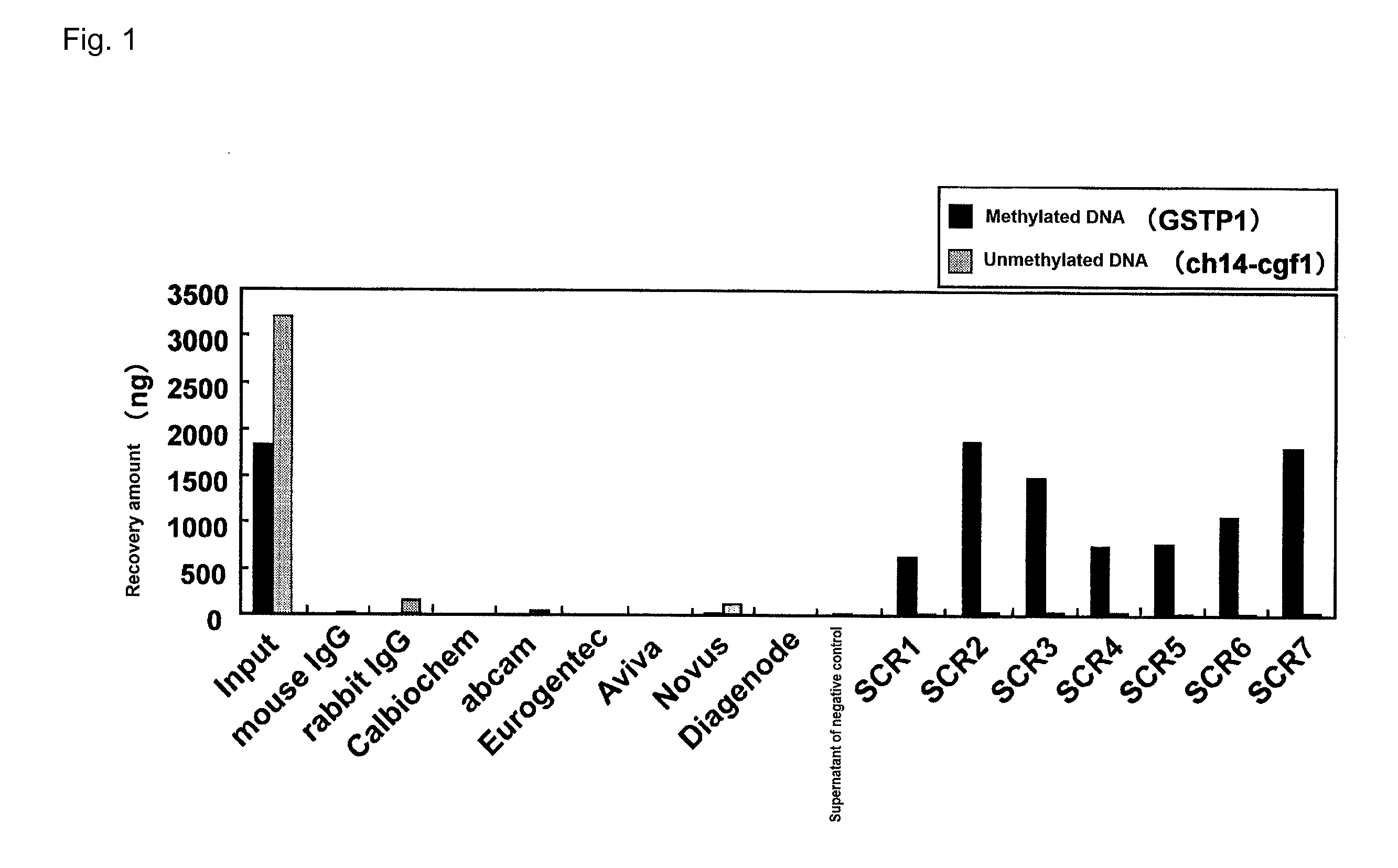
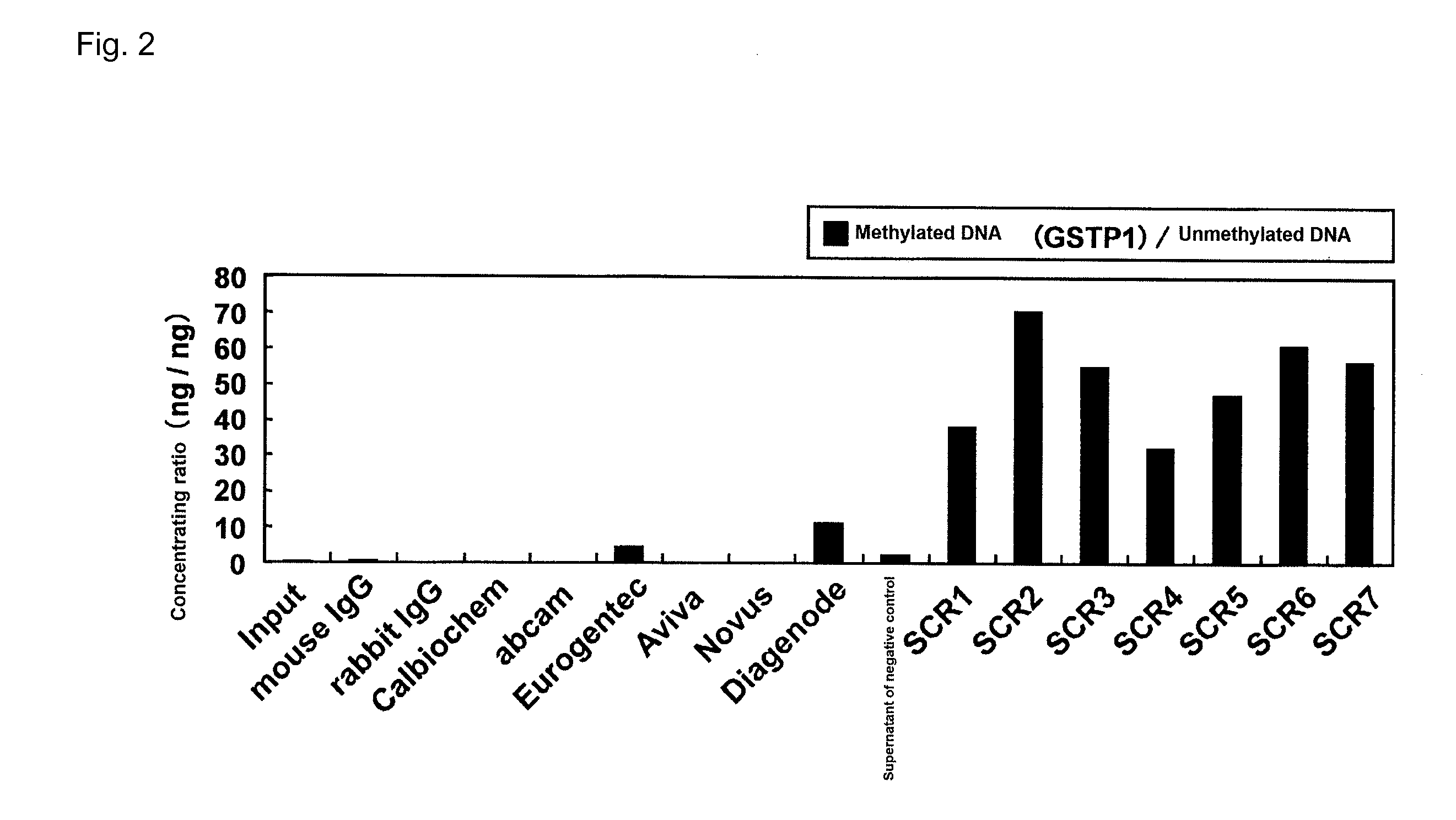
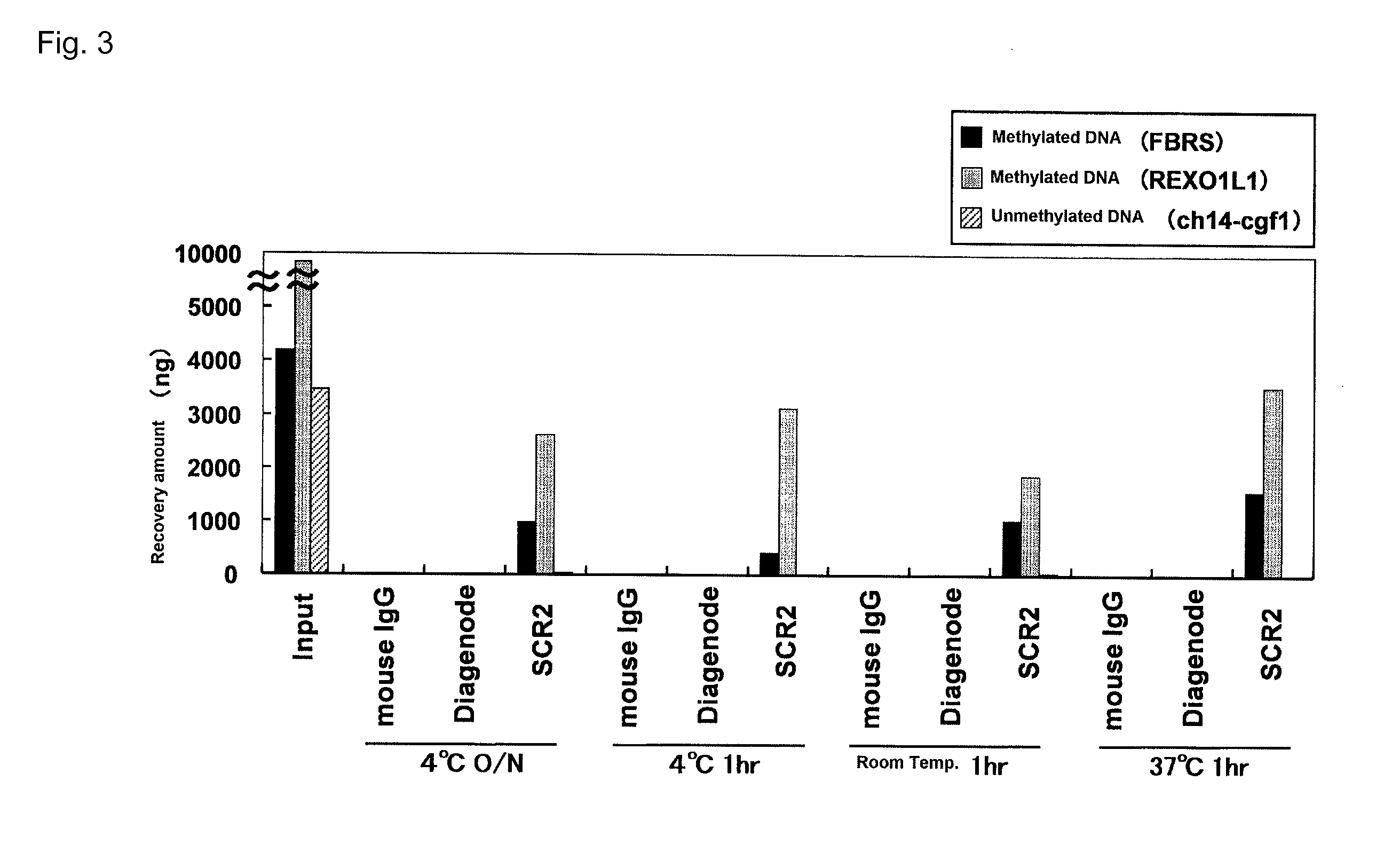
Patents
Literature
89 results about "Deoxyguanosine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
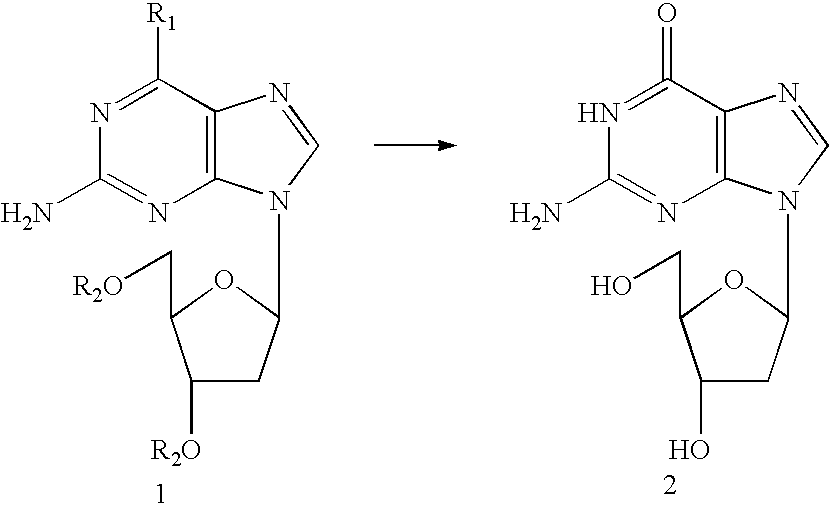
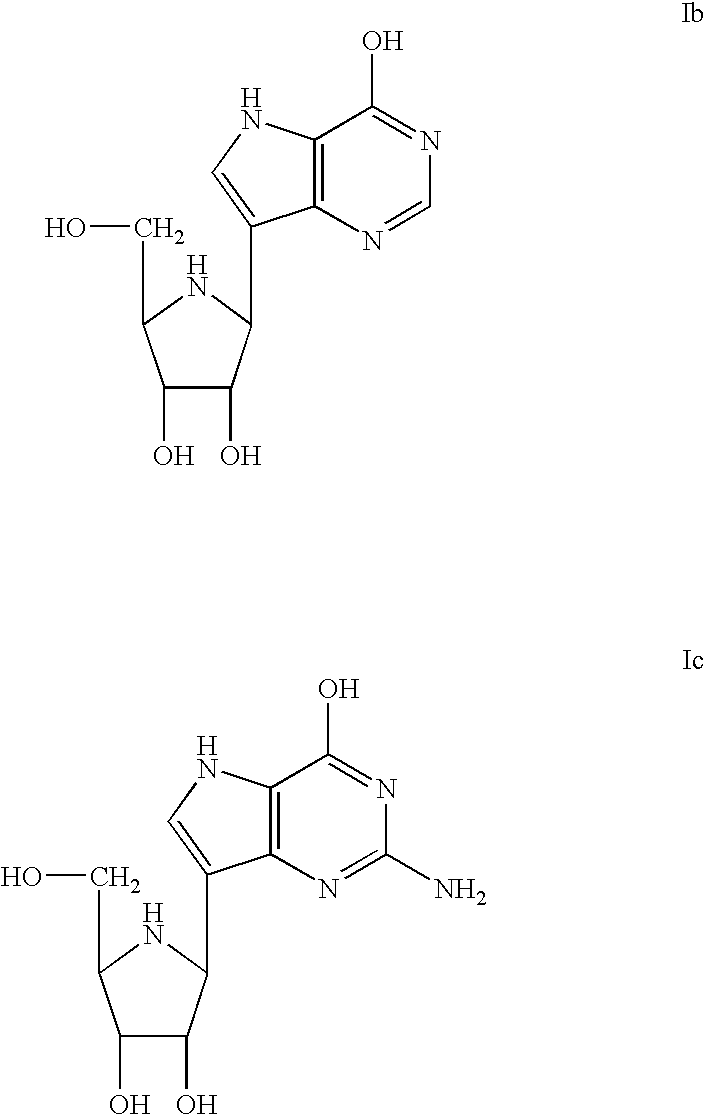
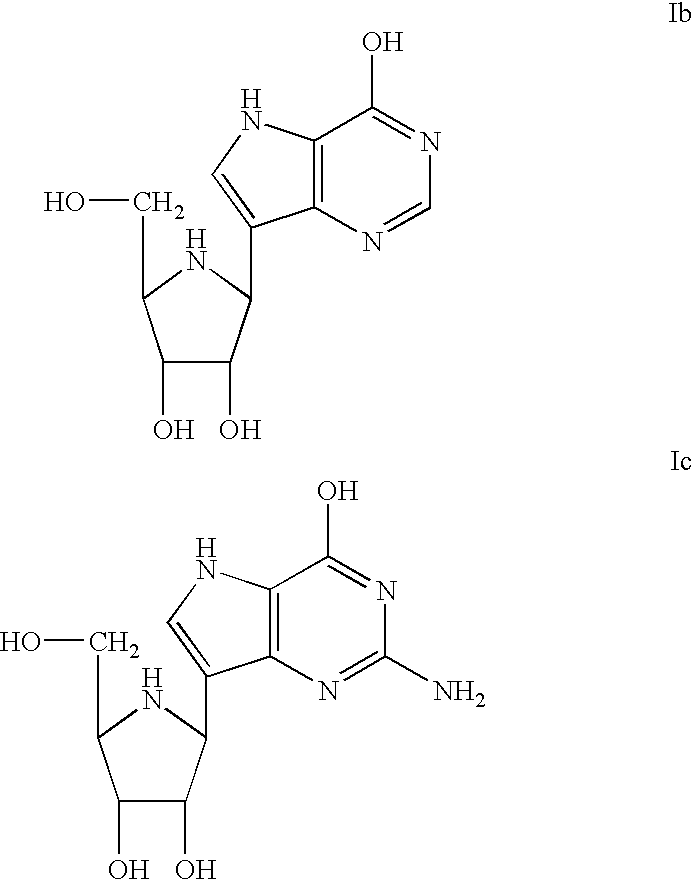
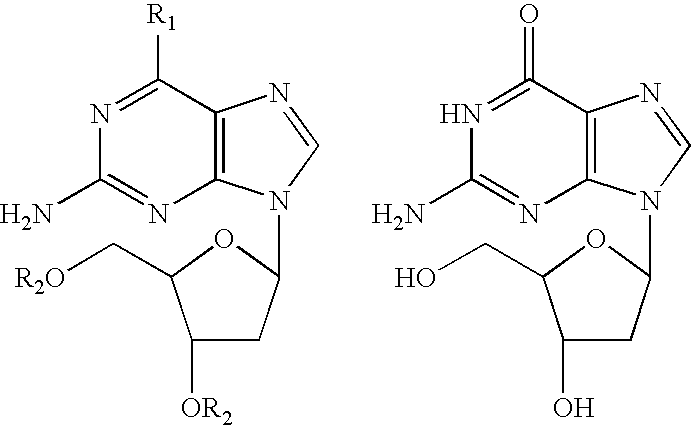
Deoxyguanosine is composed of the purine nucleobase guanine linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose. It is similar to guanosine, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the 2' position of the ribose sugar (making it deoxyribose). If a phosphate group is attached at the 5' position, it becomes deoxyguanosine monophosphate.
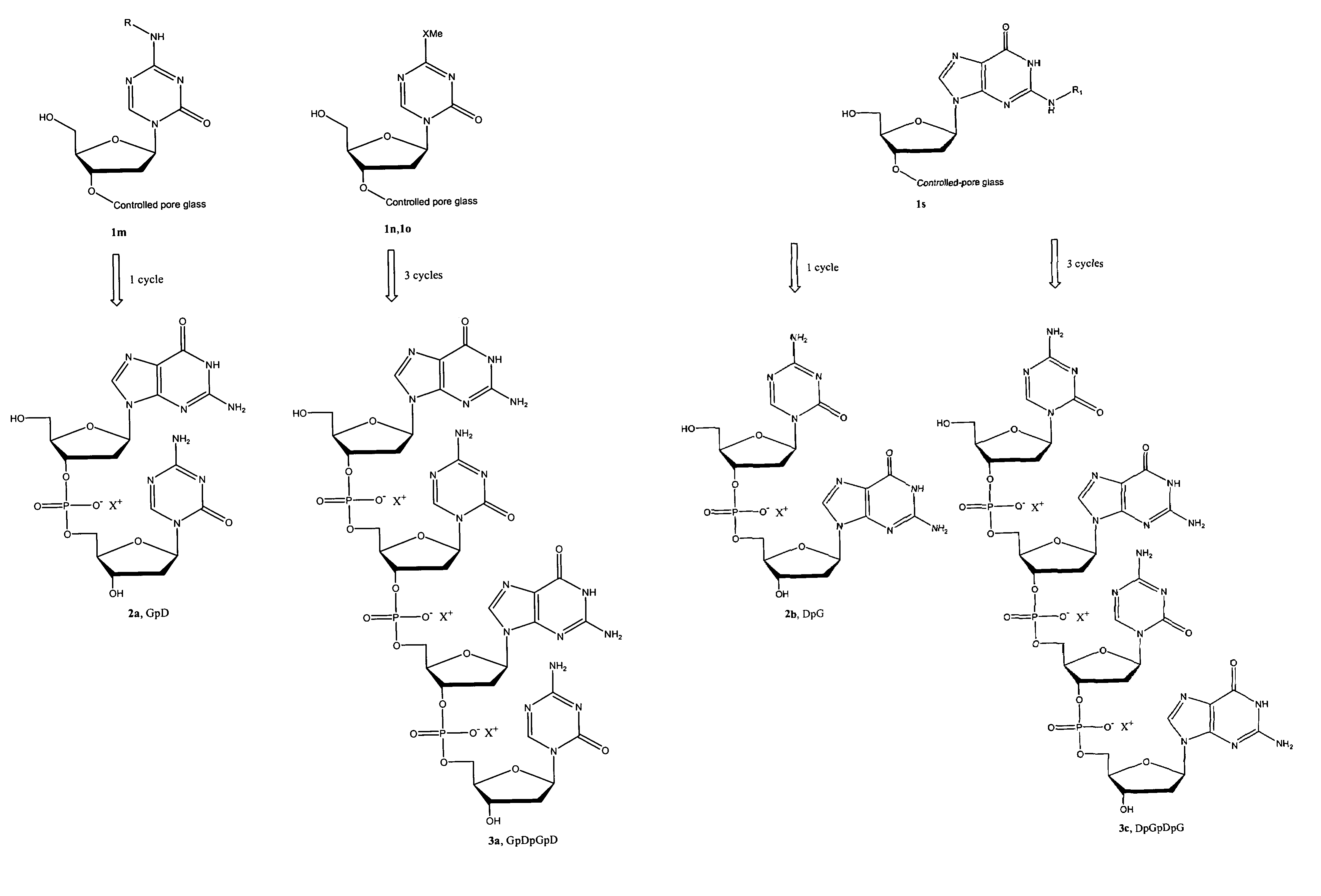
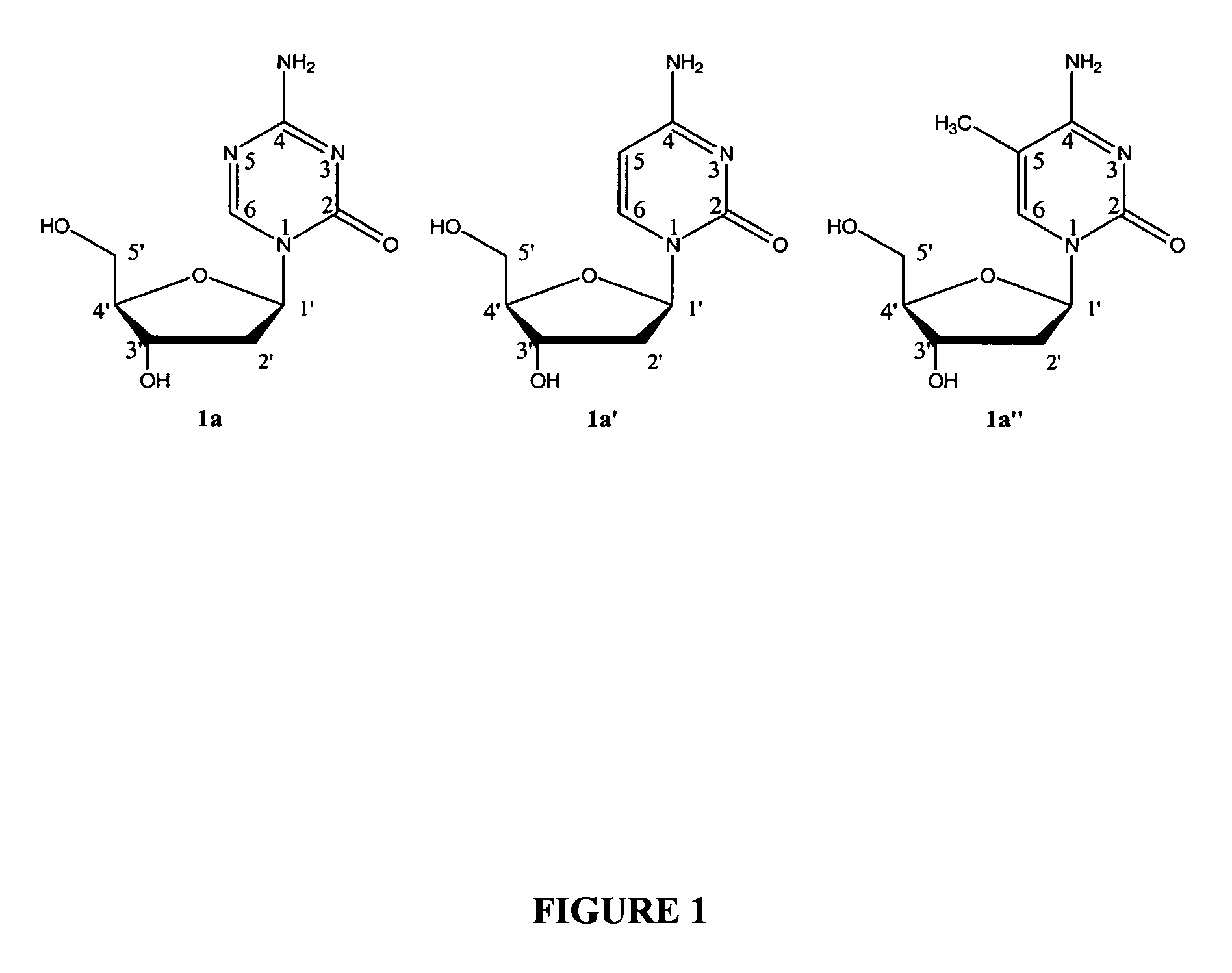
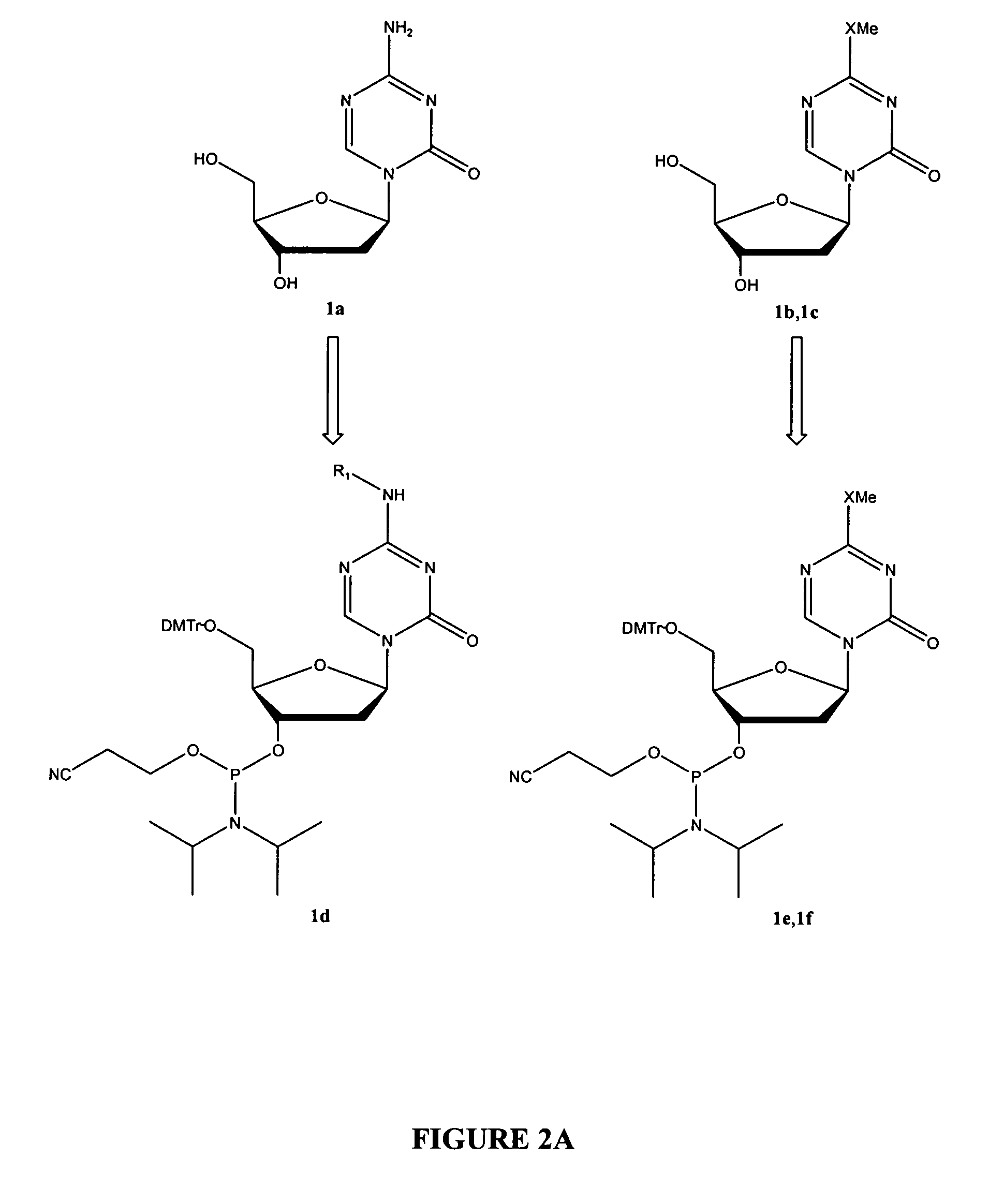
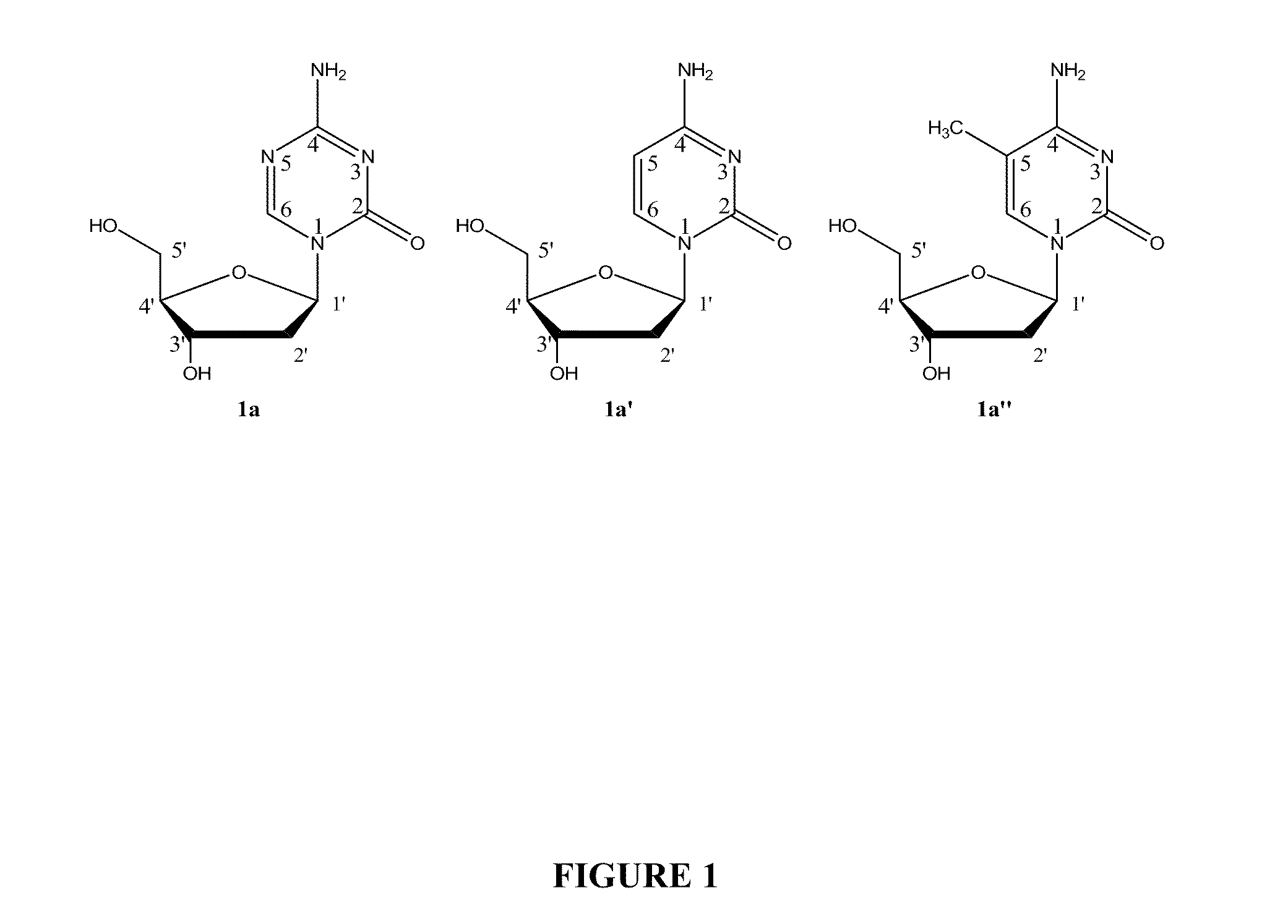
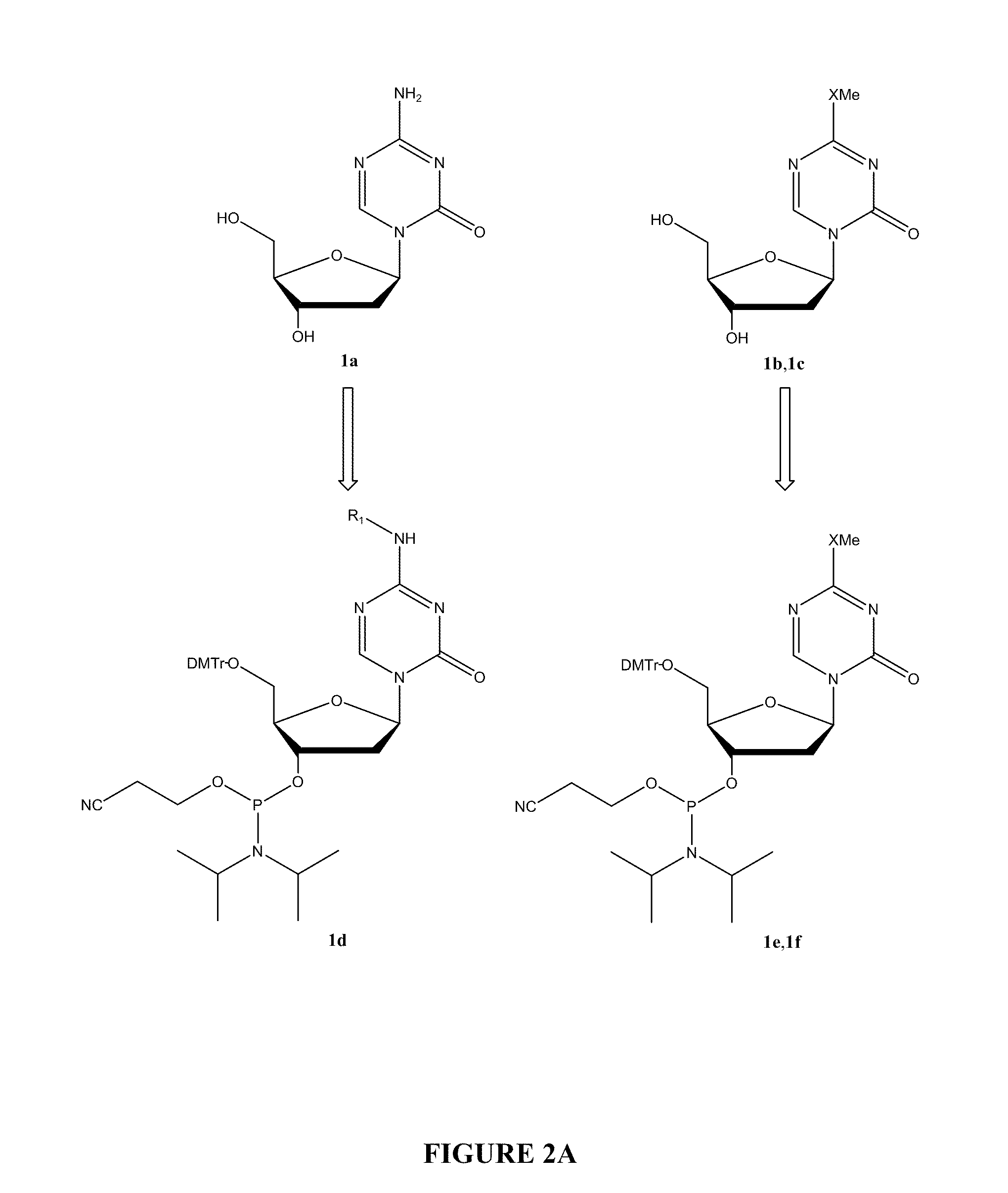
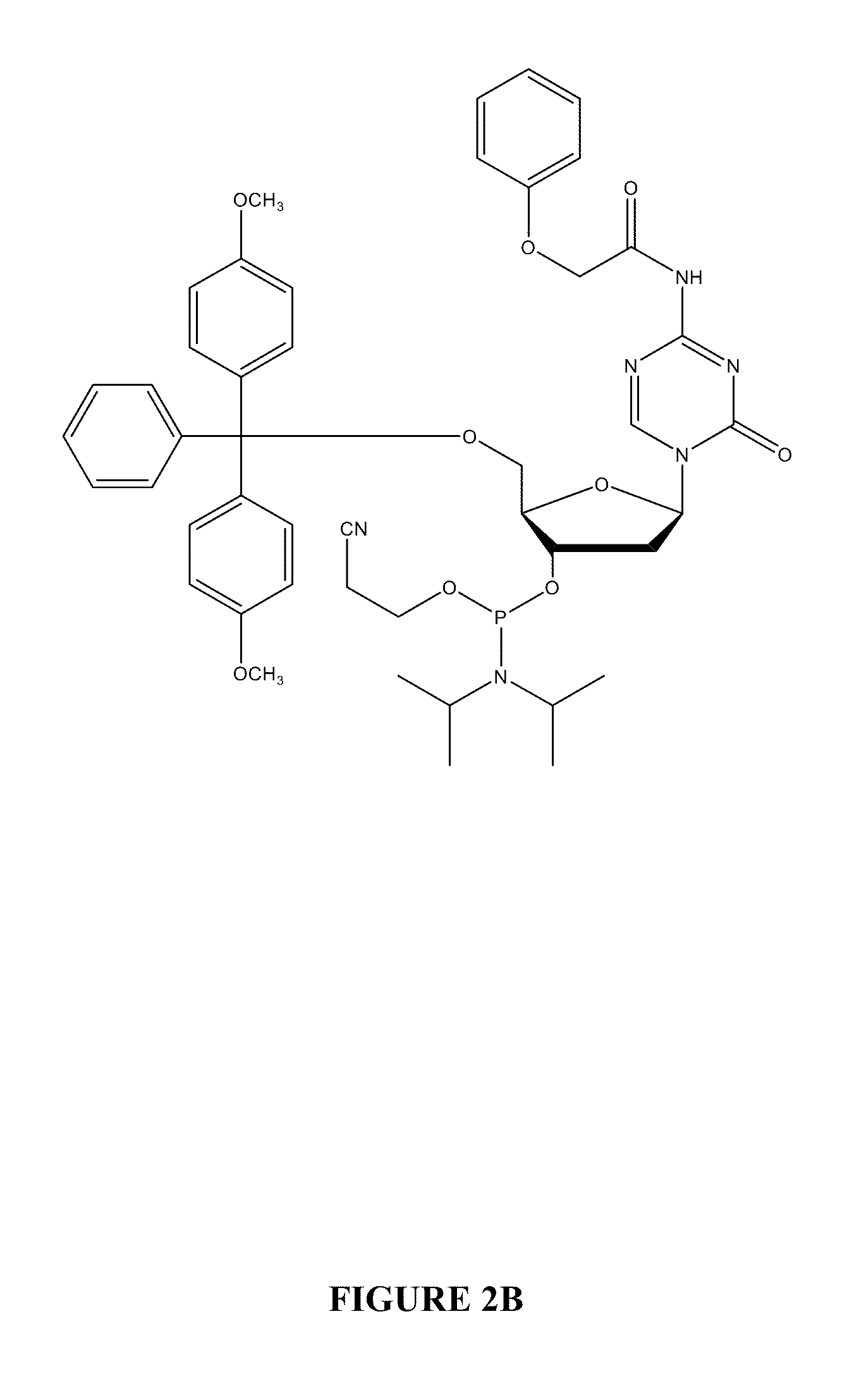
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Inhibiting T-cell proliferation
InactiveUS6656915B1Extended half-lifeEffective treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsT cellBiology
Enhancement of T-cell proliferation in a host inhibition is provided by administering 2'-deoxyguanosine and / or prodrug thereof and a PNP inhibitor. The PNP inhibitor has a Ki value of 50 nanomoles or less.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Enhancing the efficacy of reverse transcriptase and dna polymerase inhibitors (nucleoside analogs) using pnp inhibitors and/or 2'-deoxyguanosine and/or prodrug thereof
InactiveUS20050250728A1Good curative effectBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsReverse transcriptaseDNA Polymerase Inhibitor
The efficacy of reverse transcriptase and DNA polymerase inhibitors (nucleoside analogs) in a mammalian host is enhanced by administering an effective amount of PNP inhibitor of prodrug of PNP inhibitor and / or an effective amounts of 2′-de-oxyguanosine and / or prodrugs thereof.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
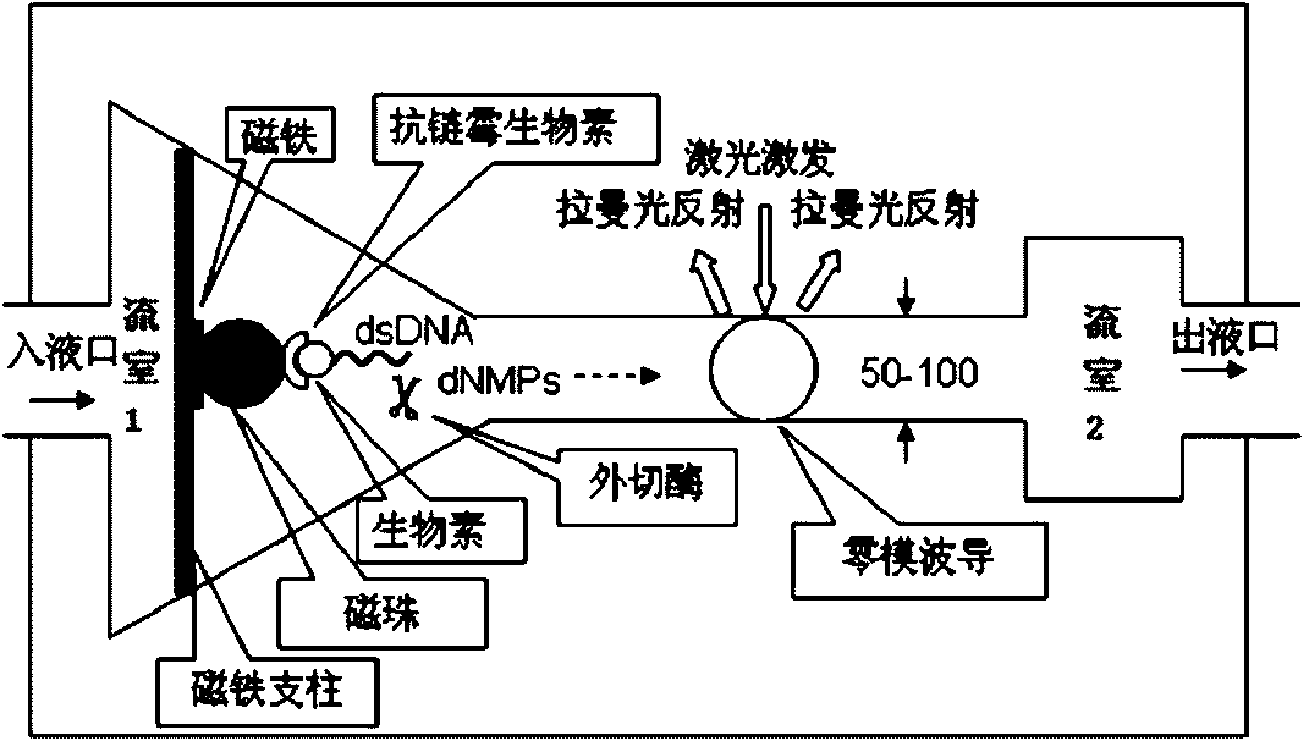
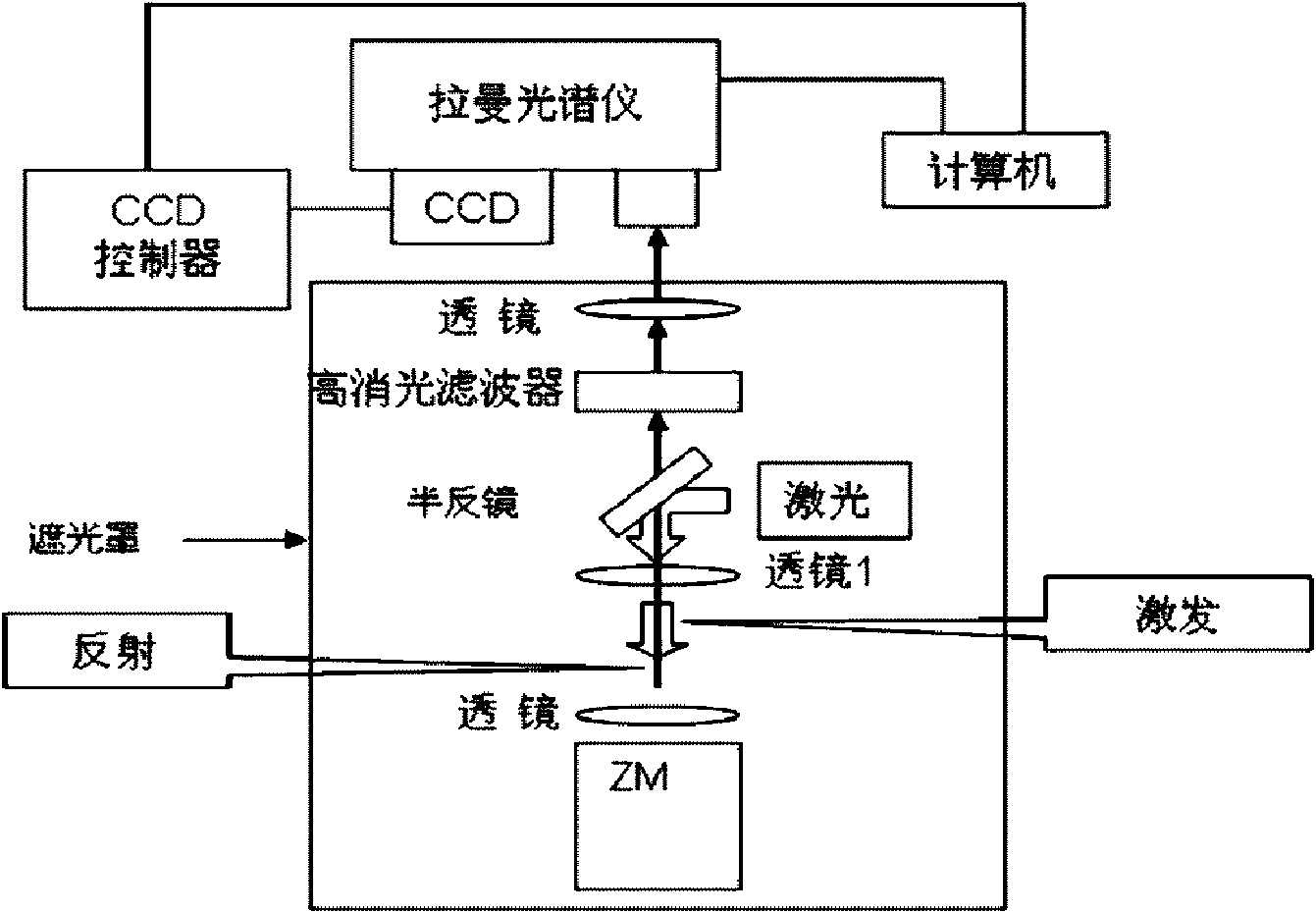
Method for testing sequence of nucleic acid single molecule
InactiveCN101654712AFast measurementHigh assay qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringPhosphoric acidWaveguide
The invention relates to a method for testing a sequence of a nucleic acid single molecule in the technical field of biology, which comprises the following steps: respectively detecting Raman spectrumsignals of deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphoric acid, deoxyguanosine 5'-phosphoric acid, deoxycytidine 5'-phosphoric acid, deoxythymidine 5'-phosphoric acid, methyldeoxycytidine 5'-phosphoric acid, adenosine5'-phosphoric acid, vernine 5'-phosphoric acid, cytidine 5'-phosphoric acid and uridine 5'-phosphoric acid and establishing a standard curve; cutting a nucleic acid molecule to be detected by exonclease and detecting the Raman spectrum signal transmitted by a cut product when passing through a zero mode waveguide by the trigger of a laser; converting the Raman spectrum signal obtained in the step2 into concrete ribotide according to the standard curve obtained in the step 1 and obtaining the concrete sequence of the nucleic acid molecule to be detected by combining the cutting direction of the exonclease. The method can directly detect a natural nucleic acid sequence without a mark and has high detecting speed and detecting quality and low detecting cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
ActiveUS20100215729A1Heavy metal active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseHuman DNA sequencing
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Inhibiting T-cell proliferation
InactiveUS20030114466A1Extended half-lifeEffective treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsT cellDeoxyguanosine
T-cell inhibition proliferation in a mammalian host by administering effective amounts of 2'-deoxyguanosine and / or prodrugs thereof; and certain PNP inhibitors.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
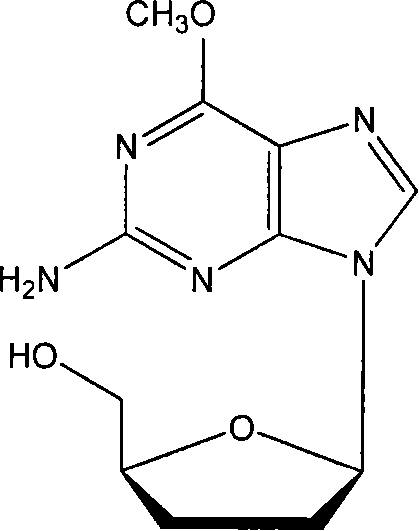
Application of 6-methocy bideoxy bideoxy guanosine in preparation of antihepatitis B medicine
InactiveCN1493301AImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemHigh resistanceHepatitis B virus
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIPINHONG PHARMA
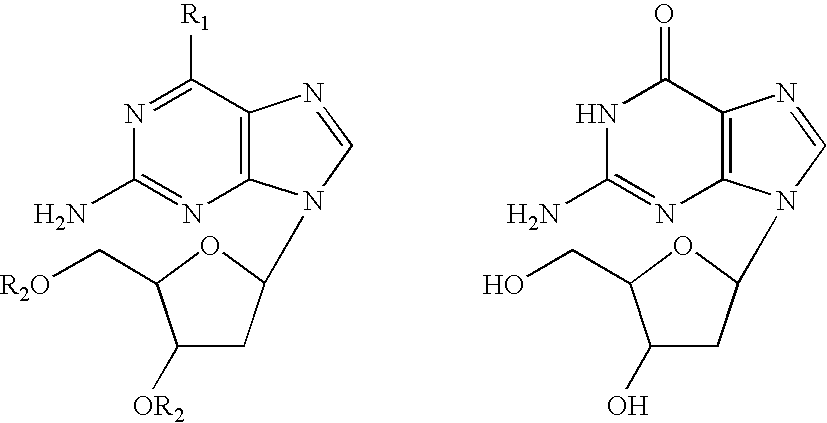
O6-alkylguanine-dna alkyltransferase inactivators and beta-glucuronidase cleavable prodrugs
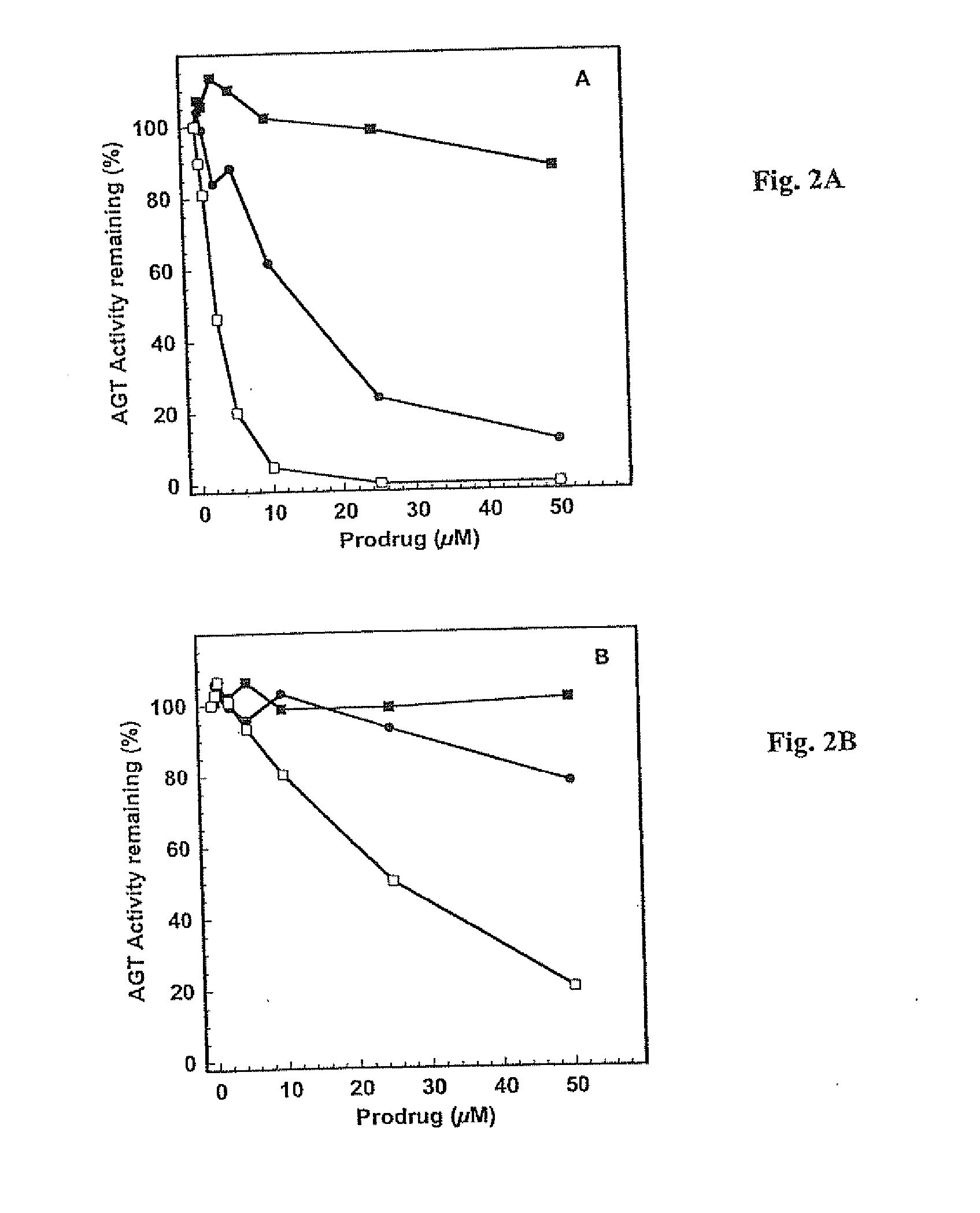
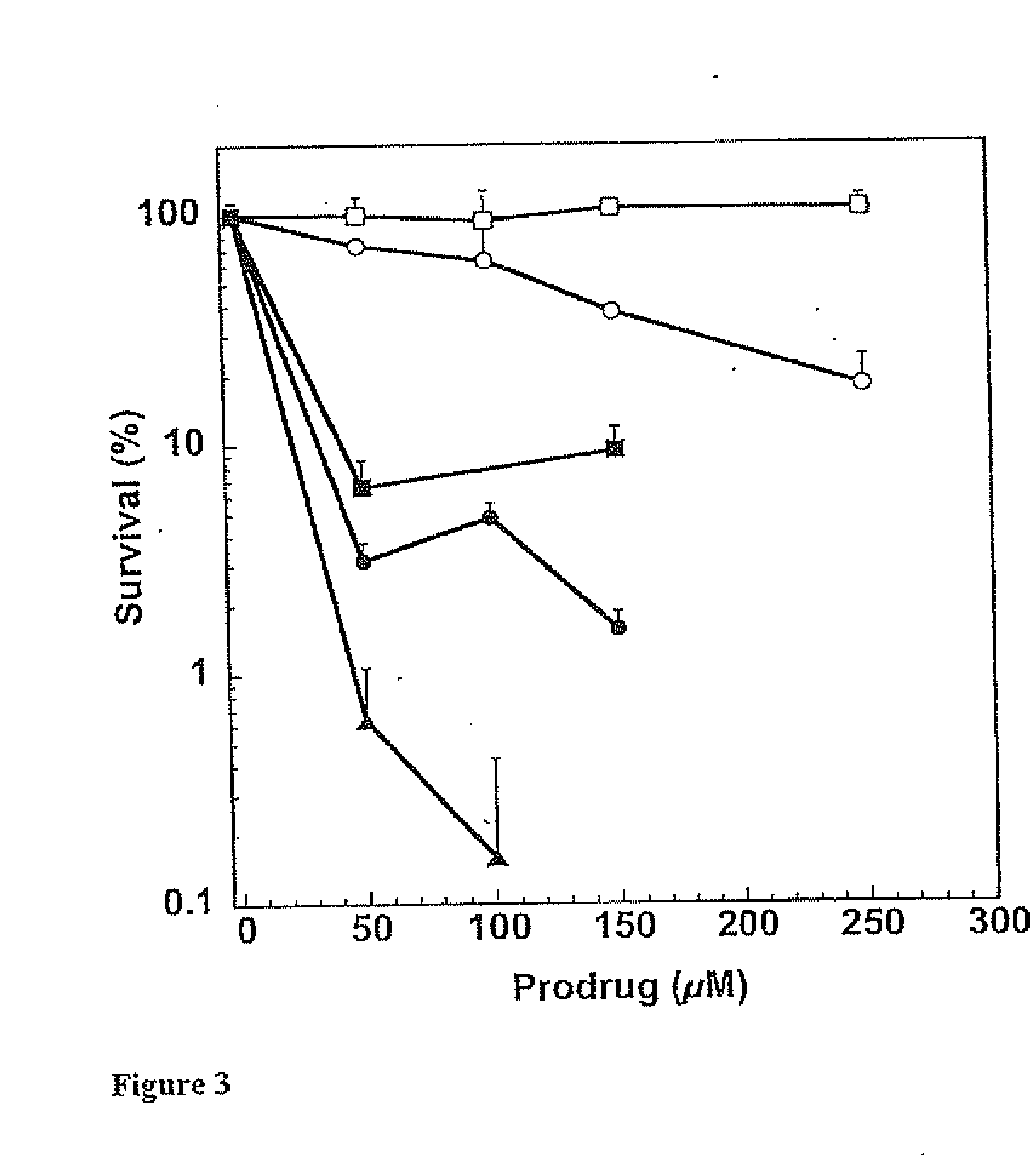
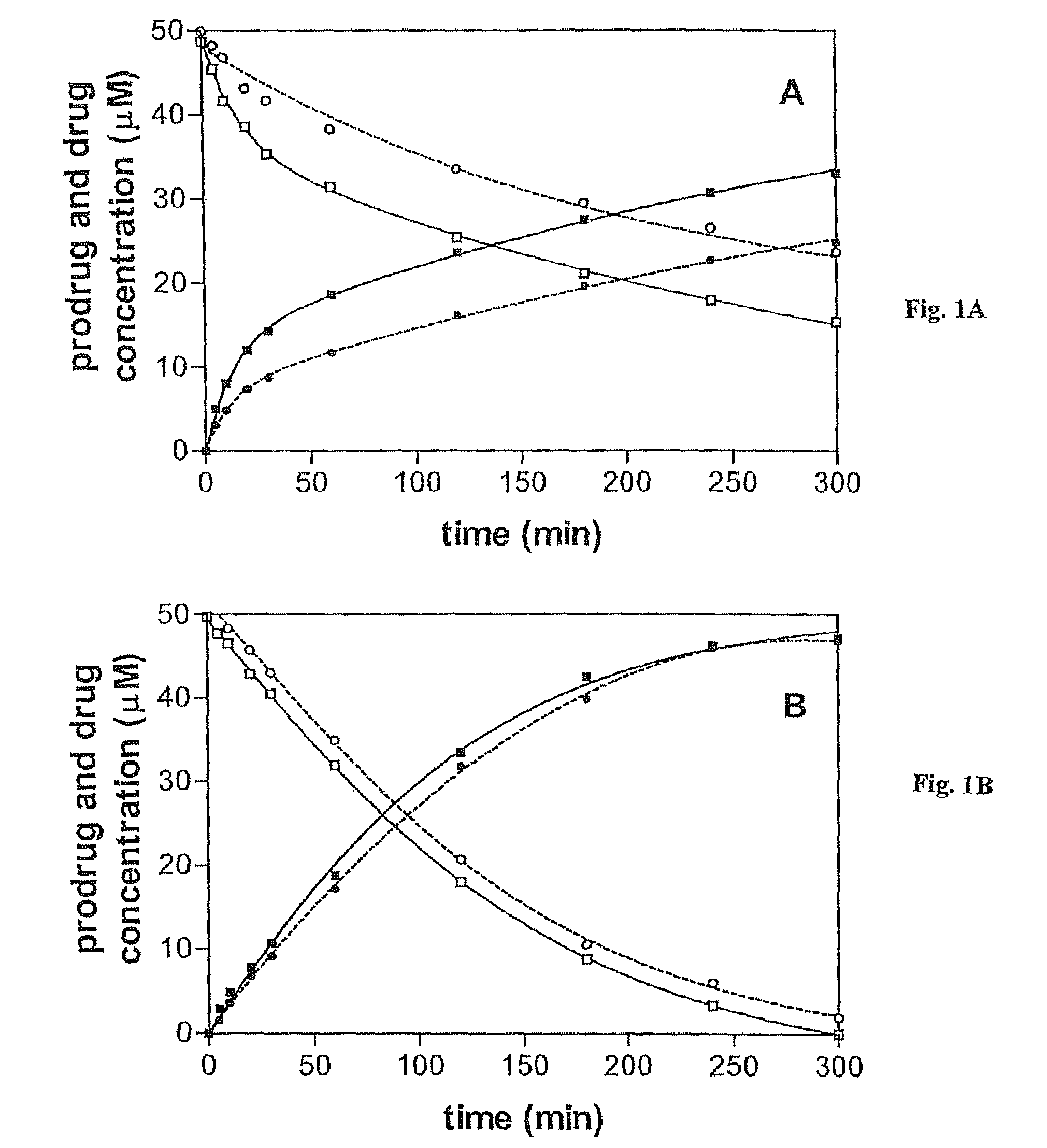
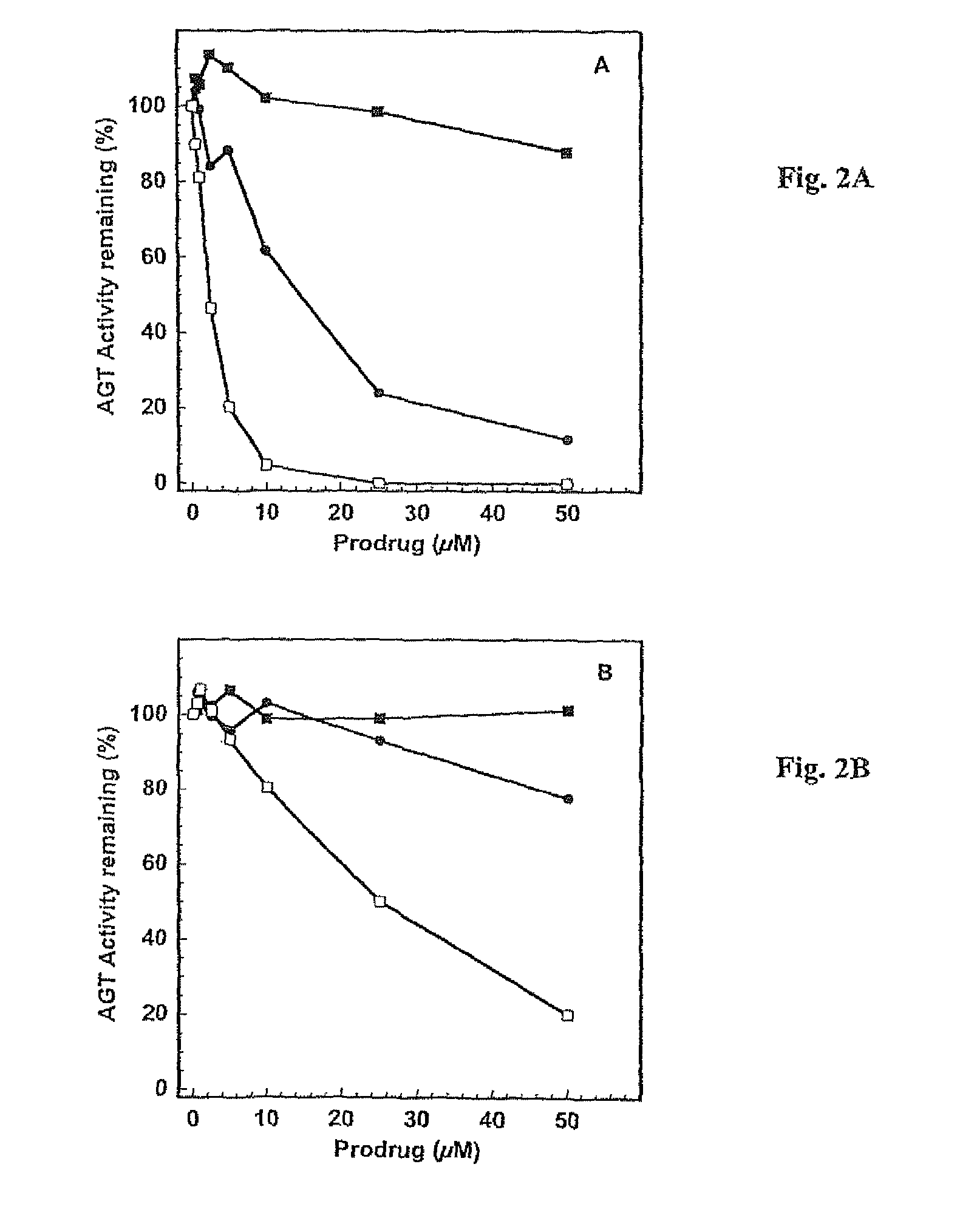
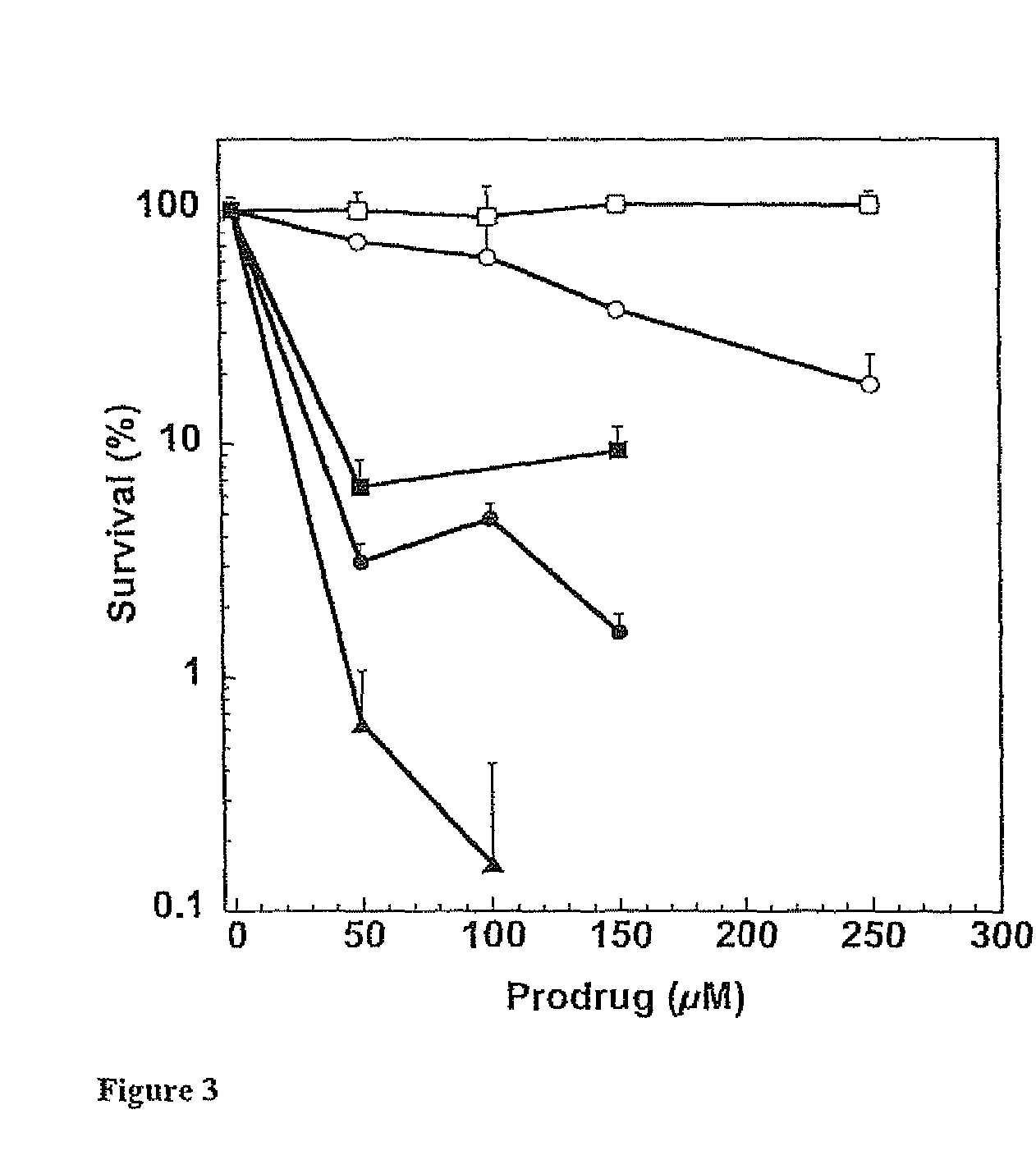
Disclosed are prodrugs of inactivators of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT). The prodrugs are cleavable by the β-glucuronidase enzyme, which is either administered to the patient or produced by necrotic tumor cells. The prodrugs are represented by the formula A-B-C, wherein A is a glucuronosyl residue linked through its 1-oxygen to the phenyl ring of B; B is a benzyloxycarbonyl group, optionally ring-substituted with one or more electron withdrawing groups; and C is an inactivator of AGT, e.g., a substituted or unsubstituted O6-benzylguanine or O6-benzyl-2′-deoxyguanosine, Also disclosed are additional inactivators of AGT, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inactivator or prodrug and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and a method of use of the inactivator or prodrug in enhancing the chemotherapeutic treatment of tumor cells in a mammal, e.g., a human, with an antineoplastic alkylating agent that causes cytotoxic lesions at the O6-position of guanine.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
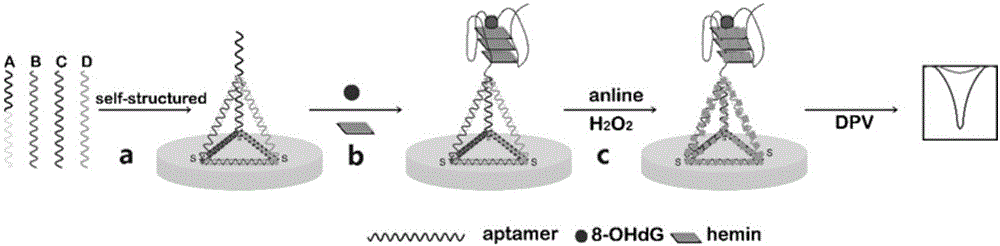
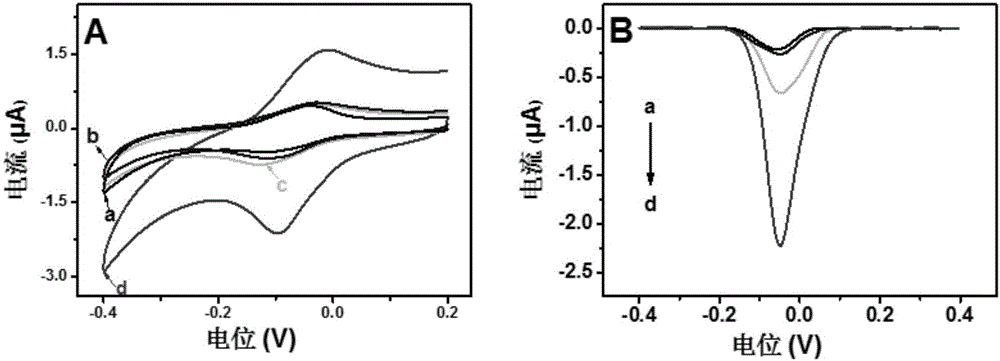
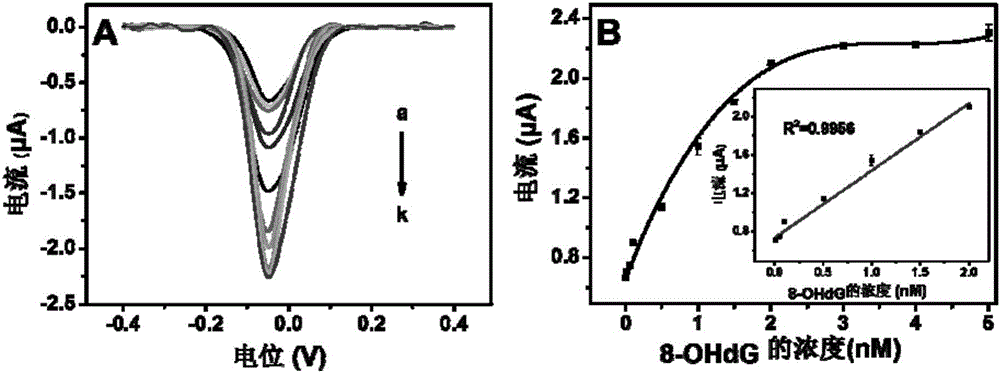
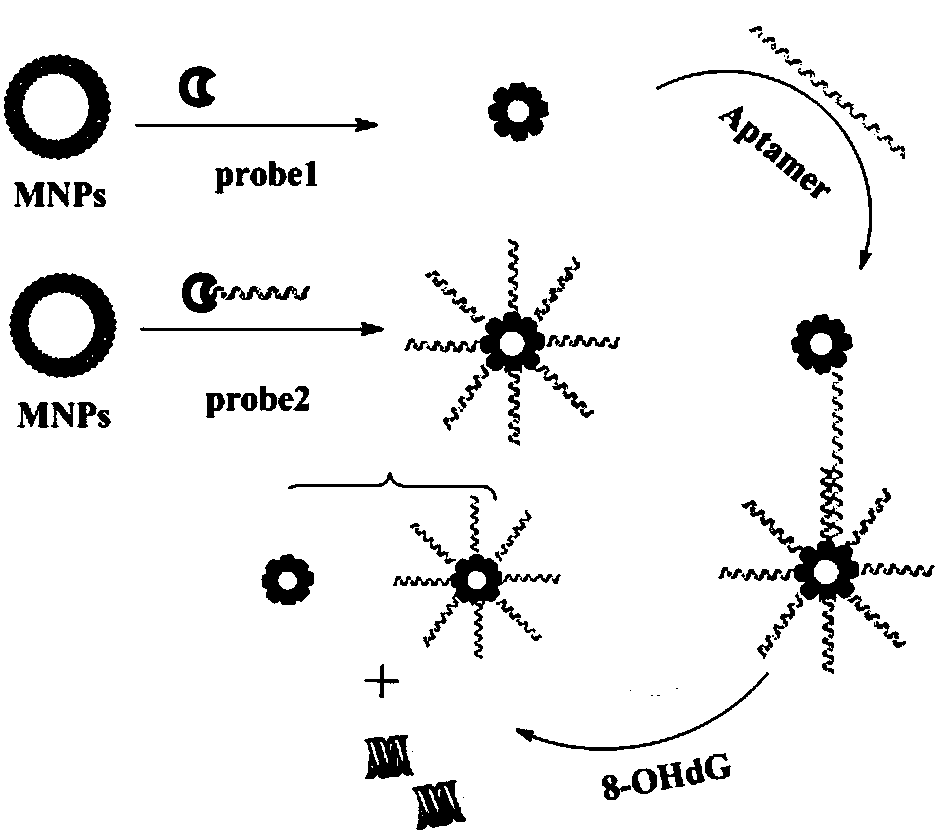
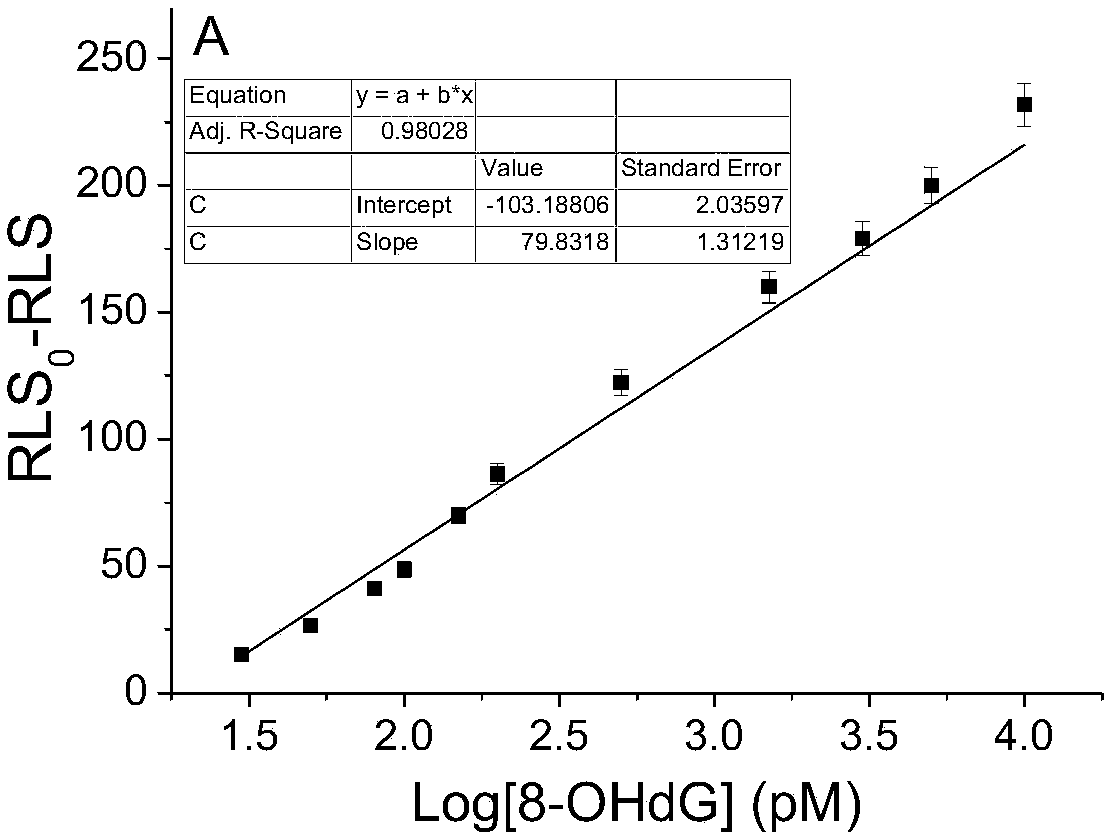
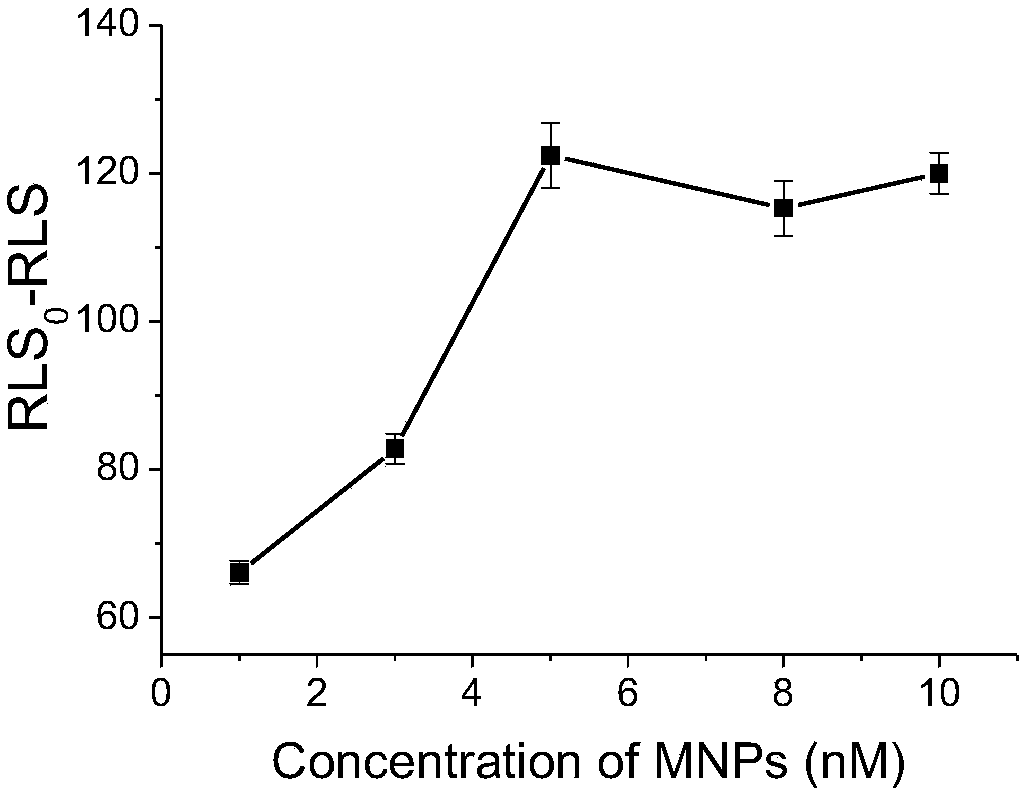
Method for quantitatively detecting activity of 8-OhdG (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine) based on aniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode
ActiveCN106442659AGuaranteed OrientationGuaranteed distanceMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerPower flow
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting the activity of 8-OhdG (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine) based on an aniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) tetrahedral structure with sulfhydryl; modifying, on a gold electrode, the DNA tetrahedral structure with the sulfhydryl to obtain an electrode of which the top end is connected with an 8-OhdG aptamer and which has the DNA tetrahedral structure with the sulfhydryl; forming a G-quadplex electrode; forming a polyaniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode; detecting a generated current signal of polyaniline by utilizing an electrochemical method, so as to detect the activity of the 8-OhdG. By using the method for quantitatively detecting the activity of the 8-OhdG based on the aniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode, the detection sensitivity on the 8-OhdG is greatly improved. In compassion with a conventional electrochemical detection method using a reduction peak of the 8-OhdG as a signal, the detection limit is decreased by two orders of magnitude. By using the method for quantitatively detecting the activity of the 8-OhdG based on the aniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode, the preparation of a complicated material and a DNA labeling probe is not needed; the defects that the preparation of the material and the DNA labeling probe causes that the detection cost is high, the operation is fussy and the reproducibility is poor can be avoided. The method for quantitatively detecting the activity of the 8-OhdG based on the aniline deposited electrochemical sensing electrode has the advantages of being low in cost, being quick, simple and convenient, and being high in sensitivity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
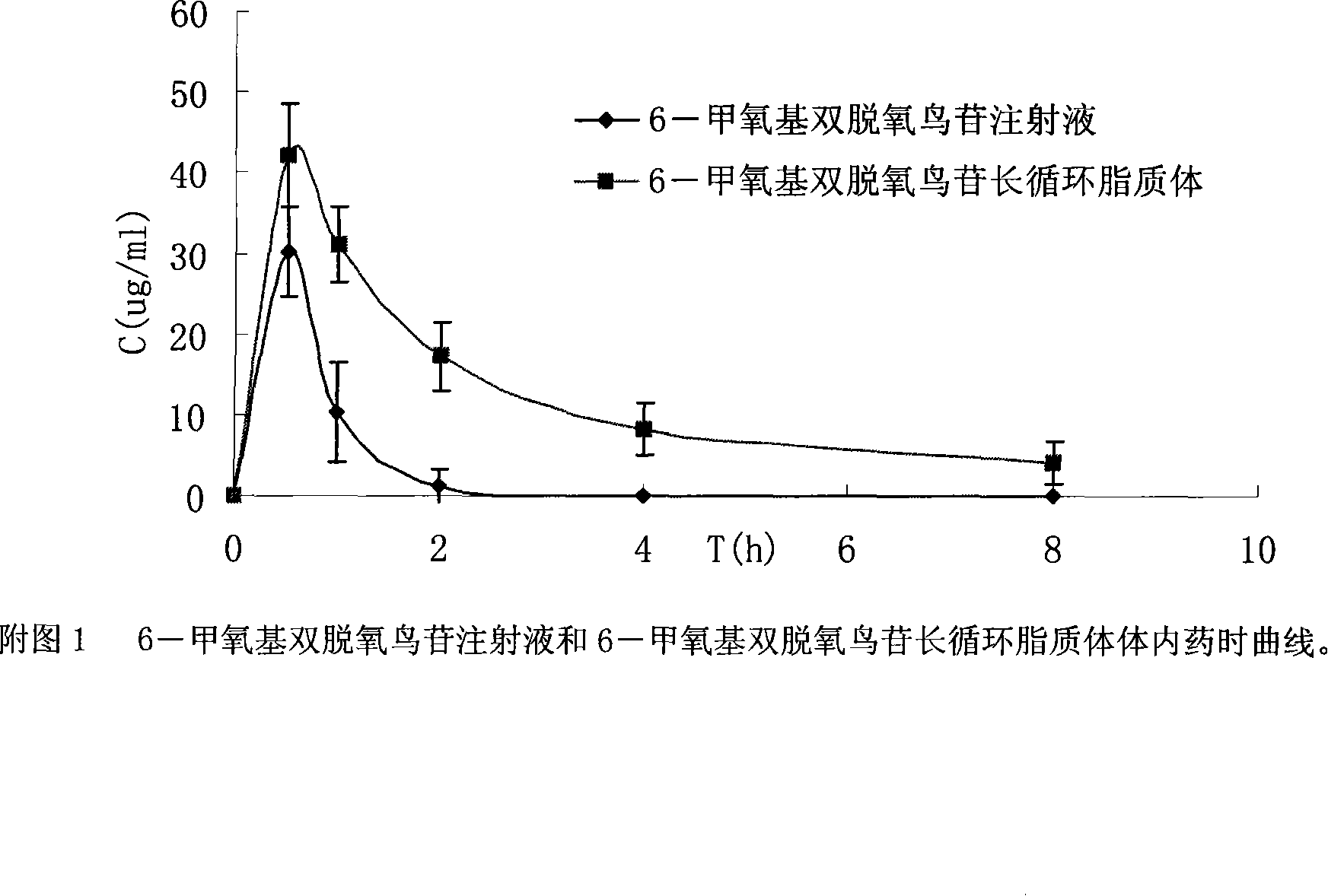
6-methocy bideoxy bideoxy guanosine long circulating liposome preparation and preparing method
The present invention relates to a liposome preparation containing 6-methoxydideoxy-guanosine. Said liposome is a vesicle of lipid double-layer membrane formed by using phospholipids as main membrane material, the metacawei is enveloped in the internal water phase of said liposome, and the outer surface of said liposome is modified by hydrophilic macromolecule, so that the time of that said liposome preparation is remained in the blood can be prolonged so as to raise the bioavailability and therapeutic effect of medicine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
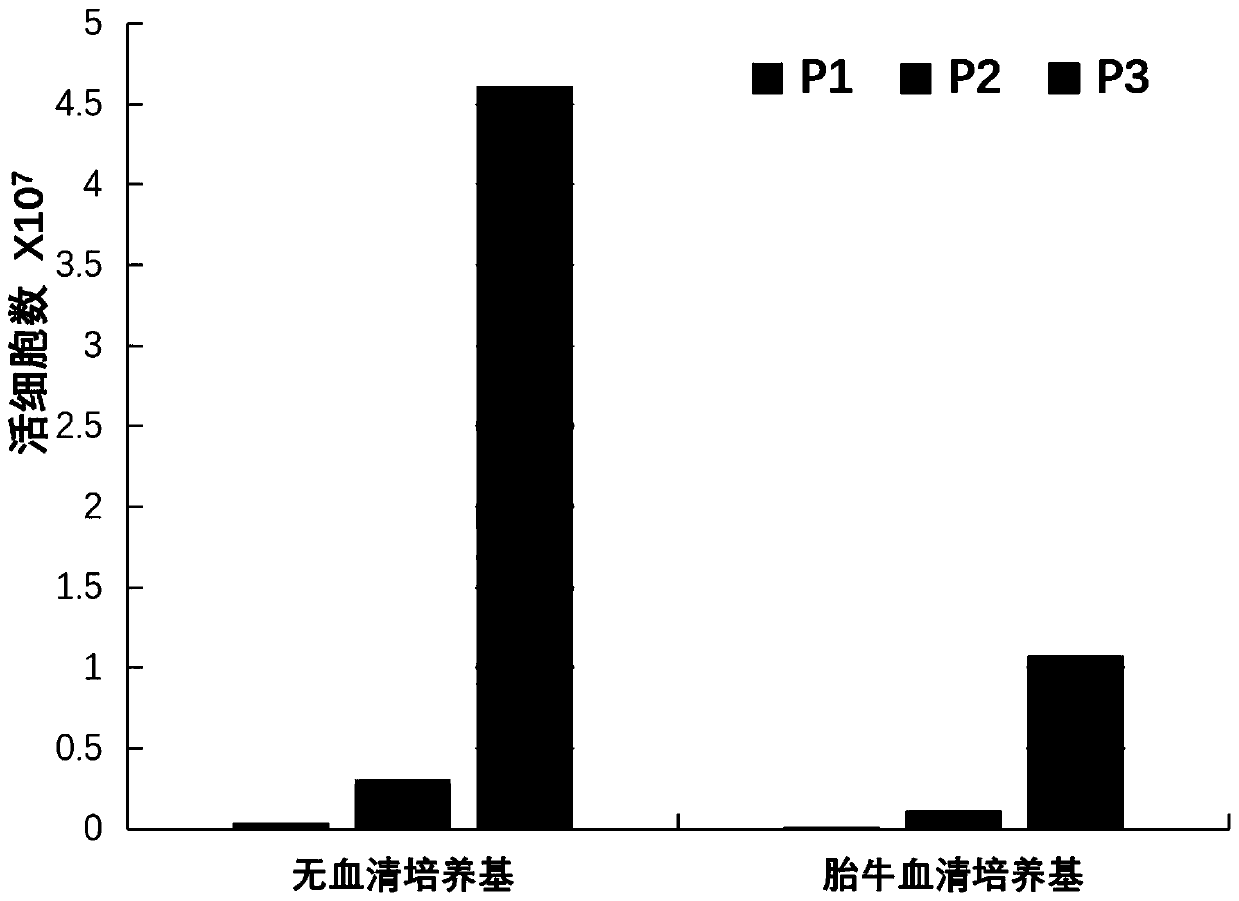
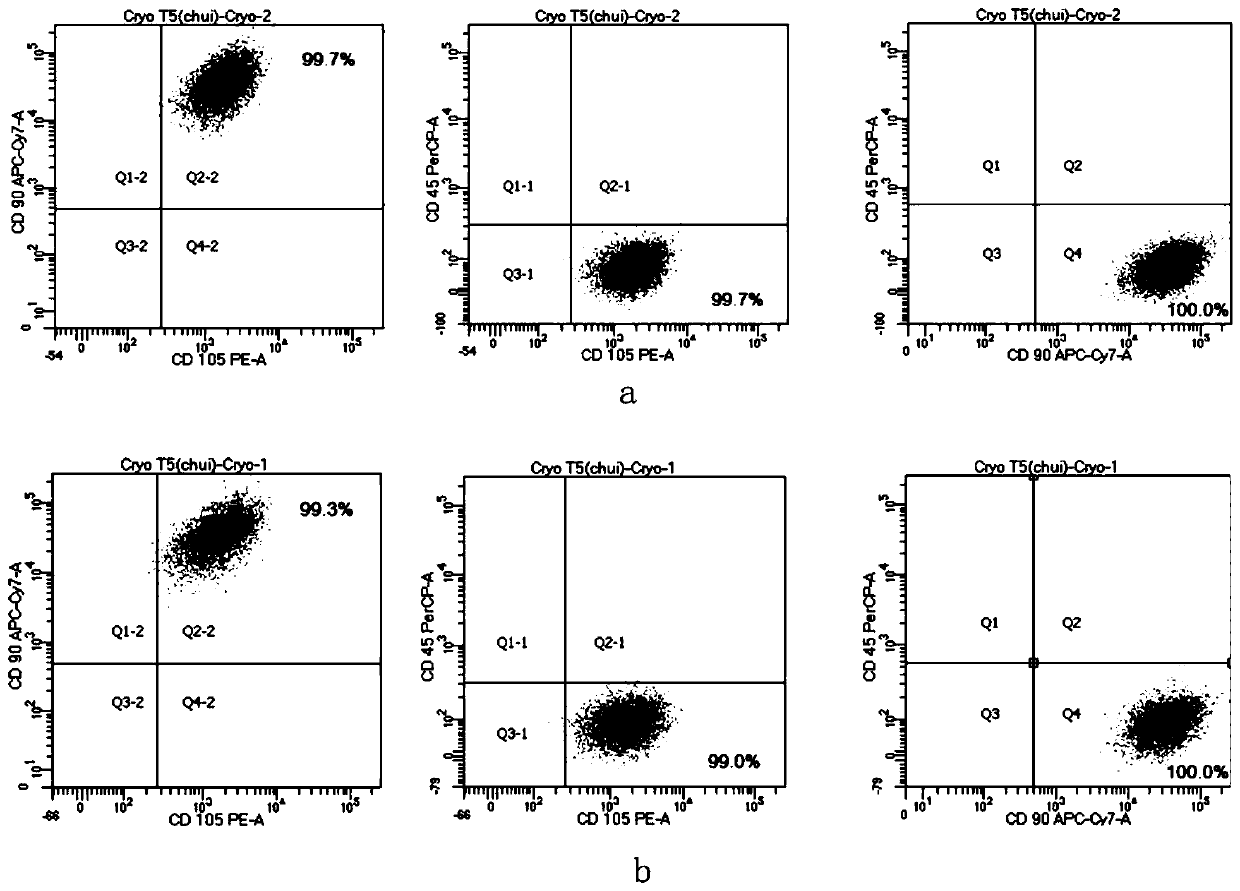
Serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells and application thereof
ActiveCN110331130AShort cycleImprove consistencyCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHeterologousCell cycle
The invention relates to a serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells and application thereof. The serum-free culture medium comprises a basal culture medium and additive components. The additive components comprise the following components: 2'-Deoxyadenosine, 2'-Deoxycytidine-HCl, 2'-Deoxyguanosine, L-glutamine, human serum albumin, recombinant human transferrin, recombinant human insulin, rhPDGF-BB, rhFGF-b, rhTGF-beta1, rhEGF, sodium selenate and hydrocortisone. The serum-free culture medium disclosed by the invention does not contain animal-derived heterologous component such asbovine serum, and can effectively replace serum to culture bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; and due to the synergistic effect of the additive components, the culture medium has the advantages of shortening cell cycle, rapid proliferation and good cell consistency while culturing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and can effectively maintain the molecular characteristics and differentiation potential of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells obtained by the culture medium are suitable for further scientific research and clinical application research.
Owner:苏州依科赛生物科技股份有限公司
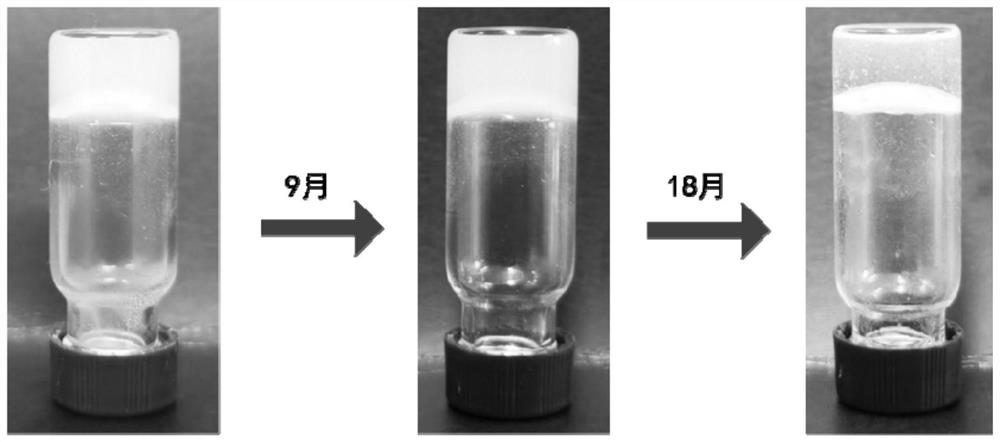
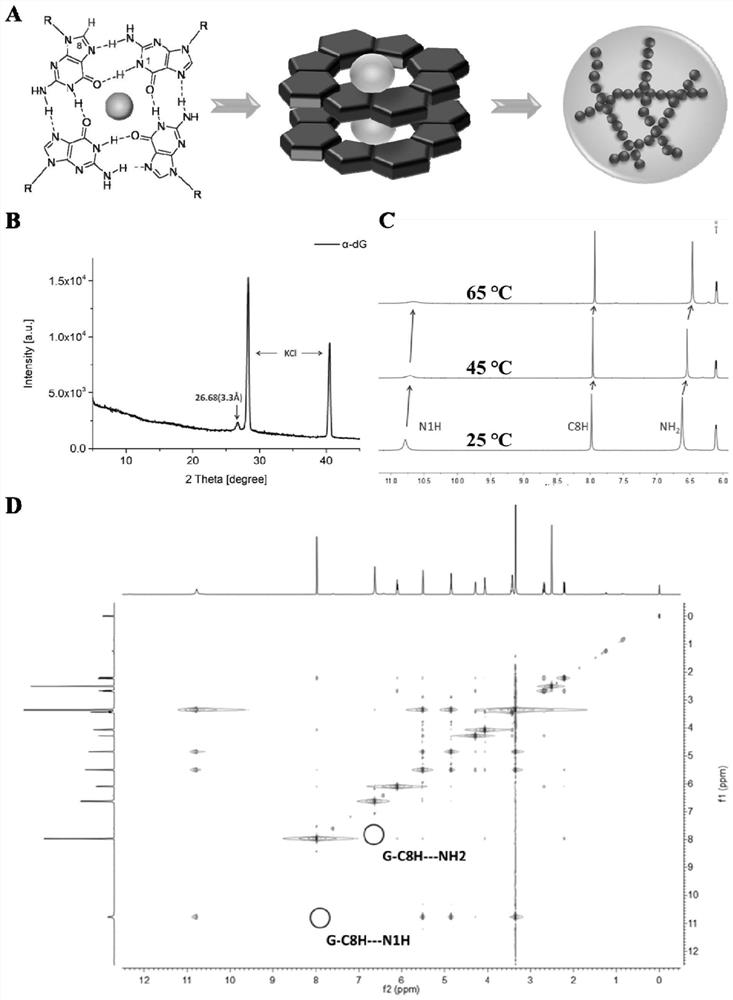
Supramolecular nucleoside hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113058076AImprove stabilityGood injectabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCoatingsDiseaseTopical treatment
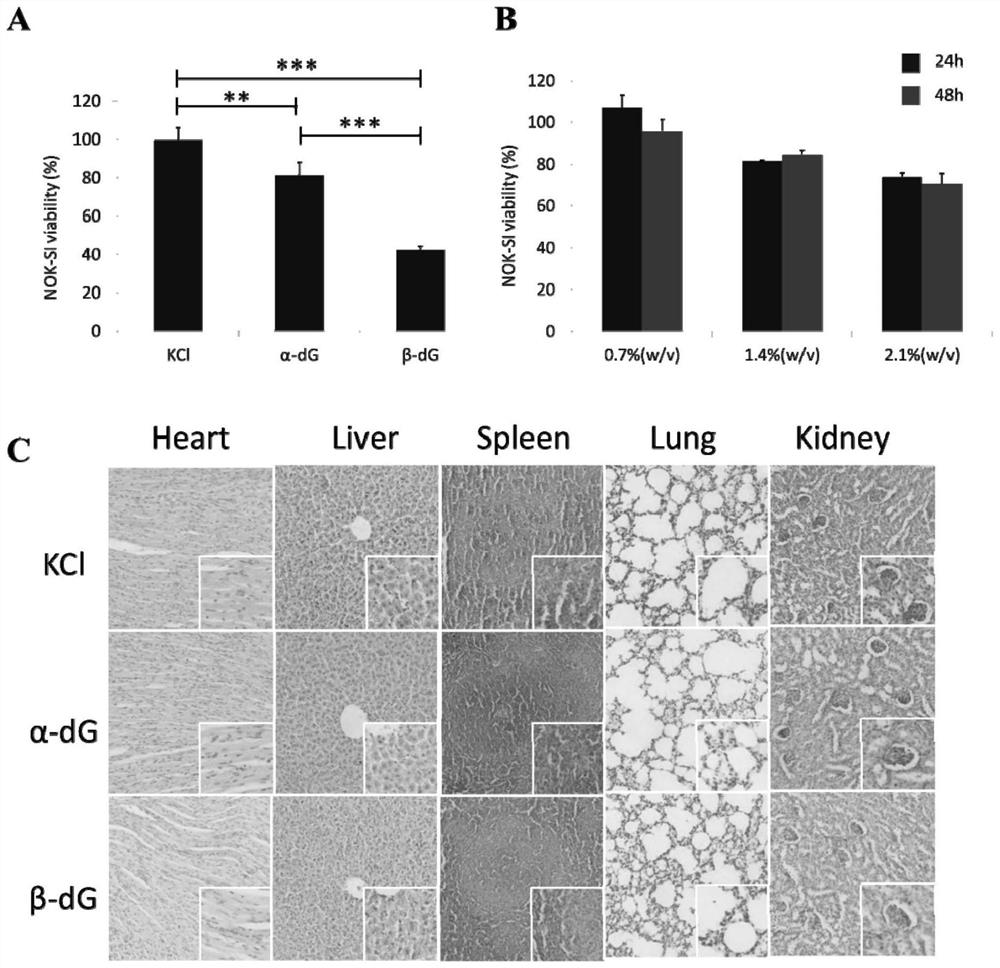
The invention provides supramolecular nucleoside hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. In a powder X-ray diffraction pattern of the hydrogel, diffraction peaks exist at 2theta diffraction angles of 26.7 degrees, 28.4 degrees and 40.5 degrees. The supramolecular hydrogel based on D-configuration alpha-deoxyguanosine is successfully constructed, the alpha-dG hydrogel has excellent stability and cannot be disintegrated and damaged after being placed for 18 months, and the problem that in the prior art, supramolecular hydrogel formed by D-type guanosine is poor in stability is solved. Besides, the alpha-dG hydrogel has good injectability, biocompatibility and drug delivery capacity, can be used as a drug carrier, and is expected to be further applied in the field of biomedicine, such as local treatment of oral mucosa diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Plant disease-resistant resistance inducer and application thereof
ActiveCN109221197AReduce the number of growthHigh activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseOxygen
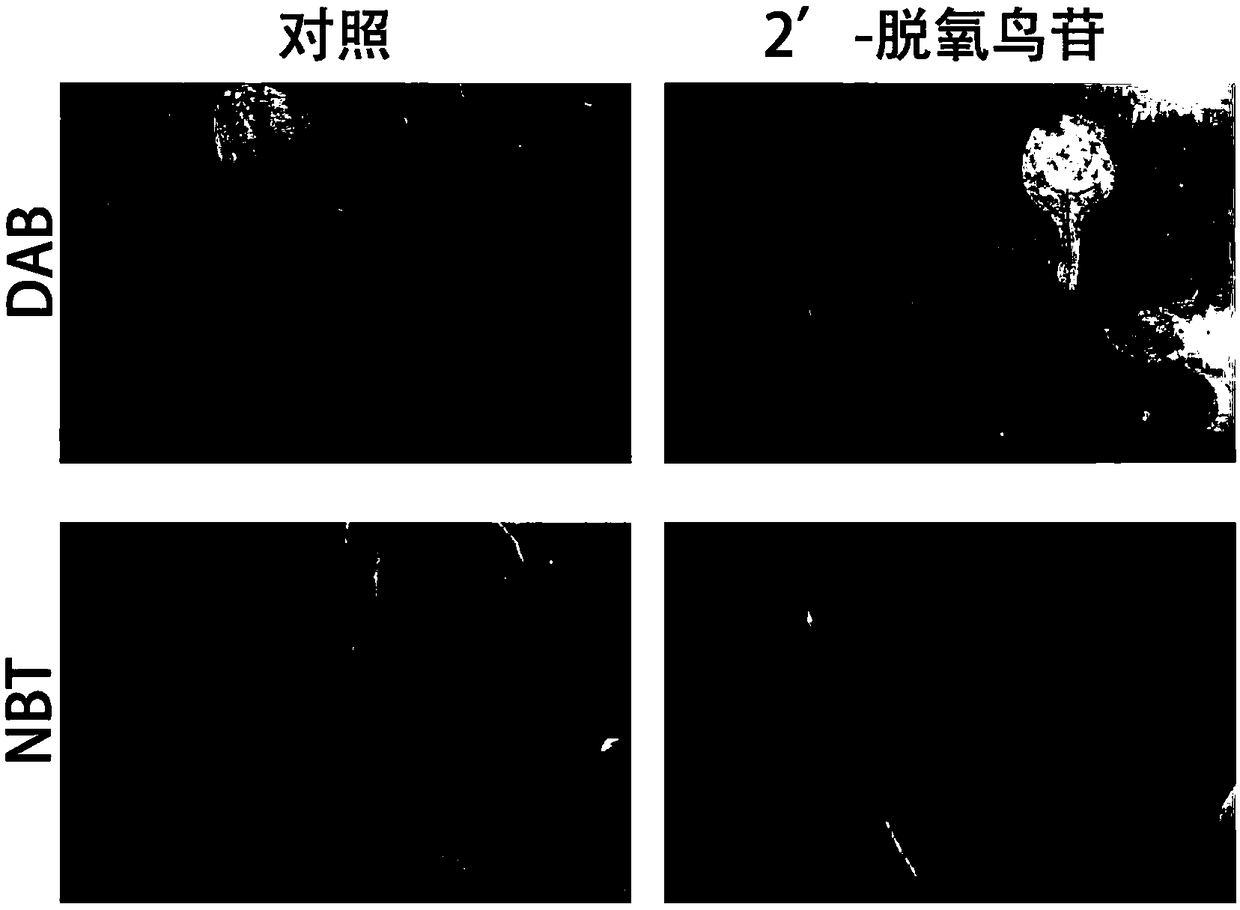
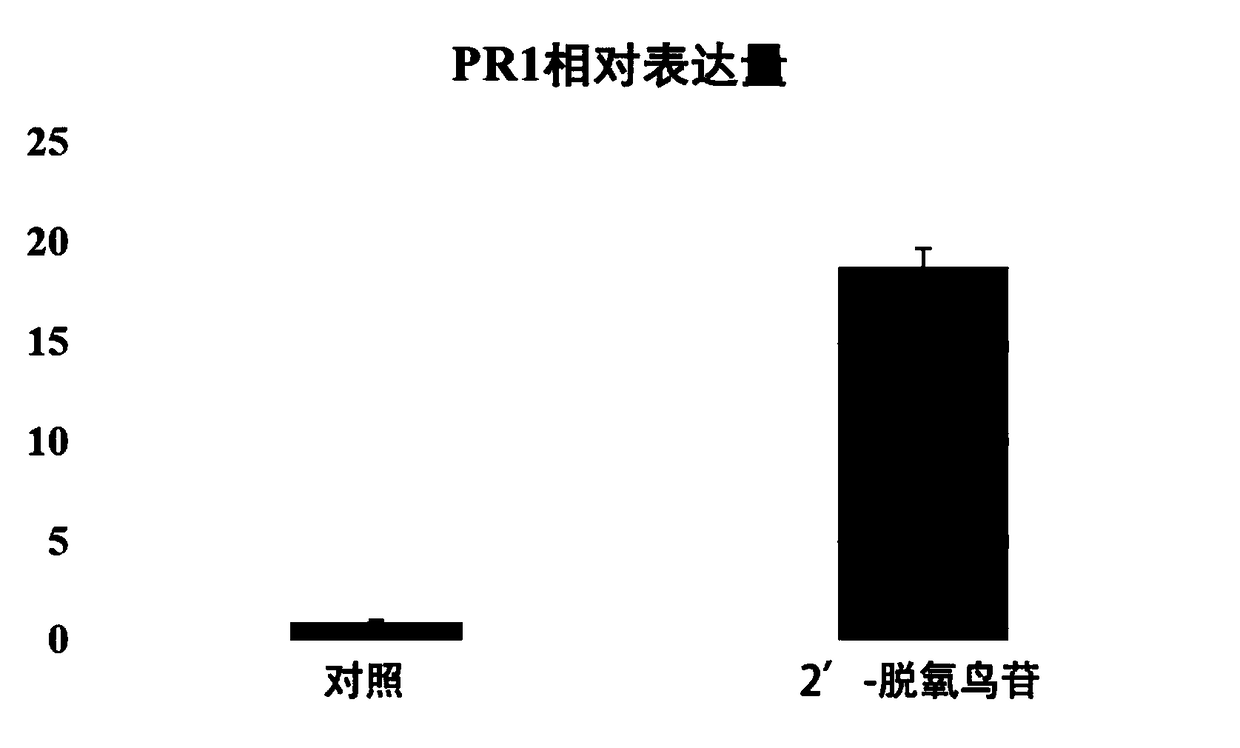
The invention discloses a plant disease-resistant resistance inducer and application thereof. Discovered that 2'-deoxyguanosine can directly cause active oxygen burst of plants and up-regulated expression of a disease-resistant gene PR1, improves the disease resistance of the plants to pathogenic bacteria and exerts the effect of the plant disease-resistant resistance inducer. 2'-deoxyguanosine iswide in source, has the characteristics of high efficiency, non pollution, low cost and the like, has a large application potential as a novel plant disease-resistant resistance inducer and accords with the requirement for sustainable and healthy development of agriculture.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Inhibiting T-Cell proliferation
InactiveUS6660719B2Extended half-lifeEffective treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsT cellDeoxyguanosine
T-cell inhibition proliferation in a mammalian host by administering effective amounts of 2'-deoxyguanosine and / or prodrugs thereof; and certain PNP inhibitors.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
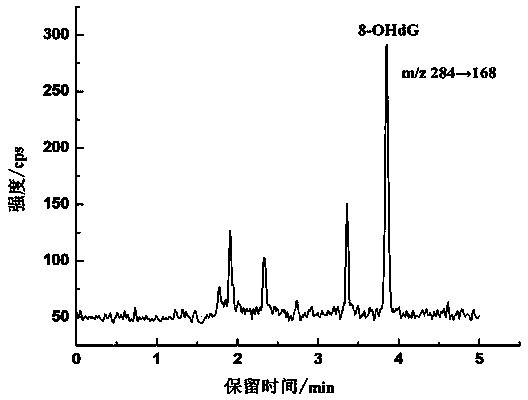
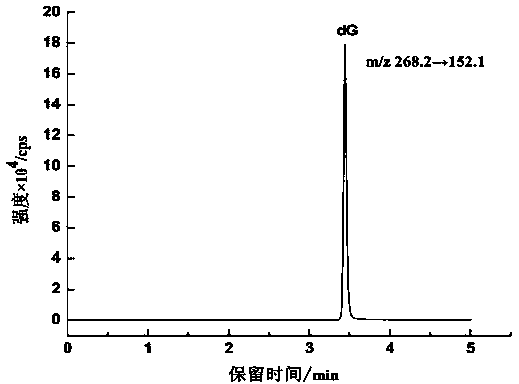
Method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 2'-deoxyguanosin (dG) in cell DNA
InactiveCN104181250AHigh sensitivityAvoid interferenceComponent separationDeferoxamine mesylateHydrolysate
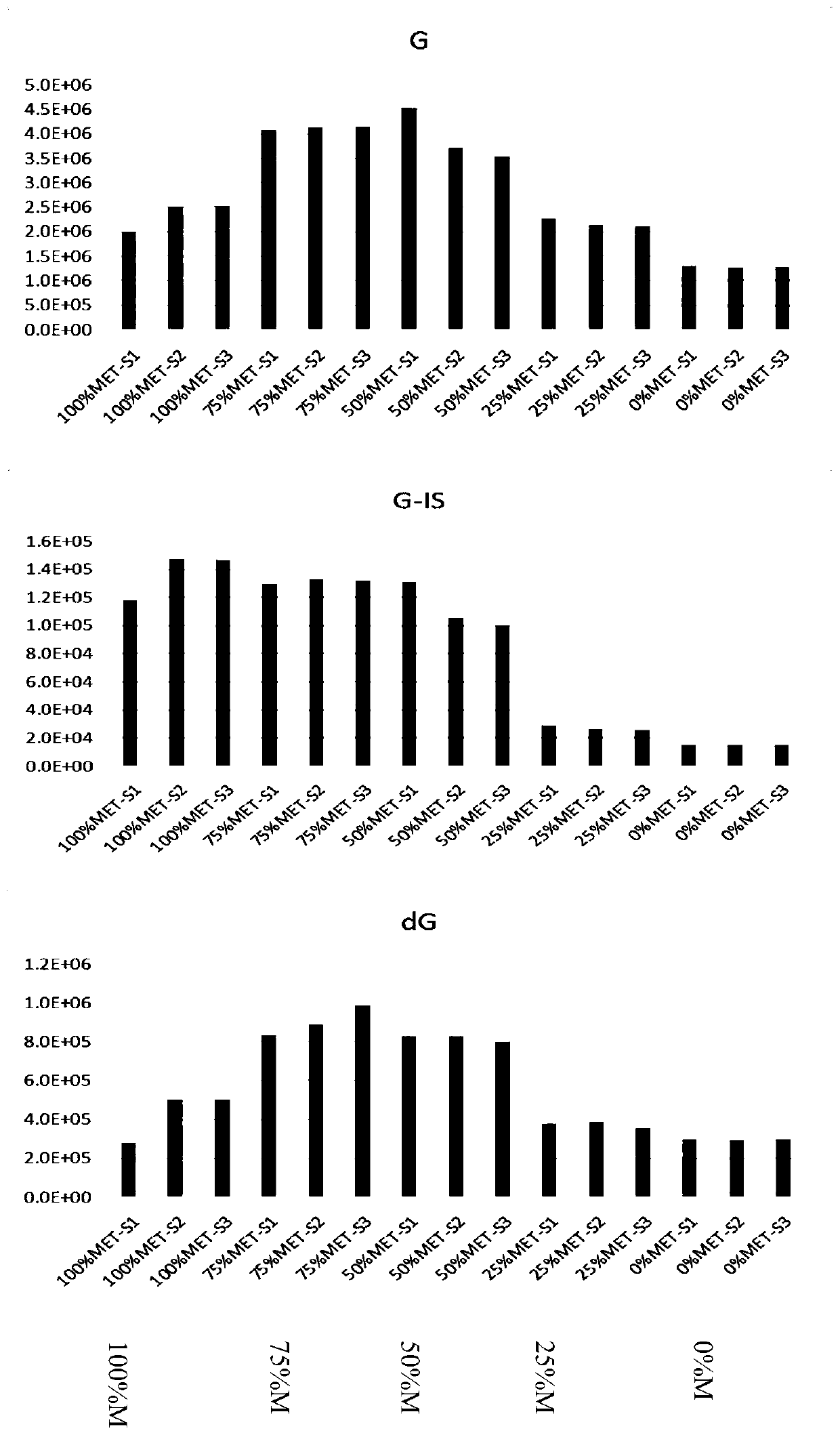
The invention belongs to a cell DNA detection technology and in particular relates to a method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 2'-deoxyguanosin (dG) in cell DNA. The method can be used for quantitatively detecting the change of the content of 8-OHdG and dG in cell DNA, caused by exposure of harmful ingredients in cigarette smoke, so that the purpose of evaluating DNA oxidation damage caused by induction of the harmful ingredients can be achieved. According to the method, deoxyribonuclease I and alkaline phosphatase are used for hydrolyzing DNA in a cell, and deferoxamine mesylate is added into enzymatic hydrolysate, so that the oxidation of dG in the enzymolysis process is avoided; enzymatic hydrolysate is detected by HPLC-MS / MS; the cell DNA oxidation damage degree is evaluated according to the value of 8-OHdG / 10<6>dG. By virtue of the method, the interference of high-concentration metal ions and artificial dG oxidation is removed, and thus the result is relatively accurate; the method is low in detection limit, high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and high in recovery rate.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2 '-deoxyguanosine by using gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatography test paper
PendingCN113447647ATo achieve the purpose of detectionGood dispersionMaterial analysisAntigenCellulose
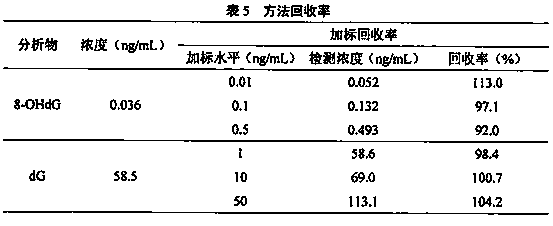
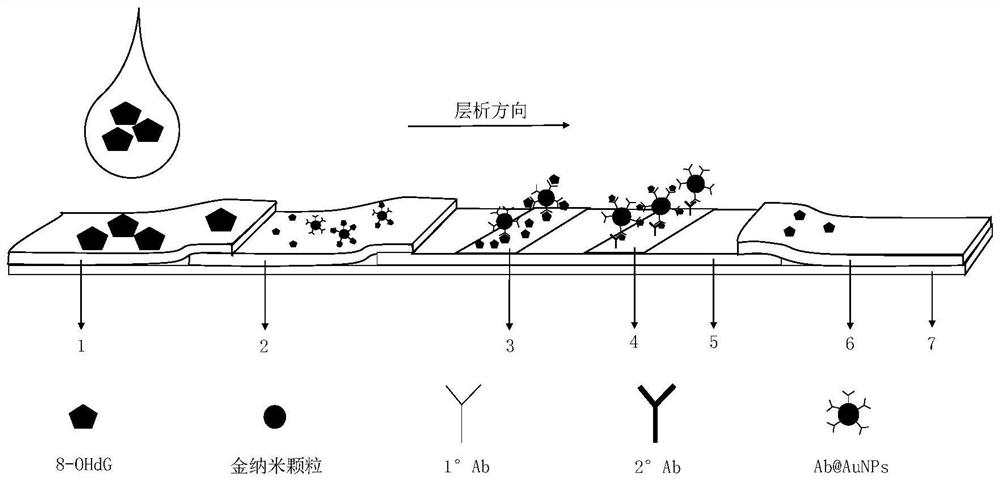
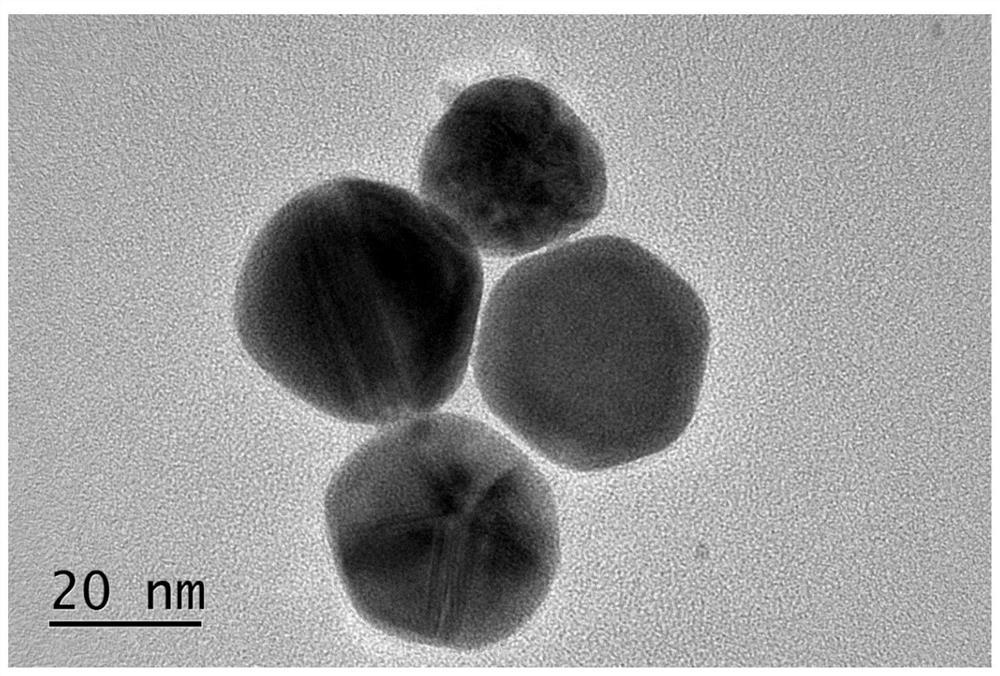
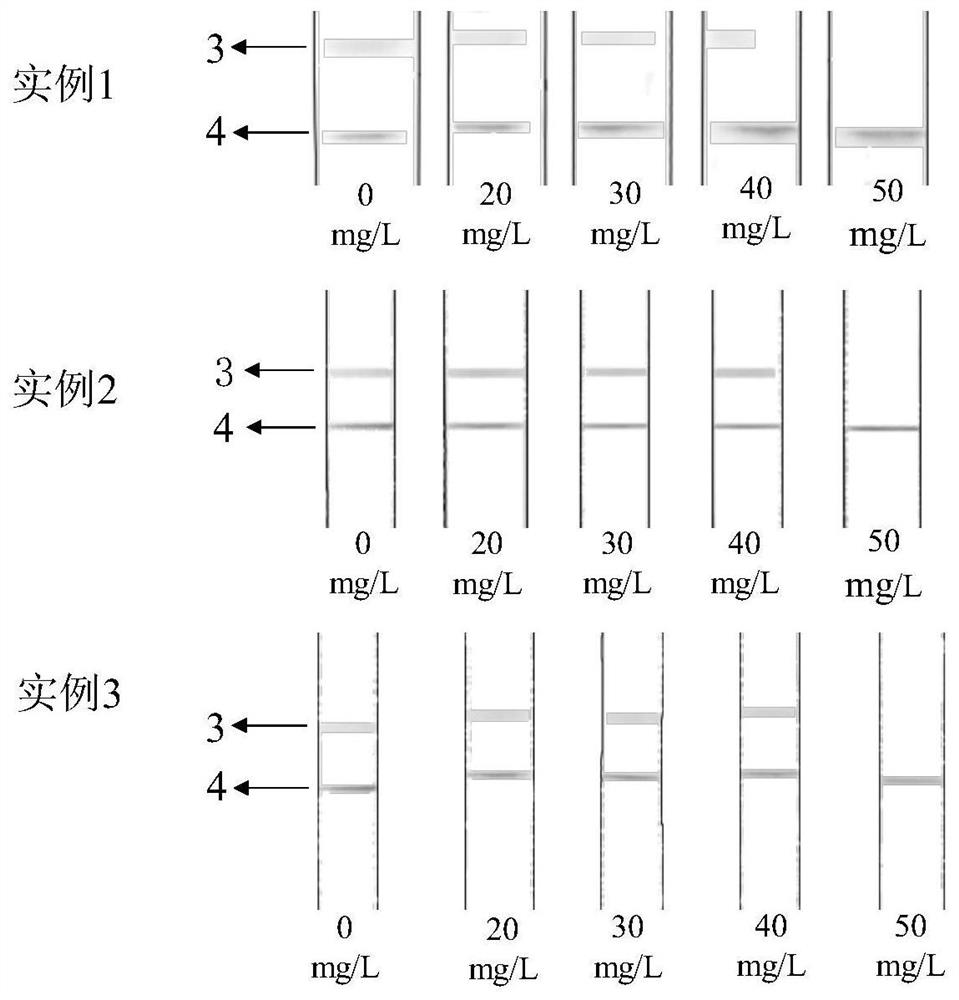
The invention relates to a method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2 '-deoxyguanosine by using gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatography test paper. The method comprises the following steps: reducing tetrachloroauric acid trihydrate by sodium citrate to prepare the gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), and coating an 8-OHdG antibody (Ab) on the outer layer of the gold nanoparticles under an alkaline condition to form Ab@AuNPs as a probe; coupling bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 8-OHdG with carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) to prepare an artificial antigen, coating a nitrocellulose membrane with the artificial antigen to form a detection line (T line), and coating a nitrocellulose membrane with goat anti-mouse IgG to form a quality control line (C line). The 8-OHdG in the object to be detected and the artificial antigen coated on the detection line compete for the 8-OHdG antibody, so that the 8-OHdG can be detected through the lightening change of the color of the detection line, and the detection limit of naked eyes is 50mg / L. According to the invention, 8-OHdG can be simply, rapidly and sensitively detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
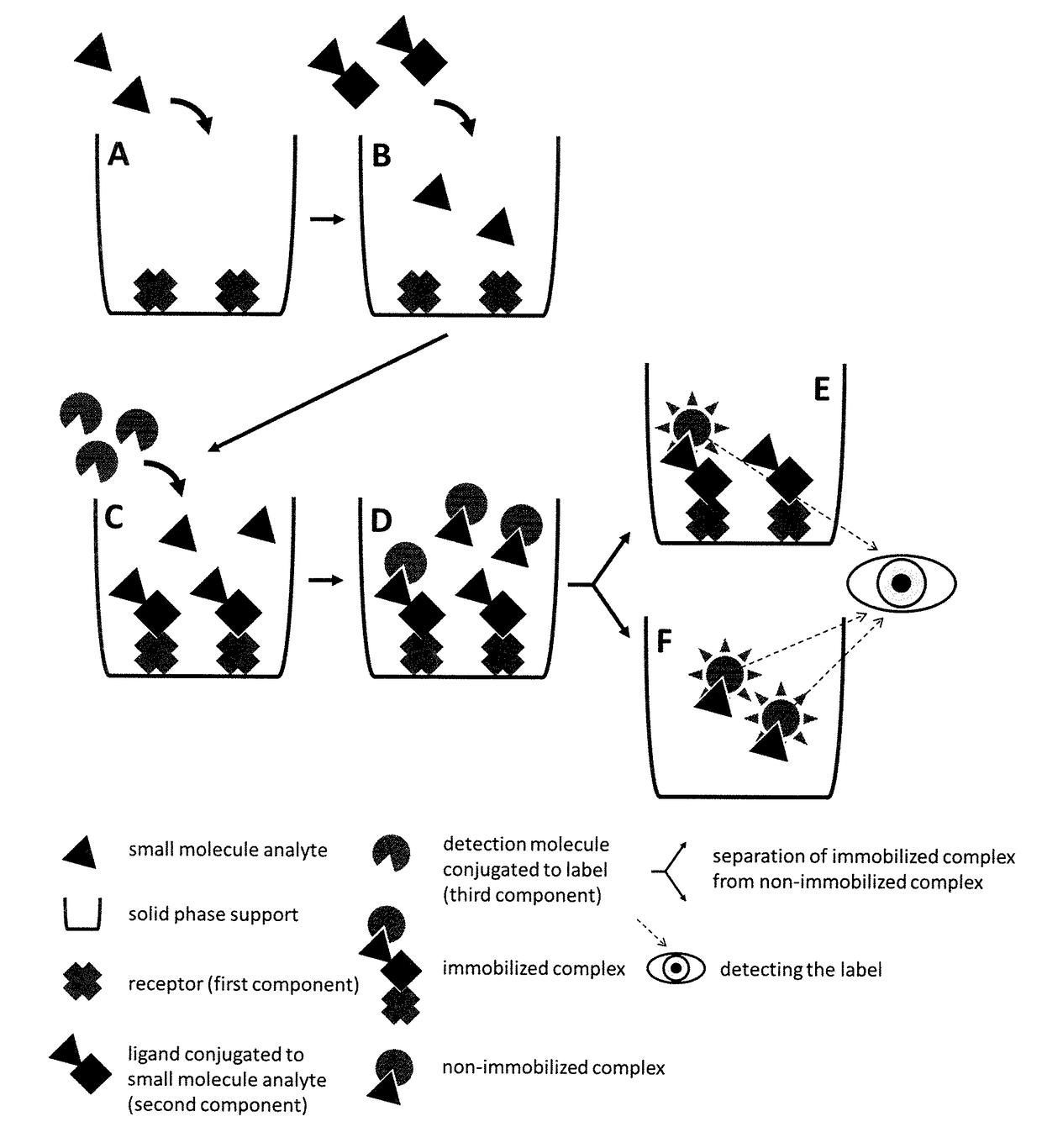
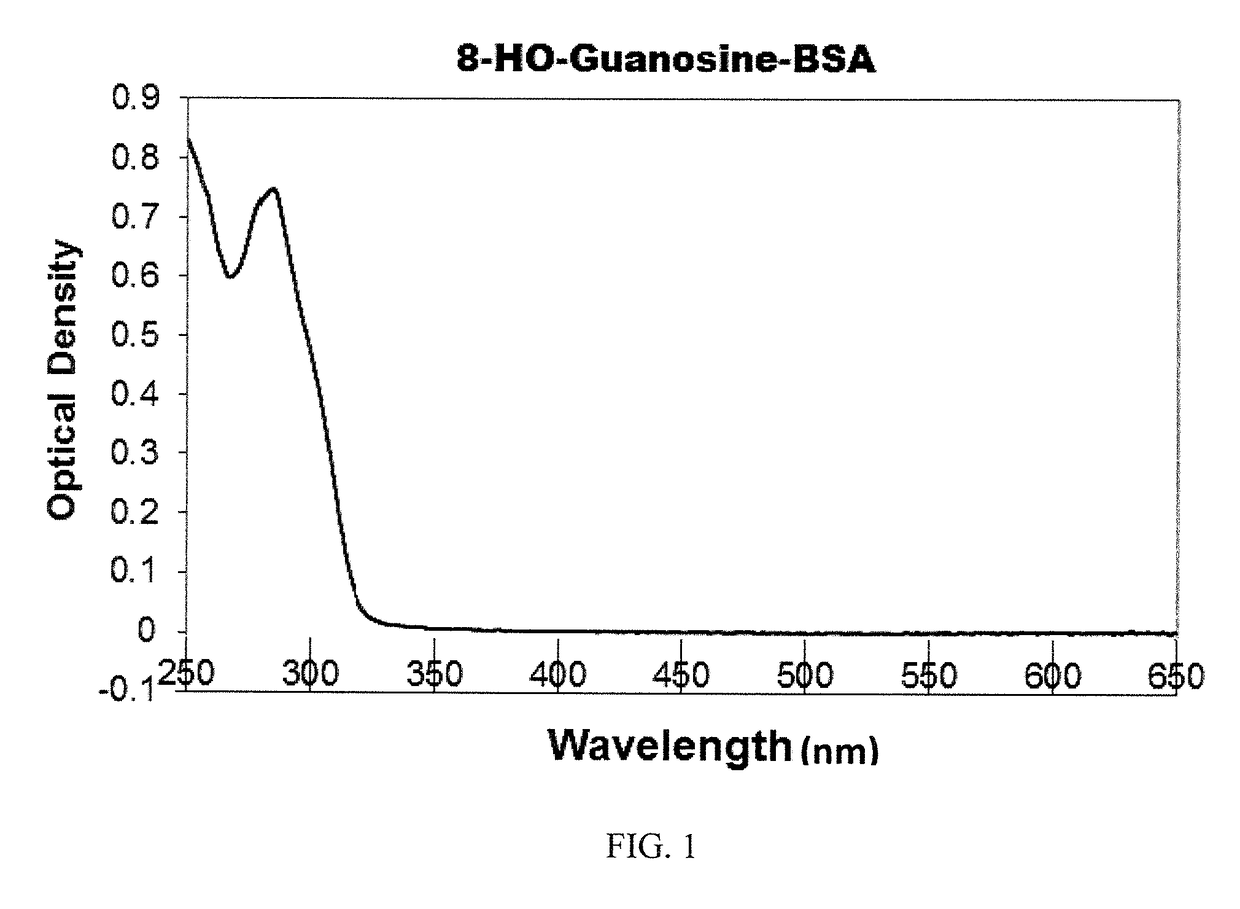
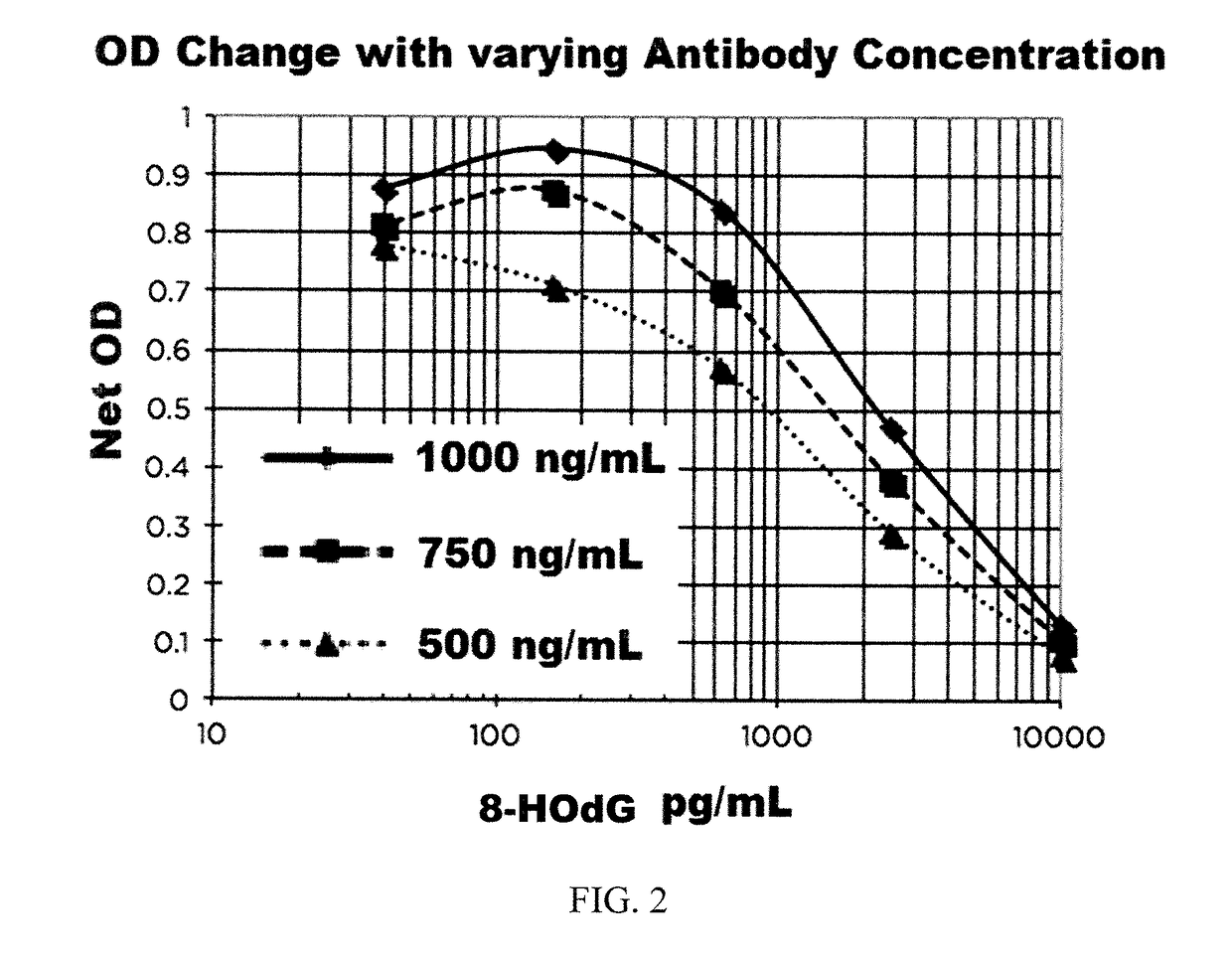
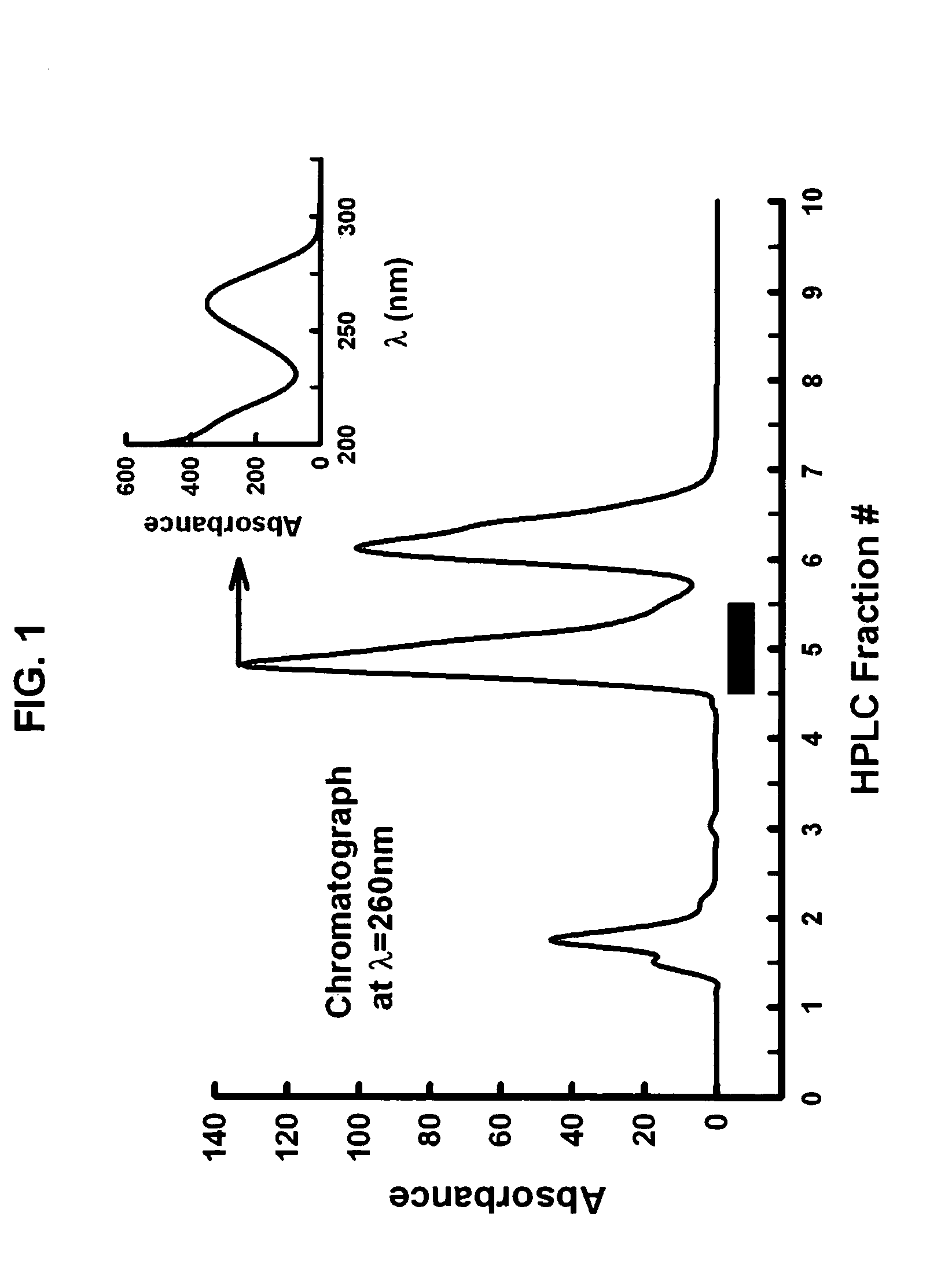
Methods and compositions relating to small molecule analyte assays
Kits and methods according to aspects of the present invention relate to the detection and quantitation of small molecule analytes including 8-hydroxyguanosine, 8-hydroxyguanine, and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine.
Owner:ARBOR ASSAYS
Use of purine nucleosides to stimulate Na/K ATPase and to treat or prevent shock
InactiveUS20050187181A1Preventing and treating septic shockHigh activityBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsInosineMedicine
This invention relates to methods of treating or preventing hemorrhagic and septic shock in an animal by administering inosine, guanosine, deoxyinosine, deoxyguanosine or a mixture thereof. Other purine nucleosides or analogs are described that have therapeutic use in treating or preventing shock. The invention also describes methods for increasing Na / K ATPase activity in erythrocytes or other cells in an animal having below normal activity of this enzyme by administering inosine, guanosine, deoxyinosine, deoxyguanosine or a mixture thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Analysis method of 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine, 8-hydroxy guanosine and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha in urine of human body
The invention relates to an analysis method of 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine, 8-hydroxy guanosine and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha in urine of a human body. The analysis method has the characteristics that the method can detect a change in in vivo typical oxidative stress biological marker caused by active oxygen relatively conveniently, rapidly and quantitatively, and can be used for evaluating in vivo oxidative damage and restoring degrees and studying a pathological process of a disease. The method employs AgilentBondEluC18 solid phase extraction column, three compounds of two different mass spectrometric detection modes, i.e., 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine, 8-hydroxy guanosine (cation mode detection) and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha (anion mode detection), in the urine can be purified simultaneously, and are subjected to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry detection by the same liquid chromatography column and the same mobile phase. The method has simple, convenient and quick pretreatment, and is high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and high in recovery rate.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Preparation method of intermediate 2'-deoxyguanosine
The invention discloses a preparation method of intermediate 2'-deoxyguanosine. A novel recombinant strain of N-nucleoside desoxyribose transferase is constructed, recombinant N-nucleoside desoxyribose transferase is synthesized through self-induction expression, a substrate is added in a dry powder feeding manner, 2'-deoxyguanosine is efficiently prepared with a biological catalysis method, the yield of prepared 2'-deoxyguanosine is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:山东格得生物科技有限公司
Nucleoside drug intermediate 2 '-deoxyguanosine production method
ActiveCN104830930ASolve the bottleneck problem of low solubilityImprove solubilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyethylene glycolDipotassium phosphate
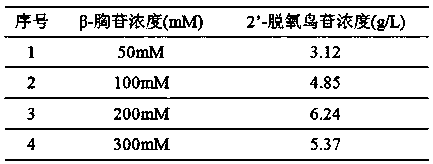
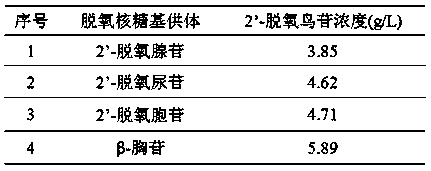
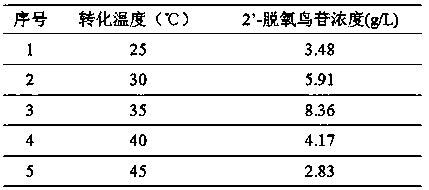
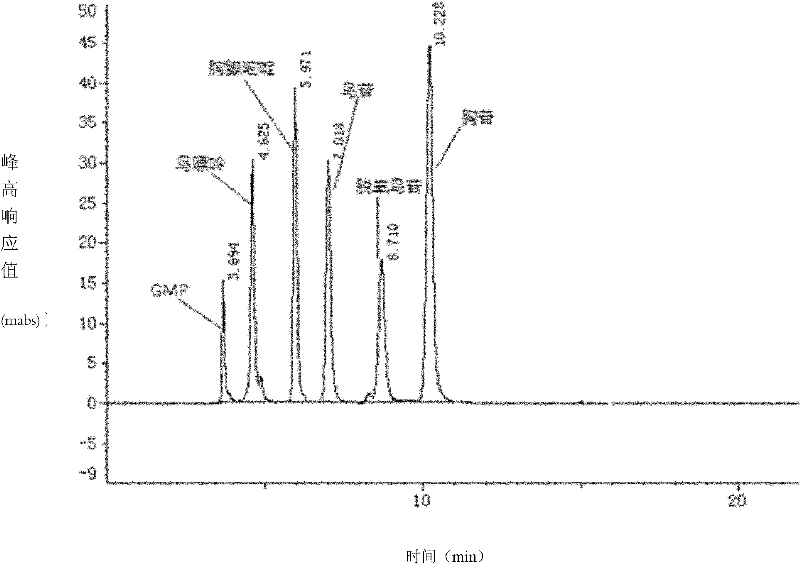
The present invention belongs to biotechnology, relates to the technical field of biological catalytic production of 2 '-deoxyguanosine, and particularly relates to a nucleoside drug intermediate 2 '-deoxyguanosine production method, according to the method, the 2 '-deoxyguanosine can be obtained by biological catalytic reaction of beta-thymidine and guanine as raw materials in the polyethylene glycol 10000 / dipotassium phosphate two aqueous phase system in the presence of lactobacillus fermenti bacteria paste as a biocatalyst, and under the condition of optimization, the addition amount of the substrate beta-thymidine reaches 16.5 g / L, the thymidine conversion rate reaches 89%, and the product 2 '-deoxyguanosine reaches 16.1 g / L.
Owner:乐山市佰尔特生物工程合伙企业(有限合伙)
Synthesis method of 2'-deoxyguanosine by adopting nucleoside phosphorylase of brevibacterium acetylium
InactiveCN102174618AHigh yieldLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentation3-deoxyribosePhosphate
The invention provides a synthesis method of 2'-deoxyguanosine by adopting nucleoside phosphorylase of brevibacterium acetylium, which comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing the brevibacterium acetylium QD96-CGMCCNo.0472; and (2) adding thalli obtained in the step (1) into a substrate solution or reaction, wherein deoxyribose receptors, deoxyribose donors and phosphate buffer solution are contained in the substrate solution, and collecting the 2'-deoxyguanosine from the reaction product. When the enzymes of the brevibacterium acetylium QD96 are used for synthesizing the 2'-deoxyguanosine, the cost can be reduced, and the 2'-deoxyguanosine can be effectively obtained; moreover, the conversion rate can reach more than 60%.
Owner:NANTONG QIUZHIYOU BIOSCI & BIOTECH +1
Self-assembled nano material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111686815ALow priceEasy to scale applicationMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFluorescenceThymidine monophosphate
The invention discloses a self-assembled nano material. formed by nucleic acid or nucleotide, an amino acid derivative or polypeptide and copper ions through self-assembly. The type of the amino acidderivative is lysine, histidine, methionine or cysteine; the chiral configuration is L-shaped or D-shaped; the polypeptide contains histidine, methionine, lysine or cysteine; the length of the peptideis 2 peptide-40 peptide; the nucleic acid is DNA; the molar ratio of guanine deoxynucleotide in DNA is 10%-100%, the total number of the nucleotides is 4-59, and the nucleotide is guanosine-5'-monophosphate, adenosine-5'-monophosphate, cytidine-5'-monophosphate, uridine-5'-monophosphate, deoxyguanosine-5'-monophosphate, deoxyadenosine-5'-monophosphate, deoxycytidine-5'-monophosphate or thymidine-5'-monophosphate. According to the invention, the simulated enzyme catalytic reaction can be monitored through a light absorption or fluorescence photometer.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for determining nucleotide metabolites in filter paper dried blood spots
The invention provides a method for determining nucleotide metabolites in a filter paper dried blood spot. The nucleotide metabolites comprise adenosine, 2'-deoxyadenosine, guanosine, 2'-deoxyguanosine, inosine and 2'-deoxyinosine. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing extraction treatment on a to-be-detected filter paper dried blood slice in an extraction working solution to obtain an extraction solution containing the nucleotide metabolite; 2) carrying out liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry detection on the extract liquor; and 3) determining the yield of the nucleotidemetabolites in the filter paper dried blood spot based on a liquid chromatography separation-mass spectrometry detection result. According to the detection method provided by the embodiment of the invention, six nucleotide metabolites in the filter paper dried blood spot can be simultaneously detected, and the detection method is used for scientific research or synchronous screening and diagnosisof ADA and PNP diseases, so that the detection cost is reduced, and the efficiency is improved. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and high accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Means for the treatment of HIV
The invention relates to a non-coding sequence of deoxyribonucleic acids comprising at least one sequence motif N1N2CGN3N4, wherein N is a nucleotide comprising A, C, T, or G, and C is deoxycytidine, G is deoxyguanosine, A is deoxyadenosine and T is deoxy-thymidine for the treatment of viral infections. In particular, the non-coding sequence of deoxyribonucleic acids is used in combination with antiretroviral therapy and / or histone de-acetylase inhibitors.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Hybridoma producing Anti-methylated DNA antibody and utilization of same
ActiveUS20120184719A1Reduce the amount of solutionSuperior binding ability and specificityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntigenPhosphate
The present invention relates to a hybridoma producing an anti-methylated DNA antibody, obtained by cell fusion of an antibody-producing cell obtained from an animal immunized with an antigen containing 5′-(5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine-3′-phospho)-2′-deoxyguanosine 3′-phosphate with a myeloma cell. The present invention also relates to a monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma and a method for immunoprecipitation of a methylated DNA using the antibody.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Sensor for detecting 8-hydroxyl-2'-deoxyguanosine as well as synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN108303527AIncrease profitHigh potential application valueScattering properties measurementsBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexSynthesis methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of sensor synthesis and the field of photochemical analysis, and in particular relates to a sensor which takes superparamagnetic nanoparticles capable of being circularly utilized as a carrier and aims at detecting 8-hydroxyl-2'-deoxyguanosine, a synthesis method of the sensor and application of the sensor to the fields of the photochemical analysis andenvironmental chemistry. The sensor is composed of superparamagnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles covered with streptavidin, and three different biotin modified single-chain deoxynucleotide sequences;one of the deoxynucleotide sequences is a deoxynucleotide sequence capable of specifically bind to the 8-hydroxyl-2'-deoxyguanosine; the streptavidin covers the superparamagnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles; the streptavidin is connected with the biotin, and the biotin is connected with the deoxynucleotide sequences. The sensor has good selectivity on the 8-hydroxyl-2'-deoxyguanosine, has strong anti-interference performance, and can be repeatedly utilized.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Anti-tumor drug prepared from combination of deoxyadenosine with other nucleosides or bases and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106074590AChange research directionReveal new lawsOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryLung cancerThymidine
The invention discloses an anti-tumor drug prepared from combination of deoxyadenosine with other nucleosides or bases and a preparation method and application thereof. The deoxyadenosine includes deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine; the other nucleotides and bases include: deoxycytidine, thymidine, adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, uridine, adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil and thymidine; The invention has the advantages that both the deoxyadenosine and other nucleosides or bases are human normal nucleotides, the drug for treating various common malignancies such as gastric cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer and genital system neoplasms is prepared from the combination of deoxyadenosine as a main drug and other nucleotides and bases as auxiliaries, and the drug has features wide spectrum, low toxicity, mechanism novelty and the like in terms of anti-tumor action; the combine drug has lower toxic and side effects than a single drug; anti-tumour effects are more multiplicative; meanwhile drug resistance of tumors can be delayed.
Owner:张始状
O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase inactivators and beta-glucuronidase cleavable prodrugs
Disclosed are prodrugs of inactivators of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT). The prodrugs are cleavable by the β-glucuronidase enzyme, which is either administered to the patient or produced by necrotic tumor cells. The prodrugs are represented by the formula A-B-C, wherein A is a glucuronosyl residue linked through its 1-oxygen to the phenyl ring of B; B is a benzyloxycarbonyl group, optionally ring-substituted with one or more electron withdrawing groups; and C is an inactivator of AGT, e.g., a substituted or unsubstituted O6-benzylguanine or O6-benzyl-2′-deoxyguanosine. Also disclosed are additional inactivators of AGT, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inactivator or prodrug and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and a method of use of the inactivator or prodrug in enhancing the chemotherapeutic treatment of tumor cells in a mammal, e.g., a human, with an antineoplastic alkylating agent that causes cytotoxic lesions at the O6-position of guanine.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
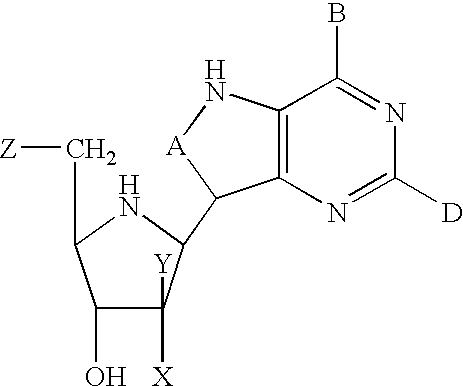
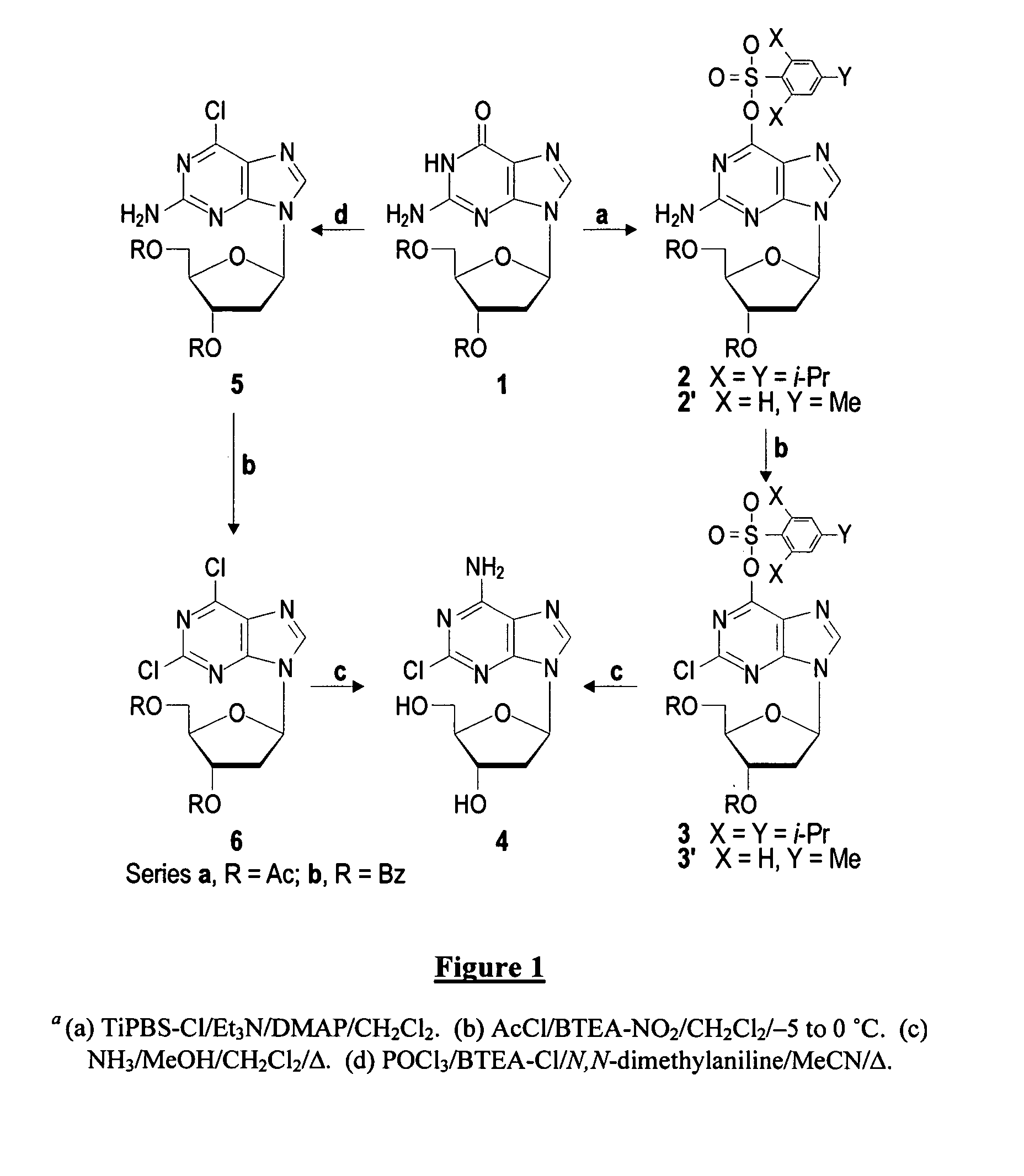
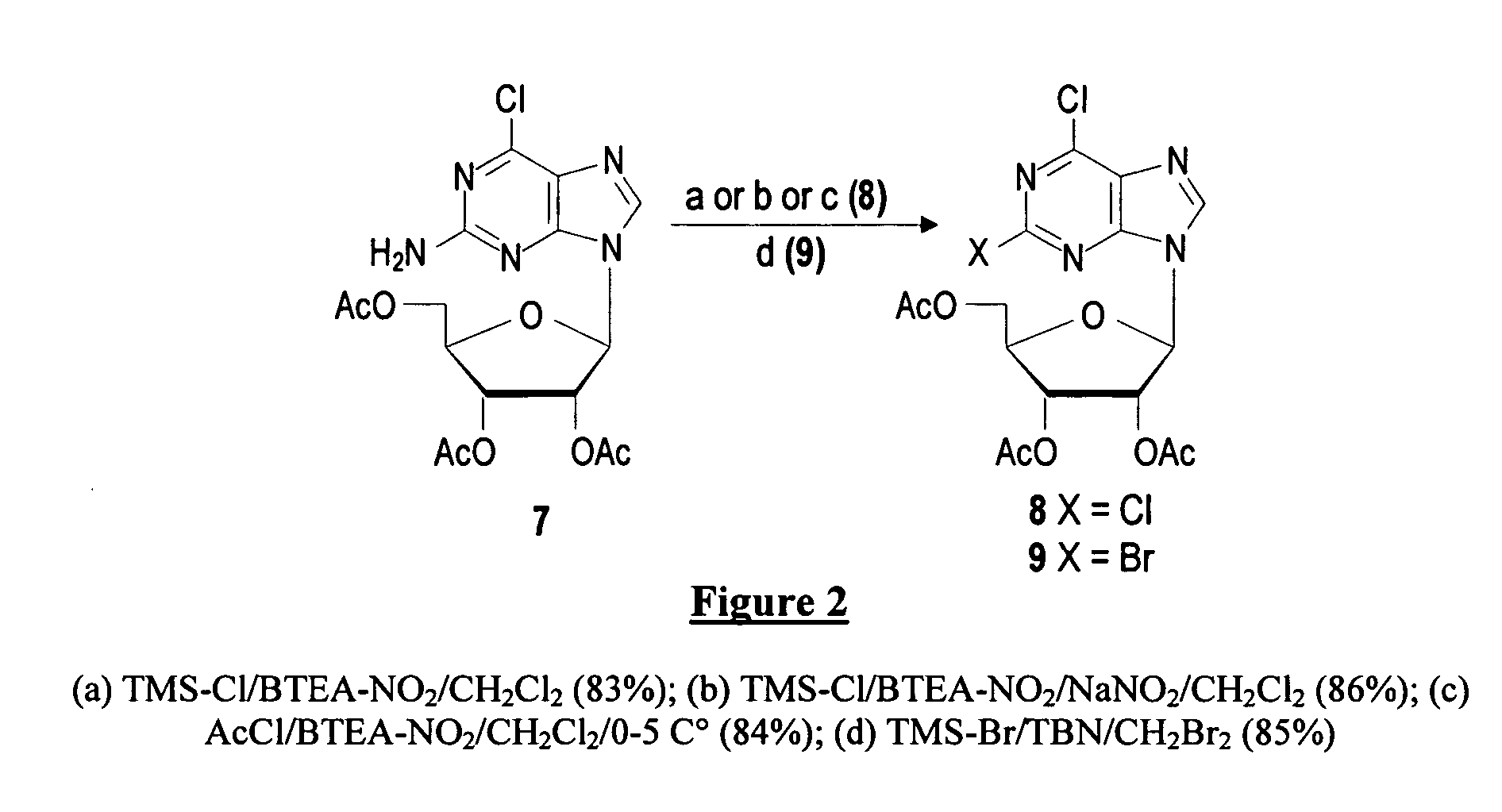
Method for the preparation of 2-halo-2'-deoxyadenosine compounds for 2'-deoxyguanosine
The present invention is a method for preparing 2-halo-6-aminopurines, and more specifically for preparing the clinical agent cladribine (2-chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine, CldAdo, 4), a drug of choice against hairy-cell leukemia and other neoplasms, from 2-amino-6-oxopurines, which are readily obtained from the naturally occurring compound 2′-deoxyguanosine. According to the methods of the present invention, the 6-oxo group of a protected 2′-deoxyguanosine (1) is converted to a 6-(substituted oxy) leaving group, or alternatively to a 6-chloro leaving group, the 2-amino group is replaced with a 2-chloro group, the 6-(substituted oxy) leaving group, or alternatively the 6-chloro leaving group, is replaced with a 6-amino group or, alternatively, a 2,6-dichloro substituted compound is selectively replaced with a 6-amino group, and the protecting groups are removed.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com