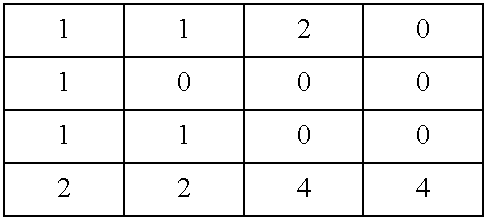Patents
Literature
79 results about "In vivo analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
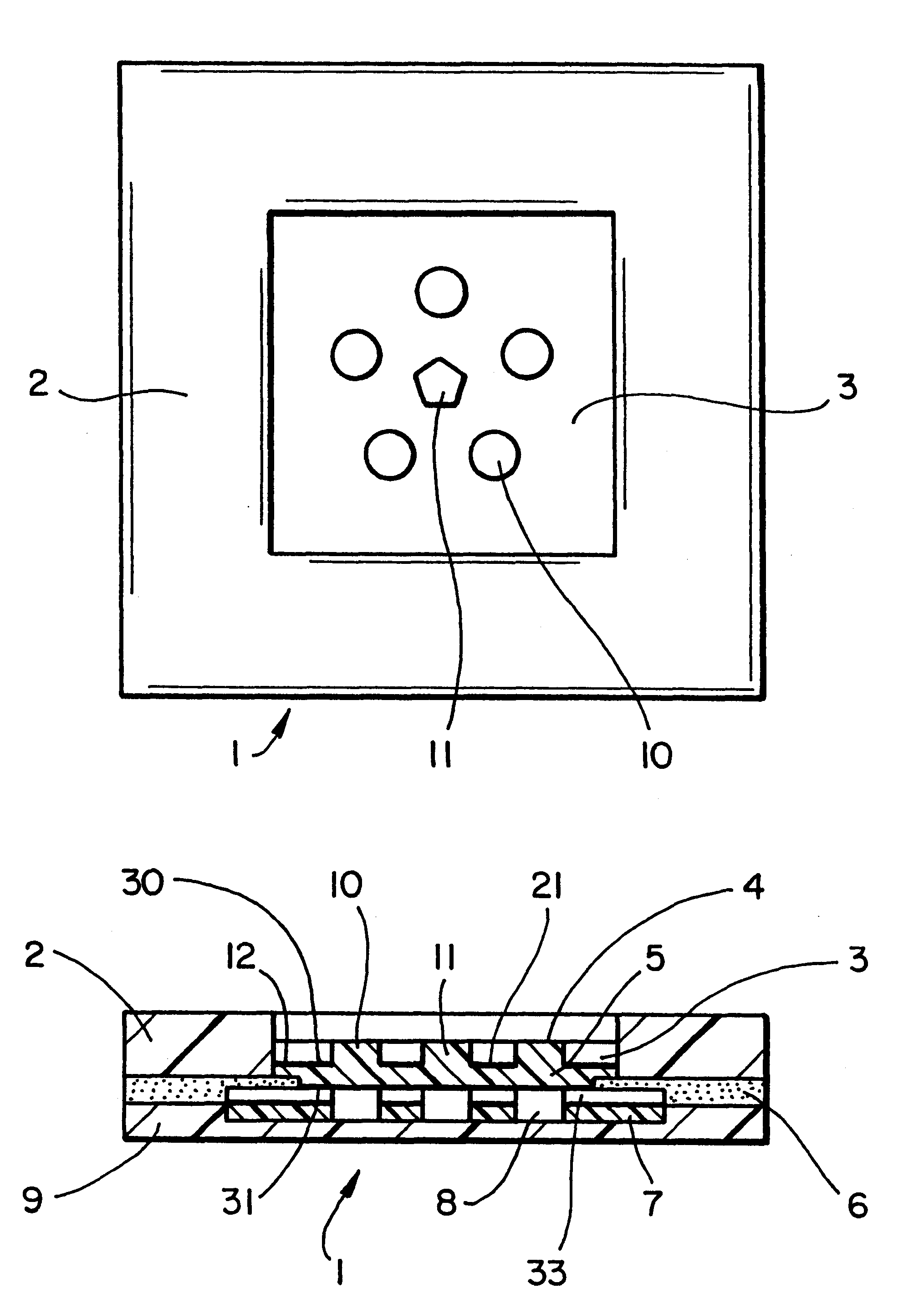
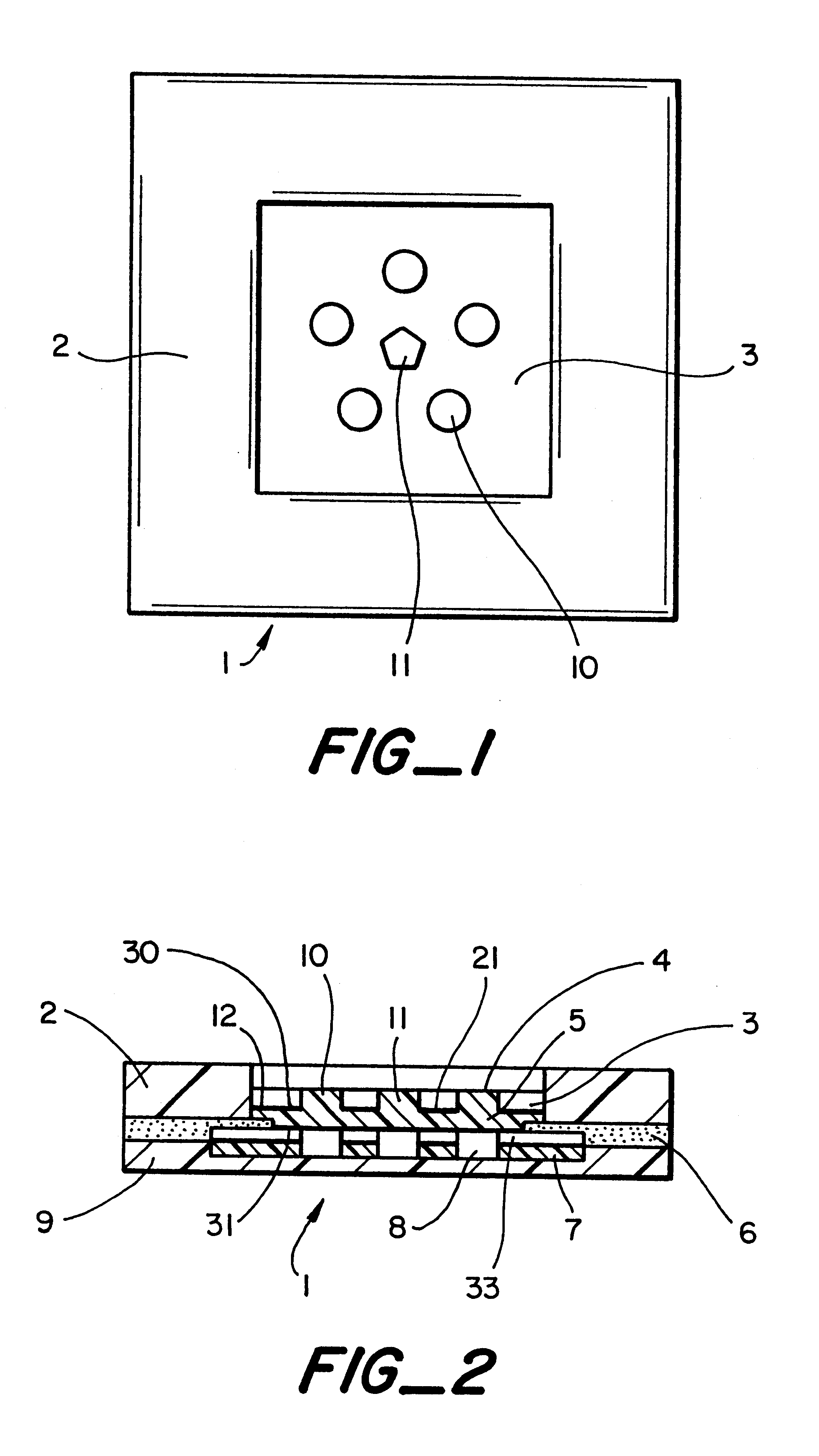
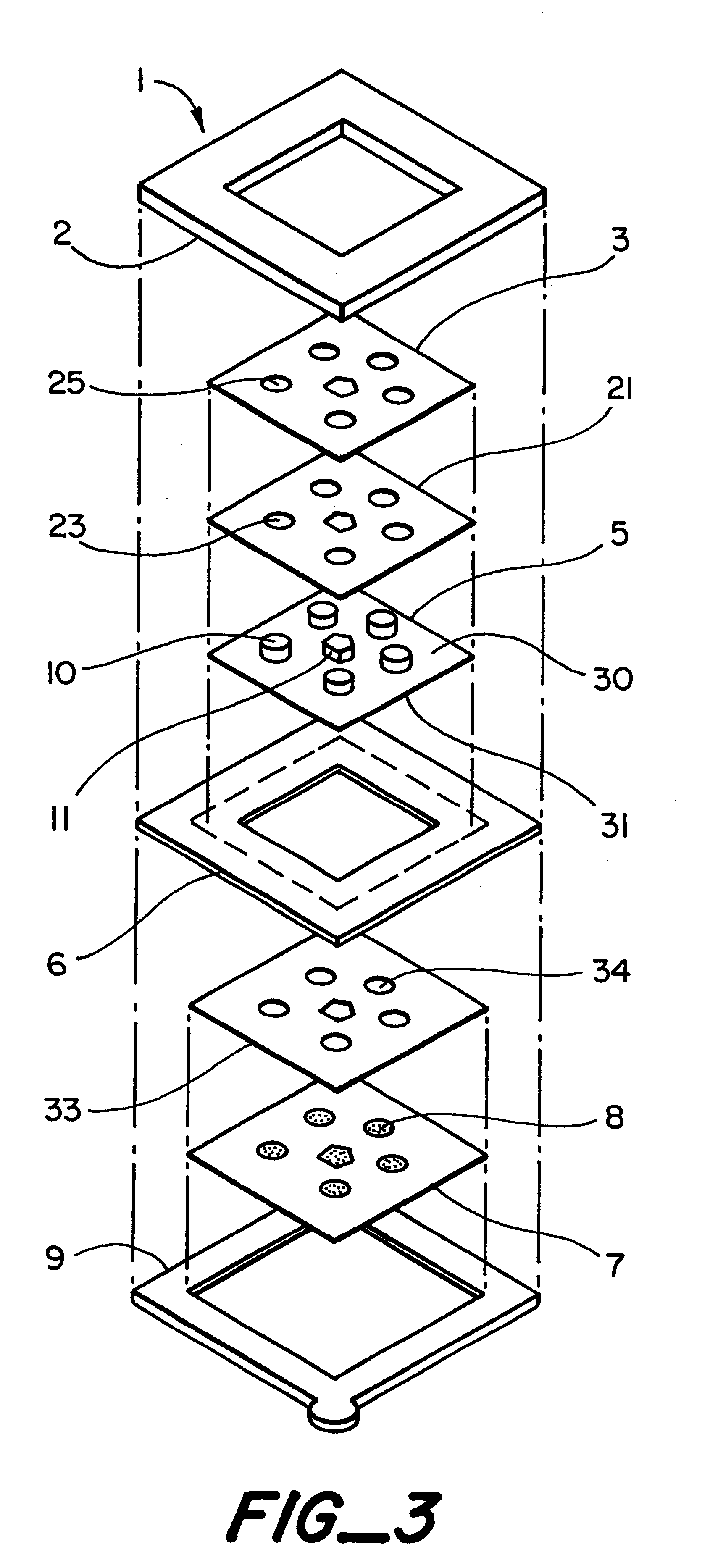
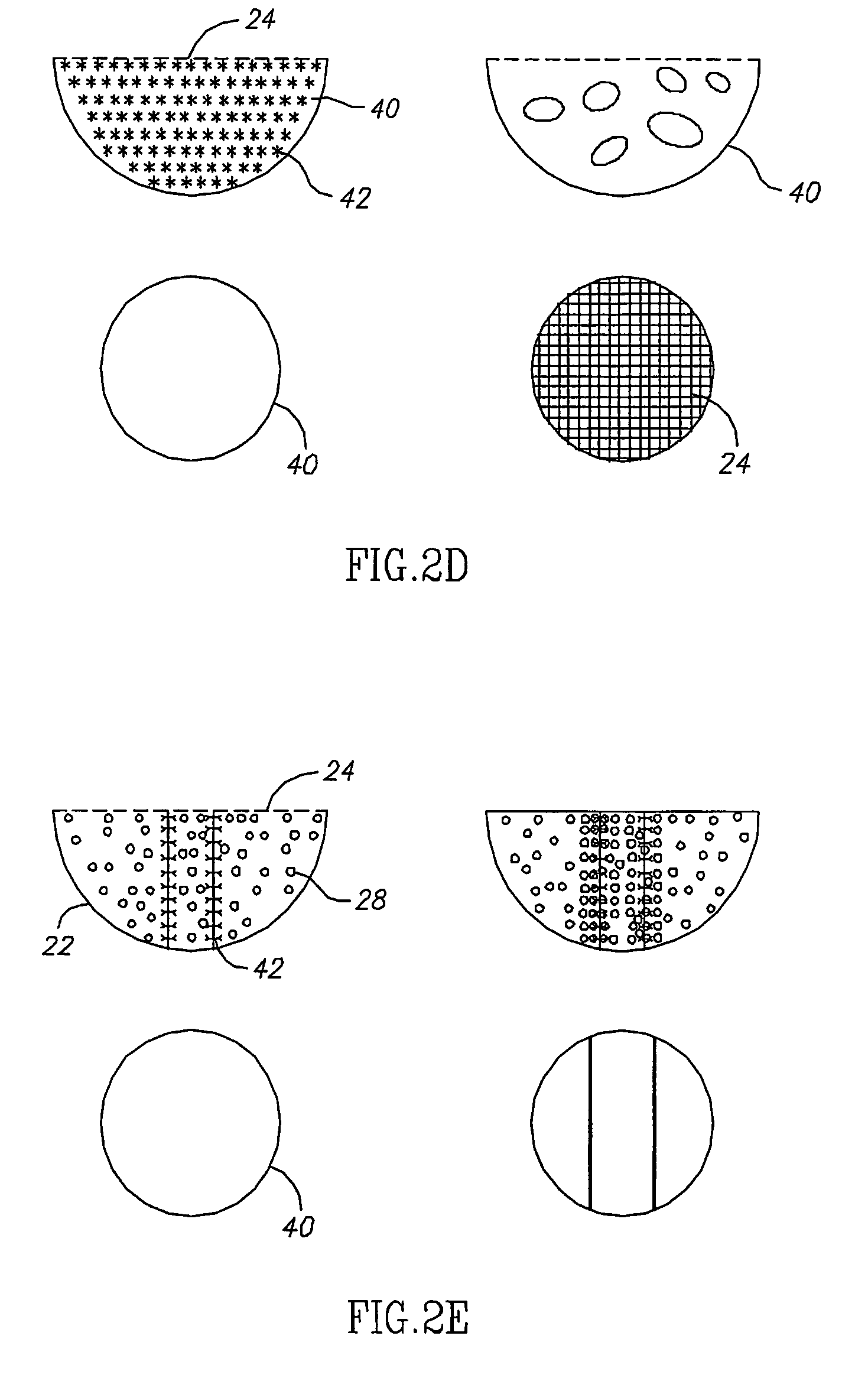
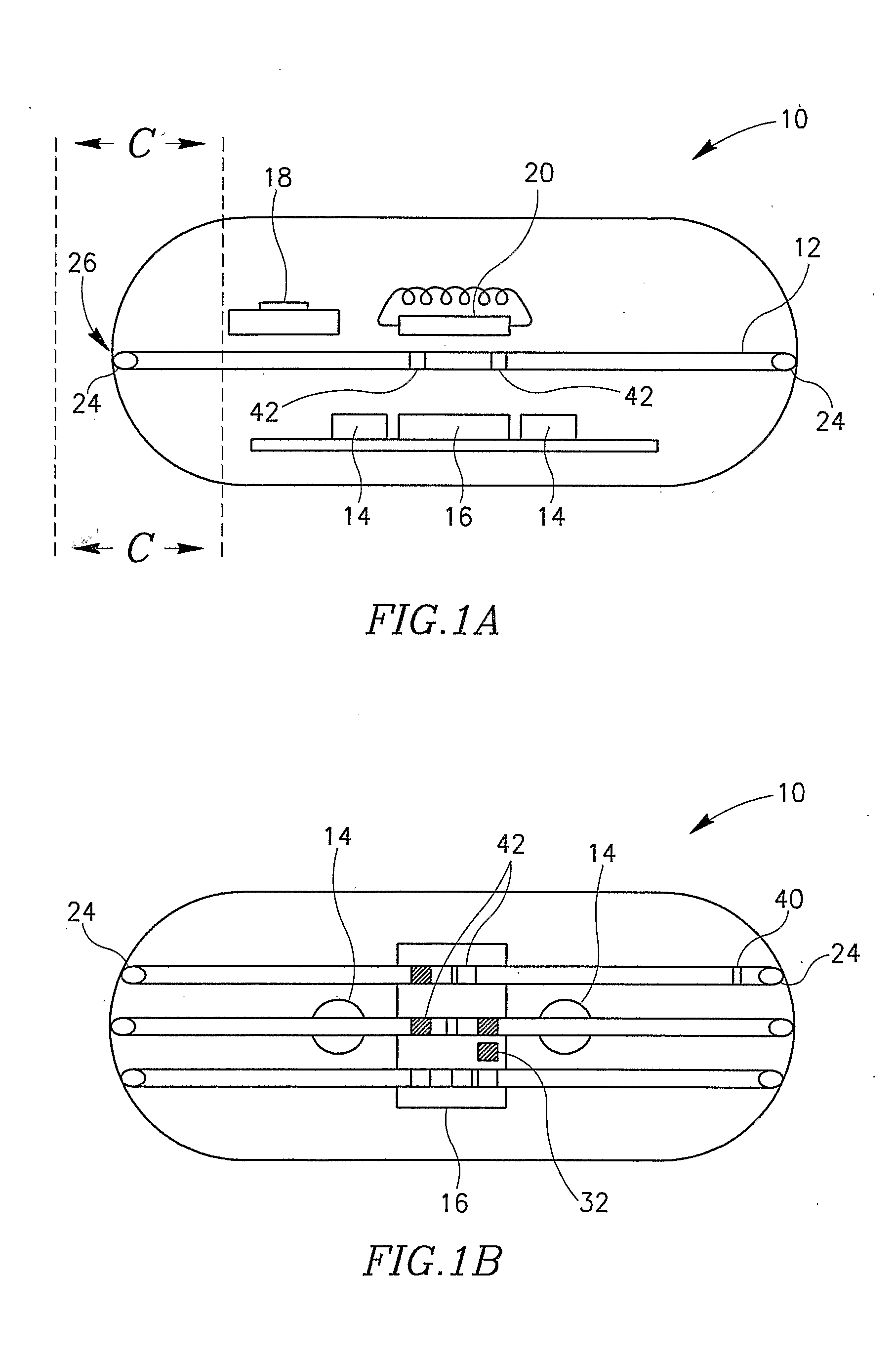
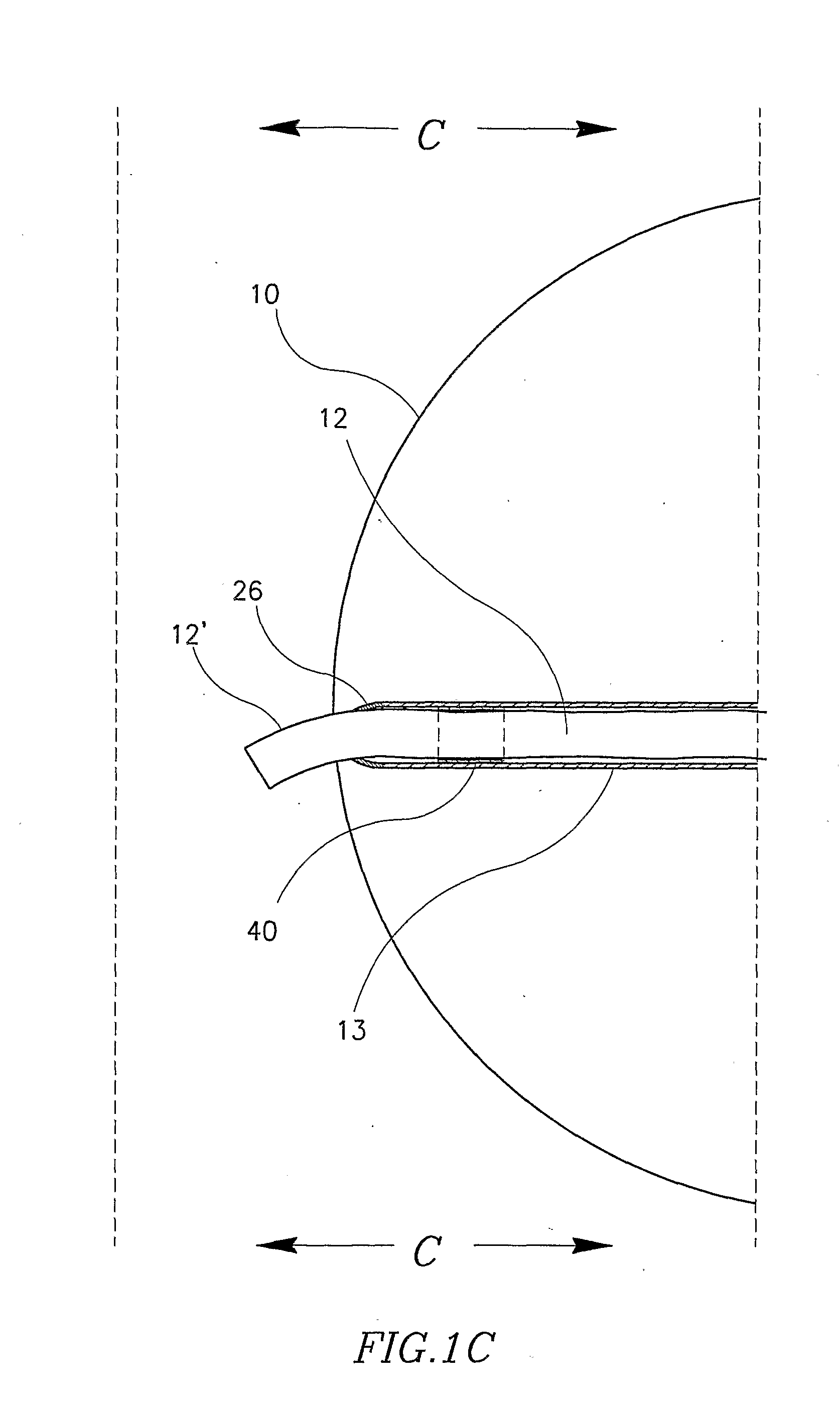
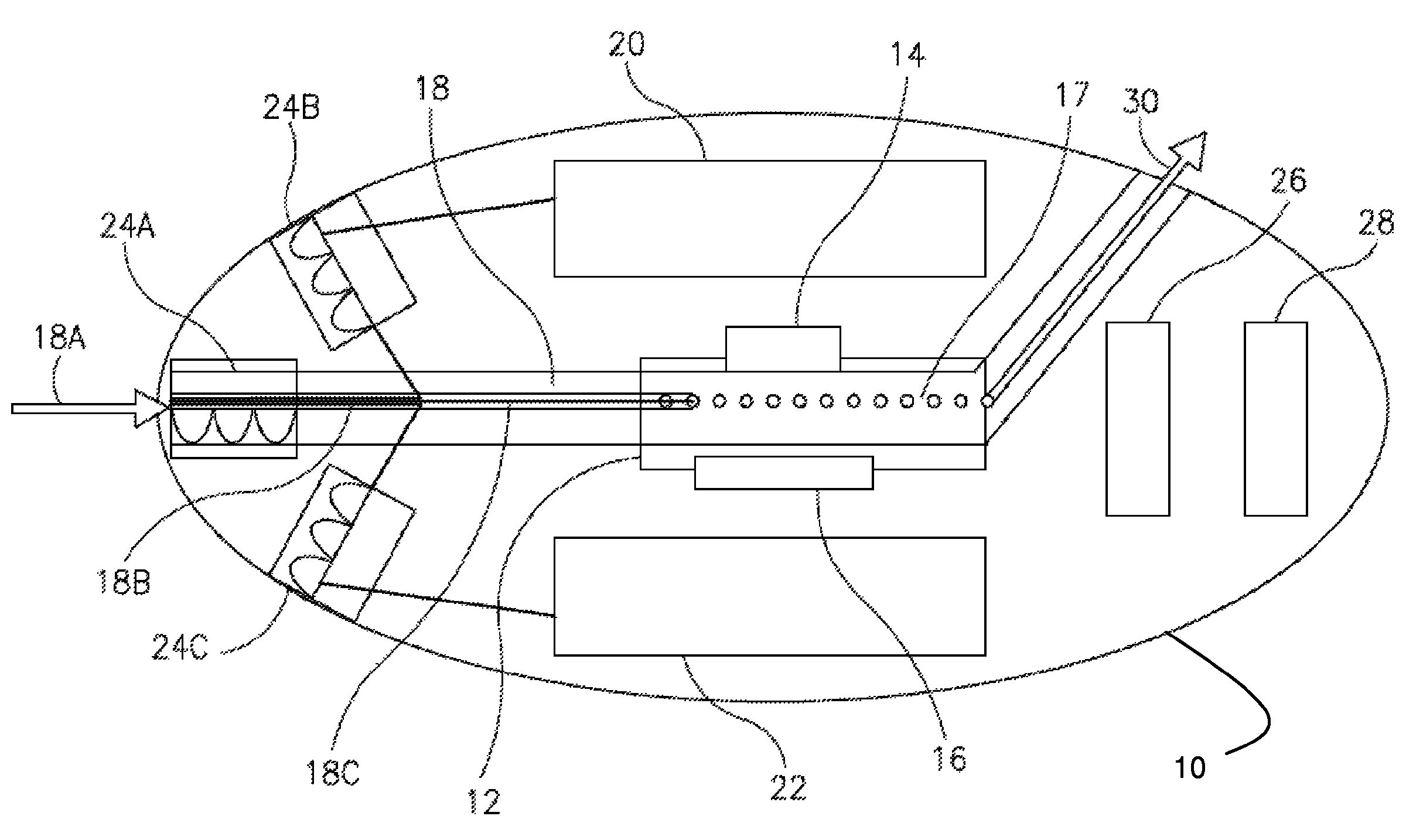
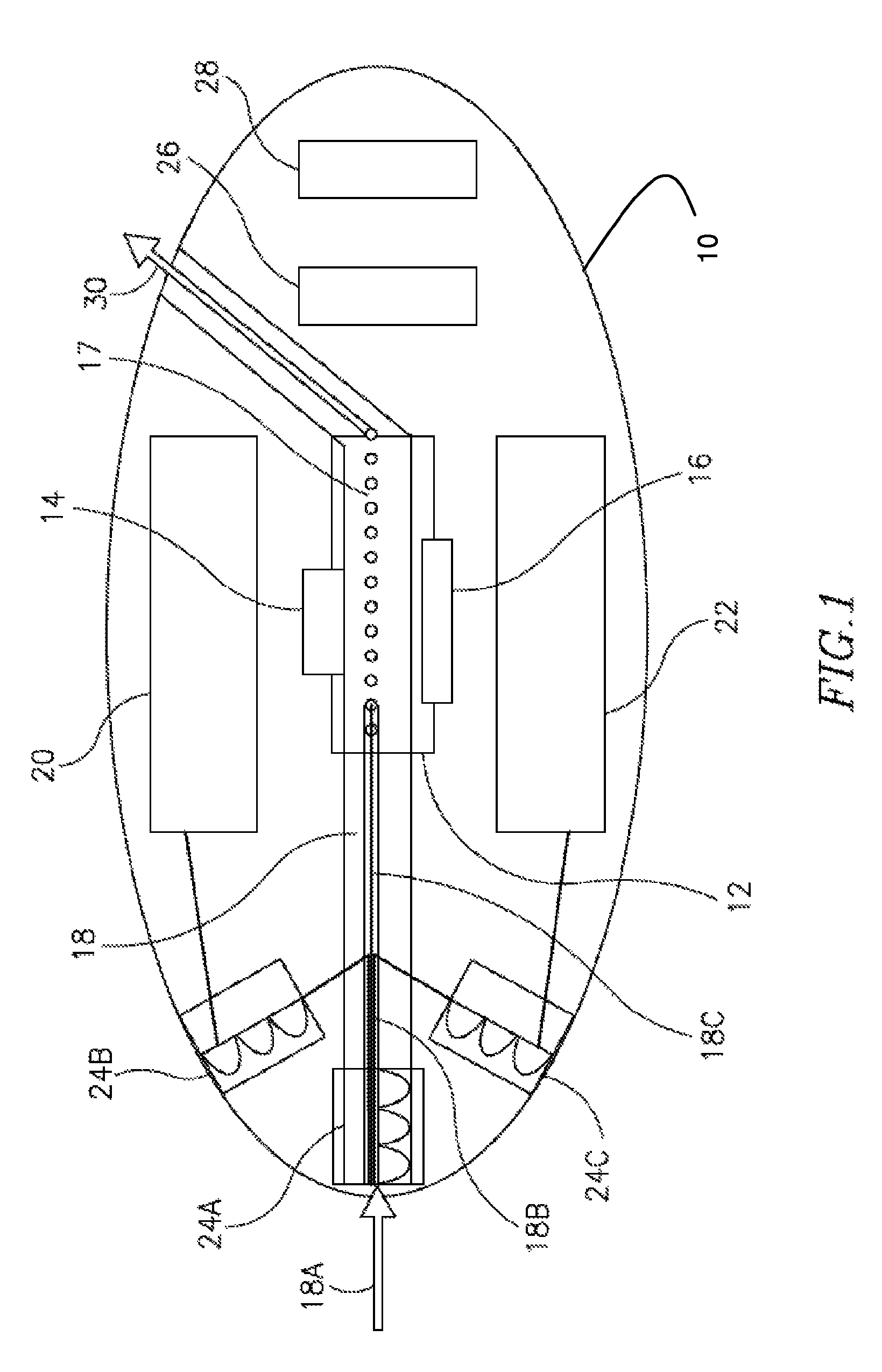
Interstitial fluid methods and devices for determination of an analyte in the body
InactiveUS6251083B1Simpler to useFacilitate increased patient complianceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalytePorous membrane
Devices and methods for utilizing dry chemistry dye indicator systems for body fluid analysis, such as glucose level provided by incorporating a porous membrane in a disposable patch. The devices also provide for microtitration of fluid samples in fixed volumetric openings containing indicator reagent. The devices provided are low cost due to efficient manufacturing methods provided.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
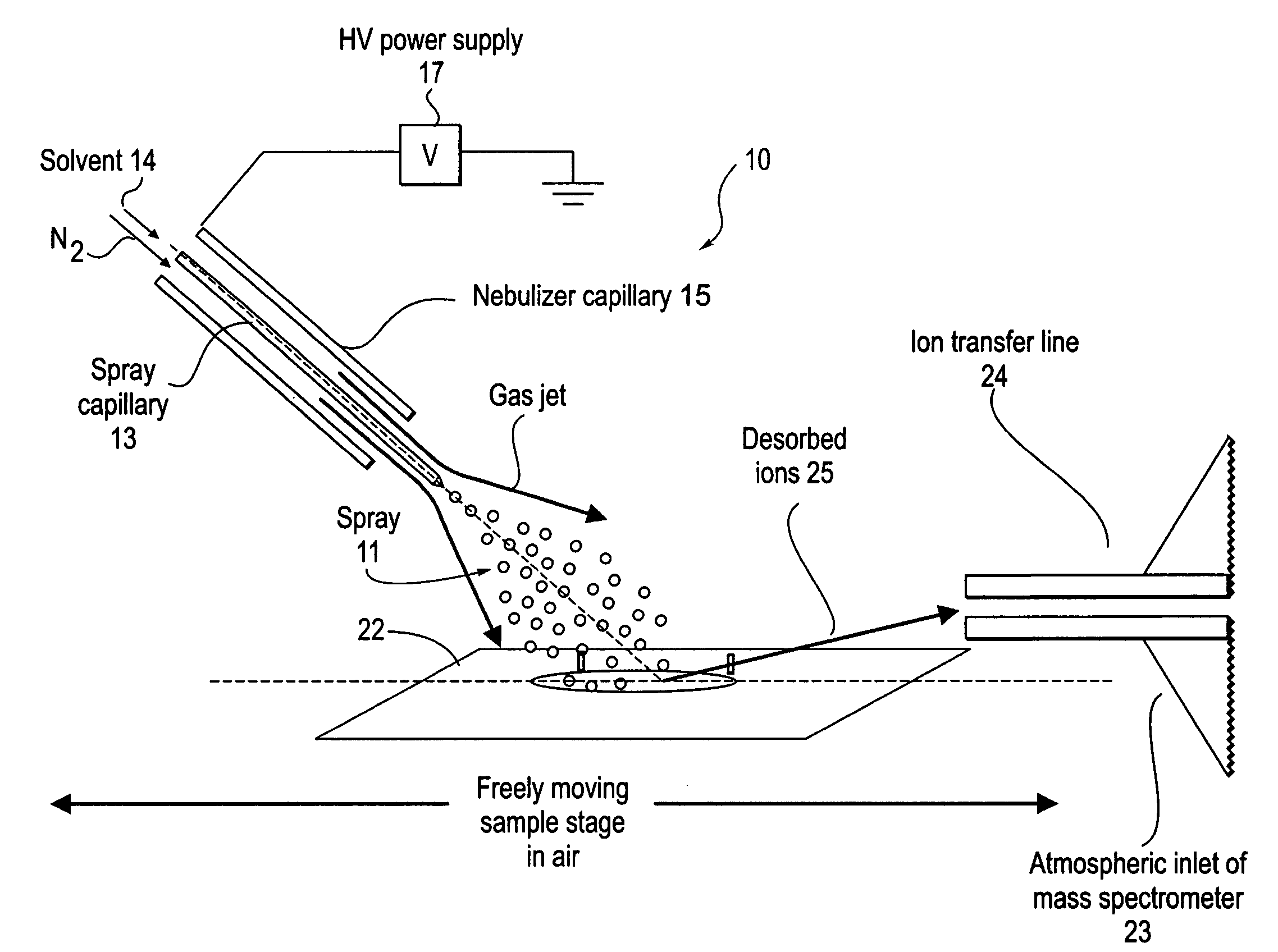
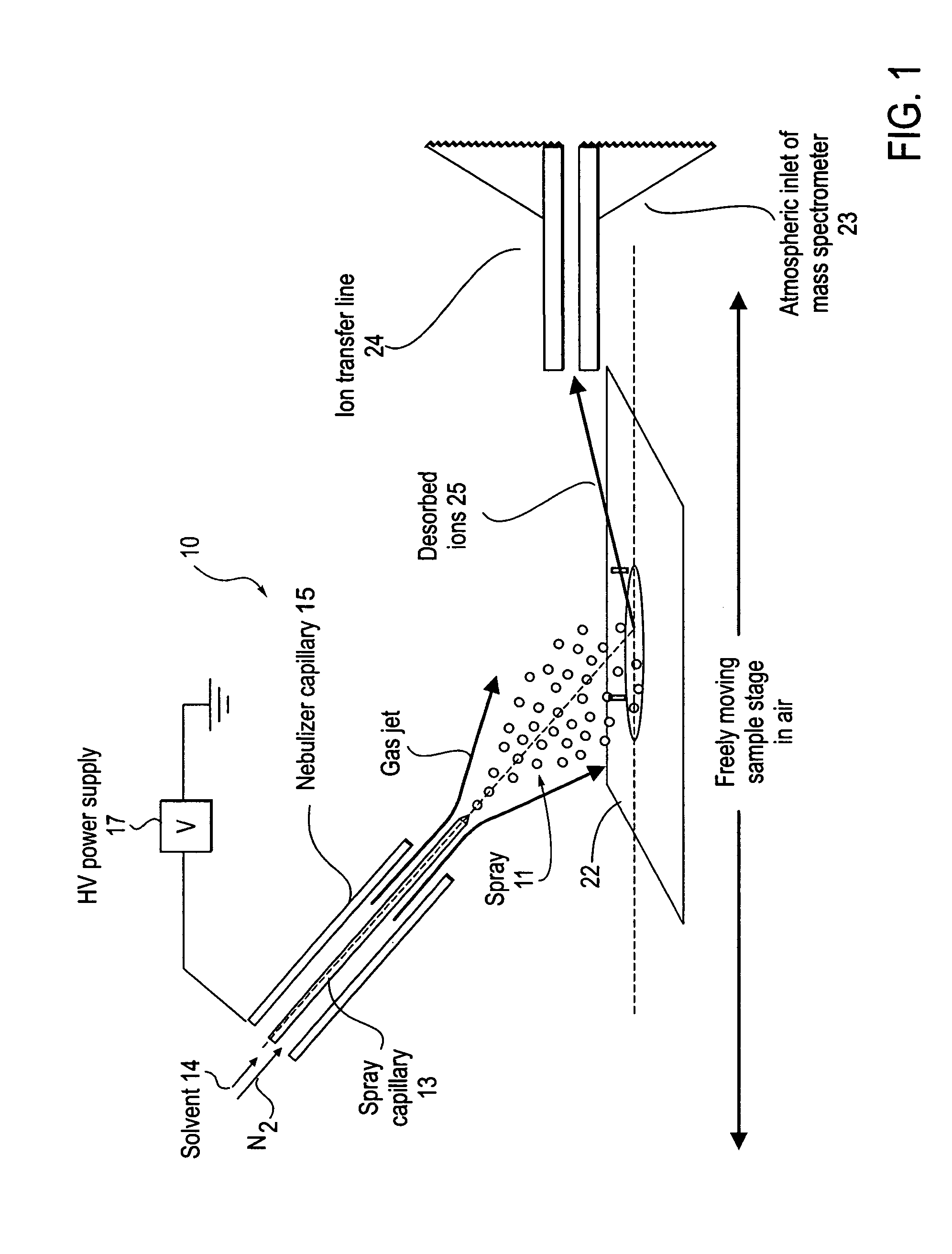
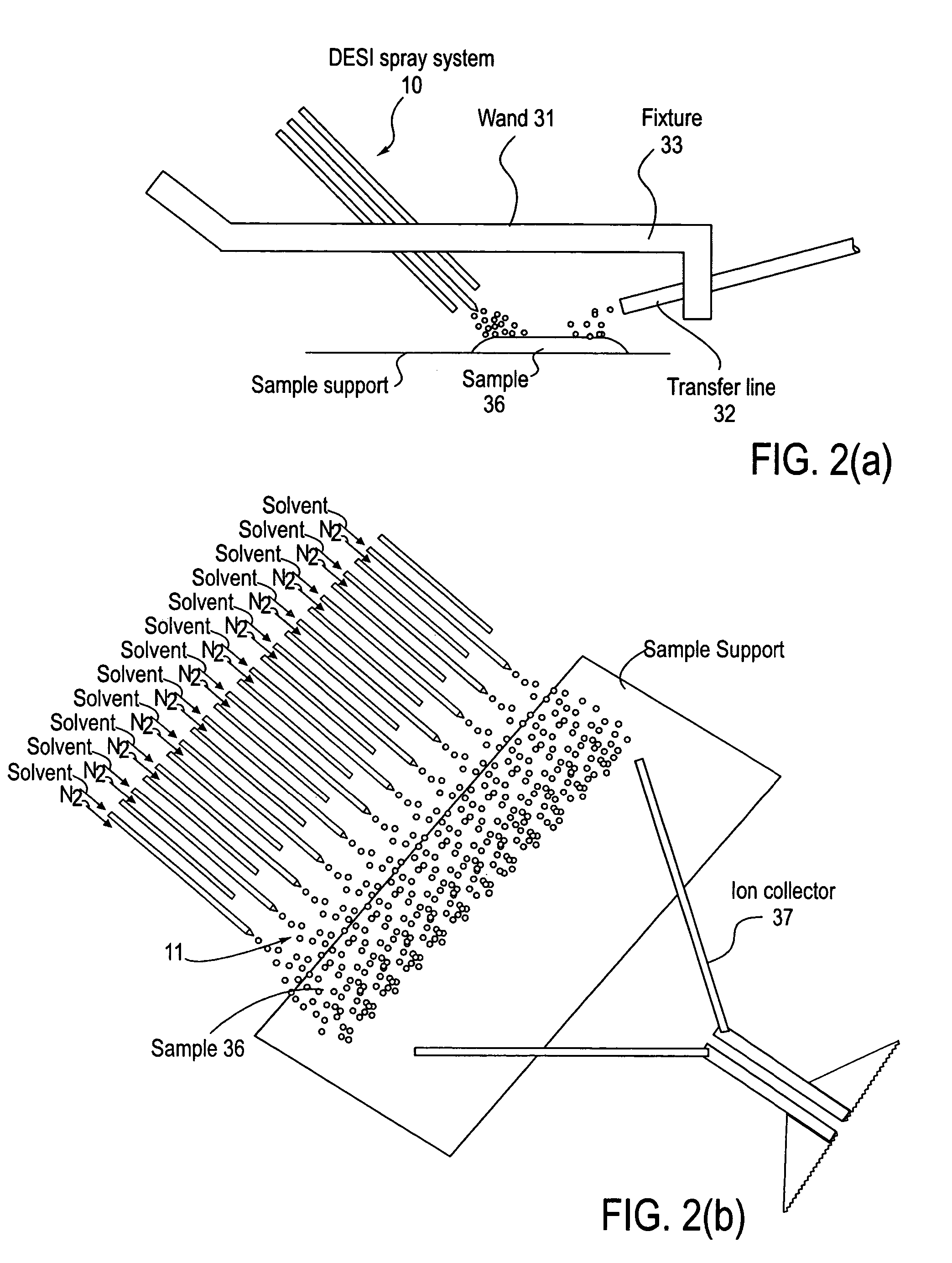
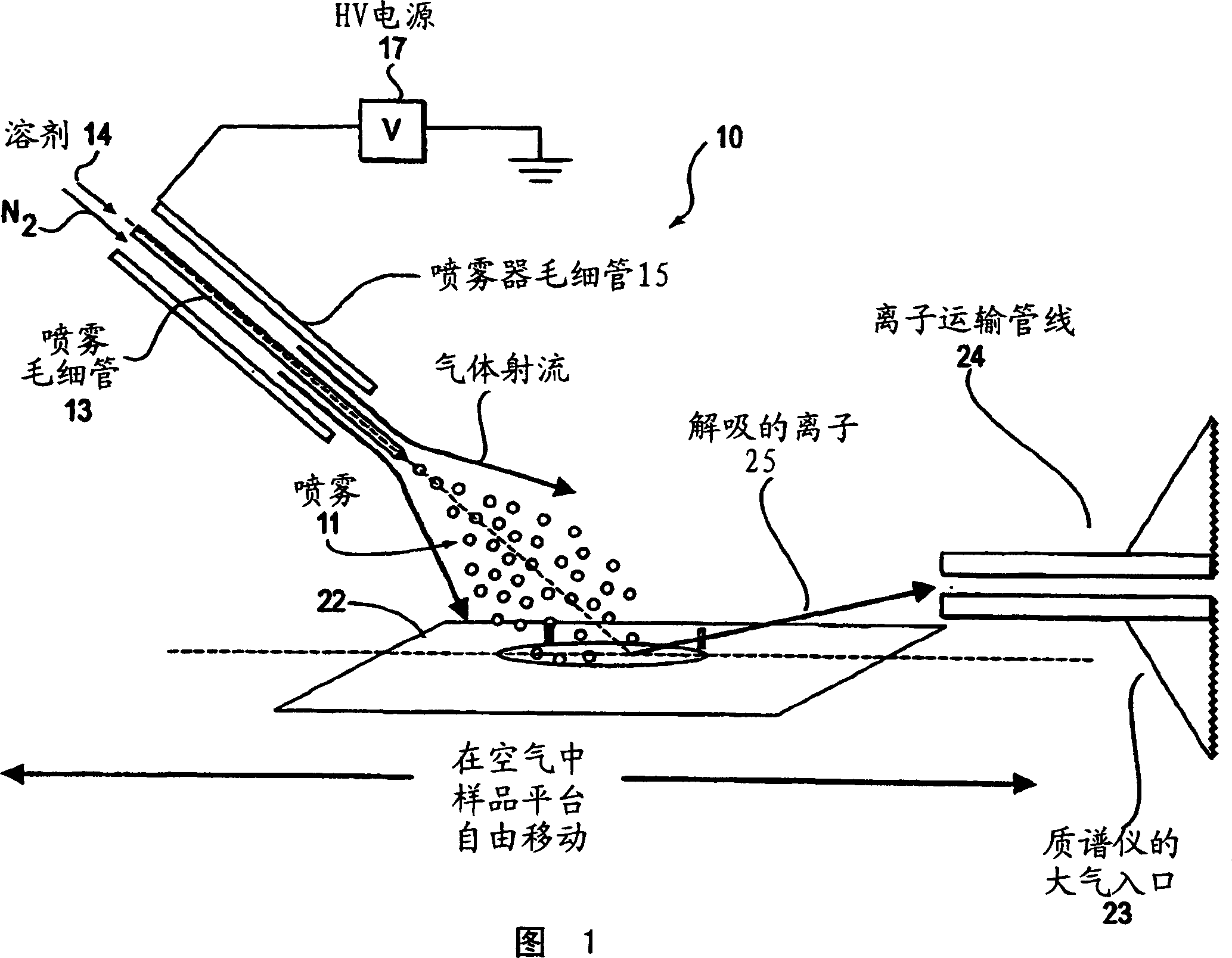
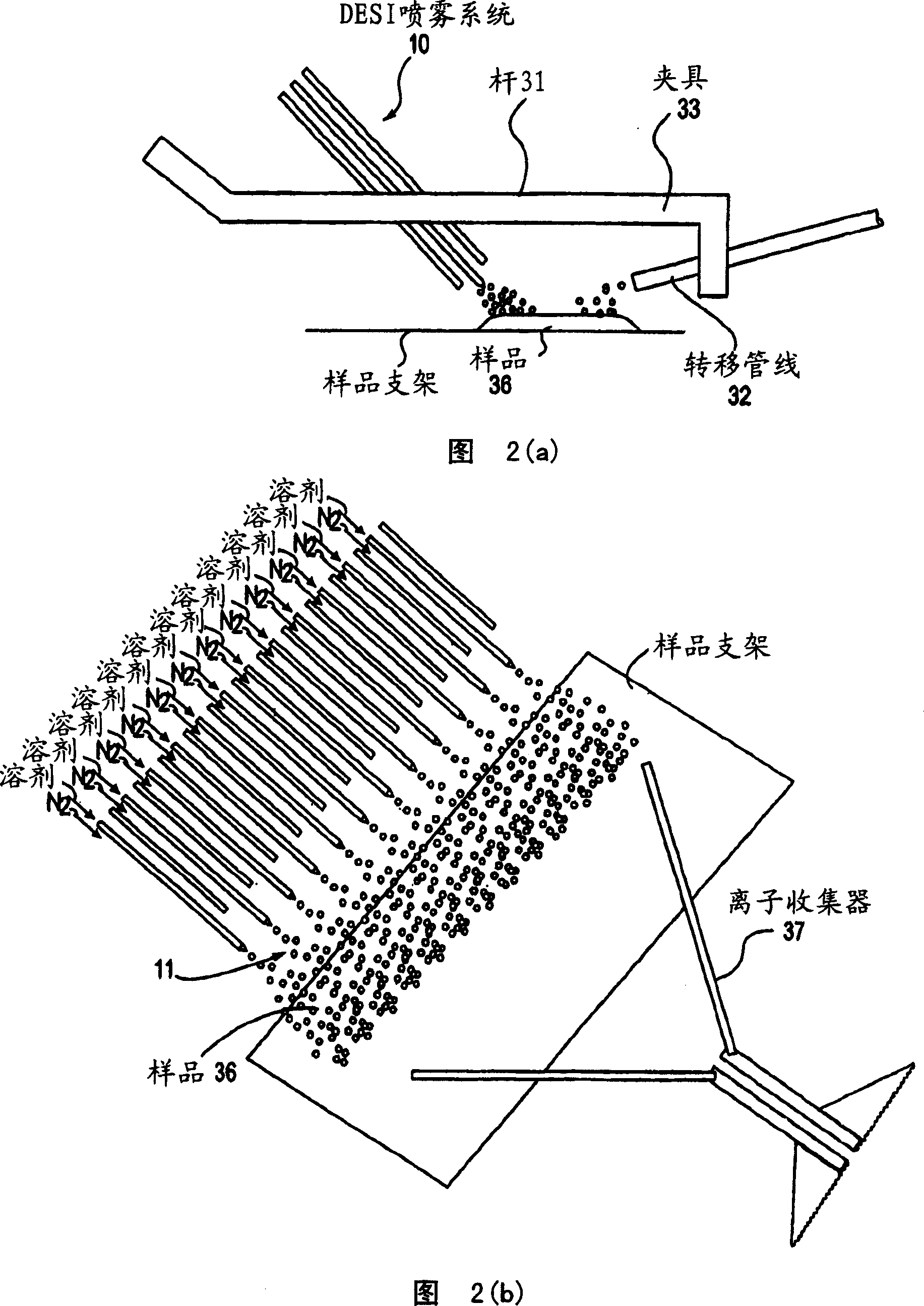
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS7335897B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLycopeneElectrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
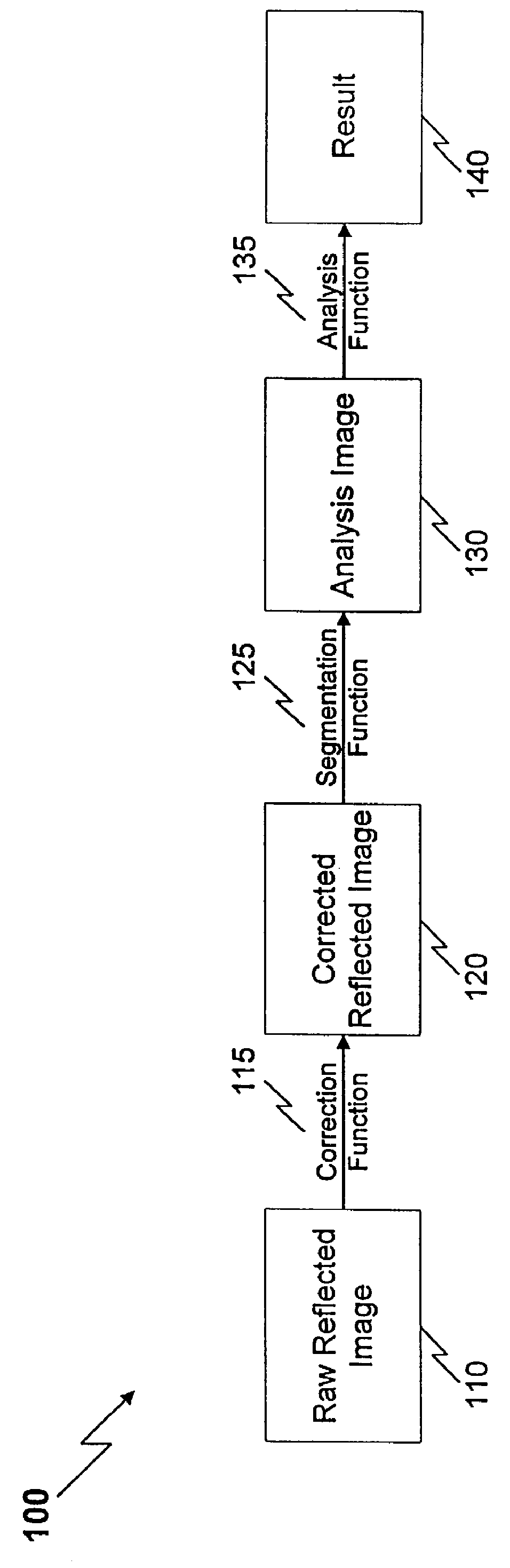
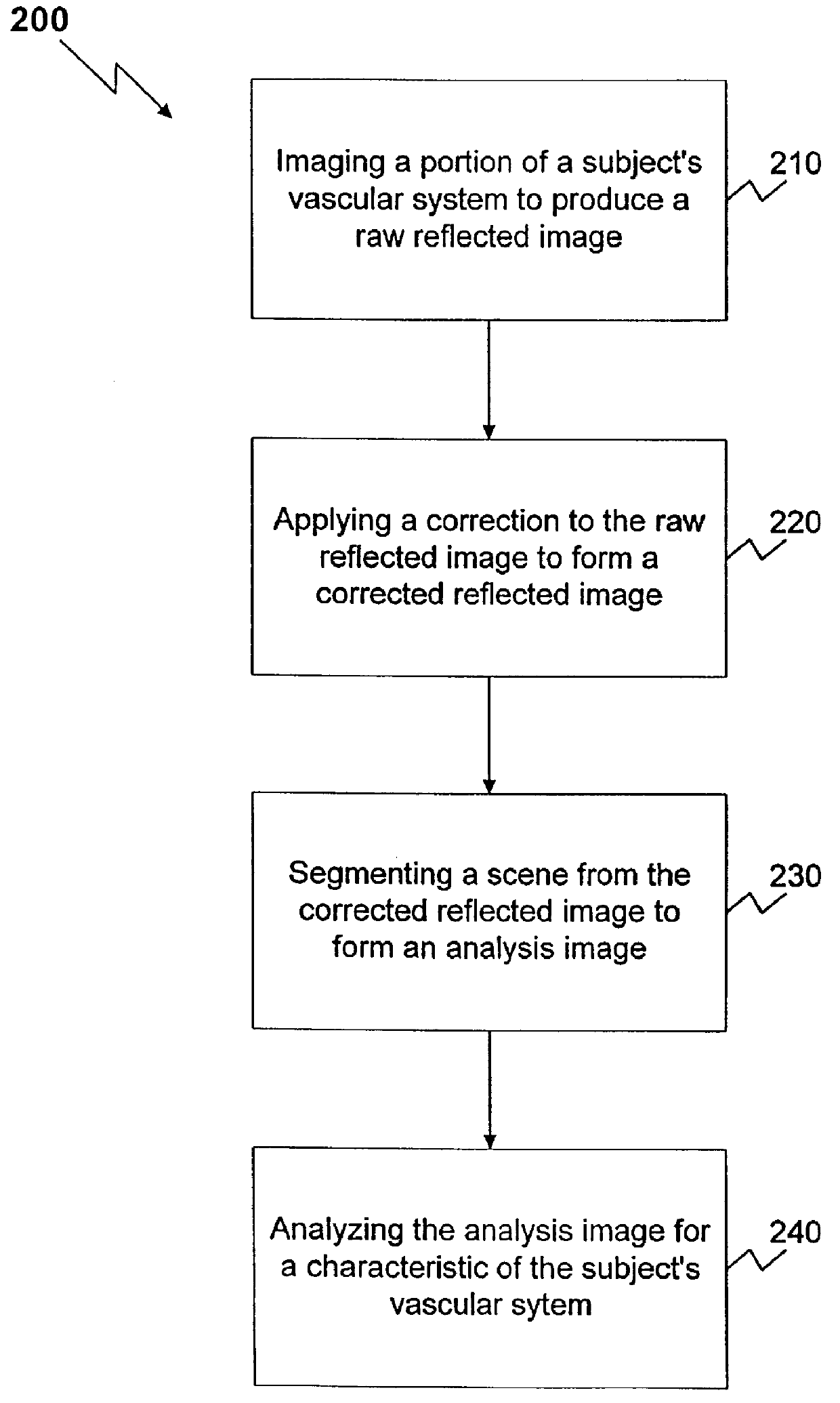
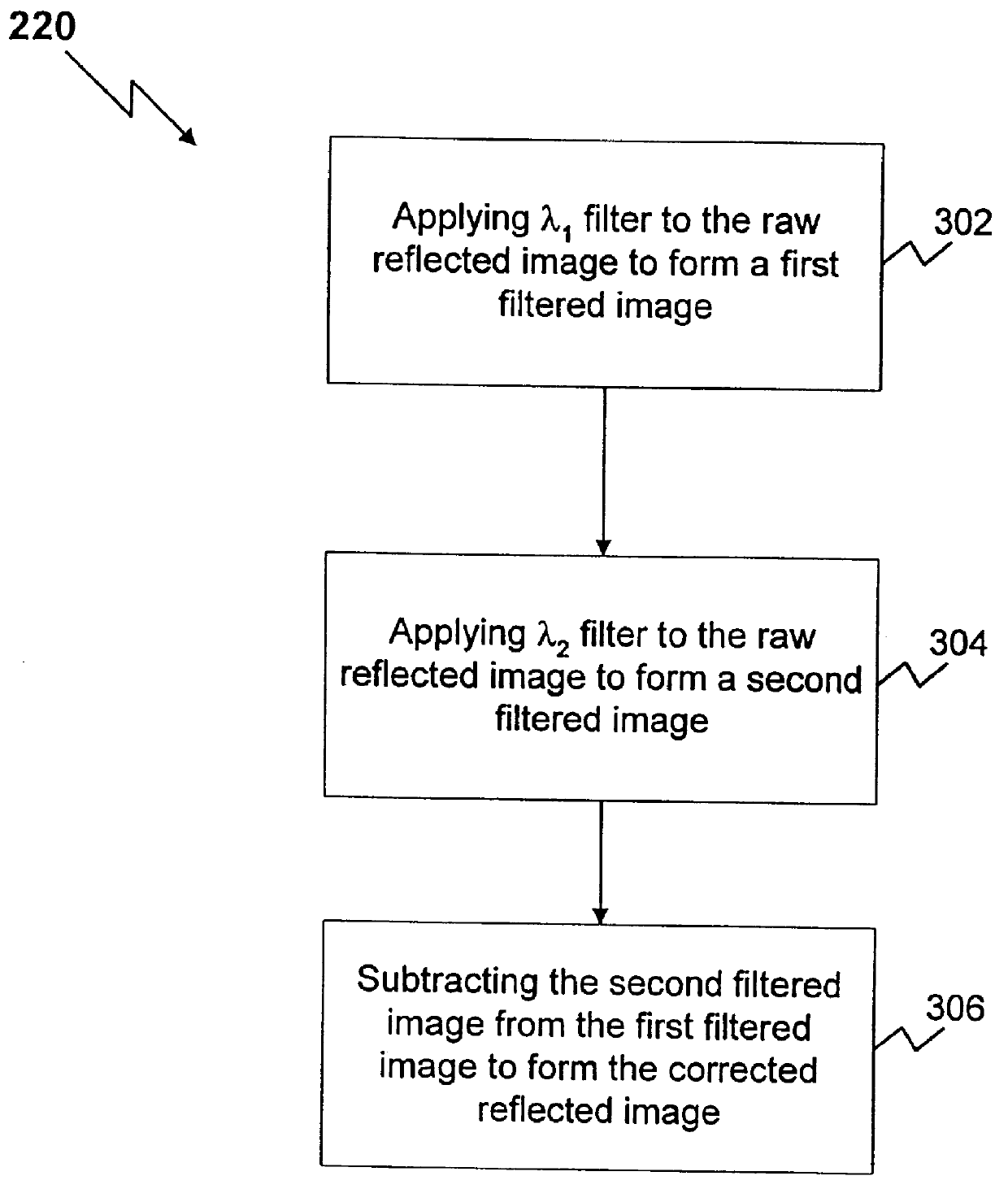
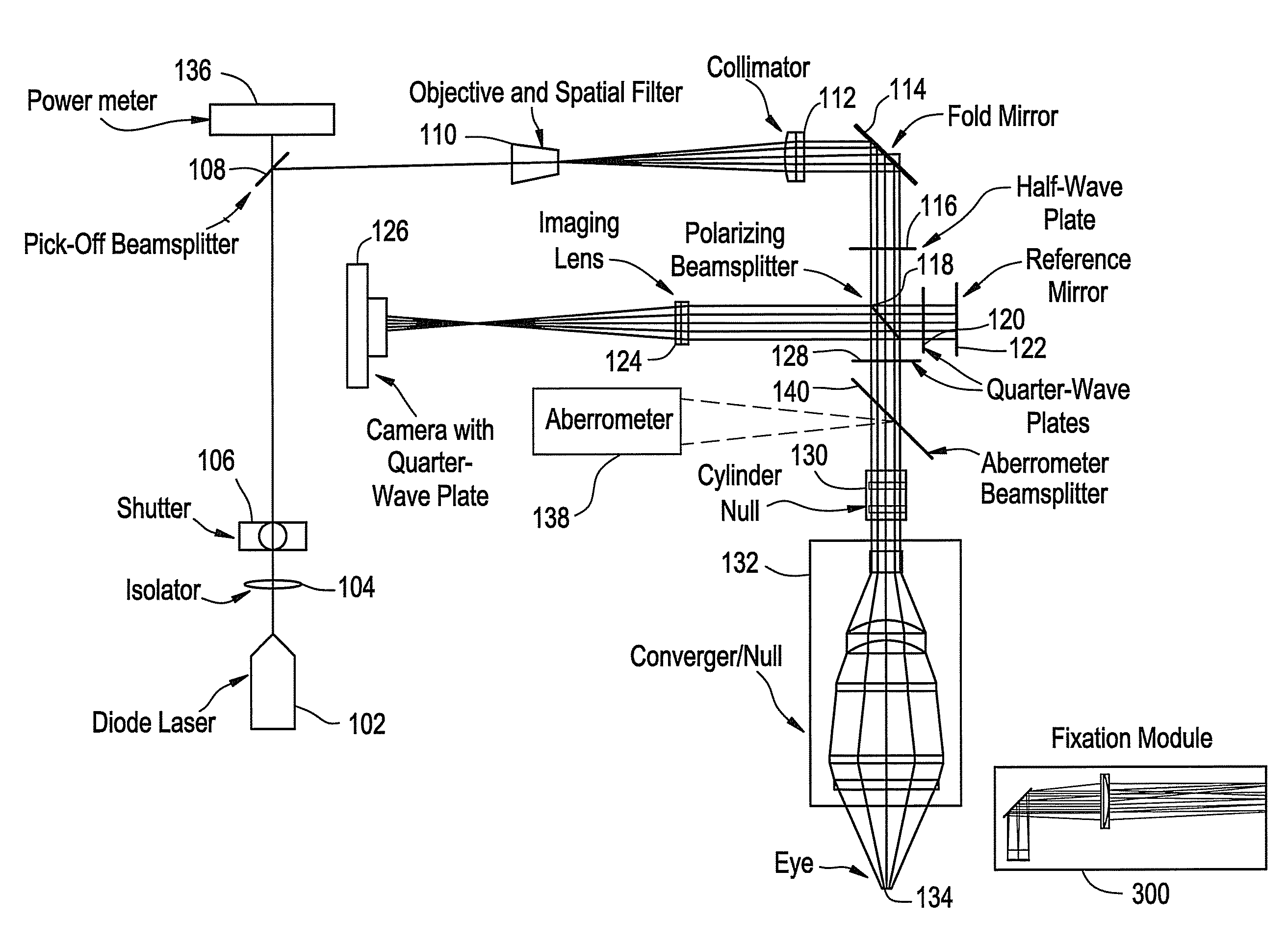
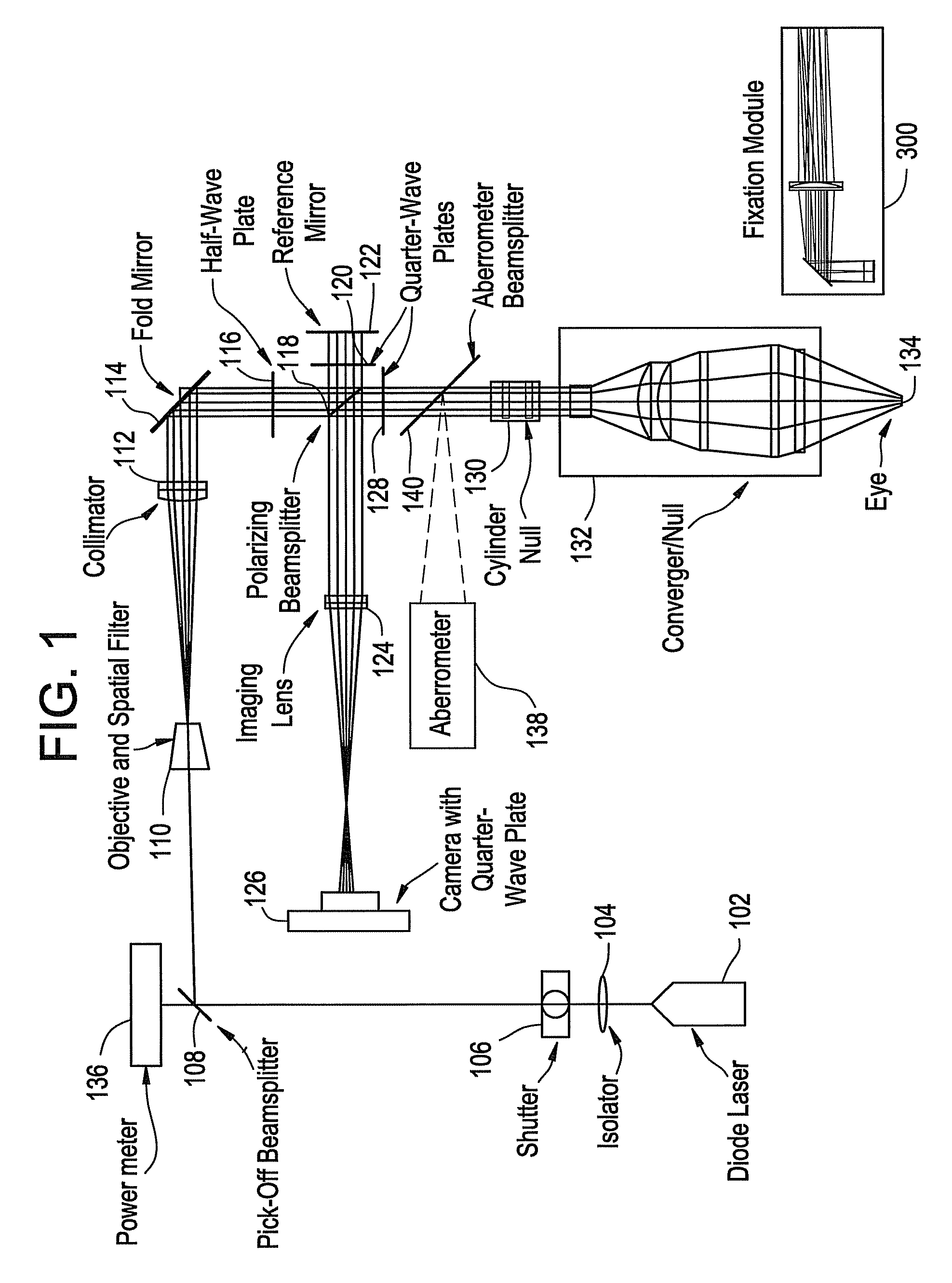
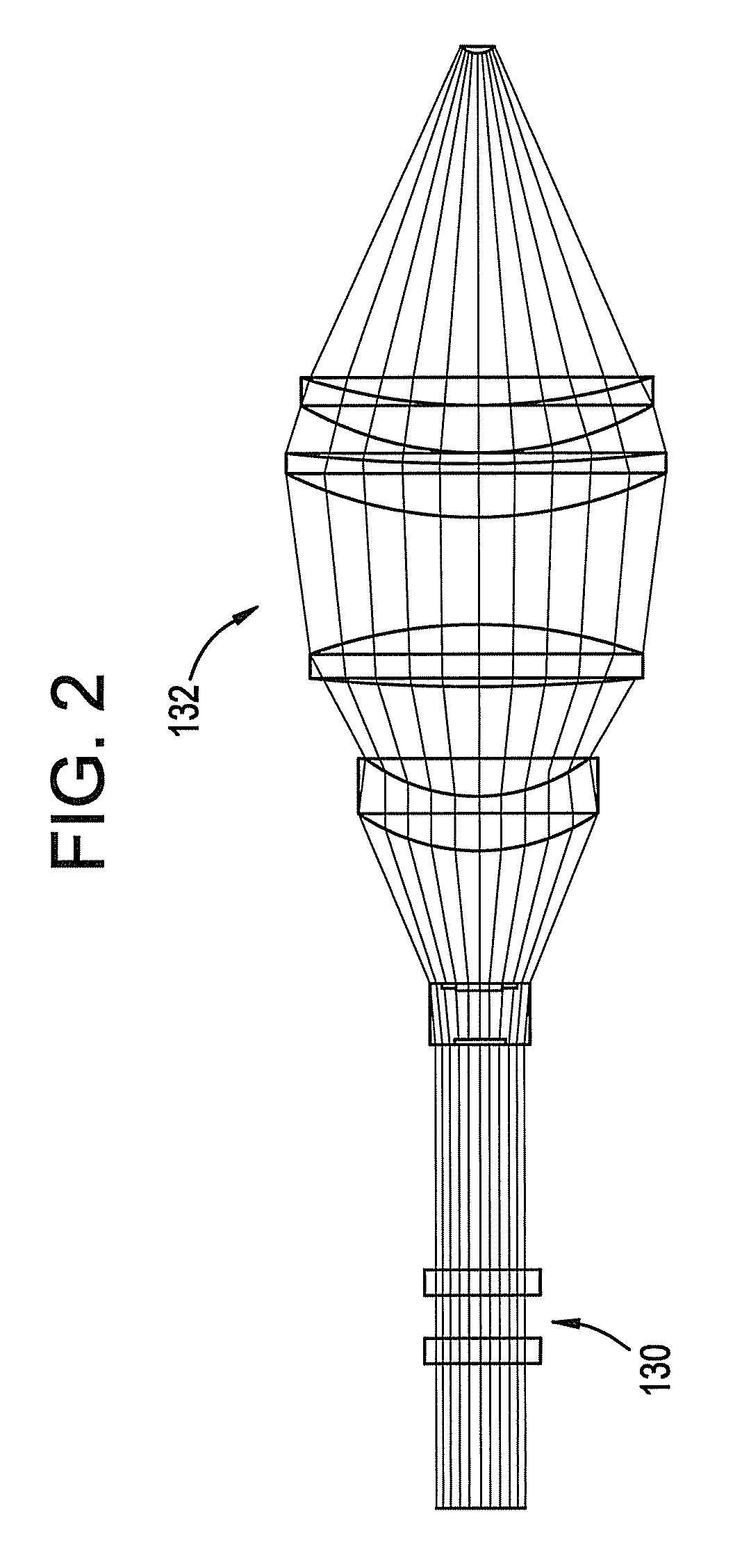
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis
InactiveUS6104939AQuick measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsWhite blood cellPolarizer
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis. Reflected imaging is used to perform non-invasive, in vivo analysis of a subject's vascular system. A raw reflected image (110) is normalized with respect to the background to form a corrected reflected image (120). An analysis image (130) is segmented from the corrected reflected image to include a scene of interest for analysis. The method and apparatus can be used to determine such characteristics as the hemoglobin concentration per unit volume of blood, the number of white blood cells per unit volume of blood, a mean cell volume, the number of platelets per unit volume of blood, and the hematocrit. Cross-polarizers can be used to improve visualization of the reflected image.
Owner:INTPROP MVM
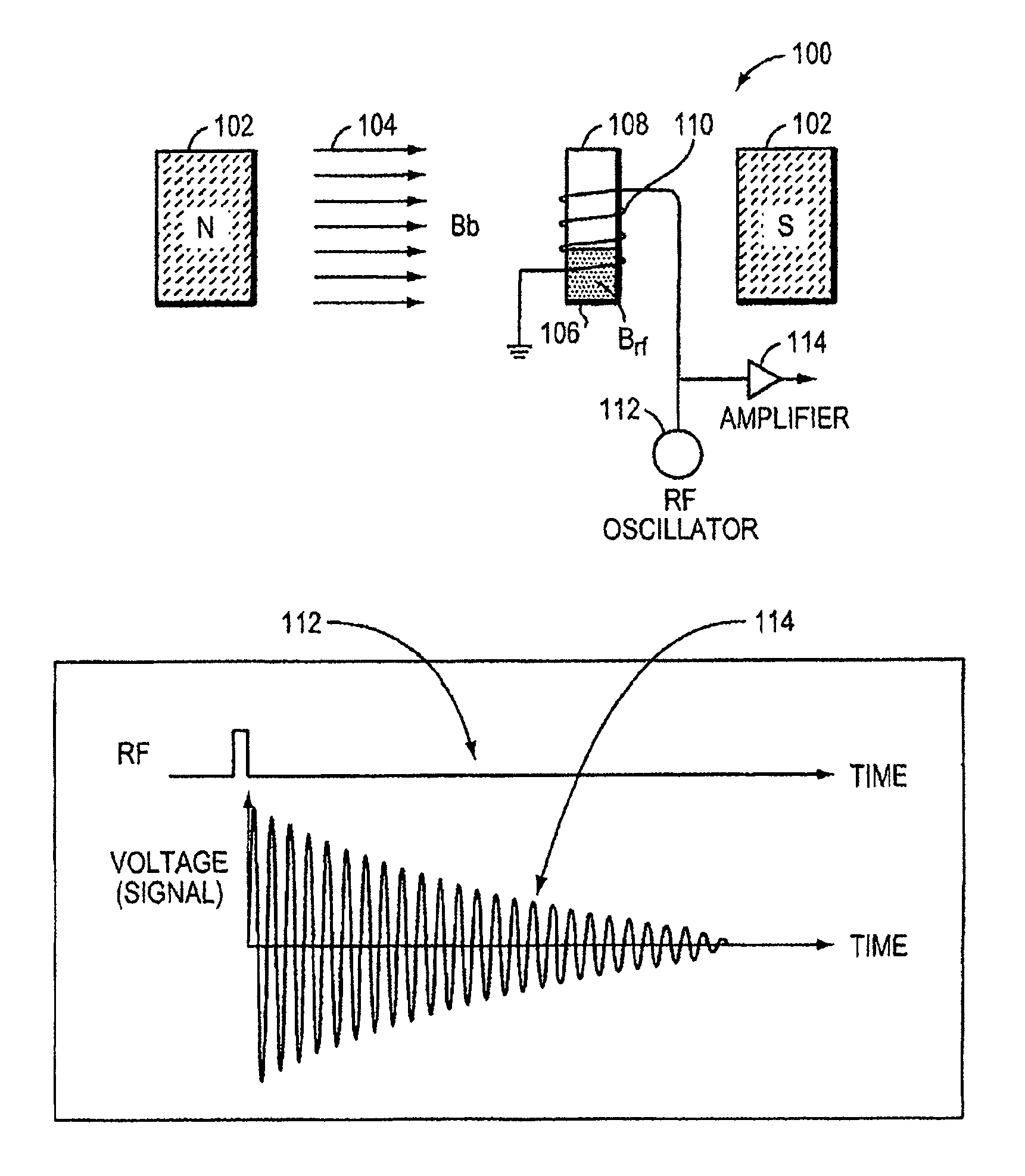
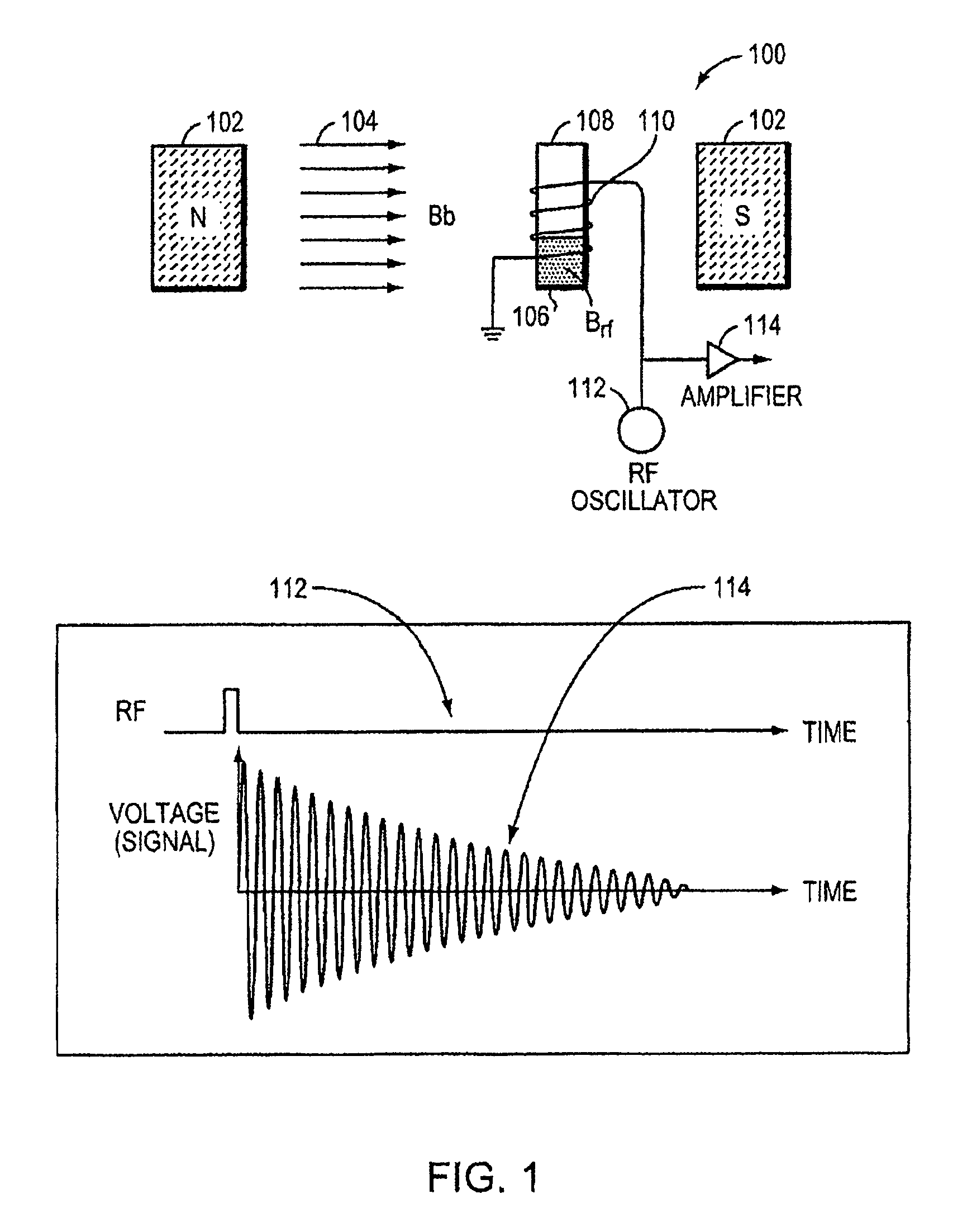
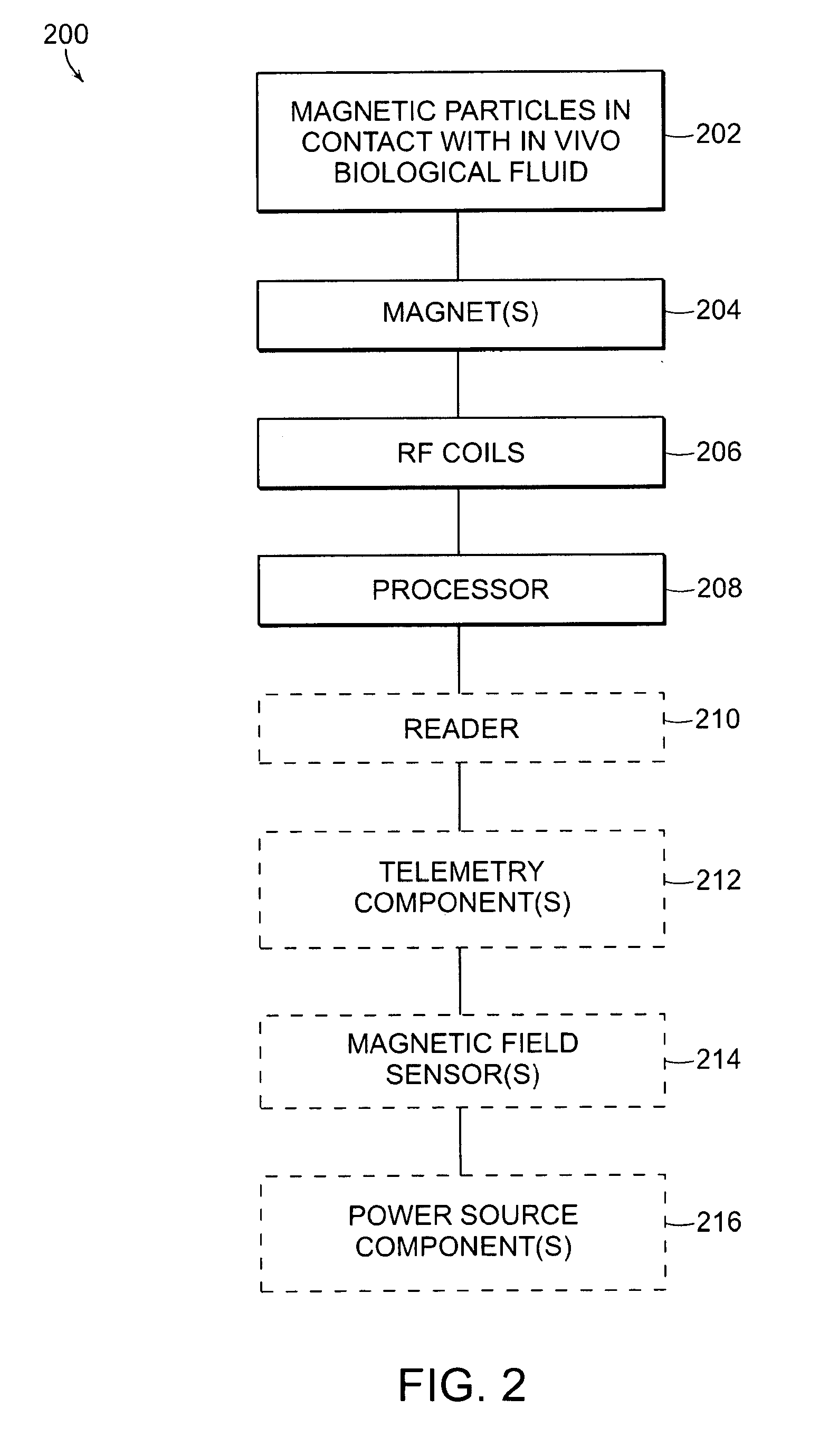
Nmr systems for in vivo detection of analytes
ActiveUS20100072994A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingAnalyteNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This invention relates generally to NMR systems for in vivo detection of analytes. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the invention relates to systems in which superparamagnetic nanoparticles are exposed to a magnetic field and radio frequency (RF) excitation at or near the Larmor frequency, such that the aggregation and / or disaggregation of the nanoparticles caused by the presence and / or concentration of a given analyte in a biological fluid is detected in vivo from a monitored RF echo response.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
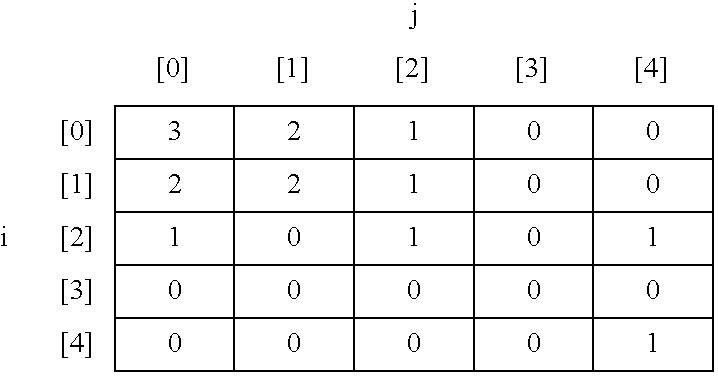
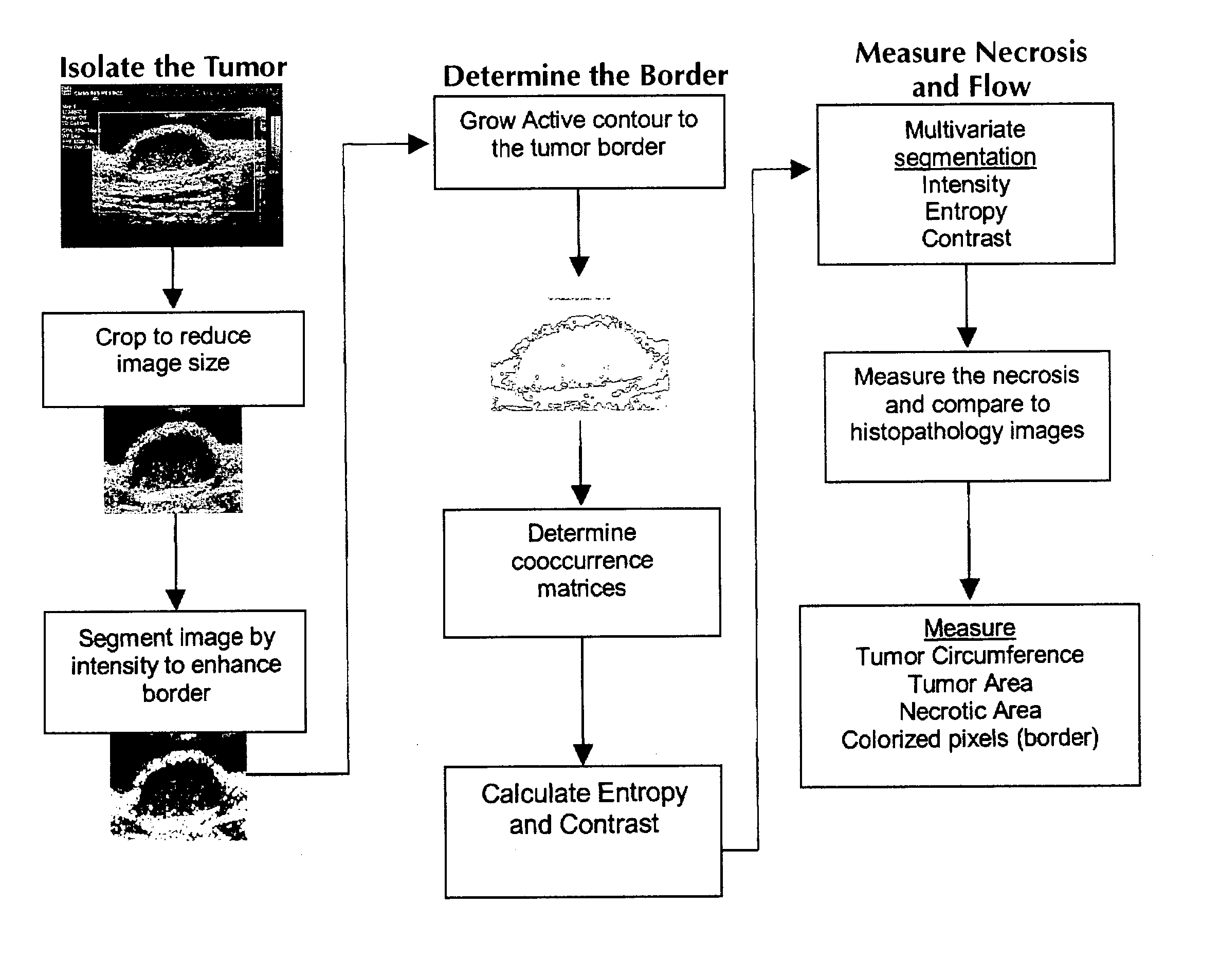
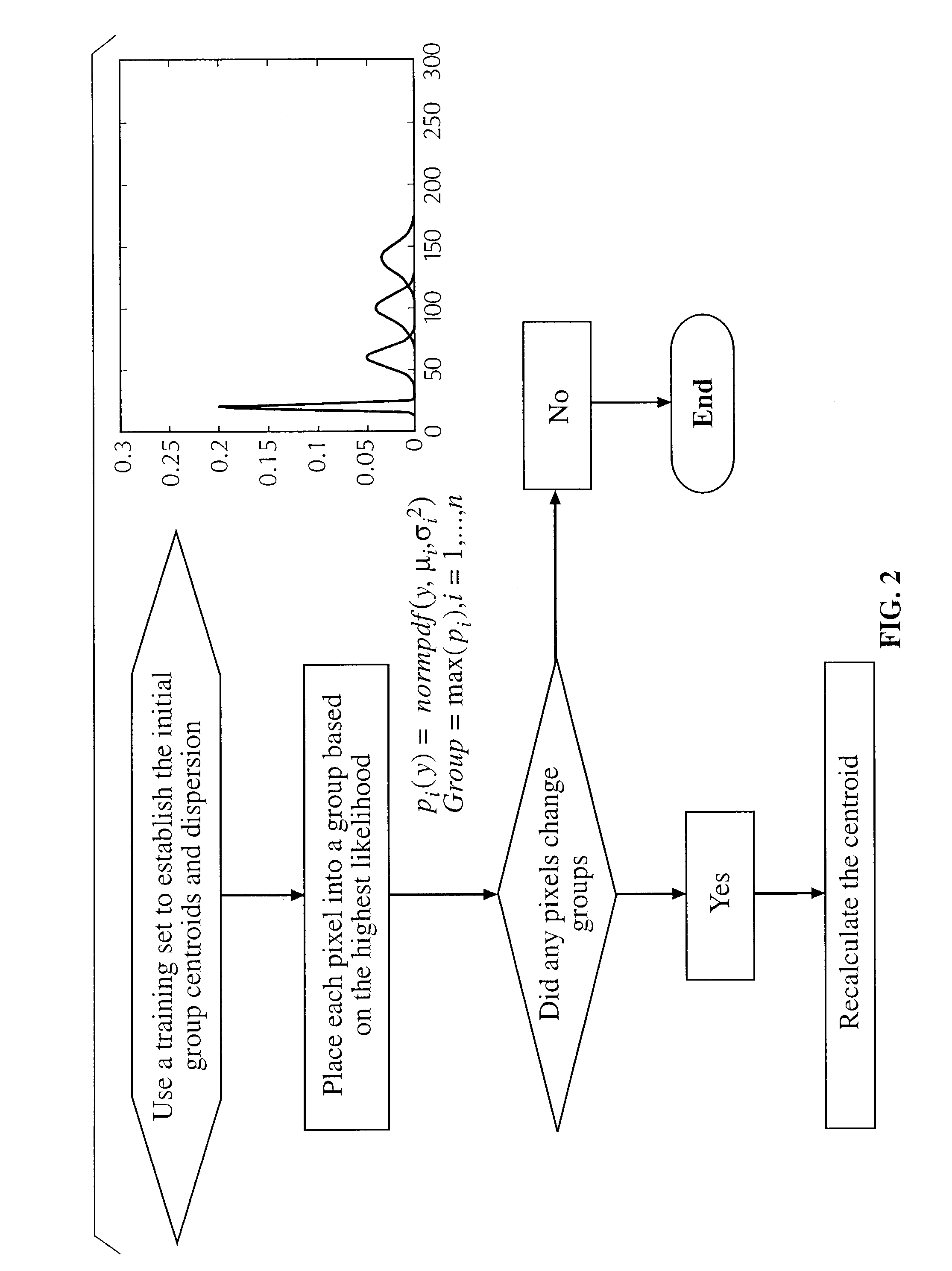
Apparatus and method for statistical image analysis
An apparatus, system, method, and computer readable medium containing computer-executable code for implementing image analysis uses multivariate statistical analysis of sample images, and allows segmentation of the image into different groups or classes, depending on a correlation to one or more sample textures, or sample surface features. In one embodiment, the invention performs multivariate statistical analysis of ultrasound images, wherein a tumor may be characterized by segmenting viable tissue from necrotic tissue, allowing for more detailed in vivo analysis of tumor growth beyond simple dimensional measurements or univariate statistical analysis. Application of the apparatus and method may also be used for characterizing other types of samples having textured features including, for example, tumor angiogenesis biomarkers from Power Doppler.
Owner:PFIZER INC
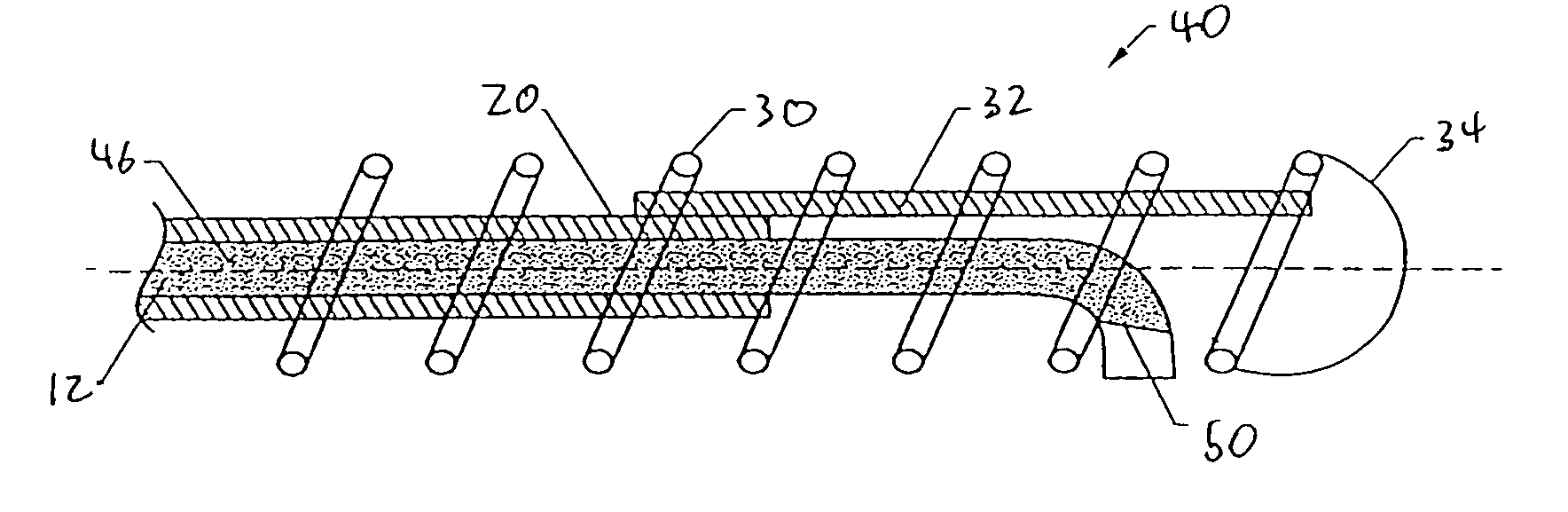
Guidewire with chemical sensing capabilities
InactiveUS7025734B1Increase production of nitric oxideIncrease production of superoxideCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineIn vivo analysis
A guidewire with a sensor which can detect NO and / or superoxide levels is disclosed. This invention can be useful for in vivo analysis of vascular health.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
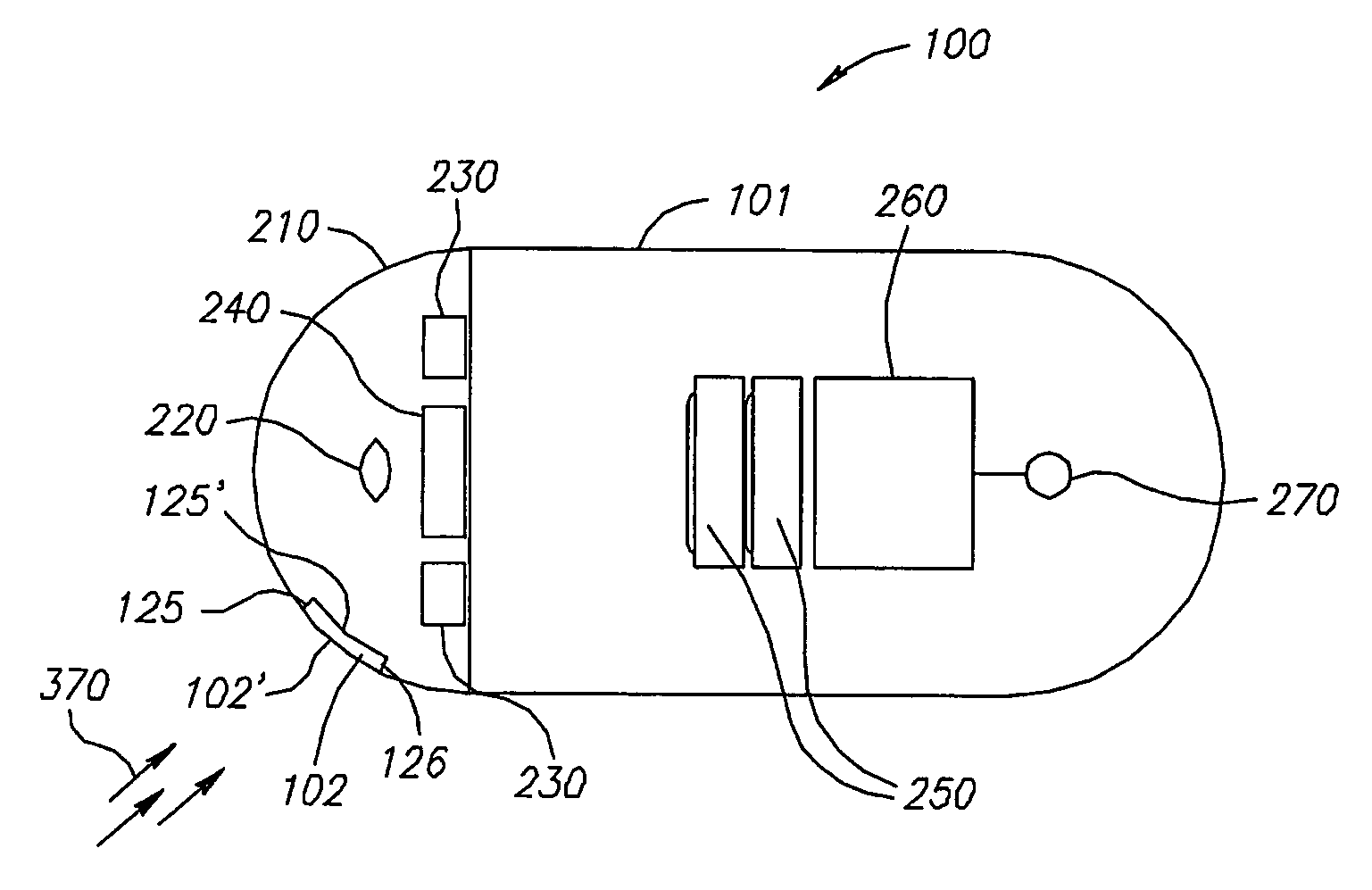
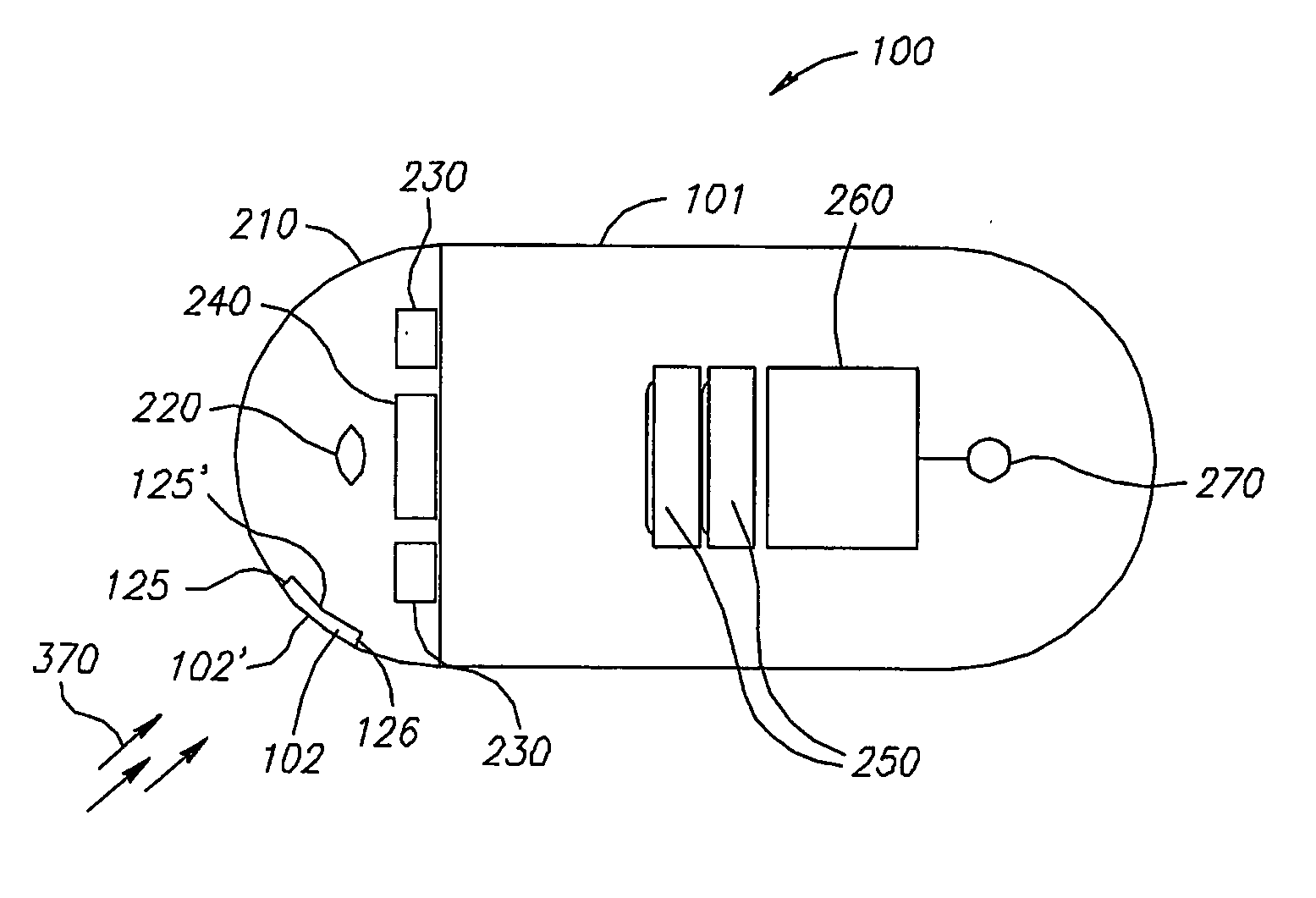
System and method for in-vivo sampling and analysis
A system for in vivo analysis which includes agglutinative particles capable of interacting with at least one analyte so as to cause an optical change; and at least one in vivo imaging system (220, 230, 240) configured for detecting the optical change in vivo. The system may be incorporated within an ingestible capsule (100).
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
System for in vivo sampling and analysis
A system for in vivo analysis which includes agglutinative particles capable of interacting with at least one analyte so as to cause an optical change; and at least one in vivo imaging system (220, 230, 240) configured for detecting the optical change in vivo. The system may be incorporated within an ingestible capsule (100).
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
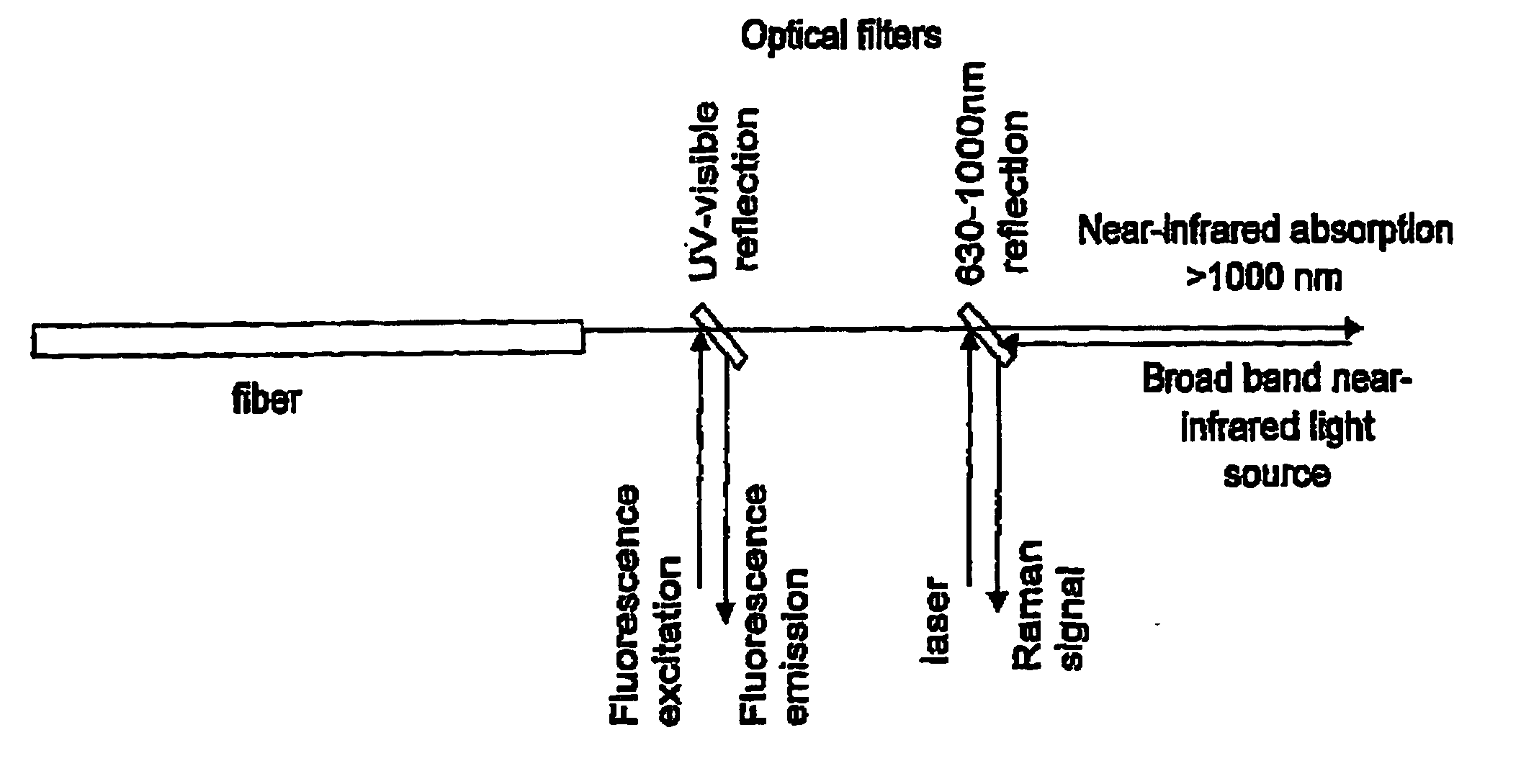
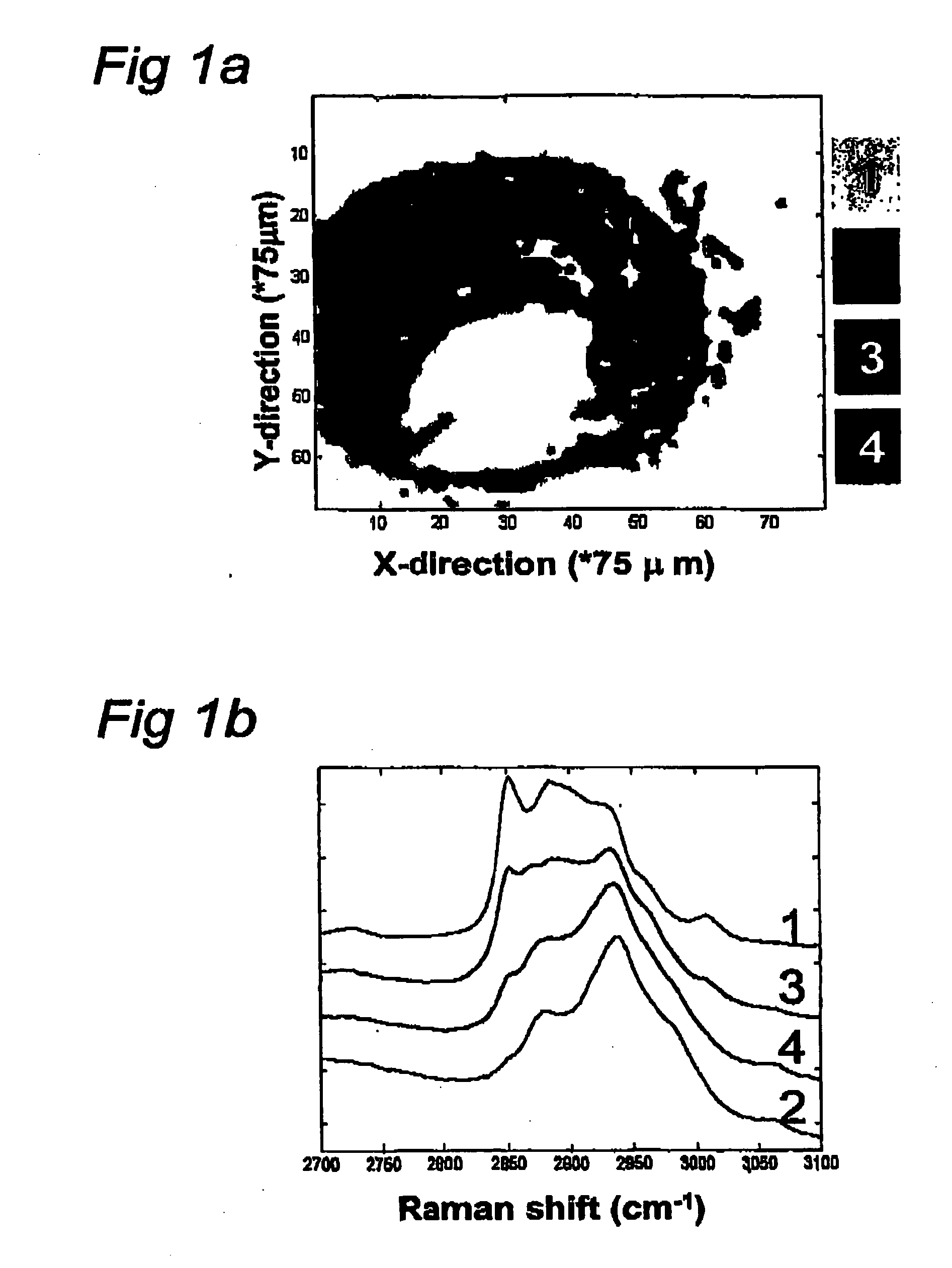
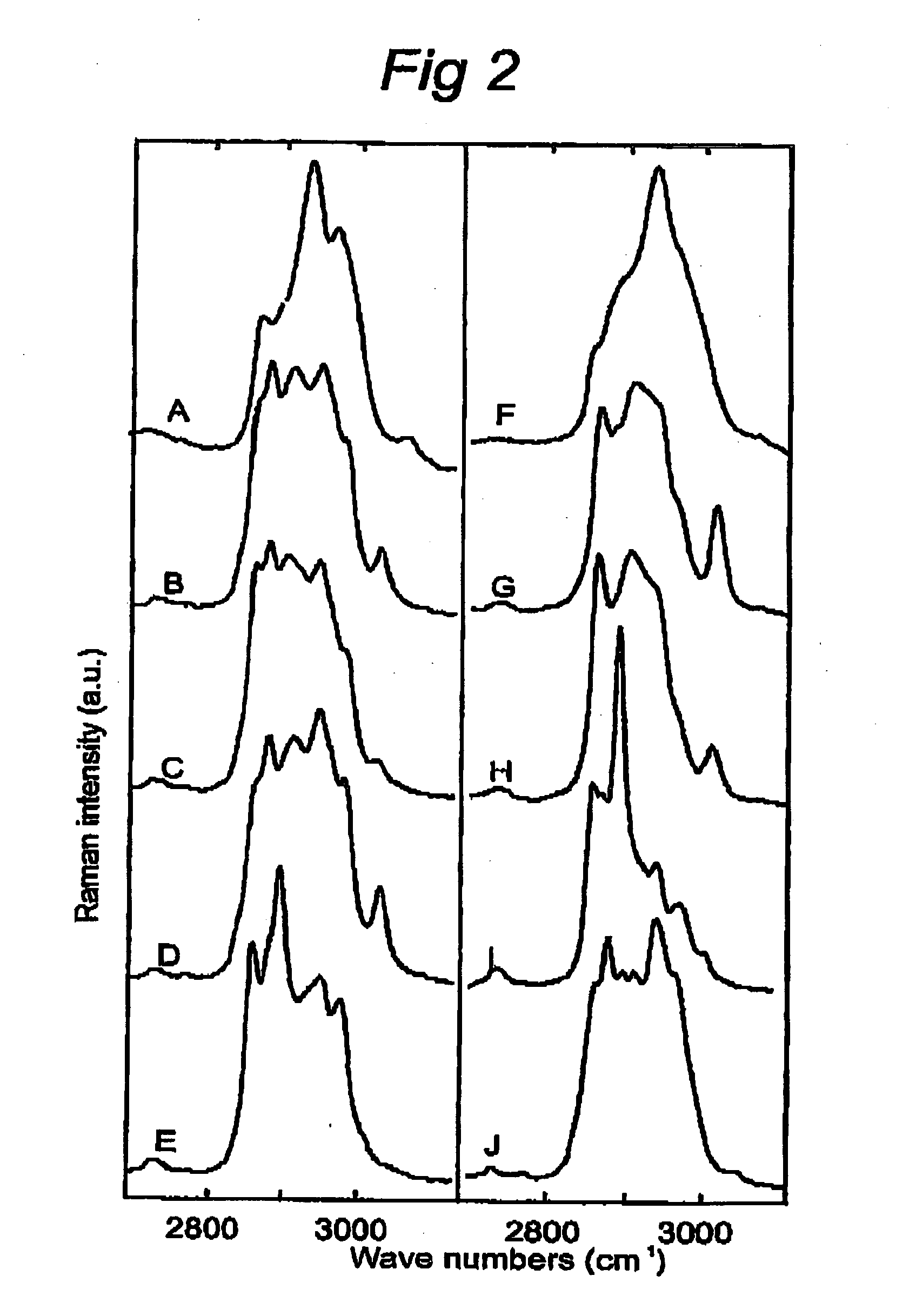
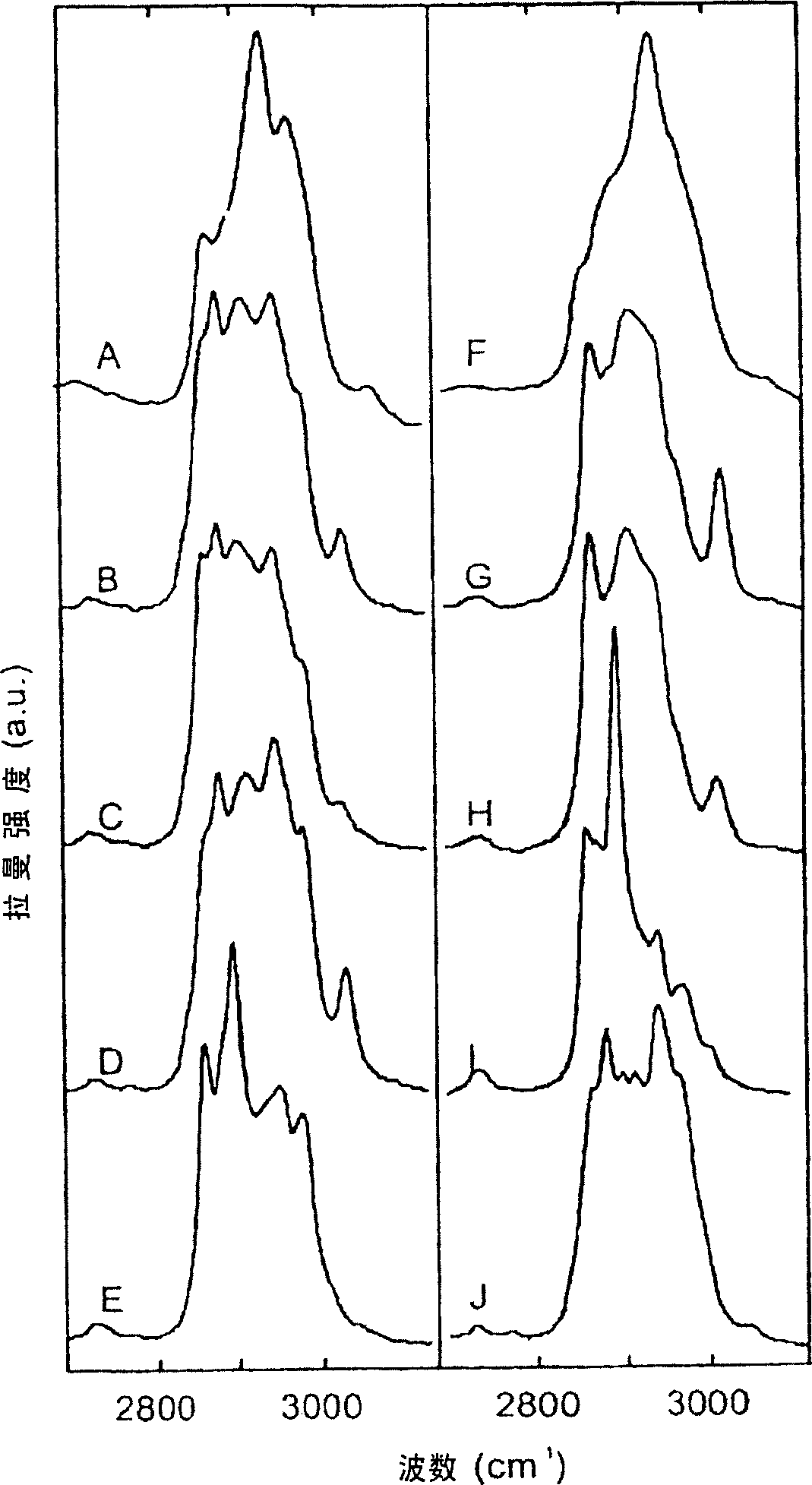
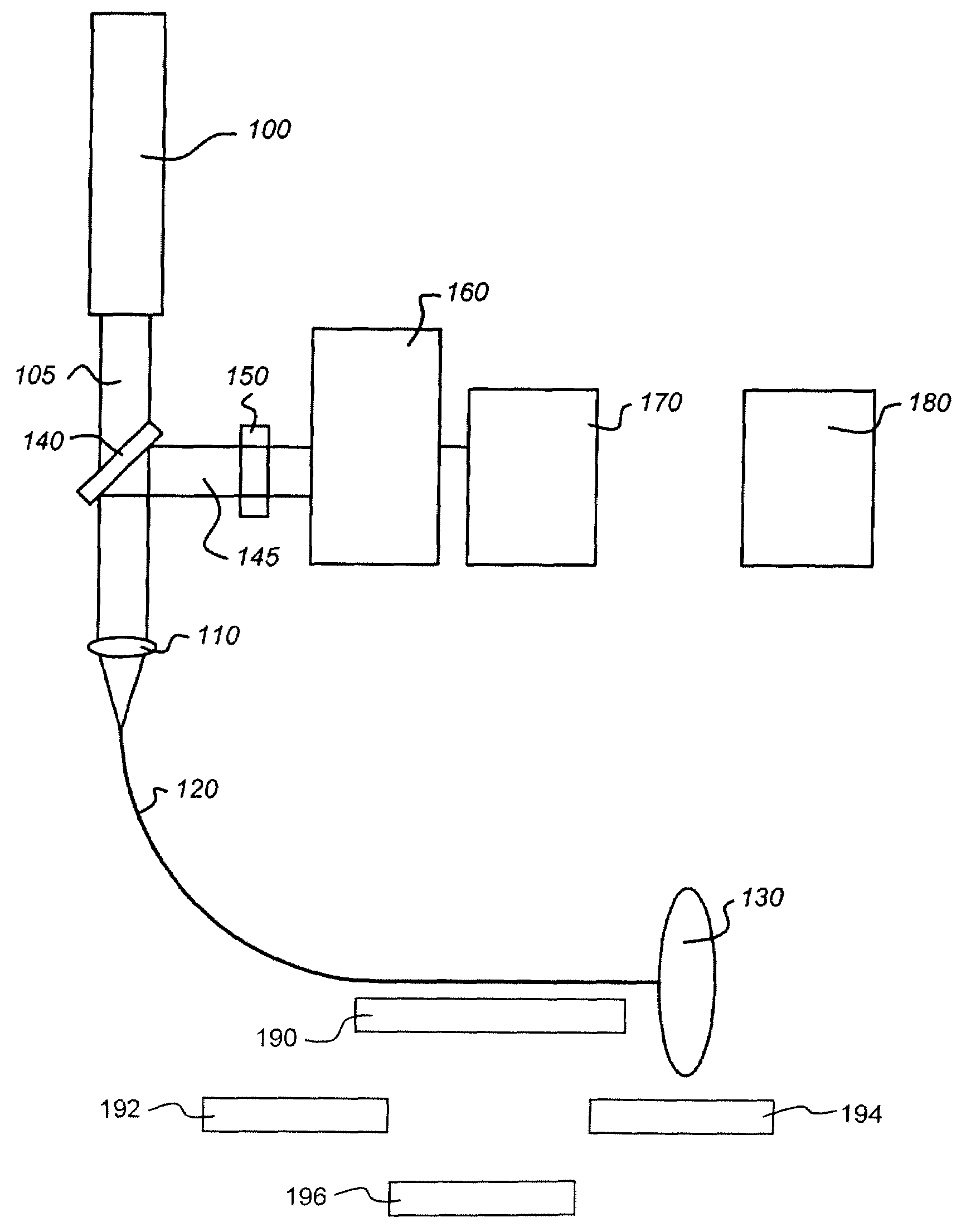
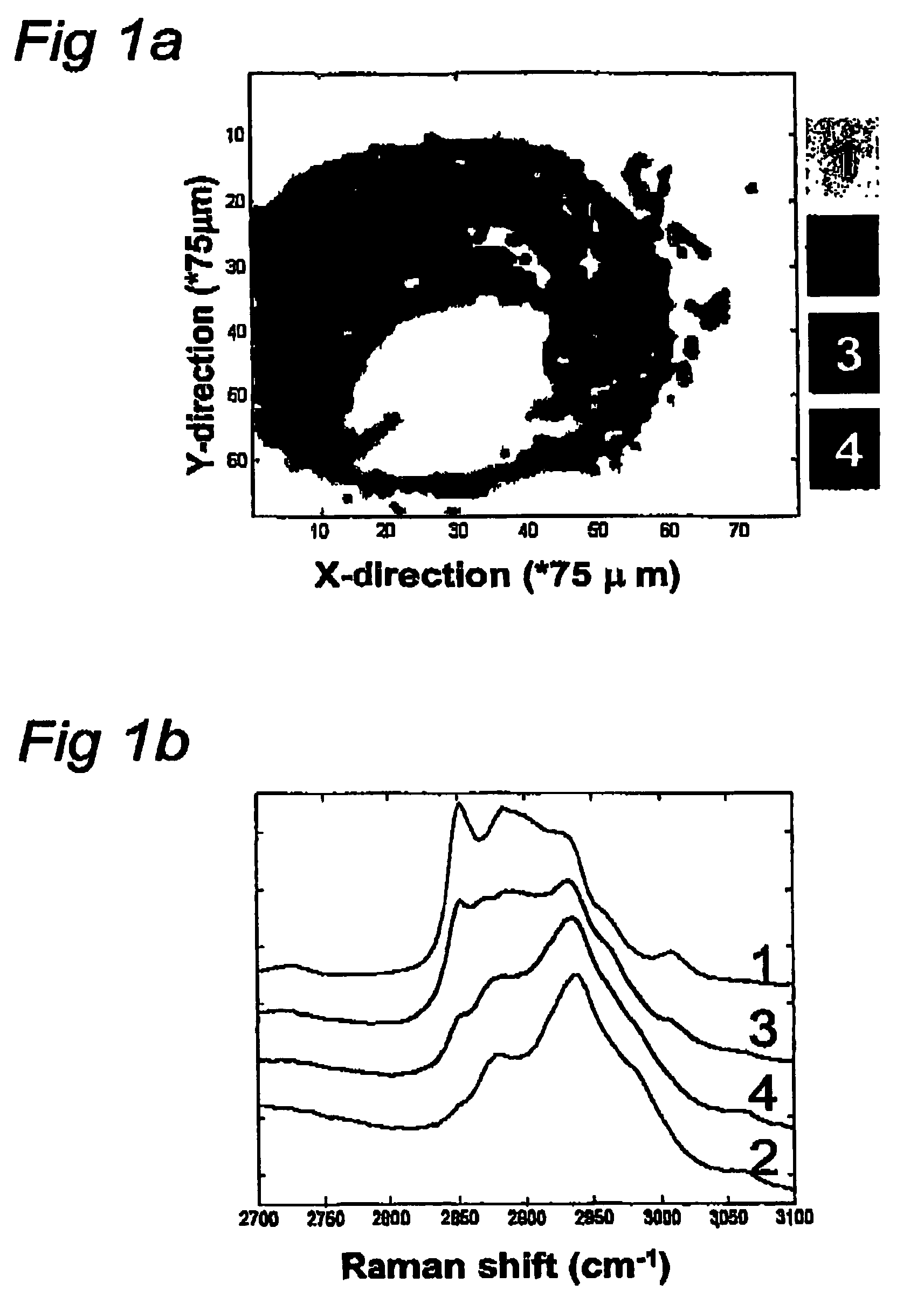
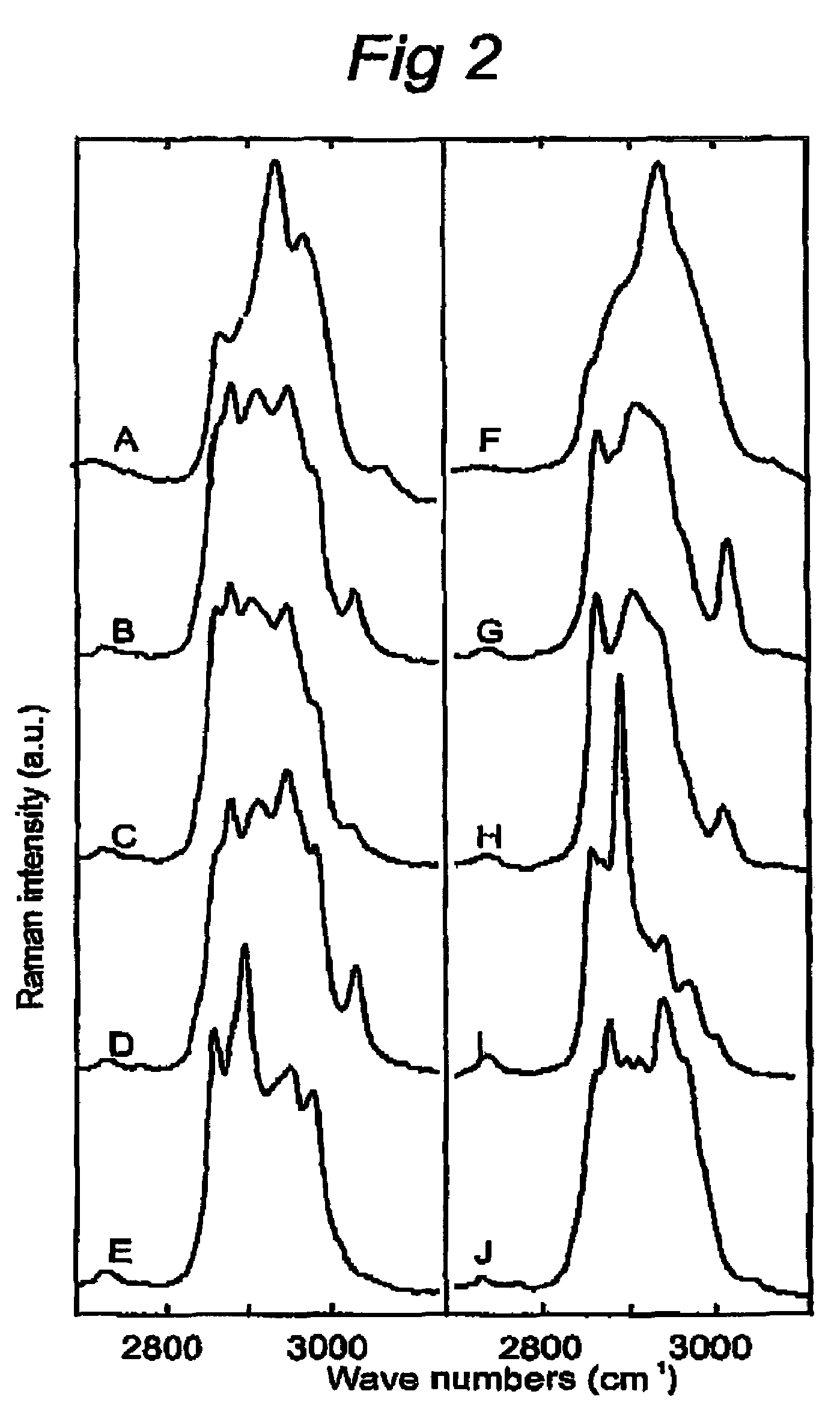
Use of high wavenumber raman spectroscopy for measuring tissue
The invention is related to the instrument for measuring a Raman signal of tissue, the instrument comprising a laser, a signal detection unit for measuring the Raman signal, and a fiber optic probe, wherein the fiber optic probe comprises one or more optical fibers for directing laser light onto the tissue and for collecting light that is scattered by the tissue and guiding the collected light away from the tissue towards the signal detection unit, wherein the fiber or fibers for collecting light have substantially no Raman signal in one or more parts of the 2500-3700 cm−1 spectral region, and wherein the detection unit records the Raman signal scattered by the tissue in said spectral region. The invention enables ex vivo, in vitro and in vivo analysis and diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaque and detection of tumor tissue with great advantages over current state-of-the-art technology.
Owner:RIVER DIAGNOSTICS
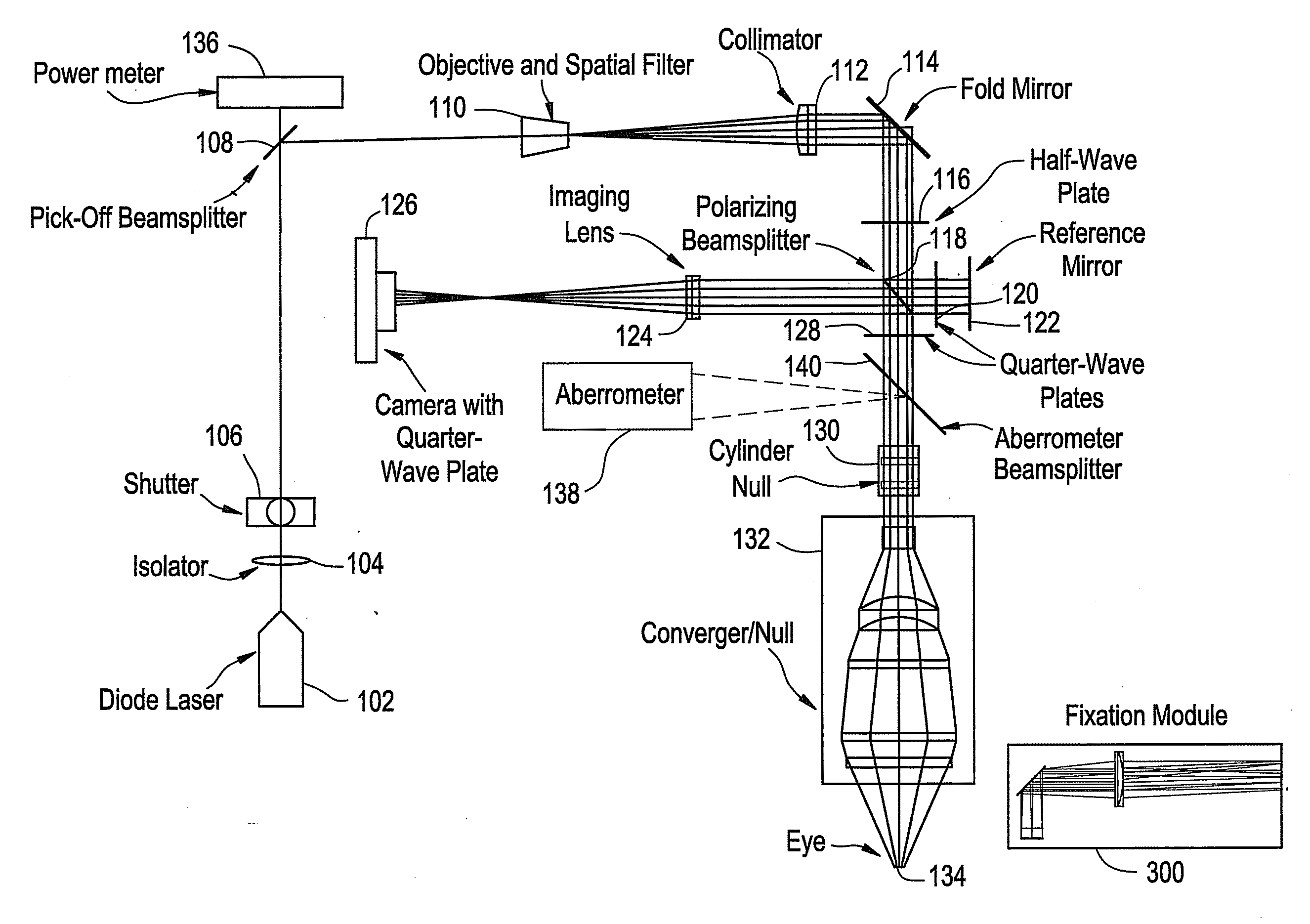
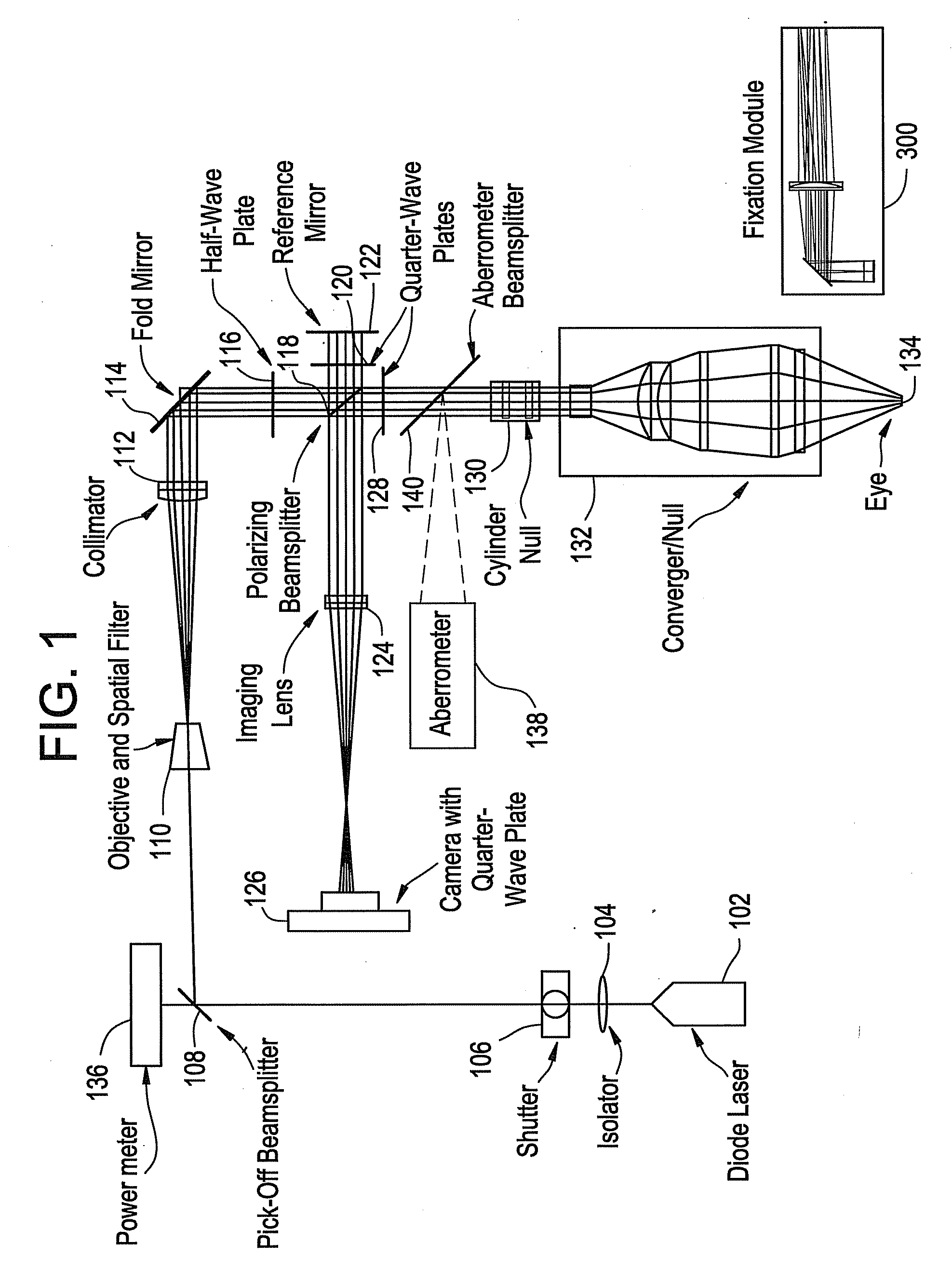
System for in vivo analysis of tear film in the human eye via phase shifting interferometry
ActiveUS20130010257A1High resolutionHigh sensitivityEye diagnosticsTemporal changePhase shifting interferometry
An in vivo method of characterizing dynamic tear films has been developed using a near infrared phase-shifting interferometer. This interferometer continuously measures light reflected from the tear film, allowing precision analysis of the dynamic surface topography. Movies showing the tear film behavior may be generated along with quantitative metrics describing the tear film surface as it changes in time.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
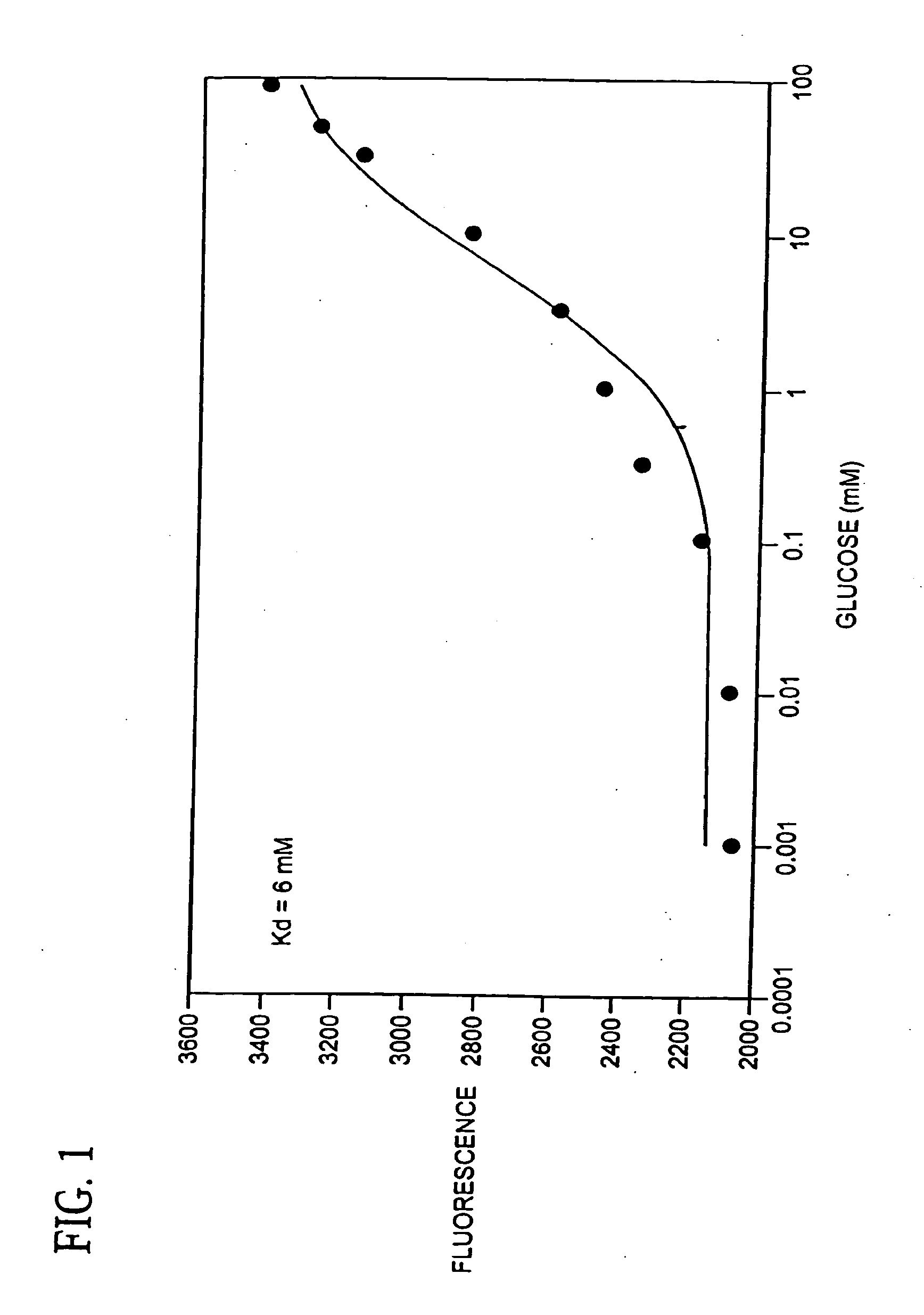
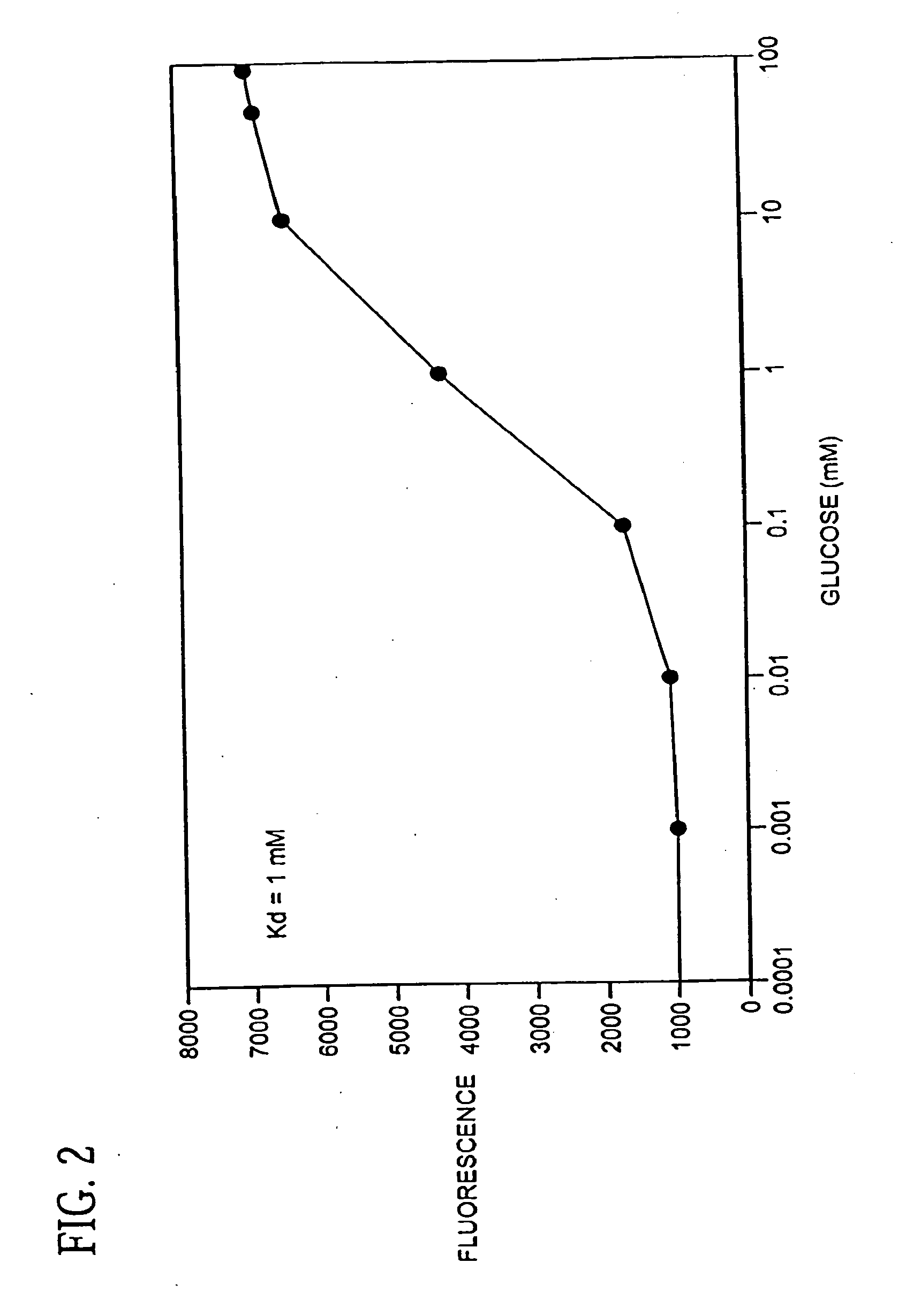
Identification of aberrant measurements of in vivo glucose concentration using temperature
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for generating an estimate of an in vivo analyte concentration and identifying whether the estimate is aberrant. In some embodiments, the system includes a sensor comprising an analyte sensor and a temperature sensing element, and a control unit programmed to identify changes in temperature that may indicate a non-physiologic condition (and result in an aberrant glucose measurement). In some embodiments, the methods include generating an estimate of analyte concentration at a particular time using the analyte sensor, and generating first and second signals indicative of temperature using the temperature sensing element. In some embodiments the methods include identifying the estimate of analyte concentration as aberrant if the magnitude of the difference between the first and second signals indicative of temperature exceeds a threshold value.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
System for in vivo analysis of tear film in the human eye via phase shifting interferometry
ActiveUS8641194B2High resolutionHigh sensitivityEye diagnosticsPhase shifting interferometryTopography
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Device,System And Method For In-Vivo Anaysis
A device, system and method of in-vivo analysis. An in-vivo device may include a chromatography unit to interact in-vivo with a body lumen substance, and a sensor to sense in-vivo a property of the chromatography unit.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Method for determining the efficacy of an anti-cancer treatment using image analysis
InactiveUS7231074B2Strong specificityHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationMultivariate statistical
An apparatus, system, method, and computer readable medium containing computer-executable code for implementing image analysis uses multivariate statistical analysis of sample images, and allows segmentation of the image into different groups or classes, depending on a correlation to one or more sample textures, or sample surface features. In one embodiment, the invention performs multivariate statistical analysis of ultrasound images, wherein a tumor may be characterized by segmenting viable tissue from necrotic tissue, allowing for more detailed in vivo analysis of tumor growth beyond simple dimensional measurements or univariate statistical analysis. Application of the apparatus and method may also be used for characterizing other types of samples having textured features including, for example, tumor angiogenesis biomarkers from Power Doppler.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Laser-induce self-assembly method for preparing high-sensitivity optical fiber SERS probe
The invention discloses a laser-induce self-assembly method for preparing a high-sensitivity optical fiber SERS probe. The method comprises the steps of conducting fusion welding on one end of an optical fiber and an output tail fiber of a laser device, and inserting the other end of the optical fiber into precious metal nano-particle sol; slowly lifting the optical fiber from the sol to be higher than the liquid level by a certain height by means of a one-dimensional precise displacement platform, so that a specific meniscus structure is formed; switching on a laser light source to enable precious metal nano-particles at the position of the meniscus to be self-assembled at the end face of the optical fiber under laser radiation, so that the optical fiber SERS probe is formed. The laser-induce self-assembly method has the advantages of being low in cost, easy to operate, short in preparation cycle, high in preparation repeatability and the like. The prepared optical fiber SERS probe has high detection sensitivity and high spectrum repeatability and has important application prospects in remote / field detection of environment pollutants, in-vivo analysis in biomedicine, real-time detection of chemical reaction process and other fields.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device, System and Method for In Vivo Analysis
Devices, systems and method for in vivo analysis. For example, an in vivo device includes: a reaction chamber to store a detecting reagent able to react with a sample collected in vivo; and optionally a labeled-substance chamber to store a labeled substance able to bind to at least a portion of a compound resulting from a reaction of the detecting reagent and the sample.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Guidewire with chemical sensing capabilities
A guidewire with a sensor which can detect NO and / or superoxide levels is disclosed. This invention can be useful for in vivo analysis of vascular health.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Use of high wavenumber raman spectroscopy for measuring tissue
The invention is related to the instrument for measuring a Raman signal of tissue, the instrument comprising a laser, a signal detection unit for measuring the Raman signal, and a fiber optic probe, wherein the fiber optic probe comprises one or more optical fibers for directing laser light onto the tissue and for collecting light that is scattered by the tissue and guiding the collected light away from the tissue towards the signal detection unit, wherein the fiber or fibers for collecting light have substantially no Raman signal in one or more parts of the 2500-3700 cm<-1 >spectral region, and wherein the detection unit records the Raman signal scattered by the tissue in said spectral region. The invention enables ex vivo, in vitro and in vivo analysis and diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaque and detection of tumor tissue with great advantages over current state-of-the-art technology.
Owner:RIVER DIAGNOSTICS
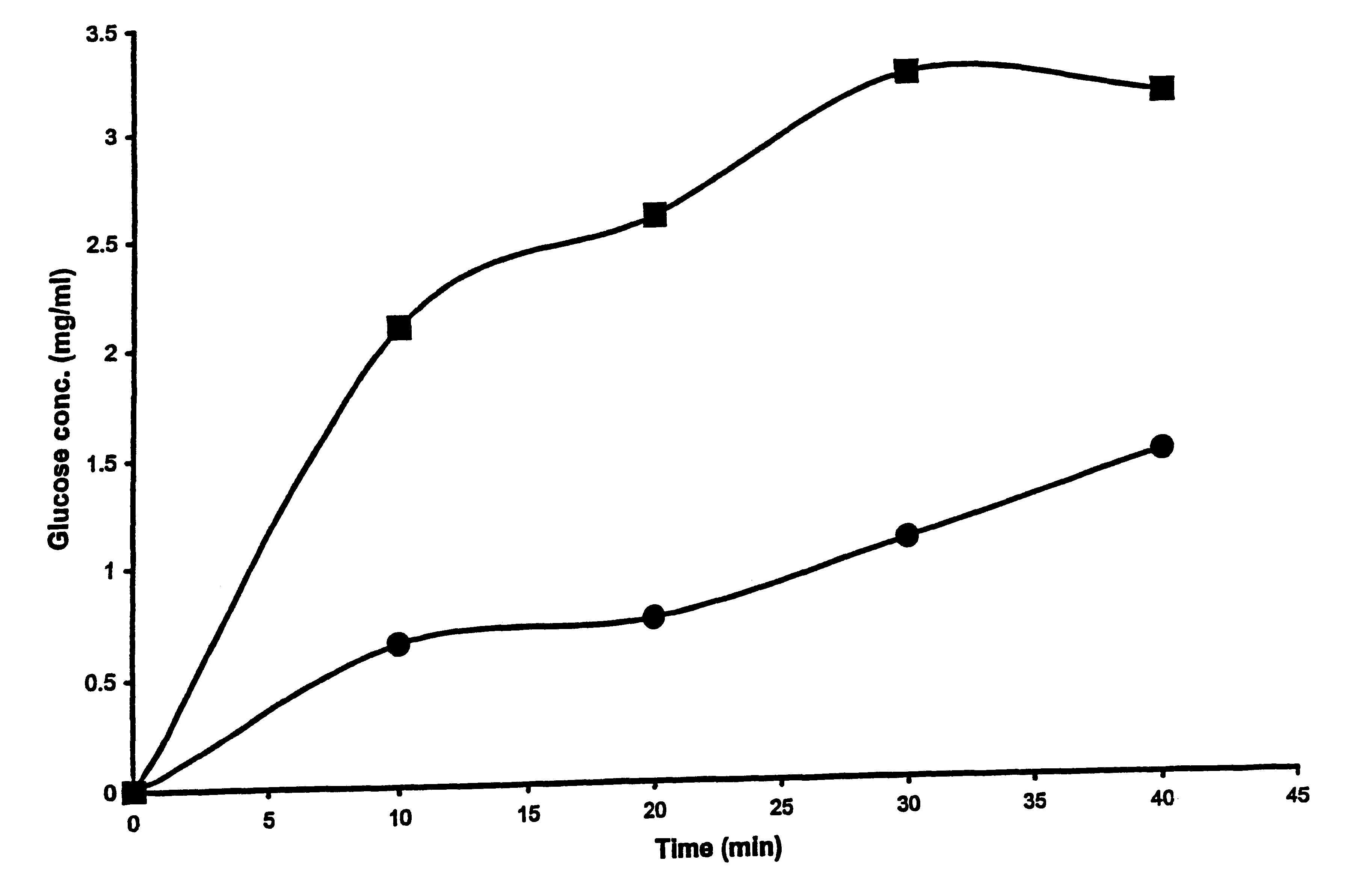
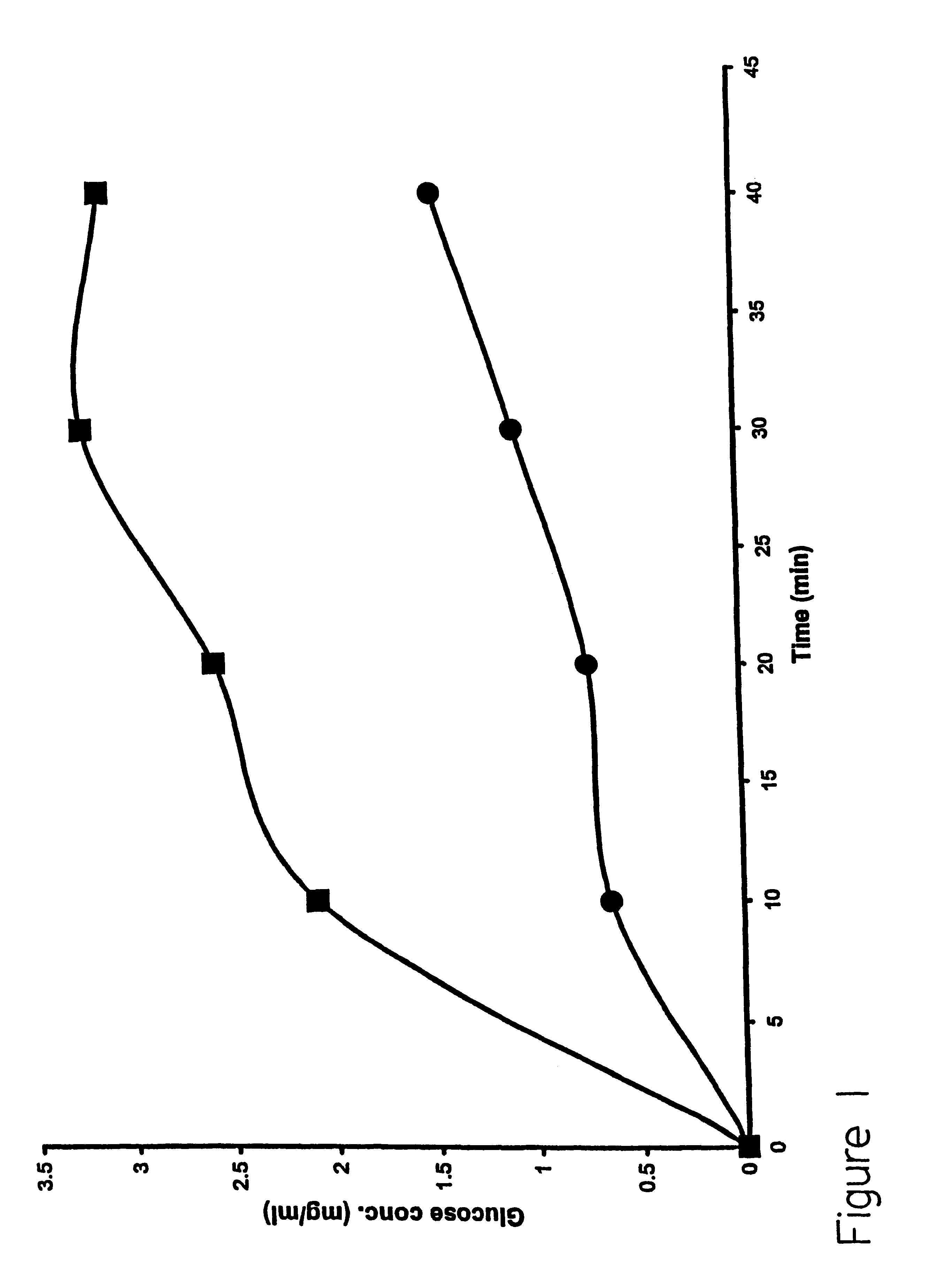
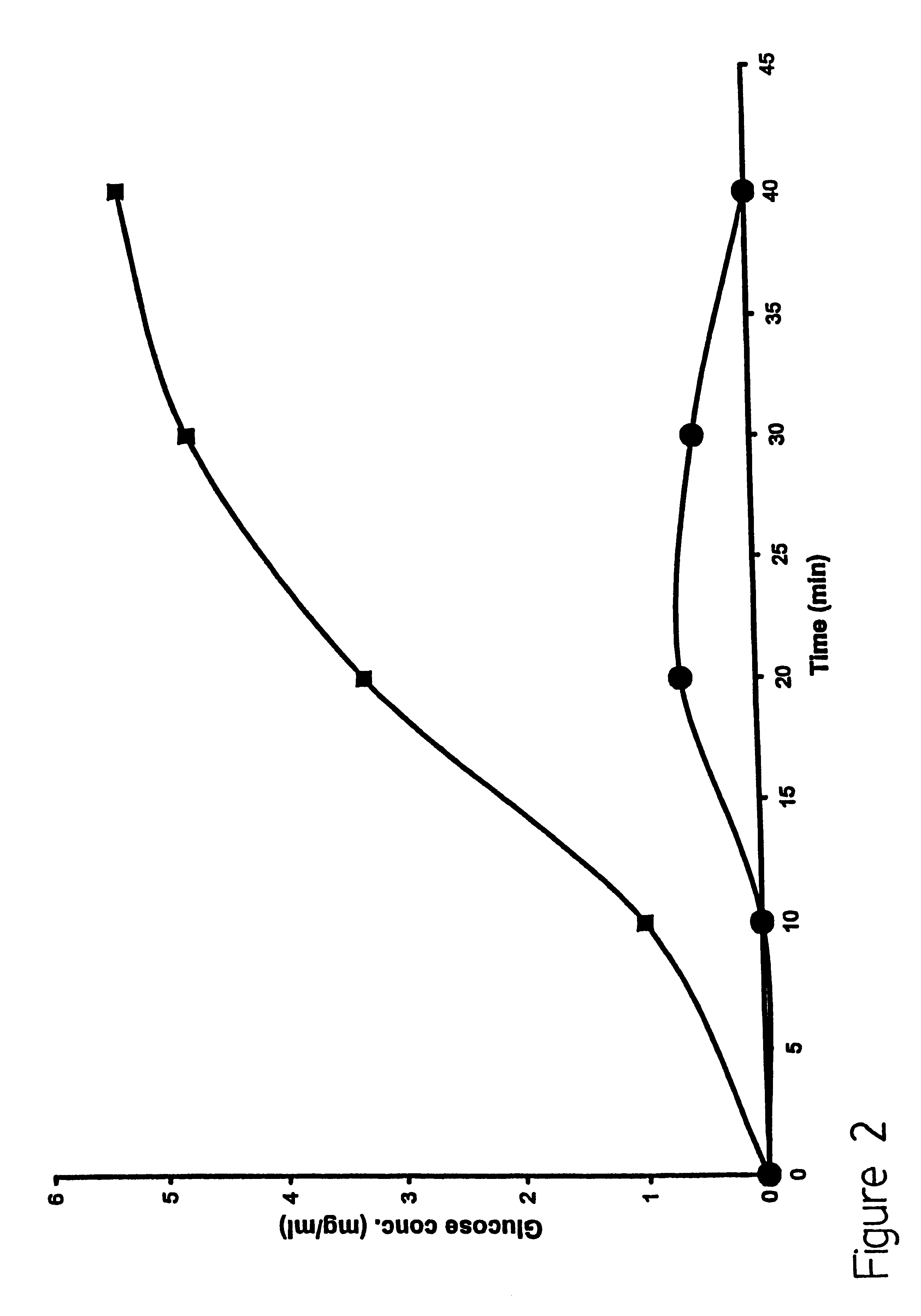
Method for transdermal sampling of analytes
The present invention discloses a method for transdermal extraction and measurement of analytes in an individual's body comprising the steps of permeabilizing the skin by electroporation in the presence of liposomes comprising negatively charged lipids, and extracting the extracellular fluid through the permeabilized skin by using suction. Analytes may be quantitated in the extracted extracellular fluid.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Device, system, and method for in-vivo analysis
A device, system and method for in-vivo analysis. An autonomous in-vivo device may include a magnet to detain at least a portion of a sample collected from a body lumen; a sensor to sense a property of the detained sample portion; and a transmitter to transmit data of the sensed property.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Use of high wavenumber Raman spectroscopy for measuring tissue
The invention is related to the instrument for measuring a Raman signal of tissue, the instrument comprising a laser, a signal detection unit for measuring the Raman signal, and a fiber optic probe, wherein the fiber optic probe comprises one or more optical fibers for directing laser light onto the tissue and for collecting light that is scattered by the tissue and guiding the collected light away from the tissue towards the signal detection unit, wherein the fiber or fibers for collecting light have substantially no Raman signal in one or more parts of the 2500-3700 cm−1 spectral region, and wherein the detection unit records the Raman signal scattered by the tissue in said spectral region. The invention enables ex vivo, in vitro and in vivo analysis and diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaque and detection of tumor tissue with great advantages over current state-of-the-art technology.
Owner:RIVER DIAGNOSTICS
Device, system and method for in-vivo analysis
InactiveUS20100322866A1Improve performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAntigenOptical property
A method for detecting the presence of a substance such as an antigen, the method including the steps of: maintaining a signaling material at a first pH within a liposome; contacting the liposome with a sample having a second pH such that if the substance is present in the sample the liposome will rupture thereby exposing the signaling material to the second pH; and detecting a change in an optical property, such as color, of the signaling material, the change caused by the exposure to the second pH.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Process, system and method for improving the determination of digestive effects upon an ingestable substance
ActiveUS20060036370A1Promote digestionIncrease conversionsMedical simulationAnimal feeding stuffBiologyIn vivo analysis
The present invention generally relates to processes, computer programs and systems, methods of making such and methods of using such for improving the determination of one or more digestive effects upon an ingestable substance. The underlying data used in this determination may originate from either an in vitro or in vivo analysis. The processes may be either partially or fully manual or automated, and combinations thereof.
Owner:VENTURE MILLING
The methods for detecting molecular interactions
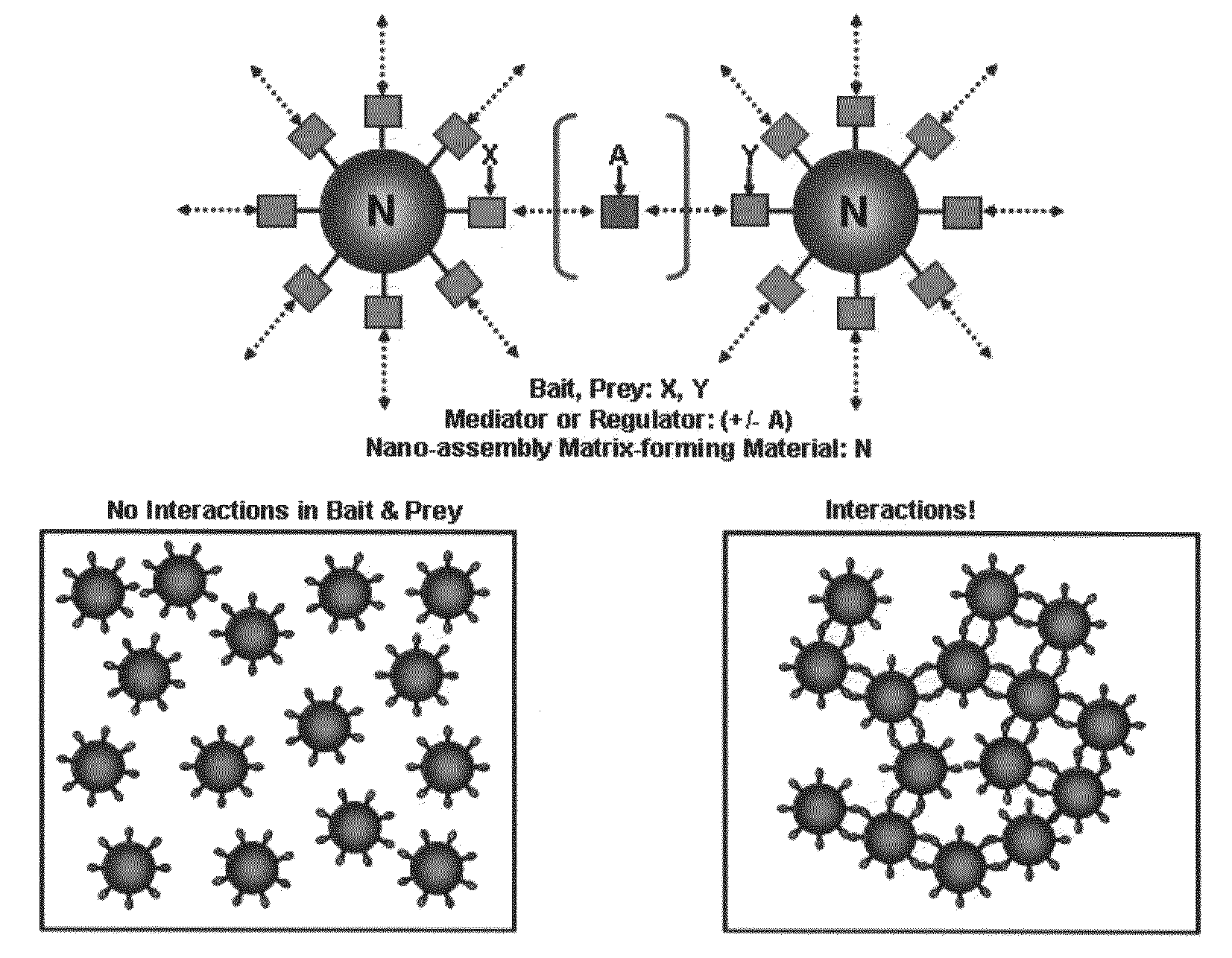
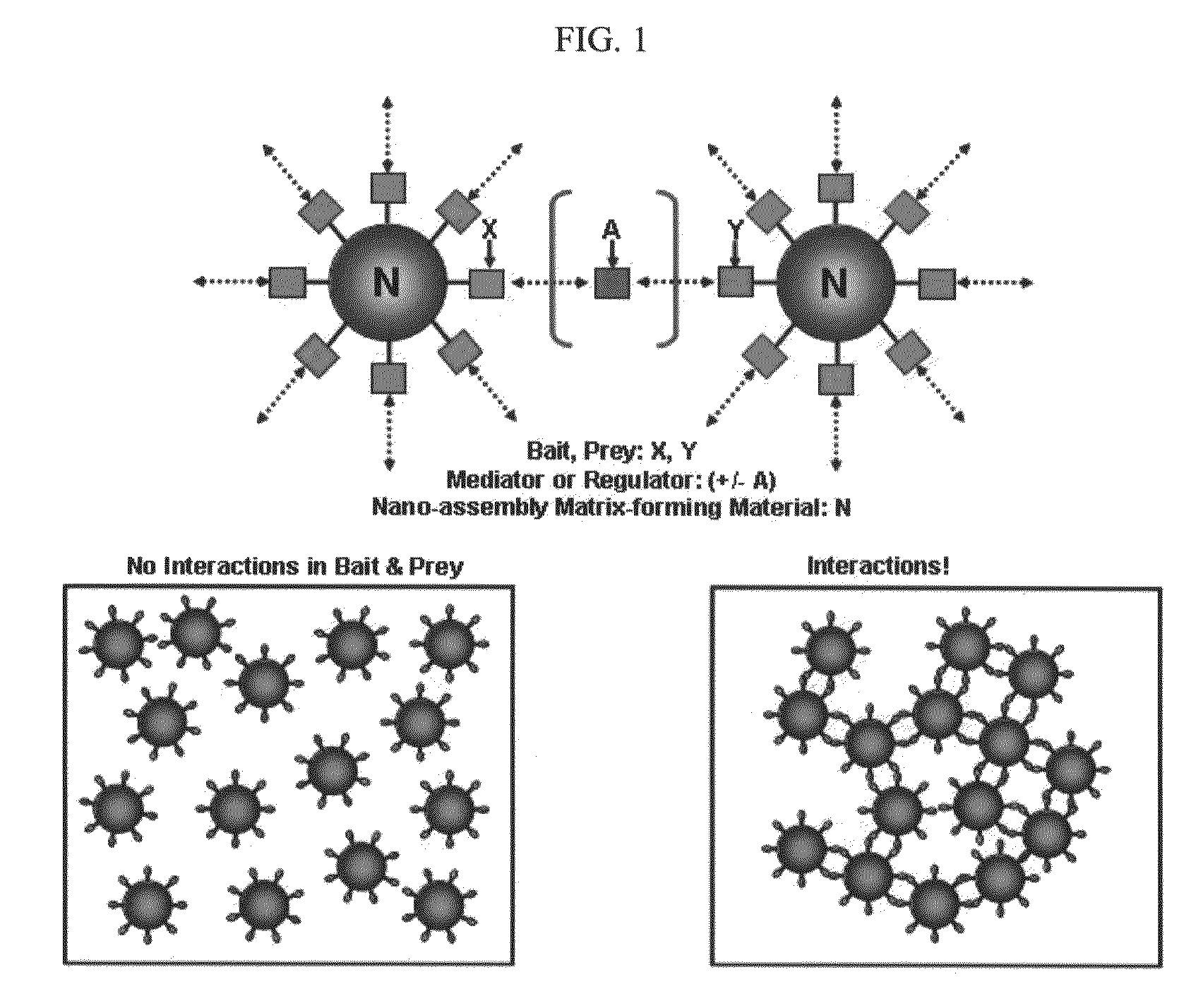
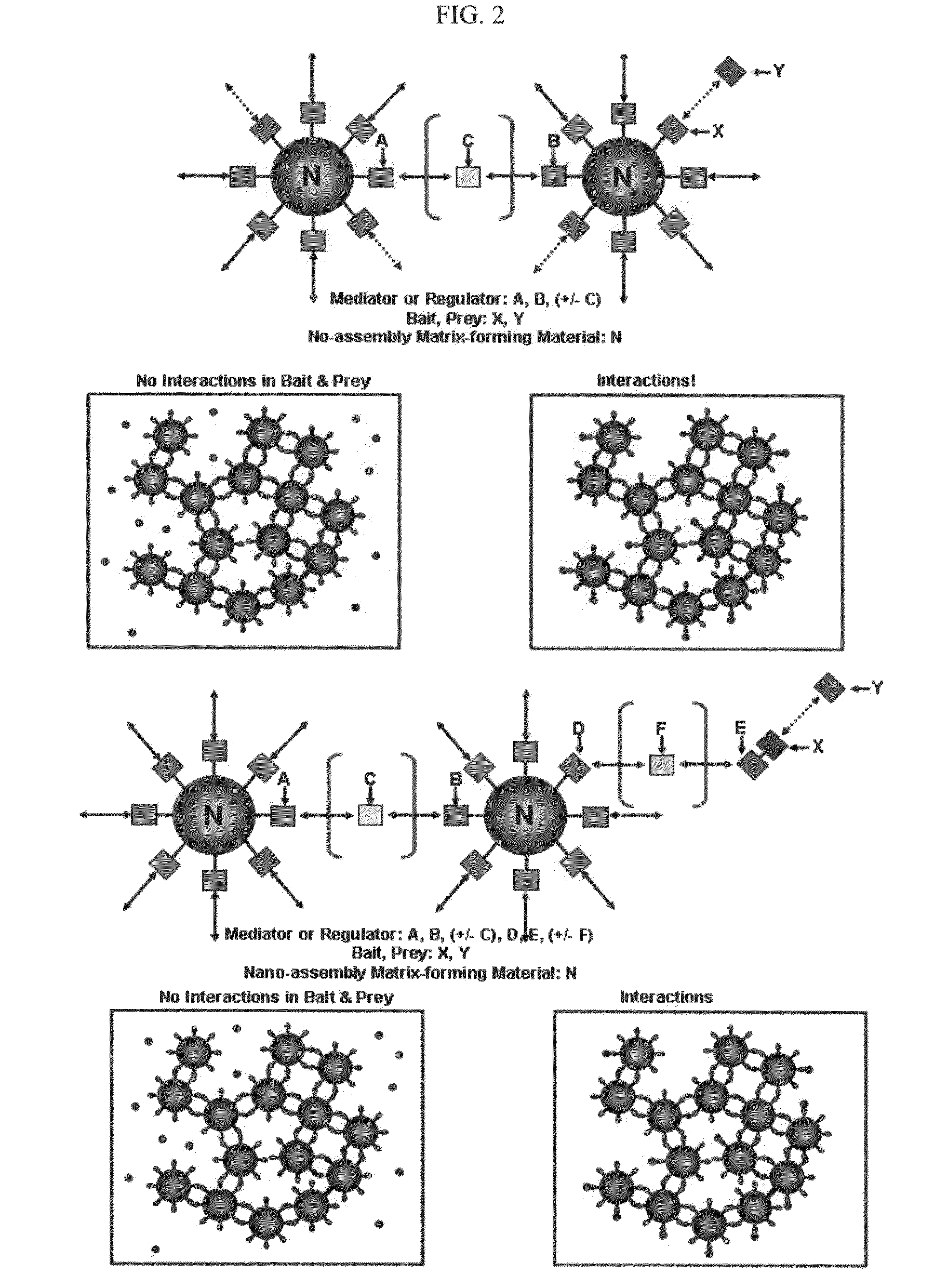
The present invention relates to methods for dynamically detecting the interactions between various materials including bioactive molecules and for detecting target molecules. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for dynamically detecting bait-prey interactions and a method for easily detecting target molecules which blocks or activates the interactions, the method comprising: allowing a material capable of forming a nano-assembly matrix, a bait and a prey to interact with each other, and analyzing whether a nano-assembly matrix is formed by the interaction between the bait and the prey in vitro or in vivo; or allowing a material capable of forming a nano-assembly matrix, a bait and a prey to interact with each other, inducing the formation of a nano-assembly matrix by a mediator (regulator) material in vitro or in vivo, and then analyzing whether the prey and the bait co-localizes on the nano-assembly matrix.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
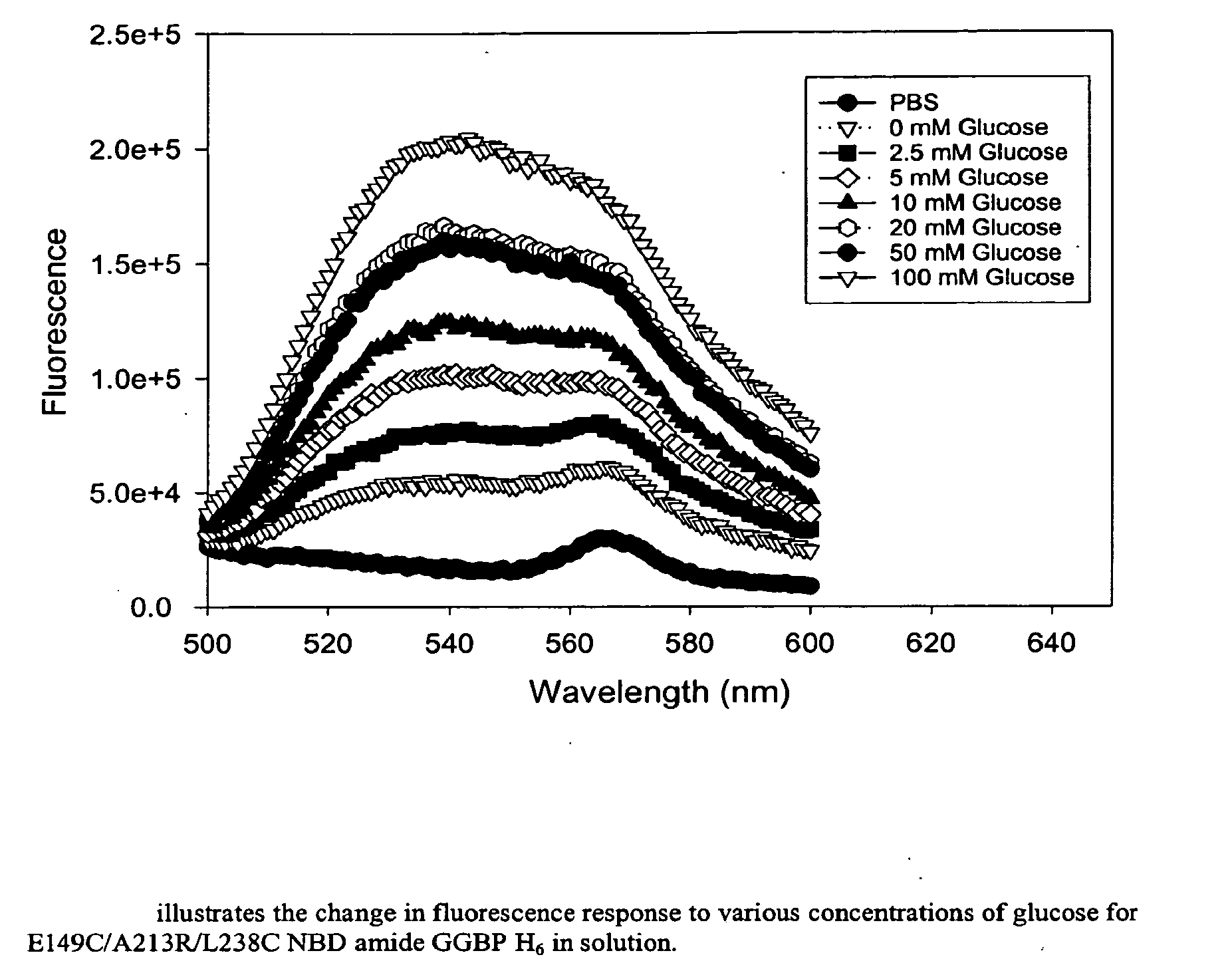
Binding proteins as biosensors
InactiveUS20070281368A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDepsipeptidesAnalyteIn vivo analysis
Owner:HSIEH HELEN VIVIAN +5
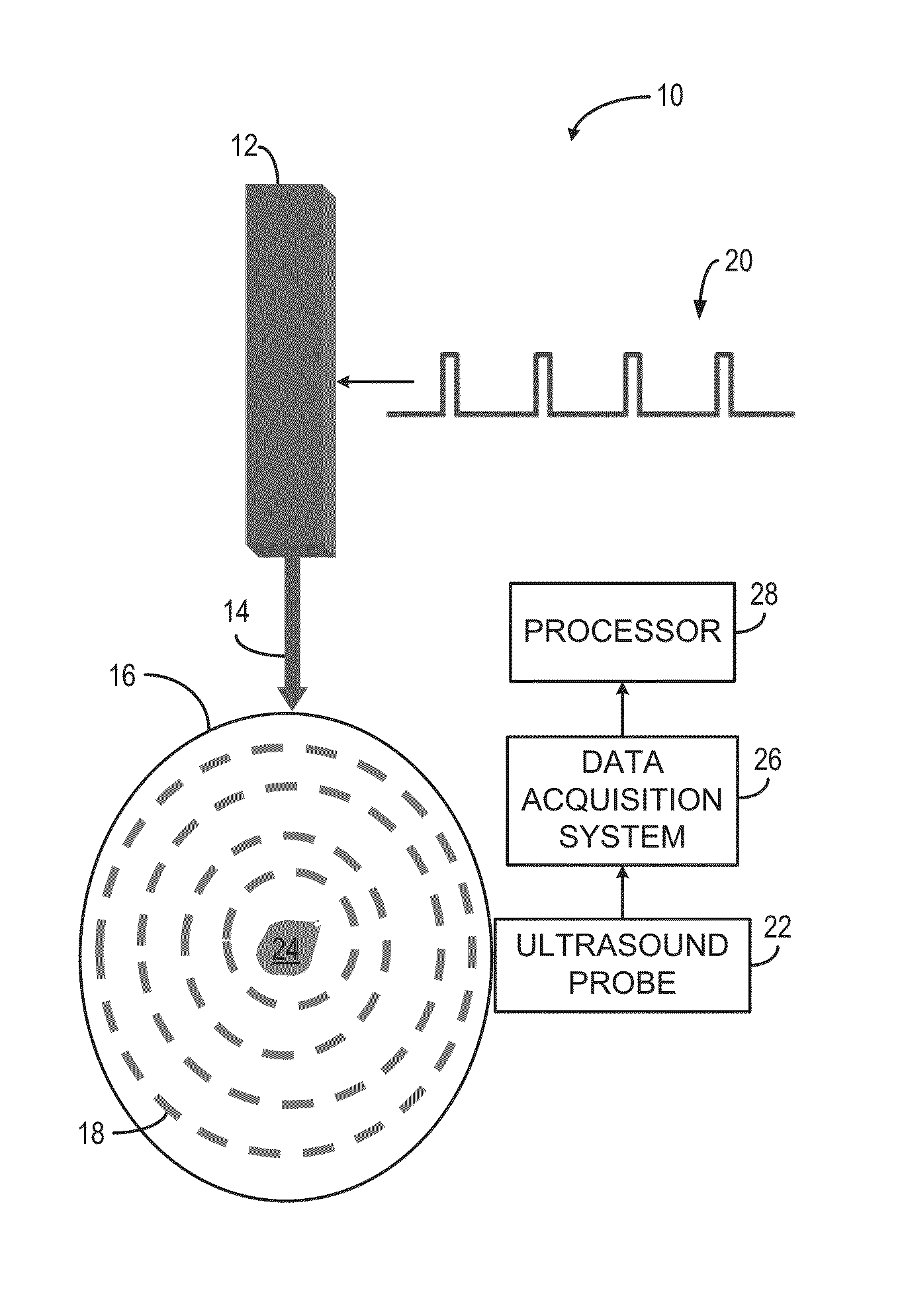
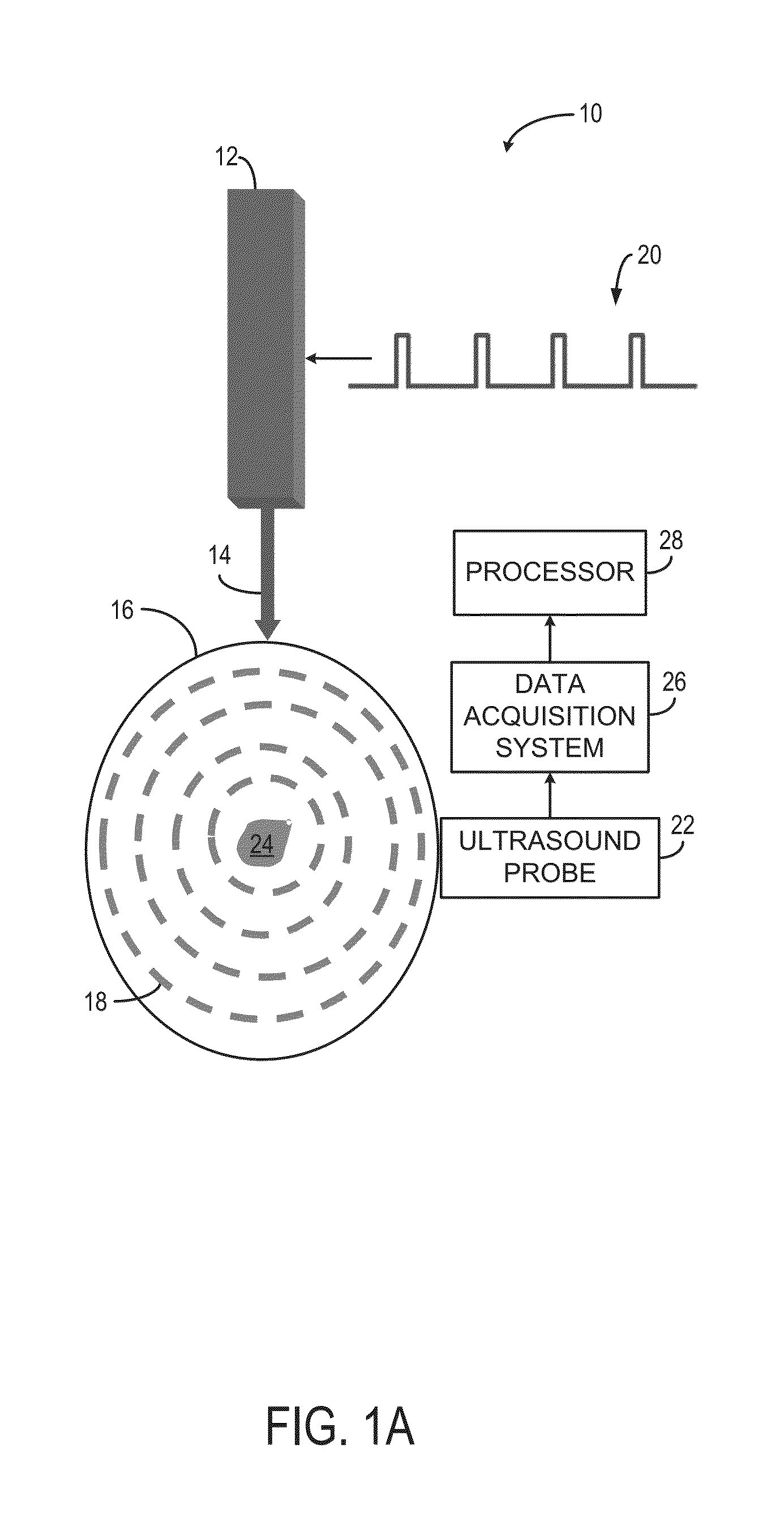
Systems and Methods for Real-Time Tracking of Photoacoustic Sensing
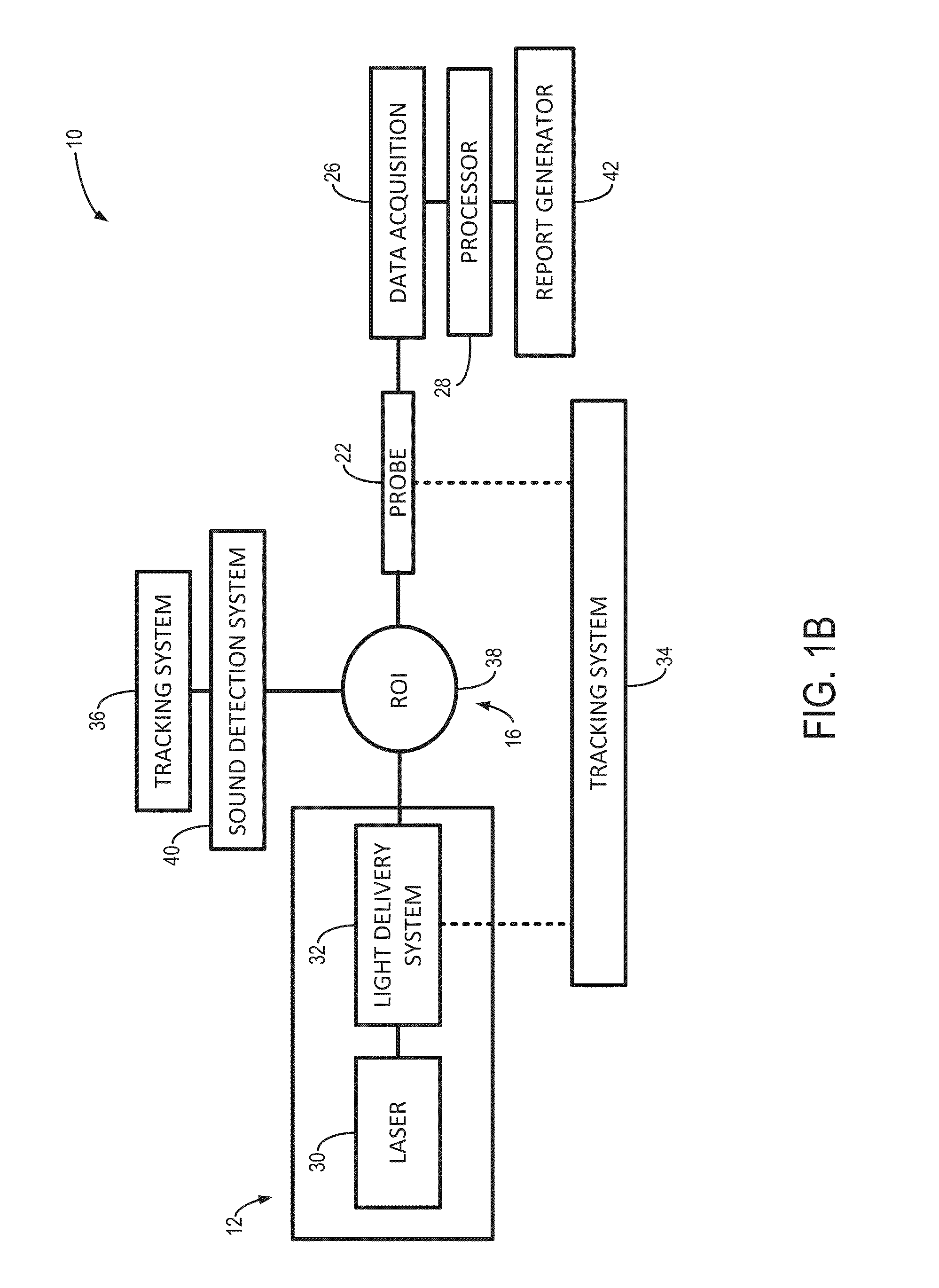
ActiveUS20150150464A1Medical imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicineIn vivo analysis
Systems and methods for real-time tracking of photoacoustic sensing are provided. In one aspect, a method for performing in vivo analysis of a subject is provided. The method includes directing an electromagnetic excitation toward a subject to be analyzed, and acquiring, with an ultrasound probe, data about resultant waves caused by the electromagnetic excitation. The method also includes processing the acquired data to extract information related to properties of tissues in the subject, and comparing the information related to the properties of tissues in the subject using a set of criteria. The method also includes generating a report about a condition of the subject based on the comparison of the information related to properties of the tissues in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
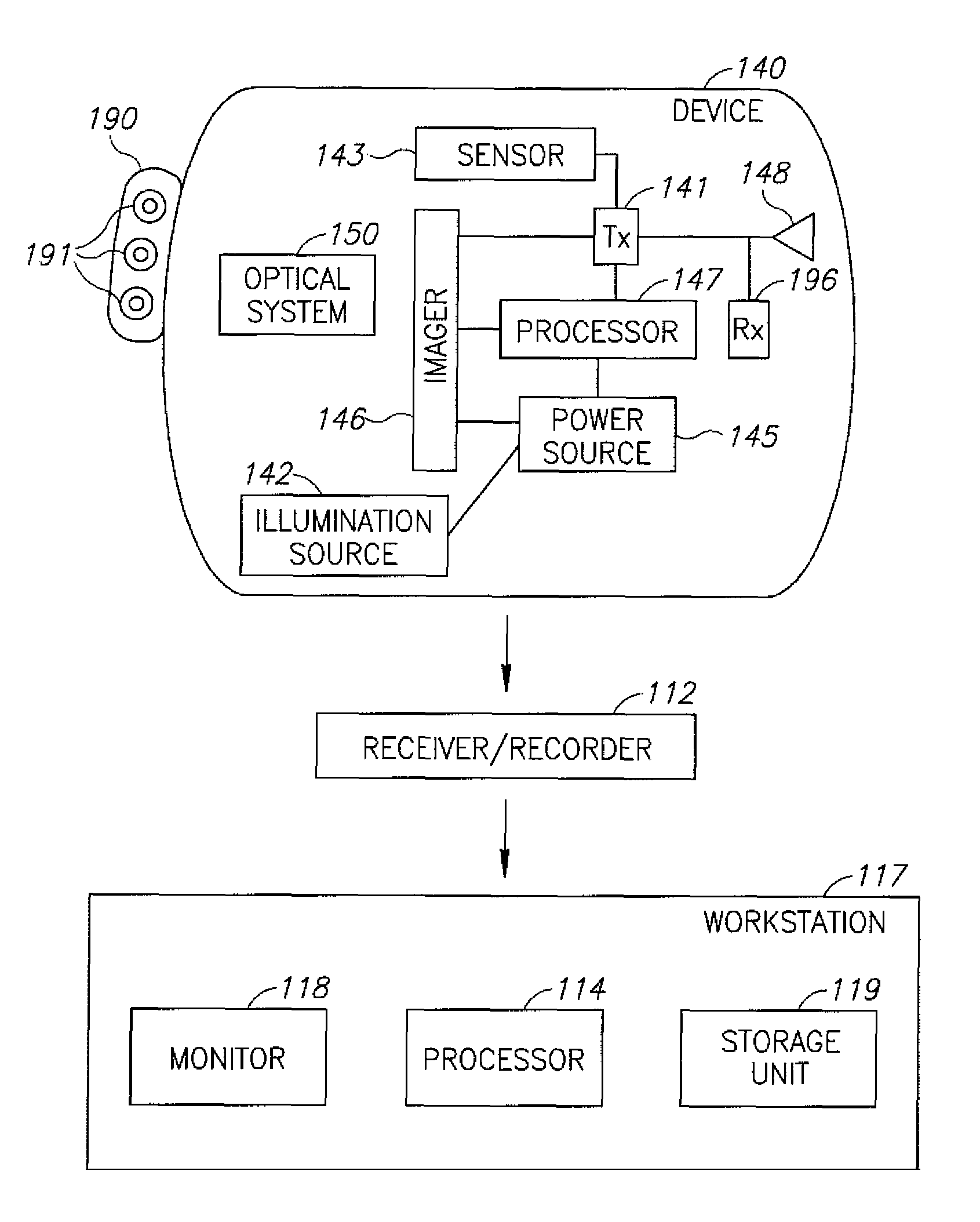
Device, system and method for in vivo analysis
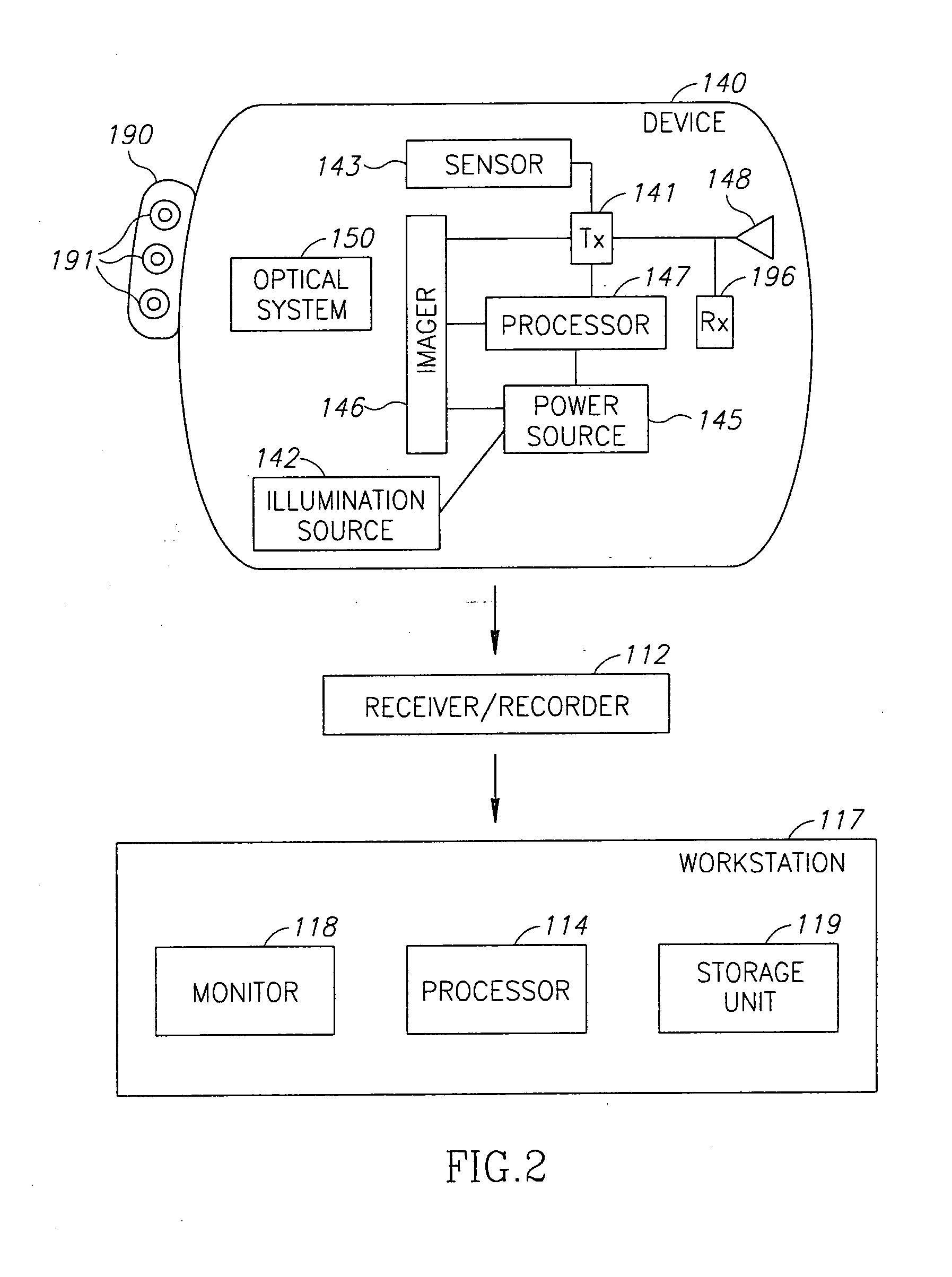
A device for in vivo analysis includes: a reaction chamber to store a detecting reagent able to react with a sample collected in vivo; and optionally a labeled-substance chamber to store a labeled substance able to bind to at least a portion of a compound resulting from a reaction of the detecting reagent and the sample. The in-vivo imaging device, typically an autonomous capsule, may have a housing, the housing comprising a window; an illumination source located within the housing to illuminate a body lumen through the window; an imager to receive light reflected from the body lumen through the window; and a transmitter to transmit image data to a receiving system. The window is coated with liposomes containing a marker such that the imager may acquire images which include the marking.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
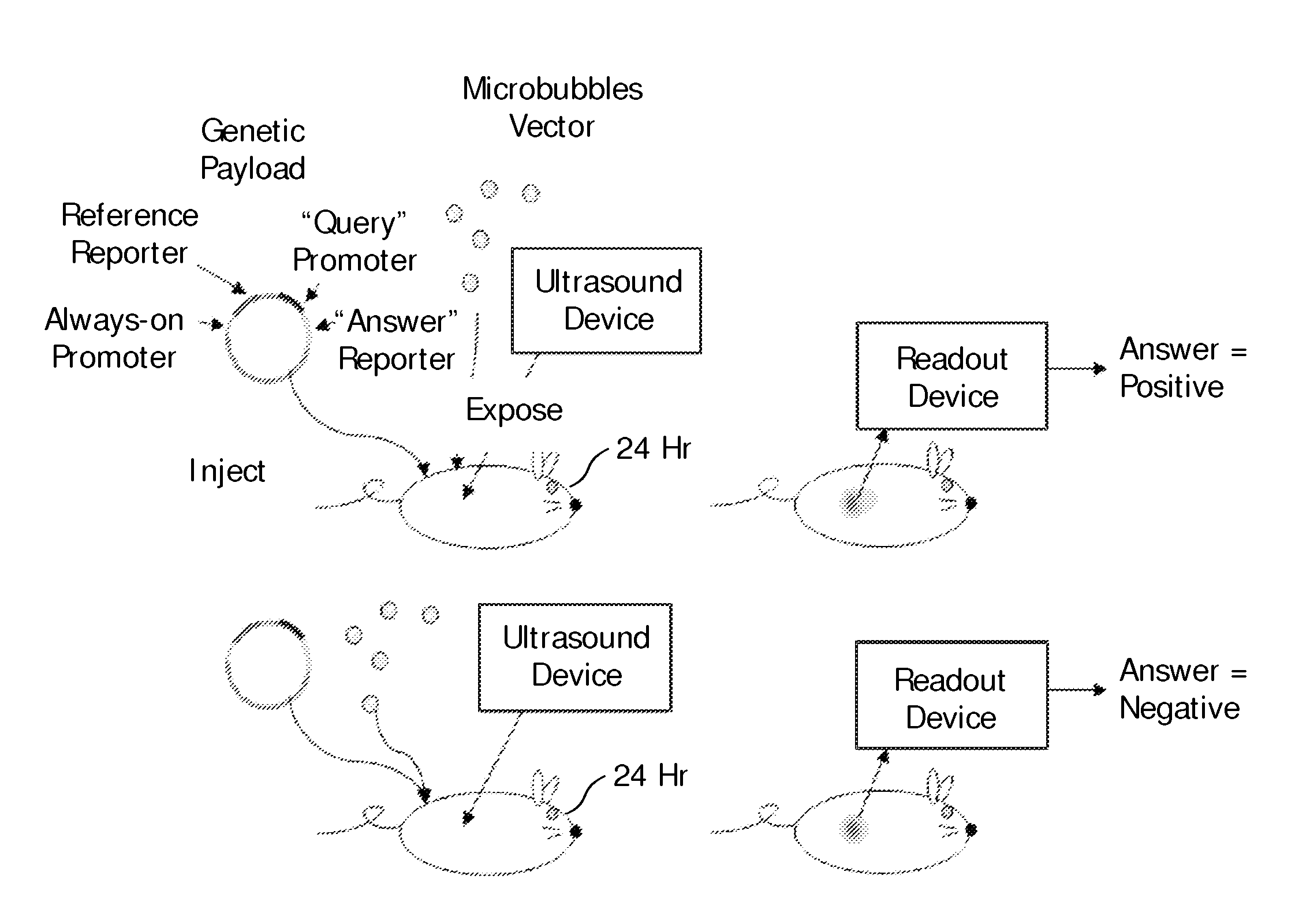
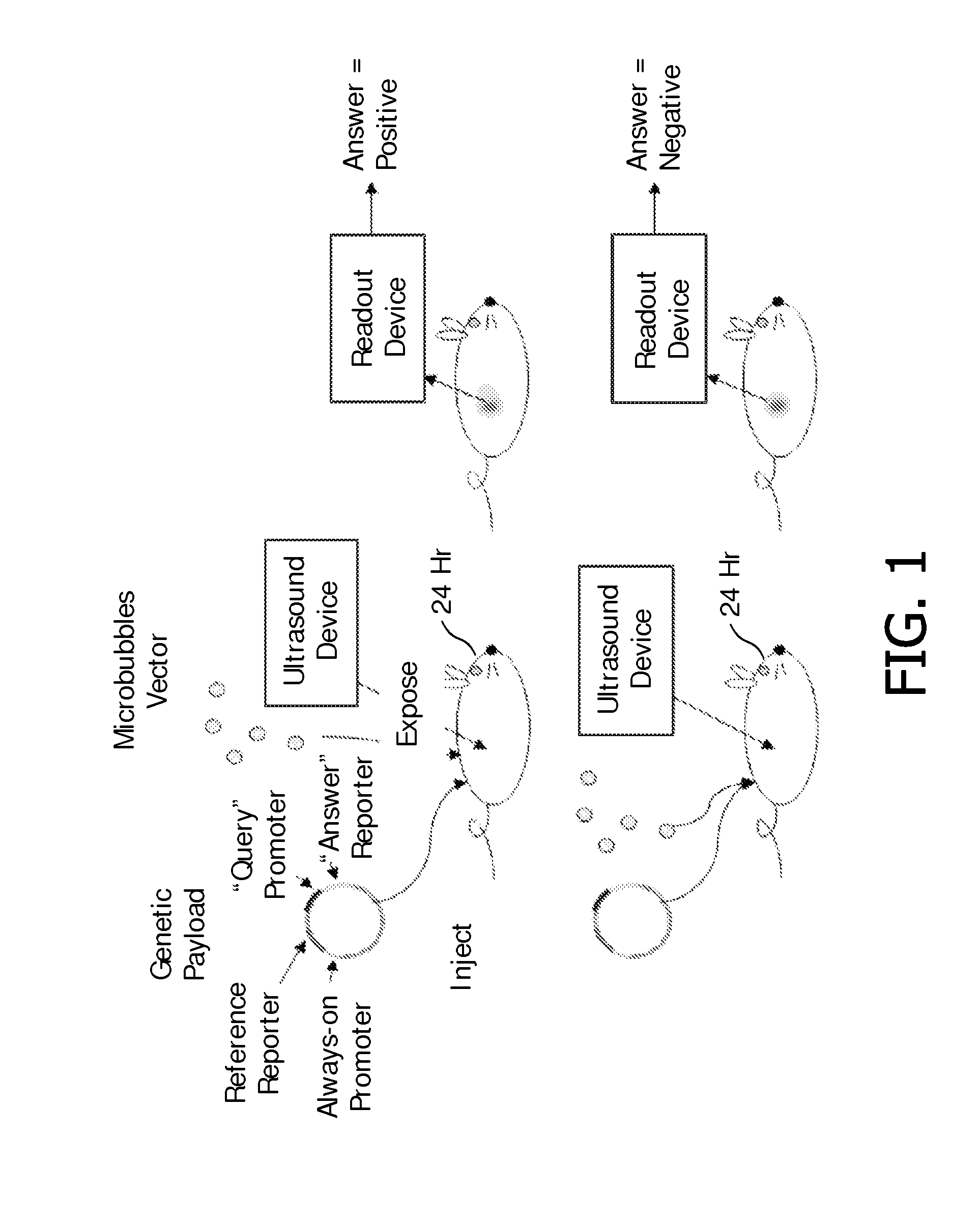
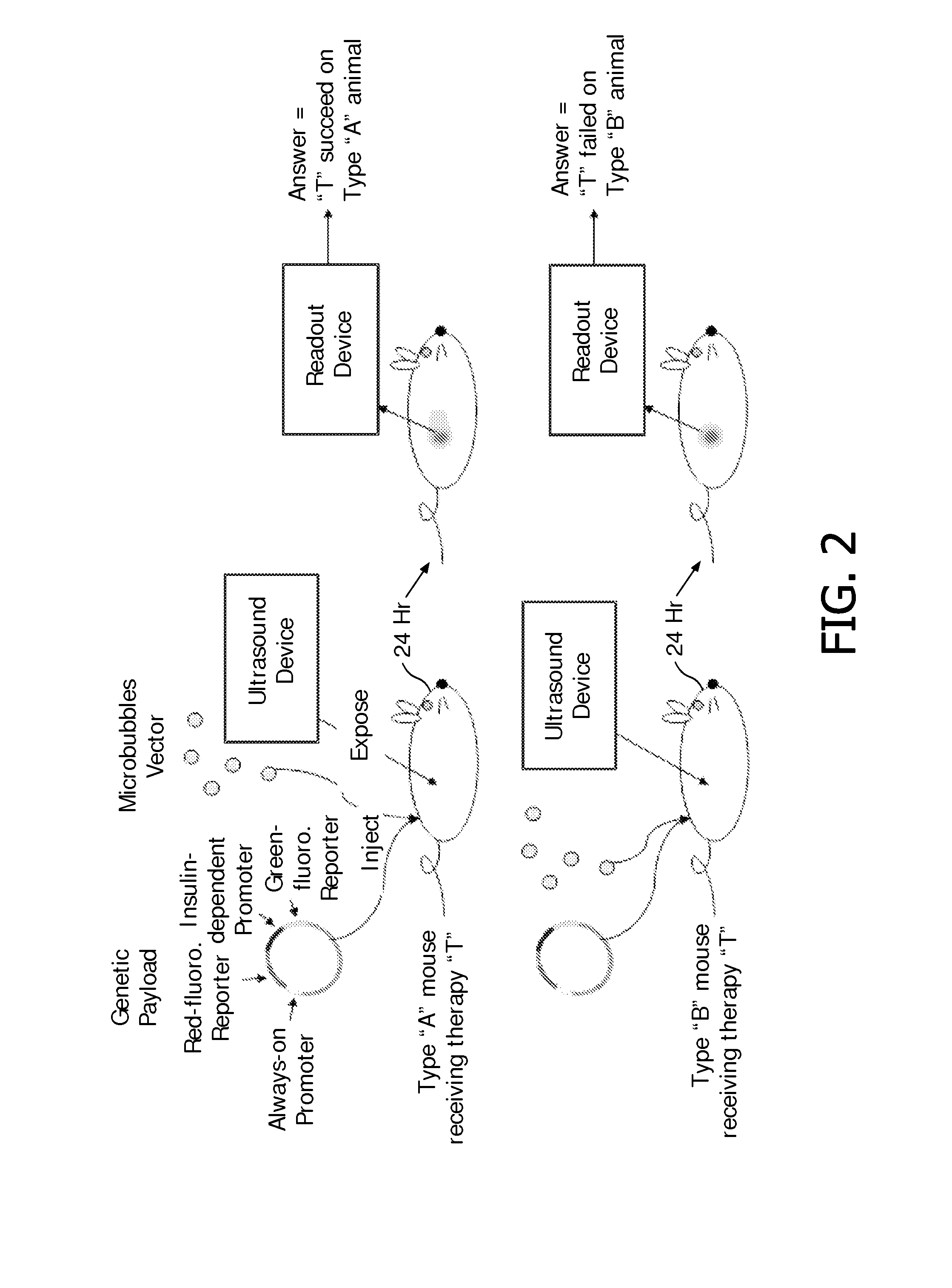
In vivo expression analysis using ultrasound-induced transfection of reporter constructs
InactiveUS20100239502A1Improve in vivo stabilityMinimizing systemic side-effectsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryLipid formationFatty acid
The invention features compositions and methods for in vivo expression analysis. The data presented herein demonstrates that ultrasound-enhanced delivery and / or expression of a composition for expression analysis comprising microbubbles vectors as well as a genetic payload, comprising a “always-on” promoter, a “reference” reporter gene, a “query” promoter and an “answer” reporter gene, enables in vivo analysis of gene expression both without requiring prior preparation (especially genetic modification) of the test subject (animal or patient) and without causing long term or systemic effects on the subject. Such an invention can be used, for example, to query the epigenotypic or phenotypic response of the individual subject to a foreign effector substance such as a pyrogen, pharmaceutical compound, pharmaceutical lead compound, an allergen, an autoimmunogene, a toxin, a polyclonal antibody, a monoclonal antibody, an antigen, a lipid, a carbohydrate, a peptide, a protein, a protein-complex, an amino acid, a fatty acid, a nucleotide, DNA, RNA, PNA, siRNA and micro RNA.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com