Extracellular polysaccharide for discoloring water-soluble dye wastewater and application thereof as coagulant aid
A technology of bacterial exopolysaccharide and coagulant aid, applied in bacteria, microorganism-based methods, textile industry wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, poor biodegradability, and low wastewater efficiency, and achieve convenient storage and sugar production. The effect of high volume and increased floc size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Cultivation of Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310 strain
[0028] Strain: Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310, deposit number: CCTCC NO: M 209258, depository unit: China Center for Type Culture Collection, deposit date: November 9, 2009.
[0029] The Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310 strain was inoculated into the 2216E liquid culture base at 15°C, and cultured in a shaker at 150rpm in the dark for 72h to ferment and produce sugar. The strain inoculation amount is 5wt%.
[0030] 2216E liquid medium formula: 1g of yeast extract, 5g of peptone, 30g of glucose, 1L of seawater for 2 months, adjust the pH to 7.5 with NaOH.
[0031] or:
[0032] The Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310 strain was inoculated into the fermentation culture based on 15°C, and cultured in a shaker at 150rpm in the dark for 72h to ferment to produce sugar. . The inoculum amount of the strain is 6wt%.
[0033] Fermentation medium formula: corn flour 20g, bran 10g, soybean meal 20g, Na 2 HPO 4 1g, KH 2 PO ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Preparation of Pseudoalteromonas.sp.SM20310 exopolysaccharide
[0035] The fermented liquid obtained in Example 1 was collected and centrifuged at 11000 rpm at 15° C. for 15 min to obtain a supernatant. Add 1:1-2:1 (v / v) absolute ethanol to the supernatant, centrifuge after the extracellular polymer is precipitated, dissolve in water, then concentrate, add 20%-25% (v%) of Chloroform and 4%-5% (v%) butanol were stirred for 20 minutes, centrifuged at 15° C. and 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove protein, and the supernatant was collected. After concentration, put it in a 14000U dialysis bag for dialysis and desalination, add 1:1~2:1 (v / v) absolute ethanol to the supernatant again, separate out the polysaccharide and then centrifuge and dry or lyophilize at normal temperature to obtain The bacterial exopolysaccharide referred to in the present invention is stored at 4°C. Before use, make it into a 0.5-3g / L solution and store it at 4°C for future use.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: the application of bacterial exopolysaccharide as coagulation aid
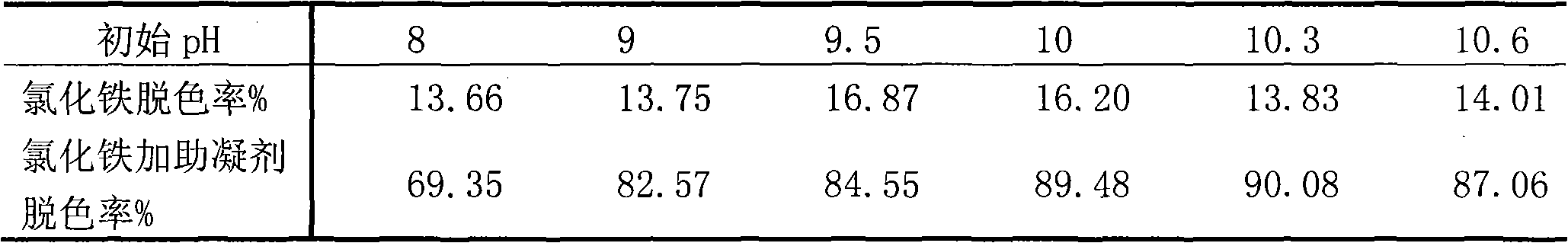
[0037] The comparison experiment of the decolorization rate of reactive brilliant red before and after adding bacterial exopolysaccharide coagulant aid at different pH is as follows:
[0038] Take the reactive brilliant red X-3B dye solution with a concentration of 100mg / L and place it in a shaker at 25°C, and use 1mol / L NaOH or HCl to adjust the initial pH of the solution to 8, 9, 9.5, 10, 10.3, 10.6, respectively. Add ferric chloride containing 55mg / L Fe(III), shake rapidly at 200rpm for 2min, then shake slowly at 60rpm for 17min, let stand for 30min, take the supernatant to measure its absorbance and calculate the decolorization rate of ferric chloride. Add the bacterial exopolysaccharide coagulant of embodiment 2 after the foregoing operation is shaken at a slow speed for 17 minutes, so that the concentration of the bacterial exopolysaccharide in the mixed solution reaches 150 mg / L, co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com