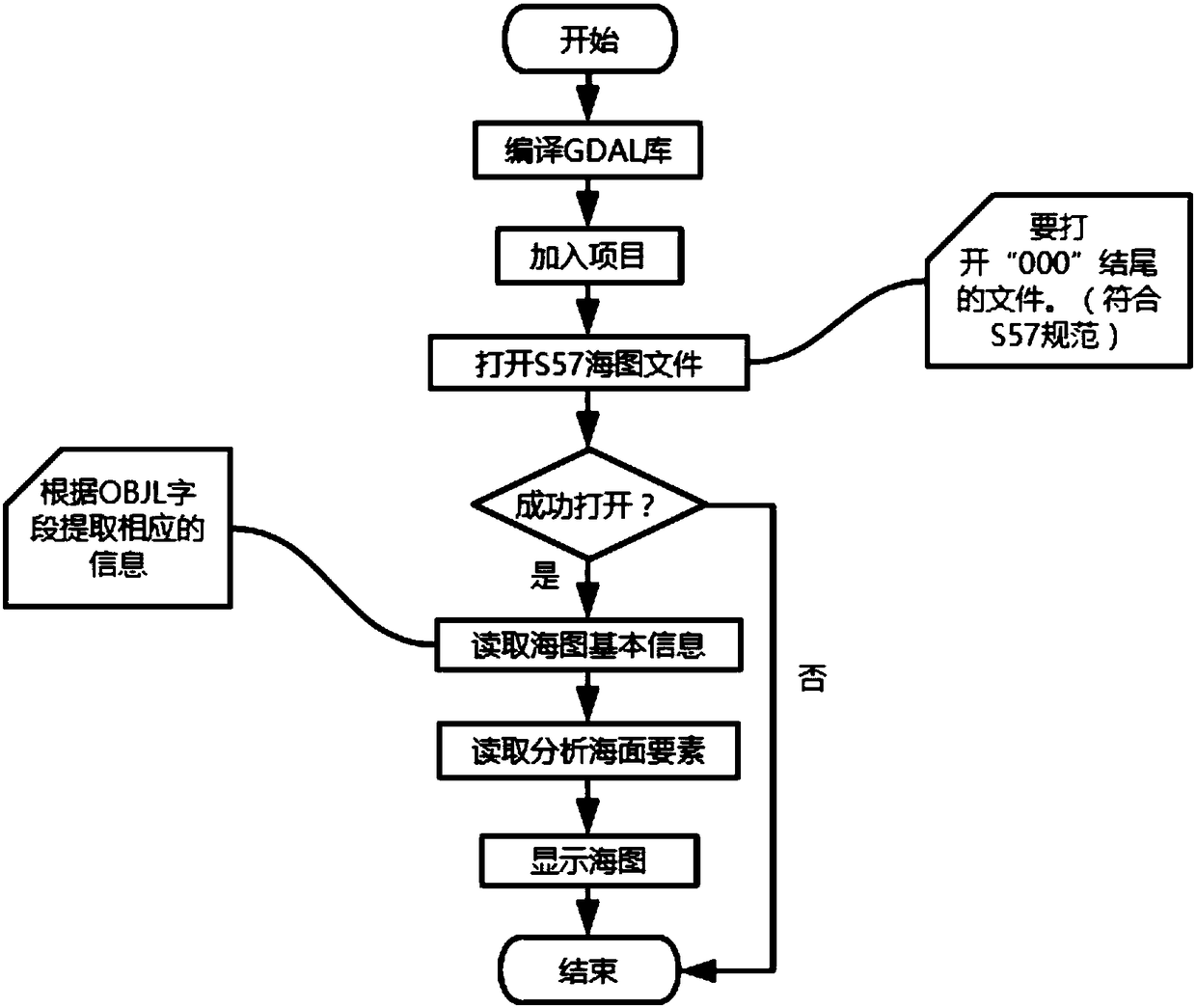
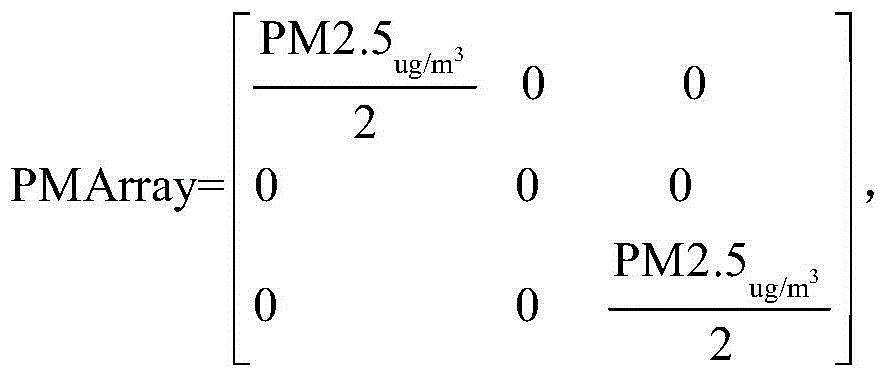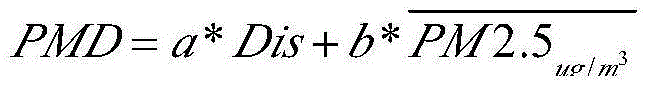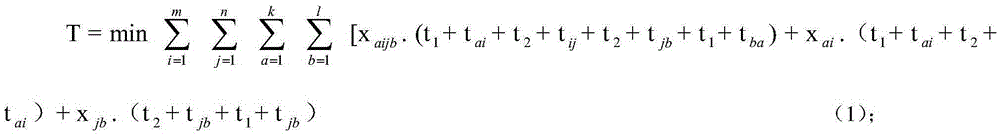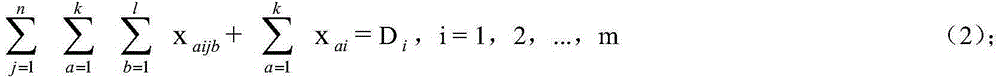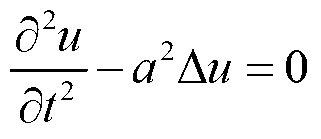Patents
Literature
302 results about "Path distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Common path of travel is the distance an occupant must travel before they have their choice of more than one exit. Exit access travel distance is the maximum distance that occupant must travel before they reach an exit.
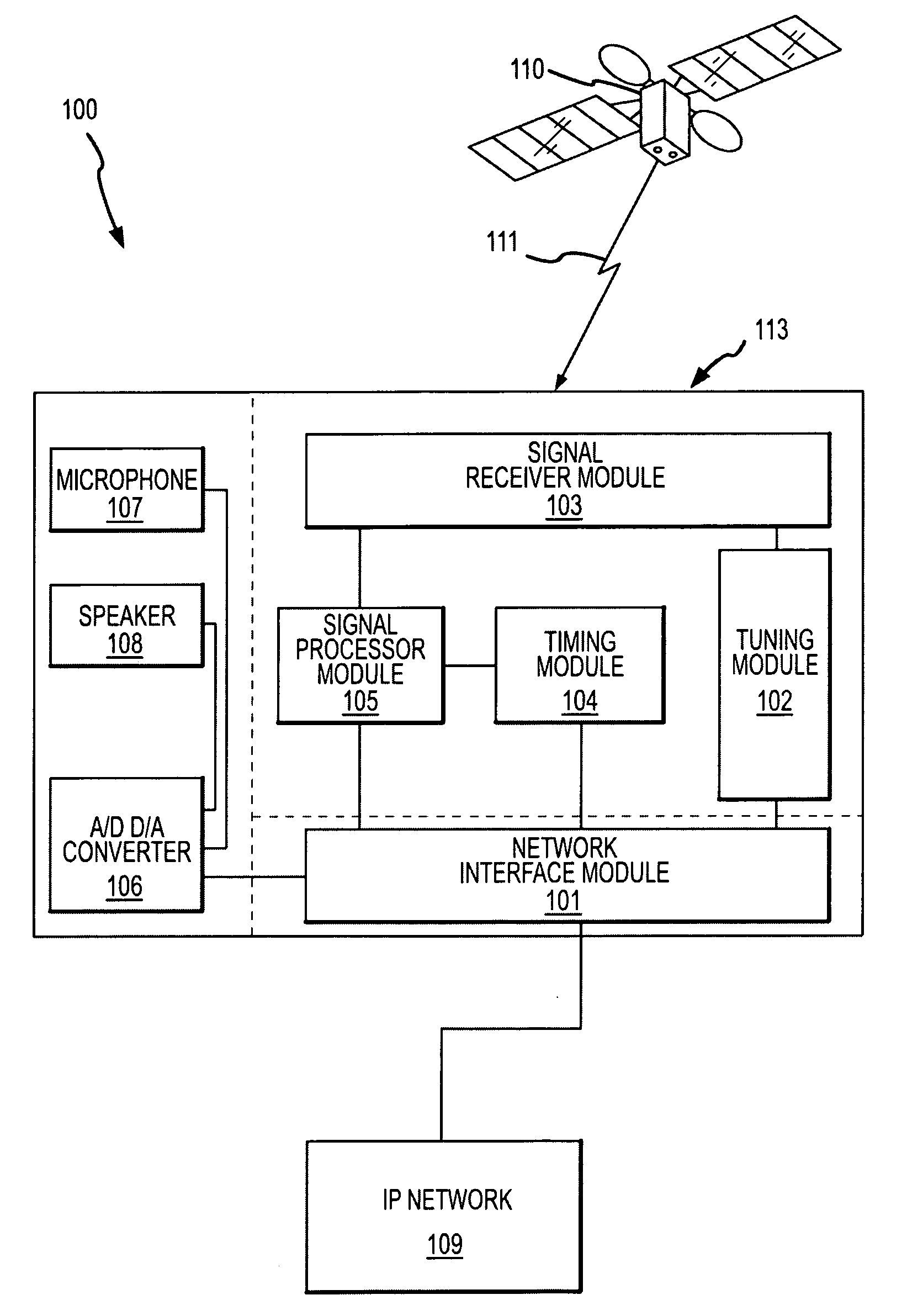
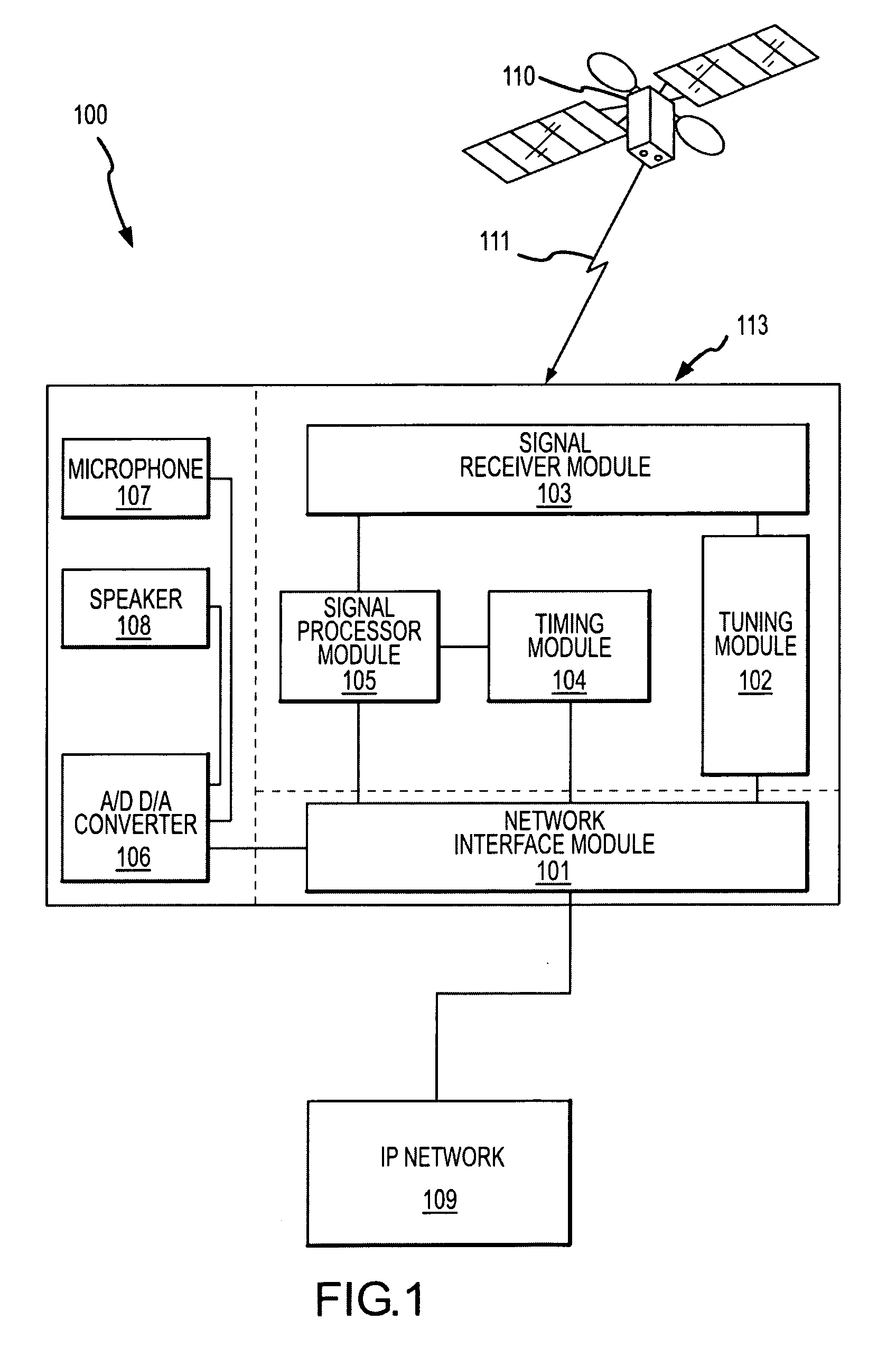
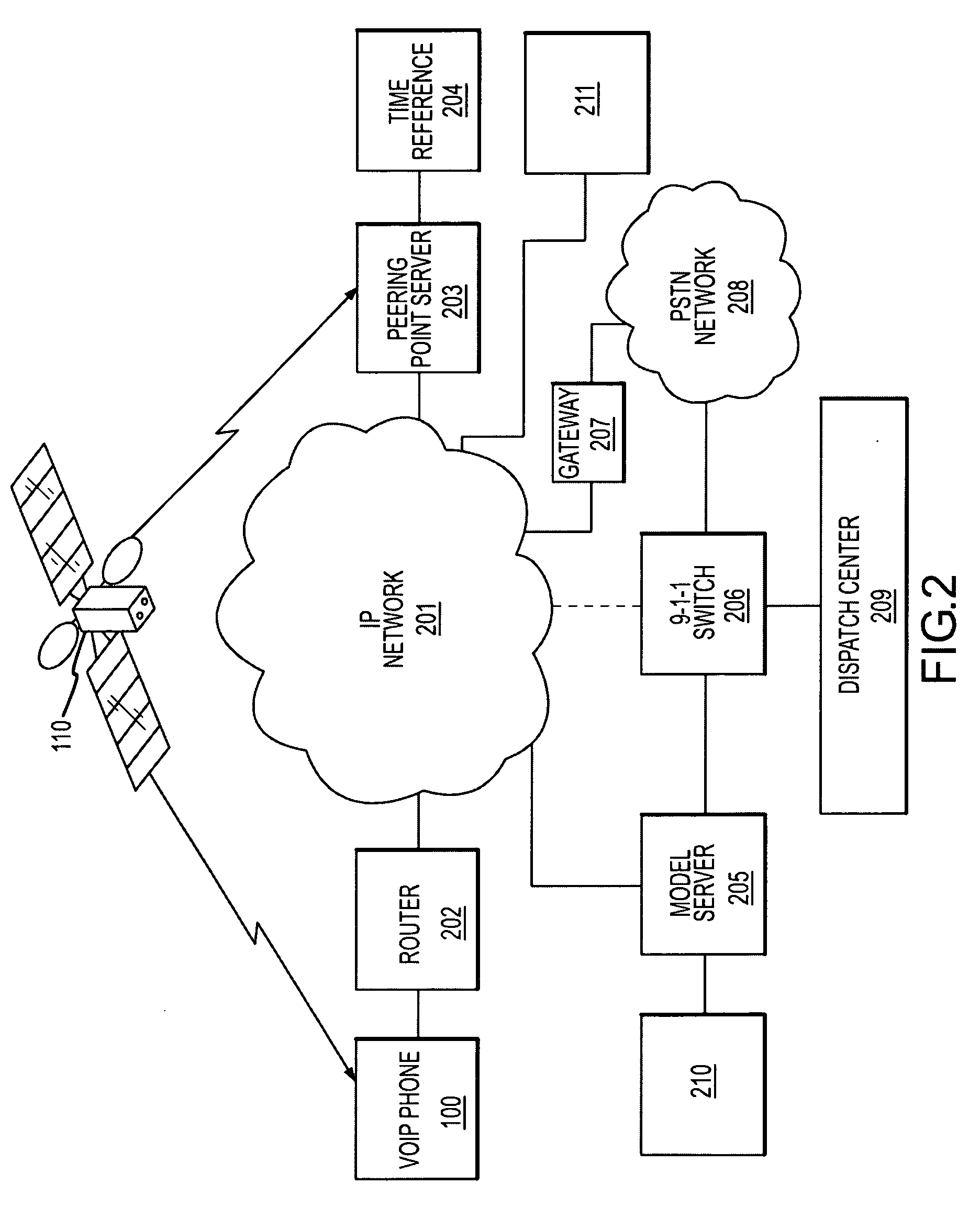
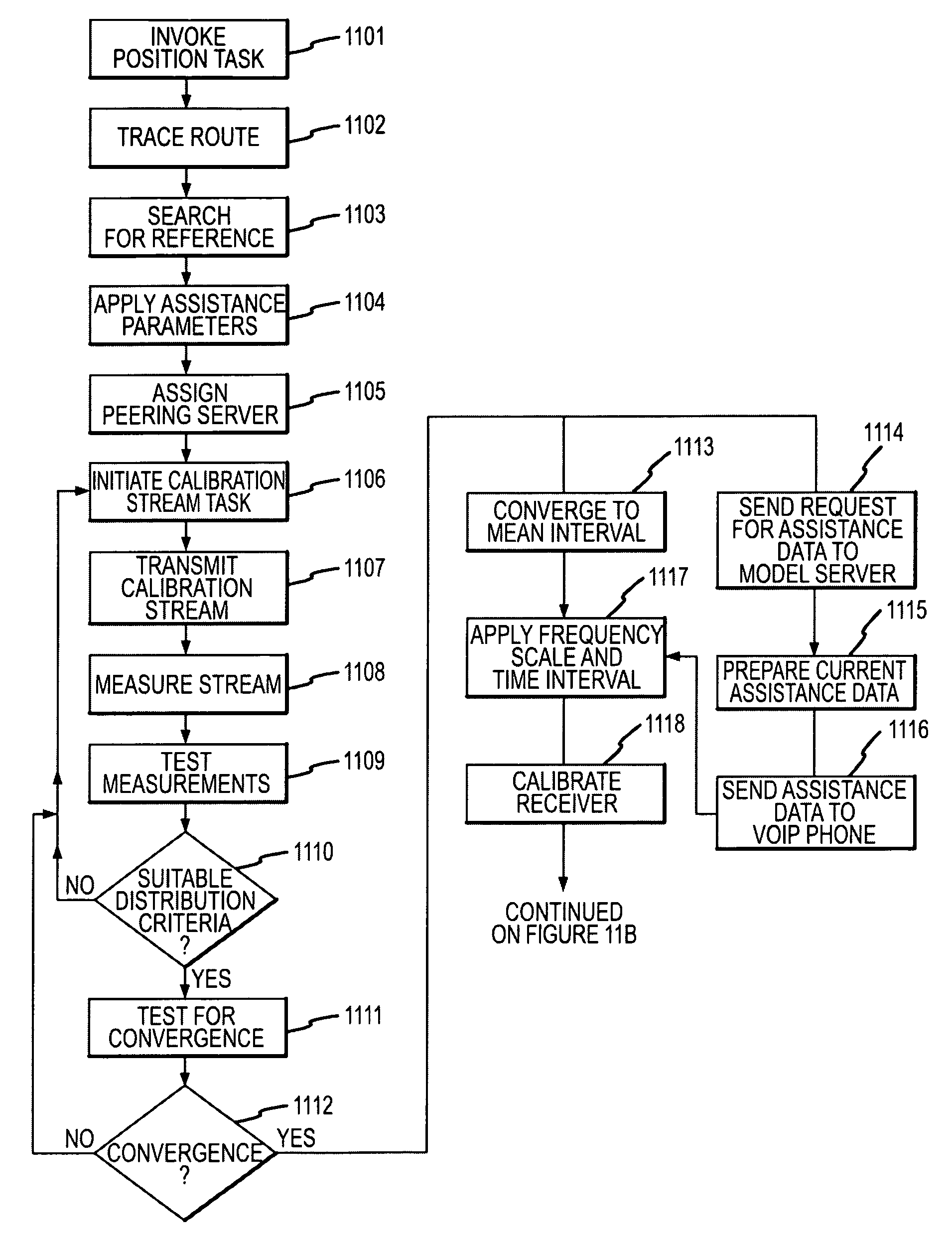
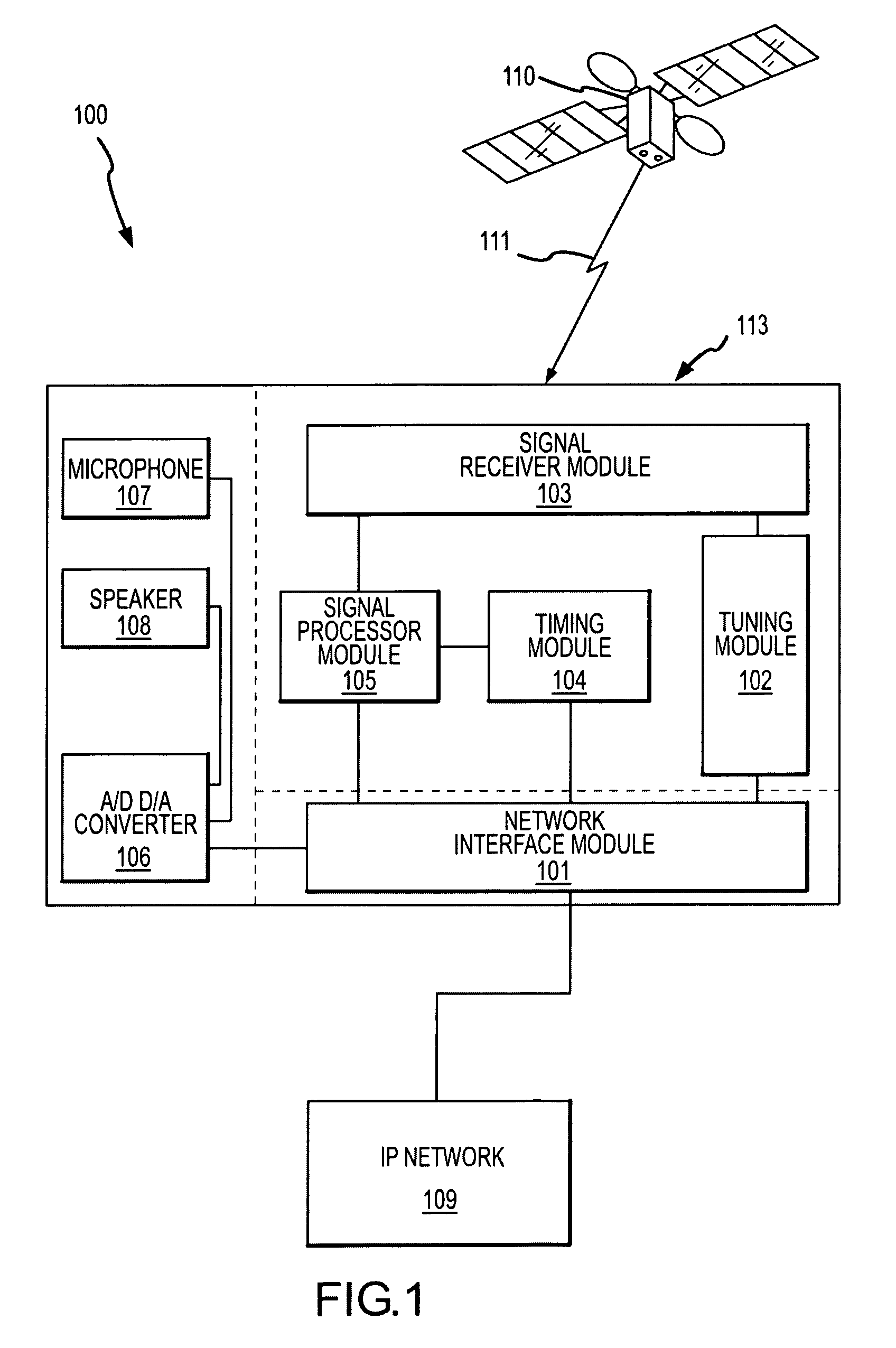
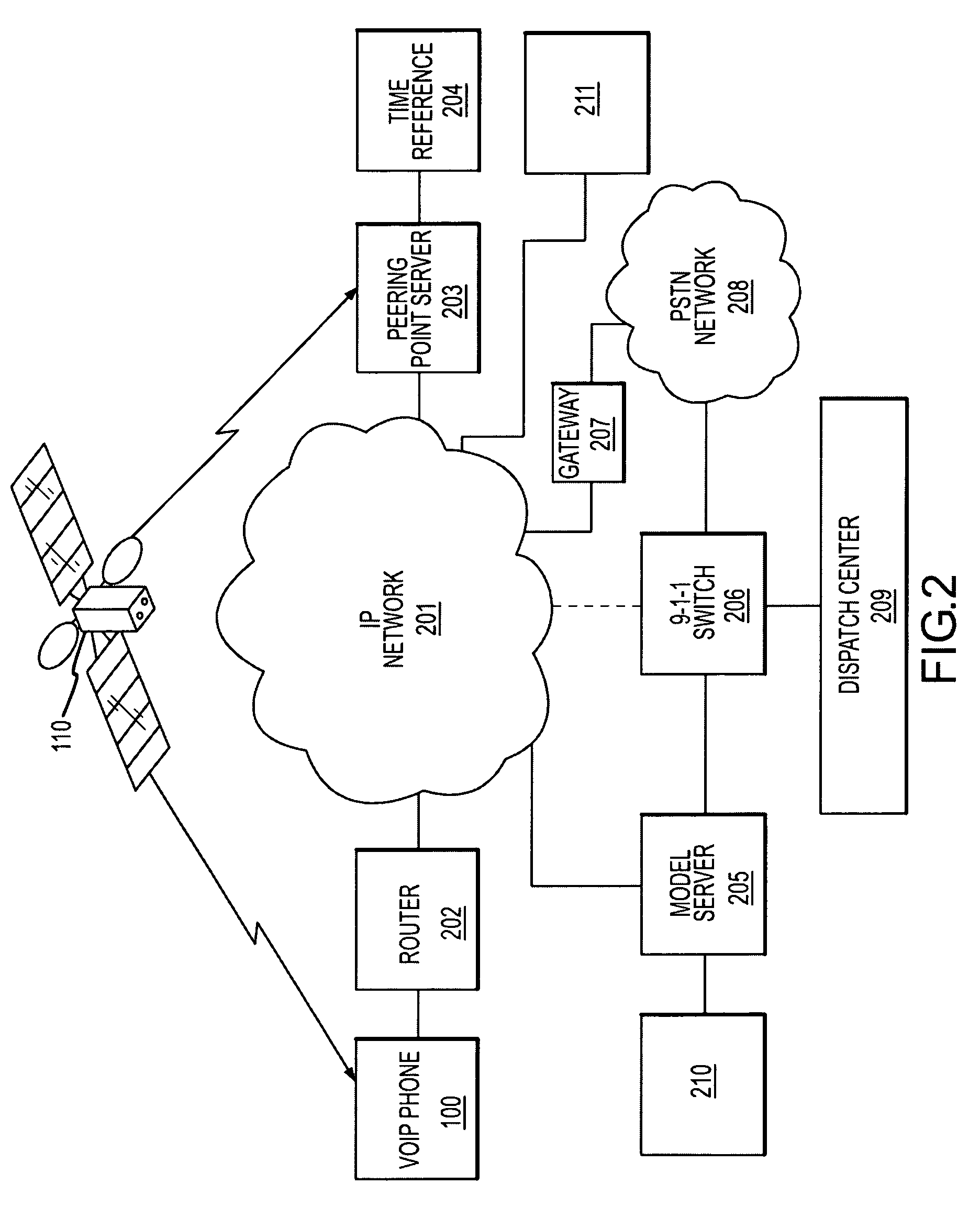
System and methods for IP and VoIP device location determination
ActiveUS20070030841A1Easy to movePrecise positioningPosition fixationData switching by path configurationGeolocationStandard methods
A method and system for precise position determination of general Internet Protocol (IP) network-connected devices. A method enables use of remote intelligence located at strategic network points to distribute relevant assistance data to IP devices with embedded receivers. Assistance is tailored to provide physical timing, frequency and real time signal status data using general broad band communication protocols. Relevant assistance data enables several complementary forms of signal processing gain critical to acquire and measure weakened or distorted in-building Global Navigation Satellite Services (GNSS) signals and to ultimately extract corresponding pseudo-range time components. A method to assemble sets of GNSS measurements that are observed over long periods of time while using standard satellite navigation methods, and once compiled, convert using standard methods each pseudo-range into usable path distances used to calculate a precise geographic position to a known degree of accuracy.
Owner:IPOSI
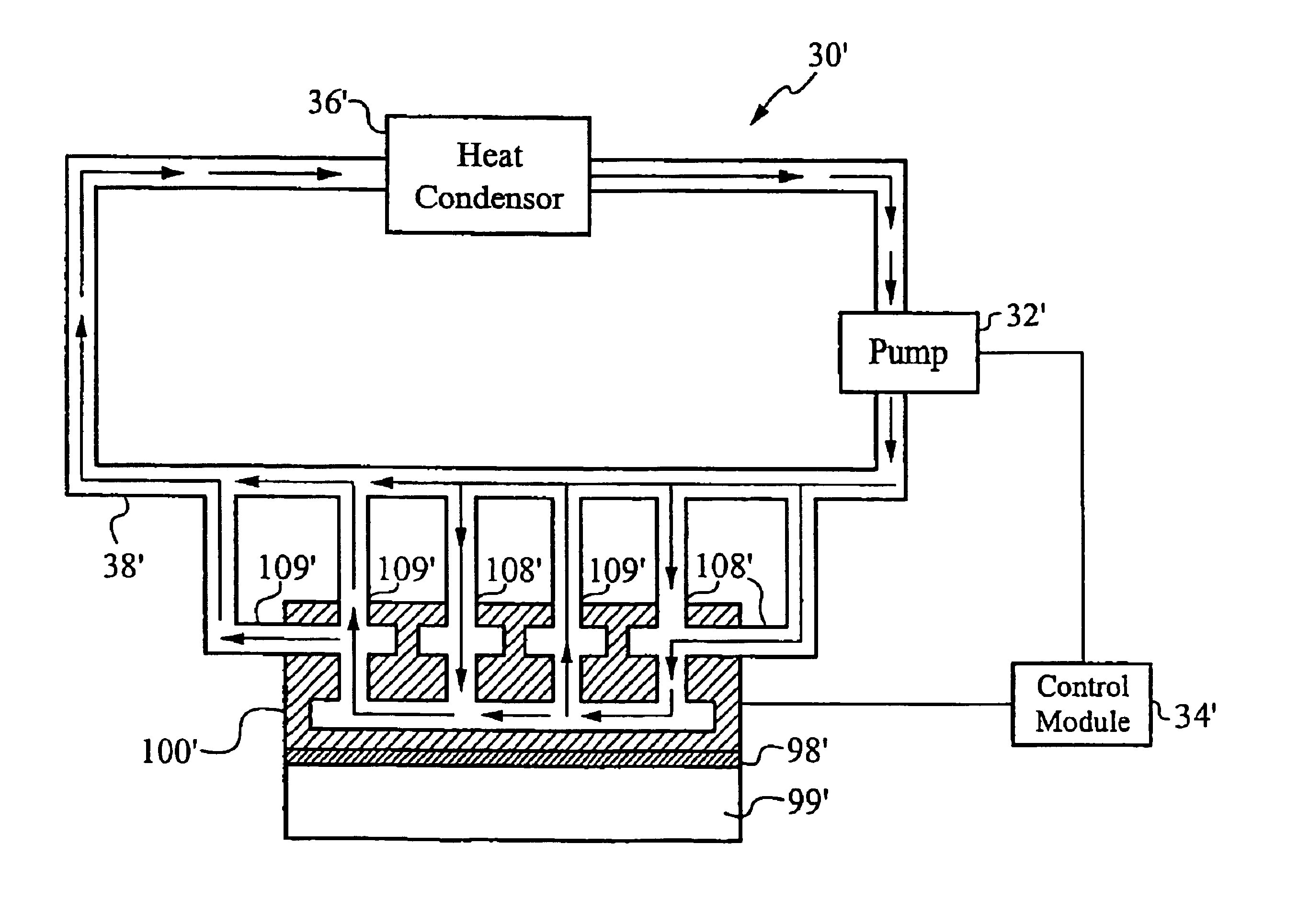
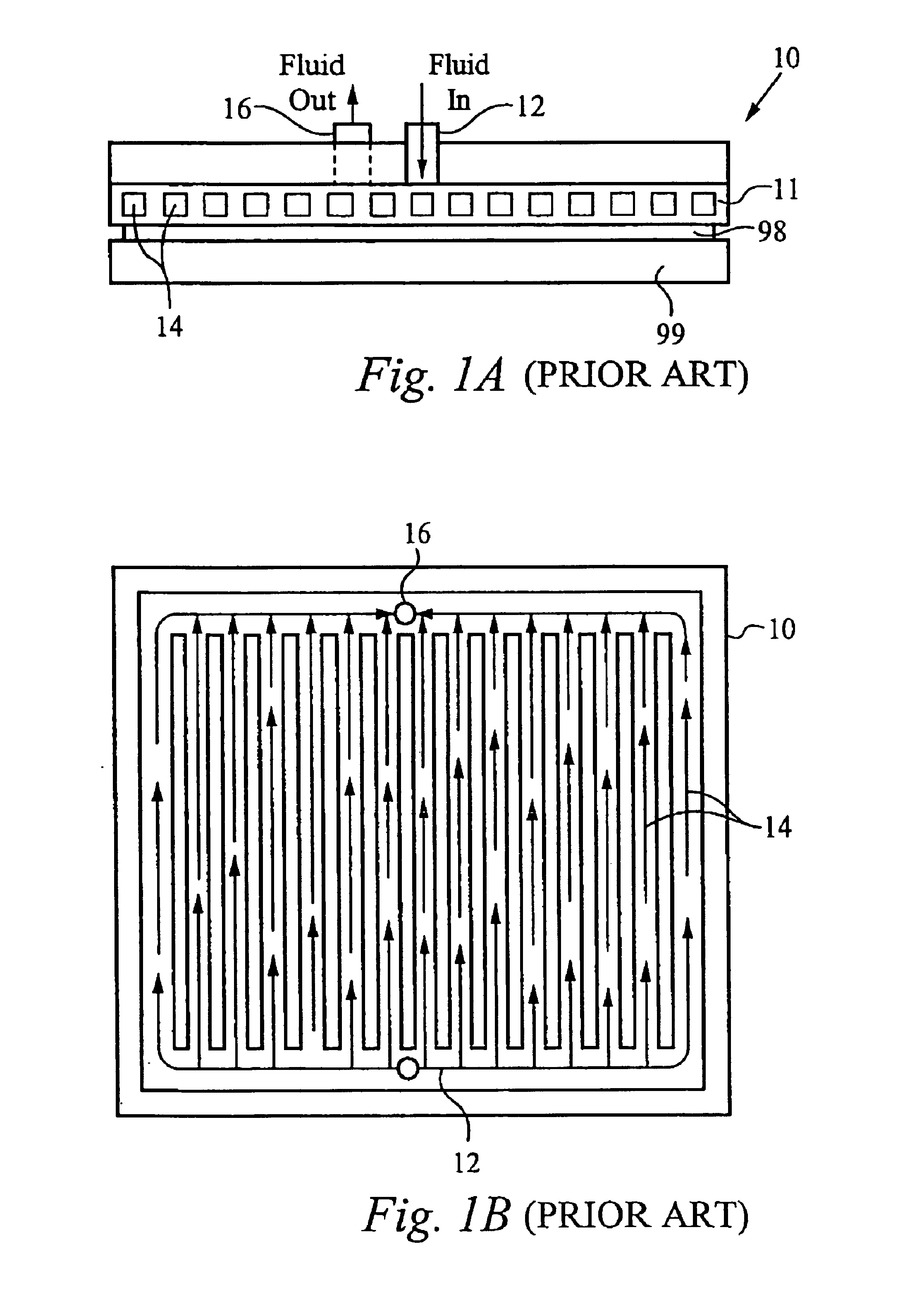
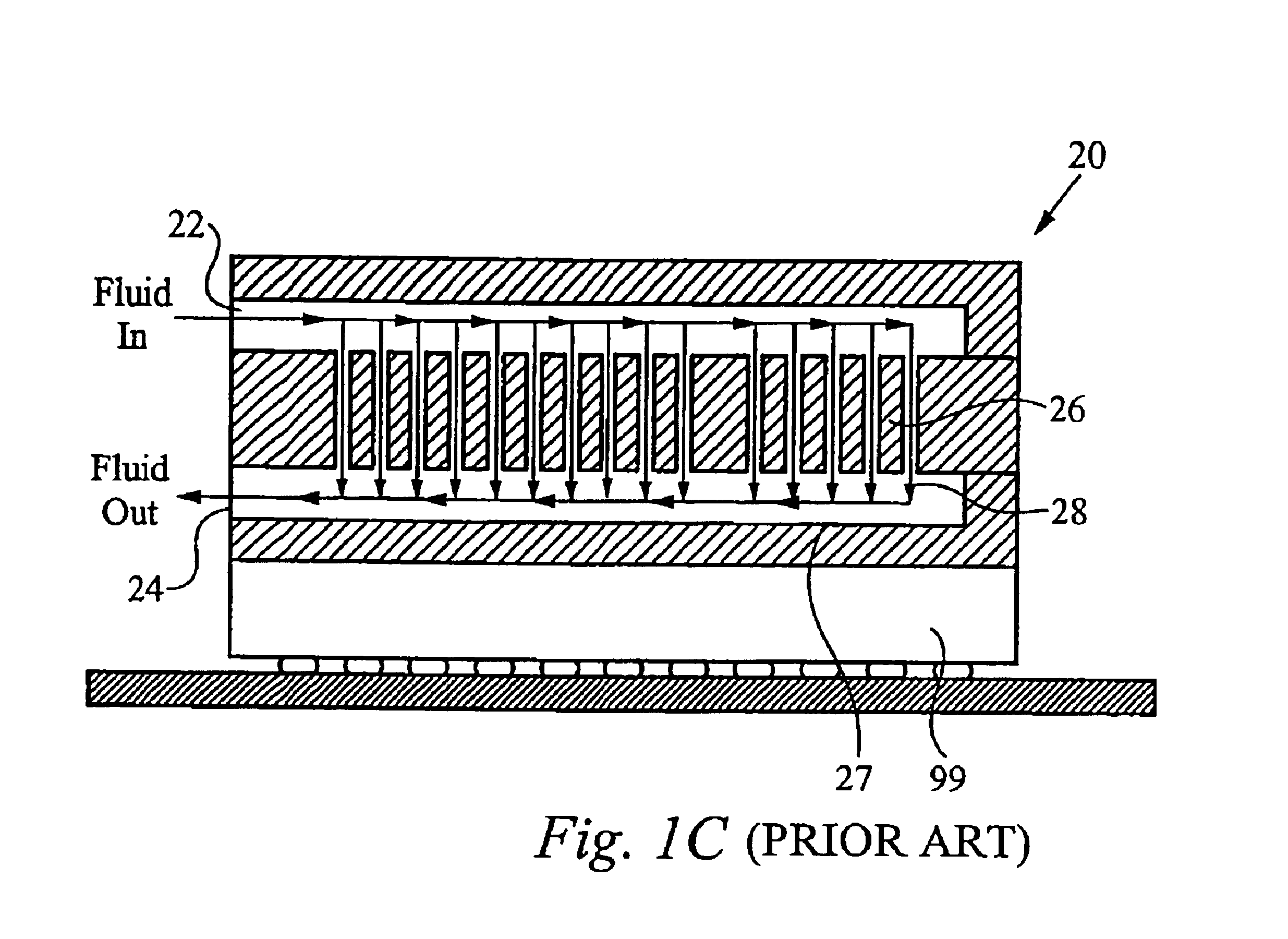
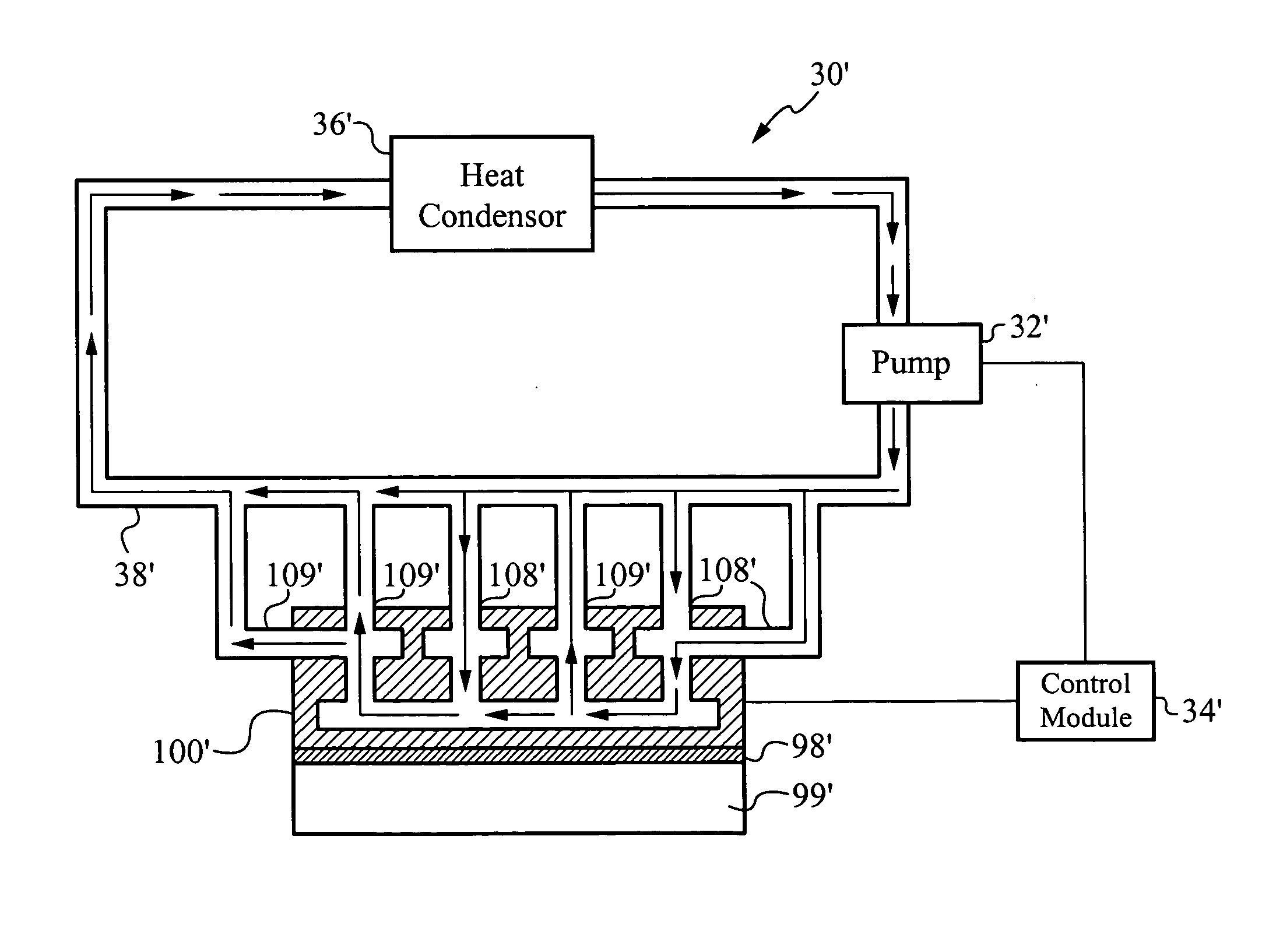
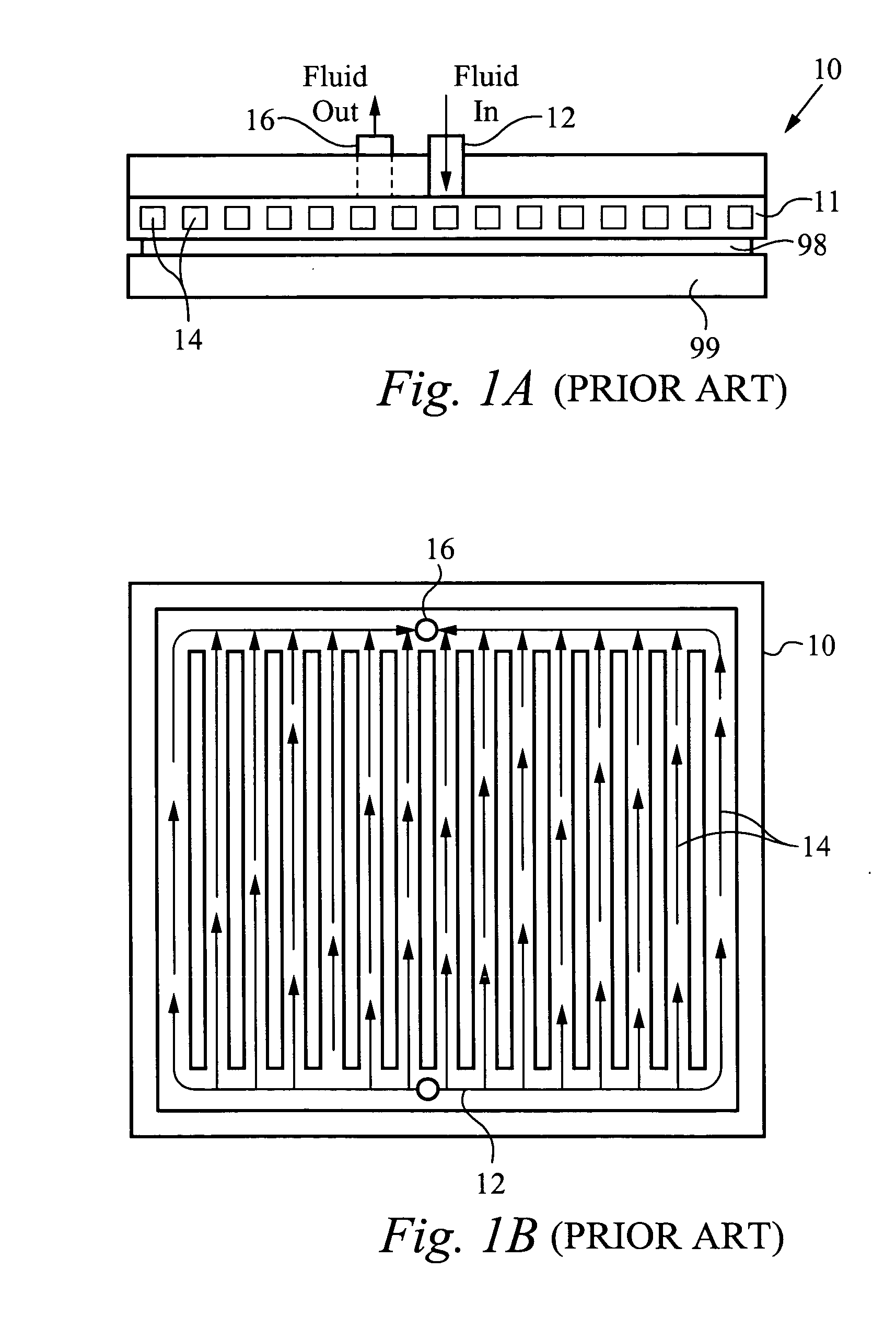
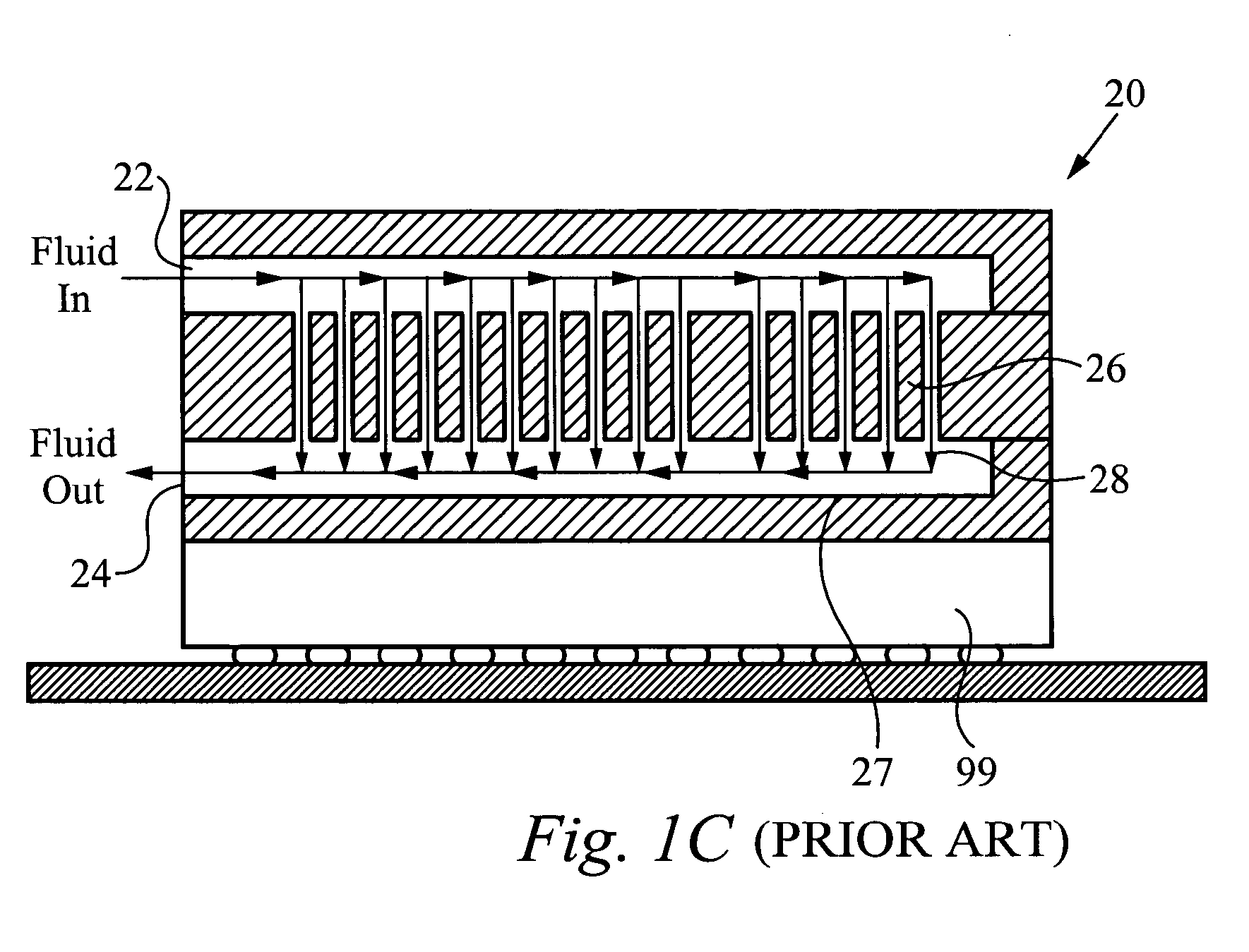
Method and apparatus for efficient vertical fluid delivery for cooling a heat producing device
InactiveUS7000684B2Minimized fluid path distanceImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterface layerPath distance
A heat exchanger and method of manufacturing thereof comprises an interface layer for cooling a heat source. The interface layer is coupled to the heat source and is configured to pass fluid therethrough. The heat exchanger further comprises a manifold layer that is coupled to the interface layer. The manifold layer includes at least one first port that is coupled to a first set of individualized holes which channel fluid through the first set. The manifold layer includes at least one second port coupled to a second set of individualized holes which channel fluid through the second set. The first set of holes and second set of holes are arranged to provide a minimized fluid path distance between the first and second ports to adequately cool the heat source. Preferably, each hole in the first set is positioned a closest optimal distance to an adjacent hole the second set.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
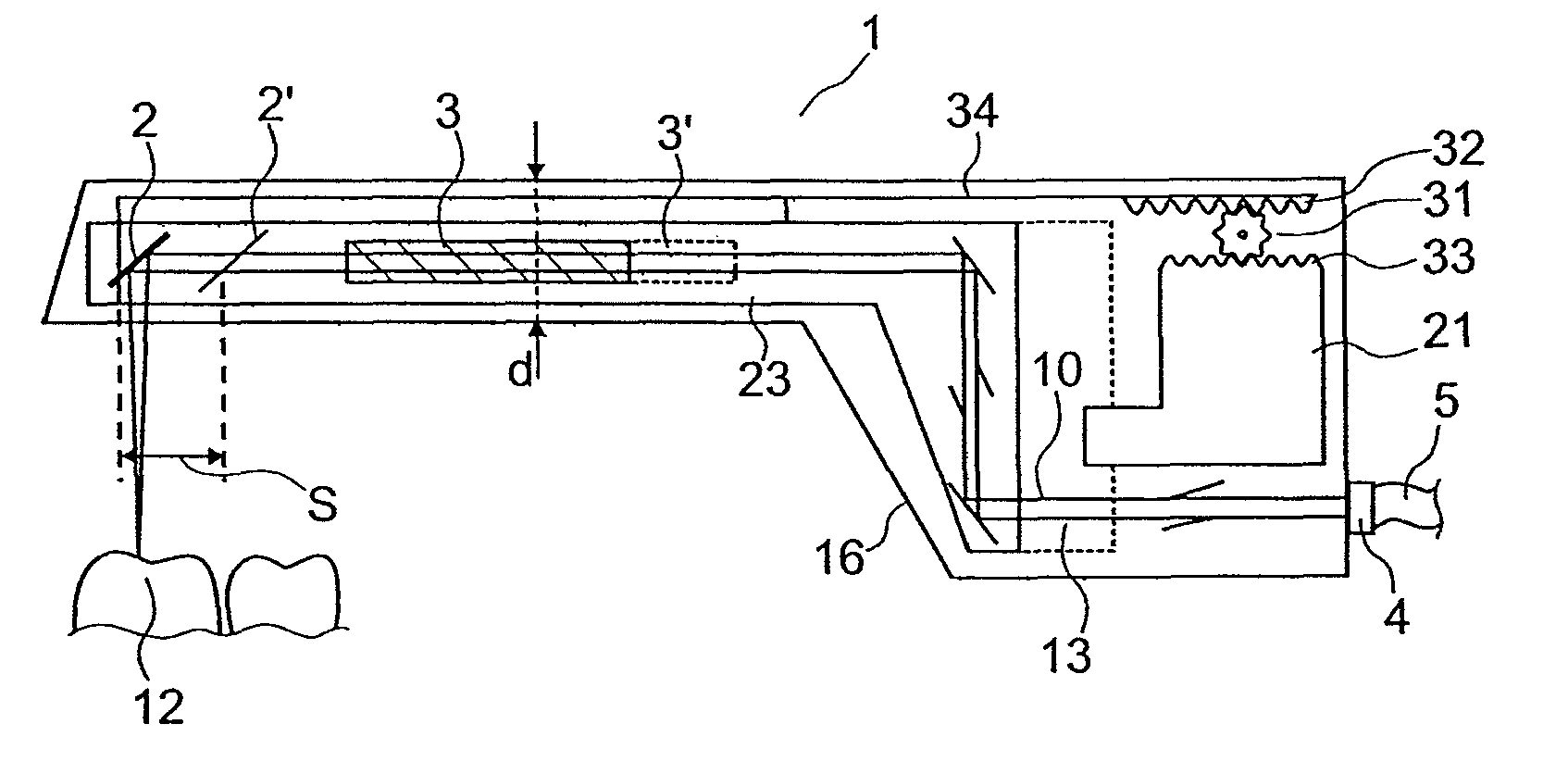
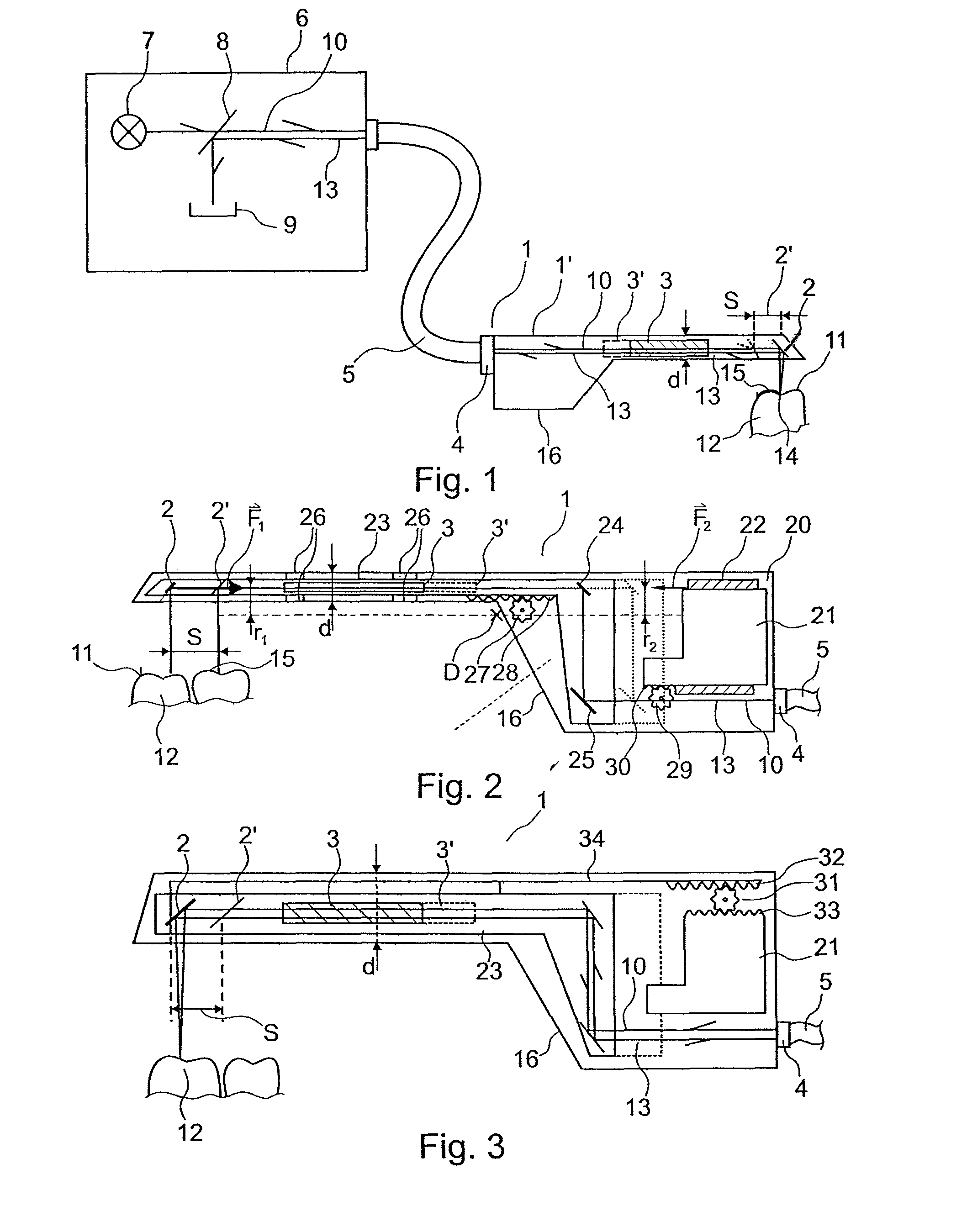
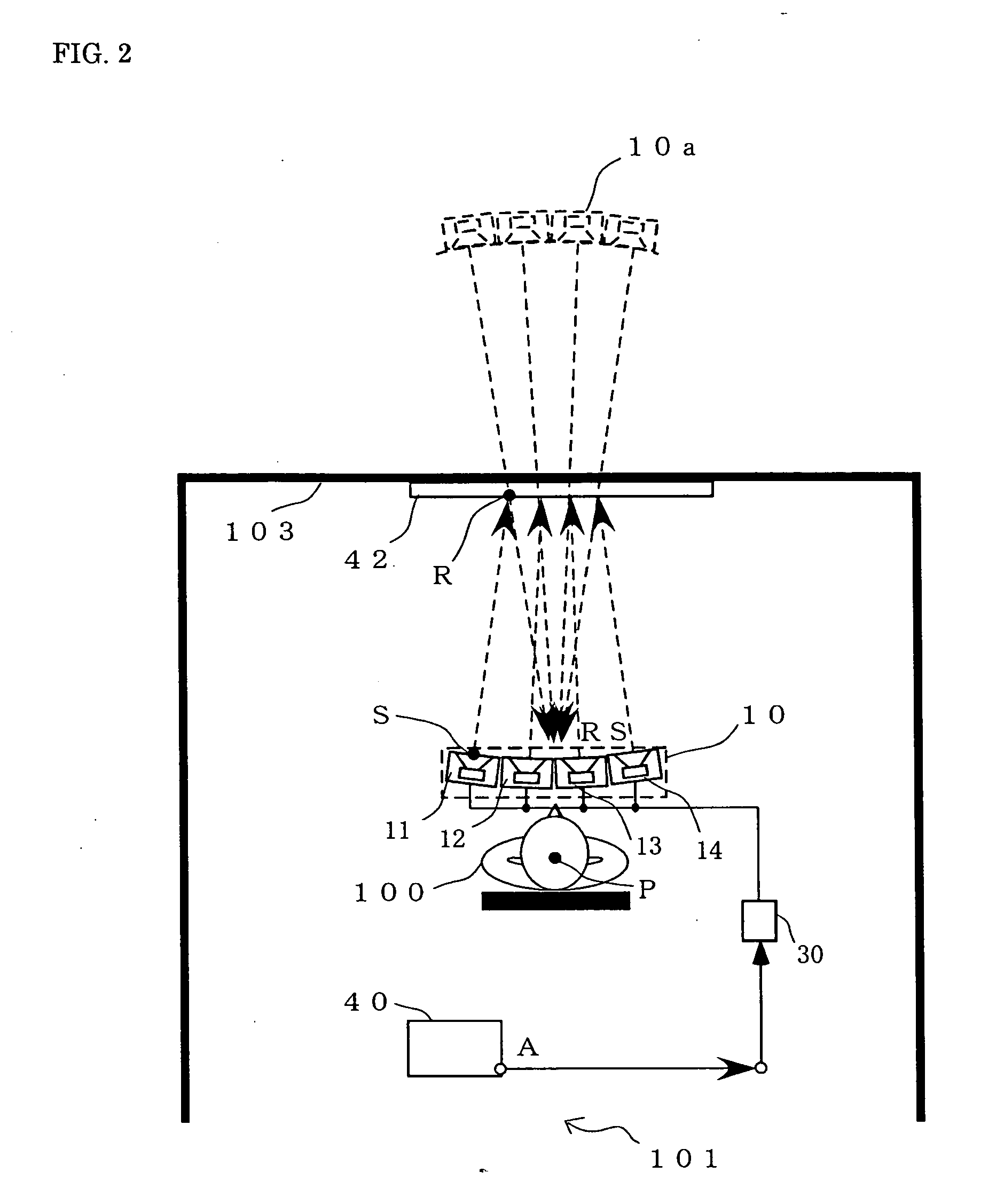
Apparatus and method for optical 3D measurement
ActiveUS7986415B2Advantageously facilitatedReduce the overall heightImpression capsDiagnostic recording/measuringLight beam3d measurement
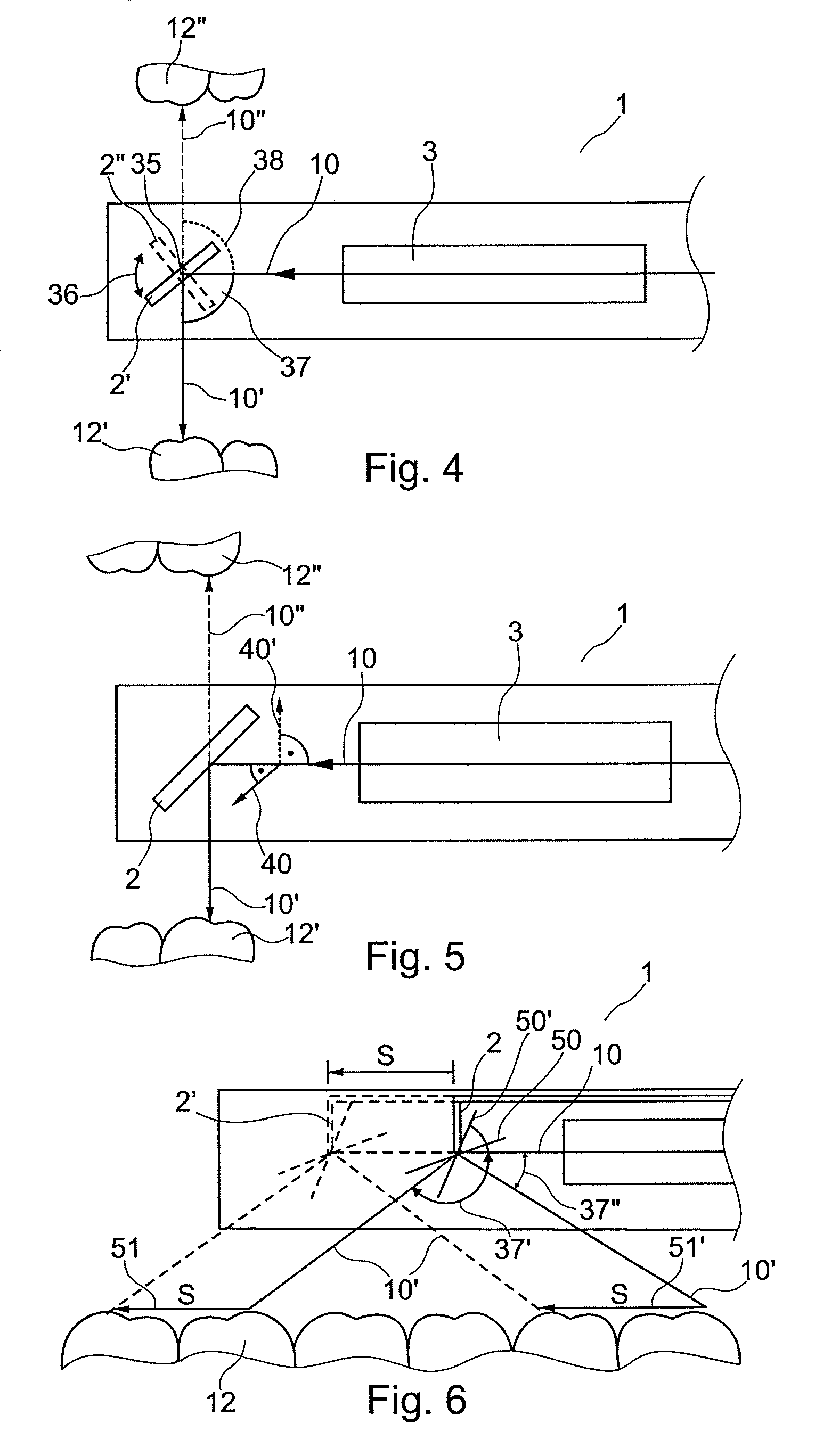
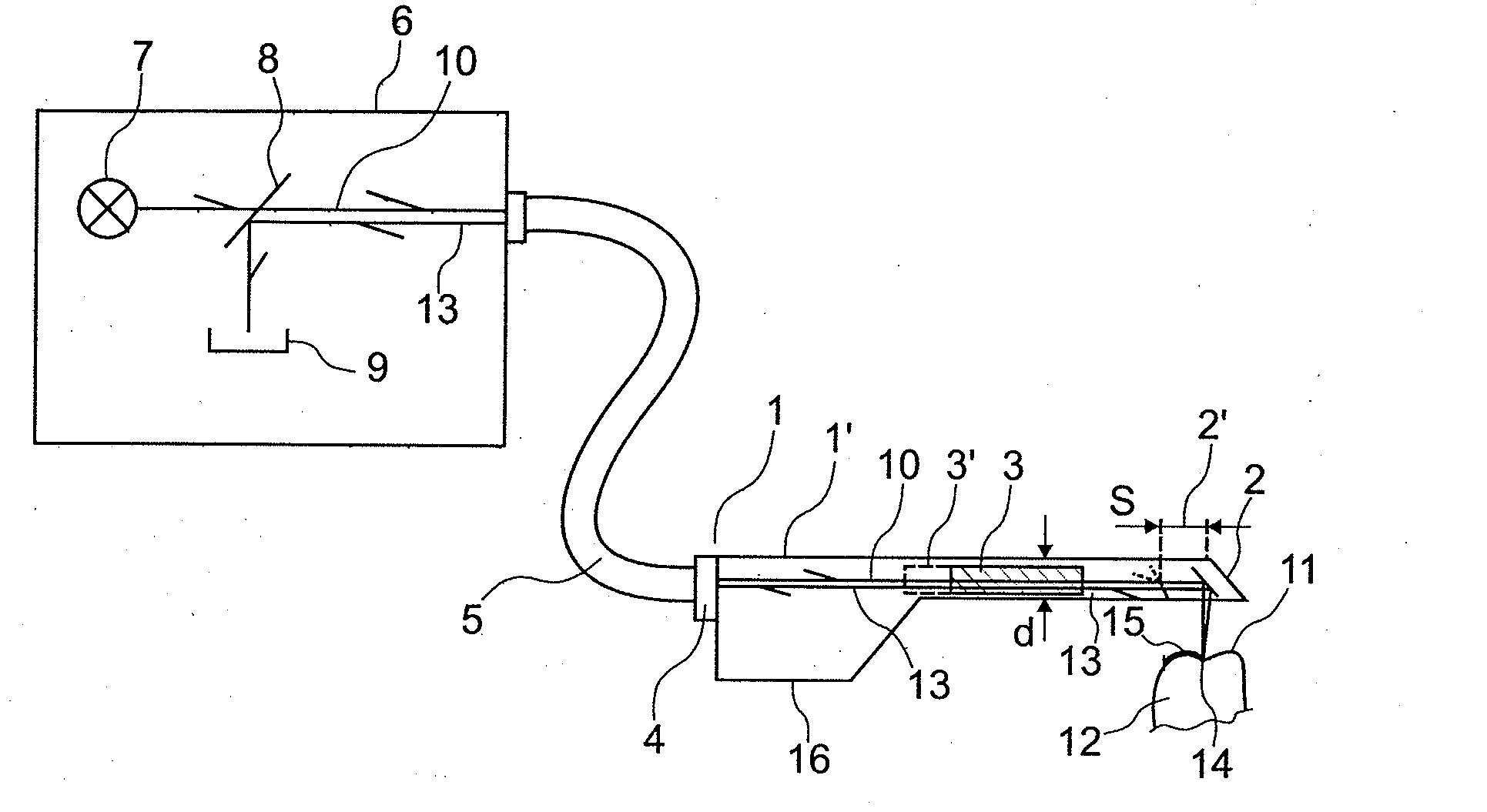
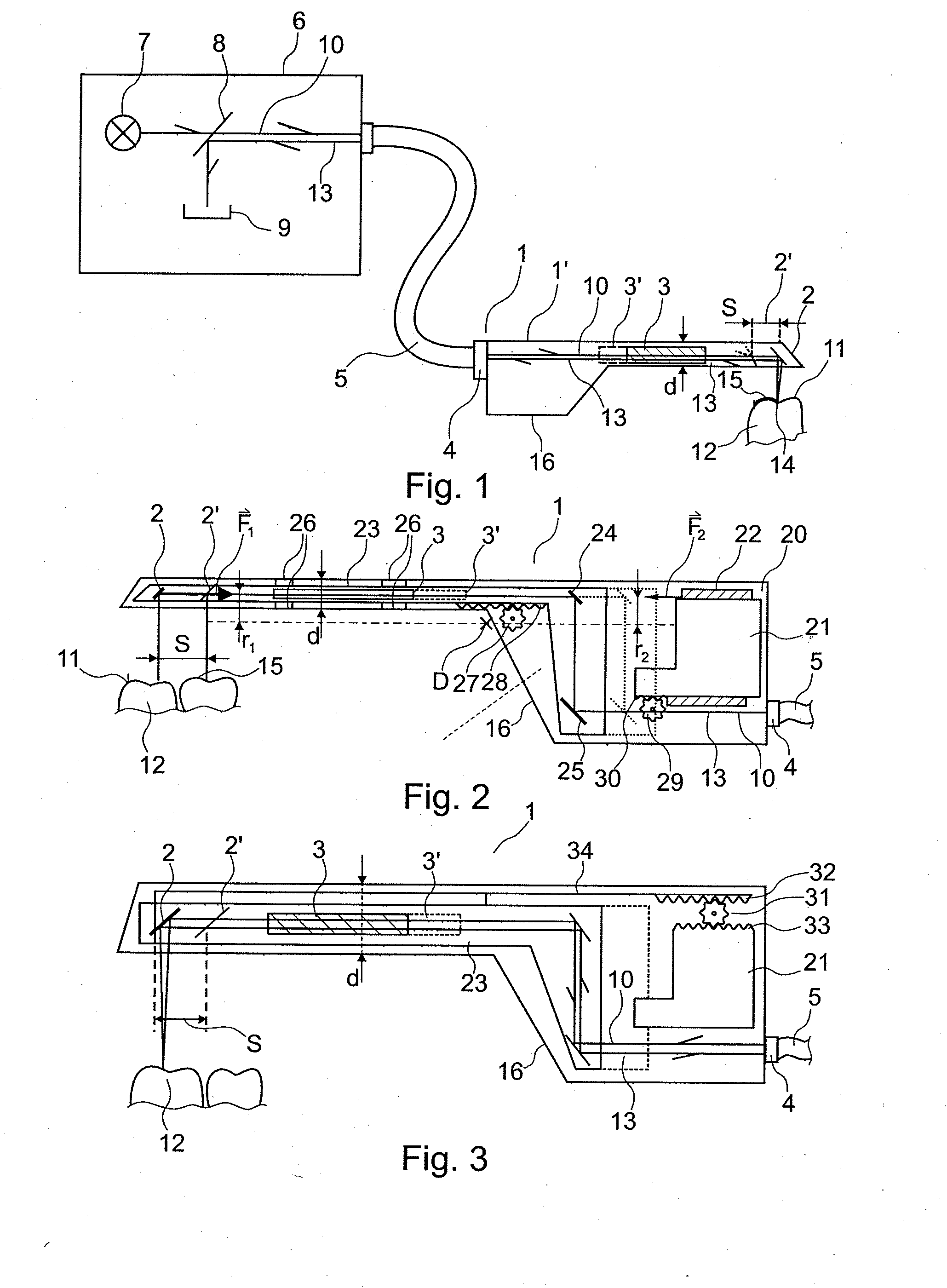
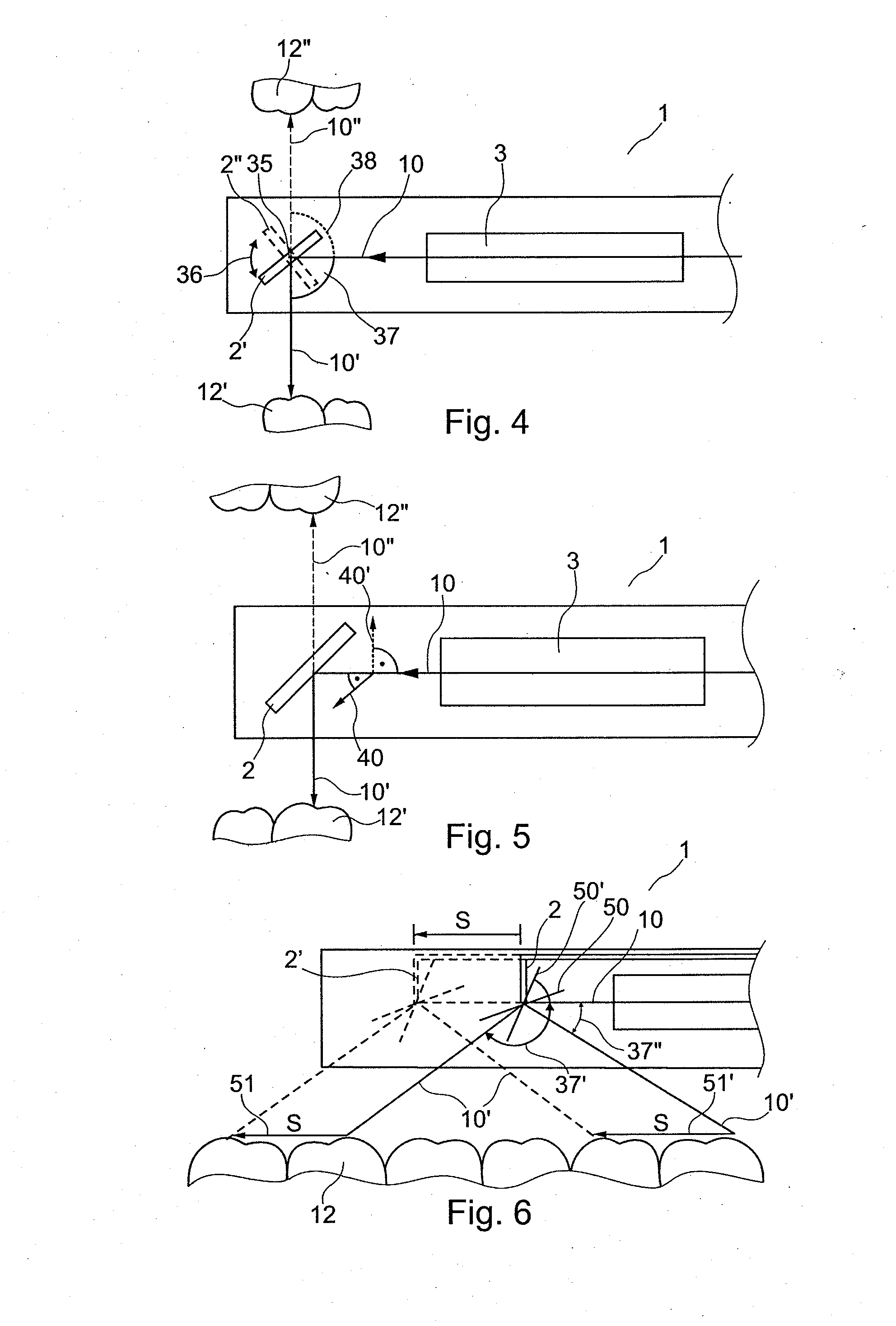
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for optical 3D measurement, comprising a first beam deflector for deflecting an illuminating beam onto a measurement object and for deflecting the observation beam which is radiated back by the measurement object, wherein the first beam deflector can move along a path distance S.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Load Distribution in Storage Area Networks
InactiveUS20080250178A1Maximum bandwidth is exceededImprove overall utilizationTransmissionInput/output processes for data processingStorage area networkLoad distribution
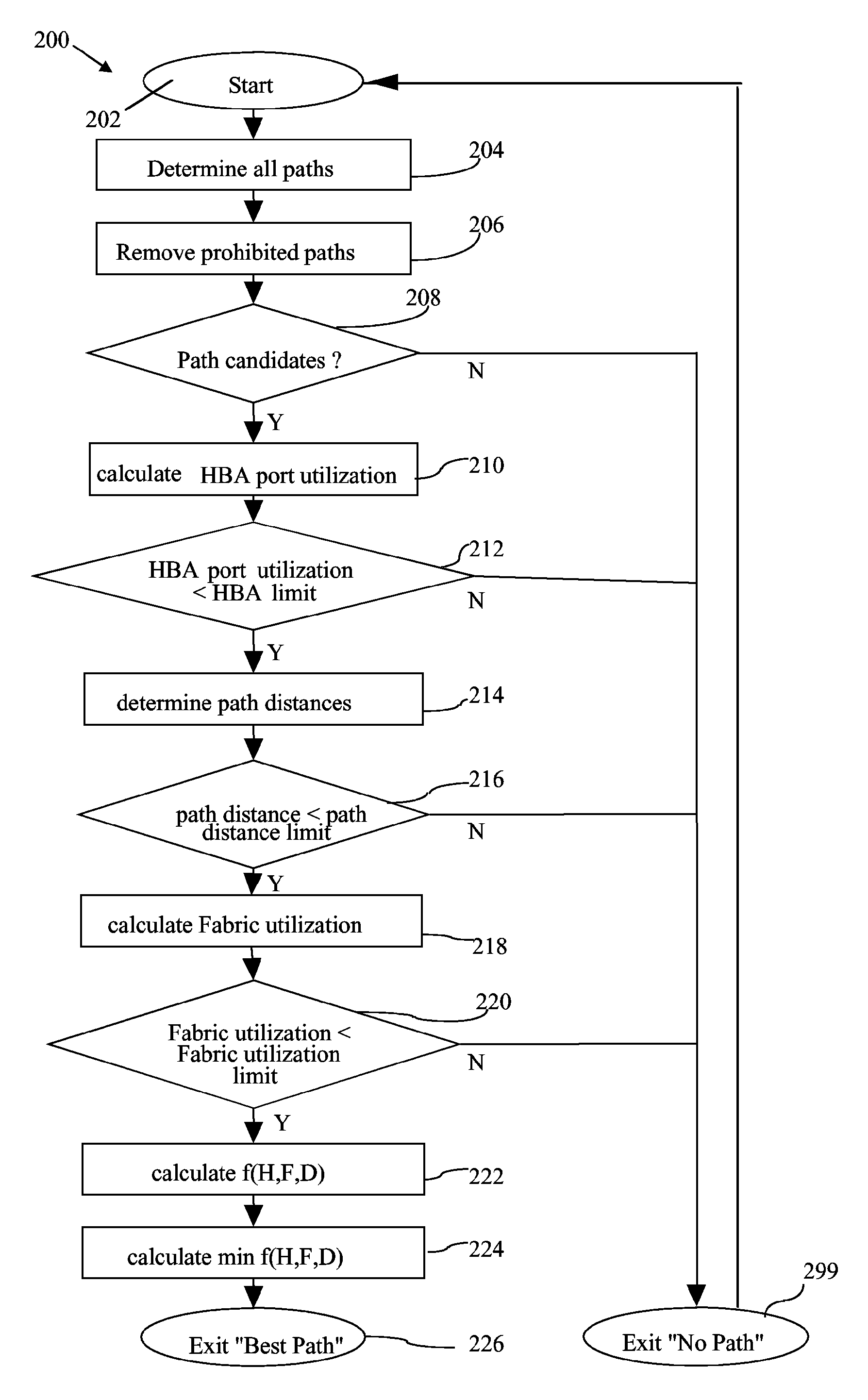
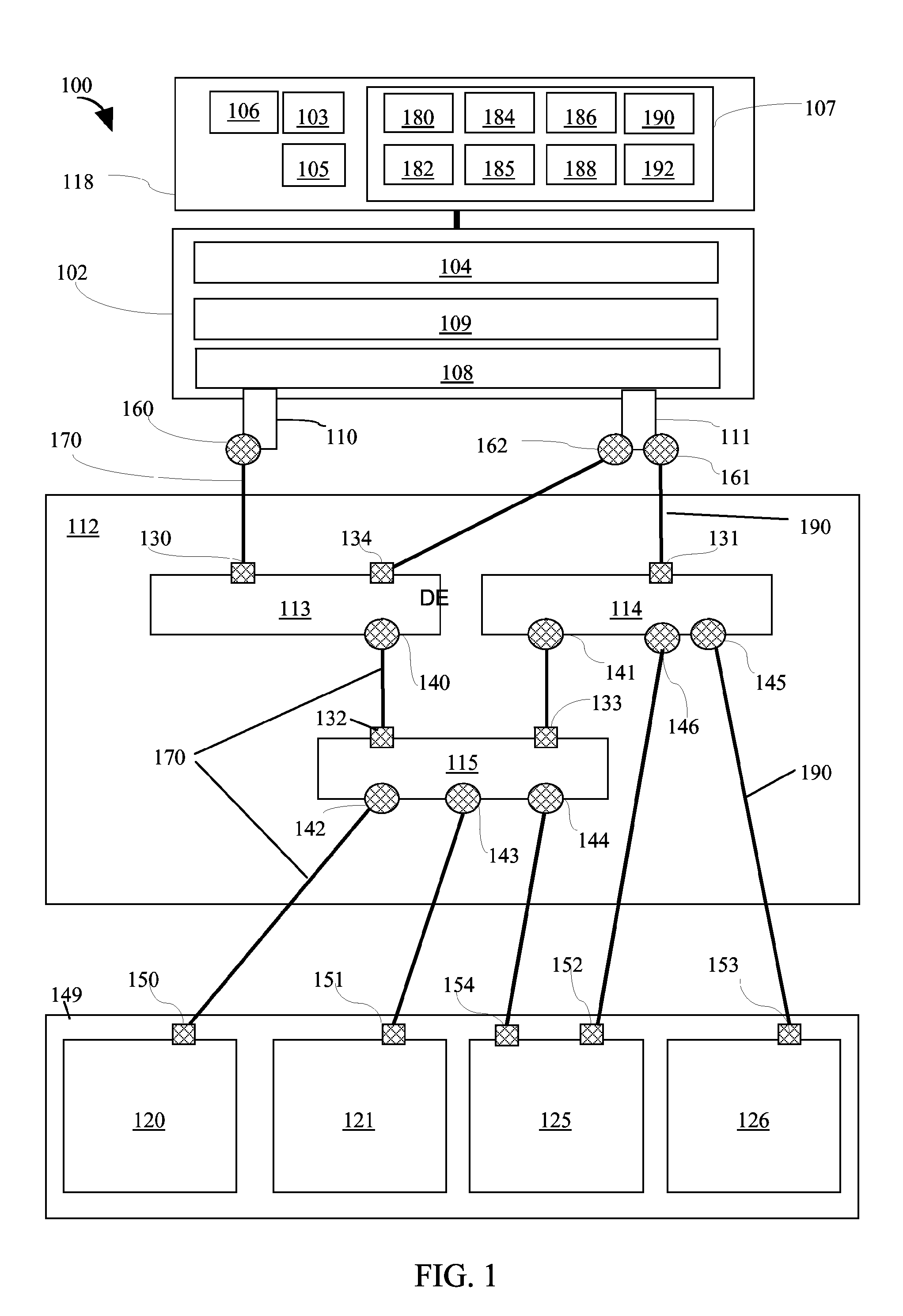
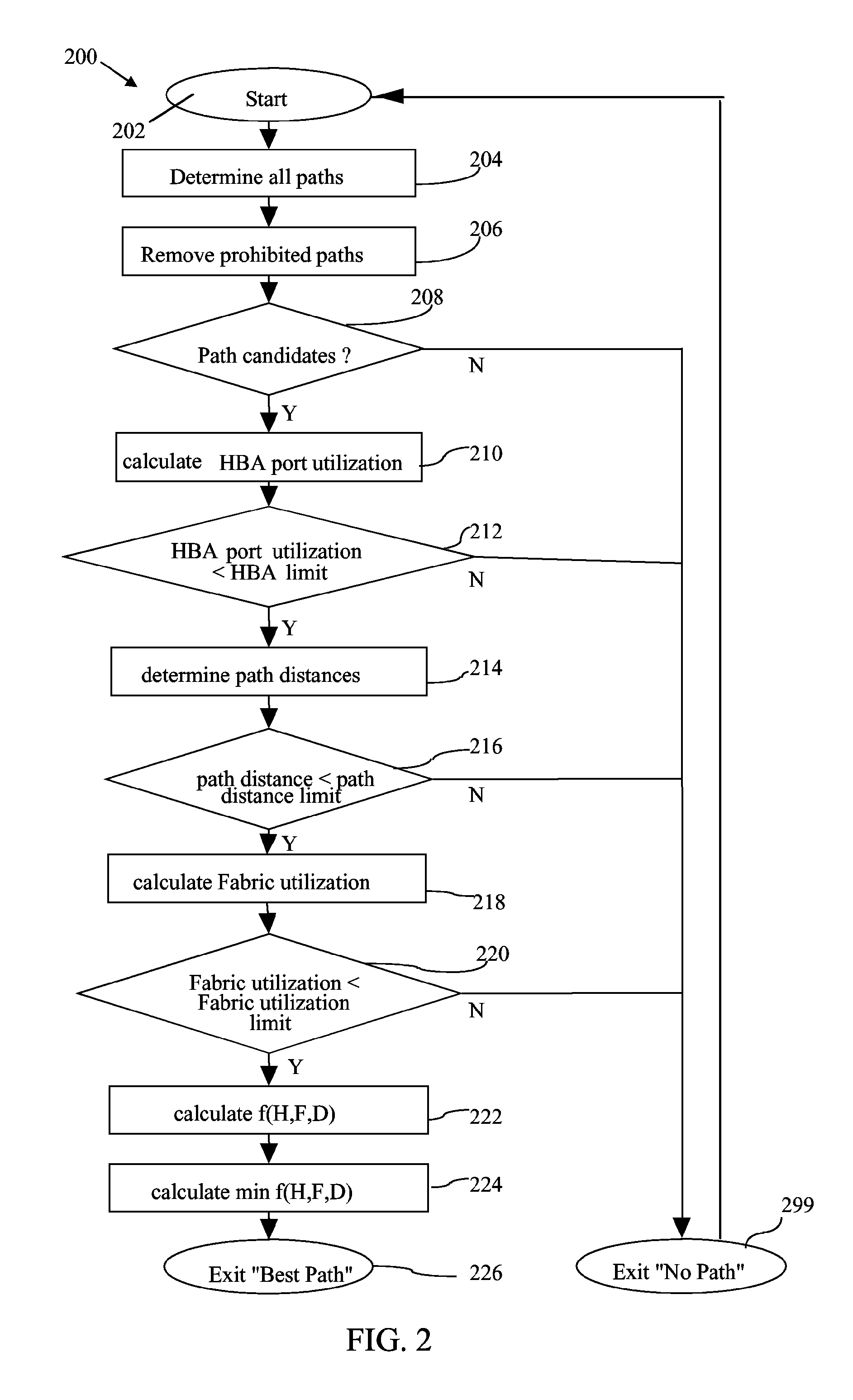
A load balancing method and system for identifying an input / output (I / O) network path from a set off I / O network paths is provided by the invention. The set off I / O network paths connect a host system via a network to a storage subsystem. The host system comprises at least one host bus adapter (HBA) and the storage subsystem comprises at least one I / O device and the network comprises at least one network device. Each of the HBA, the I / O device and the network device comprise at least one I / O port. For each I / O port of each HBA, an HBA port limit is determined. Additionally the set of I / O network paths which connect the I / O port of each of the HBA via the I / O ports of the network device to the I / O port of the I / O device is identified. Then a fabric utilization limit is determined for each I / O network path and a HBA port utilization is determined for each I / O port of the at least one HBA. All network paths are discarded for which the HBA port utilization is greater than the HBA port limit. For each of the remaining paths a network path distance is determined. All I / O network paths for which the network path distance is greater than the path distance limit are discarded. Then for each of the remaining paths a fabric utilization is determined. All I / O network paths for which the fabric utilization is greater than the fabric utilization limit are discarded and the I / O network path is determined from the remaining network paths.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for efficient vertical fluid delivery for cooling a heat producing device
InactiveUS20050211418A1Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterface layerEngineering
A heat exchanger and method of manufacturing thereof comprises an interface layer for cooling a heat source. The interface layer is coupled to the heat source and is configured to pass fluid therethrough. The heat exchanger further comprises a manifold layer that is coupled to the interface layer. The manifold layer includes at least one first port that is coupled to a first set of individualized holes which channel fluid through the first set. The manifold layer includes at least one second port coupled to a second set of individualized holes which channel fluid through the second set. The first set of holes and second set of holes are arranged to provide a minimized fluid path distance between the first and second ports to adequately cool the heat source. Preferably, each hole in the first set is positioned a closest optimal distance to an adjacent hole the second set.
Owner:COOLIGY INC
Uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under road network environment
InactiveCN103106280AExtended processing timeImprove the efficiency of solving crimesSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmRoad networks
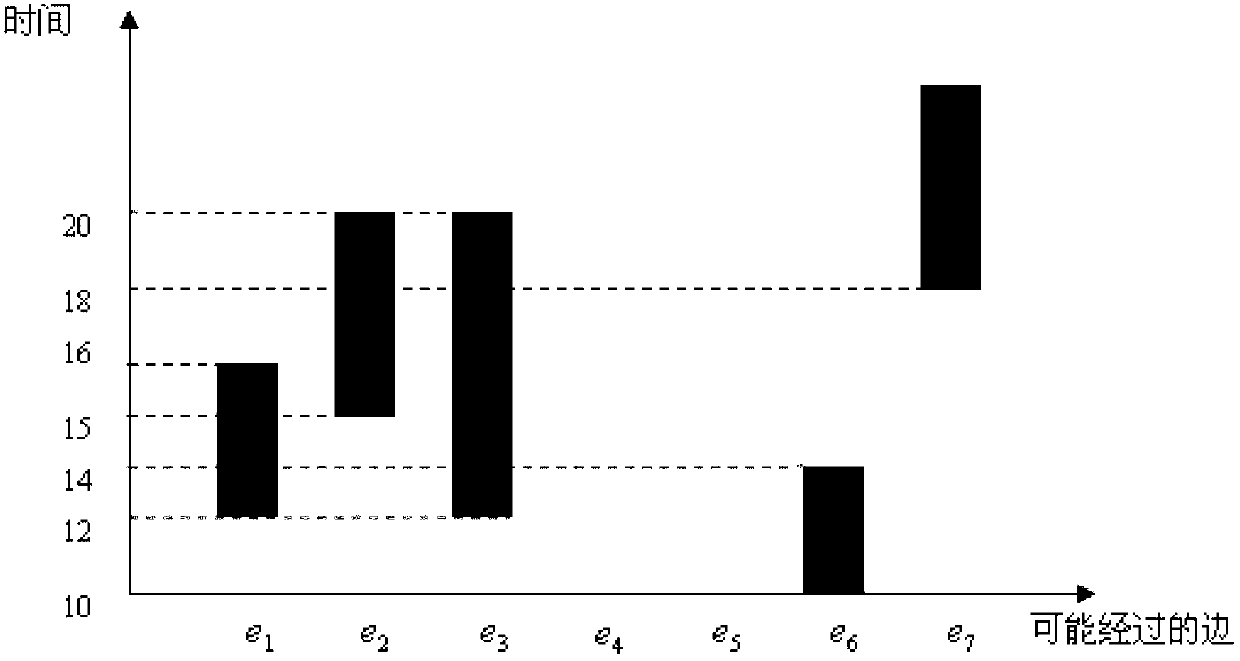
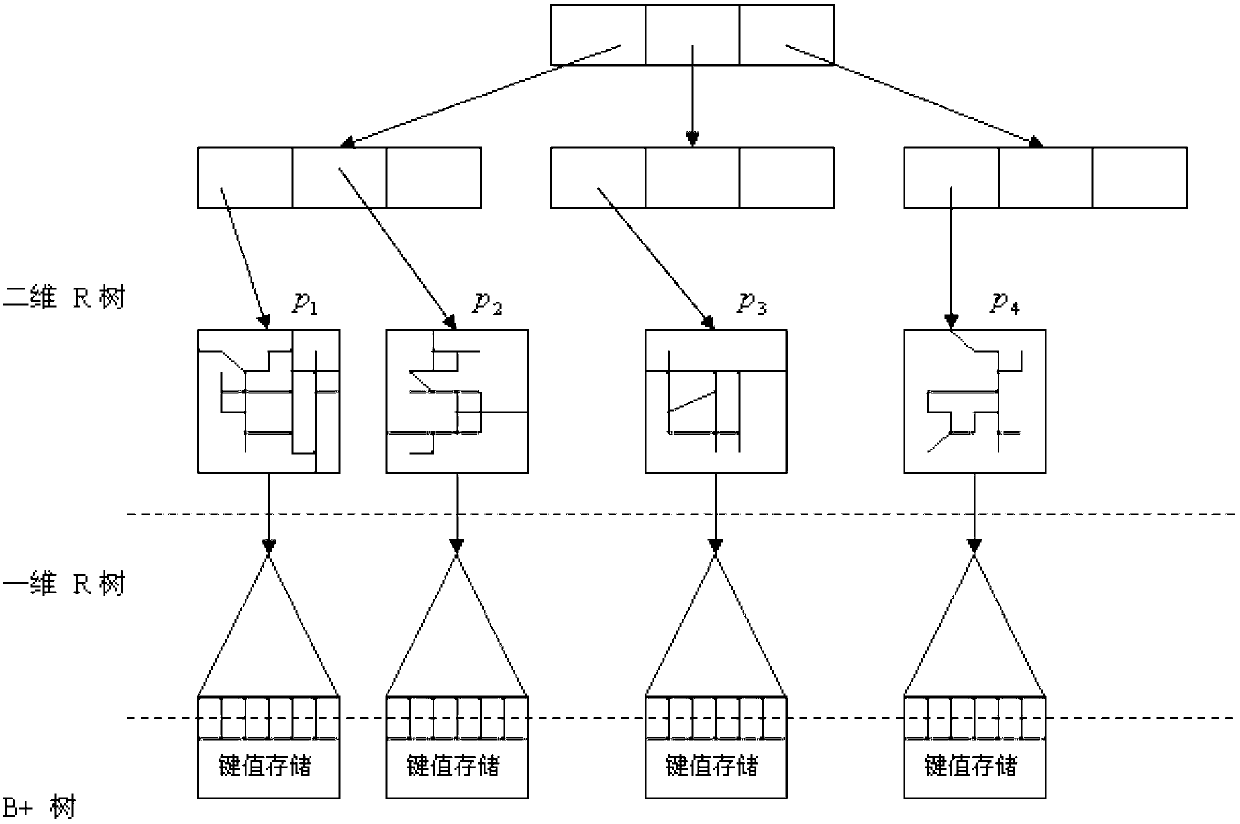
The invention discloses an uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under road network environment. The process includes that firstly, a road network is divided into divided areas with the number of K; a hash table is established according to sides and divided corresponding relations; boundary points of the divided areas are calculated, and a two-dimensional space R tree index is established; the shortest path distance among the boundary points of each dividing is calculated; a one-dimensional R tree time quantum index is established for each dividing, and a B+ tree for storing trajectory data for each one-dimensional R tree is established; then, the earliest arrival time and the latest leaving time of a certain trajectory and an uncertain trajectory are calculated, and a unit segment assemble and divided beginning and ending time are inserted into time interval components; and finally, according to the dividing of a query point, distance information of a divided boundary point and the query point is calculated, and therefore a query result is obtained. According to the uncertain space-time trajectory data range query method under the road network environment, a small amount of input / output (I / O) operations and online calculation are only needed to be performed for a part of dividing, the query results can be obtained, and the query results are high in accuracy degree and fast in response speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Self-positioning method of sensor network node based on distance size ordinal relation
The invention provides a sensor network node self-positioning method based on the relation of distance, size and sequence, belonging to the field of wireless sensor network self-positioning technique. The method of the invention is characterized in that the method sequentially comprises the steps as follows: node establishing, routine establishing and data transmission, network connecting information extracting, node relative coordinate positioning, absolute coordinate converting, compute result outputting and the like. When the relative coordinate of the node is being positioned, the relation of distance, size and sequence of the shortest path distance is used for obtaining the initial estimation topology of the node position; based on the initial estimation topology, a logarithm likelihood function of optimum node distance matrix and inverse solution Euclidean distance used as initial estimation topology; subsequently, an adjacent module comparison method is used to alternatively iterate the optimum distance matrix and the Euclidean distance; the method of the invention is not dependent on the detailed measurement value of the distance, only uses the relative sequence relation of the distances between nodes and has unique advantages.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for self-locating sensor network node within sparseness measuring set base on shortest path
InactiveCN101350635APosition fixationData switching by path configurationMultidimensional scalingNetwork connection
The present invention relates to a shortest path-based automatic positioning method of sensor network nodes on the sparse measurement set, and belongs to the technical field of automatic positioning of the wireless sensor network. The positioning method is characterized by orderly comprising node distribution, route establishment, data transmission, network connection information extraction, relative coordinate positioning of the node, absolute coordinate transformation, outward transmission of results by a computer, and so on; wherein, when the relative coordinates of the node are positioned relative to the adjacent node, a detection method of radio frequency is used for measuring the distance between the nodes; for the non-adjacent node, the distance of Freud shortest-path is used for estimating the distance between the nodes, thus the shortest-path distance matrix which comprises the adjacent node and the non-adjacent node is got; then a method of multi-dimensional scaling analysis can be adopted to acquire the initial value of topological estimation of the node position which is relatively positioned; the similar probability distribution of the unknown distance is calculated; the likelihood function of the complete-distance matrix is then used as an expected objective function for optimization, so as to eliminate the randomness, thus the relative positioning results can be acquired.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for optical 3D measurement
ActiveUS20090279103A1Advantageously facilitatedReduce the overall heightImpression capsDental toolsLight beam3d measurement
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for optical 3 D measurement, comprising a first beam deflector for deflecting an illuminating beam onto a measurement object and for deflecting the observation beam which is radiated back by the measurement object, wherein the first beam deflector can move along a path distance S.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
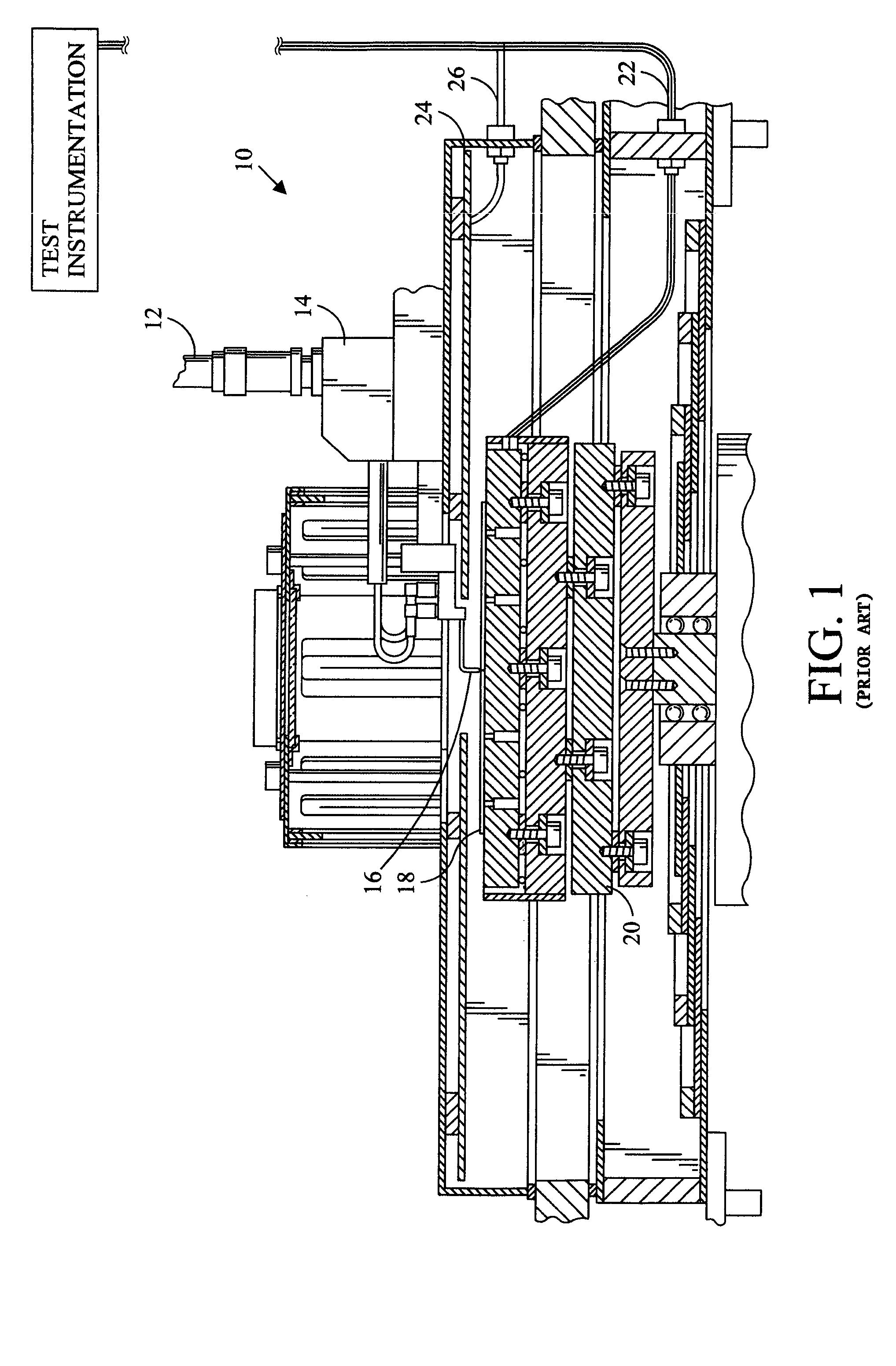
Probe station with low inductance path
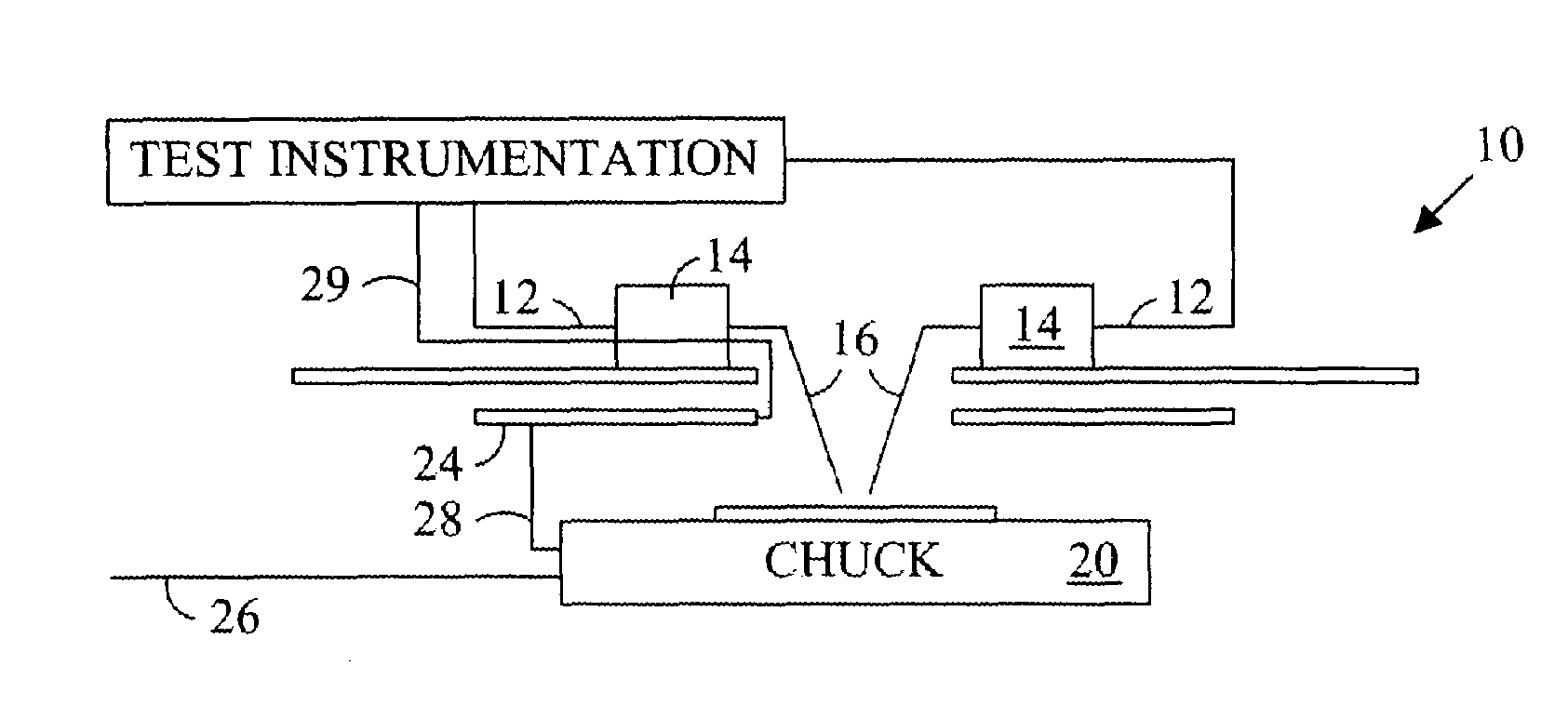
InactiveUS7250779B2Electrical measurement instrument detailsContactless circuit testingTest measurementElectrical devices
A probe assembly suitable for making test measurements using test signals having high currents. The disclosed probe assembly provides for a test signal exhibiting relatively low inductance when compared to existing probe assemblies by preferably reducing the electrical path distance between the test instrumentation and the electrical device being tested.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Reproduction system for video and audio signals
InactiveUS20050025318A1Promote reproductionLow costMicrophonesTransducers for sound channels pluralityLoudspeakerAudio frequency
A reproduction system includes speaker array composed of plural speakers having a diaphragm for reproducing an audio signal and reflection unit disposed in a chamber for reflecting a radiated sound from the speaker array. The plural speakers of the speaker array are positioned so that the vibration direction of each diaphragm may be directed towards the reflection unit, and the reflection path distance from each diaphragm to a listening point, which defines a position of the viewer / listener, via the reflection surface of the reflection unit may be equal.
Owner:ONKYO KK
Indoor map navigation route guidance algorithm
InactiveCN104215237AEasy to navigateHigh utility valueNavigational calculation instrumentsIndoor positioning systemPath distance
The invention discloses an indoor map navigation route guidance algorithm which is convenient for people to realize an optimal route and measurable time in an indoor building body. The indoor map navigation route guidance algorithm adopts a road network node pathfinding method for implementation of pathfinding between any two points of indoor map single floor, cross floors, and many buildings, and according to the indoor map navigation route guidance algorithm, a found path is shortest, at the same time, the correct direction and less turning of the path can be ensured, and the relationship between the path and locating points are corresponding. Through the calculation of the distance of each section of the path and the total route, the time required from beginning to end can be estimated. The indoor map pathfinding route is clear and beautiful in display, a user can realize convenient navigation, and the indoor navigation utility value of the user is very high.
Owner:北京掌尚无限信息技术有限公司
Two-stage clock tree synthesis with buffer distribution balancing
InactiveUS7051310B2Improve uniformityUniform signalElectrical apparatusCAD circuit designParallel computingClock tree synthesis
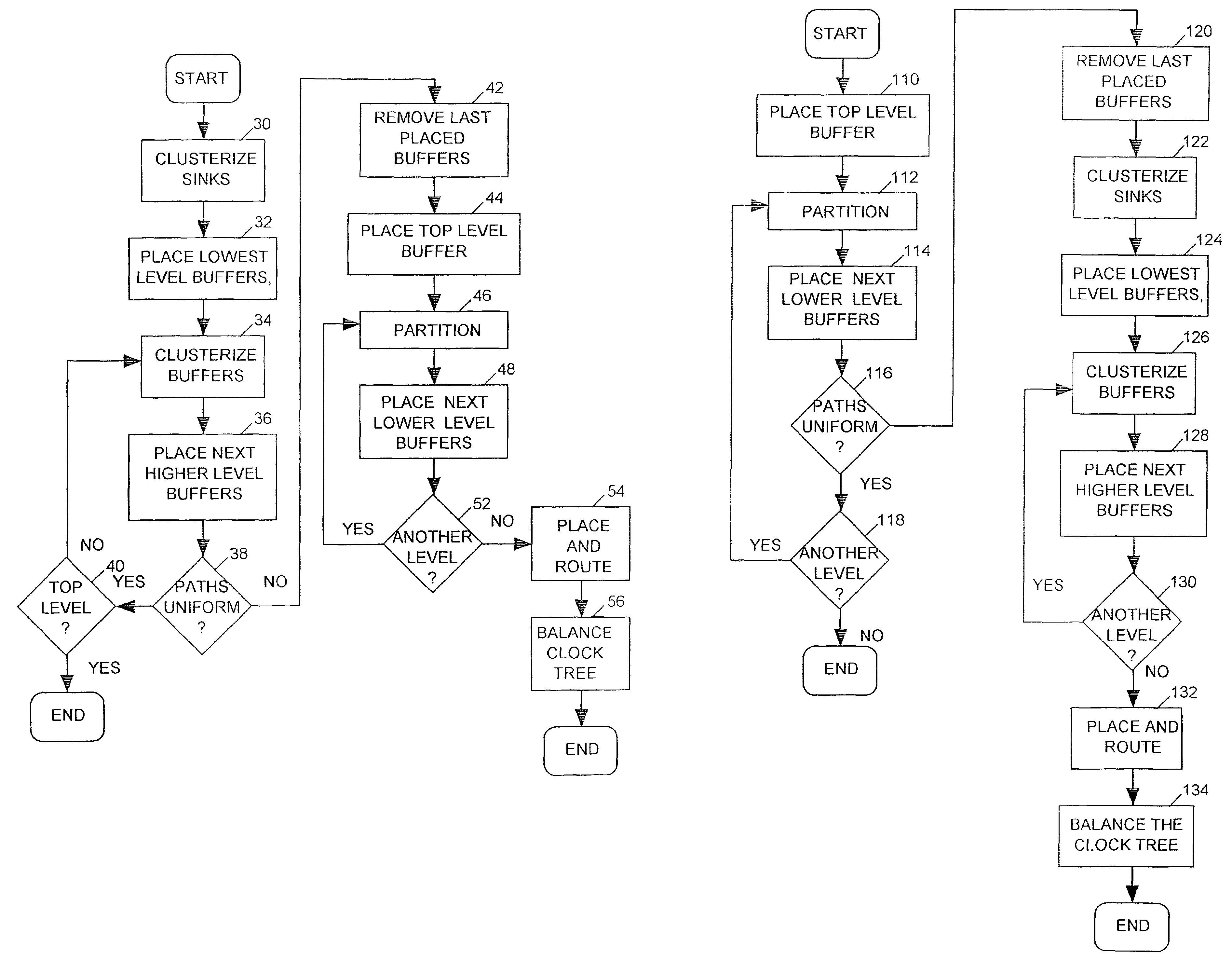
A clock tree synthesis (CTS) tool determines how to position a hierarchy of buffers for fanning out a clock signal to clocked devices (“sinks”) within an integrated circuit (IC). The tool first clusterizes the sinks and places a lowest level fan-out buffer near each cluster. The tool then iteratively places progressively higher level buffers by clusterizing a last-placed buffer level and then placing a next higher level buffer near the centroid of each lower level buffer cluster, until the tool has placed buffers at a mid-level for which variation in path distances between that level and a next higher buffer level exceeds a predetermined limit. The CTS tool then places a top level buffer at the centroid of the mid-level buffers, divides the layout into partitions, each containing a similar number of mid-level buffers, and then places a second-highest level buffer in each partition. The CTS iteratively places each next lower buffer level by dividing each partition into progressively smaller partitions and placing progressively lower level buffers in each smaller partition until it places buffers at a level having sufficient number of buffers to drive the mid-level buffers.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
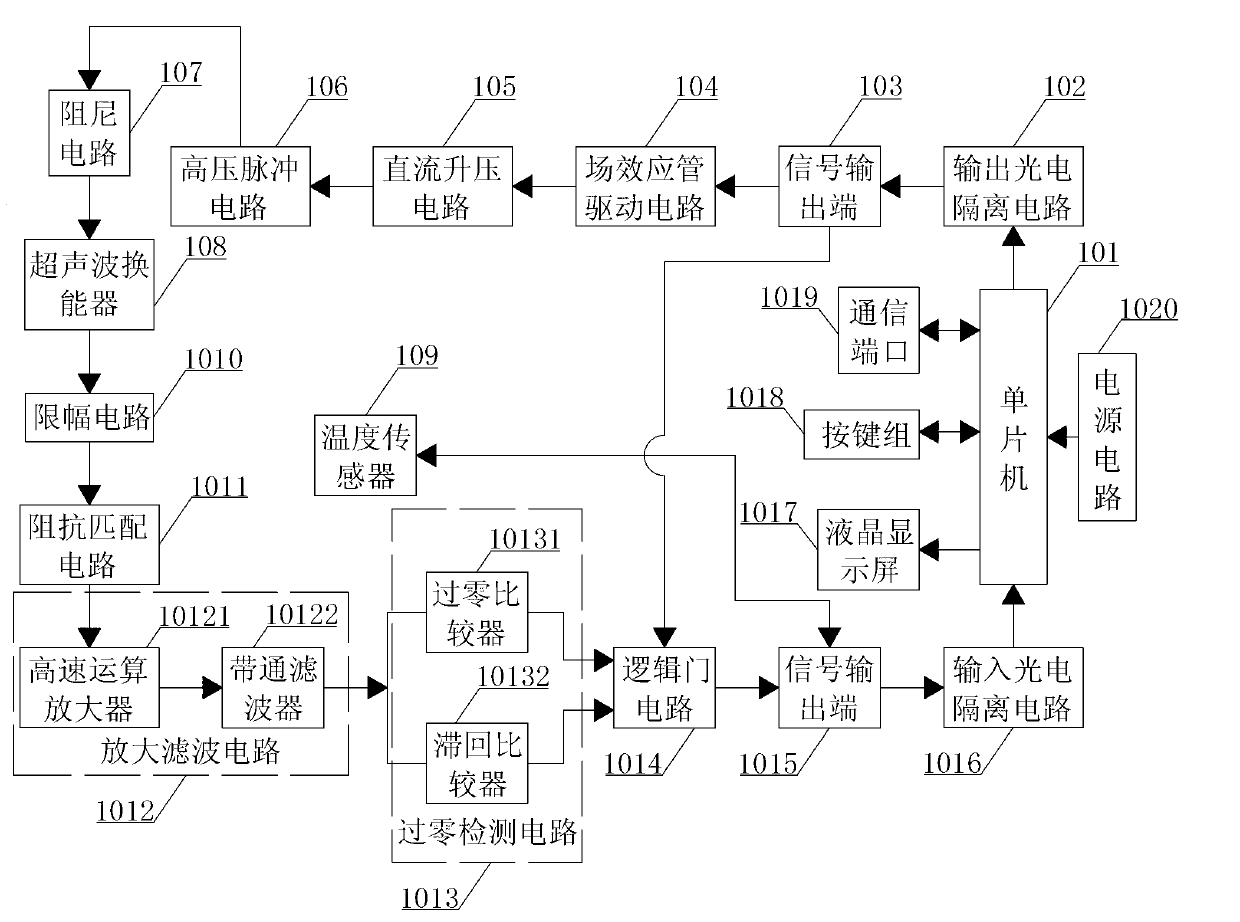
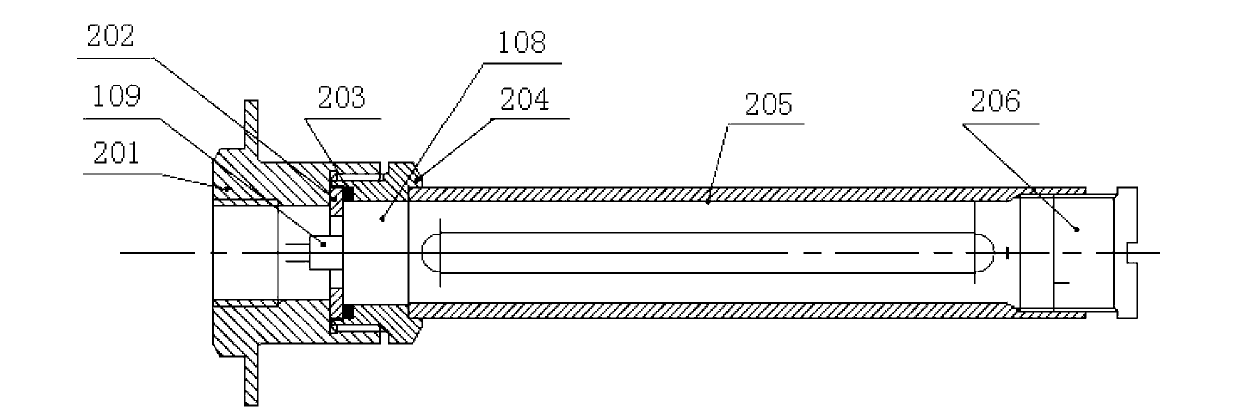
Device and method for detecting interior initial stress of steel structural member based on ultrasonic method
ActiveCN104142195AWon't breakSimple structureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesForce measurementPath distanceMaterials science
The invention provides a device and method for detecting the interior initial stress of a steel structural member based on the ultrasonic method. According to the method for detecting the interior initial stress of the steel structural member based on the ultrasonic method, the interior initial stress sigma of the steel structural member is solved by firstly calibrating the acoustic elasticity coefficient B of the fixed sonic path distance of a replica of the steel structural member in service and then detecting the change of the acoustic time t of ultrasonic waves in the steel structural member in service. An existing method for nondestructive detection of the stress of a steel structural member mainly has the disadvantages that only the change of the stress can be detected, and the intensity of the stress in the current state can not be detected; only the stress of the positions located on the surface of the steel structural member and the stress of the positions at most dozens of microns below the surface of the steel structural member can be detected, and the intensity of the stress of positions with depths of several millimeters can not be detected. The method for detecting the interior initial stress of the steel structural member based on the ultrasonic method can overcome the defects of the existing method and can be used for nondestructive detection of the interior initial stress of various steel structural members. Detections results are verified, the precision is high, the error requirement of practical engineering can be met, and the structural member can not be damaged during detection.
Owner:李祚华
System and methods for IP and VoIP device location determination
InactiveUS7961717B2Easy to movePrecise positioningPosition fixationData switching by path configurationGeolocationTime signal
A method and system for precise position determination of general Internet Protocol (IP) network-connected devices. A method enables use of remote intelligence located at strategic network points to distribute relevant assistance data to IP devices with embedded receivers. Assistance is tailored to provide physical timing, frequency and real time signal status data using general broad band communication protocols. Relevant assistance data enables several complementary forms of signal processing gain critical to acquire and measure weakened or distorted in-building Global Navigation Satellite Services (GNSS) signals and to ultimately extract corresponding pseudo-range time components. A method to assemble sets of GNSS measurements that are observed over long periods of time while using standard satellite navigation methods, and once compiled, convert using standard methods each pseudo-range into usable path distances used to calculate a precise geographic position to a known degree of accuracy.
Owner:IPOSI
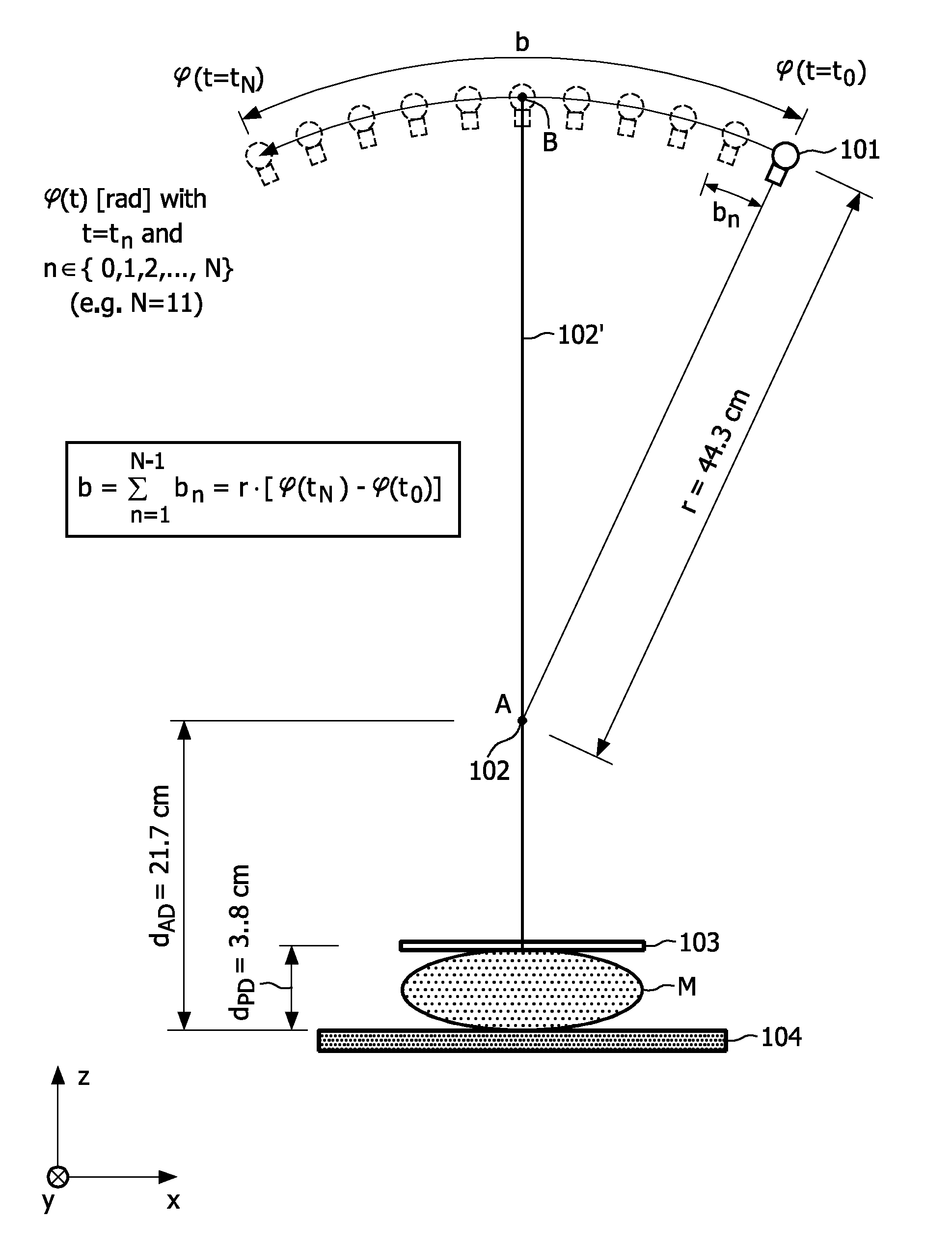
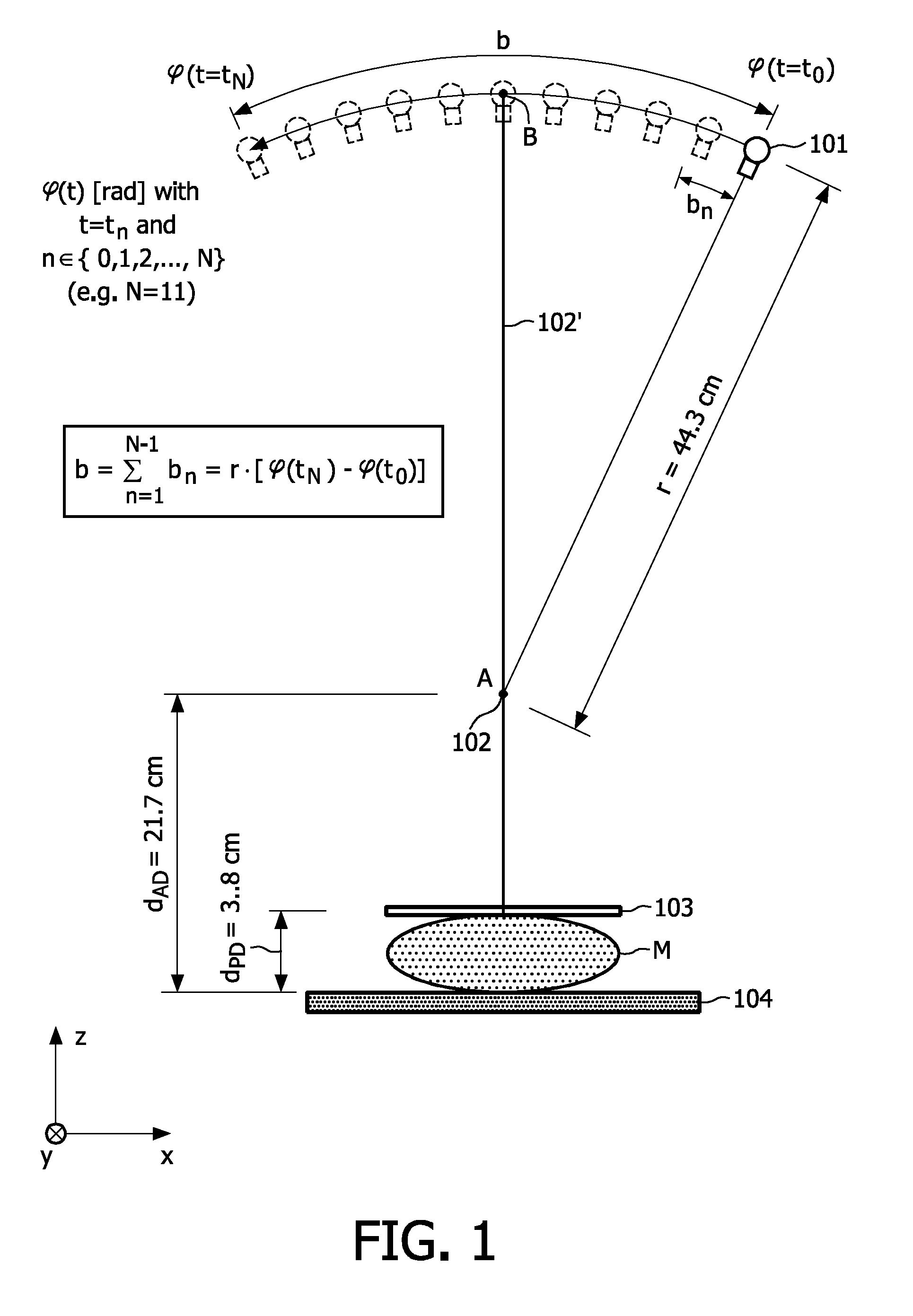
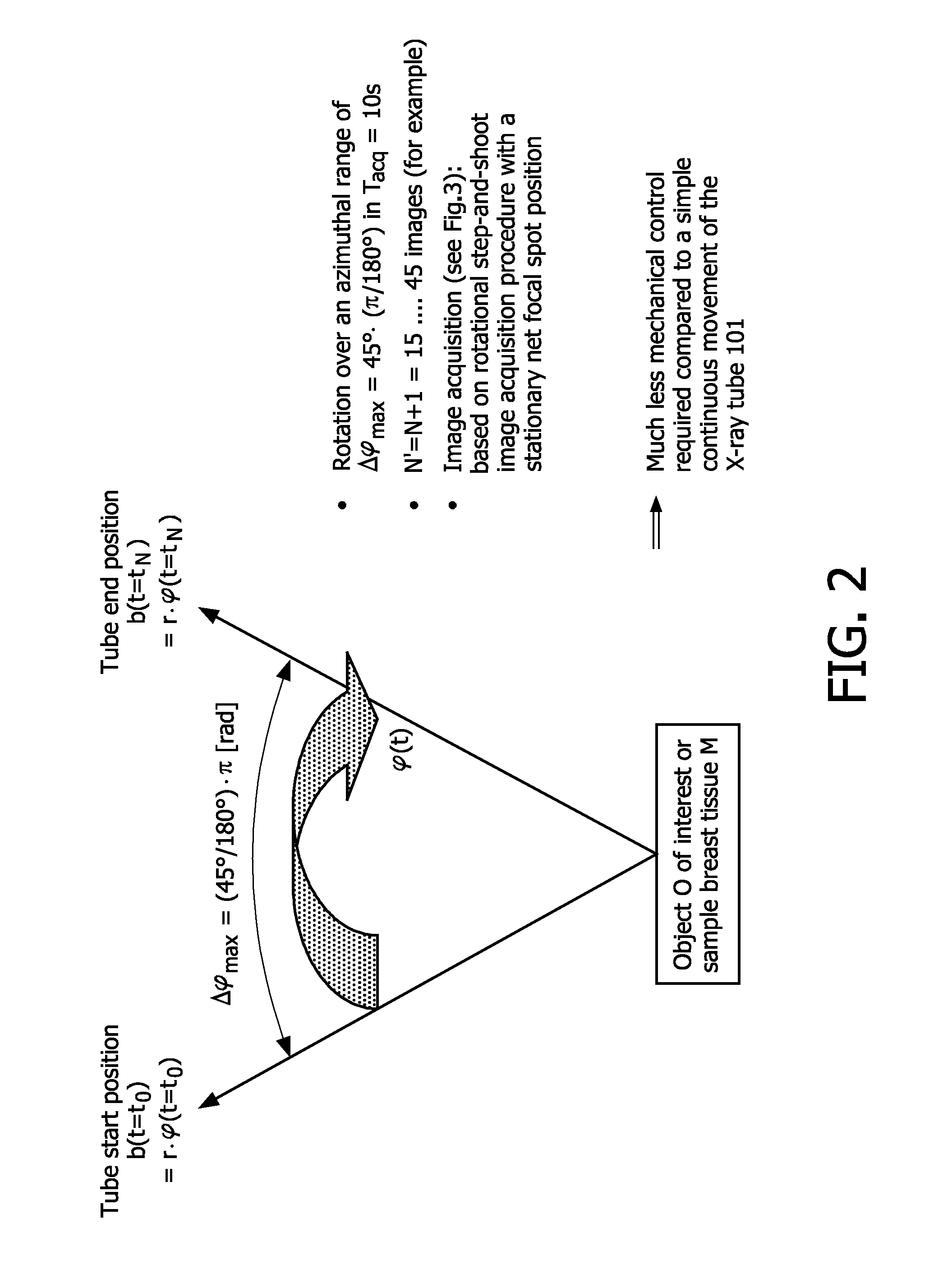
Fast tomosynthesis scanner apparatus and ct-based method based on rotational step-and-shoot image acquistion without focal spot motion during continuous tube movement for use in cone-beam volume ct mammography imaging
ActiveUS20110026667A1Improve image qualityQuality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisX-ray
The present invention generally refers to computed tomography (CT) based imaging systems and, more particularly, to a fast 3D tomosynthesis scanner apparatus and CT-based method without focal spot motion during continuous tube movement around an object of interest (O) or tissue region (M) to be examined (herein also referred to as “object”), which may advantageously be used in cone-beam volume CT mammography imaging so as to avoid motion artifacts and blurring effects. According to the present invention, said 3D tomosynthesis scanner apparatus is adapted to perform a rotational step-and-shoot image acquisition procedure for acquiring a set of 2D projection images during a continuous rotational movement of an X-ray tube (101) in an azi-muthal direction (+φ) along an arc segment of a circular trajectory when rotating around said object (O, M) and subjecting these 2D projection images to a 3D reconstruction procedure. According to the present invention, it is foreseen that, during the image acquisition time for each 2D projection image, the focal spot on the X-ray tube's anode is moved in an opposite direction (−φ)from a start position (bs) to an end position (be) with respect to the rotary X-ray tube's housing such that the azimuthal path distance (Ab) covered by the X-ray tube (101) due to the continuous rotational tube movement during this time is compensated. The 3D tomosynthesis scanner further comprises a mechanism for switching the focal spot on the X-ray tube's anode back to its start position (bs) with respect to said tube housing before starting a new image acquisition process for acquiring image data of a next 2D projection image. The superposition of the focal spot movement with respect to the tube housing and the continuous rotational movement of the X-ray tube (101) along said arc segment results in a stationary focal spot position relative to the object (O, M) and a stationary X-ray detector (104) diametrically oppositely arranged to the X-ray tube (101) with respect to said object (O) for each of the individual 2D projection images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and optical arrangement for beam guiding of a light beam with beam delay
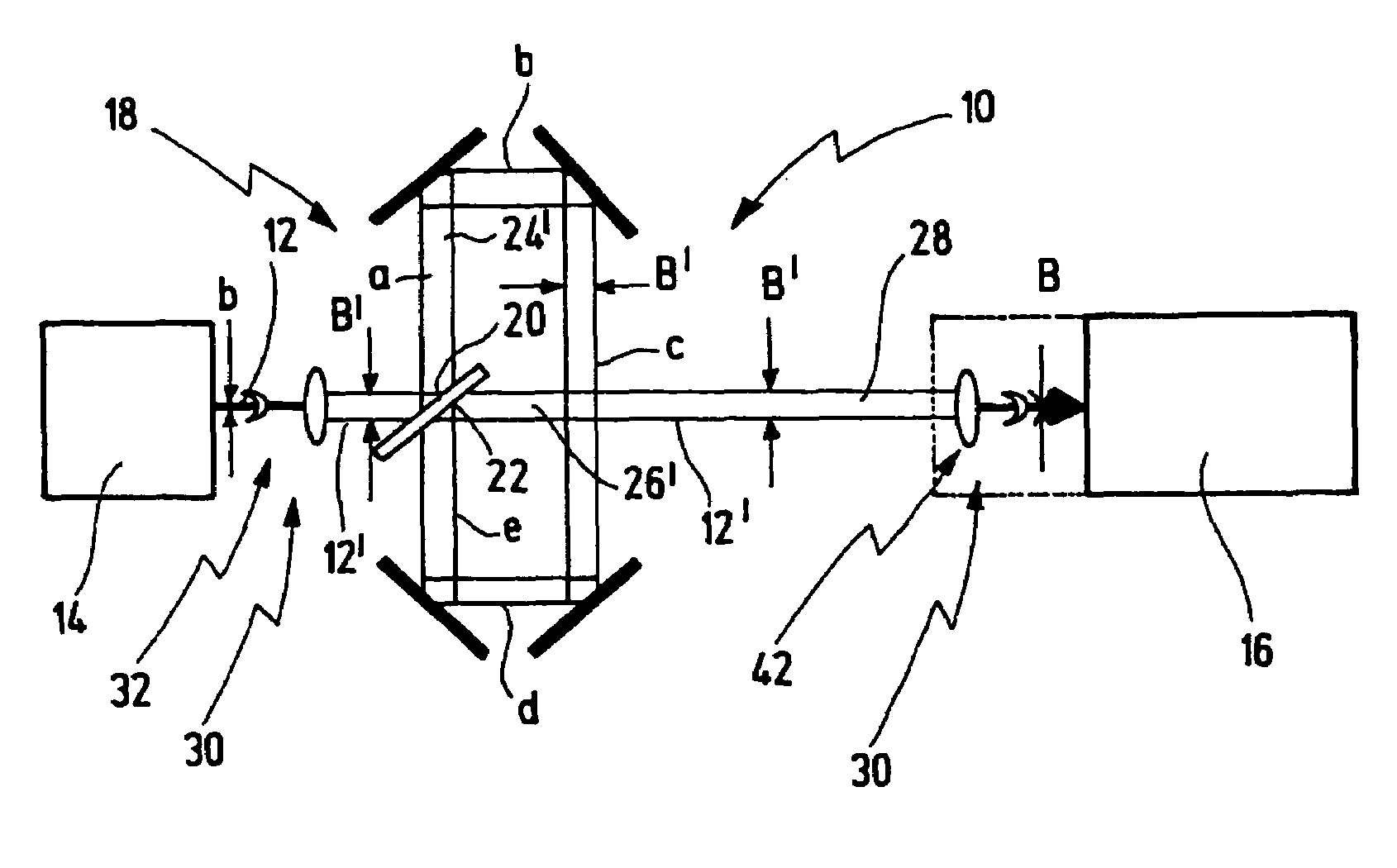
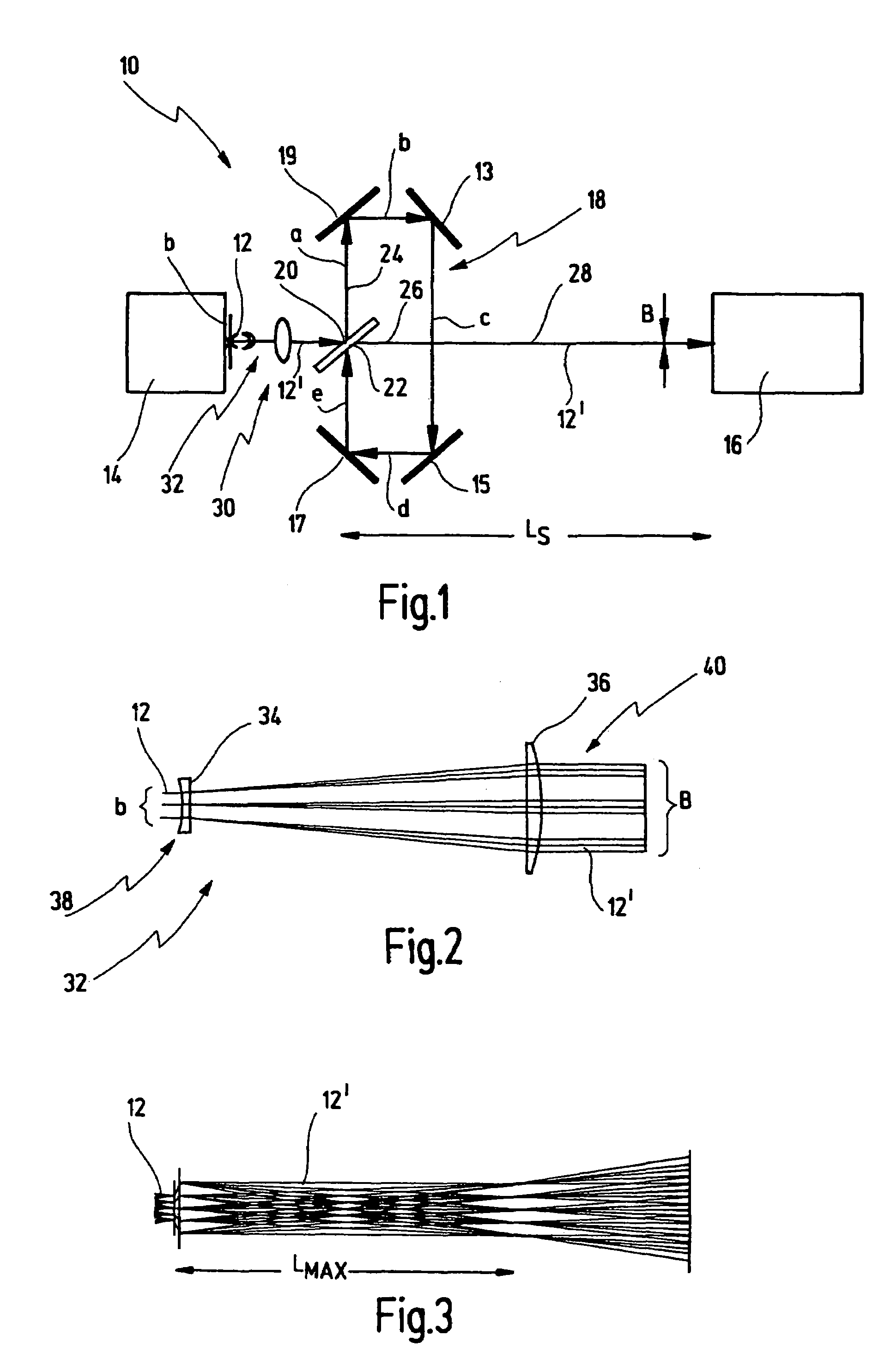
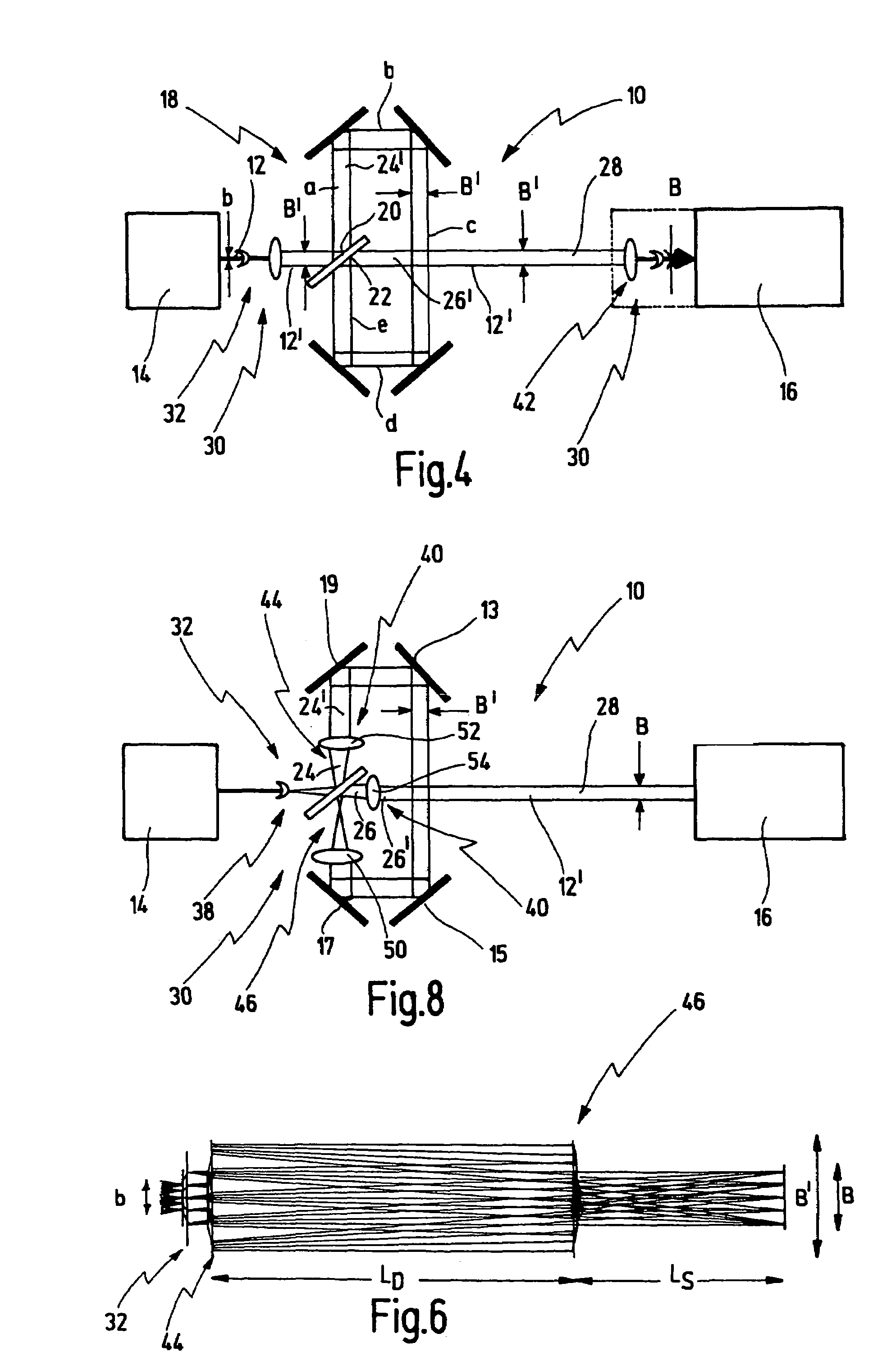
ActiveUS7321468B2Large transmission distanceLong distanceMirrorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamPath distance
A method for beam guiding of a light beam generated by a light source to a target location along a path distance LS, comprises splitting the light beam on the path distance LS at least once into a first partial beam and a second partial beam, guiding the first partial beam additionally at least once along a delay line, the first partial beam thereby covering an additional path distance LD, guiding the second partial beam only along the path distance LS, combining the first and second partial beams after the first partial beam having passed through the delay line and guiding the combined beam to the target location, wherein the light beam is guided along the path distance LS and LD in such a way that the light beam generated by the light source has a predetermined beam width B at the target location, expanding the light beam between the light source and the target location at least once to a beam width B′>B and comprising the light beam again at least once in such a way that the light beam has the predetermined beam width B at the target location.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
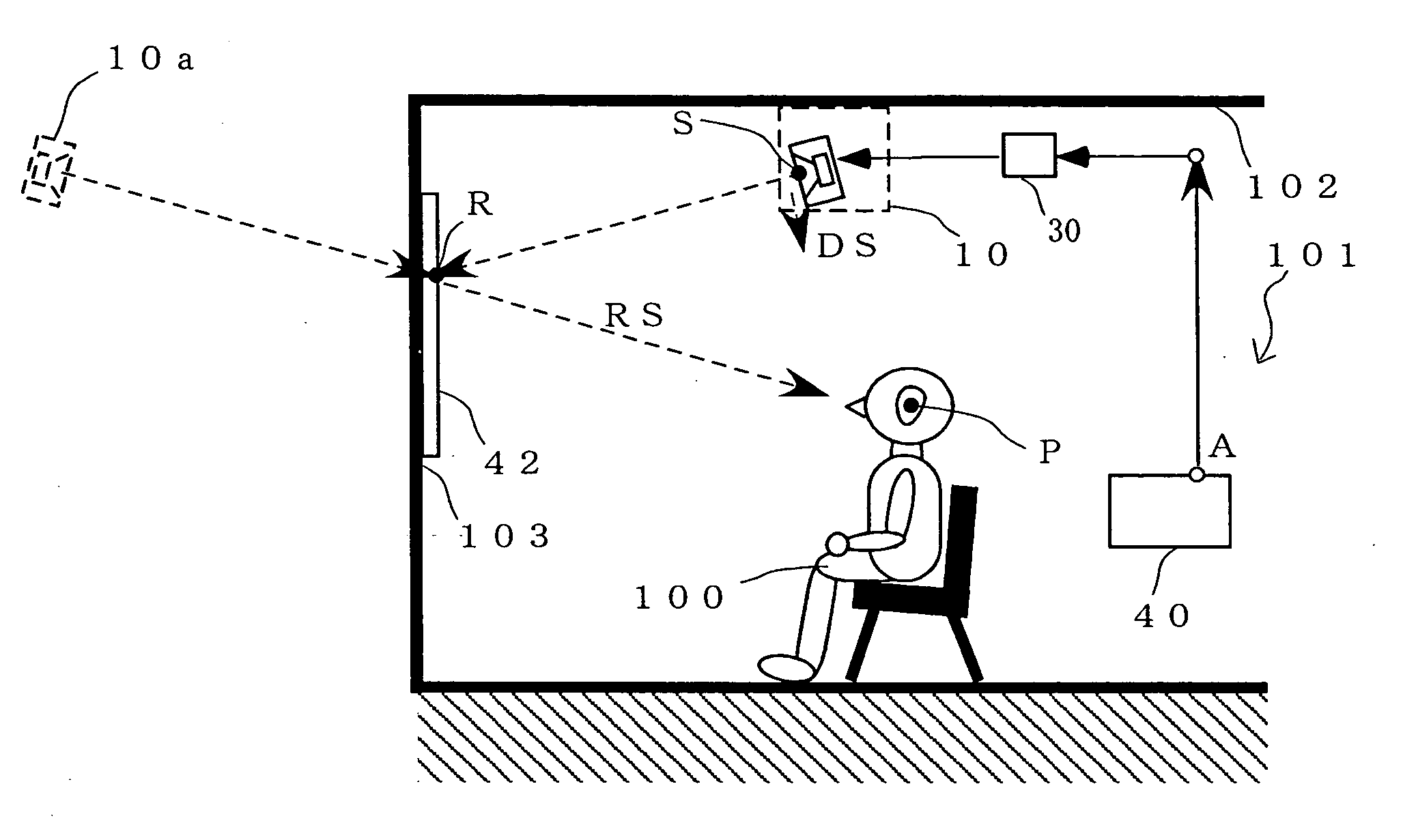
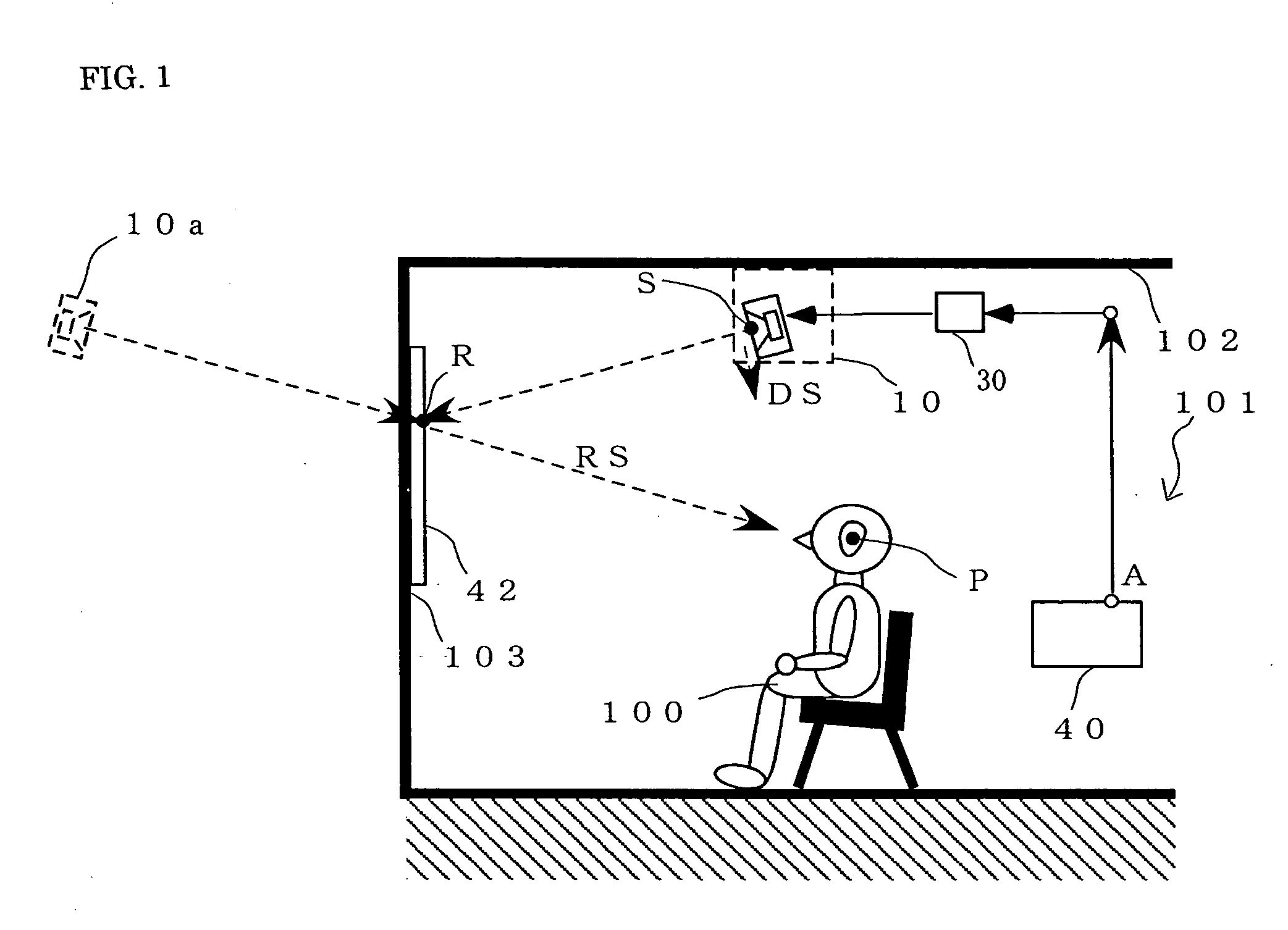
Optimizing audio processing functions by dynamically compensating for variable distances between speaker(s) and microphone(s) in a mobile device
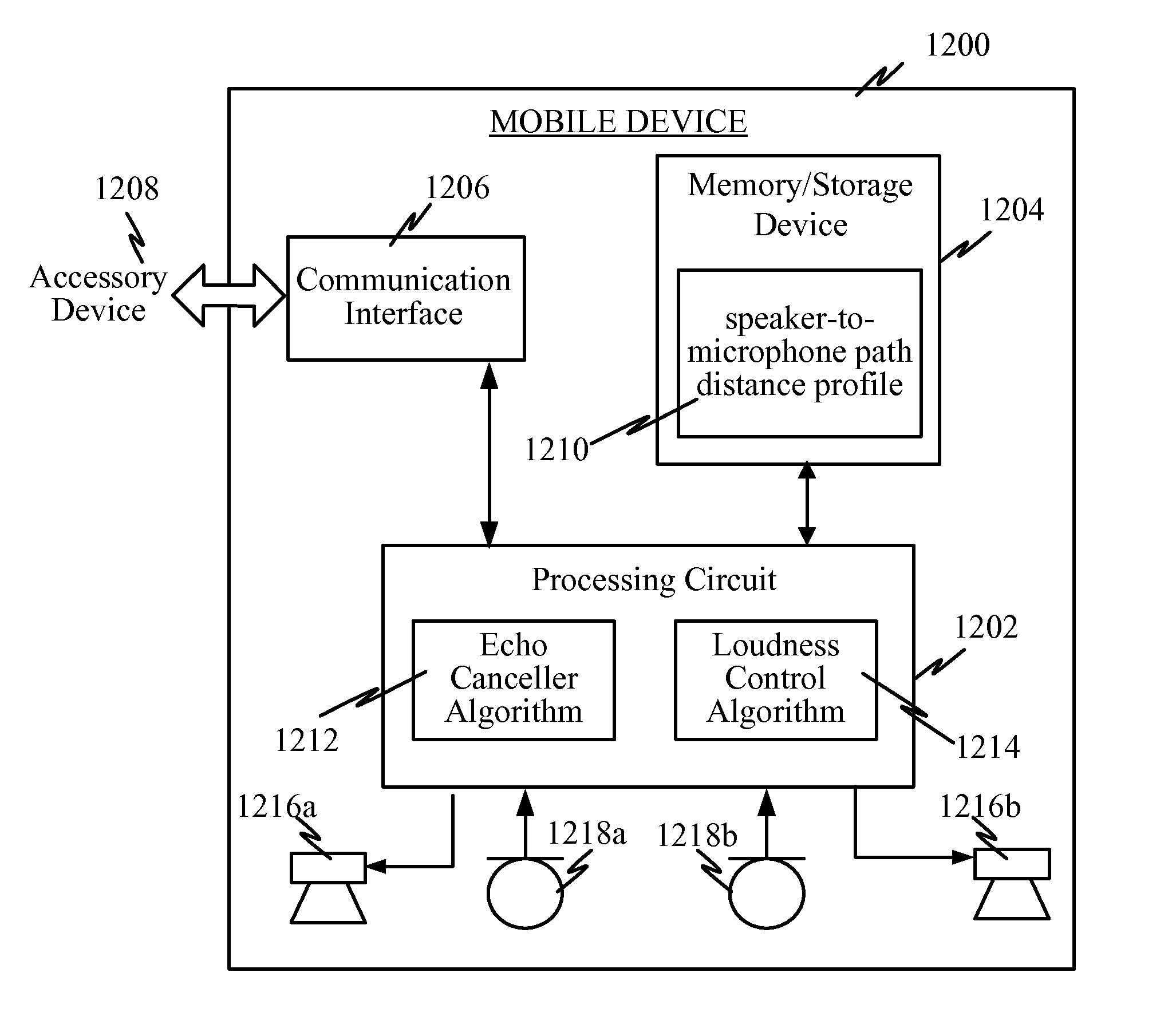
ActiveUS20130156209A1Easy to optimizeReduce and limit speaker volumeInterconnection arrangementsTransducer acoustic reaction preventionVoice communicationSound quality
Mobile communication devices, having multiple speakers and / or microphones to perform a number of audio functions, for use with mobile devices, are provided. The microphones may be housed within the communication device housing. To compensate for the unwanted signal feedback between the speakers and microphones, acoustic echo cancellation may be implemented to determine the proper distance and relative location between the speakers and microphones. Acoustic echo cancellation removes the echo from voice communications to improve the quality of the sound. The removal of the unwanted signals captured by the microphones may be accomplished by characterizing the audio signal paths from the speakers to the microphones (speaker-to-microphone path distance profile), including the distance and relative location between the speakers and microphones. The optimal distance and relative location between the speakers and microphones is provided to the user to optimize performance.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
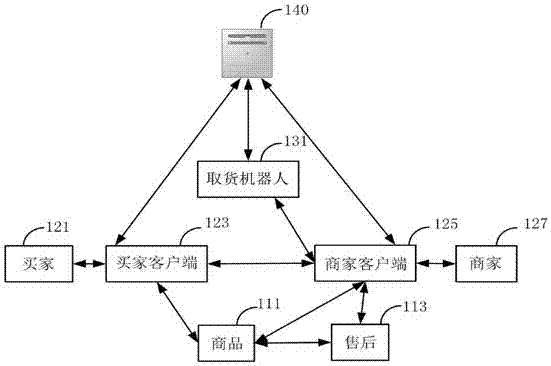
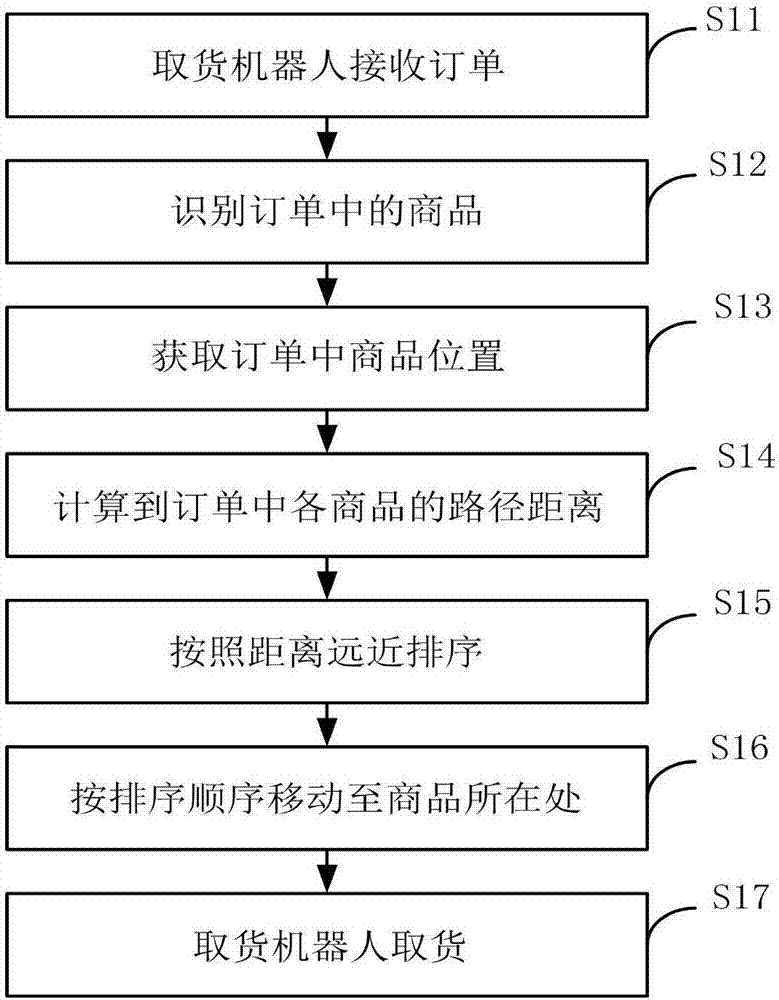
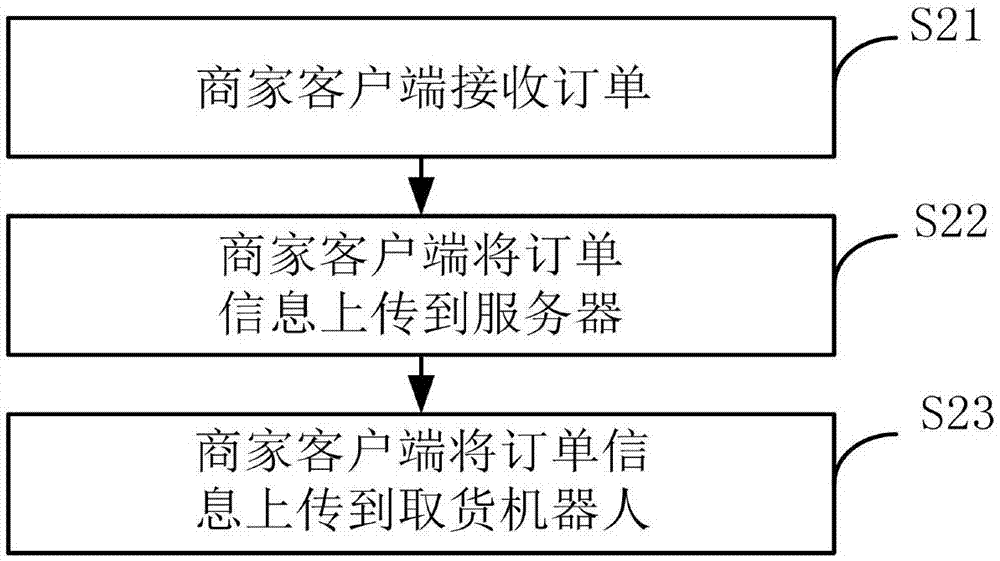
Online shopping mall robot automatic goods taking method and system
PendingCN107578303AImprove satisfactionImprove reputationBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPosition/course control in two dimensionsComputer moduleComputer science
The invention discloses an online shopping mall robot automatic goods taking method. The method includes receiving an order by a goods taking robot; identifying the goods in the order; acquiring the goods position in the order; calculating the path distance of each goods in the order; ordering according to the distance; moving to the goods positions according to the sequence; and taking the goodsby the goods taking robot. The invention further discloses an online shopping mall robot automatic goods taking system. The system includes a server comprising a first information receiving module, afirst information sending module, a first communication module, and a database module. The database module is used for calculating the driving distance, analyzing the driving path, planning the driving path and storing the data. According to the invention, the satisfaction degree of the customer is improved, and the manpower cost error rate is reduced for the merchants, and the reputation of the merchants is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SAIYI TECH DEV
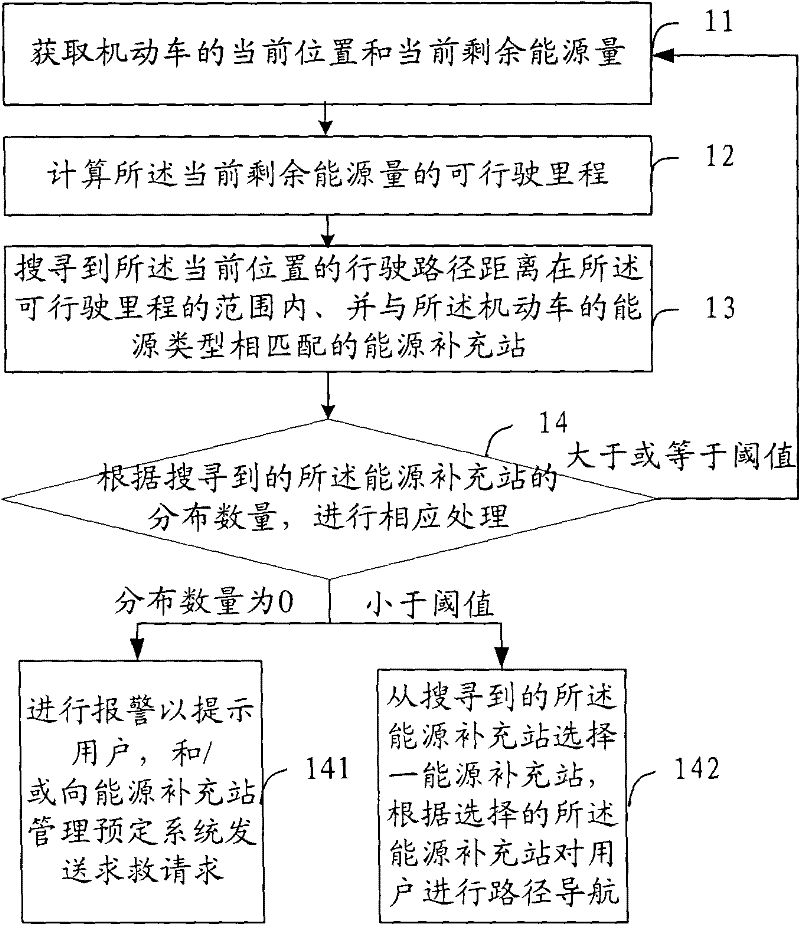
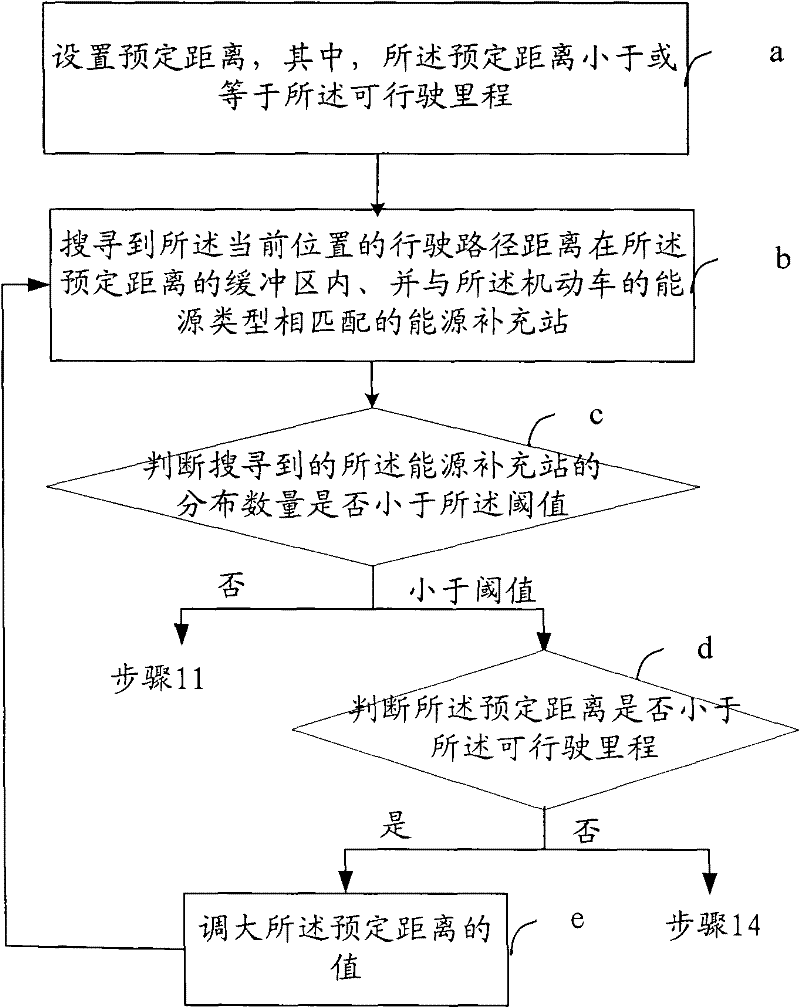
Method, device and system for managing energy of motor vehicle
The invention provides a method, a device and a system for managing energy of a motor vehicle, which relate to the field of vehicle energy management and aim at solving the technical problem that in the prior art, when distance between a starting place and a destination of the motor vehicle is relatively far, the vehicle can break down due to the fact that the energy is exhausted and cannot be replenished. The method includes: obtaining the current location and the current remaining energy quantity of the motor vehicle; calculating mileage the motor vehicle can travel with the current remaining energy quantity; searching for energy replenishing stations which are located within the mileage range the motor vehicle can travel from the current position and matched with the energy type of the motor vehicle; performing corresponding processing according to distribution number of the energy replenishing stations; and specifically selecting one energy replenishing station from the searched energy replenishing stations and performing path guidance on the selected energy replenishing station when the distribution number of the stations is smaller than a threshold value. The method, the device and the system for managing energy of the motor vehicle can improve user experience of motor vehicle driving of users.
Owner:NAVINFO
Printer
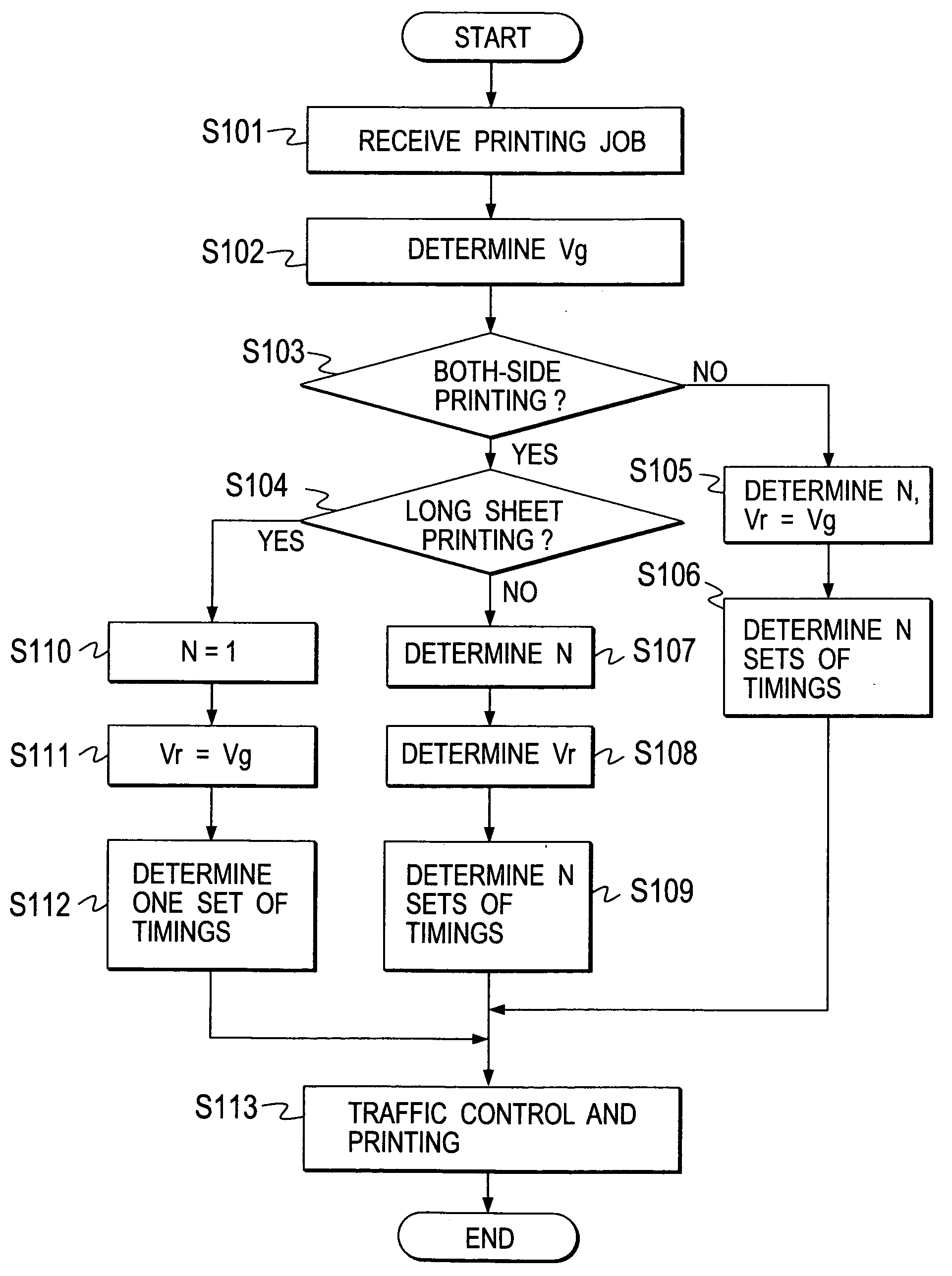
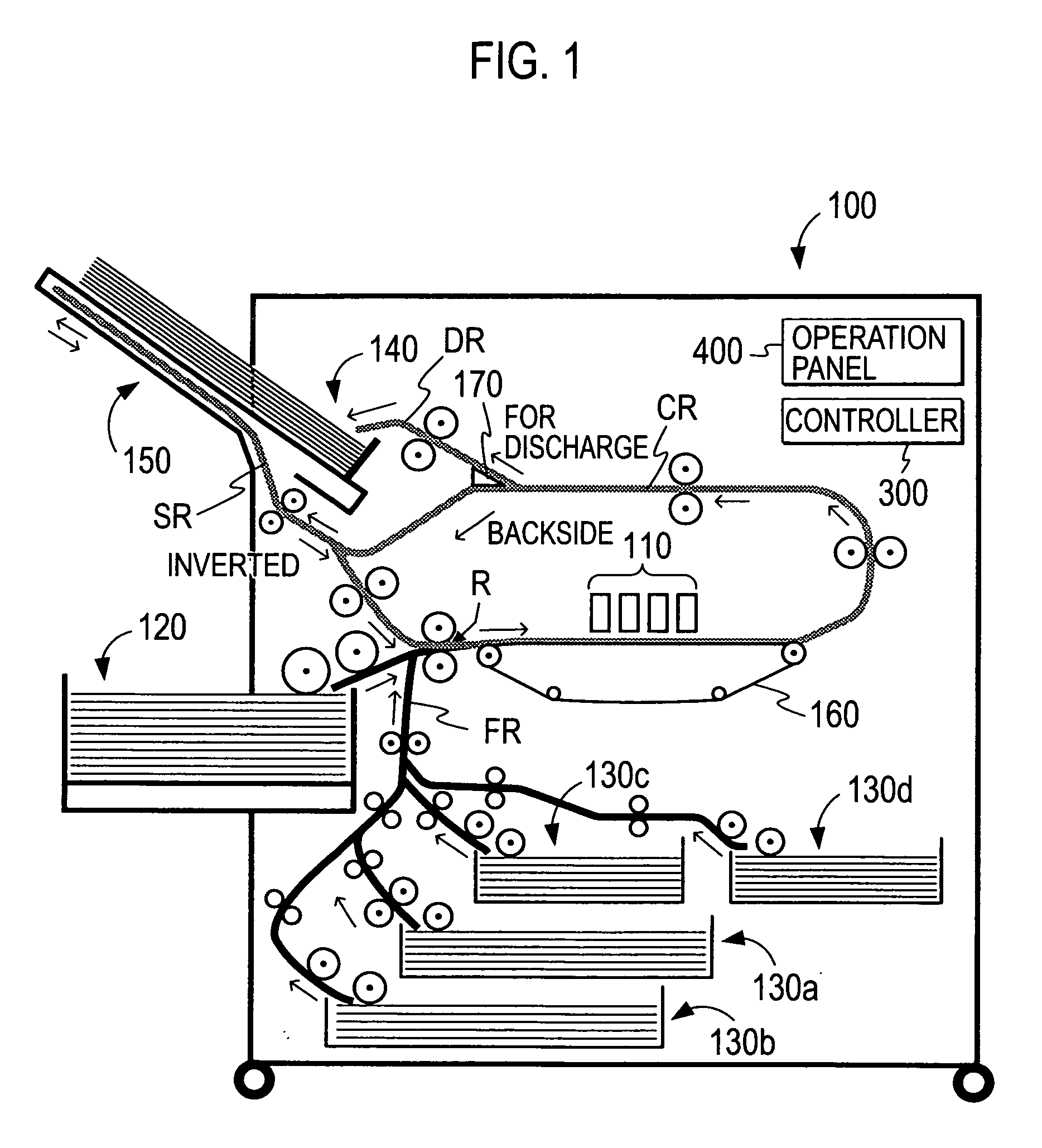
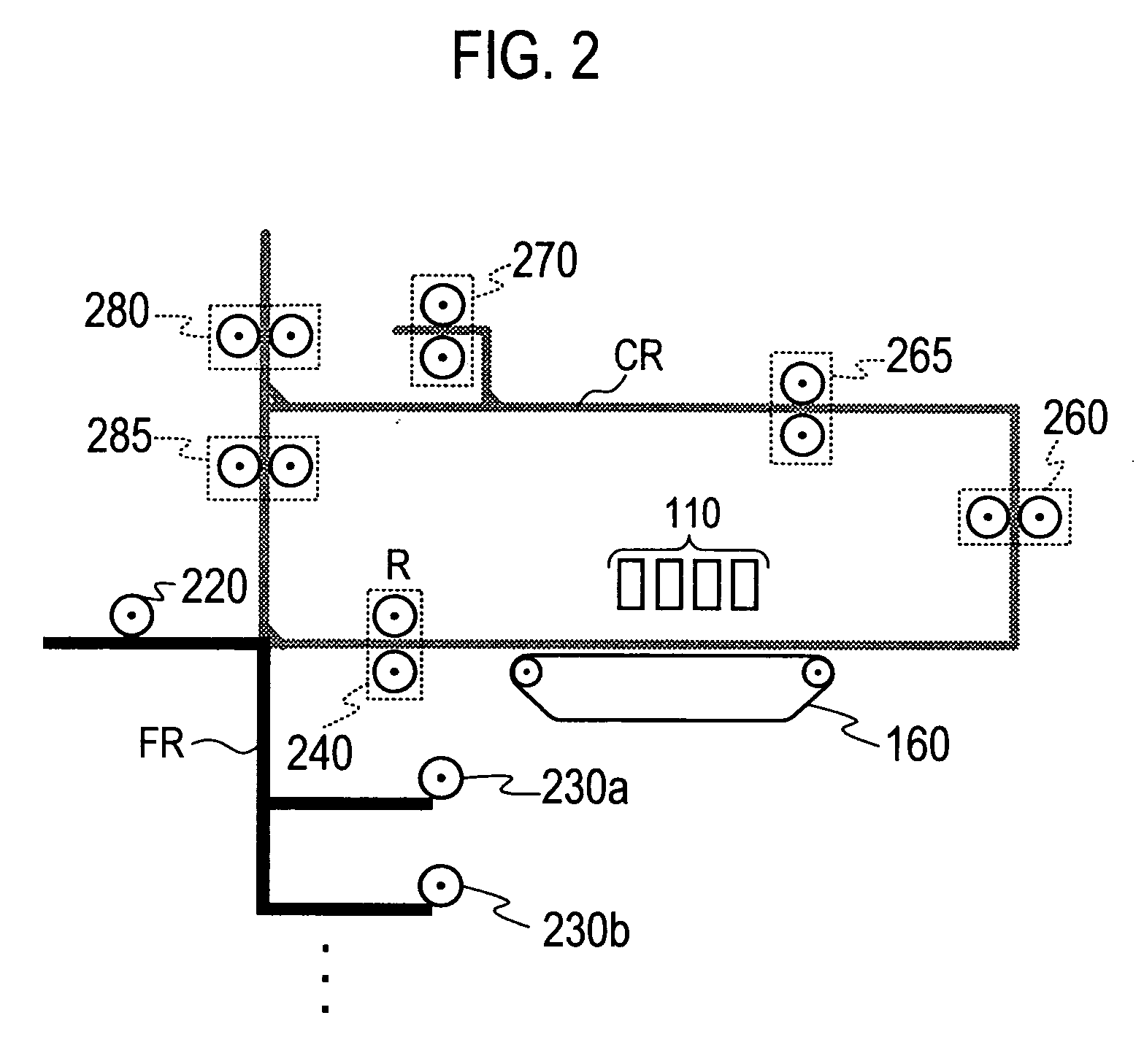
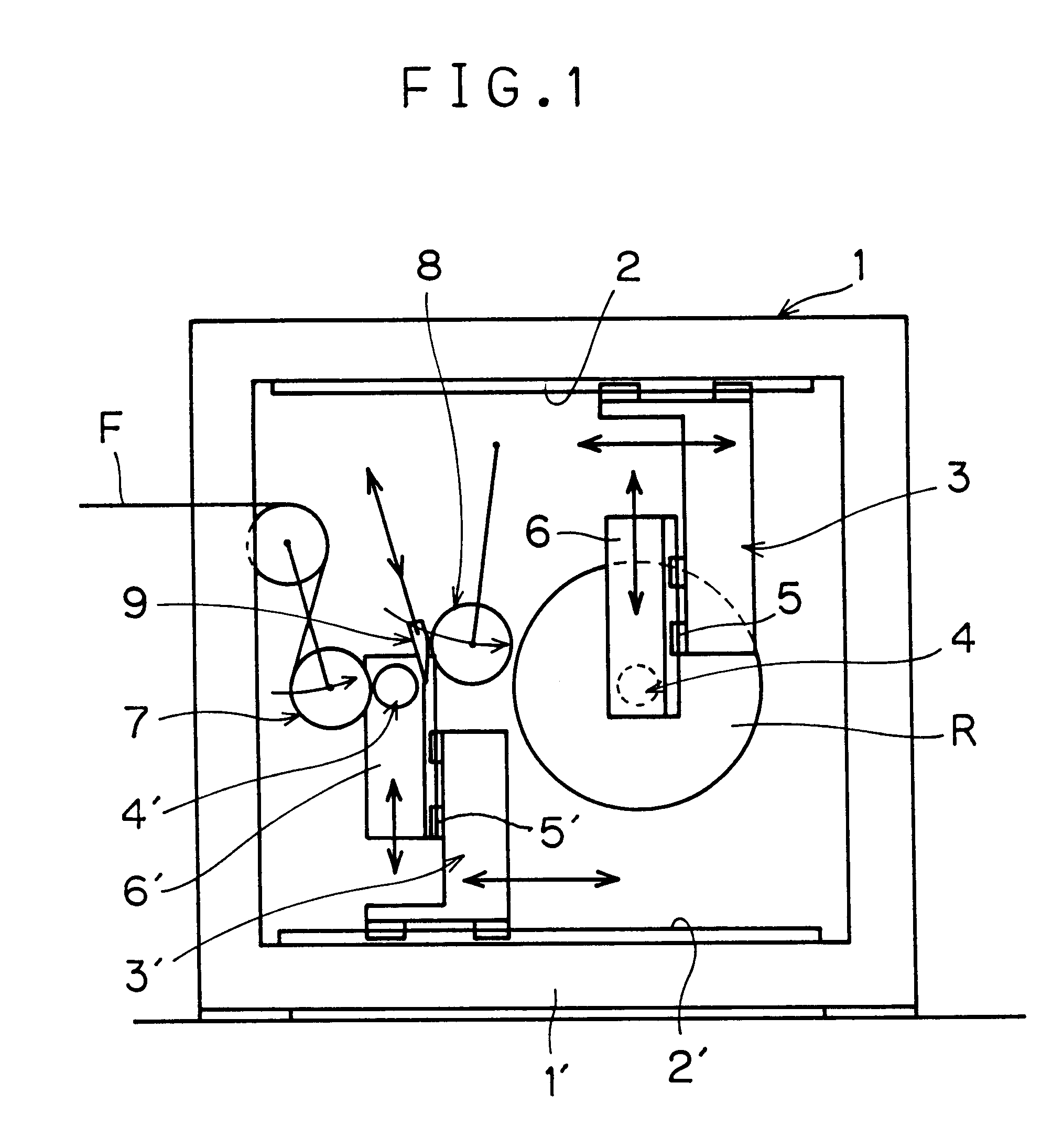
For a sheet circulating transfer route that includes a sheet transfer portion of a printing mechanism provided with a transfer belt for transfer of a sheet as positioned thereto, a transfer section provided with drive rollers for transfer of a sheet as image-formed by an image former of the printing mechanism, and a sheet invert portion operable for inversion of the sheet as image-formed, there is a drive controller adapted, in conformity to a condition that a sheet to be positioned in the printing mechanism is equal in length to or longer than a path distance from the image former to the drive rollers, to set a transfer speed of the sheet as image-formed by the drive rollers up as an identical speed to a transfer speed of the sheet as positioned by the transfer belt, and in non-conformity to the condition, to set it up as a greater speed than the transfer speed by the transfer belt.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Urban healthy trip planning method and system based on floating car method
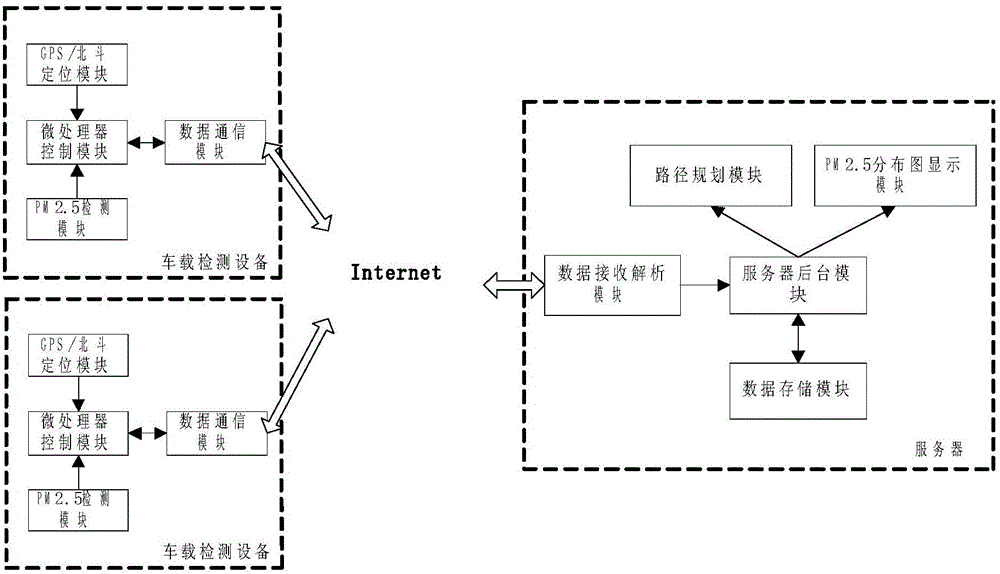
ActiveCN105043401ARealize detectionSee pollutionInstruments for road network navigationParticle suspension analysisOptimum routeComputer science
The invention discloses an urban healthy trip planning method and system based on a floating car method. The urban healthy trip planning method comprises: collecting a PM2.5 test value and a geographical coordinate at a position where a vehicle is, and sending the PM2.5 test value and the geographical coordinate to a server to form an urban PM2.5 test value data collection; showing different PM2.5 test values with different colors on an electronic map; and determining a healthy trip path according to the PM2.5 value and a path distance between a departure point and a destination. The system includes two parts of a vehicle-mounted testing device and the server. The invention can effectively solve the problems of fixed monitoring points, limited monitoring amount, high monitoring cost, long update time of monitoring data, and insufficient accuracy of the PM2.5 value at a specific location. An optimum route with excellent air quality and proper distance can be planned according to the departure point and the destination of a resident, so that a trip for the resident becomes convenient.
Owner:南京艾特斯科技有限公司
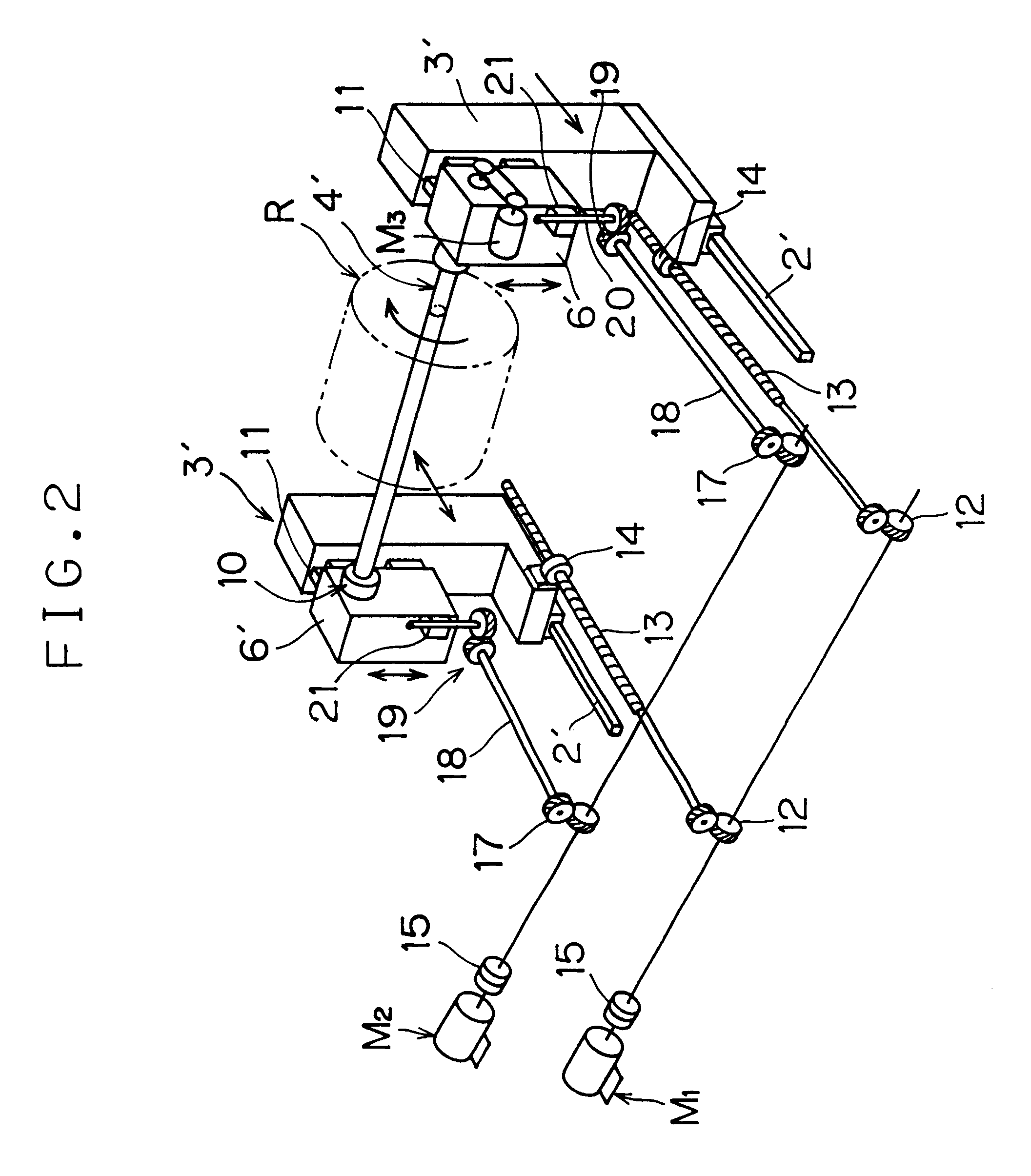
Winder for sheet material
A two-shaft linear motion type winder for winding up a sheet material, e.g. a film is provided, which can eliminate the occurrence of any mechanical loss by simplification of a transission device, shorten the path distance of the film upon roll changing, prevent the neck-in and wrinkling of the film and reduce vastly the roll changing cycle. It comprises at least a pair of upper-stage winding frames having holders for an upper winding shaft, suspended from an upper main frame to be slidingly movable back and forth in a given area; and a pair of lower-stage winding frames having holders for a lower winding shaft, disposed on a lower main frame to face upwards so as to be slidingly movable longitudinally in a given area. The holders for the upper and lower winding shafts are capable of ascending and descending vertically; and each of the upper-stage and lower-stage winding frames, upon full winding, move the one winding shaft with a full roll from a winding position to a removal position of the roll while shifting the other winding shaft to the winding position thereby enabling the roll changing; each of the frames and holders being movable individually without mutual interference.
Owner:FUJI TEKKO
Dynamic path planning method for AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) submarine topography matching
ActiveCN108871351AAvoid Low Terrain Information AreasRealize judgmentInstruments for road network navigationForecastingRelationship - FatherLandform
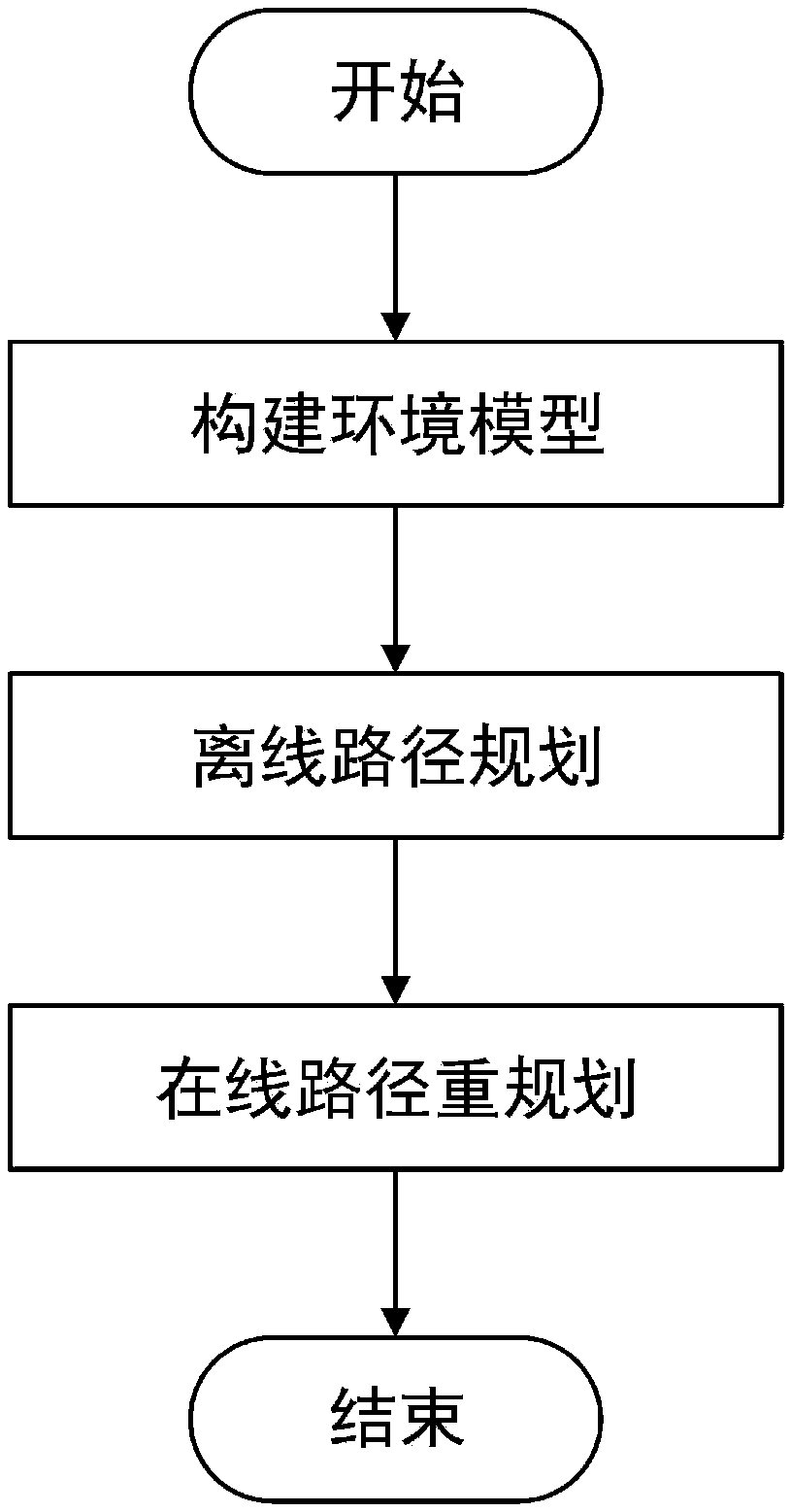
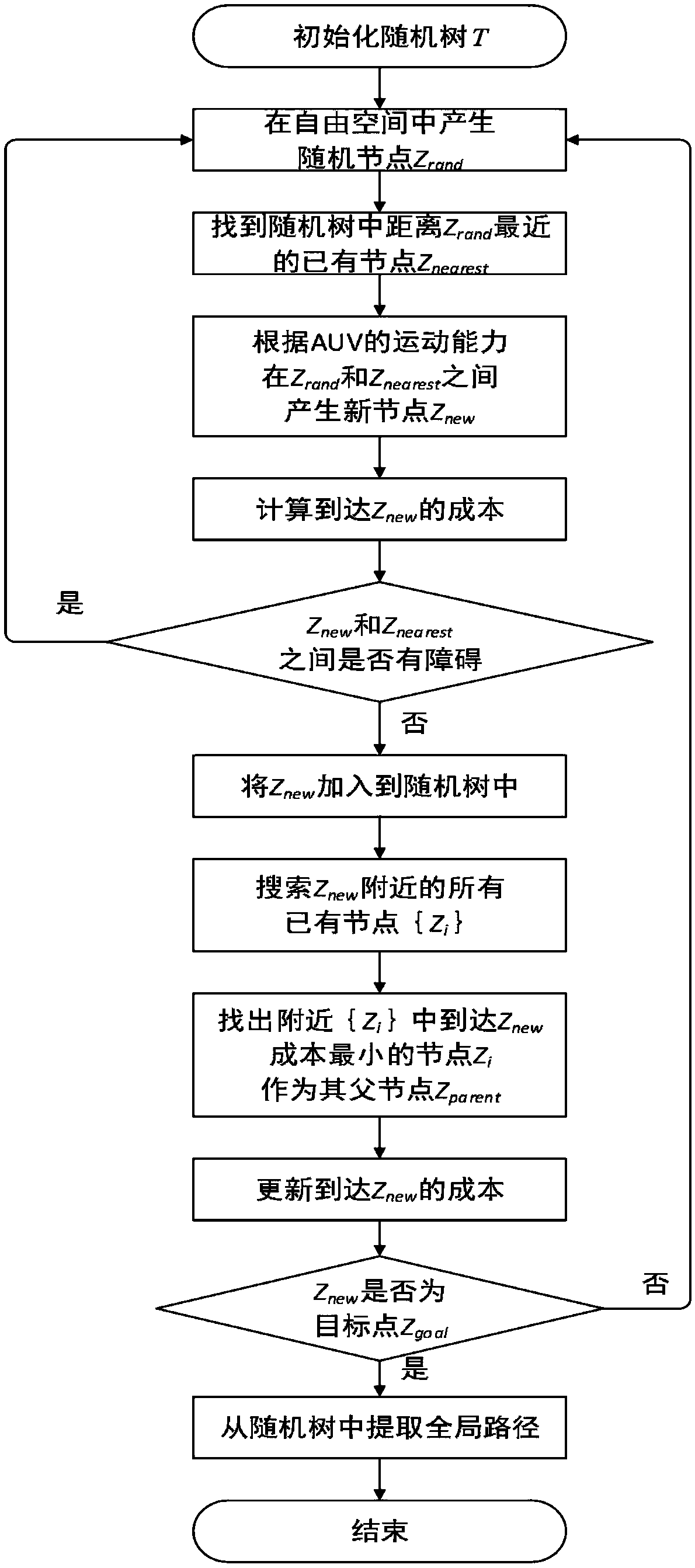
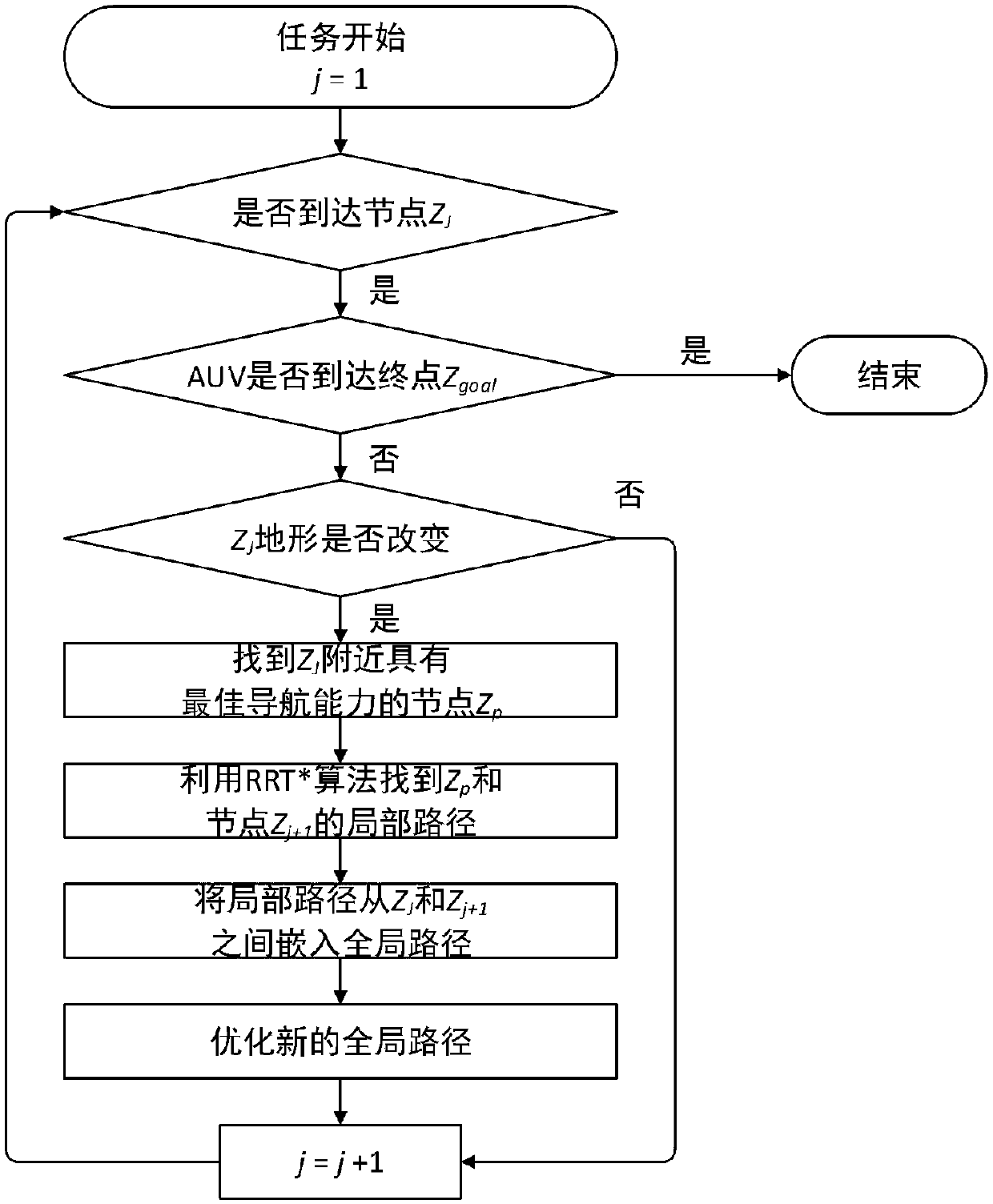
The invention discloses a dynamic path planning method for AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) submarine topography matching, and belongs to the technical field of AUV navigation. The dynamic path planning method comprises environment modeling, offline path planning and online path re-planning. An environment model is constructed by topography information and topography source confidence, whereina topography characteristic is represented with a topography standard deviation. Offline path planning is based on a rapid search random tree algorithm, improves a new node and father node selection algorithm, and processes the topography information by roulette and a mahalanobis distance so as to avoid a low topography information region. When an AUV navigates along an offline path and detects changes of the topography information, online re-planning implements judgment on the topography changes by methods of judging the topography changes, searching a local navigation optimal node, re-optimizing a global path and the like, and ensures navigation accuracy. The dynamic path planning method is applicable to long-voyage high-accuracy AUV path planning, and particularly when the topography information is changed, by modifying the path in real time, navigation accuracy and a path distance are ensured.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
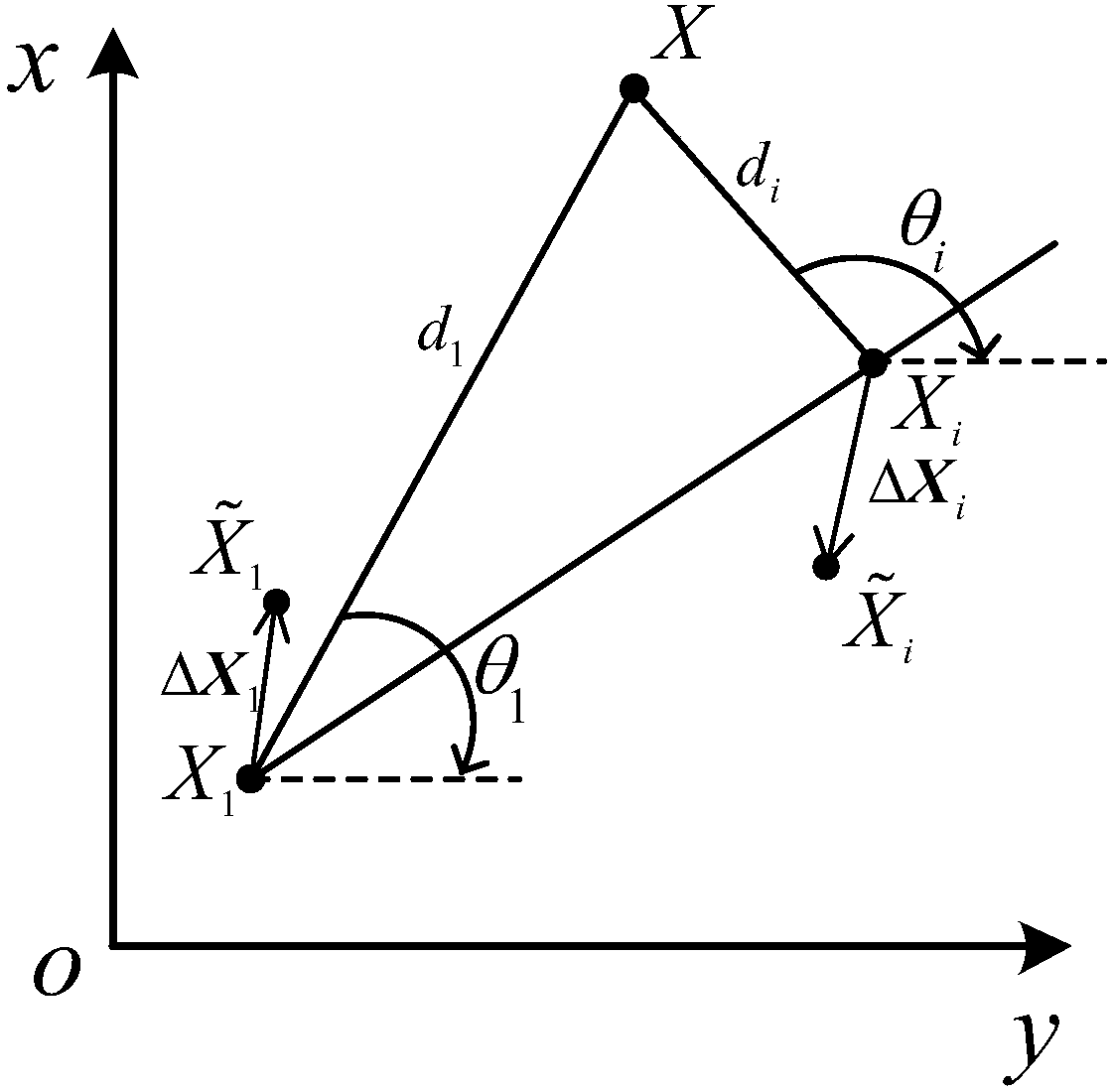
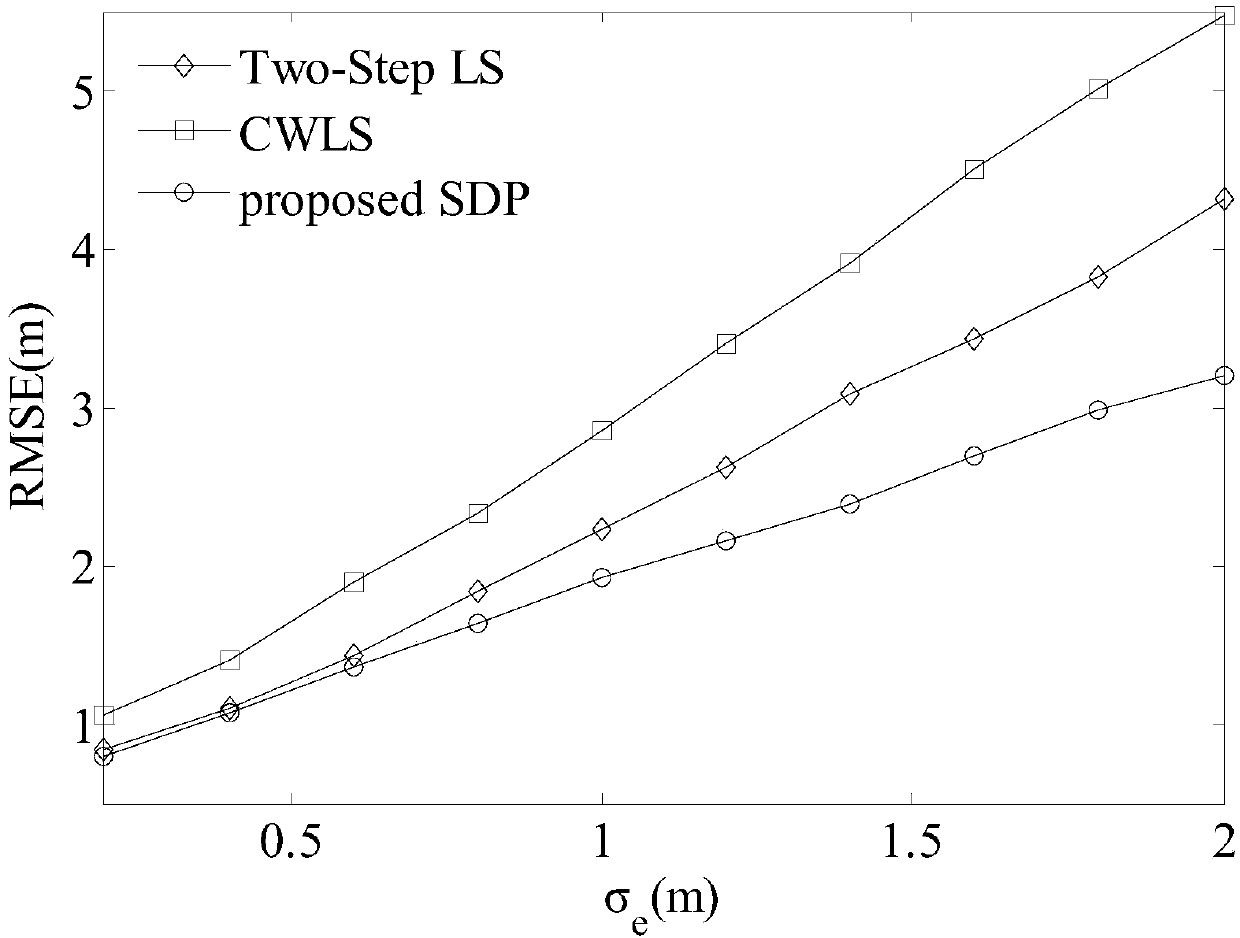
TDOA-AOA positioning method considering position error of base station
The invention relates to a TDOA-AOA positioning method considering a position error of a base station. The method comprises the following steps: 1) arranging a wireless sensor network in a two-dimensional space, and measuring, by each base station, an arrival time dereference and angles of a measurement target node and a reference node under a noise condition; 2) selecting the first base station as the reference base station, and obtaining a signal transmission path distance difference relative to the reference base station according to the arrival time dereference of signal transmission paths; 3) establishing a least square target estimation algorithm according to the measured values in the previous two steps and the known position of the base station; 4) due to the existence of the basestation error and the measurement error, analyzing the errors, and importing a weight matrix to achieve weighted least square estimation; and 5) reconstructing the weighted least square estimation, and using the semi-definite relaxation technique to transform the weighted least square into a semi-definite planning problem with linear equality constraints and linear inequality constraints via laxity rank constraints, and then solving a globally optimal solution by using an inner point method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Hybrid dynamic scheduling method used for port container truck
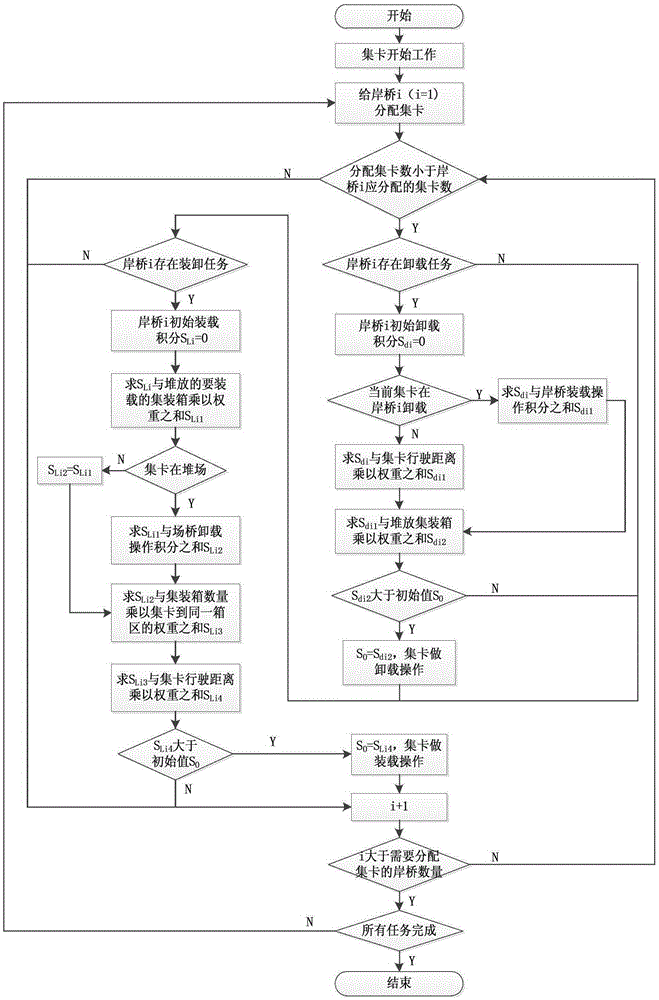
InactiveCN105427075AIncrease profitReduce empty driving distanceForecastingLogisticsProcess engineeringTruck
The invention discloses a hybrid dynamic scheduling method used for a port container truck. The hybrid dynamic scheduling method comprises the following steps: the container truck reloads containers on an import ship and unloads the containers in on export ship; a dynamic scheduling model of the container truck is established by taking total operating time as a standard, and the dynamic scheduling model is established on the premise of a known gantry crane loading plan and a known gantry unloading plan; and on the basis of shortest total operating time, an operation path of each container truck is dynamically optimized. A dynamic scheduling mode is adopted to improve the use ratio of the container truck, the no-load driving distance of container truck transportation is reduced, a next operation task is assigned according to principles including path optimization, instruction optimization and the like, a container truck transportation process is subjected to comprehensive scheduling, the container truck is selected in multiple tasks according to the selection of path distances at any moment, and a container truck service object is dynamically collocated with the operation plane of the whole wharf.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
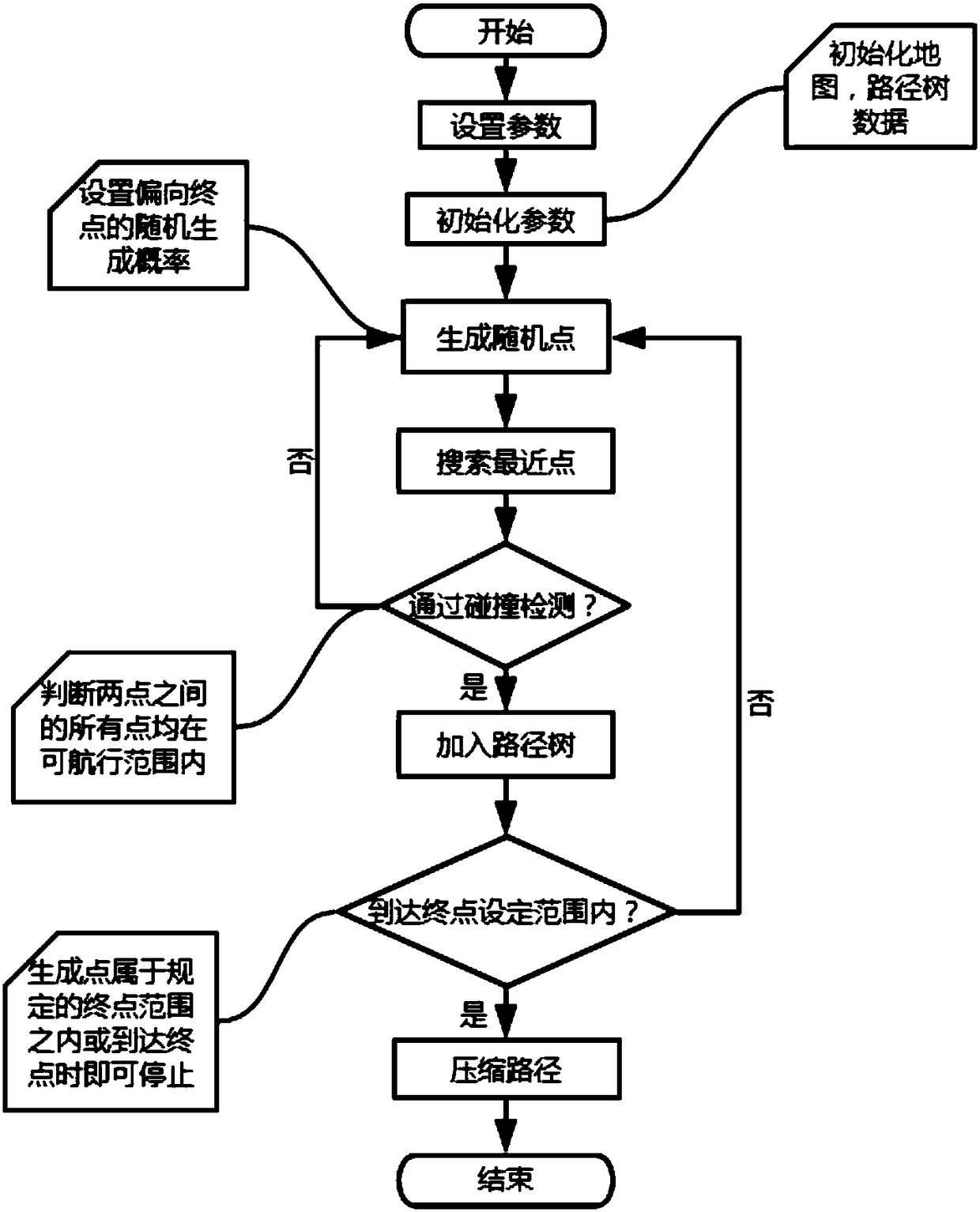
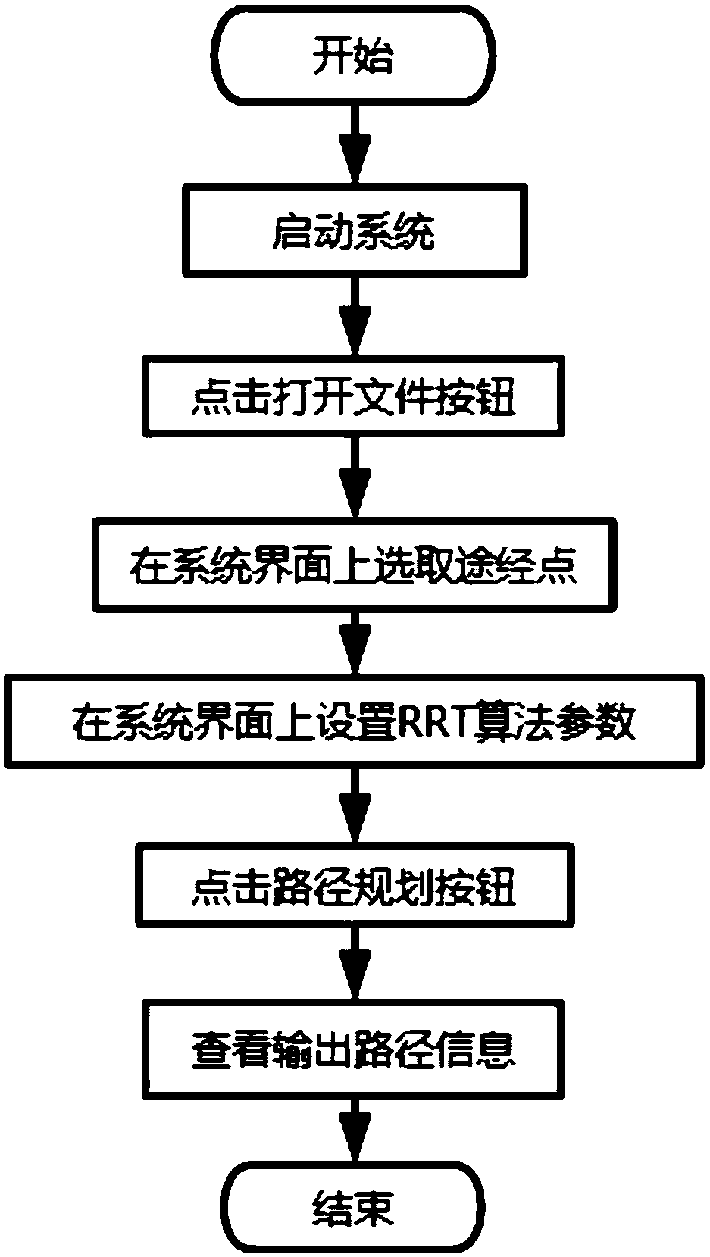
Method and system for planning sea path of unmanned ship based on RRT (rapidly-exploring random tree) algorithm
InactiveCN108507575AIndicates connectivityMature theoryNavigational calculation instrumentsControl systemPower control system
The invention discloses a method and a system for planning a sea path of an unmanned ship based on an RRT (rapidly-exploring random tree) algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining data of a sea map, so as to obtain complete information of the sea map; according to the definition of a polygon of the sea map, displaying the conditions of the sea surface, and rasterizing the original vector data, so as to obtain a complete interface of the sea map; enabling a user to set passing points on the interface of the sea map, and planning the path within the preset time threshold value by an improved RRT algorithm, so as to obtain the final asymptotically optimal effective path; converting the final effective path into the practical longitudinal and altitude information, outputting the longitudinal and altitude information of turning points on the path, and providing for a power control system of the unmanned ship to use. The method has the advantages that the RRT algorithmis further improved, the path passing the multiple preset passing points is planned, and a path compression algorithm is applied so as to effectively reduce the path distance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
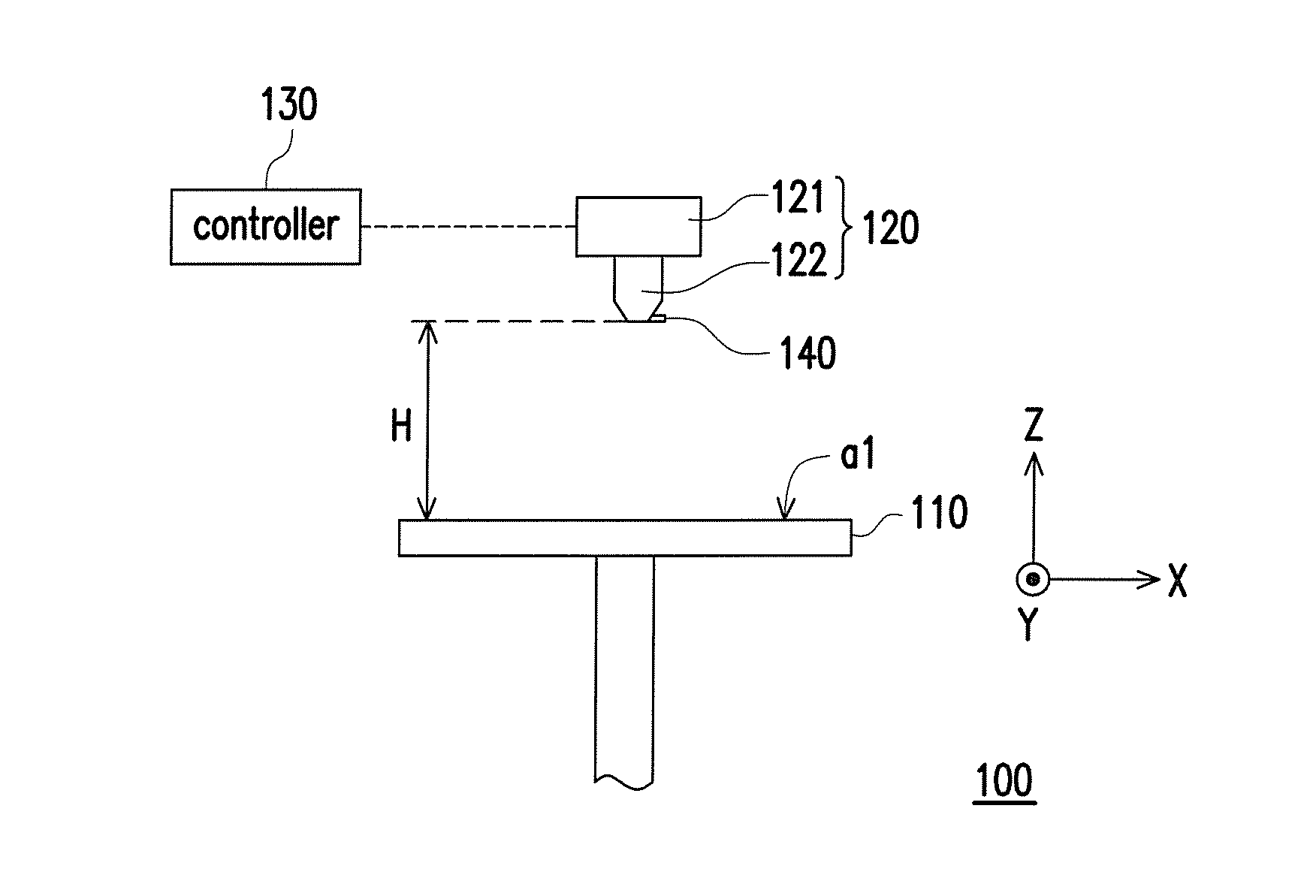
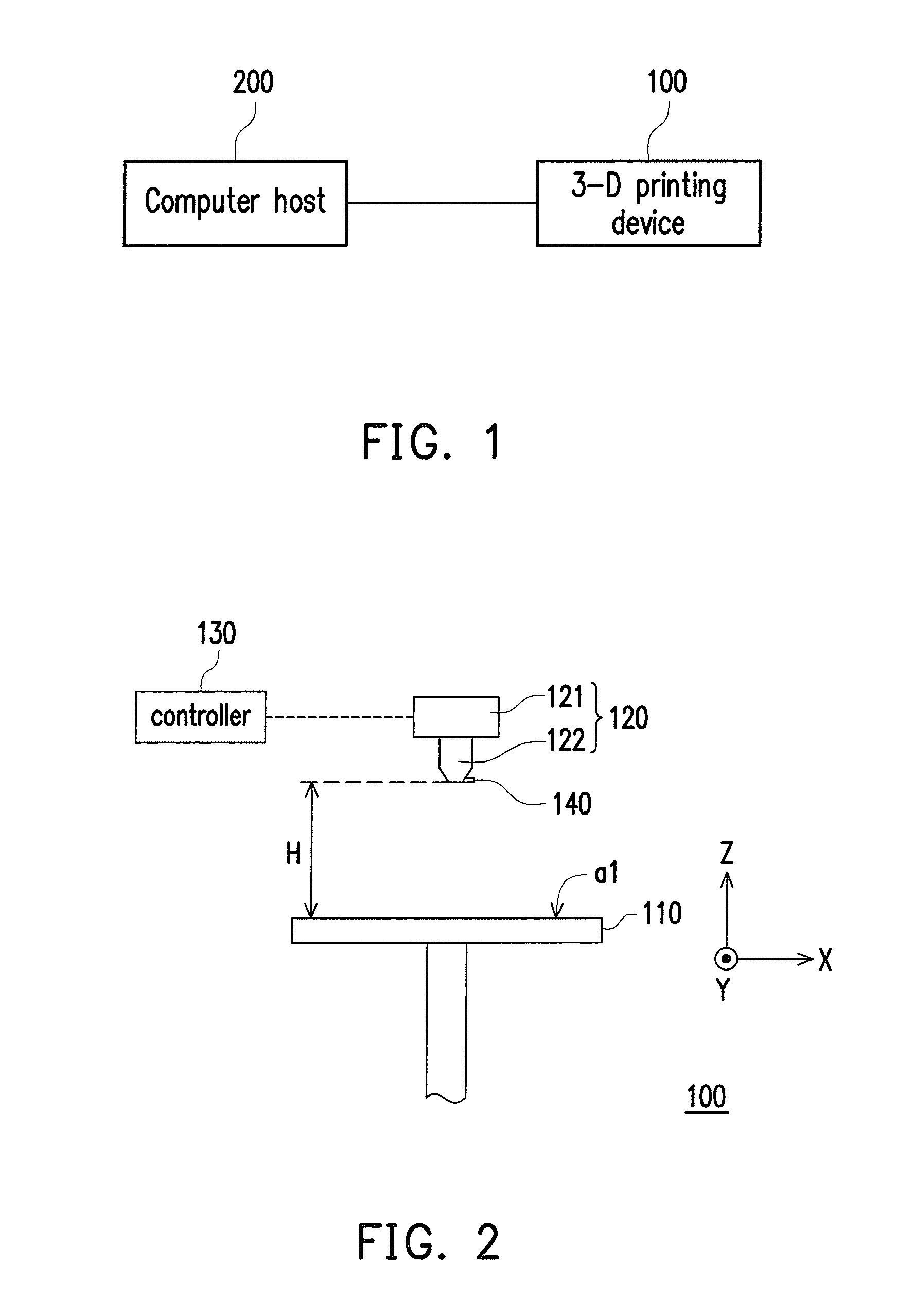
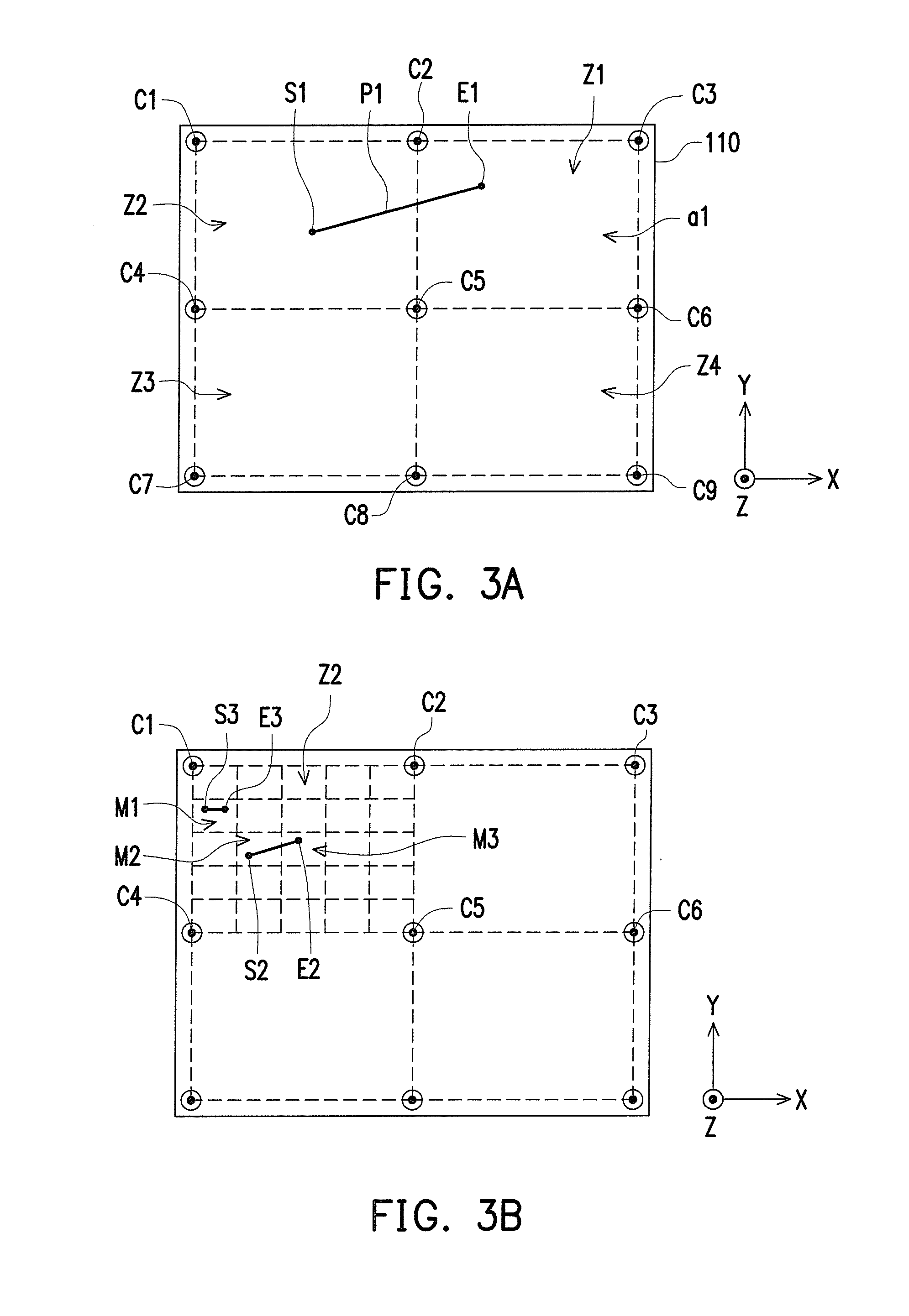
Three-dimensional printing appratus and method for calibrating printing inaccuracy thereof
ActiveUS20160354980A1Improve printing qualityAccuracy affectedProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusPath distanceSupport surface
A three-dimensional printing apparatus and a method for calibrating printing inaccuracy thereof are provided. A printing head of the three-dimensional printing apparatus is adapted for moving along a straight printing path on a datum plane and simultaneously feeding out forming material, so as to generate a layer object on a supporting surface of a platform. If a path distance of the straight printing path is greater than a threshold, a plurality of linear compensation relationships respectively corresponding to a plurality of first zones of the supporting surface are used for calculating a first compensation value of a starting point and a second compensation value of an ending point. If the path distance of the straight printing path is not greater than the threshold, a common compensation values is decided based on at least one of second zones and which is corresponding to the starting point and the ending point.
Owner:XYZPRINTING +2
GIS-based positioning method for optical cable fault points
InactiveCN106330306APrecise positioningElectromagnetic transmissionGeographical information databasesUltrasound attenuationGeolocation
The invention belongs to the field of cable fault online monitoring and particularly relates to a GIS-based positioning method for optical cable fault points. The method includes: fault positioners are mounted on an optical cable line at intervals, and marking the optical path geographic positions of the fault positioners; visually displaying the route of the optical cable line and the actual geographic positions of the fault positioners, tower connector boxes and towers on a GIS map; using the attenuation of an OTDR photometry signal to accurately obtain the light path distance between an optical cable disconnection point and a machine room; positioning the optical cable disconnection point between two adjacent fault positioners marked by optical path geographic positions; positioning the fault positioners positioning the optical cable disconnection point to actual geographical positions on the GIS map. By the GIS-based positioning method, the optical cable disconnection point can be positioned between the adjacent fault positioners marked by the actual geographic positions, and maintenance staff can maintain the optical cable disconnection point according to the positioned actual geographic positions.
Owner:XINZHOU POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER
Universal liquid concentration supersonic-detection method and universal liquid concentration supersonic-detection device
ActiveCN103278561AImprove general performanceImprove versatilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSupersonic wavesEngineering
The invention discloses a universal liquid concentration supersonic-detection method and a universal liquid concentration supersonic-detection device. The universal liquid concentration supersonic-detection method is characterized in that because of different supersonic velocities of supersonic wave in different mediums, according to known sonic path distances, sonic travel time in the detected liquid is measured; and the measured value is corrected by real-time temperature values so that percentage contents of different solutes in different solvents are obtained. Through sampling of supersonic wave propagation velocities in different solvents and solutes at different temperatures, sampling results are obtained, and through the sampling results, a corresponding relationship formula of the supersonic velocities of supersonic wave in the solutions, and the temperatures and the concentrations is worked out so that liquid concentration measurement universality is realized. Through measurement of supersonic velocities in air and in purified water under laboratory conditions, the method and the device realize correction of system hardware errors and sonic path distance errors and improve a measurement precision.
Owner:无锡煤矿机械股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com