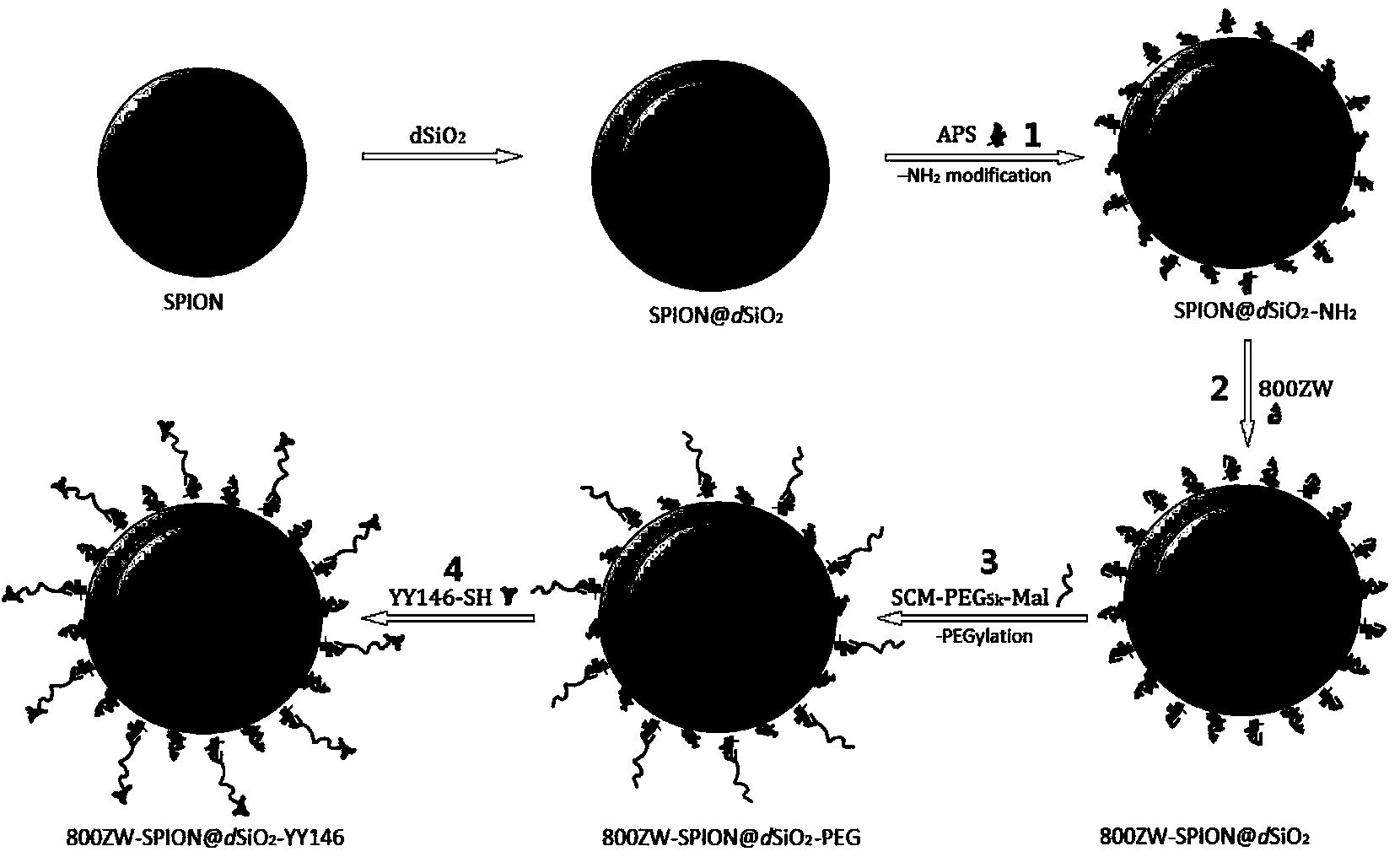
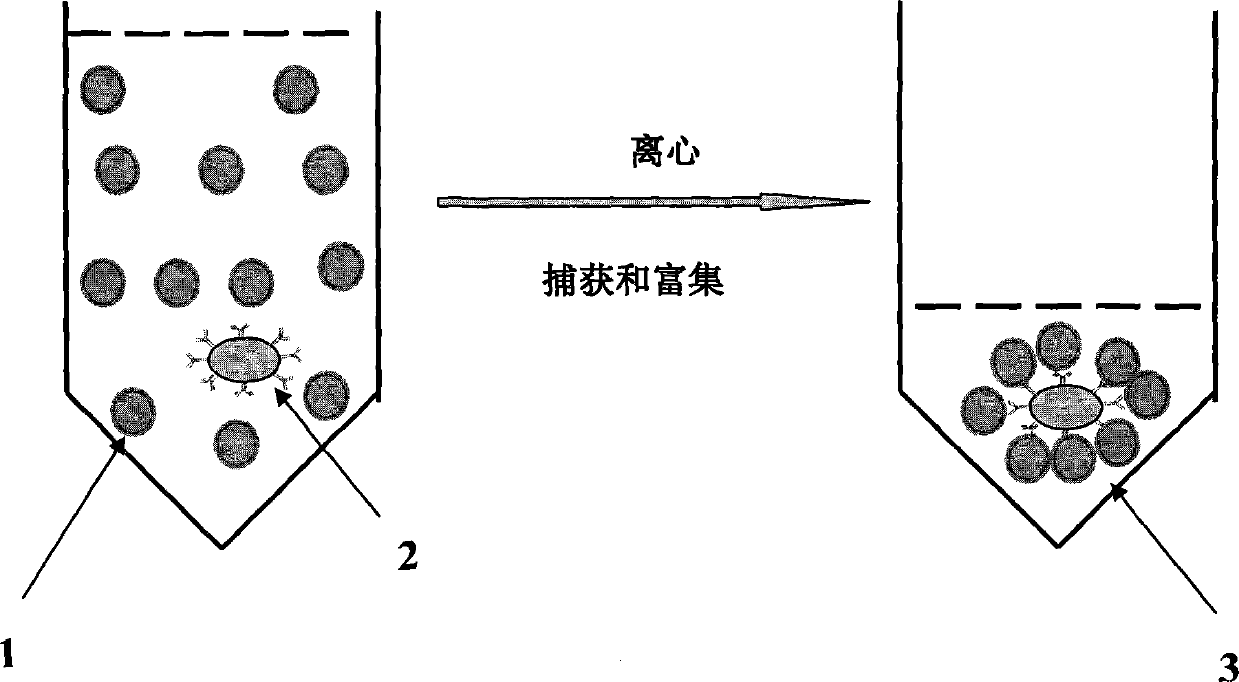
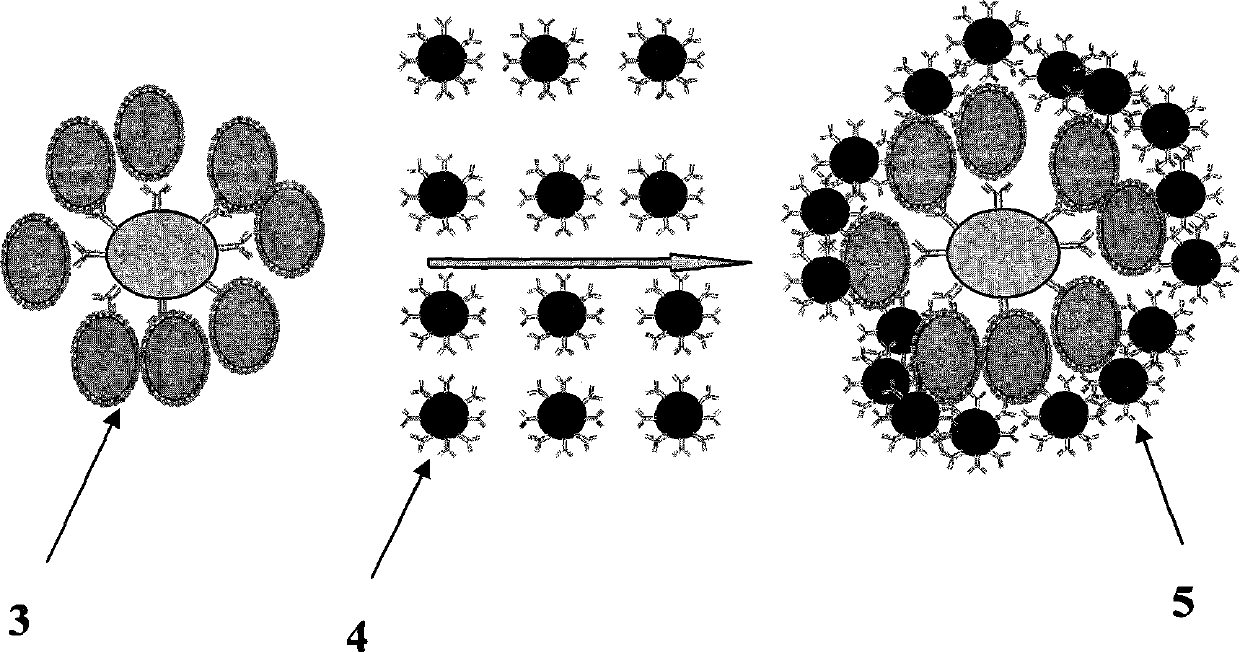
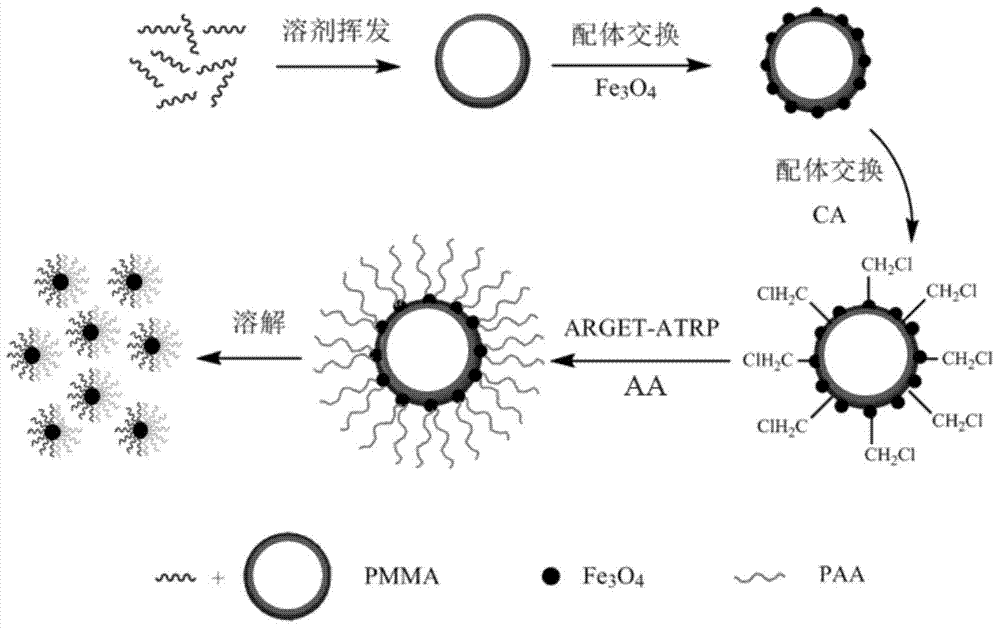
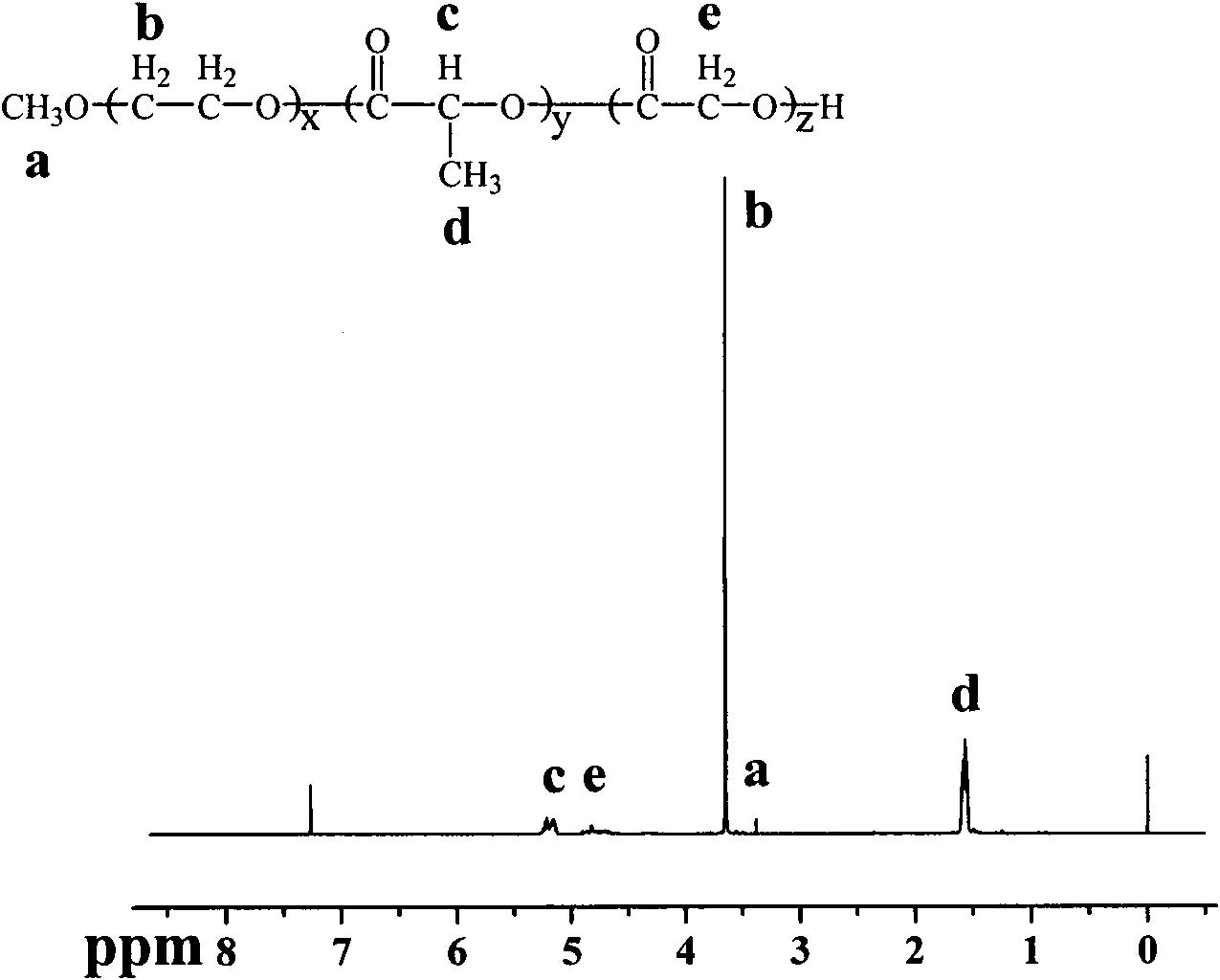
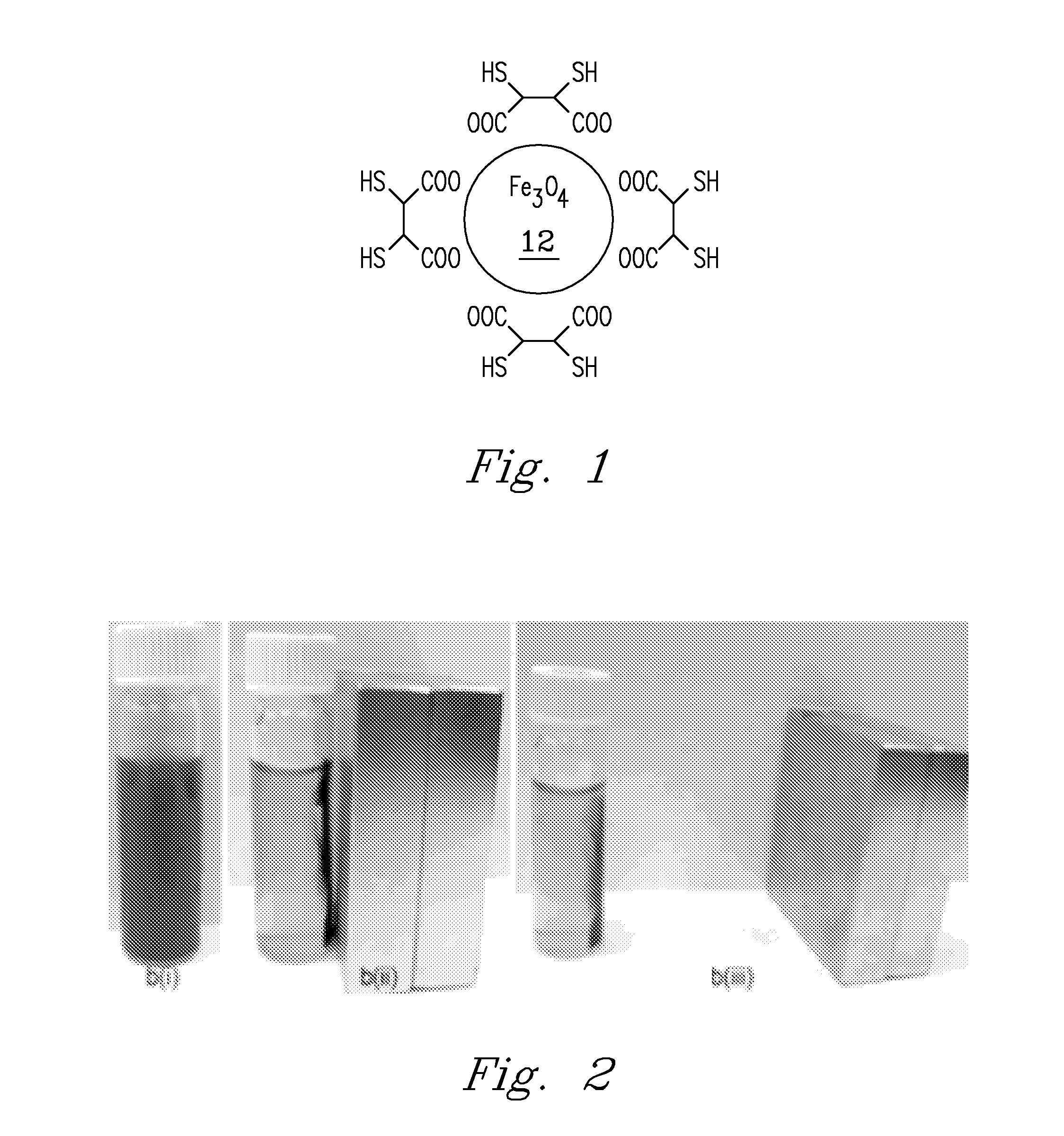
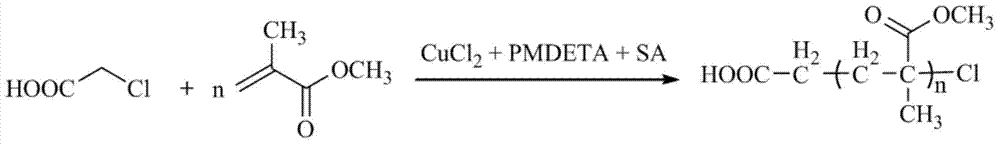Patents
Literature
127 results about "Superparamagnetic nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
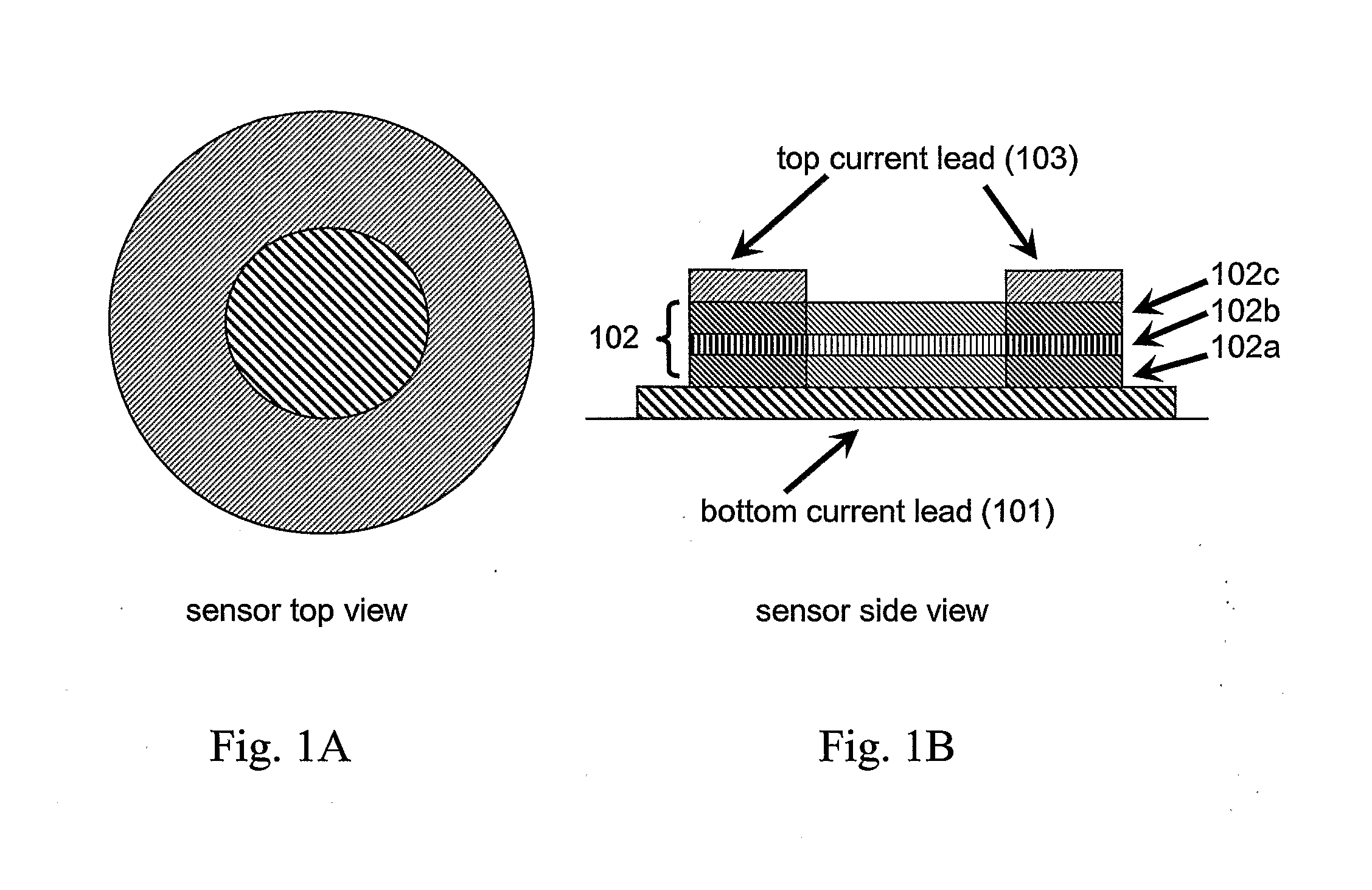
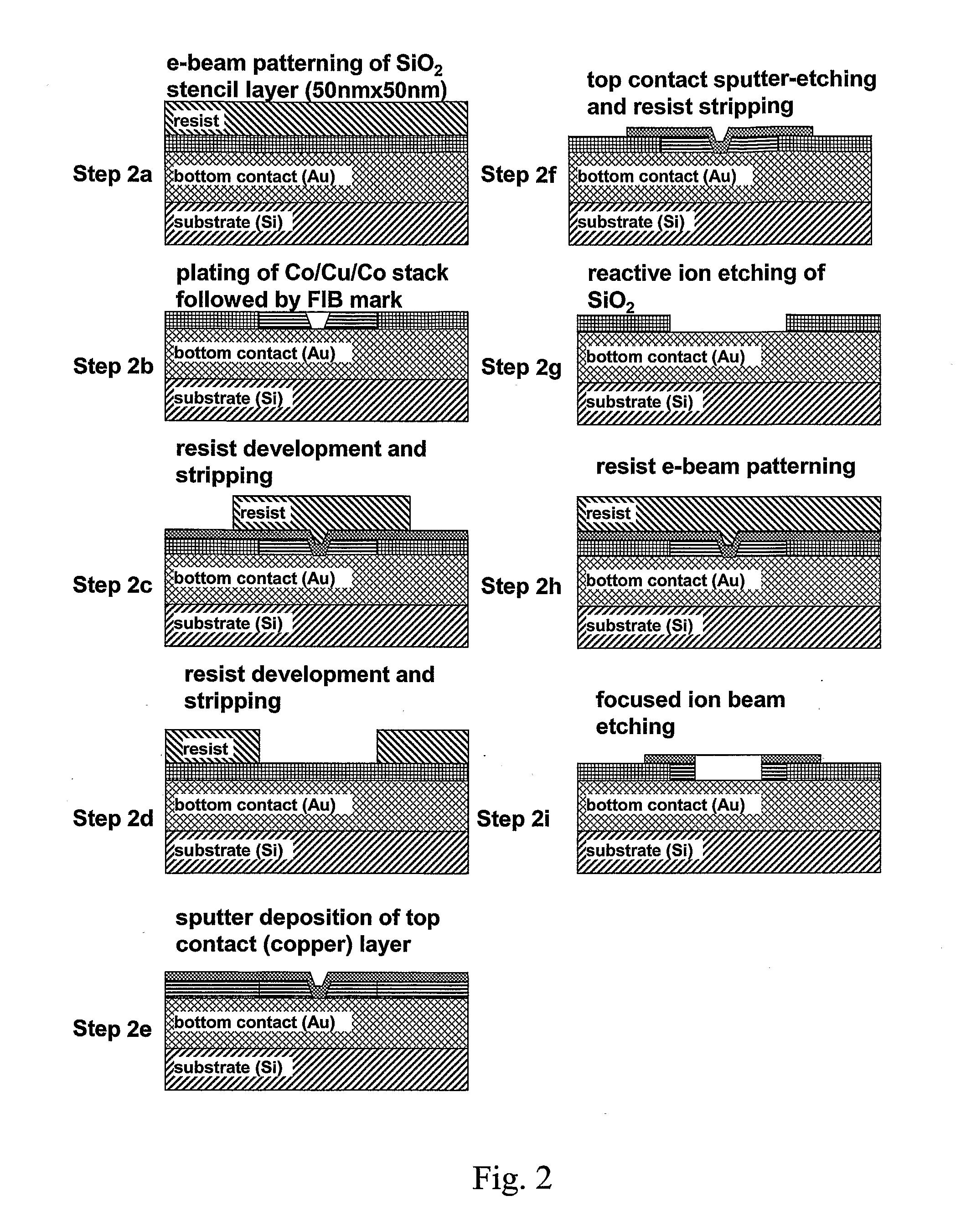
Nmr systems for in vivo detection of analytes
ActiveUS20100072994A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingAnalyteNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
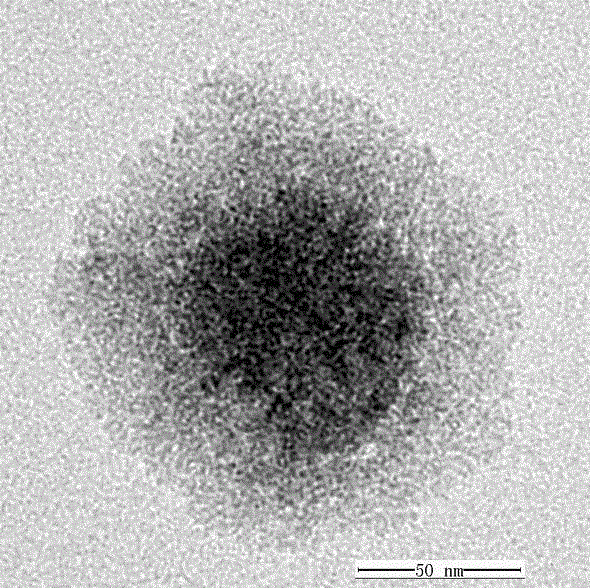
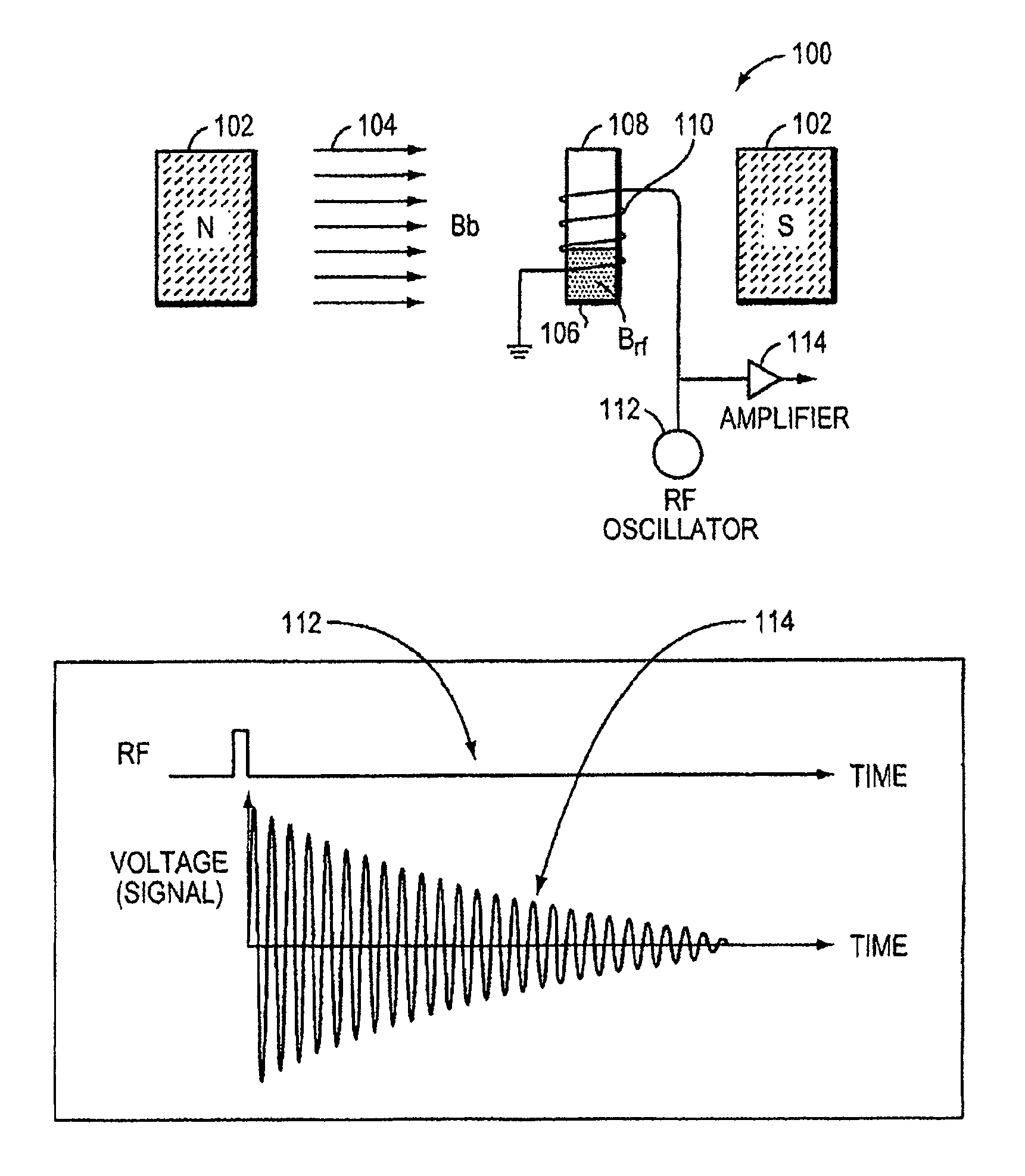
This invention relates generally to NMR systems for in vivo detection of analytes. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the invention relates to systems in which superparamagnetic nanoparticles are exposed to a magnetic field and radio frequency (RF) excitation at or near the Larmor frequency, such that the aggregation and / or disaggregation of the nanoparticles caused by the presence and / or concentration of a given analyte in a biological fluid is detected in vivo from a monitored RF echo response.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
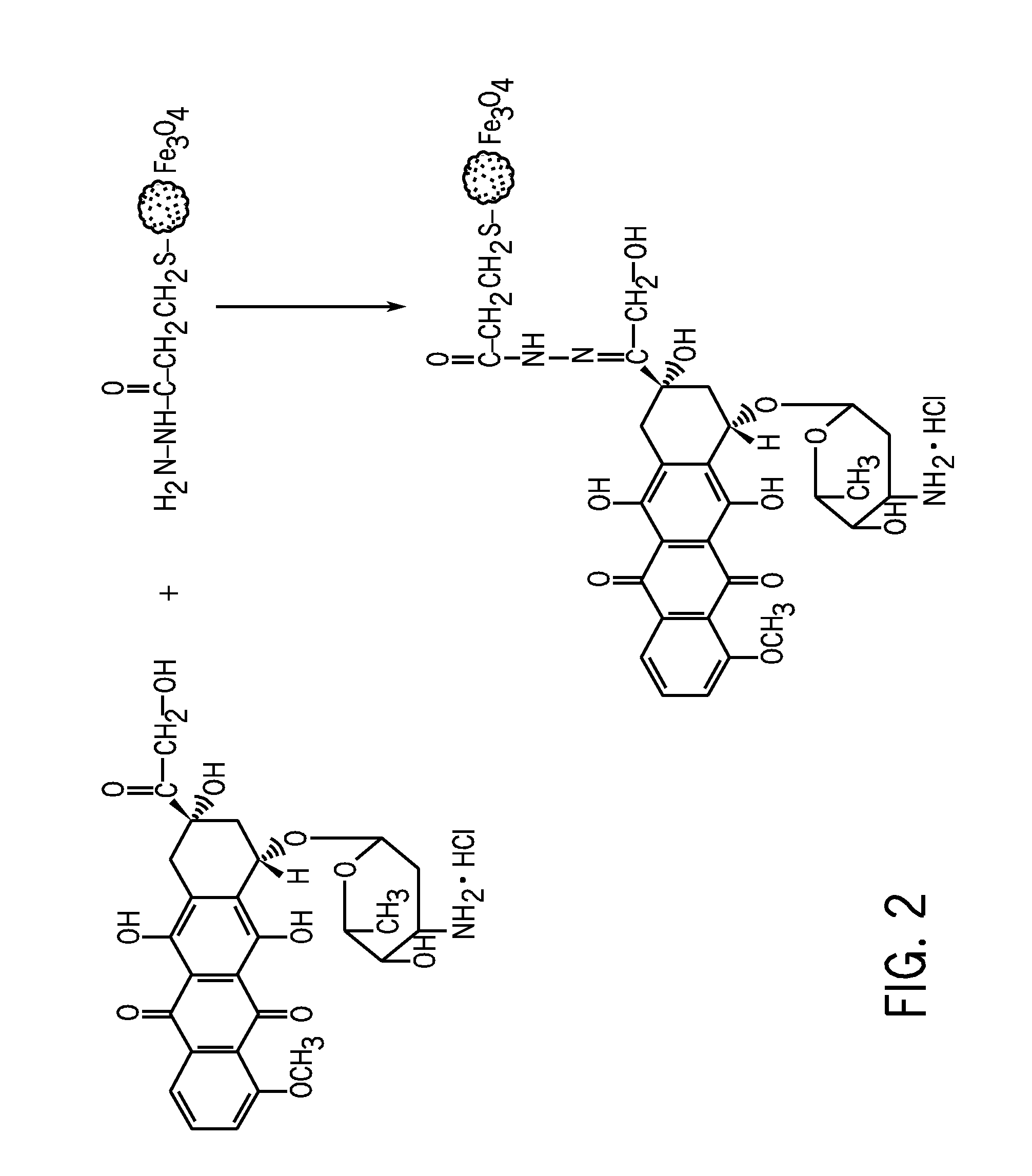
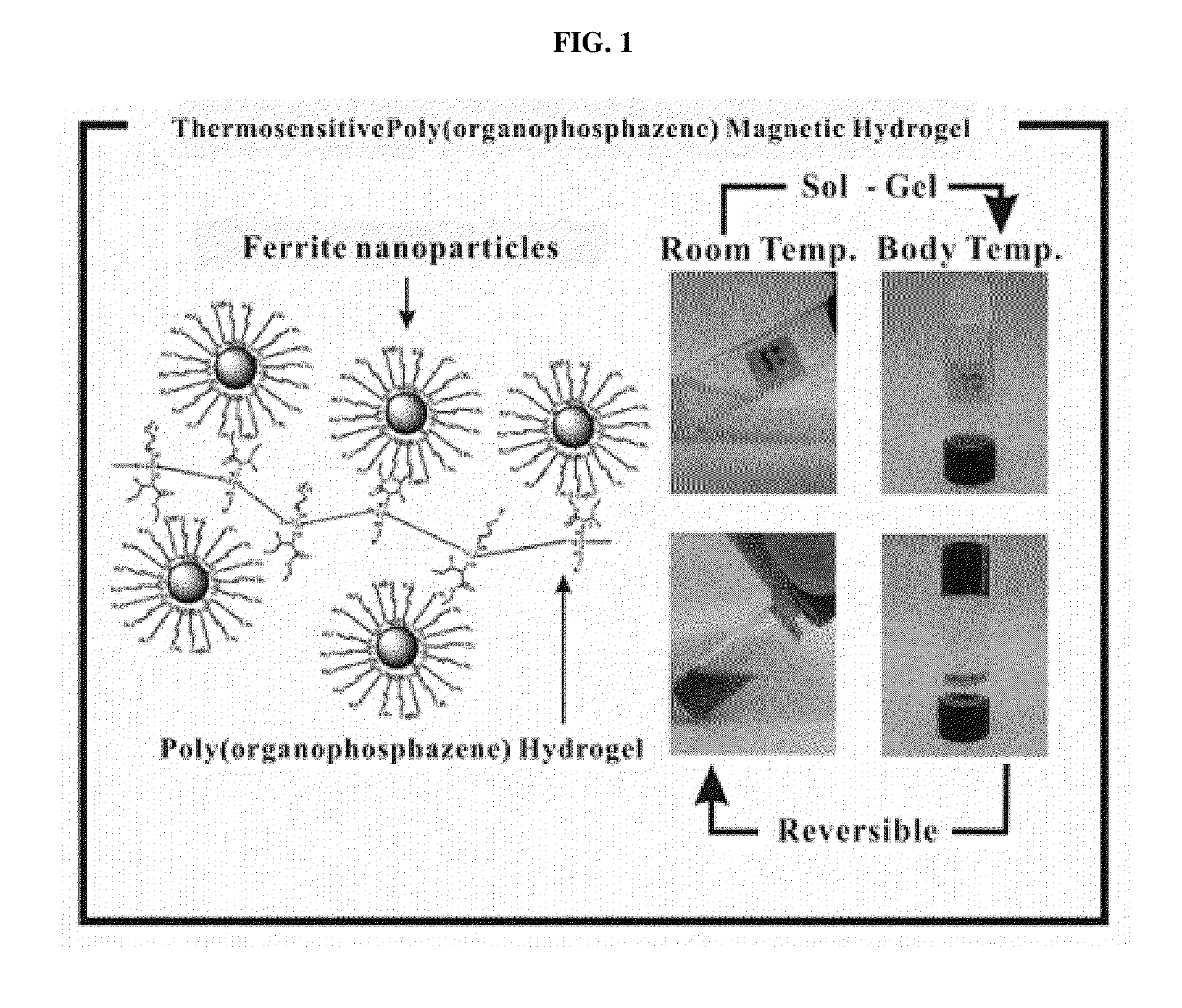
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20120121517A1Facilitated releaseImprove load effectMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideMRI contrast agentFerrite nanoparticles
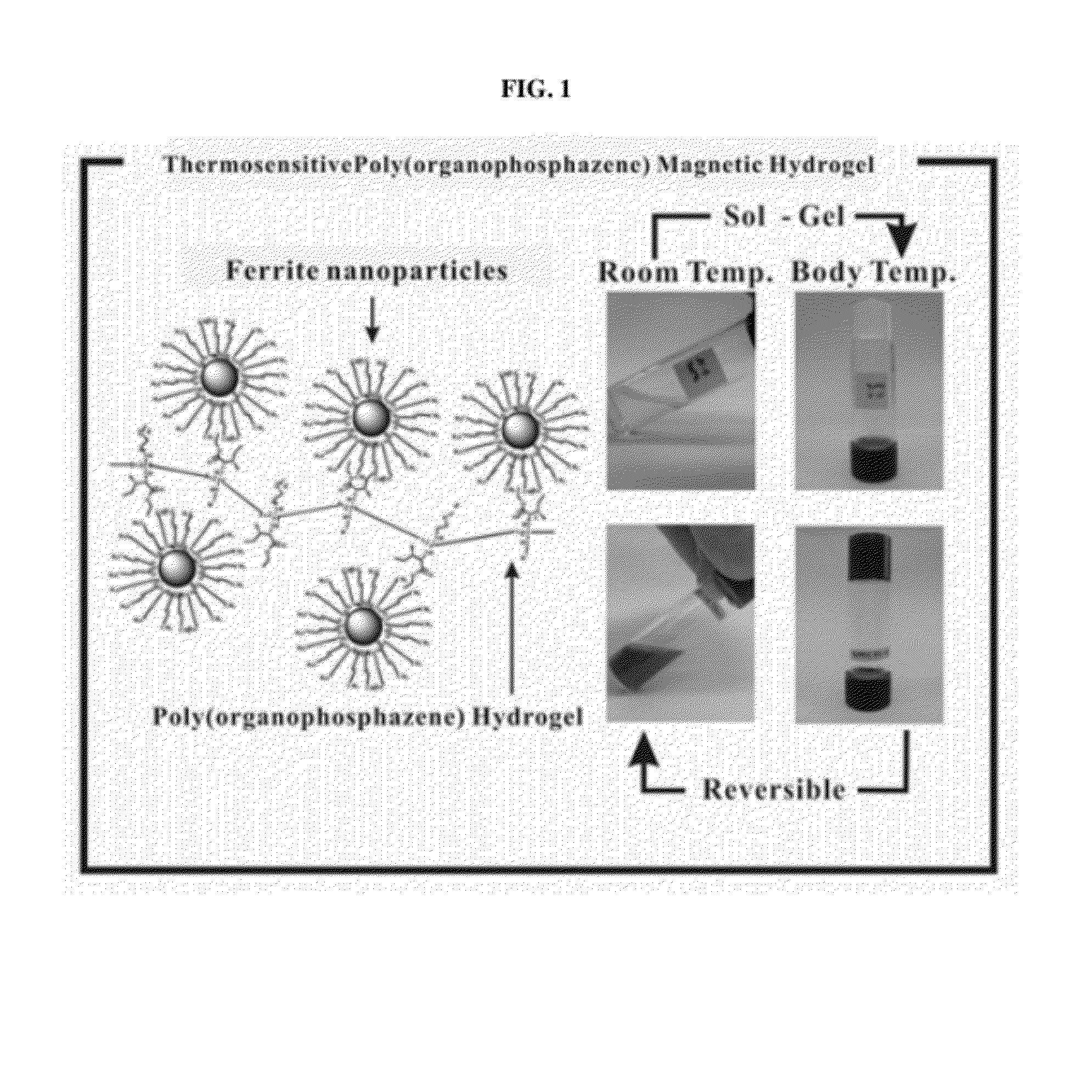
The present invention relates to a poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex including a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) and a iron oxide (Fe3O4, Magnetite)-series ferrite superparamagnetic nanoparticle, a preparation method, and uses of carrying a physiologically-active material, a bio-material and a biomaterial for cancer hyperthermia. The iron oxide is used as a MRI contrast agent for T-2 and T2* weighted image, and the poly(organophosphazene) shows a sol-to-gel behavior depending upon the temperature change. The complex is a bound-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is bonded to phosphazene-based polymer via hydrophobic binding, and a mixed-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is physically mixed with the phosphazene-based polymer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20060140871A1NanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringAbnormal tissue growthProstate cancer cell
Paramagnetic or superparamagnetic nanoparticle-ligand conjugates that include a recognition ligand that interacts with a component on the surface of a prostate cancer cell. Nanoparticle-ligand conjugates of the invention may be used for magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer, or for treatment of tumors by targeted thermal ablation.
Owner:NEW MEXICO UNIV OF
Nanoparticles that facilitate imaging of biological tissue and methods of forming the same
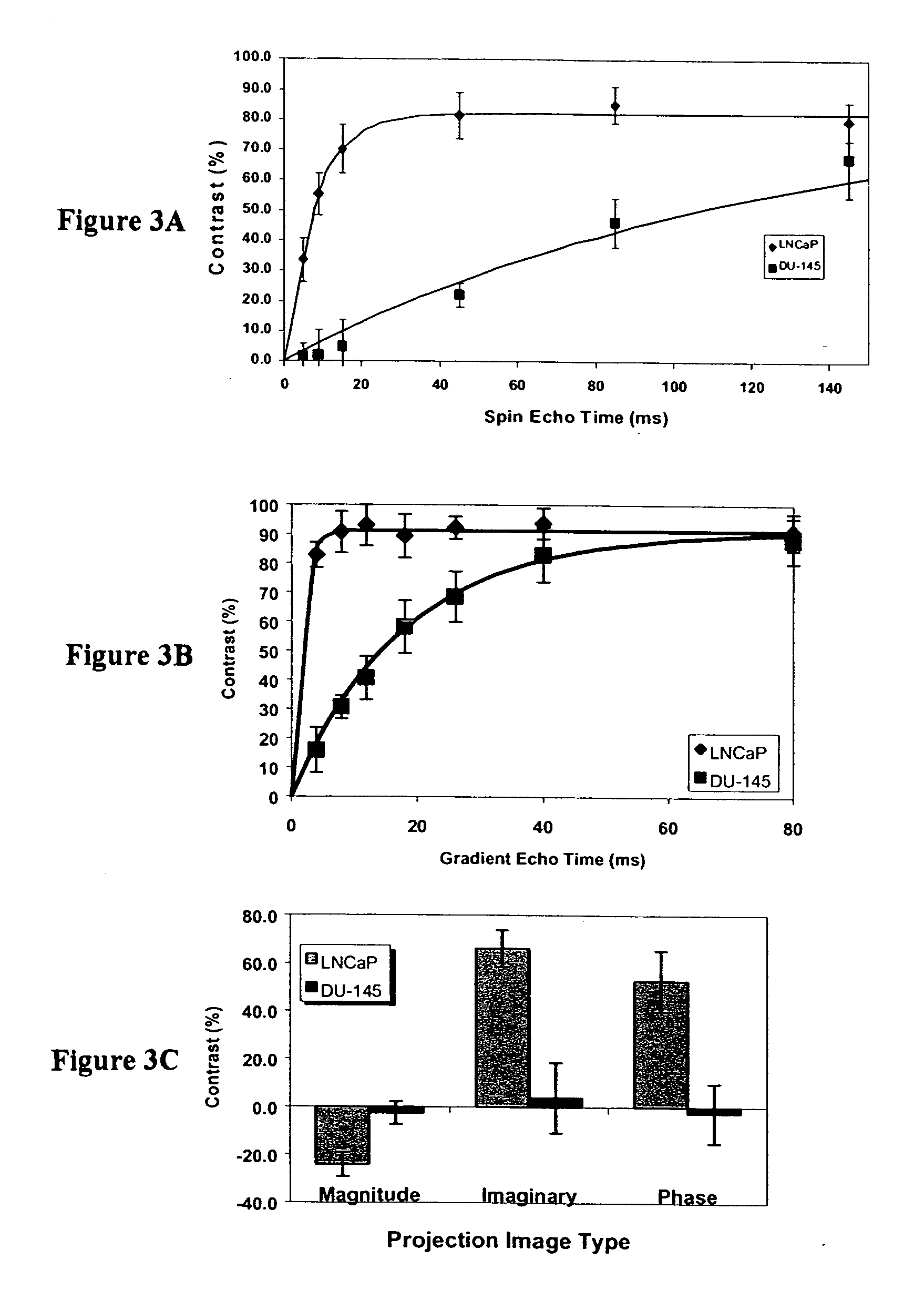
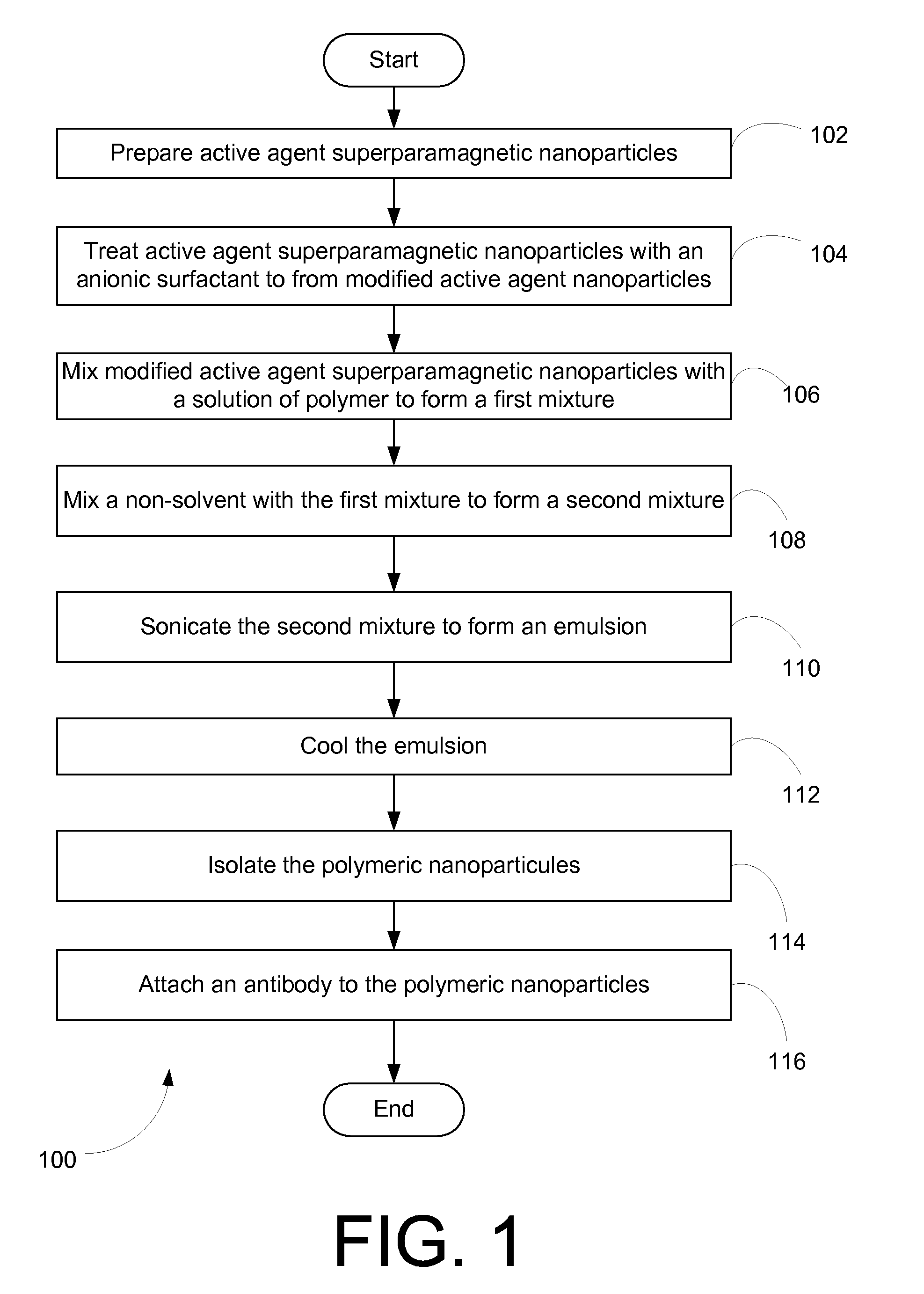
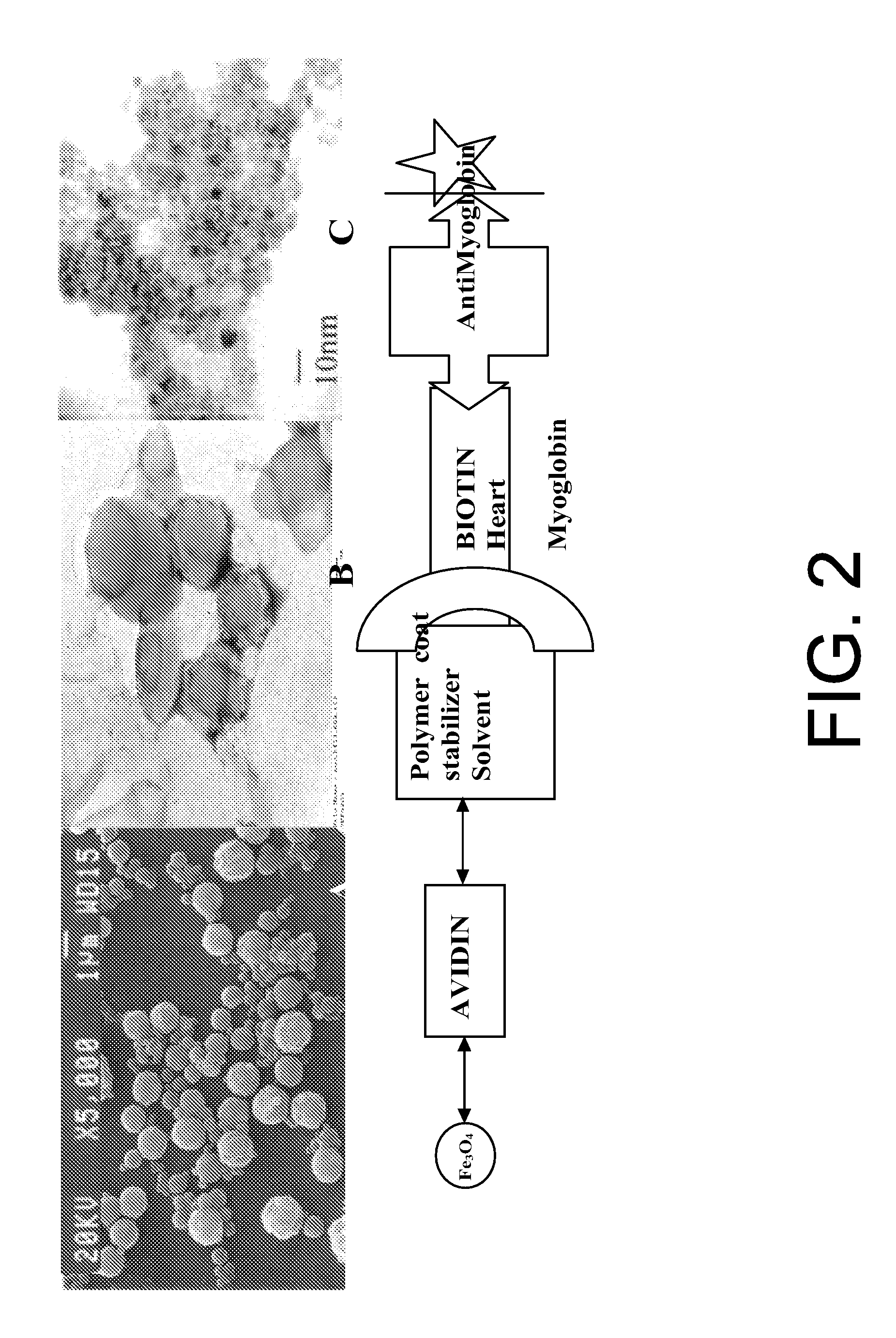
InactiveUS20090220434A1Enhance the imageGood adhesionPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesNon solventAntiendomysial antibodies
Nanoparticles that facilitate imaging of biological tissue and methods for formulating the nanoparticles are provided. In order to form suitable nanoparticles for imaging, an anionic surfactant may be applied to superparamagnetic nanoparticles to form modified nanoparticles. The modified nanoparticles may be mixed with a polymer in a solvent to form a first mixture, and a non-solvent may be mixed with the first mixture to form a second mixture. An emulsion may be formed from the second mixture and the polymeric nanoparticles may be isolated from the emulsion. In certain embodiments of the invention, an antibody may be attached to the polymeric nanoparticles to facilitate attachment of the nanoparticles to biological tissue.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Intracellular thermal ablation using nano-particle electron spin resonance heating
InactiveUS20060269612A1Reliable and sensitive resultLow costHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideResonanceNanoparticle
This invention pertains to the use of spin resonance absorption heating as a therapeutic treatment method wherein electron spin resonance absorption of superparamagnetic (SPM) nanoparticles can be used as an intracellular heating method, more preferably as an in vivo heating method that can be utilized in a variety of therapeutic contexts and can further allow for resonance imaging and internal thermometry.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Nanomagnetic detector array for biomolecular recognition
ActiveUS20100188075A1Simple designNew capabilityMagnetic measurementsMagnetic paintsSensor arrayNanoparticle
A biomolecular sensor system includes an array of magnetoresistive nanosensors designed for sensing biomolecule-conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Materials and geometry of each sensor element are designed for optimized sensitivity. The system includes magnetic field generators to apply forces to superparamagnetic nanoparticles for 1) nanoparticle manipulation, 2) sensor magnetic biasing, 3) magnetic pull-off measurement for differentiation against non-specific association, and 4) removal of all particles from the sensor array surface.
Owner:HOUSTON UNIV OF
Superparamagnetic particle imaging and its applications in quantitative multiplex stationary phase diagnostic assays
ActiveUS20190317167A1Improve responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresStationary phasePoint of care
Superparamagnetic nanoparticle-based analytical method comprising providing a sample having analytes in a sample matrix, providing a point of care chip having analytical regions, each of which is a stationary phase having at least one or more sections, labeling each of the analytes with a superparamagnetic nanoparticle and immobilizing the labeled analytes in the stationary phase, providing an analytical device having a means for exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro and a means for sensing, receiving, and transmitting response of the excited superparamagnetic nanoparticles, placing the chip in the analytical device and exciting the superparamagnetic nanoparticles in vitro, sensing, receiving, and transmitting the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles, and analyzing the response and determining characteristic of the analytes, wherein the response of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles comprises harmonics. The present invention also provides the hybrid point of care chip and analyzer to be used in the analytical method.
Owner:MARS SCI LTD
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles IN MEDICAL THERAPEUTICS and manufacturing method THEREOF
InactiveUS20110135577A1Safe and effectiveAvoid problemsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleMagnetite
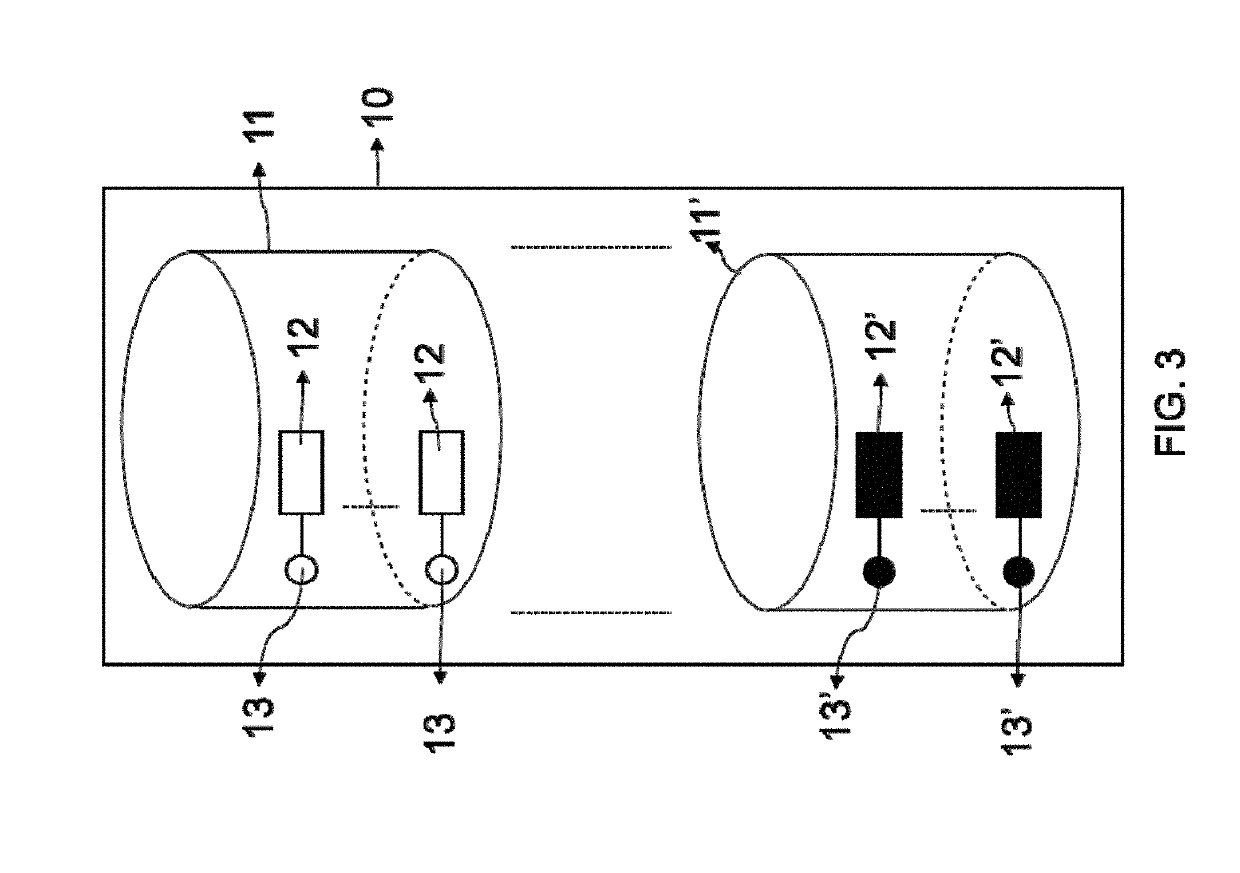
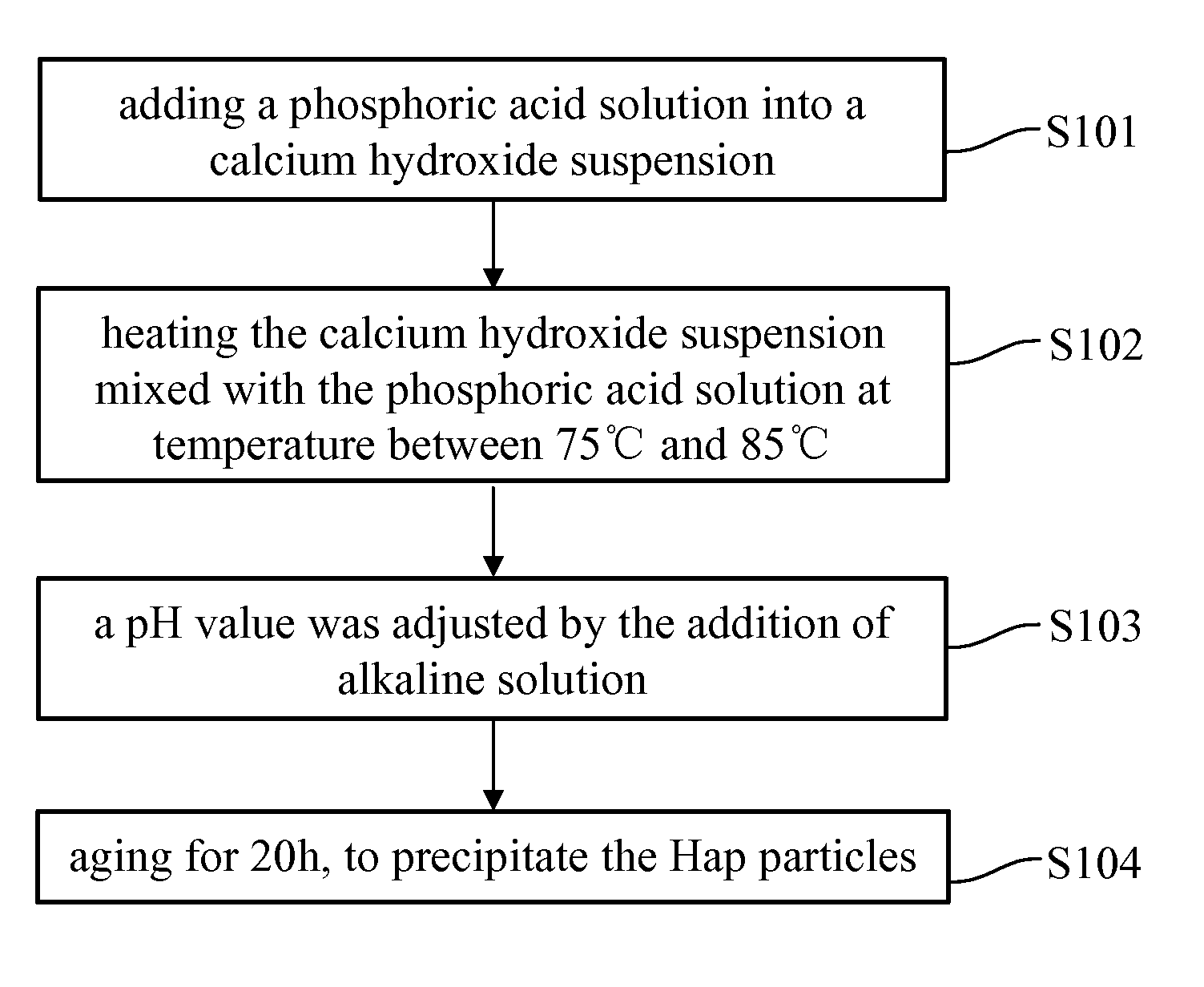
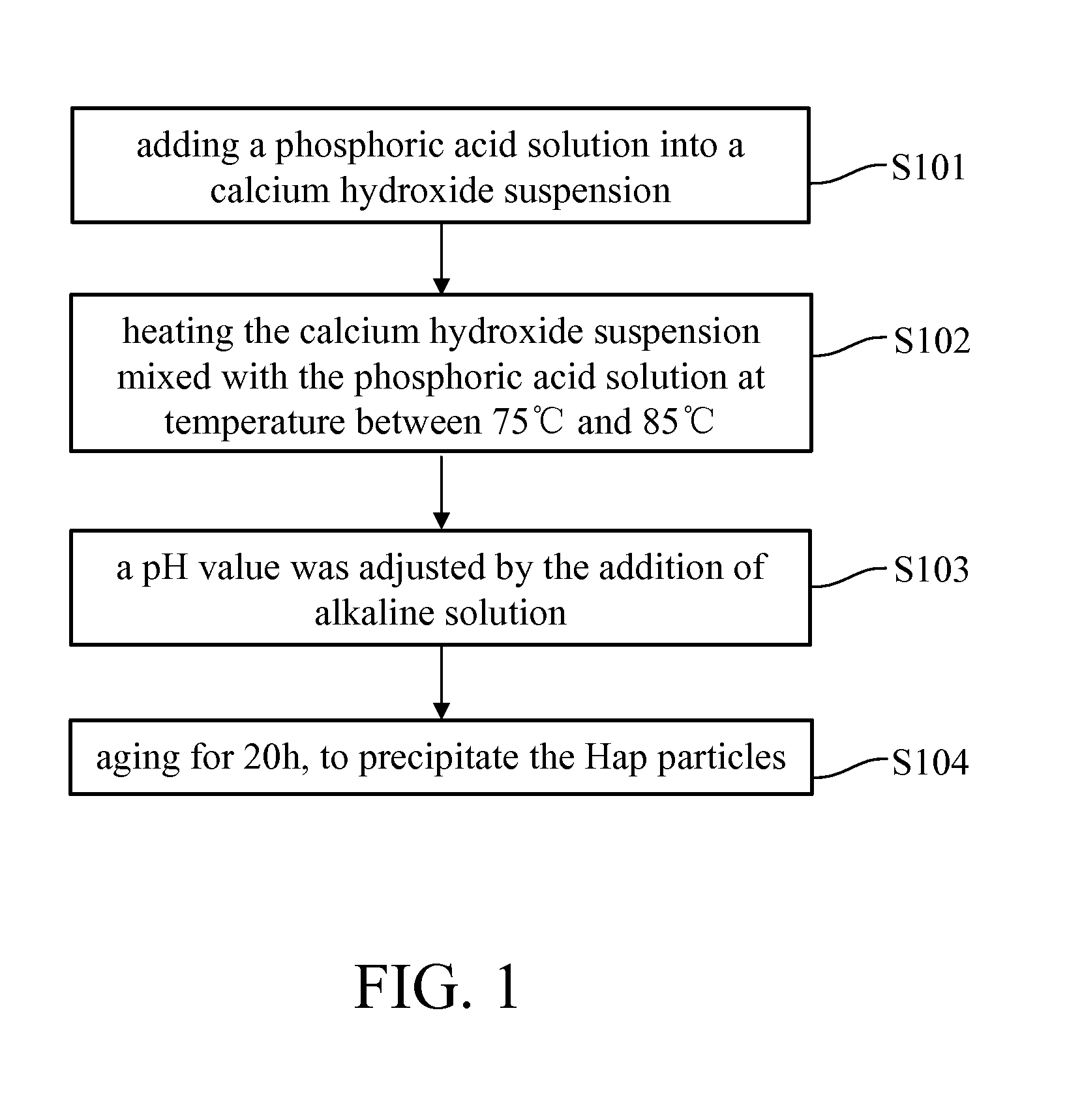
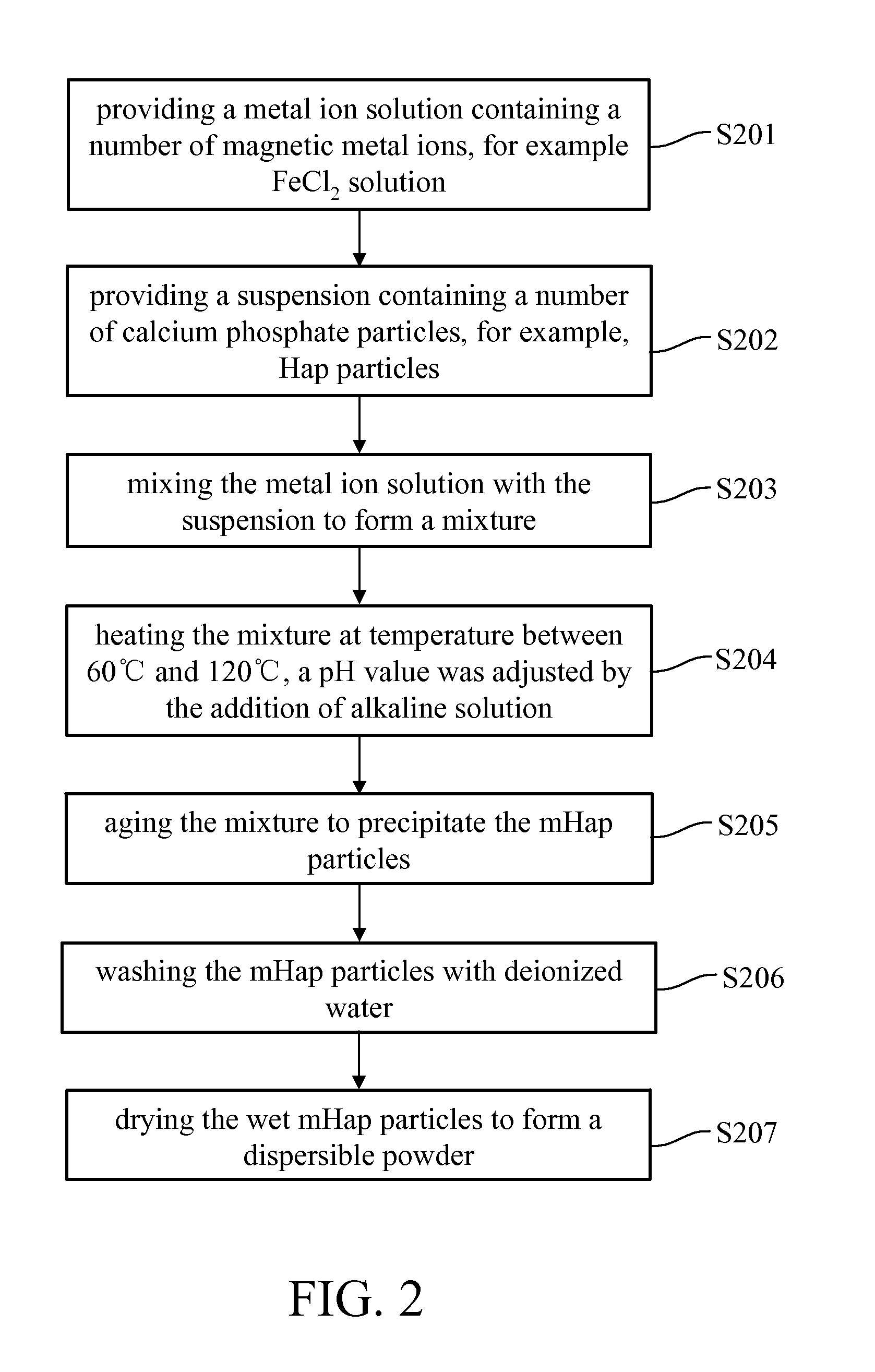
The successful transfer of therapeutic agents such as genetic materials (e.g. nucleic acid) or drug into living cells is the most important issue depending on the development of the delivery carrier. A method for manufacturing superparamagnetic nanoparticles in medical therapeutics is described to develop nano-sized calcium phosphate (CaP) mineral was rendered magnetic as delivery vehicle. The CaP-based magnetized nanoparticles (NPs) were possessed superparamagnetic property by hetero-epitaxial growth of magnetite on the CaP crystallites and also showed no harm to the cultured cells and elicited no cytotoxicity. The magnetized CaP was demonstrated to have good plasmid DNA binding affinity or drug carrying capacity. It significantly increased the expression of gene transfection and efficiency in delivery to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) under exogenous magnetic field. According to the above facts, this newly-synthesized magnetized CaP NPs has great potential as a novel non-viral targeted delivery vehicle to be applied for medical applications.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
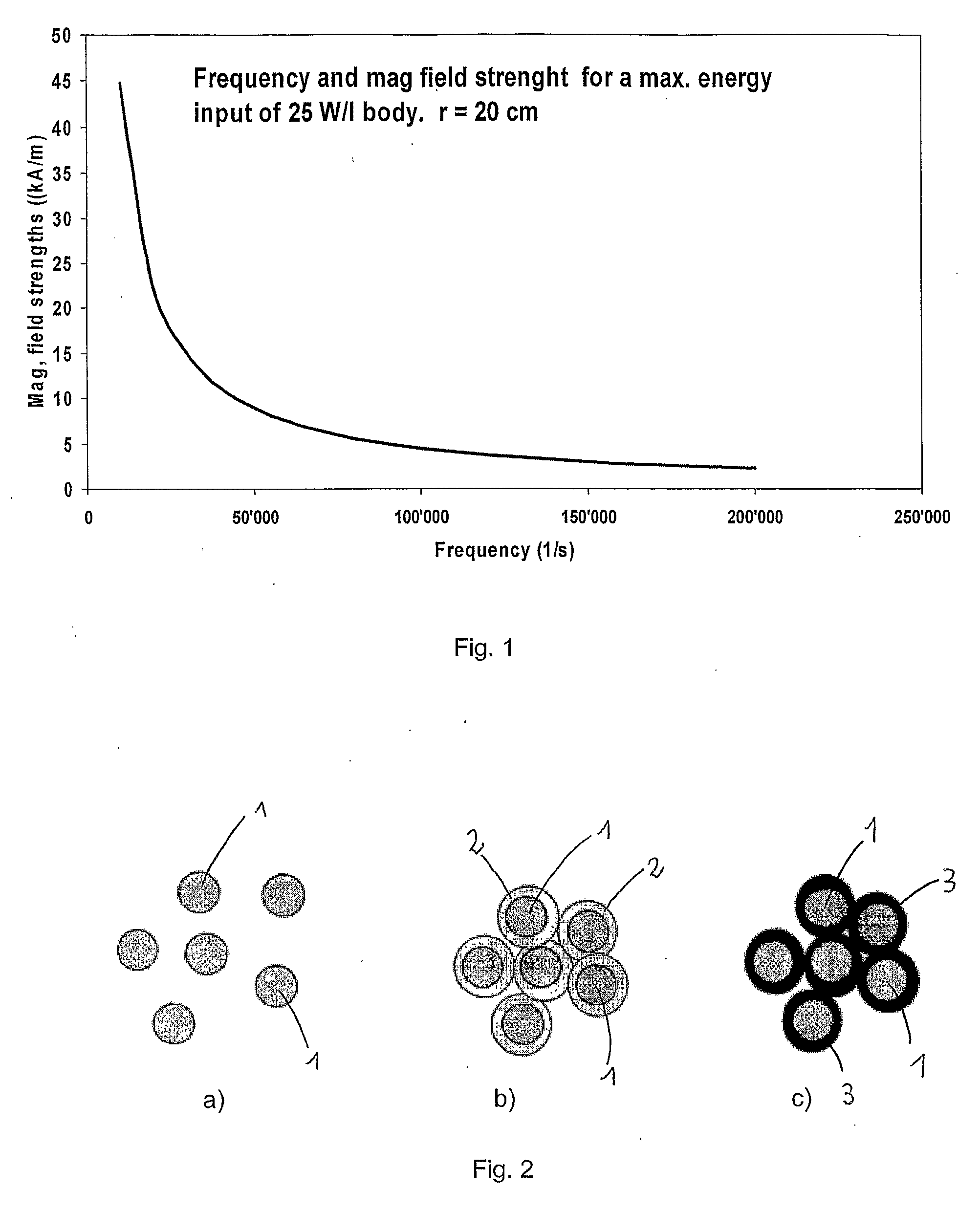
Injectable superparamagnetic nanoparticles for treatment by hyperthermia and use for forming an hyperthermic implant
The injectable formulation for treatment by hyperthermia comprises a liquid carrier and heat-generating superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles having a mean diameter not greater than 20 nm. Said injectable formulation is able to form in-situ a hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant upon contact with a body fluid or tissue. Said hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant may be useful for treating a tumor or a degenerative disc disease by hyperthermia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +2
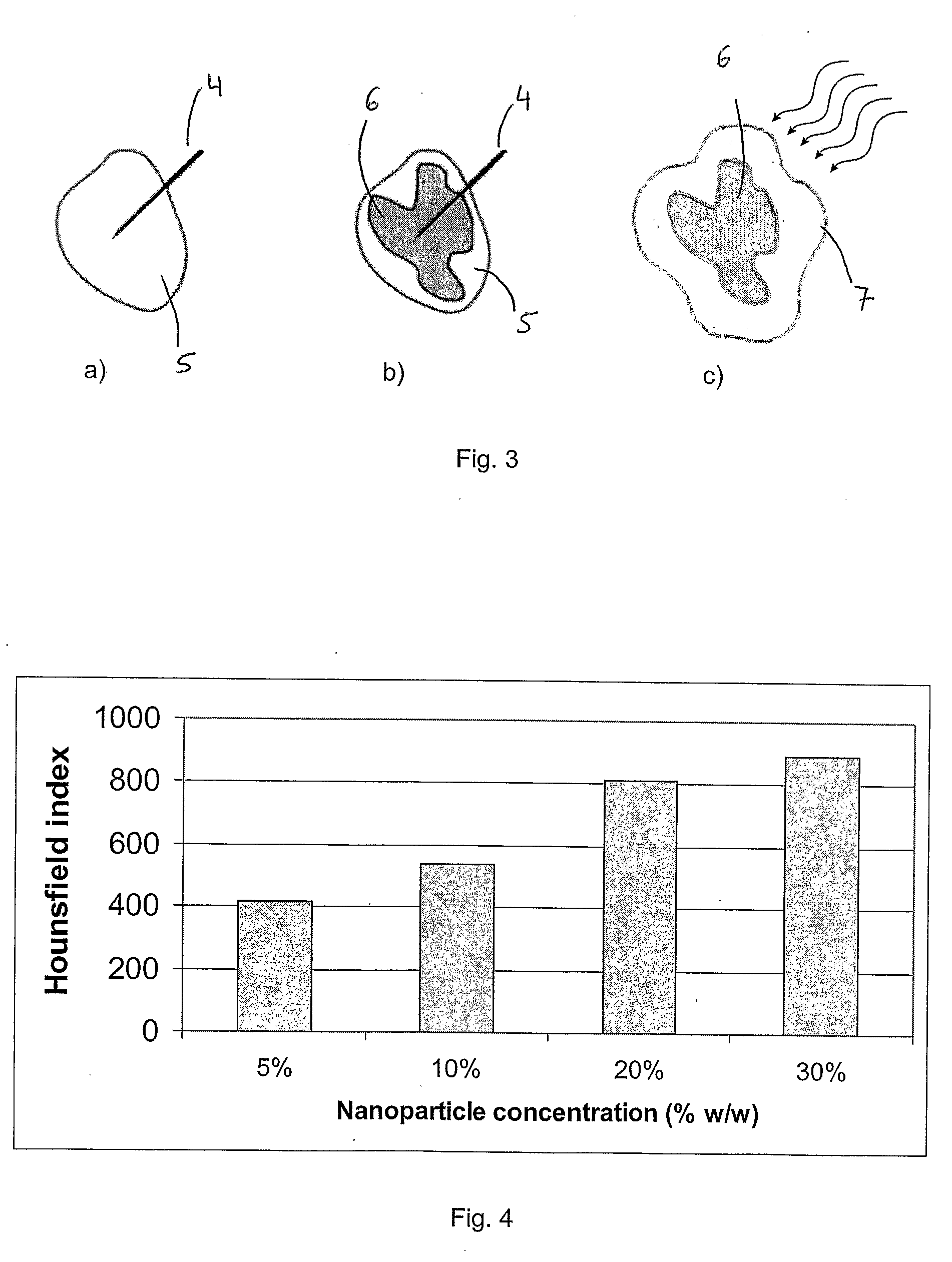
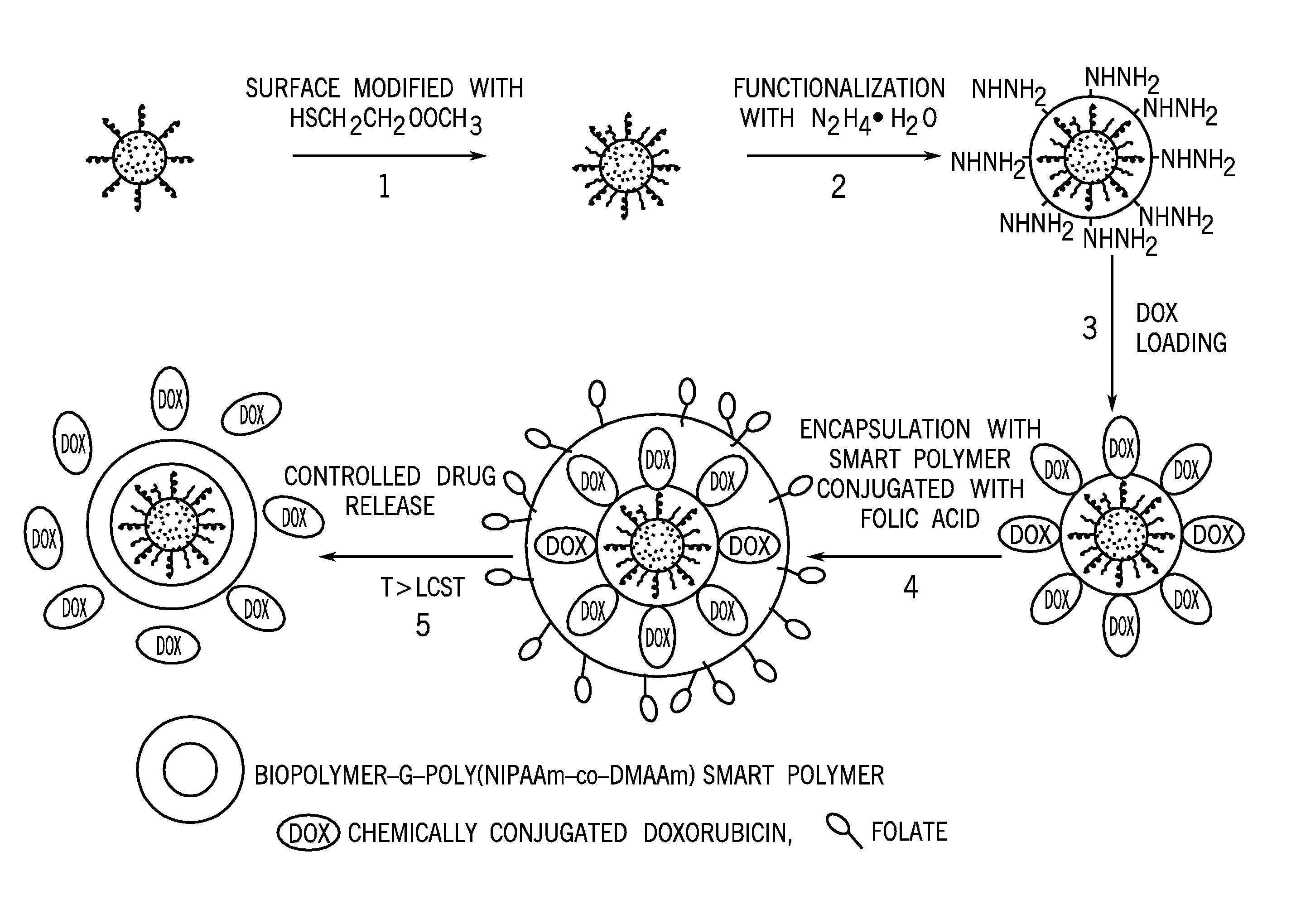
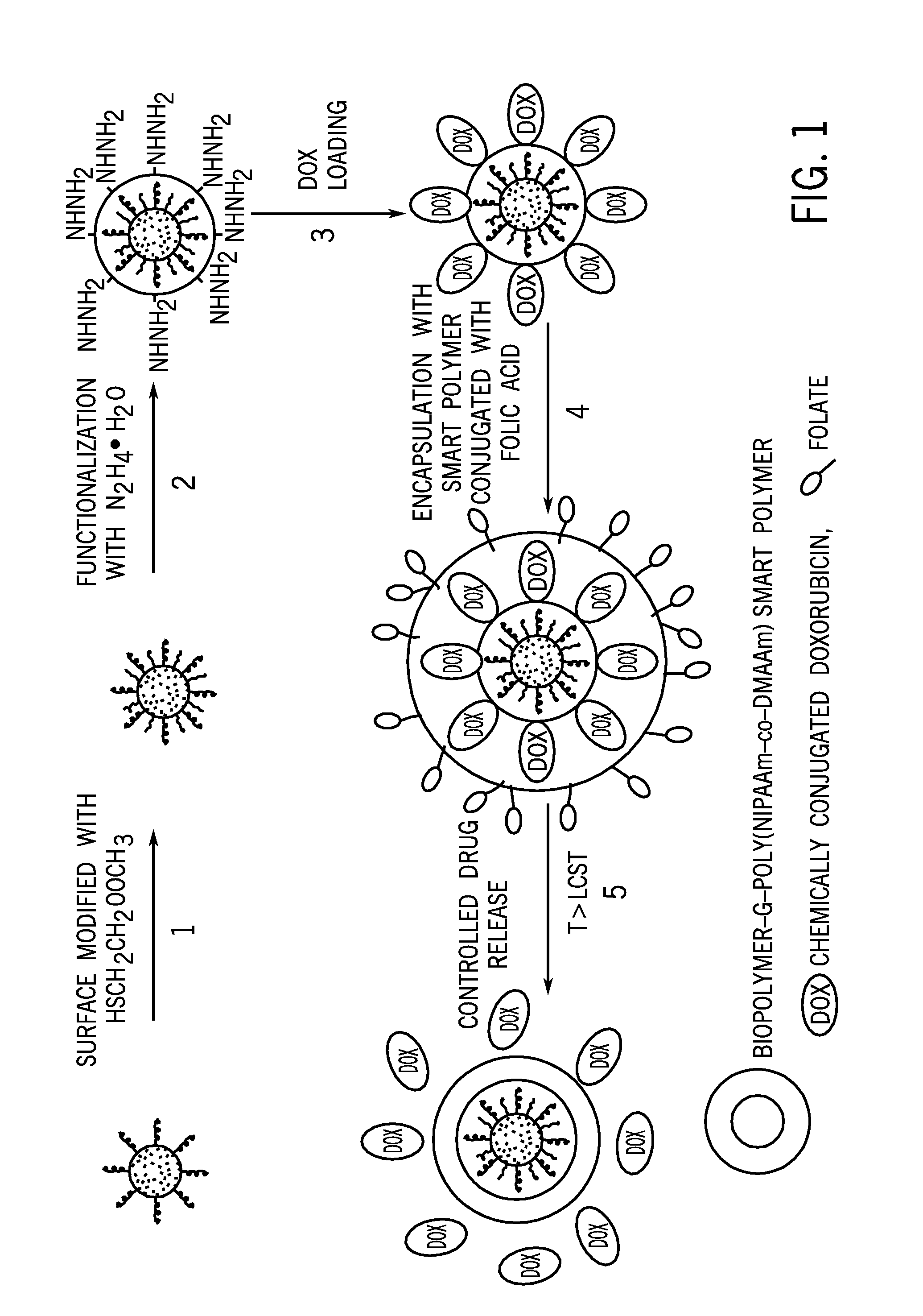
Superparamagnetic nanoparticle encapsulated with stimuli responsive polymer for drug delivery
InactiveUS20100168044A1Many possibilityReduce interactionPowder deliveryBiocideStimuli responsiveMedicine
The current invention is a novel superparamagnetic site-targeting nanoparticle comprising superparamagnetic nanoparticles encapsulated with a smart polymer. The superparamagnetic site-targeting nanoparticle comprises a functionalized superparamagnetic core that is conjugated with a therapeutic agent and then encapsulated with a smart polymer. The smart polymer can be any polymer that exhibits a reversible conformational or physio-chemical change in response to an external stimulus or stimuli.
Owner:MISRA DEVESH KUMAR
Ultrasensitive magnetic sensor based on giant faraday rotation
ActiveUS20120001625A1High constantMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesNon-linear opticsFiberOptical polarization
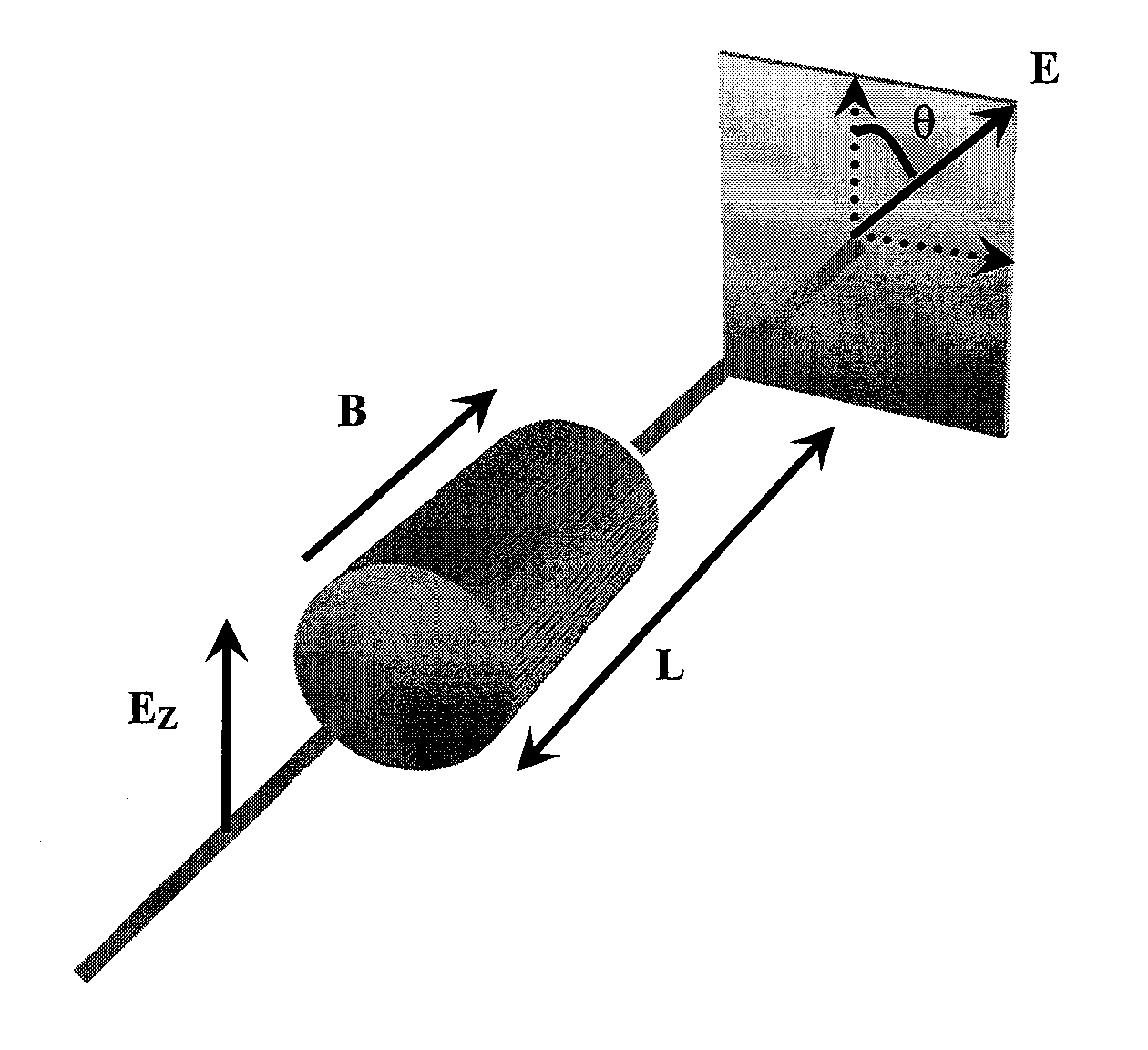
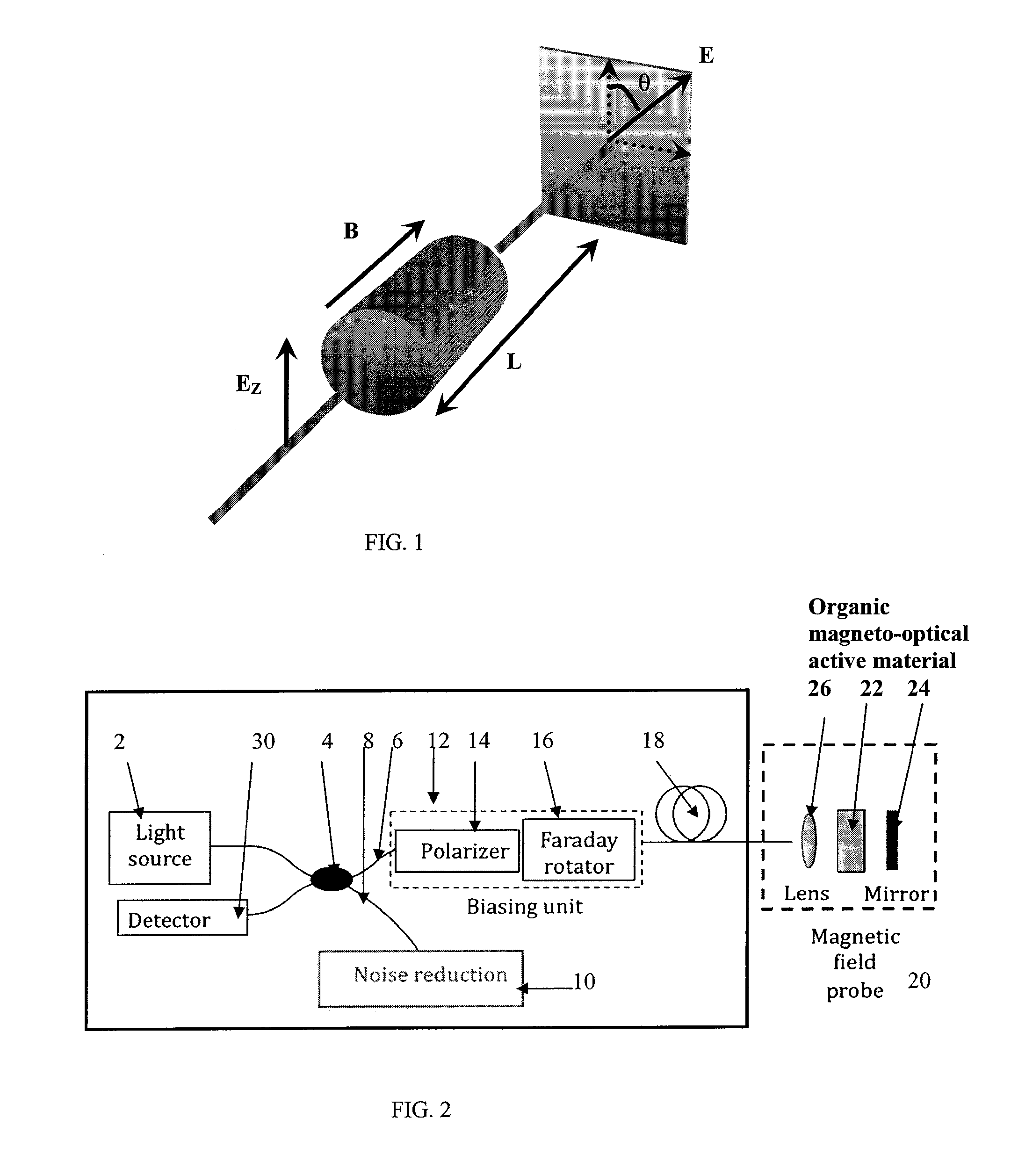
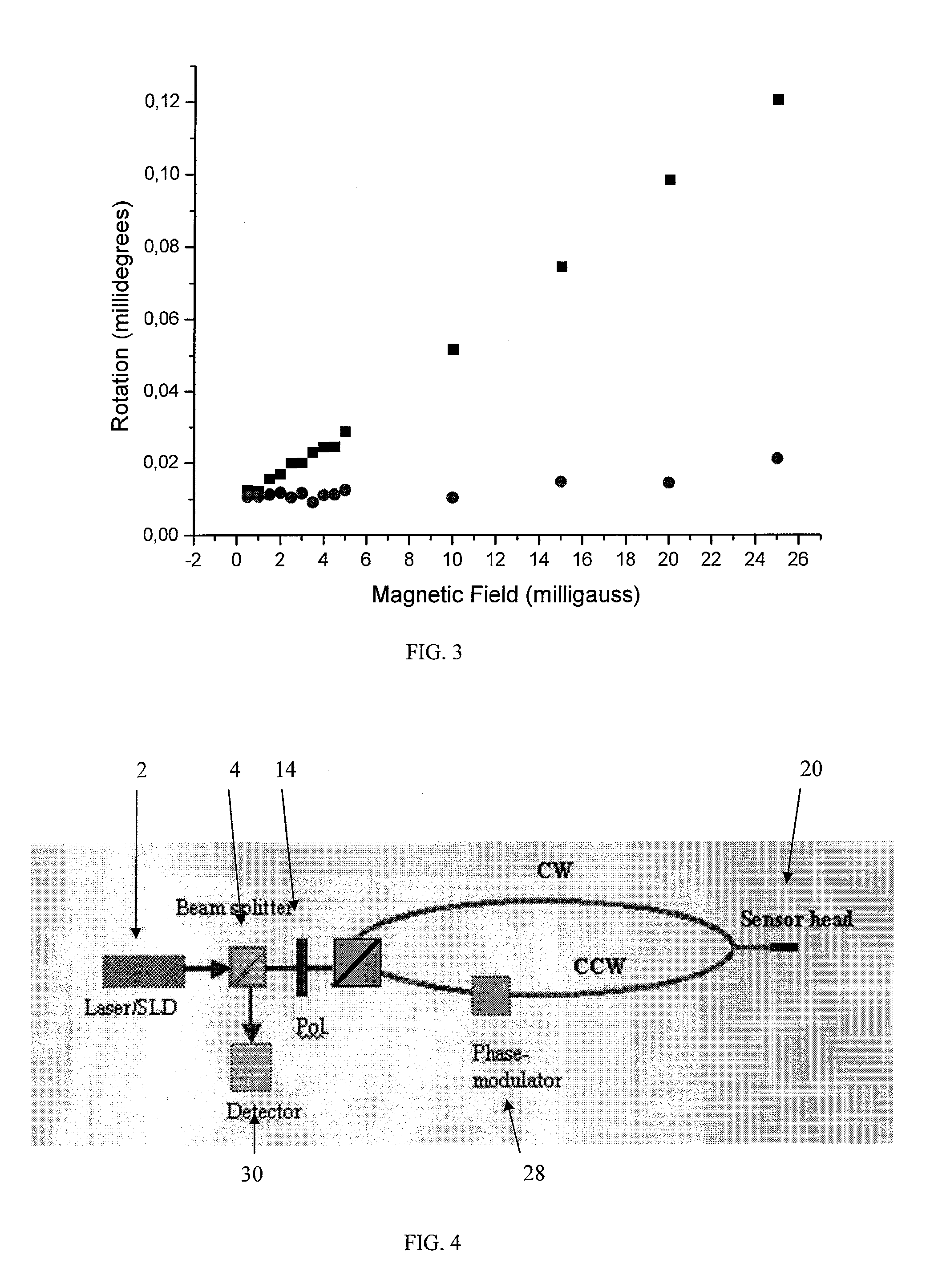
A high-resolution sensor of magnetic field sensor system and materials for use in such a system are described. The sensor systems measure a magnetic field using inorganic and / or organic magneto-optically active materials, e.g. polymer material and have an interferometer based on Faraday rotation. The polymer material is preferably in the form of a film. The polymer material has an optical property that is sensitive to the magnetic field, e.g. the Faraday rotation effect. The present invention also provides a sensor head structure comprising the above polymer material. The sensor head may be designed for use with an optical fiber or with mirrors. In particular the present invention provides a fiber Sagnac interferometer to measure the rotation of polarized plane of light. The present invention provides a fiber or mirror based Sagnac interferometer with passive phase bias applied to magnetic field sensing. This invention has the following three major aspects each being an embodiment of the present invention: 1. Sensing material: a conjugate polymer such as polythiophene and / or a polymer containing superparamagnetic nanoparticles that exhibits a giant Faraday rotation. 2. Magnetic field probe that incorporates the above polymer or polymer / nanoparticle composite, e.g. in the form of a film. 3. Sensor: The sensor combines an optical fiber-based Sagnac interferometer and the above magnetic field probe.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
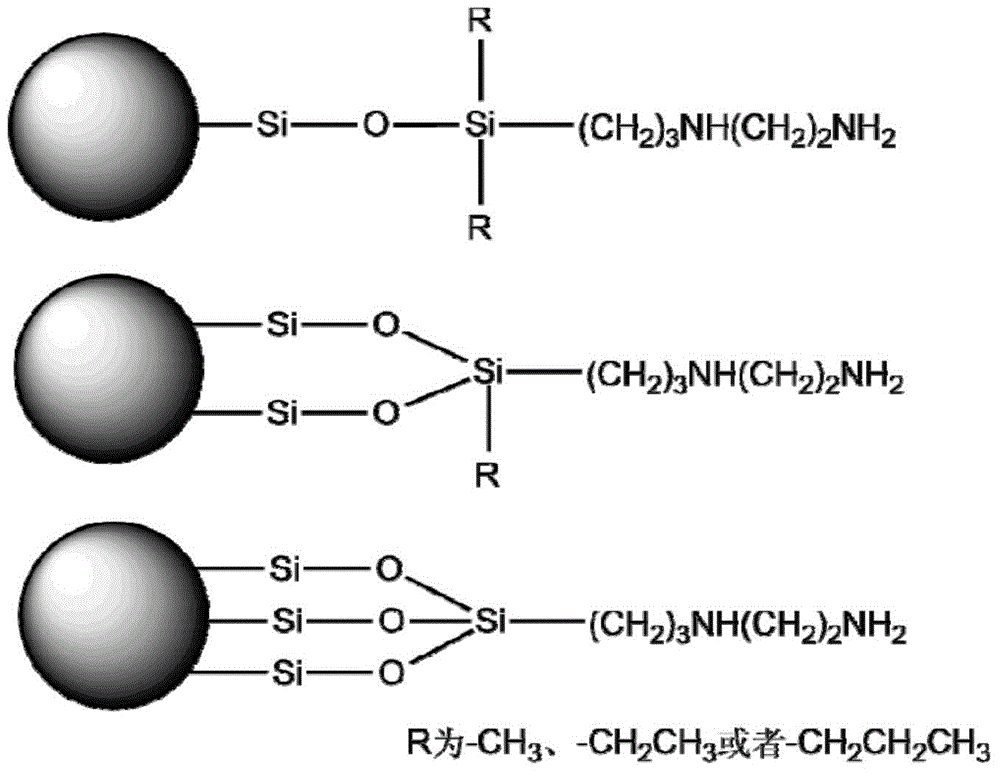
Superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by PSA and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN104525128AImprove adsorption capacityHigh ion exchange capacityCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersOrganic acidSorbent
The invention provides a superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA and a preparing method and application of the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA. According to the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA and the preparing method and application of the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA, silylanization is conducted on the surface of superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4, a silylating reagent with a PSA structure is bonded, and thus a PSA group is introduced. The superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA and the preparing method of the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA can be applied to the magnetic solid-phase extraction (M-SPE) field, and the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Fe3O4@SiO2@PSA modified by the PSA can serve as an adsorbent which is frequently used for magnetic solid-phase extraction, be applied to various pesticides such as carbamic acid ester, the organophosphorus pesticide and the herbicide and be used for absorption and extraction of target objects such as sulfonamides, organic acid and saccharides; meanwhile, the functional group of the PSA is a good binary ligand, in this way, the PSA is a good chelation material, can be used for extraction of metal ions and has high practical value and broad application prospect in the aspect of analytical investigation.
Owner:SUZHOU ENRICHING BIOTECH CO LTD
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS9017726B2Facilitated releaseImprove load effectPowder deliveryNanomedicineHybrid typeMRI contrast agent
Owner:NEXGEL BIOTECH CO LTD
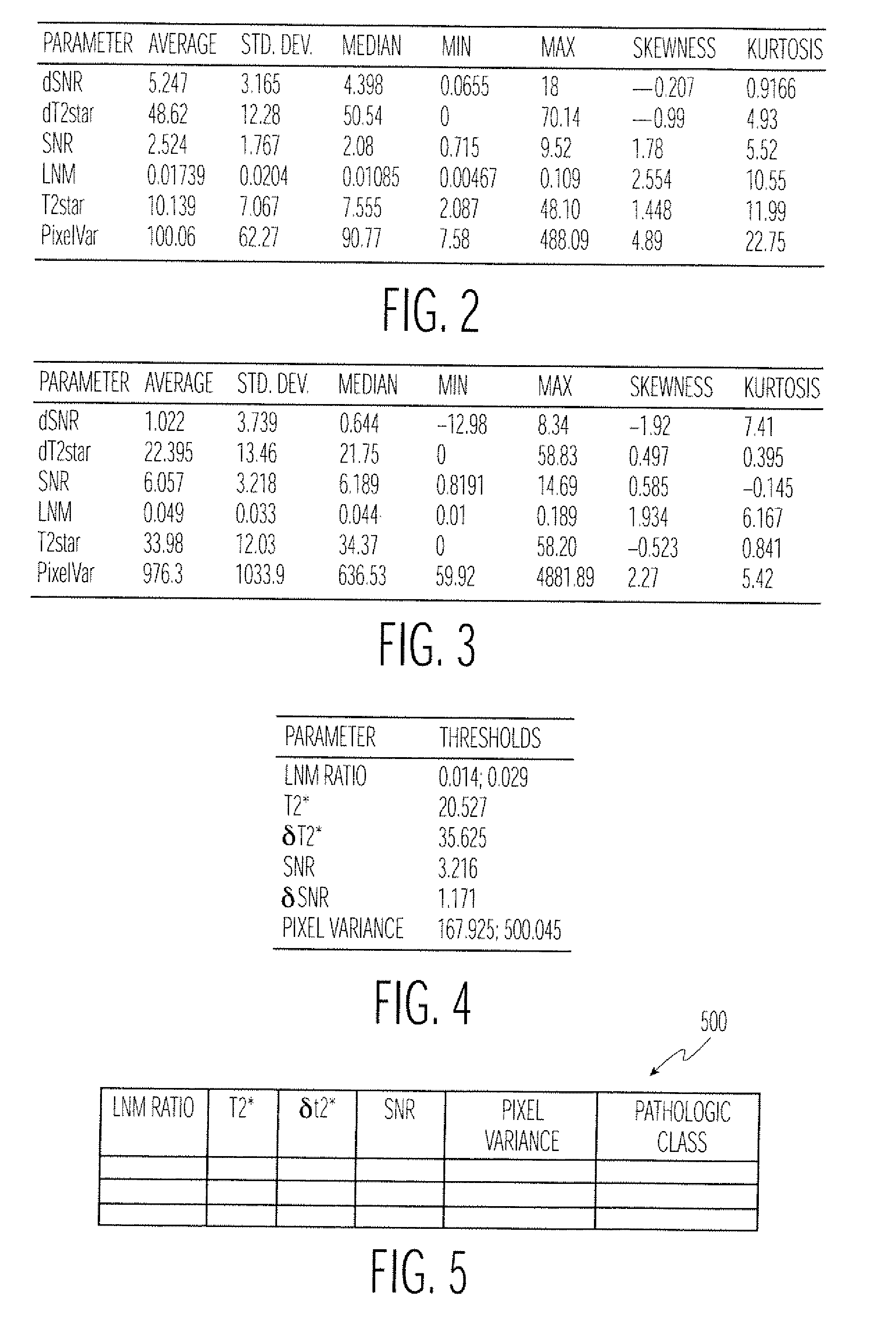
Method and Apparatus for Classifying Tissue Using Image Data
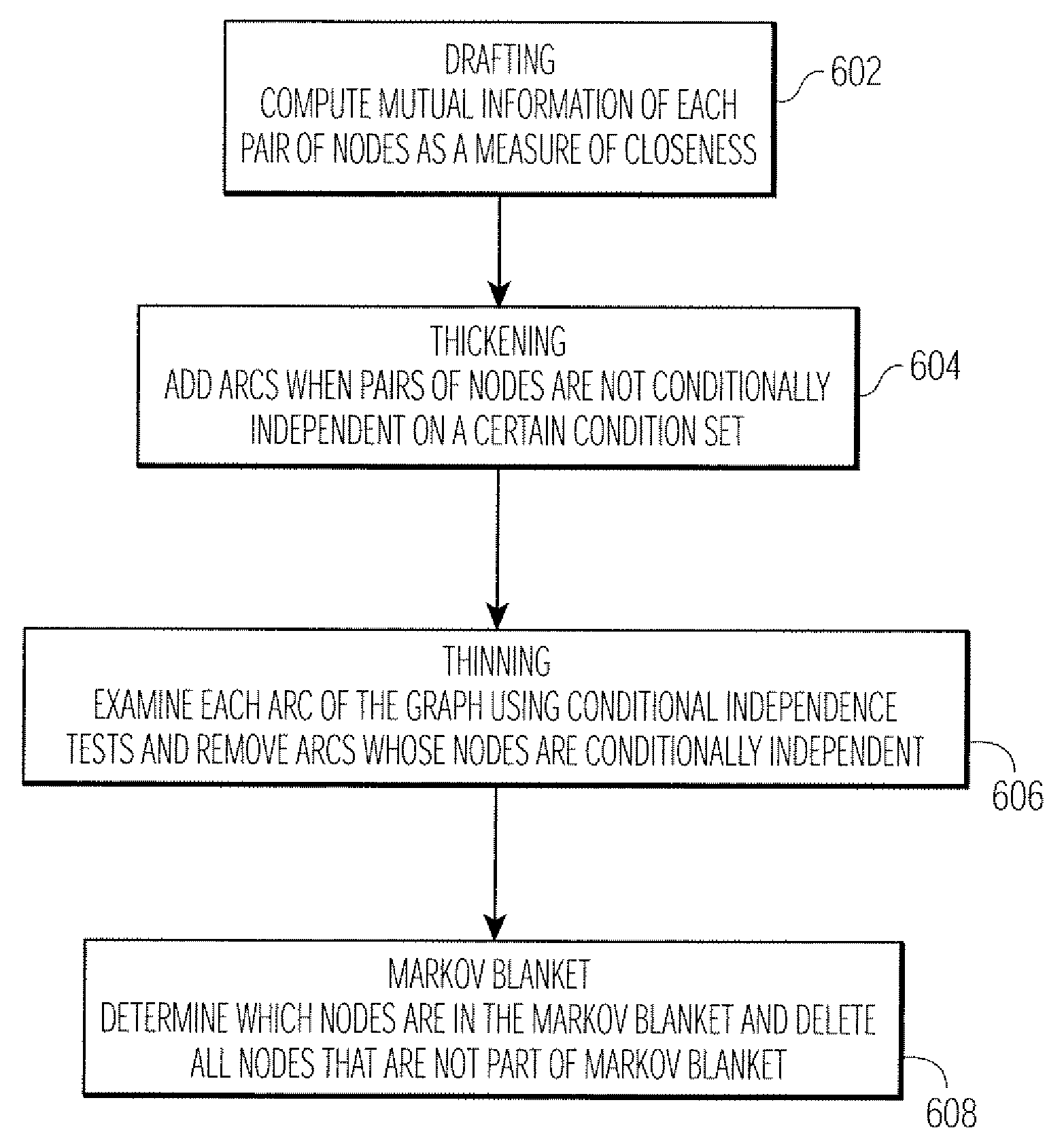
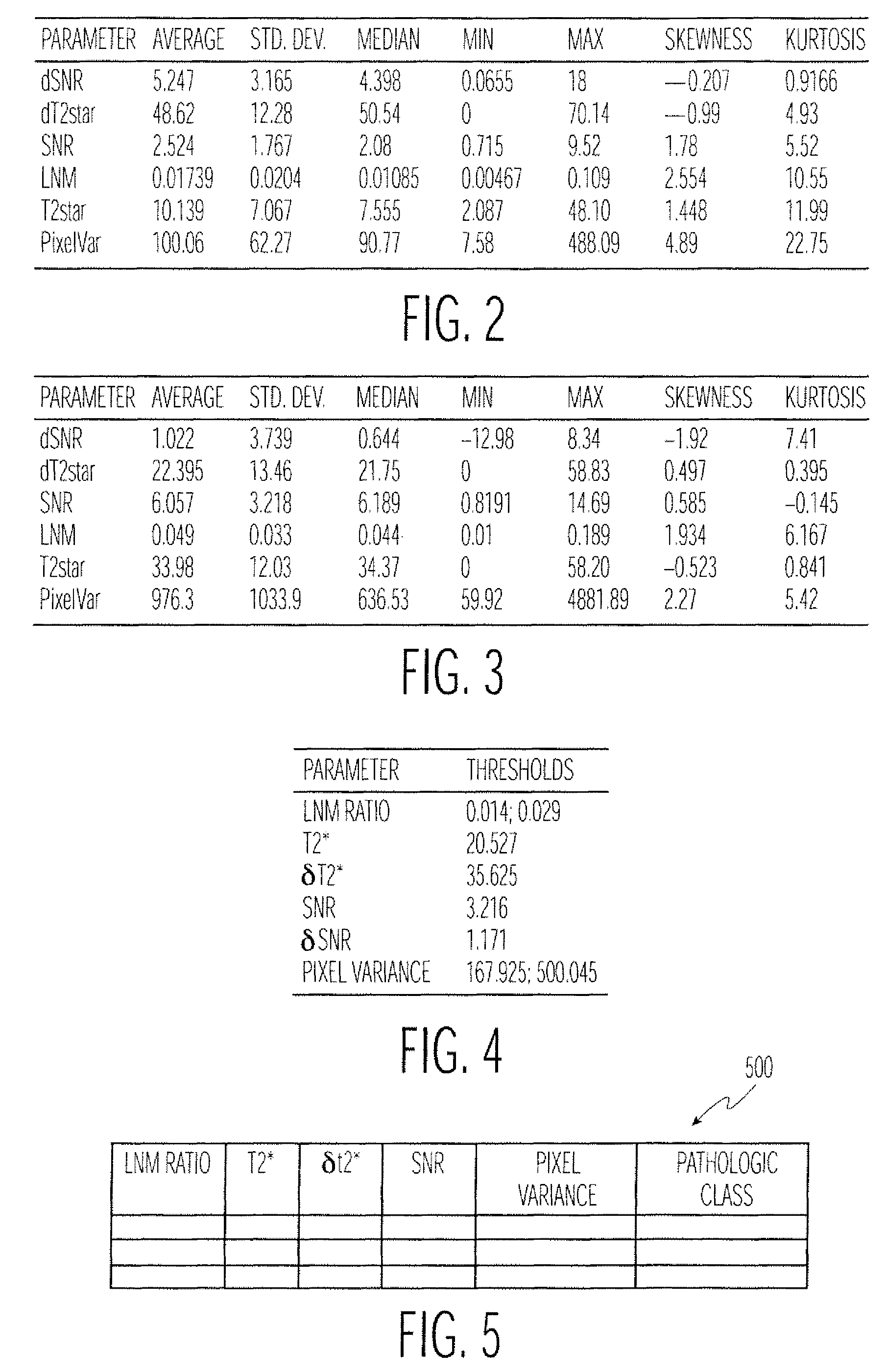
ActiveUS20070123773A1Advanced technologyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDecision model
Disclosed is a technique for classifying tissue based on image data. A plurality of tissue parameters are extracted from image data (e.g., magnetic resonance image data) to be classified. The parameters are preprocessed, and the tissue is classified using a classification algorithm and the preprocessed parameters. In one embodiment, the parameters are preprocessed by discretization of the parameters. The classification algorithm may use a decision model for the classification of the tissue, and the decision model may be generated by performing a machine learning algorithm using preprocessed tissue parameters in a training set of data. In one embodiment, the machine learning algorithm generates a Bayesian network. The image data used may be magnetic resonance image data that was obtained before and after the intravenous administration of lymphotropic superparamagnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
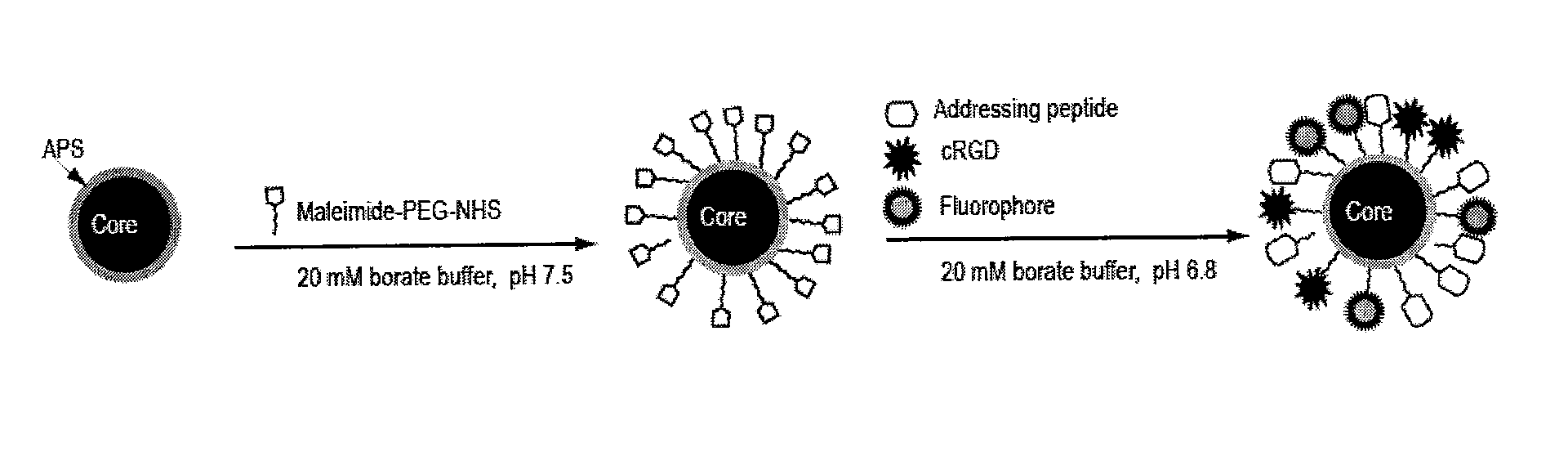
Magnetic, paramagnetic and/or superparamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention relates to nanoparticles having a mean diameter of <500 nm and comprising, at their surface, a selected material. The nanoparticles are taken up by cells under physiological conditions and can be used to isolate interaction partners of the selected material within the cells. The present invention provides important advantages in that it opens up new ways of identifying cellular components and of delivering a substance of interest specifically to a selected cell compartment. The nanoparticles are also useful as a tool of diagnosis and for the constitution of chemical libraries.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Nanosilicon dioxide/ferroferric oxide shell-core particle surface modifying method and magnetic nano material
ActiveCN104174039AImprove dispersion stabilityGood water solubilityMaterial analysis by optical meansInorganic material magnetismMicrospherePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a 'nanosilicon dioxide / ferroferric oxide shell-core particle surface modifying method and a magnetic nano material' and belongs to the technical field of medicines. A microemulsion method is adopted, ferroferric oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles with the particle size of about 15nm are added in a system of a surfactant NP-5 and cyclohexane, TEOS (Tetraethyl Orthosilicate) is introduced into a system of 30% ammonia water, so that silicon dioxide-coated ferroferric oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles are formed, then amination is carried out on the silicon dioxide-coated ferroferric oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles, and near infrared functional groups and polyethylene glycol sulfydryl functional groups are introduced under the action of covalence. The nanosilicon dioxide / ferroferric oxide shell-core particle surface modifying method comprises preparation of the nanosilicon dioxide / ferroferric oxide shell-core particles, amination on the near infrared functional groups on the surface of magnetic silicon dioxide pellets and polyethylene glycol sulfydrylation; the magnetic nano material prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be used for multimode imaging according to combination of molecular chemical substances different in size, proteins, short peptides, antibodies and radioactive elements, and diagnosis, treatment and monitoring on diseases are realized.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Magnetic resonance immune sensing method for detecting biomacromolecule
InactiveCN103278521AEasy to detectQuick checkAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBiological macromoleculePolystyrene microsphere
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance immune sensing method for detecting a biomacromolecule. Polystyrene microspheres coupled with specific antibody (1) are used to capture biomacromolecule antigens (2) in a sample and can specifically bonded with relaxation time sensing probes (4) based on superparamagnetic nanoparticles, thereby allowing the relaxation time sensing probes (4) to change from a dispersed state to an aggregate cluster state, and resulting in the change of relaxation time of surrounding water molecule protons. The detection is carried out according to a function relationship between the change amount and the biomacromolecule (2) by using a low field nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. The conjugated polystyrene microspheres-antibody conjugate (1) is employed to overcome steric hindrance of the magnetic resonance immunoreactions and increase specific binding sites. Compared with a conventional magnetic resonance immune sensing method, the method provided by the invention can significantly increased detection sensitivity of the biomacromolecule (2), is simple in sample pretreatment step and fast in analytic speed, and has very wide application prospects and development value.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Janus structure superparamagnetic nanoparticle and prepration method thereof
The invention discloses a Janus structure superparamagnetic nanoparticle and a prepration method thereof. The Janus structure superparamagnetic nanoparticle adopts a superparamagnetic nanoparticle as a core; two sides of the surface of the superparamagnetic nanoparticle are respectively grafted with polymer brushes with different properties; and the polymer brushes include hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer brushes, pH sensitive-temperature sensitive polymer brushes and the like. The Janus structure superparamagnetic nanoparticle disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small particle size, narrow distribution range, functionalized surface and the like.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method for superparamagnetic nanoparticle photocatalyst with Fe3O4-PAMAM-TiO2 core-shell structure
InactiveCN104923309AReduce direct contactReduce in quantityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNanoparticlePolyamide
The invention relates to a method for preparing a superparamagnetic nanoparticle photocatalyst with a Fe3O4-PAMAM-TiO2 core-shell structure by using polyamide-amine (PAMAM) dendrimer as a template and an isolation layer in a low-temperature aqueous solution. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, with the PAMAM dendrimer as the template, preparing a superparamagnetic Fe3O4-PAMAM nanoparticle colloidal solution by using a co-precipitation method; then adding the PAMAM dendrimer with different terminal groups and coating Fe3O4-PAMAM nanoparticles so as to form a dendrimer isolation layer; finally, dropwise adding a TiCl4 absolute ethanol solution, and carrying out normal pressure reaction and hydrothermal reaction so as to obtain the nanoparticles with the Fe3O4-PAMAM-TiO2 core-shell structure and a complete TiO2 shell layer; and carrying out washing and redispersion so as to obtain the nanoparticle photocatalyst with the Fe3O4-PAMAM-TiO2 core-shell structure.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic nano-carrier with targeted hydrophobic drug delivery to tumor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101632834ASolve solubilityReduce usageInorganic non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsNanocarriersSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical polymer material and nanobiomaterial, particularly relates to a magnetic nano-carrier with targeted hydrophobic drug delivery to tumor and a preparation method thereof. The magnetic nano-carrier is formed by encapsulating superparamagnetic nano-particles with amphiphilic segmented copolymer methoxy polye thylene glycol-poly(lactide- glycolide) (MePEG-PLGA) micelles. First, a large amount of MePEG-PLGA with good dispersion is synthesized by the improved solution polymerization process, and then the MePEG-PLGA is used as raw materials to encapsulate Fe3O4 nano-particles by the solvent evaporation process to obtain a magnetic nano drug carrier. The carrier is expected to solve the solubility problem of insoluble drugs, achieves slow release of drugs, and achieves the passive-targeting of the drugs by the EPR effect of tumor; Fe3O4 nano-particles are used in the active-targeting of the drugs to reduce the dosage and the side effect and improve the treatment efficiency; besides, the carrier can be used in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of tumor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Functionalized magnetic nanoparticle analyte sensor
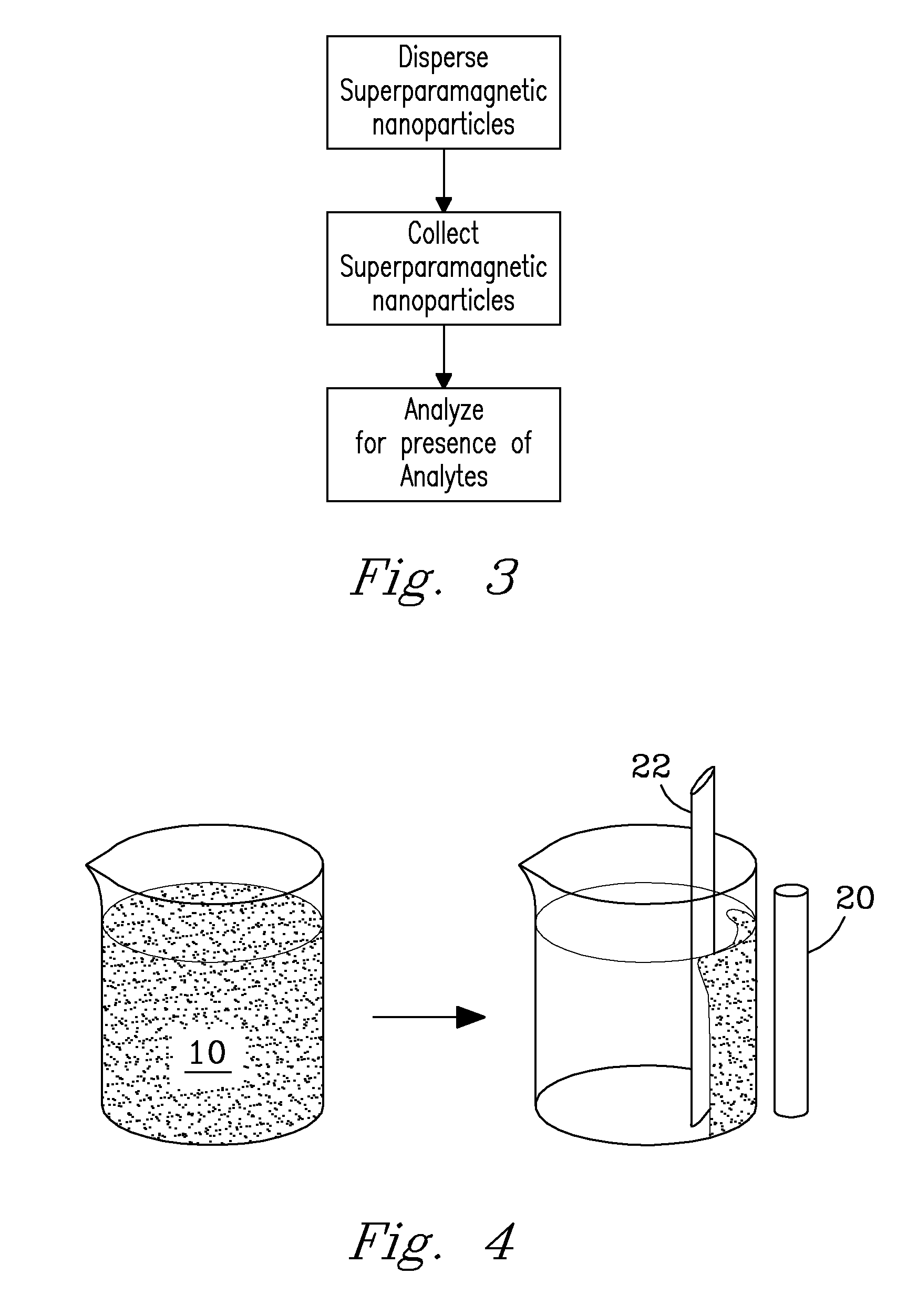
A method and system for simply and efficiently determining quantities of a preselected material in a particular solution by the placement of at least one superparamagnetic nanoparticle having a specified functionalized organic material connected thereto into a particular sample solution, wherein preselected analytes attach to the functionalized organic groups, these superparamagnetic nanoparticles are then collected at a collection site and analyzed for the presence of a particular analyte.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method and apparatus for classifying tissue using image data
Disclosed is a technique for classifying tissue based on image data. A plurality of tissue parameters are extracted from image data (e.g., magnetic resonance image data) to be classified. The parameters are preprocessed, and the tissue is classified using a classification algorithm and the preprocessed parameters. In one embodiment, the parameters are preprocessed by discretization of the parameters. The classification algorithm may use a decision model for the classification of the tissue, and the decision model may be generated by performing a machine learning algorithm using preprocessed tissue parameters in a training set of data. In one embodiment, the machine learning algorithm generates a Bayesian network. The image data used may be magnetic resonance image data that was obtained before and after the intravenous administration of lymphotropic superparamagnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
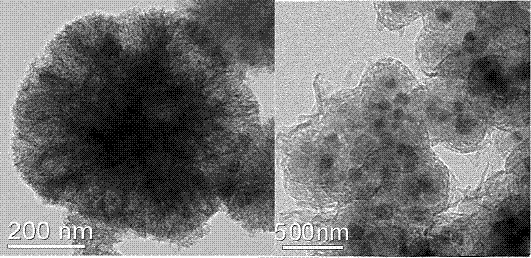
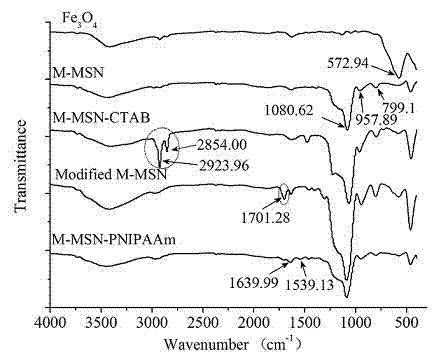
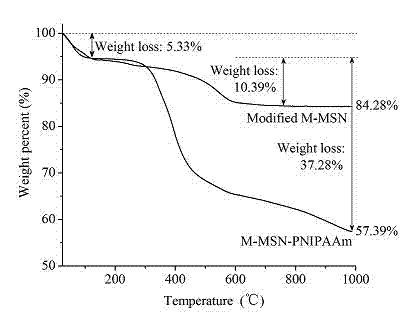
Preparation method of thermo-magnetic dual responsive mesoporous silicon microspheres
InactiveCN103495368ALow priceEasy to operateOther chemical processesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrosphereSio2 nanoparticle
The invention relates to a preparation method of thermo-magnetic dual responsive mesoporous silicon microspheres. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles; 2) preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles; 3) synthesis of magnetic responsive mesoporous silicon microspheres [M-MSN-CTAB (Magnetic-Mesoporous Silicon Nanoparticle-Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide)]; 4) modification of M-MSN-CATB; 5) preparation of the thermo-magnetic dual responsive mesoporous silicon microspheres [M-MSN-PNIPAAm (Poly N-Isopropyl Acryl Amide)]. The preparation method provided by the invention is reasonable in design method and simple and feasible in operation, and can be used for successfully preparing novel thermo-magnetic dual responsive M-MSN by taking superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a core, mesoporous silicon as a middle interlayer and a temperature sensitive copolymer as a shell. The M-MSN-PNIPAAm has the characteristics of superparamagnetism, high specific surface area and high pore volume of mesoporous silicon and temperature response. The M-MSN-PNIPAAm can be used as a carrier of medicines to prevent medicines and active components from being damaged, and purpose of targeted delivery and controlled release is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Ferroferric oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating stem cell for exosome osteogenesis
ActiveCN109745341AFacilitate depositionStimulate osteogenic activitySkeletal disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteoblastOrthopedic disorders
The invention discloses an exosome preparation derived from a stem cell. The exosome preparation is an exosome secreted by a Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating the stem cell. The invention further provides the application of the exosome preparation in preparing a pharmaceutic preparation for promoting mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation and the application of the exosomepreparation in preparing a biological agent for treating orthopedic disorders or bone repair materials. In consideration of the complicated pathophysiologic process of osteonecrosis and bone defects,the exosome preparation prepared by the exosome secreted by the Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticle stimulating the stem cell is adopted, intramuscular administration can be adopted at local bone defect parts, or local filling is performed after the exosome preparation is mixed with absorbable gel, the exosome preparation directly reaches the focus, the osteogenic activity of the mesenchymal stem cell is motivated, the deposition of osteoblasts is promoted, and the repair of the osteonecrosis or bone defects is promoted.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
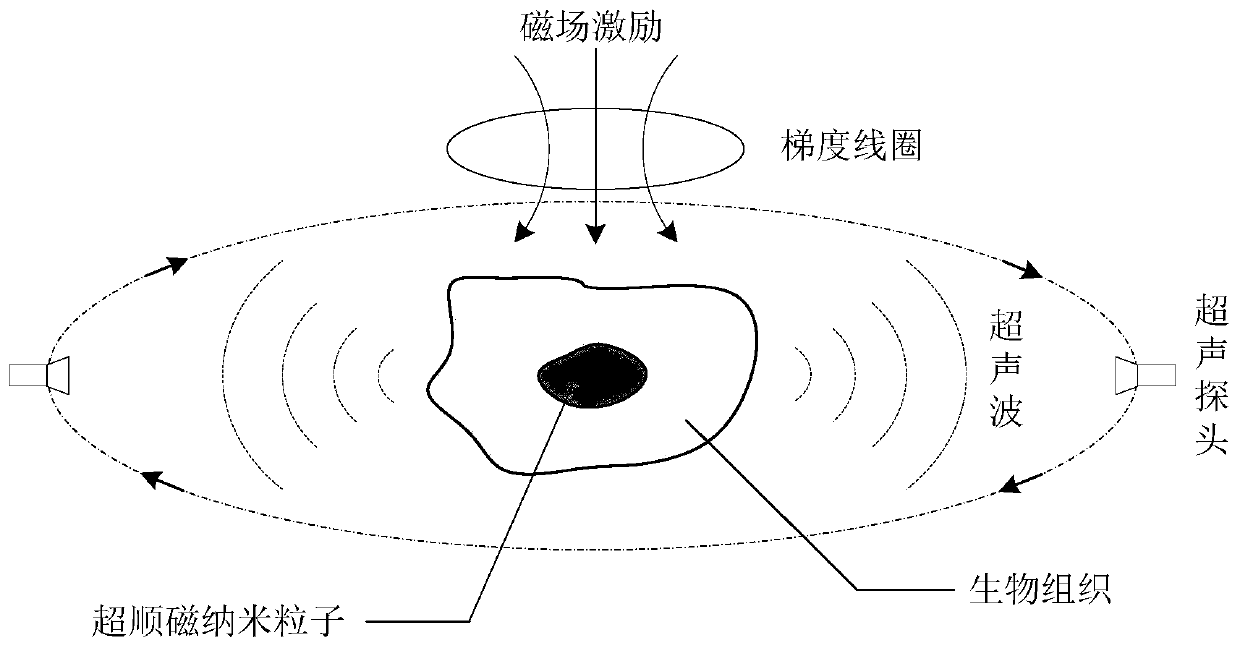
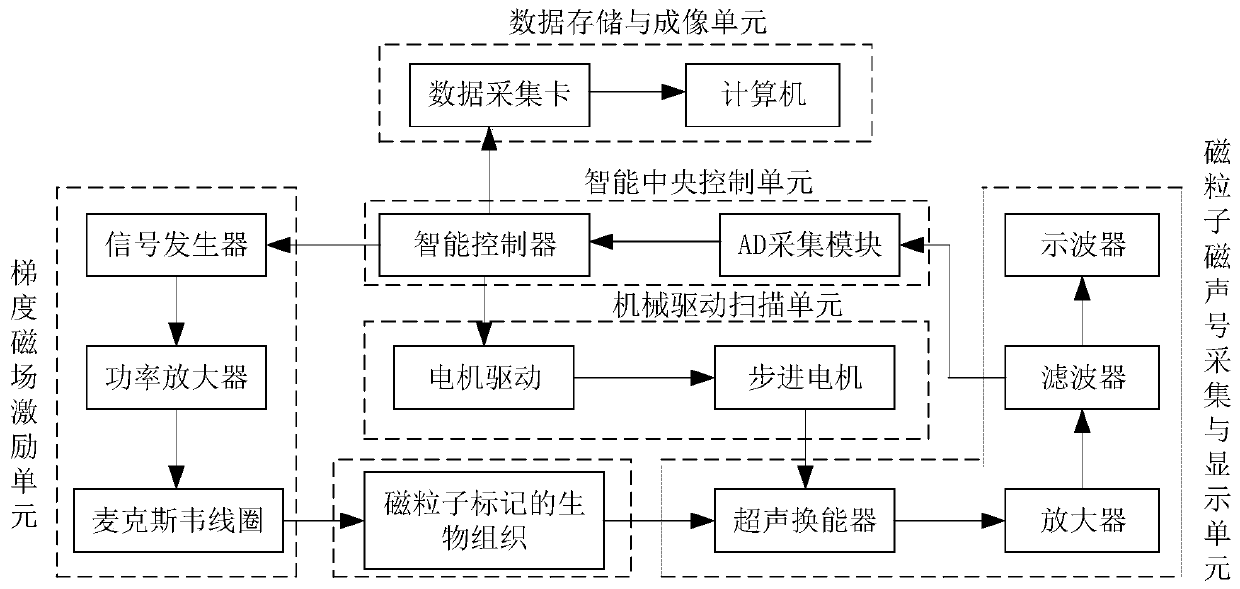
Magnetic-acoustic-magnetic particle concentration imaging device and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN110755072AExtensive research and application valueInfrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSound sourcesControl signal
The invention discloses a magnetic-acoustic-magnetic particle concentration imaging device and an imaging method thereof, and the device comprises a gradient magnetic field excitation unit which generates a gradient magnetic field and acts on an imaging body containing superparamagnetic nanoparticles; an magnetoacoustic signal acquisition and display unit which is used for acquiring magnetoacoustic signals and conditioning and displaying the acquired signals; a mechanical driving scanning unit which is used for driving the magnetoacoustic signal acquisition and display unit to perform annularscanning to receive an ultrasonic signal; an intelligent central control unit which is used for providing control signals for the gradient magnetic field excitation unit and the mechanical driving scanning unit as well as processing the acquired data; and a data storage and imaging unit which is used for further processing the acquired magnetoacoustic signals and carrying out image reconstructionon the magnetic particle concentration. A superparamagnetic nanoparticle concentration matrix is calculated by using the sound pressure information, and the ultrasonic information emitted by each point sound source is recorded through the annular scanning of an ultrasonic probe, so that the superparamagnetic nanoparticle concentrations at different positions are solved, and the whole space imagingis realized.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic Relaxometry using Brownian Randomization, Neel Relaxation, or Combinations Thereof
InactiveUS20130289383A1Saving considerable later discomfortDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineNanoparticle
The present invention can provide a method of determining the communication of substances between a first region and a second region of a patient's body. An example method according to the present invention can comprise: (a) introducing into the first region a plurality of superparamagnetic nanoparticles, having properties such that they undergo Brownian motion that randomizes the orientation of the nanoparticles according to a predetermined characteristic time; (b) after a time sufficient to allow transport of nanoparticles from the first region to the second region, subjecting the second region to an applied magnetic field of sufficient strength to induce magnetization of individual nanoparticles, and having a substantially uniform direction throughout the second region; (c) measuring the magnetic field of the second region at a plurality of times after ceasing application of the magnetic field; (d) analyzing the measured magnetic field to detect signals that correspond to decay of the magnetic field due to randomization of the nanoparticles' orientation by Brownian motion; (e) determining the presence of nanoparticles in the second region from the signals detected in step (d).
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC
Supported catalyst and preparation method thereof
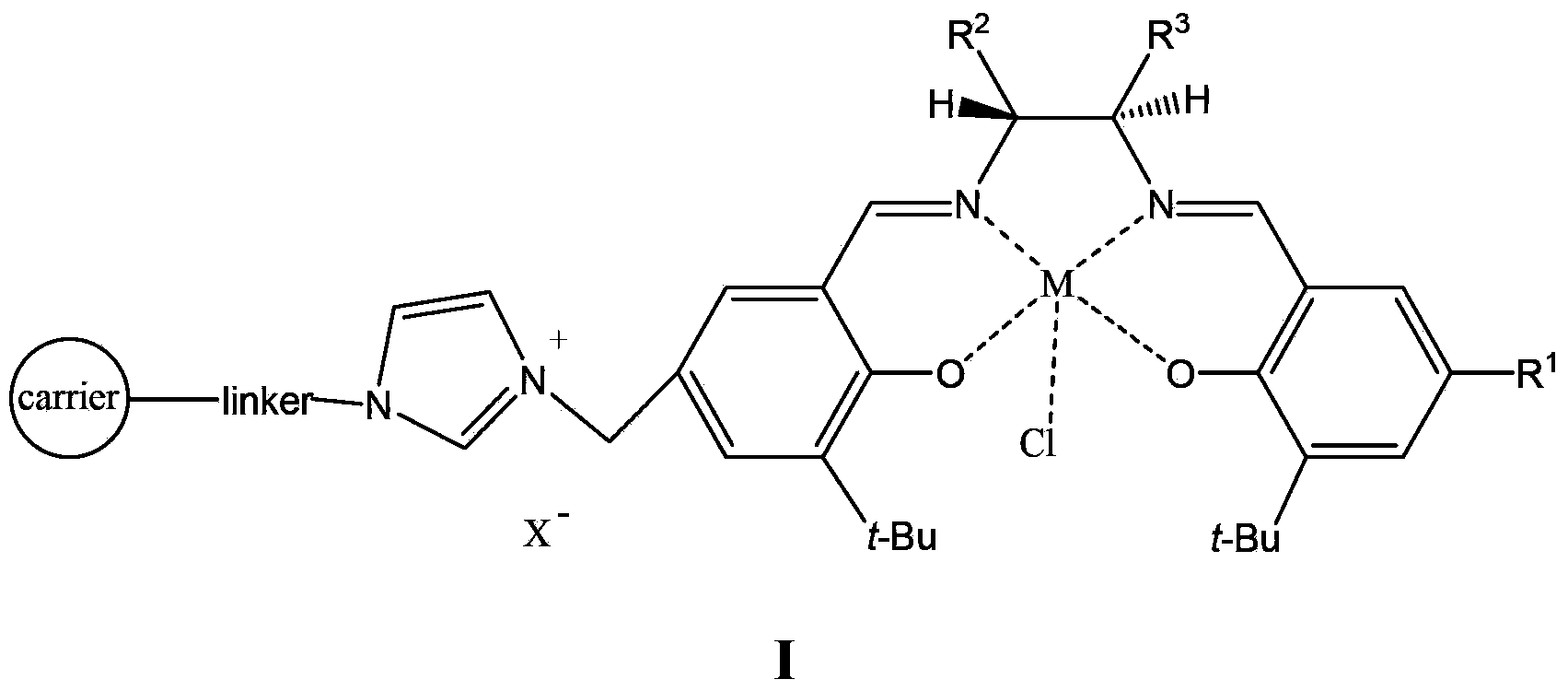
InactiveCN104117392AIncrease loadSimple preparation processOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylHalogen
The invention provides a supported catalyst with the structural formula I shown in the specification. In the formula I, a carrier is superparamagnetic nanoparticles or superparamagnetic nanoparticles wrapped by silicon dioxide; M is metal ions, X<-> is inorganic or organic negative ions; R<1> is C1-C6 alkyl, halogen substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C6-C12 aryl, halogen or C1-C6 alkyl substituted C6-C12 aryl, halogen or C1-C4 alkoxy; R<2> and R<3> are respectively C1-C6 alkyl or C6-C12 aryl, or R<2> and R<3> are connected with each other to form -(CH2)3- or -(CH2)4-; a linker is a connector. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the supported catalyst. The supported catalyst can be used as a chiral catalyst for asymmetric epoxidation reaction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISOAR PHARMA +2
Method for preparing magnetic nano carrier immobilized aldolase with high substrate tolerance
InactiveCN102517276AIncreased substrate toleranceEasy to recycle and reuseOn/in inorganic carrierChemistryPrecipitation
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnetic nano carrier immobilized aldolase with high substrate tolerance. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing super-paramagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles by co-precipitation of a mixture of ferrous and ferric iron salts, modifying the particles by using a silane coupling agent, and activating the outer surfaces of the modified particles by using glutaraldehyde to obtain surface activated magnetic nano particles; 2) stirring a purified and desalted aldolase buffer solution and a magnetic carrier at a low temperature, washing, performing freeze drying, and thus obtaining the magnetic nano carrier immobilized aldolase; and 3) catalyzing 2-deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphoric acid by using the magnetic nano carrier immobilized aldolase as a catalyst to obtain 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate and acetaldehyde. In the reaction of catalyzing the 2-deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphoric acid by using the immobilized aldolase, the tolerance of the acetaldehyde substrate is remarkably improved, and the recycling operation of enzyme is greatly simplified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing high-magnetization chitosan nanospheres
ActiveCN102580642AGood repeatabilityEasy to prepareNanotechnologyMicroballoon preparationUltrasonic emulsificationMagnetization
The invention provides a method for preparing high-magnetization chitosan nanospheres. according to the invention, an improved ultrasonic emulsification pre-crosslinking technique is adopted, namely, a chitosan solution in which superparamagnetic nanoparticles are dispersed is taken as a water phase, and liquid paraffin is taken as an oil phase, a high-magnetization and particle-size-controlled chitosan nanosphere is obtained through adjusting the composition of the oil and water phases and carrying out mixing, ultrasonic dispersion and ultrasonic pre-crosslinking,. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, high in efficiency and low in cost; the highest saturation magnetization of the obtained chitosan nanosphere can be more than 45 emu / g; and the method has great application potentials in the fields of biological medicines, enzyme engineering and magnetic separation.
Owner:ZIBO KANGBEI MEDICAL DEVICES
Method for preparing ordered magnetic nanoparticle composite film with super-high density
InactiveCN101787522AAvoid particle agglomerationPhenomena that prevent damageChemical vapor deposition coatingComposite filmHigh density
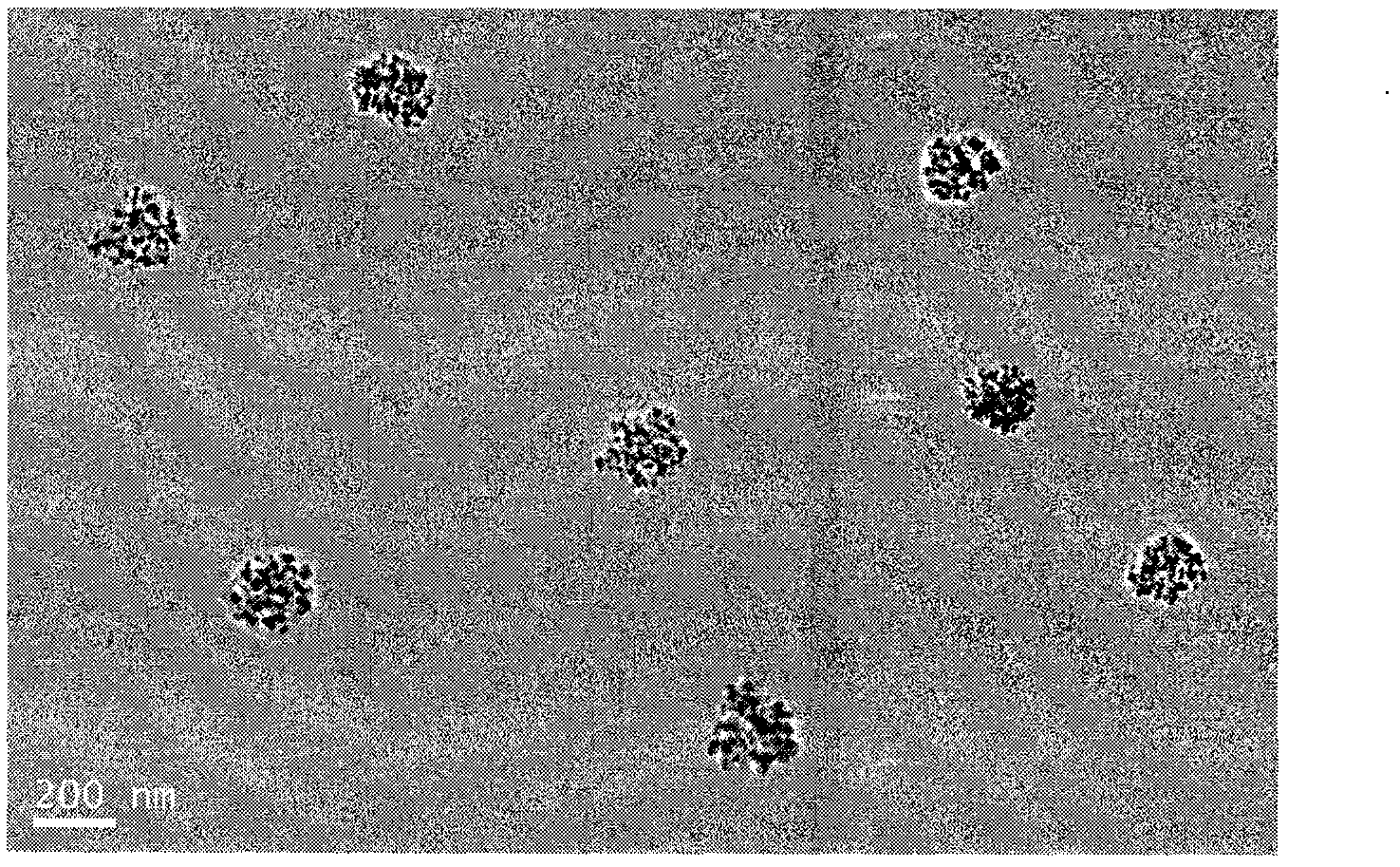
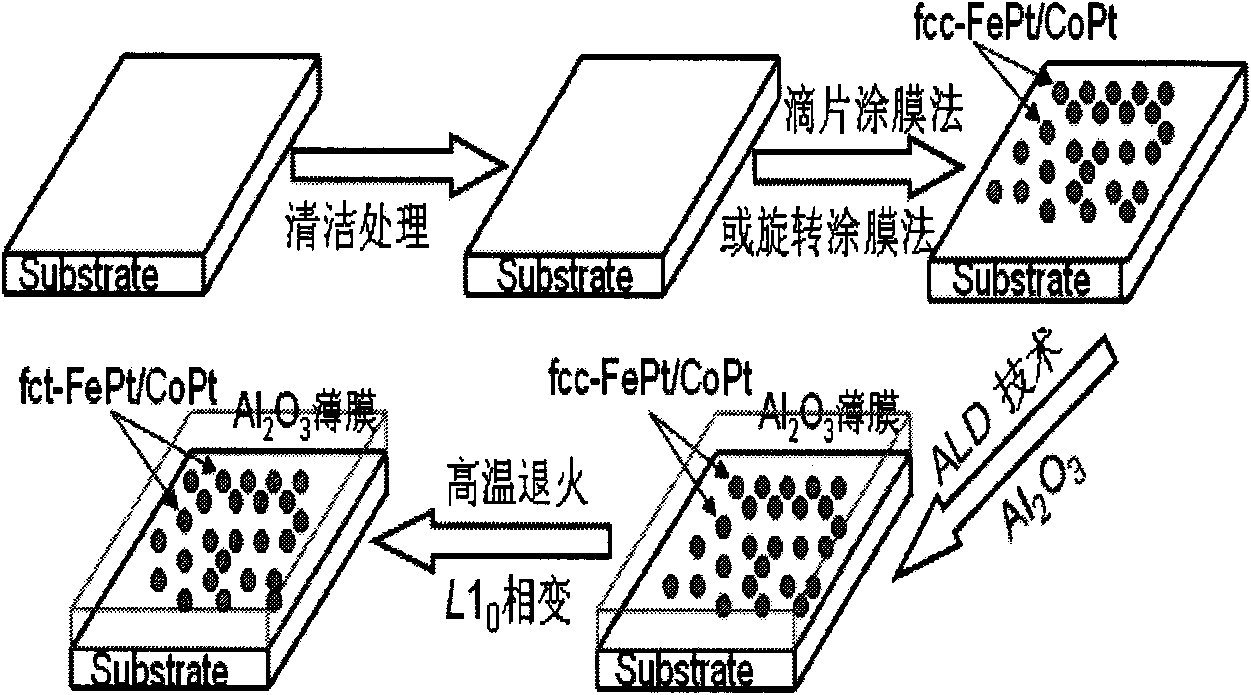
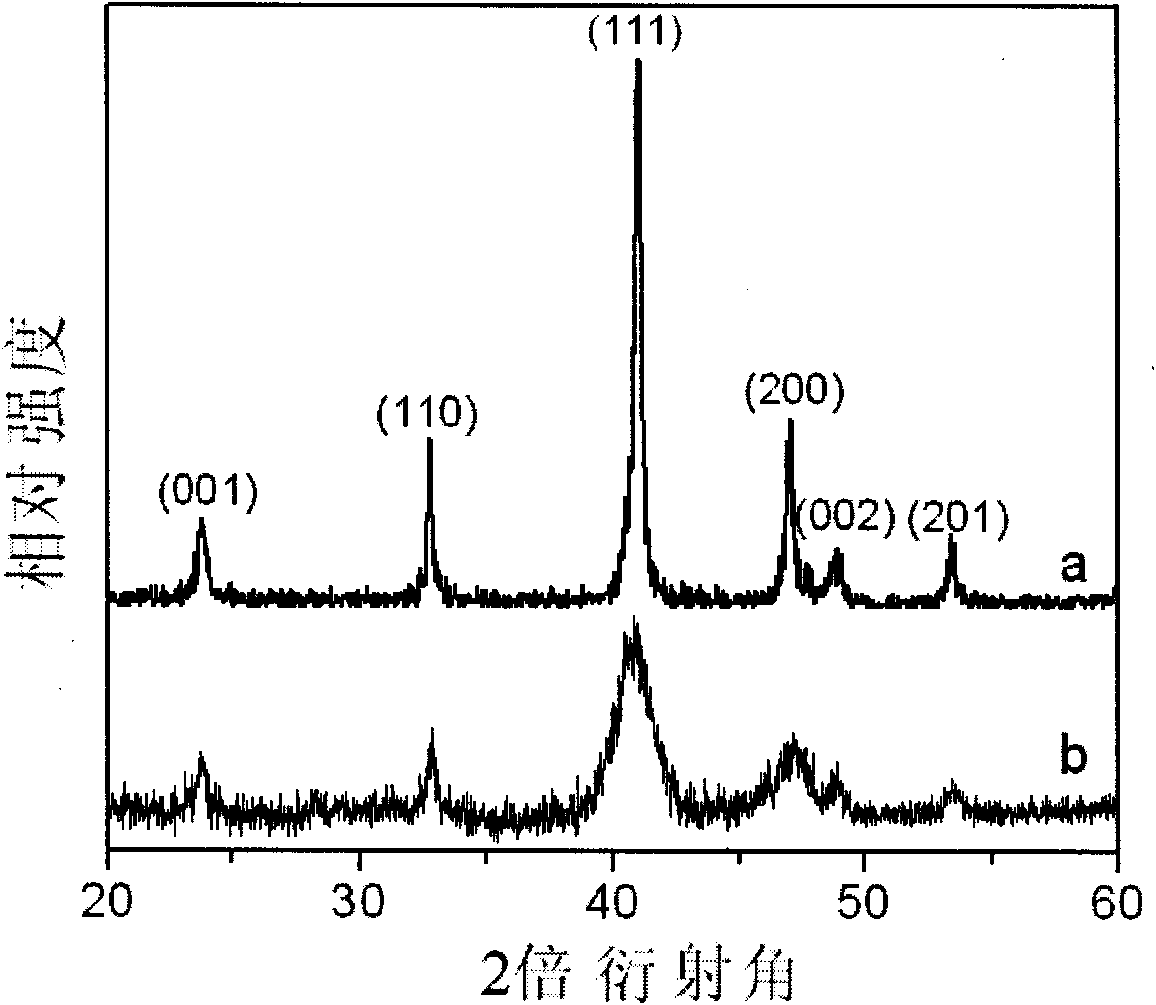
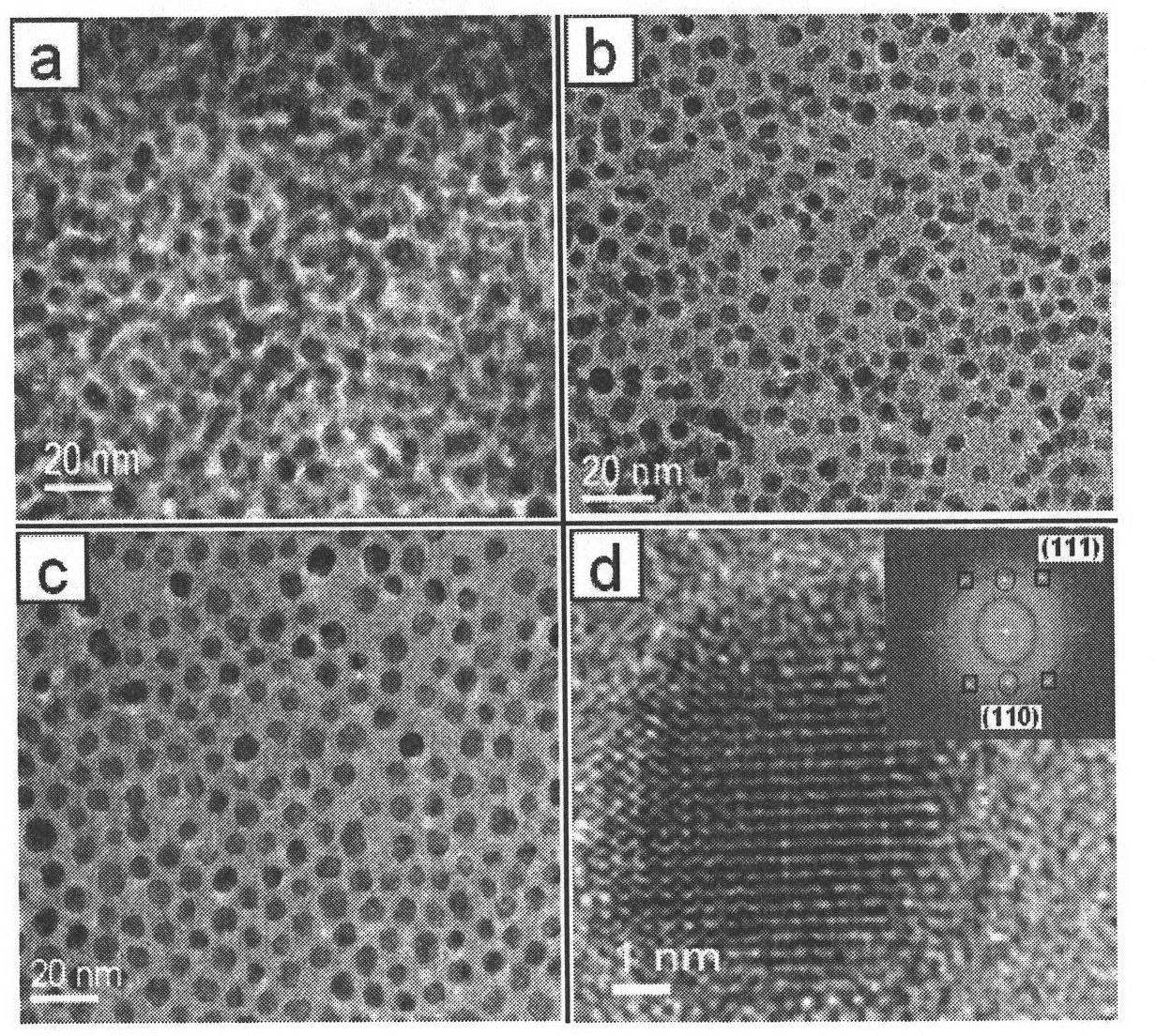
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ordered magnetic nanoparticle composite film with super-high density, which comprises the steps of: at first, preparing FePt / CoPt superparamagnetic nanoparticle; self-assembling a FePt / CoPt superparamagnetic nanoparticle-containing nonmagnetic substrate and using an atomic layer deposition technique to grow an inorganic nonmagnetic matrix film protective layer of 10-30 nanometers on the surface of the substrate containing a single layer of FePt / CoPt nanoparticle lattice; putting the deposited substrate in a tubular diffusion furnace for annealing for 30 to 90 minutes at high temperature from 600 to 750 DEG C in a reducing atmosphere of 90-97% of Ar and 10-3% of H2 to result in the composite film of FePt / CoPt ferromagnetic nanoparticles and oxides. The method can obtain the ordered FePt / CoPt nanoparticle composite film with L10 phase, good magnetic property and the magnetic coercive field up to Hc=5.9kOe.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com