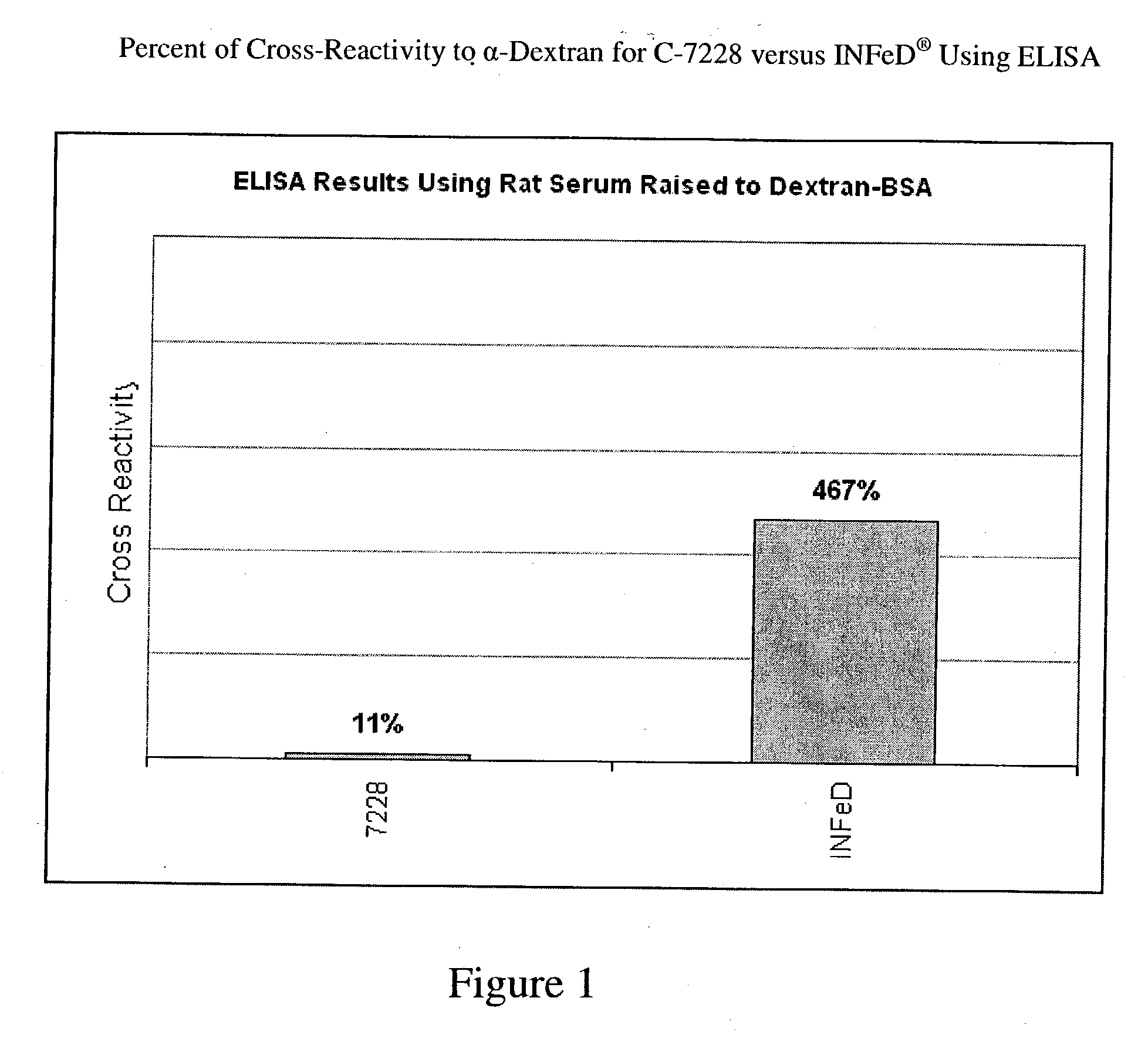
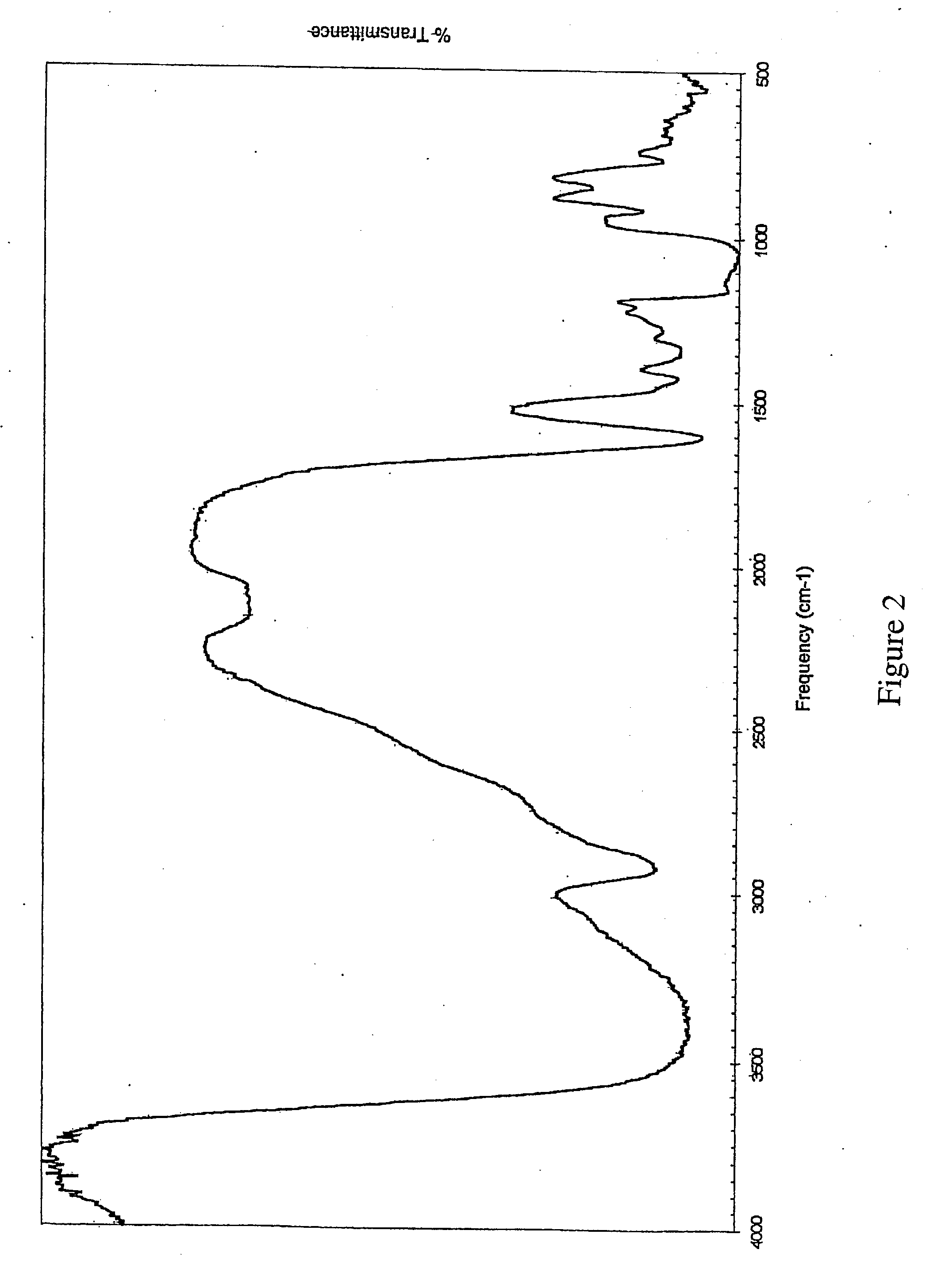
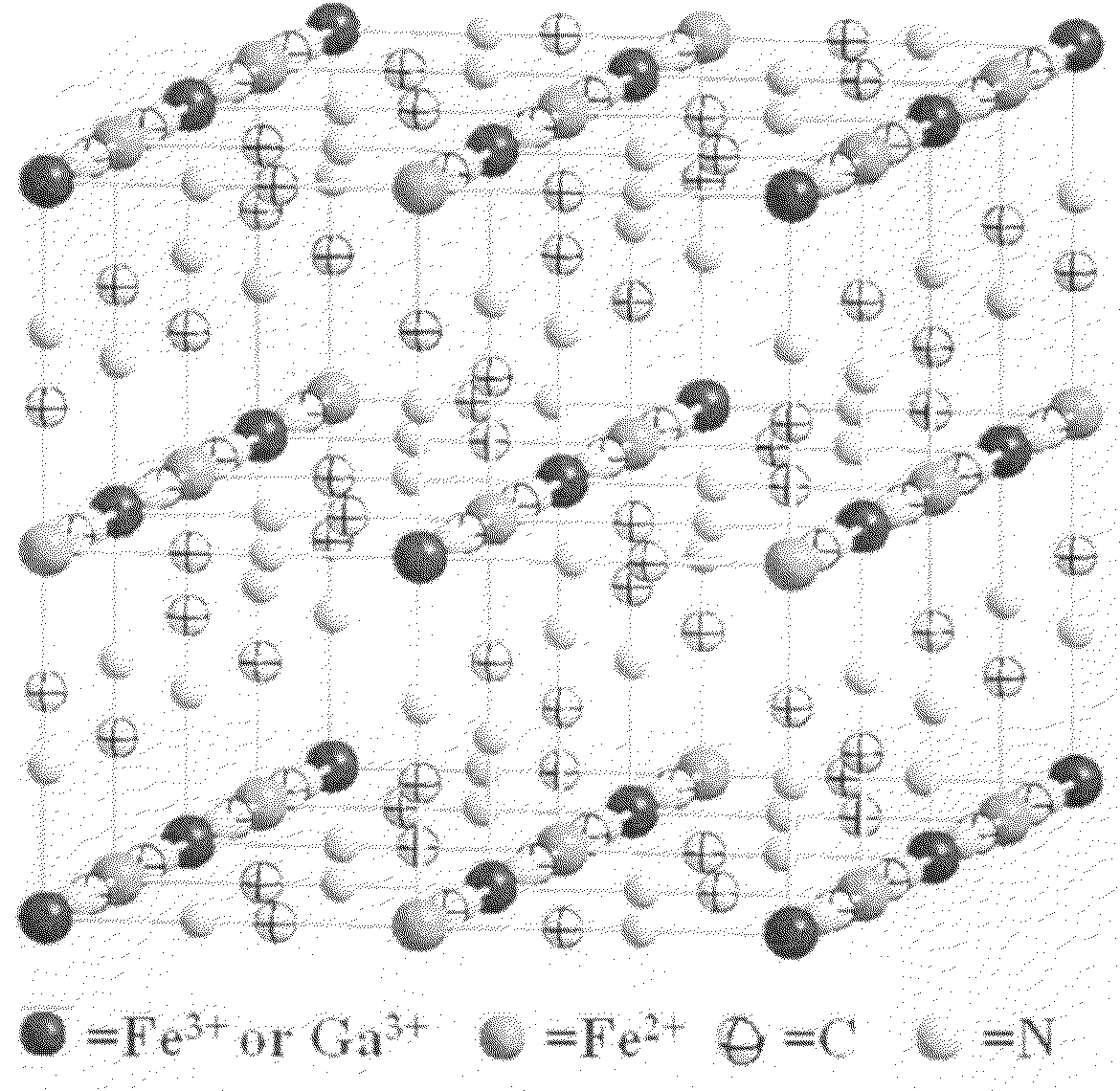
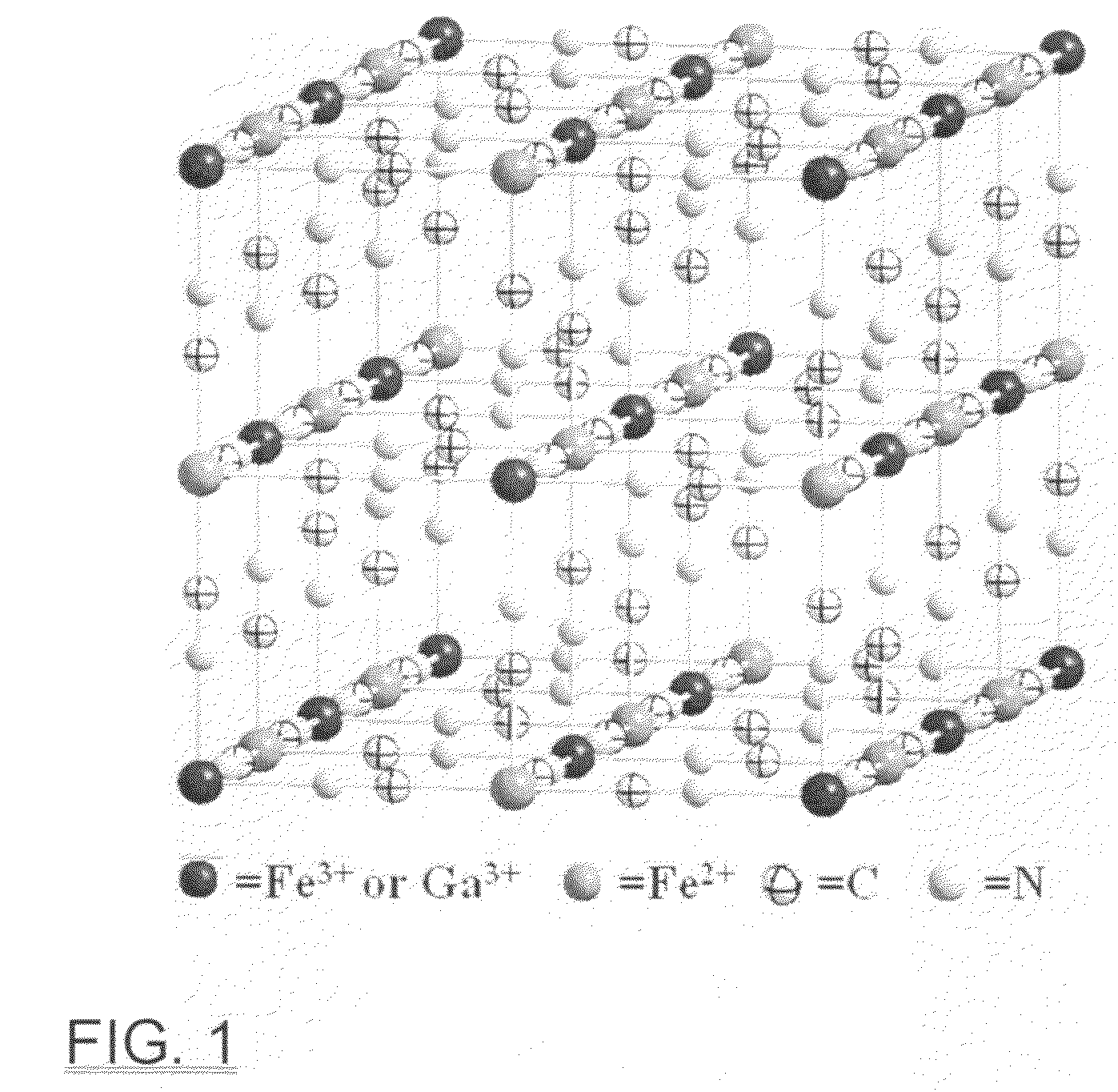
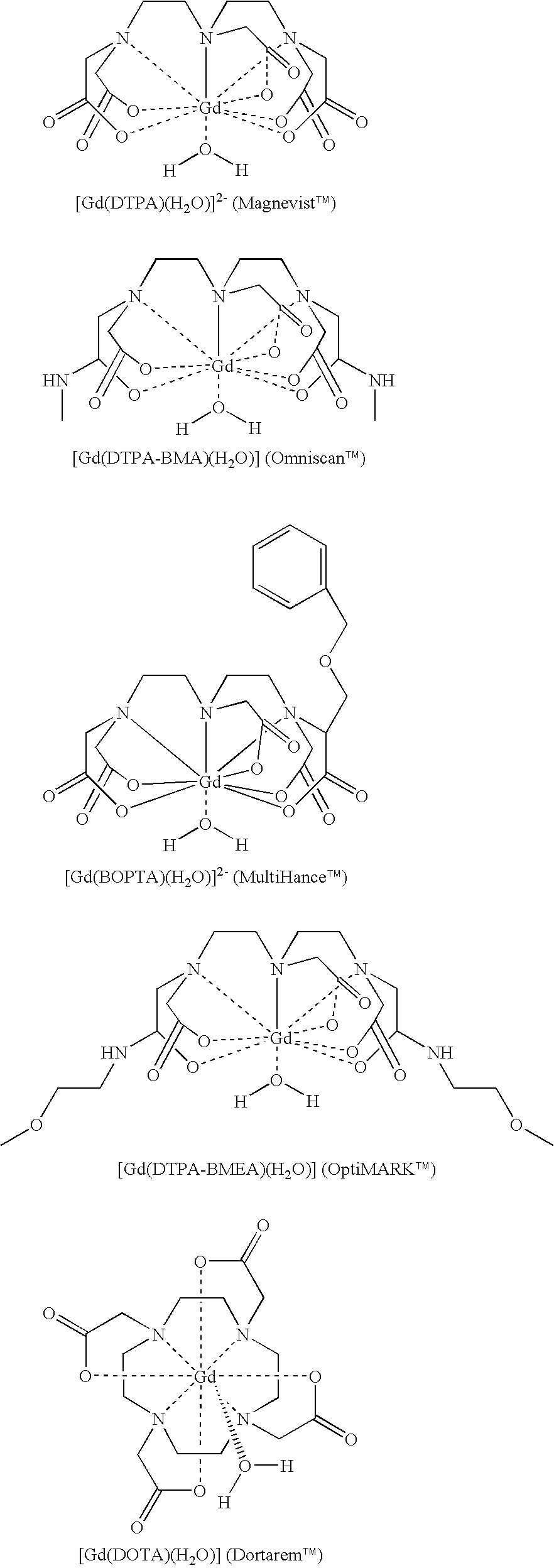
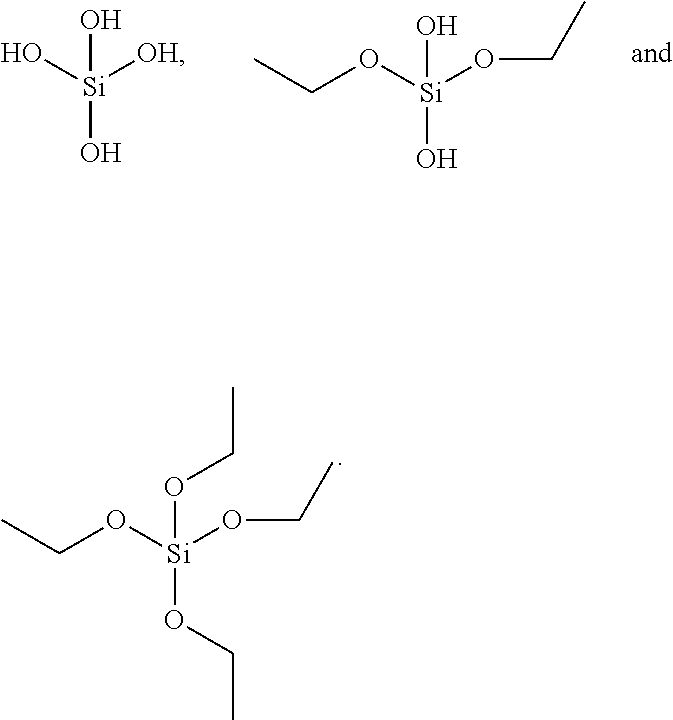
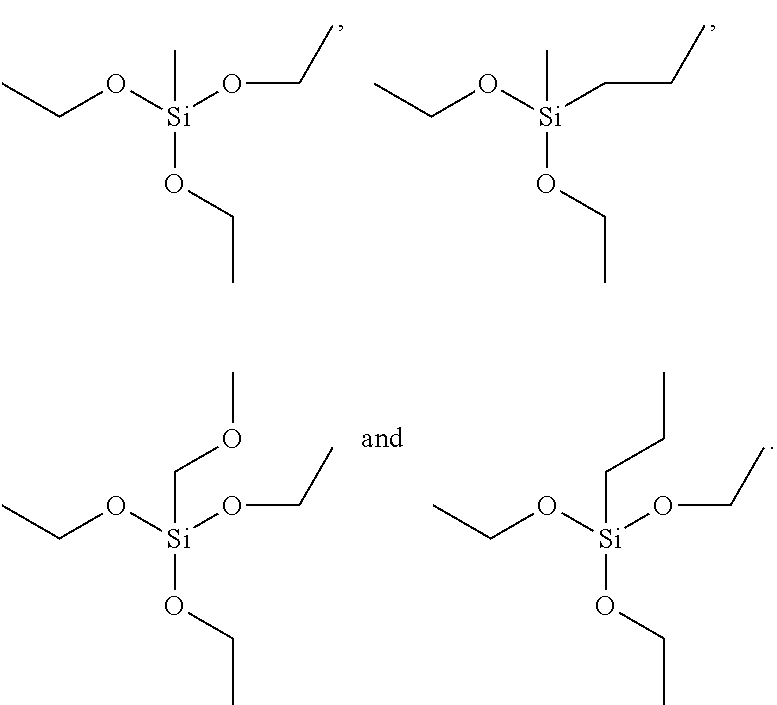
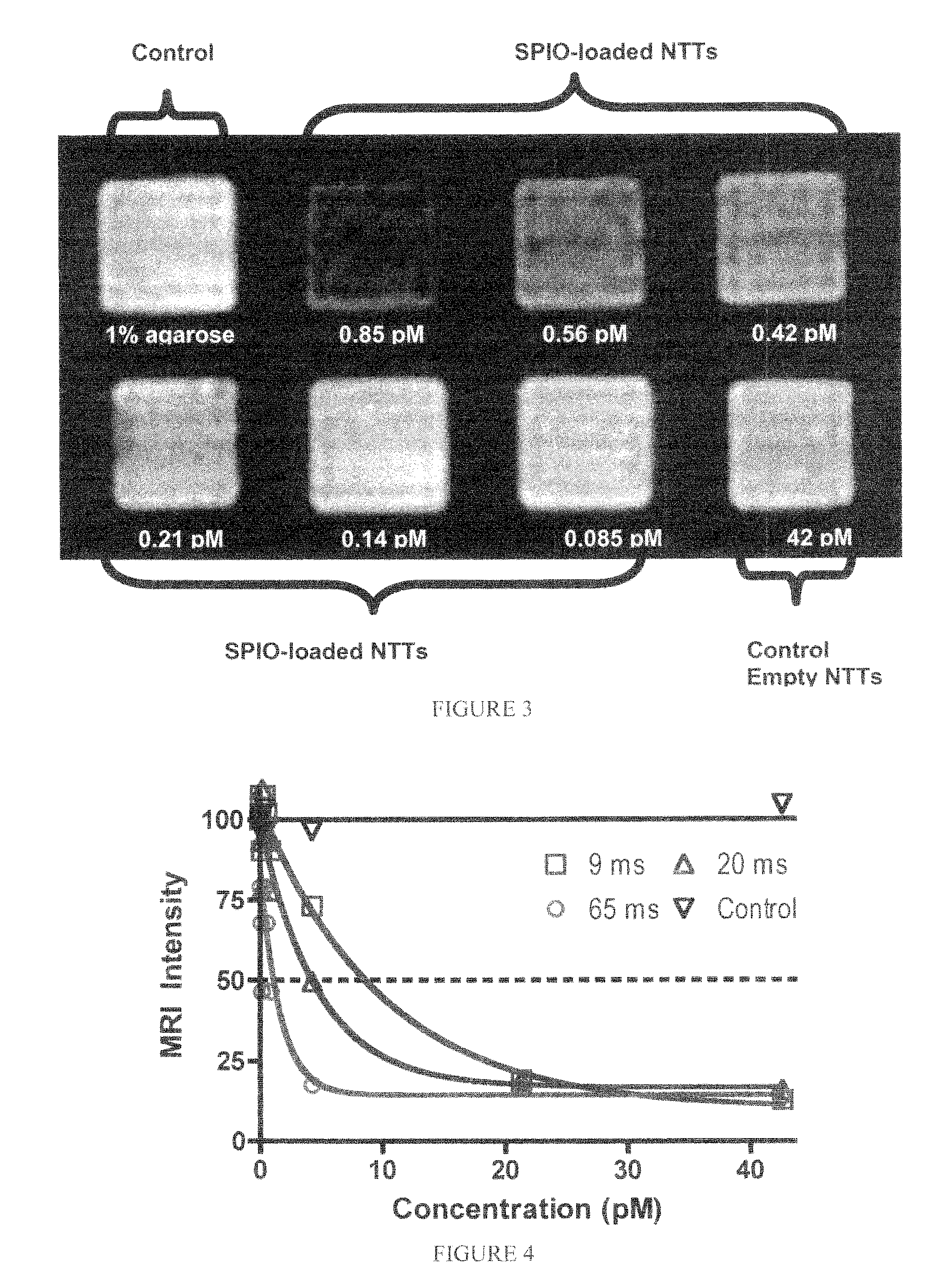
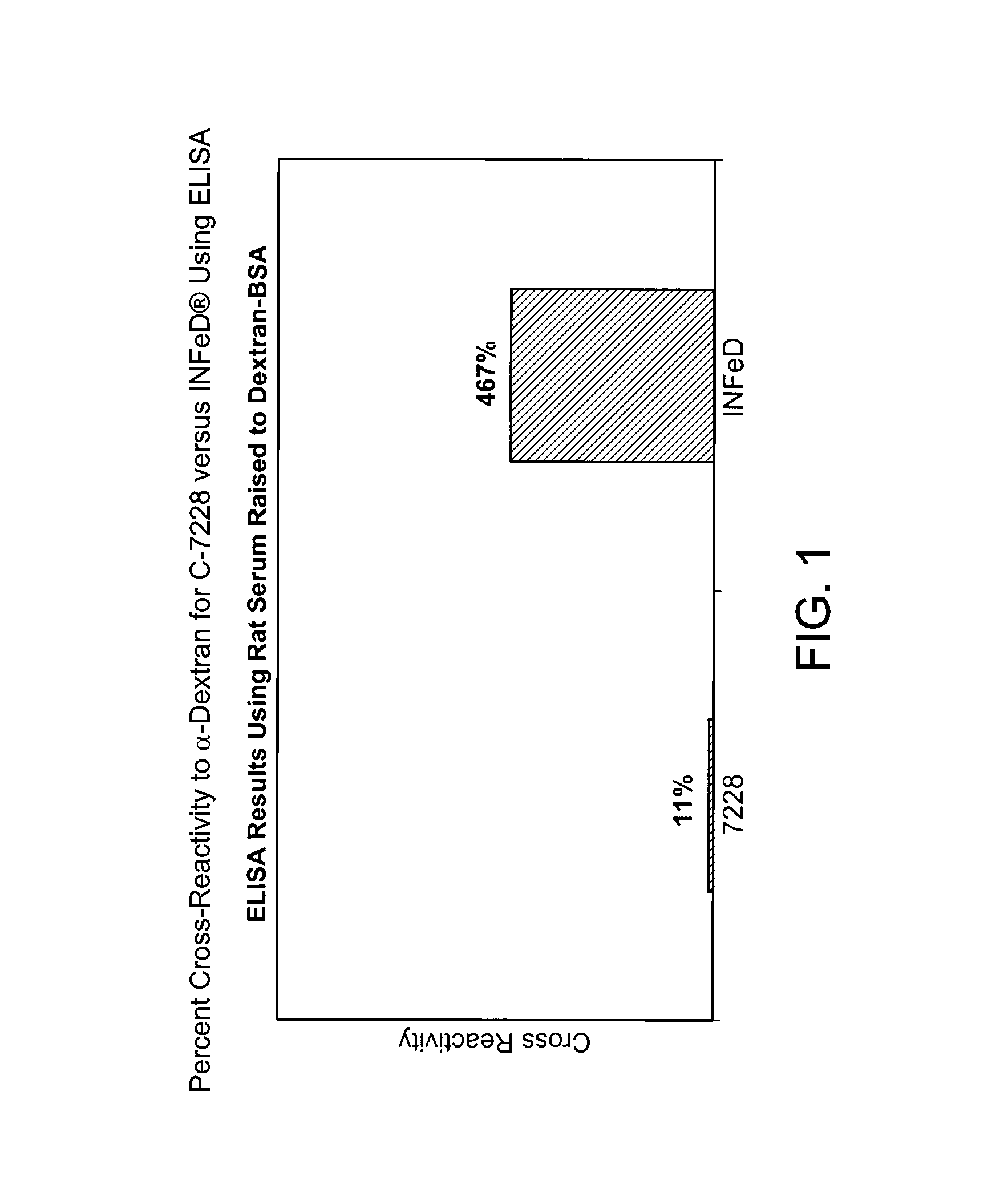
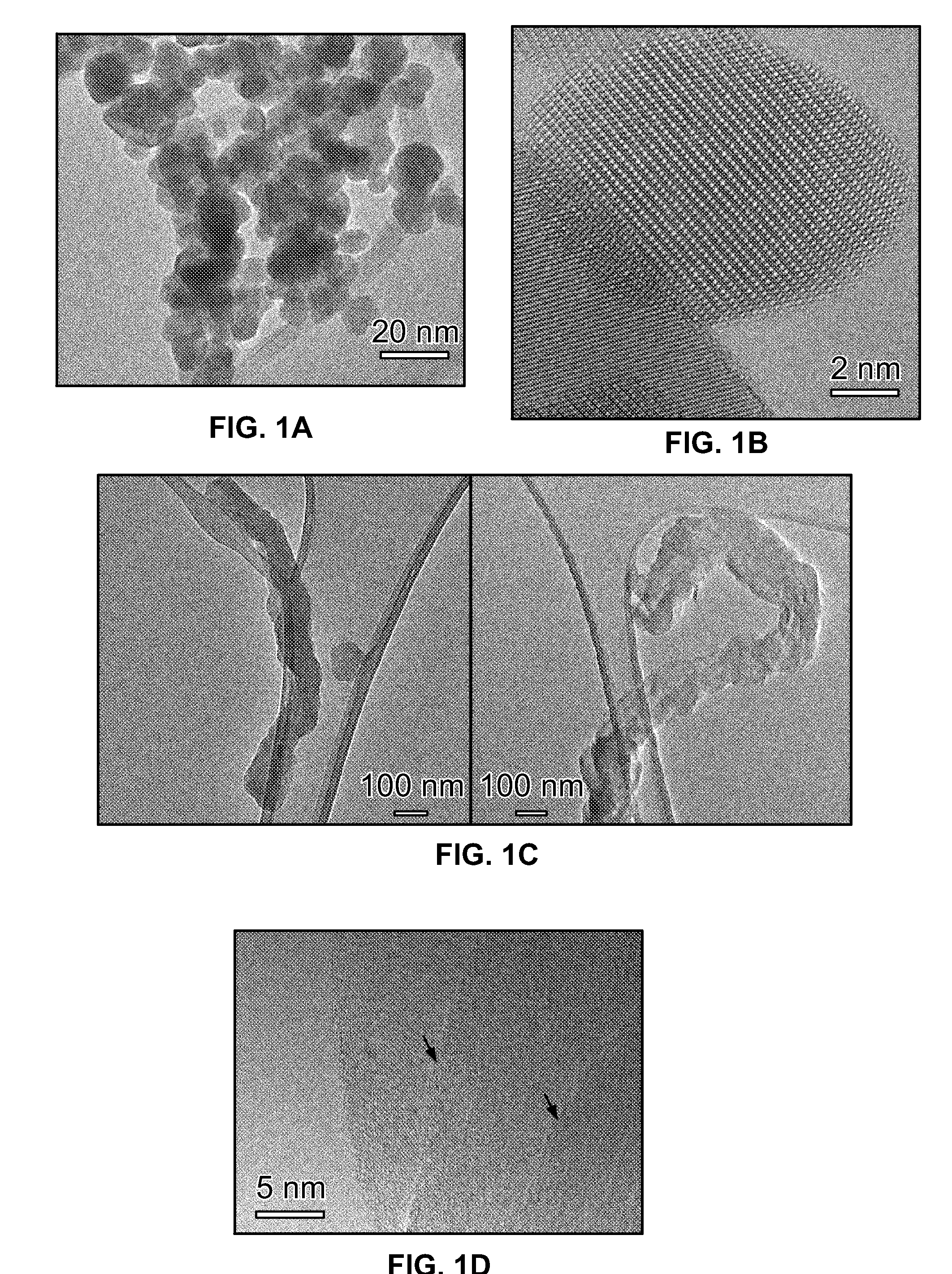
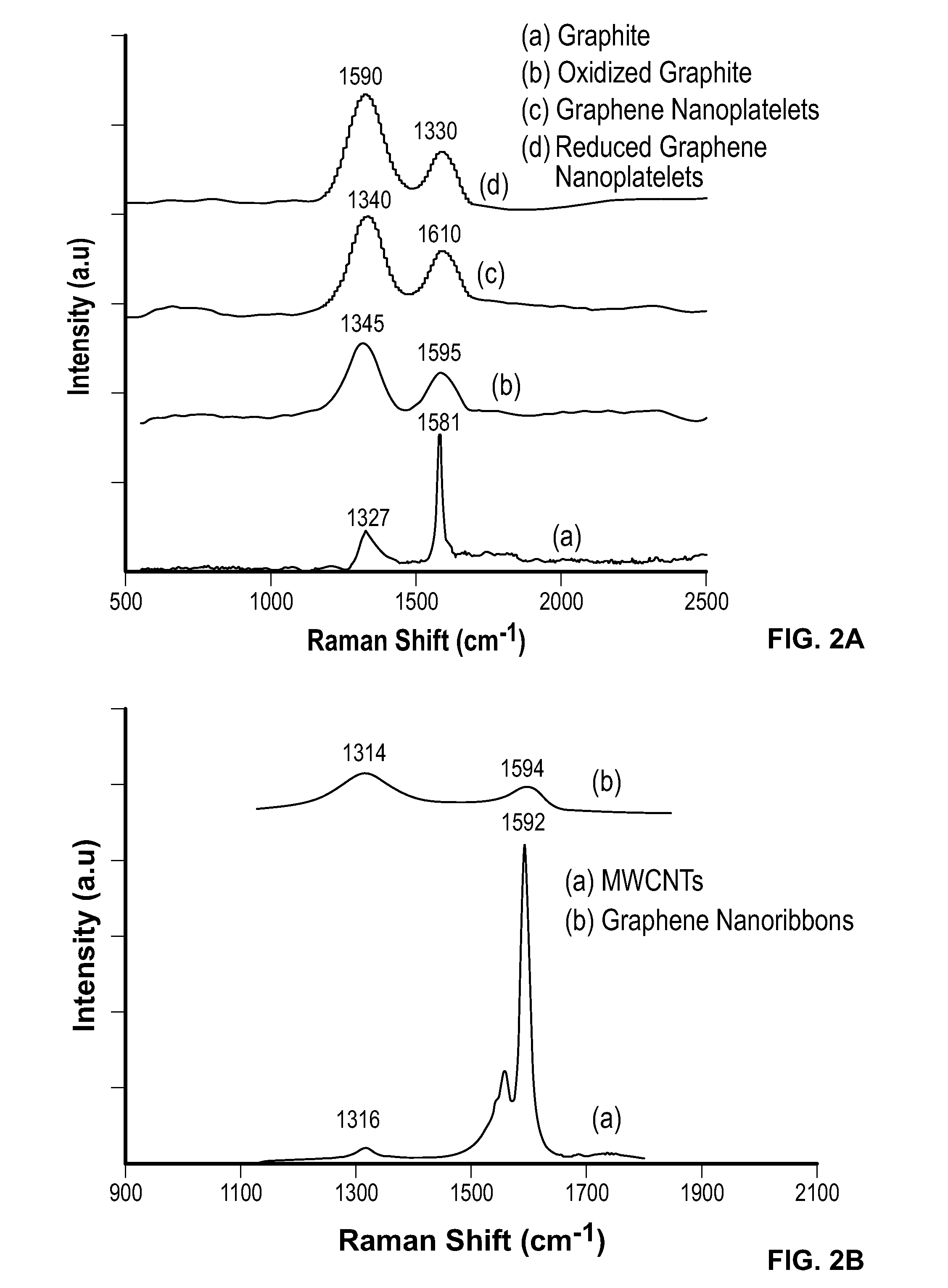
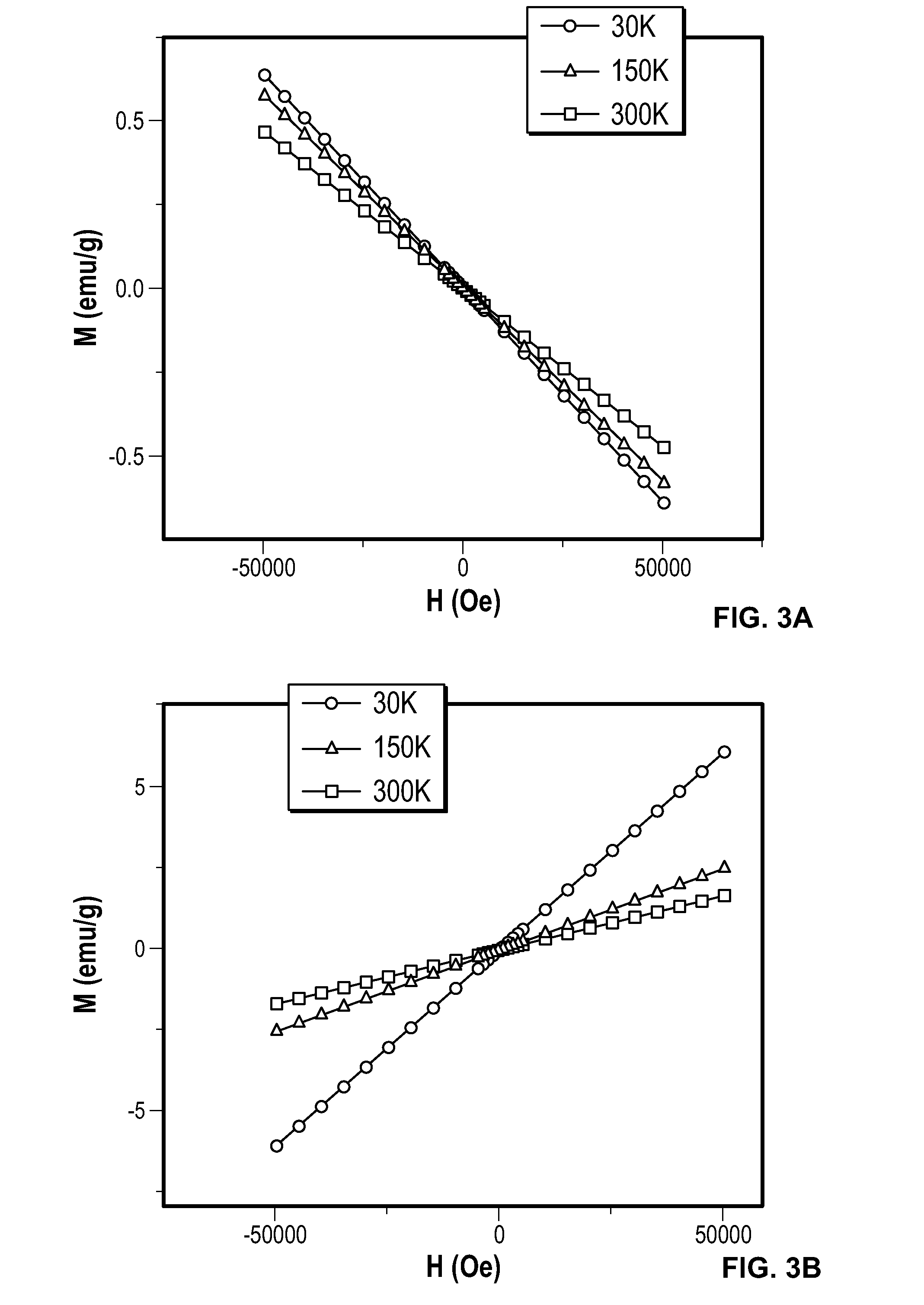
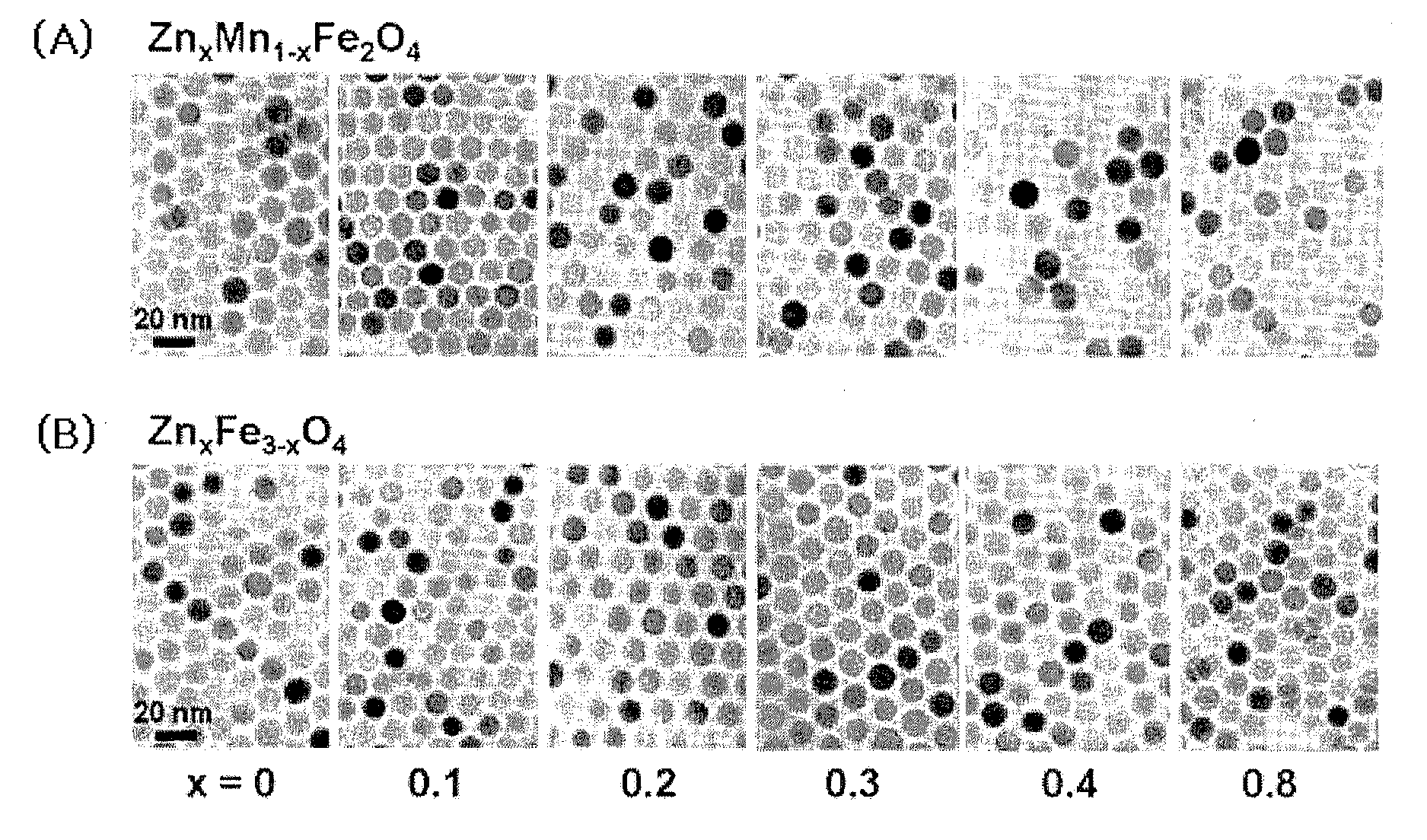
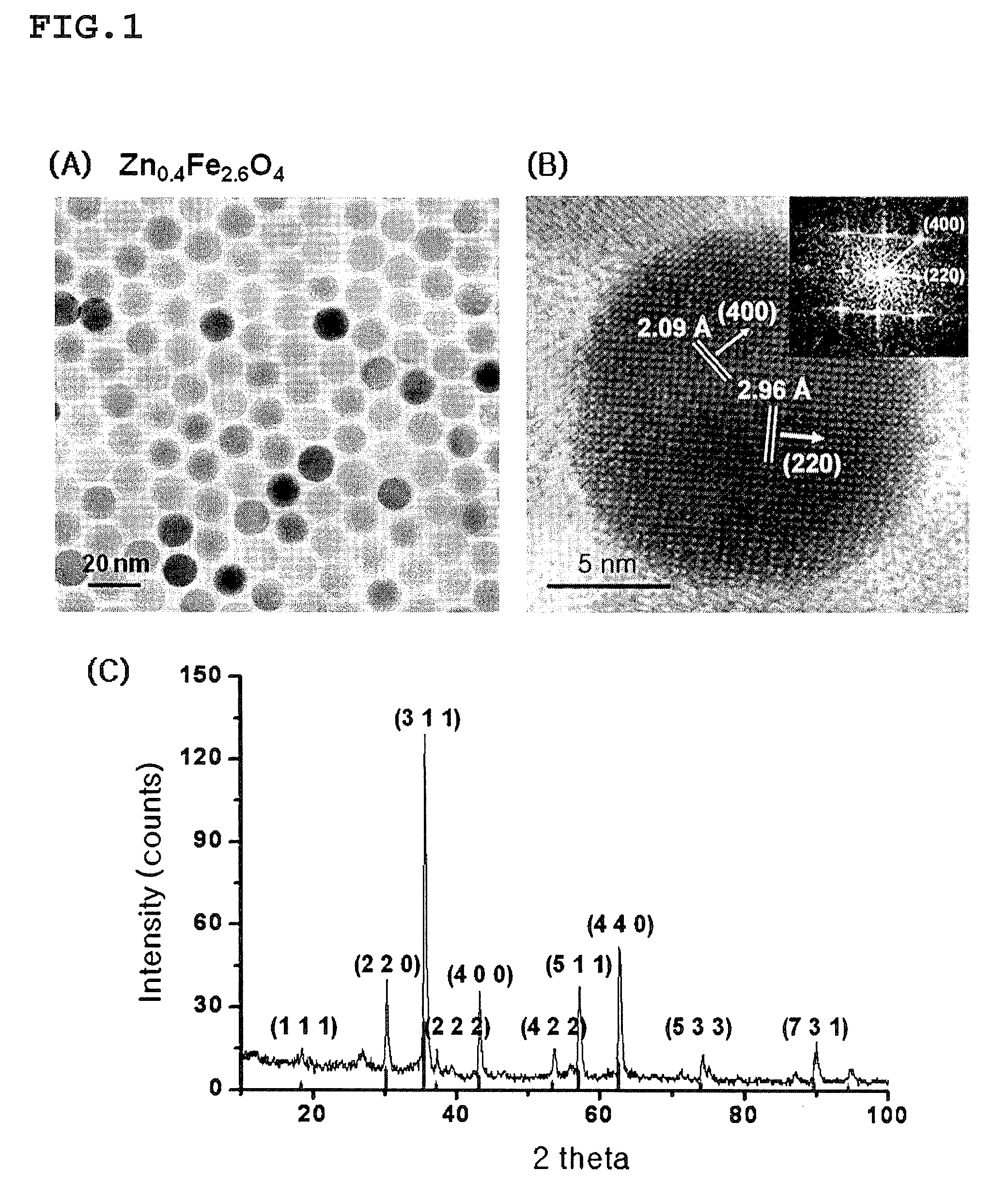
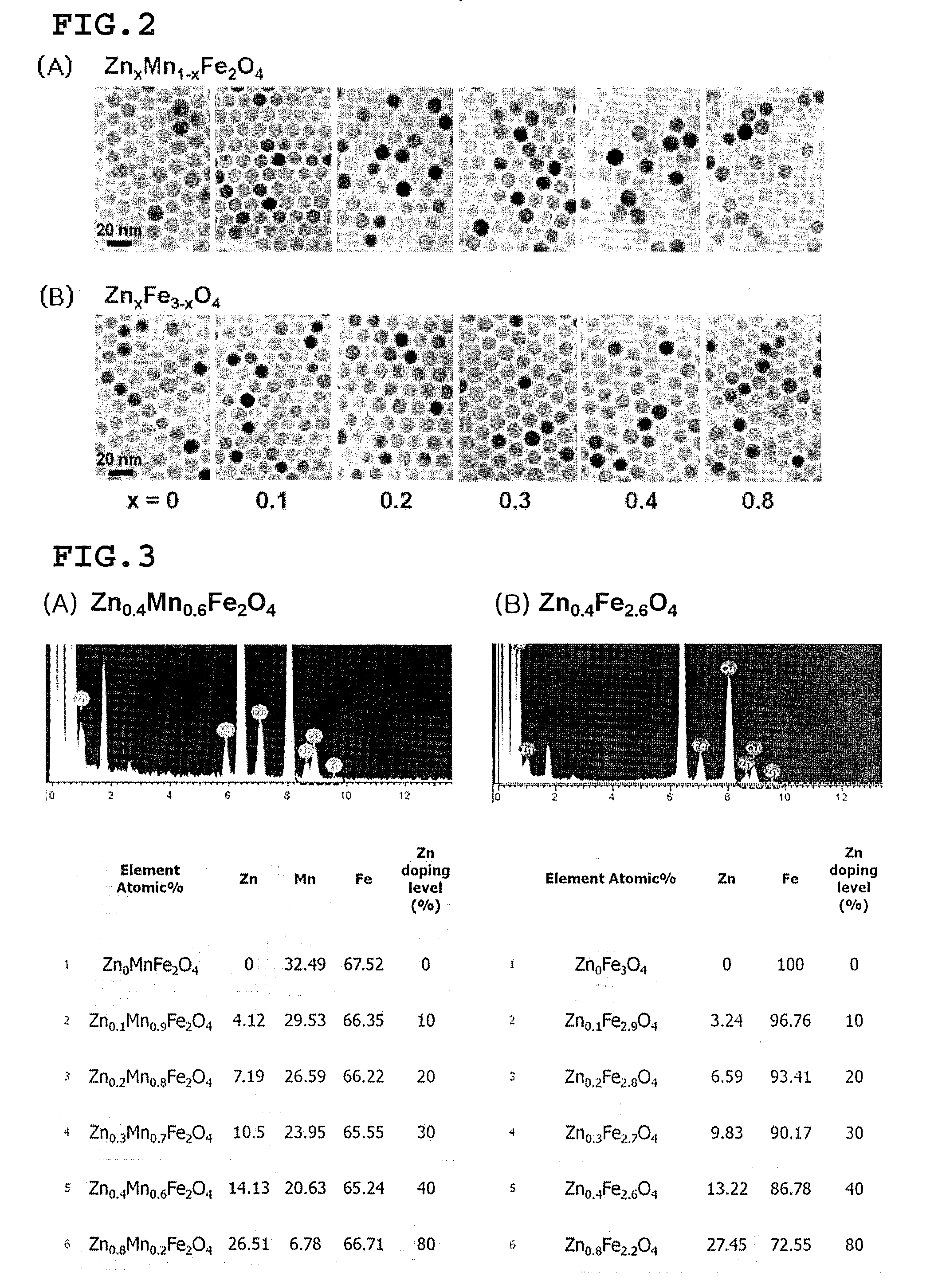
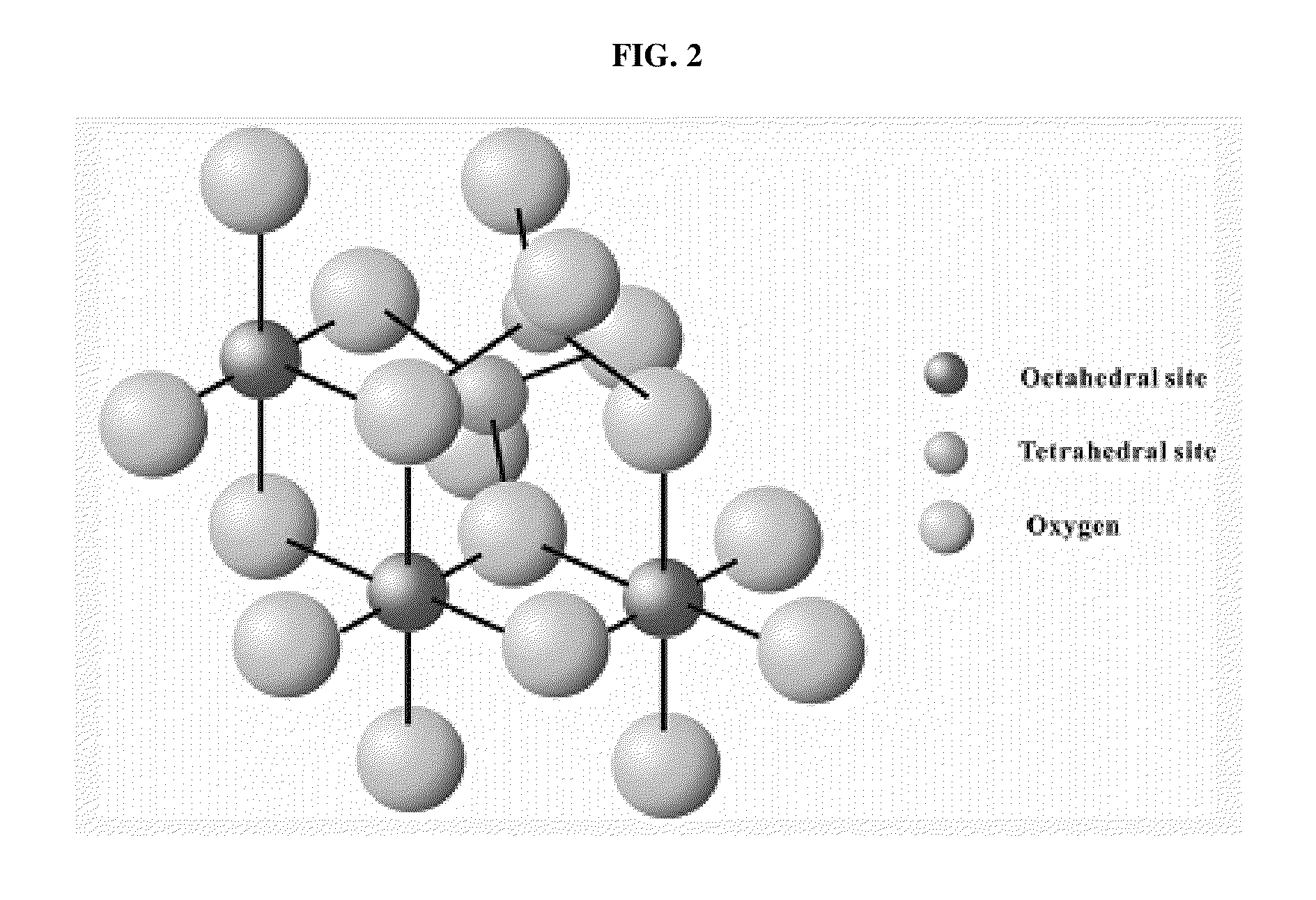
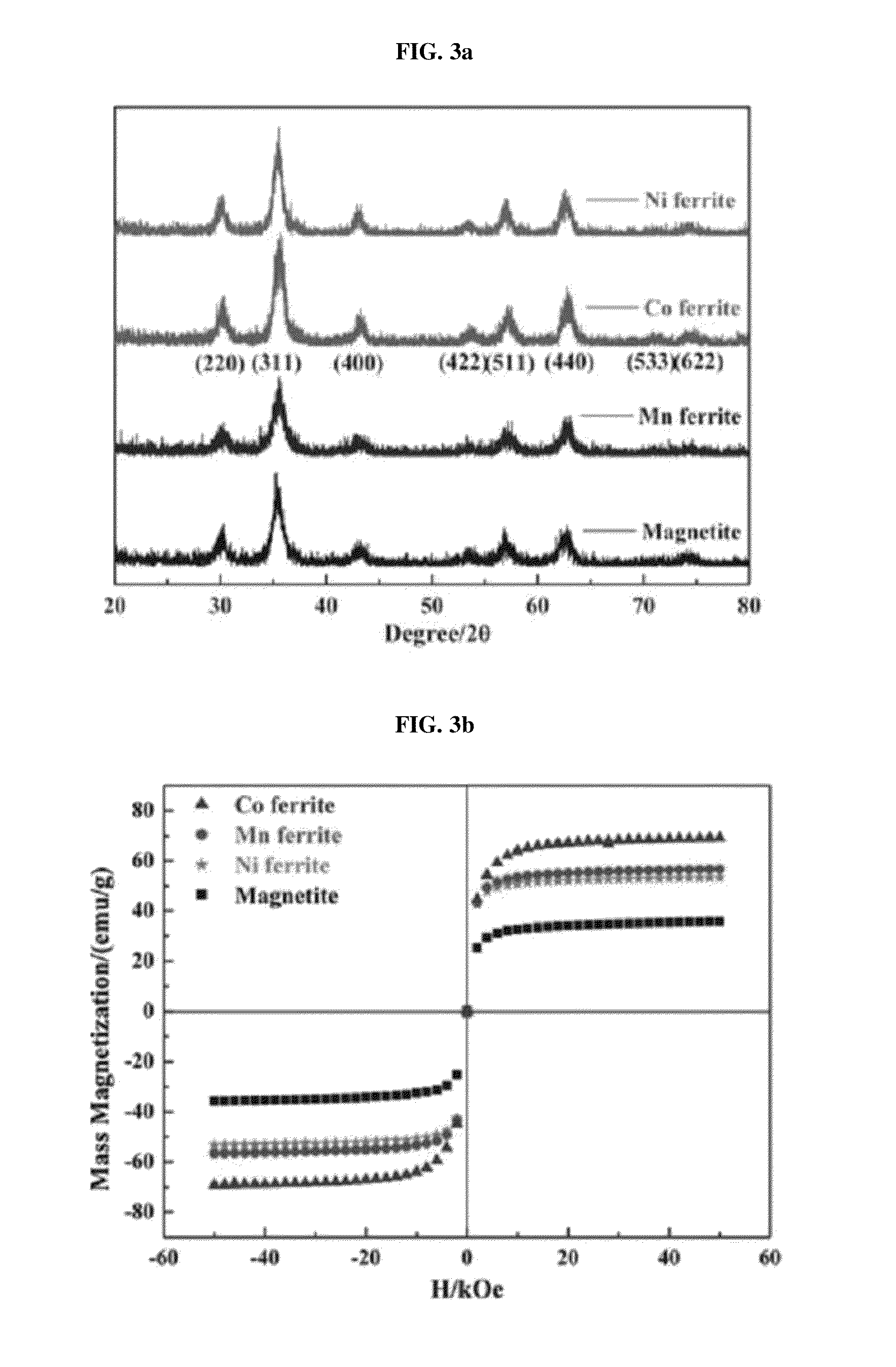
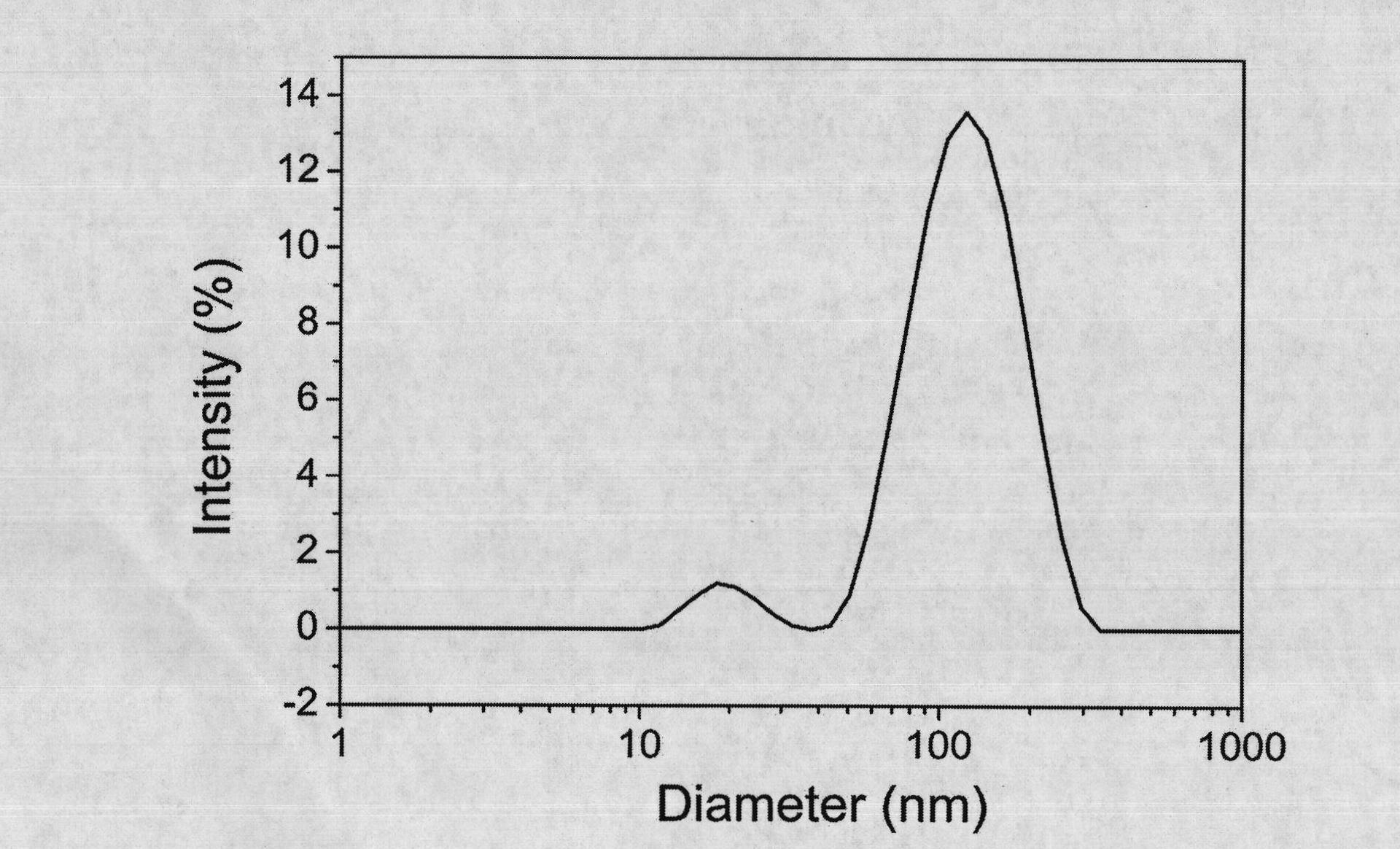
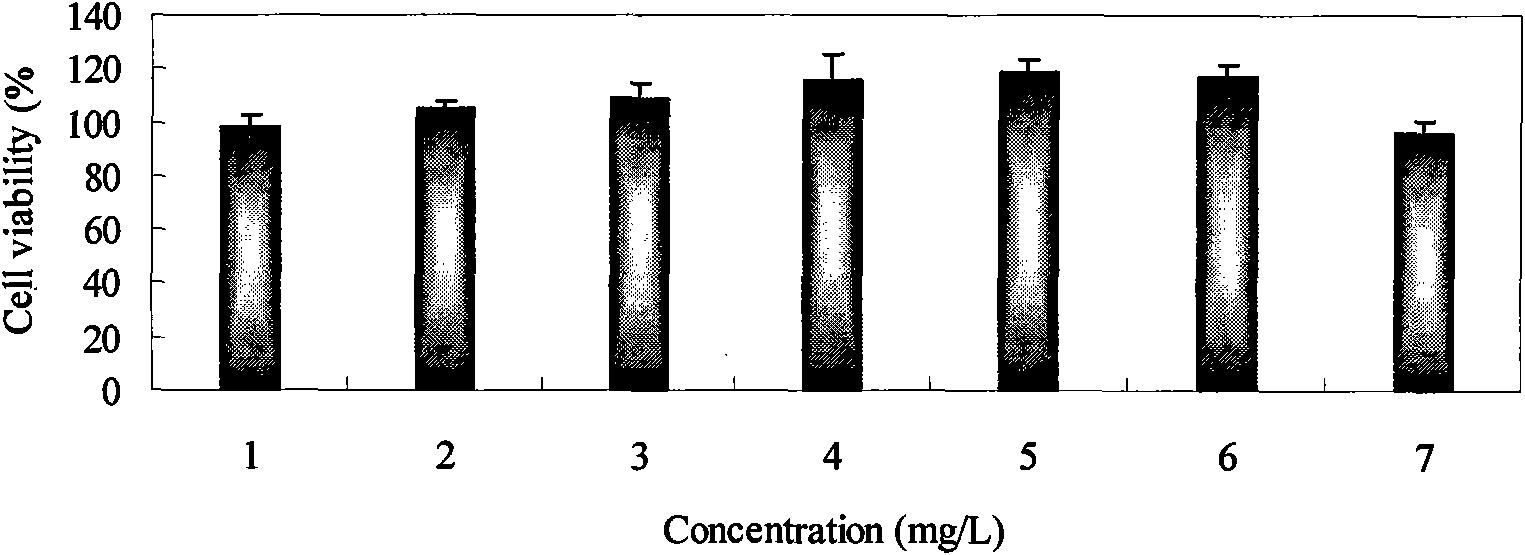
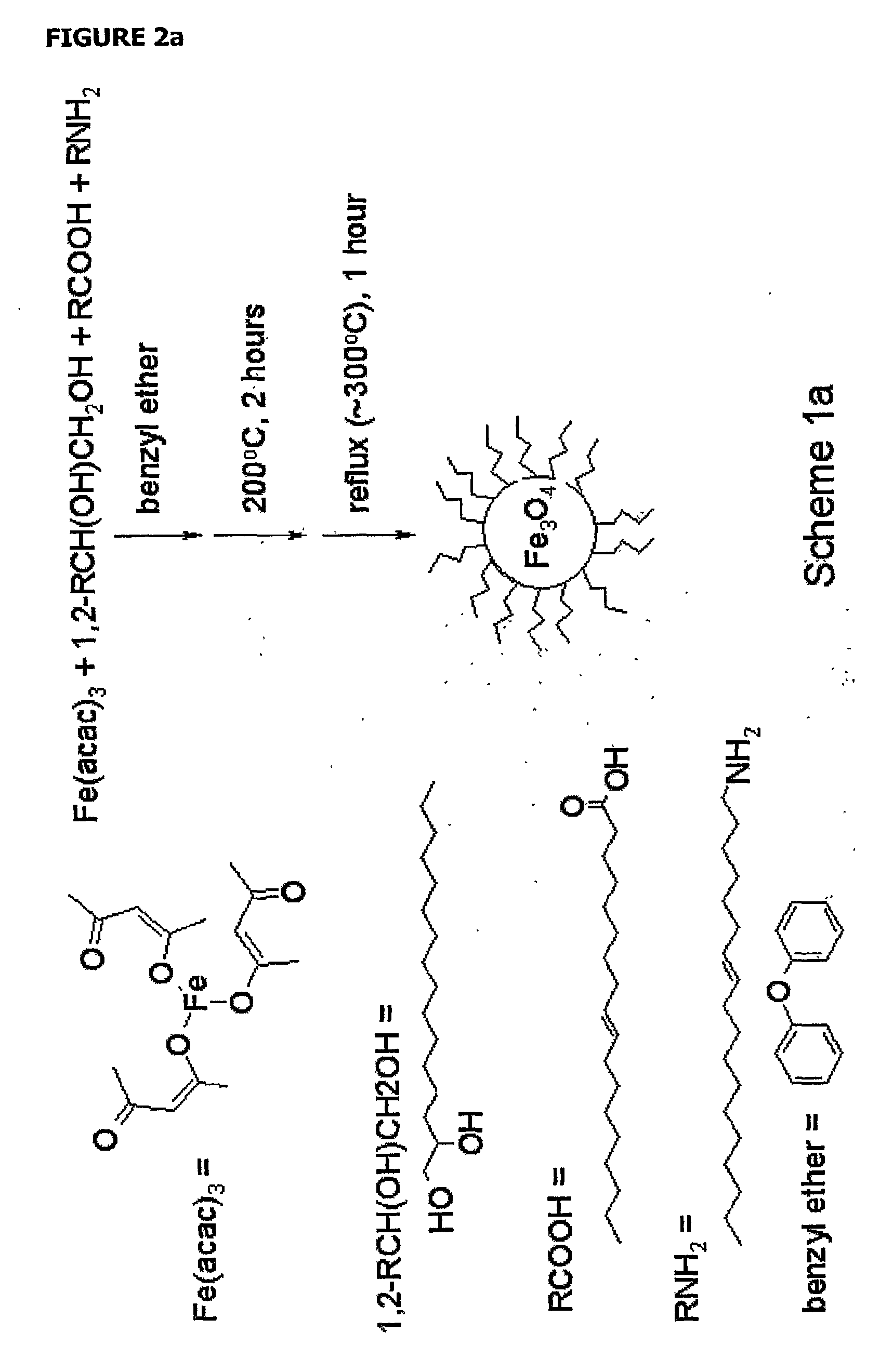
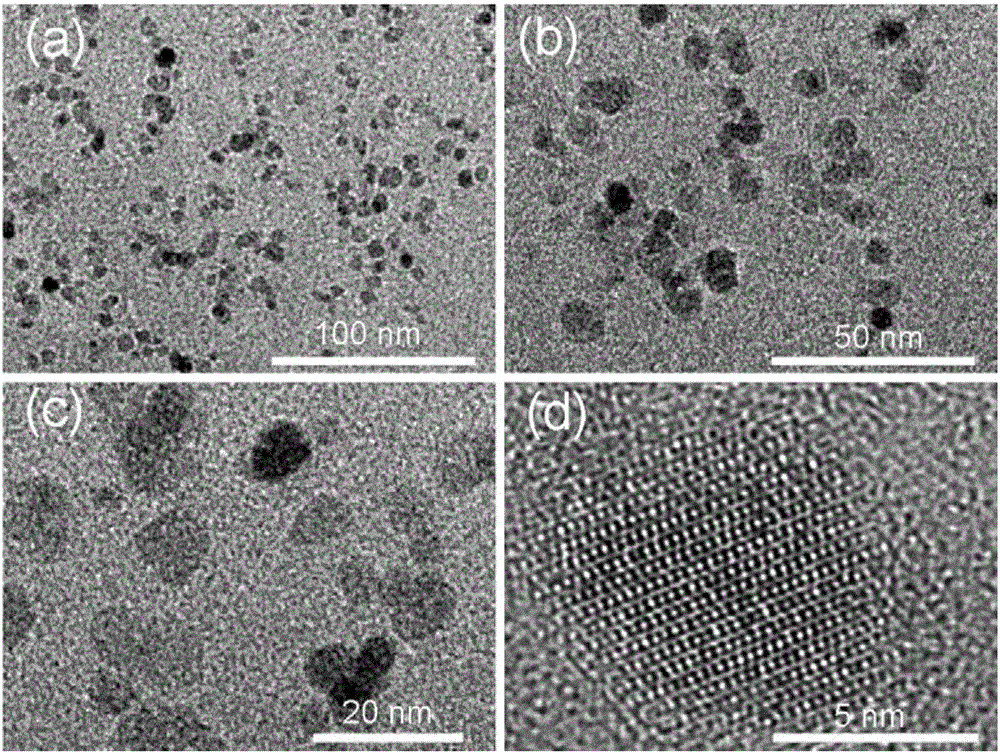
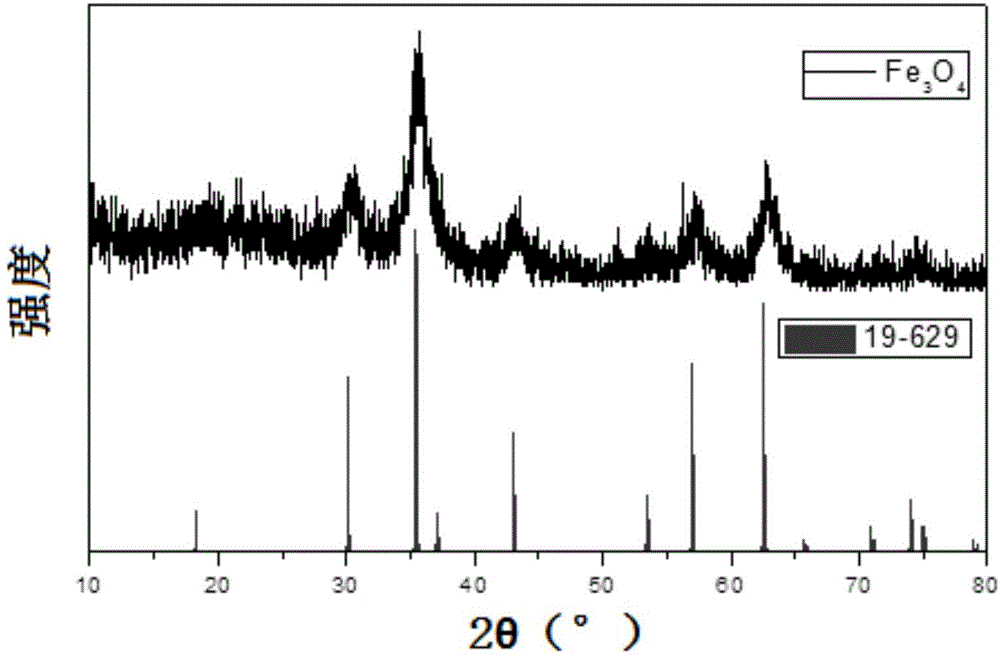
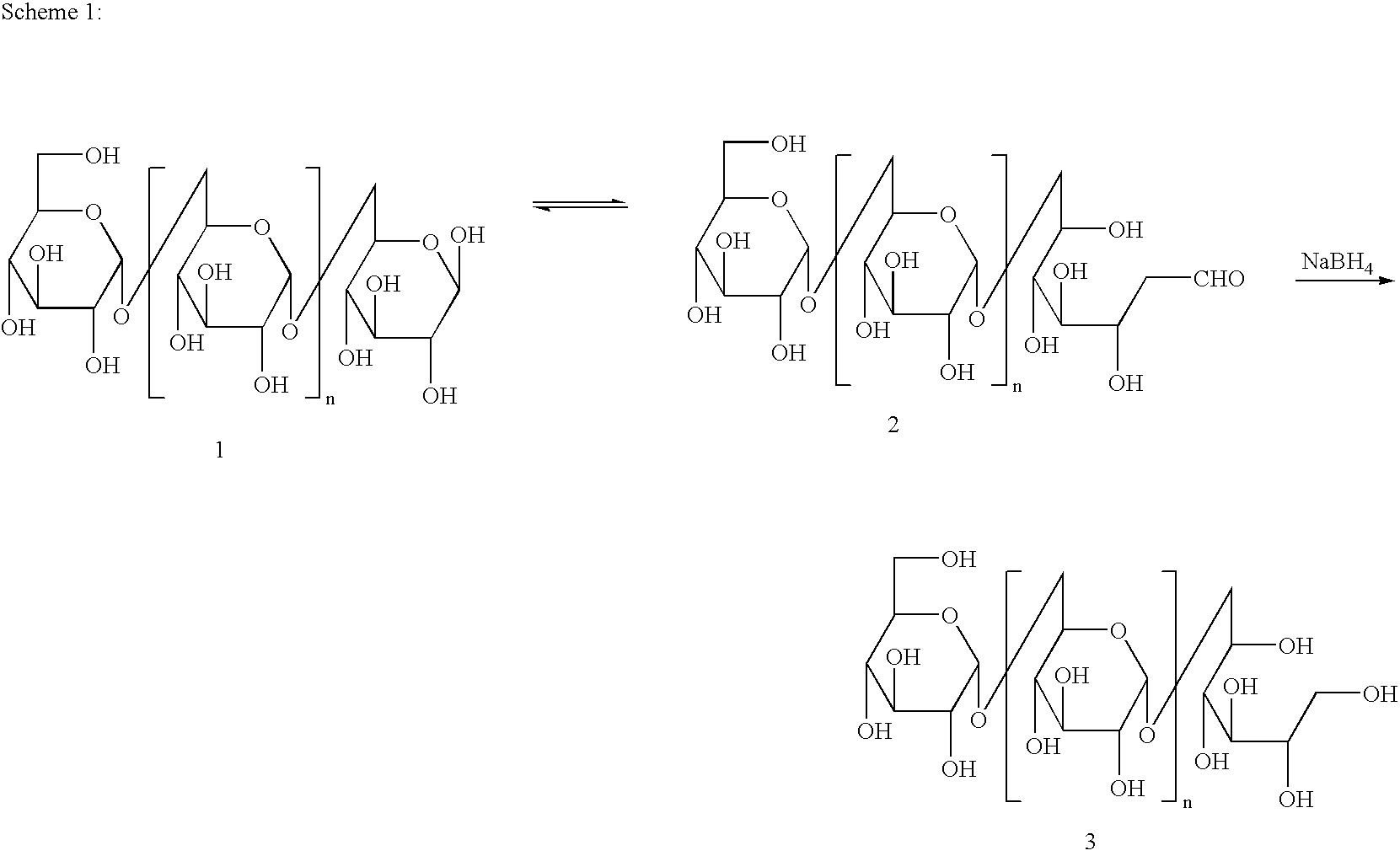Patents
Literature
309 results about "MRI contrast agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
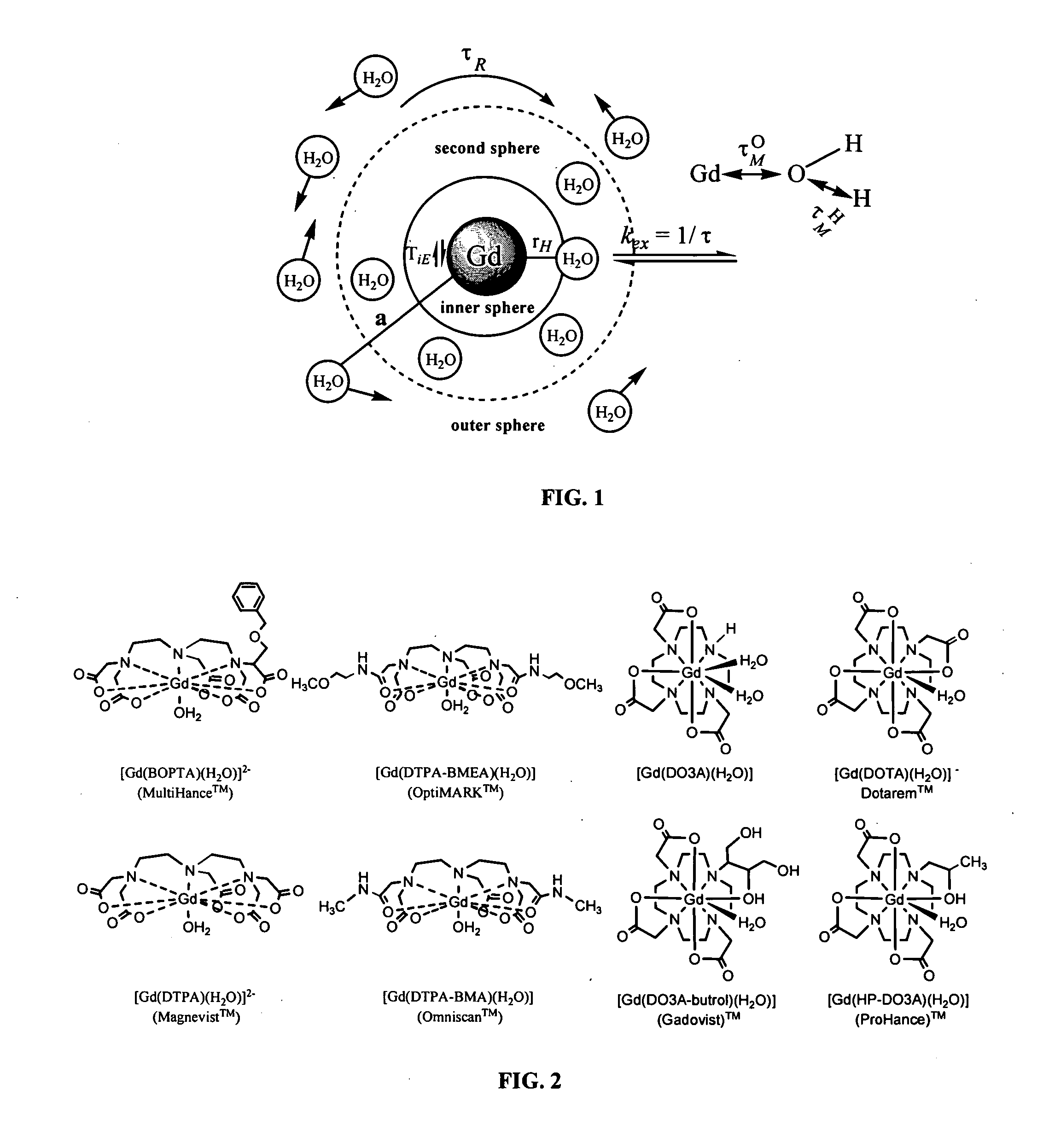
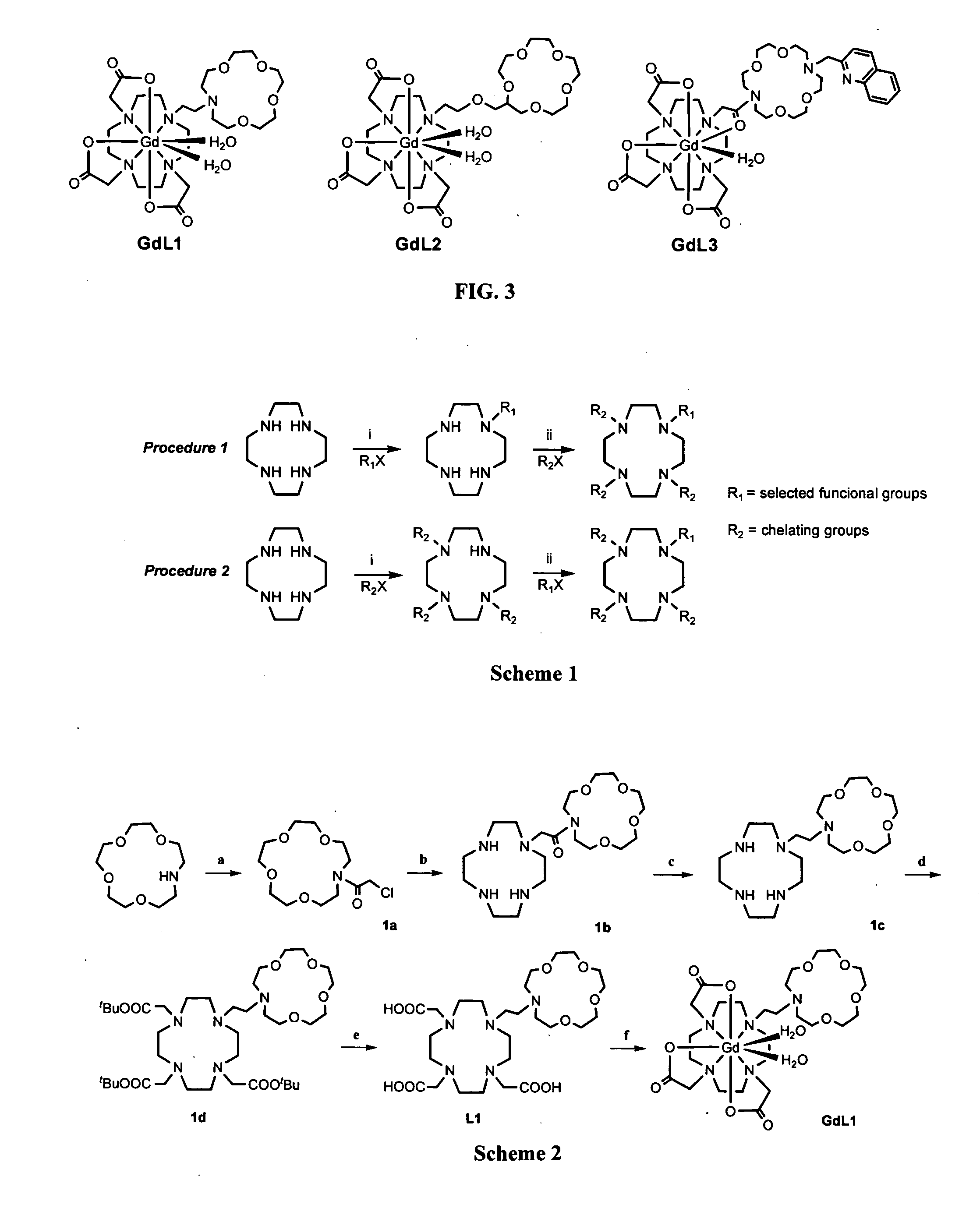
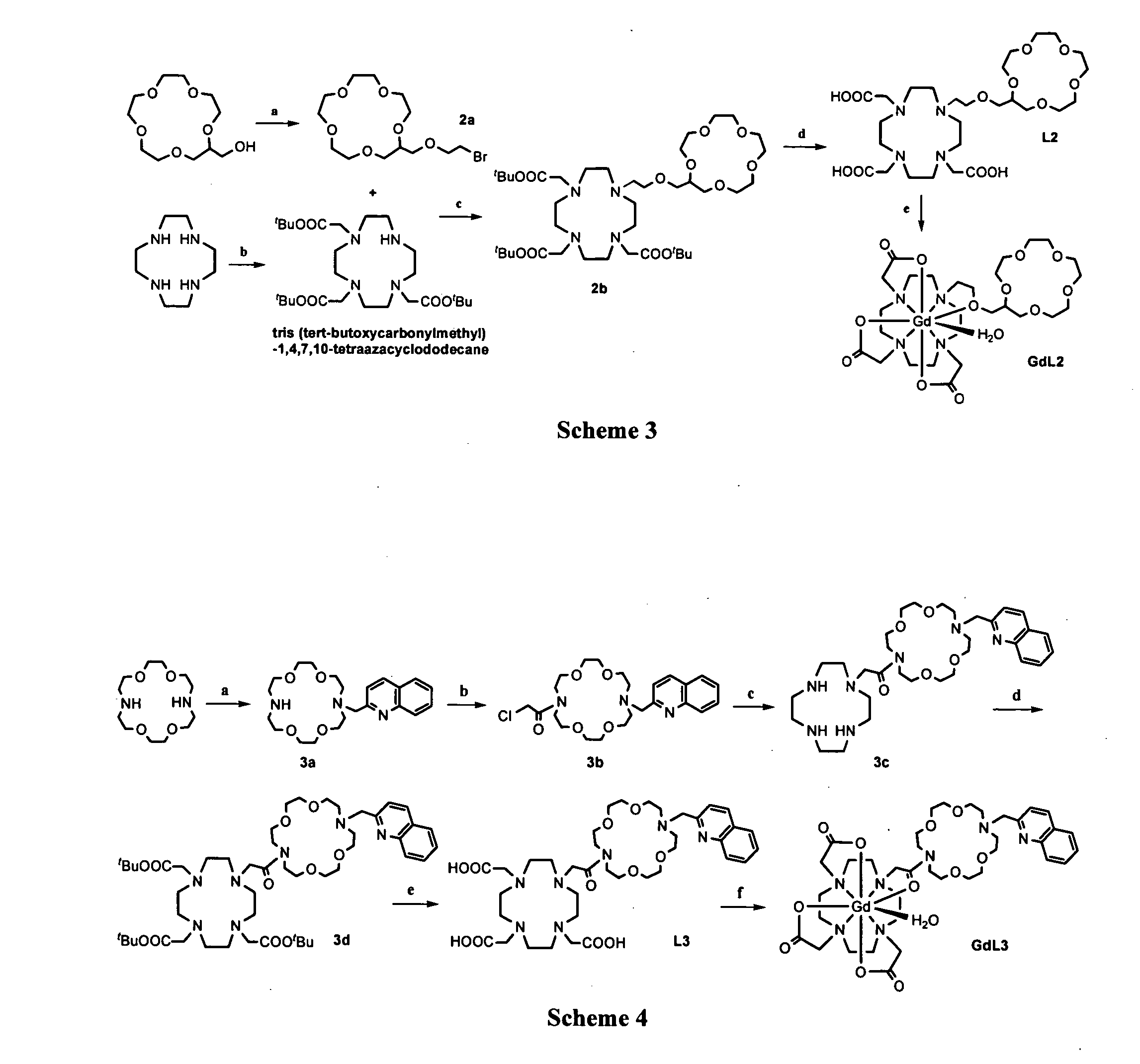
MRI contrast agents are contrast agents used to improve the visibility of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The most commonly used compounds for contrast enhancement are gadolinium-based. Such MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues following oral or intravenous administration.
Multifunctional metal-graphite nanocrystals
InactiveUS20080213189A1High resolutionShrink tumorPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsMRI contrast agentPolyethylene glycol
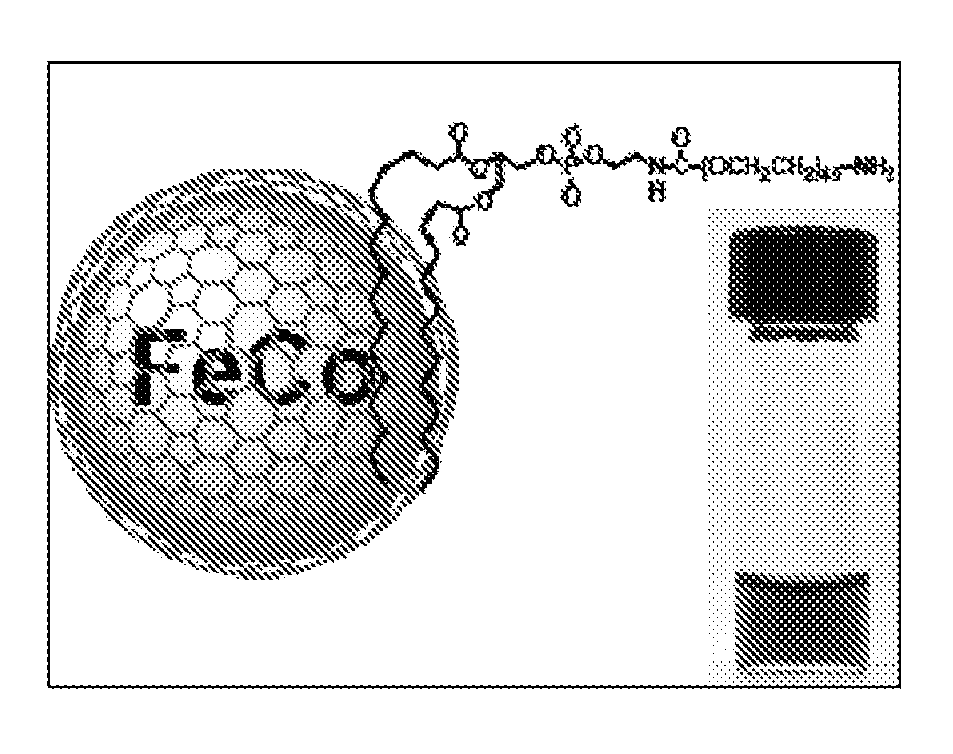
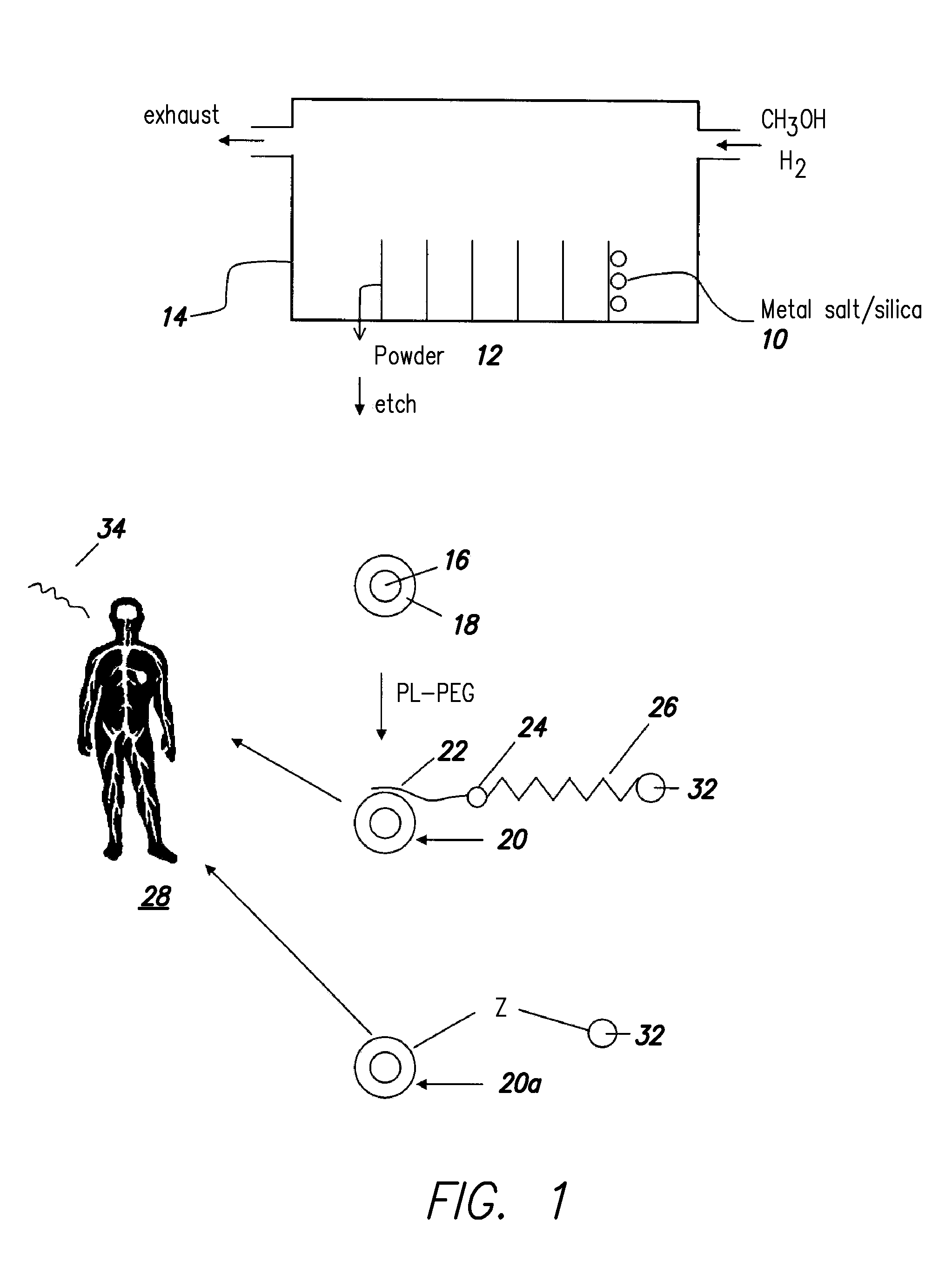
Disclosed are nanocrystals comprising metals and metal alloys, which are formed by a process that results in a layer of graphite in direct contact with the metallic core. The nanocrystals may be used in vivo as MRI contrast agents, X-ray contrast agents, near IR (NIR) heating agents, drug delivery, protein separation, catalysis etc. The nanocrystals may be further functionalized with a hydrophilic coating, e.g., phospholipid-polyethylene glycol, which improves in vivo stability. The process comprises chemical vapor deposition of metals adsorbed onto silica as a fine powder, in conjunction with a carbon containing gas, which coats the metal particles. The silica is then etched away. Preferred metals include iron, gold, cobalt, platinum, ruthenium and mixtures thereof, e.g., FeCo and AuFe. The process permits control of the alloy compositions, size, and other characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
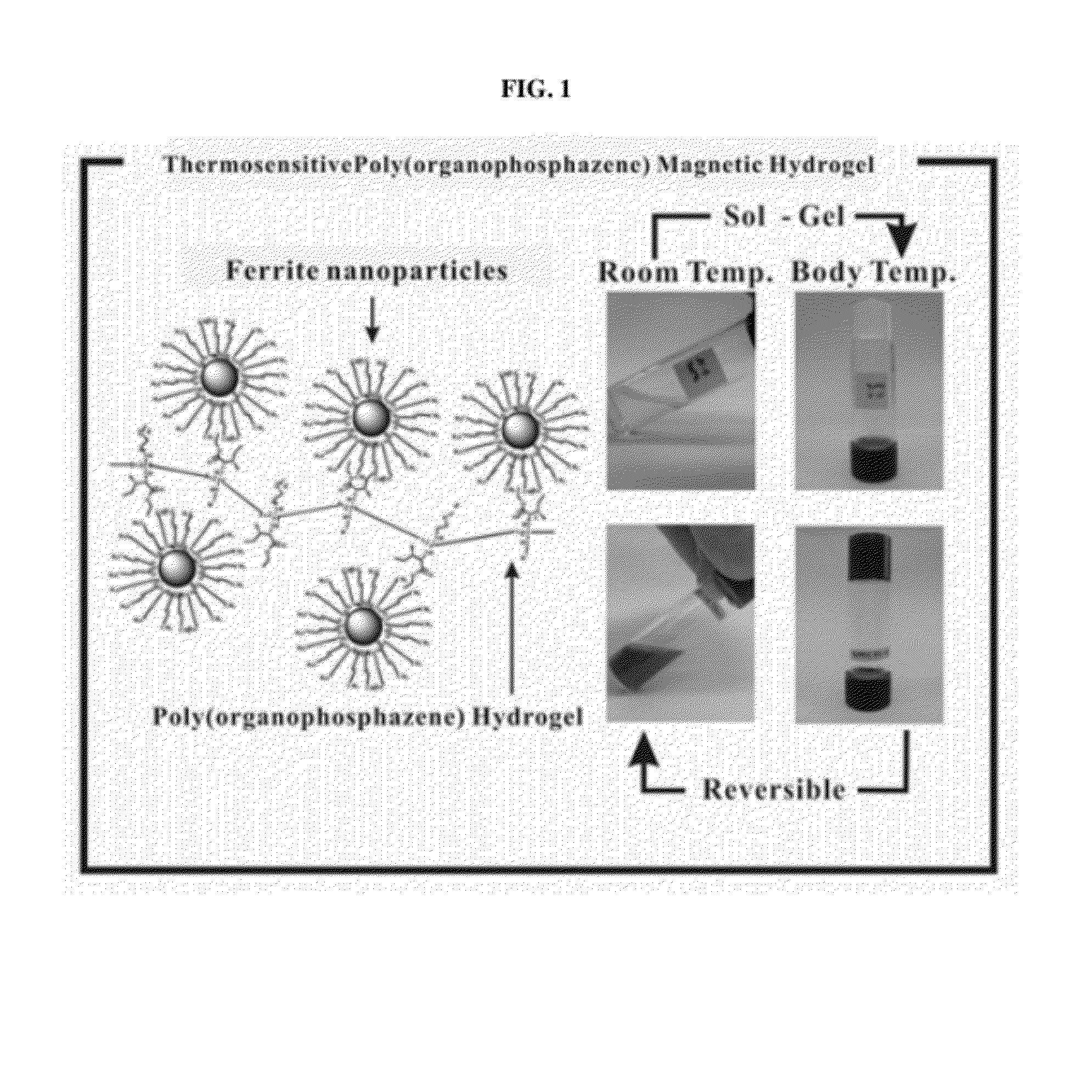
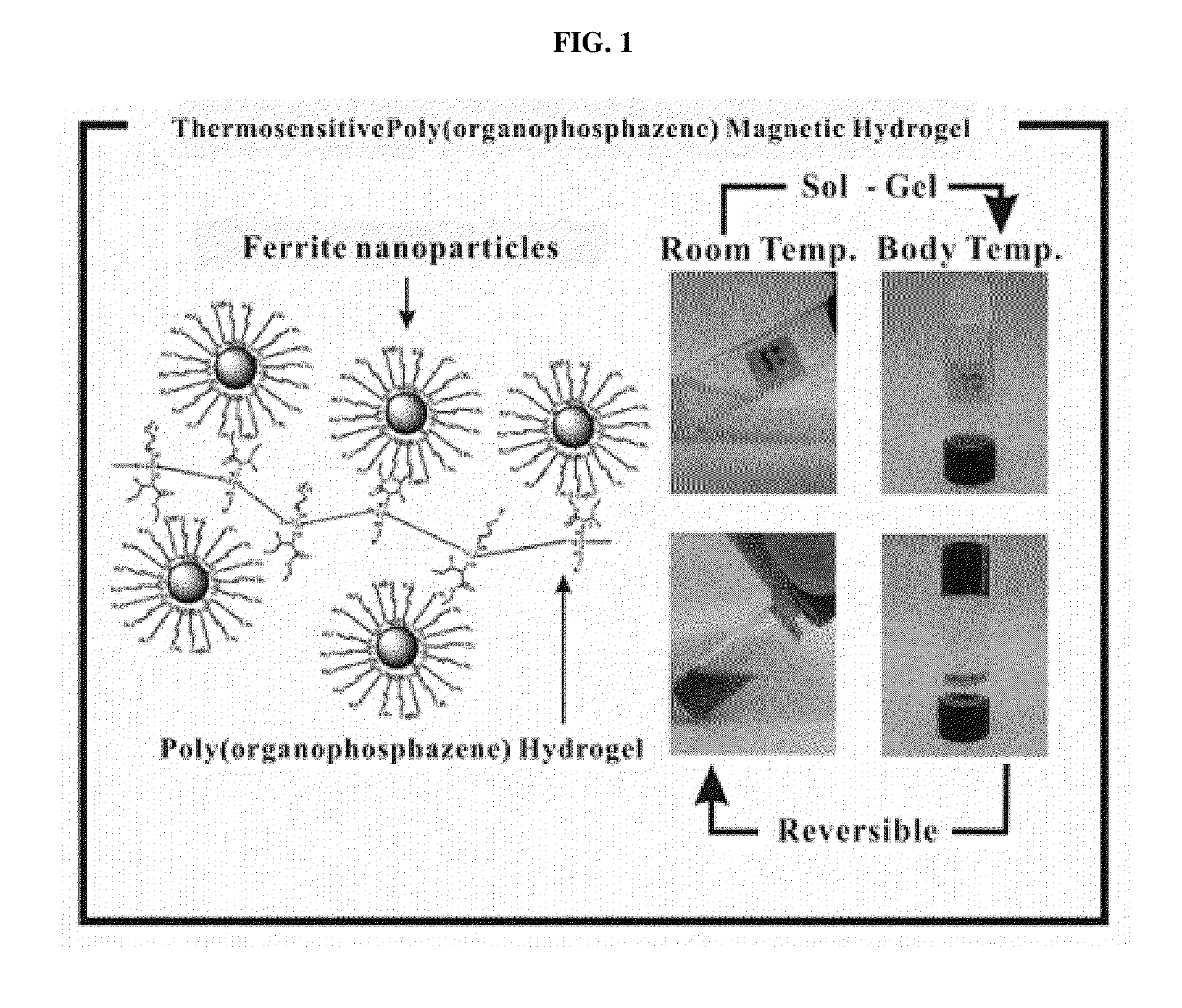
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20120121517A1Facilitated releaseImprove load effectMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideMRI contrast agentFerrite nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex including a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) and a iron oxide (Fe3O4, Magnetite)-series ferrite superparamagnetic nanoparticle, a preparation method, and uses of carrying a physiologically-active material, a bio-material and a biomaterial for cancer hyperthermia. The iron oxide is used as a MRI contrast agent for T-2 and T2* weighted image, and the poly(organophosphazene) shows a sol-to-gel behavior depending upon the temperature change. The complex is a bound-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is bonded to phosphazene-based polymer via hydrophobic binding, and a mixed-type where the superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle is physically mixed with the phosphazene-based polymer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Means and methods of multidimensional modeling in vivo spatial image of an MRI contrast agent
InactiveUS20140142914A1Analogue computers for chemical processesDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMRI contrast agentMultidimensional scaling
A method of multidimensional modeling a magnetic resonance device (MRD) contrast agent introduced within the body of a patient. The method includes: introducing into the patient body or an organ an effective measure of at least one MRD contrast agent; imaging the MRD contrast agent located at least a portion of a body and providing data defining a multidimensional image; loading or otherwise streaming the MRD image to a multidimensional printer; and multidimensionally modeling the MRD contrast agent.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
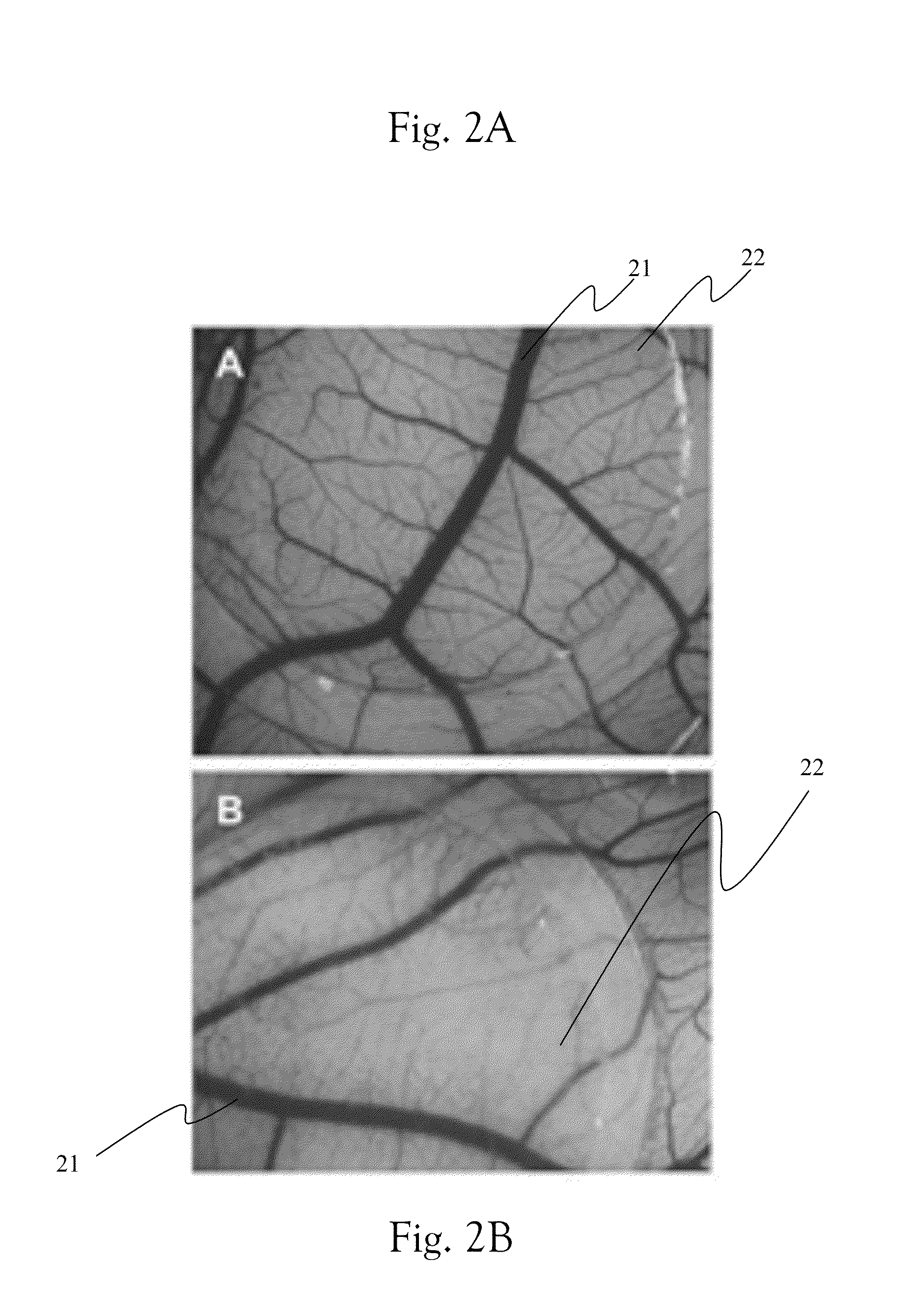
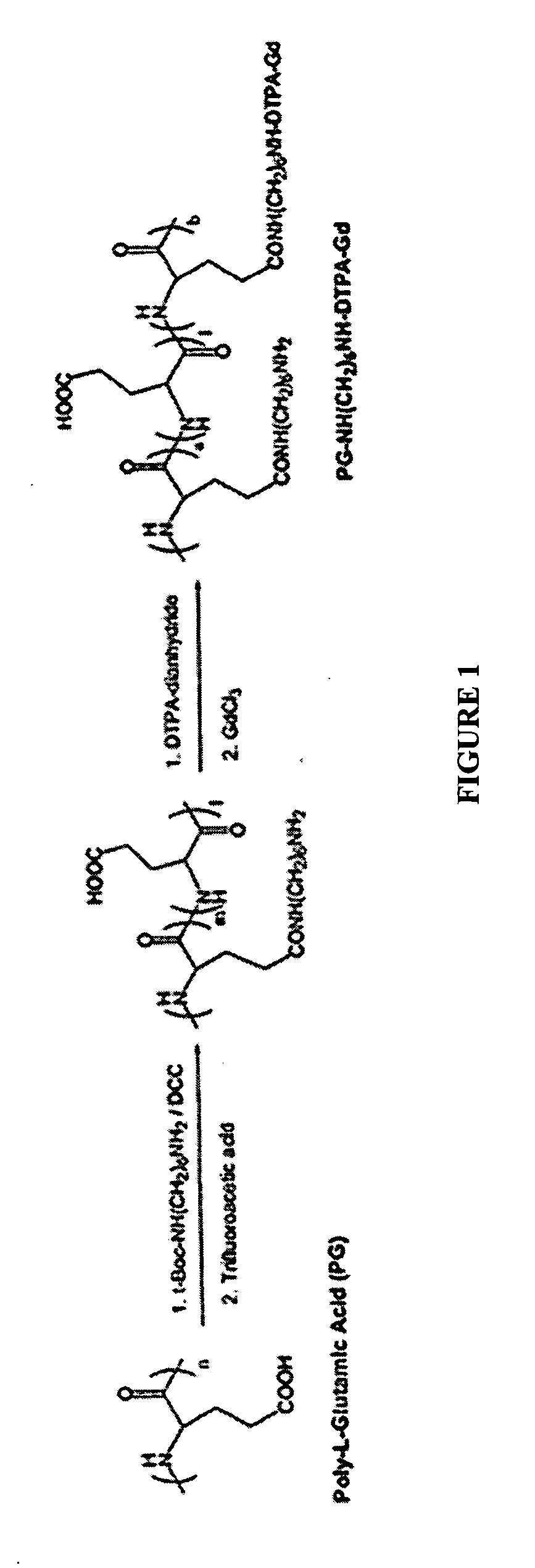
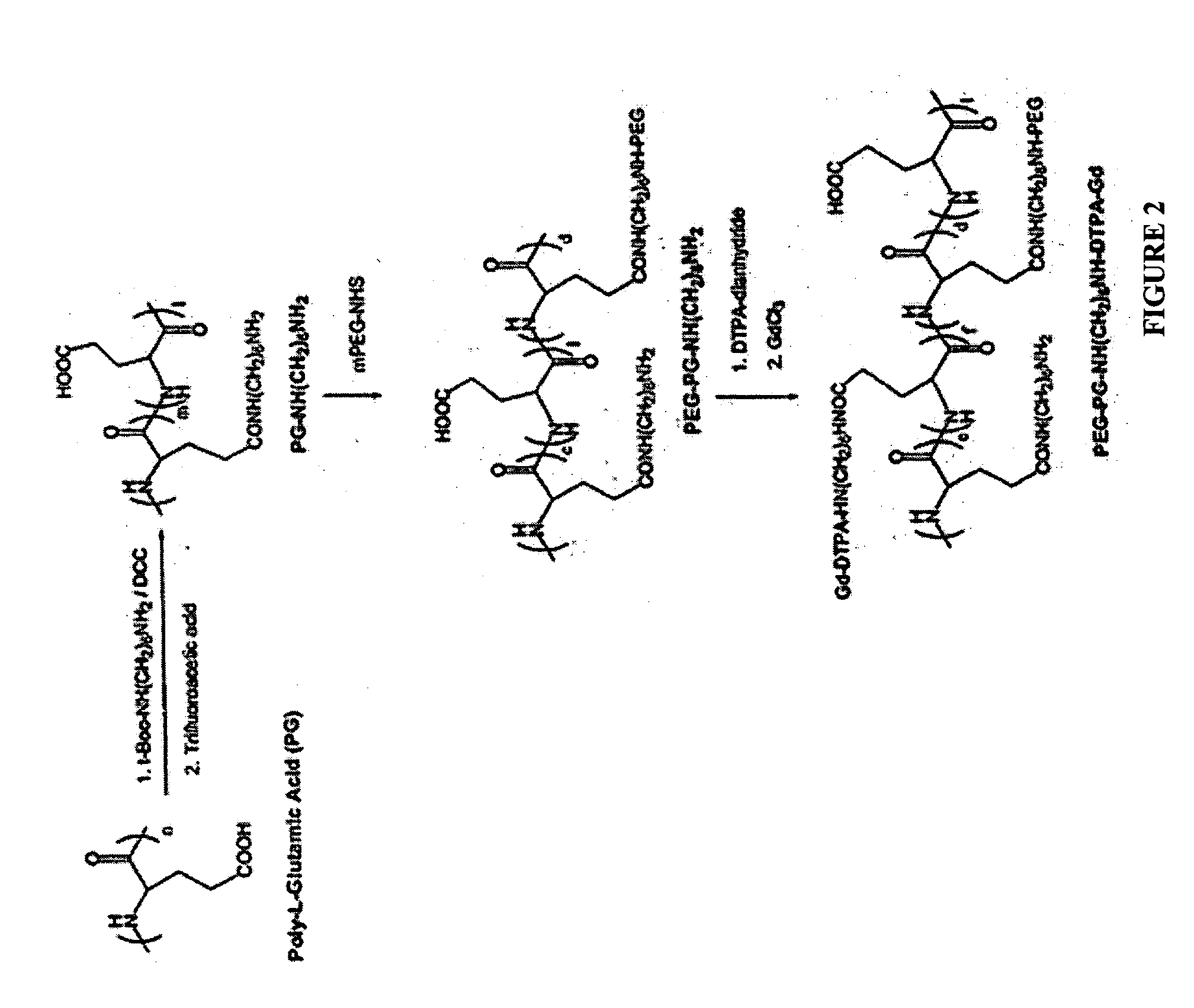
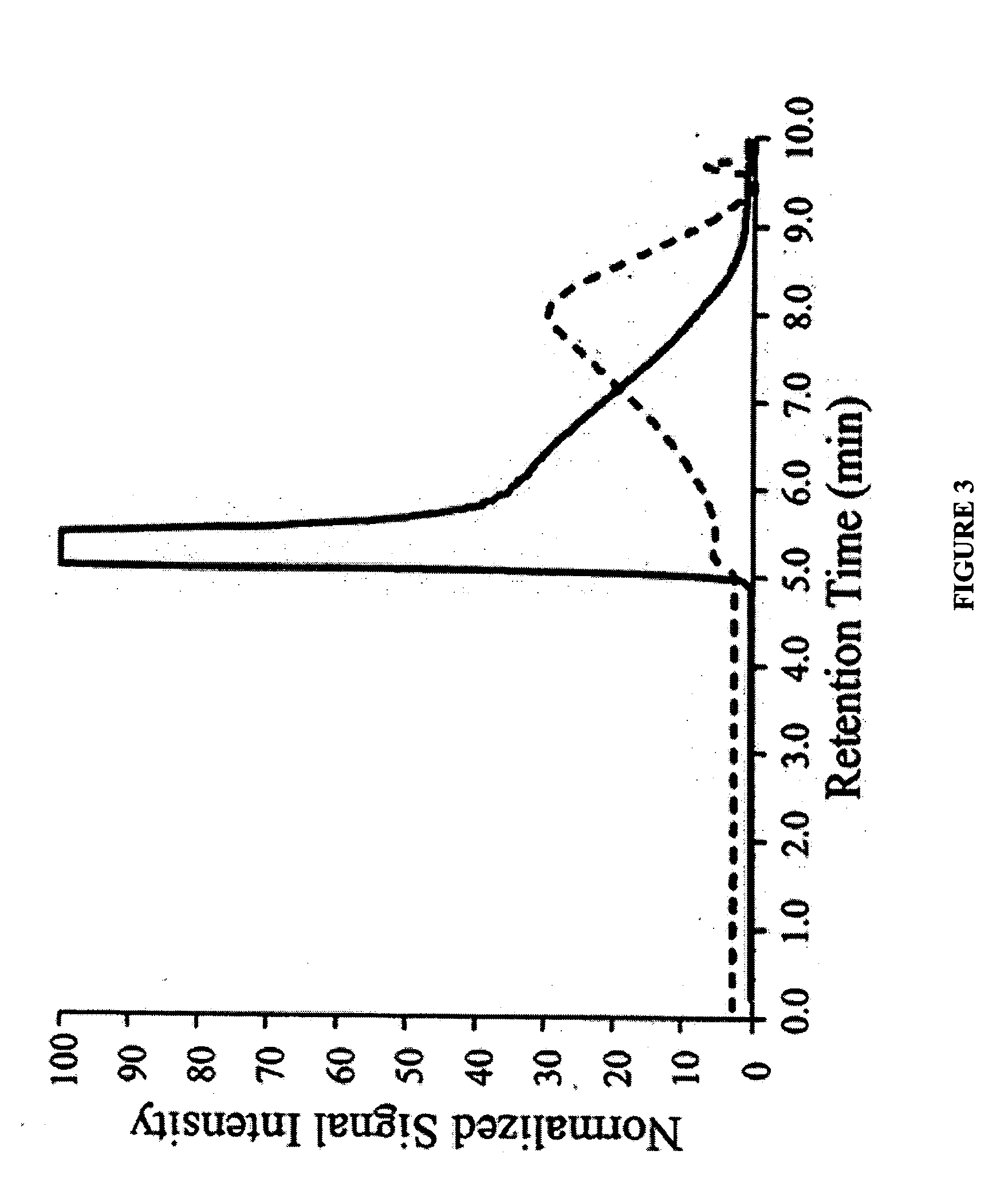
Poly (L-glutamic acid) paramagnetic material complex and use as a biodegradable MRI contrast agent
InactiveUS20050152842A1Radioactive preparation carriersNMR/MRI constrast preparationsMRI contrast agentBlood pool
The present invention includes PG polymer complexes with paramagnetic materials, such as Gd, Mn and iron oxide. The complexes may also include chelating agents which may be covalently attached to the PG polymer backbone through linkers. PEG may also be attached to the PG polymer backbone. The complexes may include targeting molecules. The complexes are useful as MRI contrast agents, particularly as blood pool agents.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Polyol and polyether iron oxide complexes as pharmacological and/or MRI contrast agents
Pharmacological compositions, and methods for administration, of the type employing an iron oxide complex with a polyol or polyether. The methods of administration may comprise parenteral administration of an effective dose of the complex formulated in a biocompatible liquid delivered at a rate of from about 1 mL / sec to less than 1 mL / min and wherein upon administration the complex provides minimal detectable free iron in a subject, and minimal incidence of anaphylaxis. The pharmacological compositions are of the type employing a polyol or polyether iron oxide complex, which, upon parenteral administration to a subject, are substantially immunosilent, provide minimal anaphylaxis and minimal free iron, and undergo minimal dissolution in vivo.
Owner:COVIS PHARM GMBH
Gadolinium containing prussian blue nanoparticles as nontoxic MRI contrast agents having high relaxivity
InactiveUS20100254912A1Low leaching rateReduce solubilityMaterial nanotechnologyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMRI contrast agentMedicine
Gadolinium+3 (Gd3+) containing (or incorporated) Prussian blue lattice contrast agents that can be used as an MRI contrast agent have unexpectedly improved r1 relaxivities of 1 or 2 magnitudes higher than the commercial Gd3+-chelates as well as exceedingly, non-toxic, low release of the Gd3+ ions into an aqueous environment at a pH of about 2 to about 7.5. The Prussian blue lattice containing Gd3+ ions therein can be used for clinical diagnosis intravenously to human beings for medical imaging. The particle sizes of the doped Prussian blue lattices are of a nanosize scale and are very stable against agglomeration.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Novel manganese comprising nanostructures
ActiveUS20140350193A1Cost advantageGood biotolerabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsNanomedicineArylMRI contrast agent
Disclosed herein are nanostructures comprising a polymeric framework comprising at least five geminal bisphosphonate groups, wherein the geminal bisphosphonate groups independently of each other are incorporated as —R3R4C(P═O(OR1)(OR2))2, wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of a negative charge, H, alkyl and aryl, and wherein at least one of R3 and R4 is a group connected to the polymeric framework with the proviso that when only one of R3 and R4 is such a connected group, the other of R3 and R4 is either a group being able to connect to the polymeric framework, or the residue of such a group, or selected from the group consisting of H, OH, OR5 and R5, wherein R5 is a lower alkyl. The polymeric framework may comprise manganese ions. Disclosed are also methods for producing such manganese containing nanostructures, compositions comprising such manganese containing nanostructures and use of such manganese containing nanostructures, i.a. as MRI contrasting agents.
Owner:SPAGO NANOMEDICAL
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents containing water-soluble nanoparticles of manganese oxide or manganese metal oxide
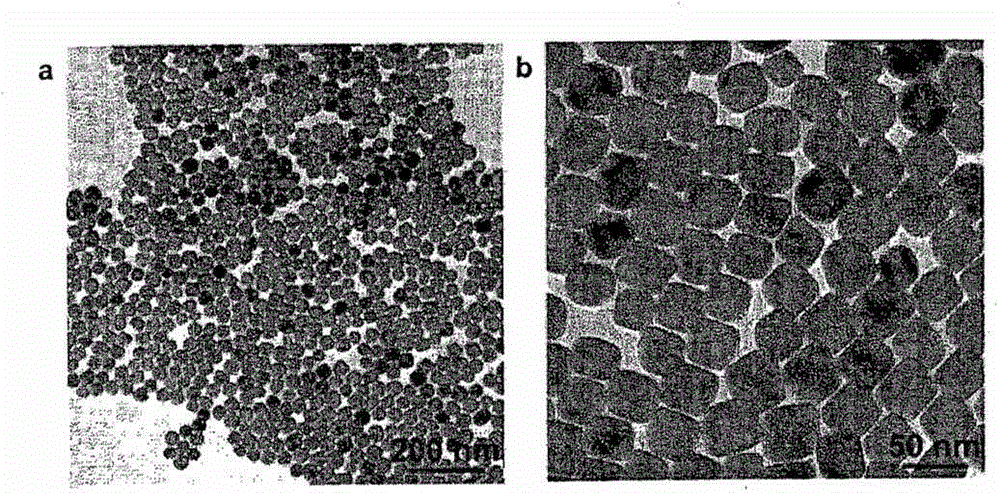
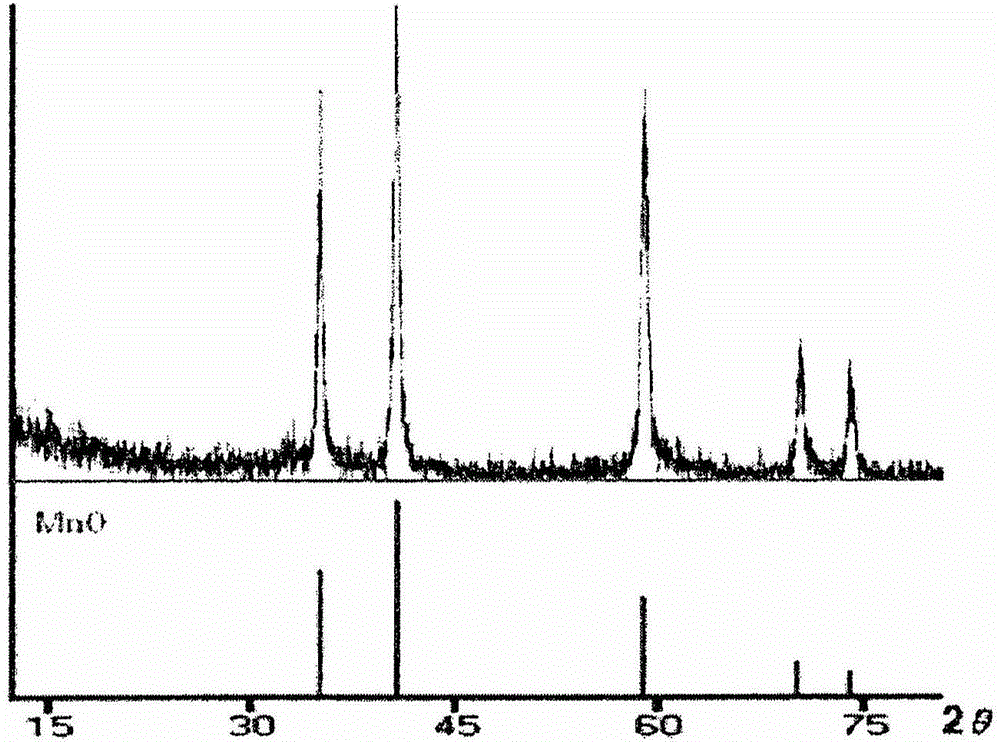
InactiveUS20090220431A1Uniform sizeImprove magnetic propertiesPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyElemental compositionMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates to a manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent, which is characterized in that: The core of it comprises 1 to 1000 nm-sized manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles which include MnO a (0<a<5) or MnMbOe (wherein M is at least one metal atom selected from the group consisting of a Group 1 or 2 element such as Li, Na, Be, Ca, Ge, Mg, Ba, Sr and Ra, a Group 13 element such as Ga and In, a transition metal element such as Y, Ta, V, Cr, Co, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Cd and Hg, and lanthanide or actinide group elements such as La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb, 0<b<5 and 0<c<10); preferably MnM′dFeeOf (wherein M′ is at least one metal atom selected from the group consisting of a Group 1 or 2 element such as Li, Na, Be, Ca, Ge, Mg, Ba, Sr and Ra, a Group 13 element such as Ga and In, a transition metal element such as Y, Ta, V, Cr, Co, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Cd and Hg, and lanthanide or actinide group elements such as La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb, 0<d<5, 0<e<5, and 0<f<15). In addition, the nanoparticles include water-soluble manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles which is characterized in that they are soluble in water themselves or stable in an aqueous media as being coated with a water-soluble ligand and they possess enhanced magnetic properties and MRI contrast effect. Also the water soluble manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles are coupled with an bioactive material such as chemical molecules or bio-functional molecules, and thus the nanoparticles can be used as an MRI contrast agent for target specificity and cell tracking.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Iron oxide nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents and their preparing method
InactiveUS20110165086A1Low toxicityHigh in ironMaterial nanotechnologyGenetic material ingredientsMRI contrast agentPolyethylene glycol
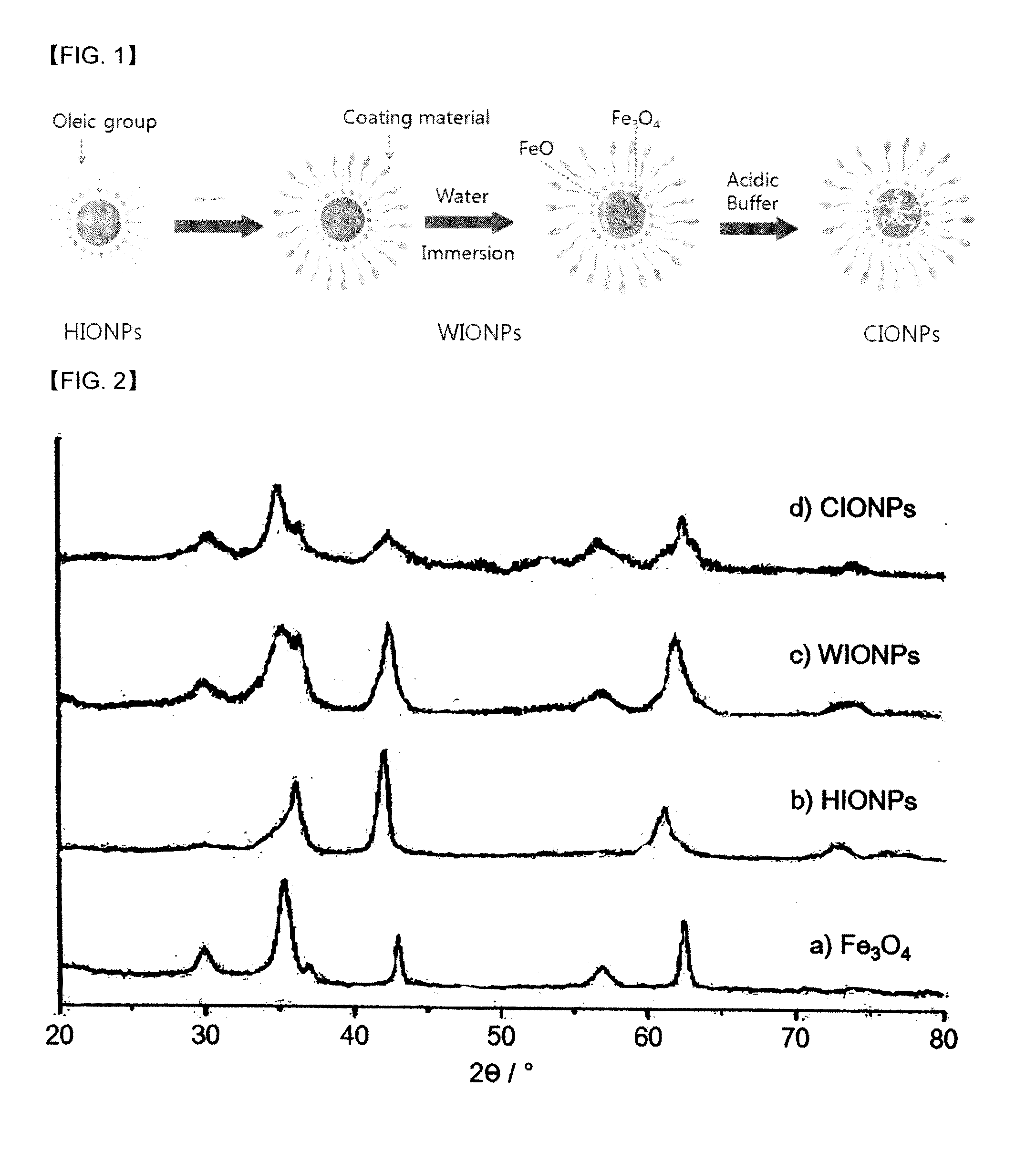
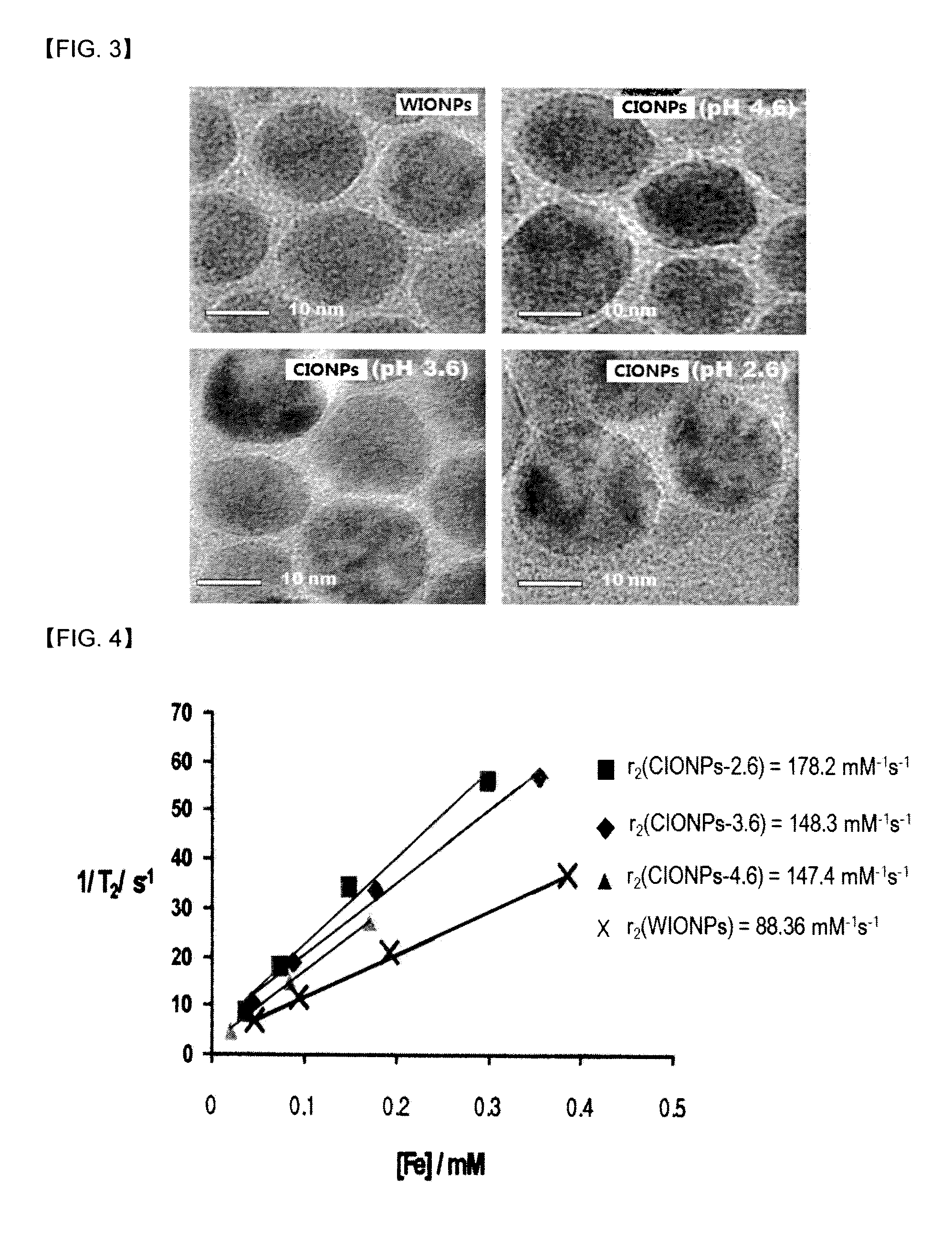
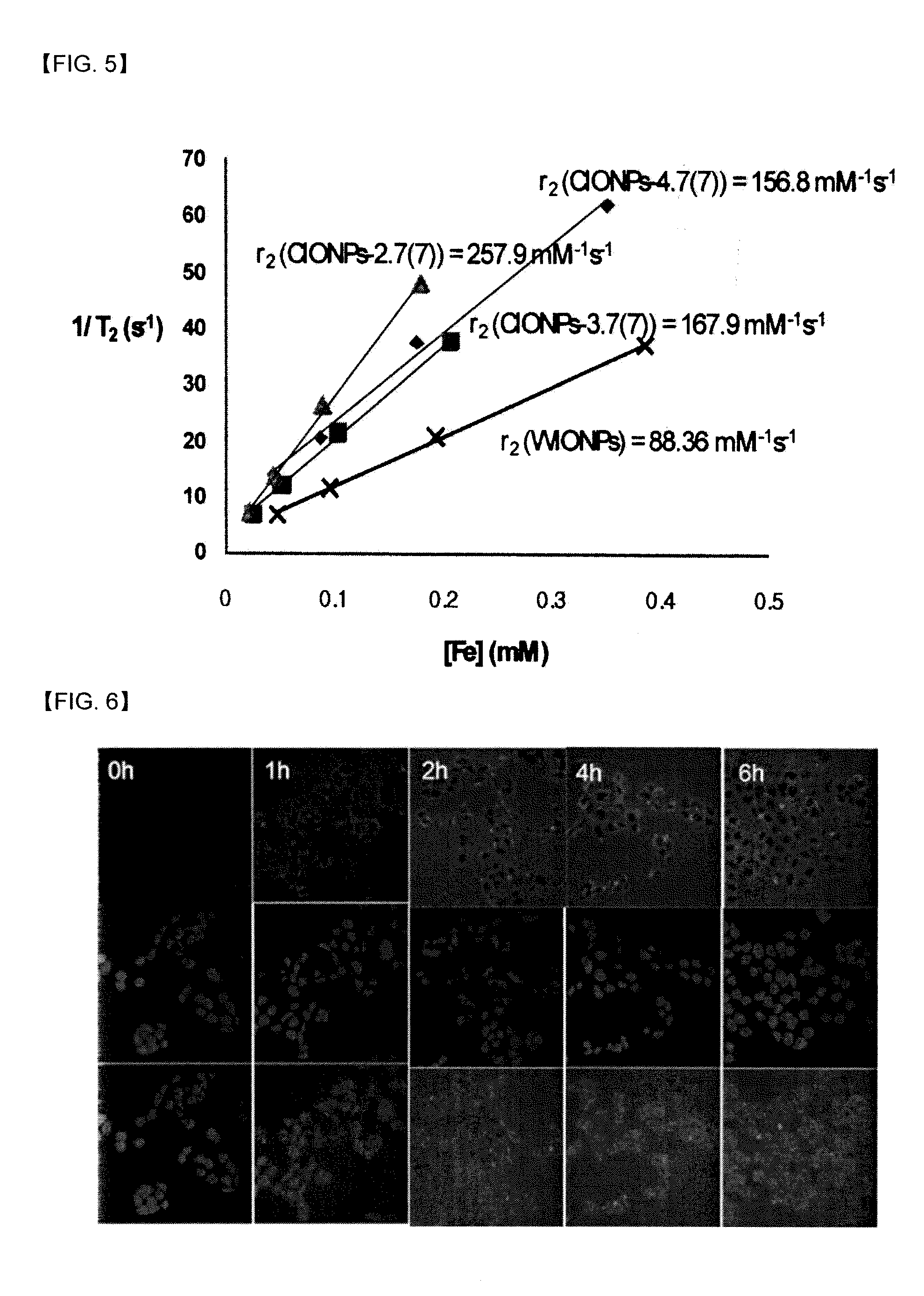
Iron oxide nano contrast agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging which have superior T2 contrast effect, and also can be used as a storage or a carrier for drugs and so on, are disclosed. The iron oxide nano contrast agents can be prepared by the steps of: coating surfaces of hydrophobic FeO nanoparticles with a coating material selected from the group consisting of polyethylene glycol-phospholipid conjugate, dextran, chitosan, dimercaptosuccinic acid and mixtures thereof in an organic solvent to form hydrophilic FeO nanoparticles having hydrophilic surfaces and dispersibility in water; dispersing the hydrophilic FeO nanoparticles in water to oxidize FeO; and exposing the oxidized hydrophilic FeO nanoparticles to an acidic buffer to dissolve and remove interior unoxidized FeO portions, and thereby to form Fe3O4 nanoparticles having an interior space.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
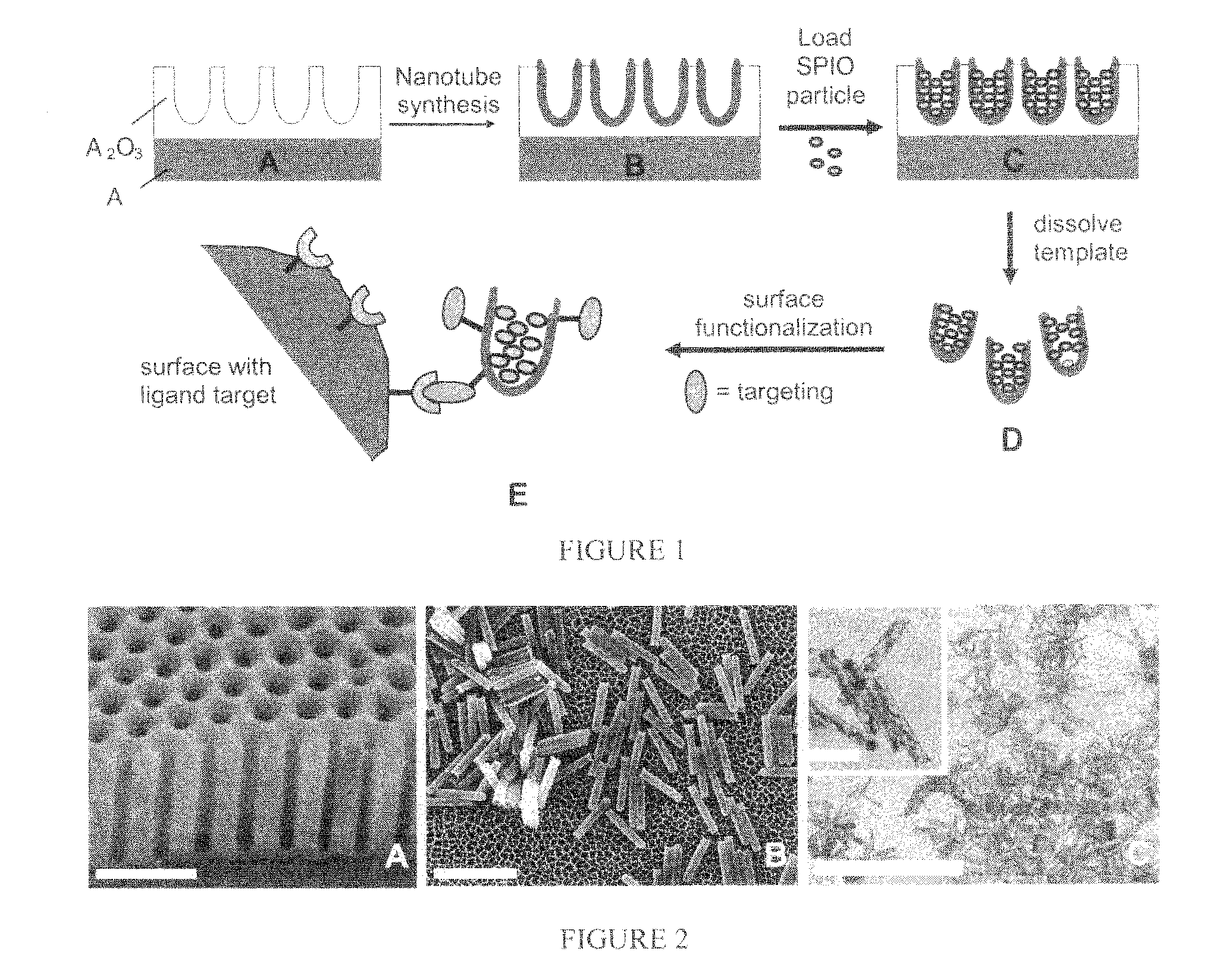
Nanotubular probes as ultrasensitive mr contrast agent
InactiveUS20080124281A1Enhanced MRI signalIncrease surface areaBiocideGenetic material ingredientsMRI contrast agentMr contrast agent
The present invention includes compositions, methods and methods for using MRI contrast agent that include a generally nanotubular carrier and an MRI contrast agent disposed within the carrier.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Polyol and polyether iron oxide complexes as pharmacological and/or MRI contrast agents
InactiveUS7871597B2Minimal detectable free ironMinimal incidenceHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideMRI contrast agentPolyol
Pharmacological compositions, and methods for administration, of the type employing an iron oxide complex with a polyol or polyether. The methods of administration may comprise parenteral administration of an effective dose of the complex formulated in a biocompatible liquid delivered at a rate of from about 1 mL / sec to less than 1 mL / min and wherein upon administration the complex provides minimal detectable free iron in a subject, and minimal incidence of anaphylaxis. The pharmacological compositions are of the type employing a polyol or polyether iron oxide complex, which, upon parenteral administration to a subject, are substantially immunosilent, provide minimal anaphylaxis and minimal free iron, and undergo minimal dissolution in vivo.
Owner:COVIS PHARM GMBH
Magnetic graphene-like nanoparticles or graphitic nano- or microparticles and method of production and uses thereof
A magnetic graphene-like nanoparticle or graphitic nano- or microparticle exhibits a high relaxivity, and is useful as a MRI contrast agent. A composition for use with MRI imaging, comprising a sufficient amount of the magnetic graphene-like nanoparticles or graphitic nano- or microparticles and one or more physiologically acceptable carriers or excipients. Methods of using the magnetic graphene-like nanoparticles or graphitic nano- or microparticles as MRI contrast agents. Methods of producing the magnetic graphene-like nanoparticle or graphitic nano- or microparticle.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents comprising zinc-containing magnetic metal oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20100143263A1Improve magnetic propertiesLow cytotoxicityBiocideNanomagnetismMRI contrast agentMetal oxide nanoparticles
The present invention relates to an MRI contrast agent that includes zinc-containing water-soluble metal oxide nanoparticles and has an improved contrast effect. The zinc-containing water-soluble metal oxide nanoparticles are characterized by addition of zinc to a matrix comprising the metal oxide nanoparticles or by substitution of metal in the matrix, resulting in the improved contrast effect of MRI. In addition, the zinc-containing metal oxide nanoparticles of the present invention include the MRI contrast agent t having hybrid structures of “zinc-containing metal oxide nanoparticle—biologically / chemically active material” in which the nanoparticle is conjugated with a bioactive material such as proteins, antibodies, and chemical materials.
Owner:INVENTERA PHARM INC
Biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene)-superparamagnetic nanoparticle complex, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS9017726B2Facilitated releaseImprove load effectPowder deliveryNanomedicineHybrid typeMRI contrast agent
Owner:NEXGEL BIOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method for nanometer graphene carrier used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent
InactiveCN102397563AImprove hydrophilicityGood biocompatibilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsMRI contrast agentRetention time
The invention relates to a preparation method for a nanometer graphene carrier used for an MRI contrast agent. According to the method, nanometer graphene oxide and hydrophilic high polymers are used as raw materials; the hydrophilic high polymers are grafted onto the surface of nanometer graphene oxide, and a contrast agent is loaded wherein. Compared to the prior art, the invention has the following advantages: by utilizing good hydrophilicity and biocompatibility of some hydrophilic high polymers and the characteristic that the system of nanometer graphene oxide and hydrophilic high polymers can enter into biological cells at a nanometer level, the contrast agent is enabled to have long in-vivo retention time, good histocompatibility and low cytotoxicity; the system shows a good application prospect in the aspect of MRI radiography.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
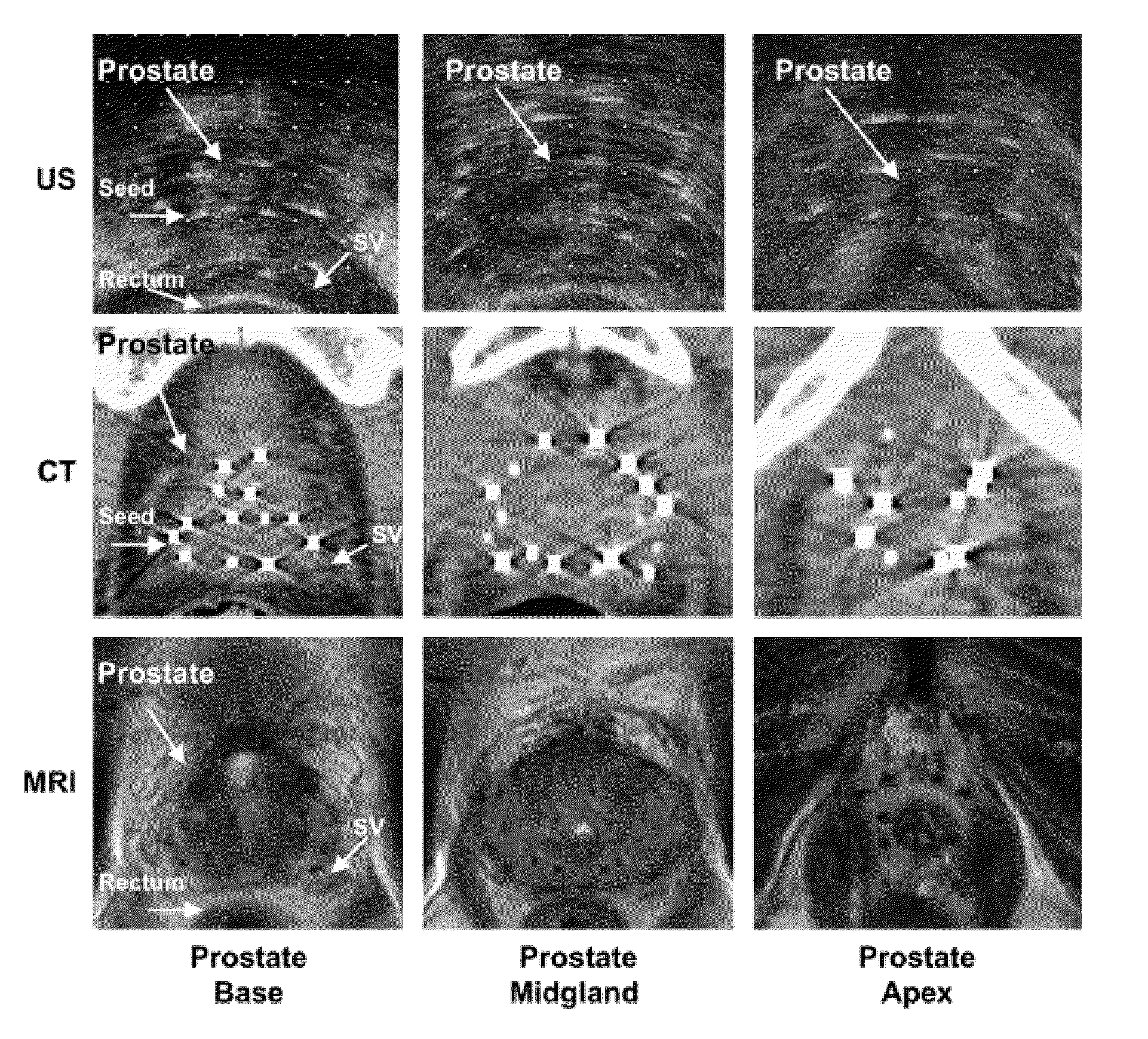
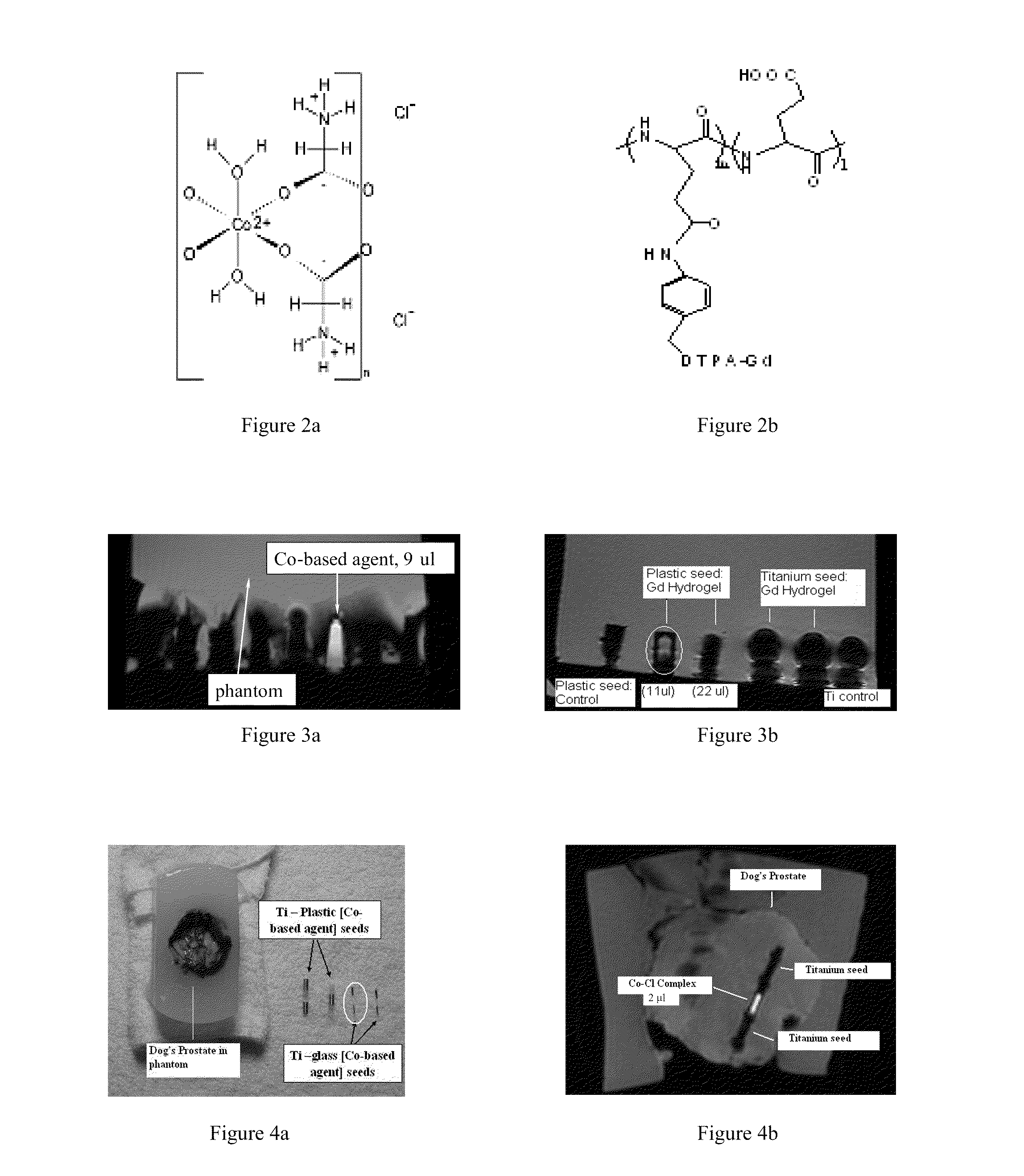
Seeds and Markers for Use in Imaging
ActiveUS20100254897A1Easy to connect and useConvenient treatmentBiocideNervous disorderMRI contrast agentBrachytherapy
A contrast marker having a casing and a novel MRI contrast agent comprising metal complexes disposed around, within, or abuting the casing is provided. Such contrast markers may be placed in a strand, with or without a therapy seed, to produce a seeded strand useful for imaging and in connection with brachytherapy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
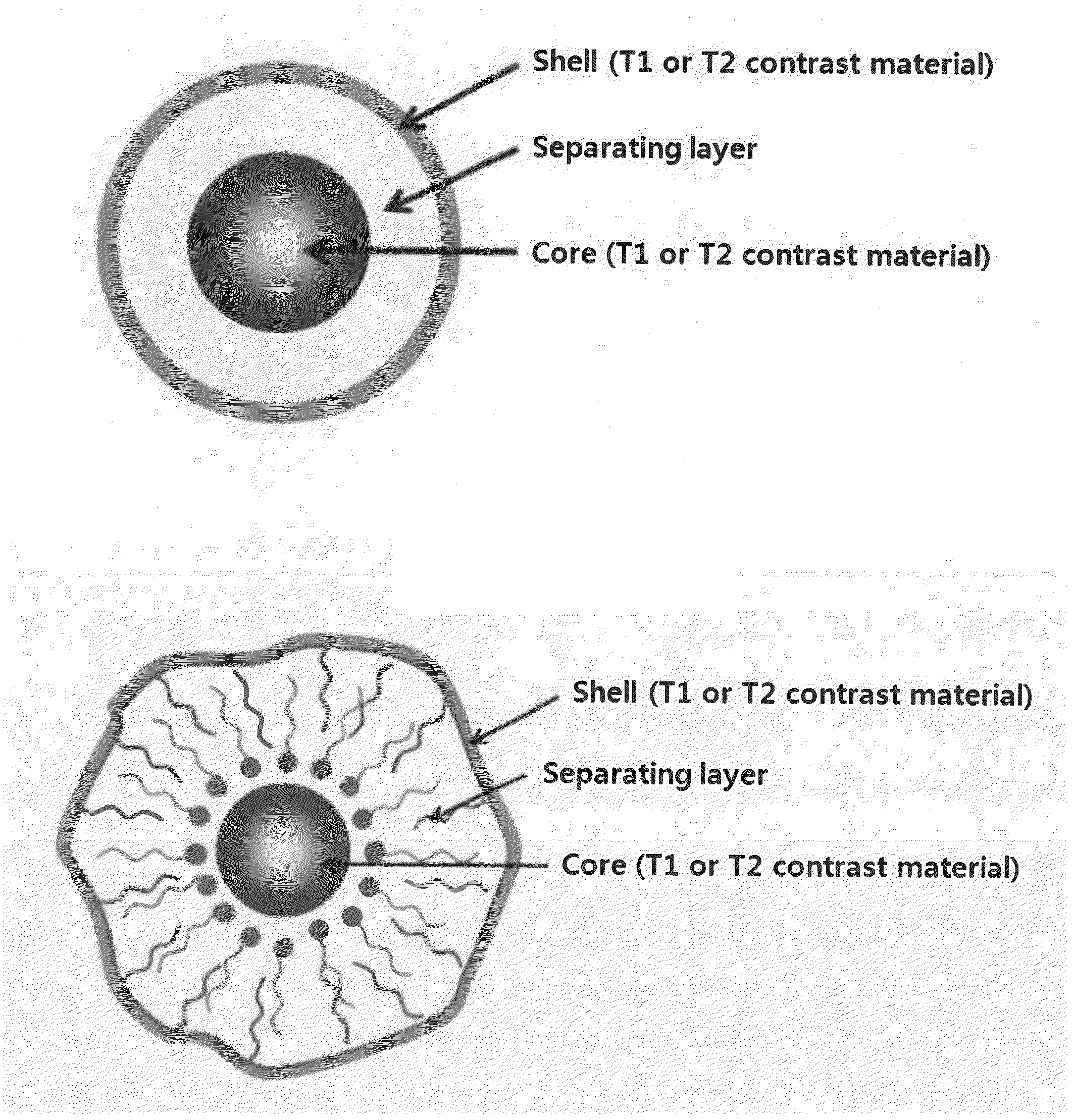
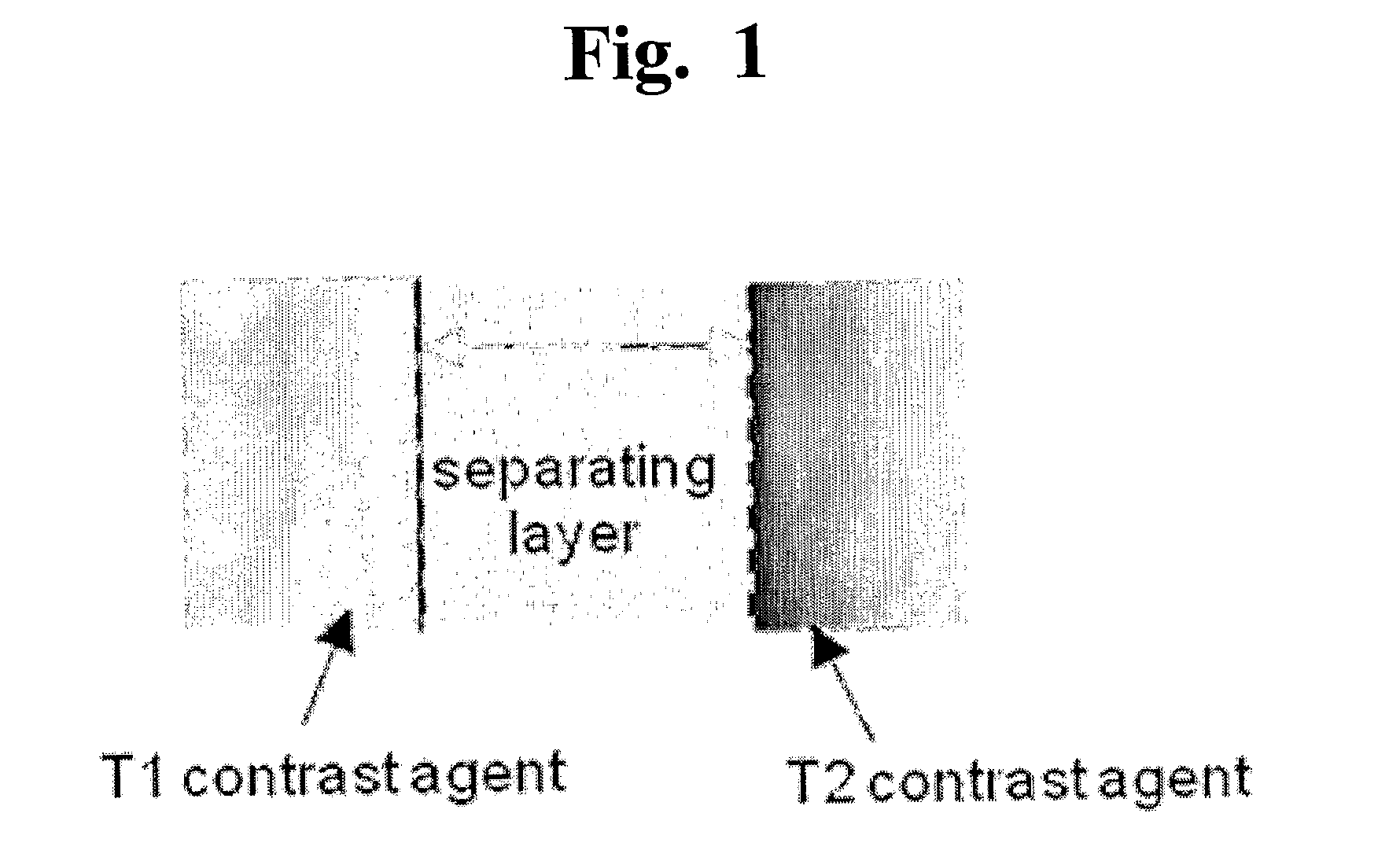
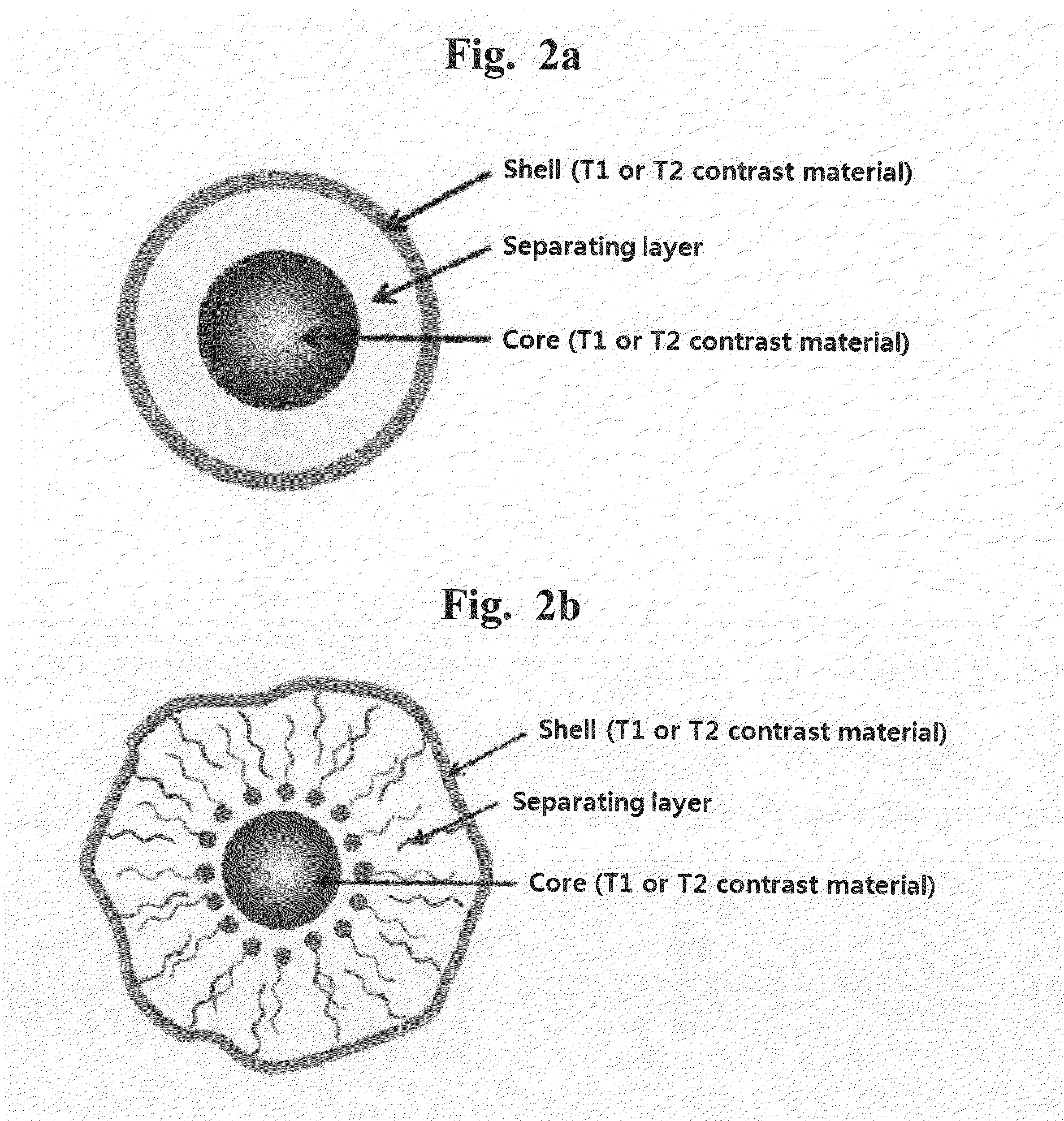
T1-T2 Dual Modal MRI Contrast Agents
The present invention relates a T1-T2 dual-modal MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast agent, comprising (a) a first layer consisting of T1 contrast material; (b) a second layer consisting of T2 contrast material; and (c) a separating layer which is present in a space between the first layer and the second layer, and inhibits a reciprocal interference between T1 contrast material and T2 contrast material, and a heat-generating composition and a drug delivery composition having the same. The T1-T2 dual-modal contrast agent of the present invention may generate both T1 and T2 signal and thus observe the signal complementarily, resulting in accurate diagnosis through reduction of misdiagnosis. Further, T1 and T2 MR imaging may be simultaneously obtained by simple operation within the same MR imaging device, enabling to remarkably reduce a diagnosis time and diagnosis cost. In addition, the particle constituting the T1-T2 dual-modal contrast agent of the present invention may be applied to hyperthermia and drug delivery systems.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
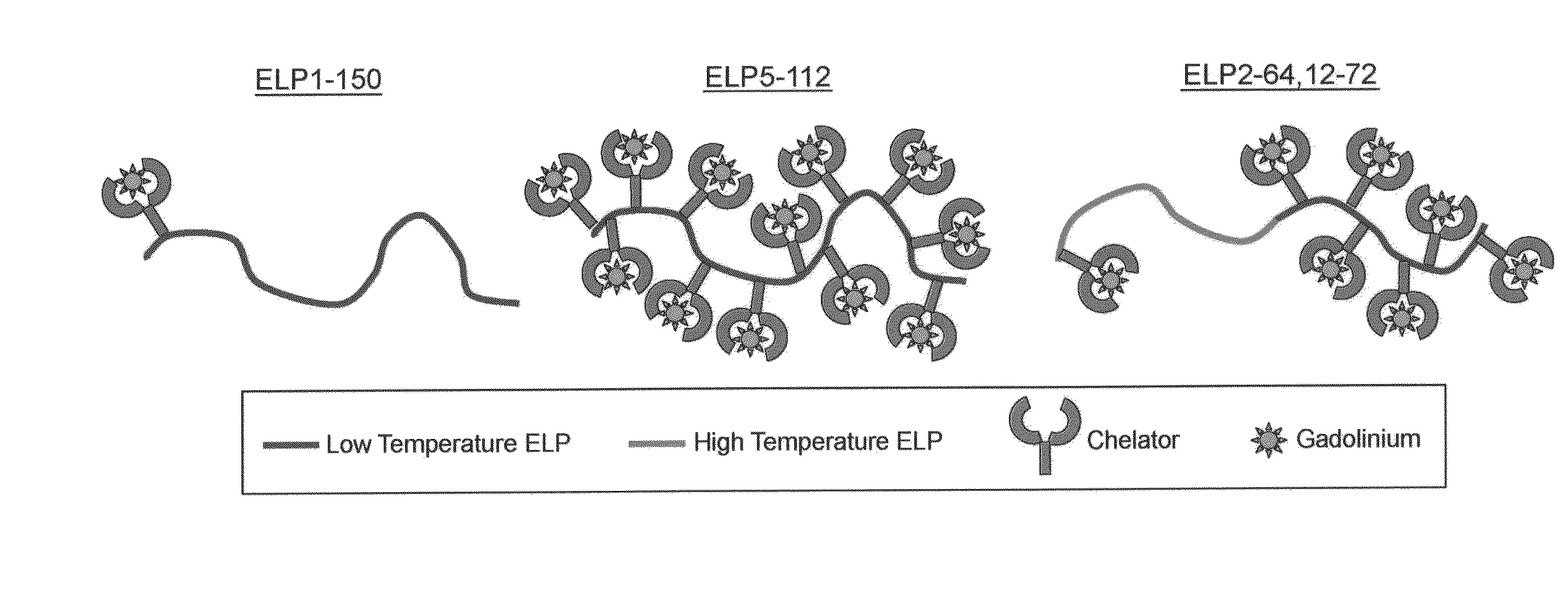
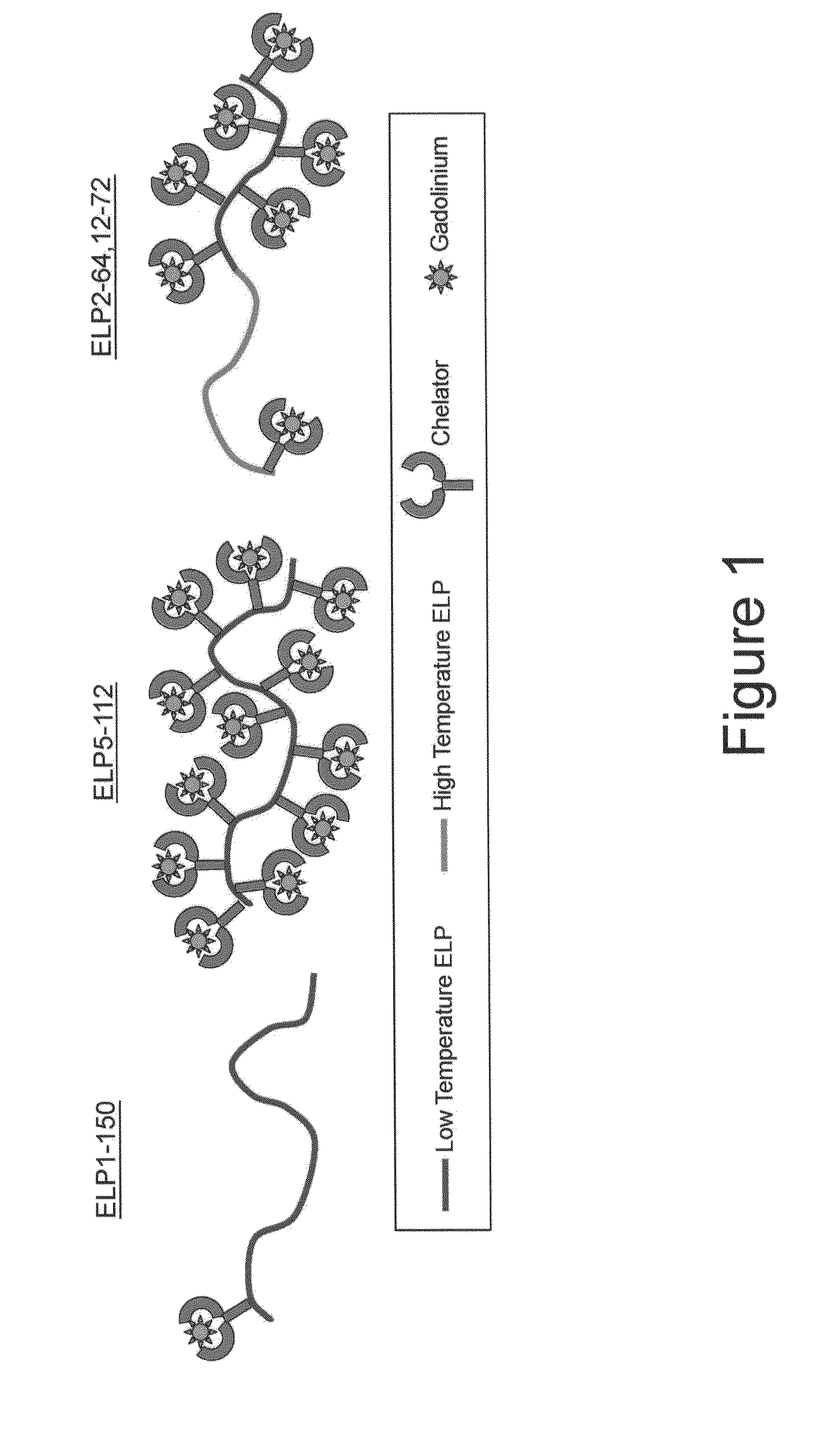
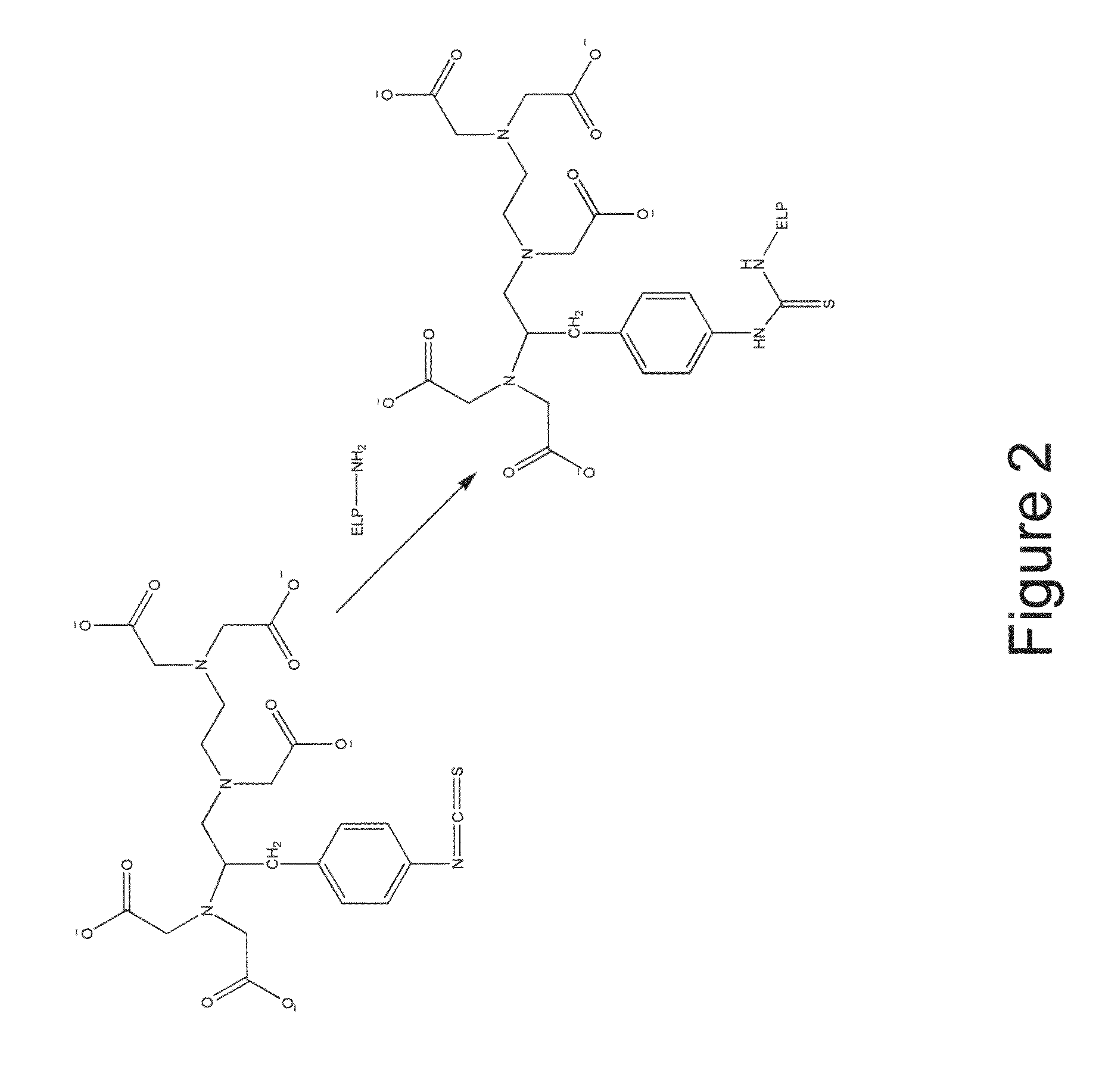
Elastin-like polypeptide and gadolinium conjugate for magnetic resonance imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast enhancement agent comprising an elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) and one or more paramagnetic metal ions is disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of preparing ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents, formulations comprising ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents, and methods of using ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents to image biological samples and to image and deliver therapeutic agents to targeted sites in vivo. In some embodiments, the ELP MRI agents can be used in methods related to blood volume determination, in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and in vascular transport determinations. The ELP MRI contrast agents can also provide information on the expression of various proteins through affinity targeting or enzymatic crosslinking in order to aid in diagnosis and in the spatial definition of pathologic tissue.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Charge neutral complexes of paramagnetic metals as intracellular magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents
InactiveUS20060078502A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove slackIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiagnostic recording/measuringMRI contrast agentDysprosium
A contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging comprising a complex of a paramagnetic cation, preferably Gd+3, Dy+3, and Fe+3 with three equivalents of a charge neutralizing chelator that provides a lipid soluble complex of the paramagnetic cation is described. The complex is retained intracellularly when introduced into a mammalian cell. A method of providing an image of an internal pathology of a patient by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by administering the MRI contrast agent or tagged cells to the patient and scanning the patient using magnetic resonance imaging to obtain visible images of the internal pathology of the patient is also set forth.
Owner:DEWANJEE MRINAL K
Preparation method of targeted MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast medium based on folic acid modified iron oxide nanoparticles
InactiveCN103143041ASimple operation processMild reaction conditionsIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetMRI contrast agent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a targeted MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast medium based on folic acid modified iron oxide nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting FA to NH2-PEG-COOH to form COOH-PEG-FA; synthesizing PEI coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4-PEI) by a hydrothermal method; performing surface modification on the Fe3O4-PEI nanoparticles by use of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FI); connecting COOH-PEG-FA to the surface of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles; and finally performing acetylation modification of the residual PEI aminos on the surface of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles to improve the biocompatibility for MRI diagnosis. The preparation method provided by the invention has simple technology and mild reaction conditions, and is easy to operate; and the prepared Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles have good colloidal stability, biocompatibility and tumor targeting performance as well as potential application value in the field of in-vivo tumor targeted diagnosis.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
D-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles and preparation method of lyophilized powder thereof
InactiveCN101698106AOvercome the problem of liquid instabilityFulfil requirementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryTumor targetSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
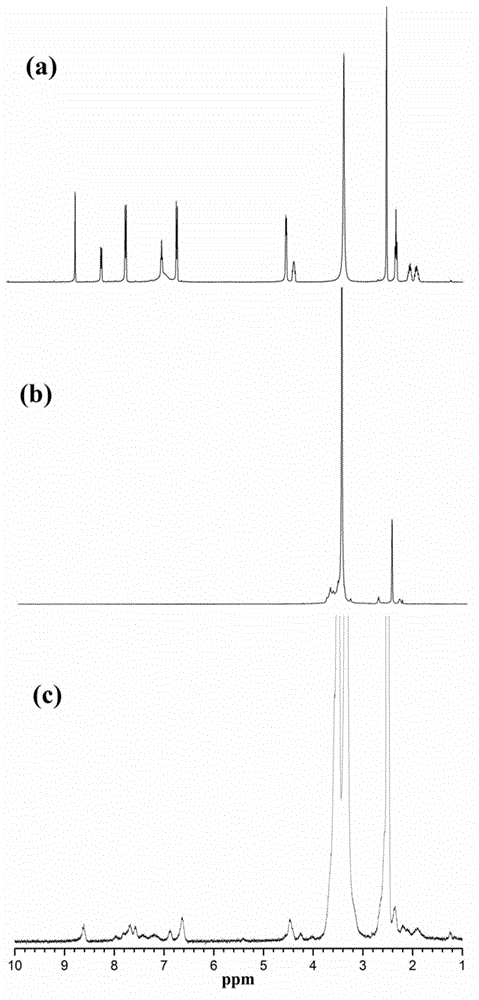
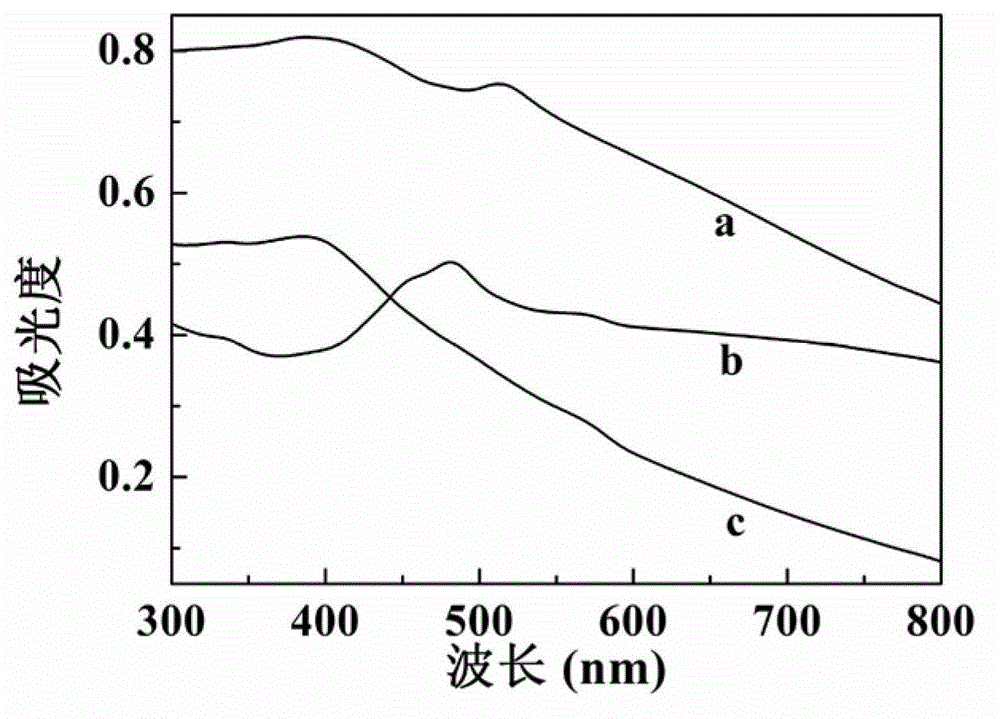
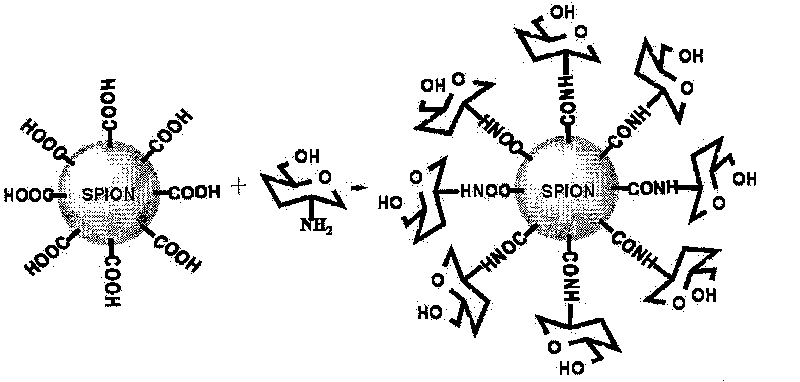
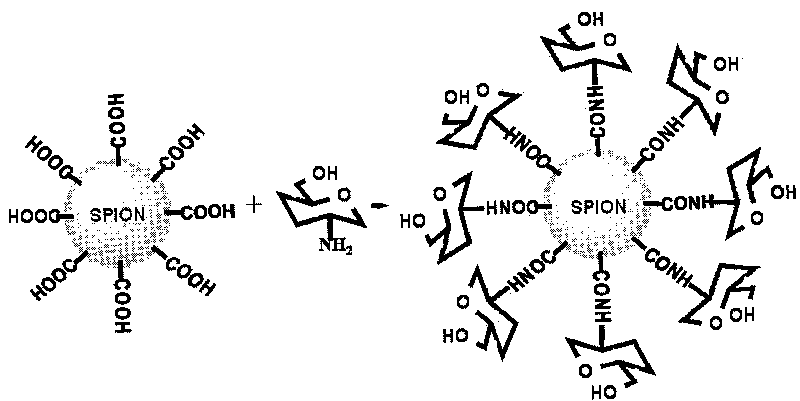
The invention relates to d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles used as a tracer for magnetic resonance, a preparation method of lyophilized powder thereof and use thereof. The d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles comprise superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, wherein the surfaces of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are modified by a substance having carboxyls; the carboxyls react with the aminos of the d-glucosamine to form amido bonds; and thus a structure that the surfaces of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are modified by the d-glucosamine is formed. The invention provides a novel tumor-targeted MRI contrast agent which has high selectivity of tumors for the tumor targeted magnetic resonance diagnostic tests and clinic tumor diagnosis. By preserving the d-glucosamine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in form of the lyophilized powder, the unstable problem of the d-glucosamine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles is solved. The d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles are sterile, anhemolytic and free from vascular stimulation and can meet the requirements of tests of cells, animals and the like.
Owner:ZHENJIANG NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Cancer cell diagnosis by targeting delivery of nanodevices
InactiveUS20090180966A1Reduced Hydrodynamic DiameterHydrodynamic diameter of increasePowder deliveryBiocideCancer cellMRI contrast agent
Macromolecular contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging are described. Biomolecules and their modified derivatives form stable complexes with paramagnetic ions thus increasing the molecular relaxivity of carriers. The synthesis of biomolecular based nanodevices for targeted delivery of MRI contrast agents are described. Nanoparticles (NP) have been constructed by self-assembling of chitosan (CHIT) as polycation and poly-gamma glutamic acids (PGA) as polyanion. NP's are capable of Gd-ion uptake forming a particle with suitable molecular relaxivity. Folic acid (FA) is linked to the NP's to produce NP-FA bioconjugates that can be used for targeted in vitro delivery to a human cancer cell line.
Owner:BORBELY JANOS +5
Nanoparticles for Imaging Atherosclerotic Plaque
InactiveUS20080206150A1Reduce contrastStrong specificityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideDiseaseScavenger
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease of the arterial walls and represents a significant health problem in developed nations. Described is a targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) contrast agent for in vivo imaging of early stage atherosclerosis. Early plaque development is characterized by the influx of macrophages, which express a class of surface receptors known collectively as the scavenger receptors (SR). The macrophage scavenger receptor class A (SRA) is highly expressed during early atherosclerosis. The macrophage SRA therefore presents itself as an ideal target for labeling of lesion formation. By coupling a known ligand for the scavenger receptor, dextran sulfate, to a MRI contrast agent, early plaque formation can be detected in vivo. Targeted MR contrast agents offer a unique opportunity to visualize early plaque development in vivo with high sensitivity and resolution, allowing or early diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
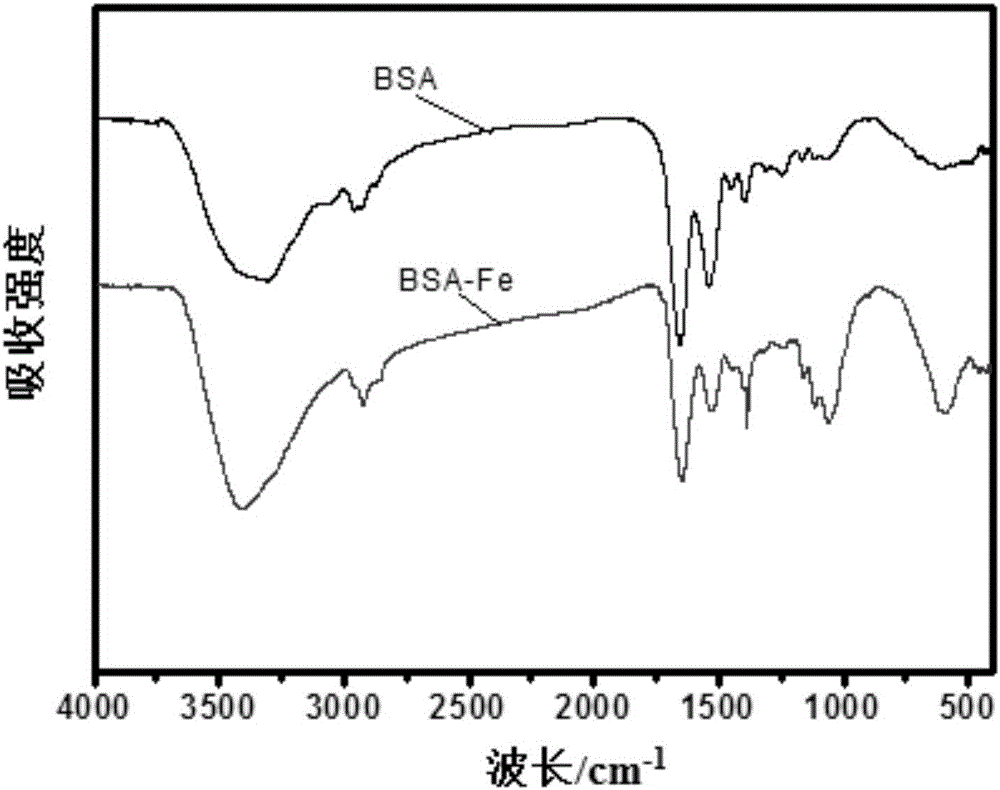
Bovine serum albumin coated ferriferrous oxide nano-particle T1-MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) contrast medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106075475AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsMRI contrast agentFerrous salts
The invention relates to a bovine serum albumin coated ferriferrous oxide nano-particle T1-MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) contrast medium and a preparation method thereof. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving bovine serum albumin into secondary water A; ultrasonically dissolving to prepare a bovine serum albumin solution; (2) adding soluble ferric iron salts and soluble ferrous salts into secondary water B and dissolving to prepare an iron source solution; (3) putting the bovine serum albumin solution into an inert atmosphere and heating and stirring; adding the iron source solution into the bovine serum albumin solution to prepare a BSA-Fe precursor; and (4) raising the temperature to 50-100 DEG C and rapidly adding concentrated ammonia water, and reacting at a constant temperature for 5min-30min to prepare the bovine serum albumin coated ferriferrous oxide nano-particle T1-MRI contrast medium. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method is simple and the controllability is good; and obtained bovine serum albumin coated ferriferrous oxide nano-particles have the characteristics of good biocompatibility, easiness of being discharged out of a body, small toxicity and good T1 imaging effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for functional kidney imaging using small dendrimer contrast agents
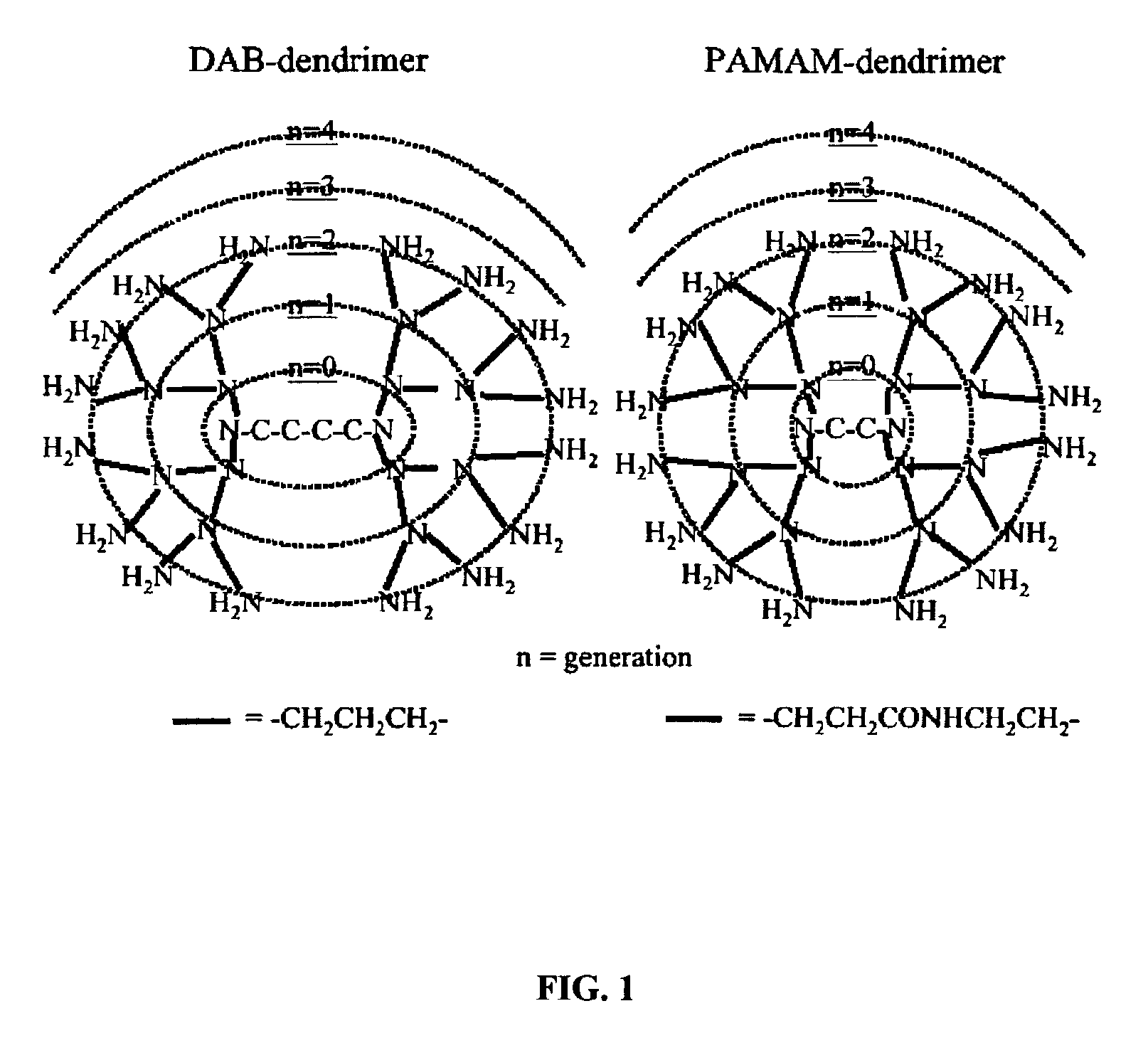
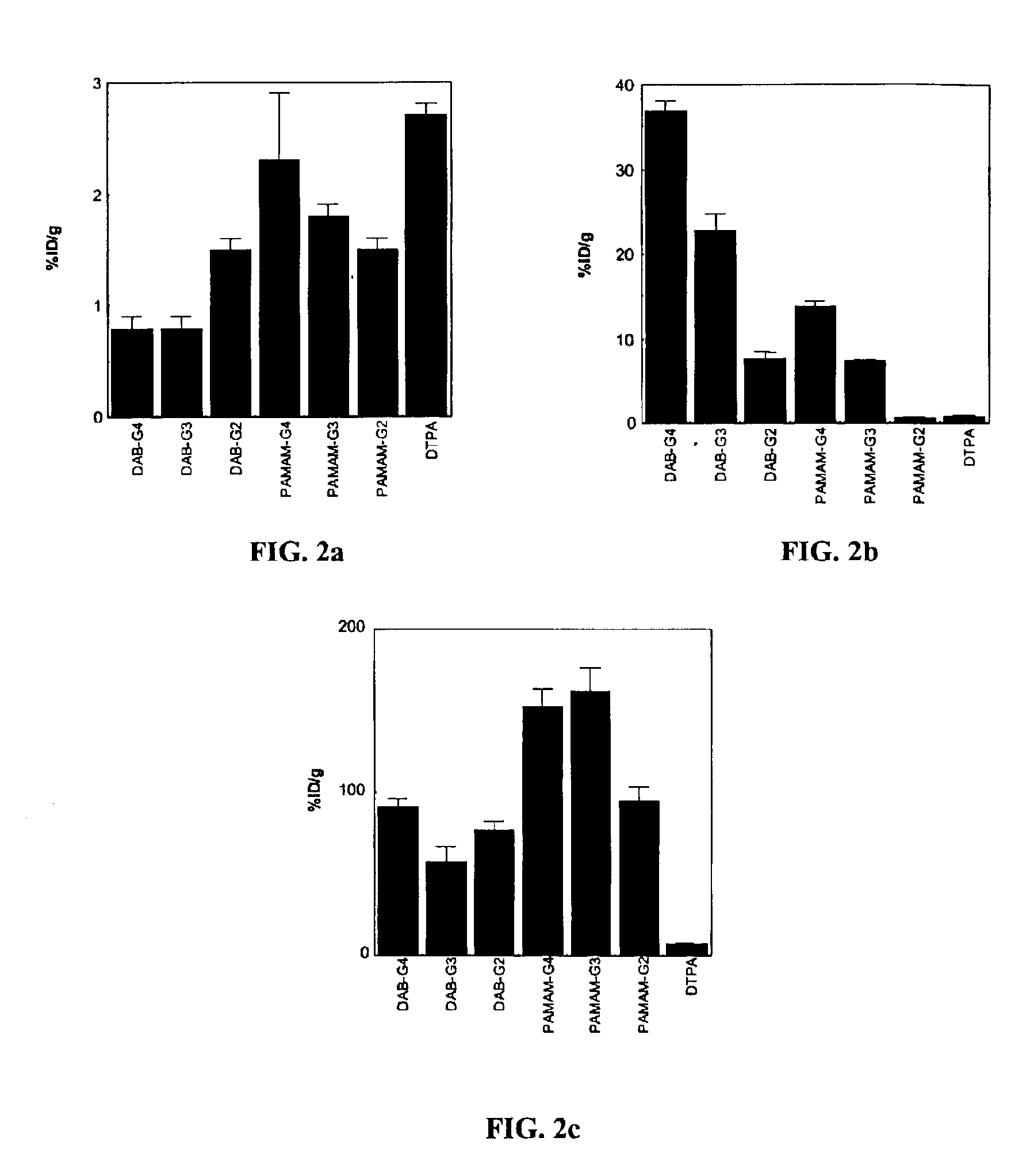
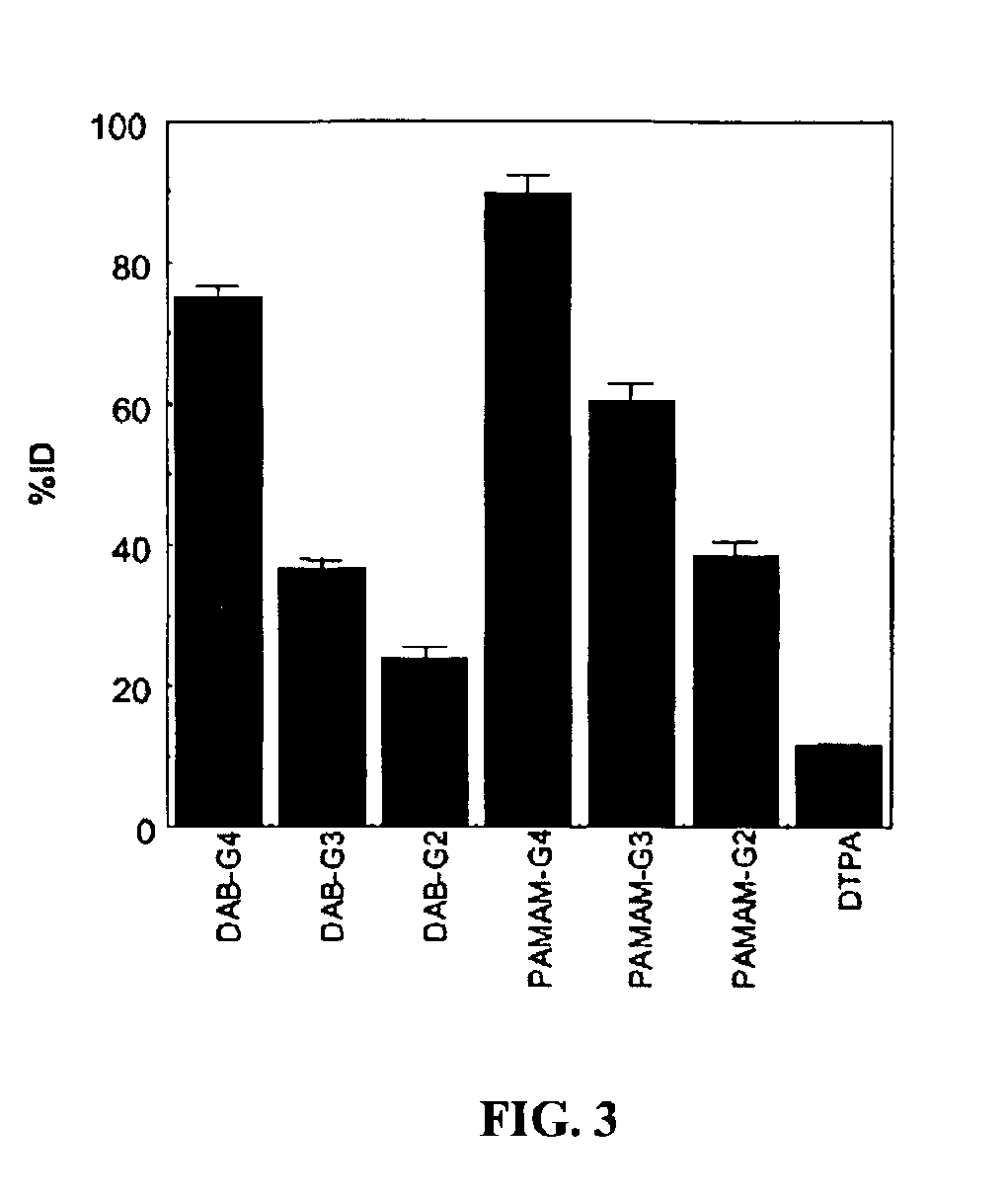
Small dendrimer-based MRI contrast agents are disclosed to accumulate in renal tubules. The accumulation enables visualization of renal structure and function, permitting assessment of structural and functional damage to the kidneys. In a disclosed embodiment, six, small dendrimer-based MRI contrast agents were synthesized, and their pharmacokinetics, whole body retention, and renal MRI images were evaluated in mice. Surprisingly, despite having unequal renal clearance properties, all of the dendrimer agents clearly visualized the renal anatomy and proximal straight tubules of the mice better than Gd-[DTPA]-dimeglumine. Dendrimer conjugate contrast agents prepared from PAMAM-G2D, DAB-G3D, and DAB-G2D dendrimers were excreted rapidly and may be acceptable for use in clinical applications.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
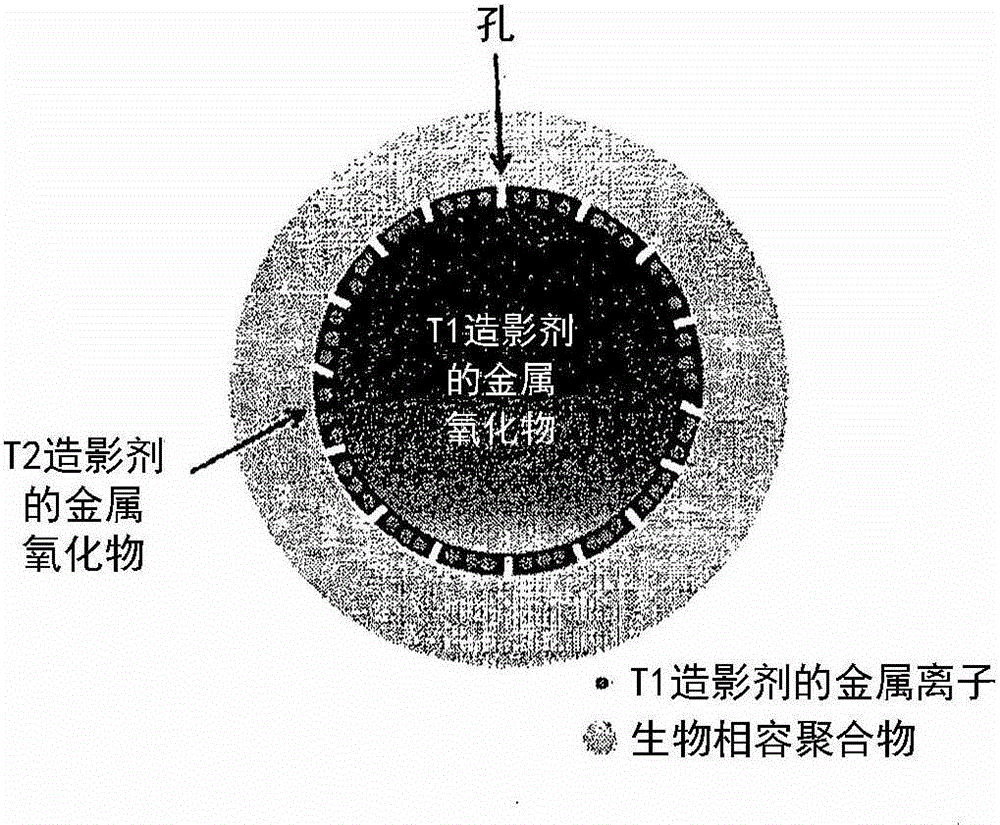
Metal oxide nanoparticle-based t1-t2 dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent
ActiveCN105188772AControl physical sizeControl formLiquid surface applicatorsInorganic non-active ingredientsDiseaseMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent, particularly a metal oxide nanoparticle-based T1-T2 dual-mode MRI contrast agent that can be used not only as a T1 MRI contrast agent but also as a T2 MRI contrast agent, and a method for producing the same. The metal oxide nanoparticle-based T1-T2 dual-mode MRI contrast agent can provide more accurate and detailed information associated with disease than single MRI contrast agent by the beneficial contrast effects in both T1 imaging with high tissue resolution and T2 imaging with high feasibility on detection of a lesion.
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Paramagnetic Complexes with Pendant Crown Compounds Showing Improved Targeting- Specificity as MRI Contrast Agents
InactiveUS20090104124A1Favorable exchange lifetimePromisingBiocideGenetic material ingredientsSolubilityMRI contrast agent
Potential magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents that are functionalized with crown compounds have been synthesized, and show target-specificity to the kidney and liver, along with excellent water solubility, high MR intensity enhancement efficiency, long resident lifetime, low dosage requirement, low cytotoxicity and prolonged excretion rate.
Owner:UNIV HONG KONG THE
Dual-Modality PET/MRI Contrast Agents
InactiveUS20110123439A1Improve imaging effectImprove magnetic propertiesPowder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsDiseaseMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates a dual-modality PET (positron emission tomography) / MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast agent, a hybrid nanoparticle comprising: (a) a magnetic signal generating core; (b) a water-soluble multi-functional ligand coated on the signal generating core; and (c) a positron emitting factor linked to the water-soluble multi-functional ligand. The contrast agent of the present invention is the dual-modality contrast agent enabling to perform PET and MR imaging and can effectively obtain images having the merits of PET (excellent sensitivity and high temporal resolution) and MR (high spatial resolution and anatomical information) imaging. The contrast agent of the present invention is very useful for non-invasive and highly sensitive real-time fault-free imaging of various biological events such as cell migration, diagnosis of various diseases (e.g., cancer diagnosis) and drug delivery.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV +1
Paramagnetic complexes with pendant crown compounds showing improved targeting-specificity as MRI contrast agents
InactiveUS20060057071A1High yieldHigh regional selectivityIron organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsSolubilityMRI contrast agent
Potential magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents that are functionalized with crown compounds have been synthesized, and show target-specificity to the kidney and liver, along with excellent water solubility, high MR intensity enhancement efficiency, long resident lifetime, low dosage requirement, low cytotoxicity and prolonged excretion rate.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for preparing supermolecule capsule with multiple drug release stimulation and MRI radiography ability
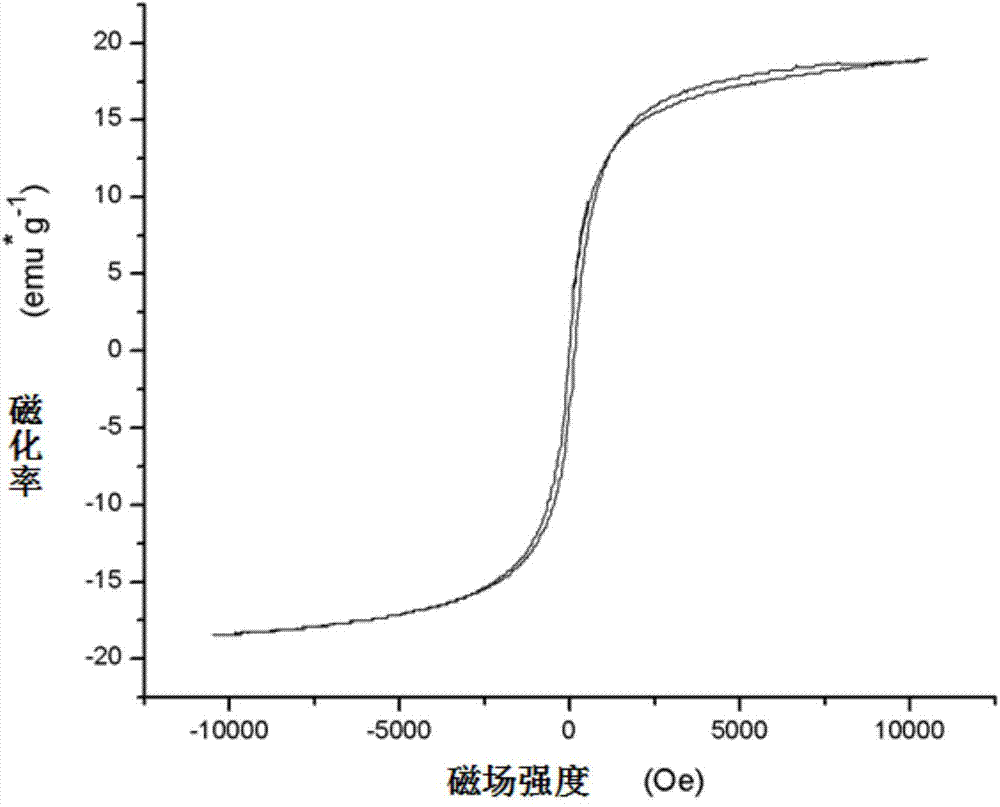
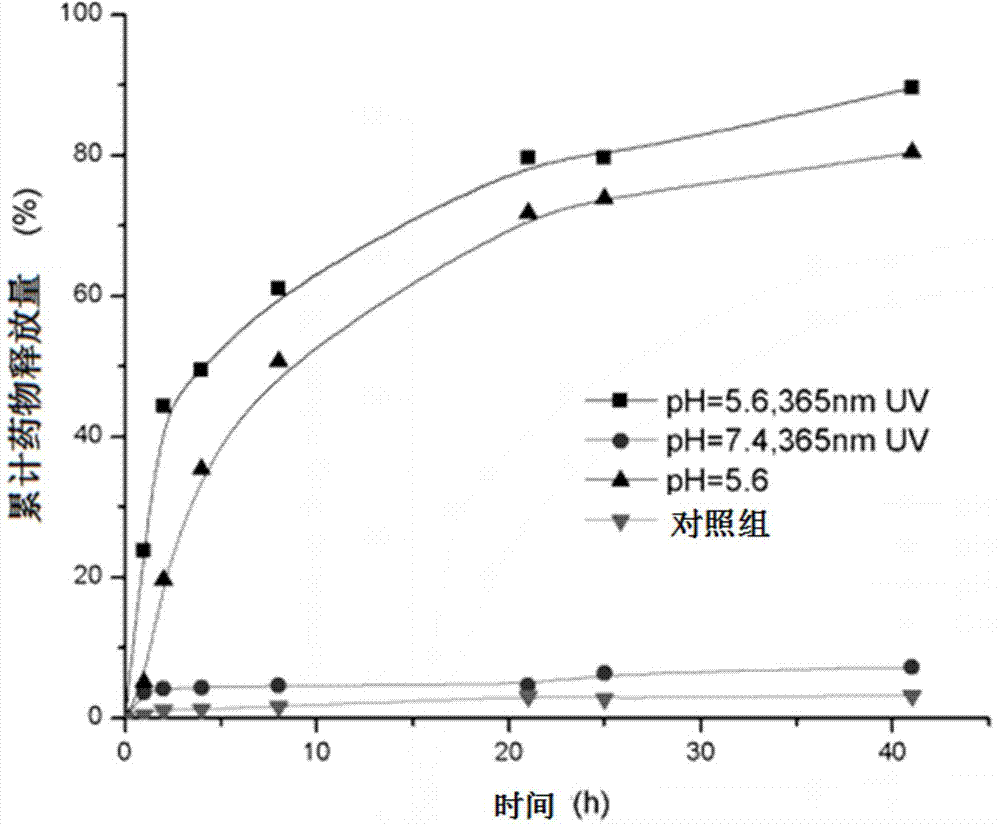
InactiveCN104758955AGood biocompatibilityGood superparamagneticEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMRI contrast agentSuperparamagnetism
The invention discloses a method for preparing a supermolecule capsule with multiple drug release stimulation and MRI radiography ability. A ferroferric oxide microcapsule is prepared as a novel multifunctional magnetic resonance noise and drug therapy medicament through a layer-by-layer self-assembly technology. Through the host-guest interaction and the Coulomb interaction of different supramolecular polymers, the medicine molecule is controllably released through the non-invasive ultraviolet radiation distributed azobenzene isomerism and the acid response Schiff base. Additionally the magnetic-targeted MRI contrast agent is obtained by encapsulating the superparamagnetic ferroferric oxide granule. The r2 relaxation rate of the microcapsule is increased by 37% to reach 125.71 mM-1S-1 compared with that of the neutral condition (92.02mM-1S-1) through the stimulation of subacidity (pH=5.6).
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com