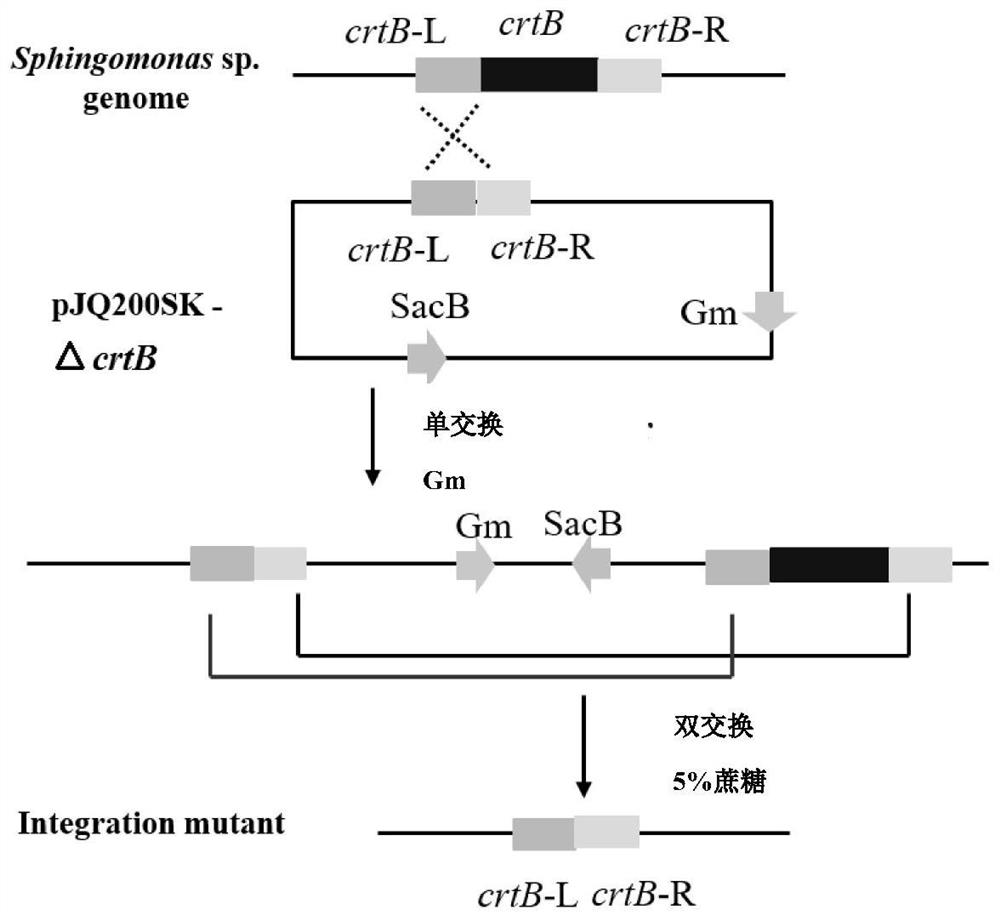
Pigment-free low molecular weight welan gum production strain and its construction method and application
ActiveCN110144318BHigh polysaccharide yieldRaise the level of fermentationBacteriaTransferasesEnzyme GeneDegradative enzyme
The invention discloses a pigment-free low-molecular weight Welan gum production strain. Sphingomonas sp. HT-1 (CCTCC NO: M2012062) is taken as an original strain to respectively construct a pigment-deficient and decapsulated-structure sphingomonas genetically engineered strain WG-1, a pigment and degrading enzyme gene-deficient sphingomonas engineered strain WG-2, and a pigment and degrading enzyme gene-deficient and decapsulated-structure sphingomonas genetically engineered strain WG-3. The yield of the Welan gum produced by the sphingomonas strain WG-2 in the invention is increased by 10% to 30% compared with the original strain, reaching 35 to 45g / L, and the molecular weight is not significantly changed (Mn: 10000 to 20000kDa). The sphingomonas strain WG-1 and the sphingomonas strain WG-3 in the invention are fermented to produce low-molecular weight Welan gum (Mn: 500 to 1000kDa), and the yield of the Welan gum produced by the decapsulated-structure strain WG-3 is increased by 20%to 30% compared with the strain WG-1, reaching 20 to 25g / L. The strain constructed by the invention can obtain Welan gum products of different molecular weight ranges, and significantly improves thefermentation level of Welan gum.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Production method of grifolan selenium compound
ActiveCN102816806BIncrease productionIncrease valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhosphate
The invention relates to a production method of a grifolan selenium compound, and relates to the food microbiological application technology field. The method comprises the steps that: rice bran and wheat bran are leached in water with a temperature of 90 DEG C to 98 DEG C for 2.5-3h under normal pressure; residuals are removed, and a juice is obtained; the obtained process liquid is used as a culture media for fermentation, wherein the rice bran application amount is 30-120g / L culture media, the wheat bran application amount is 30-120g / L culture media, an addition amount of selenium is 5-10mg / L culture media, an addition amount of potassium dihydrogen phosphate is 1.0-1.5g / L, an addition amount of magnesium sulfate is 0.5-0.80g / L, and a pH value is natural; mycelium obtained by liquid culturing is subjected to centrifugal separation, and is washed by using distilled water; the mycelium is dried to constant weight, such that the mycelium is obtained; the mycelium is subjected to conventional water extraction, deproteinization, ethanol precipitation, and lyophilization, such that a intracellular polysaccharide selenium compound can be obtained. With the method provided by the invention, the production of grifolan selenium compound by using cheap raw materials is better realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYUAN ZHONGTIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran
The invention discloses a Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with a composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran, which belongs to the technical field of microbial application technology and food biology. The Grifola frondosa strain JSU10 is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) in October 8th, 2010 with the CGMCC No. 4179 and is identified to be Grifolasp. The invention improves the positive mutation rate of the Grifola frondosa strain for rapidly growing and producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on a composite culture medium of rice bran and wheat bran by composite mutagenesis of ultraviolet rays and microwave to obtain a high-yield strain; the strain and the original strain are respectively a liquid fermentation rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium; and hypha dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutated strain are respectively improved by 39.24 percent and 42.58 percent compared with the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of white peach and phellinus igniarius wine
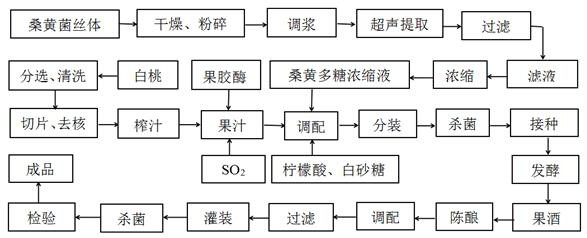
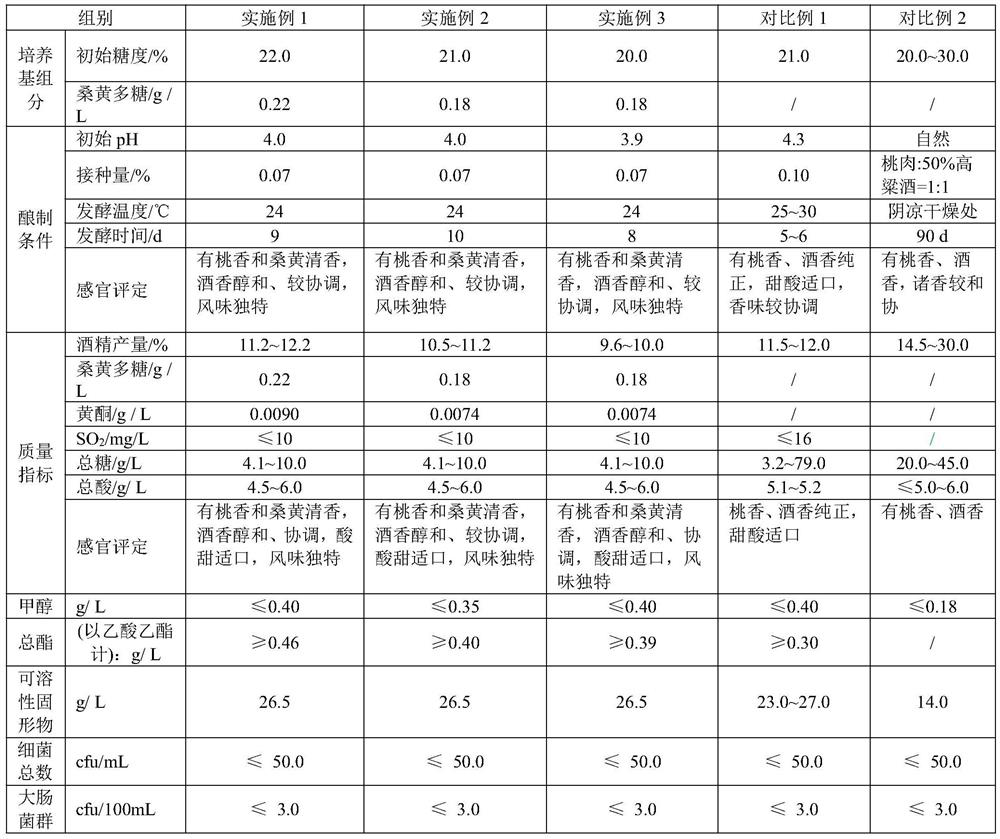
PendingCN112899109AImprove the level of brewing technologyPreserve the flavorFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFruit wine
The invention discloses a preparation method of white peach and phellinus igniarius wine. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a phellinus igniarius polysaccharide concentrated solution and white peach juice respectively, adding the phellinus igniarius polysaccharide concentrated solution to the white peach juice, regulating the concentration, initial sugar degree and pH value of phellinus igniarius polysaccharide in the white peach juice, then performing sterilizing, activating a saccharomycetes strain, inoculating the saccharomycetes strain to the white peach juice, and performing fermenting, aging, blending, filtering and sterilizing to obtain the white peach and phellinus igniarius wine. The key technical condition problems of initial sugar degree of the white peach fruit juice, initial pH of a brewing culture medium for the phellinus igniarius polysaccharide and white peach fruit wine, brewing temperature, yeast inoculation amount and brewing time and the like in the white peach fruit wine brewing process are solved, the brewing technical level of the white peach fruit wine is improved, and a new way is developed for deep processing of white peaches.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Grifola frondosa strain produced through rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid fermentation
InactiveCN103416313BIncrease productionChange the disadvantages of low utilizationFungiFungi productsMicroorganismDry weight
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe application and good bioscience and discloses a polysaccharide grifola strain produced through a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium. grifola Grifola sp.JSU1301 is preserved in the China Typical Model Cultivation Center (CCTCC) in June 25th, 2013, and is numbered CCTCC NO: M 2013286 and named a grifola Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2013286. According to the invention, a ultraviolet mutagenesis method is described with figures; a new strain capable of highly producing polysaccharide by starting with Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2011113; the new strain quickly ferments and highly produces polysaccharide in the rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium; the mycelial dry weight and the mycelial polysaccharide productivity of a shake flask are increased by 16.8% and 8.57% compared with those of a starting strain, and those of fermentation in a tank are improved by 30.9% and 29.7%, which reach the highest level at present.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for producing polysaccharide by rice husk bran composite raw material and grifola frondosa mutant strain
InactiveCN102080113BIncrease productionImproving the value of adjuvant antineoplastic therapyFungiFermentationEthanol precipitationBran
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com