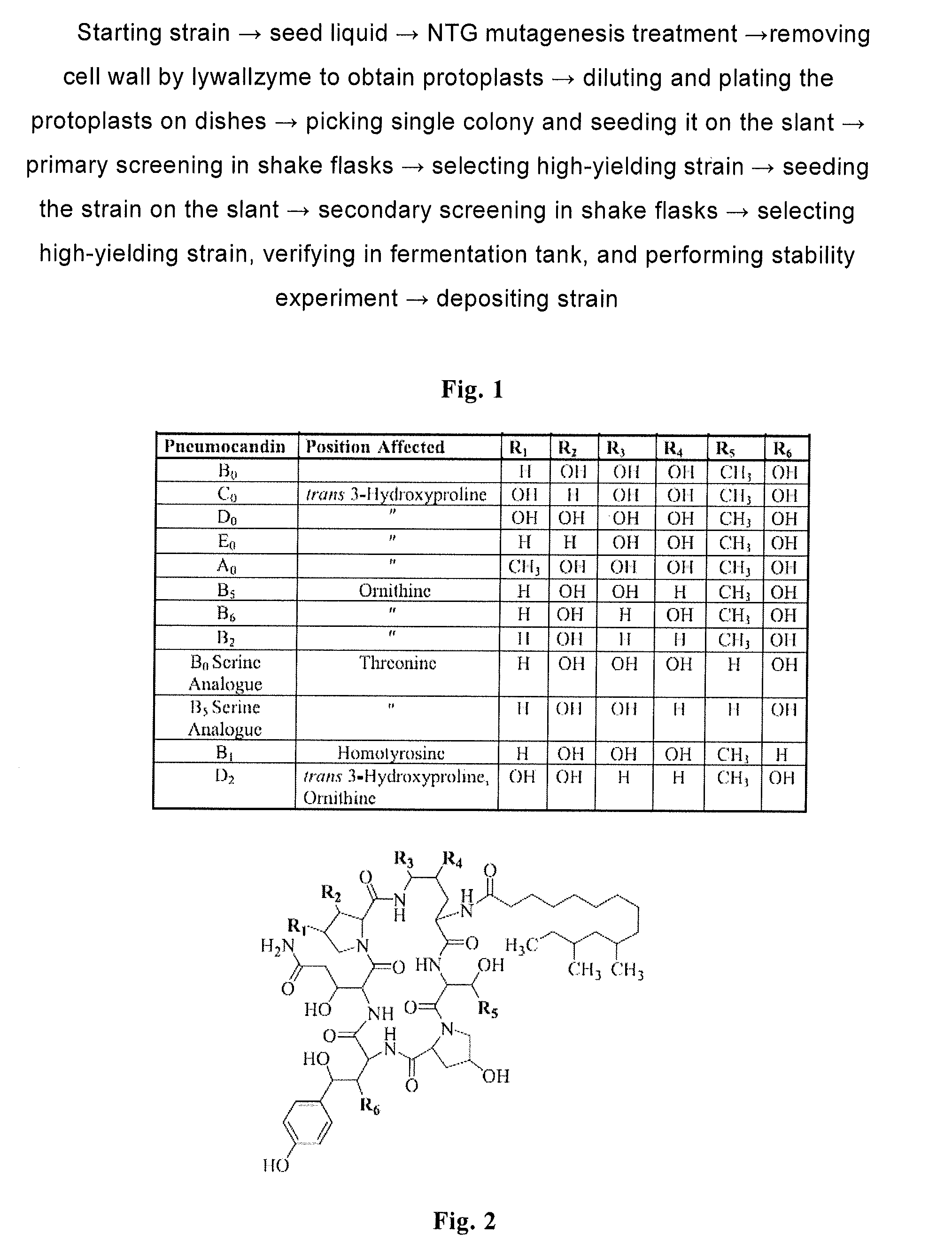
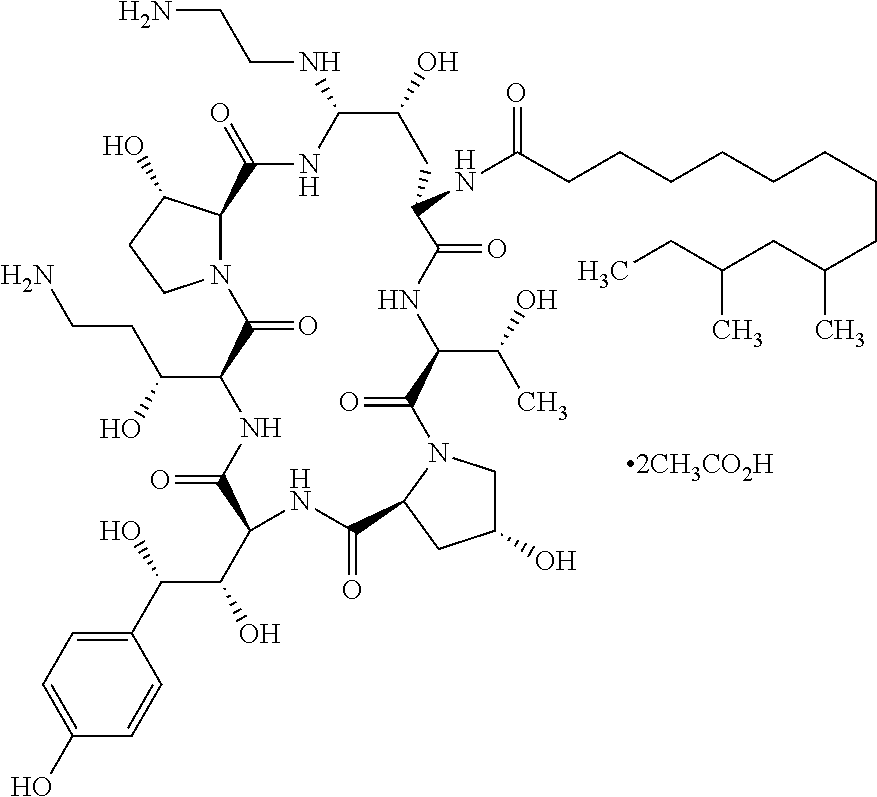
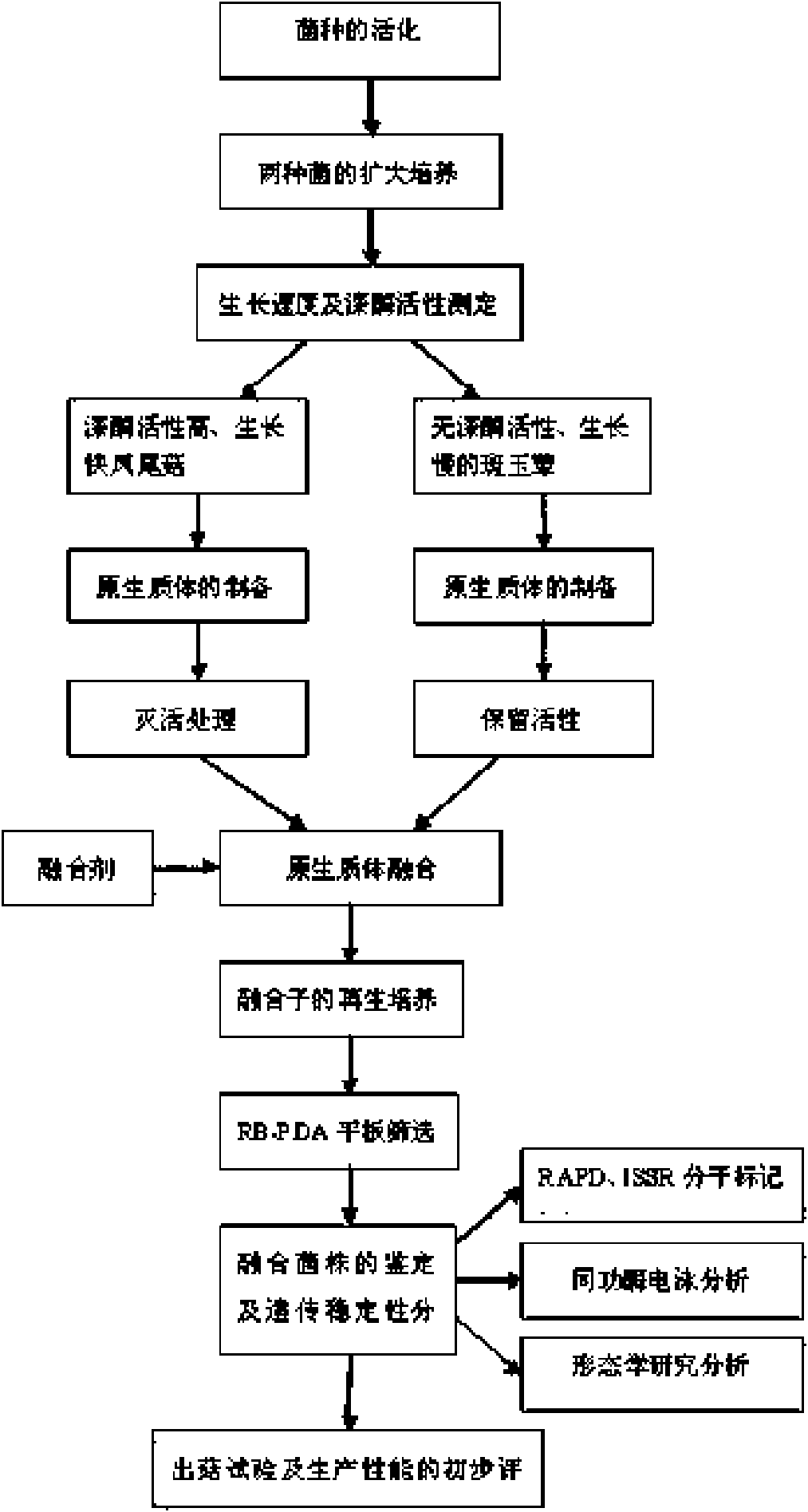
Patents
Literature
312results about "Lichen products" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
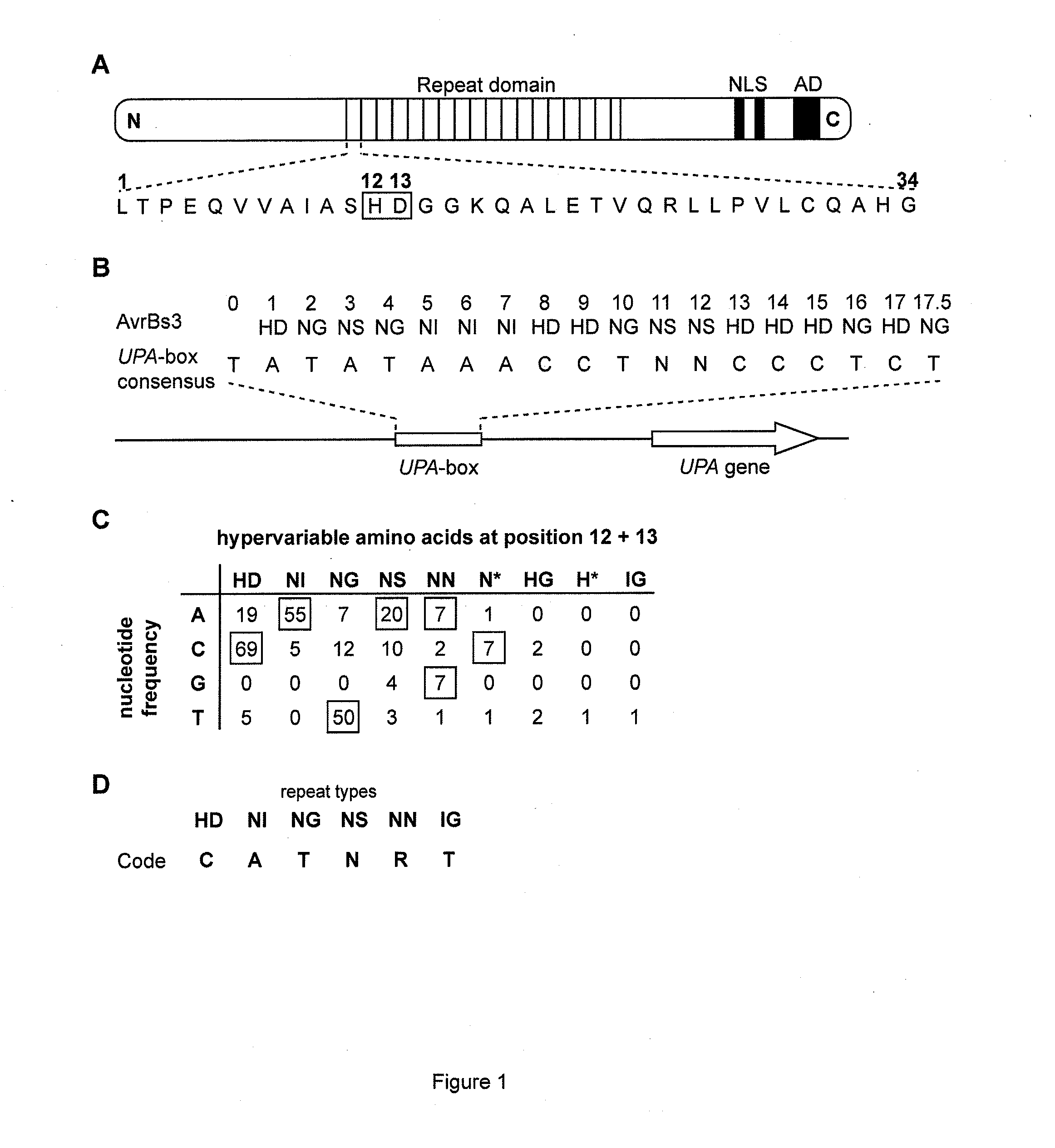
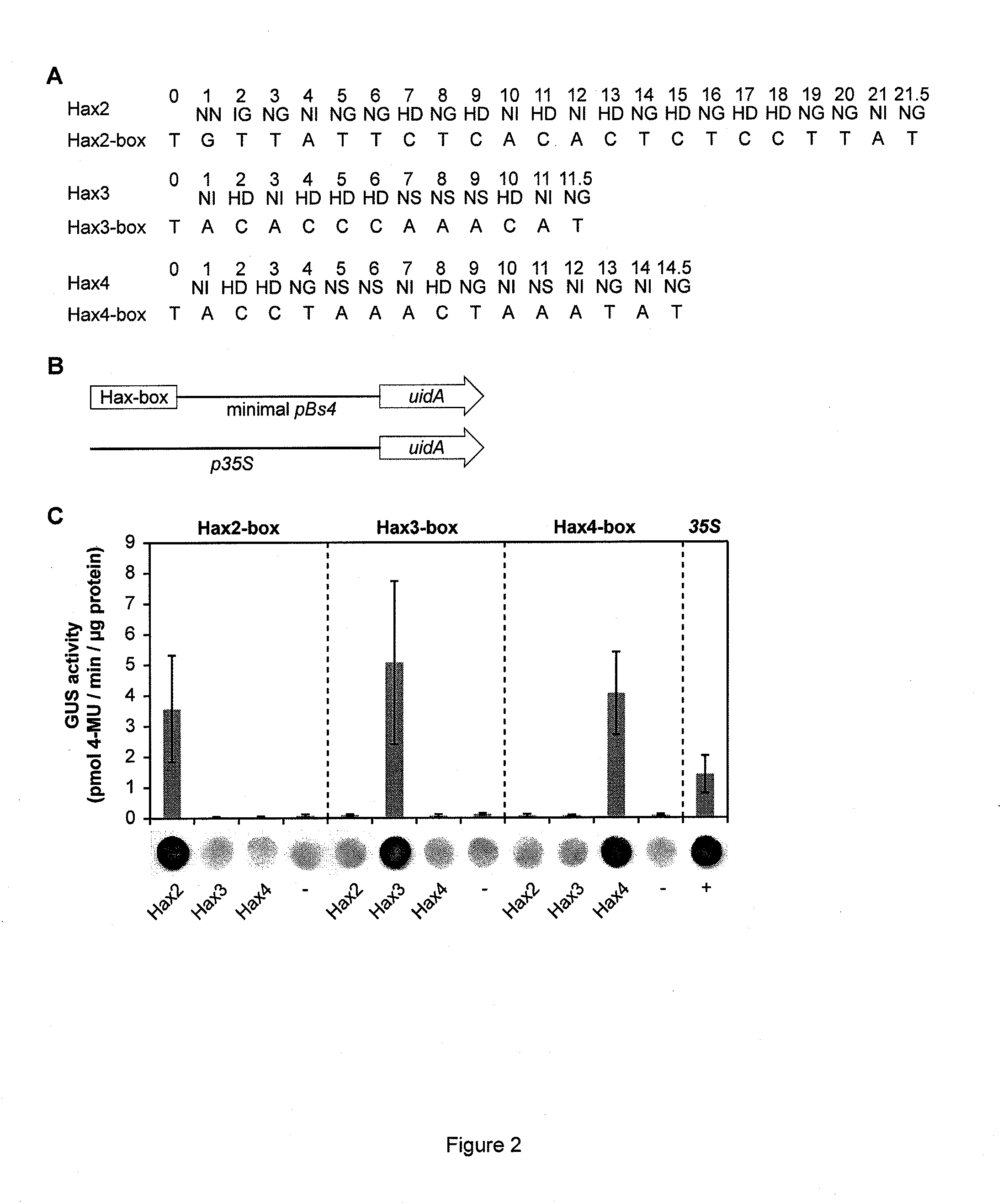
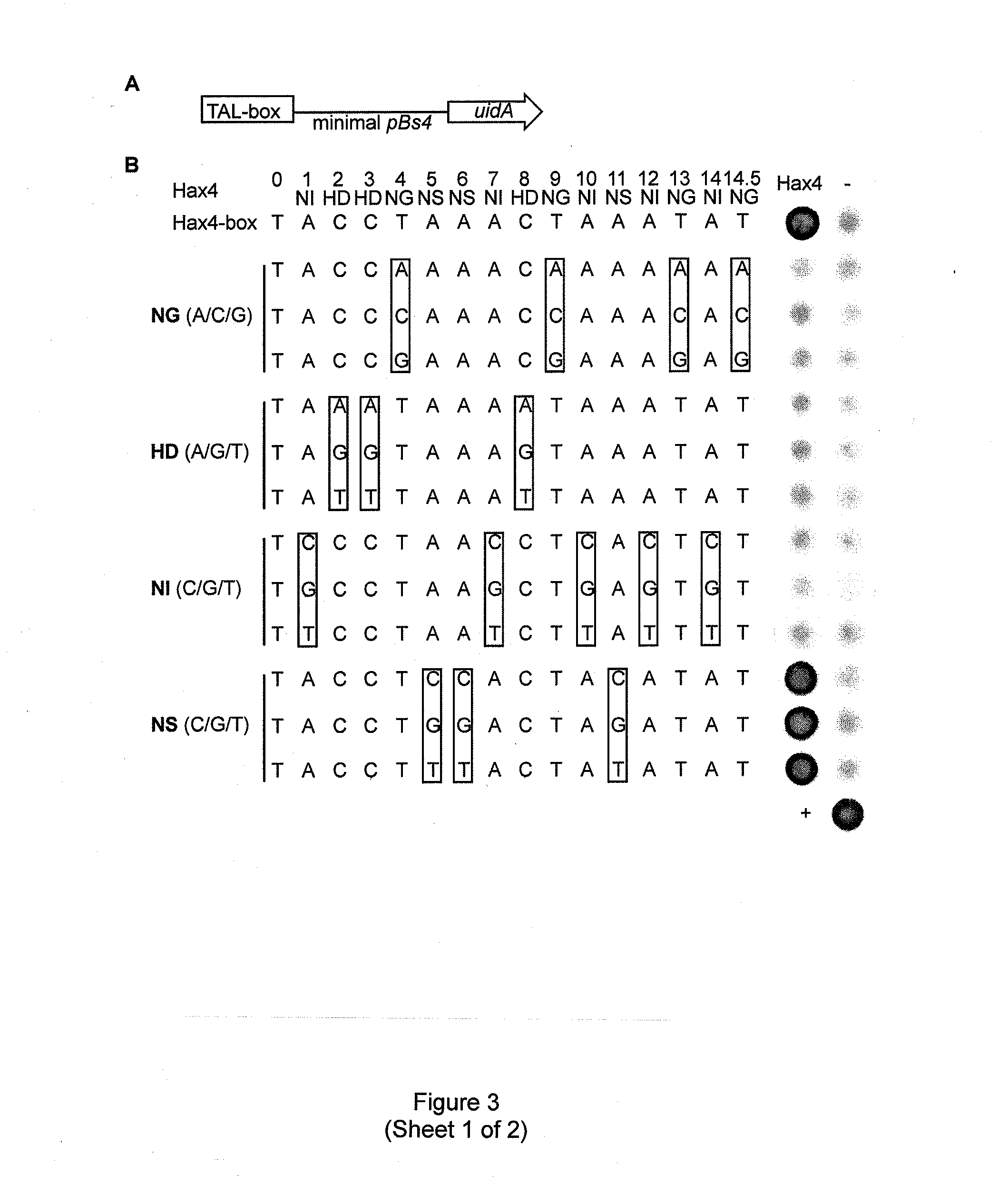
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
InactiveUS20110239315A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFungiBacteriaDNA-binding domainDna targeting
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +2
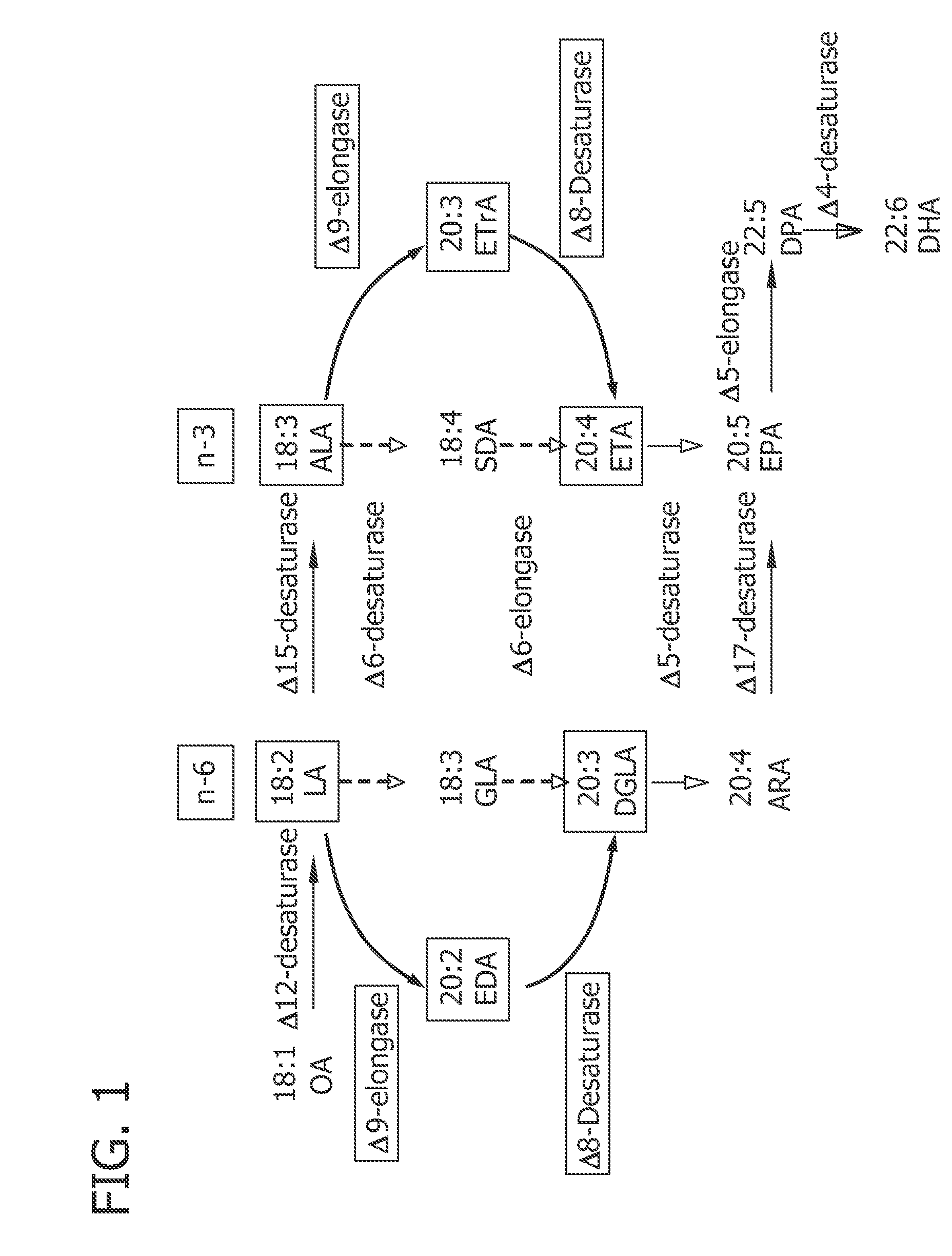
Novel delta9-elongase for production of polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched oils
The present disclosure relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding a delta 9-elongase, delta 9-elongases encoded by the isolated polynucleotides, expression vectors comprising the isolated polynucleotides, host cells comprising the expression vectors, and methods for producing delta 9-elongase and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
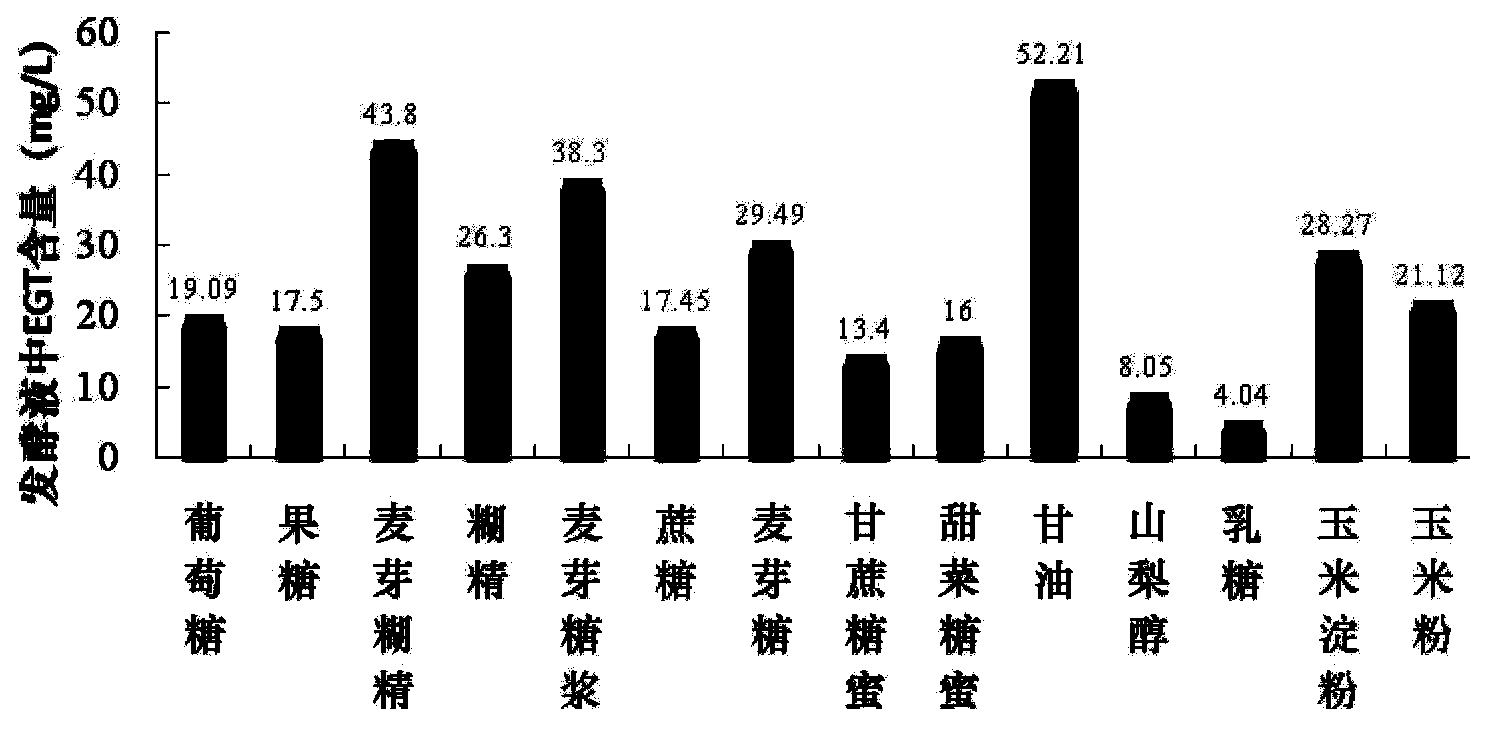
Bacterial strain producing L-erythrothioneine and method of preparing the L-erythrothioneine
ActiveCN103734022AIncrease contentRaw materials are cheap and easy to getFungi productsLichen productsMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a strain Pleurotus ostreatus TIB.BPE.10010 with the accession number being CGMCC No.6232. The invention also relates to a method of preparing L-erythrothioneine. The method comprises steps of culturing and fermenting the Pleurotus ostreatus CGMCC No.6232 to perform biosynthesis to form the L-erythrothioneine and extracting the L-erythrothioneine from mycelium cells.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Grifola frondosa strain produced through rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid fermentation
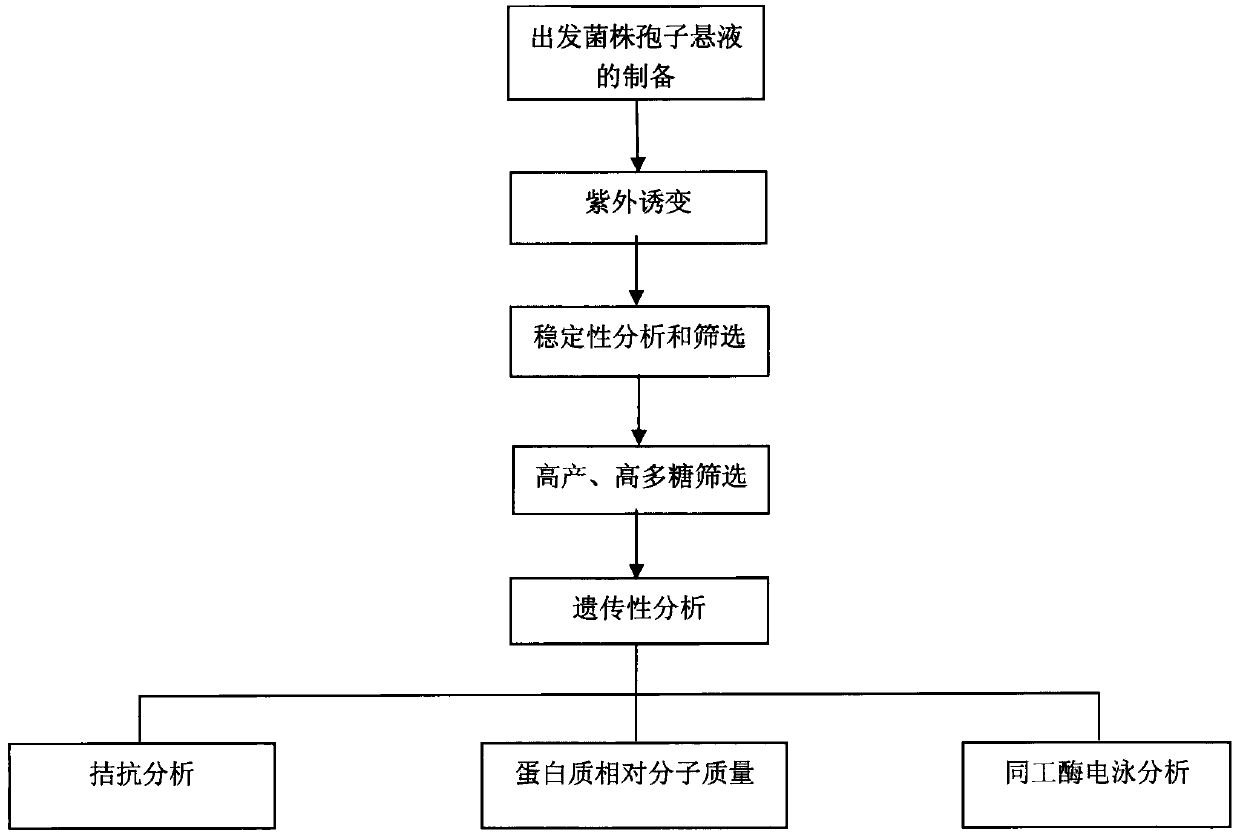
InactiveCN103416313AChange the disadvantages of low utilizationFast growthFungi productsLichen productsMutagenic ProcessFood biotechnology
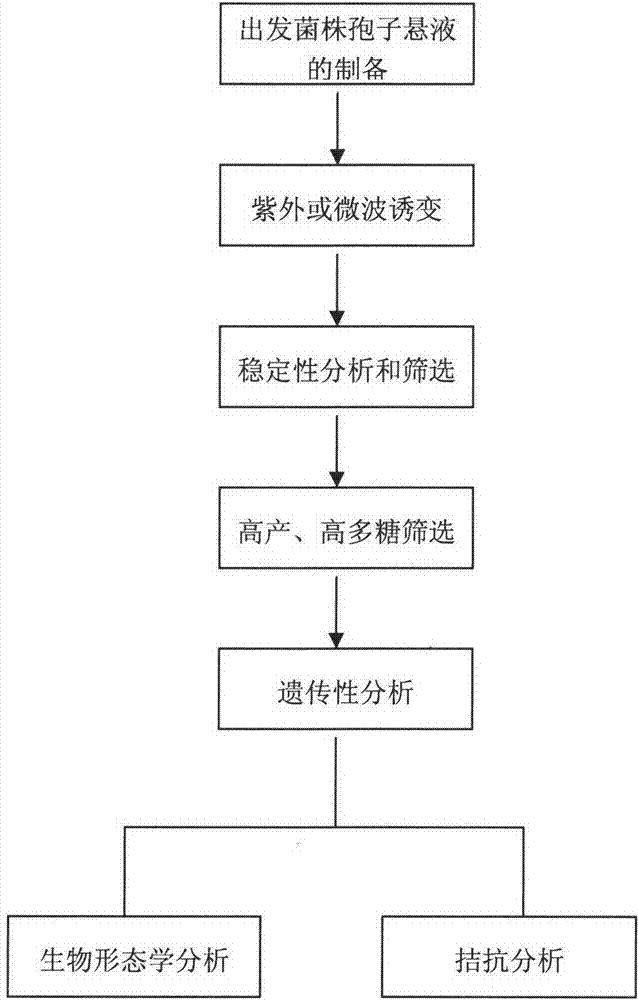
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe application and good bioscience and discloses a polysaccharide grifola strain produced through a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium. grifola Grifola sp.JSU1301 is preserved in the China Typical Model Cultivation Center (CCTCC) in June 25th, 2013, and is numbered CCTCC NO: M 2013286 and named a grifola Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2013286. According to the invention, a ultraviolet mutagenesis method is described with figures; a new strain capable of highly producing polysaccharide by starting with Grifola sp.CCTCC NO: M 2011113; the new strain quickly ferments and highly produces polysaccharide in the rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium; the mycelial dry weight and the mycelial polysaccharide productivity of a shake flask are increased by 16.8% and 8.57% compared with those of a starting strain, and those of fermentation in a tank are improved by 30.9% and 29.7%, which reach the highest level at present.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Mushrooms
A substrate for mushroom cultivation comprises a polyene fungicide, in particular, natamycin. Mushrooms cultivated in such substrates can be harvested earlier than mushrooms cultivated in substrates which do not include polyene fungicides. Alternatively, mushrooms grown in a substrate comprising a polyene fungicide achieve a greater size than mushrooms grown for the same amount of time in a substrate which does not include a polyene fungicide.
Owner:SYLVAN +1
Bacterial strain used for producing ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides by complete feed liquid fermentation of rice bran and wheat bran
The invention belongs to the field of microbial application technology and food biotechnology, and discloses a ganoderma lucidum strain used for producing polysaccharides by complete feed liquid fermentation of rice bran and wheat bran. Ganoderma lucidum JSU6161314 is stored in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 25th, June, 2013, preservation number is CCTCC M2013287, and the bacterial strain is named as Ganoderma lucidum CCTCC M2013287. According to a method disclosed in a drawing of the invention, the novel bacterial strain, which is capable of realizing high yield of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, is obtained by modifying ganoderma lucidum CFCC6043. The novel bacterial strain is used for rapid fermentation in a rice bran and wheat bran complete feed liquid culture medium and high yield of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. After fermentation, hypha dry weight and hypha polysaccharide yield increase 23.0% and 45% respectively compared with that of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
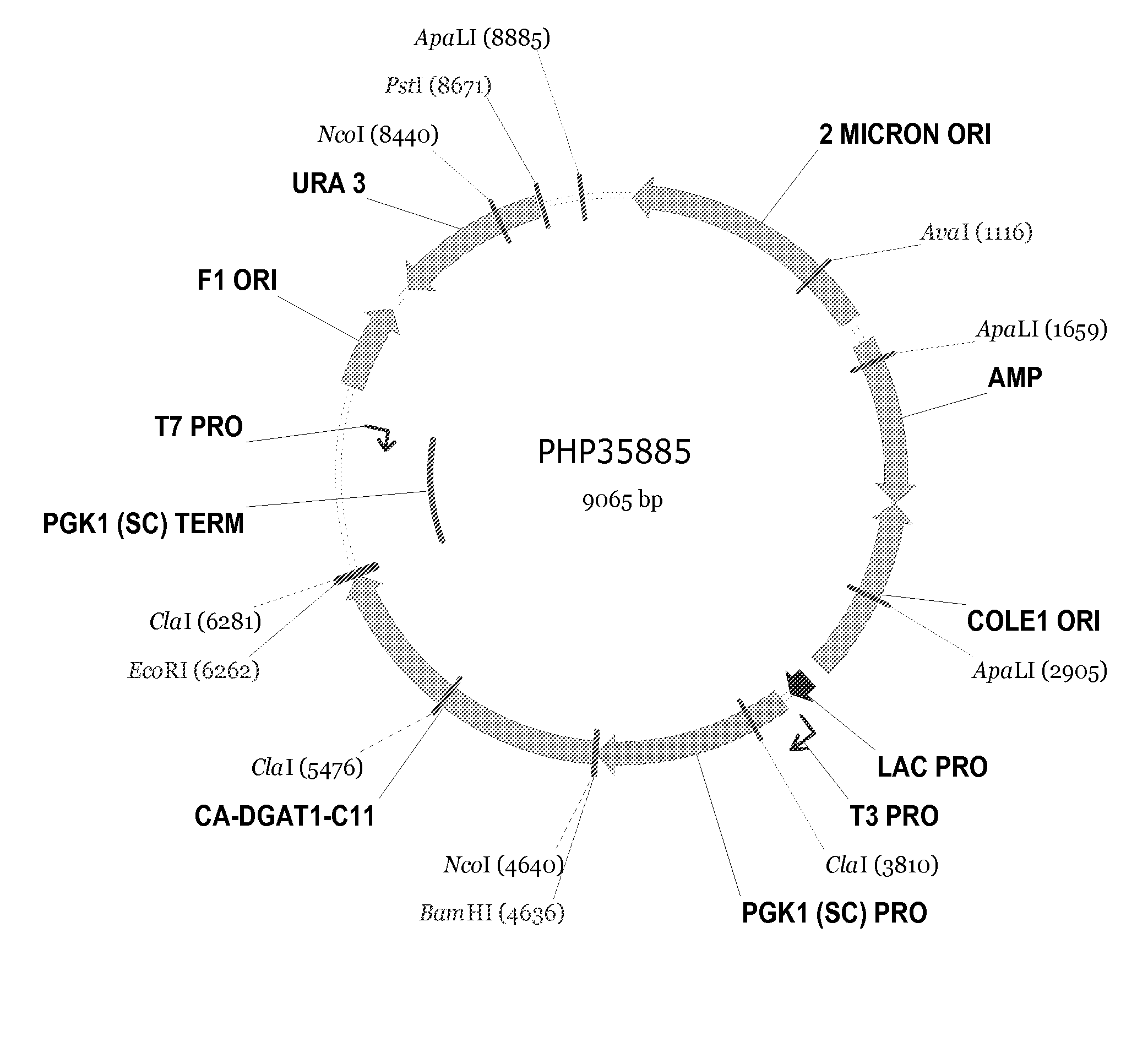
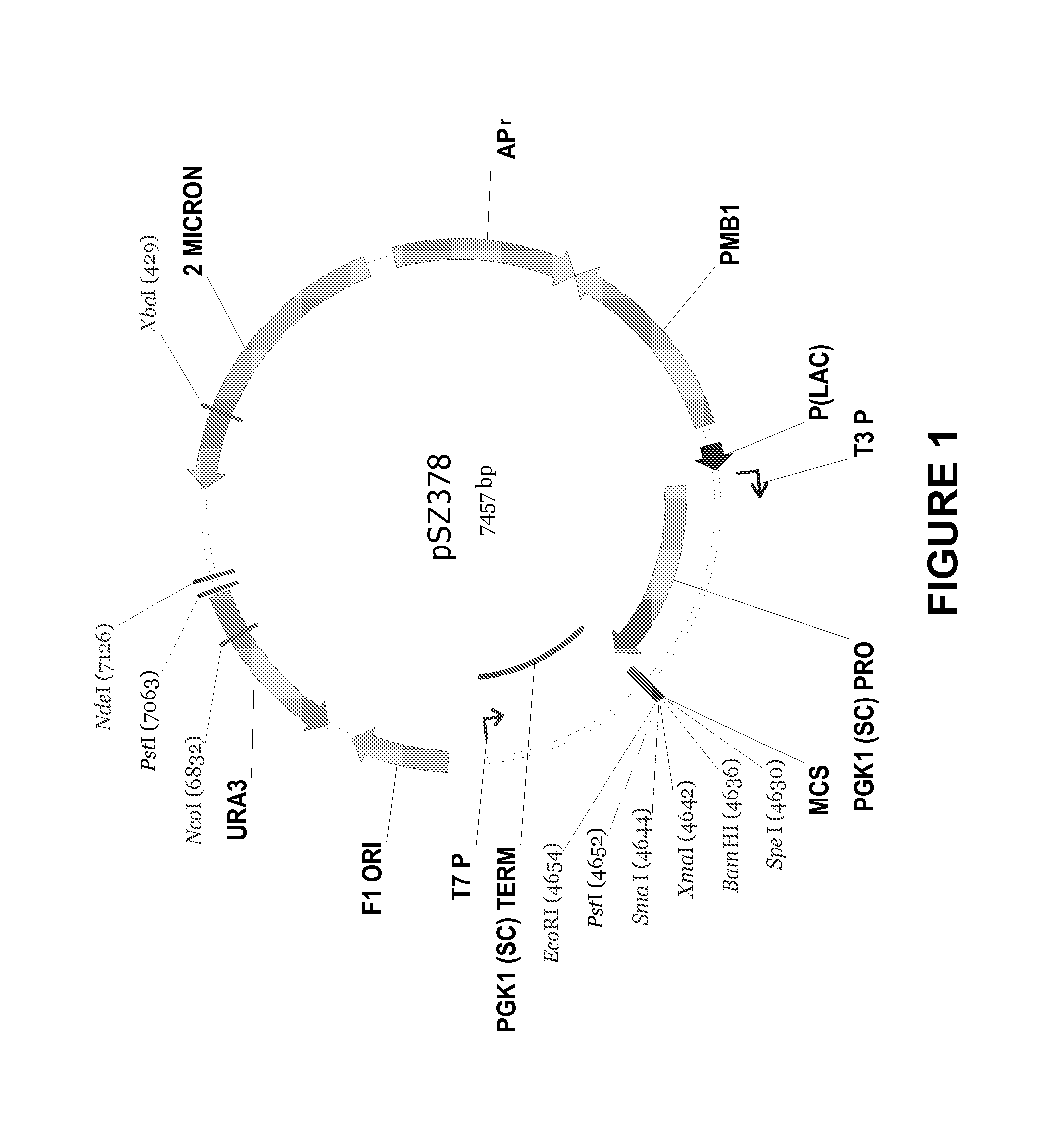
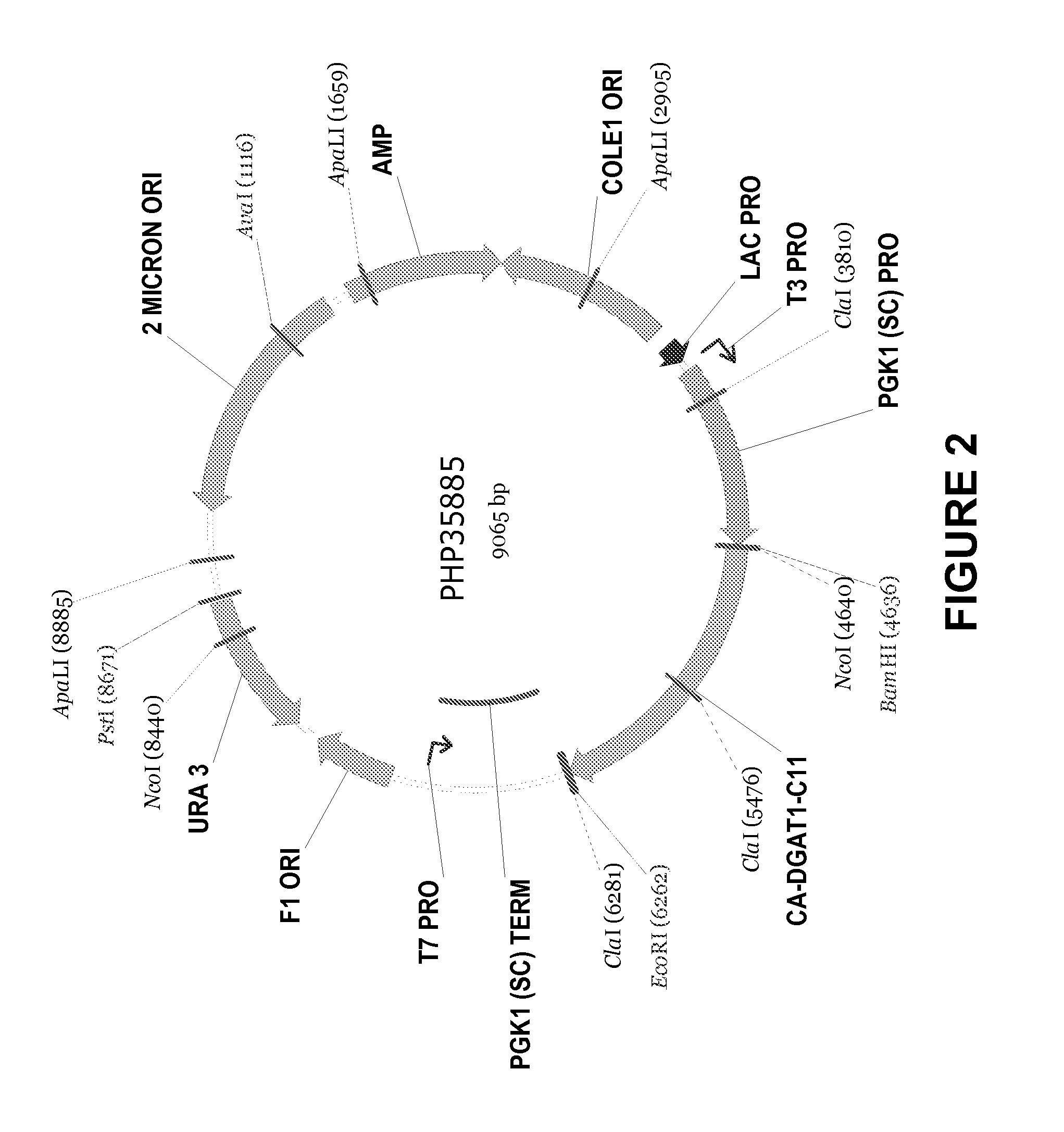
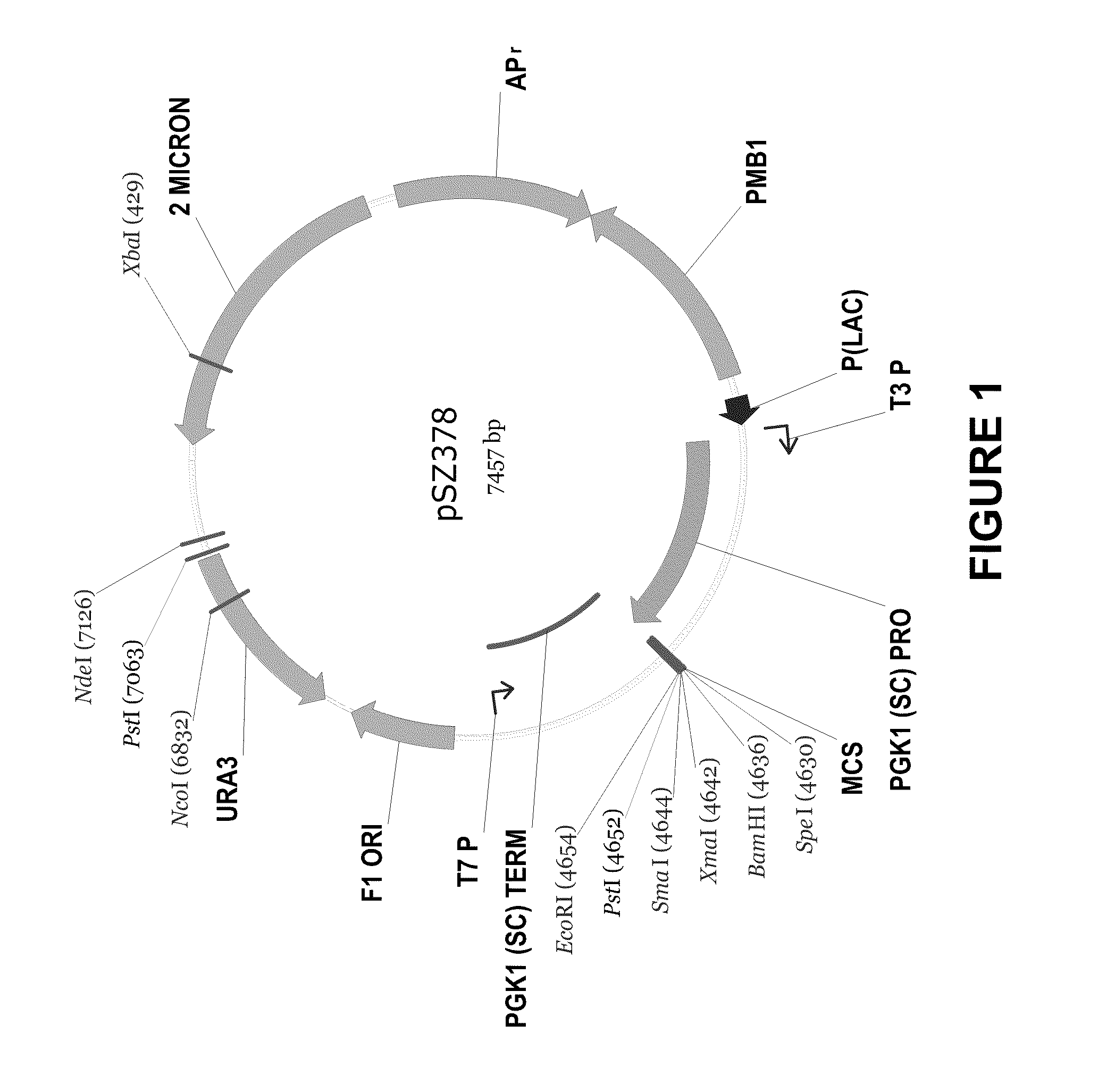
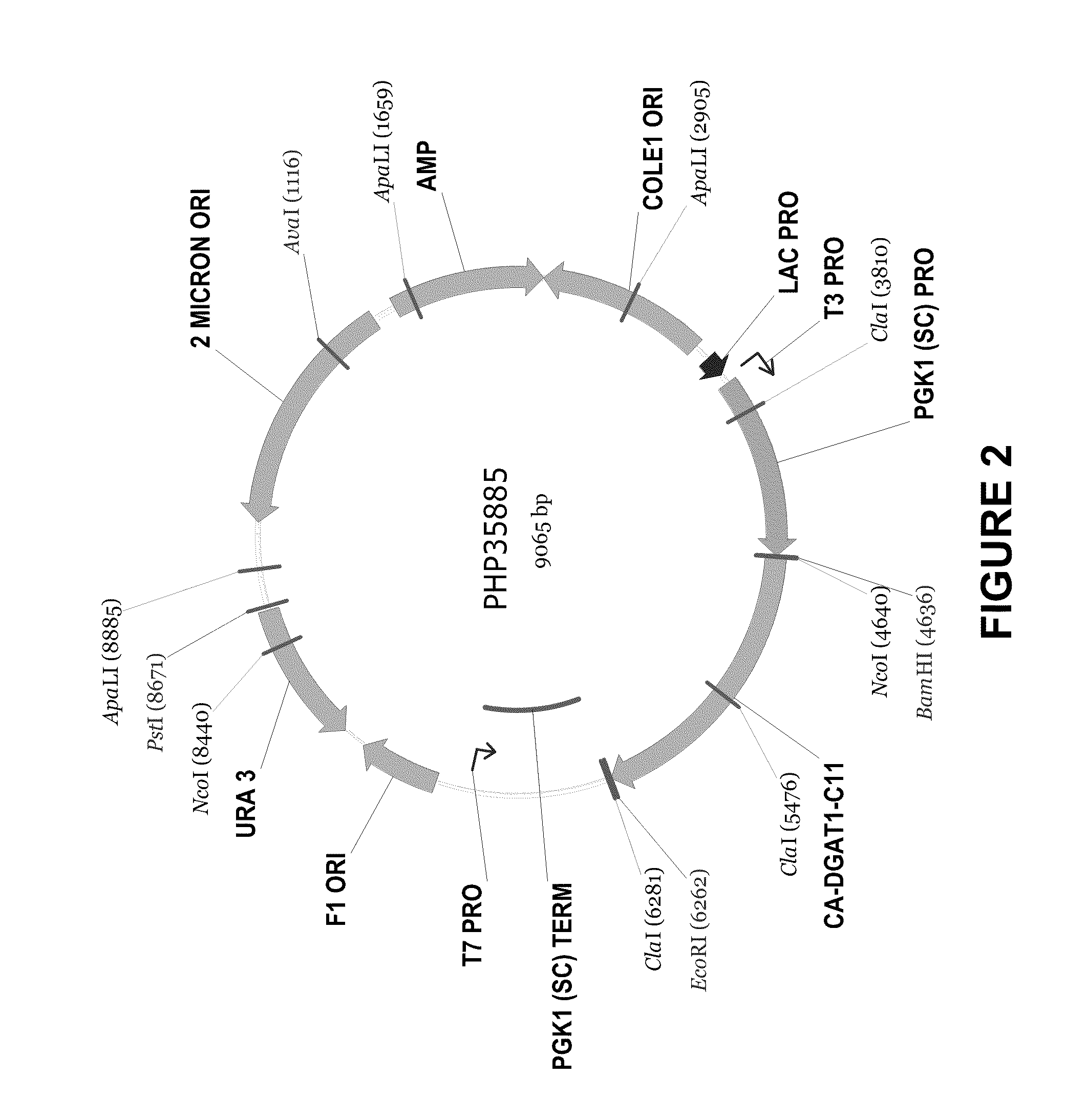
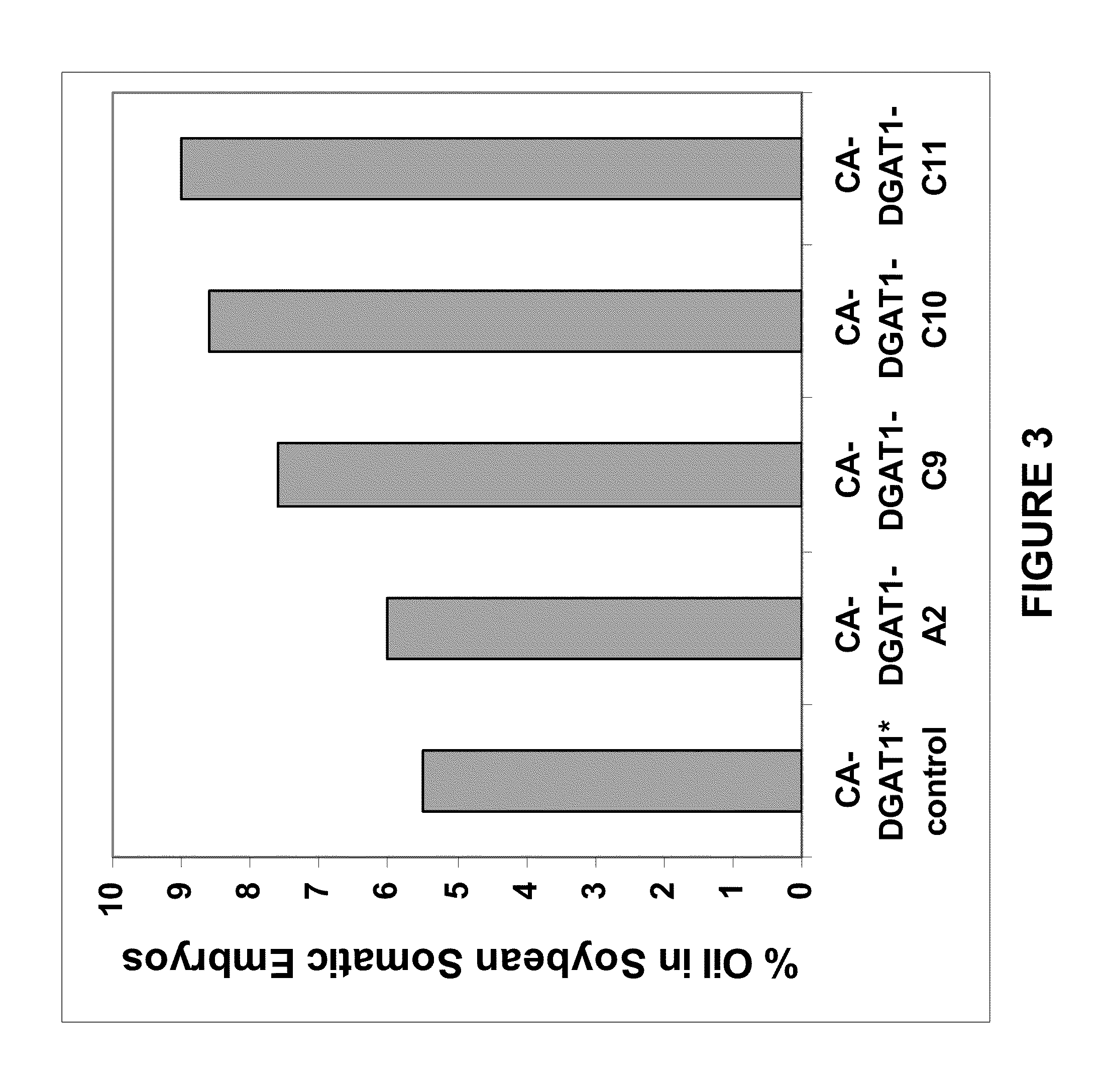
Novel dgat genes for increased seed storage lipid production and altered fatty acid profiles in oilseed plants
Transgenic oilseeds having increased total fatty acid content of at least 10% and altered fatty acid profiles when compared to the total fatty acid content of null segregant oilseeds are described. Novel DGAT genes are used to achieve the increase in seed storage lipids.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Method for breeding Poria cocos
InactiveCN1732761AGuaranteed clinical useReduce planting costsFungi productsLichen productsHyphomycetesHypha
The invention discloses a method for cultivating Poria cocos, belonging to the technique field of microbiological cultivating, which comprises: choosing good Poria cocos seeds by means of bacterial breeding, preserving and culturing the parent seeds, producing and breeding the initial species and cultivating species on the base of the former step; the parent species culturing comprising separating the parent species and culturing in the culture medium. By employing the method in this invention, bacterial filament and sclerotium can be produced, the culture medium is prepared artificially in the culture of parent species, original species and cultivating species course, and does not need natural pine and thus there is no need for trees cutting. The method is suitable for mass production and the planting cost is very low.
Owner:SAAS BIOTECH & NUCLEAR TECH RES INST
Bioreactor Paradigm for the Production of Secondary extra-Particle Hyphal Matrices
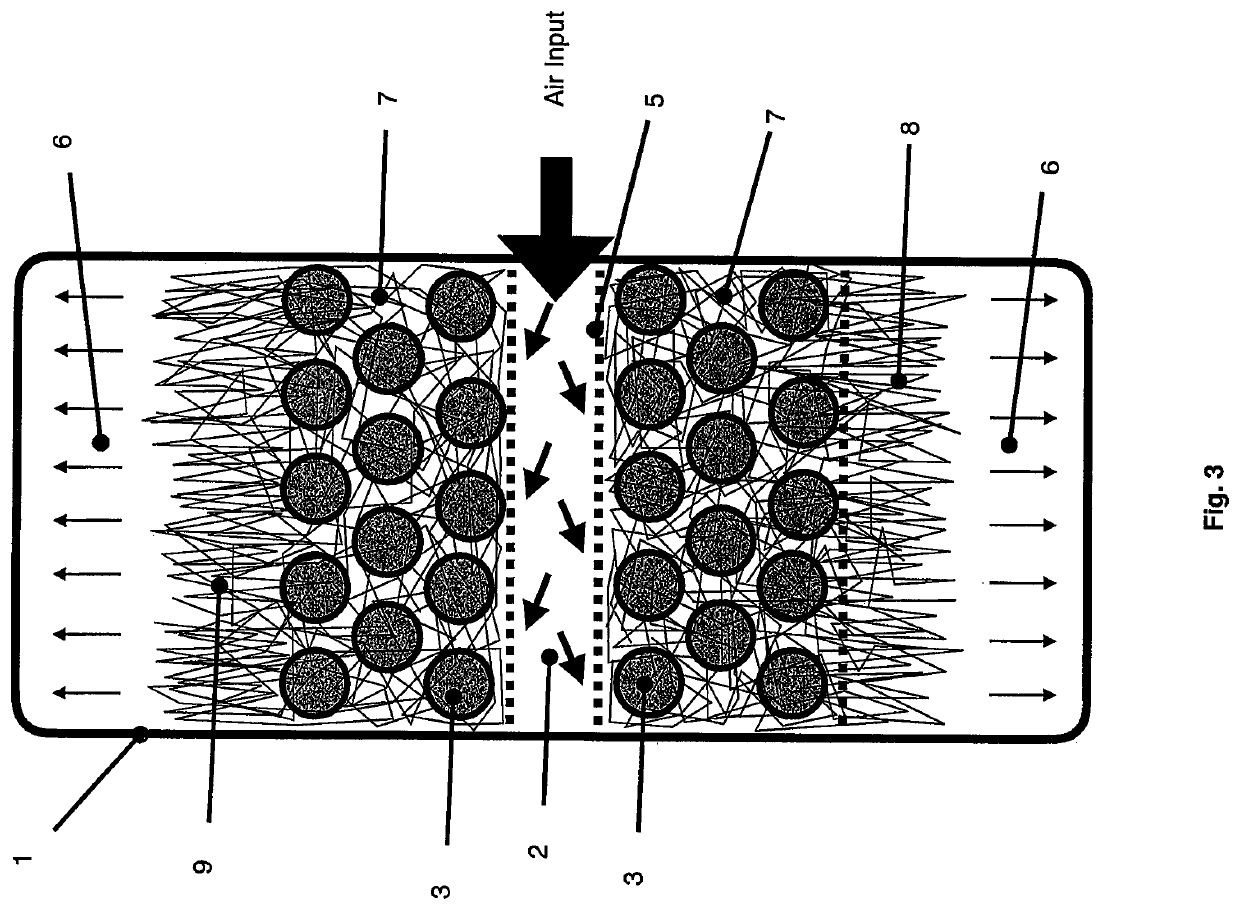
The invention describes a methodology for production of a secondary extra-particle fungal matrix for application as a mycological material, manufactured via a Type II actively aerated static packed-bed bioreactor. A pre-conditioned air stream is passed through a substrate of discrete elements inoculated with a filamentous fungus to form an isotropic inter-particle hyphal matrix between the discrete elements. Continued feeding of the air through the substrate of discrete elements and isotropic inter-particle hyphal matrixes develops an extra-particle hyphal matrix that extends from an isotropic inter-particle hyphal matrix in the direction of airflow into a void space within the vessel.
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
Mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and breeding method
InactiveCN101690463AGenetically stableIncrease productionFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyDry weight
The invention provides a mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and a breeding method. A new high-yield strain of cordyceps militaris is obtained by chemical mutagenesis, the preservation number thereof is CGMCC NO. 2909, and compared with original starting strain, the dry weight of mycelium is increased by 103%, the content of adenosine is increased by 536%, the content of polysaccharide is increased by 22.2%, the content of protein is increased by 55.5%, and the content of mannitol is increased by 37.5 %. The new strain of cordyceps militaris does not degenerate after more than 20 times of subculturing, has genetic stability, and utilizes the research of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to verify the difference on DNA level between the strain and the original starting strain. The invention also discloses the optimum process condition for extracting polysaccharide and adenosine of cordyceps militaris.
Owner:CHANGCHUN SHENGJINNUO BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Culture method of antrodia camphorata
A culture method of a fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata is provided, which includes: (a) fermenting a culture medium containing yeast at 5-35° C. for 3-30 days; (b) adding wood flour to the fermented culture medium with stirring; (c) placing the wood flour and the culture medium into a vessel; (d) sterilizing the vessel containing the wood flour and the culture medium; (e) inoculating Antrodia camphorata strains into the sterilized vessel containing the wood flour and the culture medium, and culturing at 5-35° C., to form mycelia; (f) inoculating the wood flour containing Antrodia camphorata mycelia into a wood segment; (g) placing the wood segment inoculated with Antrodia camphorata mycelia in an environment where the temperature is 5-35° C. and the humidity is 65-85%, and culturing for a period of time; and (h) removing the wood flour remained on the wood segment, then placing the wood segment in an environment where the temperature is 15-35° C. and the humidity is 80-98%, and culturing for a period of time, to form a fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata. A culture method of Antrodia camphorata mycelia, a culture method of a fruiting body of Antrodia camphorate, and a fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata cultured by the same method are also provided. The fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata cultured by the method of the present invention is thick and solid, and the content of triterpenoids is comparable to that of wild Antrodia camphorate.
Owner:TSAI TA MING
Brown mushrooms for commercial production
Hybrid Agaricus bisporus mushroom strains having one or more genetic characteristics of a wild mushroom strain deposited under ATCC accession No. PTA-6903 or a progeny thereof and having specified physical and genetic characteristics are disclosed along with methods of producing brown mushrooms for commercial use.
Owner:AMYCEL LLC
Fungus for promoting aquilaria plants to generate agilawood and application of fungus
ActiveCN103651151ANon-perishableStrong environmental toleranceFungi productsLichen productsAquilariaFomitopsis sp.
The invention discloses a fungus for promoting aquilaria plants to generate agilawood and application of the fungus. The fungus is Fomitopsis sp. ASAF01, and the preservation number in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC NO.7802. The Fomitopsis sp.ASAF01 can promote the heartwood formation of aquilaria sinensis after the Fomitopsis sp. ASAF01 is inoculated for six months, and the middle of the formed agilawood is not easy to rot. Furthermore, the strain can still grow at the temperature of 15-40 DEG C and pH value of 2-11 to indicate that the Fomitopsis sp.ASAF01 has strong environmental tolerance.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI HAINAN BRANCH
Hypsizygus marmoreus GJ5 strain as well as SSR marker primers and application thereof
ActiveCN112280687AShort detection timeReduce testing costsFungiFungi productsElectrophoresesAntagonism
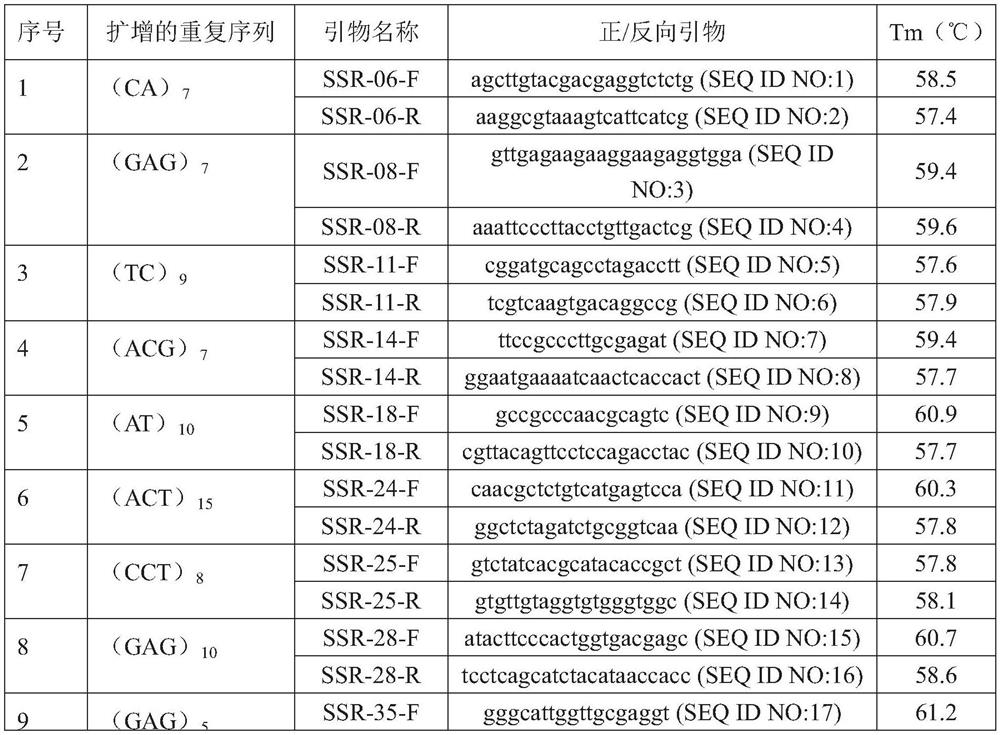
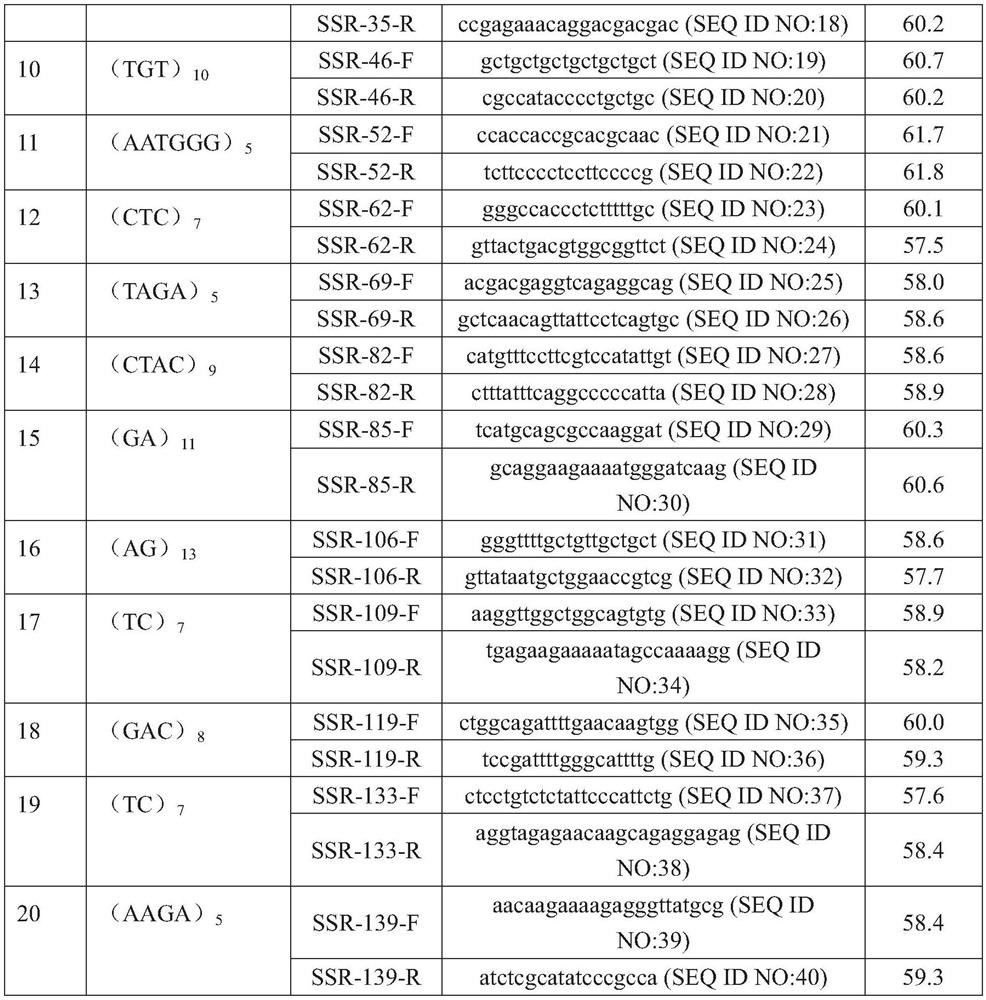
The invention discloses a hypsizygus marmoreus GJ5 strain as well as SSR marker primers and application thereof. The preservation number of the hypsizygus marmoreus GJ5 strain is CCTCC M 2020506; theSSR marker primers comprise five pairs of SSR specific marker primer combinations, and the five pairs of SSR specific marker primers form a fingerprint spectrum. The application comprises the following detection steps: extracting genome DNA of hyphae or sporocarp of a strain to be detected; carrying out SSR molecular marker amplification; carrying out electrophoresis detection; and comparing an electrophoretic band with the fingerprint spectrum, wherein the bacterial strain consistent with the fingerprint spectrum is the hypsizygus marmoreus GJ5 strain. Compared with conventional morphologicaldetection, antagonism experiments and fruiting experiment methods, the SSR fingerprint has the advantages of being short in detection time, high in accuracy, good in repeatability and the like, and the SSR fingerprint constructed through the SSR fingerprint can be used for distinguishing the hypsizygus marmoreus GJ5 strain from 23 main cultivated varieties of hypsizygus marmoreus.
Owner:东营市菇健生物科技有限公司
DGAT genes for increased seed storage lipid production and altered fatty acid profiles in oilseed plants
Transgenic oilseeds having increased total fatty acid content of at least 10% and altered fatty acid profiles when compared to the total fatty acid content of null segregant oilseeds are described. Novel DGAT genes are used to achieve the increase in seed storage lipids.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Protoplast mutation breeding method for improving cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN103215250AGood mutagenic effectEasy to operateFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention relates to a protoplast mutation breeding method for improving the cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps of activated culture of bacterial strains, solid culture of mycelia, liquid mycelia culture, mycelia enzymolysis, protoplast nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutation, protoplast regeneration culture, regenerated bacteria subculture, fermentation culture, filtering, further washing of mycelia, measurement of cordycepin content in the mycelia, preservation of the bacteria strain with high cordycepin content, measurement of the genetic stability and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the cordycepin content of the cordyceps militaris can be increased.
Owner:XUZHOU HONGYU AGRI TECH
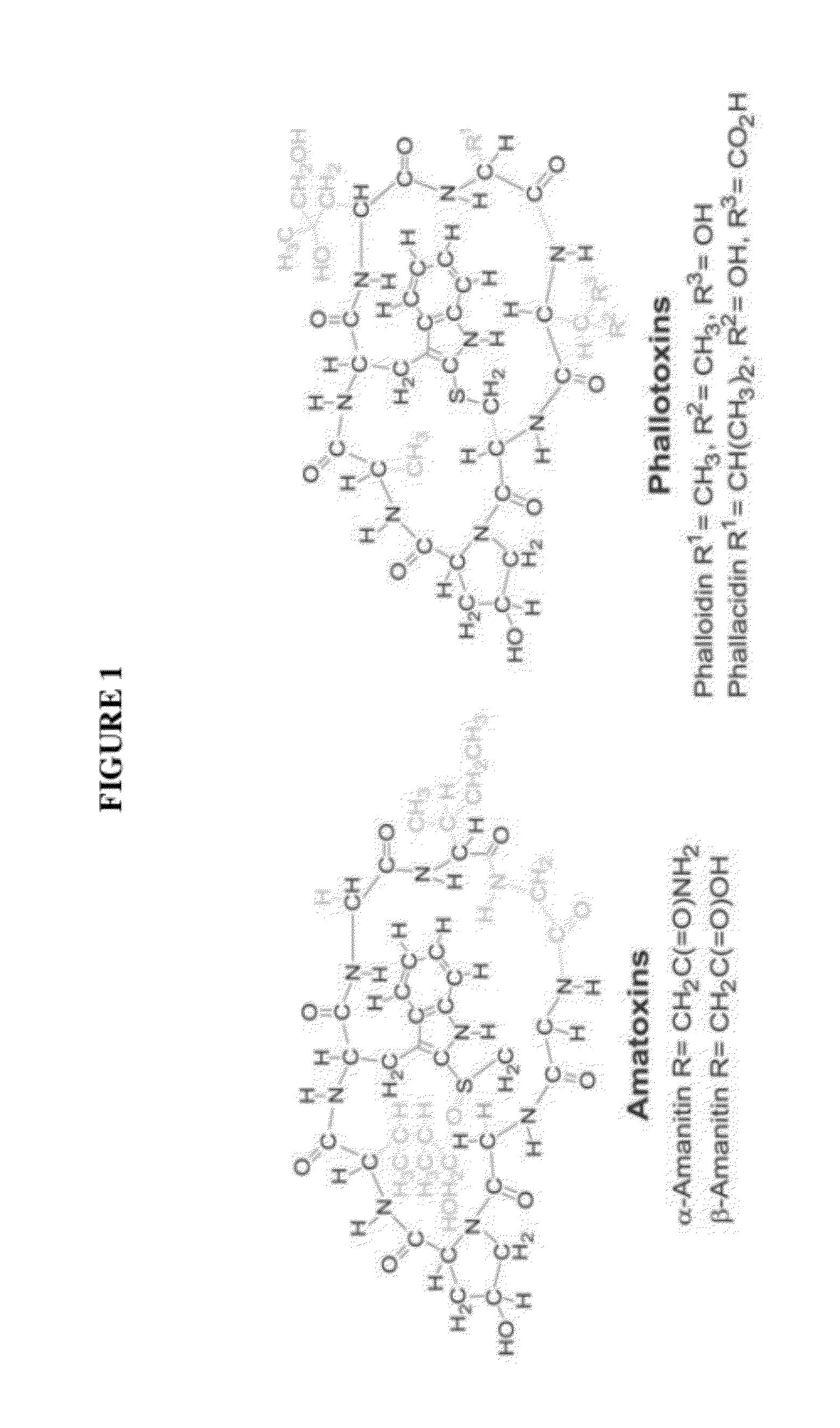
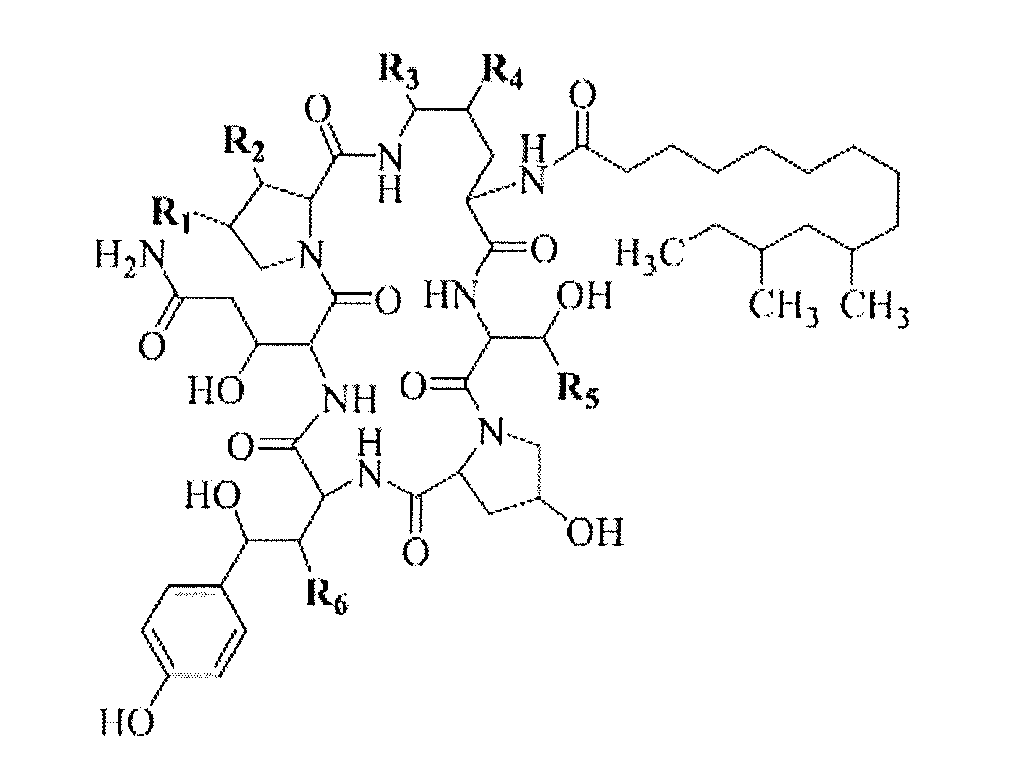
Use Of Galerina Marginata Genes And Proteins For Peptide Production
ActiveUS20120276588A1Improve concentrationIncrease concentrationSugar derivativesFungi productsCyclic peptideGalerina
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising genes and peptides associated with cyclic peptides and cyclic peptide production in mushrooms. In particular, the present invention relates to using genes and proteins from Galerina species encoding peptides specifically relating to amatoxins in addition to proteins involved with processing cyclic peptide toxins. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention also relates to methods for making small peptides and small cyclic peptides including peptides similar to amanitin. Further, the present inventions relate to providing kits for making small peptides.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Hypsizygus marmoreus strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105165635AShort training periodShort cultivation periodFungi productsLichen productsEdible mushroomMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of edible mushrooms and particularly relates to a hypsizygus marmoreus Finc-B-3 strain and application thereof. The hypsizygus marmoreus strain provided by the invention is named as Finc-B-3 and is obtained by taking a strain TNN-12 and a strain F-FG as parents to be hybridized through systematic selection, belongs to hypsizygus marmoreus and is preserved in Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences, wherein the address is No.3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.11204 and the preservation date is 20150813. Compared with the prior art, the hypsizygus marmoreus Finc-B-3 strain provided by the invention has short culture and cultivation periods, so that the production efficiency of factories is greatly improved; the unit yield is high, the yields of bottles are similar, and topographic characteristics are good, so that sub-packaging and sales of products are very easy; and the Finc-B-3 has good comprehensive performances and a wide market prospect.
Owner:青岛丰科生物科技有限公司 +2
Inonotus obliquus and method for extracting triterpennoids from same
The invention relates to Inonotus obliquus and a method for extracting triterpennoids from the same. The adopted technical scheme is that the Inonqqus obliquus LNUF 008 has the collection number of CCTCC M 209280. The method for extracting the triterpennoids from the inonotus obliquus comprises the following steps of: activating the inonotus obliquus to prepare seed liquor; inoculating the seed liquor in an inoculation amount which accounts for 2 percent of the volume of fermentation liquor into a fermentation tank liquid synthetic medium, fermenting, performing suction filter on the fermentation liquor, drying at the temperature of 45 DEG C, filtering out mycelia, pouring the mycelia into a mortar, grinding the mycelia into powder, adding an organic solvent in a volume which is 10 times mass of the powder, and immersing for 24 hours; performing ultrasonication at the temperature of 50 DEG C and the frequency of 77 KHz for 60 minutes; and centrifuging for 10 minutes under the condition of 5,000 revolutions / minute, removing sediment, collecting supernatant, and concentrating under reduced pressure to obtain a target product. The triterpennoids extracted from the inonotus obliquus have the advantages of high content and high recovery rate, and provide the feasibility for large-scale production.
Owner:辽宁储阳生物科技开发有限公司
New grey white variant strain with red pleurotus
The invention relates to a new strain of edible fungus, belonging to the technical field of edible fungus development and utilization. The new grey variant strain of edible fungus with red pleurotus: Pleurotus djamor (Rumph.: Fr.)Boedijn, is the new strain of edible fungus selectively bred through single spore cross breeding and has the number No.1933 in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center). The strain is characterized in that the color of sporophore is stable grey white, the whole sporophore is pure and transparent, the cellulose content is 5-12%, and the strain has favorable mouth feel and is used for producing the edible fungus in the high temperature season. Mycelium grows very fast and has strong ability in fighting bacteria and also has developed aerial hyphae. The hypha has clamp connection and the growth temperature of 3-45 DEG C; the temperature of sporophore differentiation is 18-35 DEG C, and the new grey variant strain is typical high temperature edible fungus. Straws, saw dust, bran, and the like are selected as cultivation materials. The edible fungus is cultivated in March to November. Cultivation materials produced in scale do not need high pressure or normal pressure sterilization, and the sporophore output is 15-25%. The strain is newly selected and bred edible fungus and has application value in the edible fungus field and ornamental fungus field.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof are provided. The fungus strain is a mutant derived from Glarea lozoyensis, and deposited in CGMCC with the accession number of CGMCC 2933. The preparation method concludes following steps: (a) mixing the culture media of Glarea lozoyensis strain ATCC 20957 with nitrosoguanidine, and obtaining mixture a; (b) mixing lywallzyme with the mixture a, and obtaining protoplasts; (c) regenerating the protoplasts, and obtaining single clones; and (d) culturing the single clones, then obtaining the mutant strain. This fungus strain has stable genetic and producing property, produces little impurities in fermentation, and is suitable to be used in industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECHWELL BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Hypsizigus marmoreus and method for establishing laccase transfer system in breeding thereof
ActiveCN101642054AConsistent agronomic traitsEstablishment of laccase conversion systemFungi productsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismTransfer system
The invention provides hypsizigus marmoreus and a method for establishing laccase transfer system in breeding thereof, belongs to the technical field of the hypsizigus marmoreus, and solves the problems that the hypsizigus marmoreus does not have laccase activity, has slow growing speed, longer production period and weak bacterial resistance in the prior art. The Hypsizigus marmoreus new strain Jinshan No.1 has the laccase activity, and is reserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 12 June, 2009 with the accession number of CGMCC No. 3120. Pleurotus pulmonarius withthe laccase activity and the hypsizigus marmoreus are subjected to protoplast fusion to establish the laccase transfer system in the hypsizigus marmoreus. The hypsizigus marmoreus new strain culturedby the method has excellent properties of high laccase activity, high growing speed, short production period and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Culture of nematoda without bacteria
An aseptic culture method for pine nematode includes such steps as culturing Pseudomonas fluorescens GcM5-1A (CCTCC No.M204065), deactivating, culturing the calli of black pine, deactivating, preparing the aseptic ova of pine nematode, preparing the culture liquid from deactivated cells and calli and aseptic water, adding said aseptic ova, and culturing at 15-40 deg.C for 4-20 days.
Owner:赵昕
Breeding method for excellent white agrocybe cylindracea
InactiveCN103828600AFirst cross-breedingCarry out cross breedingFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the field of agrocybe cylindracea, and particularly relates to a breeding method for excellent white agrocybe cylindracea. The method comprises the steps that hybridization is carried out on the white agrocybe cylindracea and the agrocybe cylindracea of a pale taupe strain, secondary hybridization is carried out on filial generations and the white agrocybe cylindracea again, and hybrids of the white agrocybe cylindracea can be obtained. The obtained hybrids of the white agrocybe cylindracea carry genes of the agrocybe cylindracea of the pale taupe strain, the excellent character of the agrocybe cylindracea of the pale taupe strain can be inherited to the white agrocybe cylindracea, and therefore the character of the white agrocybe cylindracea is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method of culturing agaricus bisporus mycelium and medium for culturing the same
InactiveUS20090235579A1Effective trainingImprove absorption efficiencyFungiFungi productsSporeLiquid medium
Owner:CJ CORPORATION
Poria wood grafting cultivation method
The present invention relates to artificial poria cultivating method. The wood cultivation process of poria features that it is realized through the following steps: selecting pine wood section, digging field, setting wood section into cellar, culturing wood primer, making wood primer, inoculating wood primer, transmitting wood primer, and separating mother seed. The present invention can cultivate robust poria in high yield and simple operation.
Owner:居学锋 +3
Enhancing inorganic carbon fixation by photosynthetic organisms
A method of enhancing inorganic carbon fixation by a photosynthetic organism. The method is effected by transforming cells of the photosynthetic organism with an expressible polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide having a bicarbonate transporter activity. Preferably, the polynucleotide further includes a plant promoter. Sequences and constructs for implementing the method are also described.
Owner:KAPLAN AARON +5
Hybrid mushroom strain B14528 and descendants thereof
ActiveUS9017988B1Reduce pathogen pressure pathogenReduce pathogen pathogen reservoirFungi productsMicroorganismsMicrobiologyAgaricus bisporus
A hybrid mushroom culture of Agaricus bisporus, designated as strain B14528, includes a representative culture of the strain, which has been deposited under NRRL Accession No. 50900. A method of producing a hybrid mushroom culture of Agaricus bisporus comprising: mating a homokaryotic line J12998-s39 with a homokaryotic line BW-s191. Additionally, mushrooms, parts of the culture and products incorporating the culture are provided.
Owner:SYLVAN AMERICA
Hybrid mushroom strain j9277, its descendants, and related methods
ActiveUS20100154079A1Improve facilitiesReduce morbidityFungi productsLichen productsDiseaseBasidiospore
A mushroom culture of Agaricus bisporus produced by hybridization of a first strain and a second strain of Agaricus bisporus, wherein at least one of said first and second strains of Agaricus is a hybrid mushroom culture of Agaricus bisporus designated strain J9277. Diverse additional strains can be developed from J9277 by various means including somatic and tissue culture selection, basidiospore selection, and hybridization to other strains of Agaricus bisporus, and the resulting derivative strains can be screened for desirable commercial characteristics. One resultant class of the mushroom Agaricus bisporus (J. Lange) Imbach is the hybrid strain J10165. It exhibits an attractive appearance that includes a smooth, bright white cap, and is biologically incompatible with strains of the Ur lineage group. A method for improving facility hygiene and reducing disease incidence at any commercial Agaricus bisporus mushroom production facility is also provided.
Owner:SYLVAN AMERICA
Soybean cultivar SW90702
A novel soybean cultivar, designated SW90702, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar SW90702, to the plants of soybean SW90702 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar SW90702 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar SW90702 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com