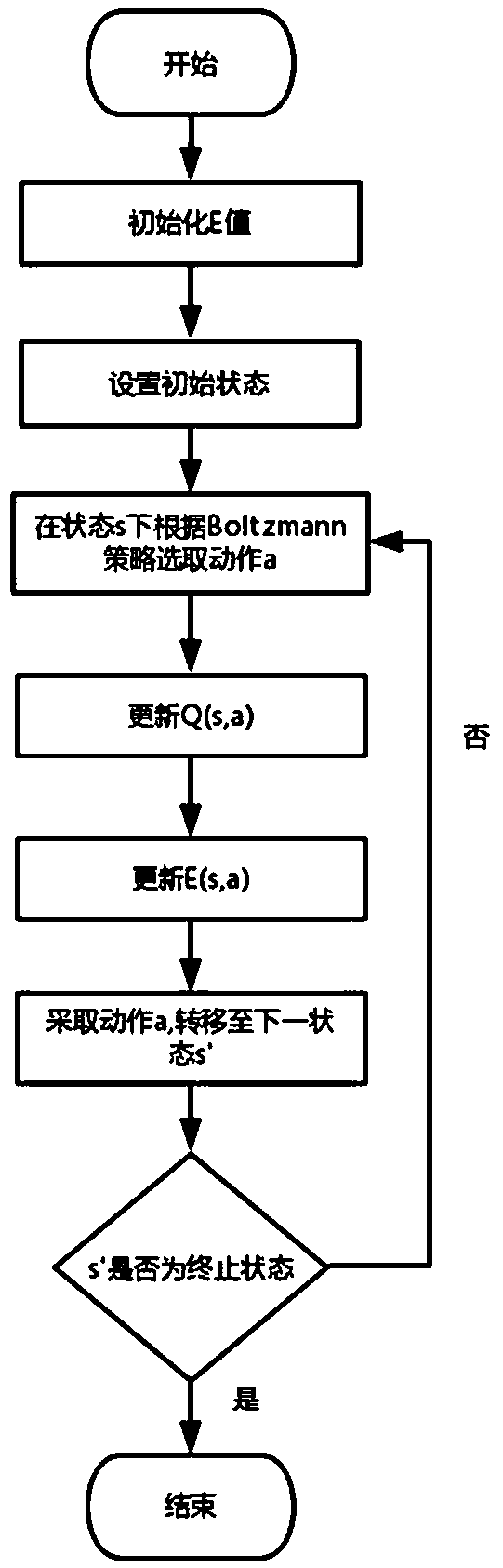
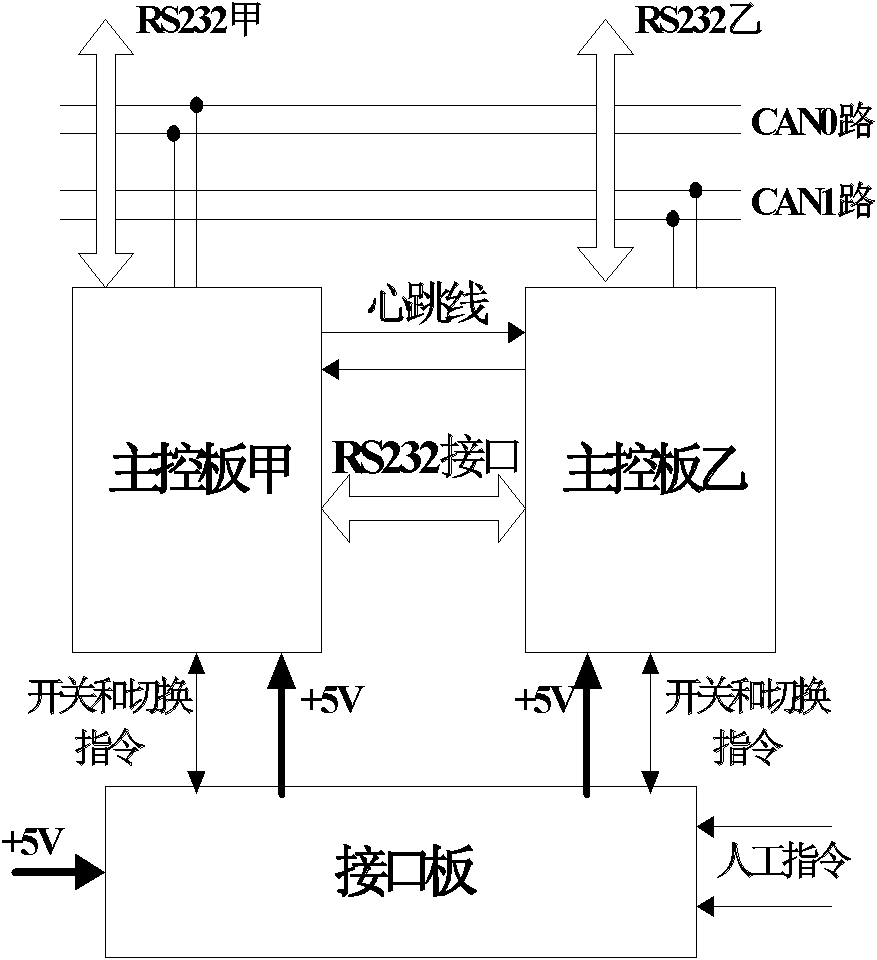
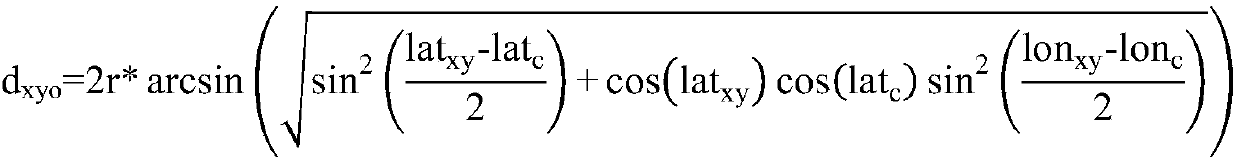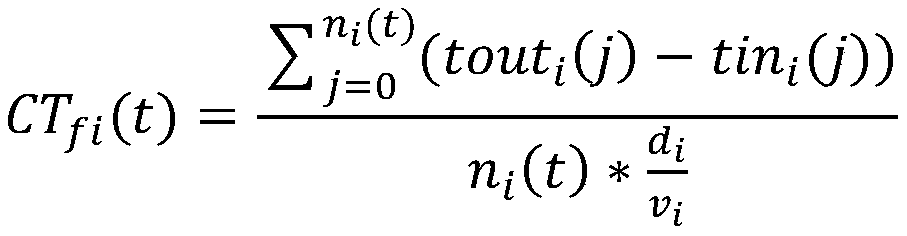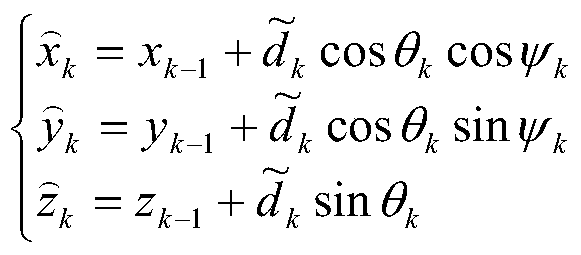Patents
Literature
47 results about "Environmental modelling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environmental modelling is the creation and use of mathematical models of the environment. Environmental modelling may be used purely for research purposes and improved understanding of environmental systems, or for providing an interdisciplinary analysis that can inform decision making and policy.
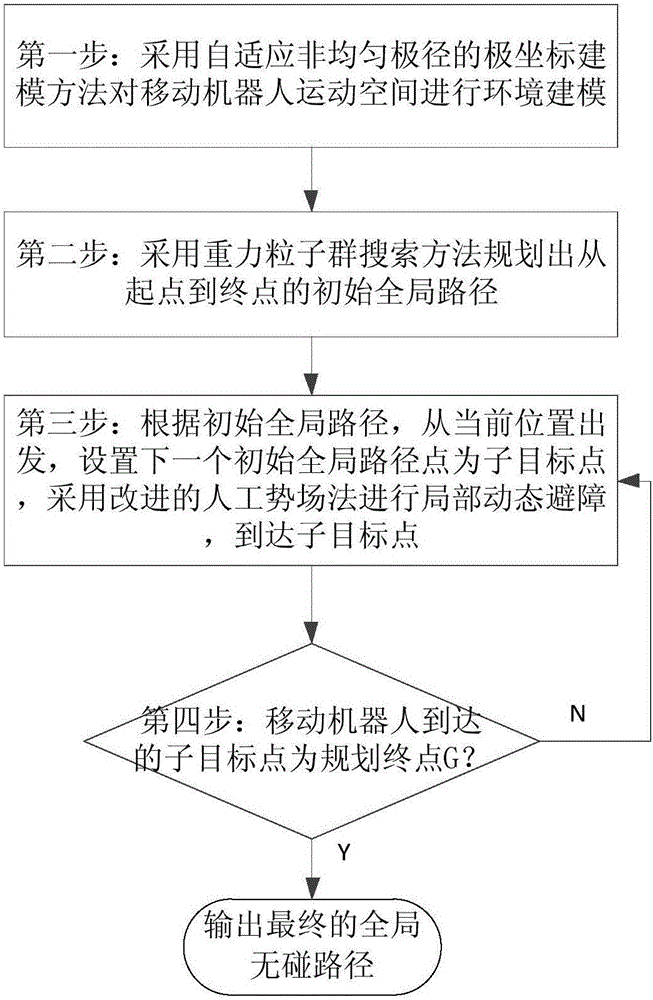
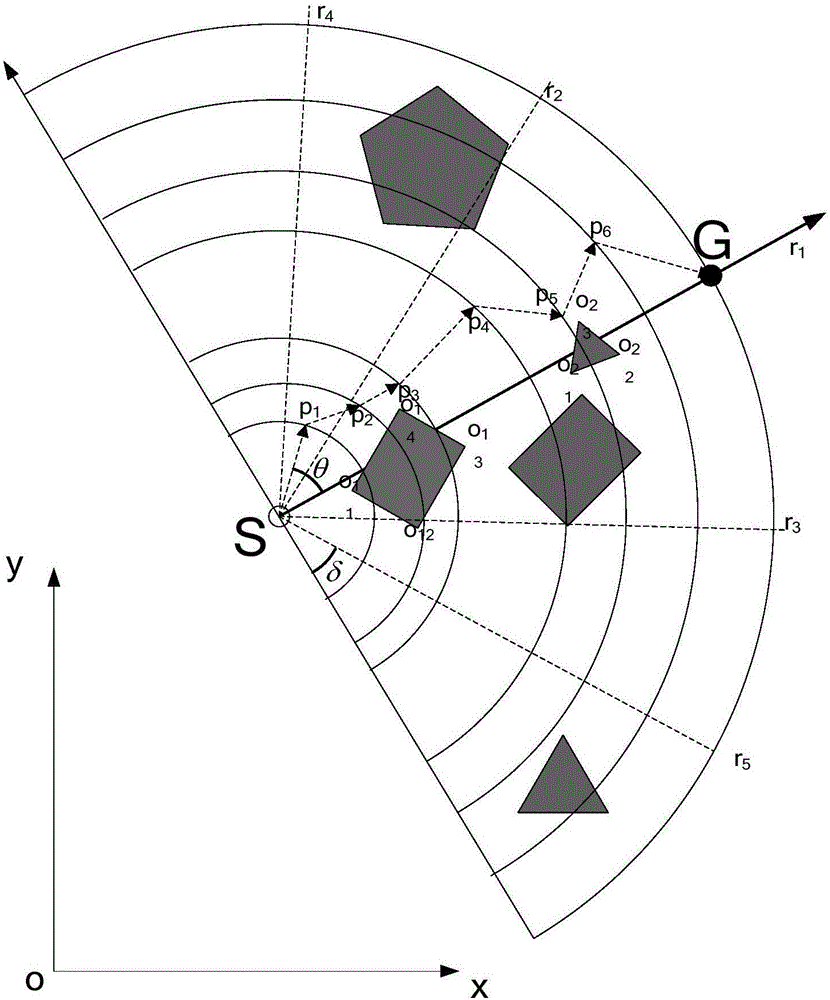
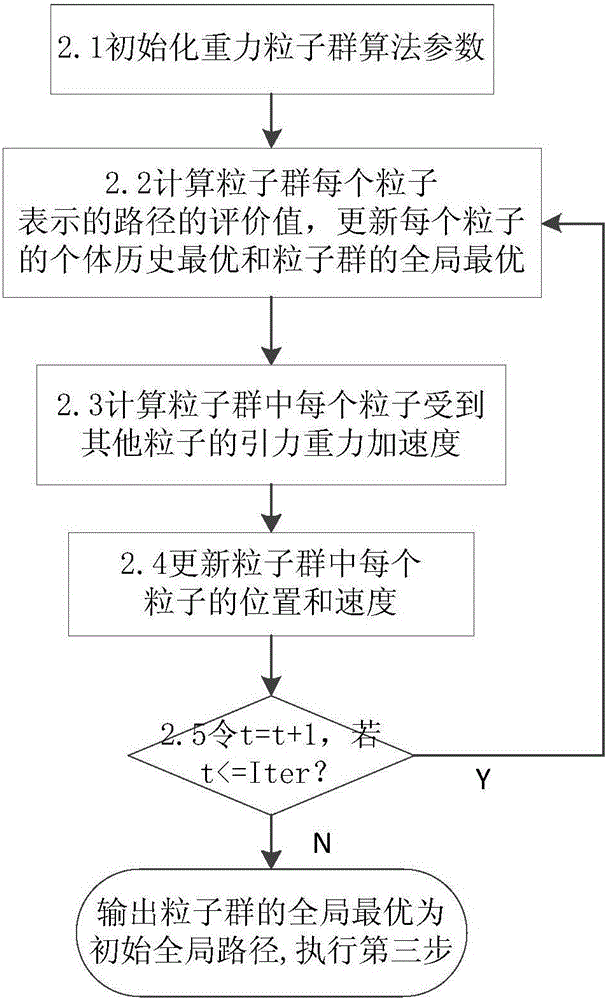
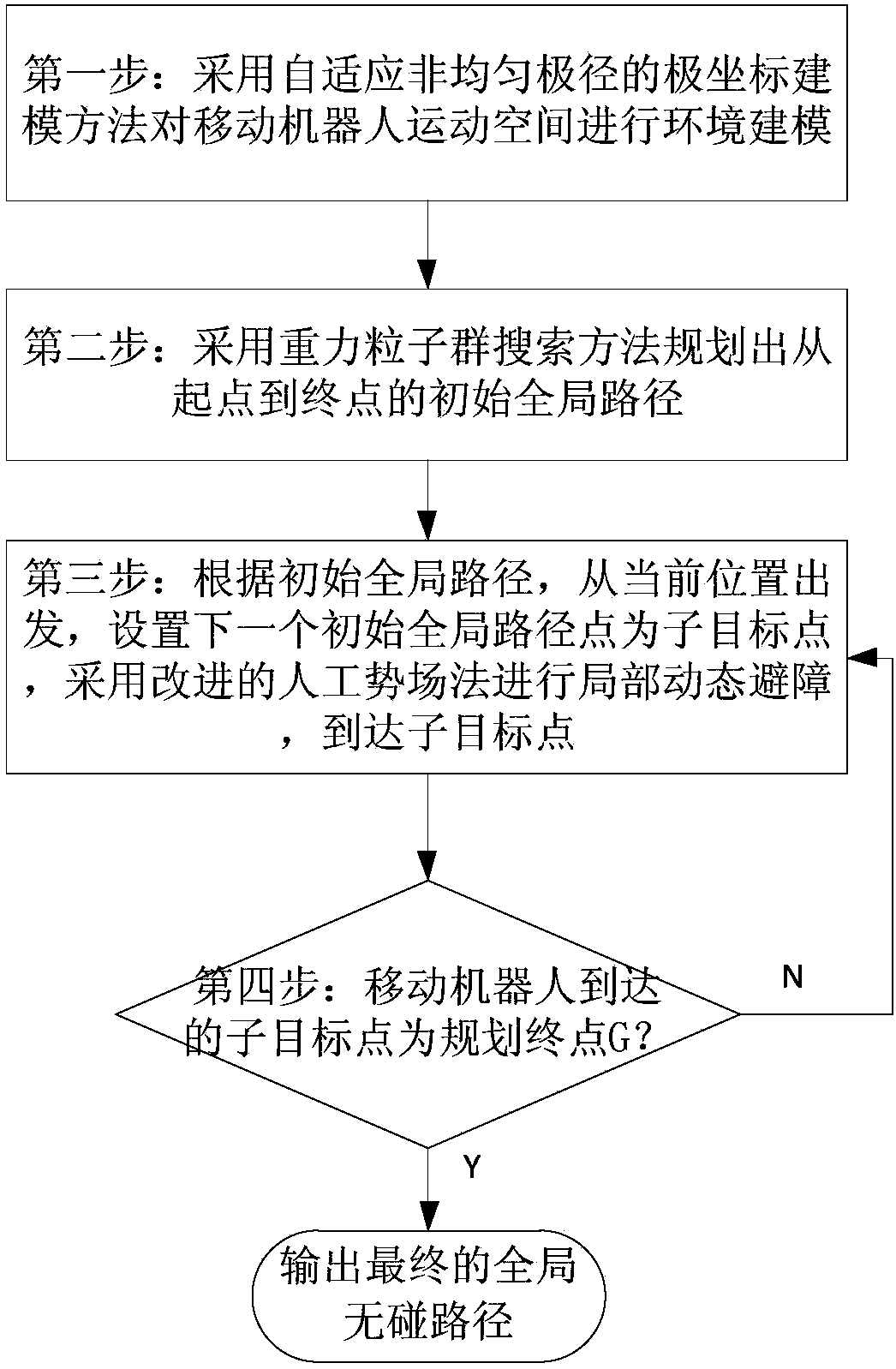
Planning method for mixed path of mobile robot under multi-resolution barrier environment
ActiveCN105717929AImprove blindnessReduce computational costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPresent methodPotential field
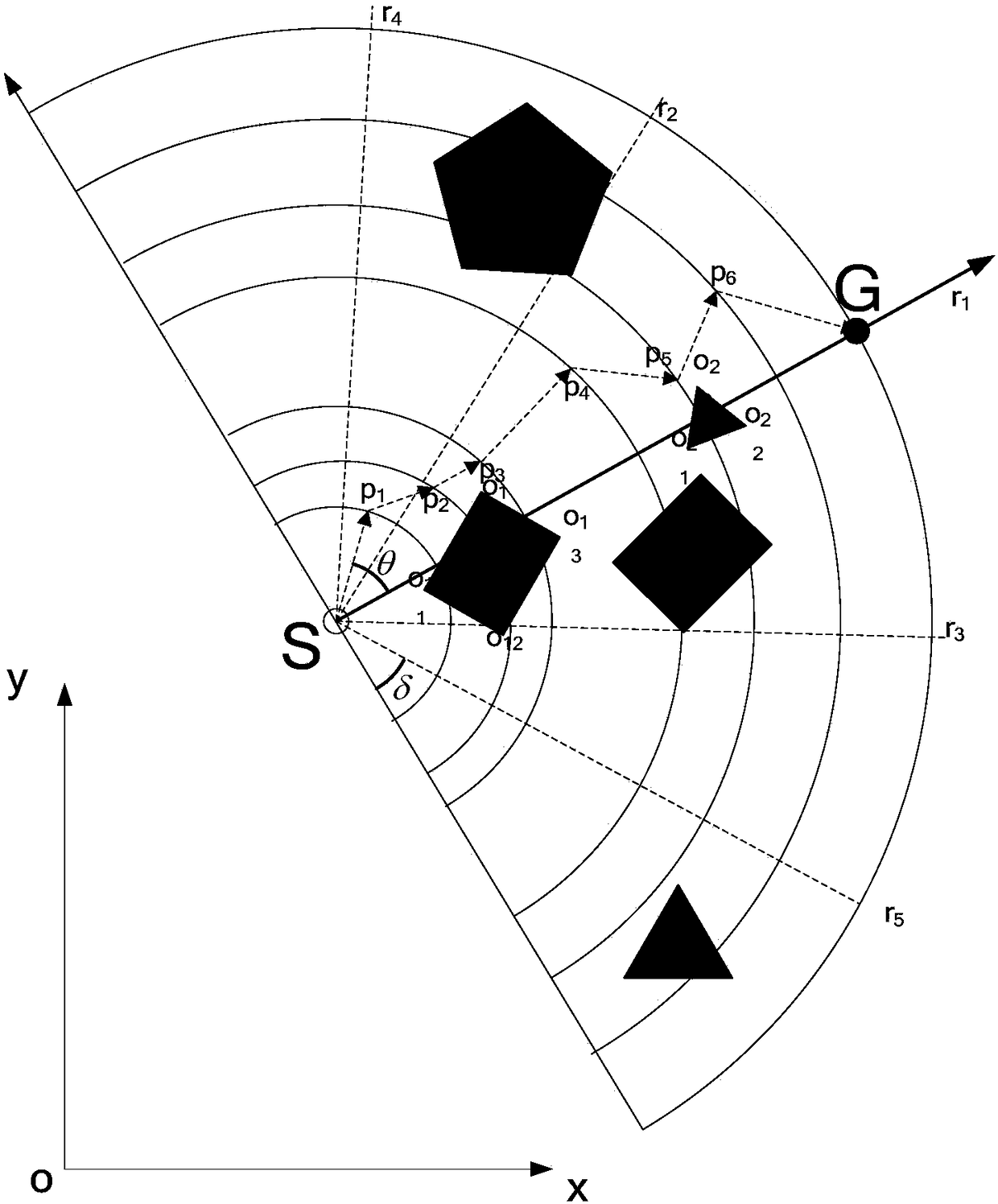
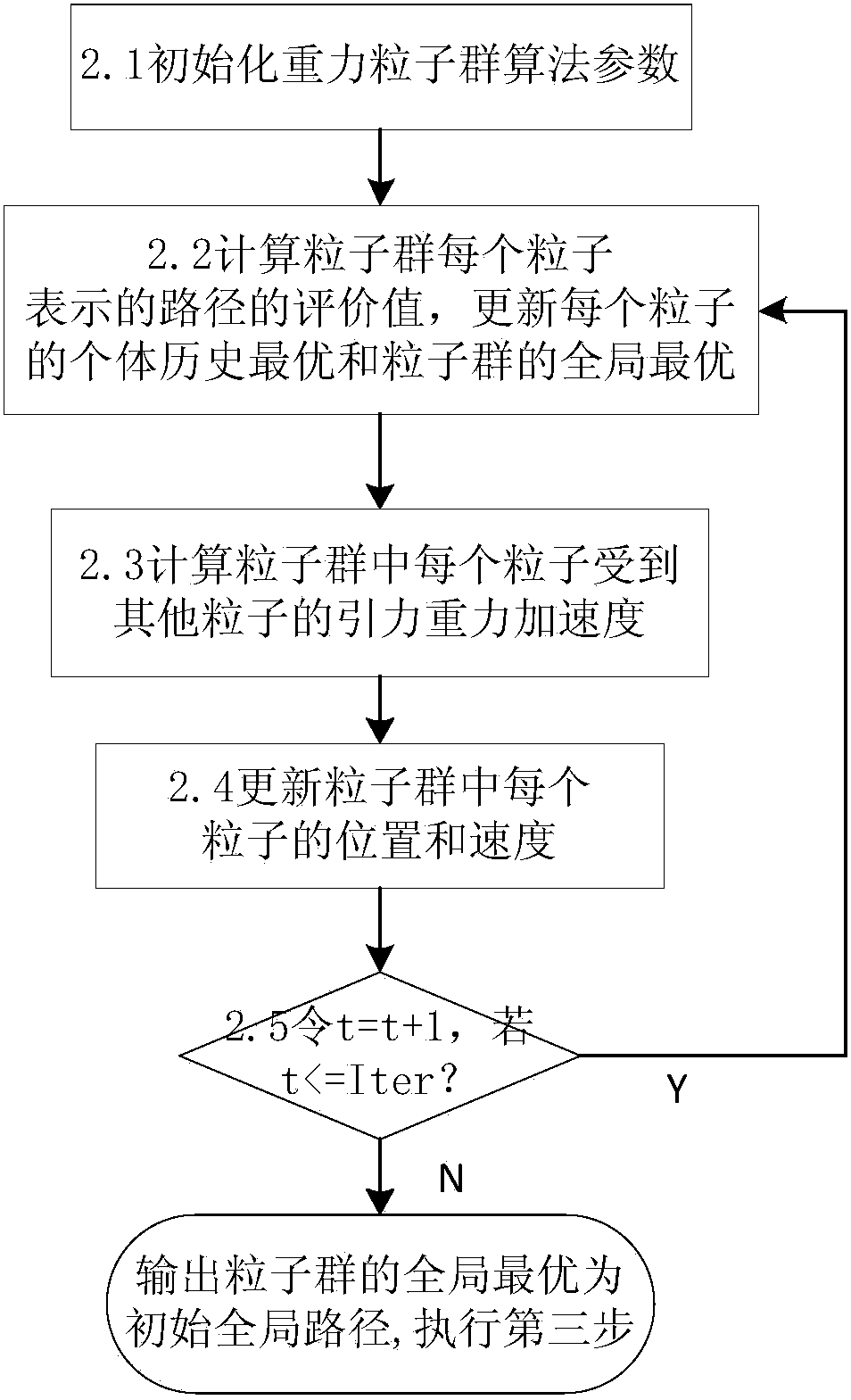
The invention discloses a planning method for a mixed path of a mobile robot under a multi-resolution barrier environment. The invention aims to solve the problems of blindness of initial planning, environment modeling lack of flexibility and poor real-time obstacle avoidance capability of the present method. According to the technical scheme, a self-adapting inhomogeneous polar-radius polar coordinate modeling method is adopted for performing environment modeling on the motion space of the mobile robot; a gravity particle swarm searching method is adopted for planning an initial overall path from starting point to ending point; according to the initial overall path, a modified artificial potential field method is adopted for performing local dynamic obstacle avoidance by estimating the minimum safe distance and safe collision-preventing angle and for arriving at each initial overall path point in turn; and a final overall collision-free path is output after arriving the planning end point. According to the planning method provided by the invention, the blindness of initial overall planning and the environment modeling flexibility can be effectively improved, the real-time obstacle avoidance capability for dynamic unknown barrier is strong, and the method is high in speed, high in precision and strong in adaptability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for planning paths of unmanned aerial vehicles on basis of Q(lambda) algorithms
ActiveCN109655066AGive full play to the flying abilitySolve the shortcomings of the lack of basis in the discretization processNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsDecision modelEnvironmental modelling
The invention provides a method for planning tasks of unmanned aerial vehicles on the basis of Q(lambda) algorithms. The method includes a step of carrying out environment modeling, a step of initializing Markov decision process models, a step of carrying out Q(lambda) algorithm iterative computation and a step of computing the optimal paths according to state value functions. The method particularly includes initializing grid spaces according to the minimum flight path section lengths of the unmanned aerial vehicles, mapping coordinates of the grid spaces to obtain airway points and representing circular and polygonal threat regions; building Markov decision models, to be more specific, representing flight action spaces of the unmanned aerial vehicles, designing state transition probability and constructing reward functions; carrying out iterative computation on the basis of constructed models by the aid of the Q(lambda) algorithms; computing each optimal path of the corresponding unmanned aerial vehicle according to the ultimate convergent state value functions. The unmanned aerial vehicles can safely avoid the threat regions via the optimal paths computed according to the ultimate convergent state value functions. The method has the advantages that the traditional Q learning algorithms and effectiveness tracking are combined with one another, accordingly, the value functionconvergence speeds can be increased, the value function convergence precision can be enhanced, and the unmanned aerial vehicles can be guided to avoid the threat regions and autonomously plan paths.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Autonomous operation forestry robot intelligent control system
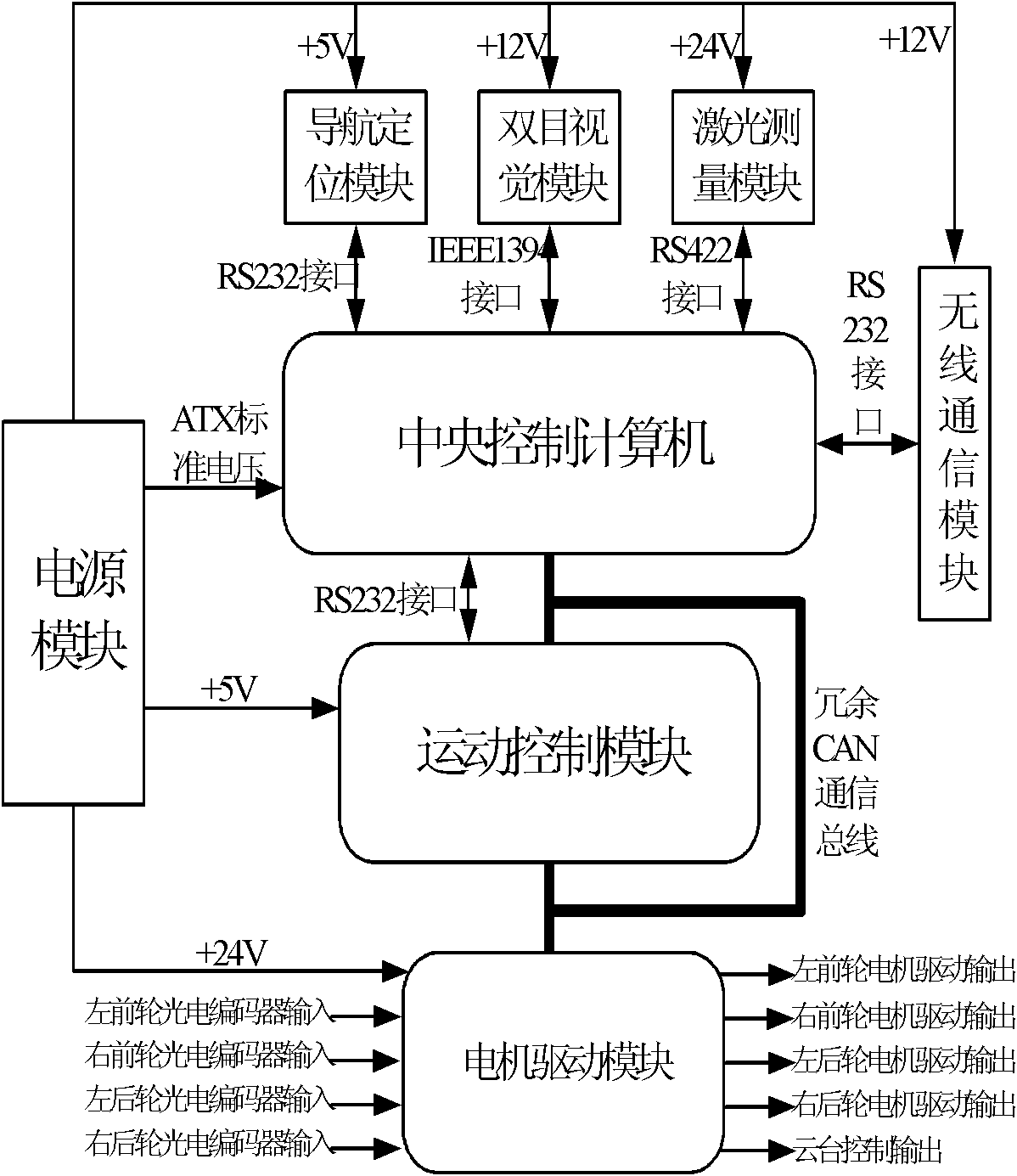
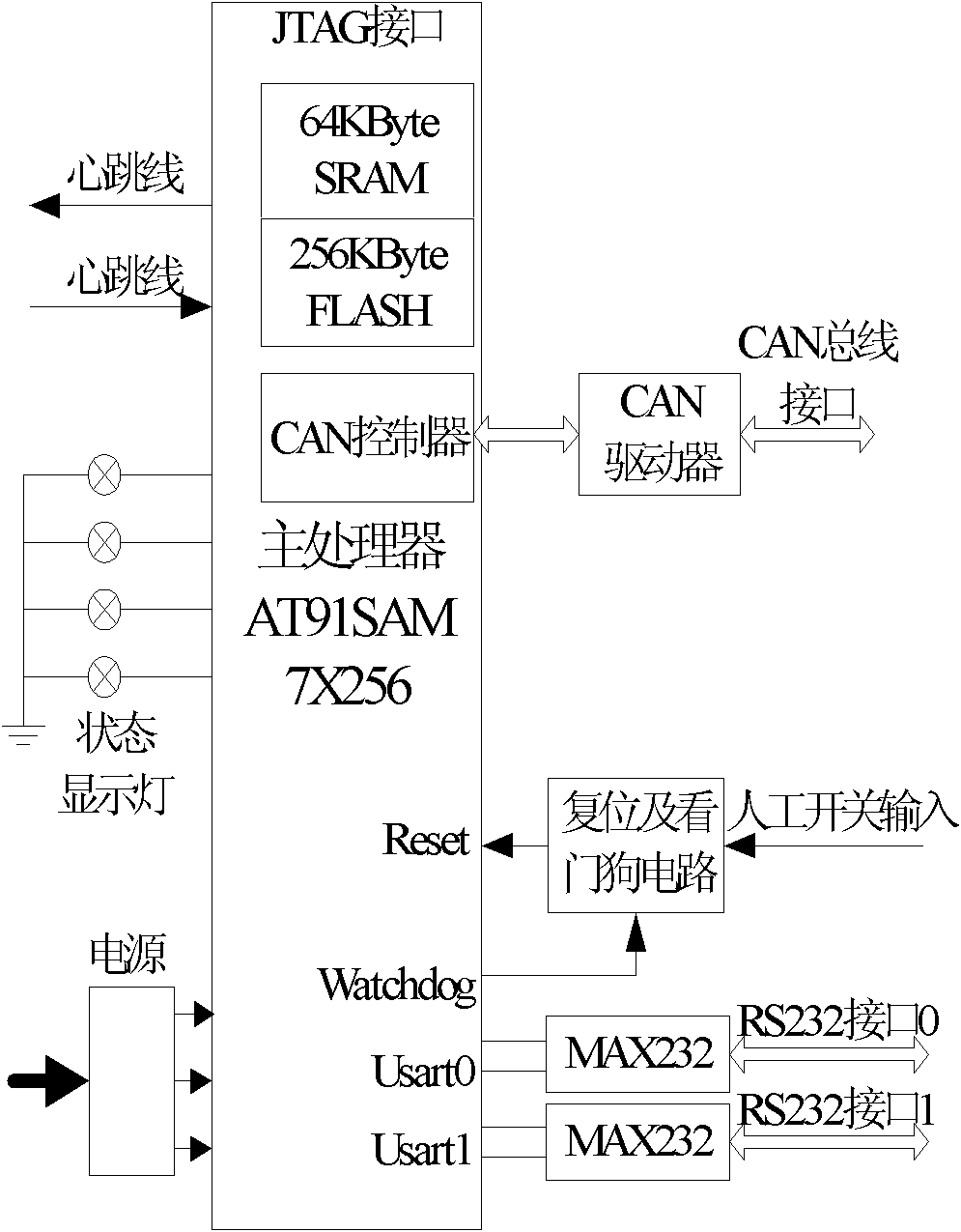
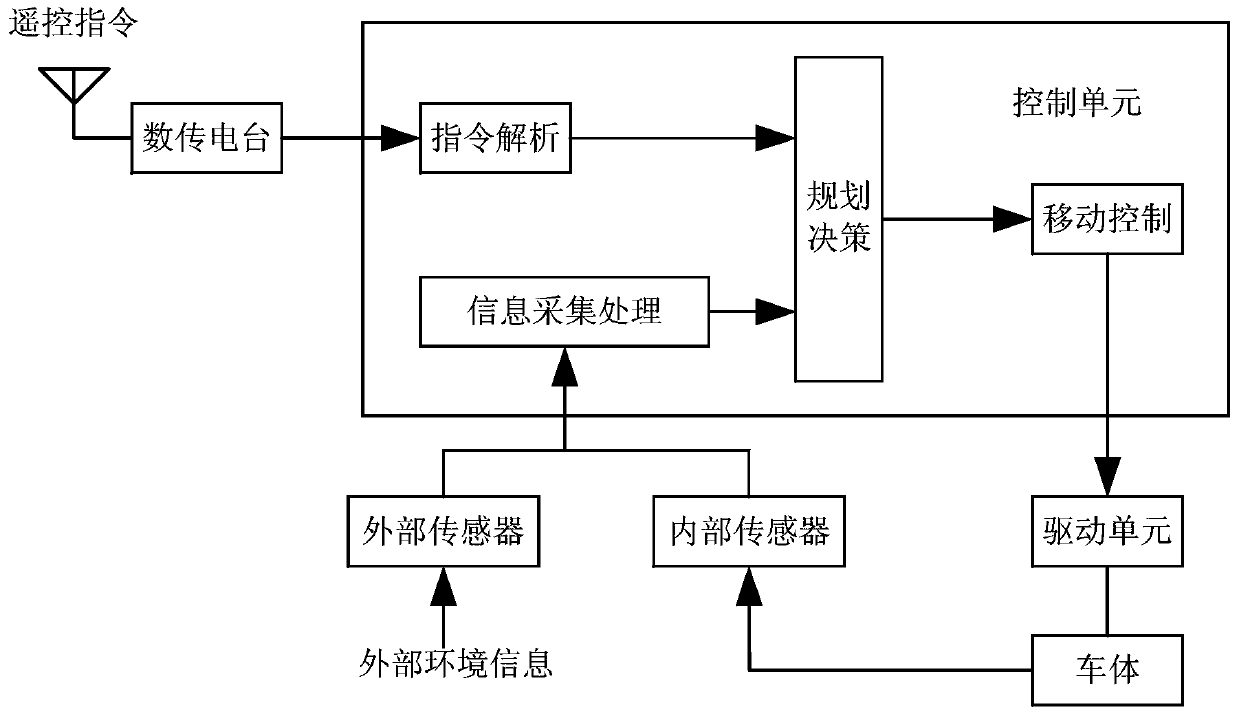
The invention discloses an autonomous operation forestry robot intelligent control system applied to the technical field of intellectualization of forestry equipment. The autonomous operation forestry robot intelligent control system comprises a central control computer, a motion control module, a navigation positioning module, a laser measurement module, a binocular vision module, a motor-driven module, a wireless communication module, a power supply module and a CAN (controller area network) communication module. Complex task scheduling and control algorithms are realized in the central control computer, and simpler control algorithms with high real-time requirements are realized in the motion control module and the motor-driven module, thus the whole processing capacity and real-time property of the system are ensured. Redundancy design is adopted on the motion control module, thus the reliability of the system is improved. The task requirements of the autonomous operation forestry robot for intelligent decision making and environmental modelling can be met, the system has the characteristics of high data processing capacity and high automation of intelligence and reliability; and the automation of intelligence of the traditional forestry robot control system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Environment modeling method applicable to navigation of automatic piloting vehicles
InactiveCN102353379AAvoid signal lossHigh precisionInstruments for road network navigationEnvironmental modellingSimulation
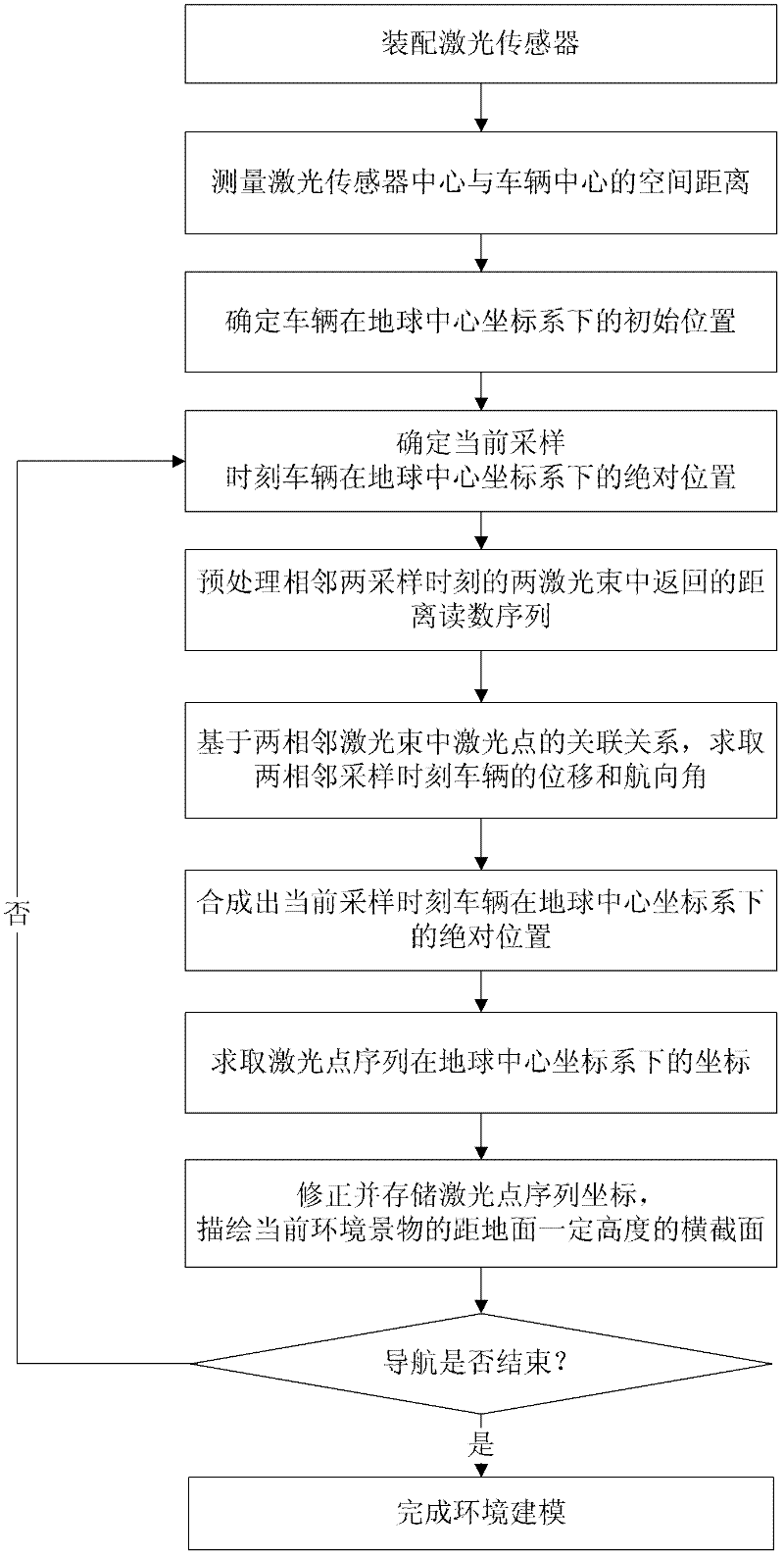
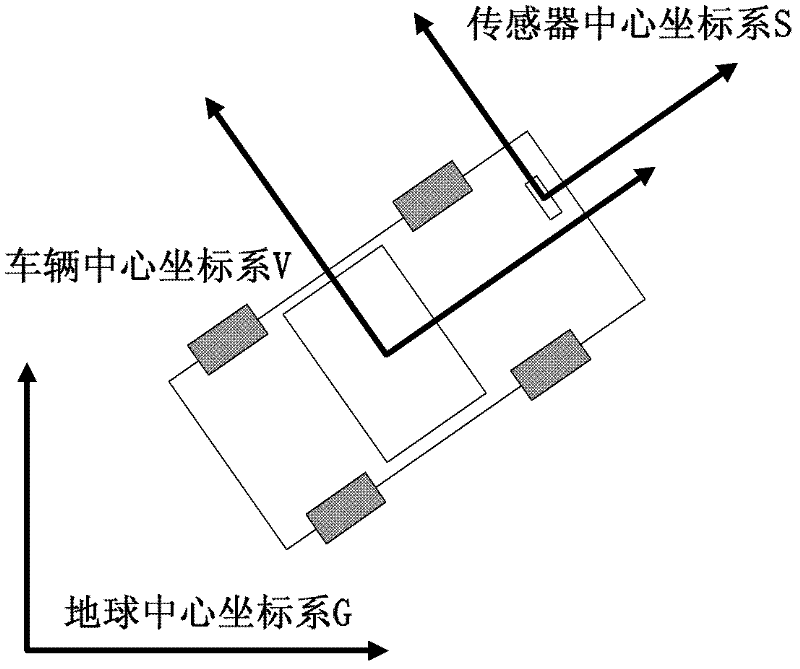
The invention provides an environment modeling method applicable to navigation of automatic piloting vehicles. One of the key problems needing to be overcome for the navigation of automatic piloting vehicles is to modeling an environment in which a vehicle pilots, to distinguish sceneries in the environment and to convert environmental information into parameterized information which can be used for intelligent obstacle avoidance and path planning of an automatic piloting vehicle. According to the invention, a laser sensor is provided at the front of the automatic piloting vehicle; a series of steps like measurement of spatial distance between the center of the laser sensor and the center of the vehicle are carried out; the whole environment is modeled by utilizing laser point sequences acquired in the driving process of the vehicle. Displacement and course angles of the vehicle are calculated by registering observation of the laser sensor at adjacent sampling time, which is a self-contained scheme and can effectively avoid the problem of LOS (lost of signals) in extreme environments in similar methods which employ a scheme bases on a constellation system; in the method provided in the invention, the laser point sequences in laser beams are processed with a method of inference based on a probabilistic graph model, which enables geometrical characteristics of scenery contours to be utilized and managed intelligently, and therefore, higher accuracy in environment modeling is obtained in the invention.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Visual feedback platform improving virtual reality immersion degree
ActiveCN105291138ASolve the problem of limited work spaceAchieve intuitive controlManipulatorVisual servoingEnvironmental modelling
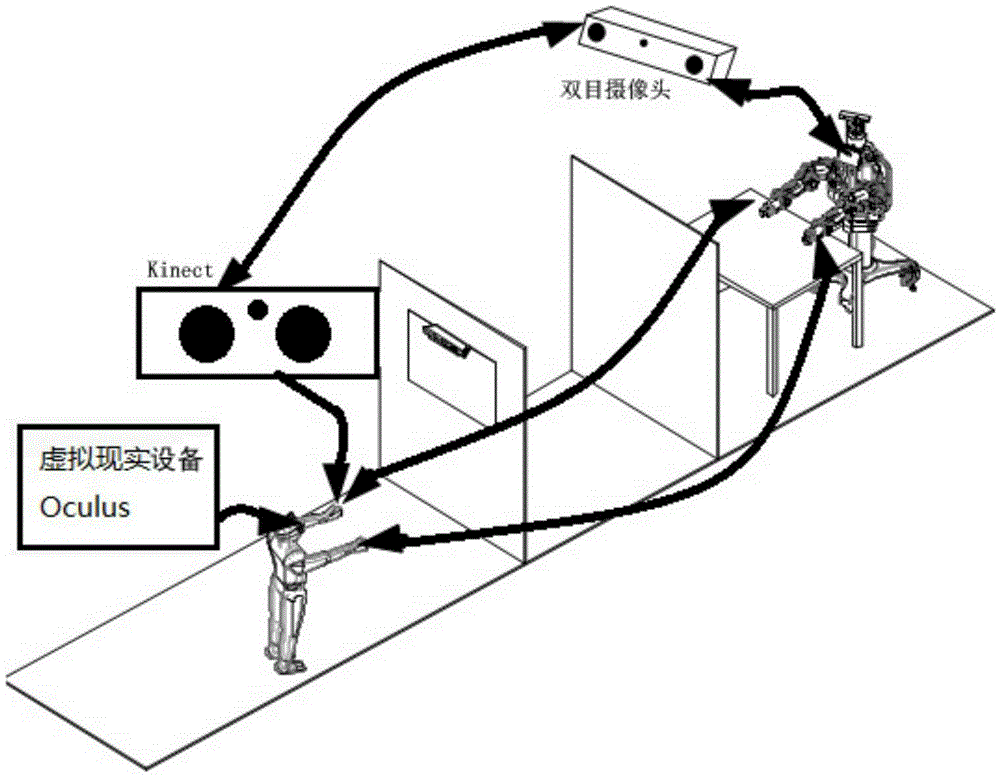
The invention discloses a visual feedback platform improving the virtual reality immersion degree. The visual feedback platform is characterized by comprising a robot, a visual servo tracking control unit and an immersion type visual feedback unit and forms a closed presence sense system with users; the visual servo tracking control unit is used for tracking movement behaviors of the users and carrying out environment modeling; the immersion type visual feedback unit receives the information of the movement behaviors of the users and environment modeling and then mixes the information with limb models of the robot into a 3D virtual reality interface, and the users wear virtual reality equipment to achieve man-machine interaction. The visual feedback platform has the advantages that the immersion degree of man-machine interaction is high, the hardware investment is small, the system is simple and the integration level is high, thereby being suitable for constructing man-machine interaction systems of robots of different functions.
Owner:创泽智能机器人集团股份有限公司
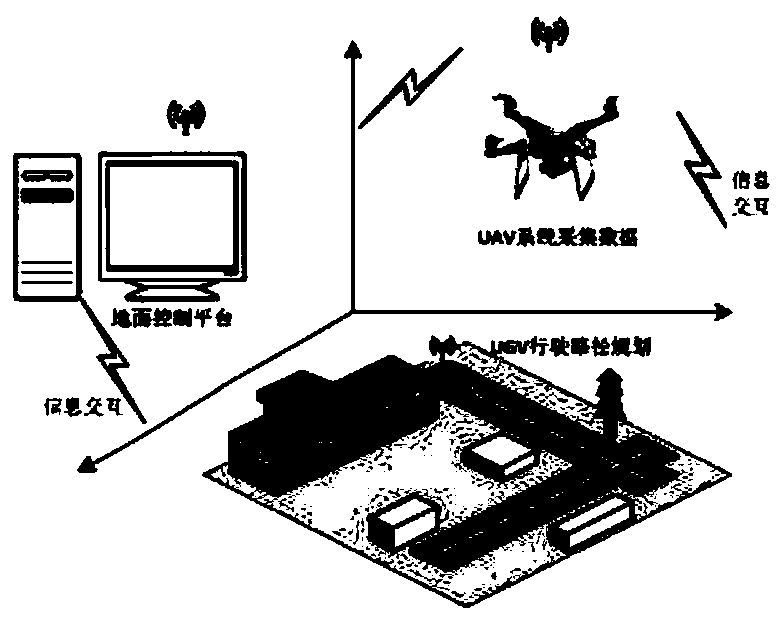
UGV driving path planning method based on UAV cooperation sensing
PendingCN111413965ARealize automatic planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsTime informationEnvironmental modelling
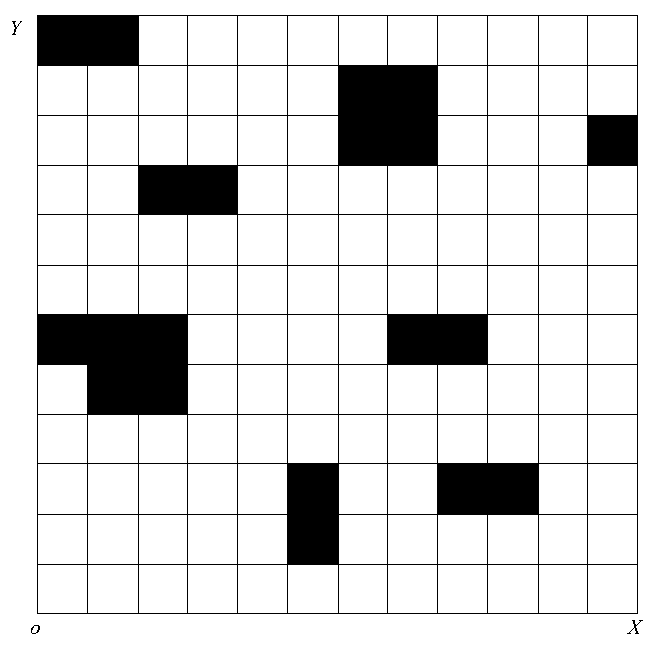
The invention discloses a UGV driving path planning method based on UAV cooperation awareness, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out environmental modeling and environmental awareness: establishing a real-time information interaction environment and obtaining scene information; converting the obtained scene information into a grid scene map, and carrying out obstacle collisionrisk prediction and avoidance; and carrying out path planning in the obtained grid scene map. Under the UAV cooperation mode, an obstacle target is effectively identified, automatic planning of a UGVdriving path is realized, a theoretical and technical support is provided for path planning problems related to intelligent transportation industries such as emergency response, target tracking and rescue, and research has certain perspectiveness and urgency.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Top-down multi-layer virtual entironment modelling approach based on from
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
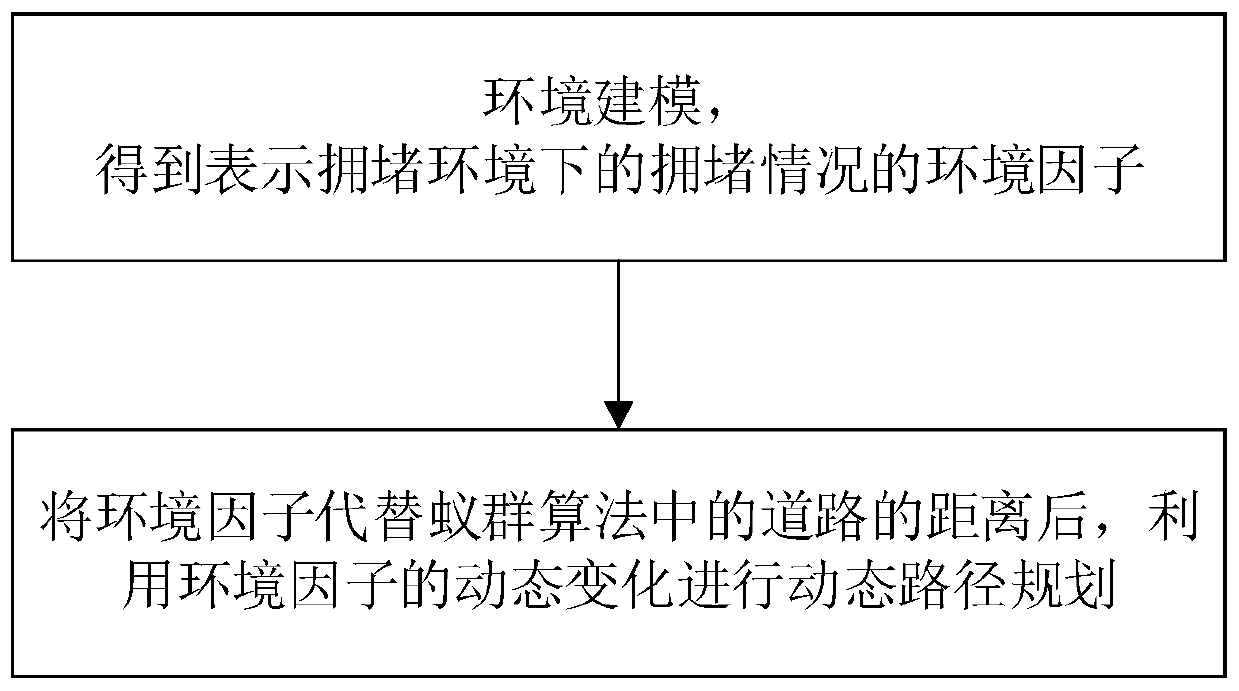
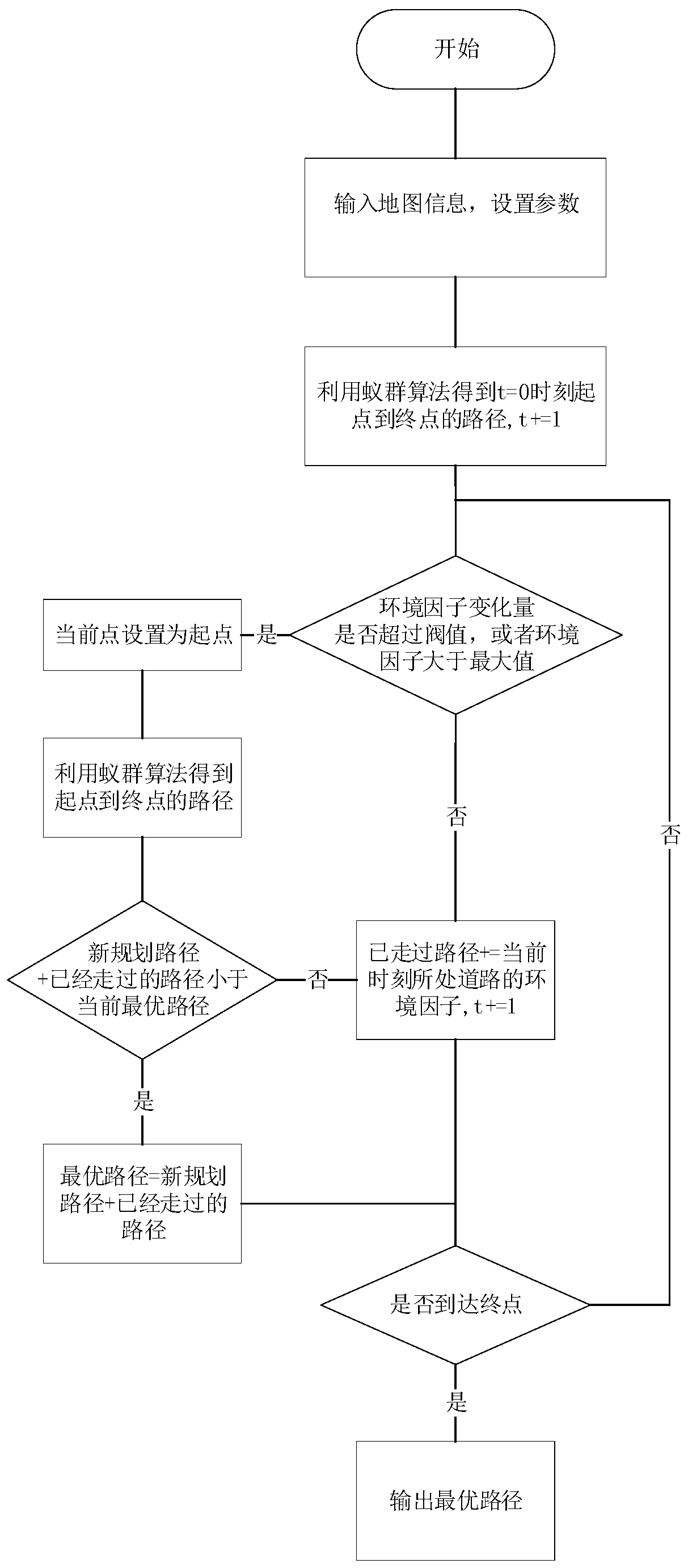
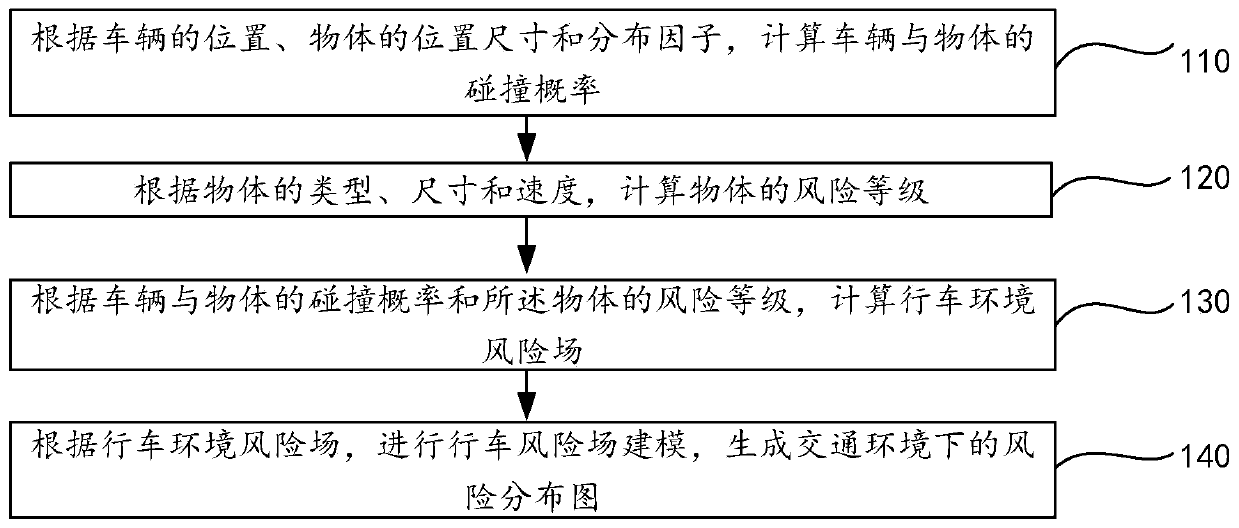
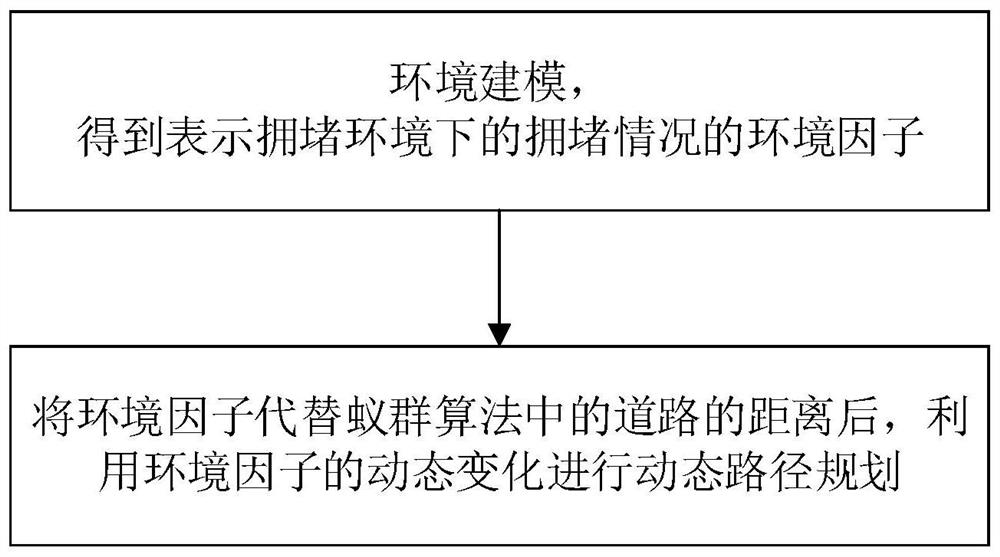
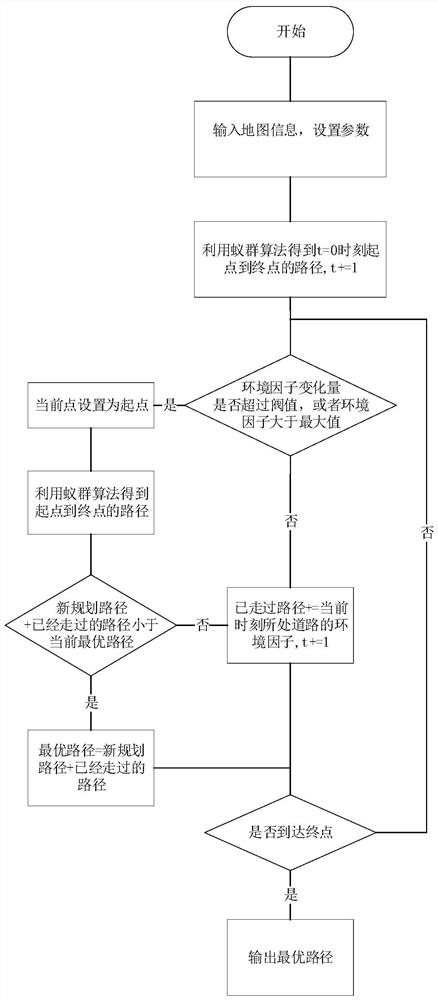
Dynamic path planning method for ant colony algorithm in congestion environment
ActiveCN110941267AMake up for the factors that do not consider the dynamic changes of environmental congestionMeet traffic jamPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEnvironmental modellingSimulation
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Traffic environment modeling method
Owner:BEIJING ZHIXINGZHE TECH CO LTD
Mobile robot path planning method based on weighted average distance vision fish school algorithm
InactiveCN105242669AImprove conveniencePosition/course control in two dimensionsLocal optimumEnvironmental modelling
The invention provides a mobile robot path planning method based on a weighted average distance vision fish school algorithm. The method comprises the steps that the population size fishnum of artificial fish, the maximum number of iterations NC, field of view visual, the largest moving step step, a crowding factor delta, the number of attempts Try_number, the number feasibility paths N and the number of path nodes n are acquired; environment modeling is carried out on the walking environment of a robot based on a grid method; and N feasibility paths are randomly generated. According to the invention, for the problems of fixed field of view, slow algorithm convergence and increased computation of a basic artificial fish school algorithm, WAD-AFSA is provided; the algorithm is applied to the path planning of the mobile robot; environment modeling is carried out through the grid method; provided WAD-AFSA and an act selection policy are used to carry out path optimization, which prevents the paths from falling into local optimum; and a corresponding simulation experiment shows that WAD-AFSA provided by the invention has a better optimization effect than the traditional artificial fish school algorithm in the aspect of mobile robot path planning.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Environment modeling and path planning method based on multi-sensor fusion
ActiveCN112762957AImprove positioning accuracyNarrow searchInstruments for road network navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryFeature vectorPoint cloud
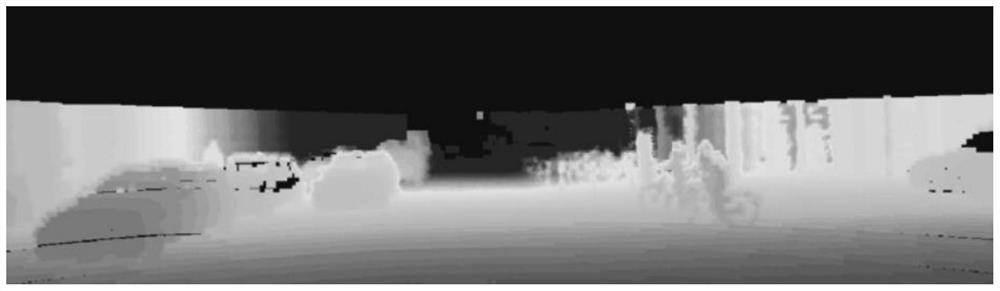
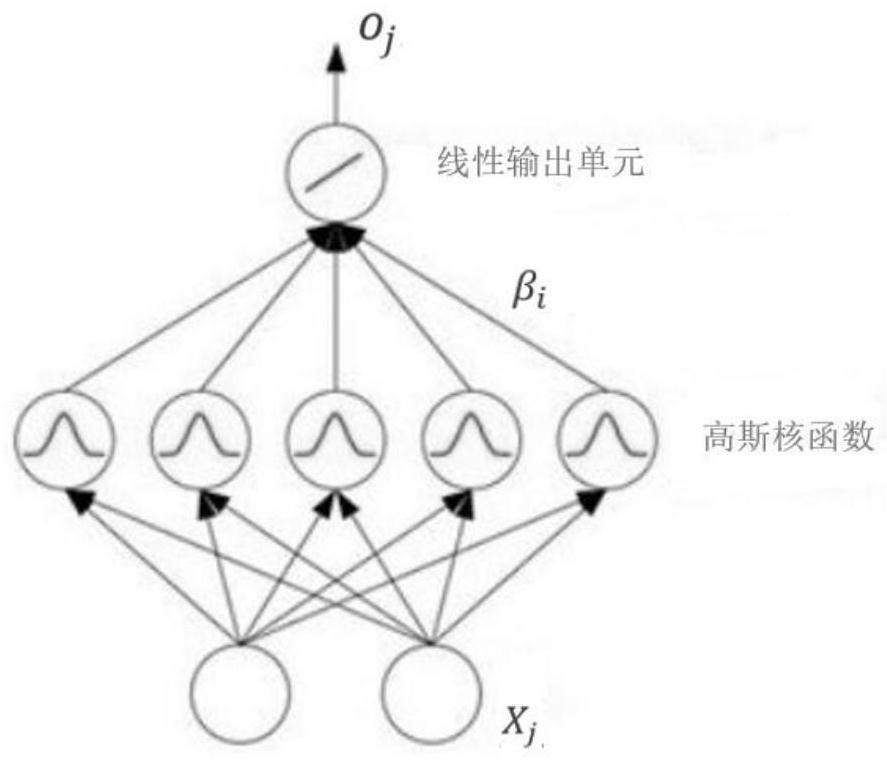
The invention discloses an environment modeling and path planning method based on multi-sensor fusion. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an image and laser point cloud data in a camera field of view on an unmanned vehicle at the same time; generating a dense point cloud depth map according to the image and the laser point cloud data; taking coordinate values in the dense point cloud depth map as input, and combining a radial basis function neural network to construct an environment model in a camera view field; and determining a path planning track point sequence of the unmanned vehicle by taking the minimum height and gradient of the track point as a target and taking an environment feature vector threshold value and a single-step length as constraint conditions. The laser point cloud data and the image of the camera are fused to serve as input data of environment model construction, the position information of the obstacles can serve as input weights to be applied to environment modeling, the positioning accuracy of the field concave-convex obstacles in the environment model can be improved, and the search time is shortened.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
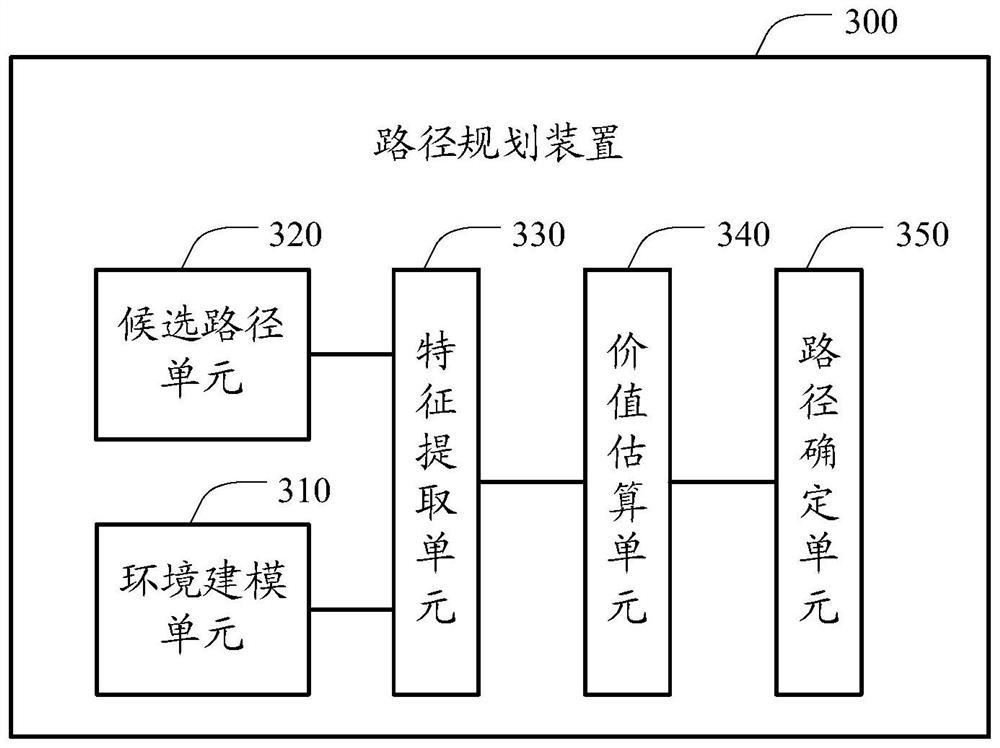
Path planning method and device and electronic equipment
ActiveCN112529254AImprove practicalityGlobalForecastingNeural architecturesPathPingFeature extraction
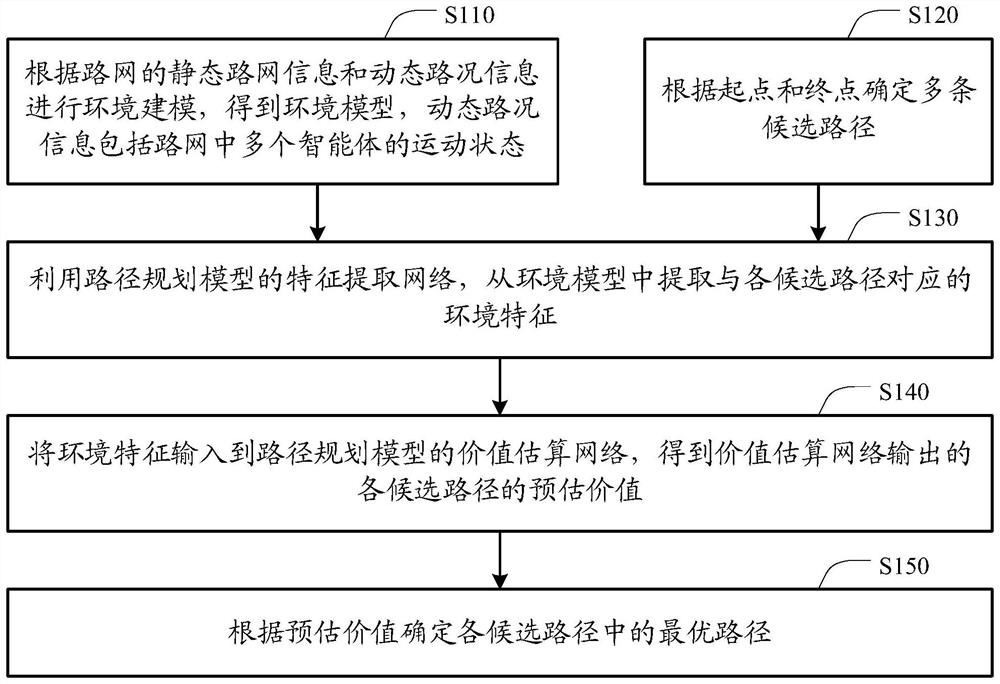
The invention discloses a path planning method and device and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: performing environmental modeling according to static road network information and dynamic road condition information of a road network to obtain an environmental model; determining a plurality of candidate paths according to the starting point and the terminal point; extracting environmental features corresponding to each candidate path from the environmental model by utilizing a feature extraction network of the path planning model; inputting the environmental features into a value estimation network of a path planning model to obtain estimated values of candidate paths output by the value estimation network; and determining an optimal path in the candidate pathsaccording to the estimated value. According to the technical scheme, the dynamic road condition information comprises motion states of a plurality of intelligent agents in a road network, and has spatial globality; when path planning is carried out, the environmental characteristics corresponding to the candidate paths determined according to the starting point and the terminal point are extractedaccording to the environmental model, so that full-path planning instead of planning in different time windows is achieved, and time globality is achieved.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
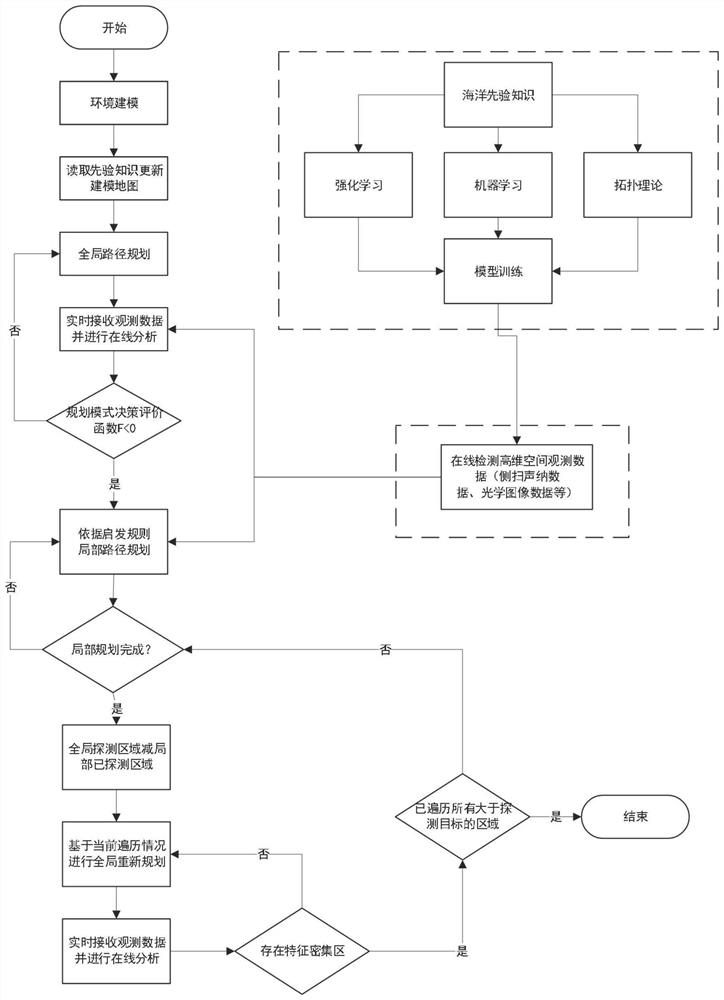
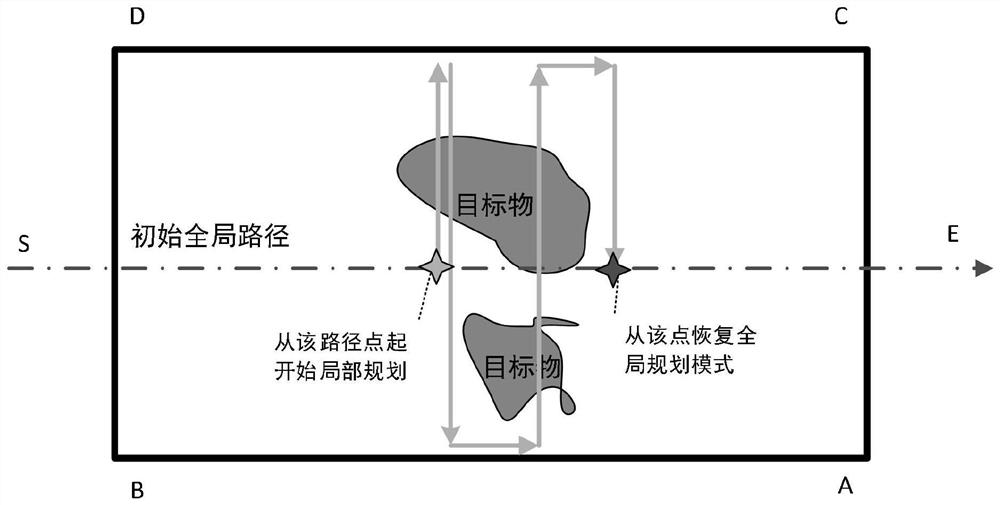
Data-driven path planning method for unmanned underwater vehicle
ActiveCN111721296AAvoid the hassle of finding heuristicsMean Time Efficiency ImprovementNavigational calculation instrumentsGlobal planningObservation data
The invention provides a data-driven path planning method for an unmanned underwater vehicle, and is mainly applied to path planning of an underwater region traversal task. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, for a task area, carrying out environment modeling by utilizing a grid method, reading priori knowledge to update a modeling map, and generating an initial global path by utilizing initial map information; during execution of the task, detecting and receiving observation data in real time, carrying out online path planning analysis, deciding a global planning mode and a local planning mode based on a planning mode decision evaluation function F, if the global planning mode and the local planning mode are switched to the local planning mode, carrying out local planning according to a heuristic rule set, and returning to an initial global planning path after traversal of a local feature dense area is completed; according to the scheme, online guidance decision makingis carried out according to underwater real-time high-dimensional space observation data, global and local planning decision making is carried out on the basis of real-time detection conditions, an adaptive planning strategy is selected through planning mode switching, the method can be suitable for more complex environments, and the time efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
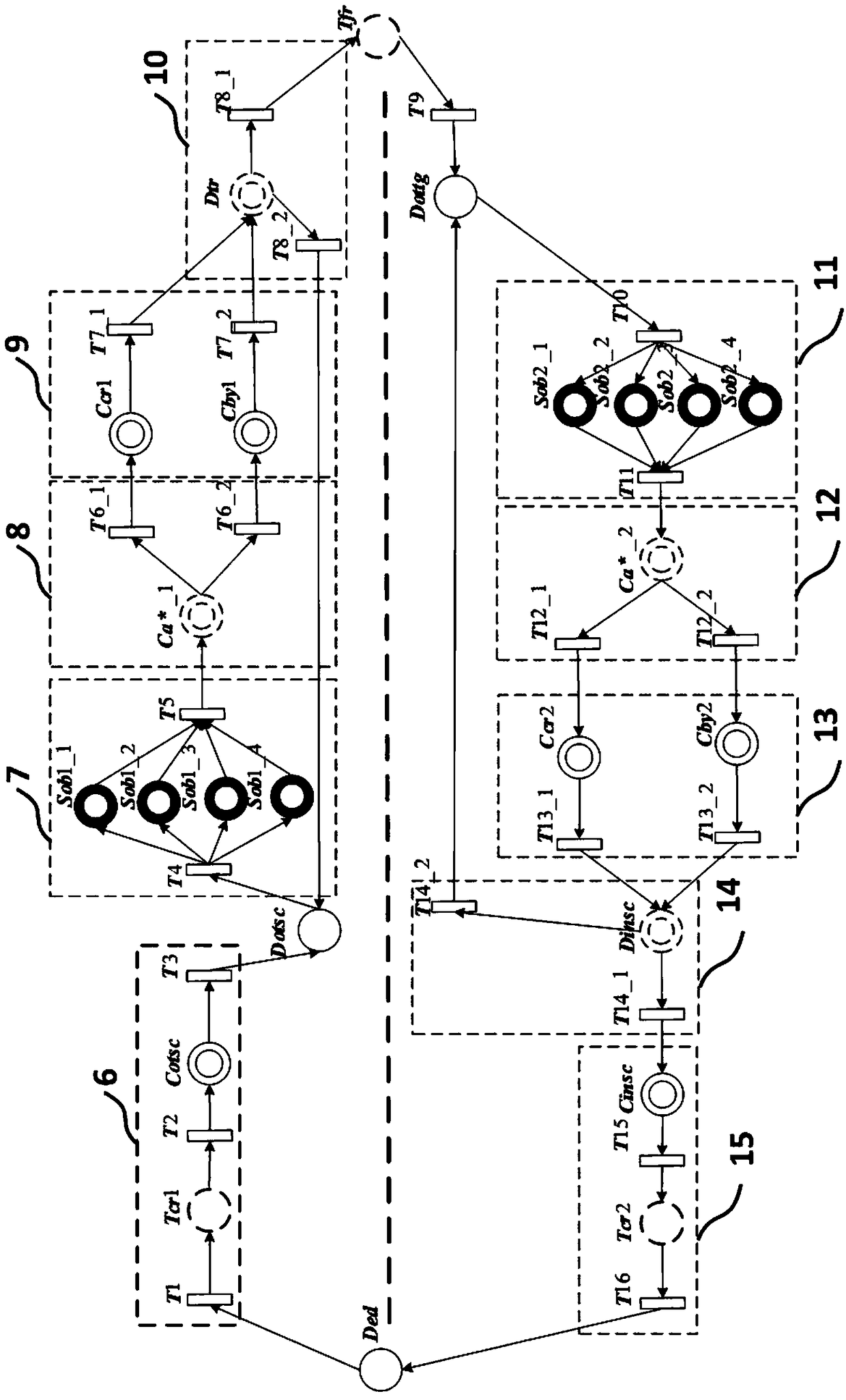
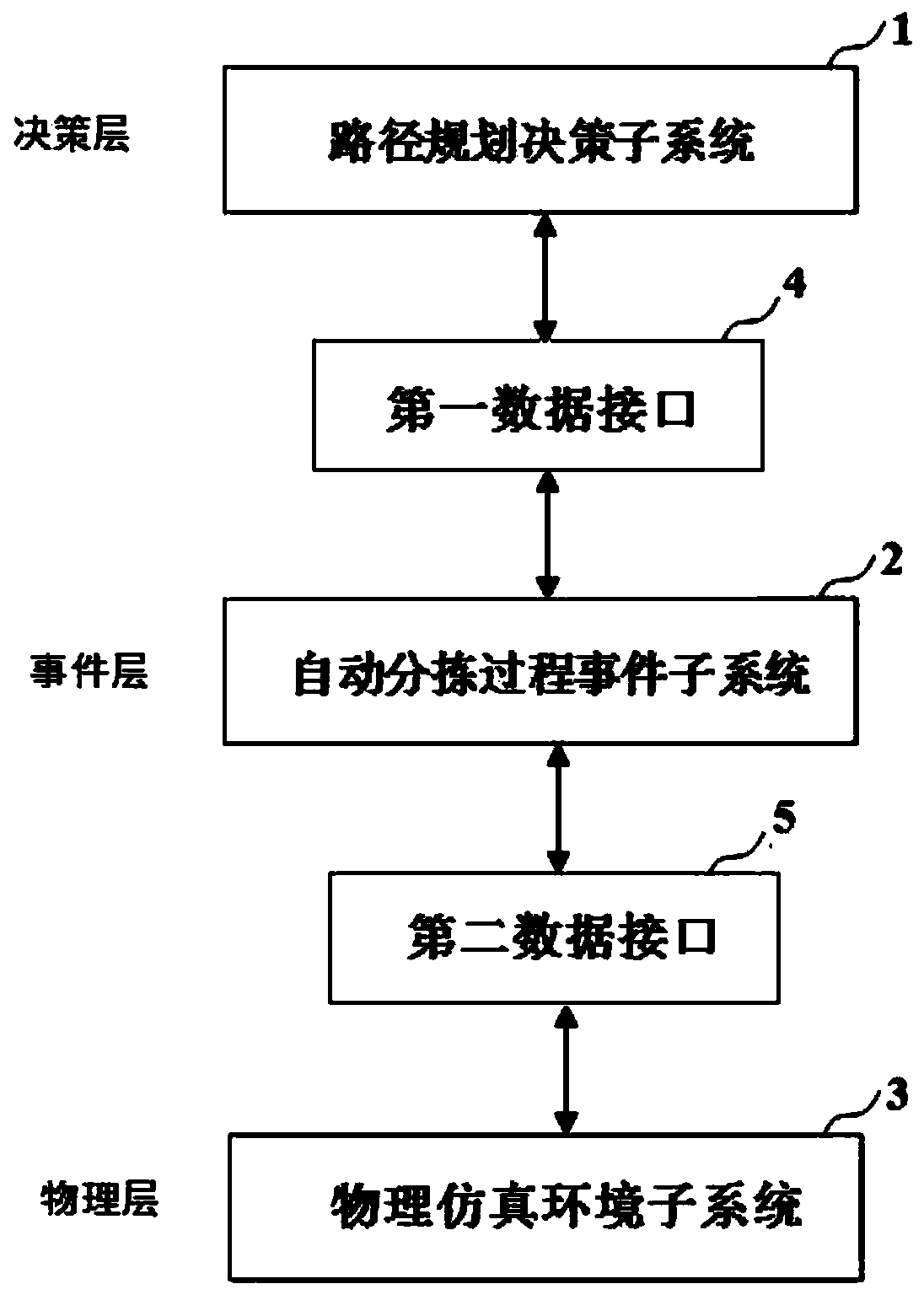
Automatic sorting control and decision making system based on M-HSTPN model
ActiveCN108873737AImplement modular modelingPowerful scientific computingSimulator controlDecision systemEnvironmental modelling
The invention discloses an automatic sorting control and decision making system based on an M-HSTPN model, and the system employs a three-layer architecture of decision-making layer-event layer-physical layer, and the system comprises a path planning decision making subsystem based on Python, an automatic sorting processing event subsystem based on HSTPNSim, and a physical simulation environment subsystem based on V-REP. The system can achieve the modeling simulation of the five types of mixed attributes in an automatic sorting process: discrete event, continuous process, time delay characteristics, random phenomenon and decision making. The system proposes a design method and design criteria for the M-HSTPN model, and achieves the modeling construction. Through the design of the HSTPNSimsoftware and an interface for Python and V-REP software, the system can process a more complex decision making problem and a more precise physical modeling problem through the powerful scientific computing and environment modeling capabilities.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Electric unmanned aerial vehicle inspection route planning method and device
ActiveCN111044044AAdvantages of the planning methodEnsure safetyInternal combustion piston enginesNavigational calculation instrumentsEnvironmental modellingUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an electric unmanned aerial vehicle inspection route planning method and device. The method comprises three steps of environment modeling, task modeling and route planning. According to the electric unmanned aerial vehicle inspection route planning method provided by the invention, carrying out spatial three-dimensional modeling on electric power facilities such as towers,lines and sites to be inspected and surrounding environments of the electric power facilities; sorting parameters such as position coordinates and shooting angles of all task points contained in an inspection task to obtain a sub-task set; and calculating an optimal route according to an environment modeling result and a task modeling result. The method has the advantages of high safety, high planning speed, high inspection efficiency and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD HUAINAN POWER SUPPLY CO +3
Three-dimensional multilayer environment model construction method based on interval estimation
PendingCN113140043AReduce space complexityOccupancy status can be judged3D modellingVoxelEnvironmental modelling
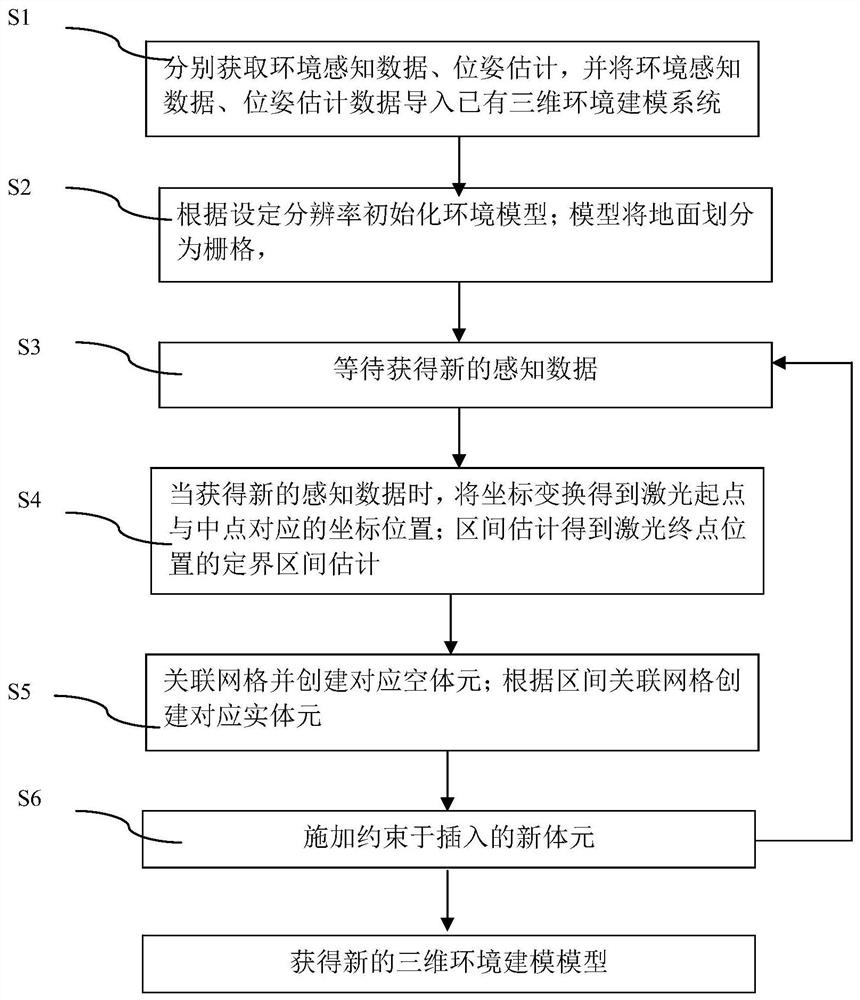
The invention discloses a three-dimensional multilayer environment model construction method based on interval estimation, which comprises the following steps: respectively acquiring environment perception data and pose estimation, and importing the environment perception data and pose estimation data into an existing three-dimensional environment modeling system; initializing an environment model according to a set resolution; enabling the the model to divide the ground into grids; waiting for obtaining new sensing data; when new sensing data is obtained, converting the coordinates to obtain coordinate positions corresponding to the starting point and the midpoint of the laser; performing interval estimation to obtain delimited interval estimation of a laser end point position; associating the grids and creating corresponding empty volume elements; creating corresponding entity elements according to the interval association grids; applying a constraint to the inserted new voxel to obtain a three-dimensional environment modeling model; and meanwhile, sending the new voxel as new sensing data. The environment model representation method has the advantages of being low in space complexity, capable of being updated in real time, capable of judging the occupancy state of any space position and the like.
Owner:江苏俱为科技有限公司
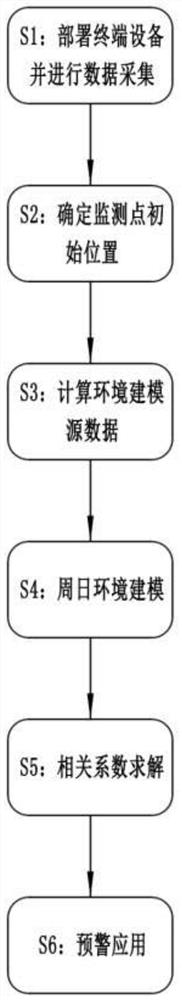
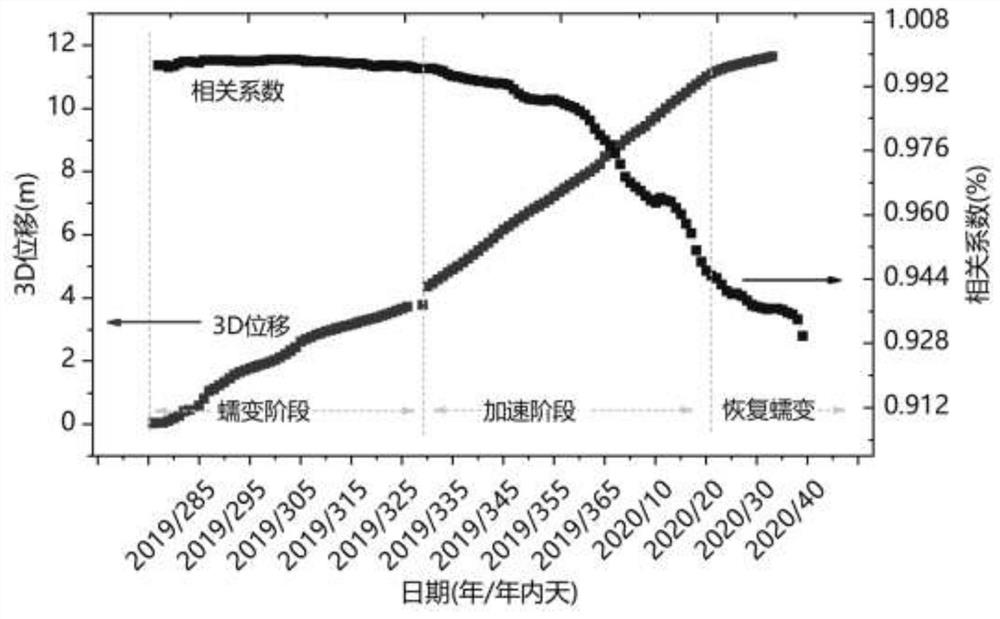
Single-station landslide deformation monitoring and early warning method based on GNSS environment model
ActiveCN111694021AMonitoring cost reductionSatellite radio beaconingAlarmsEnvironmental modellingDeformation monitoring
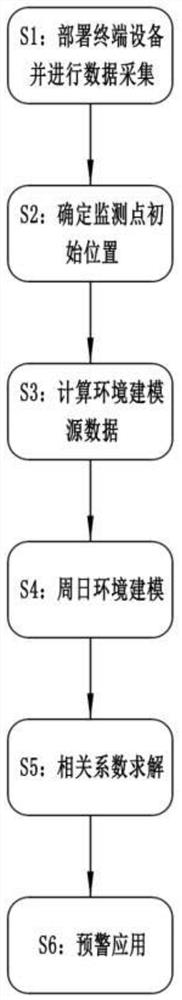
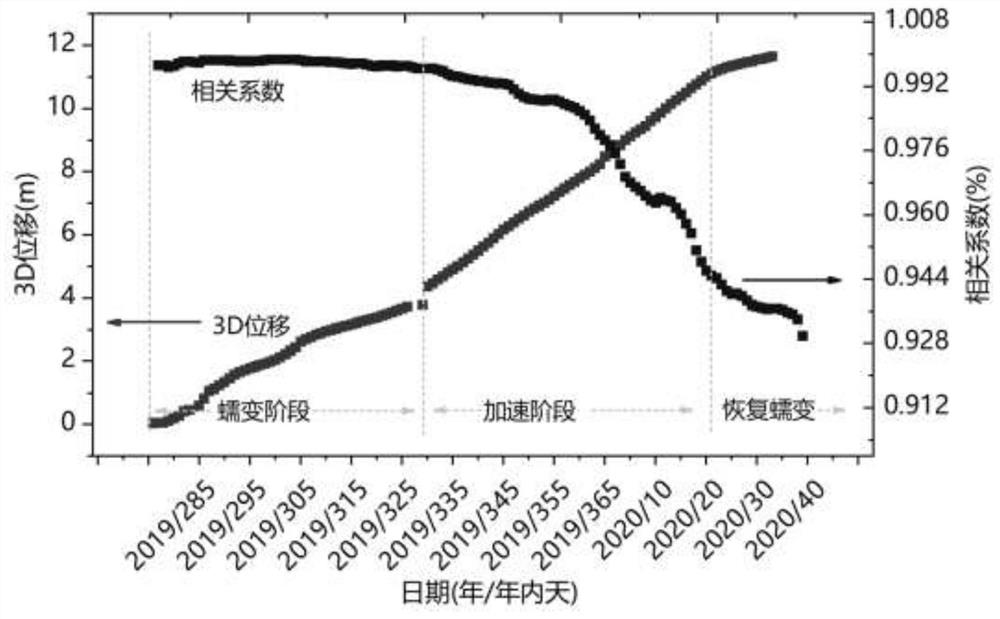
The invention discloses a single-station landslide deformation monitoring and early warning method based on a GNSS environment model. The method comprises the following steps of deploying terminal equipment and performing data acquisition, determining an initial position of a monitoring point, calculating environment modeling source data, performing weekday environment modeling, solving a correlation coefficient and performing early warning application. According to the monitoring and early warning method of the invention, a low-cost consumption-level GNSS positioning terminal is adopted to perform data acquisition and environmental modeling; the landslide acceleration state is subjected to early identification and effective early warning through the change trend of the correlation coefficient of the environment model, so that the monitoring cost is greatly reduced, and a new thought and a new method are provided for GNSS landslide monitoring and early warning.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
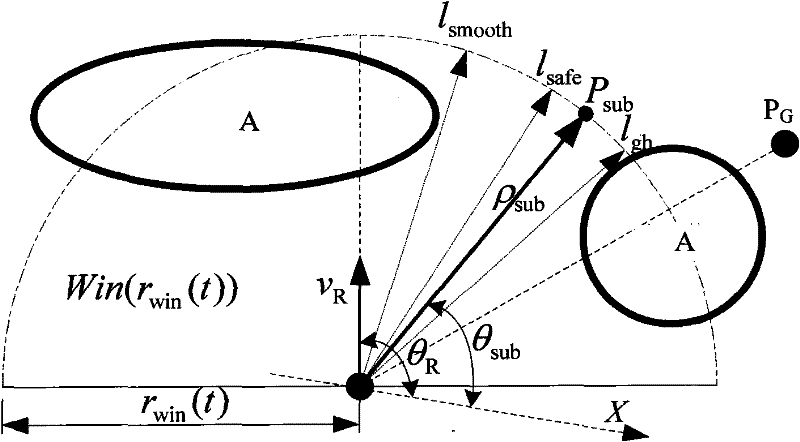
Method for planning path for mobile robot based on environmental modeling and self-adapting window
InactiveCN101738195BSolve the problem of generating obstacle avoidance paths in real timeThe problem of real-time generation of obstacle avoidance paths satisfiesInstruments for road network navigationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationLocal environment
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Natural wind-sand scouring environment modeling technology
ActiveCN108170937AAvoid layingSave human effortDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsResearch ObjectSimulation
The invention is applicable to the field of environment tests, and provides a natural wind-sand scouring environment modeling technology comprising the steps of acquiring climate state wind directionand wind speed information; acquiring a dust mixing ratio simulation data based on an area climate-dust coupling model RegCM4-Dust; computing a dust concentration; computing a wind-sand scouring flux;and computing an included angle between the wind direction and a research object, namely a wind-sand scouring angle. The natural wind-sand scouring environment is built by the wind-sand scouring fluxand the wind-sand scouring angle. According to the natural wind-sand scouring environment modeling technology provided by the invention, a numerical simulation method is used for acquiring dust concentration data, so that the arrangement of observation instruments is avoided, a lot of costs such as equipment, maintenance and labor costs are saved, and the observation time is saved; through comparing with a laboratory dust test, the technology provided by the invention can be used for assessing and evaluating the adaptation and durability of material to the natural wind-sand scouring environment, can provide a simulation environment support for the design, application and protection of the wind-sand scouring resistant material, and fills in the blank of the natural wind-sand scouring environment modeling simulation technology.
Owner:北京应用气象研究所
Scene map point and image frame matching method in environment modeling
InactiveCN113034601AEasy to buildEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a scene map point and image frame matching method in environment modeling. The method mainly adopts a monocular camera to research inverse depth estimation of map points, the inverse depth of the map points is expressed as a depth filter under Gaussian distribution assumption, and inverse depth observation information is utilized to update the map points; meanwhile, a key frame selection strategy and an observation-updating mechanism based on the depth filter are utilized, extraction and inverse depth observation of the map points are researched emphatically, map point matching is improved by adopting a rough-accurate matching mode, and in terms of setting of the real world and robustness, the semi-dense reconstruction scene after inverse depth optimization is more detailed, and the depth estimation is more accurate.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
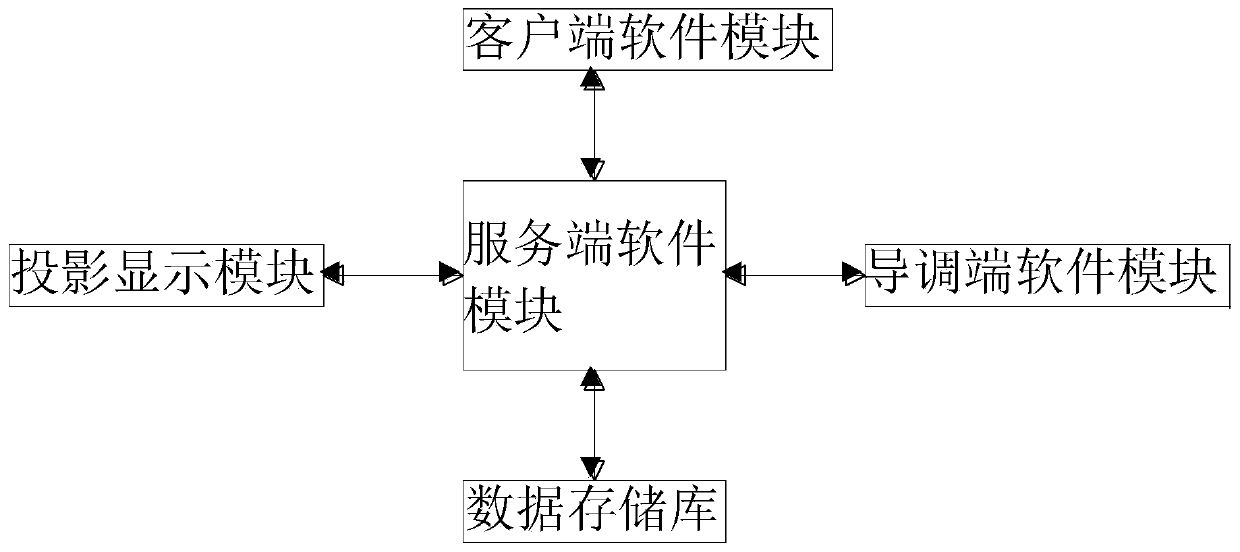
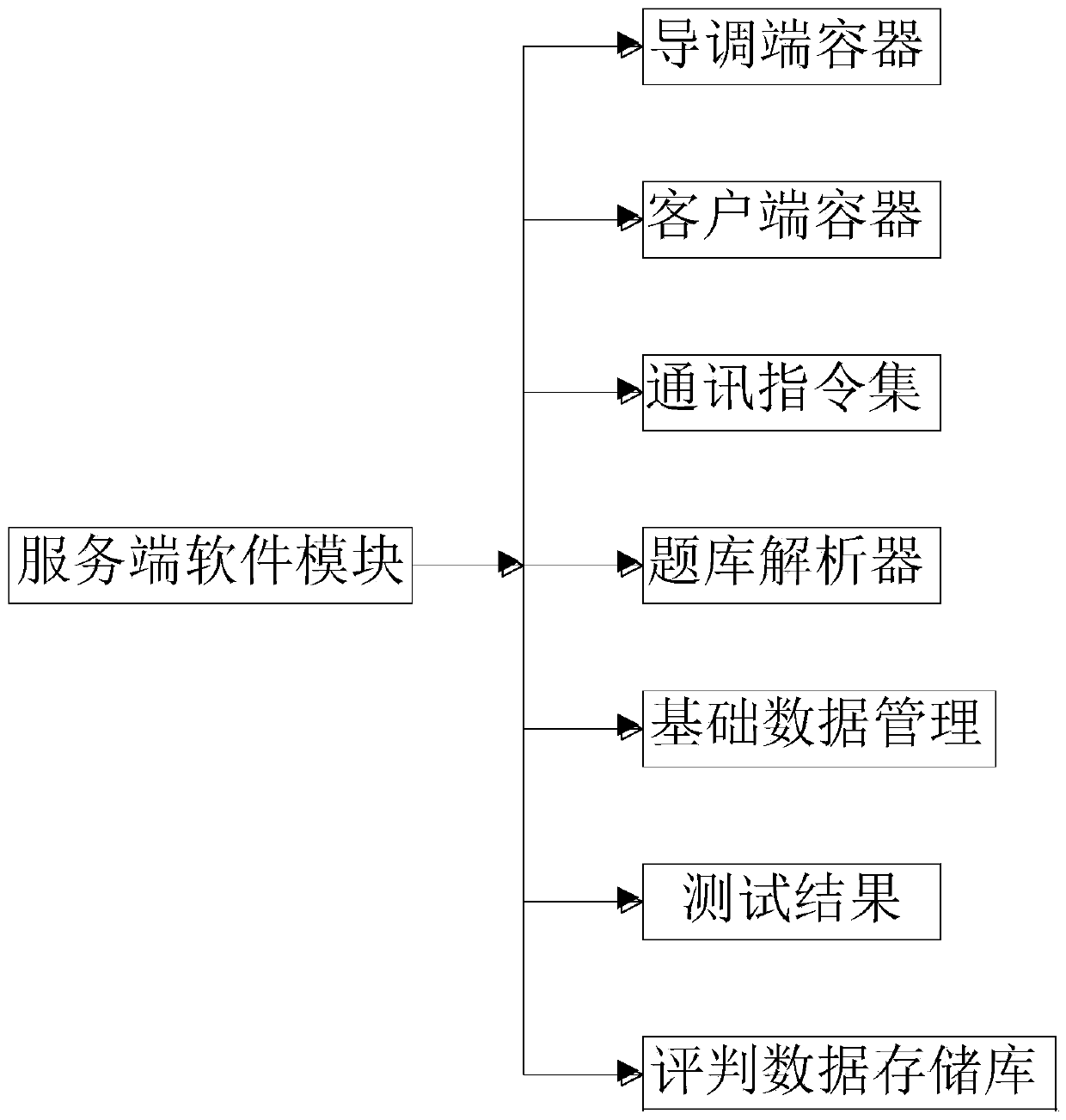
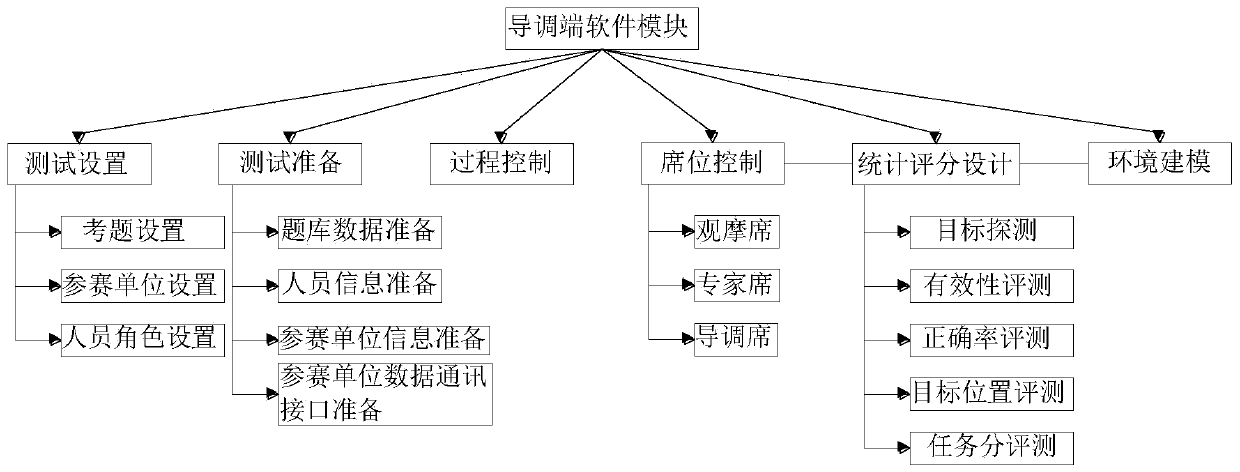
Data-based test evaluation system
PendingCN111581105AIntegrity guaranteedAvoid lossSoftware testing/debuggingEnvironmental modellingData mining
The invention relates to the technical field of test systems, and further discloses a test evaluation system based on the data. The guiding and adjusting end software module comprises a statistical score design. The statistical scoring design comprises a target detection sub-module, an effectiveness evaluation sub-module, a correct rate evaluation sub-module, a target position evaluation sub-module, a task score evaluation sub-module and the like. By setting statistic score setting, evaluation mainly comprises two evaluation bases, namely target detection and environment modeling; correspondingly, the system evaluates two subjects of each piece of to-be-tested software, namely target detection and environmental modeling, the examination question data of the two subjects are different and non-versatility, the automatic evaluation module is an independent module relative to the examination process; the to-be-tested software returns the answer to the server, then the evaluation module canoperate independently without interacting with the server, and only after the evaluation module calculates the score, the persistence related interface of the server is called to store the score in the database, so that the integrity of the data during transmission flow is ensured.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军研究院装甲兵研究所
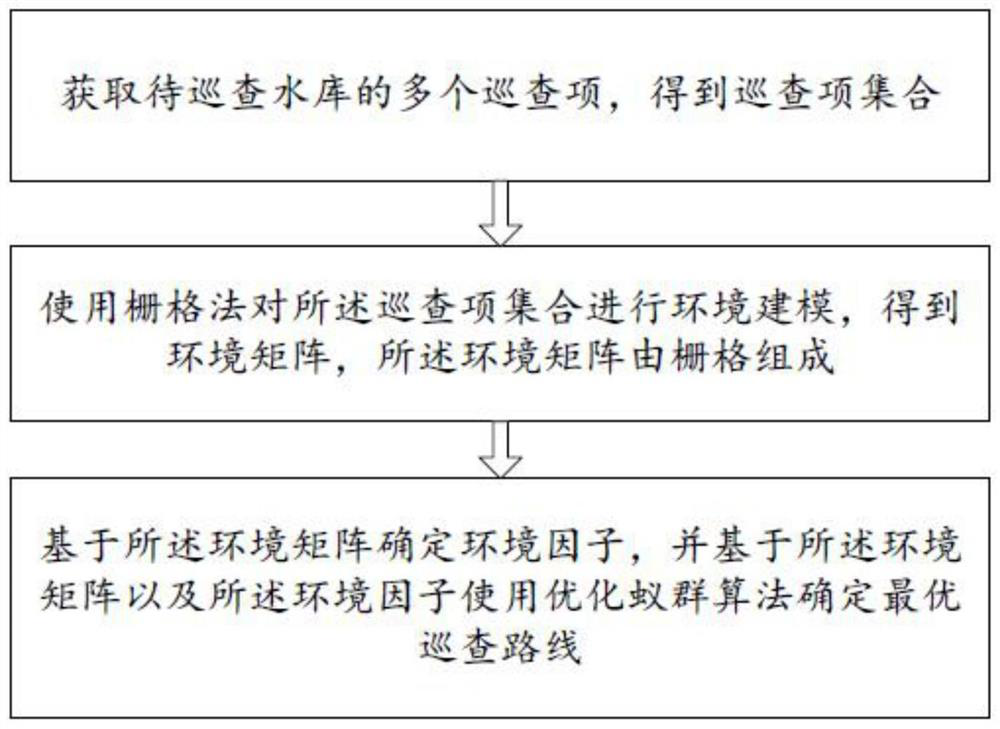
Reservoir patrol route determination method and terminal
PendingCN114298416AEfficient inspectionImprove accuracyChecking time patrolsForecastingEnvironmental modellingEnvironmental engineering
Owner:SICHUANG TECH CO LTD
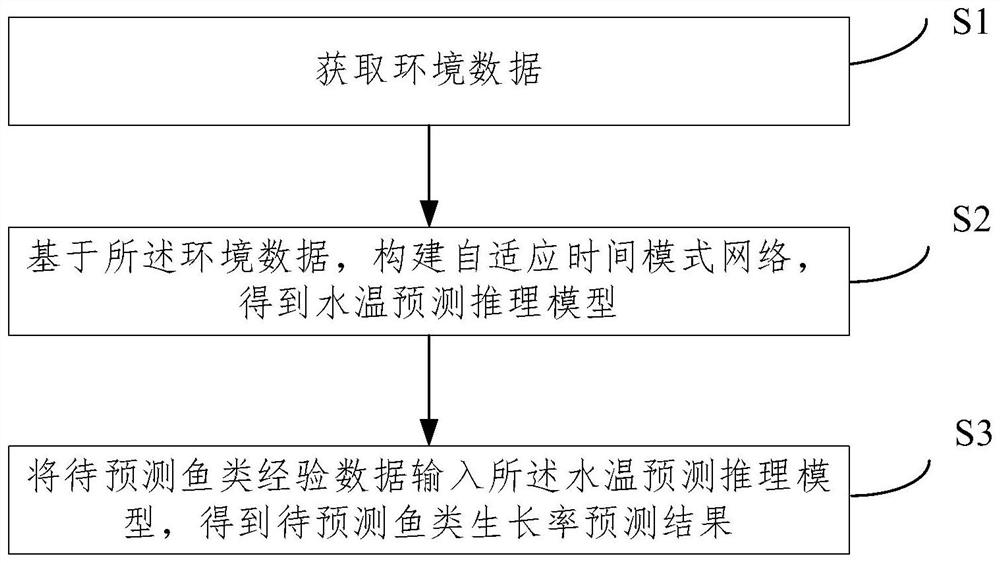
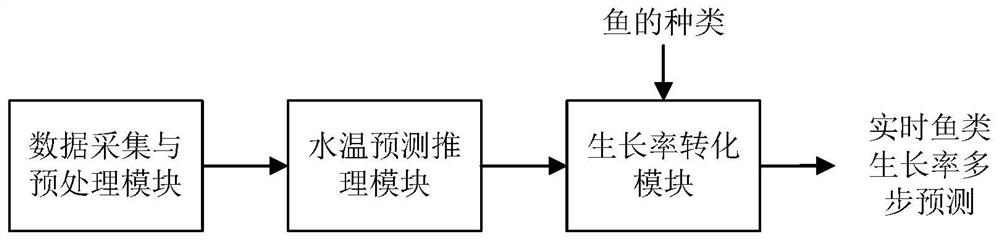
Fish growth rate prediction method and system based on environment modeling
PendingCN114386682AComprehensiveNo need to repeat trainingForecastingNeural architecturesEnvironmental modellingPredictive methods
The invention provides a fish growth rate prediction method and system based on environment modeling. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring environment data; based on the environment data, constructing an adaptive time mode network to obtain a water temperature prediction reasoning model; and inputting experience data of to-be-predicted fish into the water temperature prediction reasoning model to obtain a prediction result of the growth rate of the to-be-predicted fish. The water temperature prediction reasoning model is constructed by collecting the comprehensive environmental data, the prediction results of the growth rates of different fishes are obtained by combining the growth experience values of the different fishes, and the method has the advantages that the application range is wide, the environmental factors are comprehensively covered, and the prediction model does not need to be repeatedly trained.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for improving reliability of monocular vision localization through environmental model integrity assessment
ActiveCN109798897AImprove visual localization reliabilityHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsIntegrity assessmentData integrity
The invention discloses a method for improving reliability of monocular vision localization through environmental model integrity assessment. The method comprises, firstly, establishing an environmentexpression model; secondly, performing integrity assessment on the established environment expression model; lastly, according to the result of integrity assessment, determining whether environment modeling is completed, if so, stopping searching. Therefore, the data integrity of a finally established environment model can be improved. According to the method for improving reliability of monocular vision localization through environmental model integrity assessment, by means of the model with rich environment data, the association probability of correct data in the environment model can be improved, and further reliability of monocular vision localization can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
A Coal Mine Roadway Robot Positioning and Environment Modeling Method
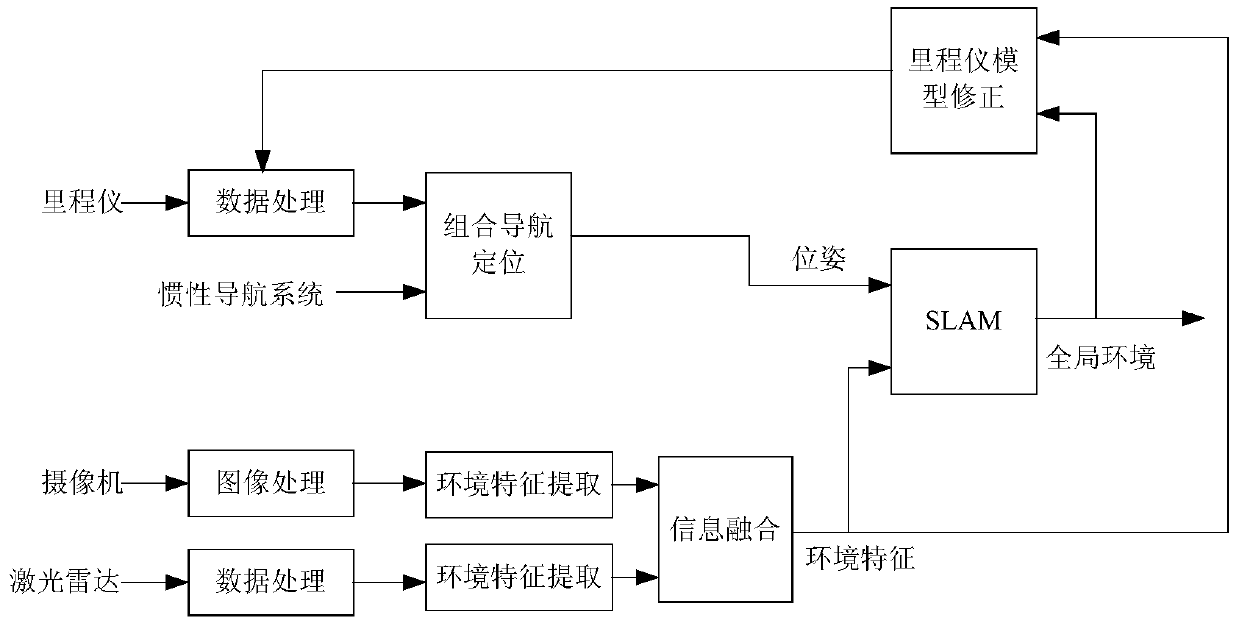
ActiveCN105573310BThree-dimensional performance and reflectionIntuitive performance and reflectionPosition/course control in two dimensionsRobot environmentEnvironmental modelling
The invention provides a method which is suitable for autonomous positioning and environment modeling of a ground mobile robot in a coal mine underground tunnel environment. The method comprises the following steps of executing a robot combined positioning algorithm; 2) performing positioning correction based on environment information; and 3) executing a robot 3D environment modeling method. The method is advantageous in that a three-dimensional model of the tunnel can be automatically generated through a coal mine tunnel measurement mobile robot; the downhole tunnel and the space relationship of the downhole tunnel can be visually and accurately represented in a three-dimensional manner; and furthermore the method has positive meaning for guiding field production and training safe production for miners.
Owner:航天科工智能机器人有限责任公司
Ant Colony Algorithm Applied to Dynamic Path Planning Method in Congested Environment
ActiveCN110941267BMeet traffic jamImprove accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEnvironmental modellingTraffic congestion
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
A single-station landslide deformation monitoring and early warning method based on gnss environment model
ActiveCN111694021BMonitoring cost reductionSatellite radio beaconingAlarmsEnvironmental modellingDeformation monitoring
The invention discloses a single-station landslide deformation monitoring and early warning method based on a GNSS environment model. Correlation coefficient solution, early warning application. The monitoring and early warning method of the present invention mainly uses a low-cost consumer-grade GNSS positioning terminal to collect data and perform environmental modeling, and identify the acceleration state of the landslide early and carry out effective early warning through the change trend of the correlation coefficient of the environmental model, which not only reduces the monitoring cost The price is greatly reduced, and it provides new ideas and methods for GNSS landslide monitoring and early warning.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Hybrid Path Planning Method for Mobile Robots in Multi-resolution Obstacle Environment
ActiveCN105717929BImprove blindnessReduce computational costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEnvironmental modellingSimulation
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
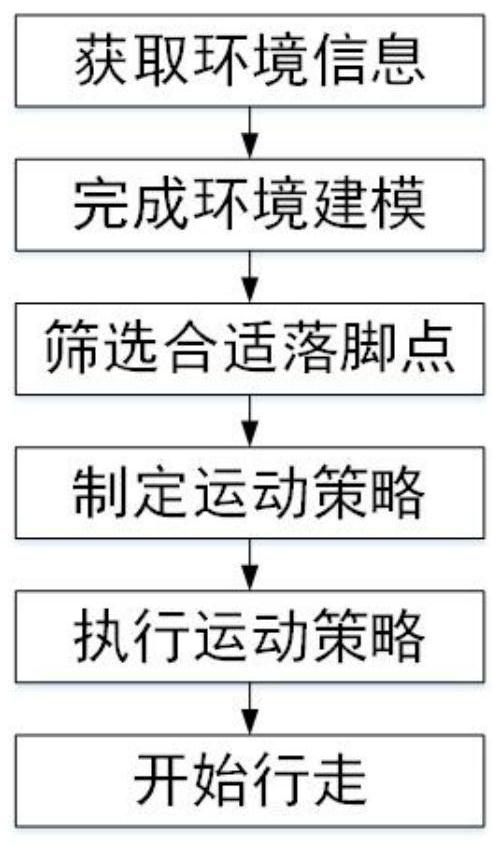
A Hexapod Robot Gait Planning Method Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
ActiveCN107562052BEasy to walkImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsHexapodEnvironmental modelling
Owner:唐开强
A Dynamic Path Planning Method for Auv Submarine Terrain Matching
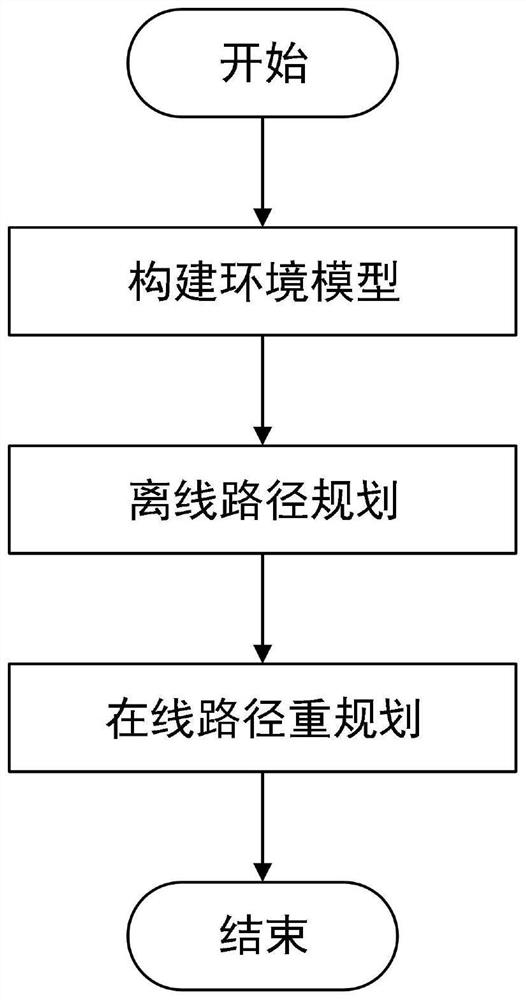
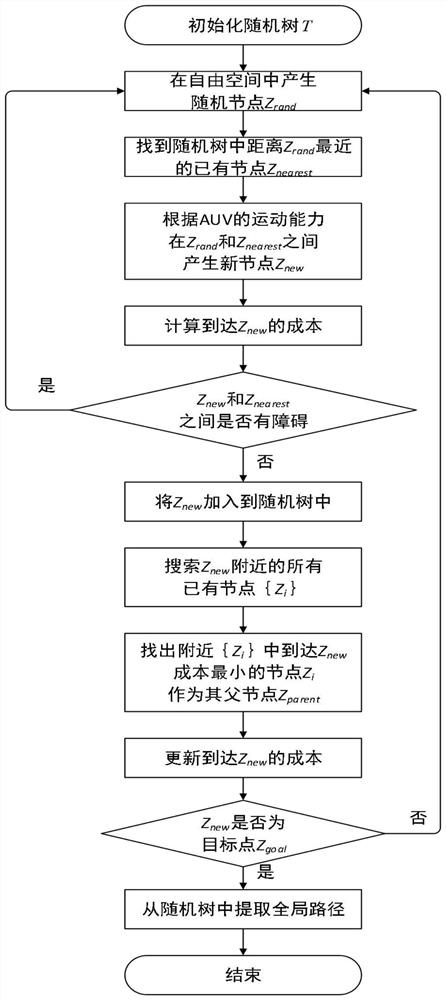
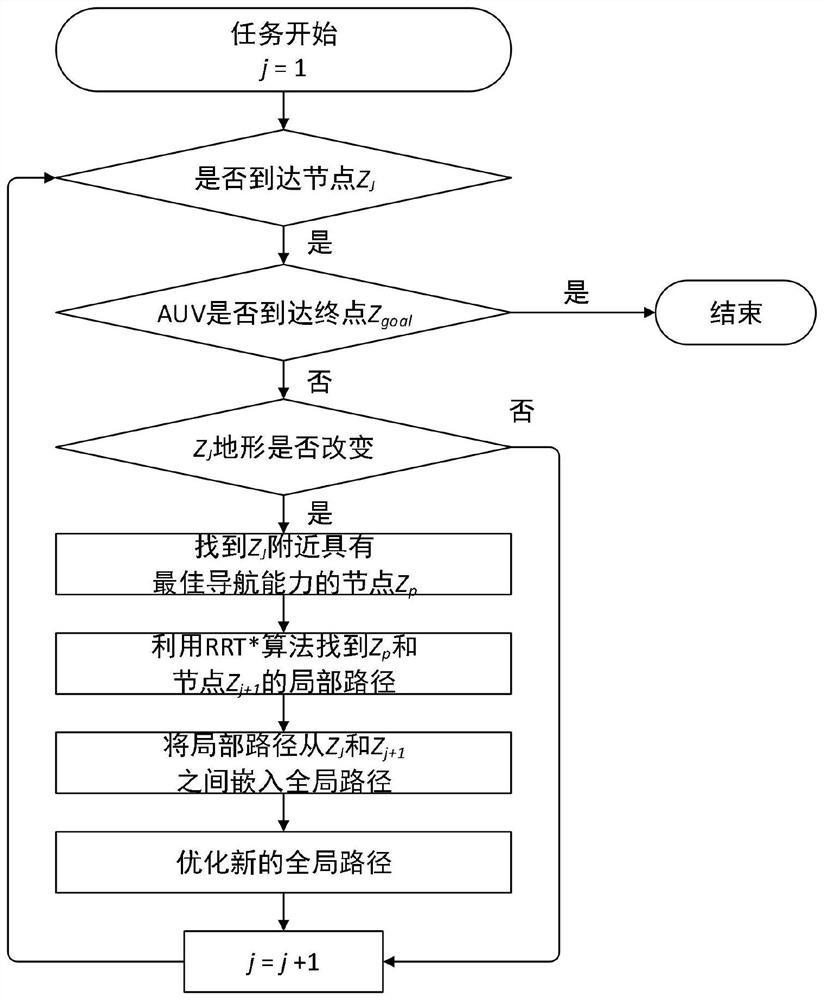
ActiveCN108871351BAvoid Low Terrain Information AreasRealize judgmentInstruments for road network navigationForecastingTerrainEnvironmental modelling
The invention discloses a dynamic path planning method for AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) submarine topography matching, and belongs to the technical field of AUV navigation. The dynamic path planning method comprises environment modeling, offline path planning and online path re-planning. An environment model is constructed by topography information and topography source confidence, whereina topography characteristic is represented with a topography standard deviation. Offline path planning is based on a rapid search random tree algorithm, improves a new node and father node selection algorithm, and processes the topography information by roulette and a mahalanobis distance so as to avoid a low topography information region. When an AUV navigates along an offline path and detects changes of the topography information, online re-planning implements judgment on the topography changes by methods of judging the topography changes, searching a local navigation optimal node, re-optimizing a global path and the like, and ensures navigation accuracy. The dynamic path planning method is applicable to long-voyage high-accuracy AUV path planning, and particularly when the topography information is changed, by modifying the path in real time, navigation accuracy and a path distance are ensured.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com