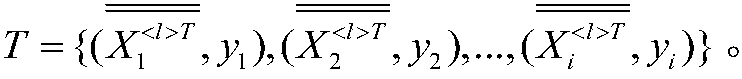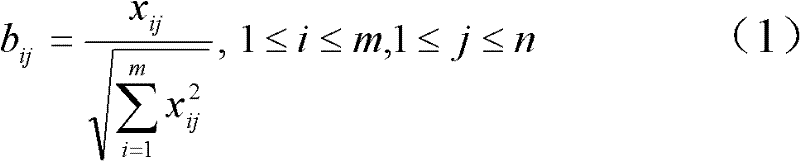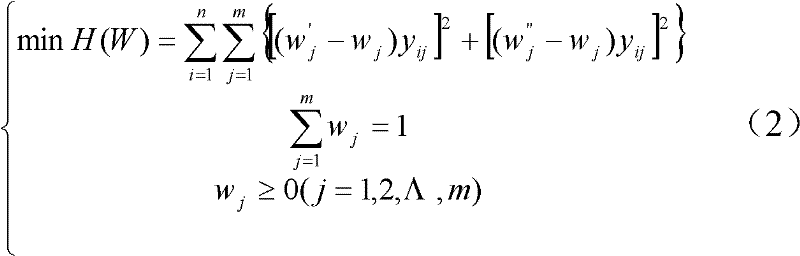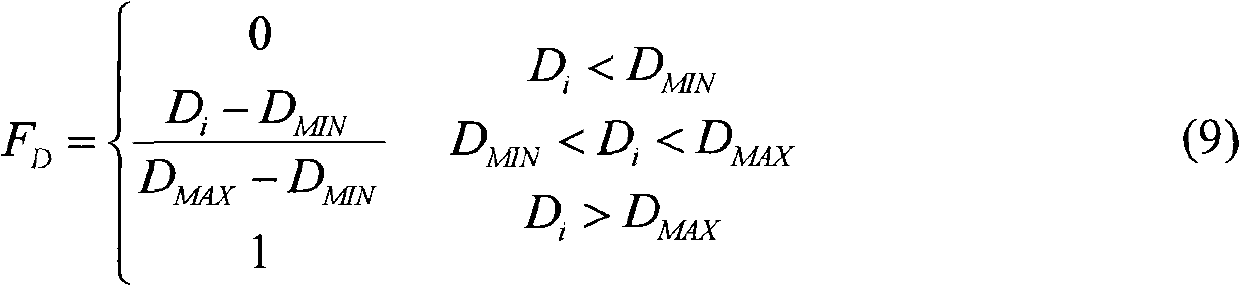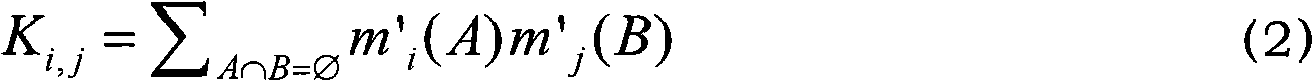Patents
Literature
1273 results about "Decision model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
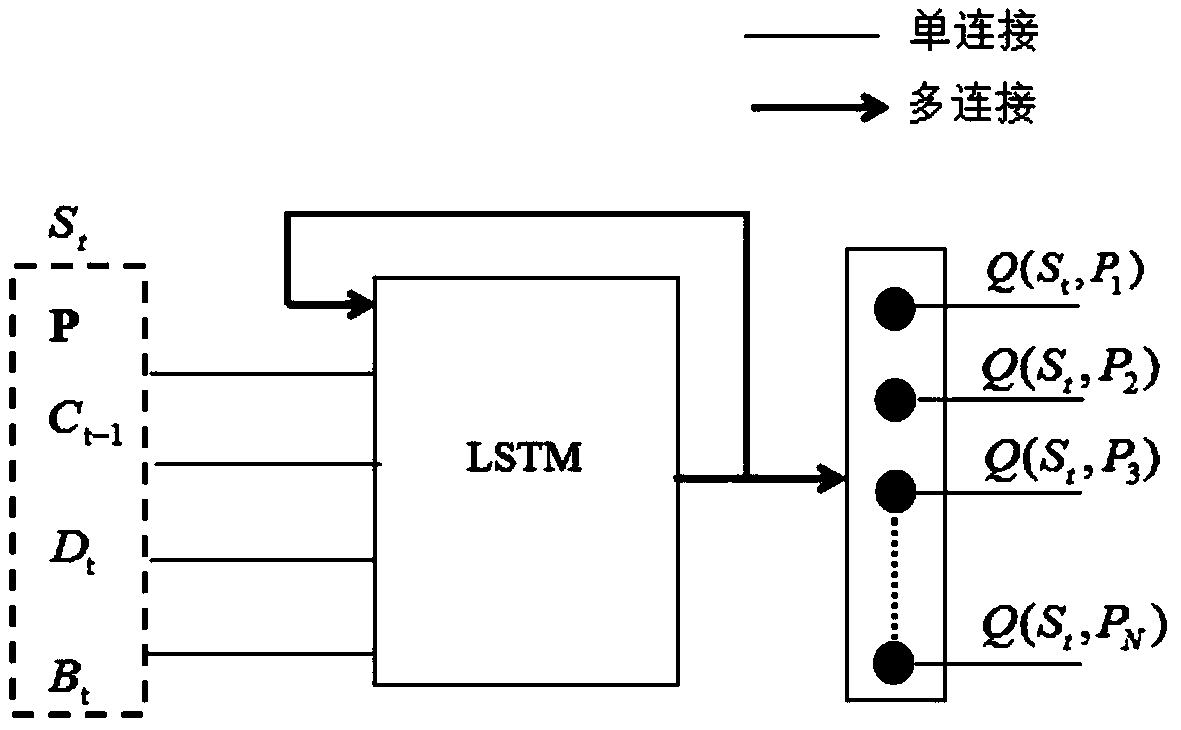
A decision method is a formal (axiomatic) system, starting with a decision model, that contains at least one action axiom. An action is of the form "IF <this> is true, THEN do <that>". An action axiom tests a condition (antecedent) and, if the condition has been met, then (consequent) it suggests (mandates) an action: from knowledge to action. A decision model may also be a network of connected decisions, information and knowledge that represents a decision-making approach that can be used repeatedly (such as one developed using the Decision Model and Notation standard).
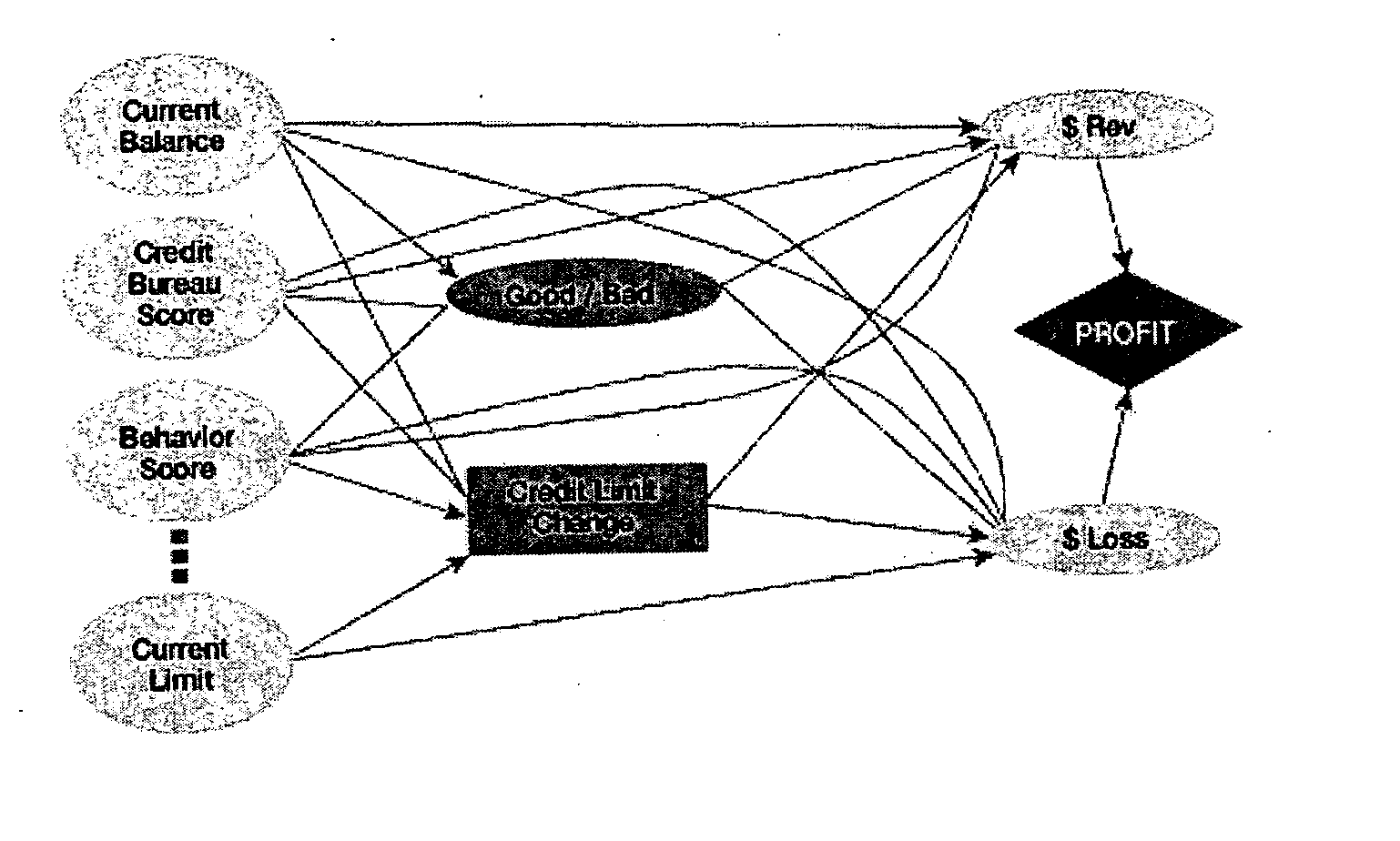
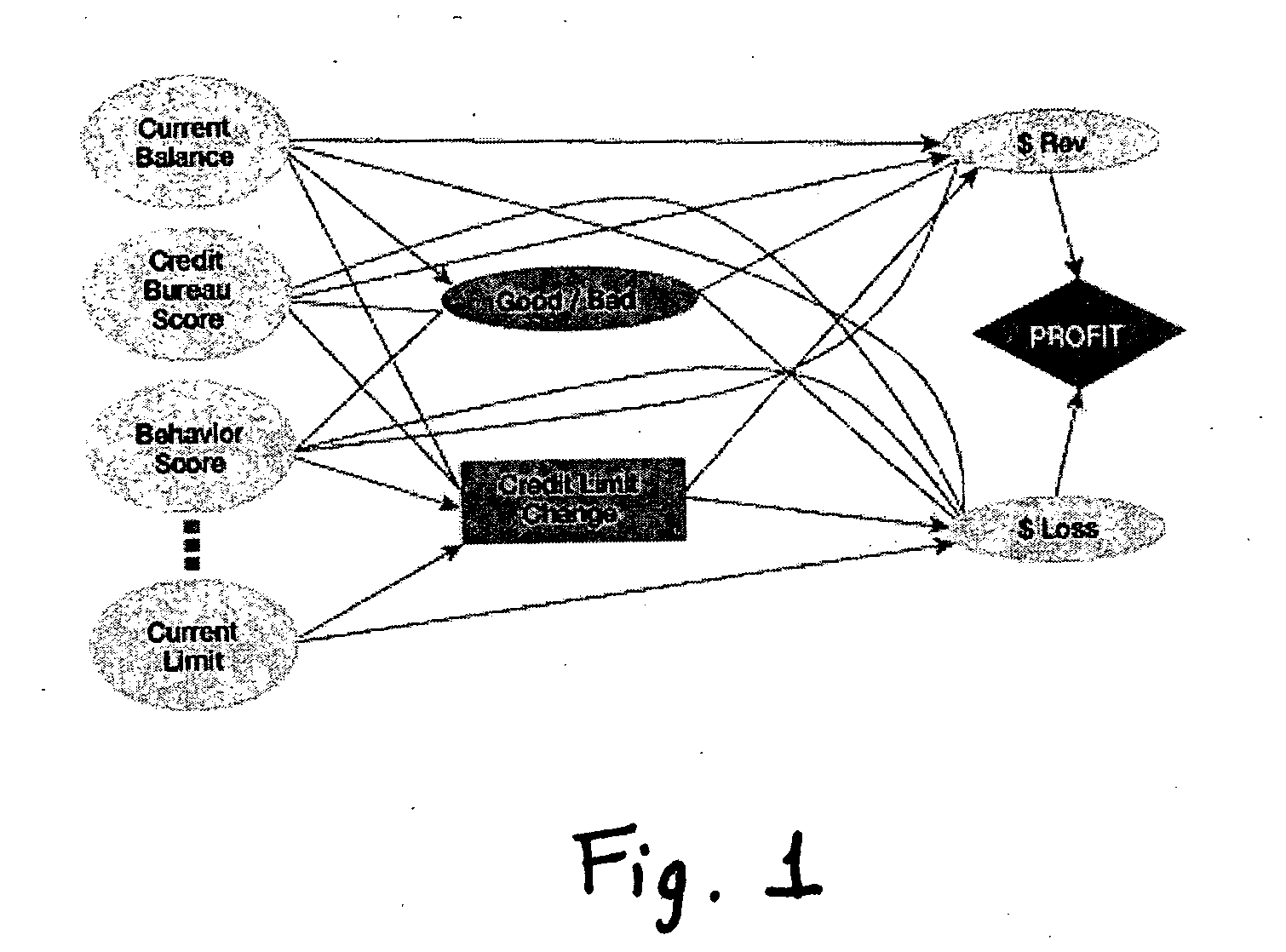
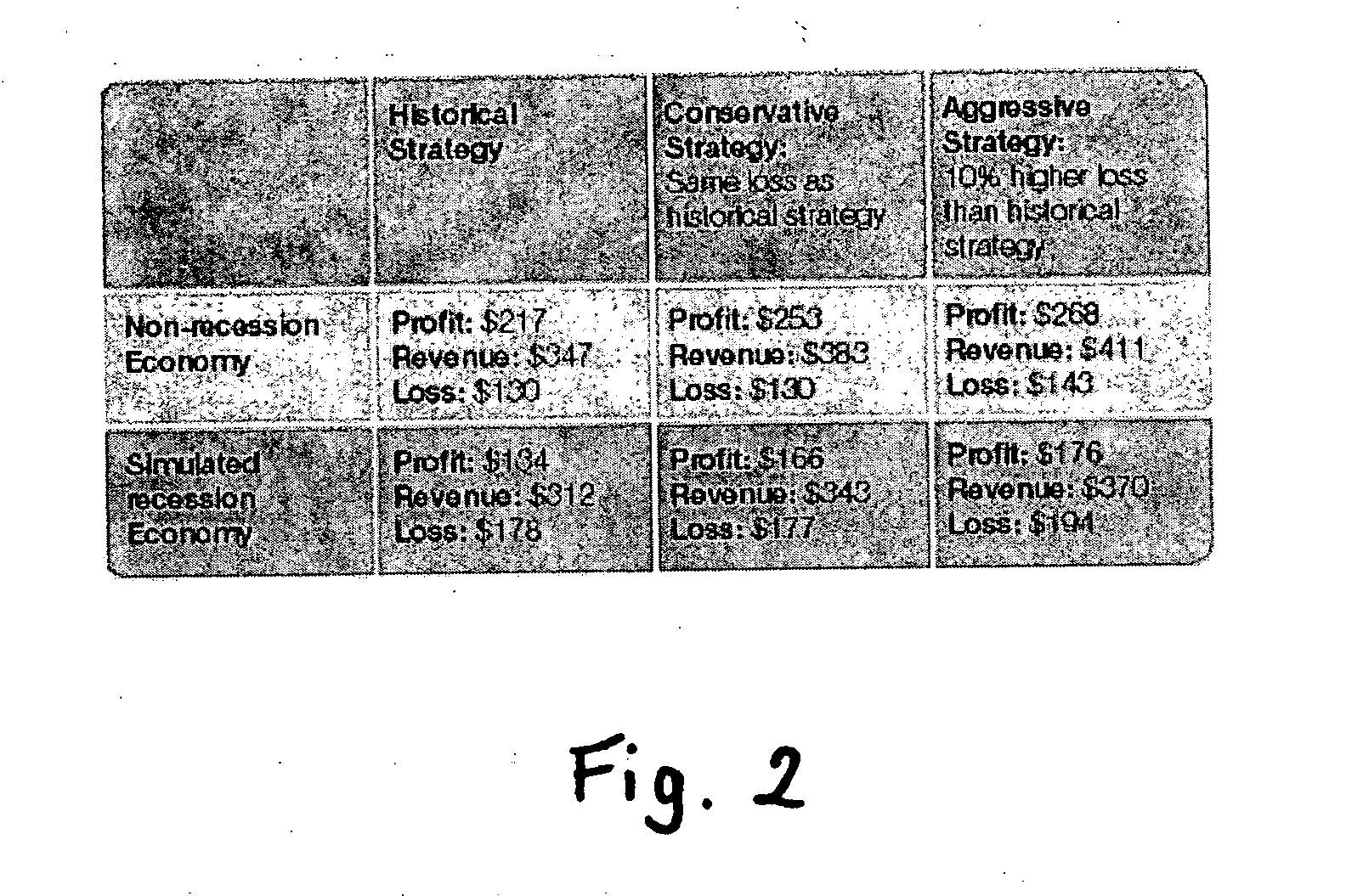
Method and apparatus for creating and evaluating strategies
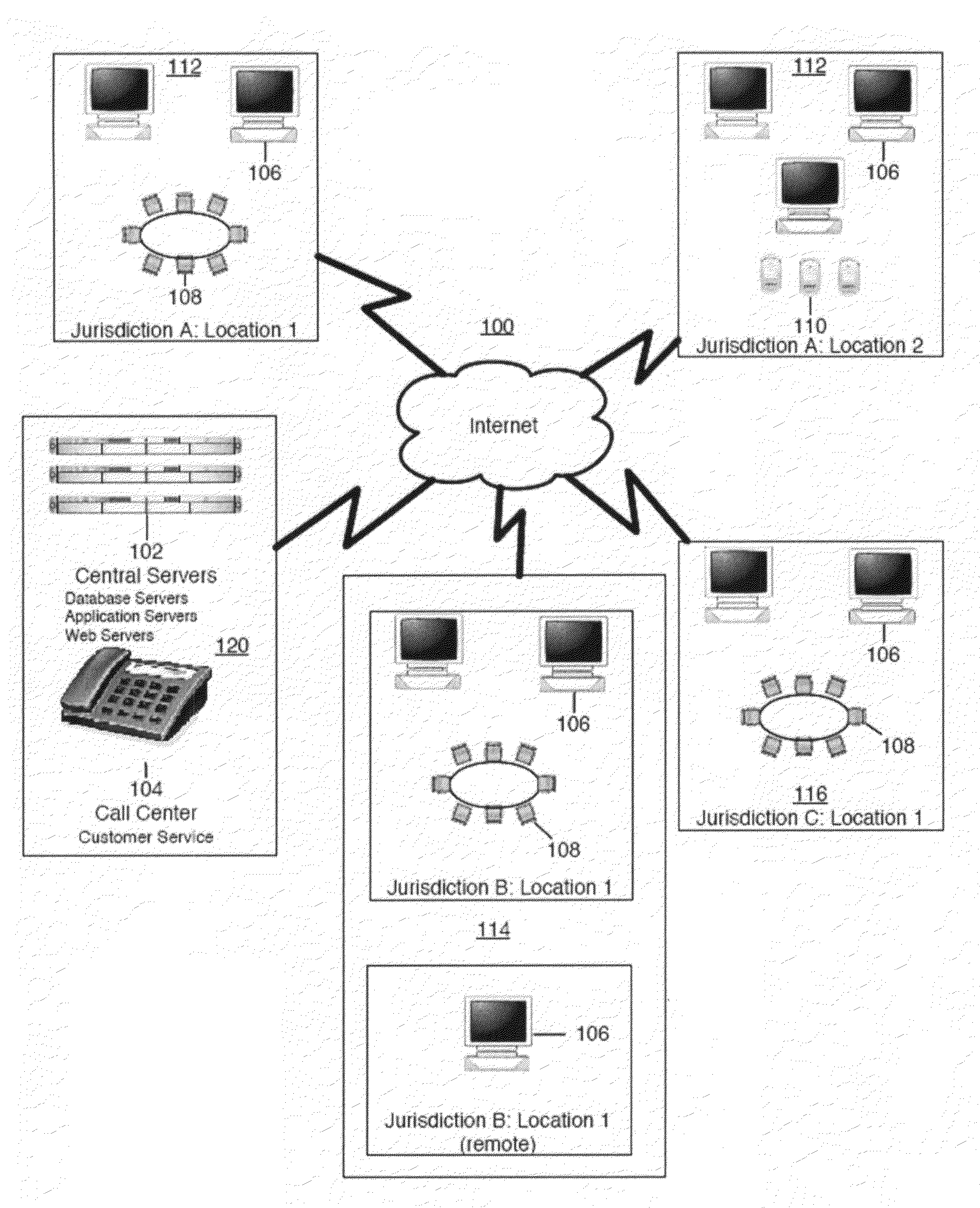
A method and apparatus for strategy science methodology involving computer implementation is provided. The invention includes a well-defined set of procedures for carrying out a full range of projects to develop strategies for clients. One embodiment of the invention produces custom consulting projects that are found at one end of the full range of projects. At the other end of the range are, for example, projects developing strategies from syndicated models. The strategies developed are for single decisions or for sequences of multiple decisions. Some parts of the preferred embodiment of the invention are categorized into the following areas: Team Development, Strategy Situation Analysis, Quantifying the Objective Function, Data Request and Reception, Data Transformation and Cleansing, Decision Key and Intermediate Variable Creation, Data Exploration, Decision Model Structuring, Decision Model Quantification, An Exemplary Score Tuner, Strategy Creation, An Exemplary Strategy Optimizer, An Exemplary Uncertainty Estimator, and Strategy Testing. Each of the sub-categories are described and discussed in detail under sections of the same headings. The invention uses judgment in addition to data for developing strategies for clients.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
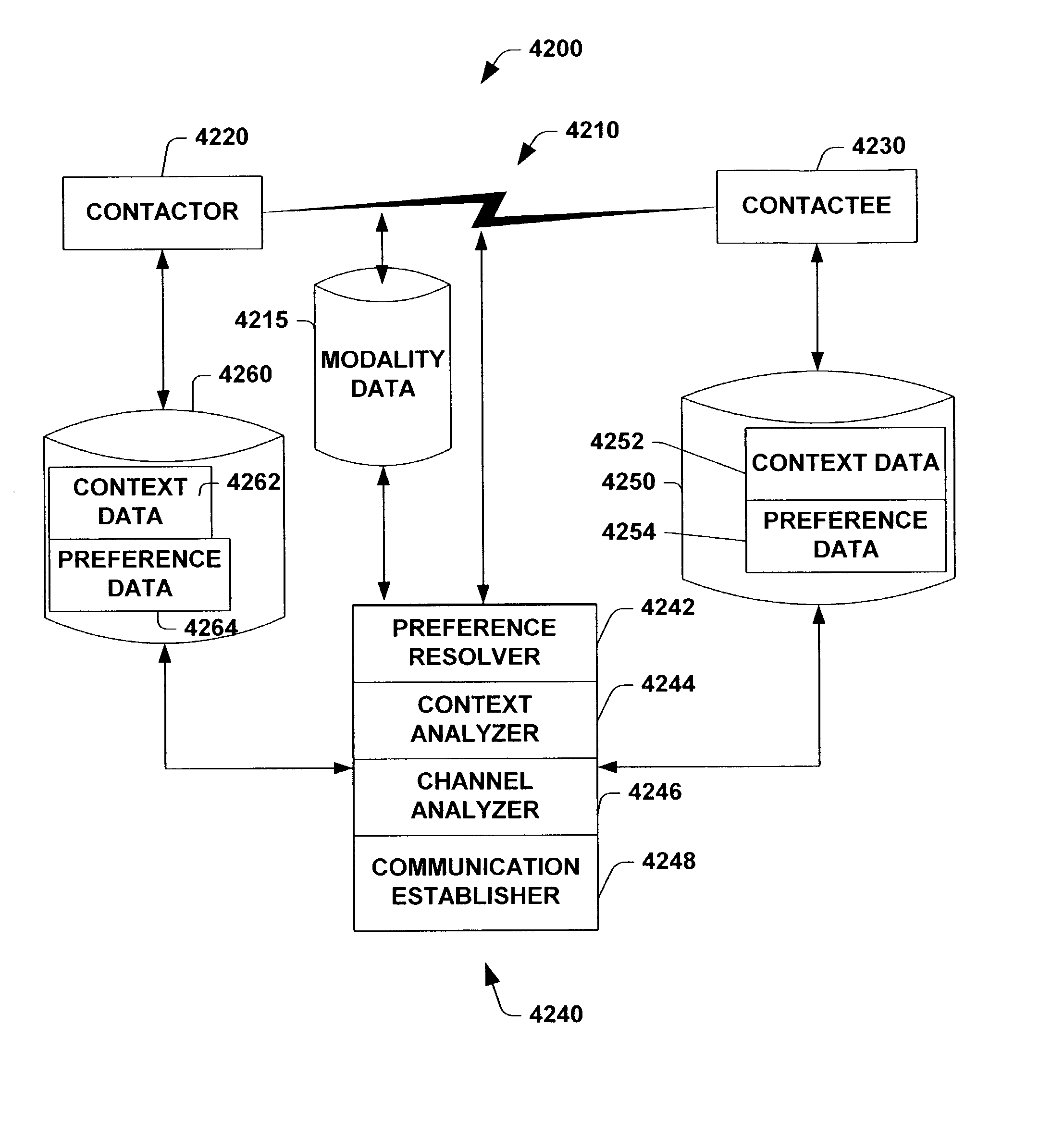
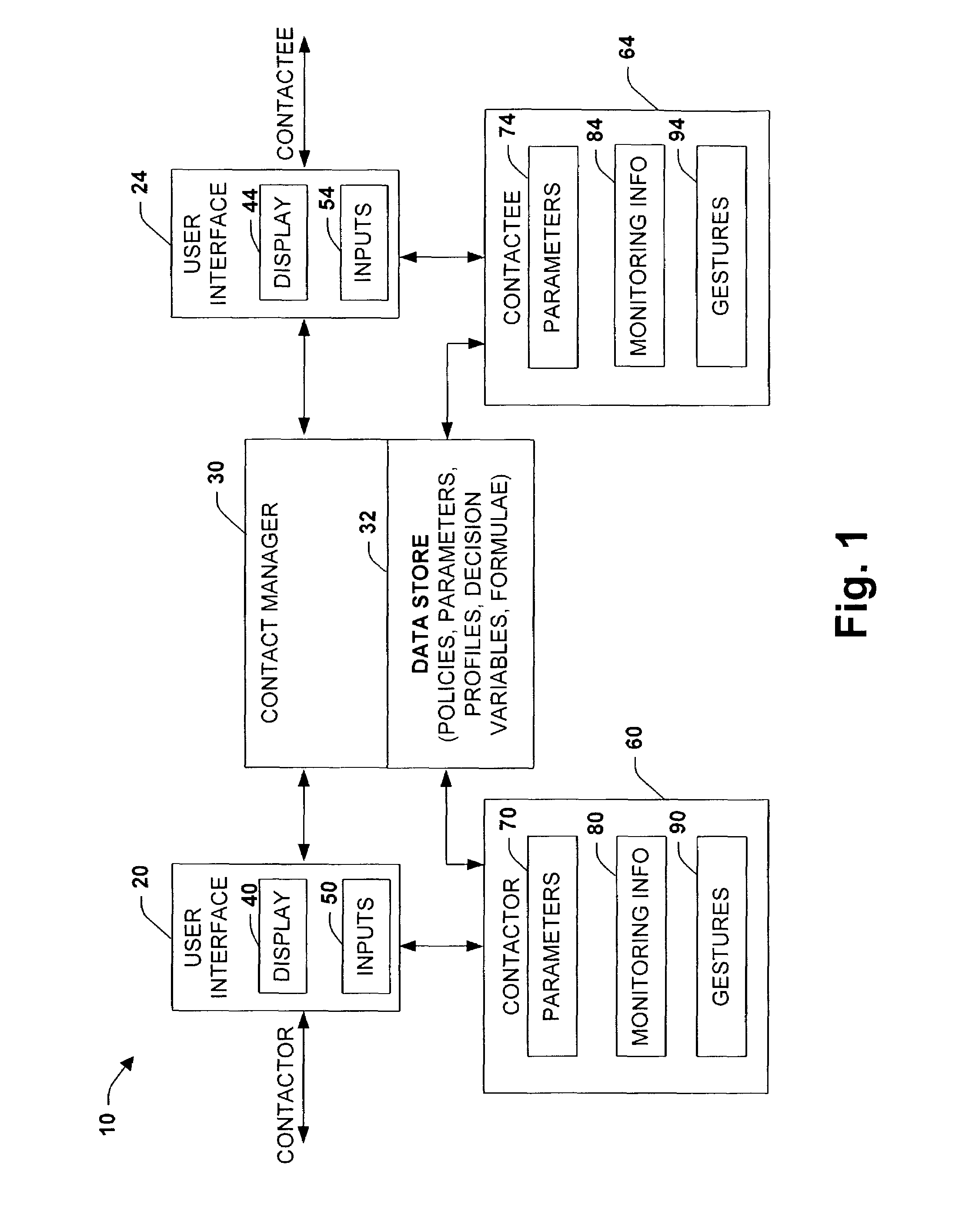
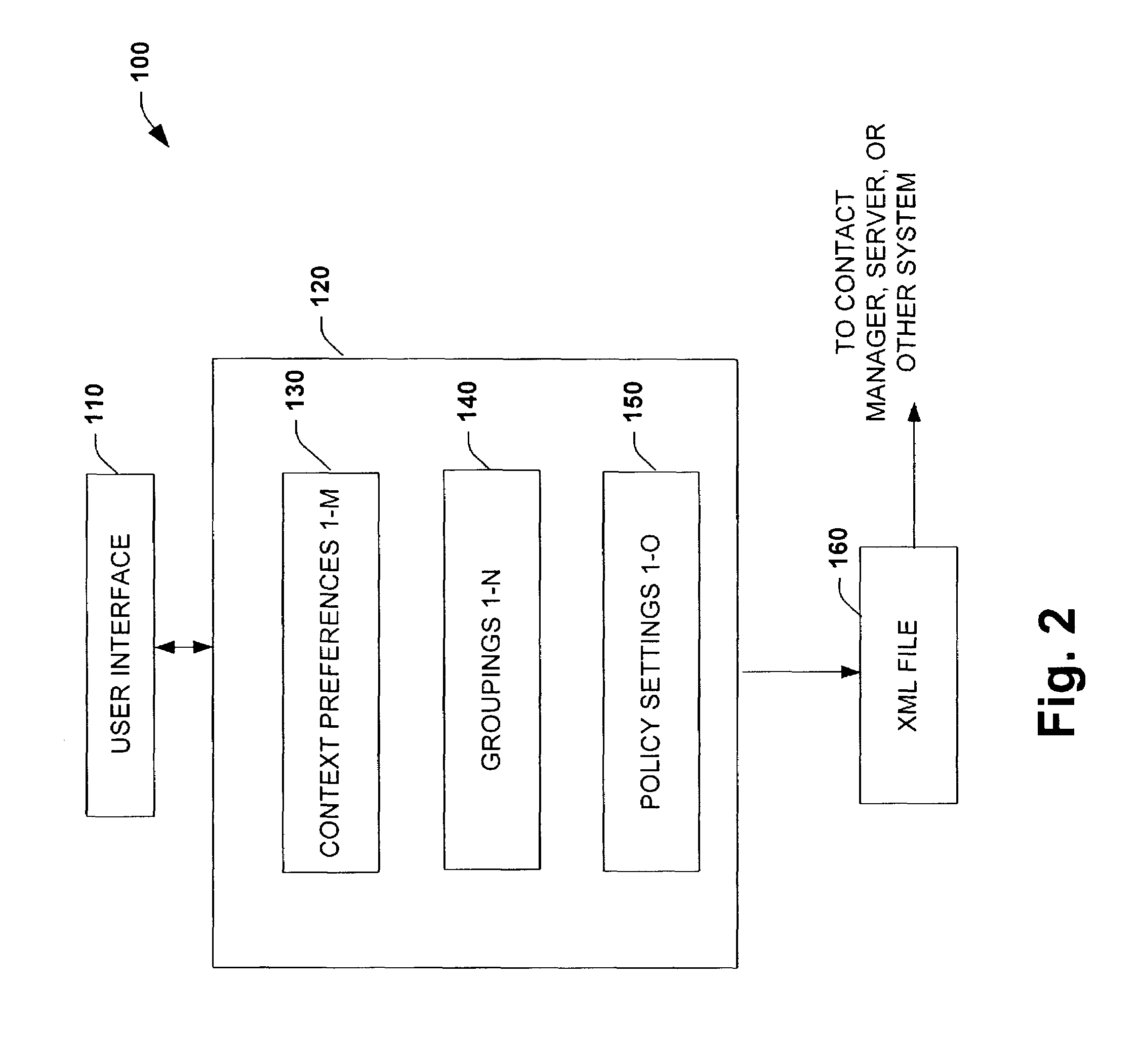
Representation, decision models, and user interface for encoding managing preferences, and performing automated decision making about the timing and modalities of interpersonal communications
InactiveUS7330895B1Increase and decrease likelihoodIncreasing and decreasing effectInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersPersonalizationDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The present invention relates to a system and methodology providing a user interface that can be employed by contactors and contactees in conjunction with a communications architecture for identifying and establishing an optimal communication based on preferences, capabilities, contexts and goals of the parties to engage in the communication. The user interface can include a graphical display having a plurality of display objects and associated input fields operable by one or more parties to a communication in order to facilitate convenient access, control, personalization and communications via the communications architecture. For example, configuration capabilities are provided in the user interface to enable operational adjustments to one or more operating parameters, communications groupings, policies and / or context preferences relating to a preferred modality of communication and to potential parties of communication between the contactors and contactees. User interface controls are also provided for defining deterministic policies and for encoding preferences for cost-benefit analyses.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
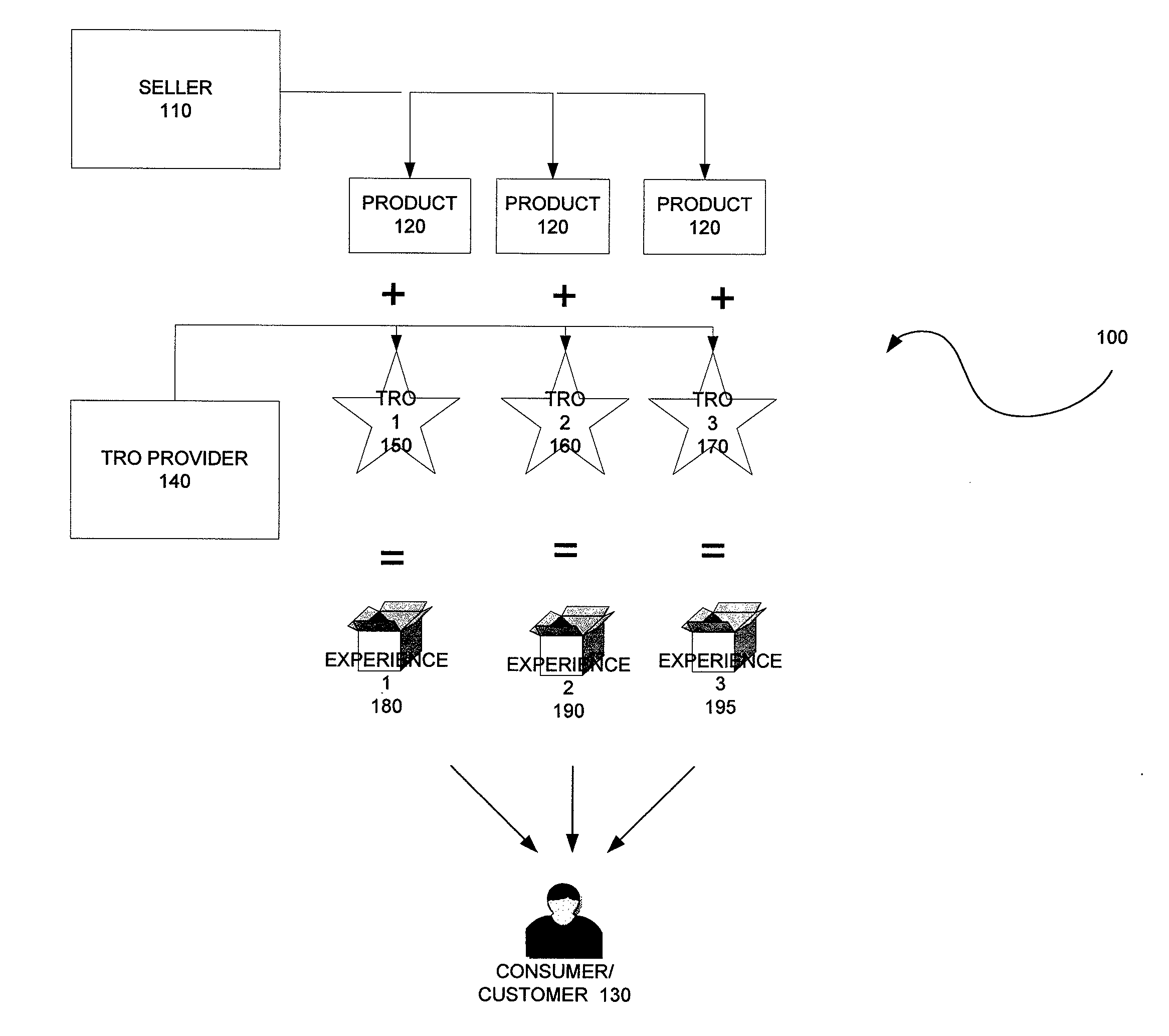
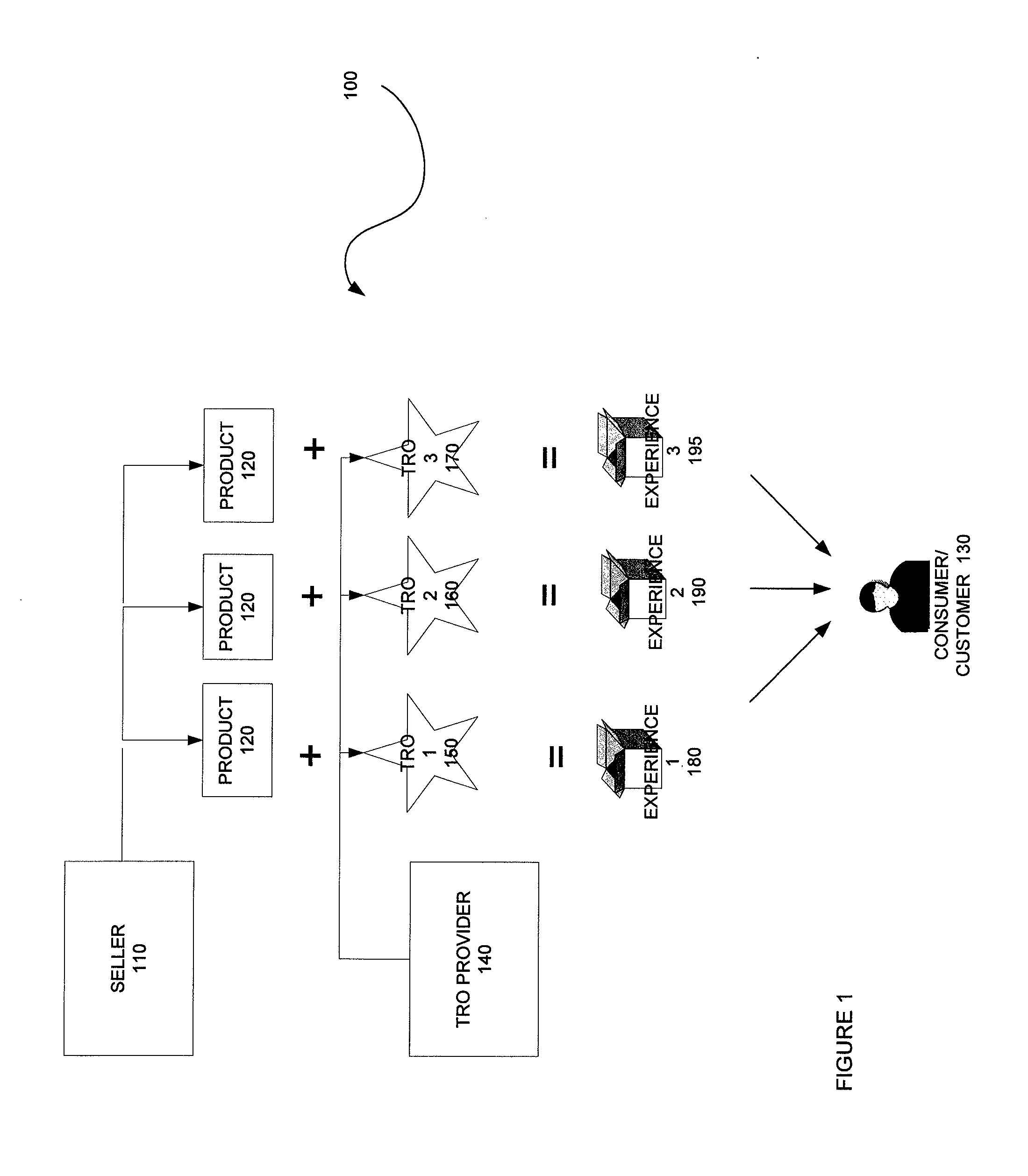
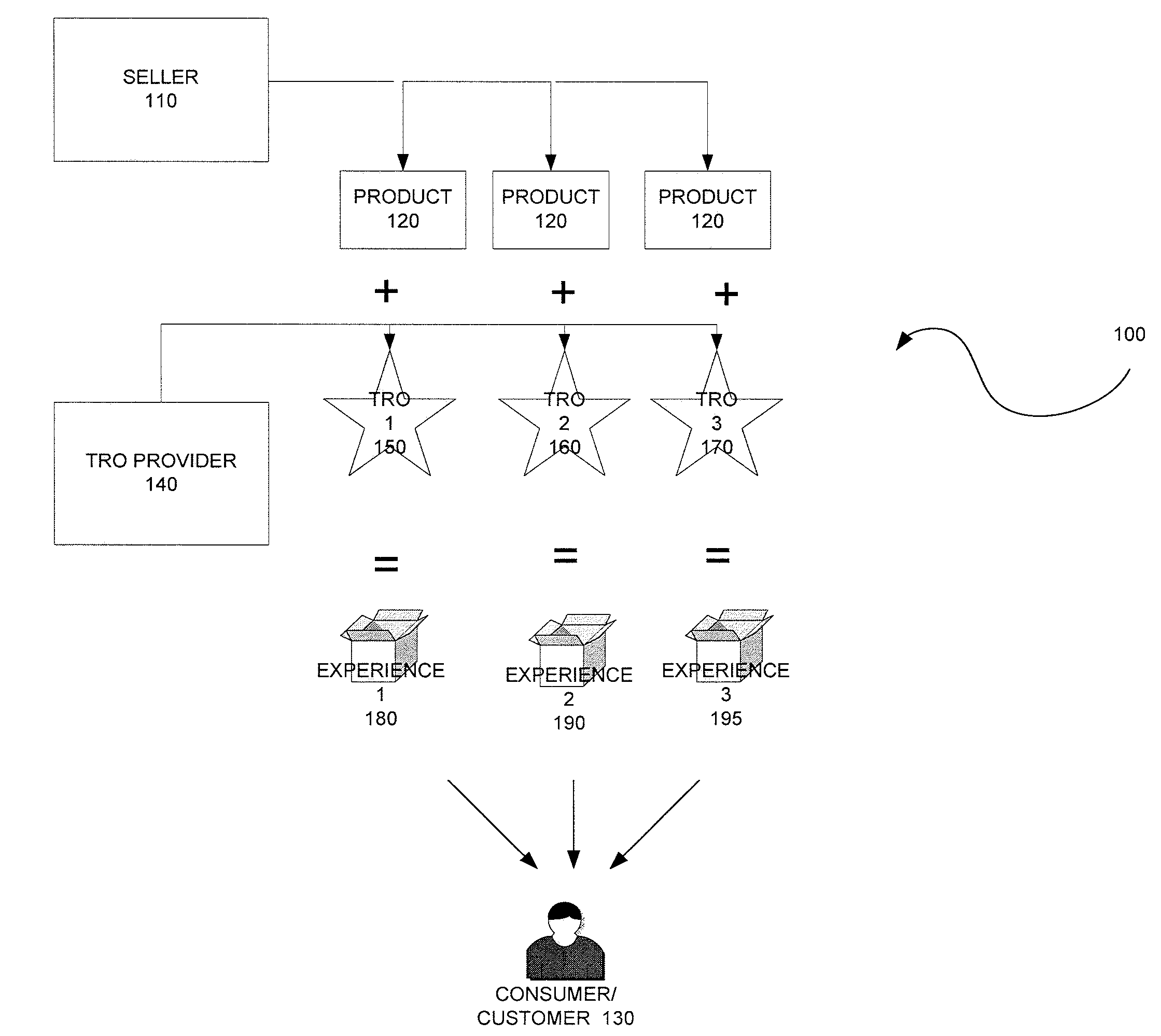
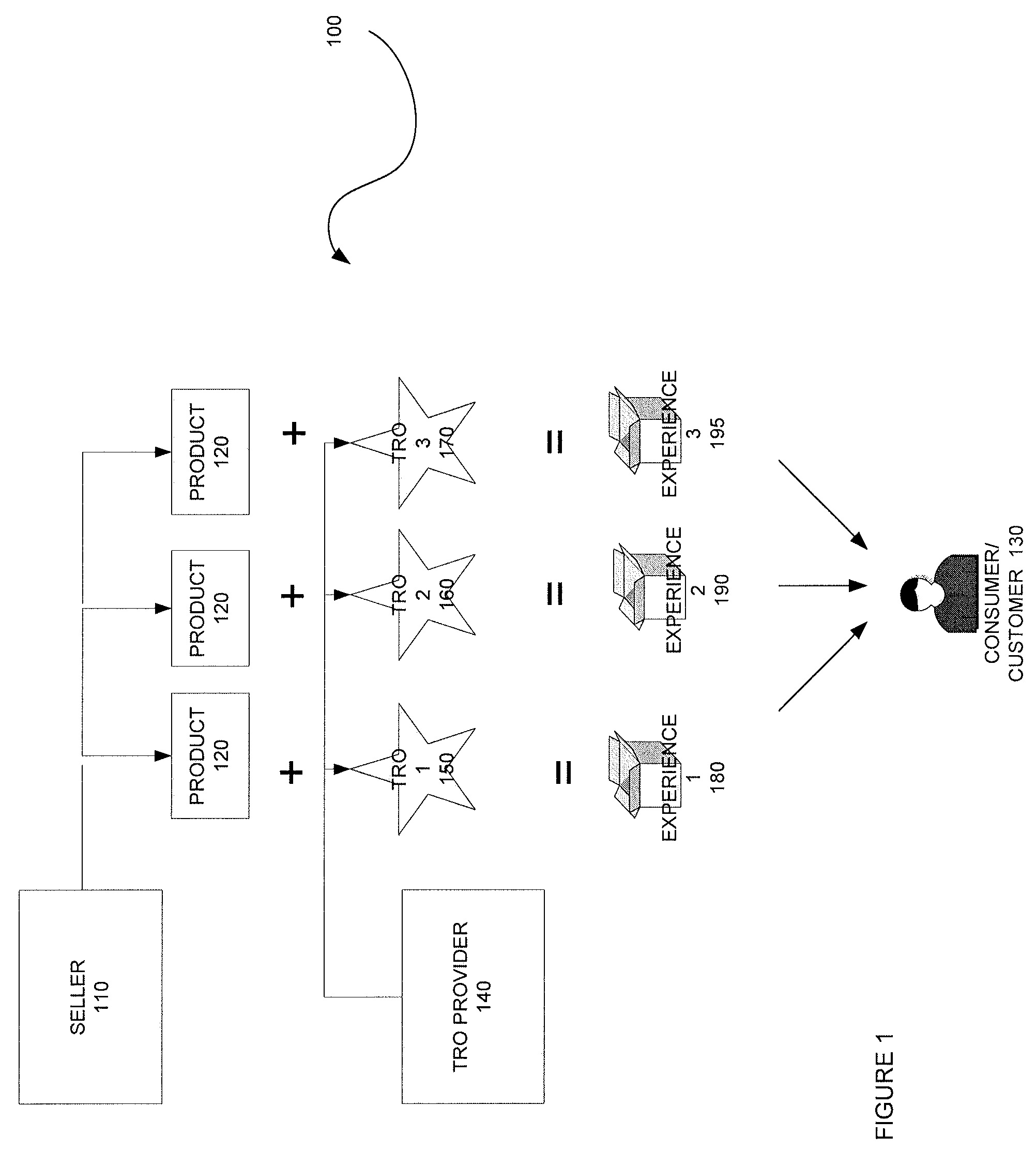
Method, system and components for obtaining, evaluating and/or utilizing seller, buyer and transaction data
ActiveUS20090119160A1Discounts/incentivesSpecial data processing applicationsDecision modelWeb analytics
Methodologies, systems, components and software are provided that perform web analytics to measure visitor to consumer conversion continuously throughout surfing, through conversion and past completion of a purchase on-line. In accordance with at least one embodiment, such methodologies, systems, components and software may be utilized to determine efficacy of a plurality of parameters relating to one or more Transaction Related Offerings (TROs). In accordance with at least one embodiment of the invention, such methodologies, systems, components and software may be utilized to configure one or more Consumer Behavior Decision Models (CBDMs) and / or generate consumer behavior data.
Owner:BUYSAFE
Automated method and system for a gaming opportunity
InactiveUS20080261701A1Reduce manual operationsReduce processing costsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesDecision modelData source
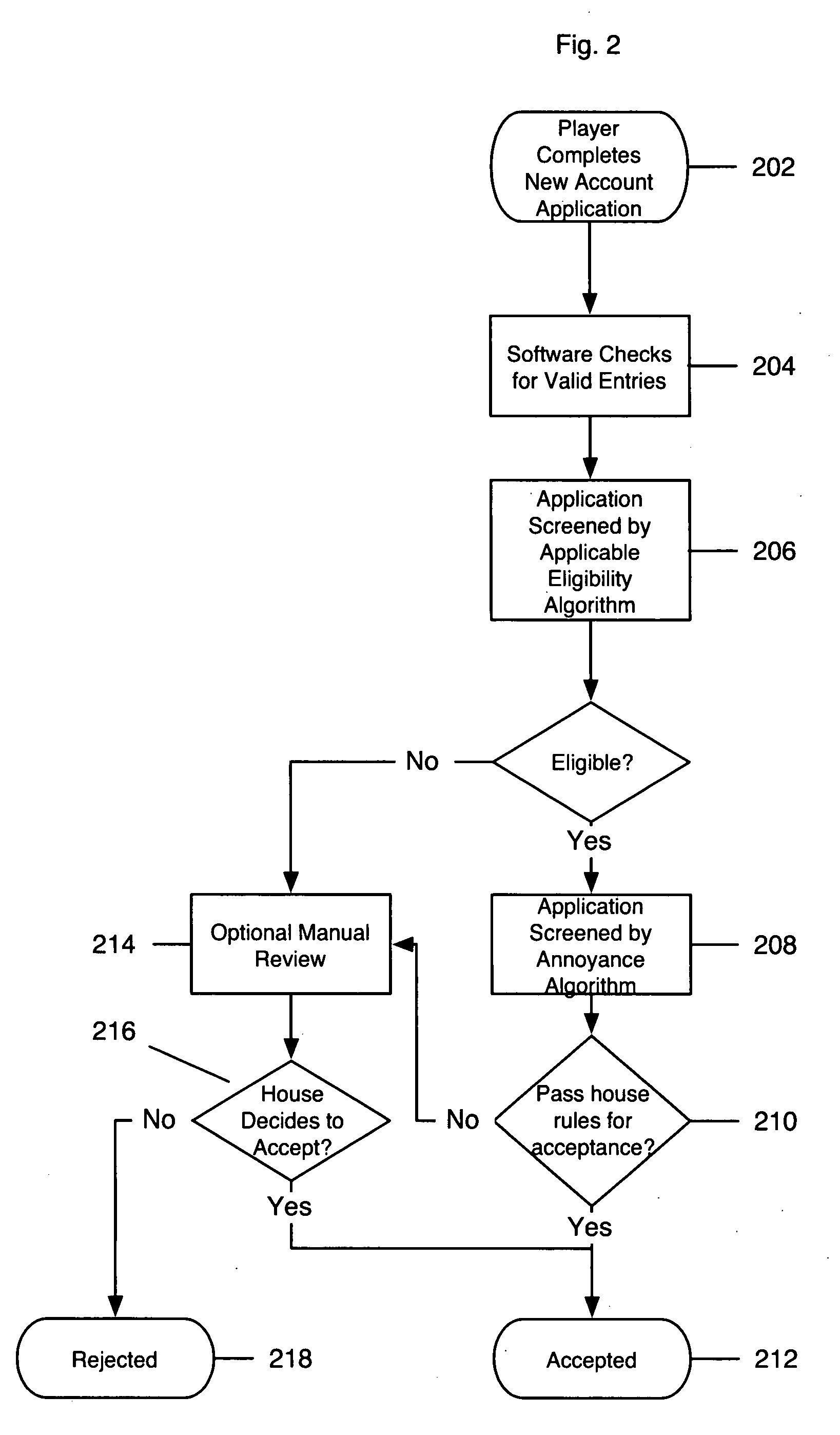
A method and system of screening a player for a gaming opportunity, including obtaining disparate data of a player from a plurality of data sources, weighting the player data based on at least one business rule, and applying the weighted player data to at least one decision model to generate at least one composite score indicative of a scale of eligibility of the player for the gaming opportunity.
Owner:TECH ASSURANCE LAB
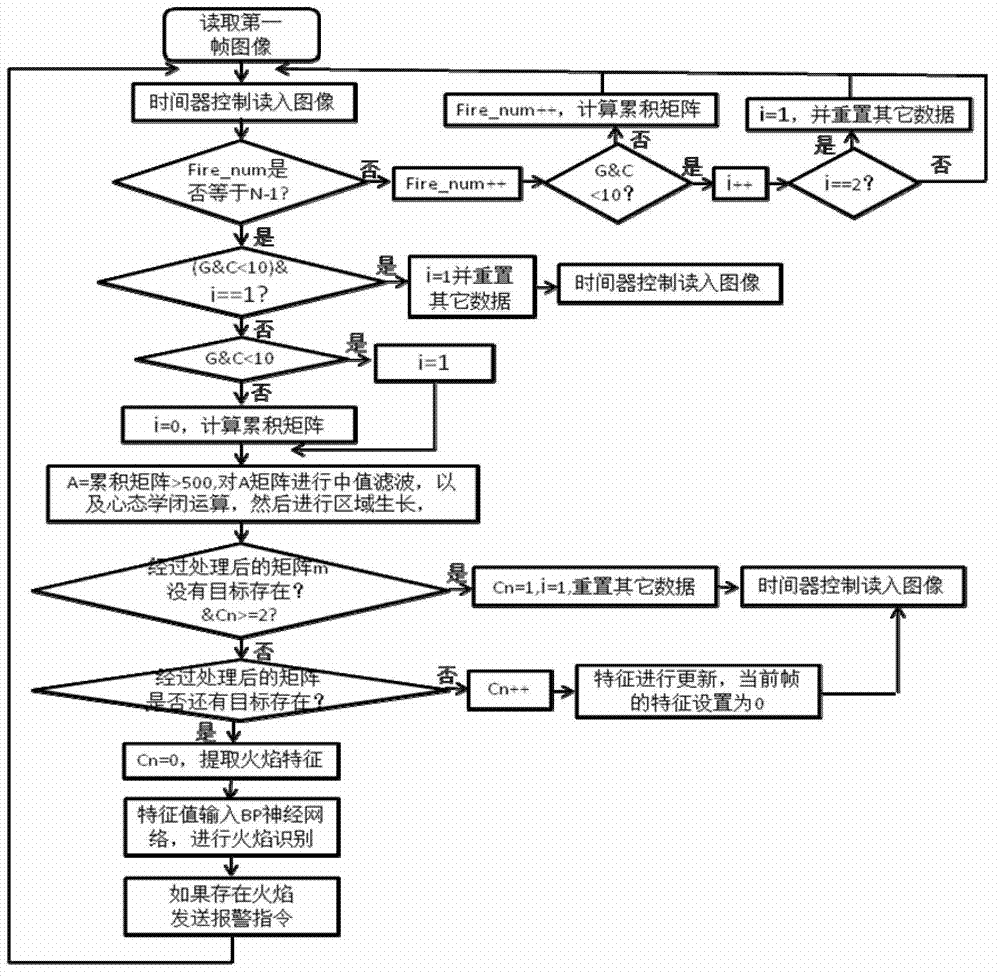
Video flame detecting method based on multi-feature fusion technology
InactiveCN103116746AExcellent capture qualityChoose from a wide range of applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision modelMulti target tracking
The invention provides a video flame detecting method based on a multi-feature fusion technology. The video flame detecting method includes firstly using a cumulative geometrical independent component analysis (C-GICA) method to capture a moving target in combination with a flame color decision model, tracking moving targets in current and historical frames in combination with a multi-target tracking technology based on moving target areas, extracting color features, edge features, circularity degrees and textural features of the targets, inputting the features into a back propagation (BP) neural network, and further detecting flames after the decision of the BP neural network. According to the video flame detecting method, spatial-temporal features of the moving features, color features, textural features and the like are comprehensively applied, the defects of algorithms of existing video flame detecting technologies are overcome, and reliability and applicability of the video flame detecting method are effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
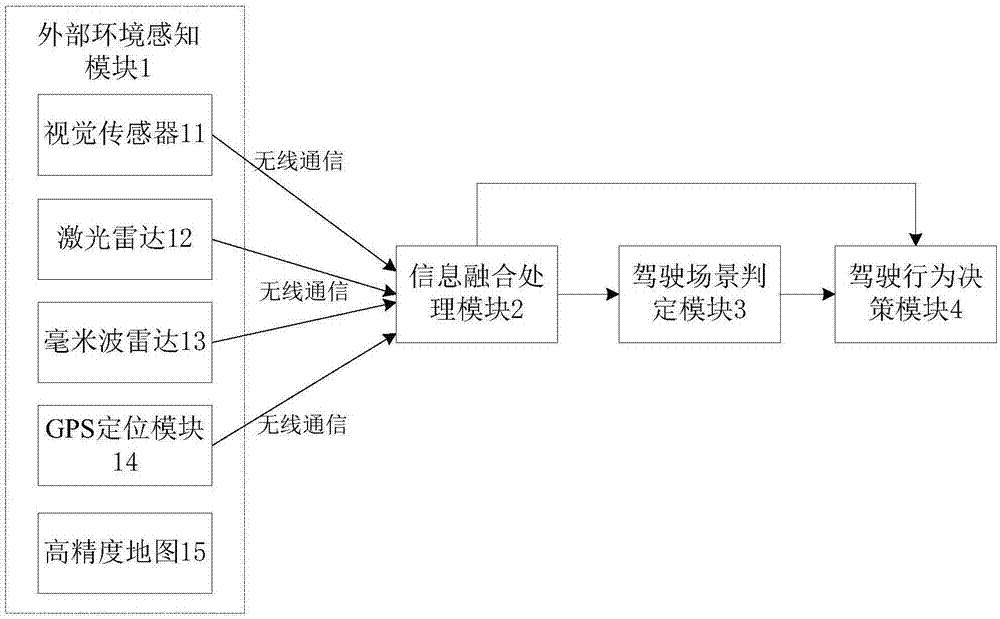
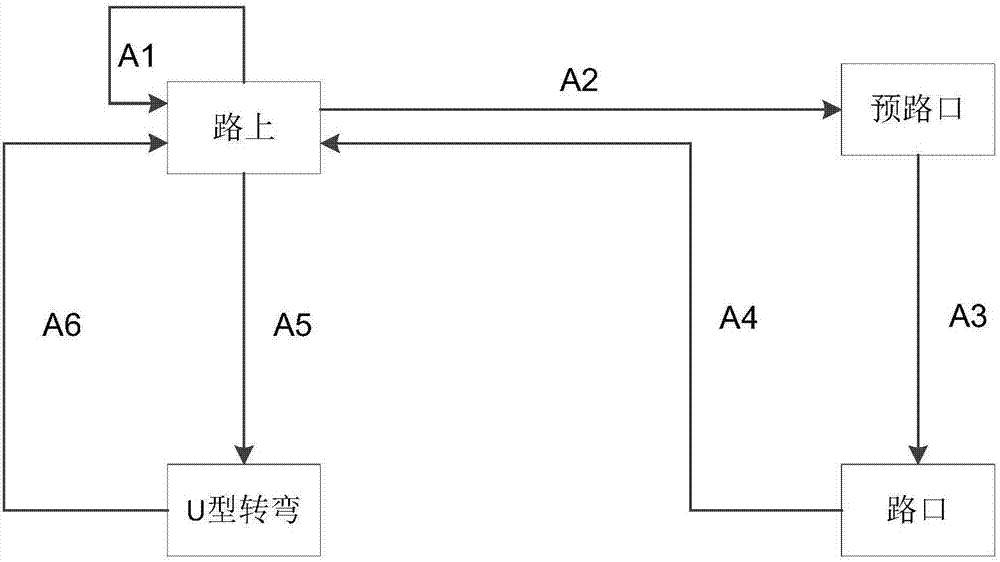
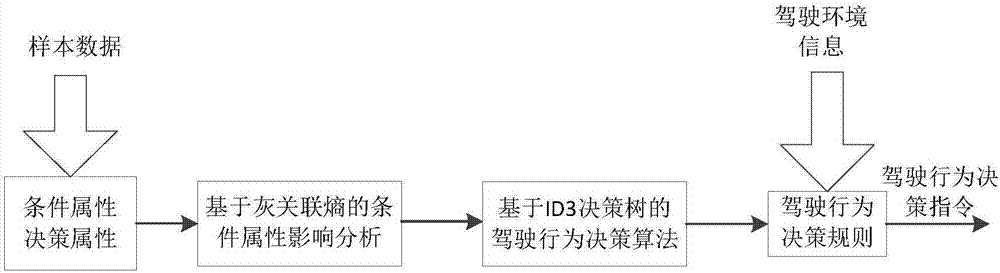
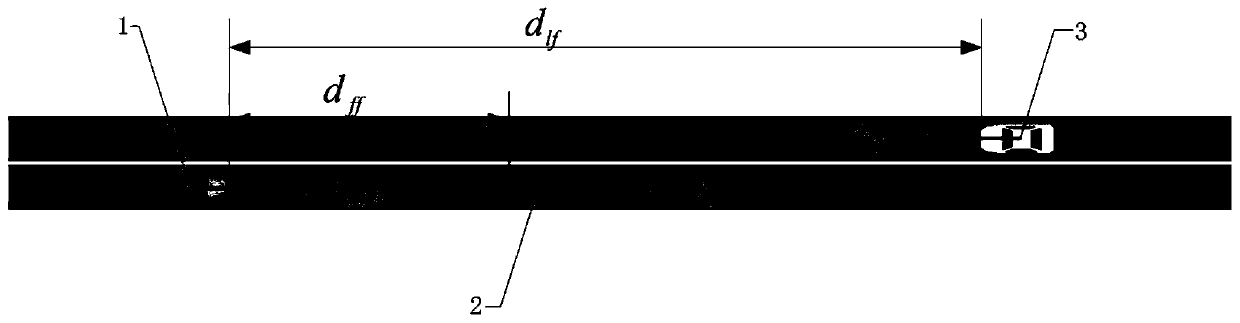
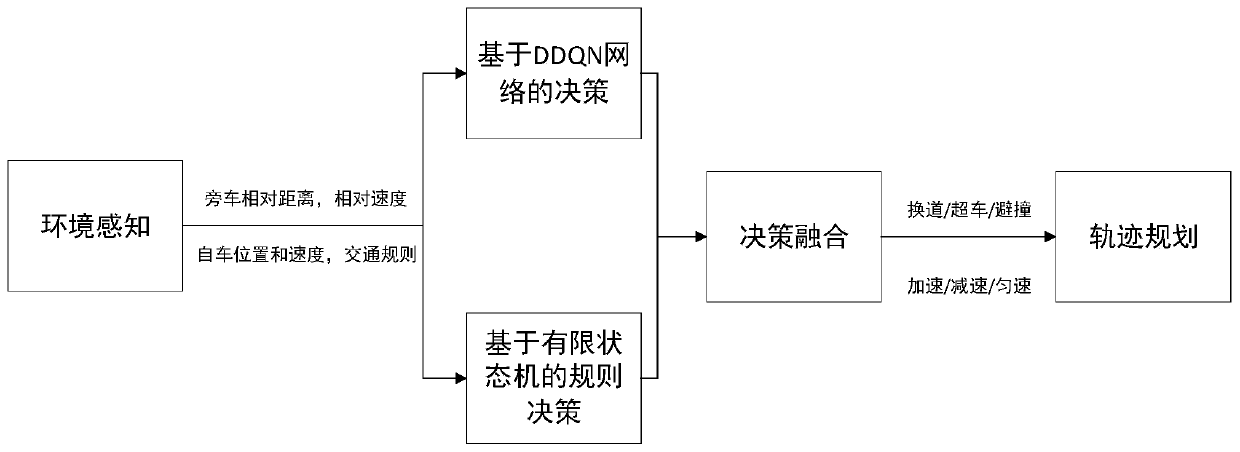
Driving behavior decision system of automatic driving public traffic vehicle
InactiveCN107272687AImprove driving safetyReduce traffic accidentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesDecision modelEngineering
The present invention discloses a driving behavior decision system of an automatic driving public traffic vehicle. The system comprises an external environment perception module, an information fusion processing module, a driving scene determination module and a driving behavior decision module. The external environment perception module comprises a vision sensor, a laser radar, a millimeter wave radar, a GPS location module and a high-precision map. The driving behavior decision module employs a limitation state machine model, and the driving behavior decision module employs a driving behavior determination decision model based on an ID3 decision tree; and the information fusion processing module performs fusion processing of the environment information sent by an external environment perception module and sends the information after fusion processing to the driving scene determination module and the driving behavior decision module. The driving behavior decision system of the automatic driving public traffic vehicle can improve the driving safety of the automatic driving public traffic vehicle and effectively reduce the probability of traffic accidents.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAYLION TECH CO LTD
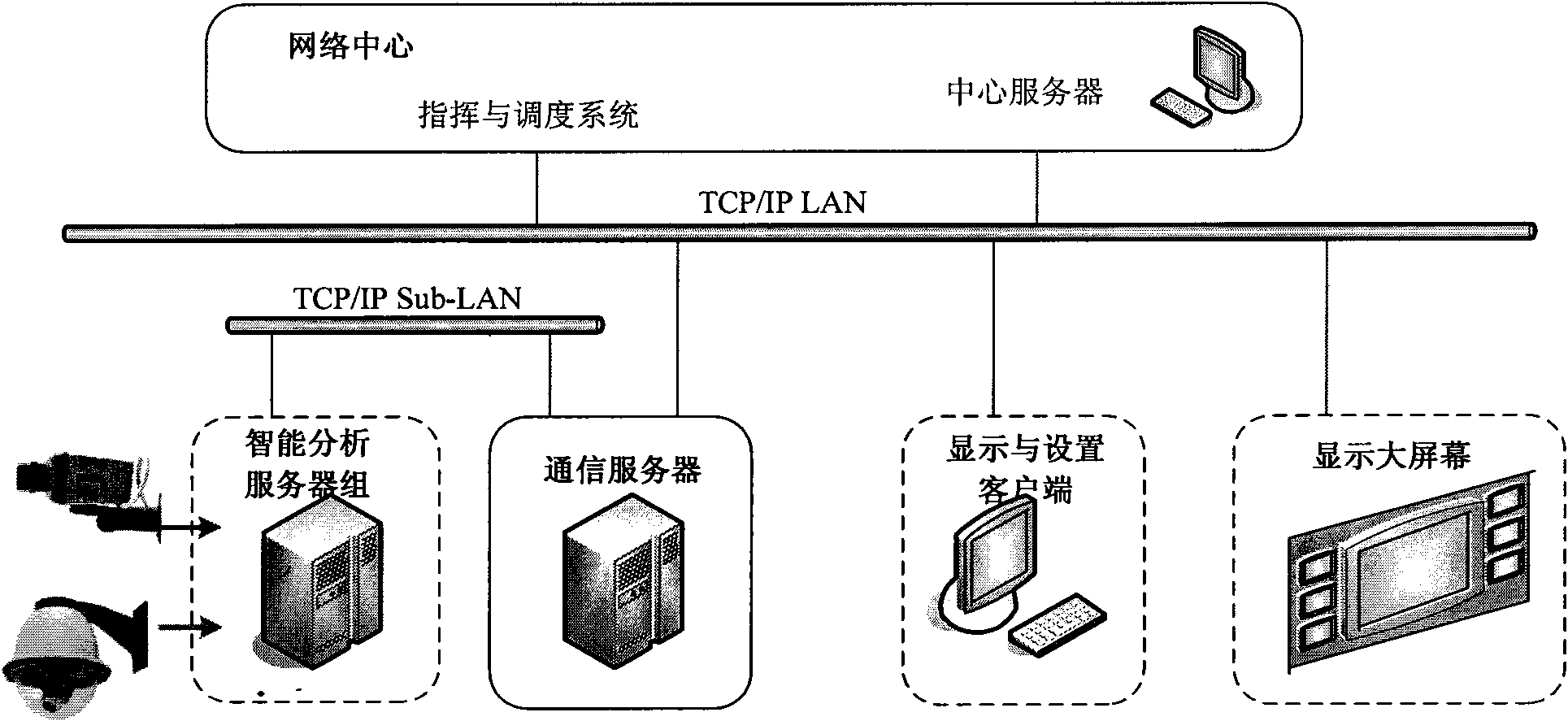
System and method for monitoring crowd situation
The invention relates to a system and a method for monitoring crowd situation. The system comprises a signal acquisition unit, a signal preprocessing unit, a crowd situation analysis center, a client and a transmission network, wherein the crowd situation analysis center is used for comprehensively analyzing feature extraction results output by the signal preprocessing unit to extract the quantity, the density and the flow direction of the crowd in the region, and obtaining a dredging and managing model of the crowd in the monitoring region according to sentiment indexes and congestion spots obtained by estimation; and the client can be used for displaying monitoring signals, preprocessed results of the signal preprocessing unit and comprehensive analysis results of the crowd situation analysis center, and giving an alarm. The technical scheme of the invention can realize the purpose of early warning the crowd congestion situation of important exits and entrances or square regions, then compute a decision model for dredging and managing the crowd in the monitoring regions, and set flow control schemes for different monitoring regions, thus the crowd situation of large public places can be simultaneously displayed, analyzed, responded and processed in real time.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAIYANG TECH CO LTD
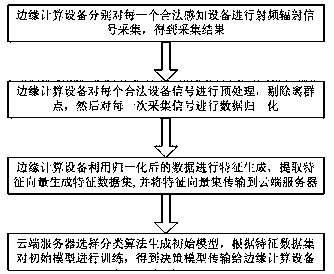
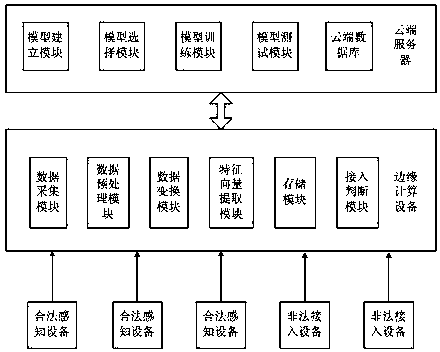
Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing
ActiveCN107770263AReduce computational complexityReduce latencyTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementComputation complexityData set
The invention discloses an Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing. The method comprises the steps that an edge computing device carries out radio frequencyradiation signal collection on each legal sensing device, thereby obtaining collection results; the edge computing device preprocesses each legal device signal, removes outliers and carries out datanormalization on collected signals of each time; the edge computing device generates features through utilization of the normalized data, extracts feature vectors to generate feature data sets and transmits the feature vector sets to a cloud server; and the cloud server selects a classification algorithm to generate a data model, trains the data model according to the feature data sets and transmits an obtained decision-making model to the edge computing device. According to the method and the system, the data processing and access judgment are carried out at the edge computing side, and the method and the system are applicable to an Internet of things device interconnection scheme with limited resources and have the advantages of low computing complexity and high authentication accuracy.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
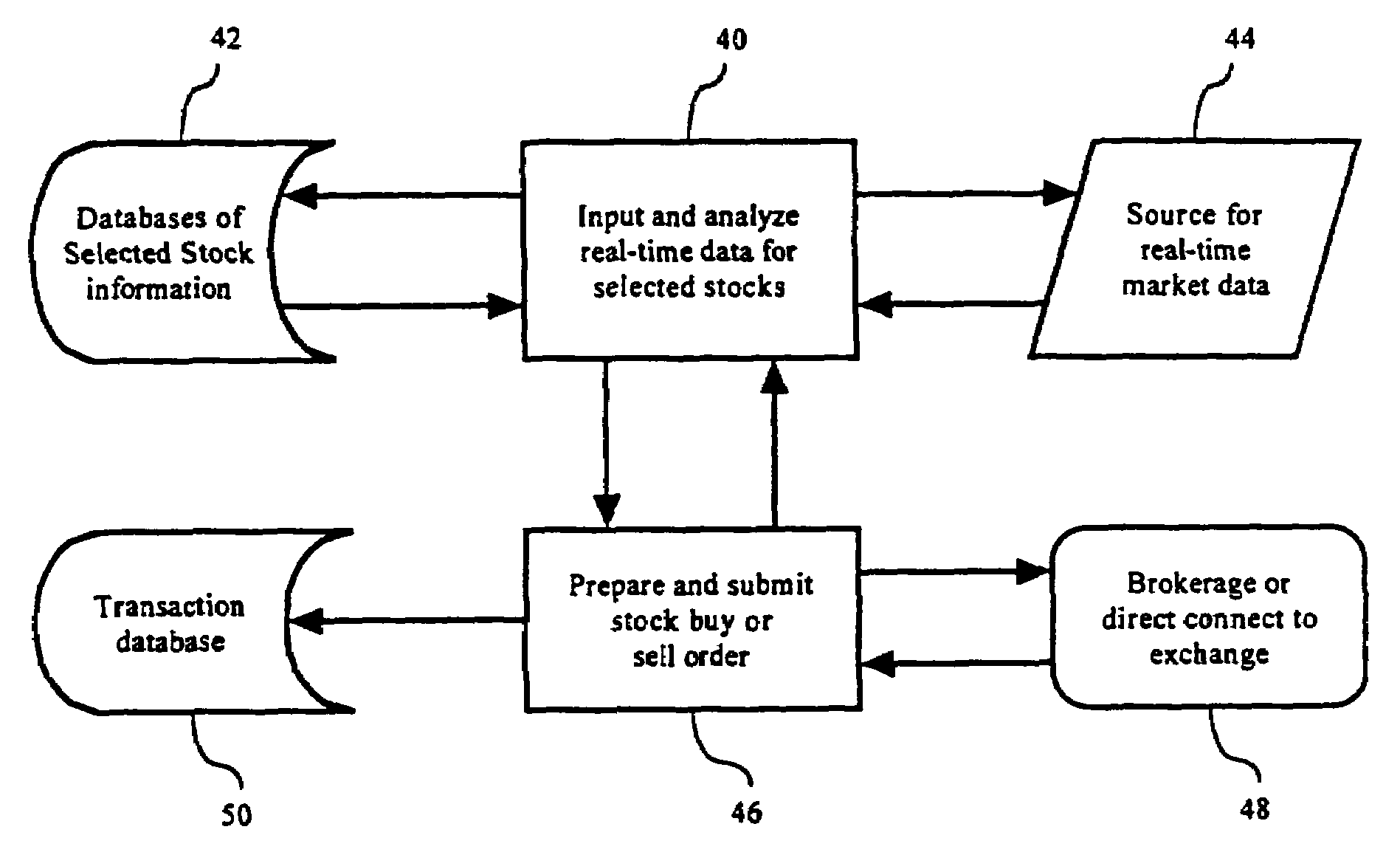
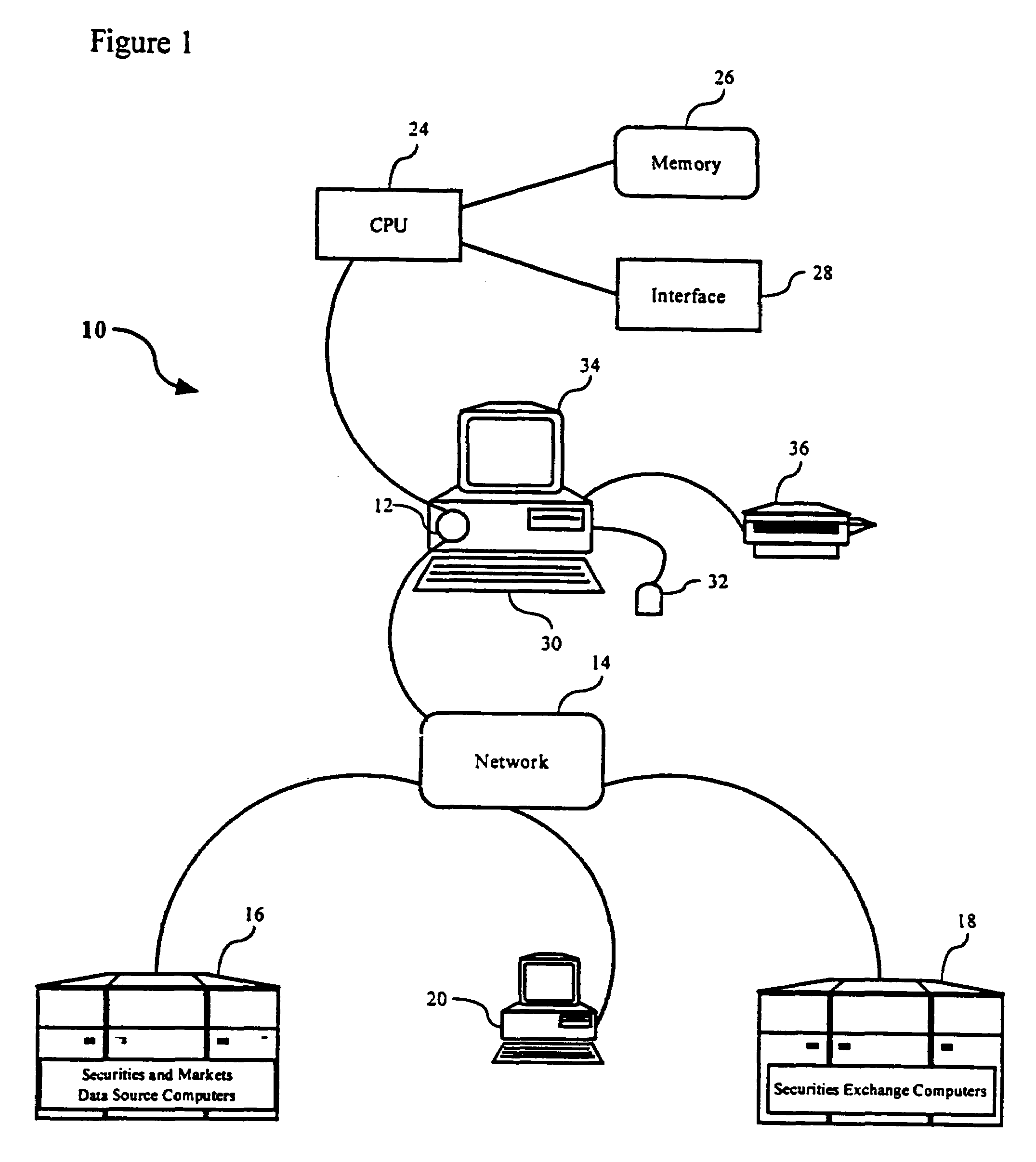
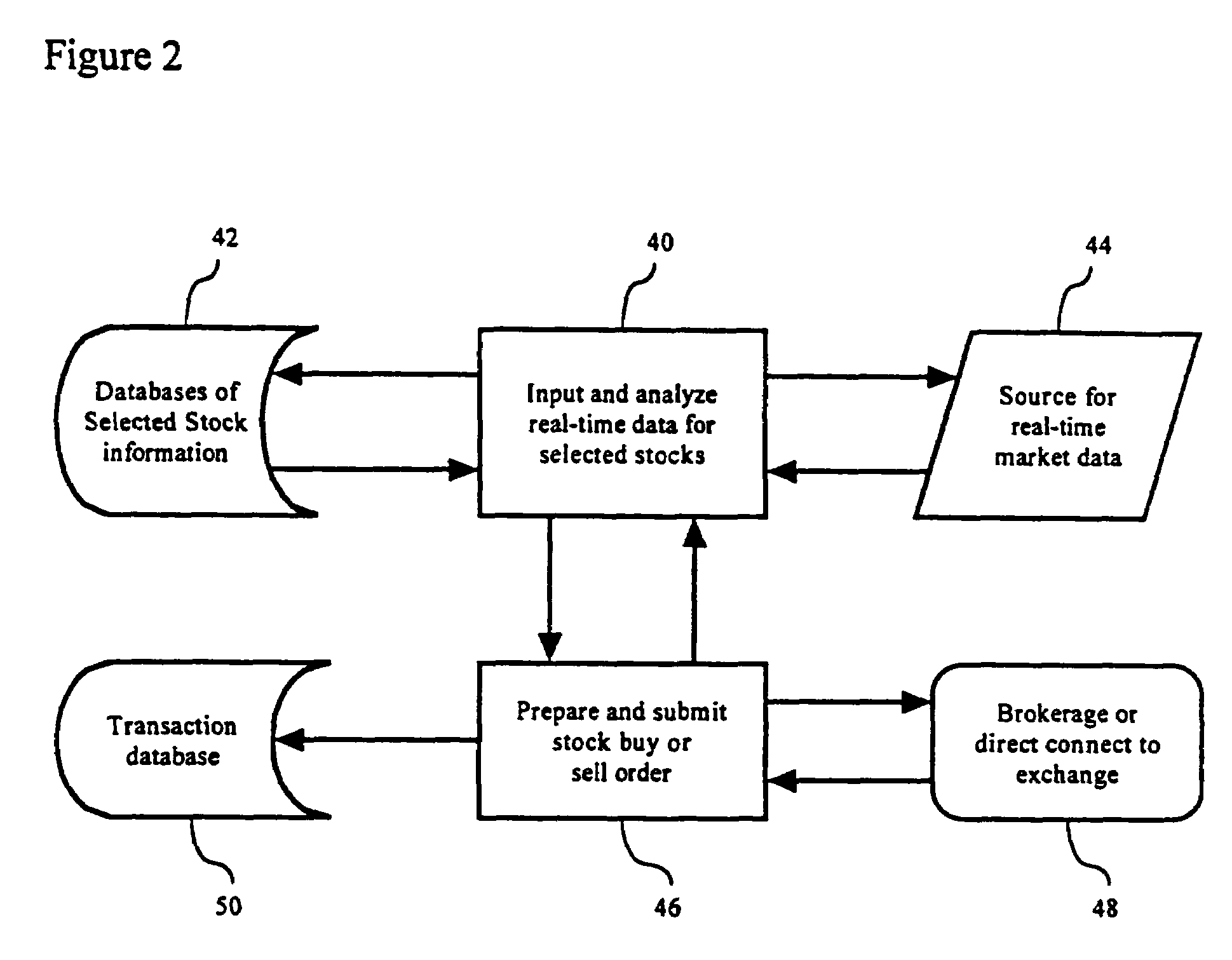
Method and apparatus for automated trading of equity securities using a real time data analysis
Owner:AMBURN DEAN
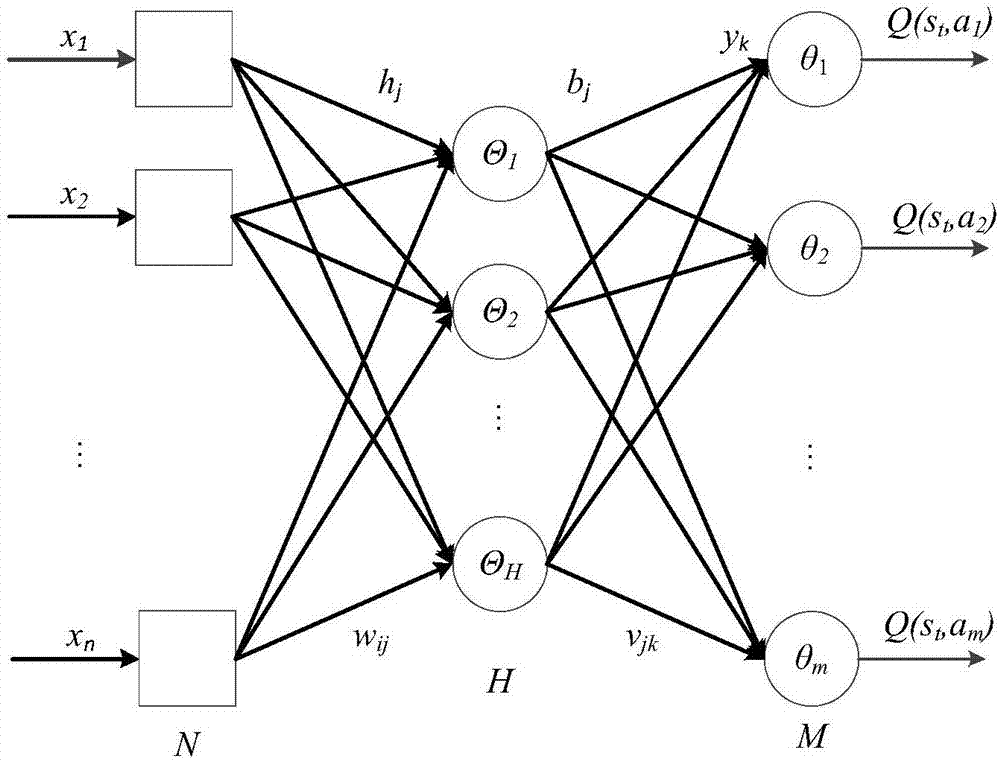
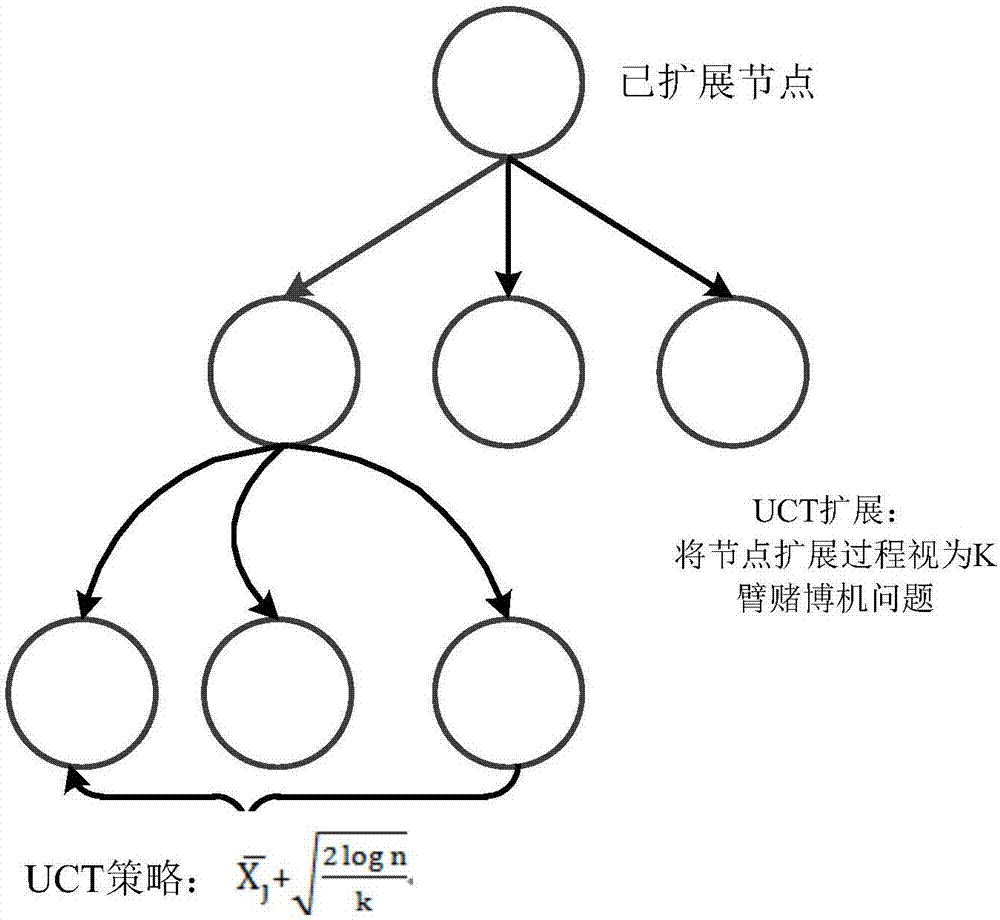
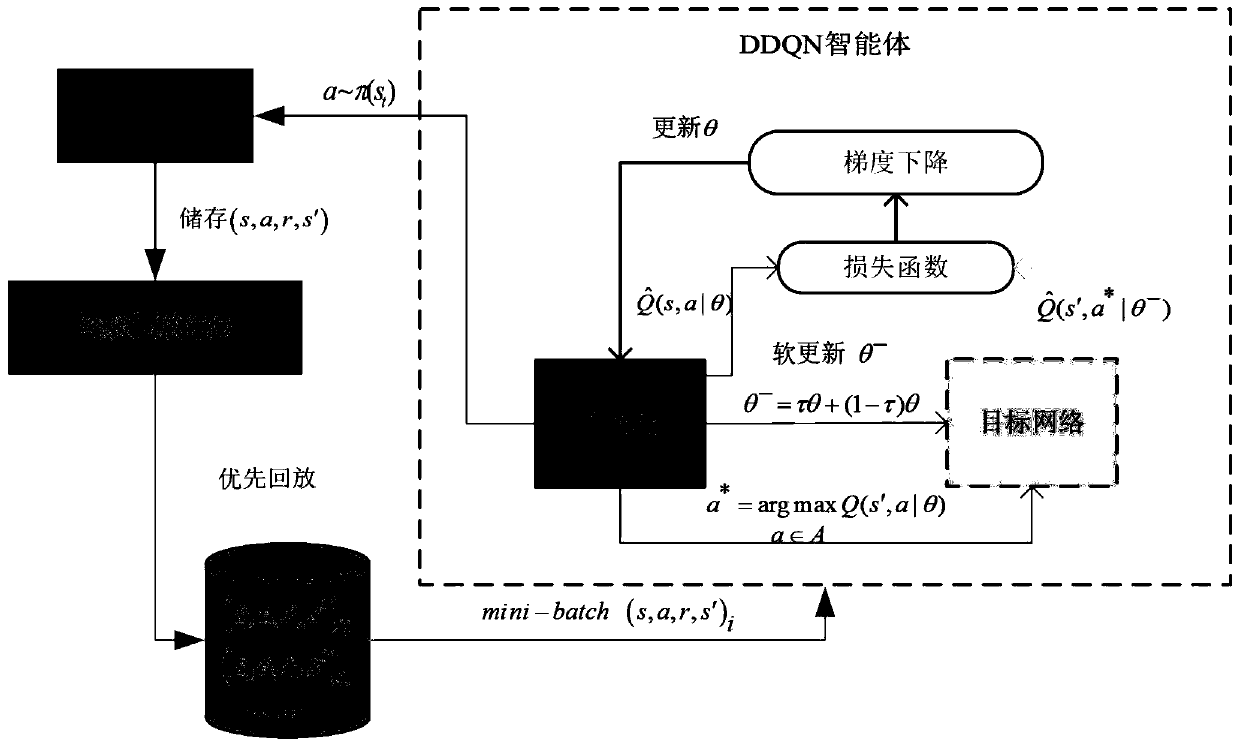
Neural network and Q learning combined estimation method under non-complete information
InactiveCN107038477AImprove the game levelReasonable strategyInference methodsNeural learning methodsDecision modelNerve network
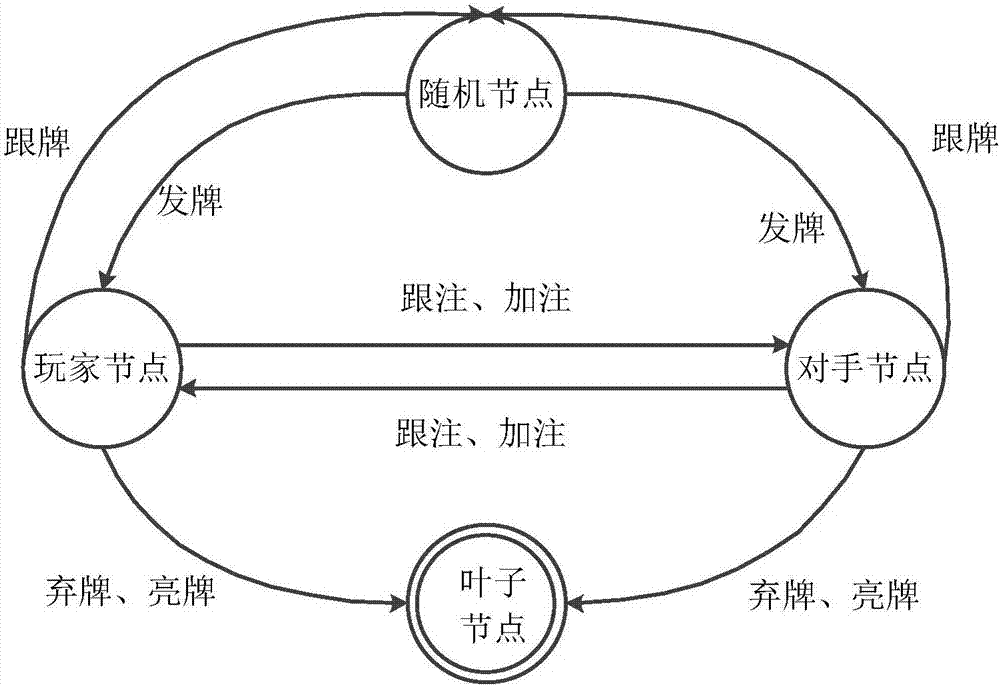
The invention provides a neural network and Q learning combined estimation method under non-complete information, and the method comprises the steps: 1, converting the non-complete information into a partly observable Markov decision-making model; 2, converting the non-complete information gaming into complete information gaming through the Monte Carlo sampling technology; 3, calculating Q learning delay return value through a Q learning algorithm based on former n steps, an algorithm combining a neural network and the Q learning and an algorithm UCT based on an upper limit confidence interval; 4, carrying out the fusion of the Q value obtained at a former step, and obtaining a final result. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method can be used in various types of non-complete information gaming, such as the Chinese poker and Texas Hold'em poker, and improves the gaming level of an intelligent agent. Compared with the conventional related research, the method greatly improves the precision.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
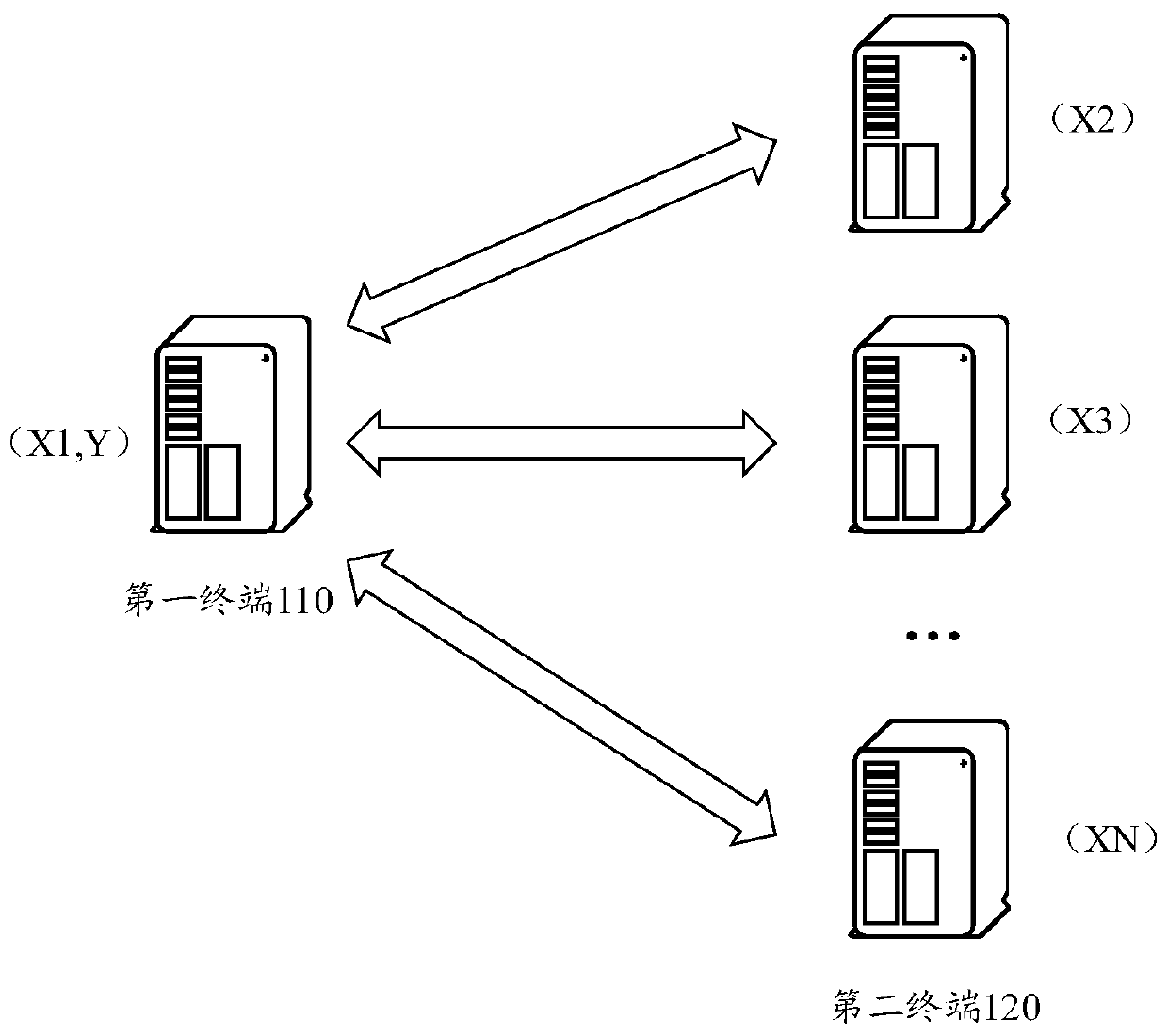
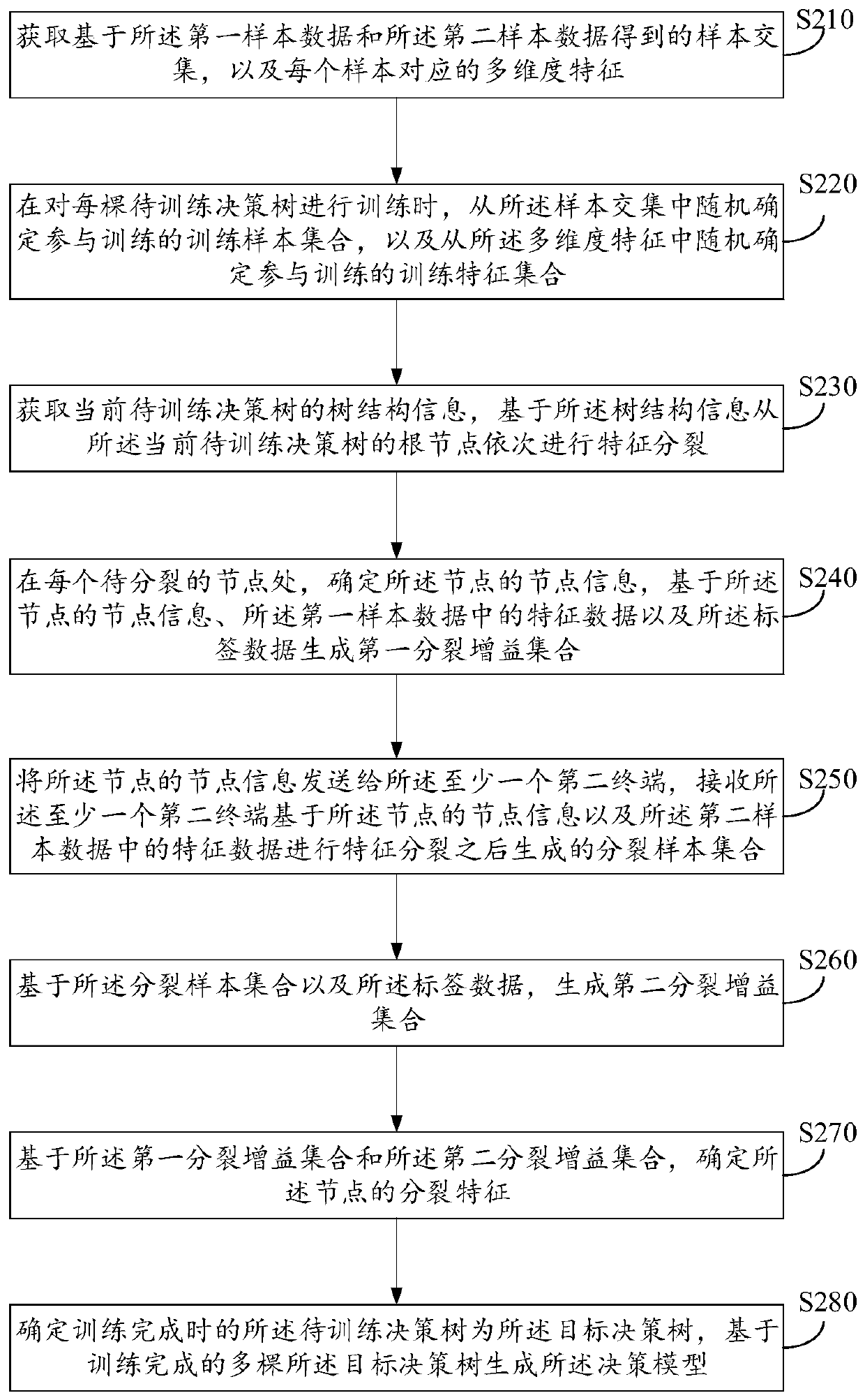
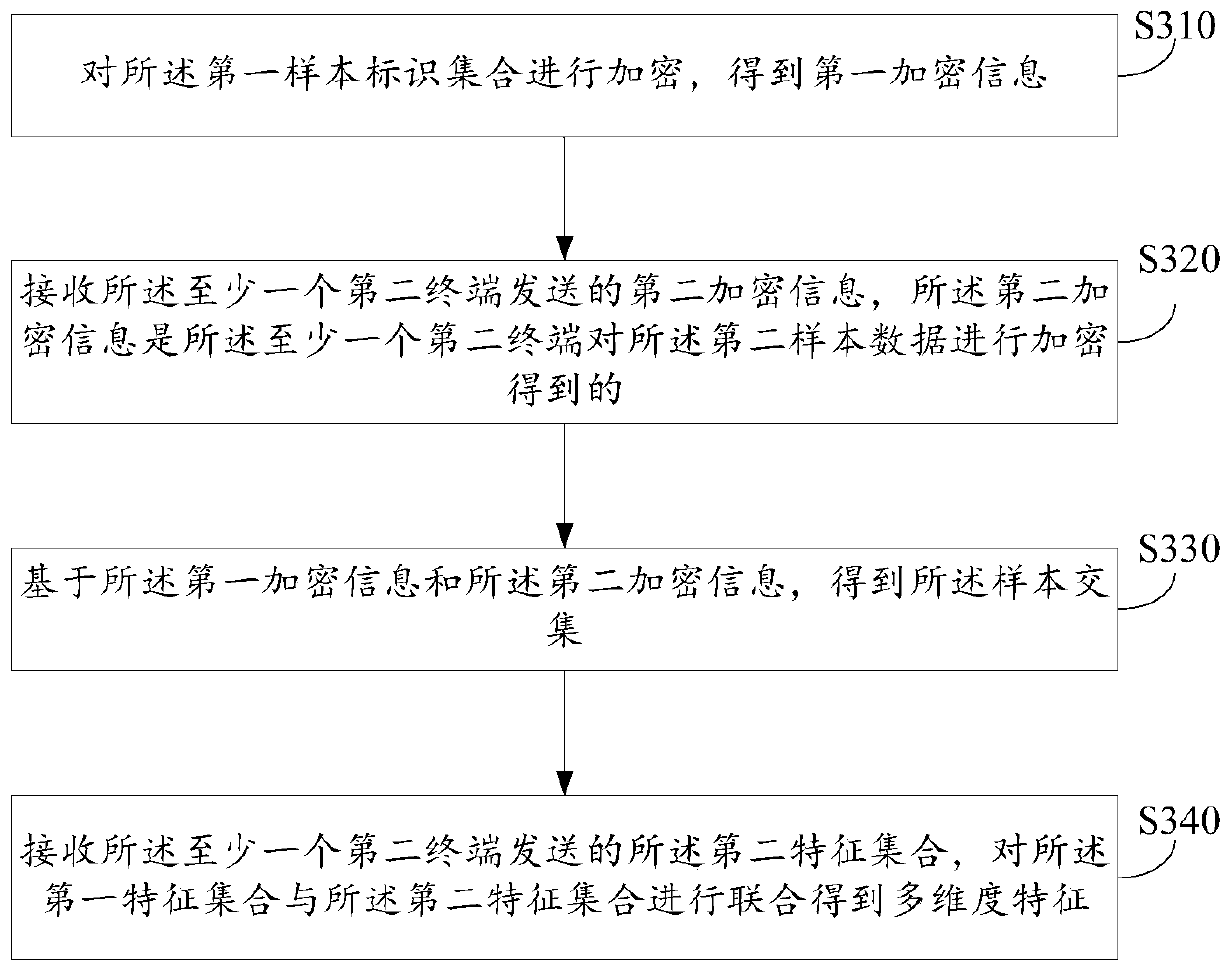
Decision model training method, prediction method and device based on longitudinal federation learning
ActiveCN111598186AAvoid safety hazardsAvoid leaked issuesCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision modelFeature set
The invention relates to a decision model training method, prediction method and device based on longitudinal federated learning. The training method comprises the steps that a training sample set participating in training and a training feature set are randomly determined; at each node of the current decision tree to be trained, determining node information of the node, and generating a first split gain set; receiving a split sample set generated by at least one second terminal; generating a second split gain set based on the split sample set and the label data; determining a splitting feature of the node based on the first splitting gain set and the second splitting gain set; and generating the decision model based on the plurality of trained target decision trees. According to the method and the device, the problem that the label data is leaked in the transmission process can be avoided, the safety of the node data of each participant is improved, and the data privacy of each participant node is protected.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method for comprehensively evaluating electric energy quality
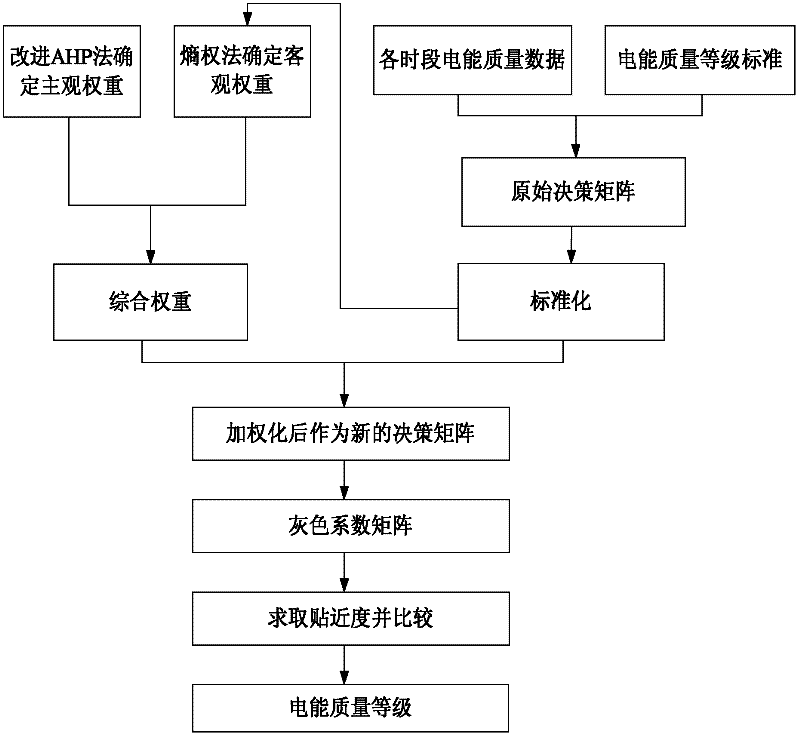
InactiveCN102542347AClear physical meaningFacilitate decision-makingData processing applicationsPower qualityDecision model
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively evaluating the electric energy quality by applying a TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution) of a grey correlation coefficient matrix, which comprises the following steps of: taking electric energy quality data at all time intervals and standard data at all grades as an original decision matrix; determining subjective weights through an improved AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process); determining objective weights through an entropy method; establishing a least square method decision model to obtain a comprehensive weight, so that the deviation of decision results under the subjective weights and the objective weights of all indexes is the least; carrying out standardization and weighted standardization on the decision matrix and obtaining the grey correction coefficient matrix by utilizing the grey theory; taking the grey correction coefficient matrix as a decision matrix of the TOPSIS to obtain the distance between positive ideal solutions and negative ideal solutions of all schemes and the relative closeness of the positive ideal solutions and the negative ideal solutions; and comparing the electric energy quality closeness at all the time intervals with the standard closeness at all the electric energy quality grades to finally obtain the electric energy quality grades at all the time intervals. With the adoption of the method, the electric energy quality evaluation result can be objectively and reasonably obtained under the situation of poor information, so that the practicability and the feasibility are stronger.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
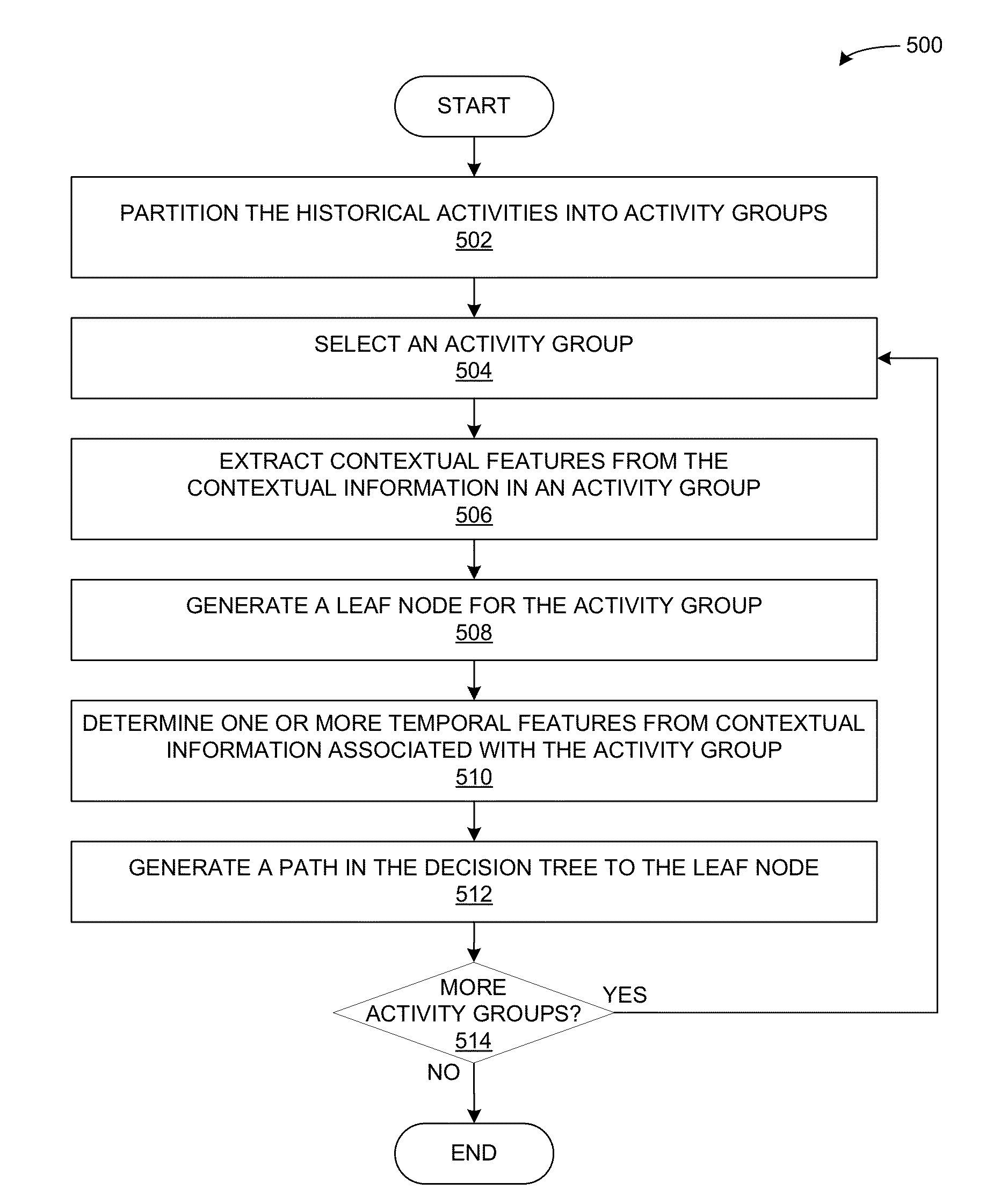
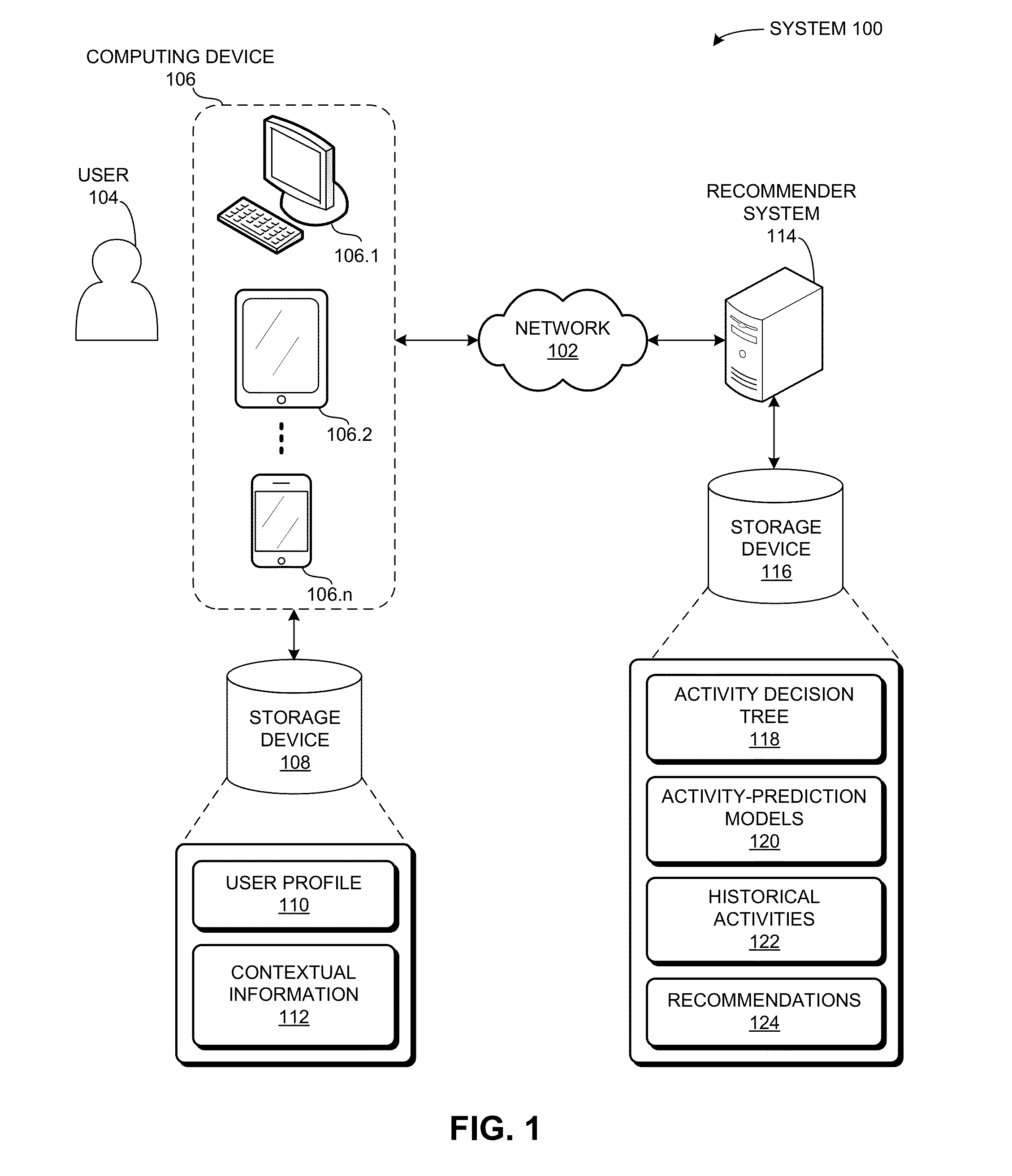
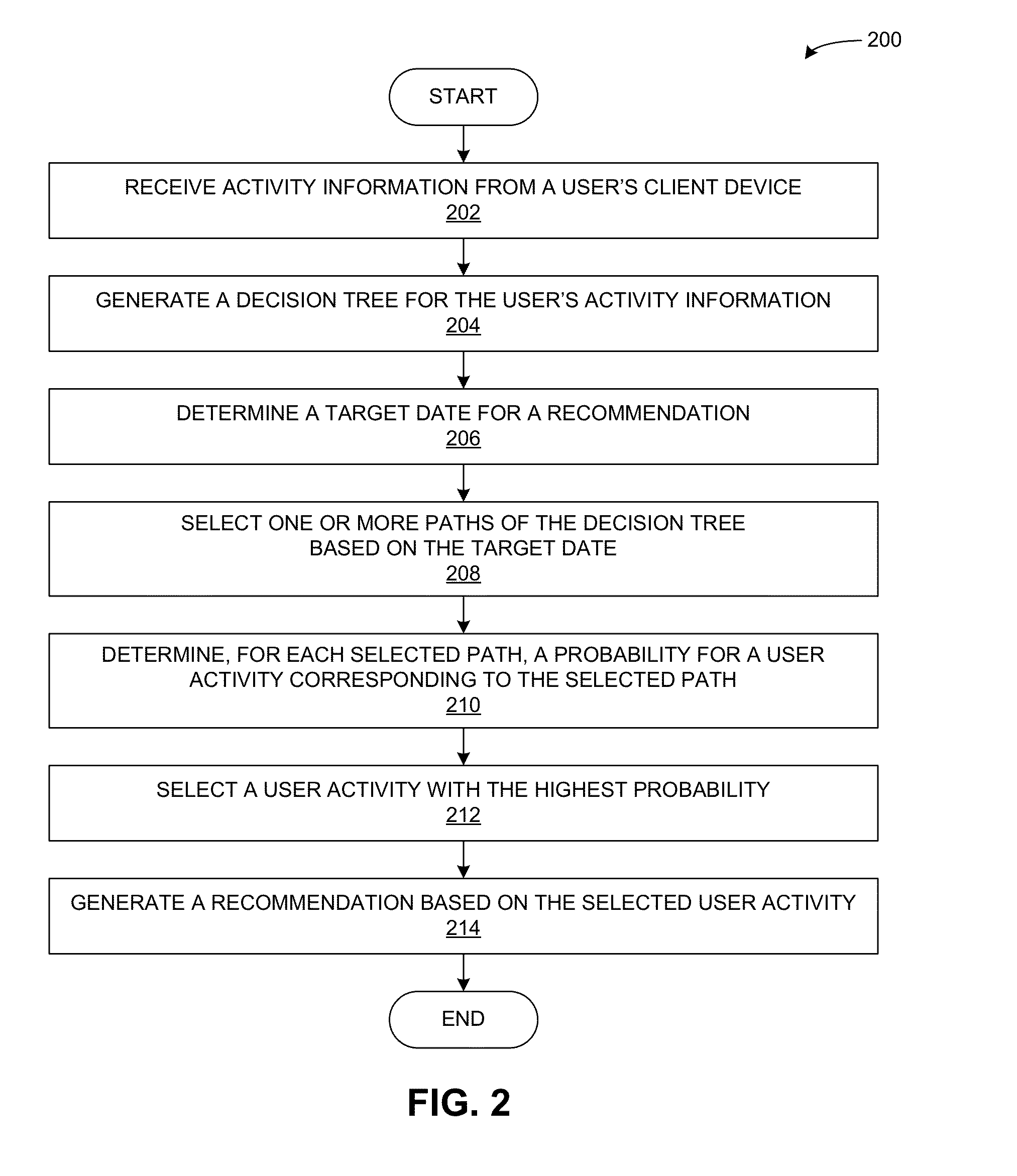
Performance-efficient system for predicting user activities based on time-related features
A recommender system uses an activity decision tree to model the changes in a user's behavior according to a plurality of time-related features. The system determines historical activities for the user, and generates a decision tree for the user's historical activities. Each leaf node of the decision tree is associated with an activity-prediction model that computes a probability for a corresponding activity. The system selects a path of the decision tree from a root node to a leaf node of the decision tree based on a target time. The selected path traverses two or more non-leaf nodes that are each associated with a temporal decision model that compares the target time against a temporal classifier. The system then determines a probability for a user activity based on an activity-prediction model of the selected path.
Owner:XEROX CORP
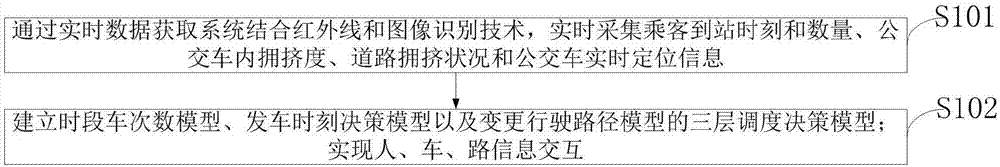
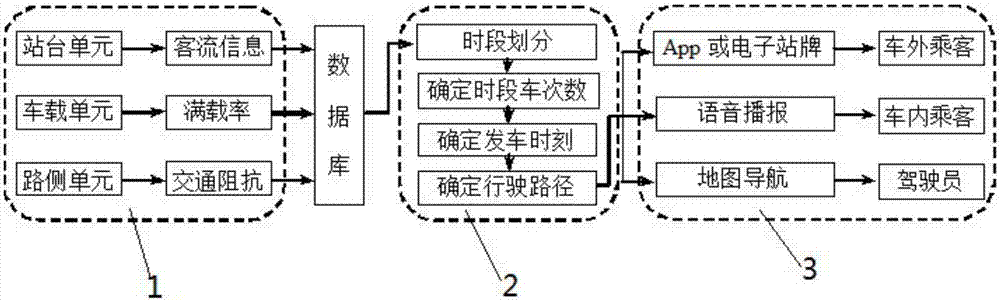
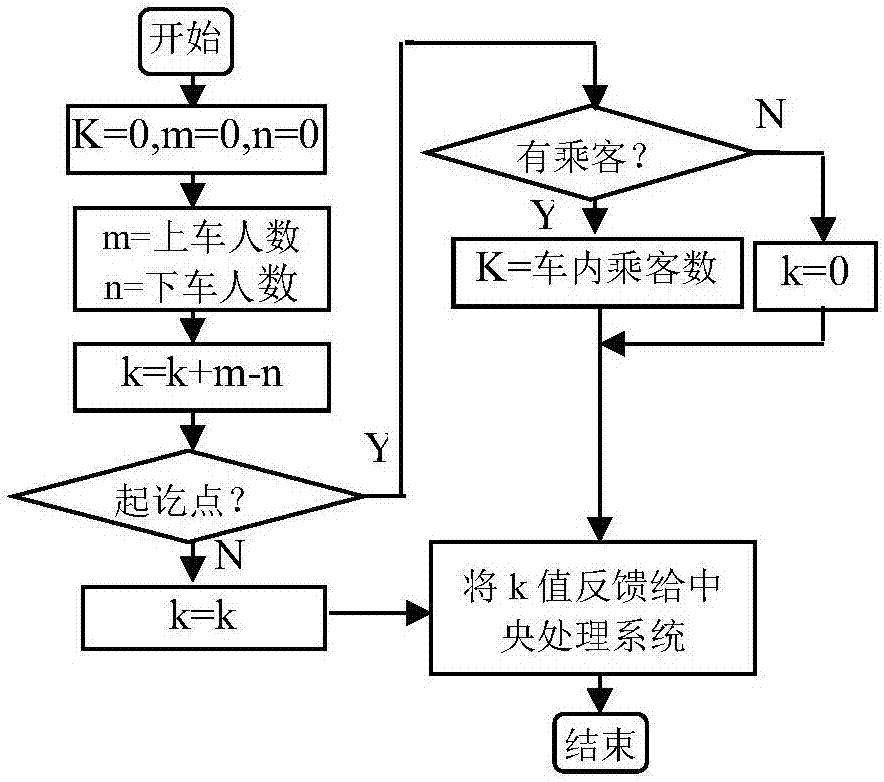
Urban bus dynamic scheduling optimization method and system
ActiveCN107330547AImprove operation scheduling efficiencyLow costForecastingResourcesDecision modelOperational costs
The present invention belongs to the data processing technology field, and discloses an urban bus dynamic scheduling optimization method and system. The method comprises: on the basis of obtaining information such as degree of congestion of a bus, a road congestion condition, bus real-time location and the like, establishing a three-layer scheduling decision model comprising a time frame bus-times model, a departing time decision model and a path changing model; realizing information interaction of people, vehicles and roads through an internet technology; determining optimal time frame bus times through the time frame bus-times model from the beginning of balancing bus operating cost, passenger waiting time and riding comfort; taking the maximum total meeting times and the minimum total meeting stations of an area as a target regulation departing moment through the departing time decision model so as to effectively reduce the probability of transferring and waiting; and employing the idea of being far away from a jamming road by employing the path changing model to effectively improve the running speed and reduce the following station passenger waiting time, and arranging response stations to allow passengers having missed the stations to get off.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
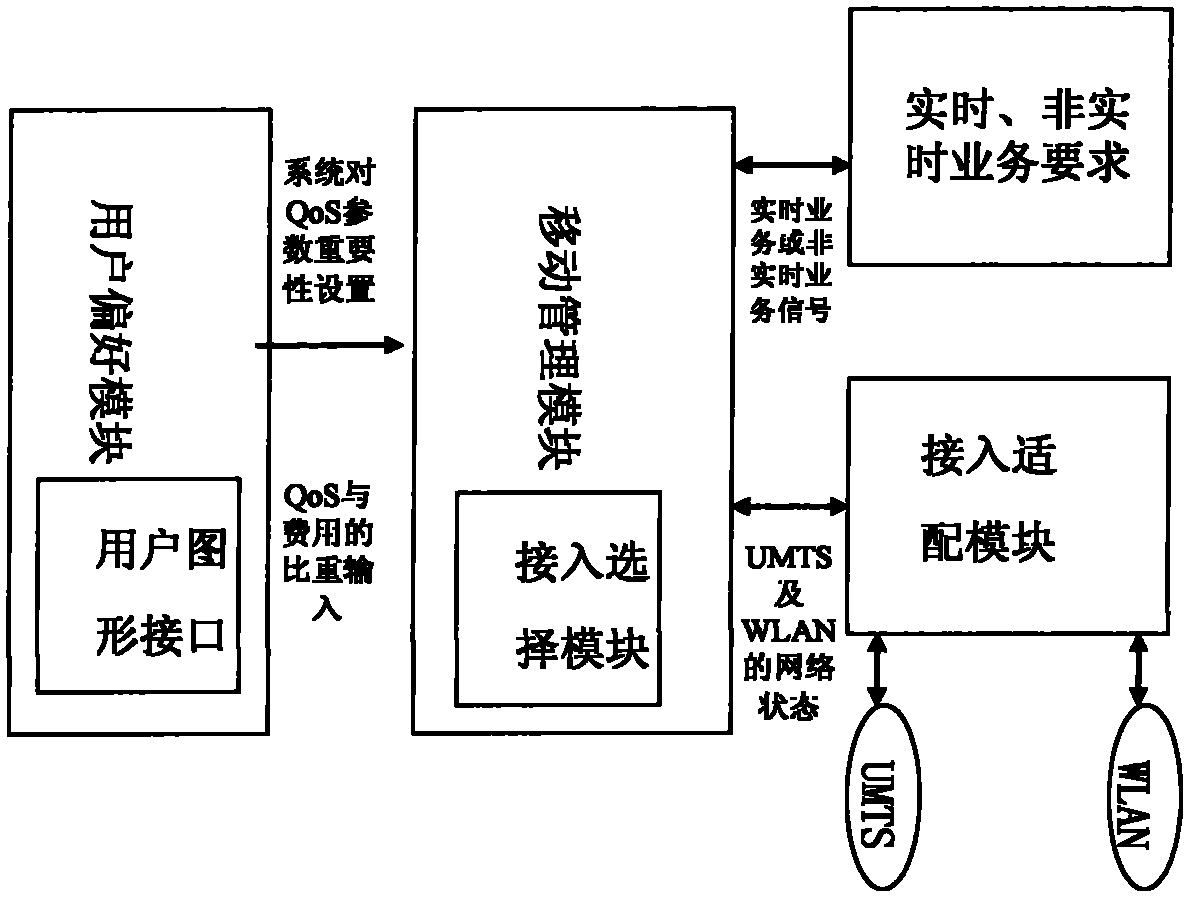
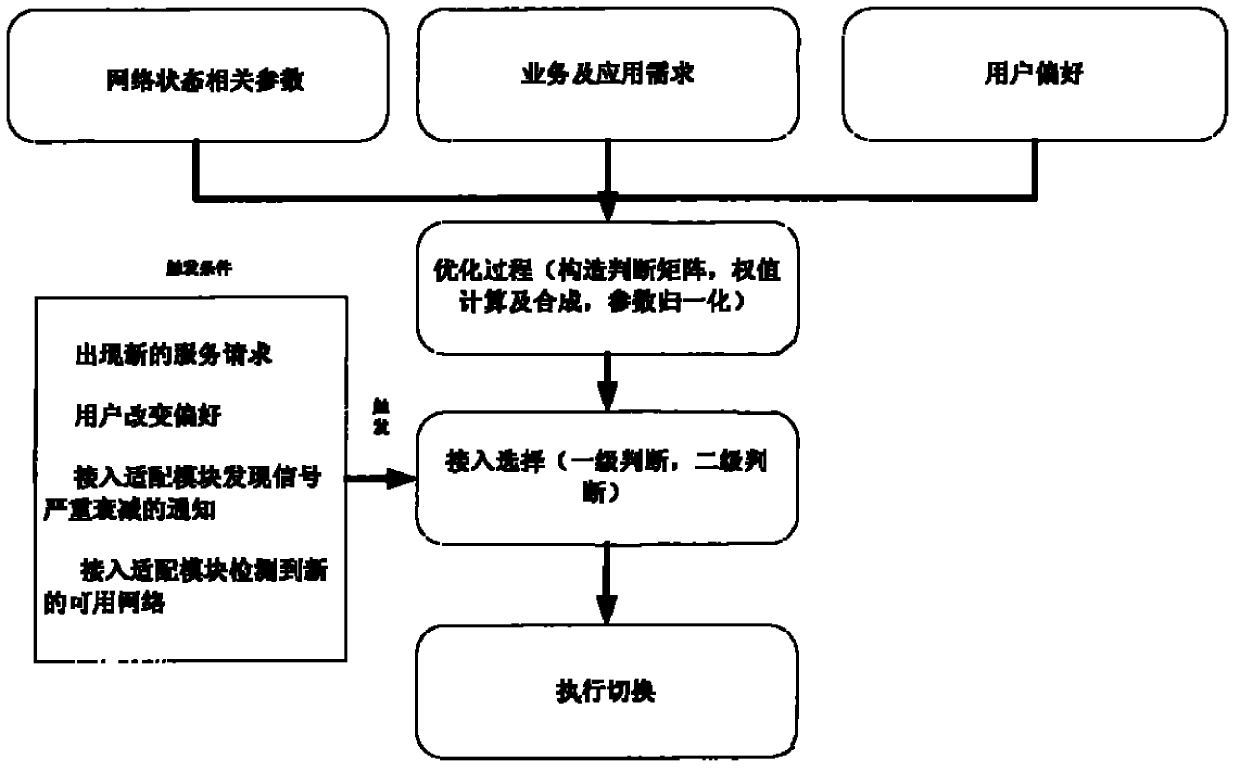
User-based multi-access network selection method being used under wireless heterogeneous network environment
The invention discloses a user-based multi-access network selection method being used under a wireless heterogeneous network environment and provides a dynamic multi-access selection method which is combined with an object cost function and the analytic hierarchy process by starting from user interests and fully considering cost, QoS and stability of pre-access to a network. A network selection decision model is established by analyzing and judging influencing factors; furthermore, the method has the advantages of the multi-factor-based network selection method, and can correctly and effectively carry out network selection and be conveniently realized in a user terminal.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
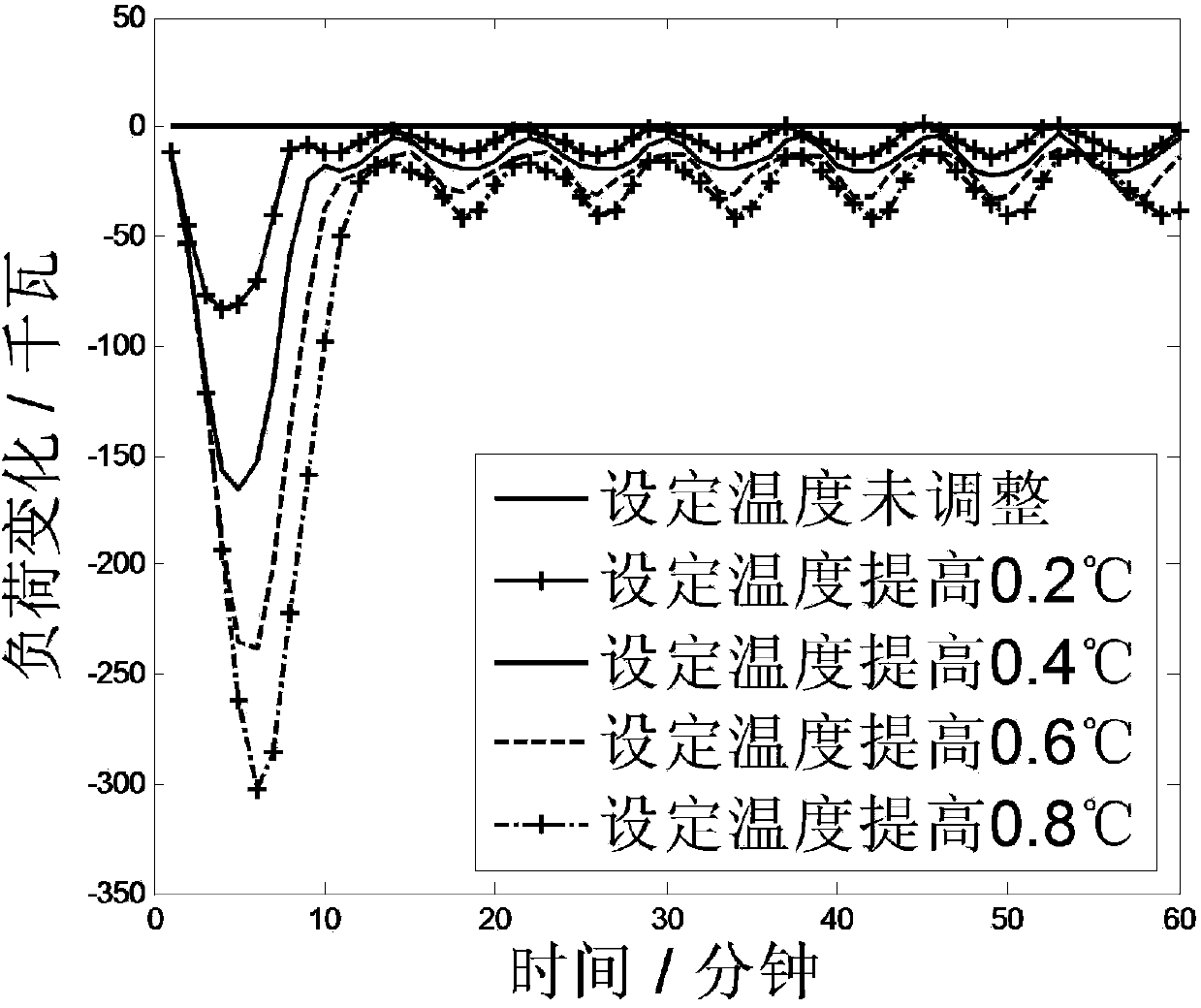
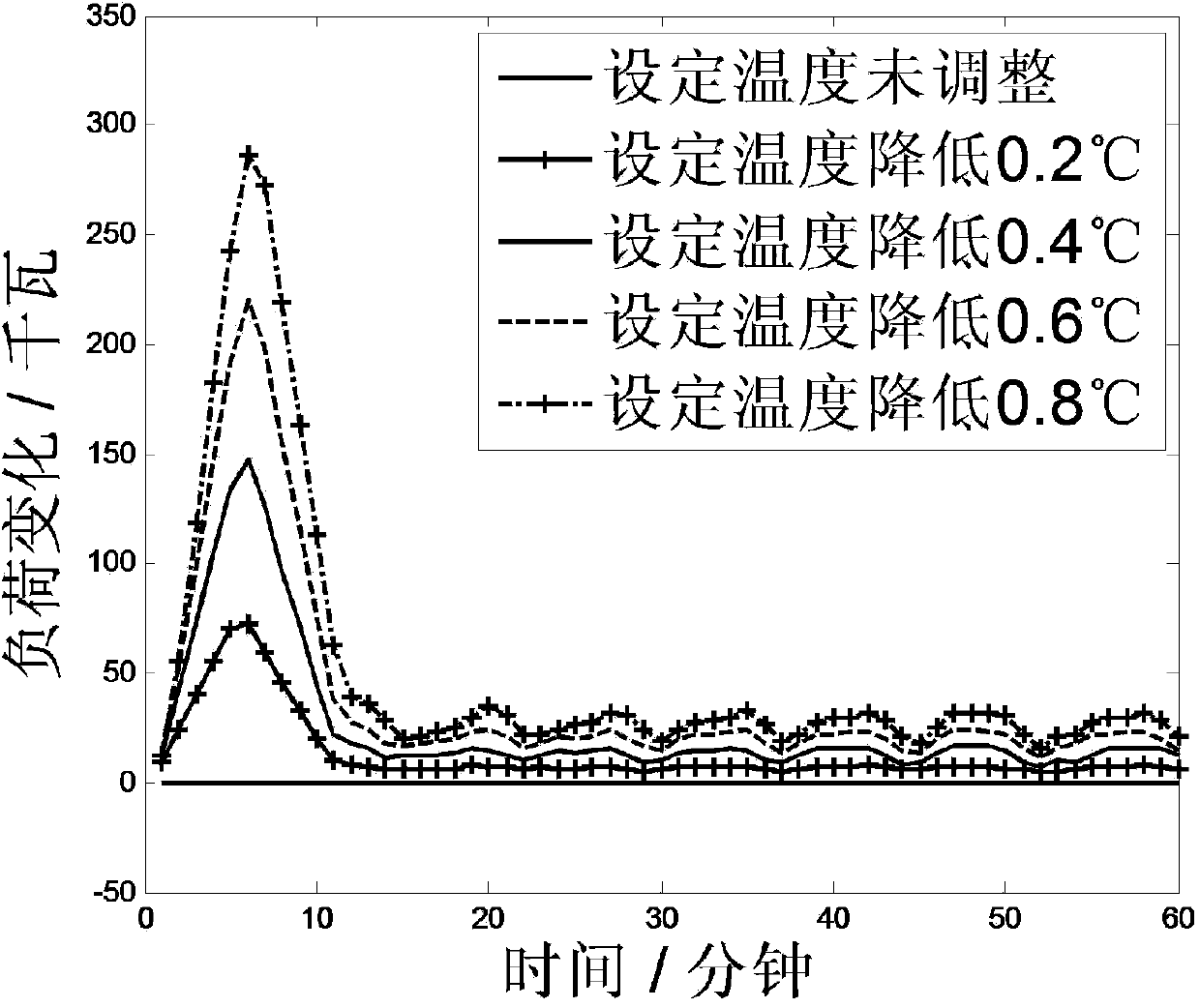
Aggregation air conditioning load scheduling method based on temperature set value adjustment
ActiveCN104214912ALittle or no impact on comfortReduce peak loadSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusDecision modelPower system scheduling
The invention discloses an aggregation air conditioning load scheduling method based on temperature set value adjustment. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring the temperature set value and outdoor temperature prediction value of each air conditioner aggregation group through a bilateral information channel; (2) adjusting and estimating the load increase / decrease scheme of each air conditioner aggregation group based on the temperature set values; (3) acquiring a load increase / decrease target issued by a superior scheduling department; (4) establishing an aggregation air conditioner scheduling decision model, and solving; (5) issuing an air conditioner control command through the bilateral information channel. By adopting the aggregation air conditioning load scheduling method, load increase / decrease service can be provided for electric power system scheduling on the premise of not influencing the user comfort by using air conditioning equipment of a user, so that the user turns from an electric energy user to a participant of an electric power system and participates in running of the electric power system; meanwhile, by using the method, technical guidance can be provided for the innovation of the scheduling mode of a power grid scheduling department.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multi-source data fusion method in clustering wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101556651AReduce reliabilityFast convergenceNetwork topologiesCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision modelWireless mesh network
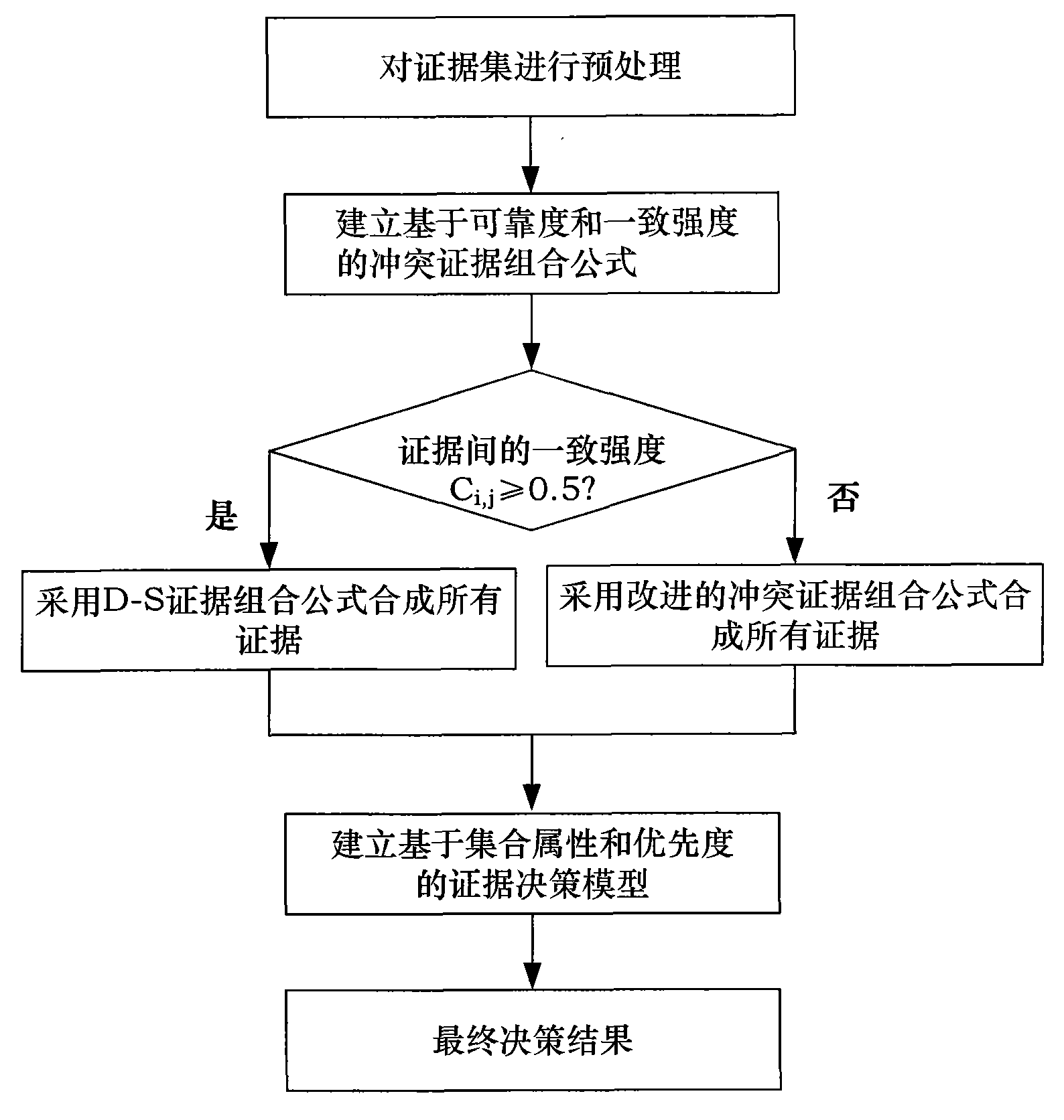
The invention discloses a multi-source data fusion method in a clustering wireless sensor network, which comprises the following specific contents: a distributive data fusion structure is adopted; at all cluster-head nodes, an evidence set is preprocessed according to reliability degree of the member nodes in the cluster; based on the consistent intensity and the value of primitive supporting degree of the evidence, the evidence conflicts are distributed, the evidence combination sequence is optimized, the rules of conflicting evidence combination are established to synthesize all evidences; in connection with the evidence combination results, the value of the fine confidence interval of the primitive proposition is obtained by utilizing the uncertainty measure and the property supporting degree of the set; and then an evidence decision model is constructed based on the priority sequence of the fine confidence interval, and the final diagnosis is made. The method can improve the identifying accuracy ratio of the detected goal by the clustering wireless sensor network, and simultaneously and effectively reduce the transmitting volume of redundant data in the network and satisfy the application demands of the clustering wireless sensor network in the fields such as pipe leakage diagnosis, target tracking, environment detecting and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Question-answering system combining emotion recognition and output
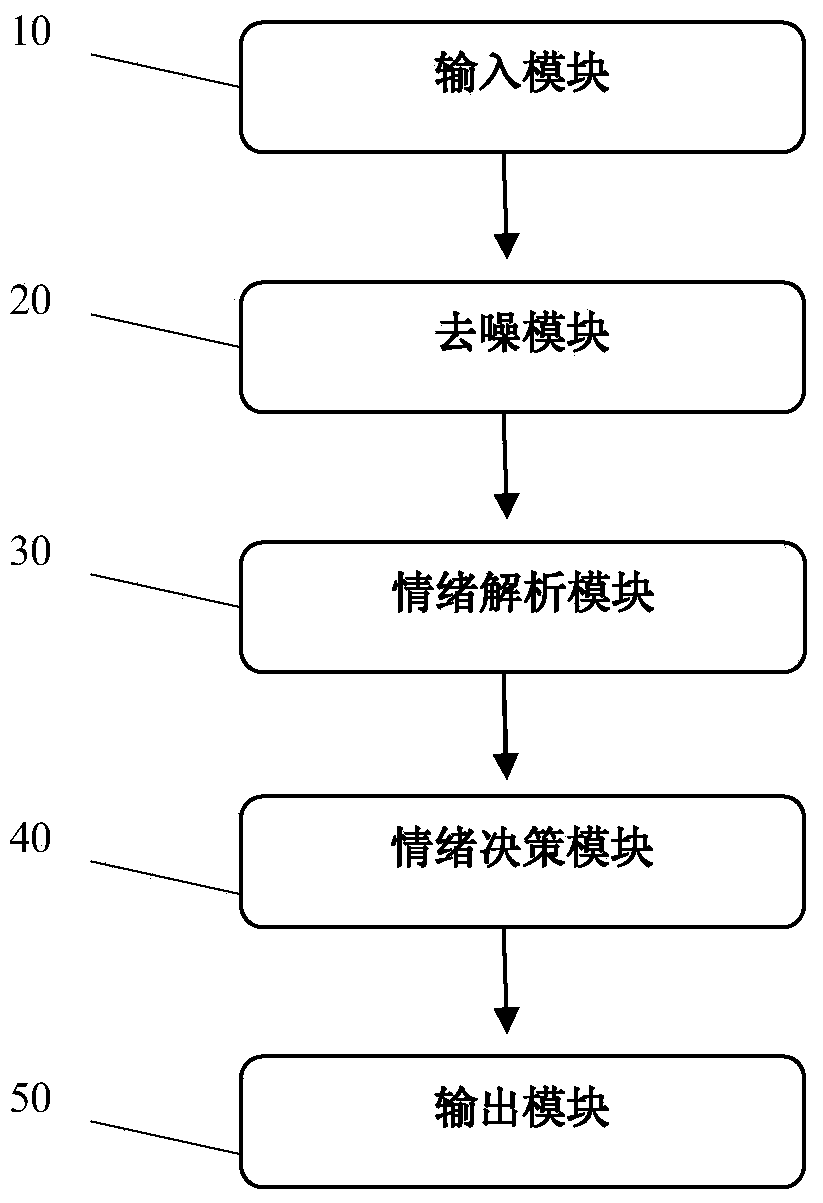
ActiveCN103593054AImprove experienceAccurate guessInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDecision model
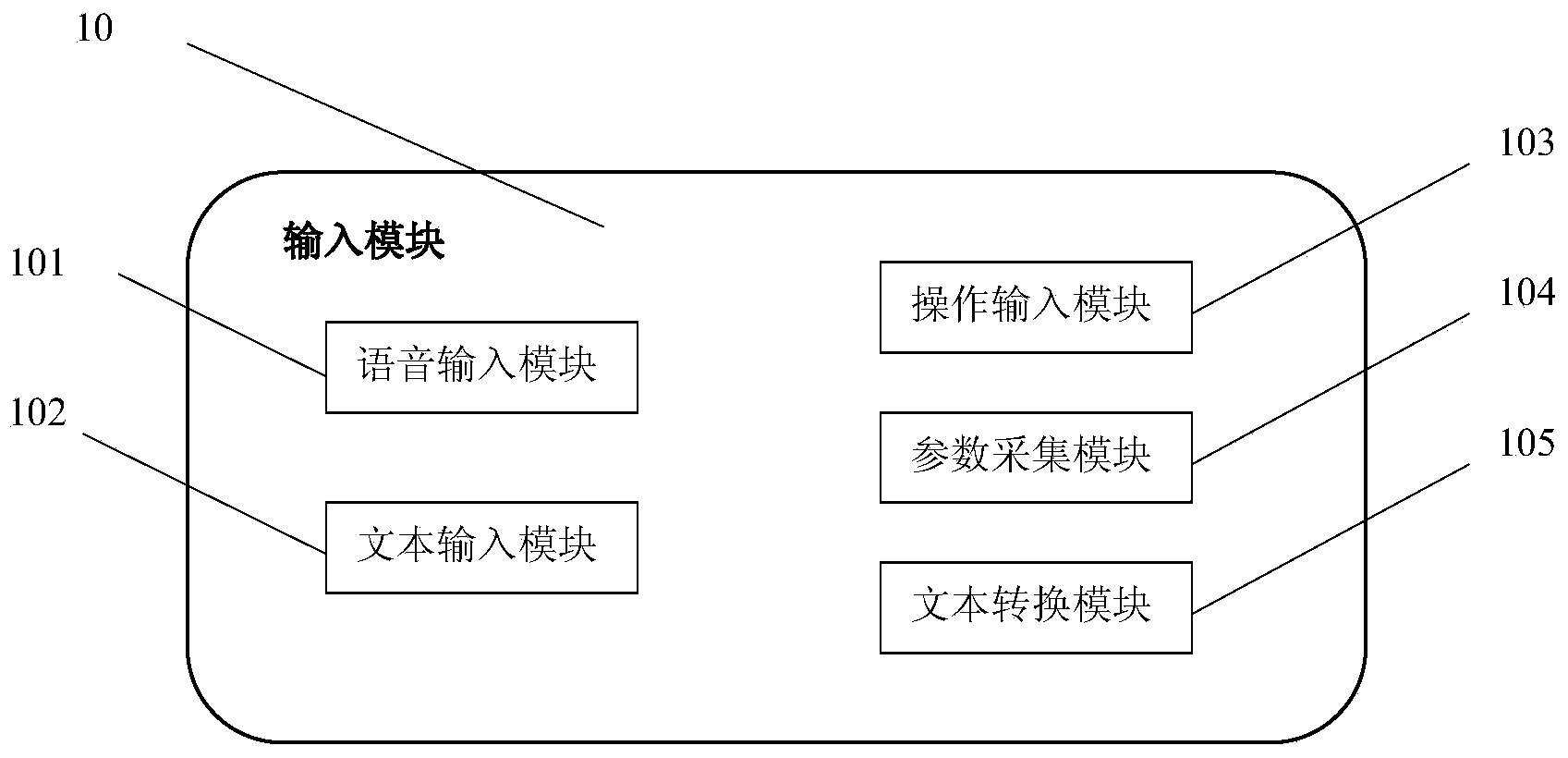
The invention provides a question-answering system combining emotion recognition and output. The question-answering system comprises an input module, a denoising module, an emotion analysis module, an emotion decision module and an output module. The input module is used for inputting user questioning information and user parameter information and converting the user questioning information and the user parameter information into standard text formatting information. The denoising module is used for carrying out denoising and module structuralization processing on the text formatting information. The emotion analysis module is used for building an emotion feature point model and extracting emotion feature points from the user questioning information through the emotion feature point model. The emotion decision module is used for building an emotion decision model and judging the current emotion of a user and the current circumstance where the user is located based on the emotion feature points of the user through combinatorial computing by combining the records and habits of the user. The output module is used for outputting a corresponding result according to the current emotion of the user. The emotion information of the user is combined, the user intention is speculated more accurately, intimate answers are given according to the actual situation of the user, and user experience is greatly promoted.
Owner:BEIJING GUANGNIAN WUXIAN SCI & TECH
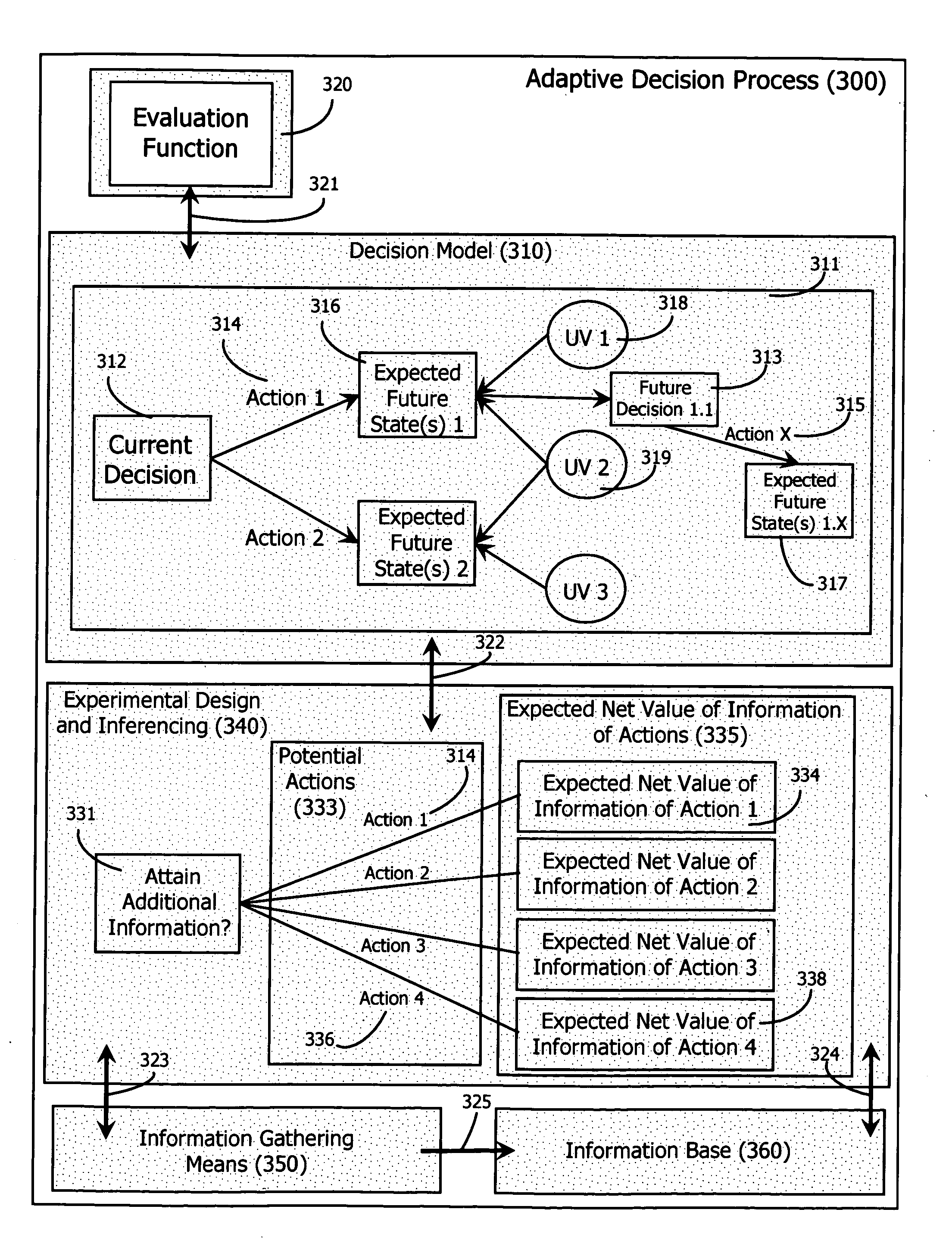
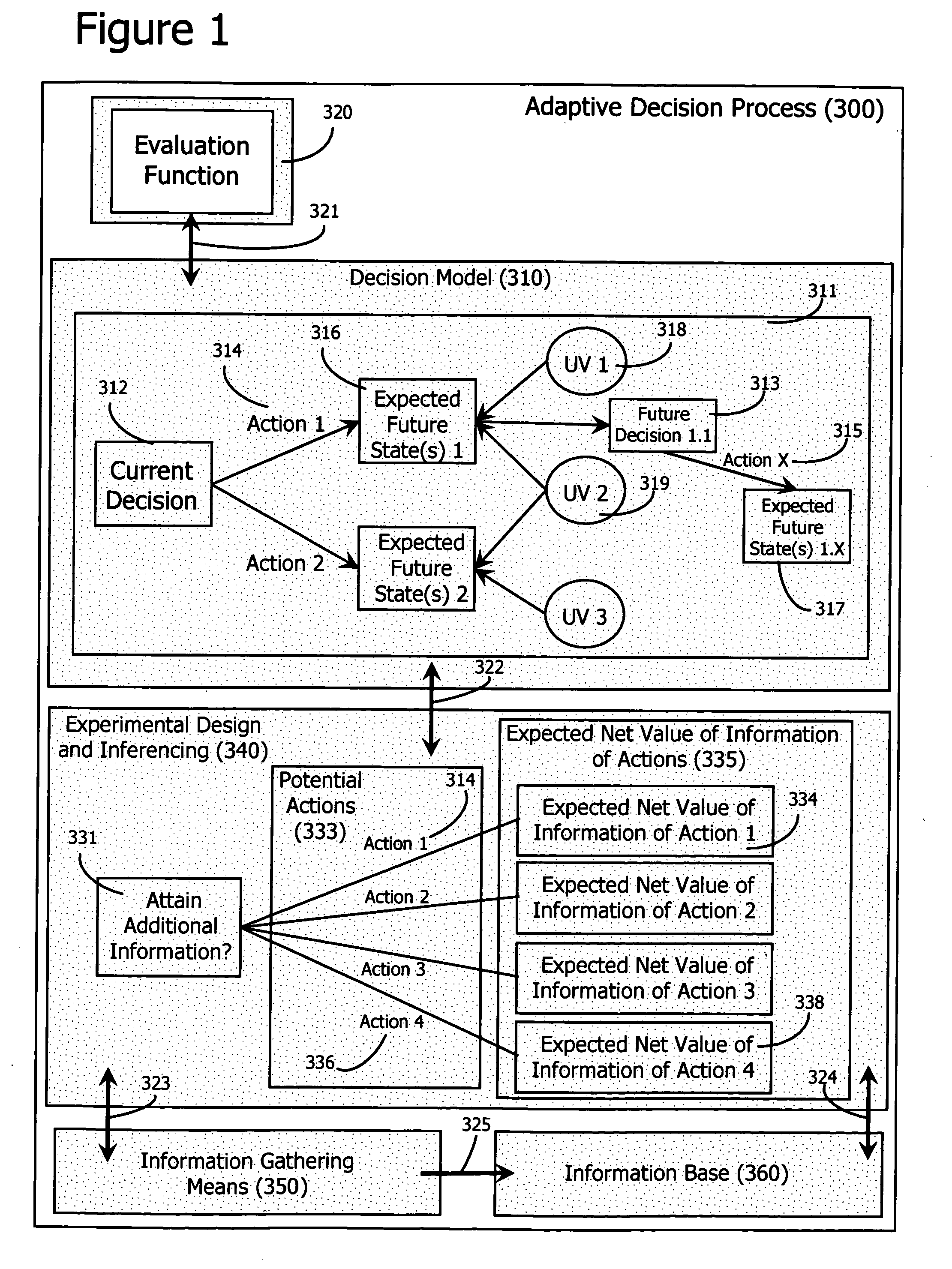
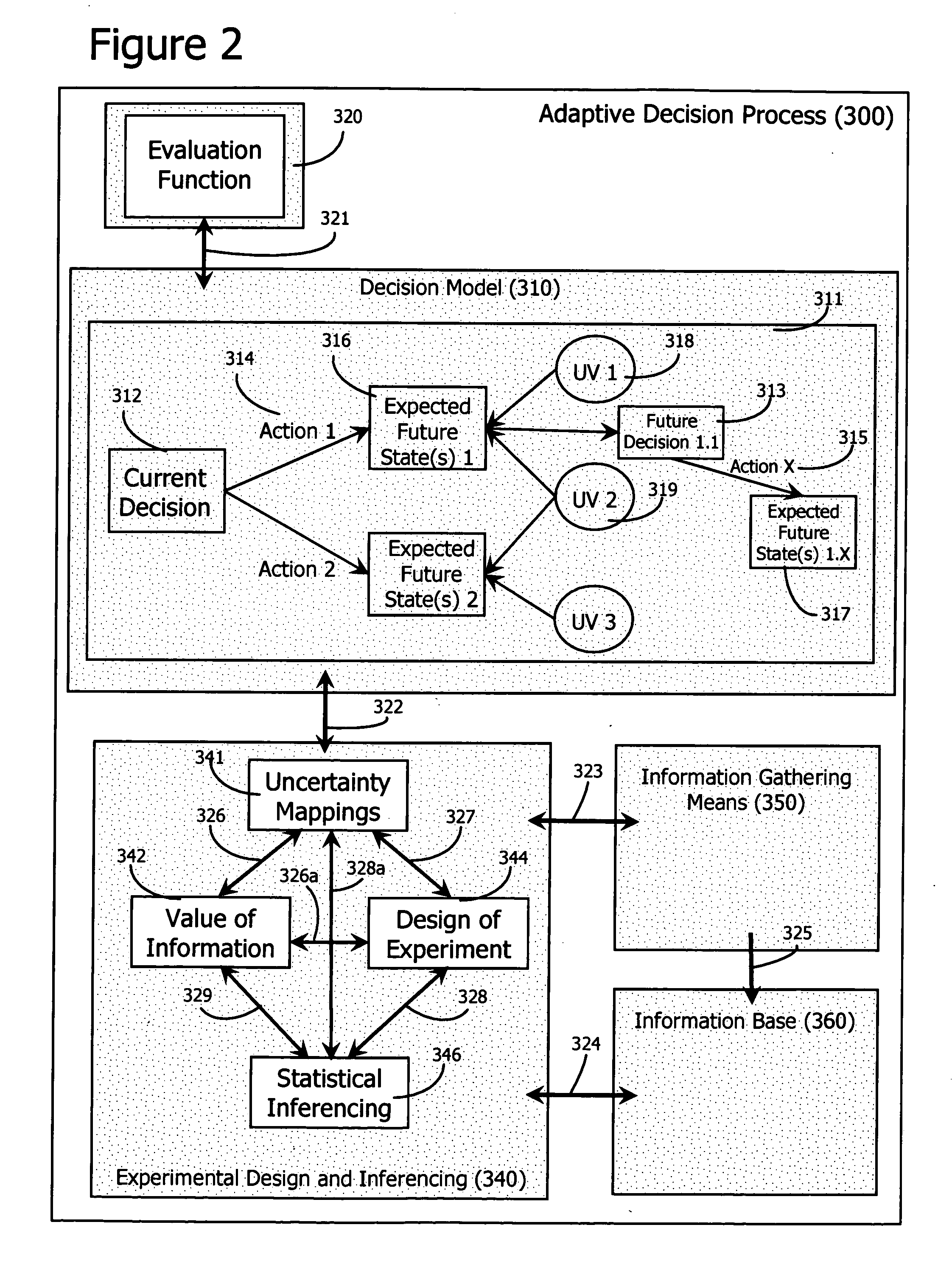
Adaptive decision process
InactiveUS20060184482A1Probabilistic networksSpecial data processing applicationsDecision modelClosed loop
An adaptive decision process is disclosed for more effectively and efficiently determining and conducting information gathering and evaluation associated with decisions. The adaptive decision process integrates decision analysis, value of information analysis, design of experiment models, and the inferencing of gathered information, including experimental results. The process enables an automatic, adaptive, closed-loop process for attaining additional information and assimilating the attained information into the decision model.
Owner:MANYWORLDS CONSULTING
Automatic detection confirmations method for urban traffic incident
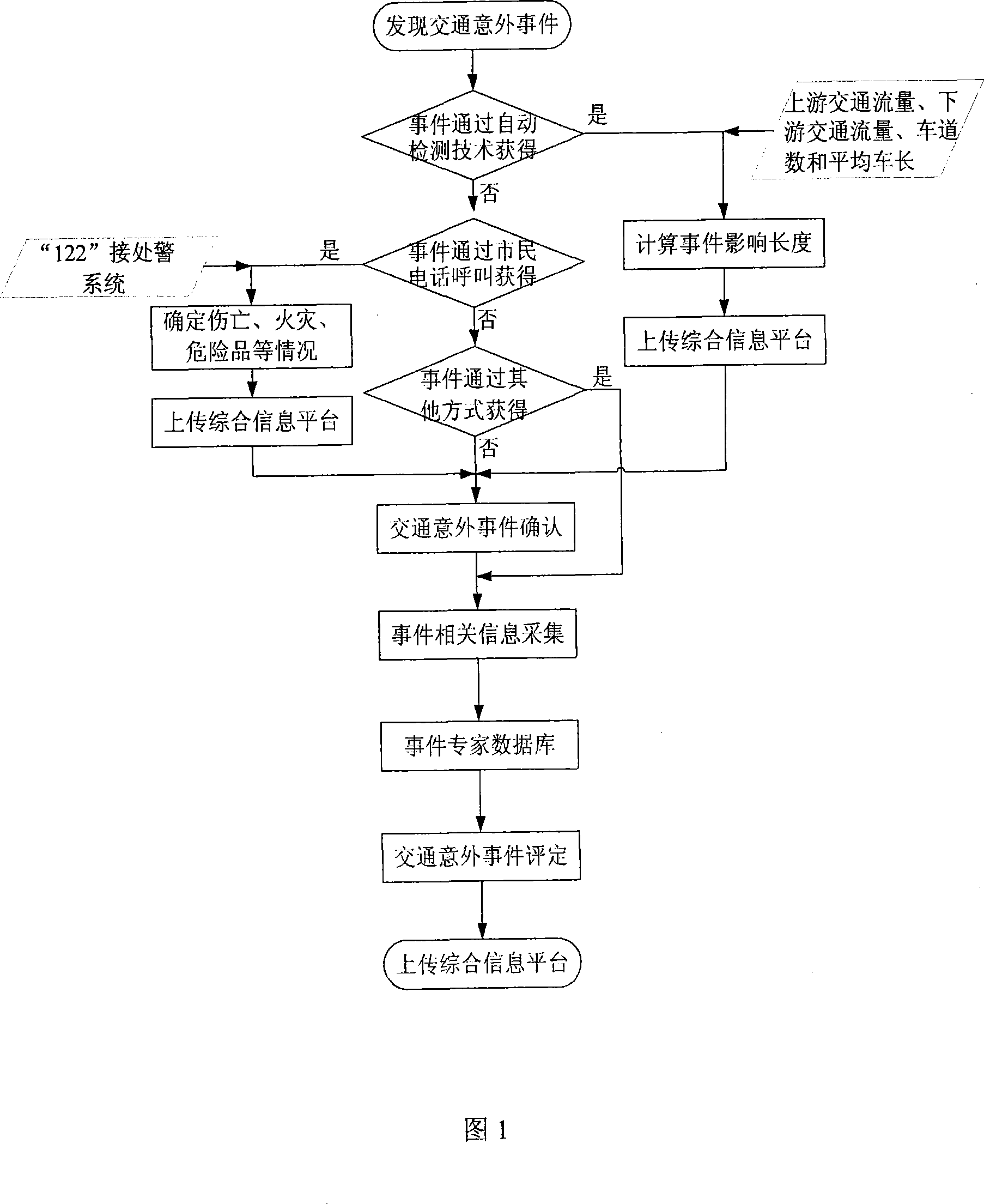
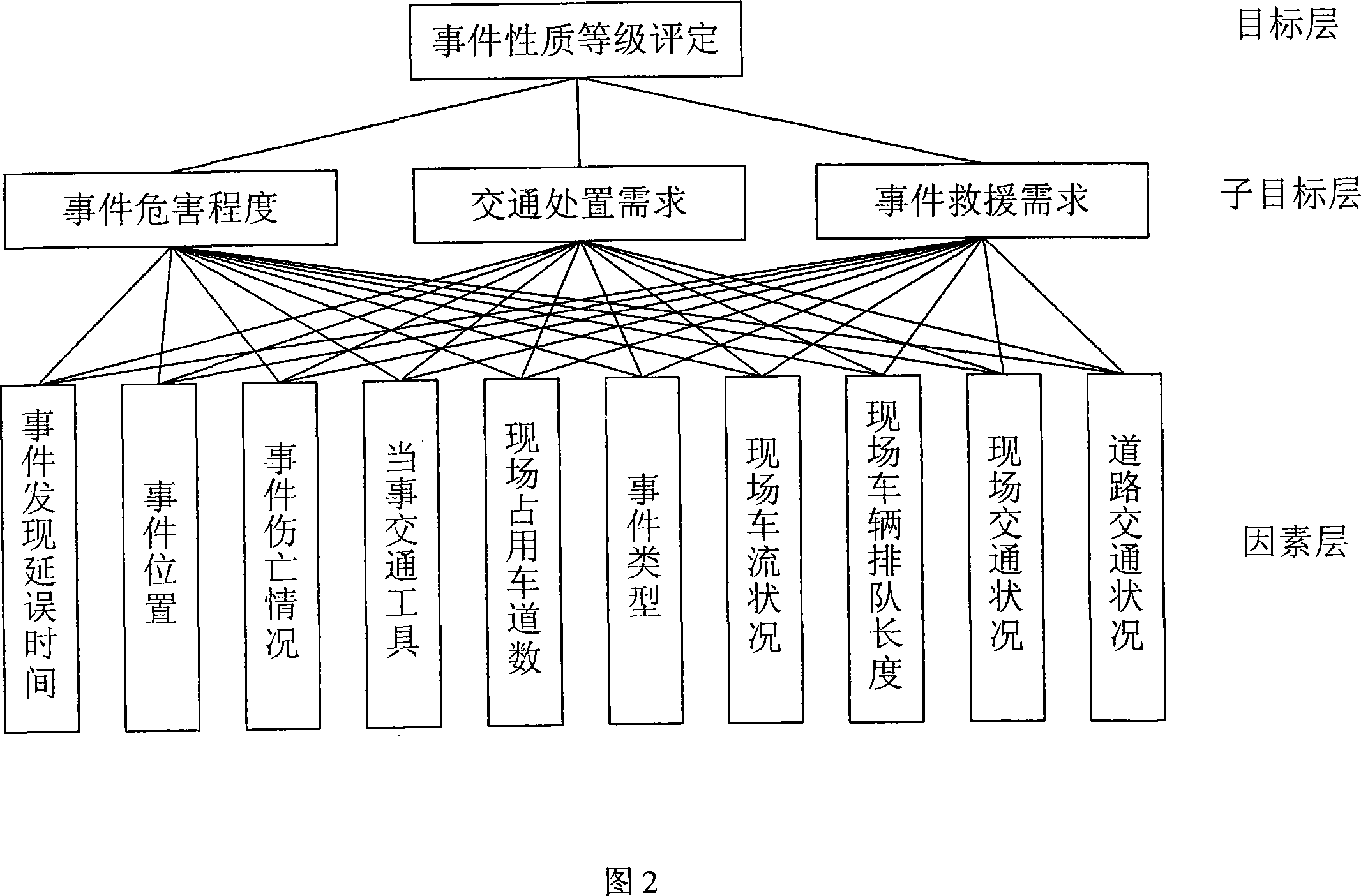
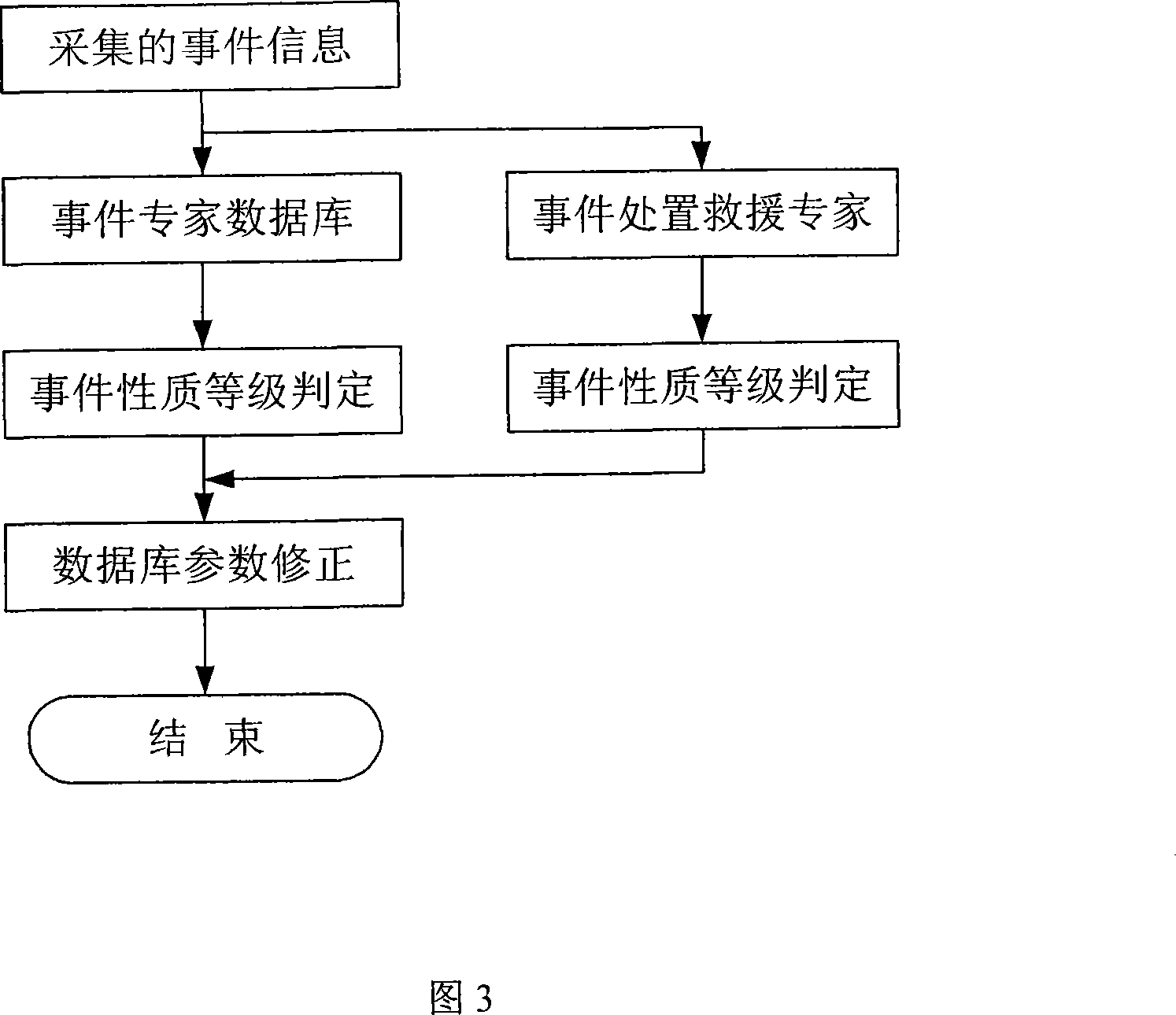
InactiveCN101159098AEasy to detectEasy to confirmData processing applicationsDetection of traffic movementDecision modelTraffic accident
The invention relates to an automatic detection identification method of city traffic accidents and reaches the object that rapid disposal capacity of the city traffic accidents is improved through the comprehensive application of the traffic accident automatic detection technique and the non-automatic detection technique and the casualties and property loss caused by the city traffic accidents is reduced through the comprehensive application of traffic accident automatic detection technique and non-automatic detection technique. The concrete method is that traffic accident influent length L=(V<up-Vdown)l / n is identified through the method that data are read and is transmitted to traffic comprehensive information platform; accident site image information collected by city traffic monitoring system is read; whether the traffic accident happens or not is judged by the video mode recognition technique; traffic accident special database transmits the index information and accident detection signals such as rank valuation, accident hazard degree, traffic disposal demand and accident rescue demand to traffic comprehensive information platform to be processed according to the relational traffic accident data and the indexes such as phrase vague decision model, generation traffic accident class, accident hazard degree, traffic disposal demand and accident rescue demand.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Vehicle control method and apparatus and method and apparatus for acquiring decision-making model
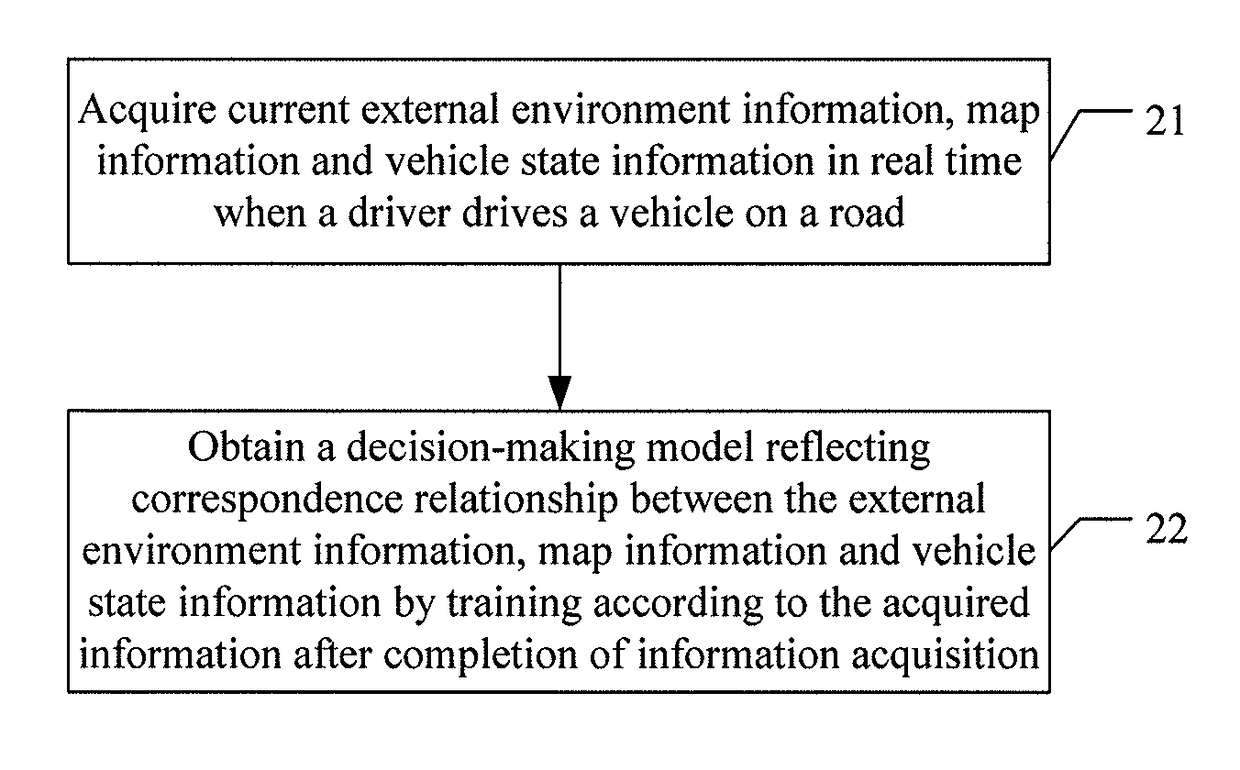
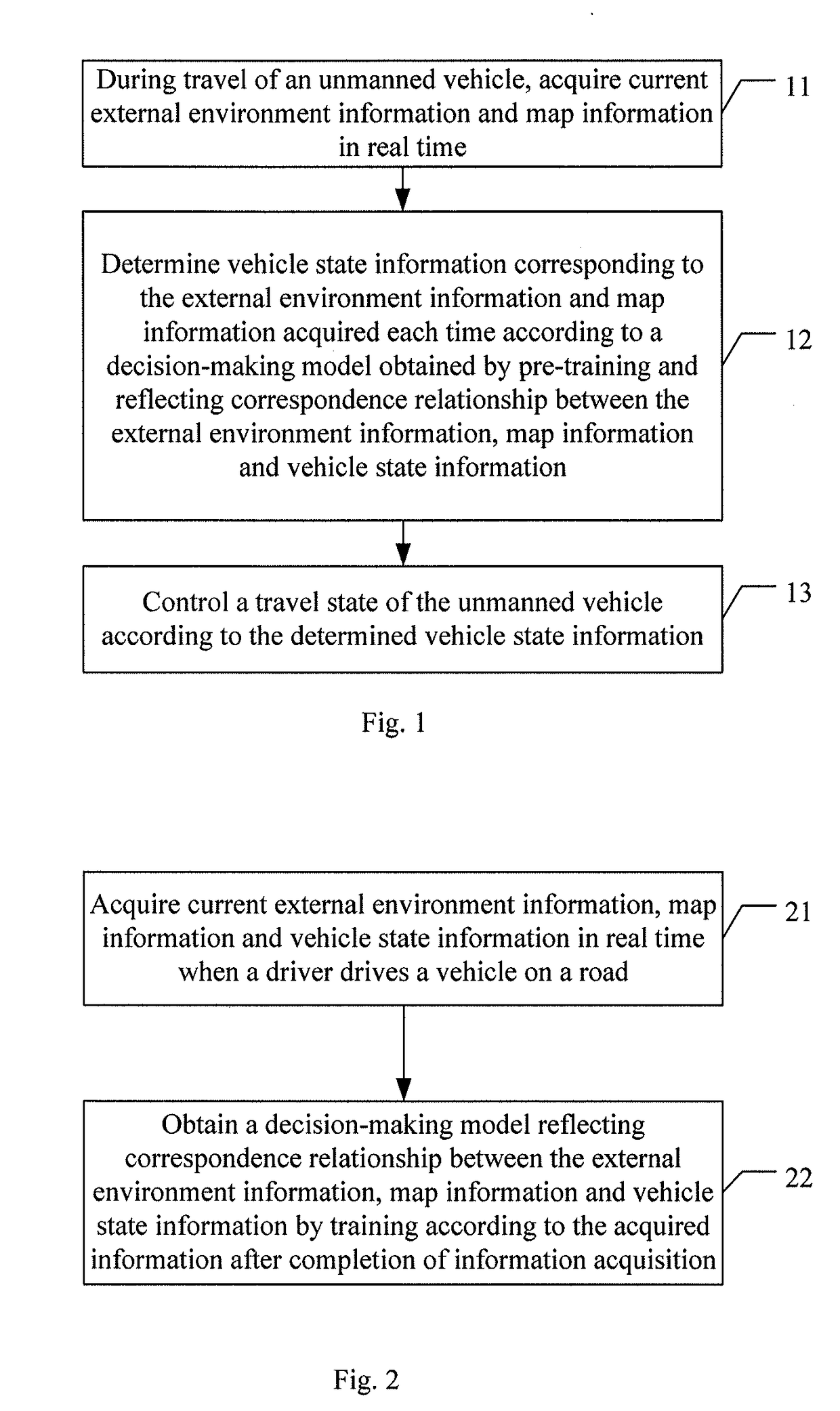
ActiveUS20170357257A1Improve abilitiesImprove securityHybrid vehiclesAutonomous decision making processWorkloadDecision-making models
The present invention discloses a vehicle control method and apparatus and a method and apparatus for acquiring a decision-making model. The vehicle control method, comprising: during travel of an unmanned vehicle, acquiring current external environment information and map information in real time; determining vehicle state information corresponding to the external environment information and map information acquired each time according to a decision-making model obtained by pre-training and reflecting correspondence relationship between the external environment information, map information and vehicle state information, and controlling a travel state of the unmanned vehicle according to the determined vehicle state information. Application of the solution of the present invention can improve security and reduce the workload.
Crop planting management system and method based on cloud services
InactiveCN110347127ARealize intelligenceRealize scientificProgramme total factory controlDiseaseDecision model
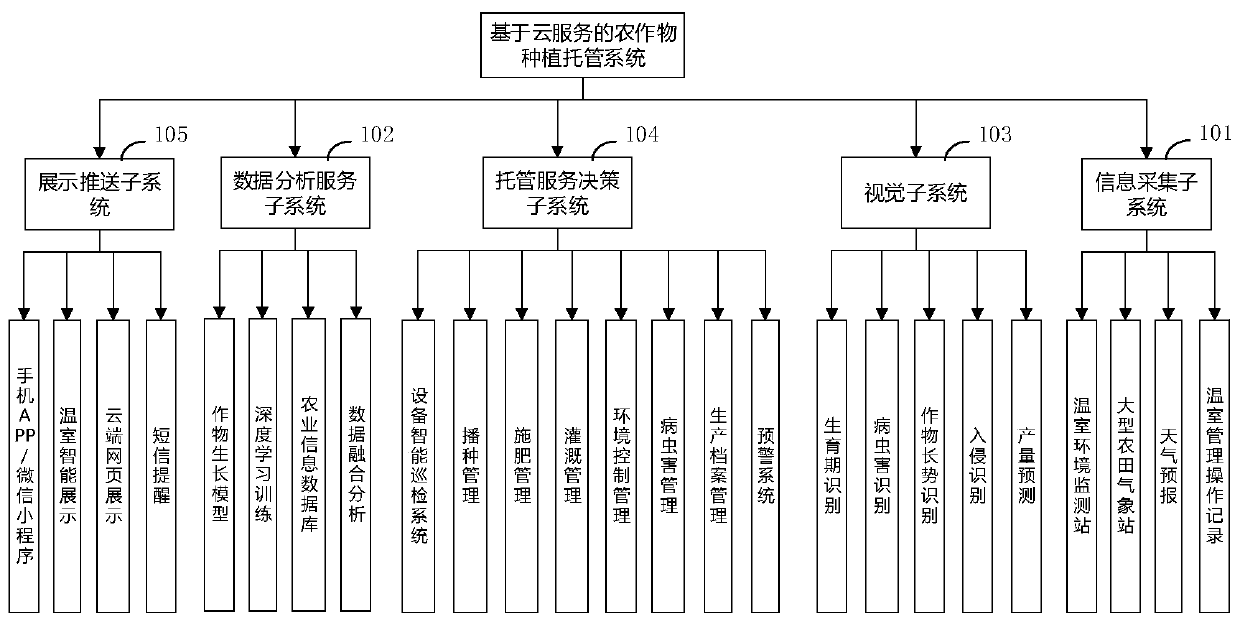
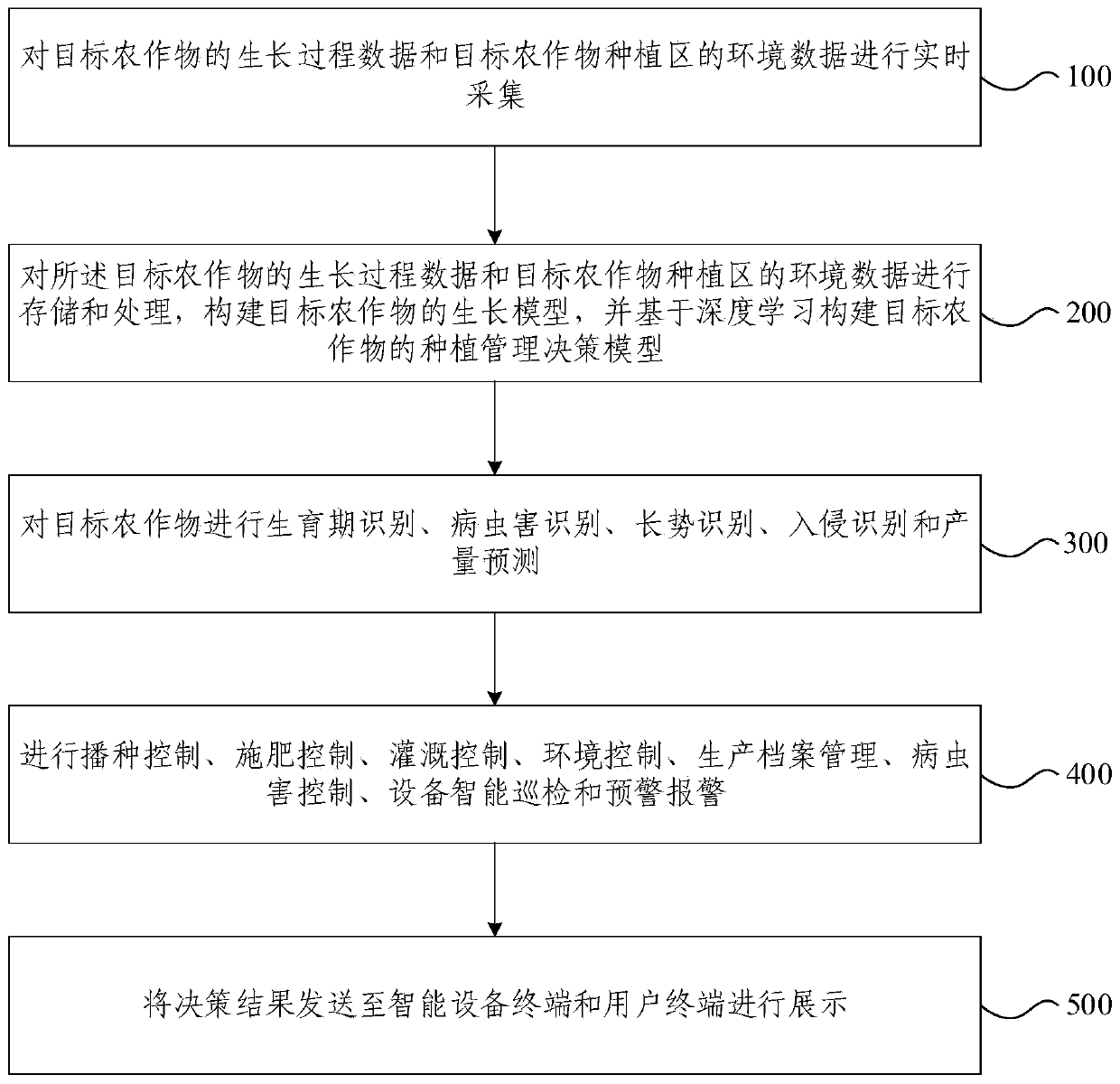
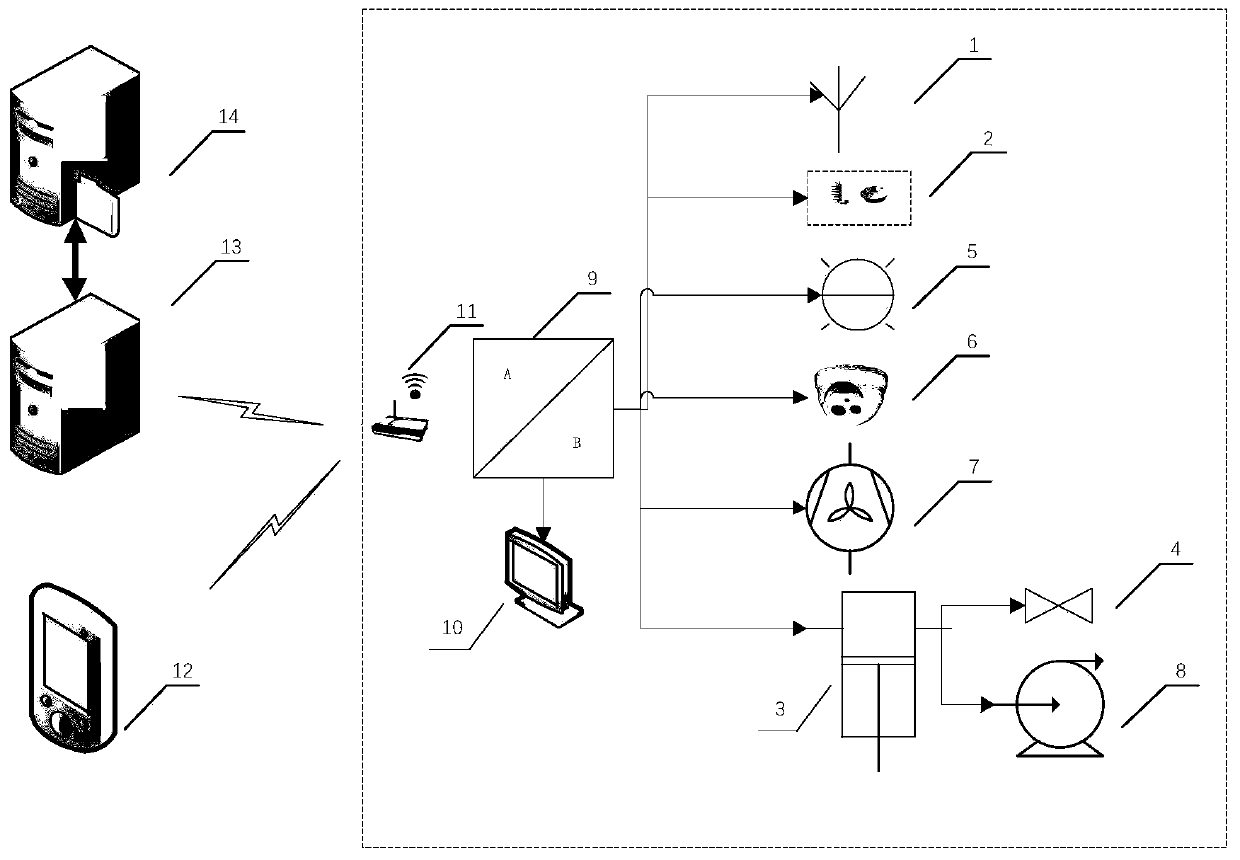
Embodiments of the invention provide a crop planting management system and method based on cloud services. The system comprises an information acquisition subsystem used for acquiring growth process data of target crops and environment data of a target crop planting area in real time, a data analysis service subsystem used for storing and processing the data acquired by the information acquisitionsubsystem and building a planting management decision model of the target crops based on deep learning, a visual subsystem used for performing growth period recognition, disease and pest recognition,growth vigor recognition, intrusion recognition and yield prediction on the target crops, a management service decision subsystem used for realizing seeding control, fertilization control, irrigationcontrol, environment control, production archive management, disease and pest control, intelligent equipment patrol and early warning, and a display pushing subsystem used for sending a decision result to an intelligent equipment terminal and a user terminal for displaying. The crop planting management system and method based on cloud services can be used for realizing intelligent, scientific andunmanned agricultural planting management.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
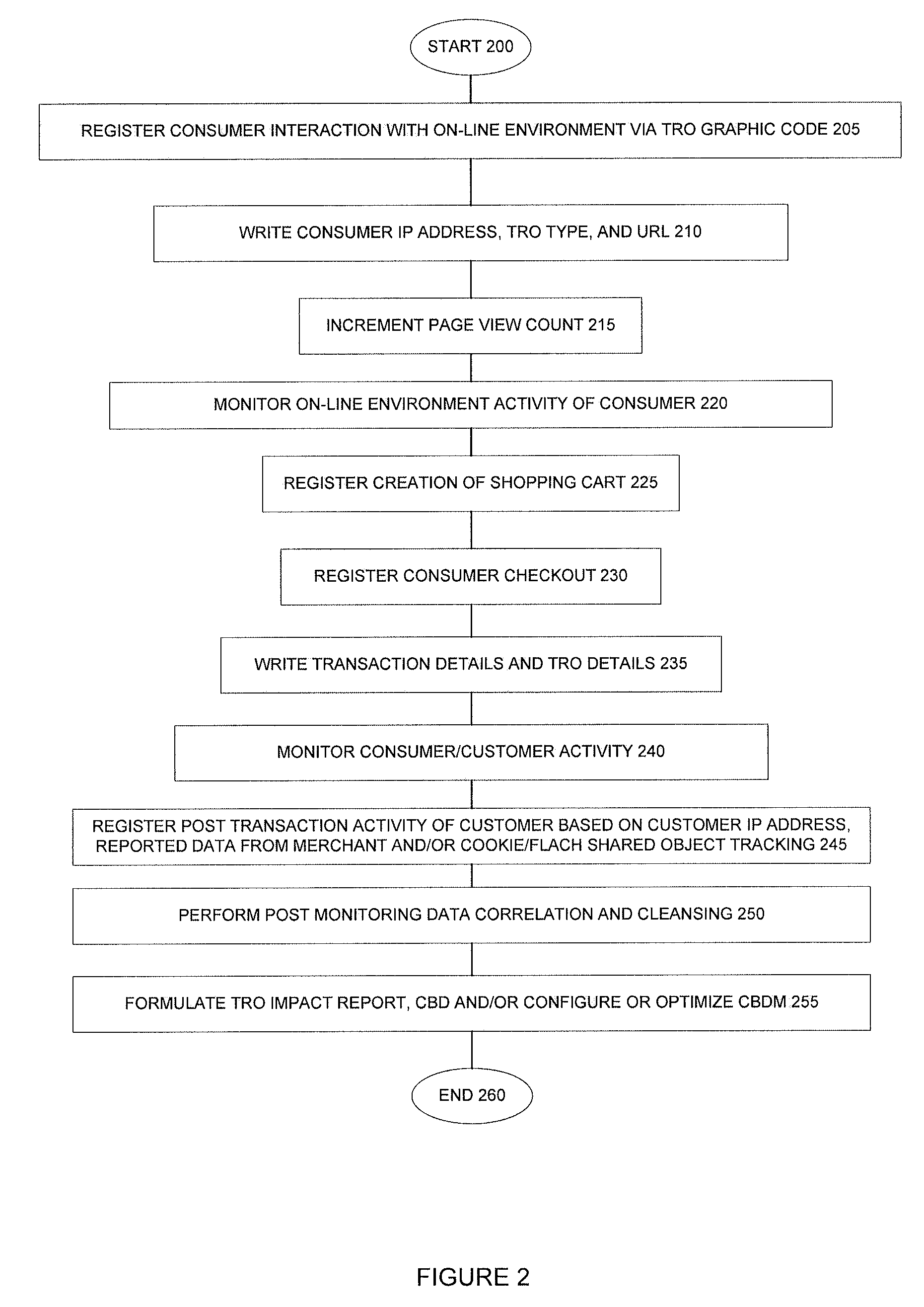
Method, system and components for obtaining, evaluating and/or utilizing seller, buyer and transaction data
Methodologies, systems, components and software are provided that perform web analytics to measure visitor to consumer conversion continuously throughout surfing, through conversion and past completion of a purchase on-line. In accordance with at least one embodiment, such methodologies, systems, components and software may be utilized to determine efficacy of a plurality of parameters relating to one or more Transaction Related Offerings (TROs). In accordance with at least one embodiment of the invention, such methodologies, systems, components and software may be utilized to configure one or more Consumer Behavior Decision Models (CBDMS) and / or generate consumer behavior data.
Owner:BUYSAFE
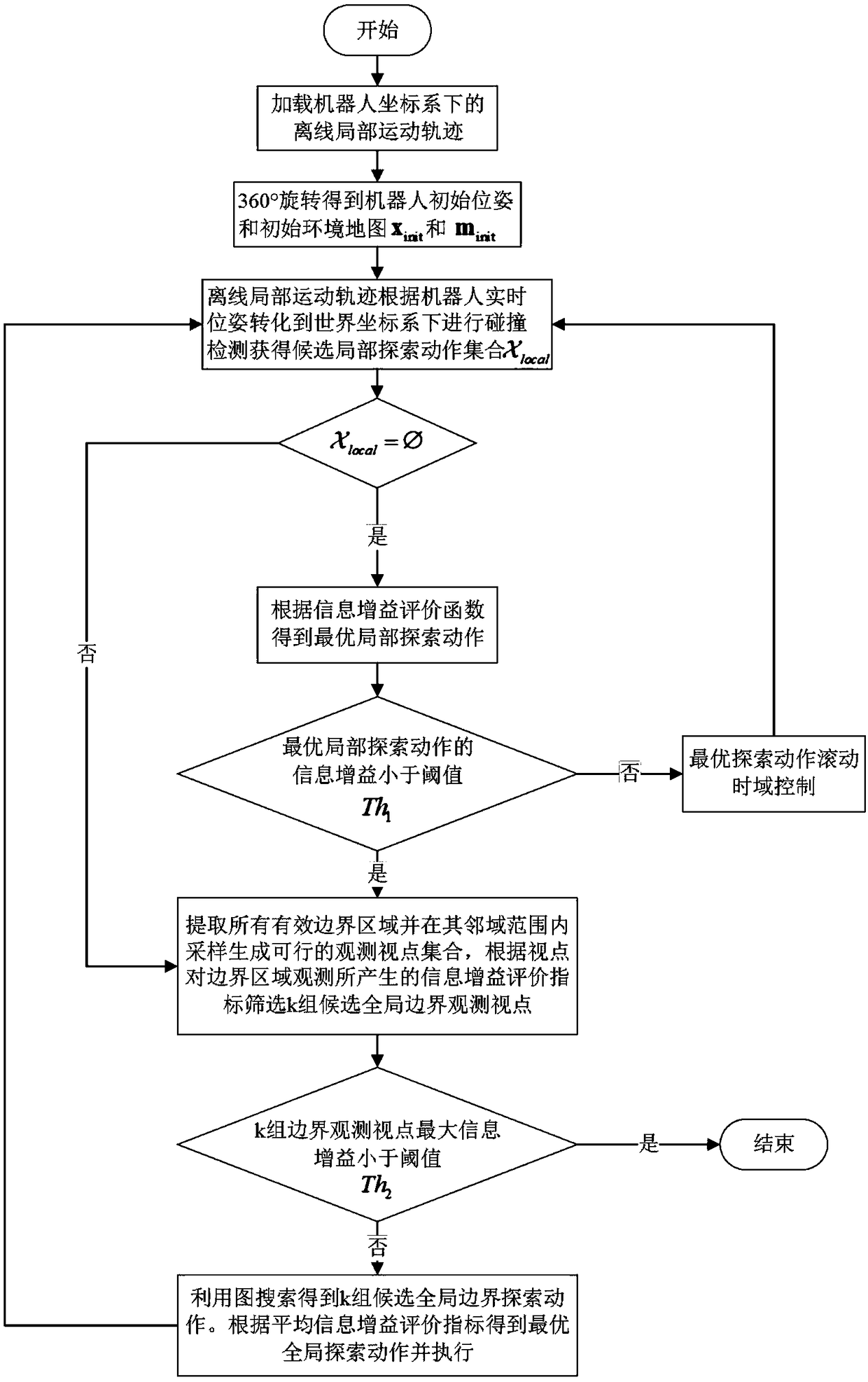
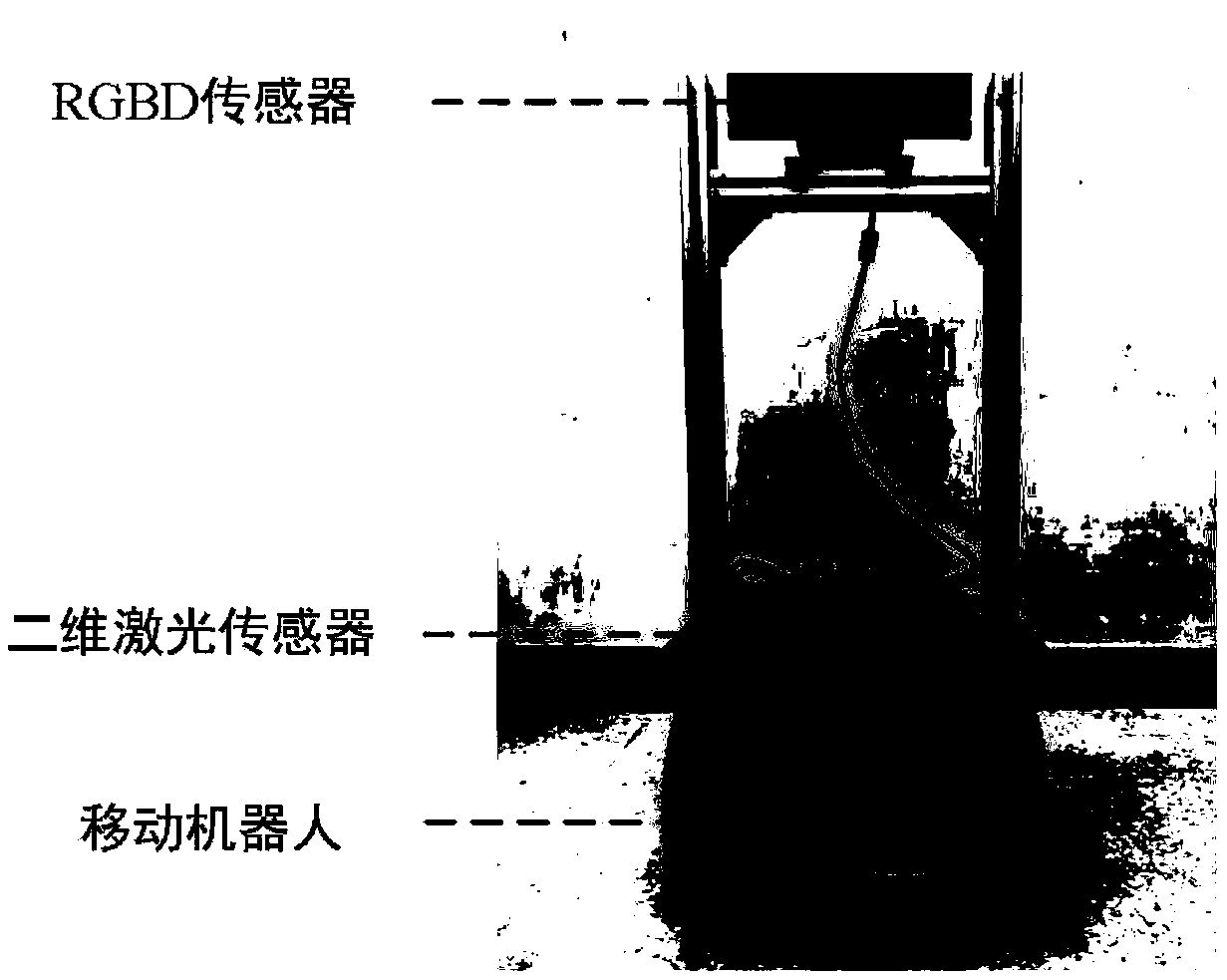
Method for constructing three-dimensional map by mobile robot in unknown environment
ActiveCN109341707AIntegrity guaranteedAchieve a full buildInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsDecision modelInformation gain
The invention discloses a method for constructing a three-dimensional (3D) map by a mobile robot in an unknown environment, and proposes a multi-exploration strategy method combining information gainguided local exploration strategy and global boundary exploration strategy for a problem of constructing a map of an indoor unknown 3D environment. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing an autonomous exploration and 3D map construction system framework of the mobile robot, which comprises a map construction module and an exploration decision planning control module; secondly, establishing an information gain guided decision model based on a Shannon information theory and designing an information gain objective function calculation applied to multi-step exploration action evaluation; and finally, constructing a local exploration strategy by using an offline local motion trajectory, realizing a multi-strategy exploration method by combining with the information gainguided global boundary exploration strategy, and dynamically switching the two strategies during exploration according to real-time construction situations of the 3D map. Experimental results show that the method provided by the invention ensures integrity of map construction while rapidly constructing the 3D map.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
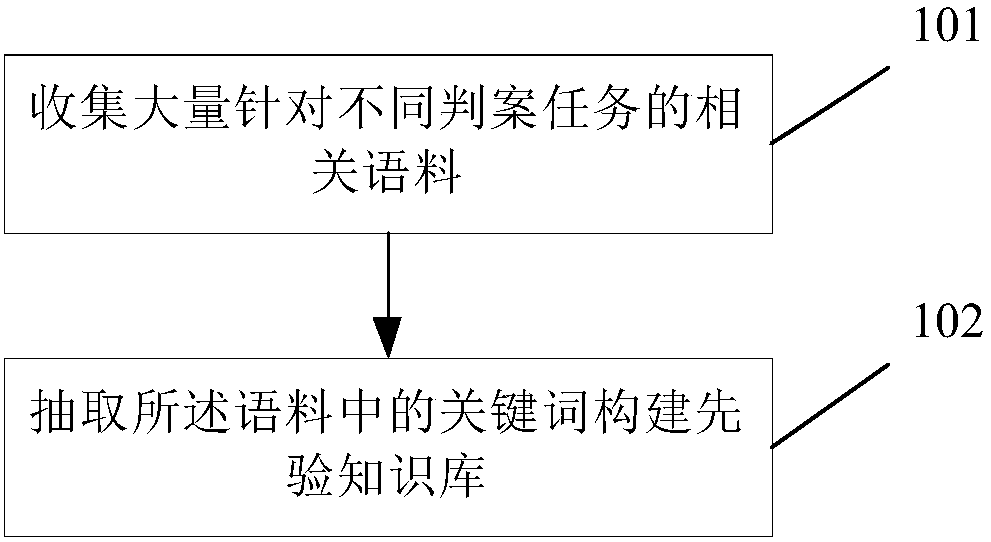
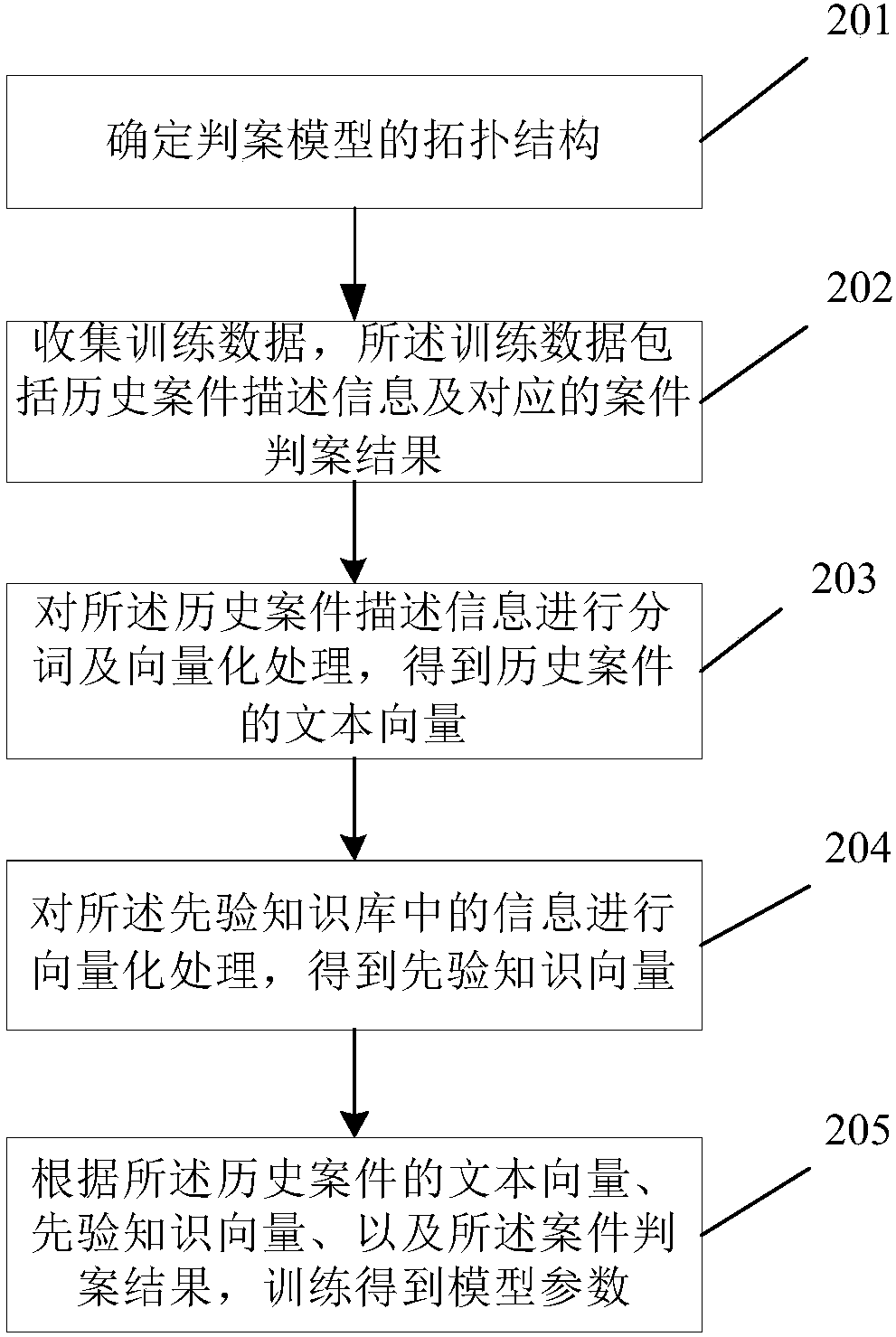
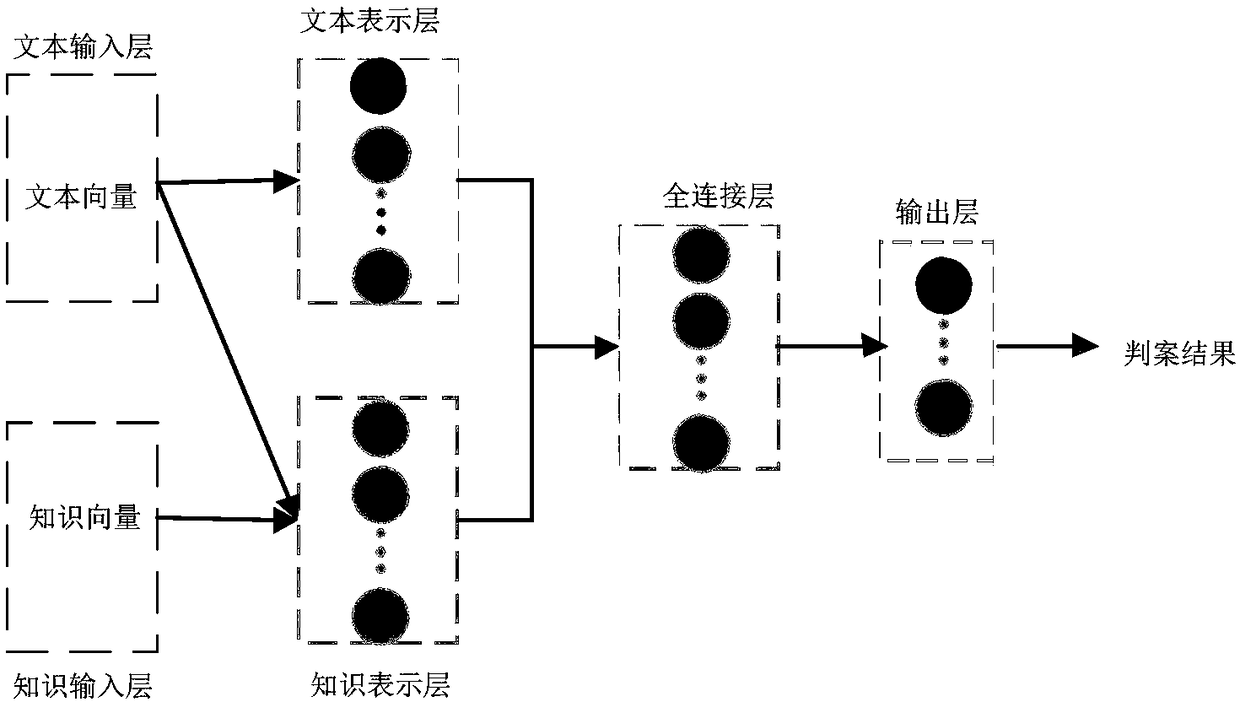
Automatic case decision method and system
InactiveCN108133436AReduce workloadAvoid influenceData processing applicationsKnowledge representationDecision modelDecision methods
The invention discloses an automatic case decision method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining related data of a to-be-decided case; carrying out word segmentation and vectorization on the related data of the to-be-decided case so as to obtain a text vector of the to-be-decided case; vectorizing information in a pre-constructed prior knowledge base so as to obtain a prior knowledge vector; and inputting the prior knowledge vector and the text vector of the to-be-decided case into a pre-constructed case decision model, and obtaining a case decision result accordingto output of the case decision model. By utilizing the method and the system, the case decision efficiency can be improved, influences of subjective factors such as knowledge background of judicial officials and the like can be avoided, and the case decision fairness and authority can be improved.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD +2
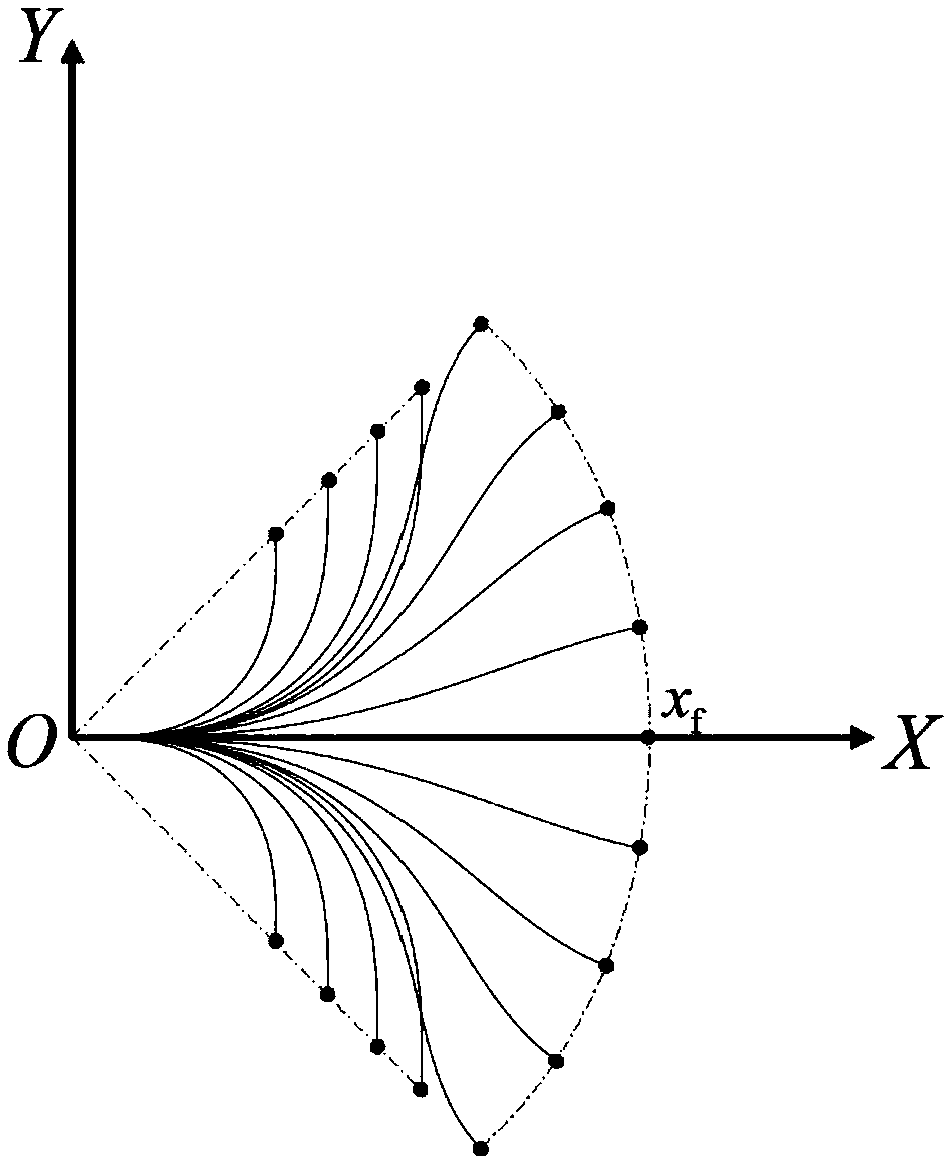
Method for planning paths of unmanned aerial vehicles on basis of Q(lambda) algorithms
ActiveCN109655066AGive full play to the flying abilitySolve the shortcomings of the lack of basis in the discretization processNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsDecision modelEnvironmental modelling
The invention provides a method for planning tasks of unmanned aerial vehicles on the basis of Q(lambda) algorithms. The method includes a step of carrying out environment modeling, a step of initializing Markov decision process models, a step of carrying out Q(lambda) algorithm iterative computation and a step of computing the optimal paths according to state value functions. The method particularly includes initializing grid spaces according to the minimum flight path section lengths of the unmanned aerial vehicles, mapping coordinates of the grid spaces to obtain airway points and representing circular and polygonal threat regions; building Markov decision models, to be more specific, representing flight action spaces of the unmanned aerial vehicles, designing state transition probability and constructing reward functions; carrying out iterative computation on the basis of constructed models by the aid of the Q(lambda) algorithms; computing each optimal path of the corresponding unmanned aerial vehicle according to the ultimate convergent state value functions. The unmanned aerial vehicles can safely avoid the threat regions via the optimal paths computed according to the ultimate convergent state value functions. The method has the advantages that the traditional Q learning algorithms and effectiveness tracking are combined with one another, accordingly, the value functionconvergence speeds can be increased, the value function convergence precision can be enhanced, and the unmanned aerial vehicles can be guided to avoid the threat regions and autonomously plan paths.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Automatic driving overtaking decision-making method based on reinforcement learning under opposite double lanes
ActiveCN110969848AEnsure safetyGuaranteed comfortInternal combustion piston enginesDetection of traffic movementDecision modelEngineering
The invention discloses an automatic driving overtaking decision-making method based on reinforcement learning under opposite double lanes. The method comprises the following steps of collecting the traffic state of an automatic driving vehicle through a sensor; inputting the collected traffic state into a trained decision model; enabling the decision model to select a corresponding driving actioninstruction from the action space according to the input information and output the driving action instruction, and driving the vehicle automatically to form a new traffic state after the driving action; calculating a reward value of the driving action through a reward function, and storing the original traffic state, the driving action, the reward value and the new traffic state into an experience playback pool as transfer samples; calculating a loss function value of the decision model, and optimizing parameters of the decision model according to the transfer sample and the loss function value; and repeating the steps until the automatic driving is finished. The safety and comfort of the overtaking decision-making process of the automatic driving vehicle are ensured, and the humanization and robustness of decision-making are improved through a reinforcement learning decision-making method.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
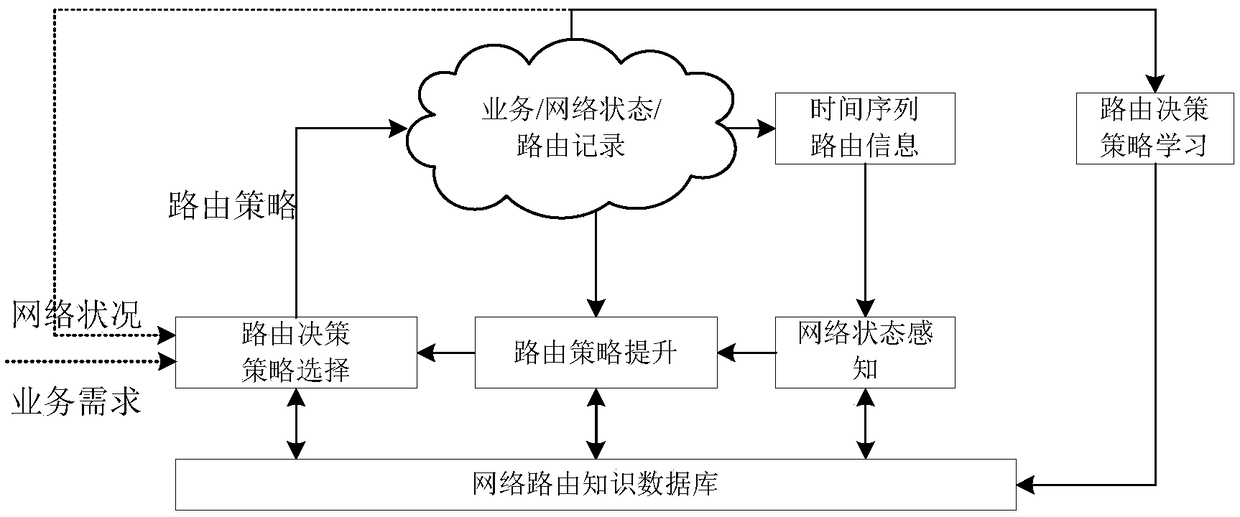
Fast routing decision algorithm based on Q learning and LSTM neural network
ActiveCN108667734ASolve the problem of slow convergence and long training processSave time and costData switching networksRouting decisionDecision model
The invention discloses a fast routing decision algorithm based on Q learning and a LSTM neural network. The algorithm is mainly divided into two stages including model training and dynamic routing decision; and the model training stage is mainly used for calculating an optimal or a relatively better path which satisfies a constraint condition according to different QoS requests through a heuristic algorithm. Then, input and corresponding output of the heuristic algorithm are combined to form a training set of a machine learning model, and the training set is taken as a target Q value of different routing to train a decision model. On the basis, when a controller receives a new QoS request, correspondingly, the machine learning model jointly takes the current network state and the constraint condition in the request as input of the model, corresponding Q value can be calculated quickly through the routing decision model in which LSTM and Q learning are combined, and prediction is completed and an optimal path can be output. Time for the process is greatly reduced in comparison with the heuristic algorithm, but the result is very similar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-time scale coordinated control method for independent microgrid with hybrid energy storage
InactiveCN109149567AFast solutionImprove robustnessSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingDecision modelMicrogrid
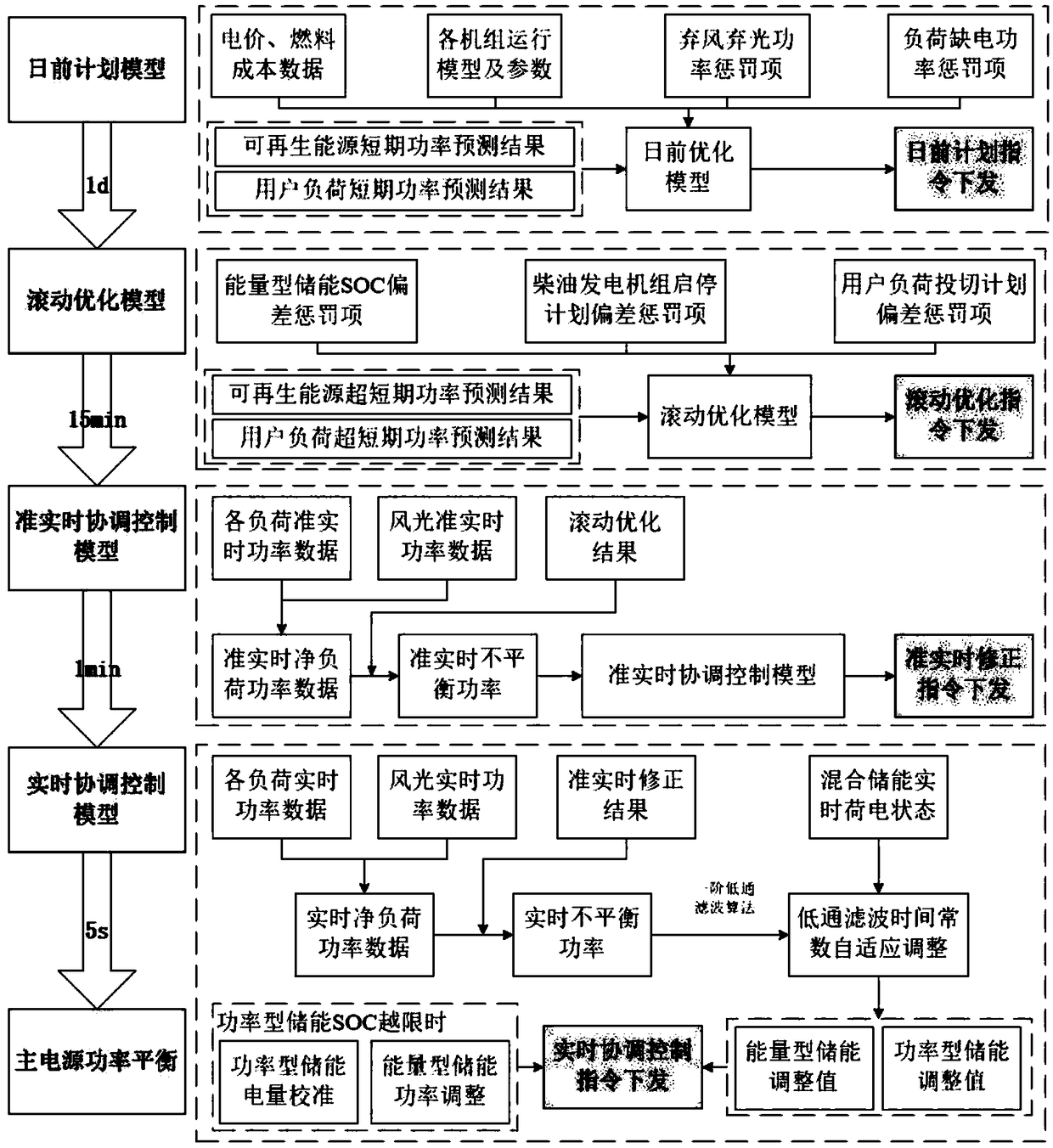
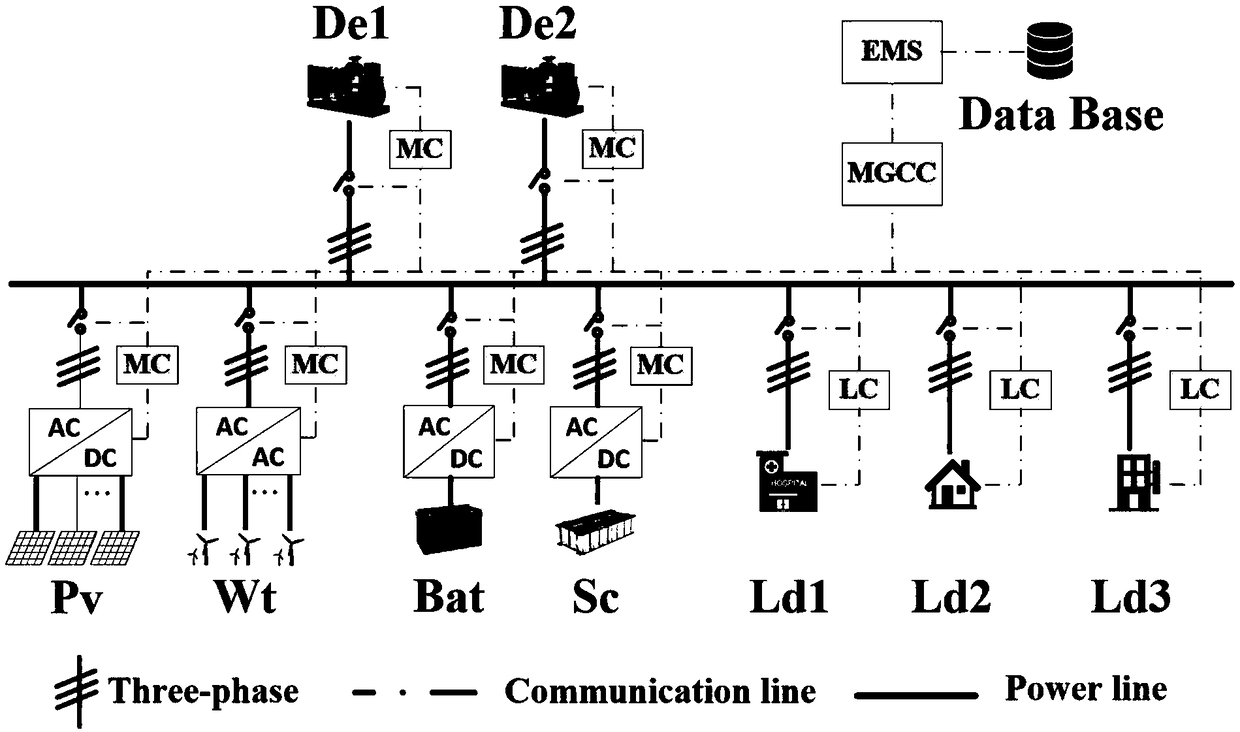
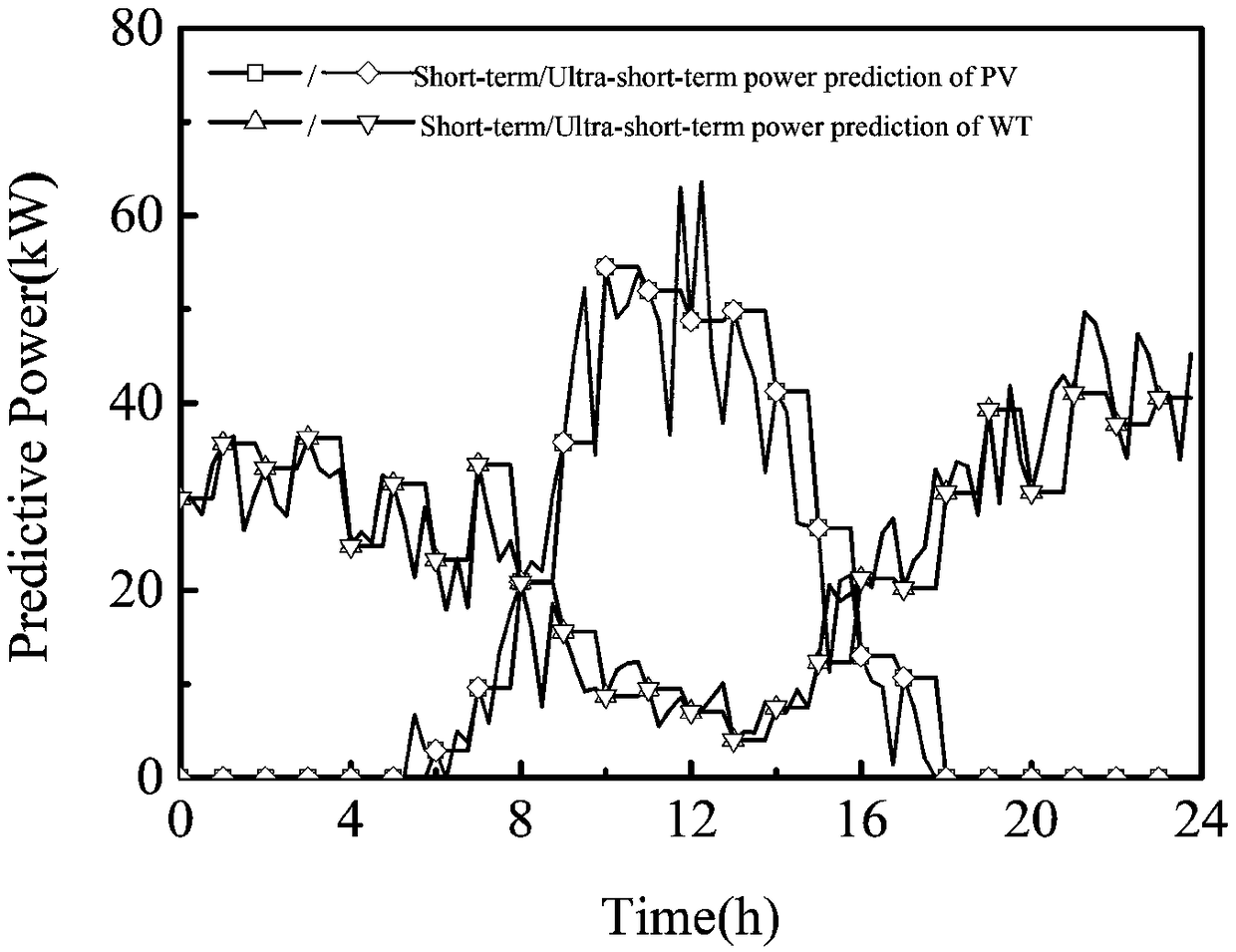
The invention discloses an improved multi-time scale coordinated control method for independent microgrid containing hybrid energy storage, this method is based on the day-ahead planning decision model, The intra-day rolling optimization model based on model predictive control, the quasi-real-time coordinated control model based on comprehensive criteria and the real-time coordinated control modelare constructed. Firstly, the day-ahead planning decision-making model takes the operation economy as the optimization objective, the operation restriction of distributed generation and the safety and stability of the system as the constraint conditions. Then the controllable unit start-stop plan deviation and load switching plan deviation are introduced into the rolling optimization model as soft constraints, which allow to revise the unit start-stop plan and load switching plan before the day. Secondly, a comprehensive criterion is introduced into the quasi-real-time coordinated control todecide the priority of distributed generation. Finally, in the real-time coordinated control, the hybrid energy storage system adopts the improved first-order low-pass filter algorithm to compensate the second-order unbalanced power adaptively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Unmanned vehicle urban intersection left turn decision-making method based on conflict resolution
ActiveCN110298122AImprove rationalityImprove adaptabilityControlling traffic signalsForecastingDecision modelVehicle driving
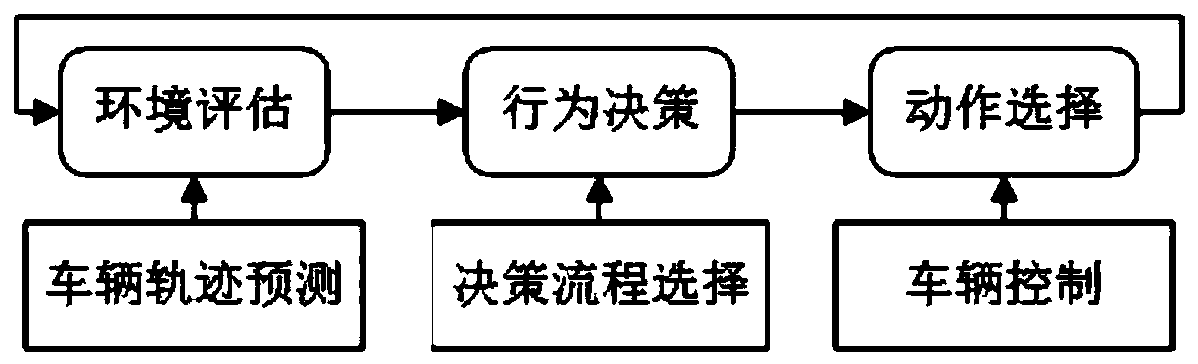
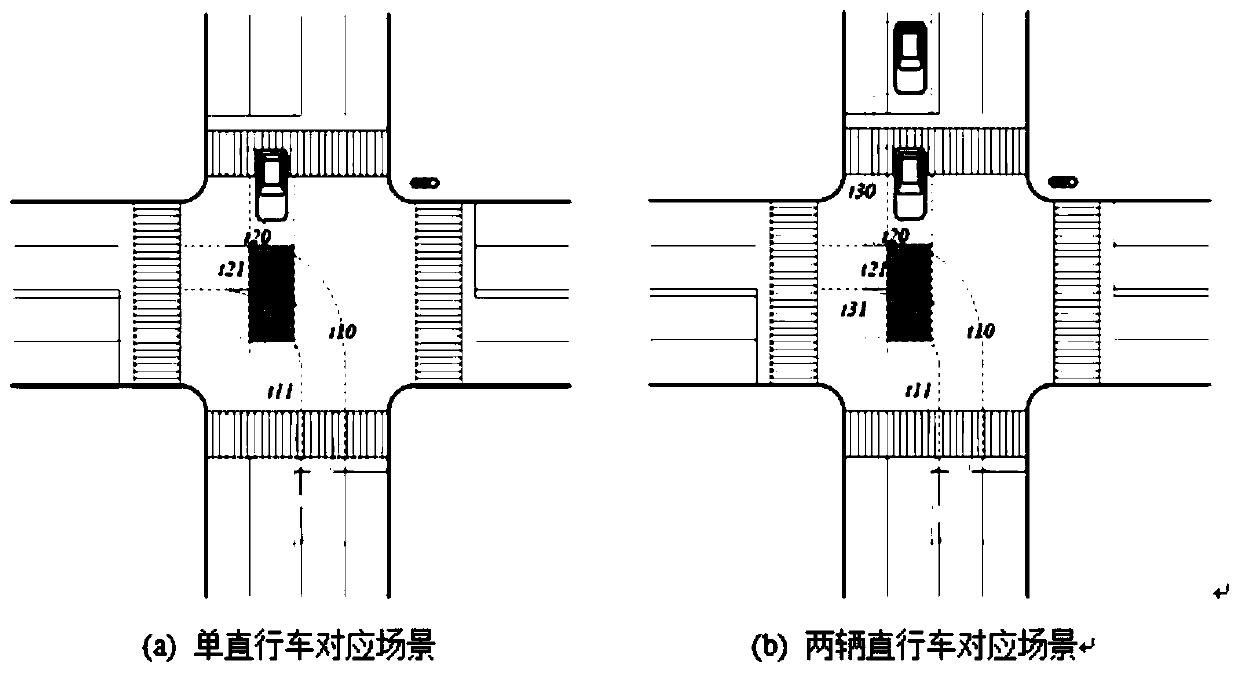
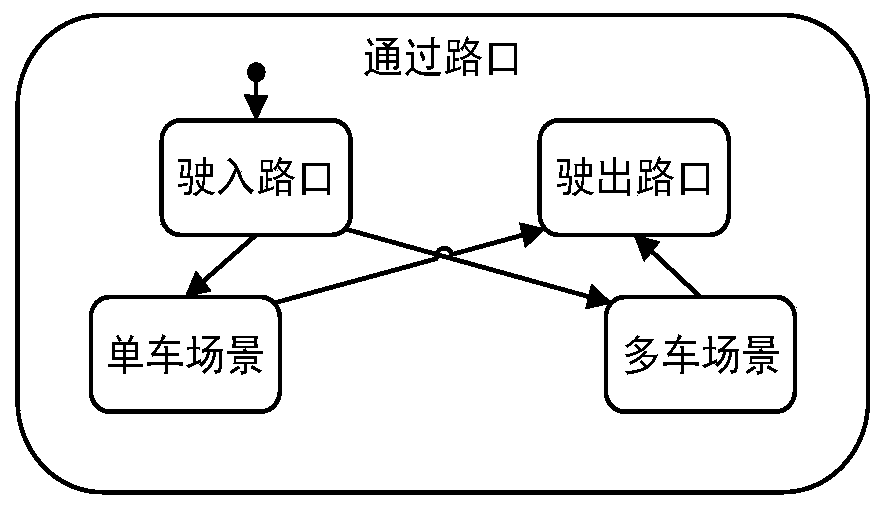
The invention discloses an unmanned vehicle urban intersection left-turn decision-making method based on conflict resolution. The method comprises the steps of track prediction for straight vehicles at an intersection, decision-making process selection of a behavior decision-making module corresponding to different scenes, and vehicle control parameter selection corresponding to an action selection module. According to the invention, the decision-making framework of the left turn of the unmanned vehicle at the intersection is divided into environment assessment, behavior decision-making and action selection; prediction of intersection straight driving motion tracks is realized by using a Gaussian process regression model, decision-making processes under different left-turn scenes are formulated, and an unmanned vehicle driving action selection method considering multiple factors is provided; and the decision-making process of the left turn of the unmanned vehicle at the intersection isstructured and clarified, so that the reasonability and the adaptability of the decision-making model are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com