Method for concurrently improving spirulina biomass and polysaccharide yield
A technology of spirulina and biomass, applied in the field of spirulina to accumulate biomass and polysaccharides, can solve the problems of affecting cell growth and photosynthetic carbon fixation efficiency, the yield of polysaccharides is not significantly improved, and the production of spirulina polysaccharides is affected. Good sustainability, promotion of industrial production, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
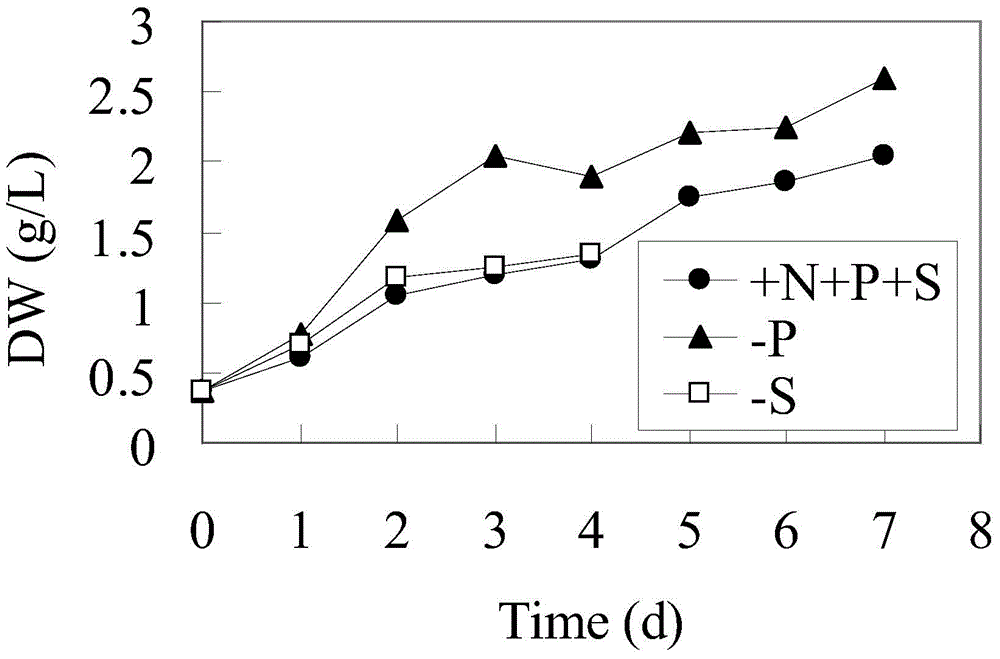
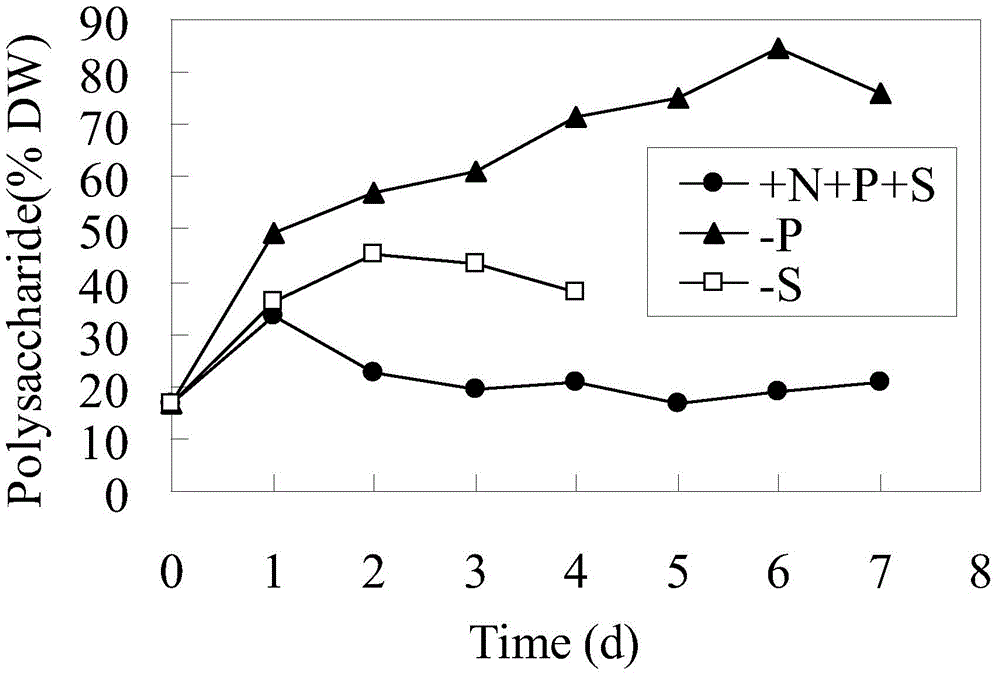
[0021] The accumulation of biomass and polysaccharides in Spirulina was investigated under P-limited and S-limited conditions.
[0022] The algae cultivation and polysaccharide accumulation processes were carried out in a 500mL cylindrical bubbling photobioreactor (glass material, diameter 50mm, height 400mm).
[0023] 1) Cultivation of algal species
[0024] Spirulina cells are cultured in a nutrient-rich medium (Zarrouk). The medium is prepared with deionized water, and each liter of water contains: NaHCO316.8g, K2HPO40.5g, NaNO32.5g, K2SO41g, NaCl1g, MgSO4 7H2O0.2g, CaCl2·2H2O0.04g, FeSO4·7H2O0.01g, H3BO32.86mg, MnCl2·4H2O1.86mg, ZnSO4·7H2O0.22mg, Na2MoO4·2H2O0.39mg, CuSO4·5H2O0.08mg. The initial inoculation density OD560 is 0.5, the culture temperature is 30±2°C, continuous single-row illumination, the light intensity is 200 μmolm–2s–1, and the air flow rate is 0.4vvm.
[0025] 2) Simultaneous accumulation of algal cell biomass and polysaccharides
[0026] Centrifuge th...
Embodiment 2
[0034] To investigate the effect of N limitation on biomass and polysaccharide accumulation of Spirulina in small-scale indoor cultivation.
[0035] The cultivation of the algae species is the same as that of the algae species in Example 1. The polysaccharide accumulation process was carried out in a 6L plastic square basin with a water depth of 8cm.
[0036] Centrifuge the cells cultivated to an OD560 of 3 at 4000 rpm for 5 min, discard the supernatant, wash the algae mud once with NaNO3-free Zarrouk medium (Zarrouk-N) and resuspend it in Zarrouk-N, adjust the cell density to 0.5 for OD560, Inoculate in a 6L plastic square basin, and stir the algae solution with a submersible pump with a power of 5W. The culture temperature is 23±2°C, under natural conditions, and the maximum light intensity on the surface of the algae liquid does not exceed 84.5 μmolm–2s–1 for 90% of the time.
[0037] Nutrient-rich conditions (+N): add NaNO32.5g per liter of algae liquid.
[0038] N limi...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Large-scale cultivation of Spirulina using N limitation in an outdoor racetrack pond for enhanced biomass and polysaccharide yields.
[0043] The process of algae cultivation and polysaccharide accumulation was carried out in an outdoor 1-acre track pool with a water depth of 30 cm and a water velocity of 20 cm / s.
[0044] 1) Cultivation of algal species
[0045] Spirulina cells are cultured in nutrient-rich natural mother liquor alkali medium (MYJ), and the culture medium is prepared with underground fresh water. Each liter of water contains: 6g of mother liquor alkali (containing about 3.4g of NaHCO3) produced by Ordos plateau natural alkali lake, NaNO31g , KCl0.5g, H3PO40.12g, FeSO4·7H2O0.01g, MgSO4·7H2O0.01g. The initial inoculation density OD560 was 0.3, the culture temperature was 32±5°C, the natural conditions were lighted, and the maximum light intensity on the surface of the algae liquid was 3000 μmolm–2s–1.
[0046] 2) Simultaneous accumulation of algal cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com