Method for preparing and purifying grifola frondosa polysaccharide with high antioxidant activity
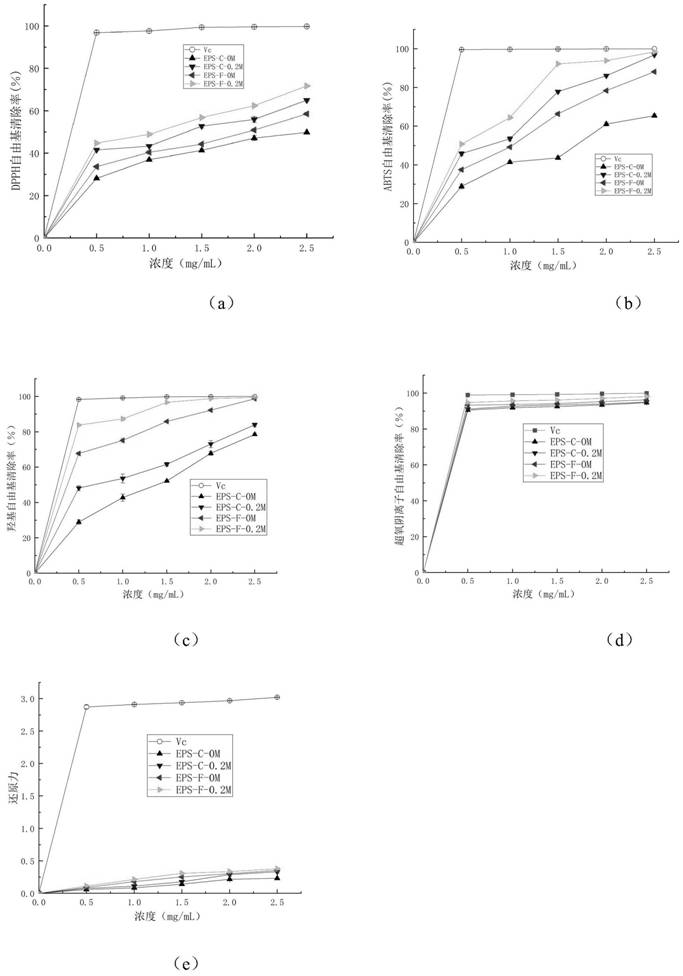
A technology of Grifola frondosa polysaccharide and oxidation activity, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, and adding compounds to stimulate growth, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory application in the market, limited production of acidic polysaccharide components, etc. , to achieve the effect of improving in vitro antioxidant activity, safety and non-toxic stability, and improving reducing ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1 (control group)
[0065] Grifola frondosa seed culture: cut the Grifola frondosa grown on the PDA plate into 1cm 2 Take 3 to 5 small pieces of different sizes and inoculate them into the seed medium in a 100mL / 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, culture at 160r / min and 28°C for 5 days.
[0066] Fermentation culture of Grifola frondosa: add 150mL fermentation medium to a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask, inoculate 15mL of seed liquid, culture at 160r / min, 28°C for 8 days.
[0067] The seed medium contains 200 g of potatoes, 20 g of glucose, 5 g of peptone, 2 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1 g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, and vitamin B per L. 1 0.02g, pH natural. The fermentation medium contains 22g of glucose per L, 3g of peptone, 1.2g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.8g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, vitamin B 1 0.12g, pH natural.
[0068] Wherein the extraction method and assay method of Grifola frondosa polysaccharide are:
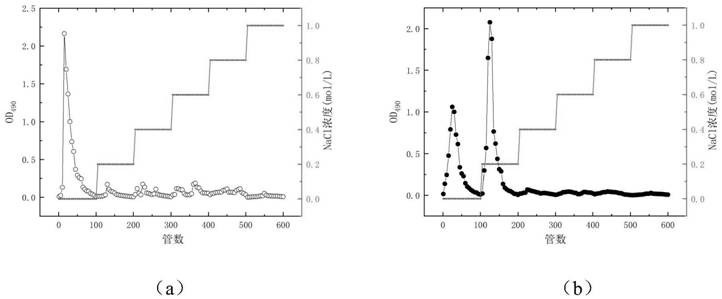
[0069] Take 1 mL of the abo...
Embodiment 2
[0071]The culture medium and culture method are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that on the 0-2d of the fermentation culture of Grifola frondosa, 0-0.2mmol / L of exogenous additive farnesol is added, and the fermentation liquid of Grifola frondosa after adding farnesol continues to ferment to 8d. After the fermentation is finished, the mycelia of Grifola frondosa is obtained and the polysaccharides in the fermentation broth are extracted. Wherein, the extraction method and assay method of the polysaccharide of Grifola frondosa fermented liquid are the same as Example 1, and the polysaccharide content of measured Grifola frondosa fermented liquid is (0.8371 ± 0.0532) g / L, which has increased by 66% relative to the control group. Such as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0073] The culture medium and culture method are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that on the 0-2d of the fermentation culture of Grifola frondosa, 0.2-0.4mmol / L of exogenous additive farnesol is added, and the fermentation liquid of Grifola frondosa after adding farnesol continues to ferment to 8d. After the fermentation is finished, the mycelia of Grifola frondosa is obtained and the polysaccharides in the fermentation broth are extracted. Wherein, the extraction method and assay method of the polysaccharide of Grifola frondosa fermented liquid are the same as Example 1, and the polysaccharide content of measured Grifola frondosa fermented liquid is (1.0058 ± 0.0128) g / L, which has increased by 98% relative to the control group. Such as image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com