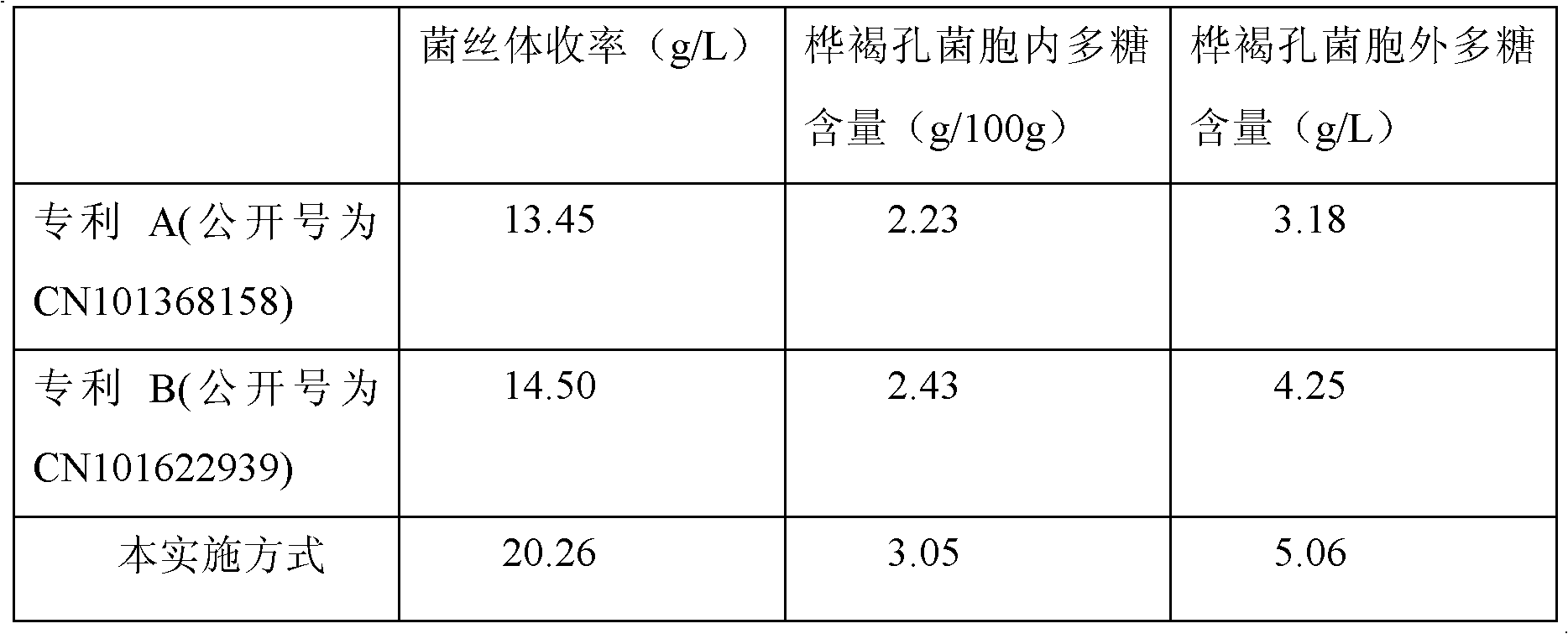
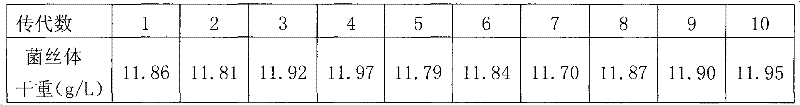
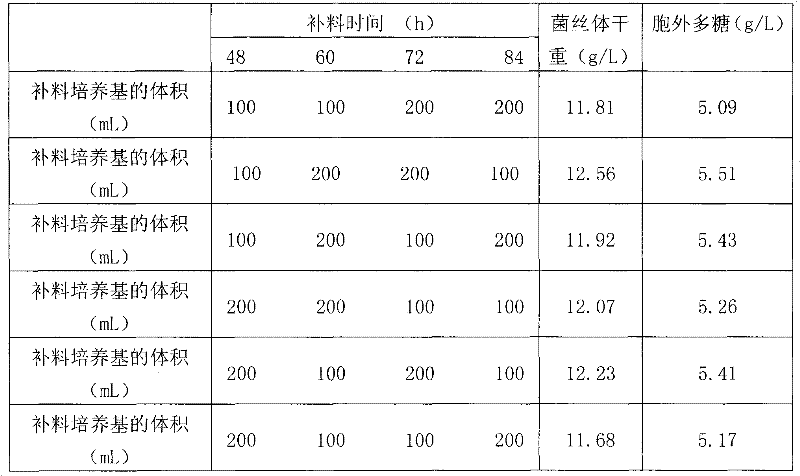
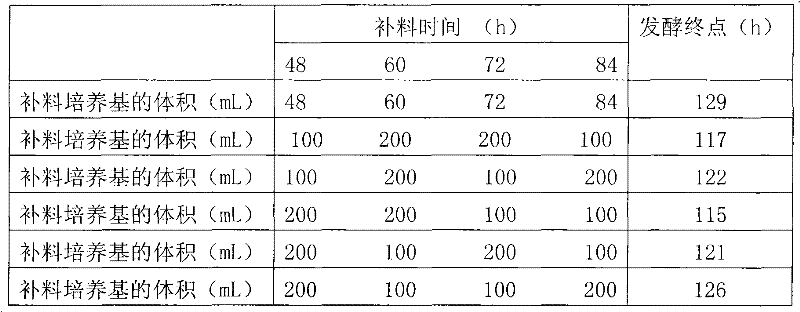
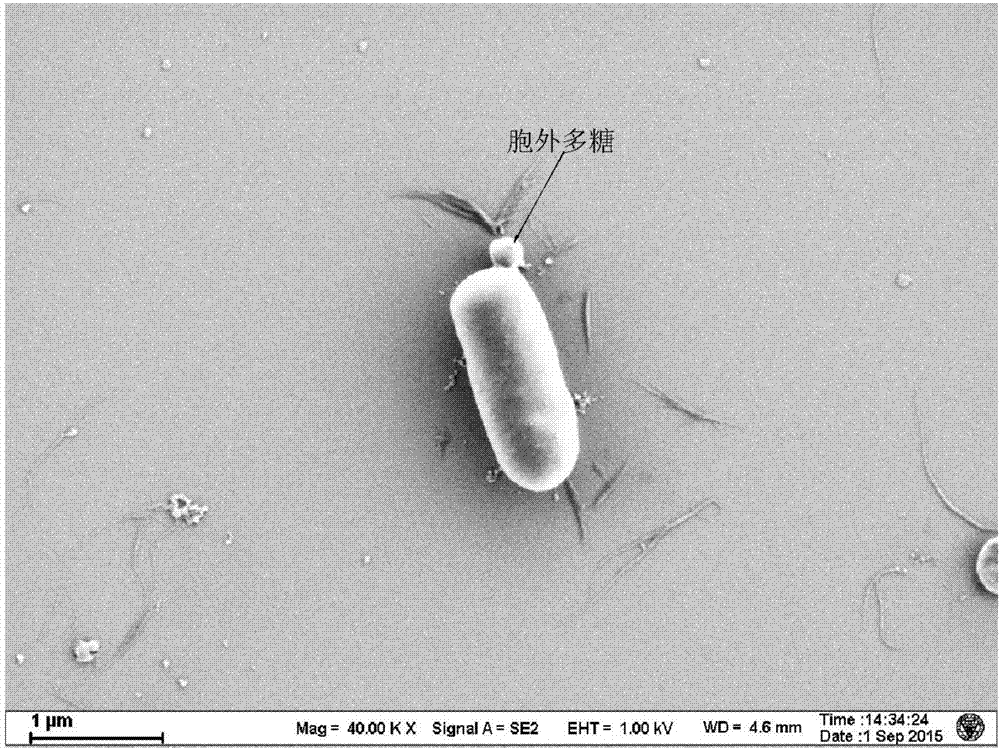
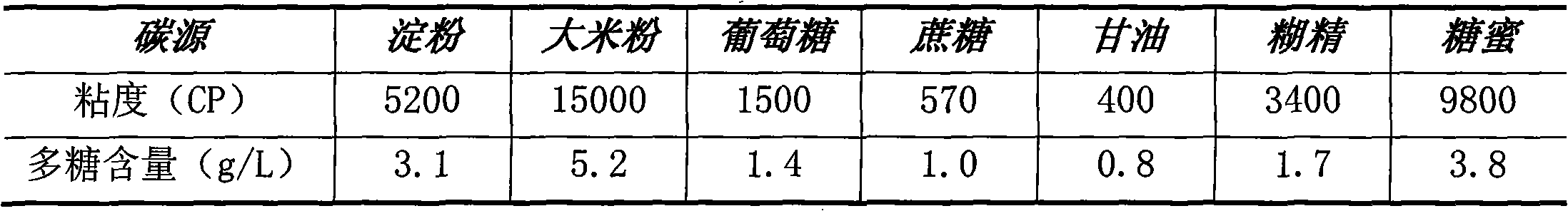
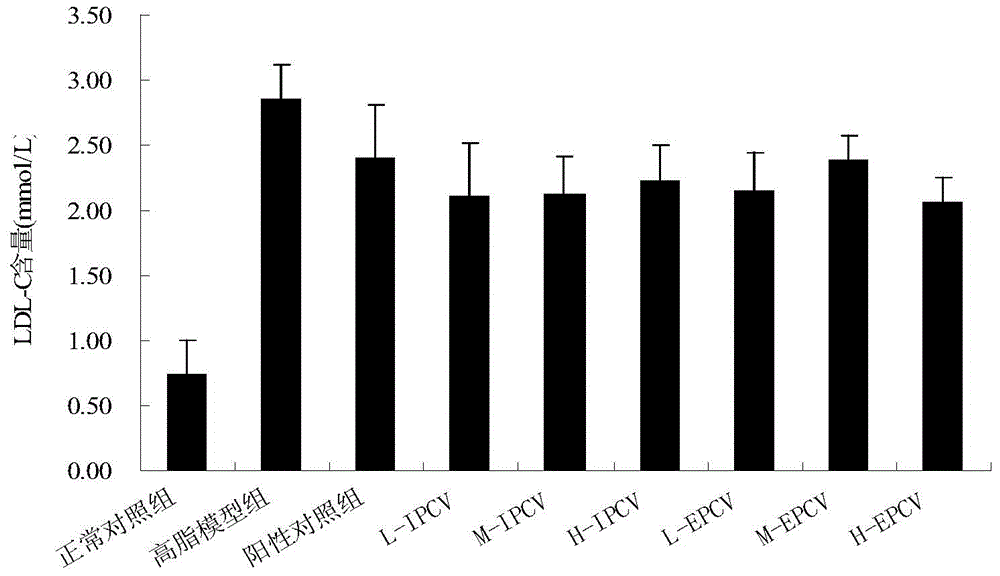
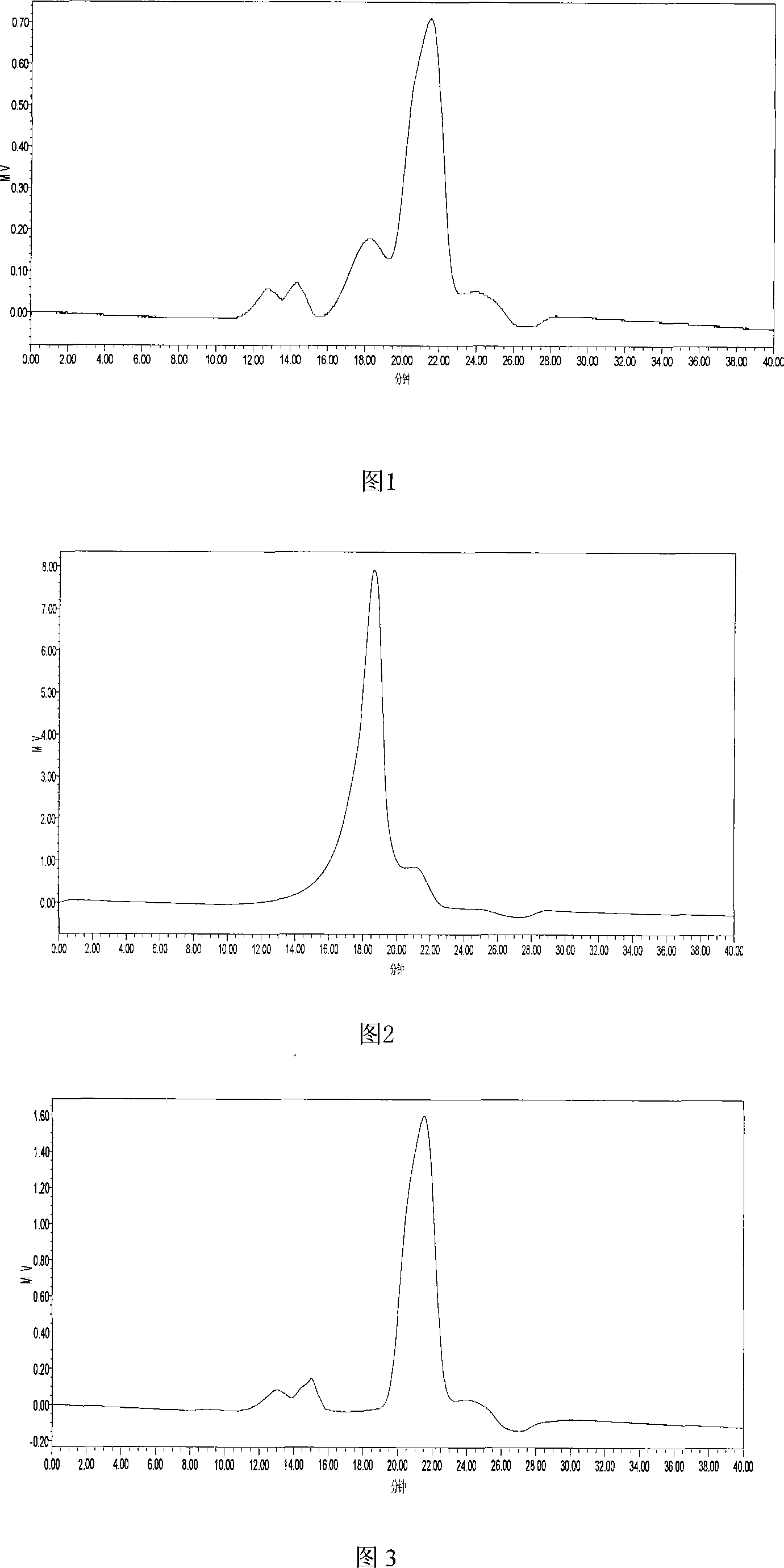
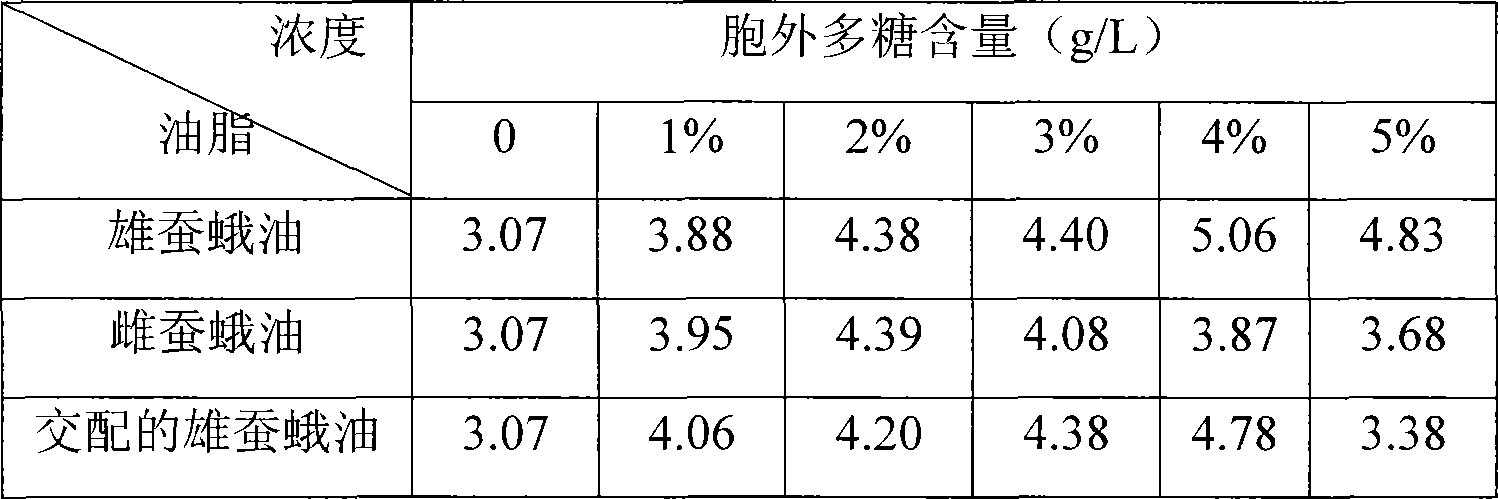
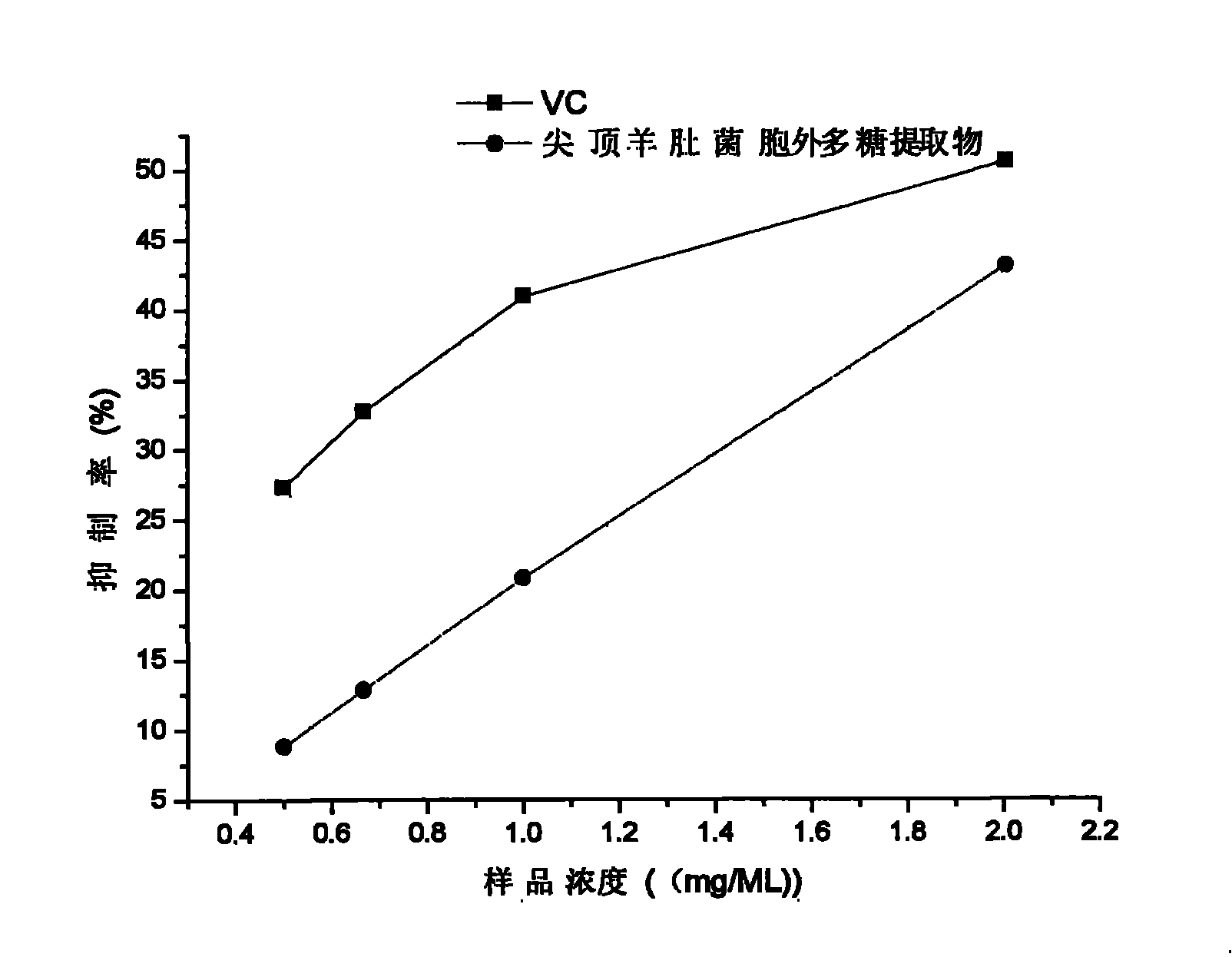
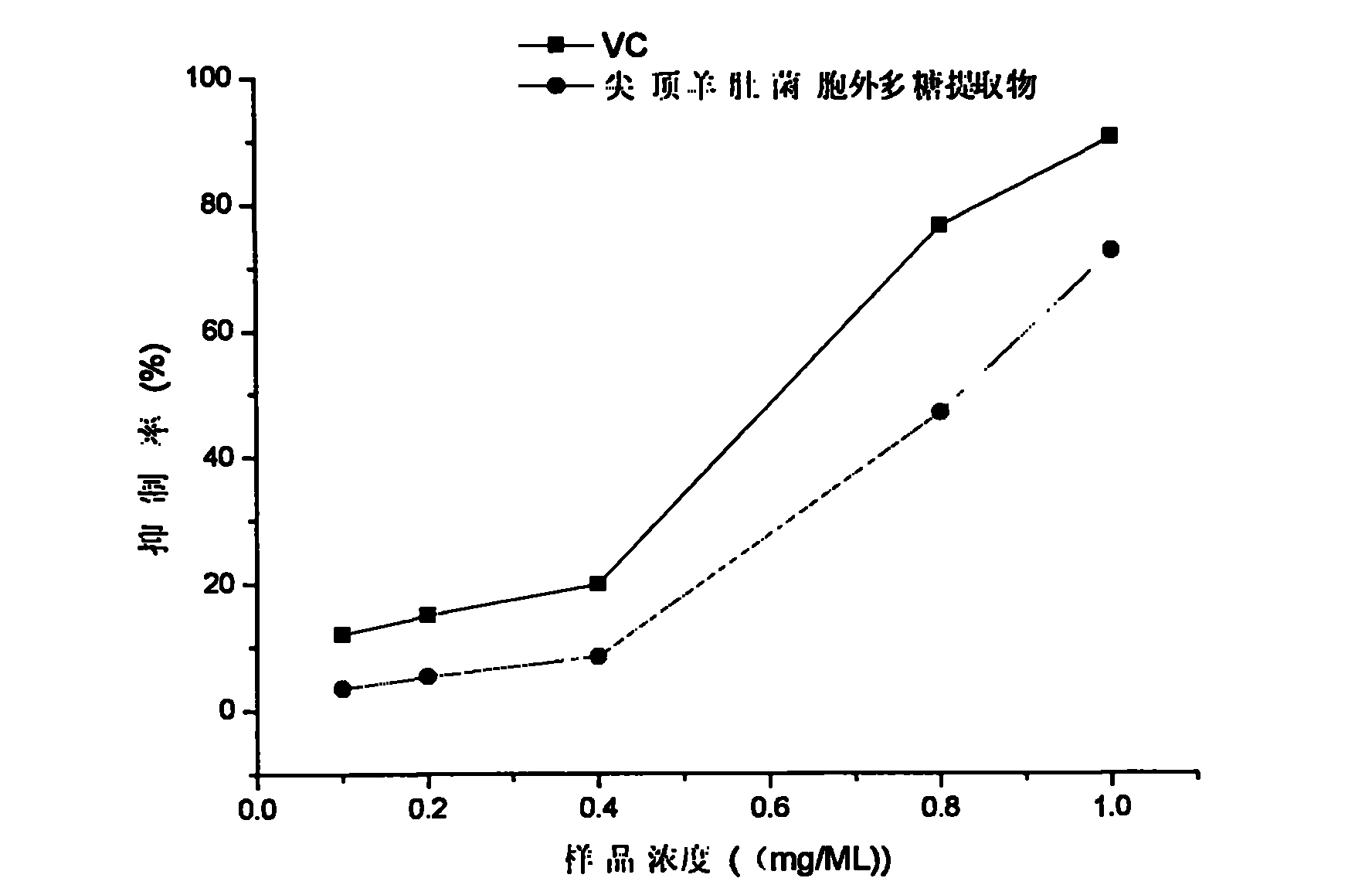
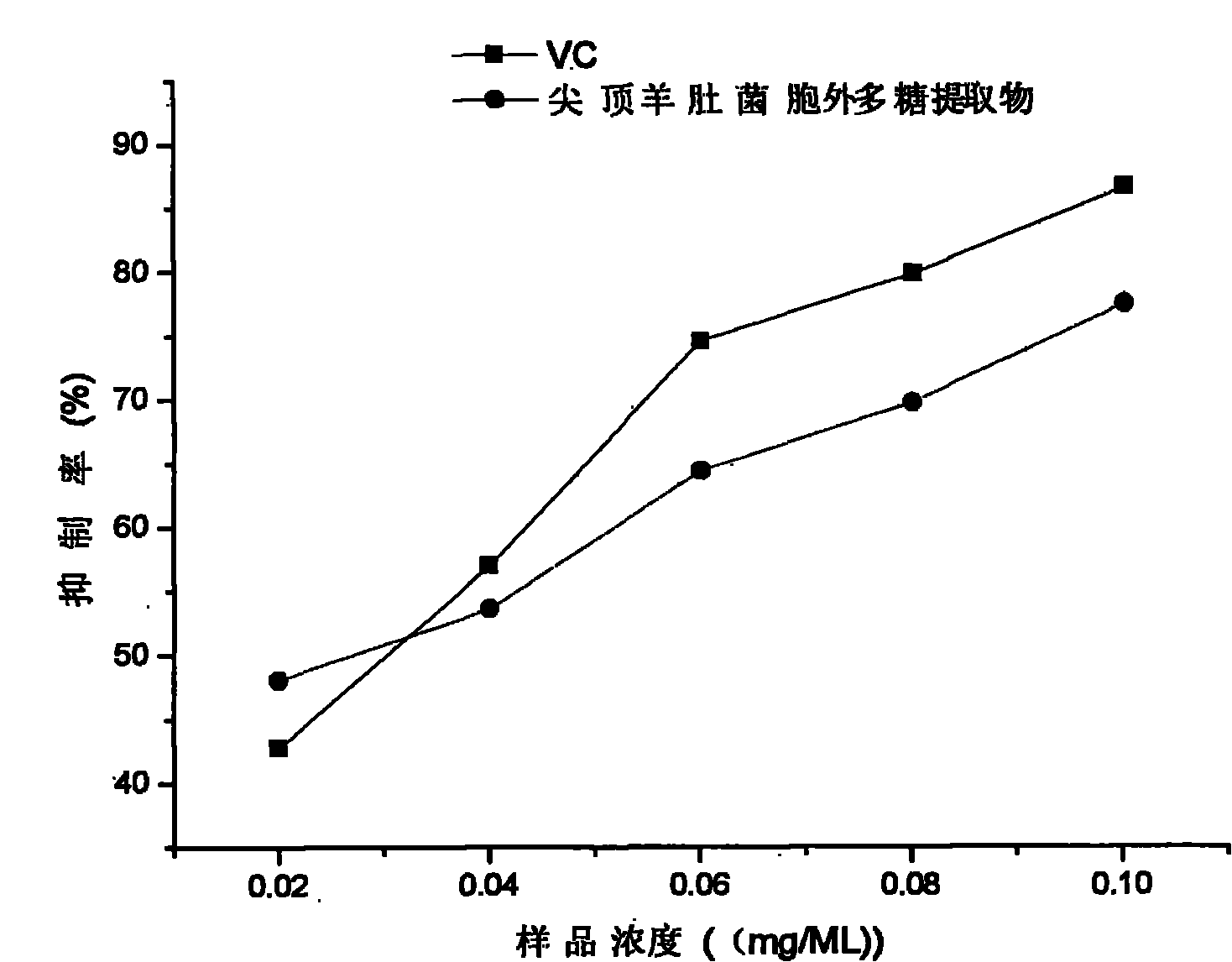
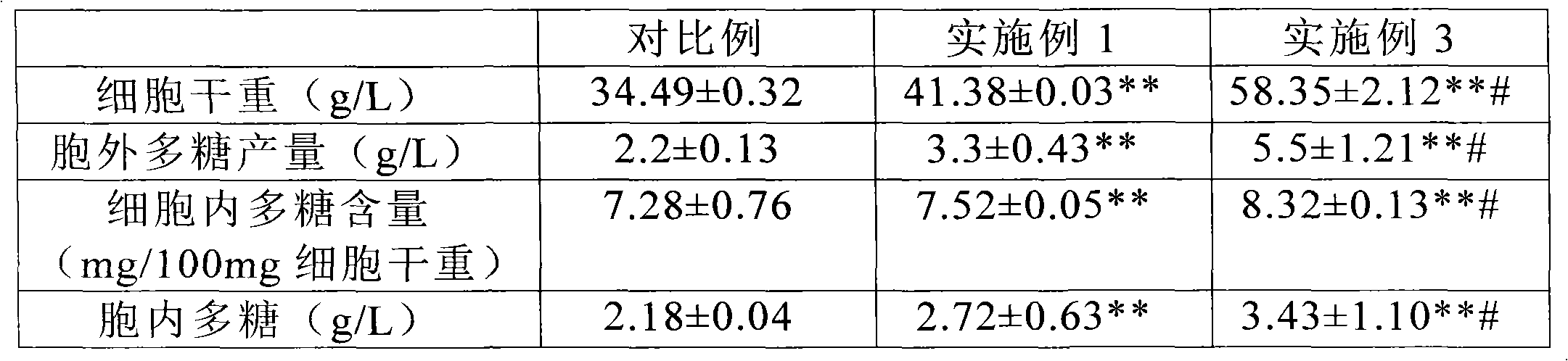
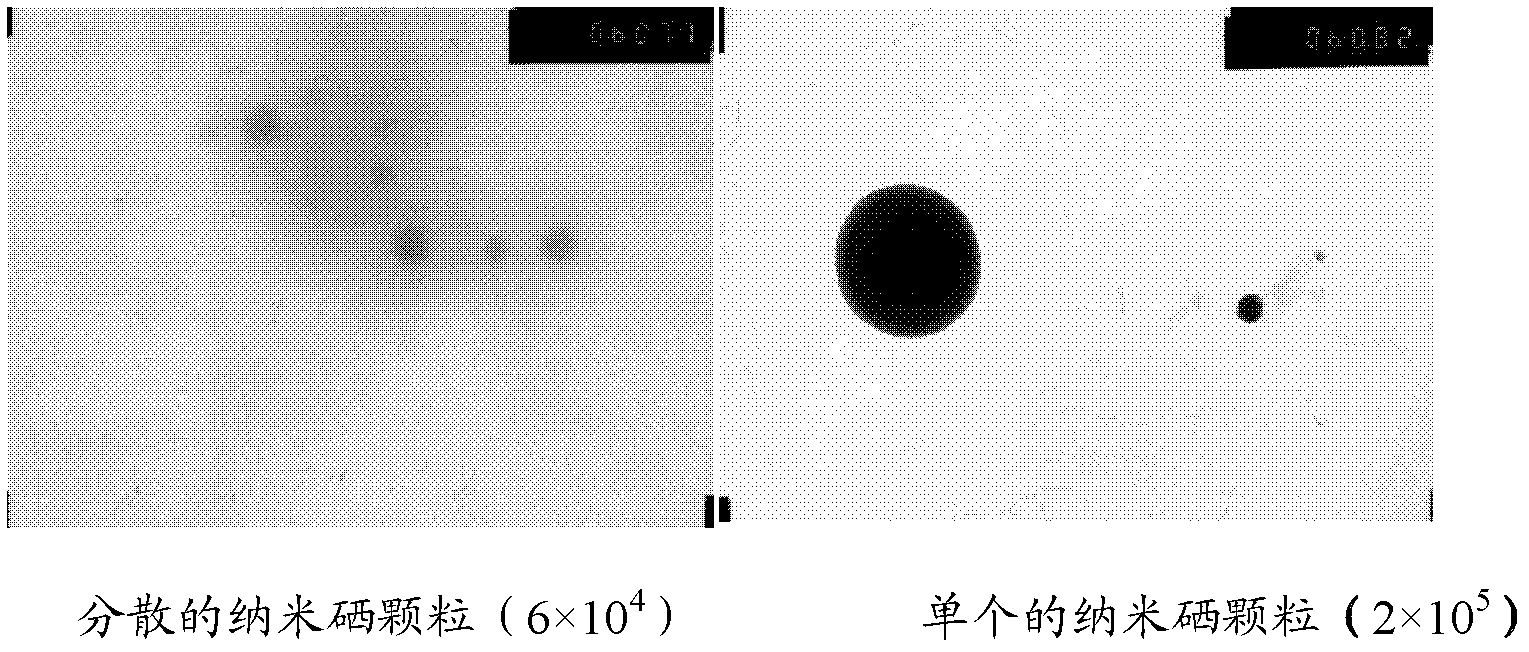
Patents
Literature
401 results about "Extracellular polysaccharide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
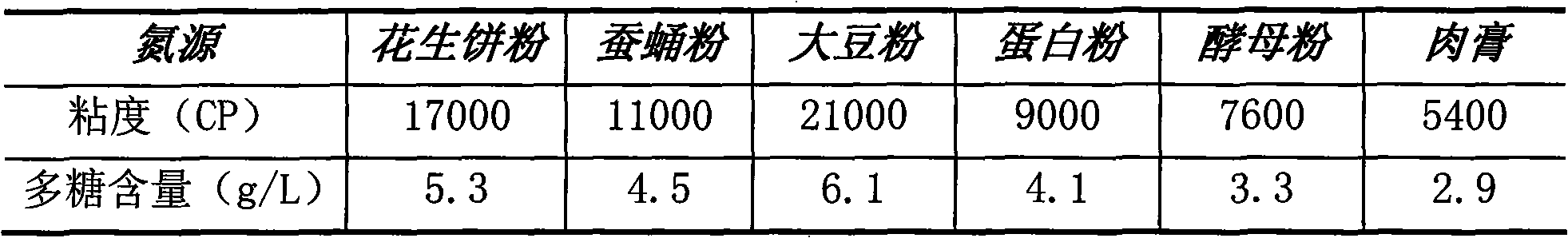
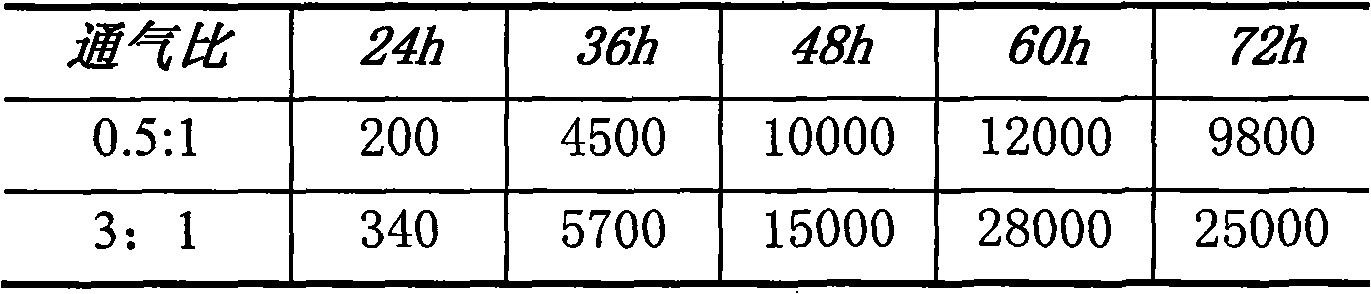
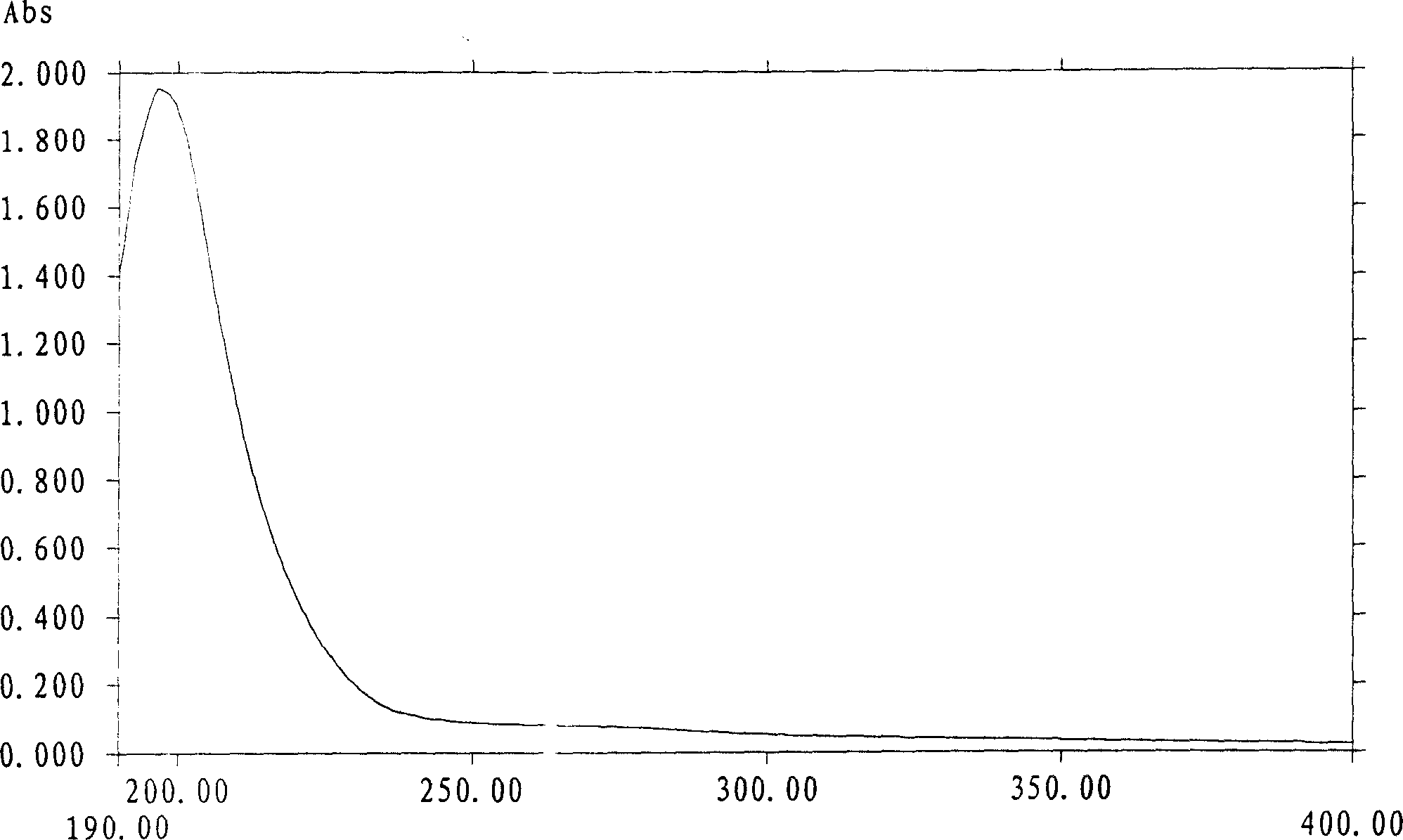
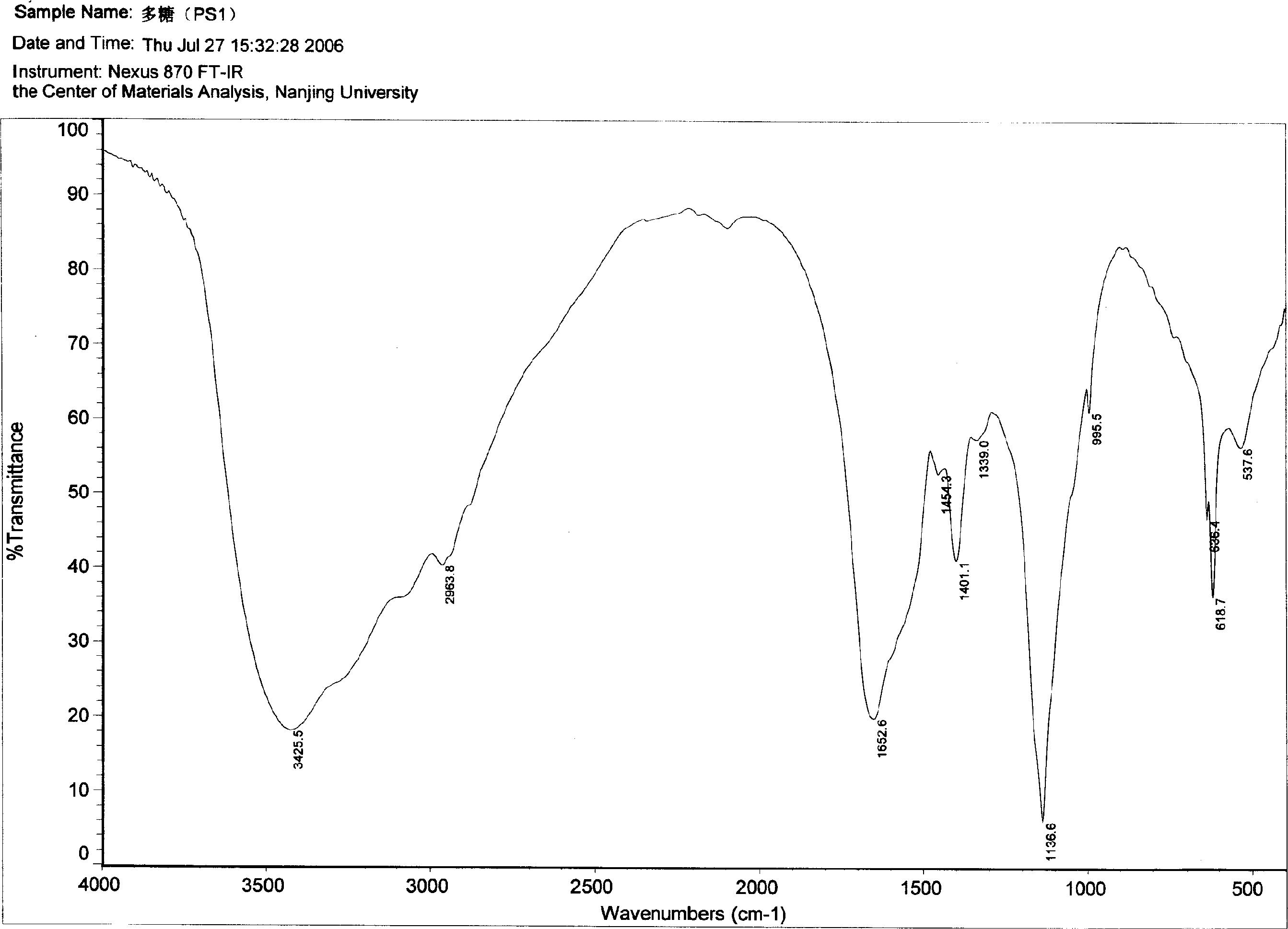
Extracellular polysaccharide. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) Extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) matrix Microbial EPS are the key components for the aggregation of microorganisms in biofilms, flocs and sludge. They are composed of polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and other biological macromolecules.
Biofilm extracellular polysachharide solvating system
The invention provides a solvating system for the removal of biofilms which solvates the extracellular polysaccharide matrix holding it to a surface. The aqueous solvating system comprises water, a metal ion sequestering agent, and a solvating agent for an extracellular polysaccharide matrix, which is gentle enough to be used directly on human tissues, but which may also be used on hard or soft non-tissue surfaces to breakdown, and / or remove biofilms.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
High-temperature stable hydrogel mask
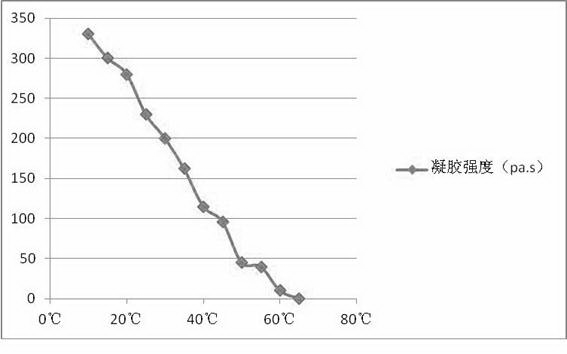
ActiveCN104042449AFast conditioningFast absorptionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPlanting seedSeaweed extract
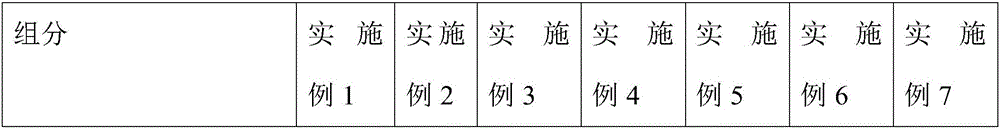
A high-temperature stable hydrogel mask comprises a carrier net cloth and hydrogel. The hydrogel comprises the following components by weight: 0.1%-1% of a cellulose derivative water-soluble polymer, 0.5%-2% of seaweed extract natural water-soluble polymer, 0.1%-2% of extracellular polysaccharide natural water-soluble polymer generated by microbial fermentation, 0.1%-2% of plant seed or root extracted natural water-soluble polymer, 0.1%-2% of electrolyte required by cross-linking initiation, 0.5%-5% of a skin conditioner, 0.1%-1% of a transdermal absorption promoter, 5%-20% of polyol, 0.1%-1% of a preservative and the balance of pure water. The high-temperature stable hydrogel mask meets the requirements for physicochemical indexes of mask in Light Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China ''QB-T2872-2007 mask''. The hydrogel on the carrier net cloth maintains stable in the temperature range of -15 to 55 DEG C, and improves the stability of the product during transport and storage.
Owner:NOX BELLCOW COSMETICS CO LTD
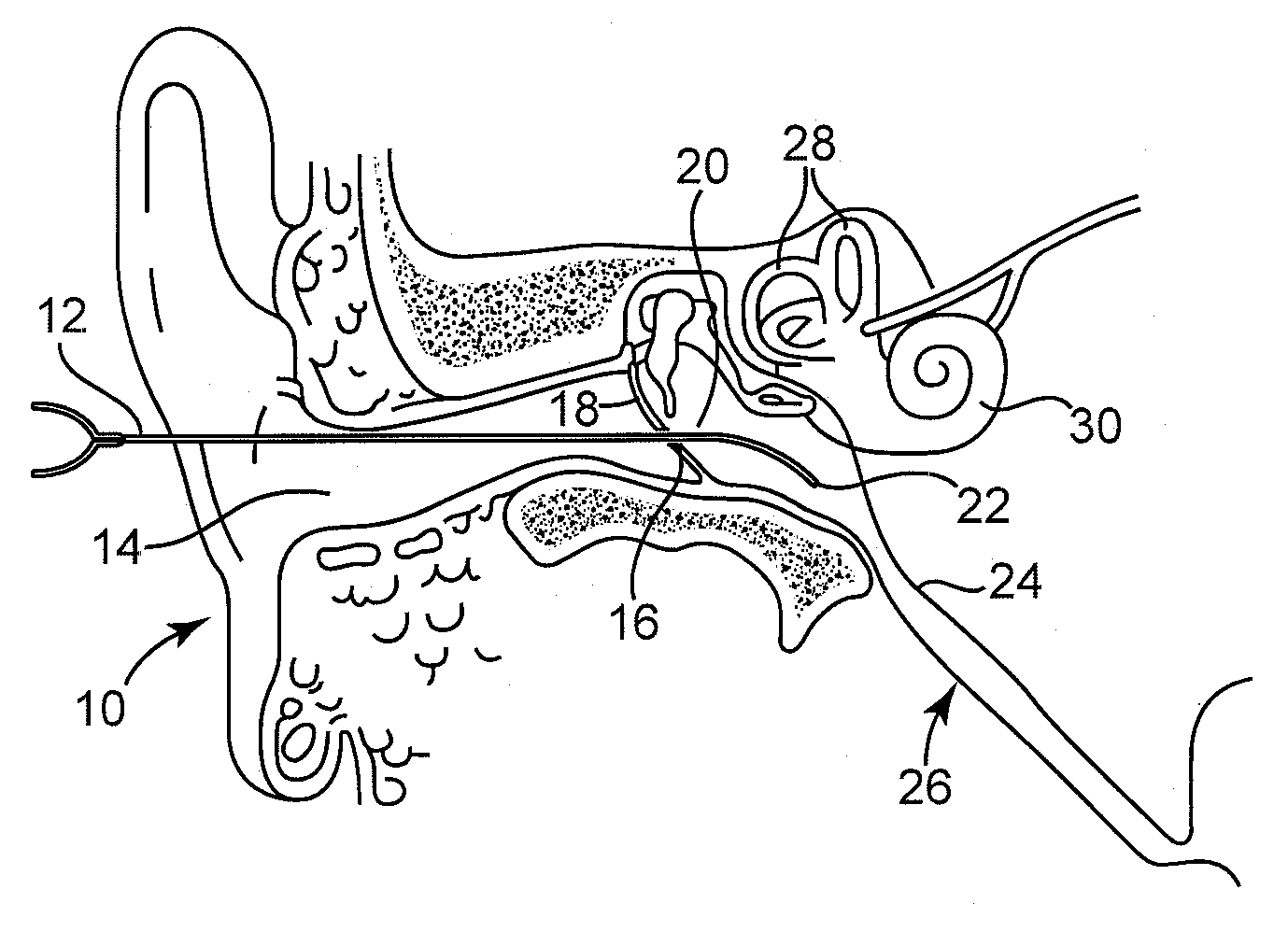
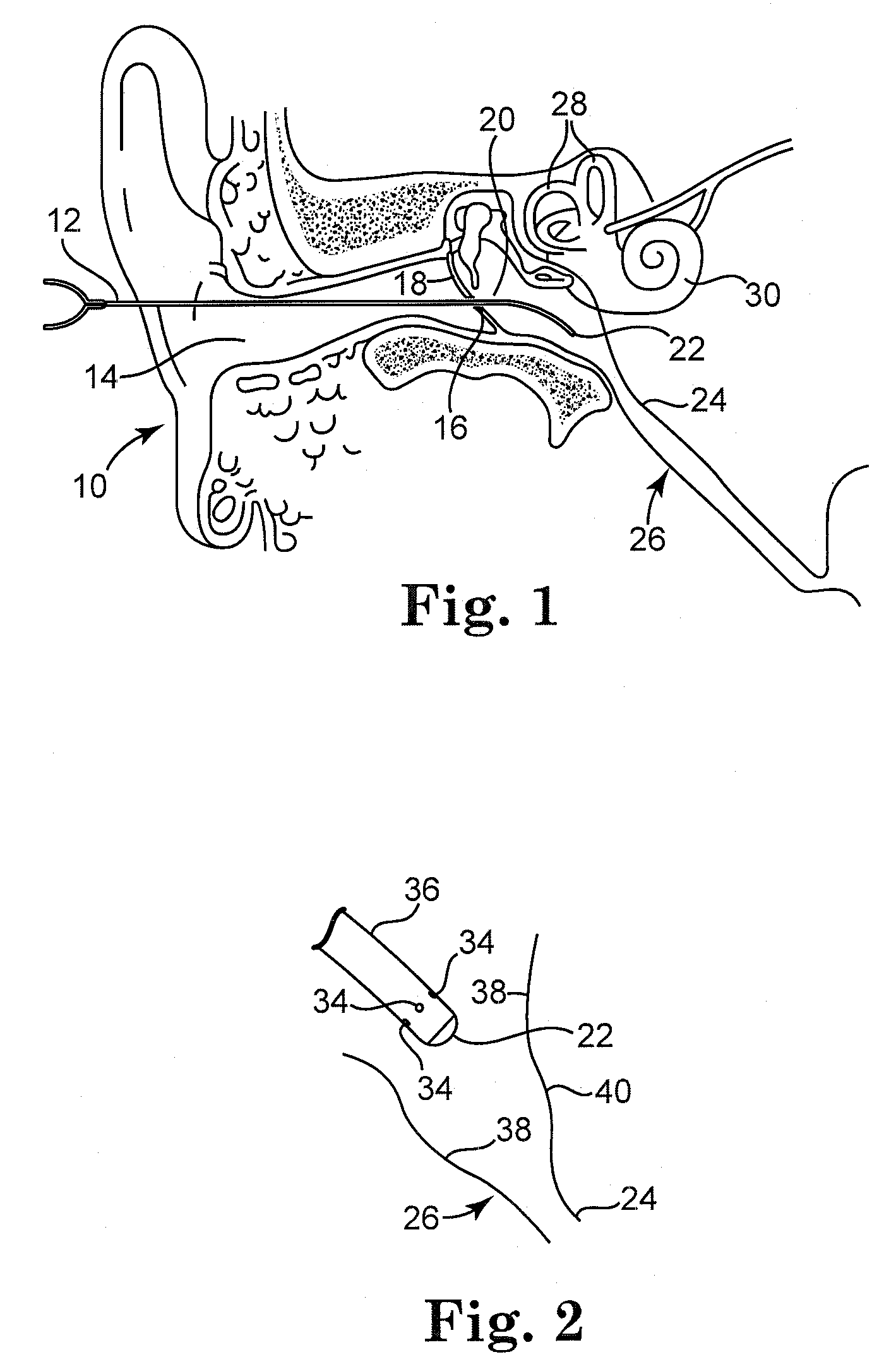
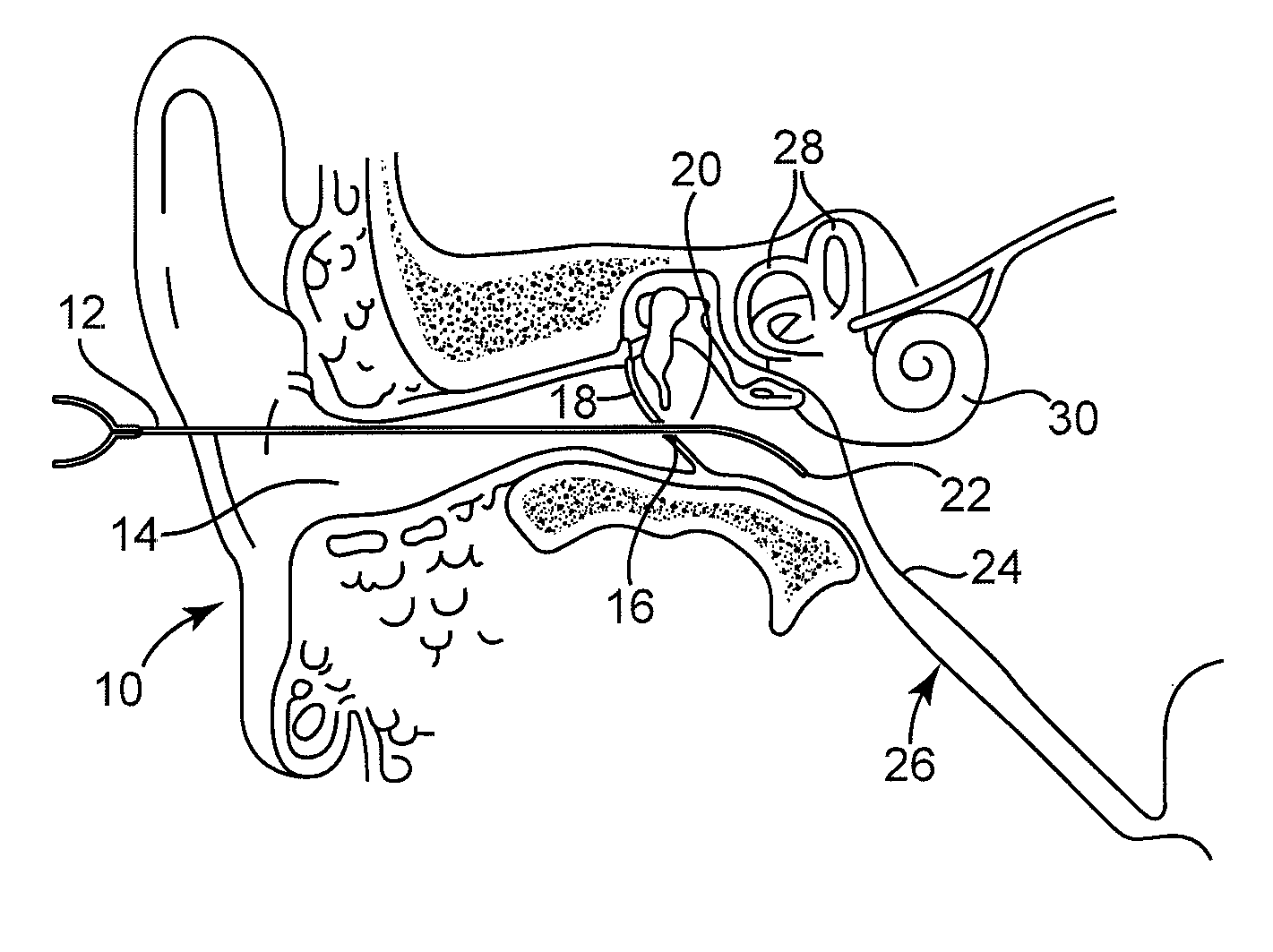
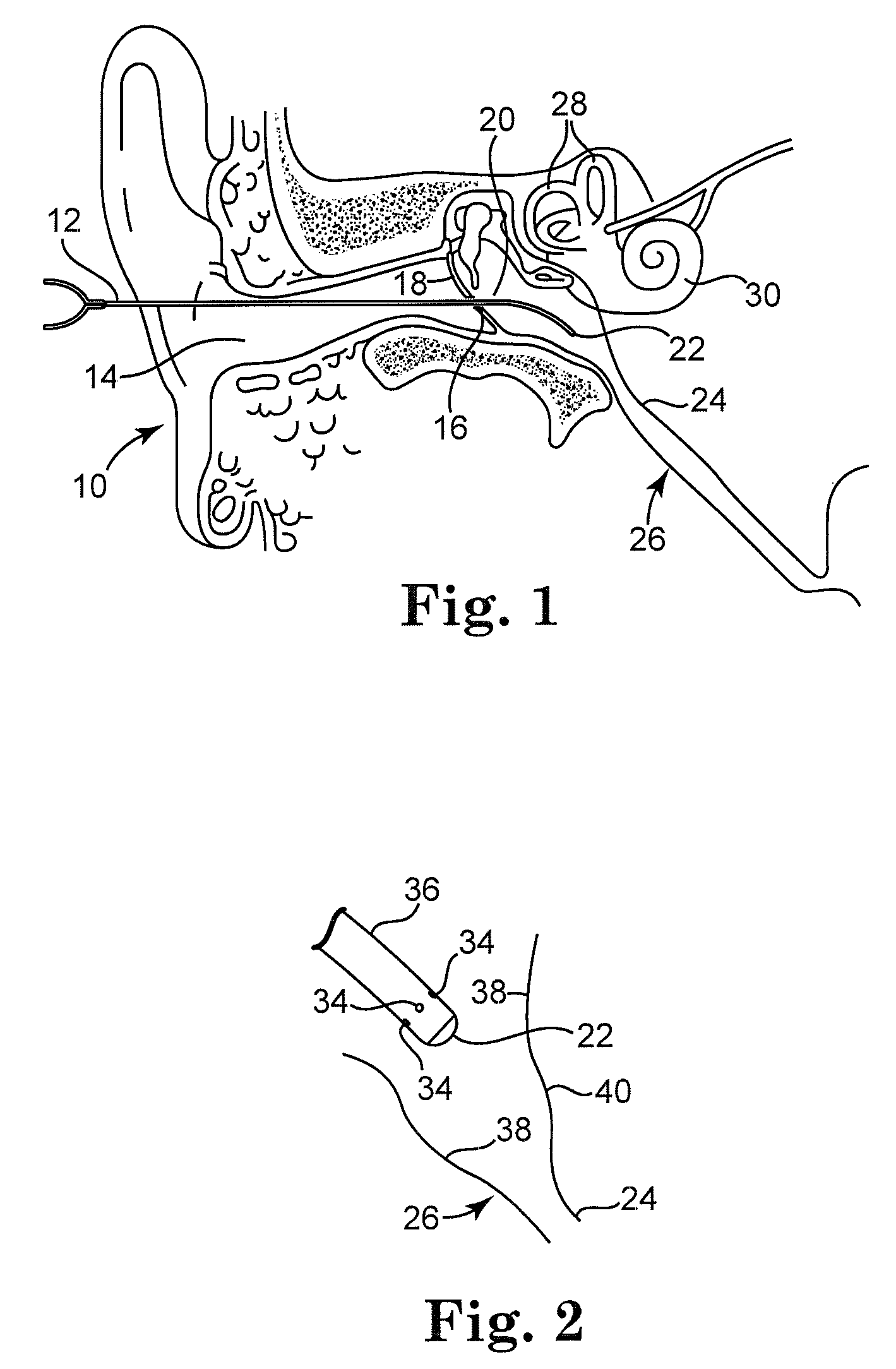
Extracellular polysaccharide solvating system for treatment of bacterial ear conditions
ActiveUS20070264353A1Discourage bacterial recolonization and biofilm reformationEfficiently disruptedAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsBacteroidesBiofilm
Chronic otitis media and other bacterial ear conditions may be treated by applying a solvating system containing a metal ion sequestering agent and surfactant to a bacterial biofilm in the middle or inner ear. The solvating system disrupts the biofilm and aids in its removal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Novel Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and Extracellular Polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
Extracellular polysaccharide solvating system for treatment of bacterial ear conditions
ActiveUS7976873B2Discourage bacterial recolonization and biofilm reformationEfficiently disruptedAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiofilm
Chronic otitis media and other bacterial ear conditions may be treated by applying a solvating system containing a metal ion sequestering agent and surfactant to a bacterial biofilm in the middle or inner ear. The solvating system disrupts the biofilm and aids in its removal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Culture medium and method for submerged fermentation of inonotus obliquus
InactiveCN102115350AHigh yieldEnhance Inonotus obliquus intracellular polysaccharideHorticultureFertilizer mixturesPhosphateMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a culture medium and method for submerged fermentation of inonotus obliquus, relating to a culture medium and method for microbial submerged fermentation, and solving the problems of low yield of traditional inonotus obliquus submerged fermentation mycelia and low output of intracellular polysaccharide and extracellular polysaccharide of the inonotus obliquus as the activeingredient for the submerged fermentation. The culture medium for submerged fermentation is prepared from the following components: carboxymethyl cellulose, glucose, soybean meal, yeast extract, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, magnesium sulfate, vitamin B1 and the balance of water. The method for the submerged fermentation comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a culture medium for the submerged fermentation of inonotus obliquus; (2) inoculating the inonotus obliquus; and (3) carrying out submerged fermentation at two stages. By means of the culture medium and the method for the submerged fermentation of the inonotus obliquus in the invention, higher mycelium yield and intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides can be obtained. The mycelia polysaccharide obtained by the invention is 1.4 times higher than that of wild fruiting bodies, and the content of other active ingredients is higher than or equal to that of the wild fruiting bodies. The culture medium and method provided by the invention can be used for providing a rapid and abundant seed liquid for the large-scale artificial culture of the inonotus obliquus.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Production and cultivation of glossy ganoderma with tea branch, tea, stem material
The invention relates to a production process method for mythic fungus cultivation by tea branches, tea and peduncle-replaced materials. The production process method is characterized in that the proportions are as follows: 33-53% of tea branches, 17-27% of peduncles, 18-48% of wheat bran, 1-2% of brown sugar, 0.5-1% of gypsum and 0.1-0.5% of calcium superphosphate. A plurality of wasted tea branches generated during the cutting process in tea garden, tea and peduncles in the tea making process are sufficiently utilized; furthermore, special inducible factors such as tea polysaccharides, vitamin, trace elements, etc. that are rich in the tea branches and tea peduncles can be utilized to produce the mythic fungus with the 1.5-2.5% of the content of the tea polysaccharides which is higher than that of the current mythic fungus cultivated by the replacing material such as tree sawdust, cotton seed shell, etc. by 24.5-35.8%; meanwhile, the tea can prompt the synthesis of extracellular polysaccharide of mythic fungus, improves the quality and medicinal efficacy of the mythic fungus, cultivates the mythic fungus by the tea branches, tea and peduncle-replaced material, increases new replacing material for the mythic fungus cultivation, prompts the development of Chinese mythic fungus production, and is beneficial to the execution of the Chinese natural forest protection engineering.
Owner:AGRI ECOLOGY INST FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
New Poria cocos strain and liquid fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102199543AMeet needsIncrease production capacityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention provides a new Poria cocos strain and a liquid fermentation method thereof and relates to the field of Poria cocos liquid fermentation. The invention provides the Poria cocos strain conserved in the China center for type culture collection, wherein the CCTCC NO is M 2010361. The invention also provides a Poria cocos liquid fermentation method and the method comprises the following steps: a) preparing a fermentation seed: inoculating the Poria cocos strain of which CCTCC NO is M 2010361 in seed culture medium to obtain the Poria cocos seed; and b) fermenting: inoculating the seed obtained in the step a) in Poria cocos liquid fermentation culture medium to ferment and obtain fermentation liquor, namely the Poria cocos fermentation product. By adopting the fermentation method, the mycelium yield or extracellular polysaccharide yield of Poria cocos liquid fermentation can be increased, the demand of the market on Poria cocos can be met and a foundation is laid for the developments of the health food and medicine which are related to Poria cocos.
Owner:CHENGDU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Lactobacillus plantarum strain capable of producing extracellular polysaccharide
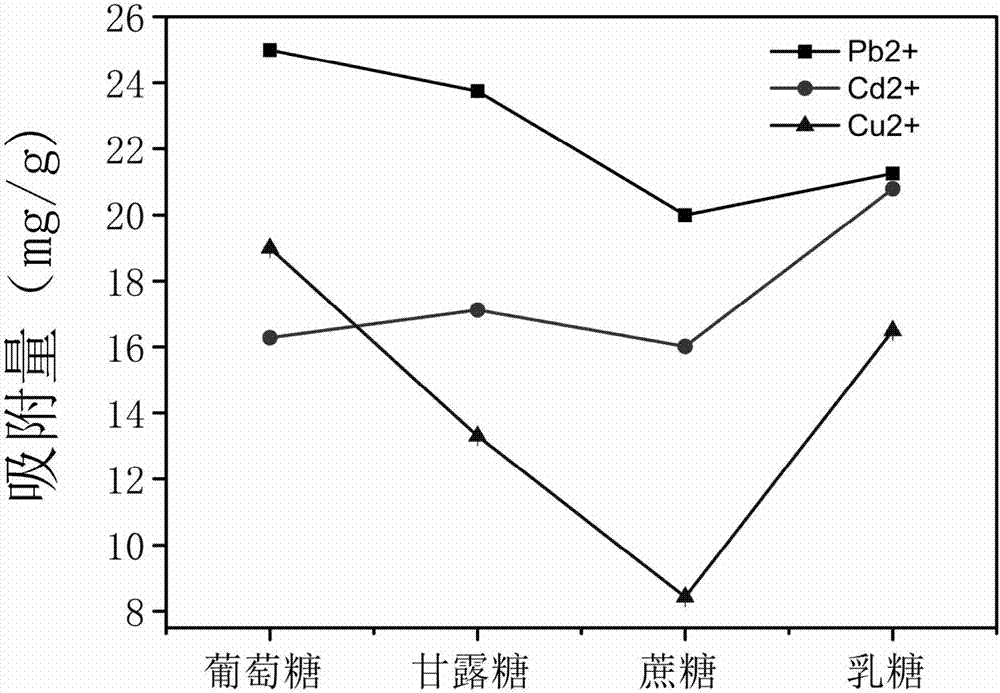
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum strain LCC-605 capable of producing extracellular polysaccharide, which is stored in China Center for Type Culture Collection (No. CCTCC-M-2016491) on September 18, 2016. Compared with the strain in the prior art, the extracellular polysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strain LCC-605 is found to be able to self-assemble to form nanoparticles, and has the highest capacity to adsorb heavy metal and methylene blue. The adsorptive capacities to methylene blue, Pb<2+>, Cd<2+> and Cu<2+> are 3,029 mg / g, 1,513 mg / g, 2,097 mg / g and 2,987 mg / g, respectively. The extracellular polysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strain LCC-605 can be used for bioremediation to control the heavy metal and dye pollution in the environment, and has environmental friendliness and sustainable developability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
Bread and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105794907AHigh nutritional valueSimple structurePre-baking dough treatmentBakery productsFood additiveNutritive values
The invention provides bread. The bread is prepared from the following ingredients: high-gluten flour, sour dough, water, olive oil, fresh yeast and table salt; and the bread is especially prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 29-30 parts of high-gluten flour, 50-51 parts of sour dough, 15-16 parts of water, 3-4 parts of olive oil, 1 part of fresh yeast and 1 part of table salt. The bread has the following beneficial effects: firstly, ingredients of the fermented milk are natural and relatively high in protein and calcium contents, so that nutritive values of the bread products are increased; secondly, the proteins are broken down by self-metabolisms of the lactobacillus floras in the fermented milk so as to produce amino acid flavoring precursors to benefit flavor-improvement of the bread, and textural structure of the bread is improved by extracellular polysaccharides produced by the metabolisms; thirdly, a diversified microbial environment is created by co-fermentation of the lactobacillus floras in the fermented milk with the industrial yeasts, so that growth of miscellaneous bacteria is inhibited and shelf lives of the food products are thereby prolonged; and fourthly, no food additive is added into the bread, so that a bread product which is natural, healthy and relatively good in taste is prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INM FOOD
Method for preparing functional extracellular polysaccharide of lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN102250984AAntioxidantFunctionalMicroorganism based processesAntinoxious agentsPhosphorylationUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing functional extracellular polysaccharide of lactic acid bacteria, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: inoculating a Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain fermentation agent for culture, performing ultrafiltration concentration, precipitation and ethanol extraction on fermentation liquor, centrifuging a precipitate, and performing freeze drying to obtain powdery crude extracellular polysaccharide; performing separation and purification by using a diethylaminoethanol (DEAE) cellulose ion exchange column and SepharoseCL-6B gel column chromatography in turn, desalting, performing ultrafiltration concentration, precipitating by using an ethanol solution, and performing freeze drying on a precipitate to obtain pure extracellular polysaccharide; and performing phosphorylation and selenide formation on the pure extracellular polysaccharide. The method has the advantages that: the extracellular polysaccharide produced by the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain is subjected to selenide formation and phosphorylation modification by a dry heating method, and the functional extracellular polysaccharide of lactic acid bacteria with obvious antioxidant and immunity enhancing effects is obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WEIRUTANG NUTRITION & HEALTH CONSULTING CO LTD
Paenibacillus polymyxa extracellular polysaccharide and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, in particular to Paenibacillus polymyxa extracellular polysaccharides and application thereof. The extracellular polysaccharide has strong auxiliary suspension effect on diatomite, kaoline and calcium carbonate and protective action on live bacteria. The Paenibacillus polymyxa extracellular polysaccharide has wide application prospect in the aspects of processing and use of pesticides, medicaments, food, petroleum extraction, water treatment, microorganism live bacteria preparations.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation for amylovorin of bacillus and application thereof
InactiveCN1908182AIncrease productionHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsLymphocyteWhite blood cell number
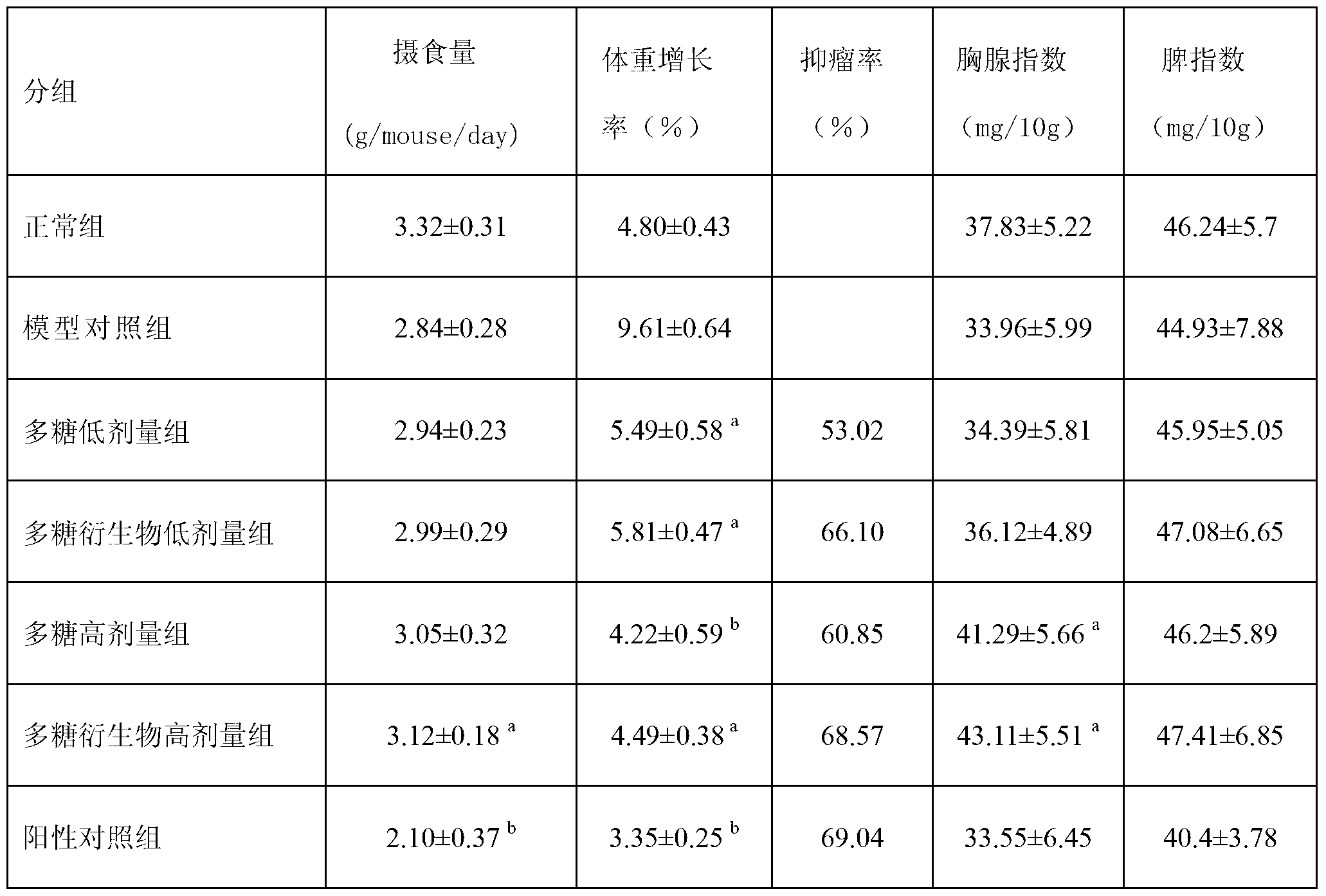
the invention discloses a preparing method of extracellular polysaccharide of Bacillus subtilis and application in the tumour facet, which is characterized by the following: inhibiting tumour from growing; accelerating the growth of macrophage, leucocyte and lymph cell; fitting for health or immune adjusting drug.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Viable type lactobacillus fermented litchi juice beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103815483AShort half-lifeAvoid destructionFood ingredient functionsFood preparationBiotechnologyLychee fruit
The invention discloses a viable type lactobacillus fermented litchi juice beverage and a preparation method thereof, and the prepared litchi juice beverage is rich in active lactobacilli. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing litchi juice, adding DMDC into the litchi juice, allowing the litchi juice to stand still for 2 to 3 hours at a room temperature, adjusting the pH value to a range of 6 to 7, and adding lactobacilli to carry out fermentation so as to obtain the fermented litchi juice beverage. The preparation method utilizes DMDC to carry out a sterilization treatment on litchi juice at a room temperature, thus the flavor and nutrient destruction caused by the conventional pasteurization is avoided, and the fermentation effect of lactobacilli is not influenced either. The fermented litchi juice beverage is rich in active lactobacilli; the thickening effect can be achieved and the pulp precipitation phenomenon can be avoided without any thickening agent and stabilizing agent, because lactobacilli can generate a large amount of extracellular polysaccharide; and at the same time the beverage has a proper sweet and sour taste, a smooth and sticky mouth feel, and a rich litchi flavor, is accord with the food safety and sanitation standards, is also accord with the natural and healthy food theory, and has a very good market prospect.
Owner:SERICULTURE & AGRI FOOD RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Repairing gel containing growth factors and preparation method of repairing gel
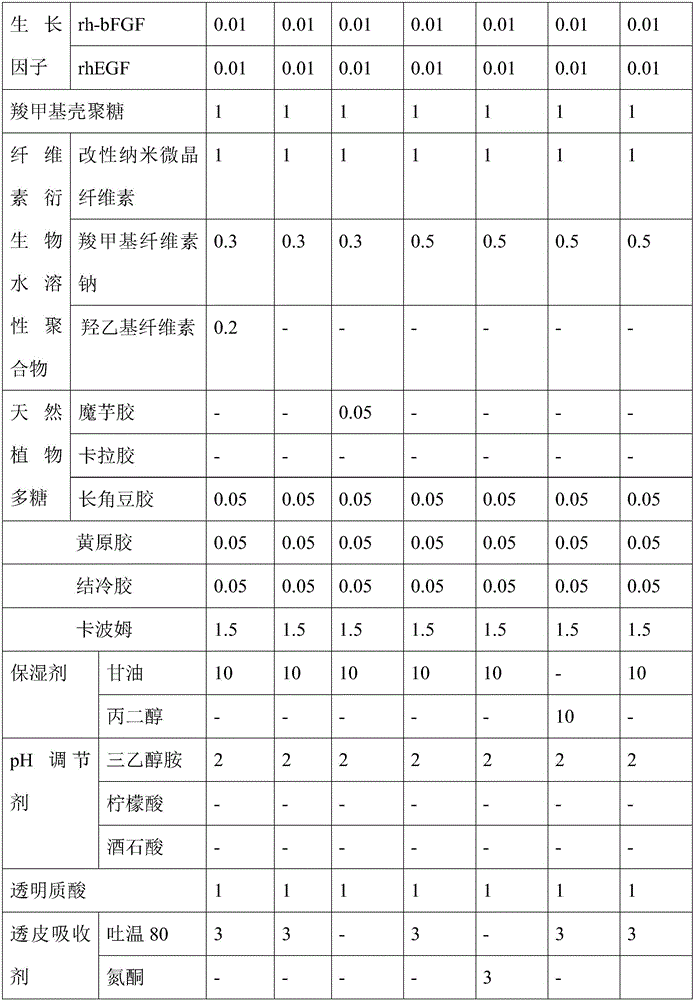
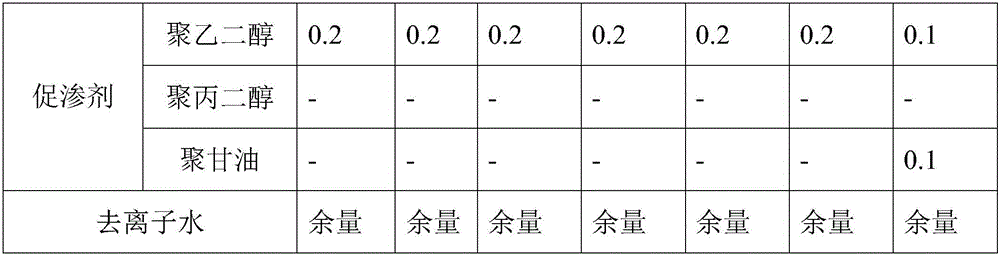
The invention belongs to the medicine field, and particularly relates to repairing gel containing growth factors and a preparation method of the repairing gel .The repairing gel is prepared from 0.001%-0.02% of the growth factors, 0.05%-1% of alkaline polysaccharides, 0.5%-2% of a cellulose derivative water-soluble polymer, 0.05%-2% of natural plant polysaccharides, 0.01%-1% of a natural water-soluble polymer of extracellular polysaccharides, 0.1%-2% of carbomer, 12%-40% of a wetting agent, 0.05%-4% of a pH regulating agent, 0.01%-2% of hyaluronic acid, 0.6%-3% of a transdermal absorption agent, 0.1%-0.3% of a penetration enhancer and the balance deionized water .The repairing gel has the excellent antibacterial effect and the good moisture absorption performance and can significantly increase the cure rate of a wound surface, shorten the healing time of the wound surface and prevent scar formation.
Owner:湖北兵兵药业(集团)有限公司
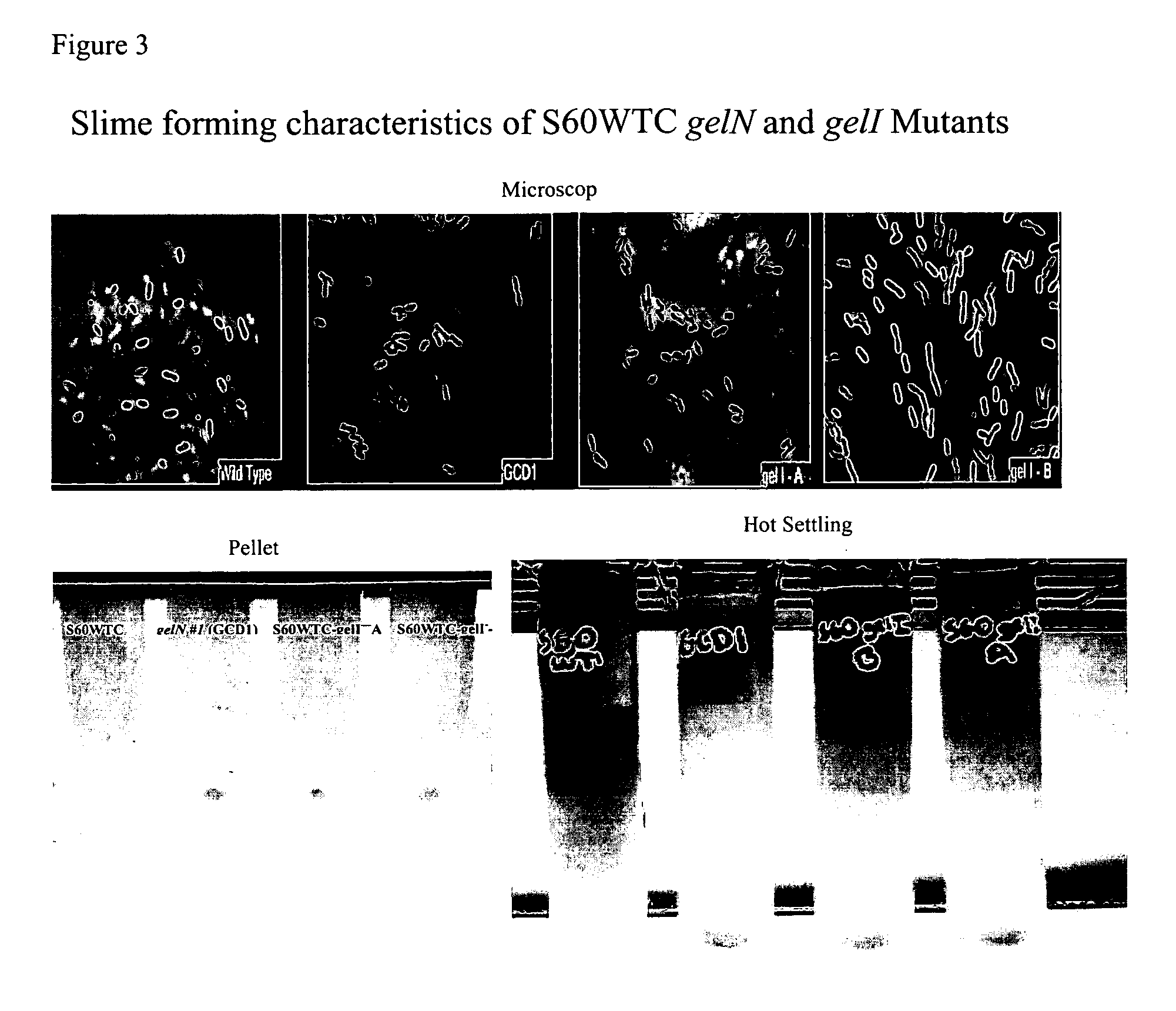
Targeted gene deletions for polysaccharide slime formers
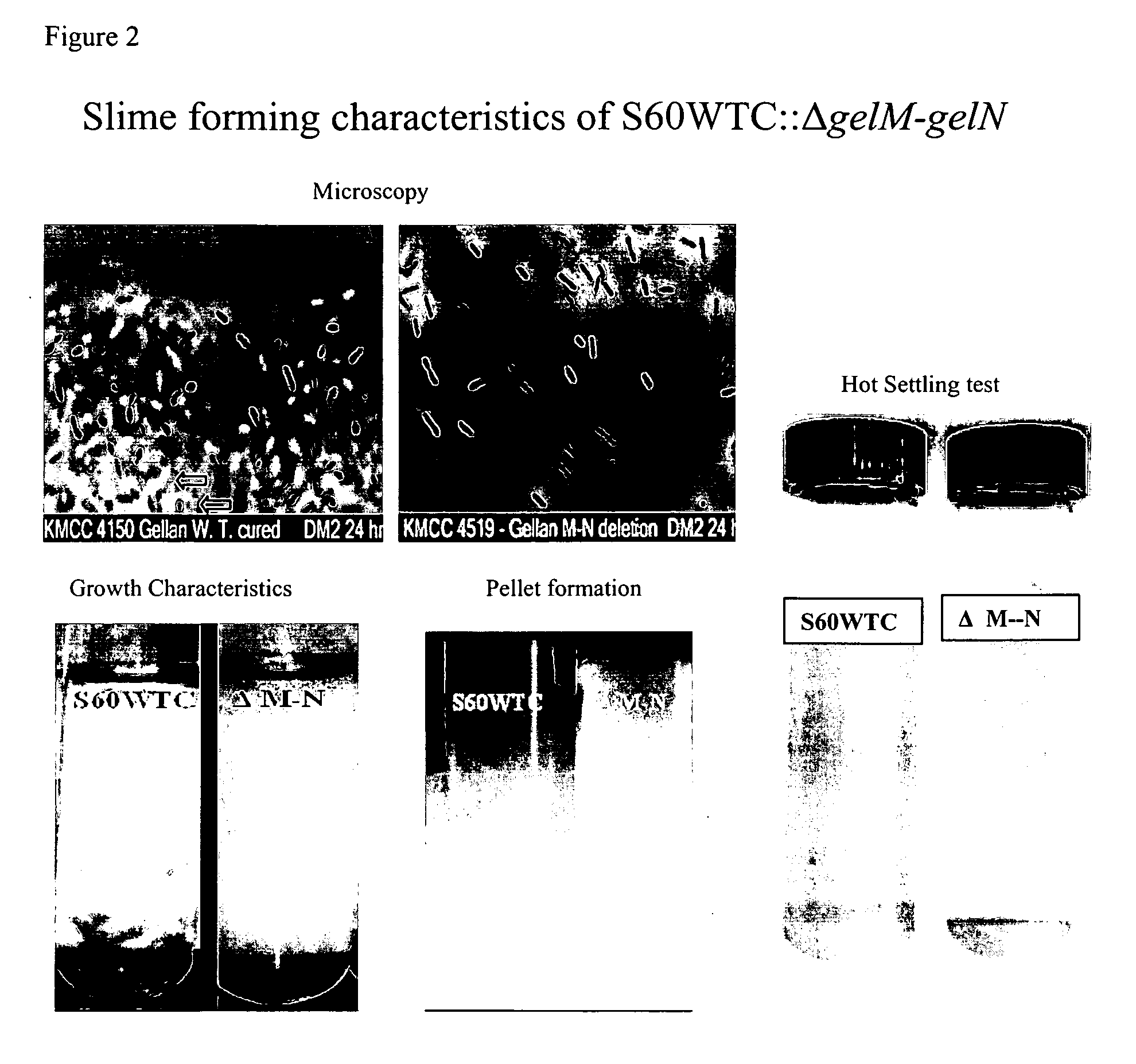
Sphingomonas strains have extracellular polysaccharide (e.g., gellan, diutan) that is firmly attached to the cell surface. This attachment may limit polysaccharide production by impairing uptake of nutrients into the cell or due to limited sites for polysaccharide biosynthesis on the cell surface. Two genes for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelM and gelN in gellan-producing strains and dpsM and dpsN in diutan-producing strains, have been inactivated by deletion mutations and shown to produce polysaccharide that is not firmly attached to the cell surface, i.e., slime form. Another gene for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelI in gellan producing strains, was inactivated by insertion mutation and also shown to produce the slime phenotype. The homologous gene dpsi in the diutan producing strain should also be involved in the attachment of the polysaccharide to the cell surface. The slime characteristic was demonstrated by the ability of the cells to be centrifuged and the lack of cell clumping as seen under the microscope or in diluted suspensions. The diutan slime mutants had somewhat increased productivity and the recovered diutan product had significantly improved rheology. Gellan slime mutants had lower broth viscosity which facilitates mixing during fermentation; however, the recovered gellan product had lower gel strength than the gellan produced from a capsular strain. A deletion in a gene gelR, which encodes a protein with homology to surface proteins and outer membrane proteins and weak homology to proteins with polysaccharide degradation activity, was shown to restore higher gel strength to the slime form of gellan, and to produce gellan of higher gel strength than that of the capsular gellan producing strains.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Method for producing polysaccharides by fermenting yellow serofluid with edible and medicinal fungi
InactiveCN101831471AIncrease productionHigh activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologySubmerged fermentation
The invention relates to a method for producing polysaccharides by fermenting yellow serofluid with edible and medicinal fungi, which belongs to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of biological extraction. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing yellow serofluid; preparing the culture medium; inoculating and culturing the seed liquid and the production culture medium; extracting fungus intracellular polysaccharides from mycelia; and extracting fungus extracellular polysaccharides from the fermentation filtrate, and the like. In the invention, waste yellow serofluid generated in the production process of bean products is used as the basic raw material, and the method of submerged fermentation of the edible or medicinal fungi is used, thus the nutritional components are maximally biotransformed. The invention has the advantages of low investment, low material cost, simple operation, high polysaccharide yield and the like, reduces the environmental pollution and lowers the production cost by about 50%. The invention can be popularized in bean product and biochemical enterprises.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Solid fermentation method of lactarius deliciosus mycelium and application of solid fermentation extractive thereof
InactiveCN102503647AImproving Solid Fermentation MethodsNot easy to loseFertilizer mixturesFood additiveMicrowave
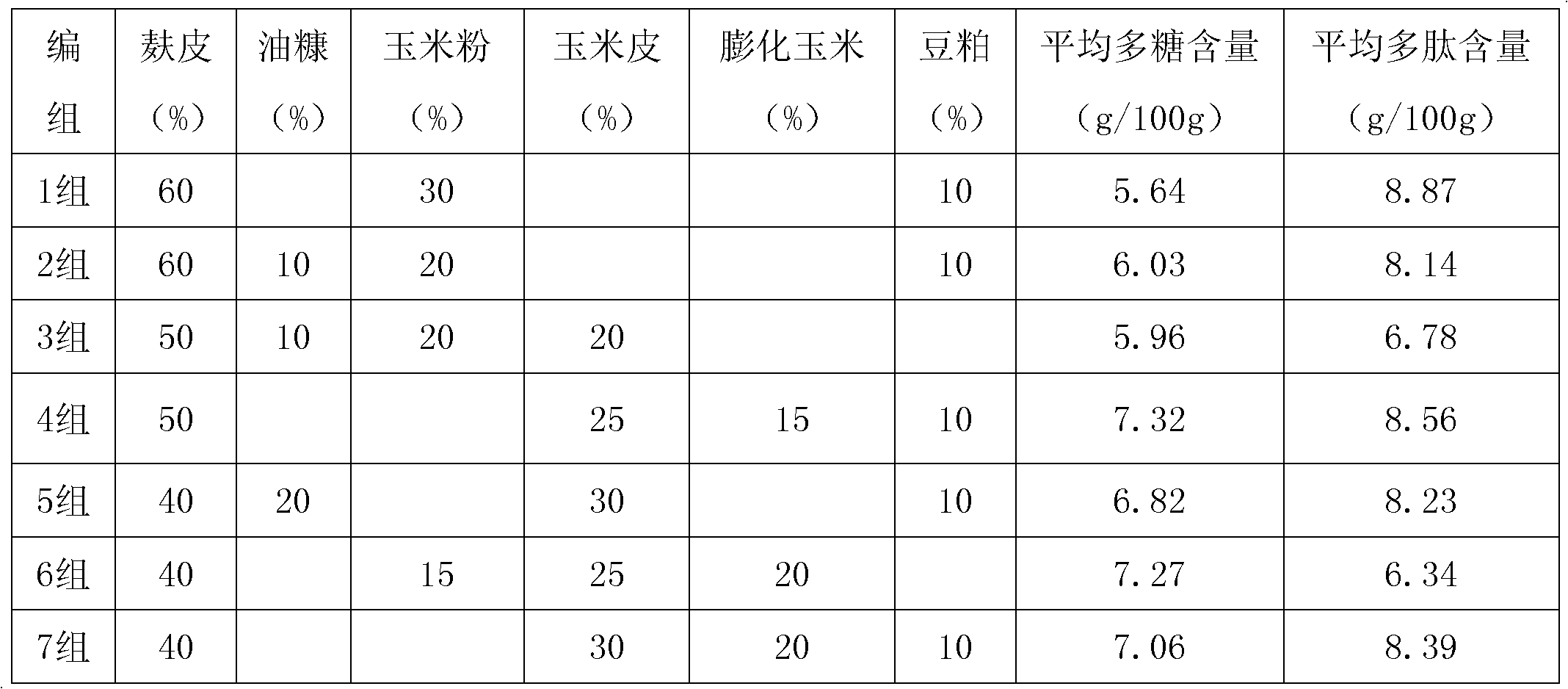
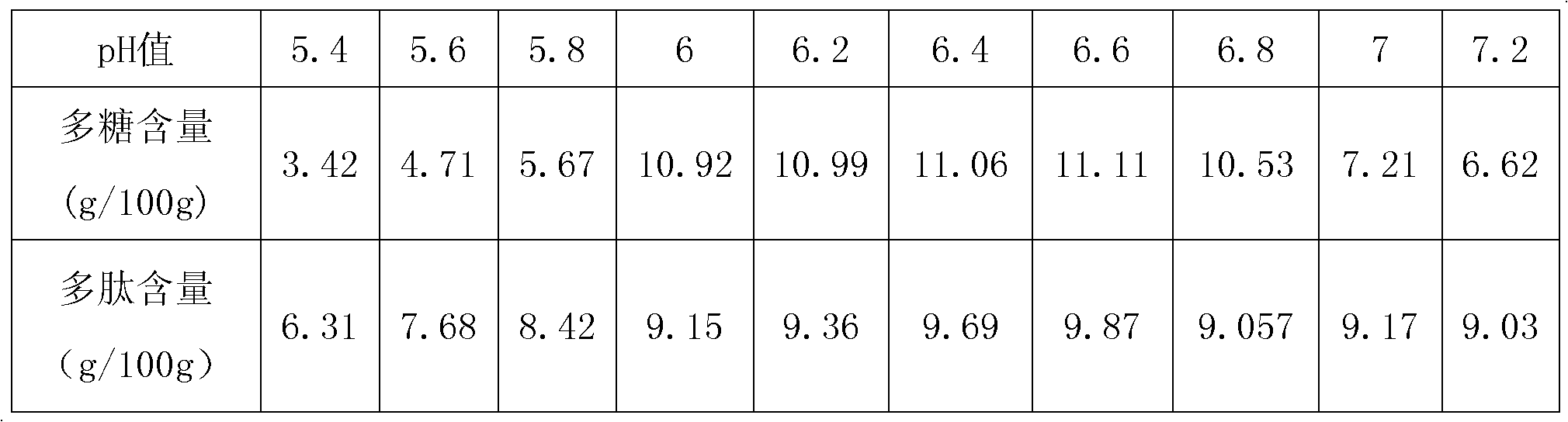
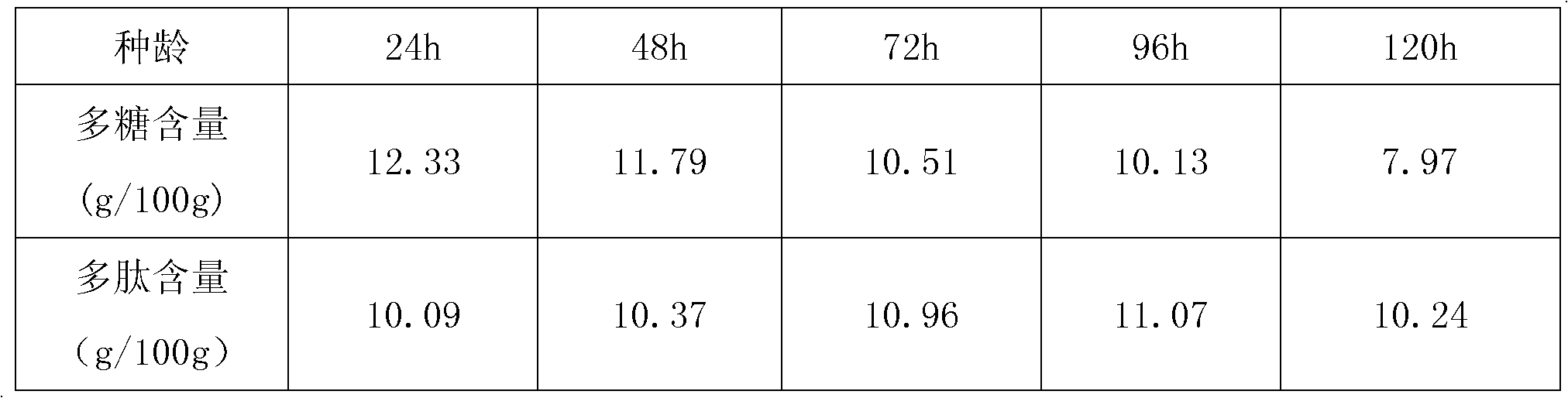
The invention relates to the technical field of solid fermentation, in particular to a solid fermentation method of lactarius deliciosus mycelium and an application of solid fermentation extractive thereof. The solid fermentation method of lactarius deliciosus mycelium comprises the steps of: performing solid fermentation on the lactarius deliciosus mycelium by a culture medium of the invention under certain culture conditions, wherein the certain culture conditions are as follows: the carbon-nitrogen ratio of the culture medium is 1:5 to 1:8, the temperature is 18-37 DEG C, the pH is 5-8, the day age of strain is 24-120 h, the inoculation amount is 10-30%, and the fermentation period is 2-7 d. The product obtained after the solid fermentation procedure of the solid fermentation method is extracted by such methods as ultramicro pulverization, enzyme treatment and microwave or ultrasonic, and the like so as to obtain an extractive containing polysaccharide and polypeptide. The extractive can be used as a food additive to be applied in the healthcare field and can be also used as a feed additive to be applied in the animal feed field. According to the invention, a proper dosage of plant Chinese medicinal herb additives can be added in the culture medium to improve the yield of the mycelium and the intracellular and extracellular polysaccharide and polypeptide so as to reinforce the pharmacological activity of the extractive.
Owner:肖兵南
Extracellular polysaccharide for discoloring water-soluble dye wastewater and application thereof as coagulant aid
InactiveCN101921715AEffectively removes chromaReduced settling timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynthetic Polymeric MacromoleculesDyeing wastewater
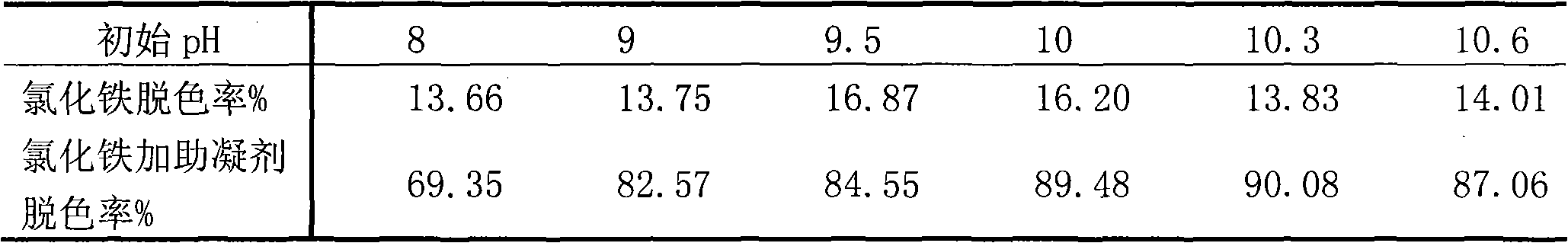
The invention relates to an extracellular polysaccharide coagulant aid for discoloring water-soluble dye wastewater, successfully solving the problems of low efficiency of processing the water-soluble dye wastewater by independently using inorganic coagulant aids as well as high cost and poor biodegradation of artificially synthesized high-polymer coagulant aid by compounding with various inorganic coagulant aids. The preparation method of the extracellular polysaccharide as the coagulant aid comprises the following steps of: firstly inoculating the strains of Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310 of Antarctic sea ice bacteria in a 2216E fluid medium or a fermentation medium, fermenting for 72 h at 15 DEG C under the condition of 150-rpm light avoidance, and collecting a fermentation fluid; extracting an extracellular polymer of the fermentation fluid by utilizing an alcohol precipitation method, and then removing proteins by using an Sevag method to obtain a crude product of the extracellular polysaccharide; and drying and storing the dried crude product, compounding the crude product to a solution with a certain concentration before being used, and then adding by adopting a wet method. When being used for processing the water-soluble dye wastewater, the extracellular polysaccharide as the coagulant aid is added after the inorganic coagulant aids are added, thereby higher floc settling speed and wastewater discoloring efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for extracting tremella polysaccharide and tremella protein
InactiveCN102876750AAchieve serializationEase of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingTremella
The method relates to a method for extracting tremella polysaccharide and tremella protein. The method comprises the steps of (1) activated culture and fermentation culture of tremella fuciformis berk bacteria; (2) concentration with an ultrafiltration membrane and fragmentation tremella fuciformis berk spores; (3) preparation of a polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system; (4) extraction of the polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system; (5) preparation of the tremella polysaccharide via freeze drying; and (6) second extraction of the polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system, filtration with the ultrafiltration membrane and preparation the tremella protein via freeze drying. The method can realize continuous and large-scale production of the tremella fuciformis berk spores and extraction of the tremella polysaccharide, and is convenient for industrialized production of the tremella polysaccharide. The obtained product has not only intercellular polysaccharide of the tremella fuciformis berk spores but also extracellular polysaccharide produced by the liquid fermentation of the tremella fuciformis berk spores, thereby increasing the yield of the tremella polysaccharide. Besides, the tremella polysaccharide and the tremella protein can be separated at the same time, so that the disadvantages of complex operations and pollutions of organic solvents in a conventional sevag method can be prevented; and the purity of the polysaccharide can be increased.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Application of lachnum extracellular polysaccharide phosphorylated derivative and application thereof in preparation of antitumor drugs
InactiveCN103319619ASignificant anti-tumor functionThe preparation method is simple and economicalOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectPhosphorylation
The invention discloses an application of lachnum extracellular polysaccharide phosphorylated derivative and an application thereof in preparation of antitumor drugs. The lachnum extracellular polysaccharide phosphorylated derivative is obtained by performing phosphorylated decoration on extracellular polysaccharide generated by lachnum with strain preservation number of CCTCC No: M2011196. As shown by an experiment, the extracellular polysaccharide phosphorylated derivative generated by lachnum with strain preservation number of CCTCC No: M2011196 not only has excellent antitumor function, but also has no toxicity or side effect, and the preparation method is simple and economic, so that the lachnum extracellular polysaccharide phosphorylated derivative can be used for preparing tablet or capsule antitumor drugs.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing extracellular mucopoly-saccharide using rhamnose lactobacillus and product
InactiveCN1781950AWide range of usesHigh fermentation yieldBacteriaFermentationLactobacillus rhamnosusPapermaking
The present invention relates to process of producing extracellular mucopolysaccharide with rhamnose lactobacillus as initial strain and glucose and lactose as carbon source and including the steps of compounding material, expanding culturing and fermentation, separation, washing, dewatering and drying. The extracellular mucopolysaccharide consists of pyruvic acid in 1 weight portion, D-glucose in 2 weight portions, D-galactose in 1 weight portion and L-rhamnose in 4 weight portions, and is colorless and smell-less solid of molecular weight 30-60 MDa. Compared with other kinds of lactobacillus extracellular polysaccharide, rhamnose lactobacillus extracellular mucopolysaccharide has higher fermentation yield, the biological effects of resisting tumor, raising immunity, resisting blood coagulation, resisting virus, etc. and wide application in food, medicine, papermaking, preservation and other fields.
Owner:天津市工业微生物研究所有限公司
Coriolus versicolor polysaccharide extracts and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104450826AGood hypolipidemic effectReduce the index of atherosclerosisOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderFreeze-dryingUltrafiltration
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to coriolus versicolor polysaccharide extracts and a preparation method and application of the coriolus versicolor polysaccharide extracts. After submerged fermentation culture of coriolus versicolor mycelia, mycelia and fermentation broth are separated from fermentation products, the mycelia are baked, smashed, sieved, degreased and dried and then are subjected to hot water extraction and concentration, and an extraction concentrated solution is obtained; after small molecules of the fermentation broth are ultrafiltered out, the fermentation broth is concentrated, and an ultrafiltration concentrated solution is obtained. The ultrafiltration concentrated solution and the extraction concentrated solution are subjected to deproteinization, ethanol precipitation, hydrogen peroxide decoloration, dialysis and vacuum freeze drying at last, so the coriolus versicolor intercellular polysaccharide extracts and the coriolus versicolor extracellular polysaccharide extracts are obtained. The preparation process is simple, high-efficiency and high-quality mass production can be achieved, and the extracts are harmless to the human body, have the good physiological effect of reducing blood fat and can be used for developing blood fat reducing medicine or health-care food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for highly effective production and separating purification of Chinese caterpillar fungus extracellular polysaccharide
The main aim of the invention is to provide a cultivation method of producing aweto extracellular polysaccharide in a highly efficient industrialized way and use the membrane dialysis technology to rapidly purify extracellular polysaccharide single component with biological activity. And the purity is more than or equal to 95 percent. The purify technology does not use any organic solvent and chemical reagent to ensure that the chemical structure of the aweto extracellular polysaccharide is not destroyed, thereby maintaining the biological activity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Morchellaconica extracellular polysaccharide extractive and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101870740AAntioxidant is goodLife-prolonging and anti-aging effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsFiltrationCentrifugation
The invention belongs to the biological technical field, which discloses a morchellaconica extracellular polysaccharide extractive and a preparation method and application thereof. The extractive is liquid fermentation liquor which is obtained by fermenting and culturing morchellaconica liquid and separating mycelium through centrifugation and vacuum filtration. The liquid fermentation liquor is concentrated to 1 / 3 to 1 / 6 of the original bulk to obtain concentrated solution and the concentration temperature is 50 to 70 degrees centigrade. The protein of the concentrated solution is removed and the concentrated solution is centrifuged. Activated extract is obtained. Polysaccharide in the concentrated solution is dialyzed and settled in 95 percent of ethanol at 0 to 10 degrees centigrade for 12 to 25 hours, the bulk of which is once to 5 times larger than the bulk of the activated extract. The pH value is 4 to 8. Flocculent white substance is precipitated after still placement. White sedimentation is obtained after centrifugation separation, which is frozen and dried to obtain the morchellaconica extracellular polysaccharide extractive. The invention has simple preparation process and allows mass production. The extractive has no harm on human body and good antioxidant and anti-aging action and can be used for preparing antioxidant and anti-aging medicine or health care food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Truffle wine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102676342AIncrease productionImprove polysaccharideFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationMyceliumFood science
The invention belongs to the technical field of foods or medicine and provides a truffle wine and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method enables truffle mycelium to be improved by 69%, truffle extracellular polysaccharide yield is improved by 150%, and bacterial intracellular polysaccharide is improved by 57%. The preparation method is simple and easy to operate and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:郭景龙
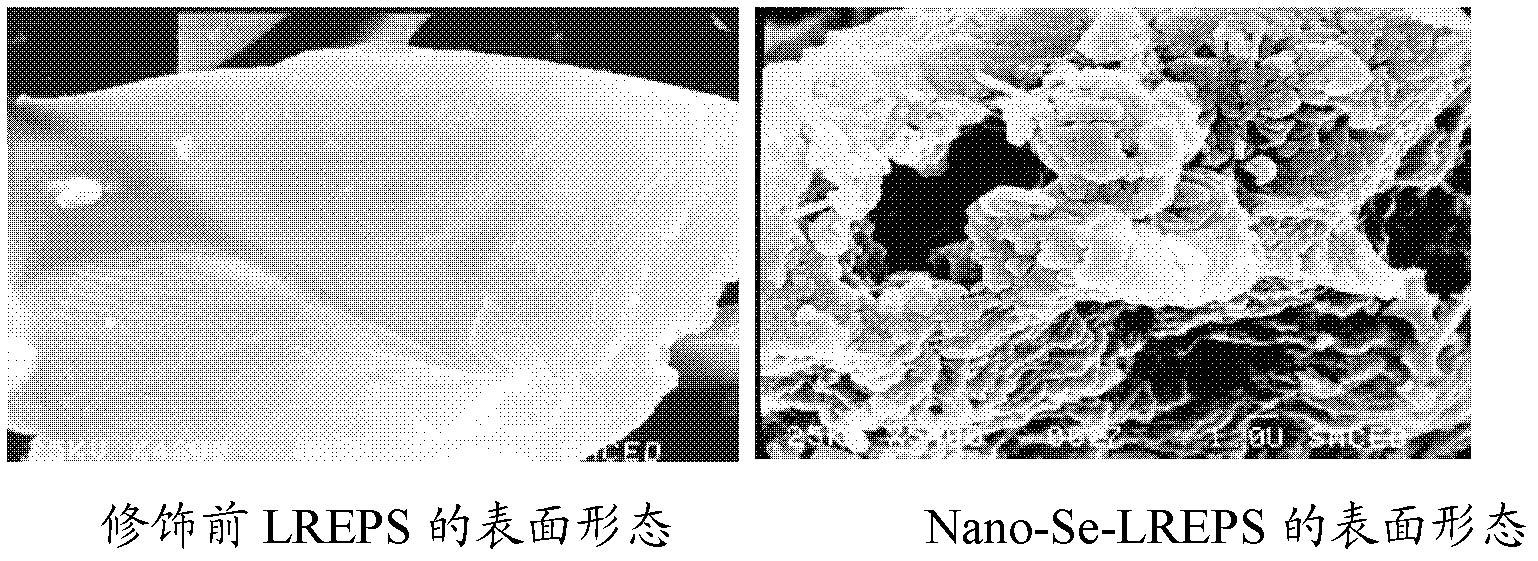
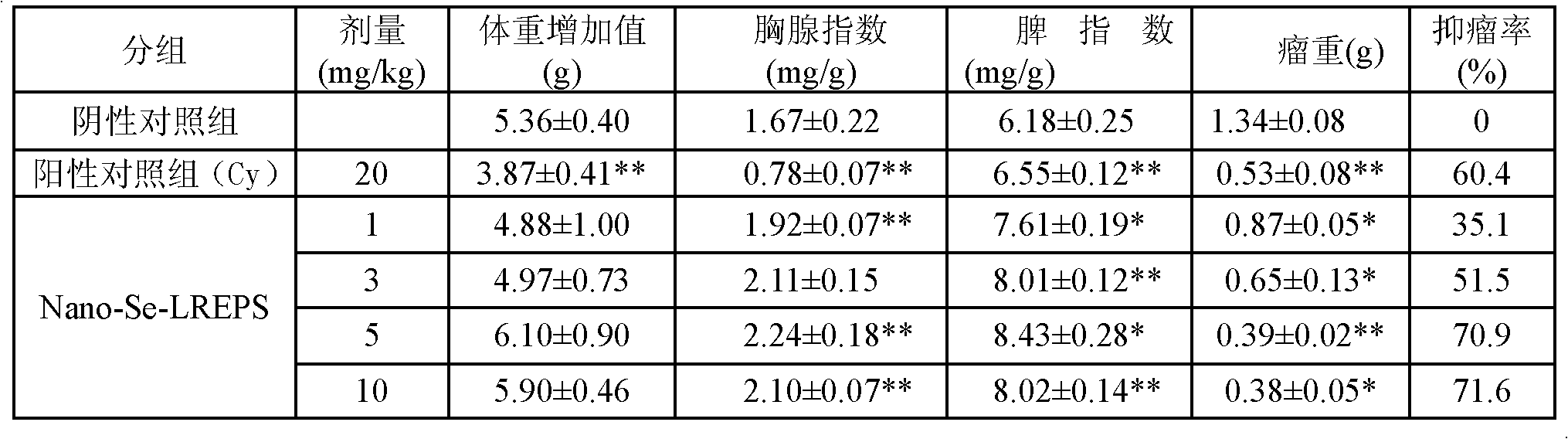
Nano selenium micromolecular microbial polysaccharide as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102643361AFast productionQuality improvementImmunological disordersAntineoplastic agentsVitamin CFreeze-drying
The invention provides a nano selenium micromolecular microbial polysaccharide, which is prepared under ultrasonic condition by taking micromolecular Caragana rhizobia extracellular polysaccharide as a raw material through uniformly dispersing and co-acting with selenium dioxide and a reducing agent. The production method specifically comprises the steps of: preparing a micromolecular bacterial polysaccharide solution with a proper concentration, uniformly mixing micromolecular Caragana rhizobia polysaccharide with vitamin C, slowly dropwise adding selenium dioxide to the mixed system, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion and reaction, dialyzing and freeze-drying. The nano selenium micromolecular microbial polysaccharide product prepared by the preparing process has the selenium content up to 15.2-16.4mu g / mg, selenium average grain size about of 380 nm and polysaccharide yield more than70%. Mouse test shows that the nano selenium micromolecular polysaccharide has excellent anticancer activity, and can be applied to preparing anticancer medicaments and health products.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
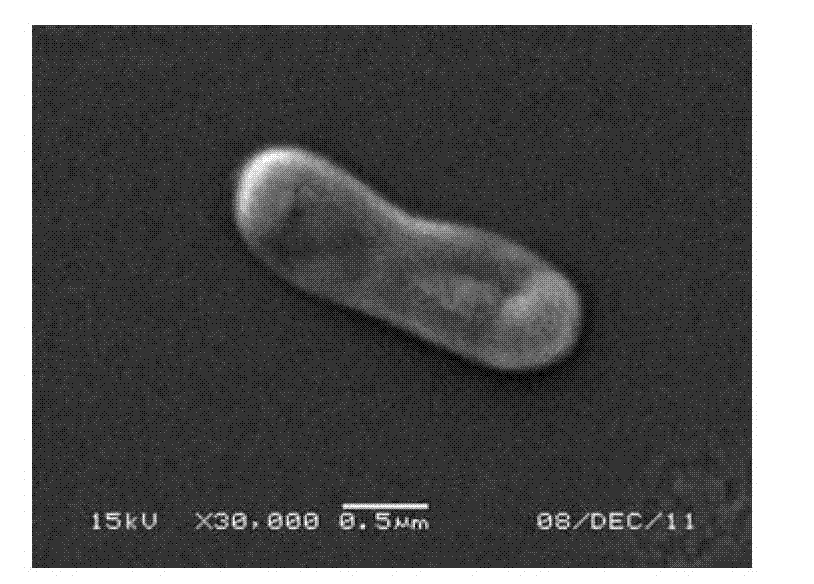
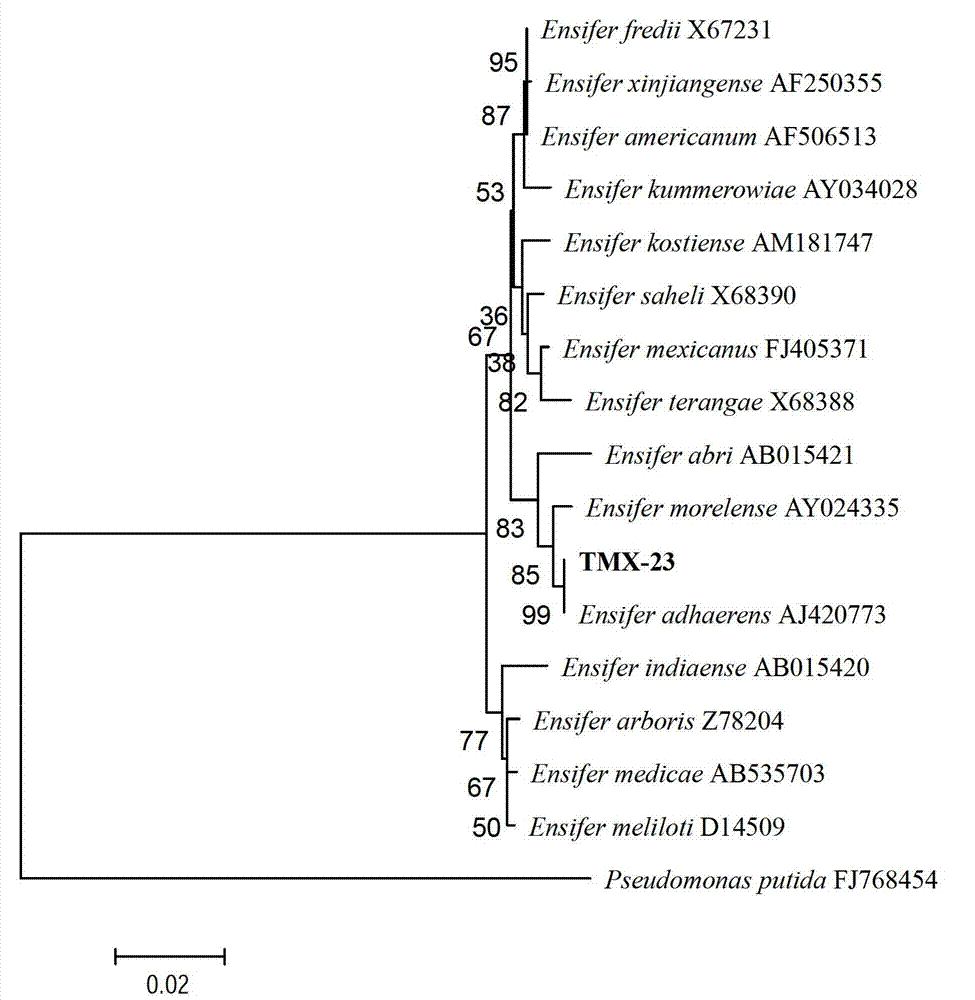
Ensiferadhaerens and application thereof
InactiveCN102851237AHas the ability to fix nitrogenHas PGPR activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBenzoic acid
The invention discloses Ensiferadhaerens CGMCC 6315 which is a bacterium having a nitrogen-fixing capability. The strain is also a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR), and can produce indoleacetic acid (IAA), extracellular polysaccharide (EPS), siderophore, salicylic acid (SA), 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA), hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and ammonia. Under the stress condition of a salt containing sodium chloride, soybeans inoculated with the E.adhaerens CGMCC 6315 can have a higher germination rate in comparison with a control group which is not inoculated with the strain.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com