A Dynamic Path Planning Method for Auv Submarine Terrain Matching
A terrain matching and dynamic path technology, which is used in road network navigators, data processing applications, forecasting, etc., can solve problems such as poor terrain navigation ability without considering matching areas, inability to consider real-time terrain information, and inability to modify paths in real time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
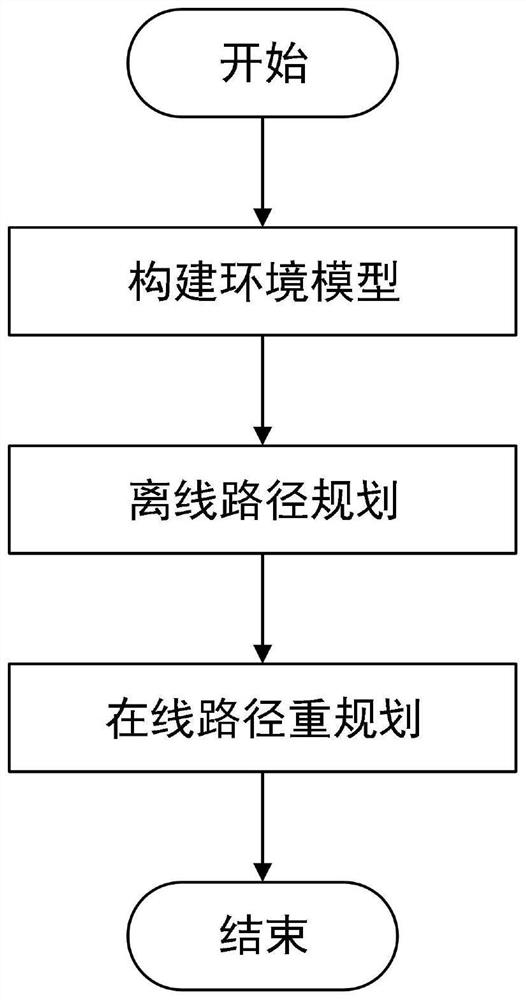
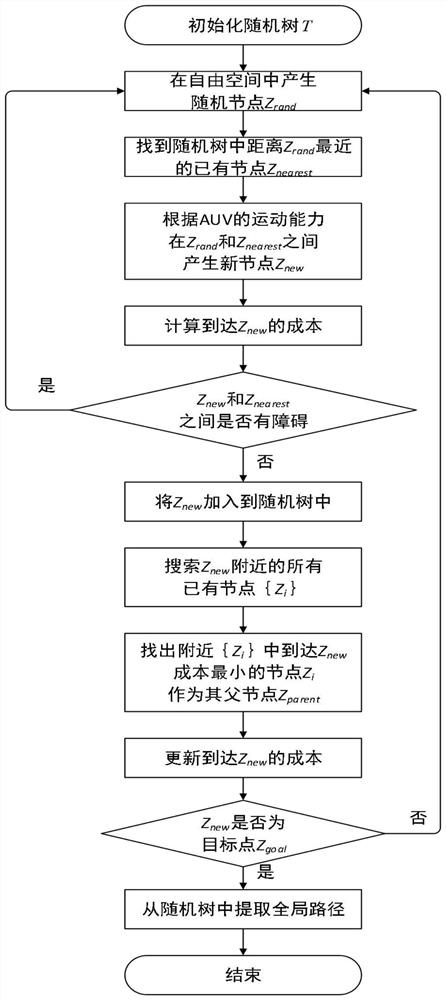
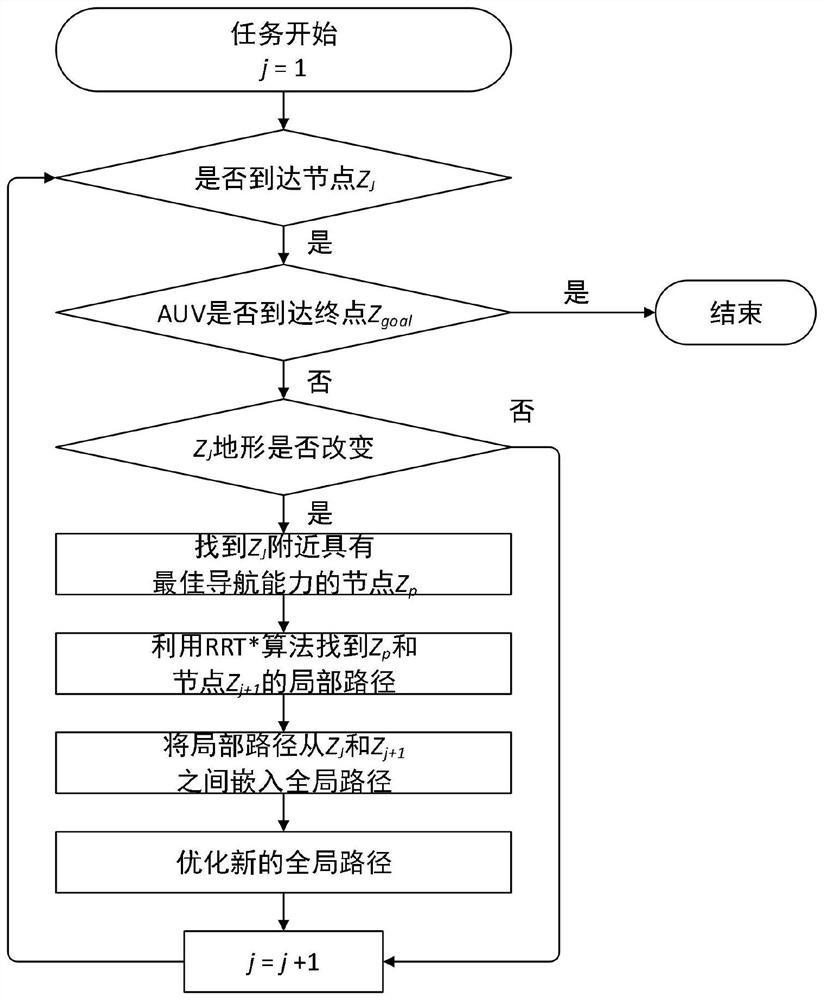
[0060] This paper deals with a dynamic path planning method, including environment modeling, offline path planning and online path replanning. Simulate the physical environment and navigation capabilities using obstacles, terrain information, and terrain source confidence. Offline path planning consists of four steps: generate random nodes, generate new nodes, select the best parent node and calculate path cost. Online path replanning consists of four steps: identifying changing terrain, finding local optimal nodes, local path planning, and refining the entire path. Finally, a seabed path with higher navigation accuracy and shorter distance is obtained.
[0061] Content of the present invention is realized like this: comprise the following steps:
[0062] 1. Construct the environmental model of the seabed. For the physical environment map of the seabed, it is gridded first, so as to become a grid map with height h(i,j) for point (i,j). Then, the navigation ability of each ...
Embodiment 2
[0107] figure 1 The system flow of the present invention has been expressed, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0108] (1) According to the surveyed and mapped seabed terrain map, it is gridded, and the terrain features of each grid point are extracted for path planning and terrain matching.
[0109] (2) Before the AUV performs the task, the offline path planning algorithm is used for global path planning.
[0110] (3) After the AUV starts to execute the task, it uses the online path re-planning algorithm for real-time global path optimization to achieve navigation accuracy.
[0111] (4) After the AUV reaches the destination, the entire dynamic path planning method ends.
[0112] figure 2 It is a flow chart of the offline path planning algorithm of the present invention, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0113] (1) Use the starting point z init Initialize the random tree T=(V,E), where V represents the nodes in the random tree a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com