Patents
Literature
72 results about "Clock tree synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
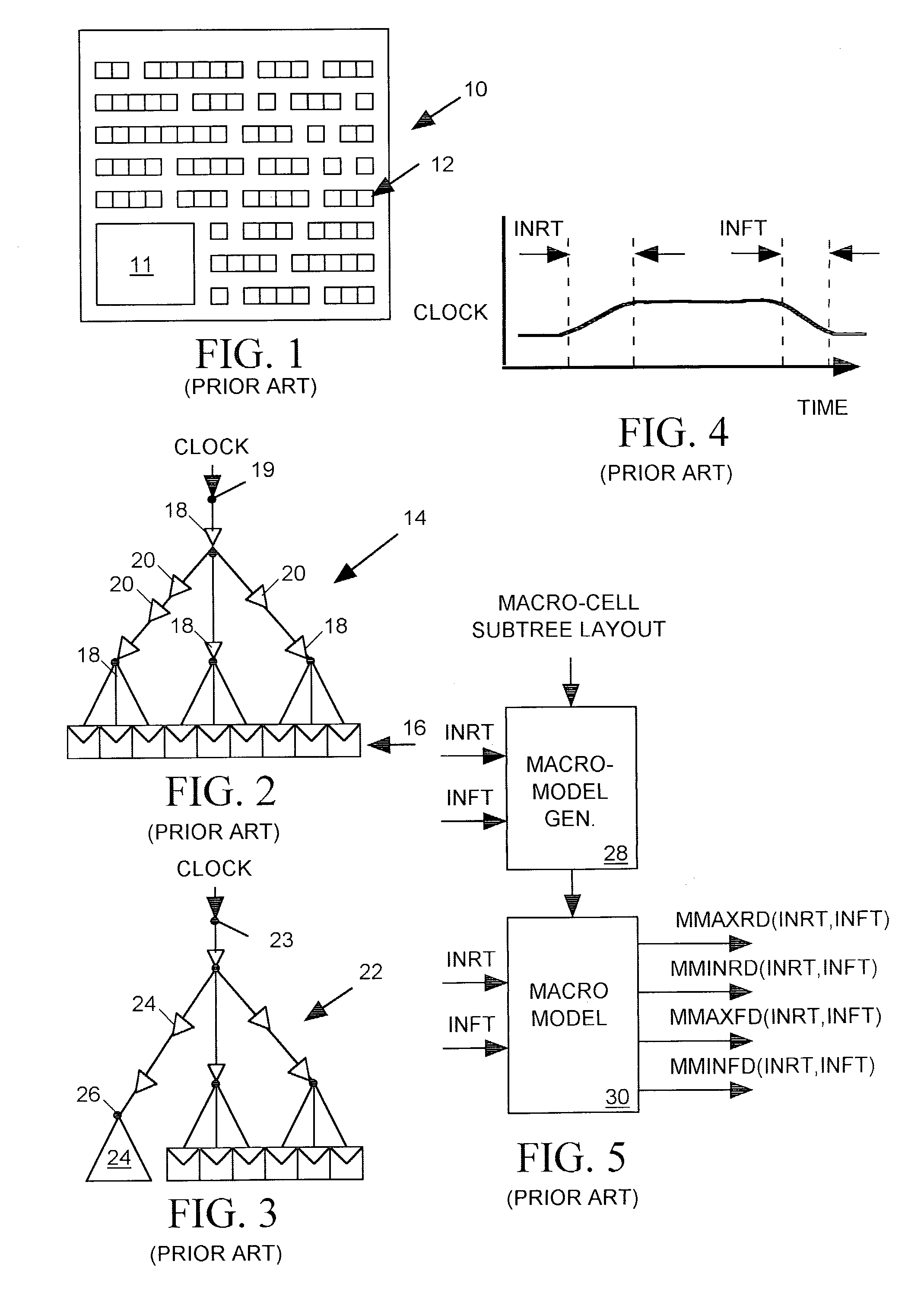
CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) CTS is the process of insertion of buffers or inverters along the clock paths of ASIC design in order to achieve zero/minimum skew or balanced skew.
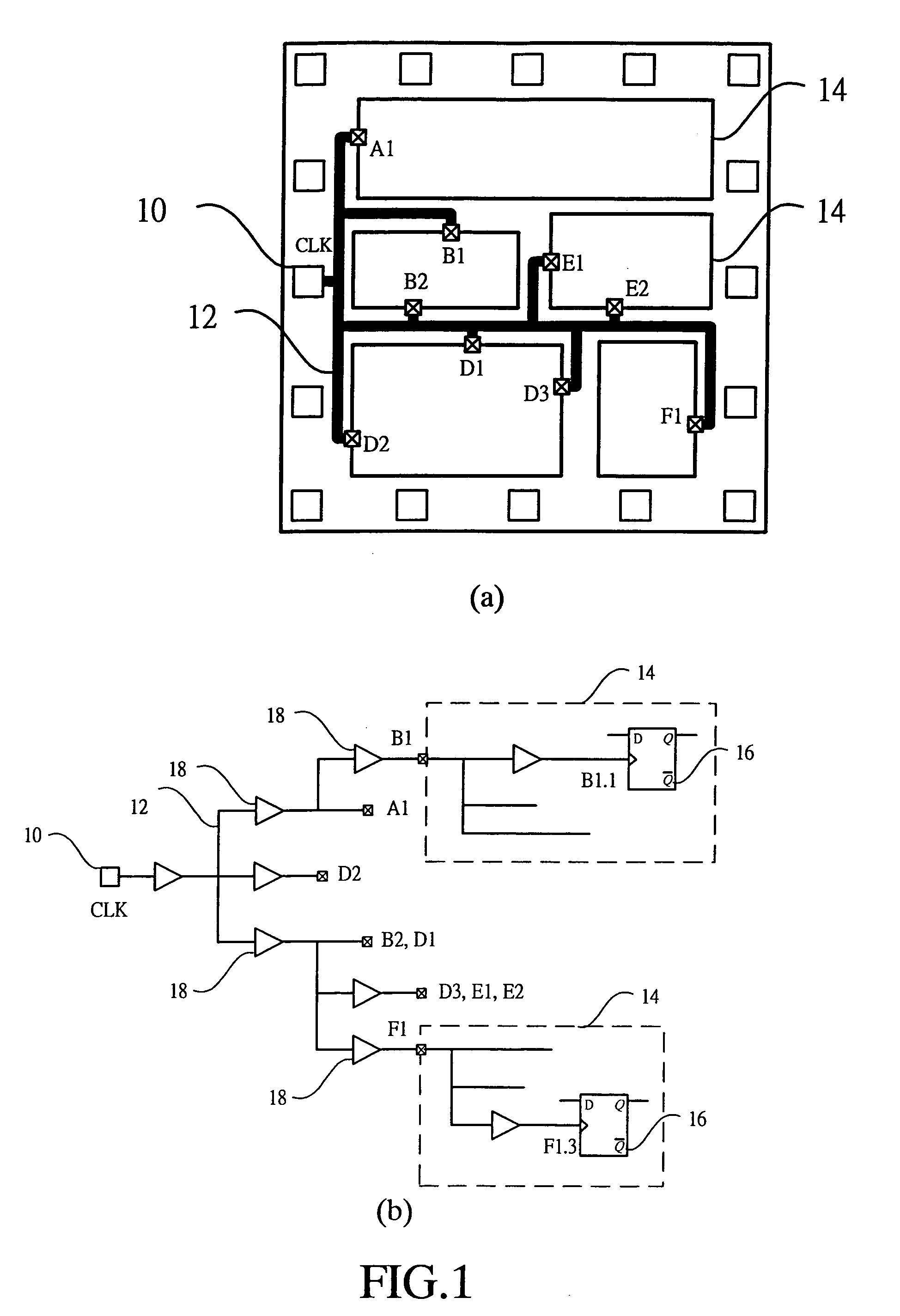
Gated clock tree synthesis method for the logic design
A gated clock tree synthesis (CTS) method is provided for the purpose of synthesizing a gate array logic circuit to allow optimal topological arrangement of the gate array on the logic circuit. This in turn allows the logic circuit to operate more efficiently. The logic circuit includes at least one clock generator, a plurality of control gates each having one input end connected to a control signal and the other input end connected to receive the output clock signal from the clock generator, a plurality of first logic elements that are directly driven by the output clock signal from the clock generator, and a plurality of second logic elements that are driven by the gated clock signal outputted from each of the control gates under control by the control signal. The gated CTS method comprises the steps of grouping the first logic elements into a plurality of groups, connecting each group of the first logic elements via a first buffer to one of the control gates, connecting each of the second logic elements via a second buffer to the clock generator, and connecting one input end of each of the control gates to the clock generator.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
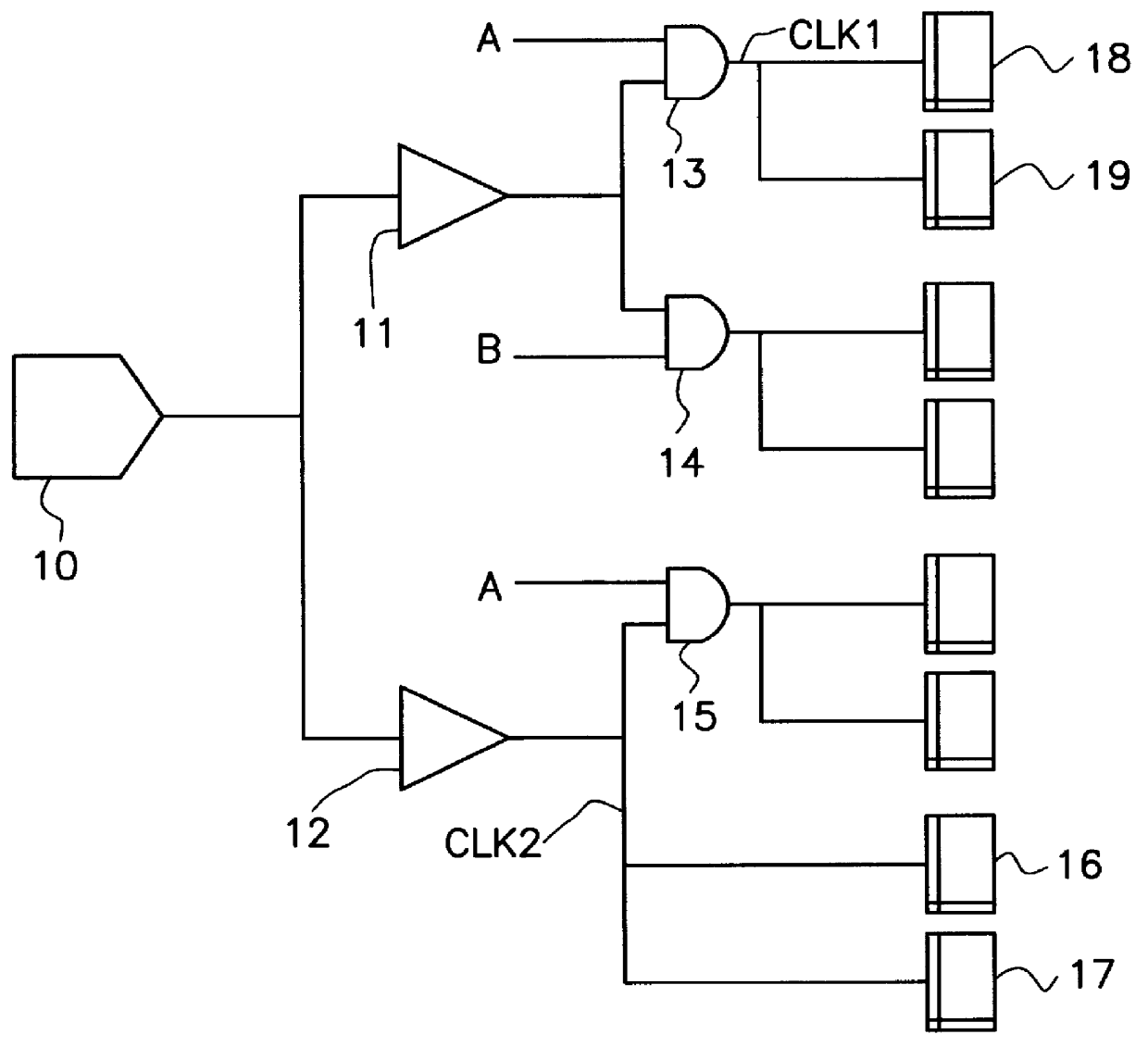
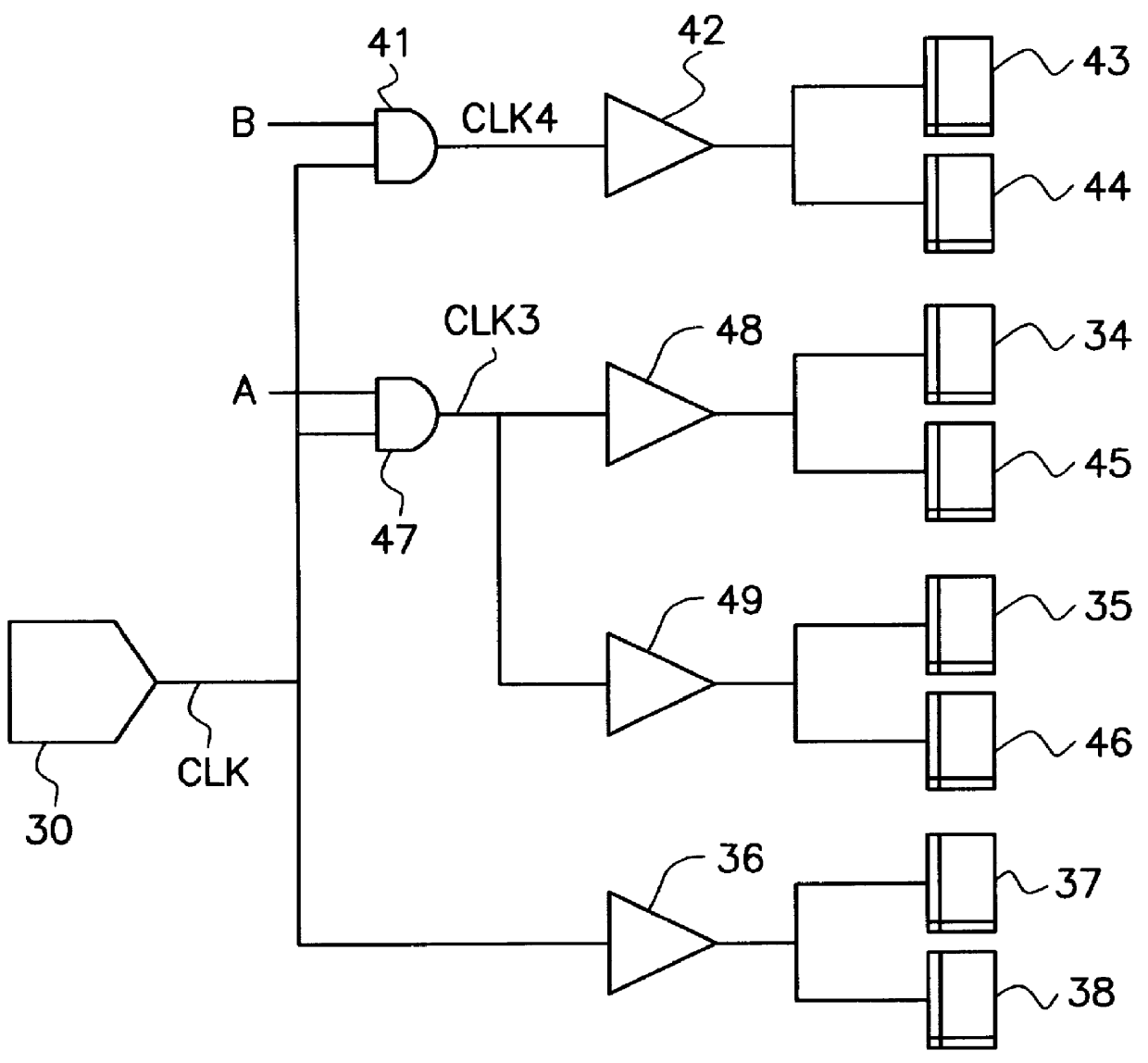
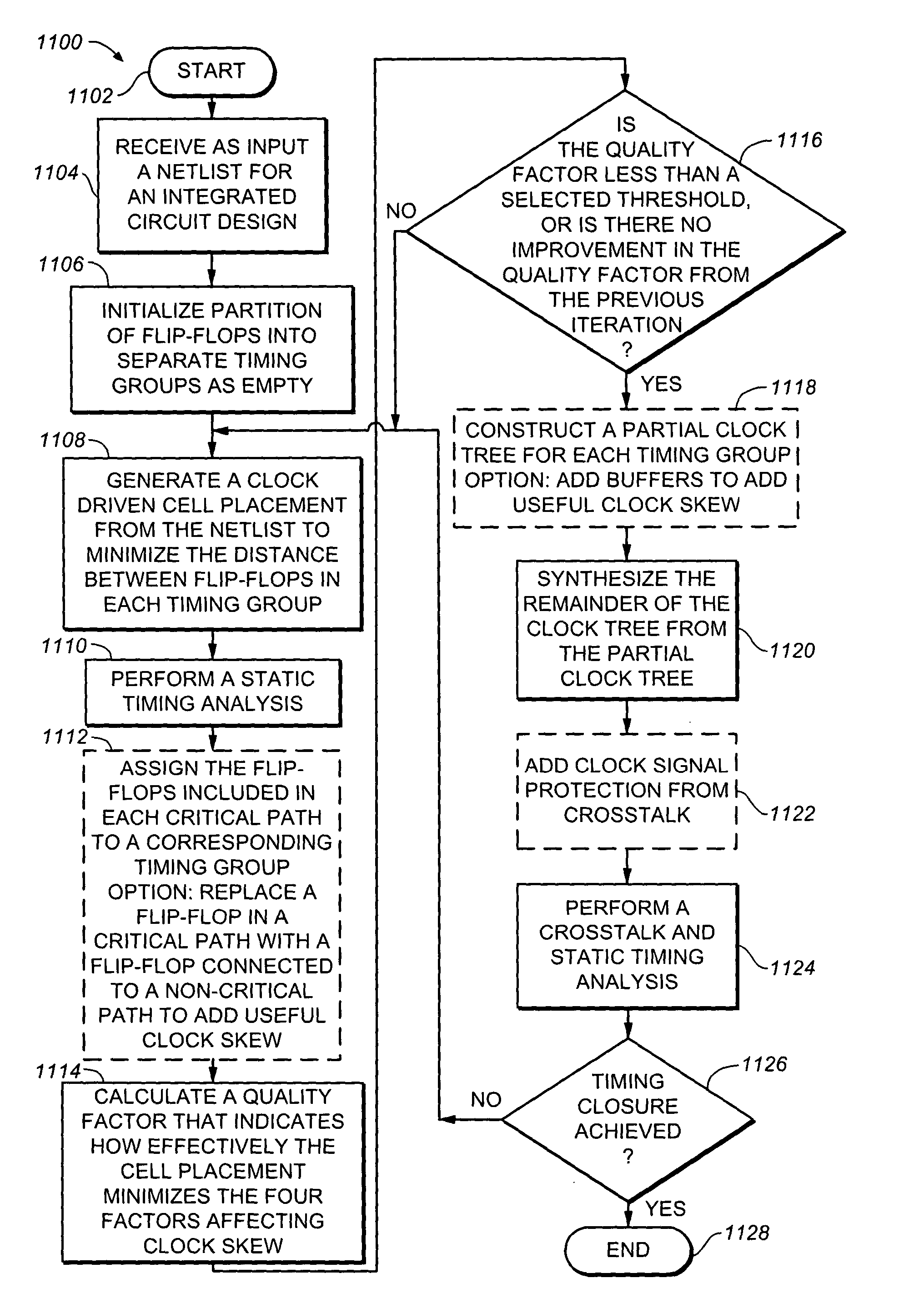
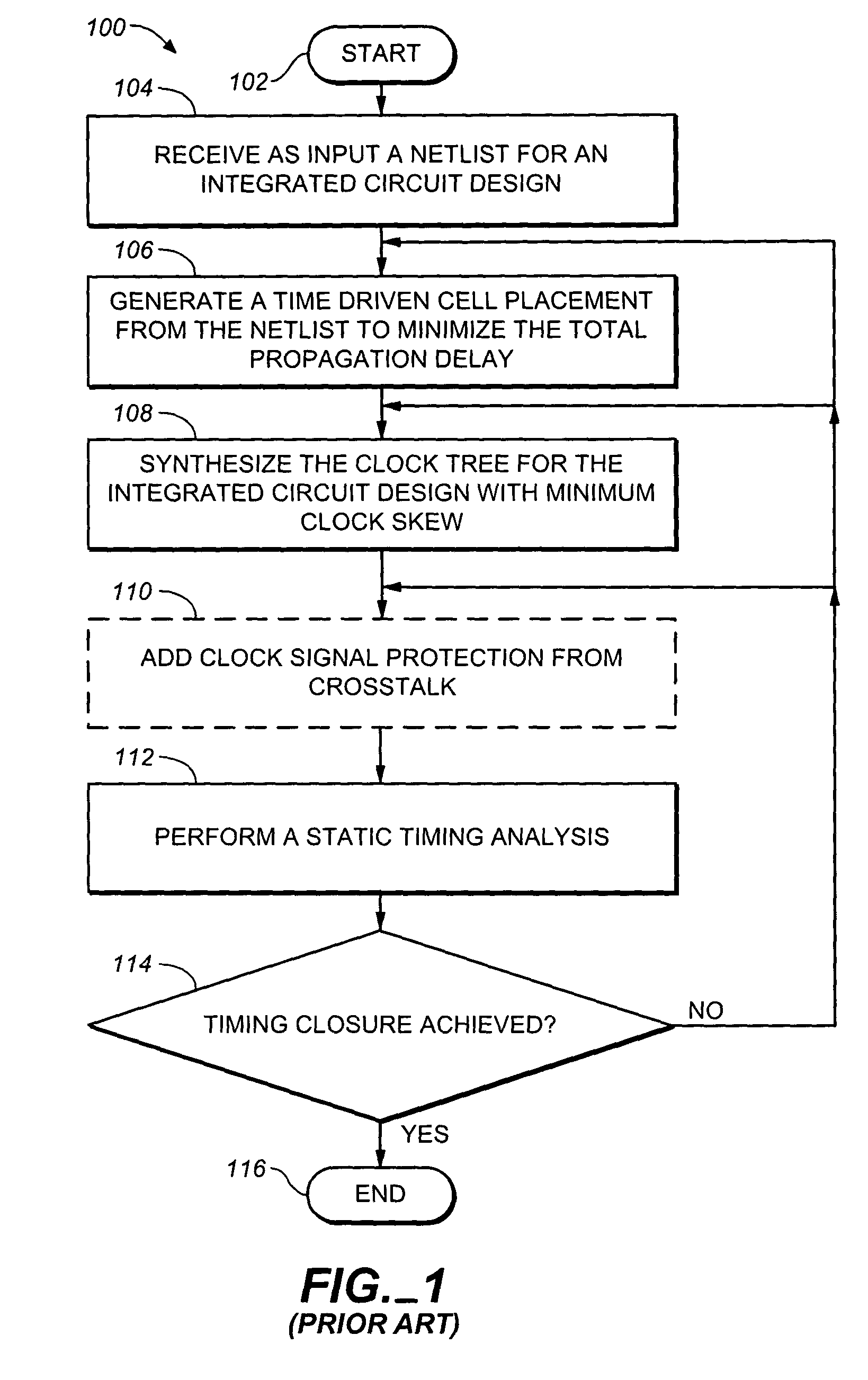
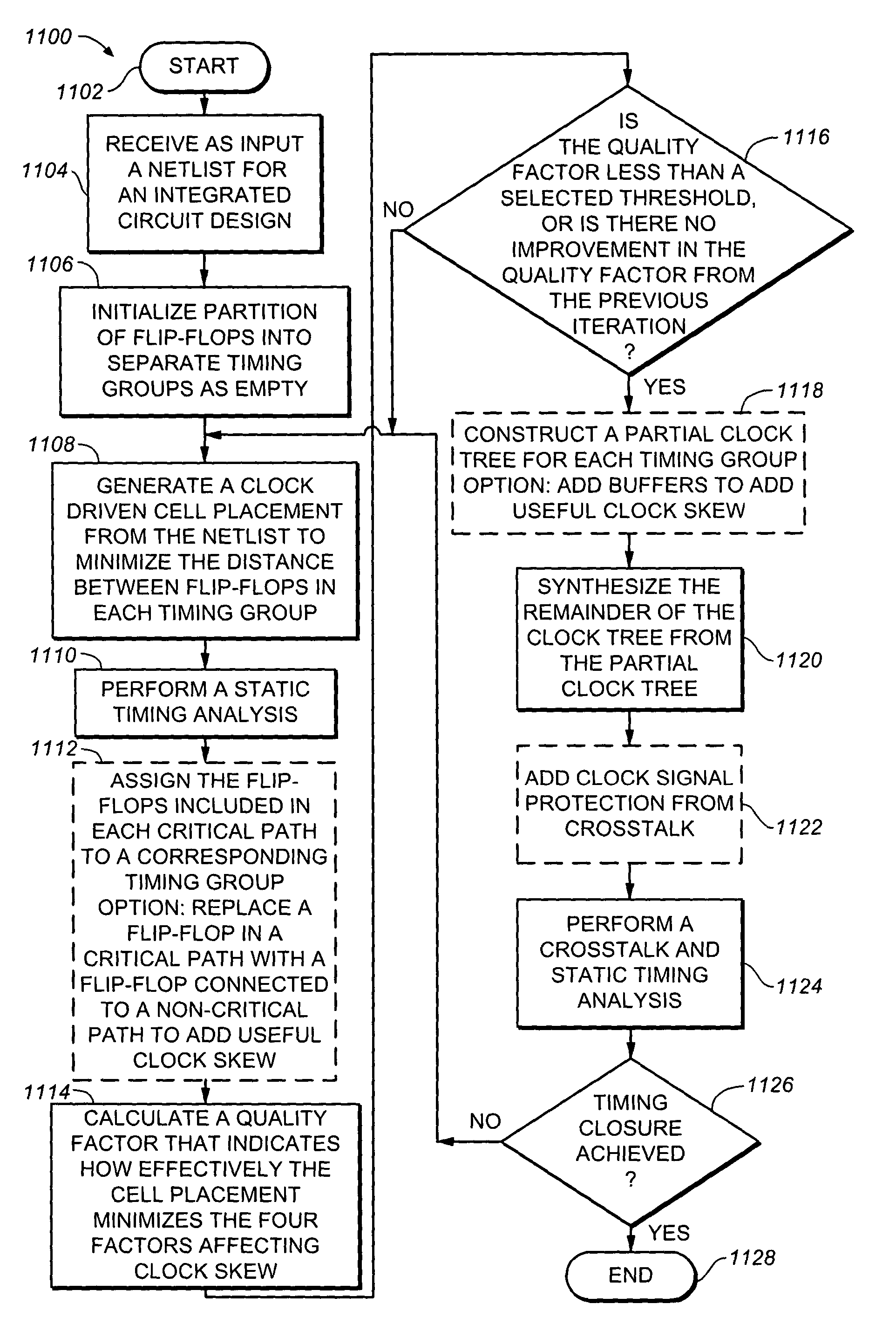
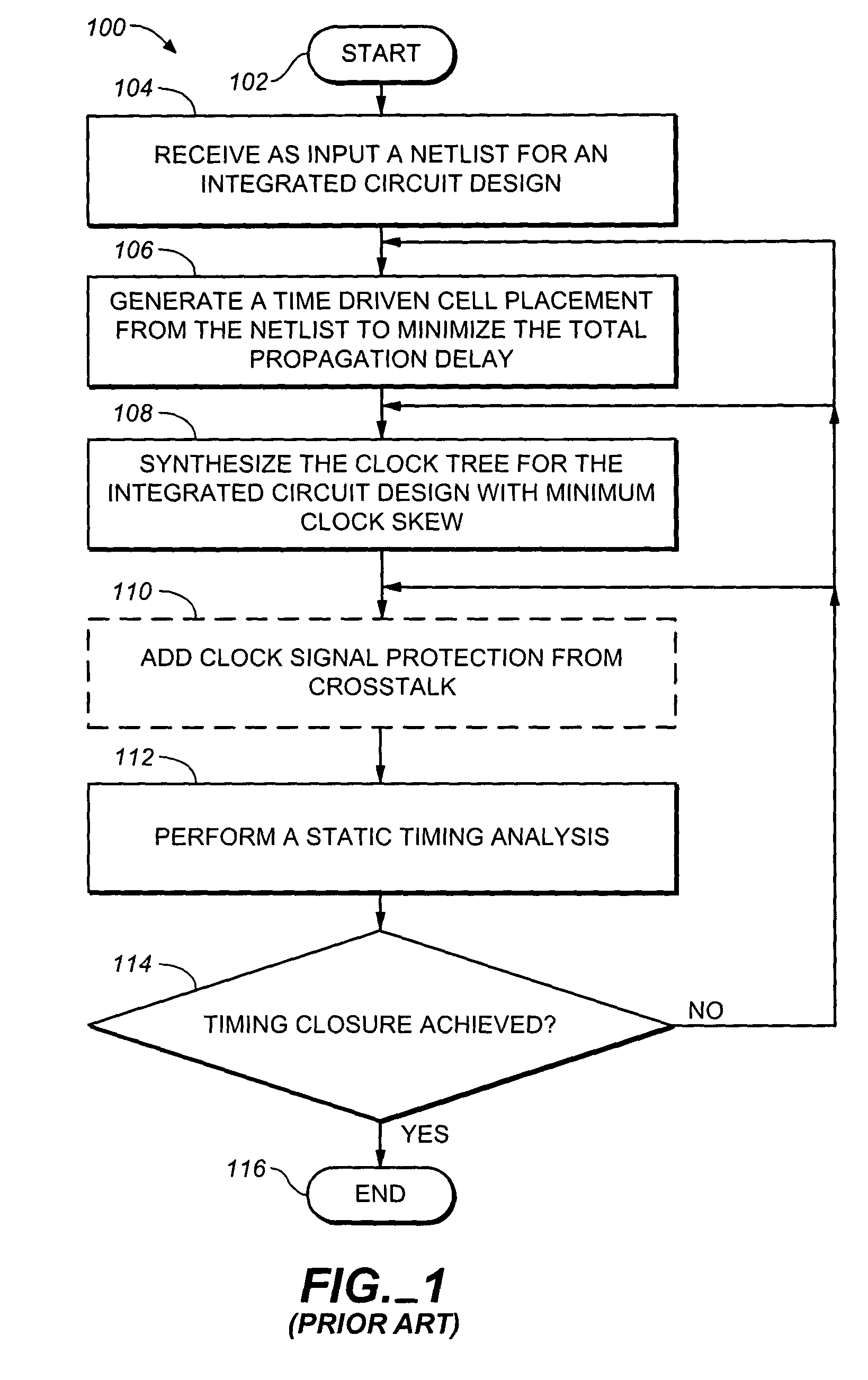
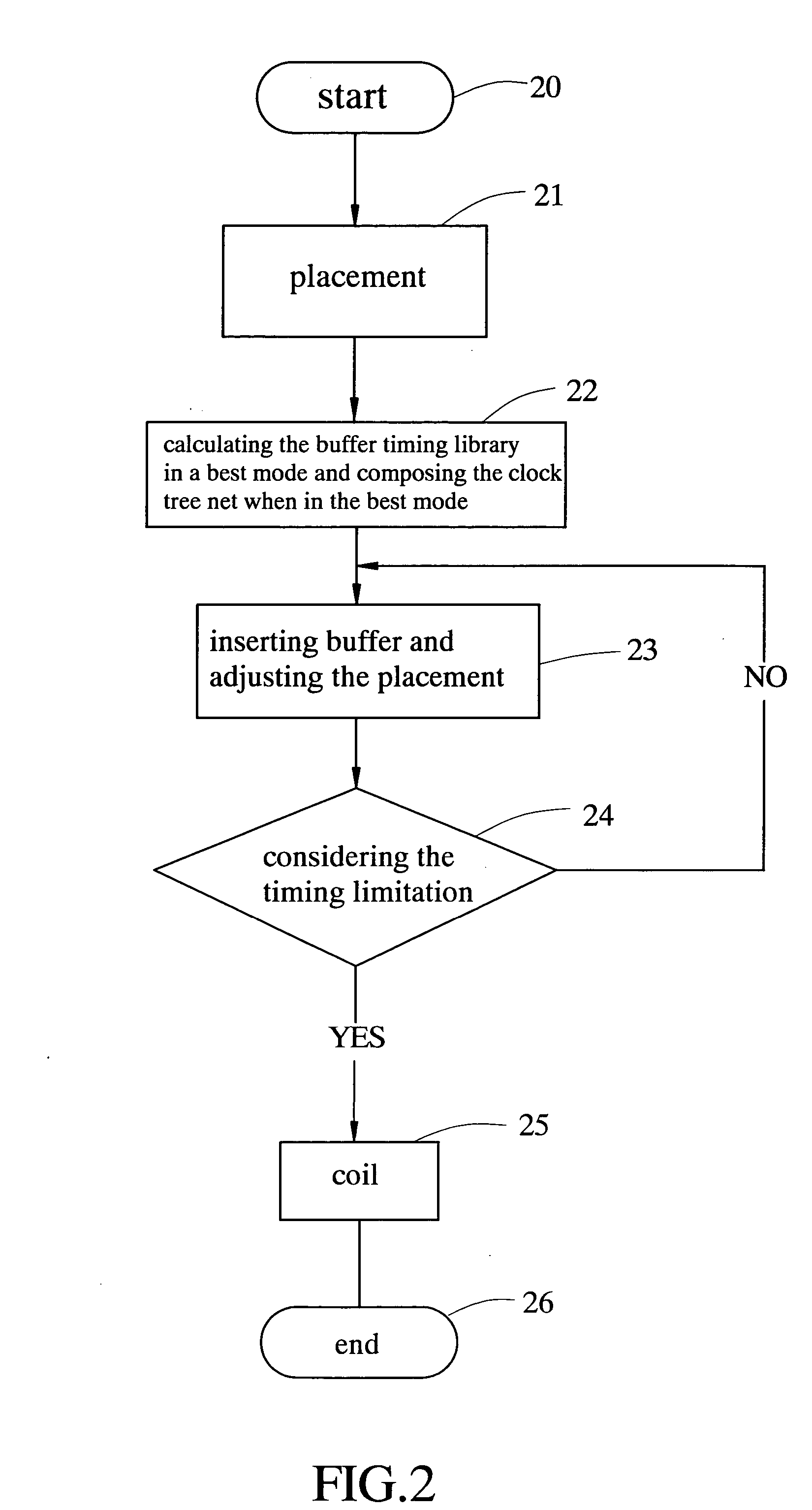
Method of clock driven cell placement and clock tree synthesis for integrated circuit design
ActiveUS20050050497A1Delay and maximum distanceFunction of delay and maximumComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPropagation delayEngineering
A method of cell placement and clock tree synthesis includes steps of: (a) identifying critical paths in an integrated circuit design; (b) partitioning the integrated circuit design into a timing group for each of the critical paths; (c) assigning each flip-flop in a critical path to a timing group corresponding to the critical path; (d) performing a cell placement to minimize a function of propagation delay and maximum distance between flip-flops within each timing group; and (e) constructing a clock sub-net for each timing group.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
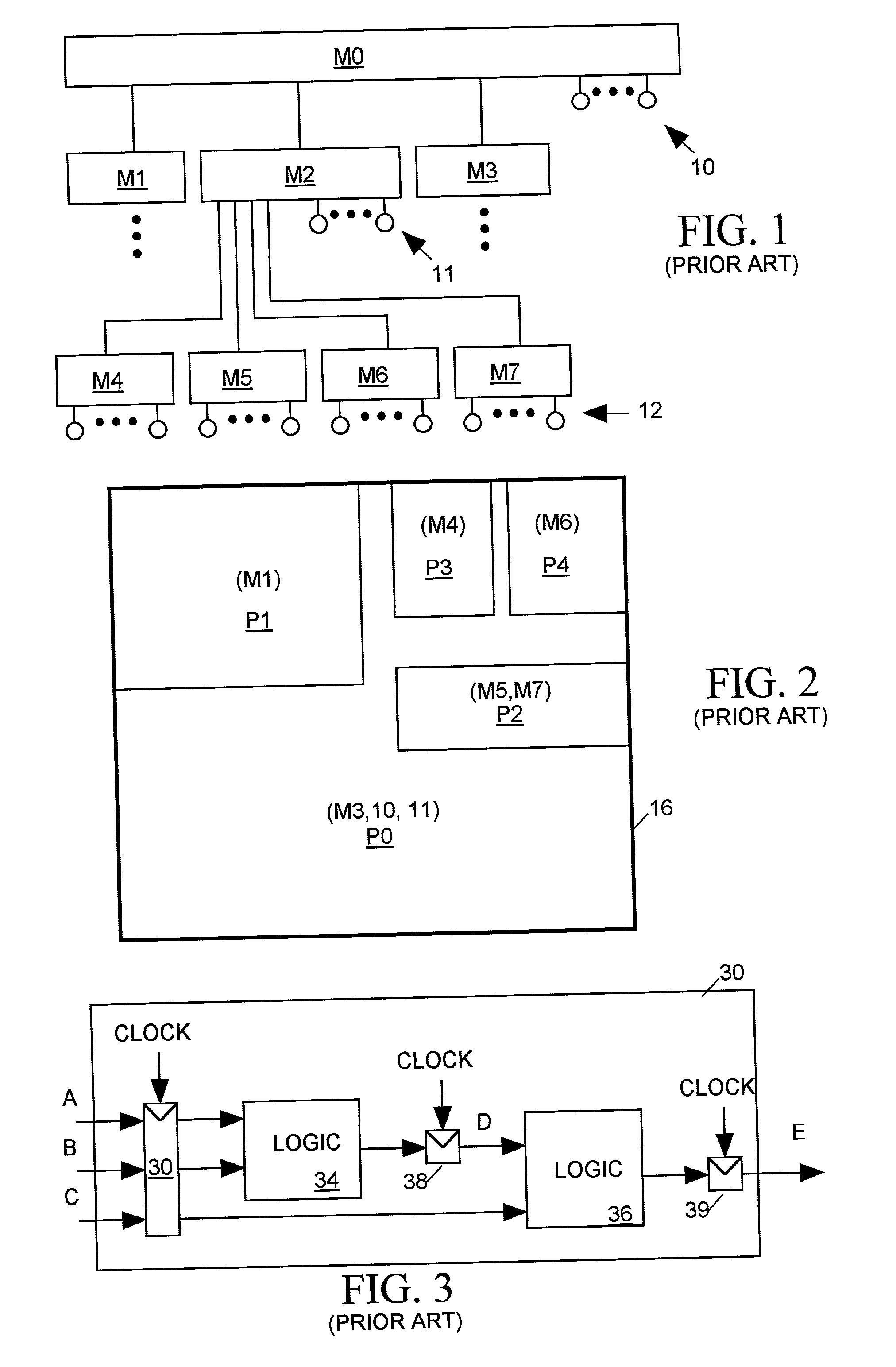
Clock tree synthesis for a hierarchically partitioned IC layout
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Processor performance optimization method based on clock planning deviation algorithm
InactiveCN103324774AHigh frequencySpecial data processing applicationsLayout planningStatic random-access memory
The invention discloses a processor performance optimization method based on the clock planning deviation algorithm, which comprises the following steps: the layout planning phase, the layout phase and the follow-up phase, wherein in the layout planning phase, grouping SRAM (static random access memory) according to the path relation between an SRM (shared resource module) preceding-stage or backward-stage register and multiple SRM; clock deviation planning is performed in the layout phase, and the layout phase is divided into two phases, namely before clock tree synthesis and after clock tree synthesis; before clock tree synthesis, SRAM clock delay is adjusted according to the average surplus capacity between SRAM and multiple paths of the preceding-stage or backward-stage register, and planning the clock jitter of the register by adopting the partial surplus capacity borrowing algorithm; after clock tree synthesis, handling a large number and few time sequence violations respectively by adopting the clock tree algorithm correction and the engineering change; in the follow-up phase, to handle the storage time violation after wiring, the restoring scheme based on distributed multi-scenario time sequence analysis, and combining an ECO (engineering change order) and a script is adopted.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
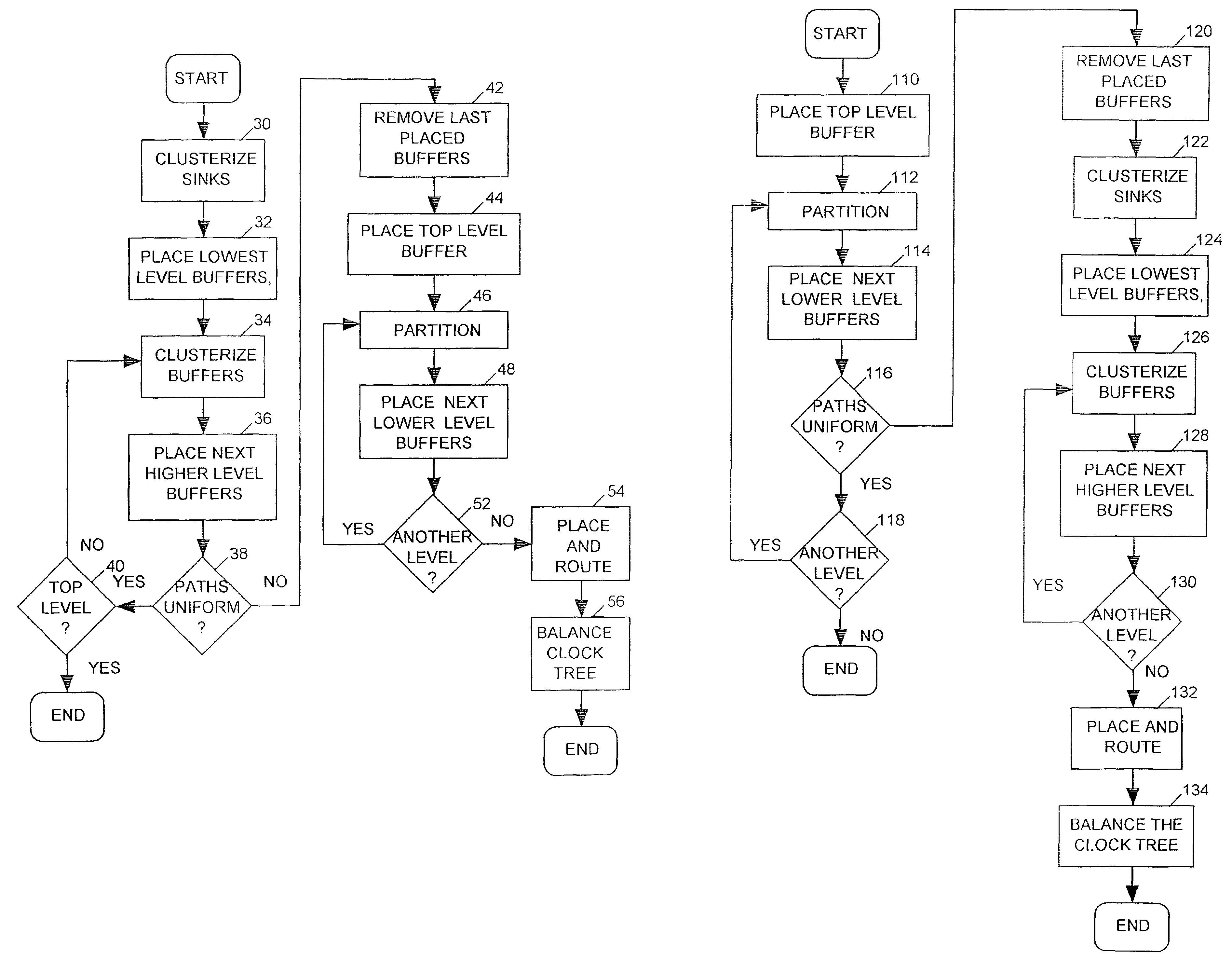
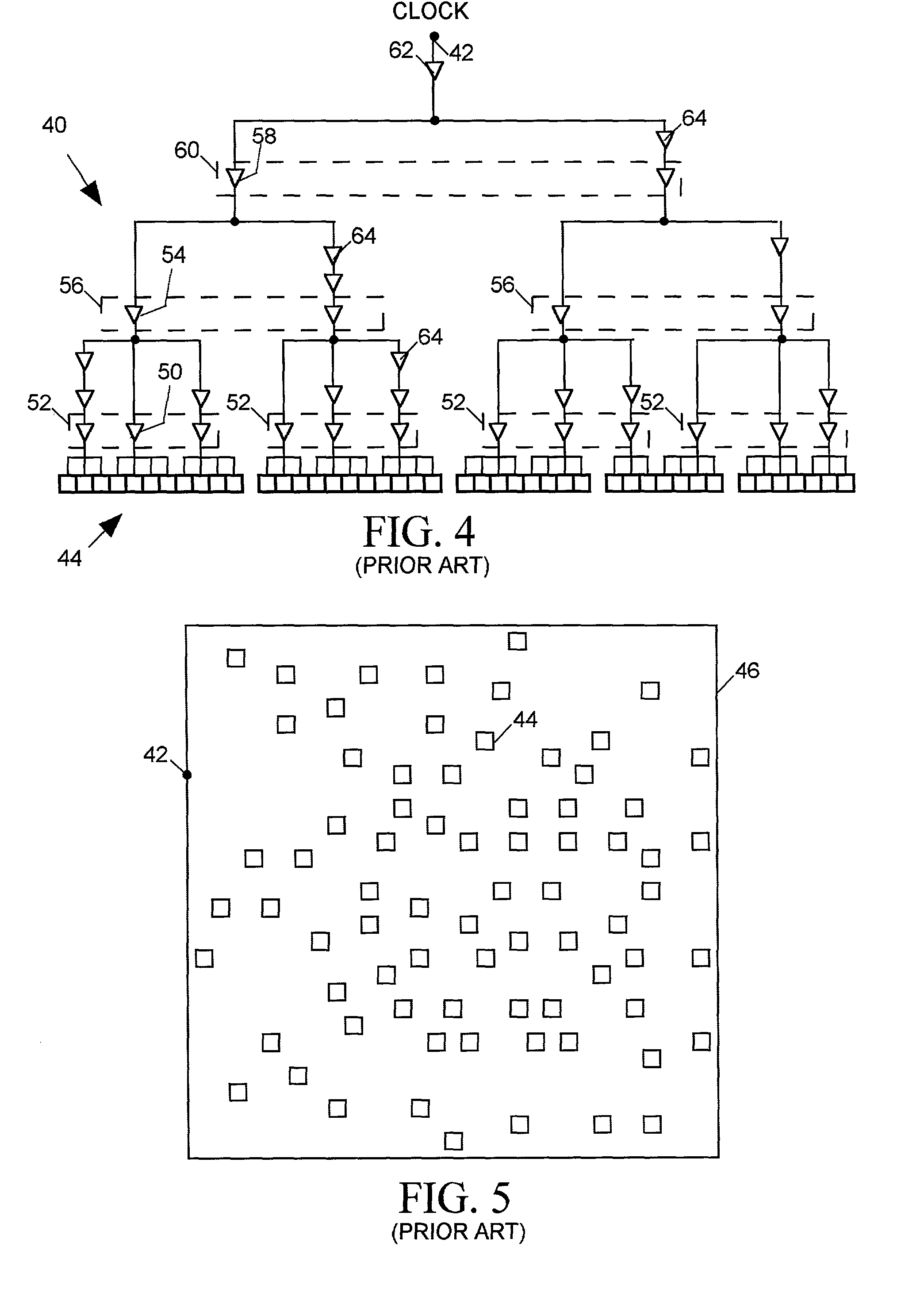
Two-stage clock tree synthesis with buffer distribution balancing
InactiveUS7051310B2Improve uniformityUniform signalElectrical apparatusCAD circuit designParallel computingClock tree synthesis
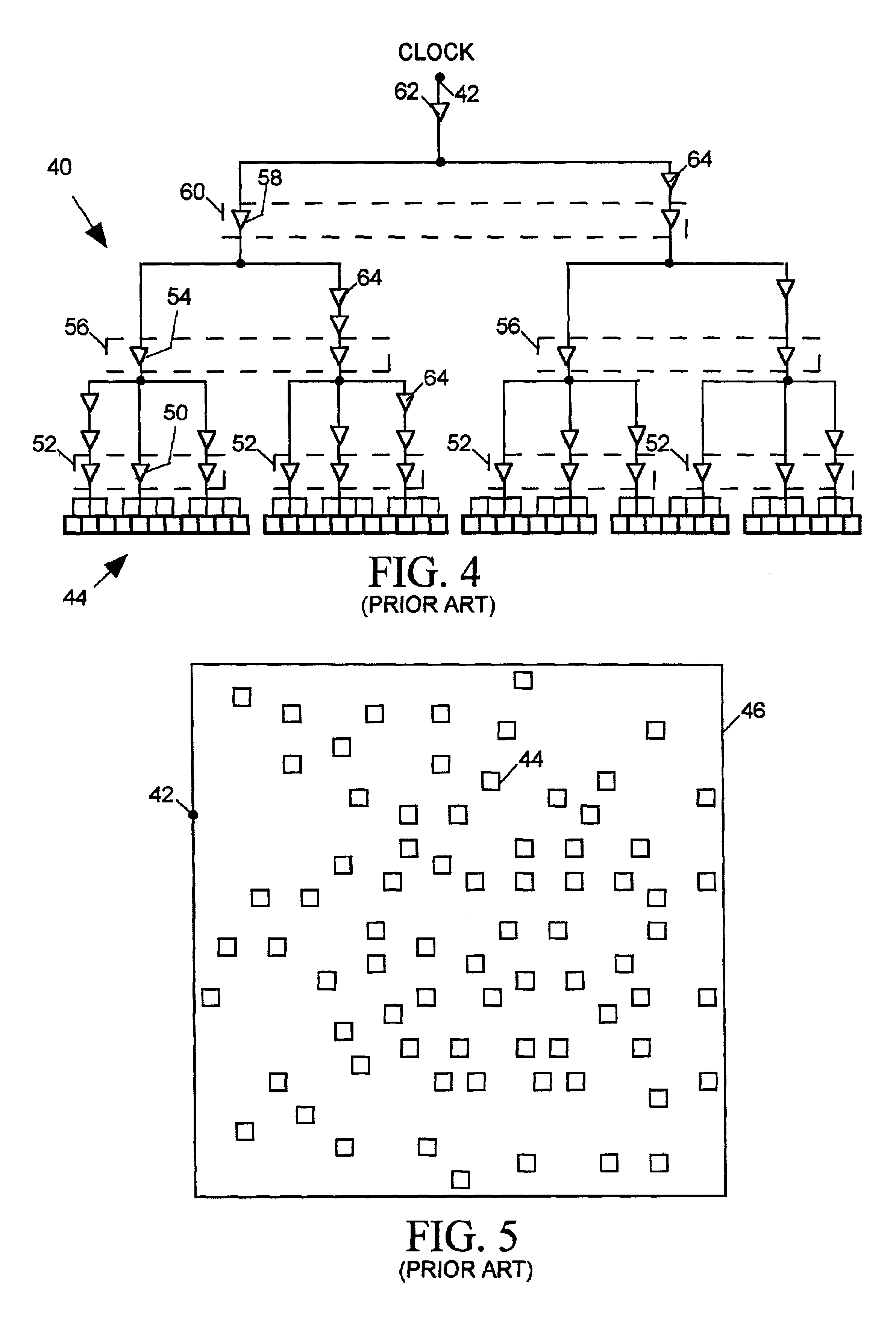
A clock tree synthesis (CTS) tool determines how to position a hierarchy of buffers for fanning out a clock signal to clocked devices (“sinks”) within an integrated circuit (IC). The tool first clusterizes the sinks and places a lowest level fan-out buffer near each cluster. The tool then iteratively places progressively higher level buffers by clusterizing a last-placed buffer level and then placing a next higher level buffer near the centroid of each lower level buffer cluster, until the tool has placed buffers at a mid-level for which variation in path distances between that level and a next higher buffer level exceeds a predetermined limit. The CTS tool then places a top level buffer at the centroid of the mid-level buffers, divides the layout into partitions, each containing a similar number of mid-level buffers, and then places a second-highest level buffer in each partition. The CTS iteratively places each next lower buffer level by dividing each partition into progressively smaller partitions and placing progressively lower level buffers in each smaller partition until it places buffers at a level having sufficient number of buffers to drive the mid-level buffers.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method of clock driven cell placement and clock tree synthesis for integrated circuit design
ActiveUS7039891B2Delay and maximum distanceFunction of delay and maximumComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPropagation delayEngineering
A method of cell placement and clock tree synthesis includes steps of: (a) identifying critical paths in an integrated circuit design; (b) partitioning the integrated circuit design into a timing group for each of the critical paths; (c) assigning each flip-flop in a critical path to a timing group corresponding to the critical path; (d) performing a cell placement to minimize a function of propagation delay and maximum distance between flip-flops within each timing group; and (e) constructing a clock sub-net for each timing group.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Clock tree synthesis for low power consumption and low clock skew
InactiveUS20060053395A1Reduce power consumptionReduces clock skew of clock skewPower supply for data processingCAD circuit designSynthesis methodsClock tree synthesis
A method for low power clock tree synthesis using buffer insertion, removal and resizing for high-speed VLSI design is proposed. The developed tool can be embedded in the existing clock tree synthesis design flow to ensure satisfying both the specifying database constrains and the clock skew constrains. For a given clock tree netlist, the location information of buffers, the parameters of wires and the buffers' timing and power library are all included. The buffer delay and wire delay of the clock tree are calculated first. Then the feasible solution is solved if the input netlist is not feasible for the given constrains. Finally, a modified low power clock tree netlist, which satisfies the timing specifications, is obtained using our proposed method.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
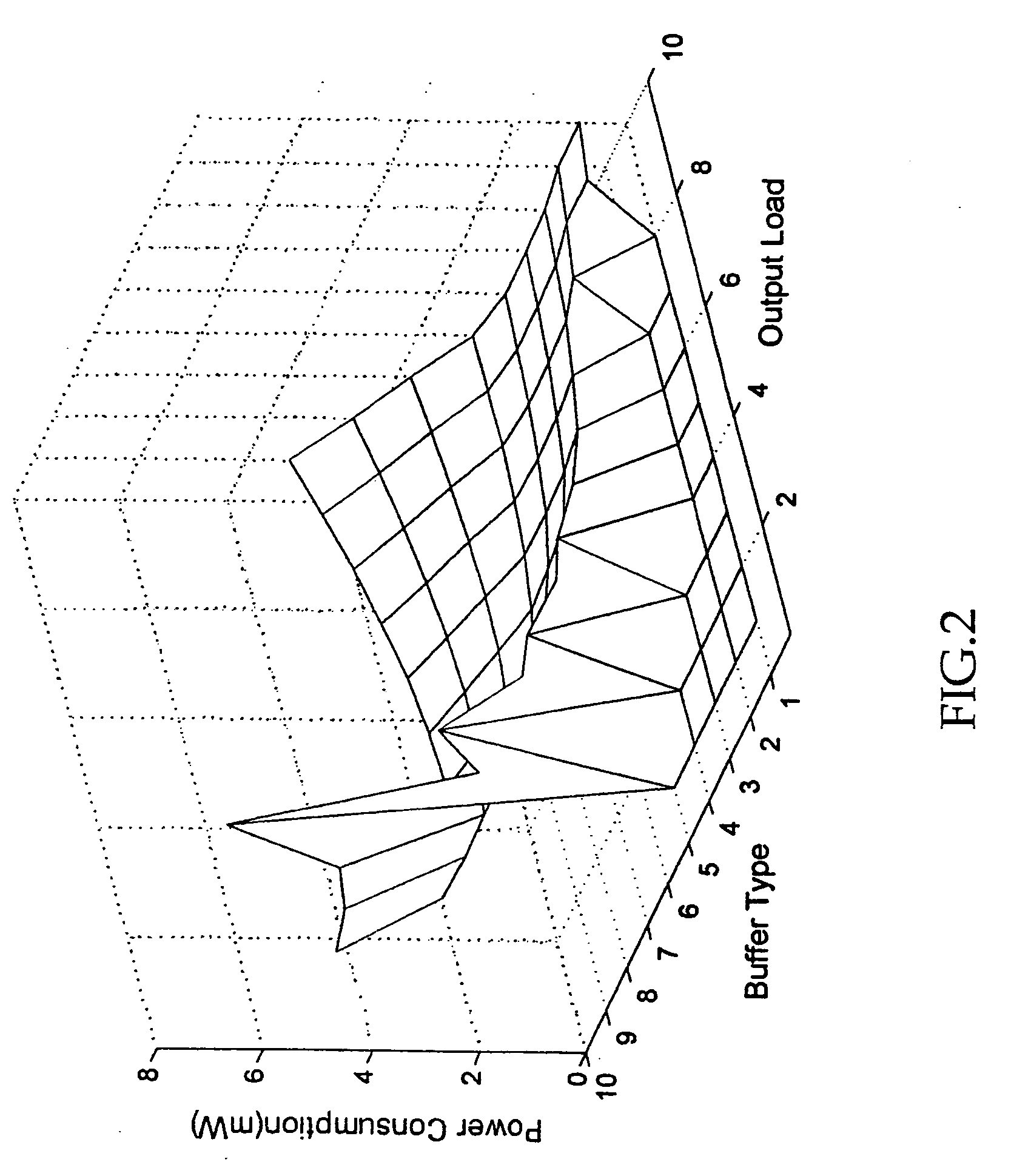
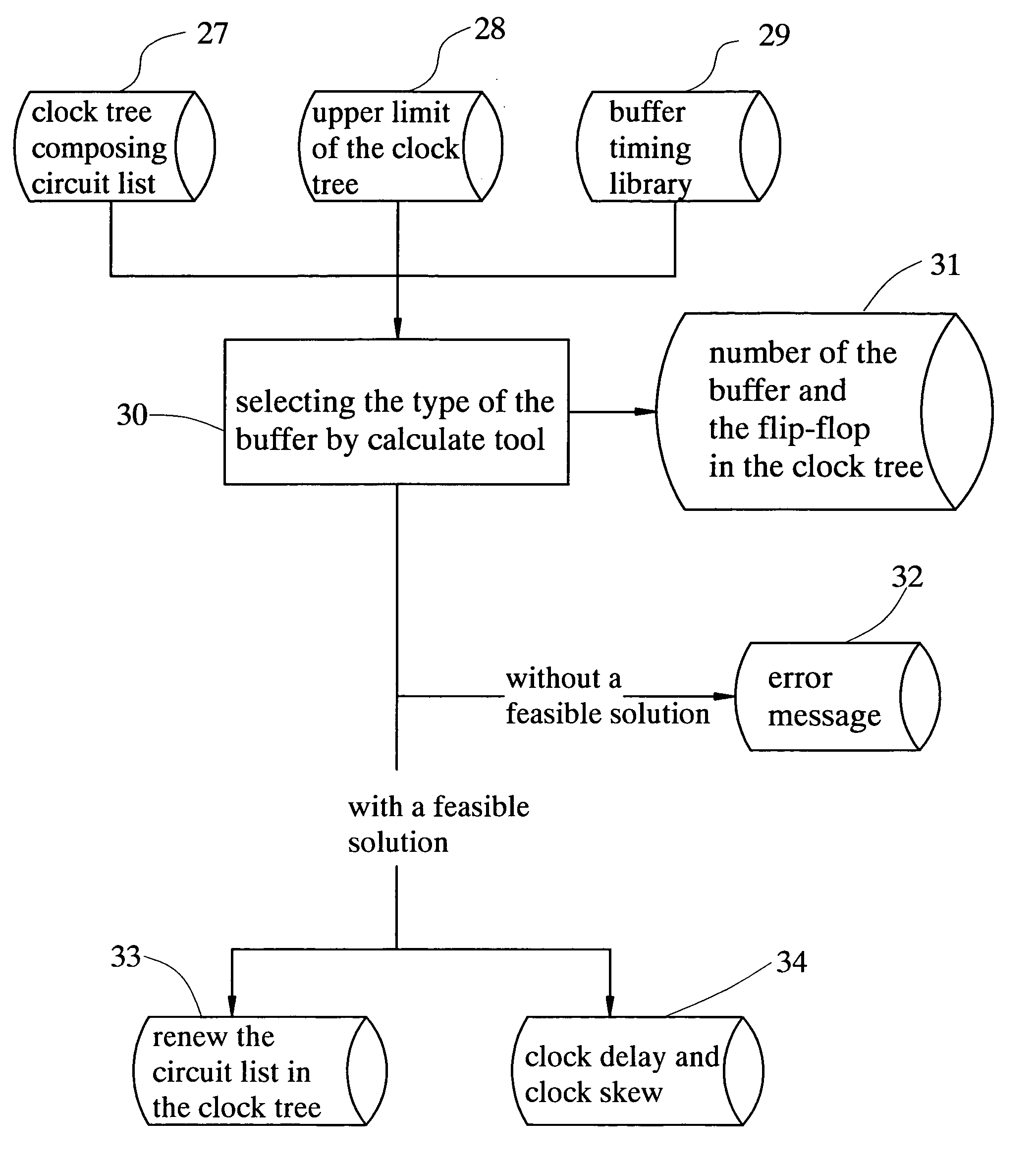
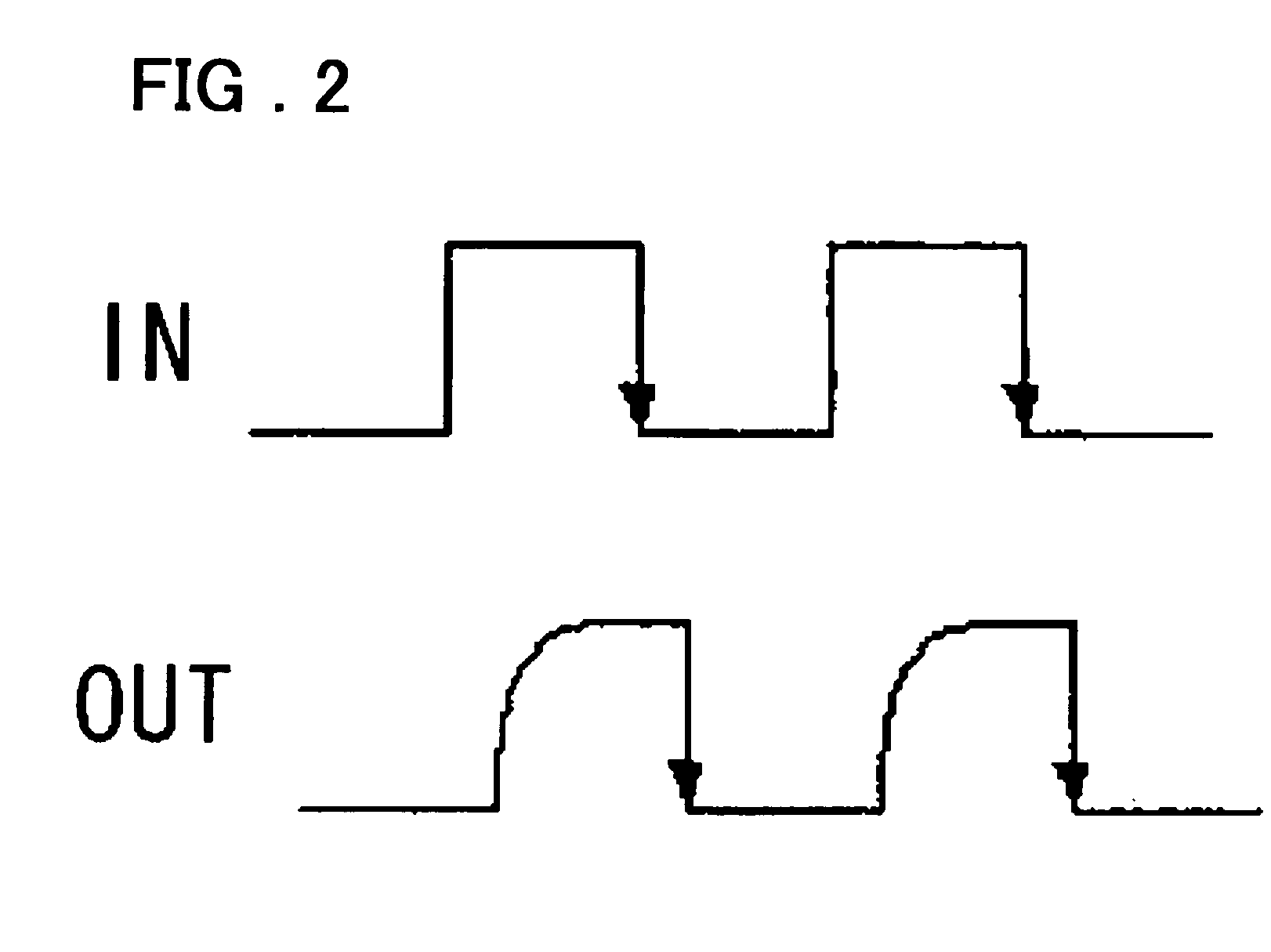
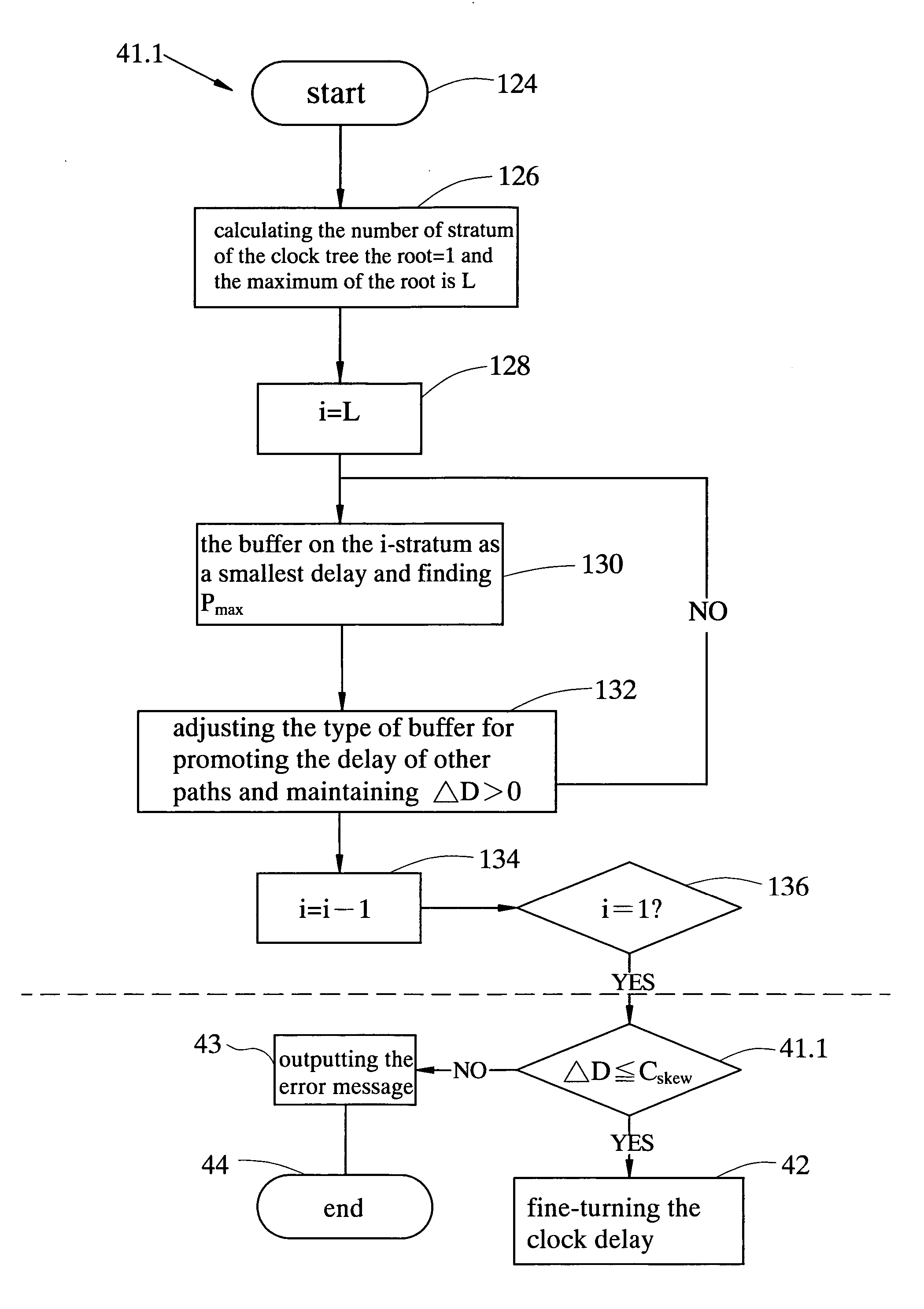
Method and apparatus for rapidly selecting types of buffers which are inserted into the clock tree for high-speed very-large-scale-integration
InactiveUS7191418B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityClock tree synthesis
A method and apparatus for rapidly selecting types of buffers which are inserted in the clock tree for high-speed VLSI design is disclosed. The developed tool can be embedded in the existing clock tree synthesis design flow to ensure minimizing the clock delay and satisfying the clock skew constrains. Given the clock tree netlist, the inserted buffers location information, the wire electrical parameters and a buffers timing library, the components delay (buffer delay and wire delay) of the clock tree can be calculated first. Then, for each I / O pin, the path delay, the clock delay and the clock skew can be obtained. Finally, using the method, a modified clock tree netlist satisfying the timing specifications can be constructed.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
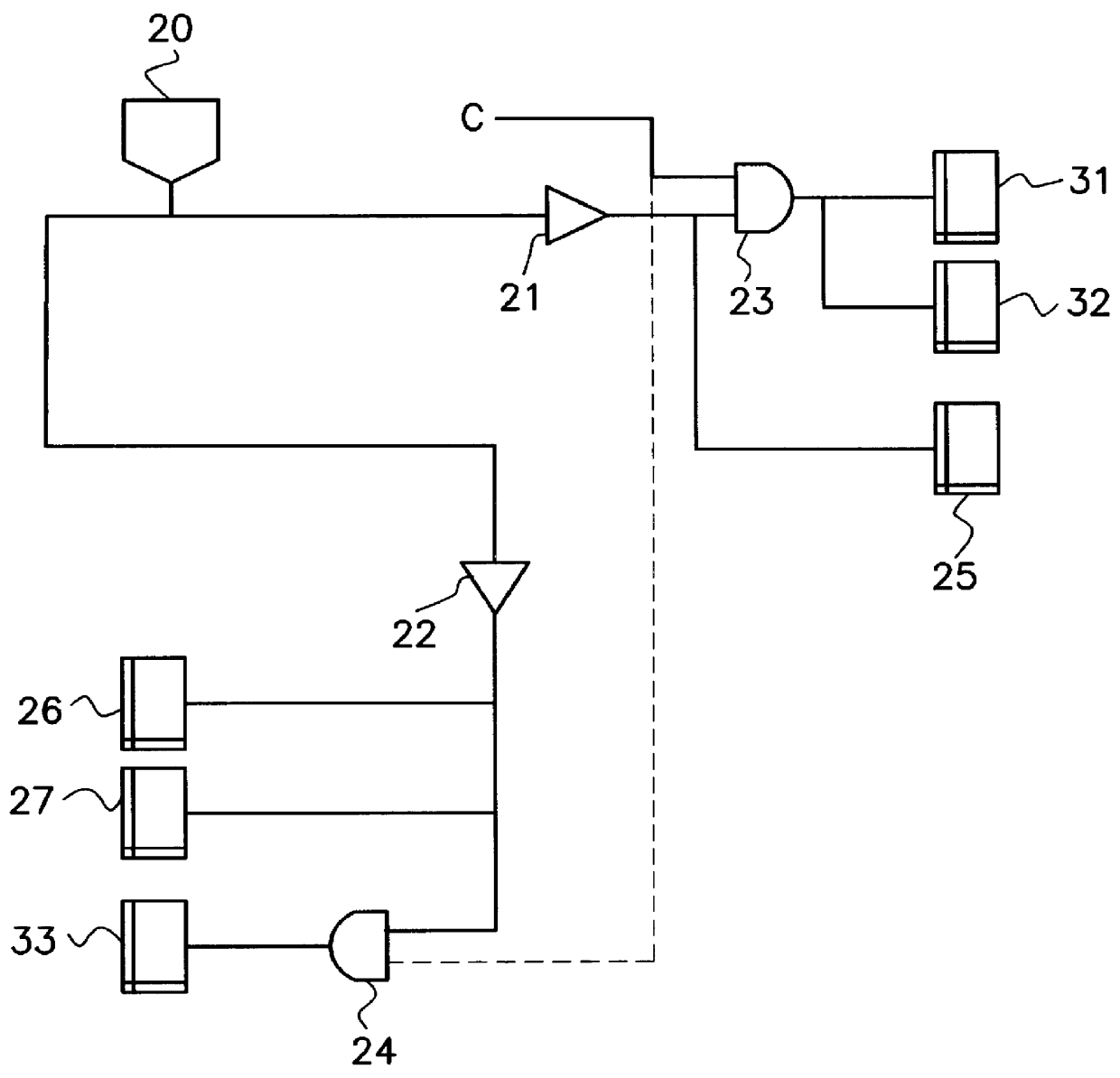
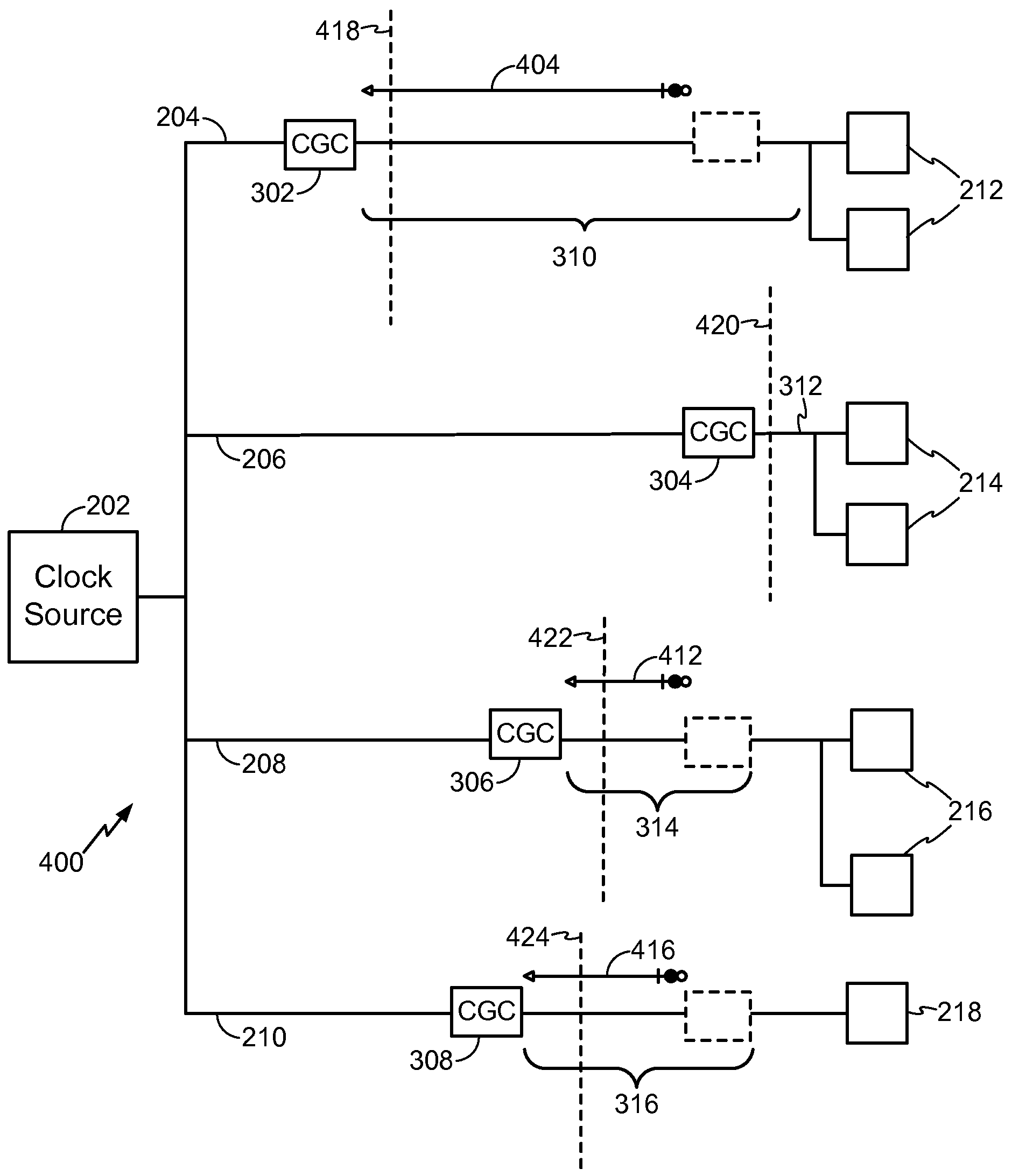
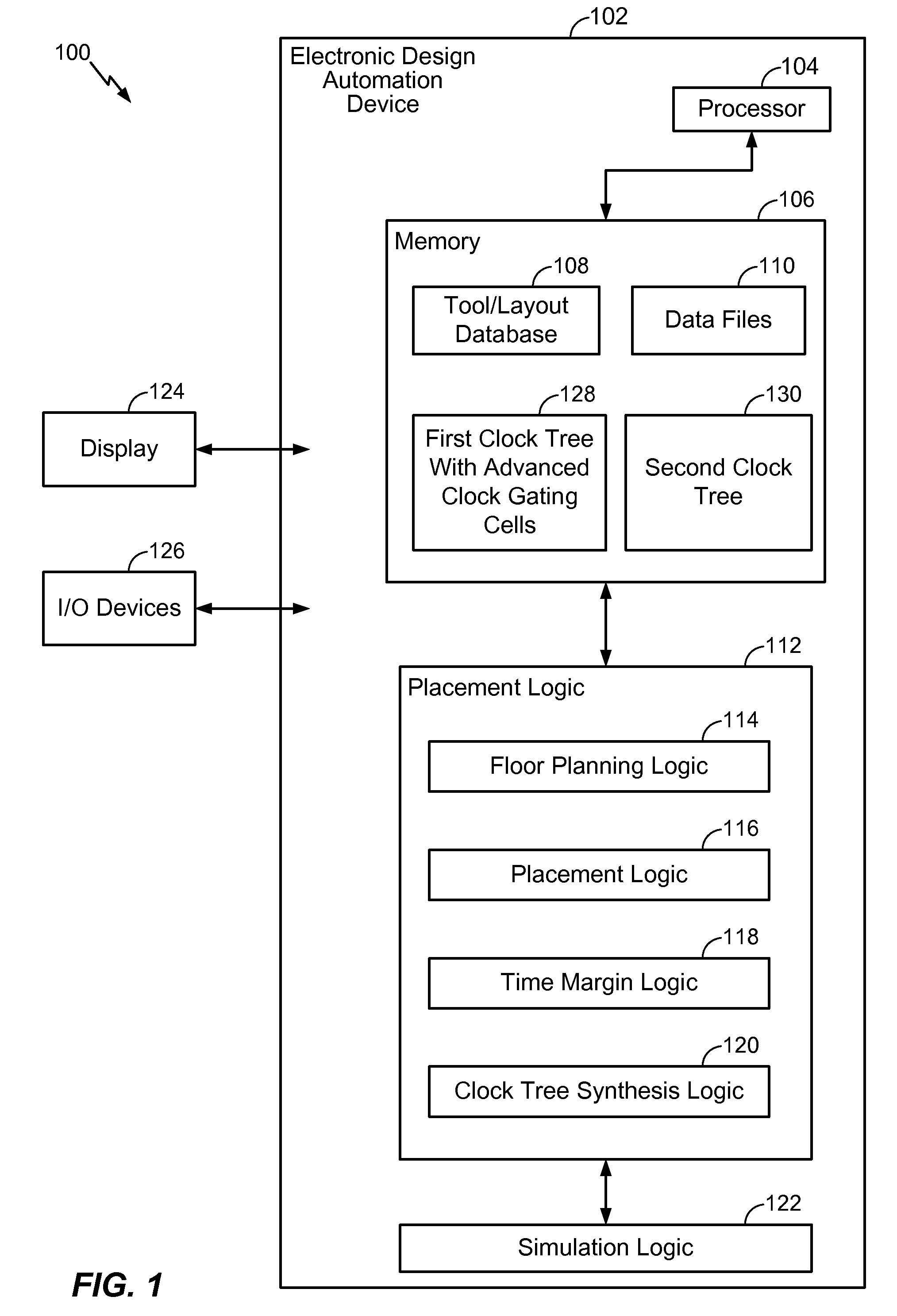
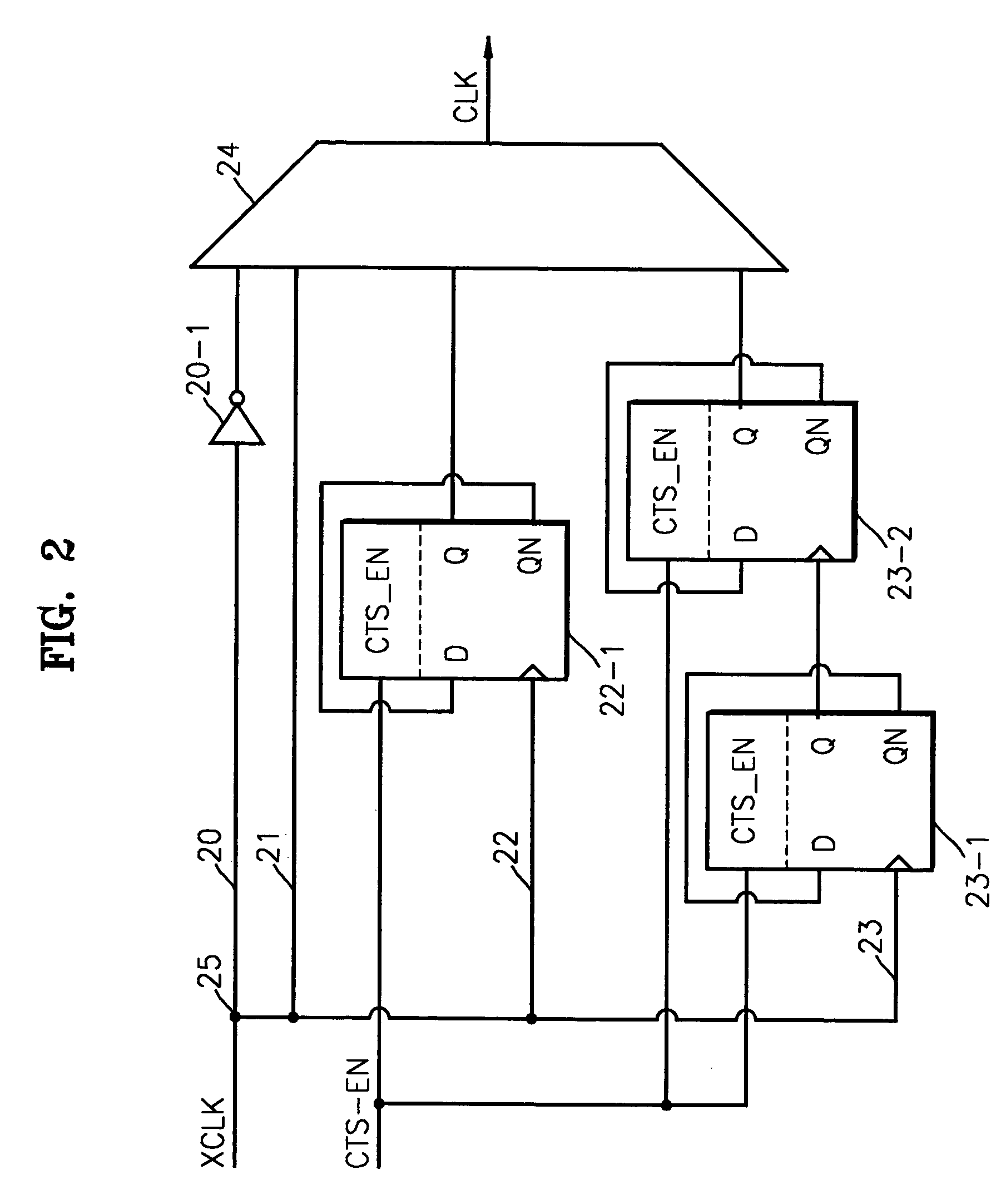
System and Method of Clock Tree Synthesis
ActiveUS20100231282A1Save powerSynchronisation information channelsElectric pulse generatorTiming marginClock tree synthesis
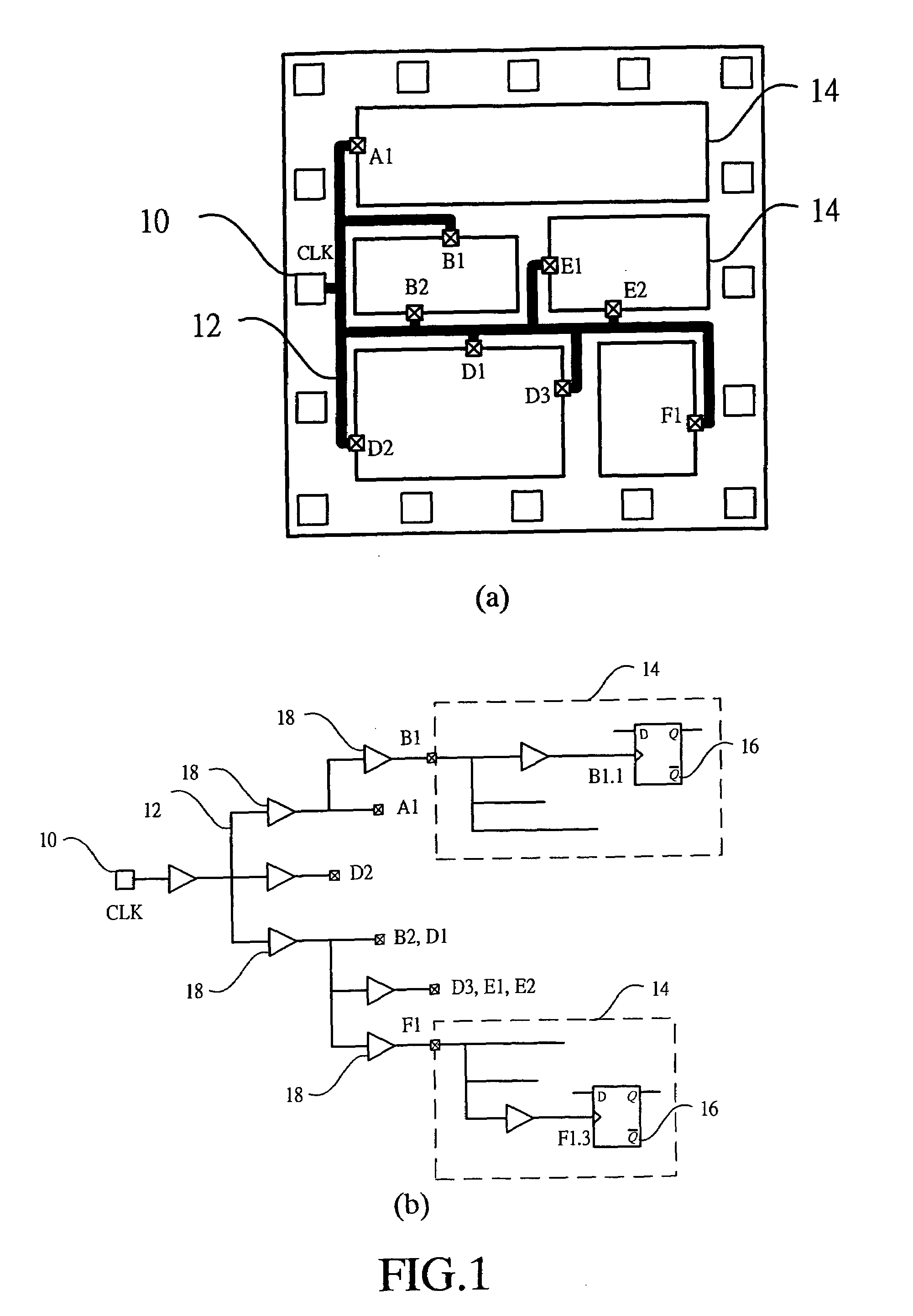
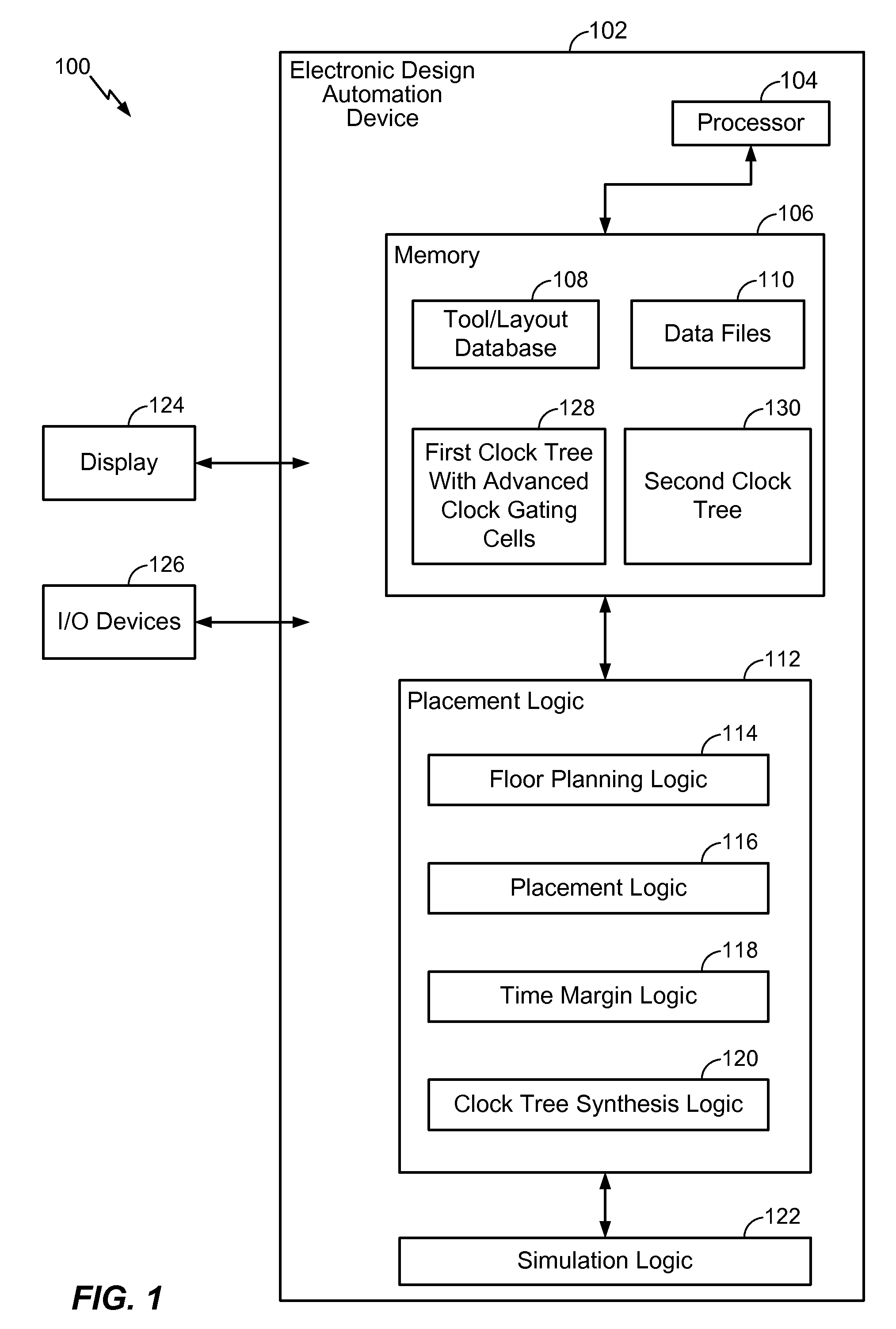
In a particular embodiment, a method of generating an advanced gating cell clock tree includes determining a timing margin for a path between a clock gating cell and a digital data storage element such as a latch or flip flop. The circuit contains a clock source and when the timing margin for the path meets a predetermined threshold, the clock gating cell is automatically moved closer to the clock source. In a particular embodiment, the timing margin is automatically determined. A clock tree synthesis is performed to insert one or more buffers into the path and create an advanced gating cell clock tree.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Logic synthesis device and logic synthesis method
InactiveUS6910202B2Unnecessary loadUnnecessary load can be avoidedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer aided designSynthesis methodsTheoretical computer science
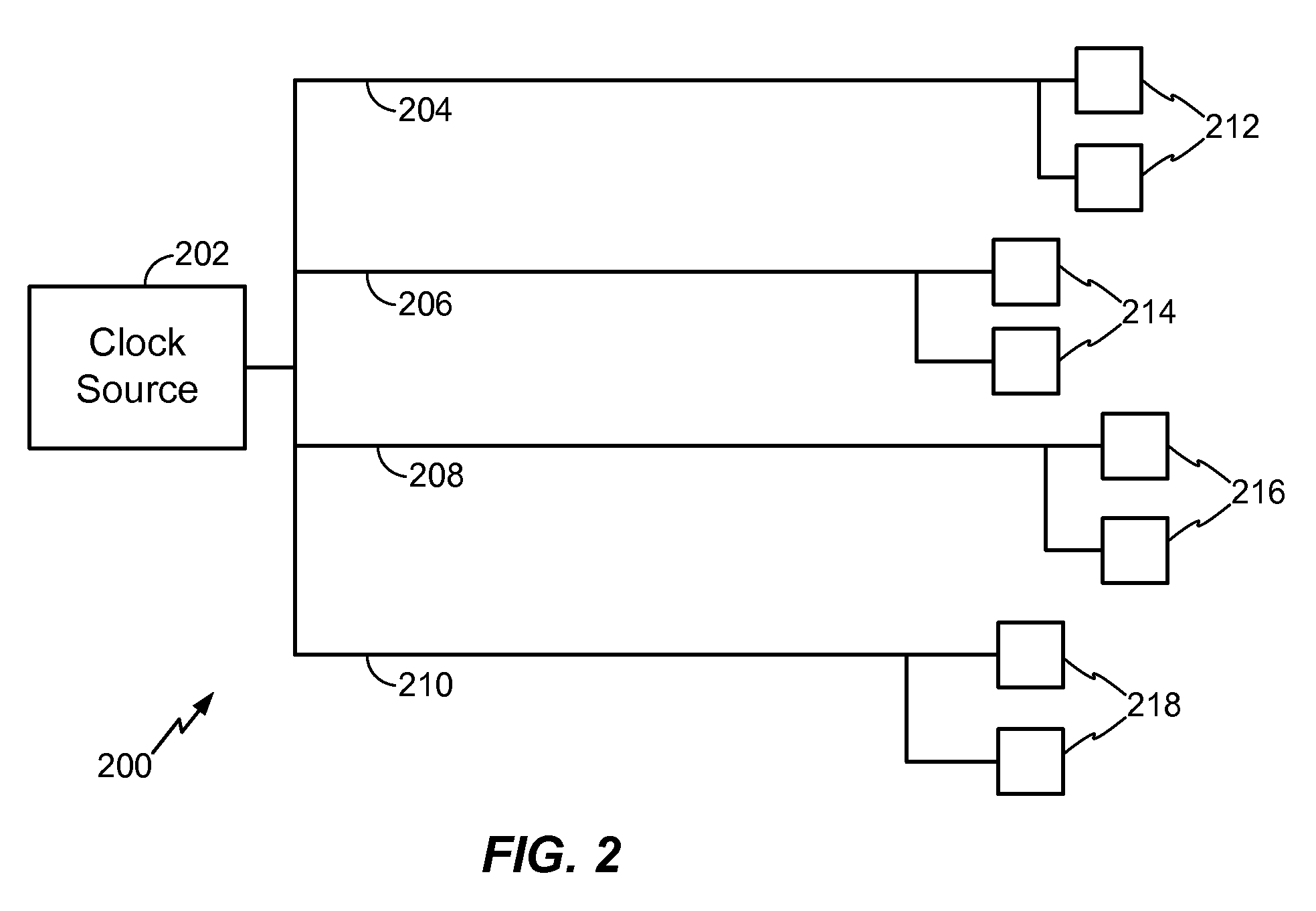
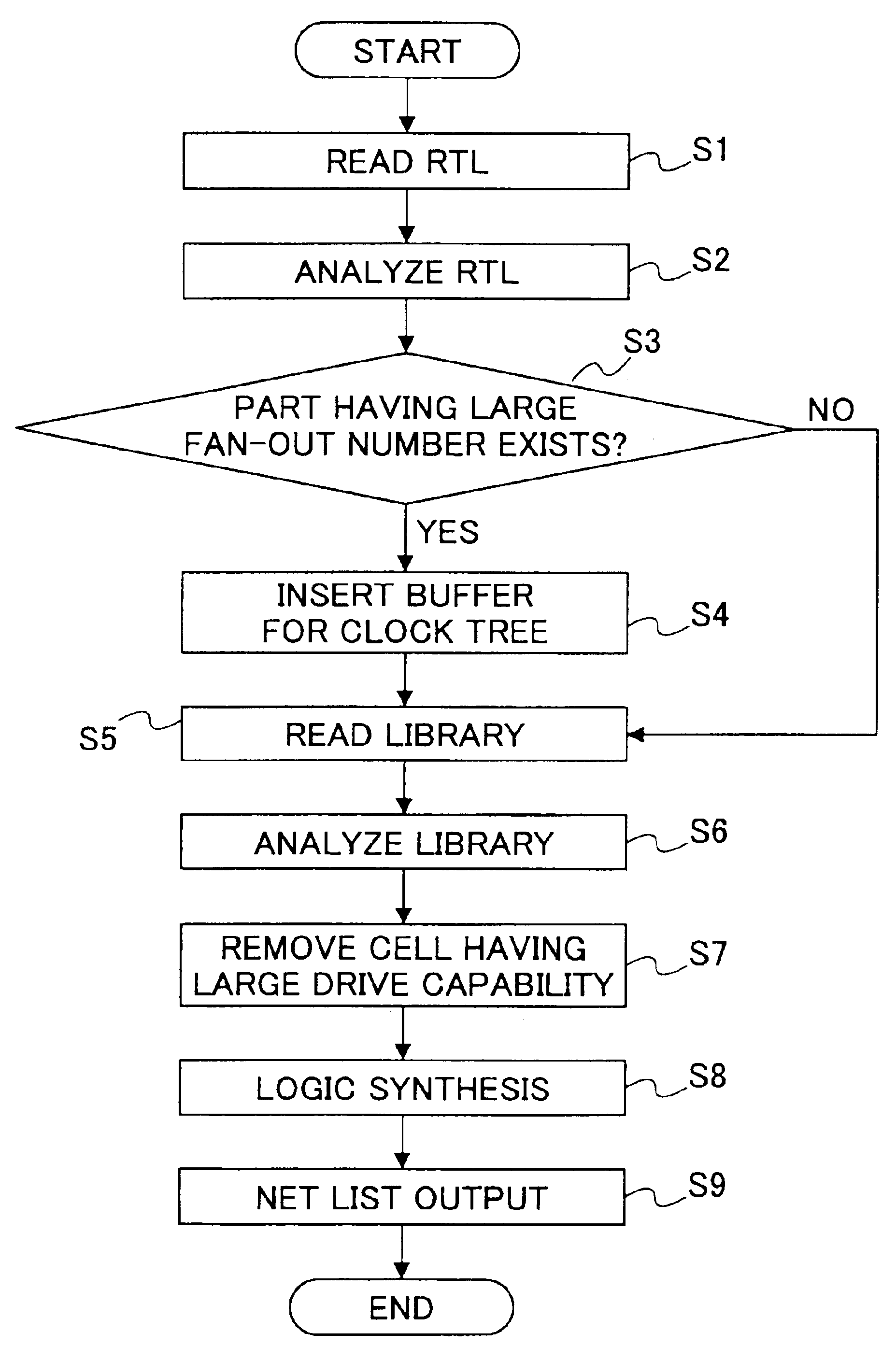
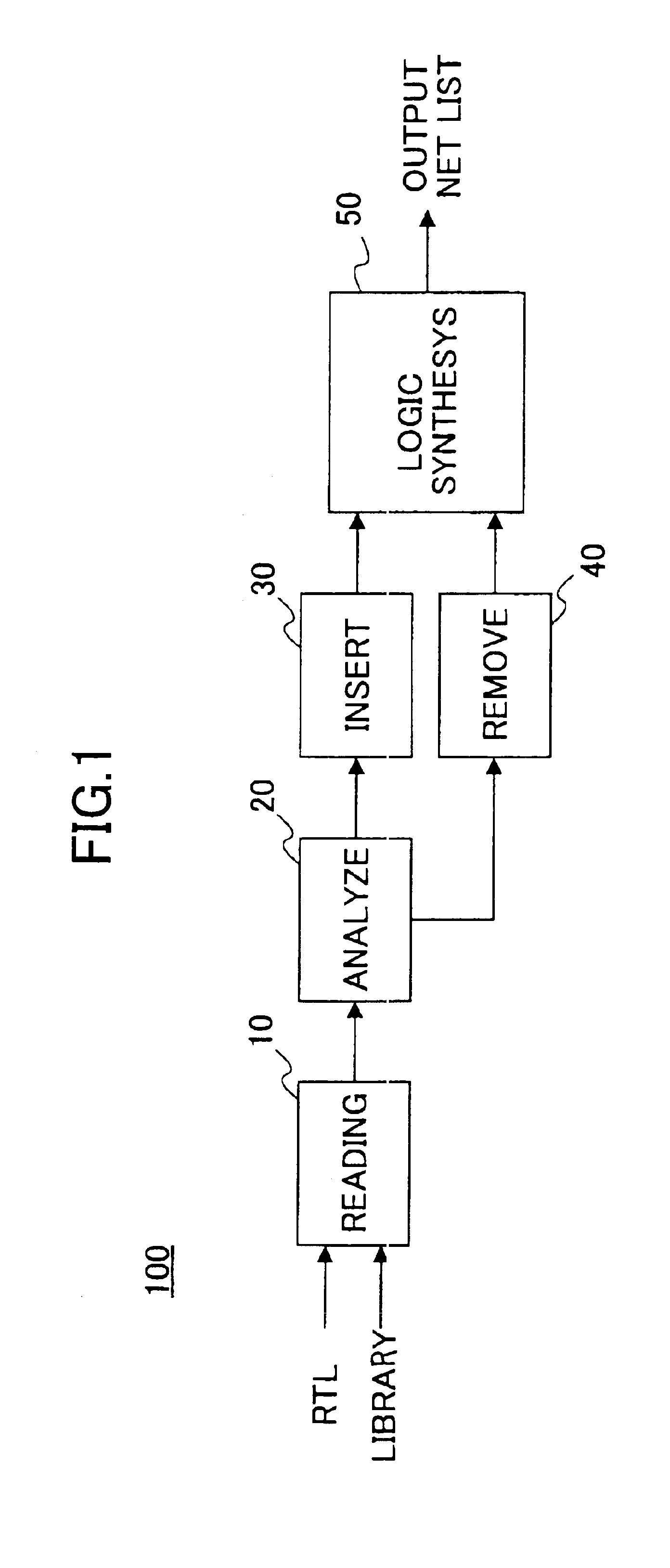
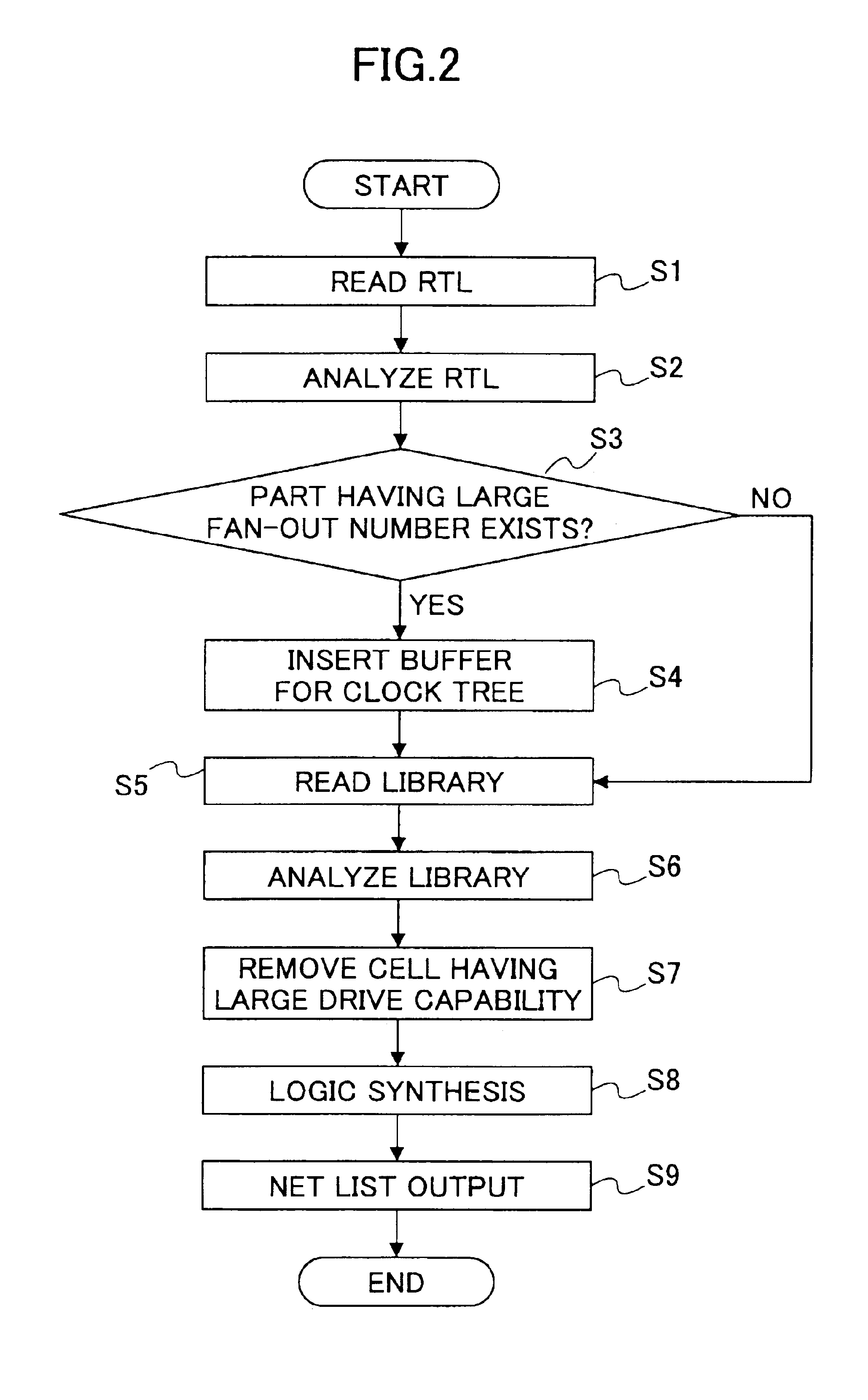
An analysis part analyzes a description of a logic design; an extraction part extracts a part of the description of the logic design having a fan-out number beyond a predetermined value, based on the analysis; an insertion part inserts a buffer for clock tree synthesis for performing an adjustment on the part extracted by said extracting part, the adjustment being performed at a time of subsequent layout process; and a logic synthesis part performs logic synthesis on the description of the logic design obtained after the insertion performed by said inserting part.
Owner:RICOH KK
Clock tree synthesis for low power consumption and low clock skew
InactiveUS7216322B2Reduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingCAD circuit designSynthesis methodsClock tree synthesis
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
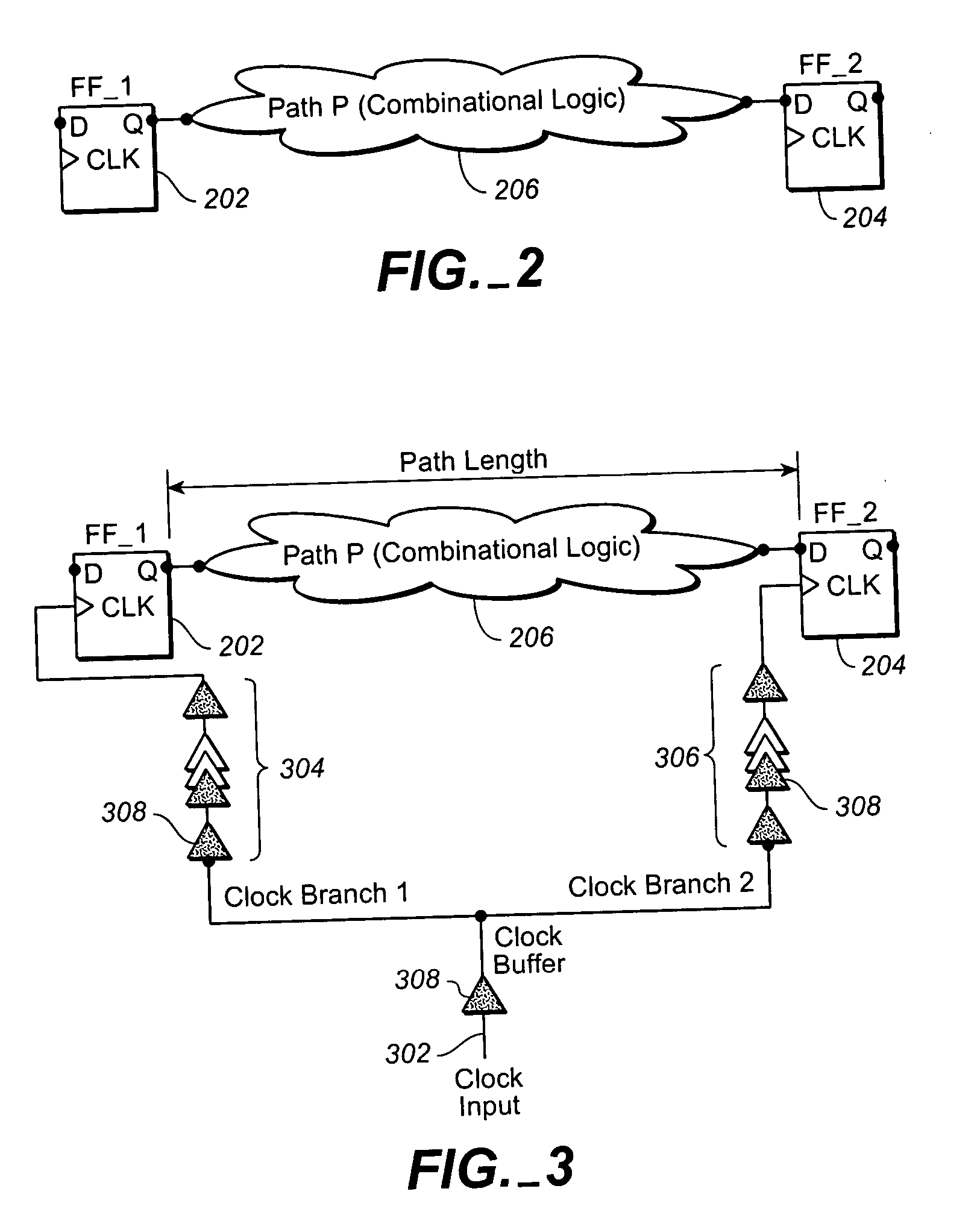
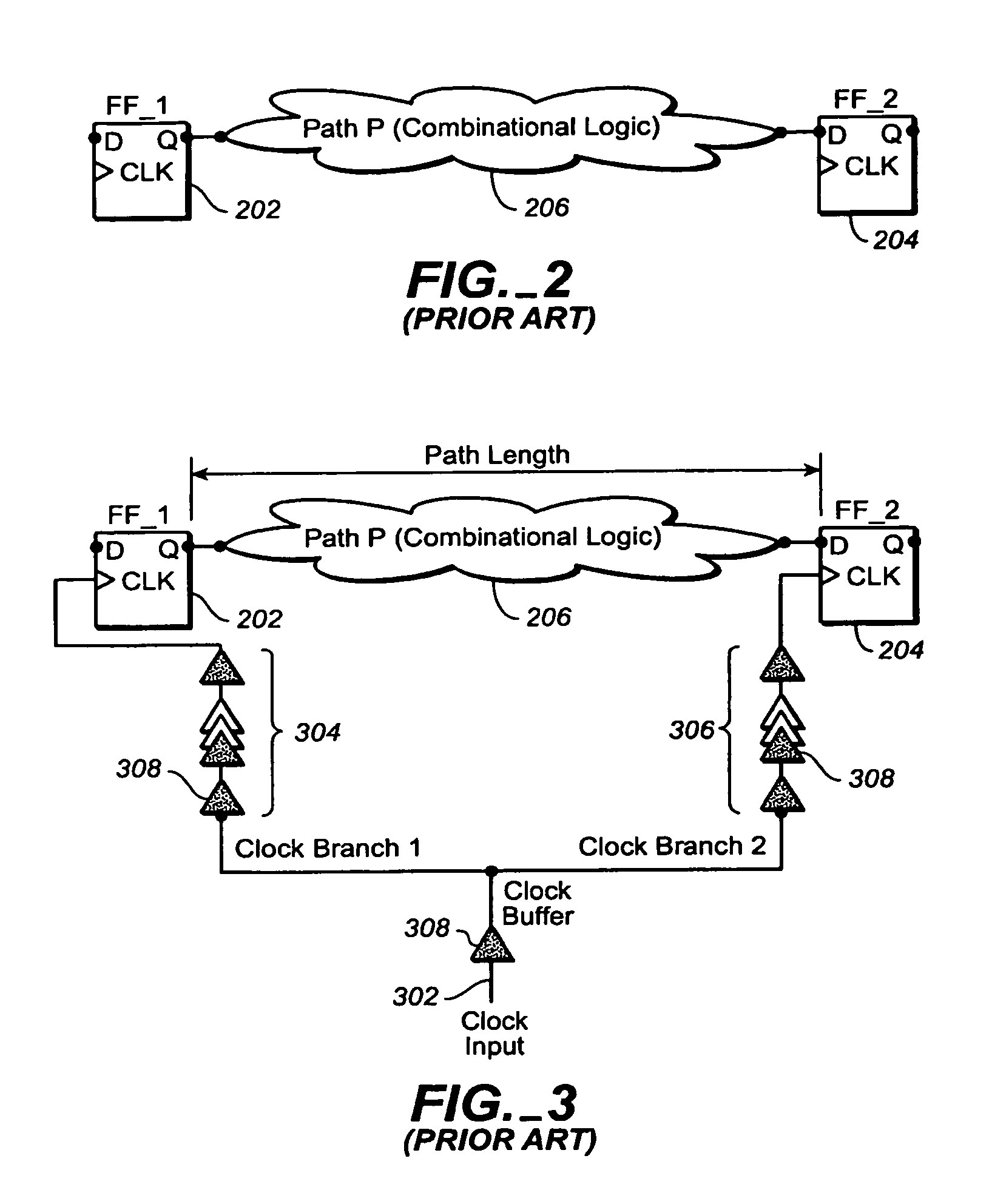
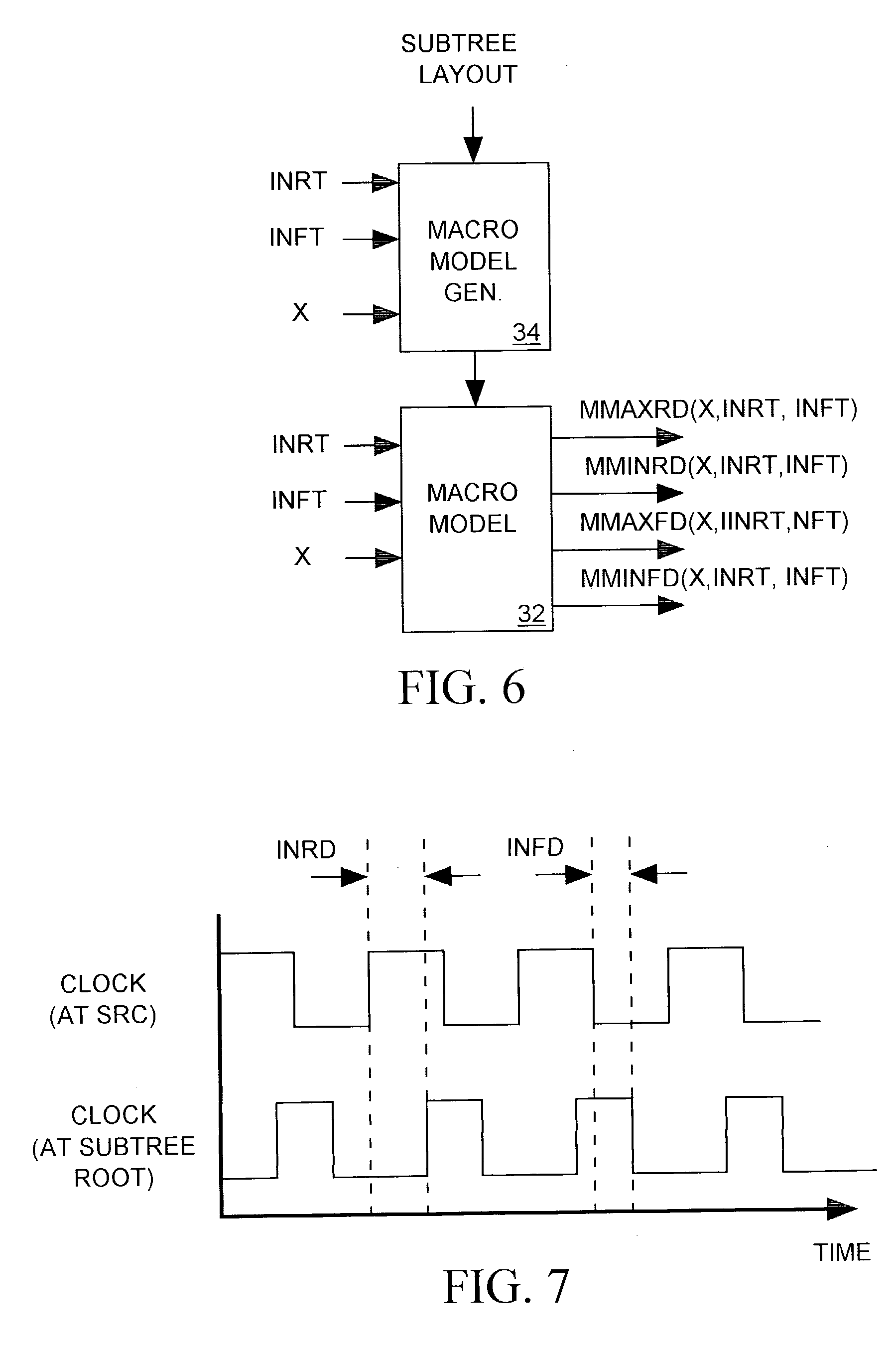
Method for analyzing path delays in an IC clock tree
ActiveUS6981233B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationClock tree synthesisTransition time
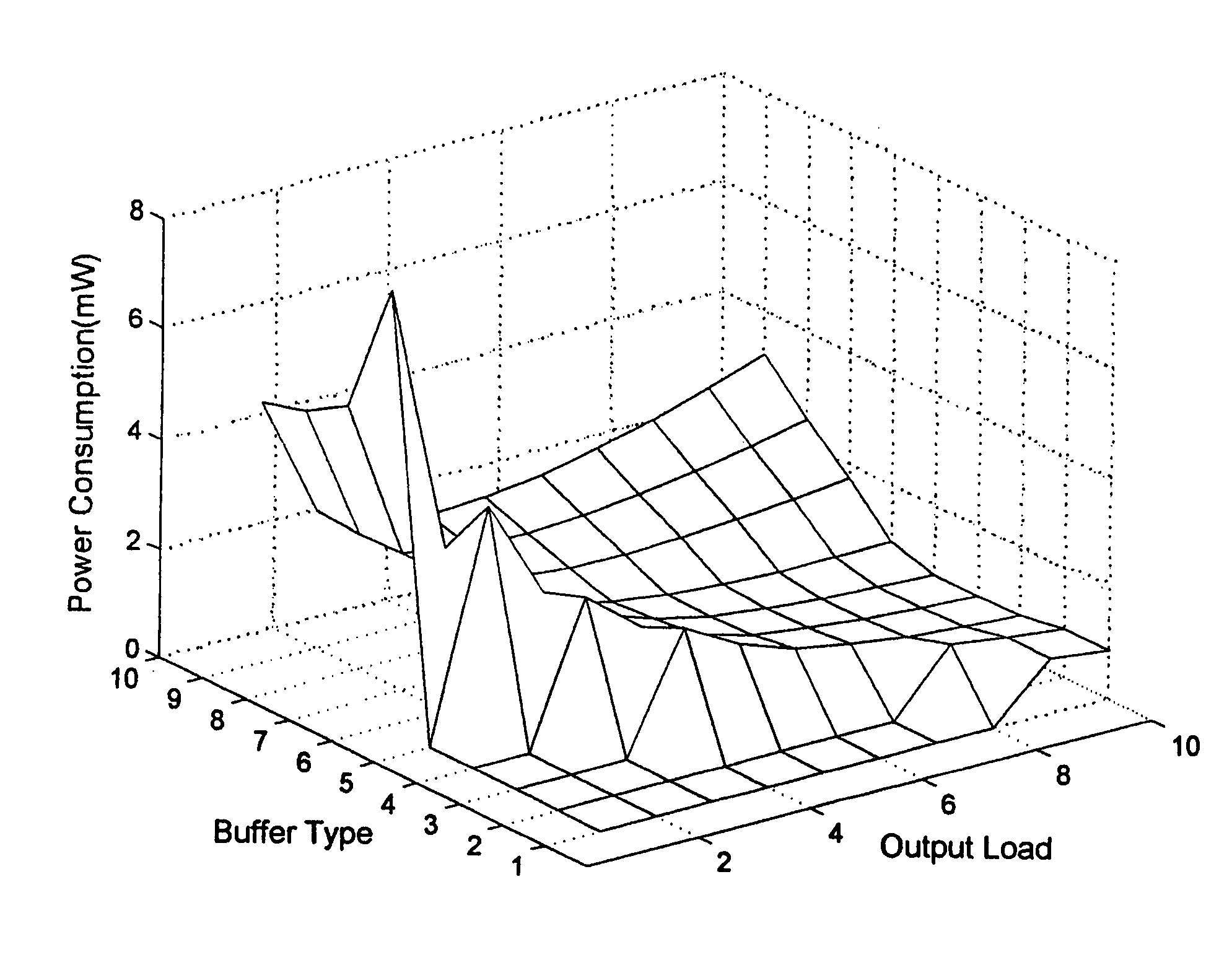
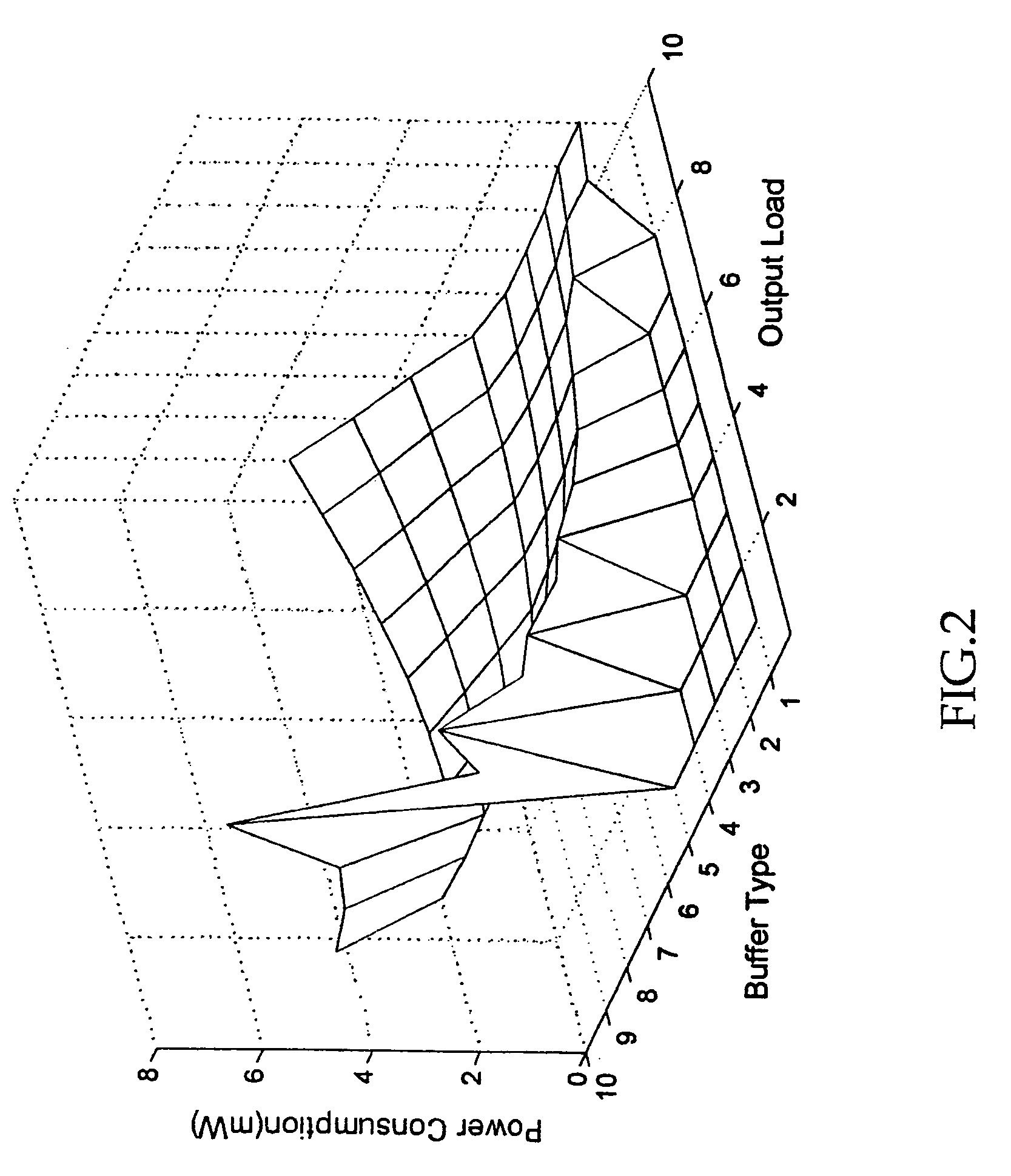
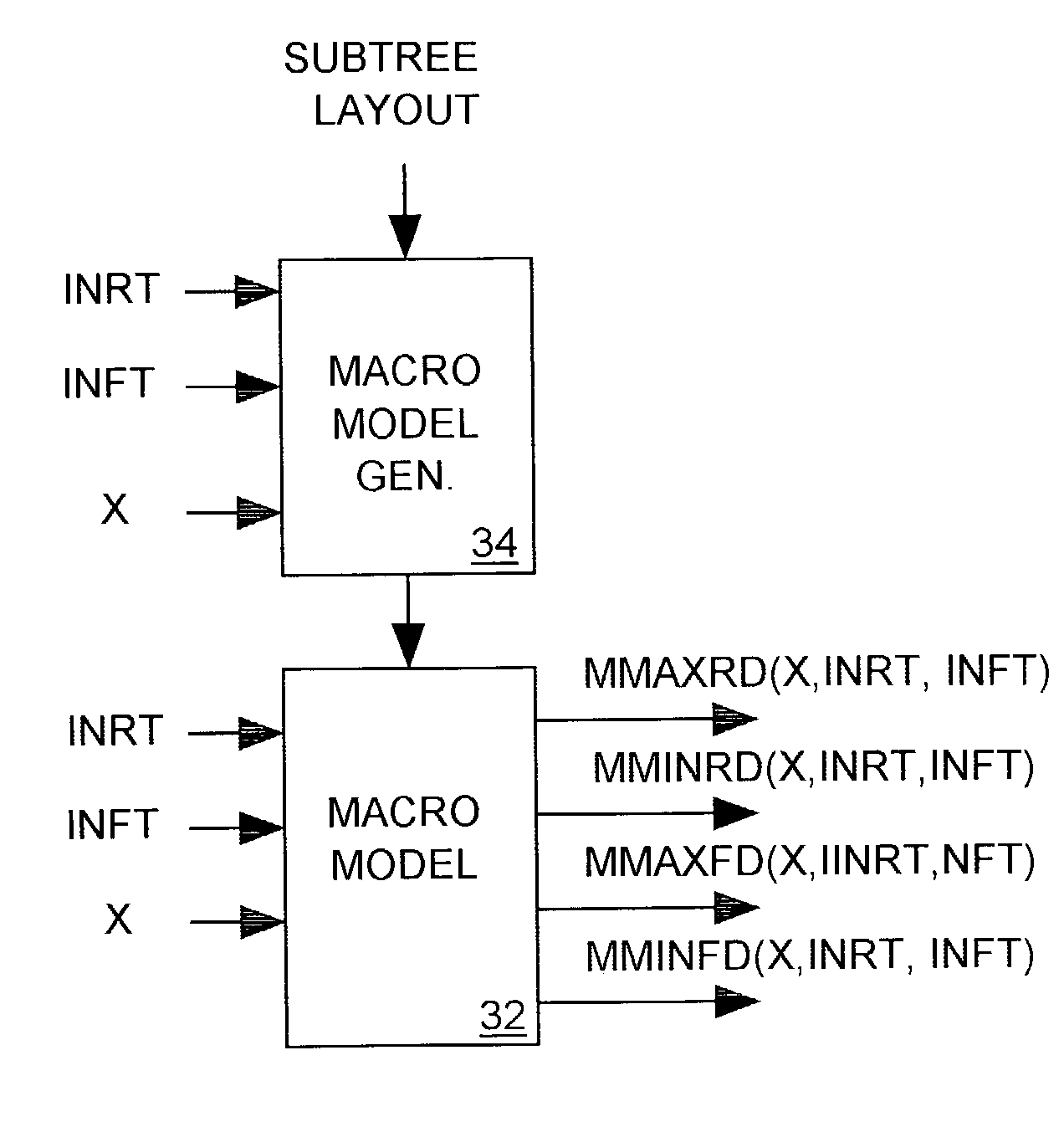
A macro-cell is incorporated into an integrated circuit (IC) design to describe a fixed arrangement of cells to be included in the IC. The IC includes a clock tree for delivering a clock signal from its root to all clocked devices (sinks) within the IC external to the macro-cell, and to a root of a clock tree subtree included within the macro-cell for delivering the clock signal from its root to sinks residing within the macro-cell. A model of the subtree depicts the maximum and minimum delays of the clock signal's rising and falling edges between the subtree root and the sinks within the macro-cell as functions of the clock signal's rising and falling edge transition times as they arrives at the subtree root and also as functions of the relative amount of delay the rising and falling edges experience as they pass from the clock tree root to the subtree root. A clock tree synthesis tool uses the subtree model to determine the maximum and minimum rising and falling edge path delays though the subtree when estimating the maximum and minimum amounts by which the clock tree delays the clock signal's rising and falling edges as they pass from the clock tree root to any sink of the IC.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
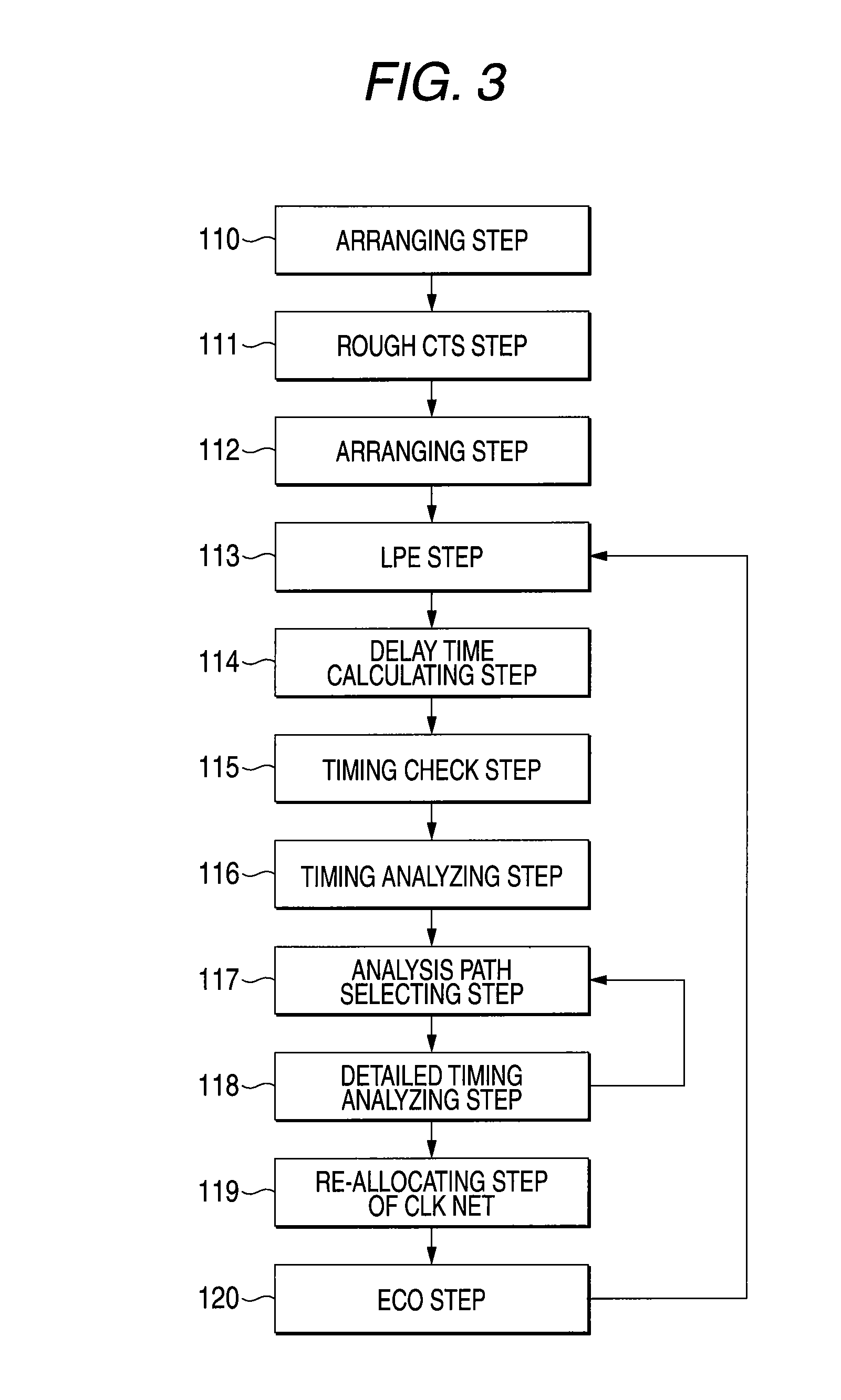
Semiconductor device and method of designing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080129362A1Run at high speedReduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorGenerating/distributing signalsPropagation timeClock tree synthesis
A semiconductor device designing method of the present invention corresponds to a method for designing a clock synthesization type semiconductor device, which is comprised of: a rough CTS (clock tree synthesis) step for performing the CTS within an adjustable range in multiple phases; a timing check step for judging whether or not transmission / reception of data are carried out under normal condition based upon a propagation time of data and an arrival time of a clock signal between flip-flops; a detailed timing analyzing step for judging whether or not the transmission / reception of the data can be carried out under the normal condition by switching a phase of a clock signal, or by increasing / decreasing a buffer in a half way of the clock tree as to supply timing of the clock signal; and a re-allocating step of a CLK net, for allocating a phase of such a clock signal which does not cause a timing violation every flip-flop based upon the result of the detailed timing analyzing step.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
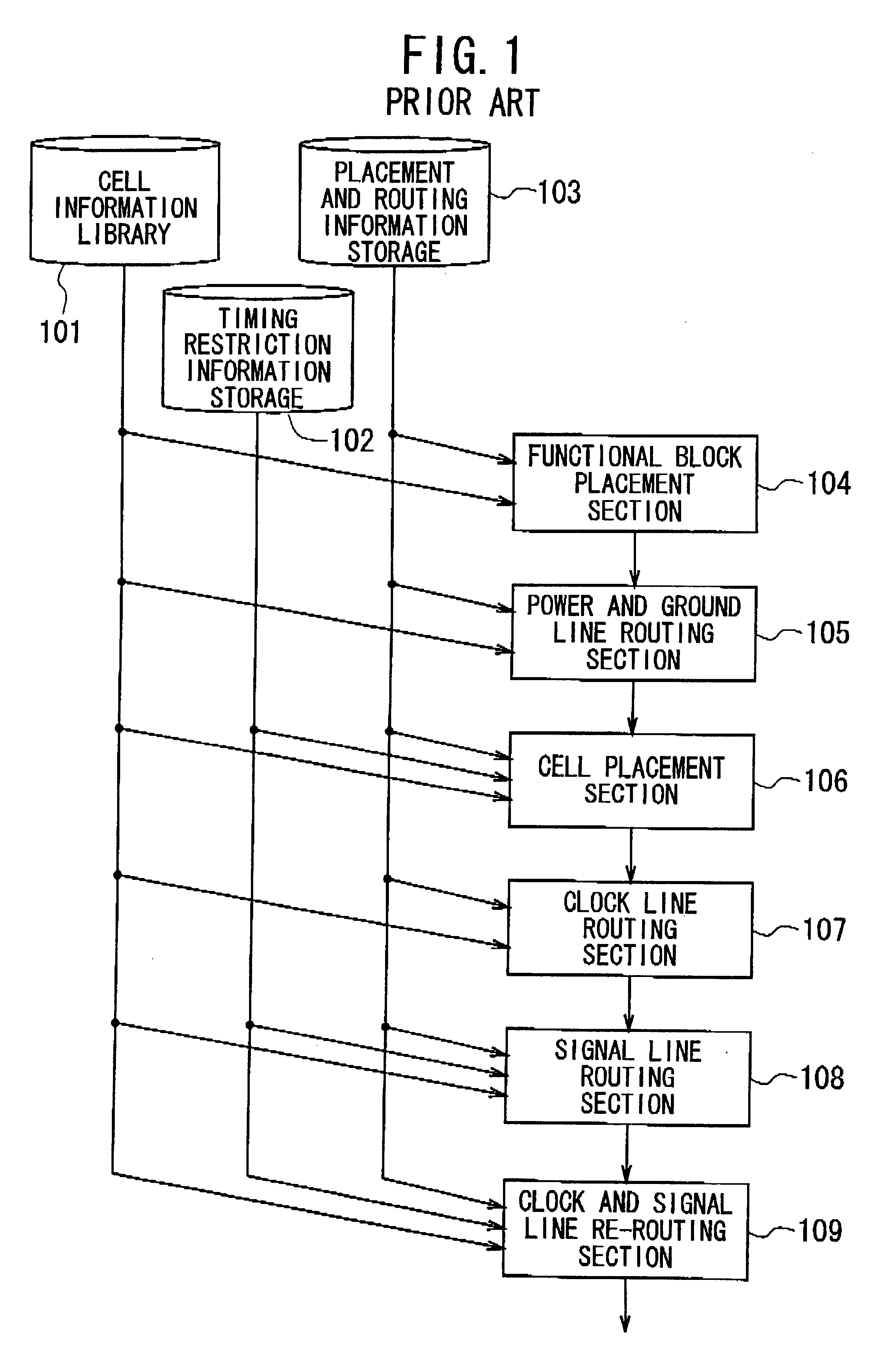
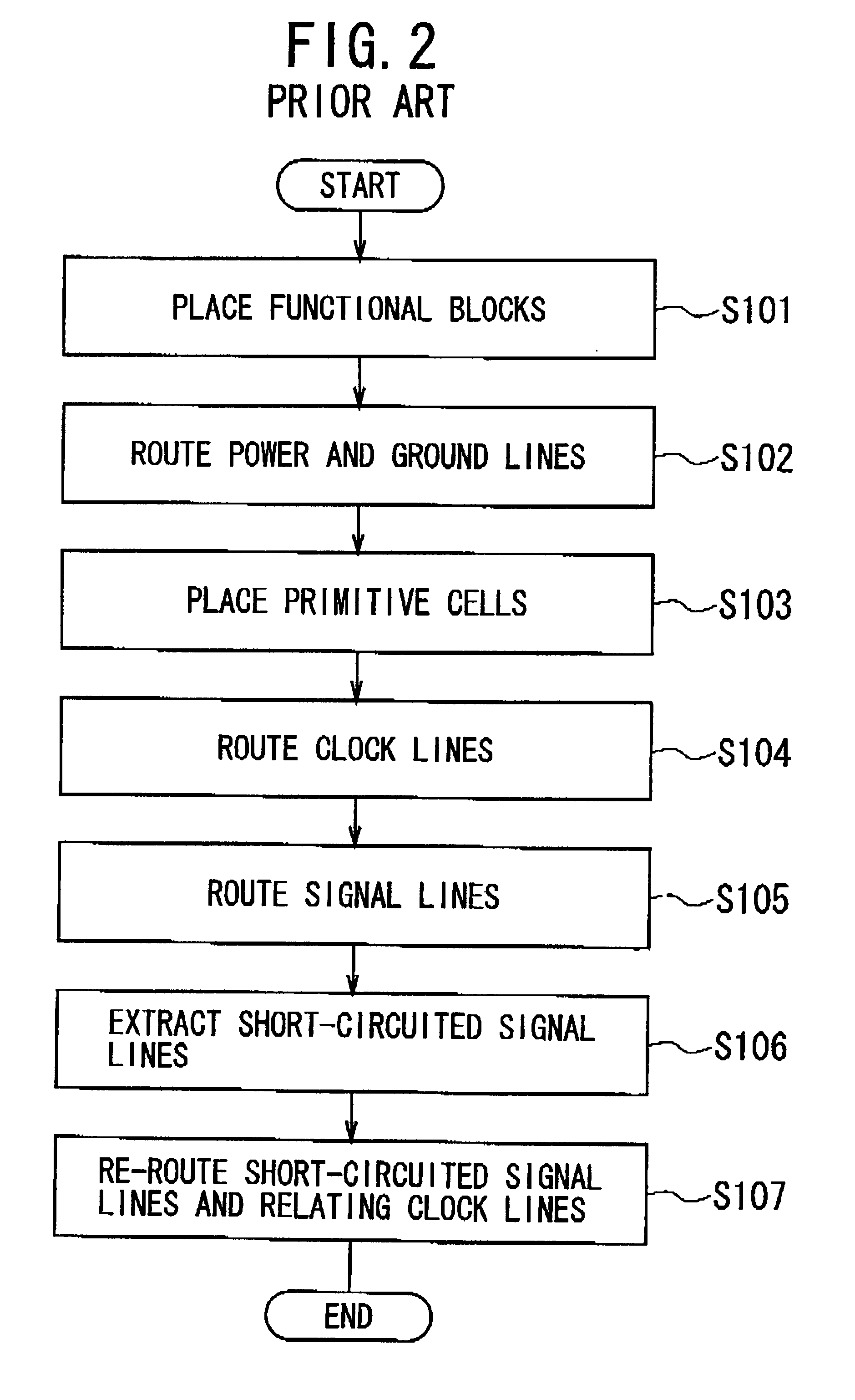
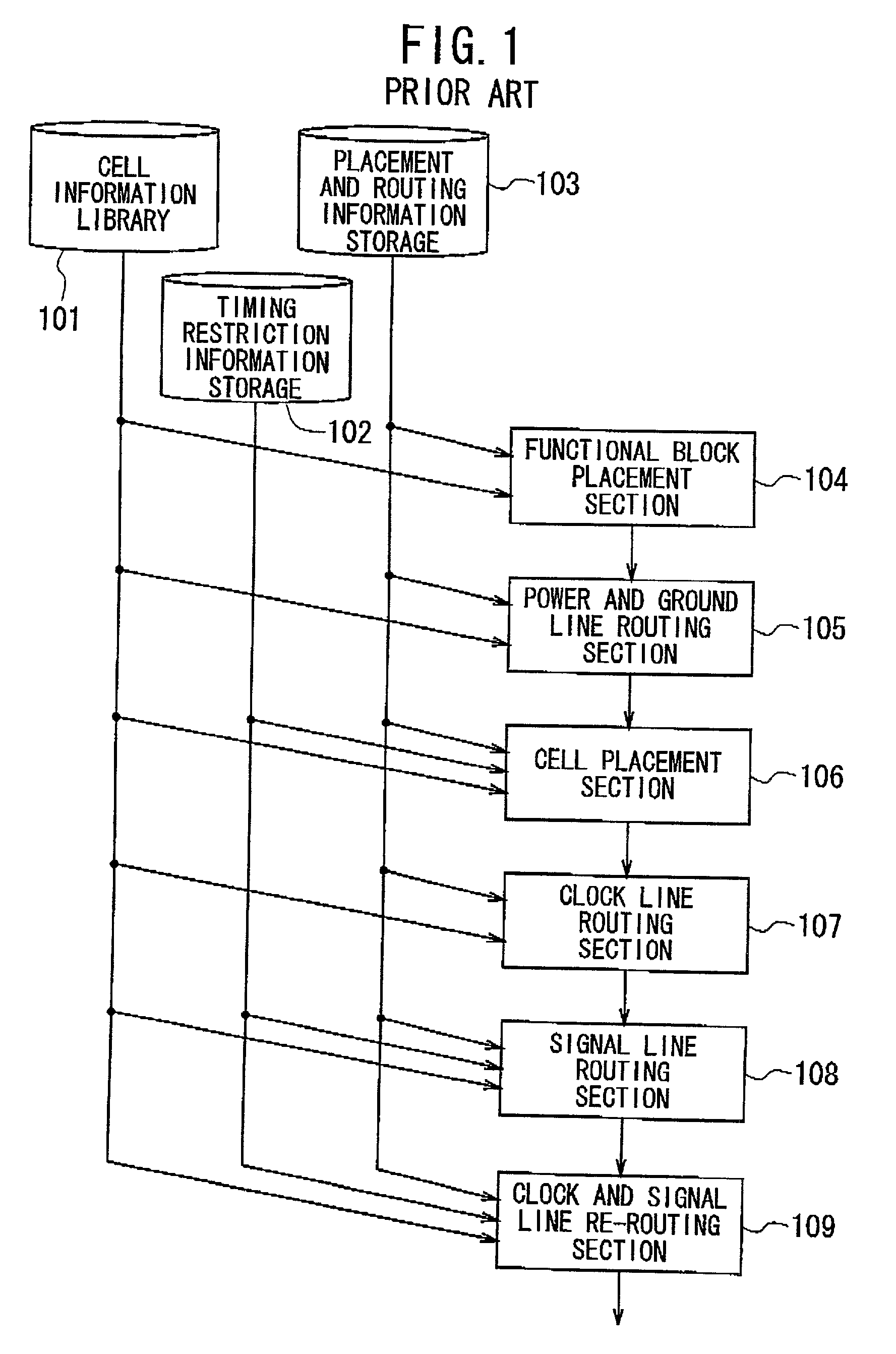
Method of designing layout for integrated circuit
InactiveUS6519750B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designIntegrated circuit layoutEngineering
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
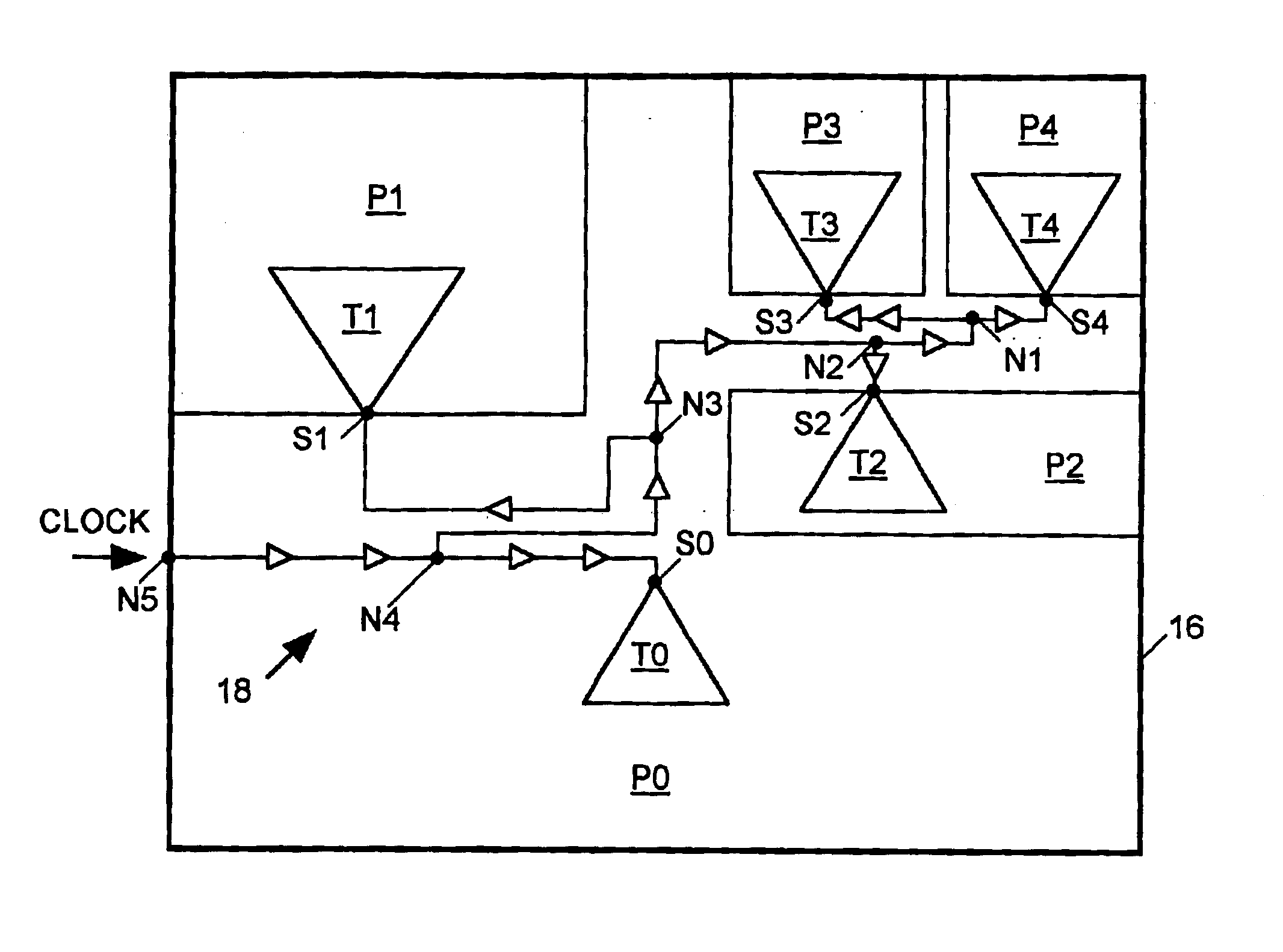
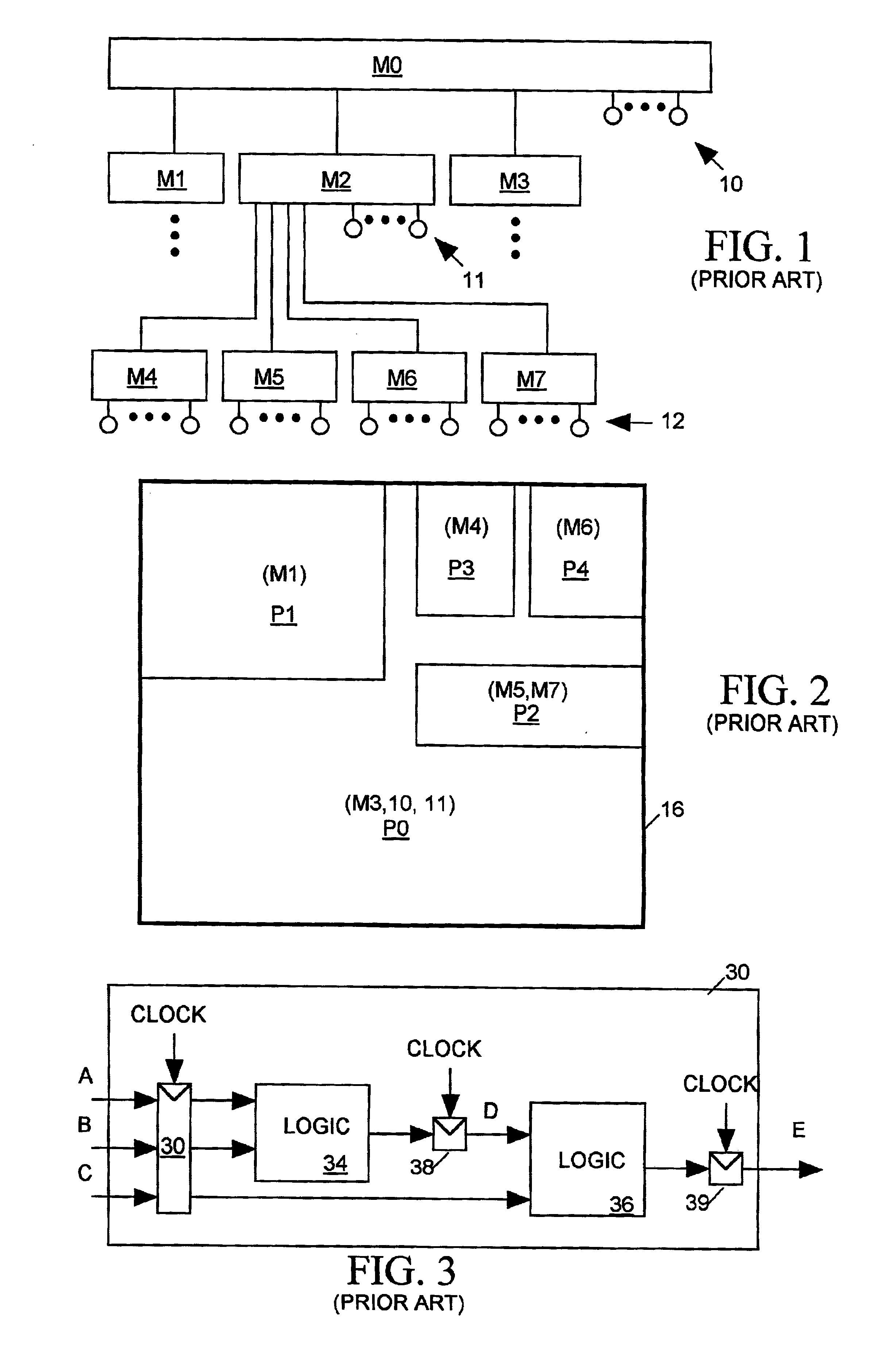
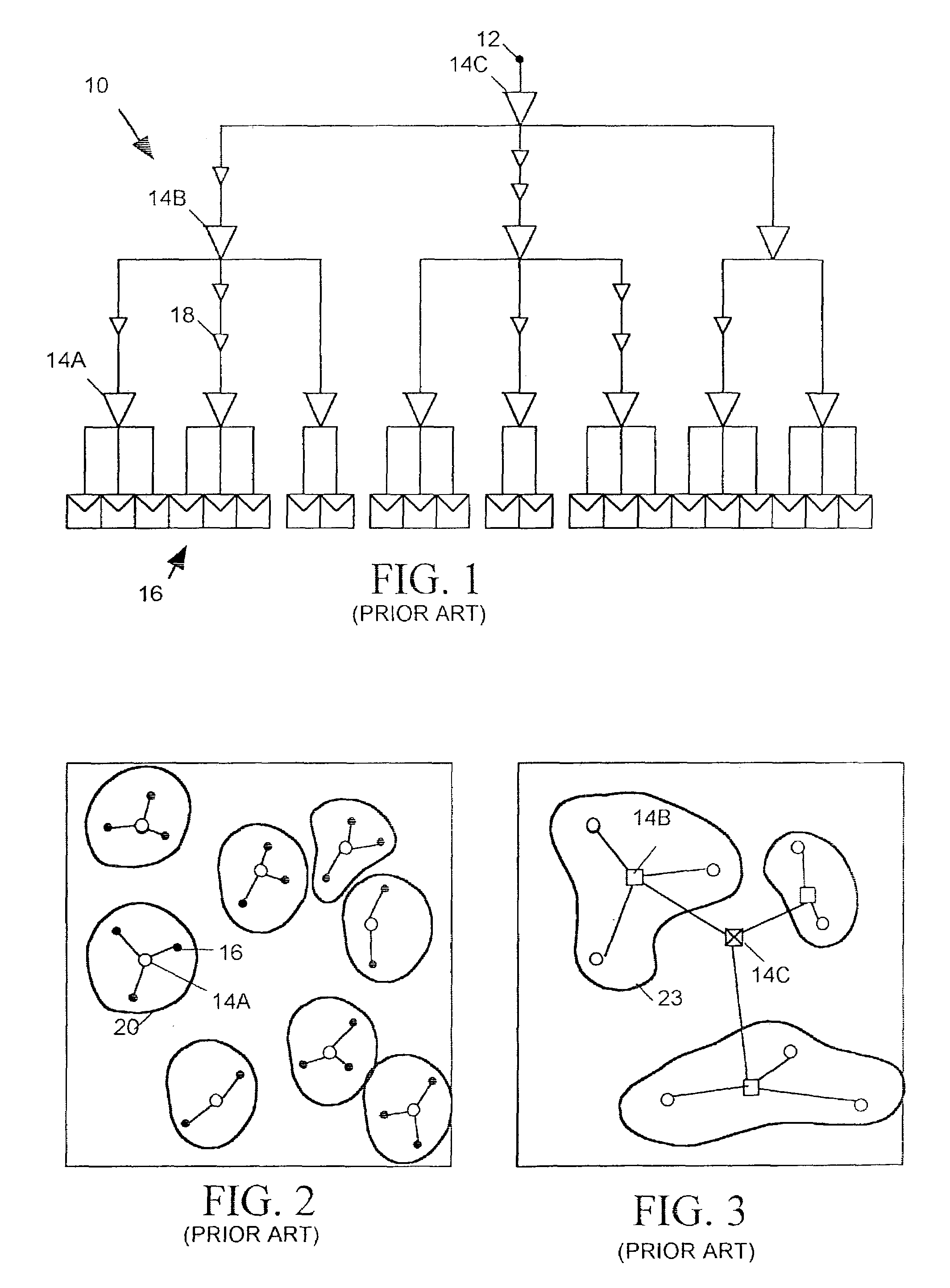
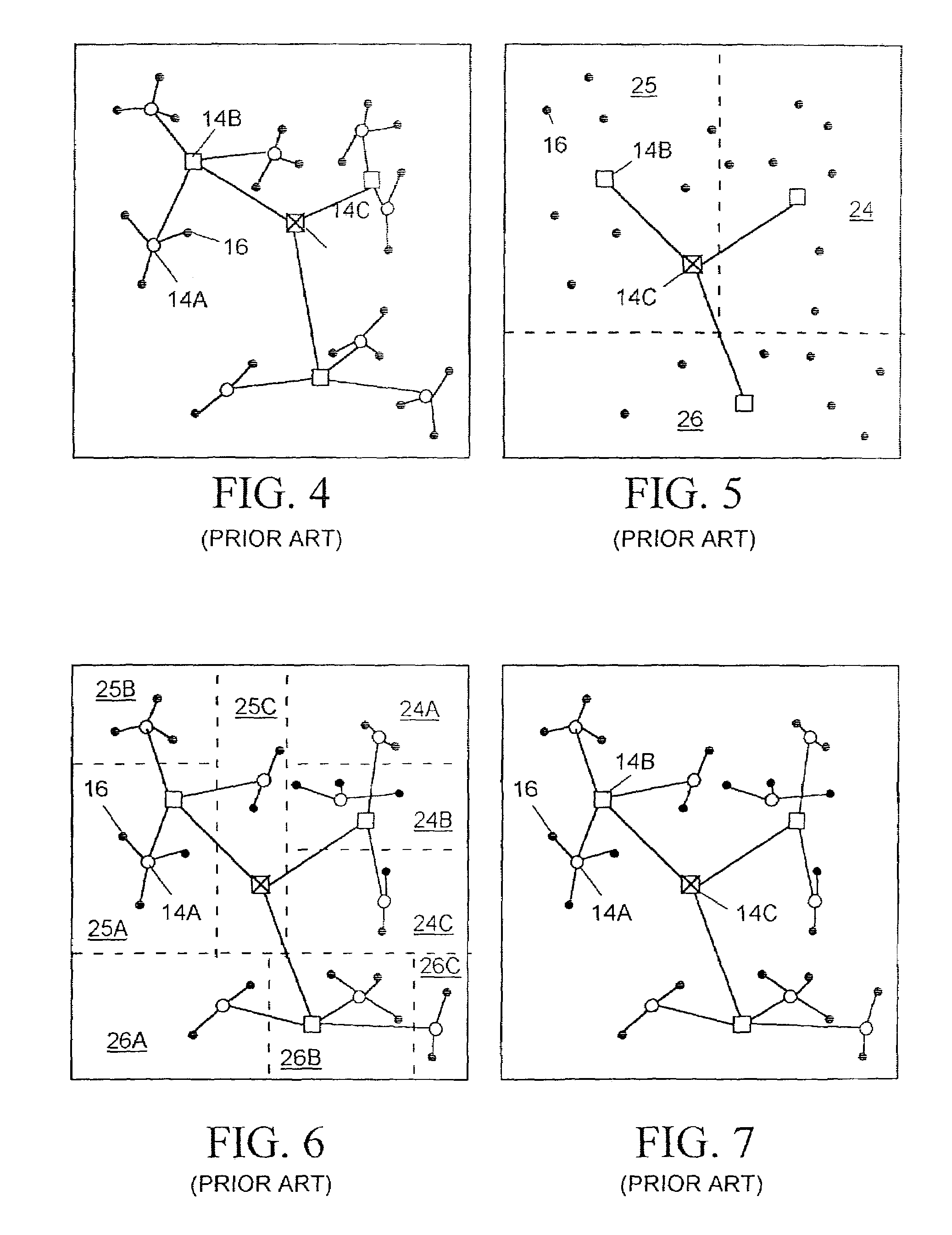
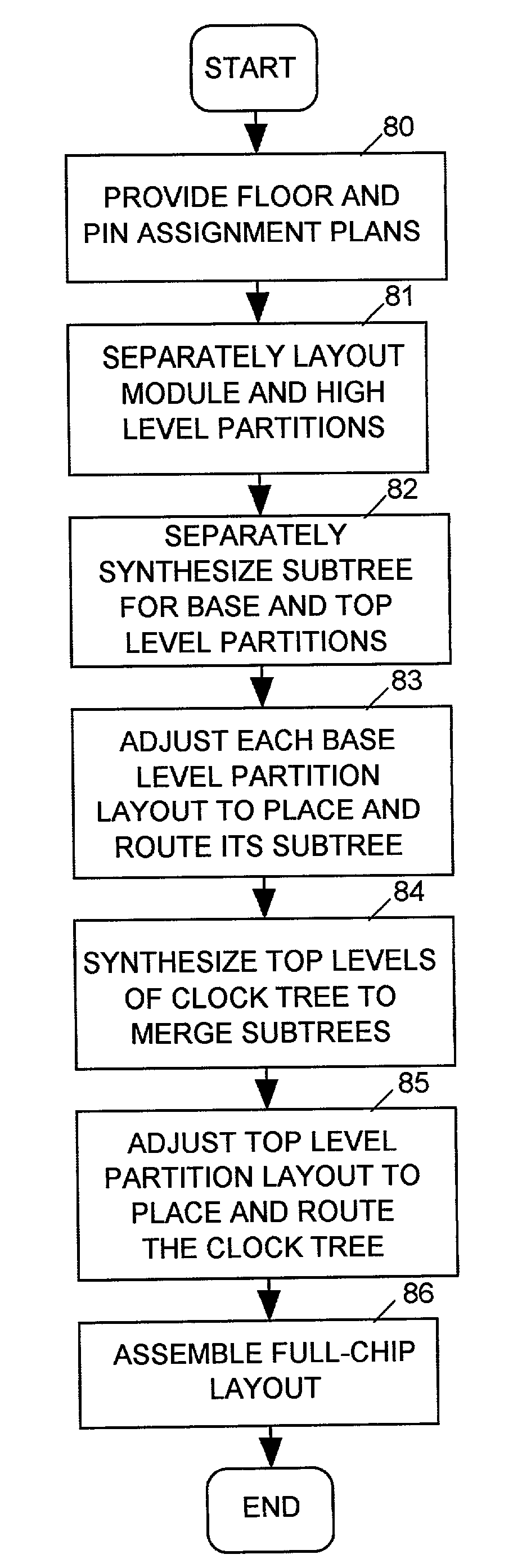
Clock tree synthesis for a hierarchically partitioned IC layout
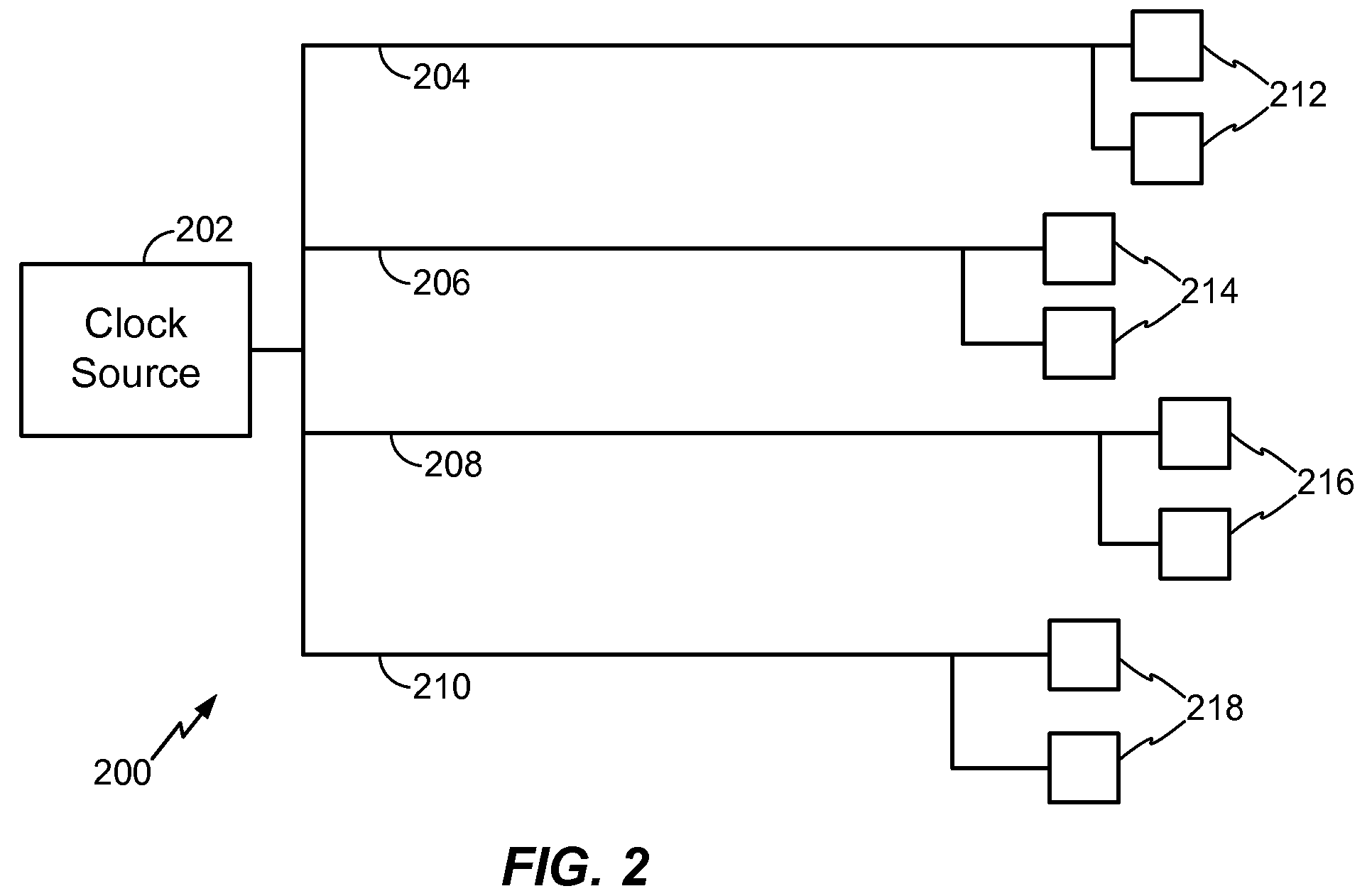
A method is disclosed for synthesizing a clock tree for a partitioned integrated circuit (IC) layout comprising a plurality of base level partitions and a top level partition each occupying a separate area of a semiconductor substrate, The base level partitions include syncs to be clocked by edges of a clock signal applied to an entry node within the area occupied by the top level partition. In accordance with the method, a plurality of independently balanced subtrees are separately synthesized. Each subtree resides within the area occupied by a separate base level partition and includes a start point at a perimeter of the area occupied by that base level partition and a network of buffers and signal paths for conveying a clock signal edge from the start point to each sync included within that area. Thereafter a top level portion of the clock tree is synthesized. The top level portion of the subtree resides within the substrate area containing the top level partition and conveys the clock signal from the entry point to the start point of each synthesized subtree.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Application specific integrated circuit link
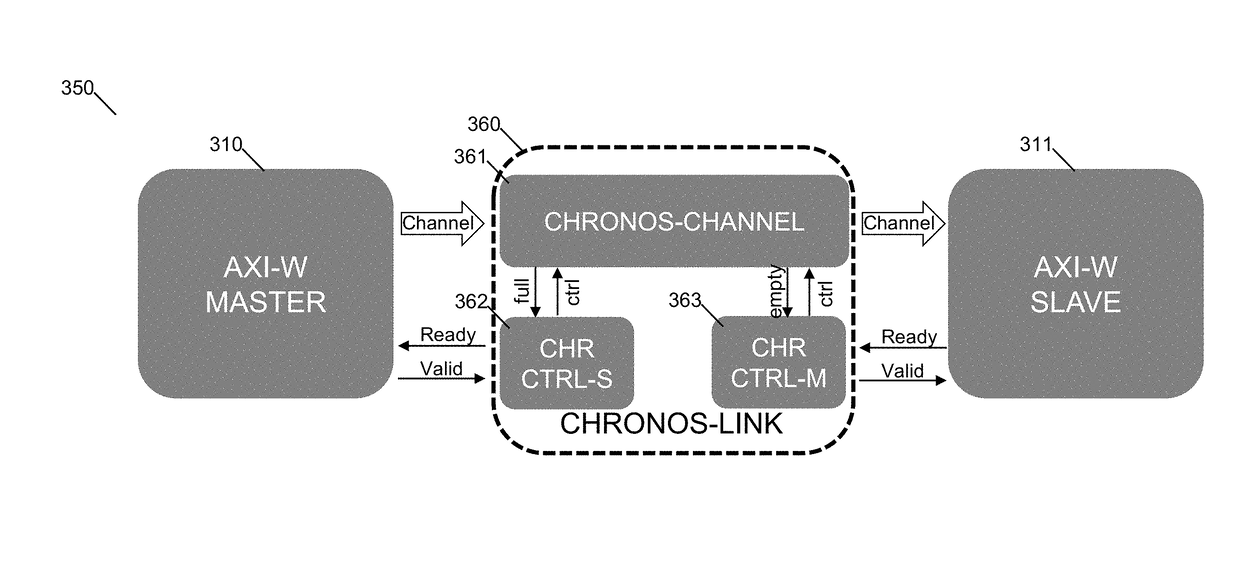
ActiveUS9977853B2Reduce overheadEfficient data transferCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsIntellectual propertyClock tree synthesis
Systems and methods for application specific integrated circuit design using Chronos links are disclosed. A Chronos Link is an ASIC on-chip and off-chip interconnect communication protocol that allows interfaces to transmit and receive information. The protocol may utilize messages or signals to indicate the availability and / or readiness of information to be exchanged between a producer and a consumer allowing the communication to be placed on hold and to be resumed seamlessly. A method includes inserting gaskets and channel repeaters connected to interfaces of multiple intellectual property (IP) blocks in order to replace traditional links with Chronos Links; performing simplified floorplanning; performing simplified placement; performing simplified clock tree synthesis (CTS) and routing; and performing simplified timing closure.
Owner:CHRONOS TECH LLC
Clock design apparatus and clock design method
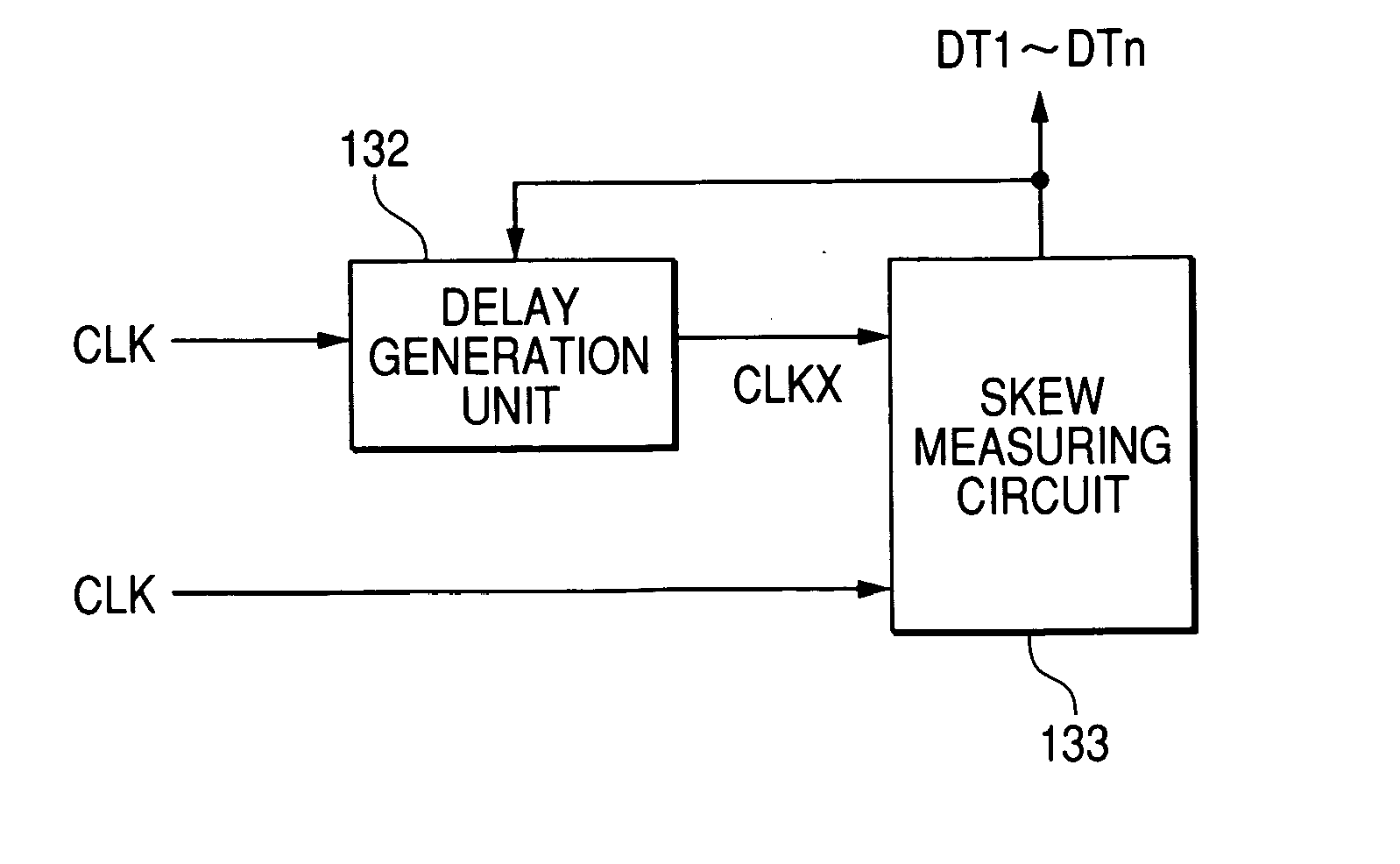
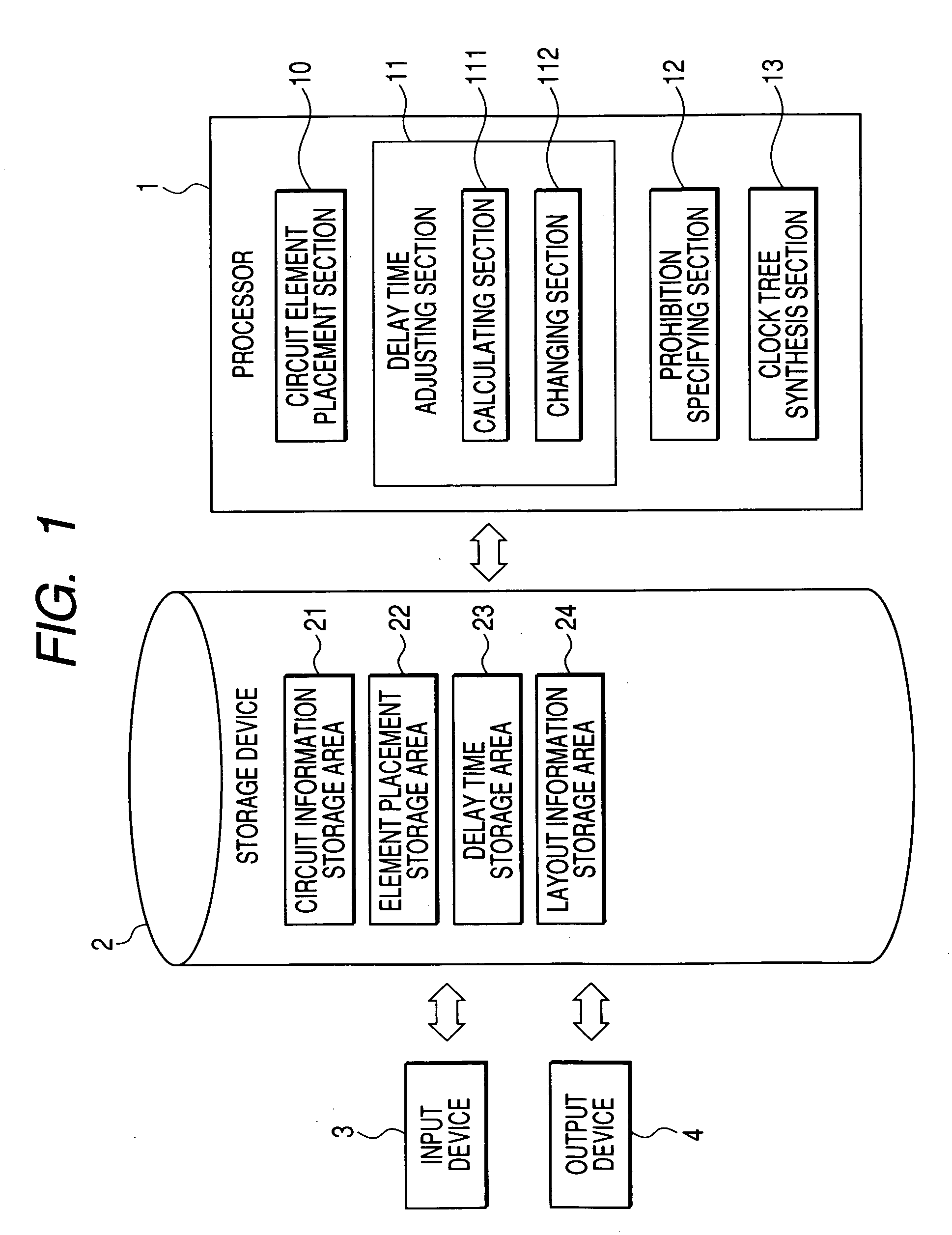
InactiveUS20060253821A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDelayed timeClock tree synthesis
A clock design apparatus includes a delay time adjusting section, a prohibition specifying section and a clock tree synthesis section. The delay time adjusting section is configured to adjust signal delay time of signal propagation paths on a semiconductor integrated circuit to be designed. The prohibition specifying section is configured to specify a part of the signal propagation paths as a circuit prevented from being changed. The clock tree synthesis section is configured to synthesize a clock tree of the semiconductor integrated circuit in accordance with the specification made by the prohibition specifying section.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
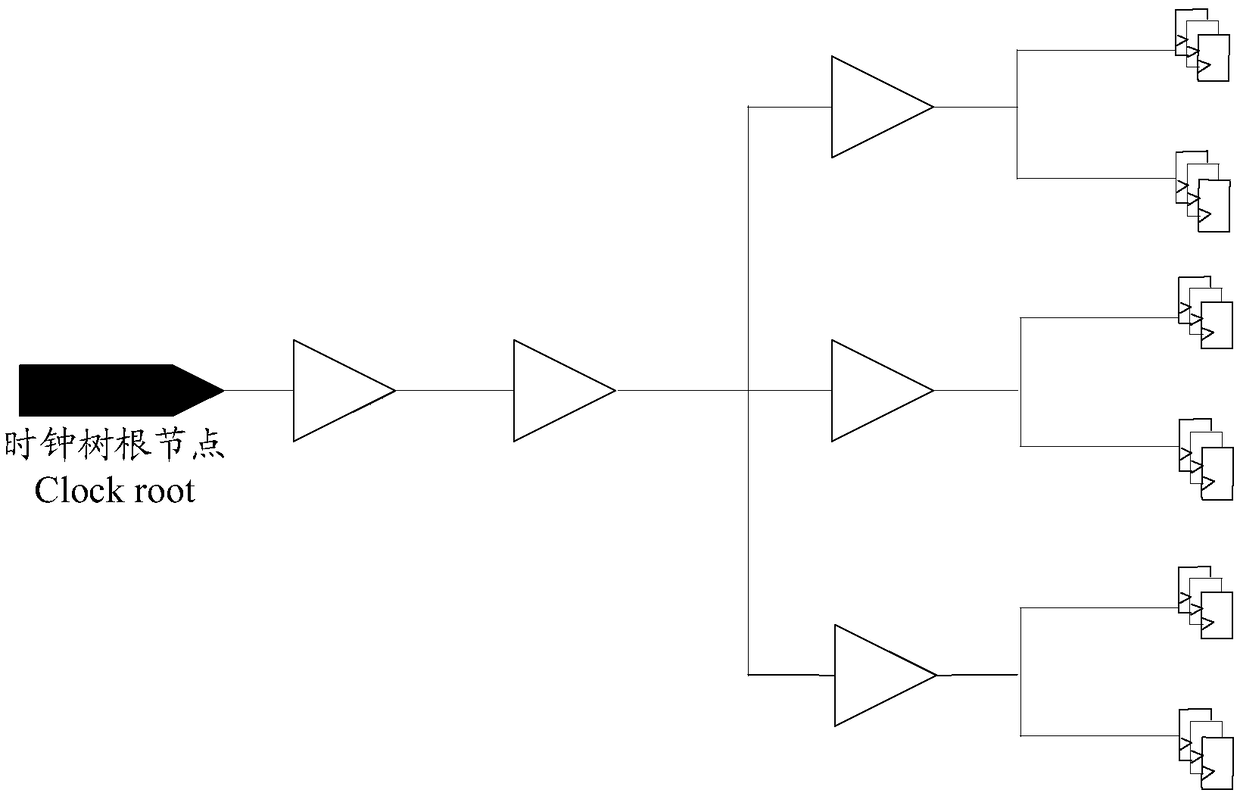
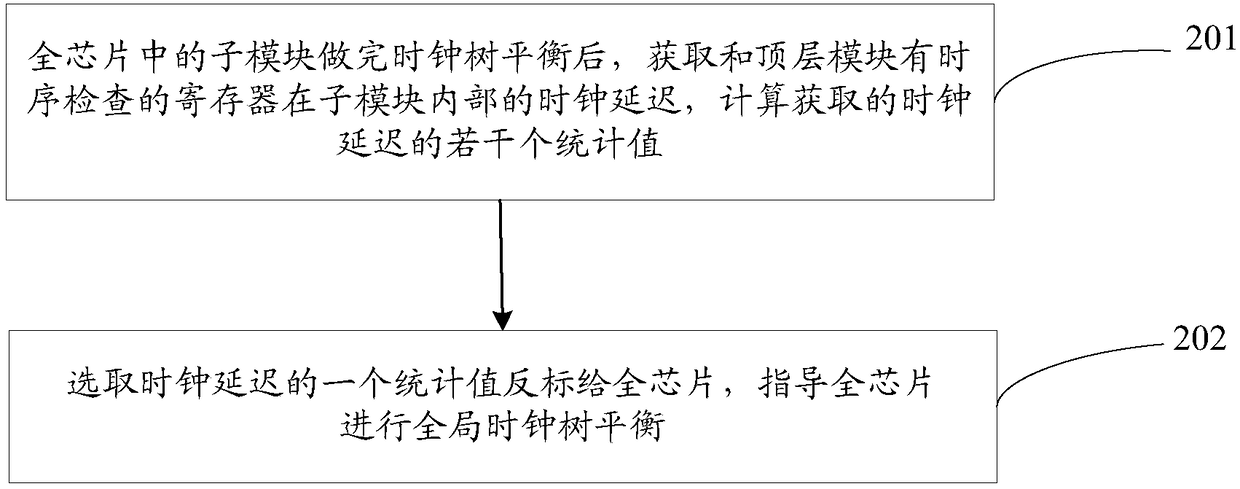
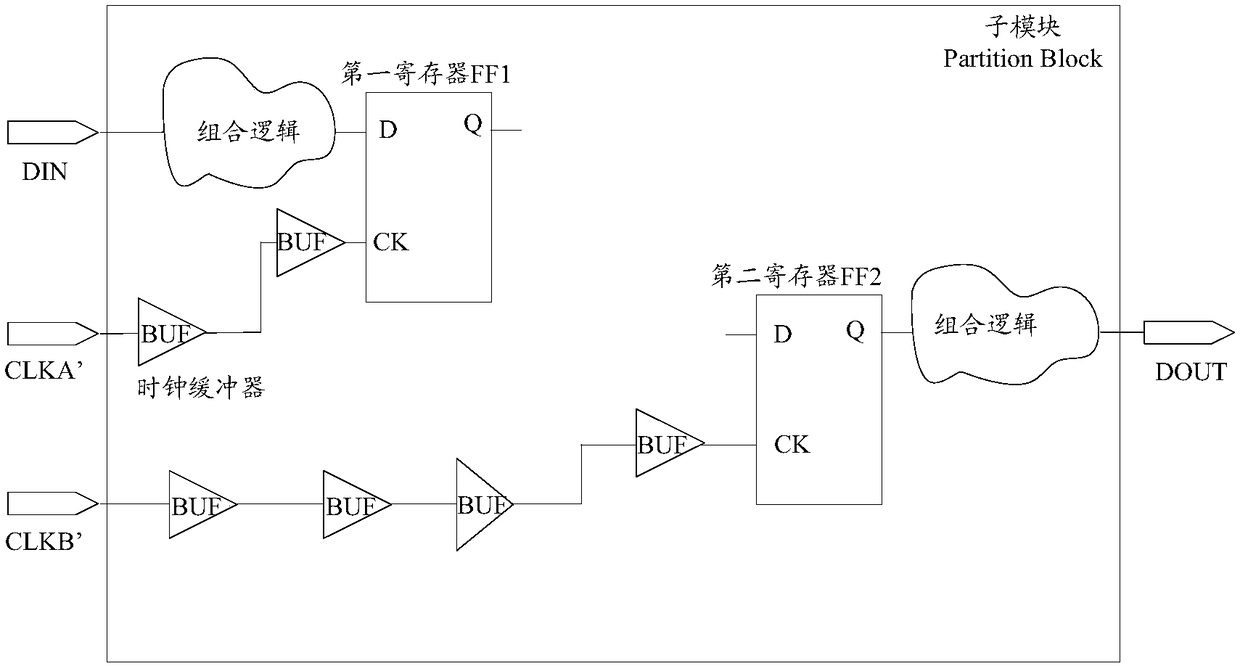
Clock tree synthesis method and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveCN108984806AFaster Timing ClosureImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsProcessor registerDesign cycle
The invention discloses a clock tree synthesis method and a computer-readable storage medium. The method comprises a step of obtaining clock latency of registers which have timing check with a top-level module in sub-modules after the clock tree balance of the sub-modules in a full chip is completed, and calculating several statistical values of the grabbed clock latency, and a step of selectinga statistical value of the clock latency and carrying out back-annotation of the statistical value to the full chip, and guiding the full clock to carry out global clock tree balance. According to the method and the computer-readable storage medium, by obtaining clock latency values of the registers at the interfaces of the sub-modules and the top-level module in the sub-modules and carrying outback-annotation of the values to the full chip to carry out global clock tree balance, the clock latency of a large number of unrelated registers that have no logical interaction with the top-level module in the sub-modules is omitted, the accuracy of a back annotation value is improved, thus a large number of timing violations do not occur at the interfaces of the sub-modules and the top-level module, the speed of the timing convergence of the full chip is increased, and a design cycle is shortened.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Moving clock gating cell closer to clock source based on enable signal propagation time to clocked storage element
ActiveUS8572418B2Save powerSynchronisation information channelsCAD circuit designTiming marginPropagation time
In a particular embodiment, a method of generating an advanced gating cell clock tree includes determining a timing margin for a path between a clock gating cell and a digital data storage element such as a latch or flip flop. The circuit contains a clock source and when the timing margin for the path meets a predetermined threshold, the clock gating cell is automatically moved closer to the clock source. In a particular embodiment, the timing margin is automatically determined. A clock tree synthesis is performed to insert one or more buffers into the path and create an advanced gating cell clock tree.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
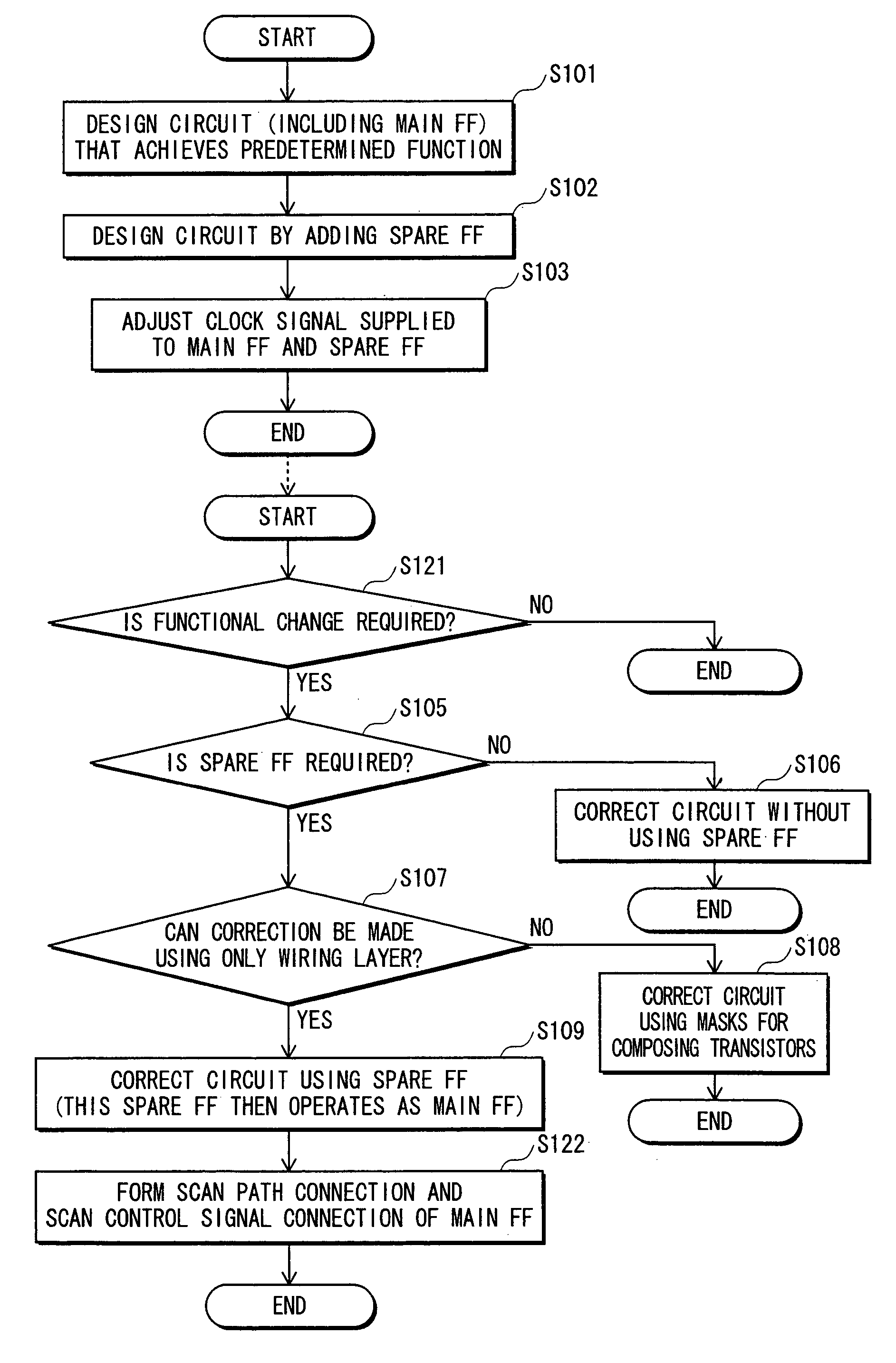
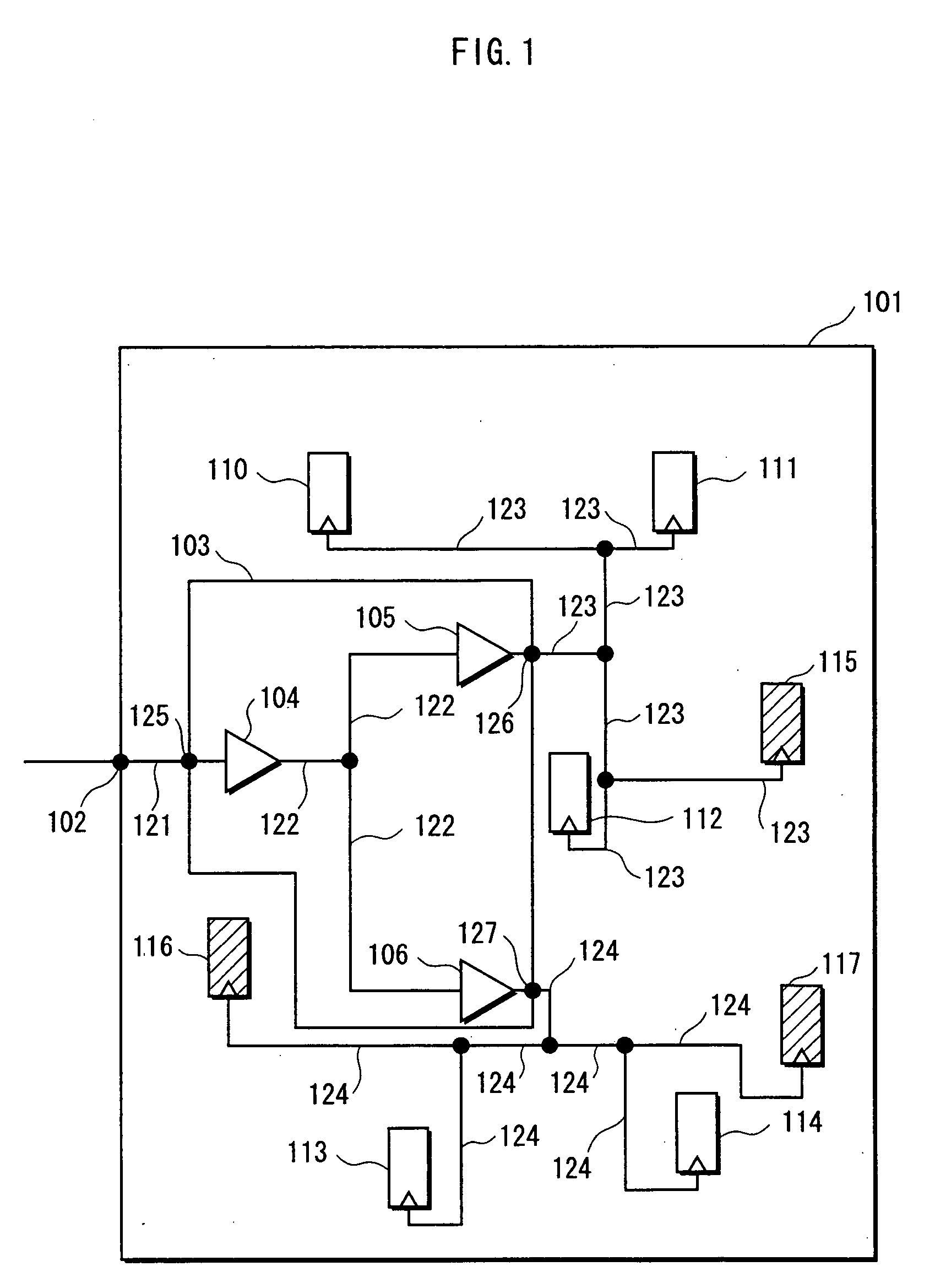
Semiconductor integrated circuit
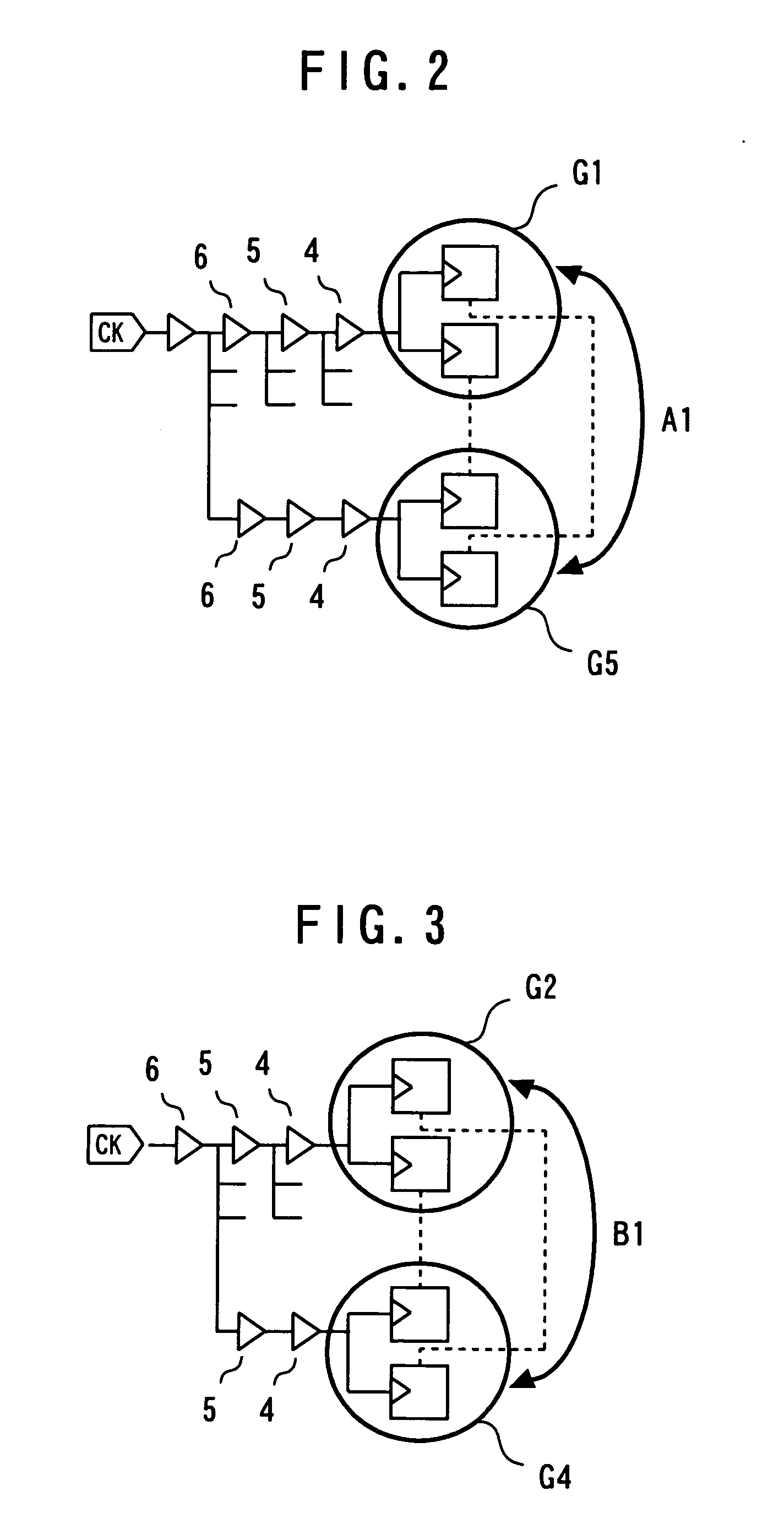
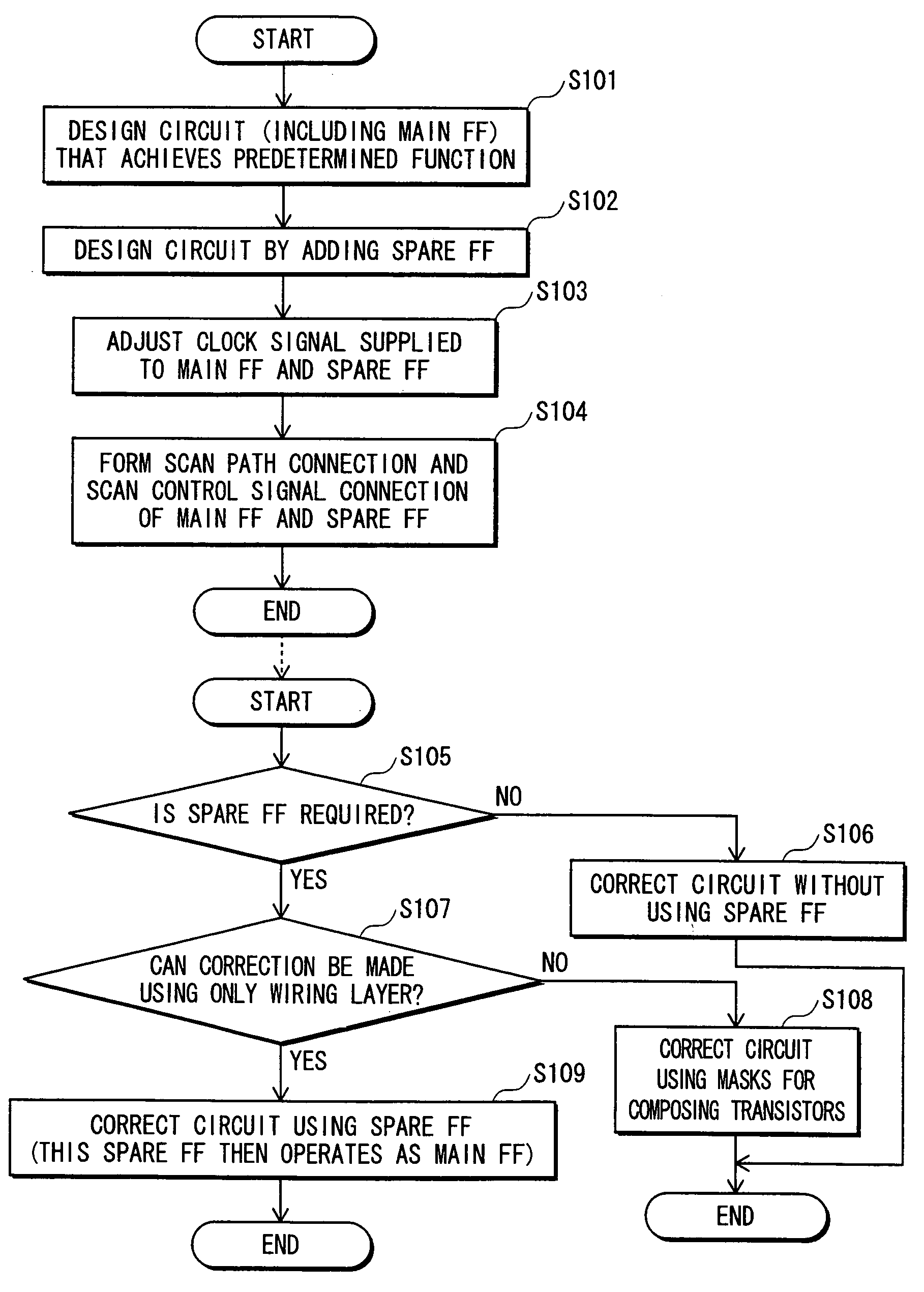
To provide a semiconductor integrated circuit in which a clock signal supplied to each flip-flop will not be adversely affected when a functional change is made using a spare flip-flop. The semiconductor integrated circuit includes a plurality of main flip-flops which contribute to a predetermined function, a plurality of spare flip-flops, and a clock tree synthesis circuit that generates a clock signal which is adjusted for synchronizing the plurality of main flip-flops and the plurality of spare flip-flops and supplies the adjusted clock signal to the plurality of main flip-flops and the plurality of spare flip-flops.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multi-mode scheduler for clock tree synthesis
ActiveUS20140181766A1CAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTheoretical computer scienceClock tree synthesis
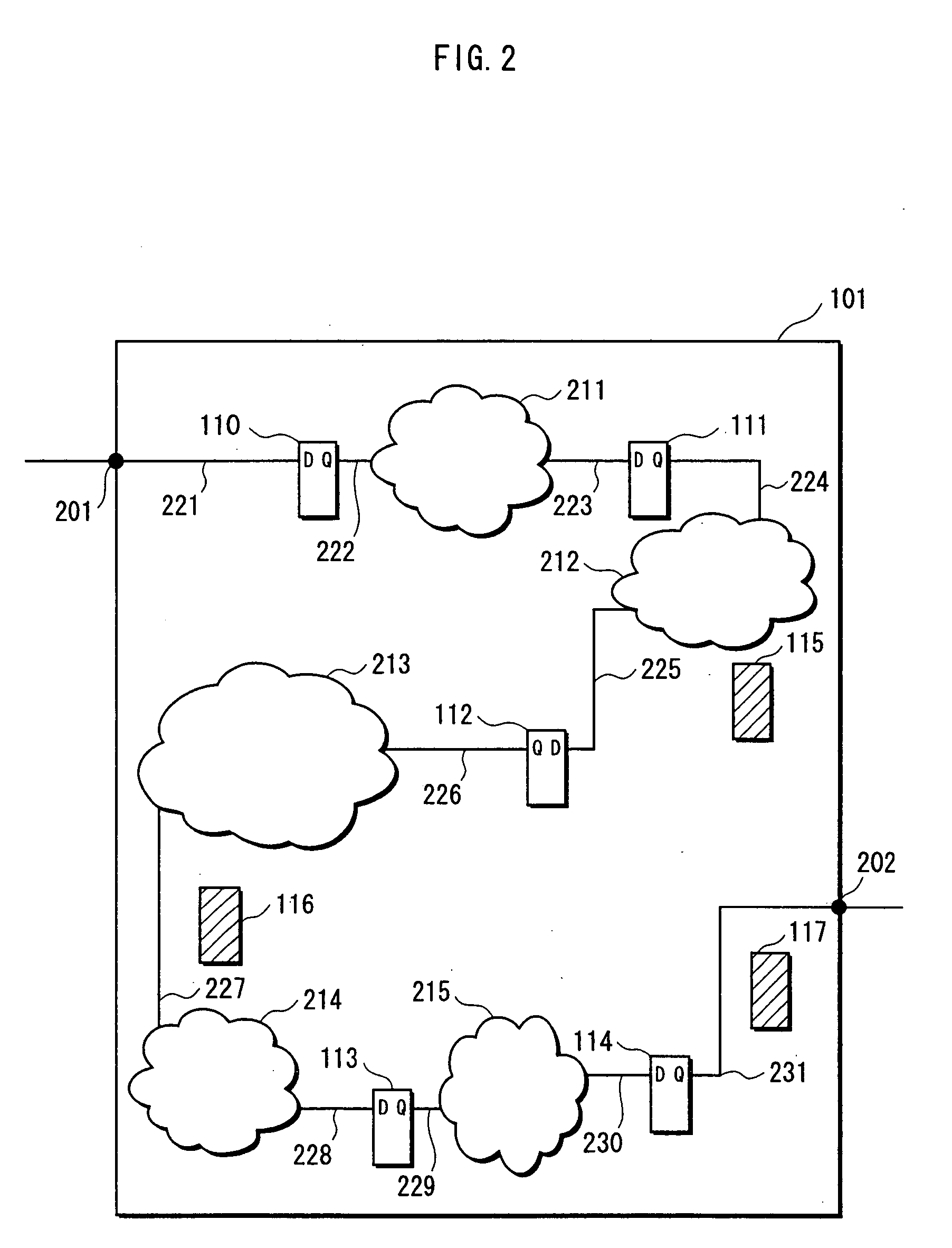
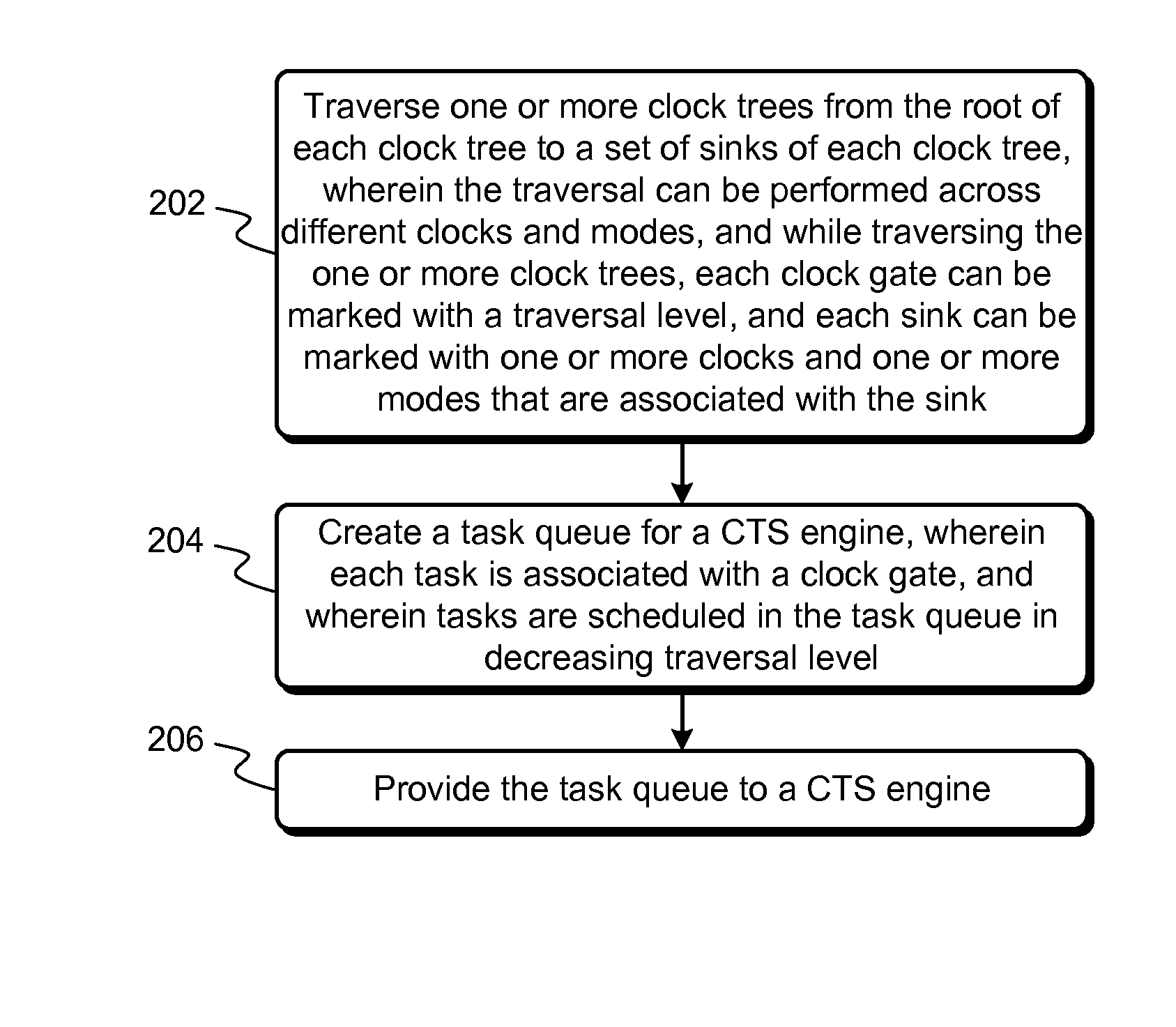
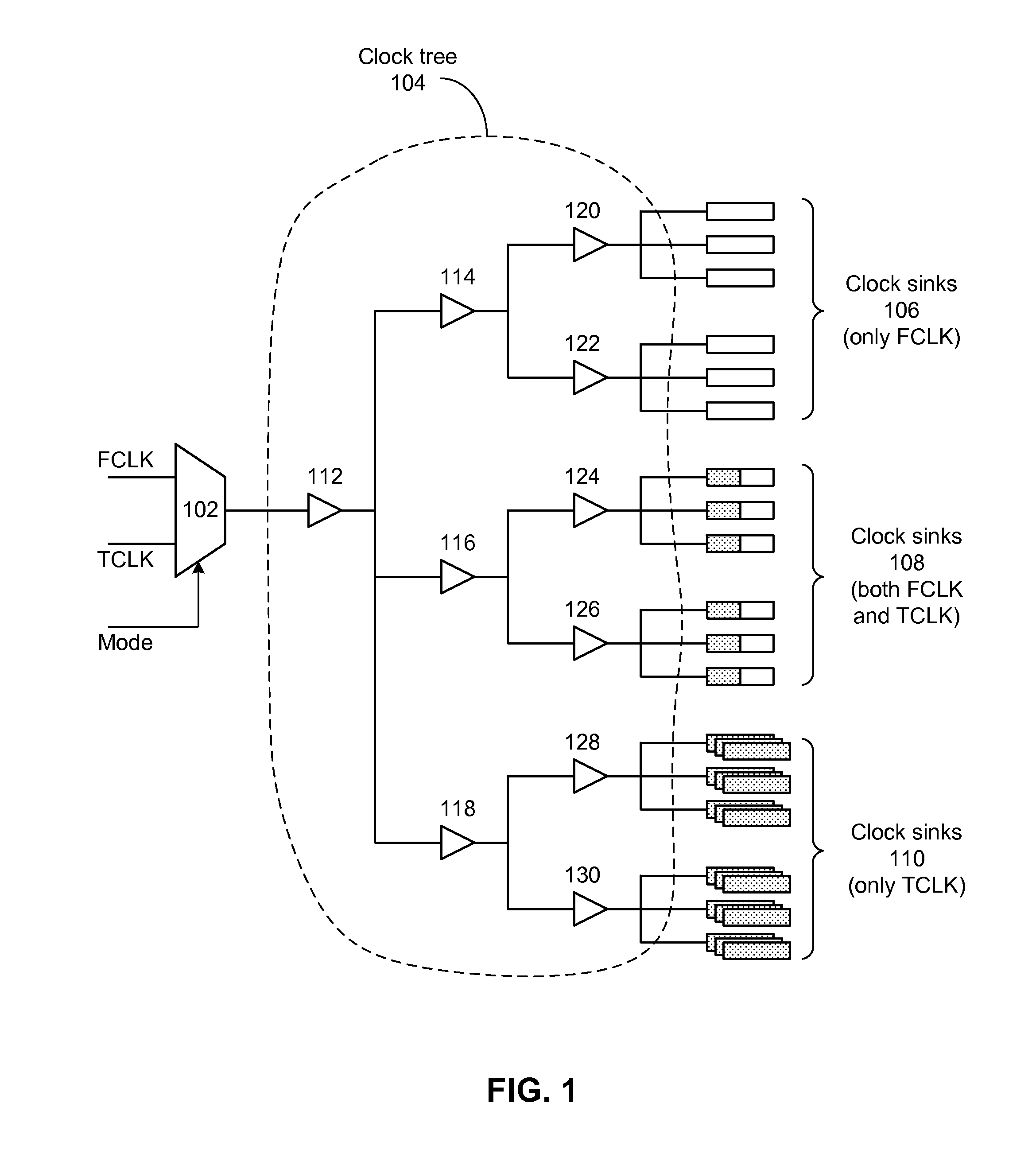
Techniques and systems for performing clock tree synthesis (CTS) across multiple modes are described. Some embodiments traverse one or more clock trees from the root of each clock tree to a set of sinks of the clock tree. During the traversal, each clock gate can be marked with a traversal level, and each sink can be marked with one or more clocks and one or more modes that are associated with the sink. A task queue can then be created based on the information collected during the clock tree traversal and populated with different types of tasks based on skew balancing requirements across different modes, and the task queue can be provided to a CTS engine to achieve high-quality skew-balanced clock trees across all modes.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Clock forming method for semiconductor integrated circuit and program product for the method
InactiveUS20070094627A1Improved on-chip-variation resistanceEasy to limitDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designElectrical resistance and conductanceData connection
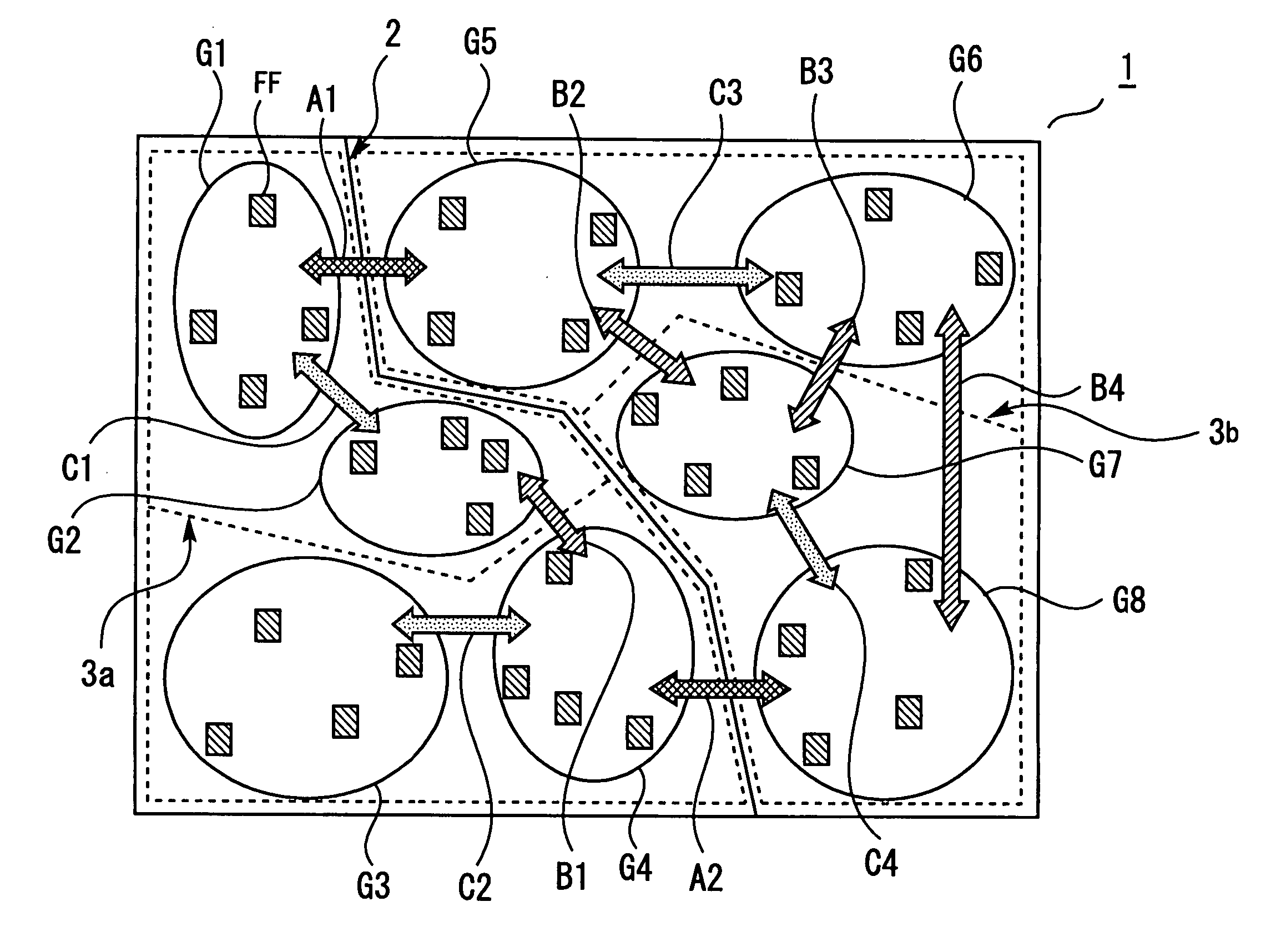
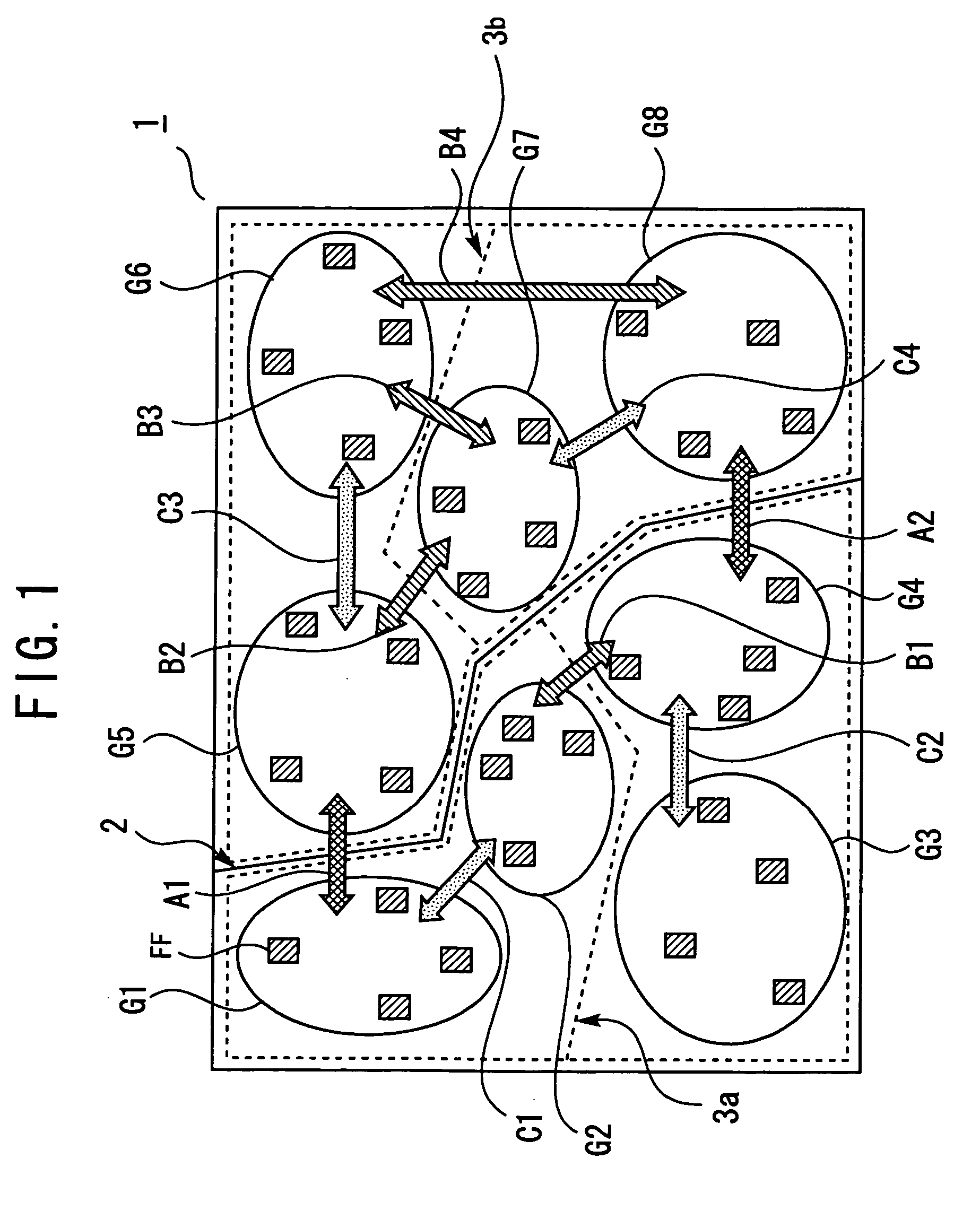
Regions G1 to G8 each including a predetermined number of flip-flops (FF) are divided into two groups. This dividing is performed so that the number of data connection channels intersected by a boundary is minimized. In the case of intersection of two data connection channels (A1, A2), the number of data connection channels intersected by the boundary is two, the minimum number. After grouping of all the regions (G1 to G4, G5 to G8), clock tree synthesis (CTS) is performed. If clock forming is performed in this way, the increase in clock skew on an actual device can be limited and on-chip variation resistance can be increased.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit
To provide a semiconductor integrated circuit in which a clock signal supplied to each flip-flop will not be adversely affected when a functional change is made using a spare flip-flop. The semiconductor integrated circuit includes a plurality of main flip-flops which contribute to a predetermined function, a plurality of spare flip-flops, and a clock tree synthesis circuit that generates a clock signal which is adjusted for synchronizing the plurality of main flip-flops and the plurality of spare flip-flops and supplies the adjusted clock signal to the plurality of main flip-flops and the plurality of spare flip-flops.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus, generator, and method for clock tree synthesis
InactiveUS7231620B2Batteries circuit arrangementsDigital storageClock tree synthesisComputer science
A clock tree synthesis (CTS) apparatus, generator, and method for synthesizing a clock tree includes a plurality of clock signal generators that output different clock signals generated from a reference clock signal. The clock signal generators includes an additional logic circuit that is not recognized as an end point of the reference clock signal when the clock tree is synthesized. In one example, the clock signal generator is a flip-flop and the additional logic circuit is a tri-state buffer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
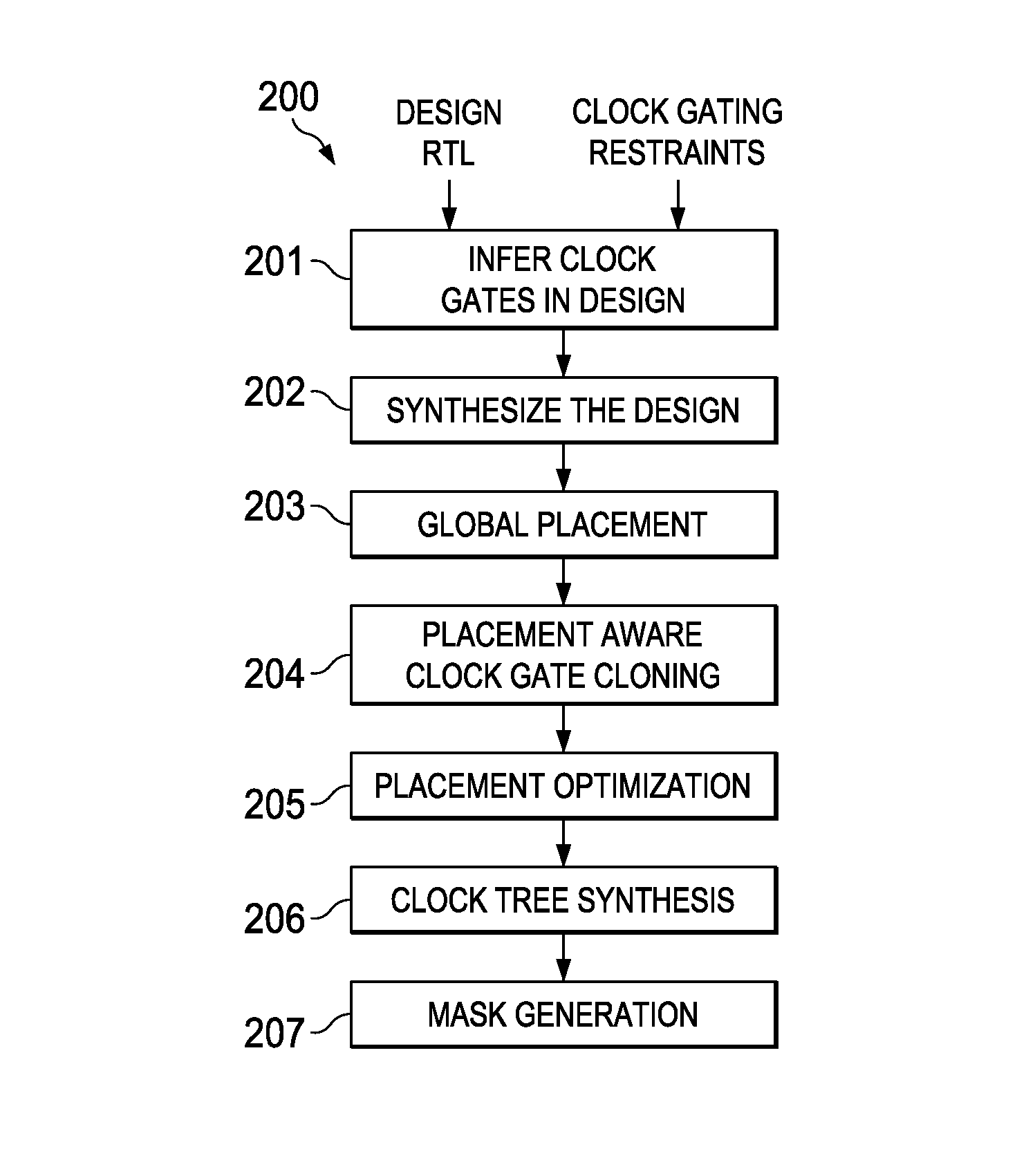
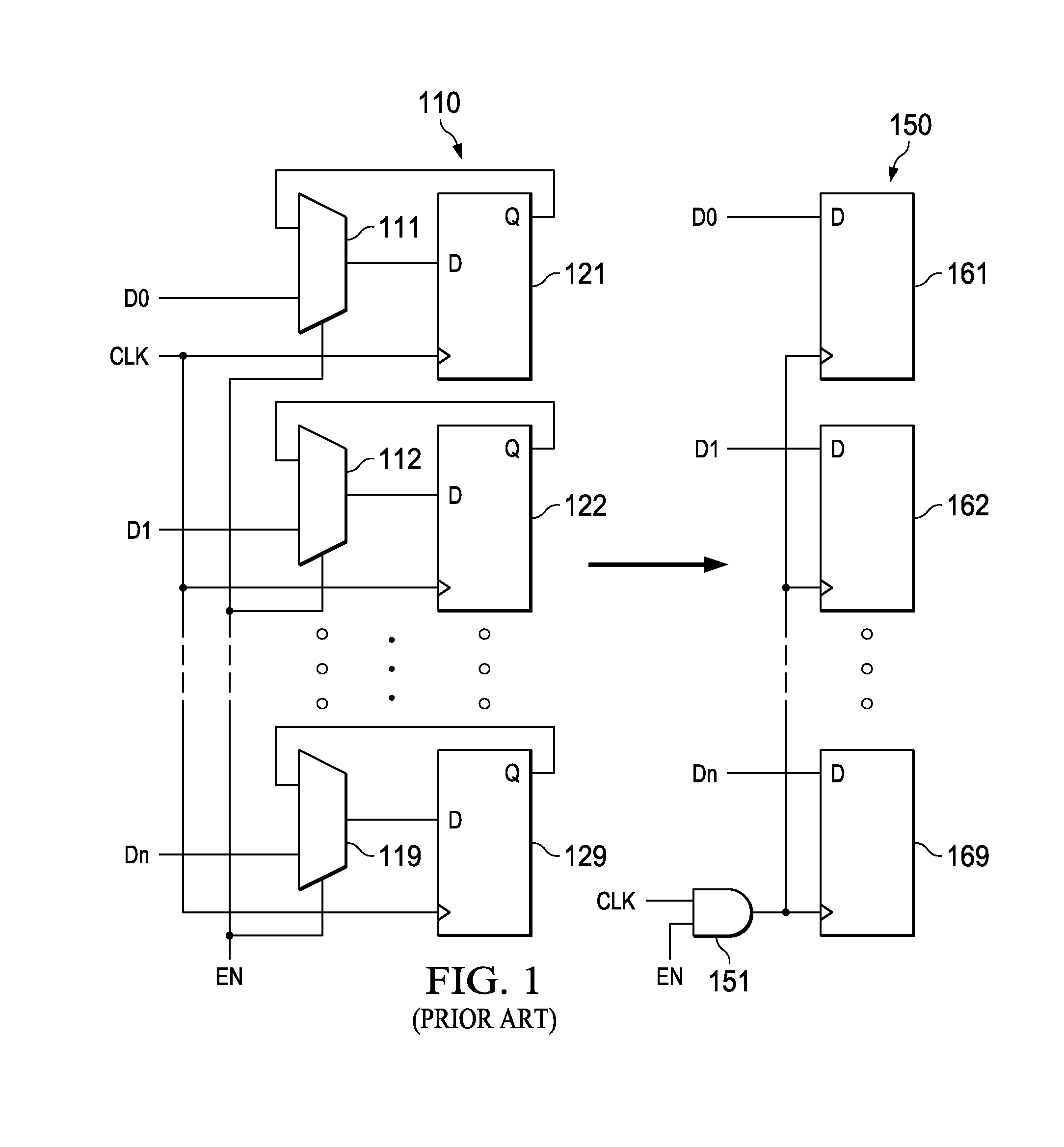
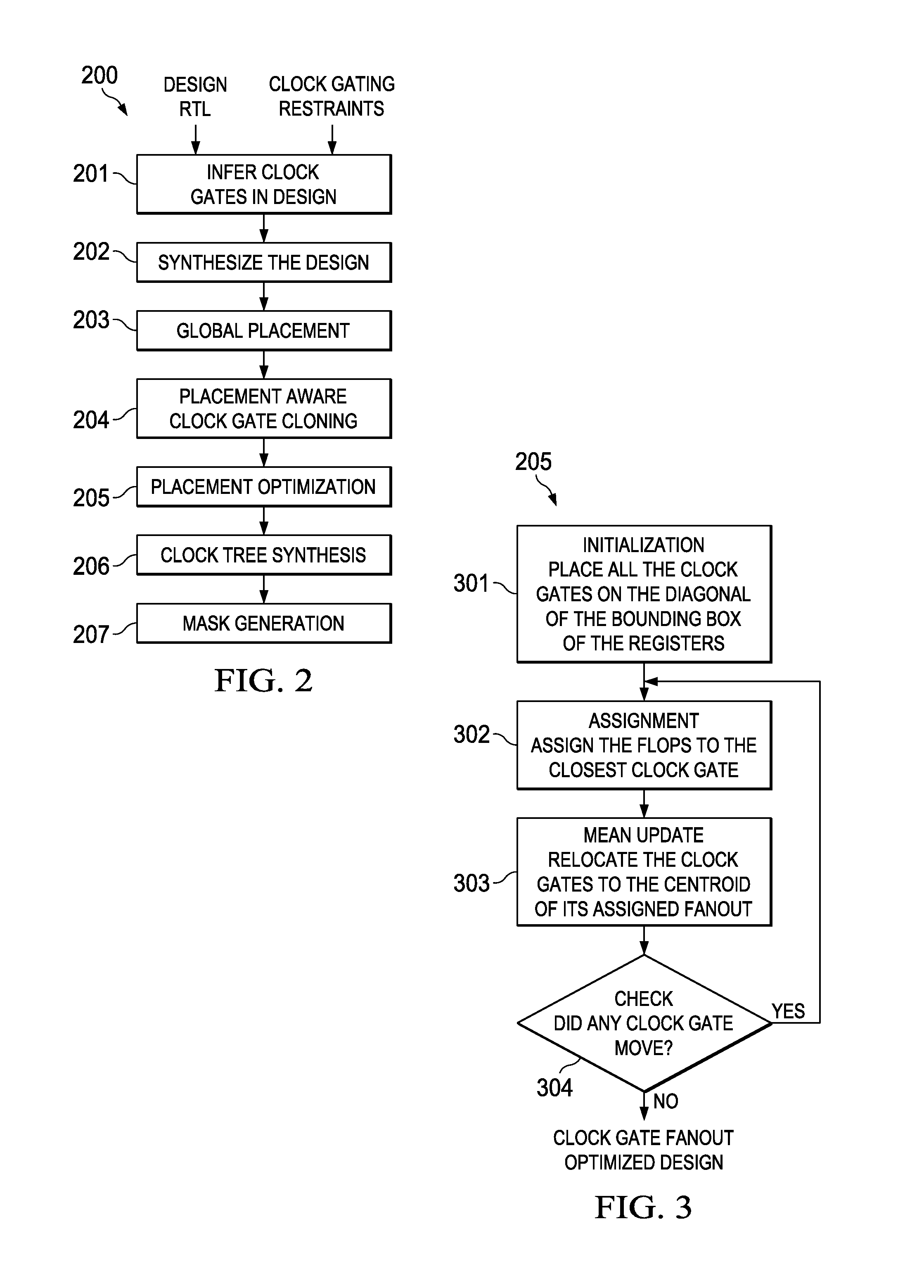
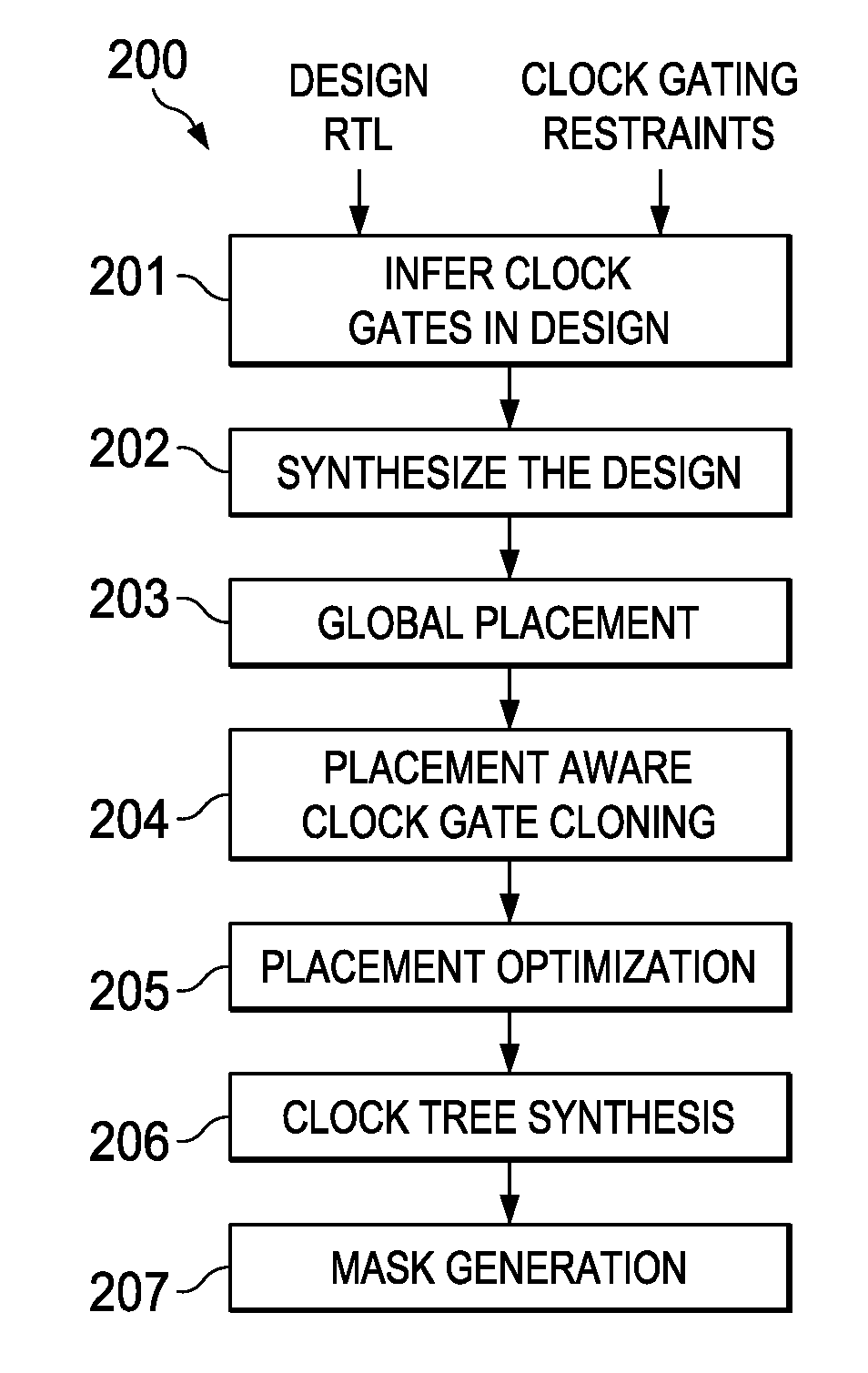
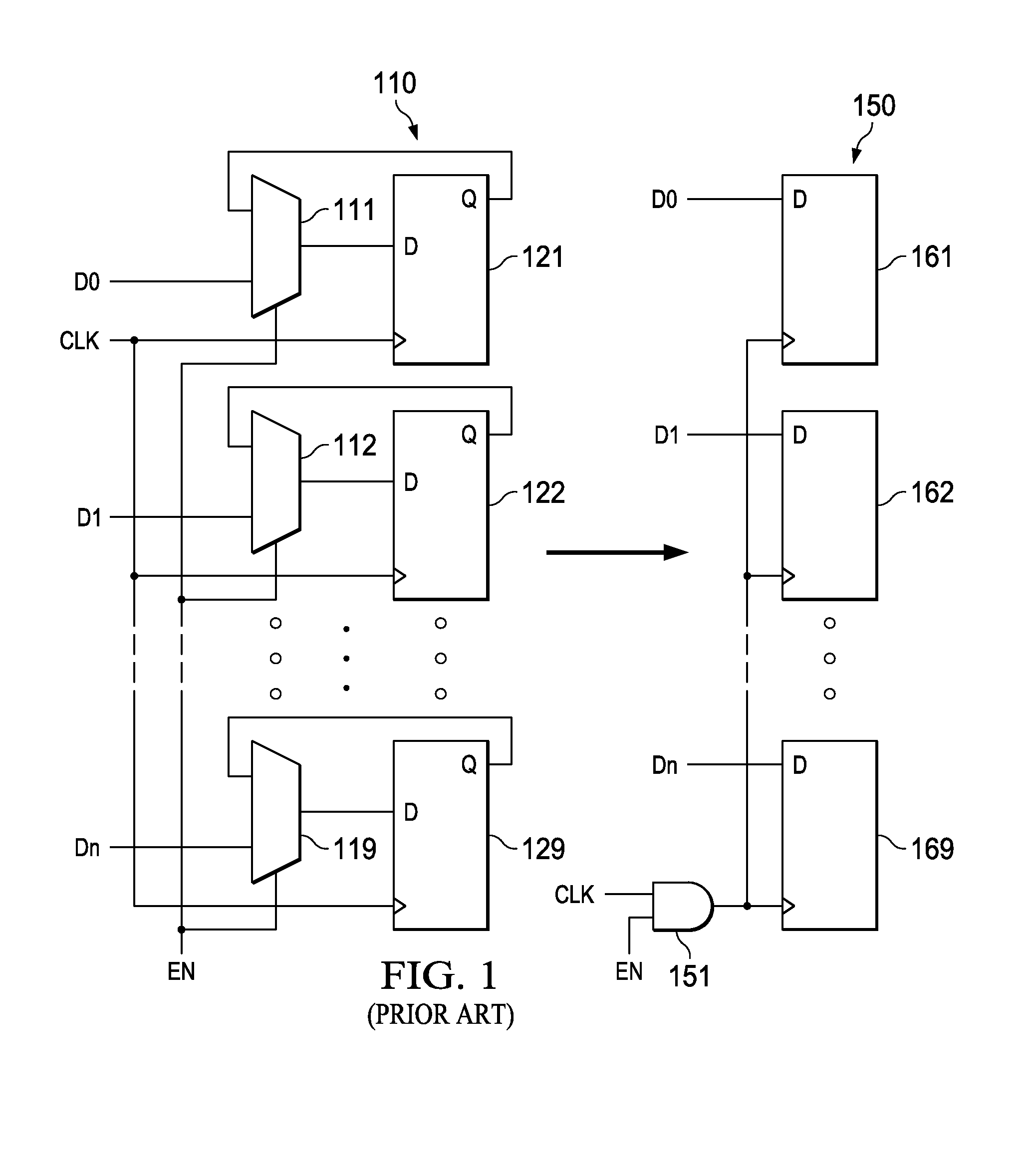
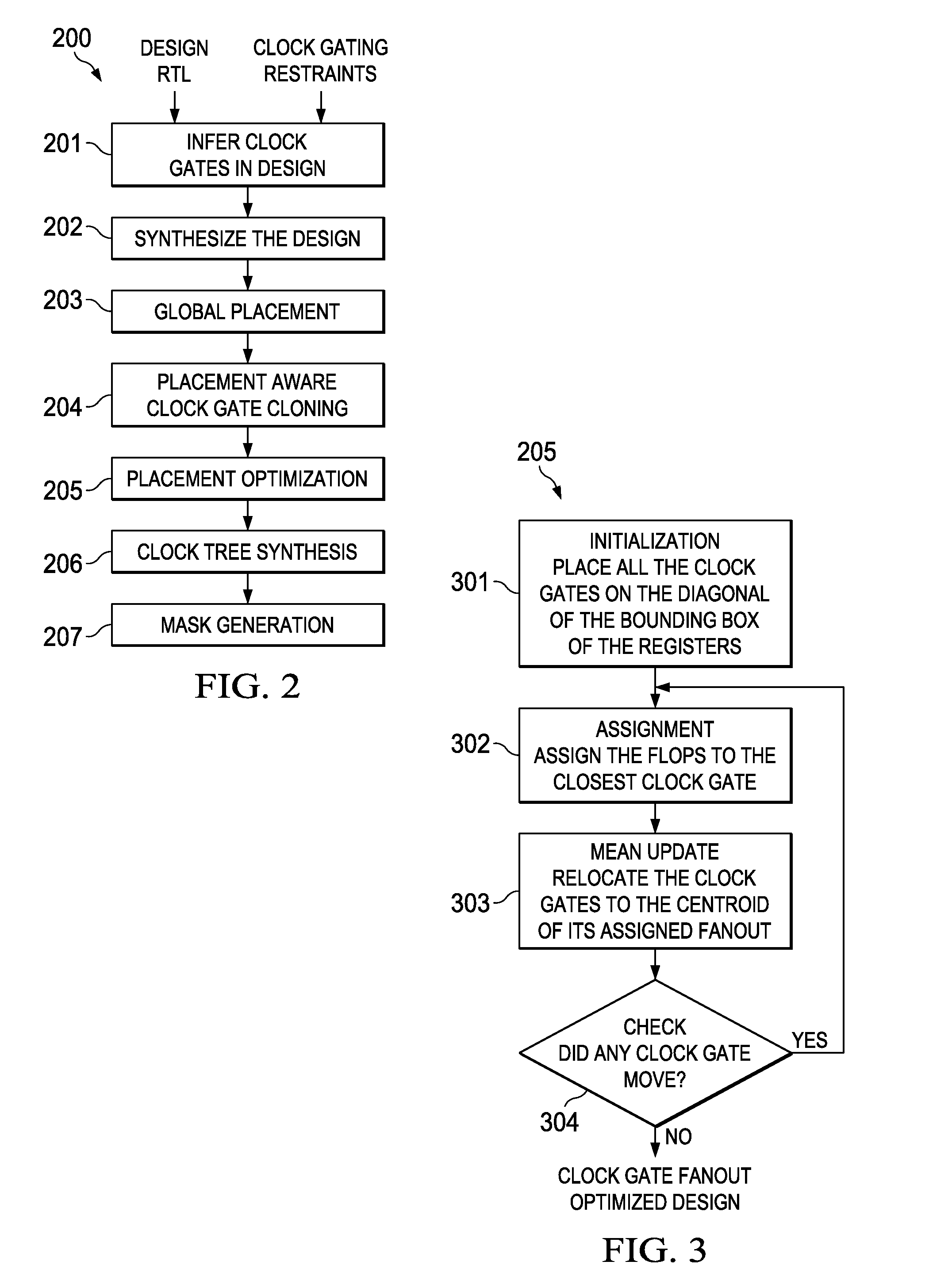
Placement aware clock gate cloning and fanout optimization
ActiveUS8661374B2Quality improvementEasy to synthesizeCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCluster algorithmProcessor register
Gating clocks has been a widely adopted technique for reducing dynamic power. The clock gating strategy employed has a huge bearing on the clock tree synthesis quality along with the impact to leakage and dynamic power. This invention is a technique for clock gate optimization to aid the clock tree synthesis. The technique enables cloning and redistribution of the fanout among the existing equivalent clock gates. The technique is placement aware and hence reduces overall clock wire length and area. The technique involves employing the k-means clustering algorithm to geographically partition the design's registers. This invention improves the clock tree synthesis quality on a complex design.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Placement aware clock gate cloning and fanout optimization
ActiveUS20130174104A1Improve placement qualityCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCluster algorithmProcessor register
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of designing layout for integrated circuit
InactiveUS20010021992A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designIntegrated circuit layoutEngineering
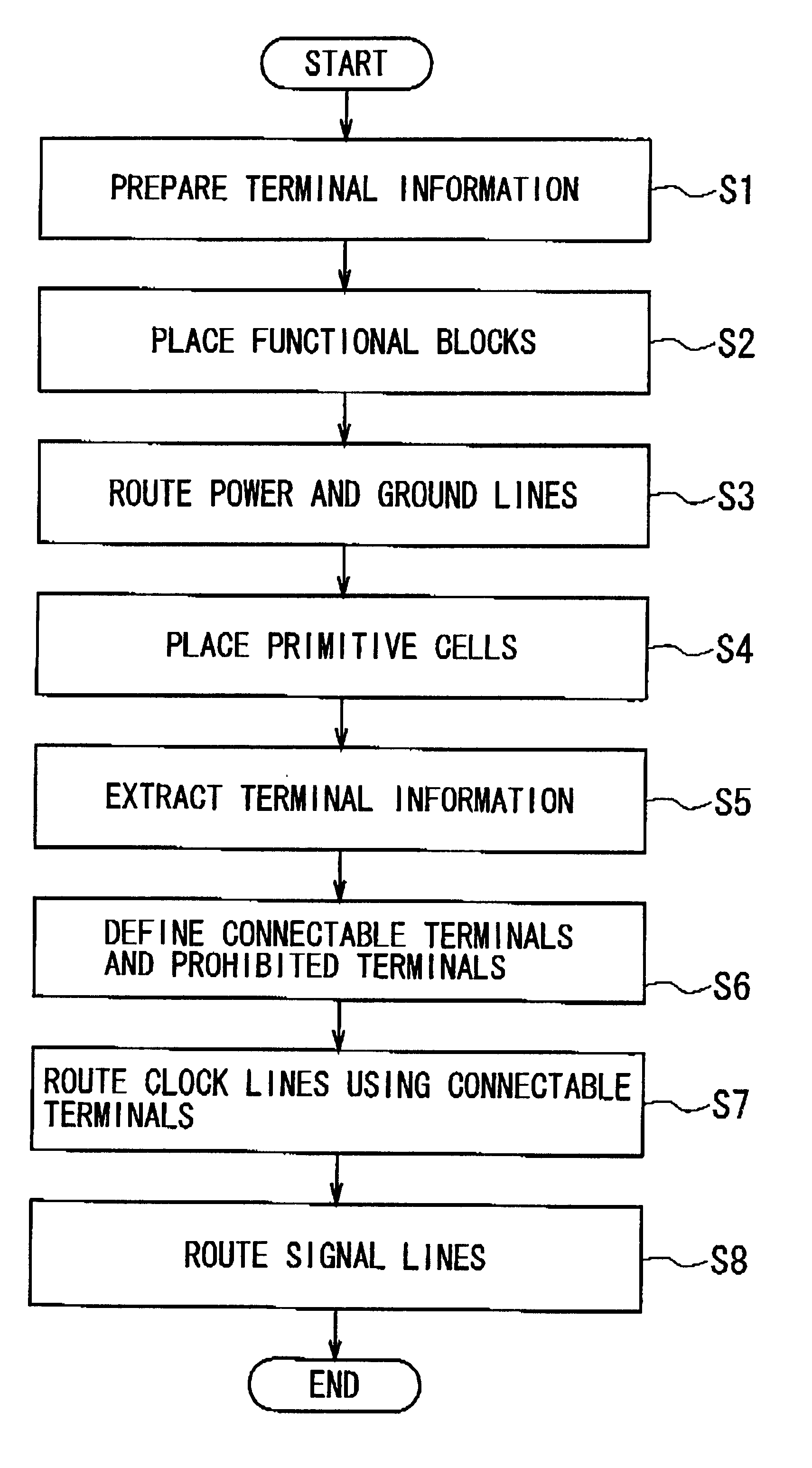
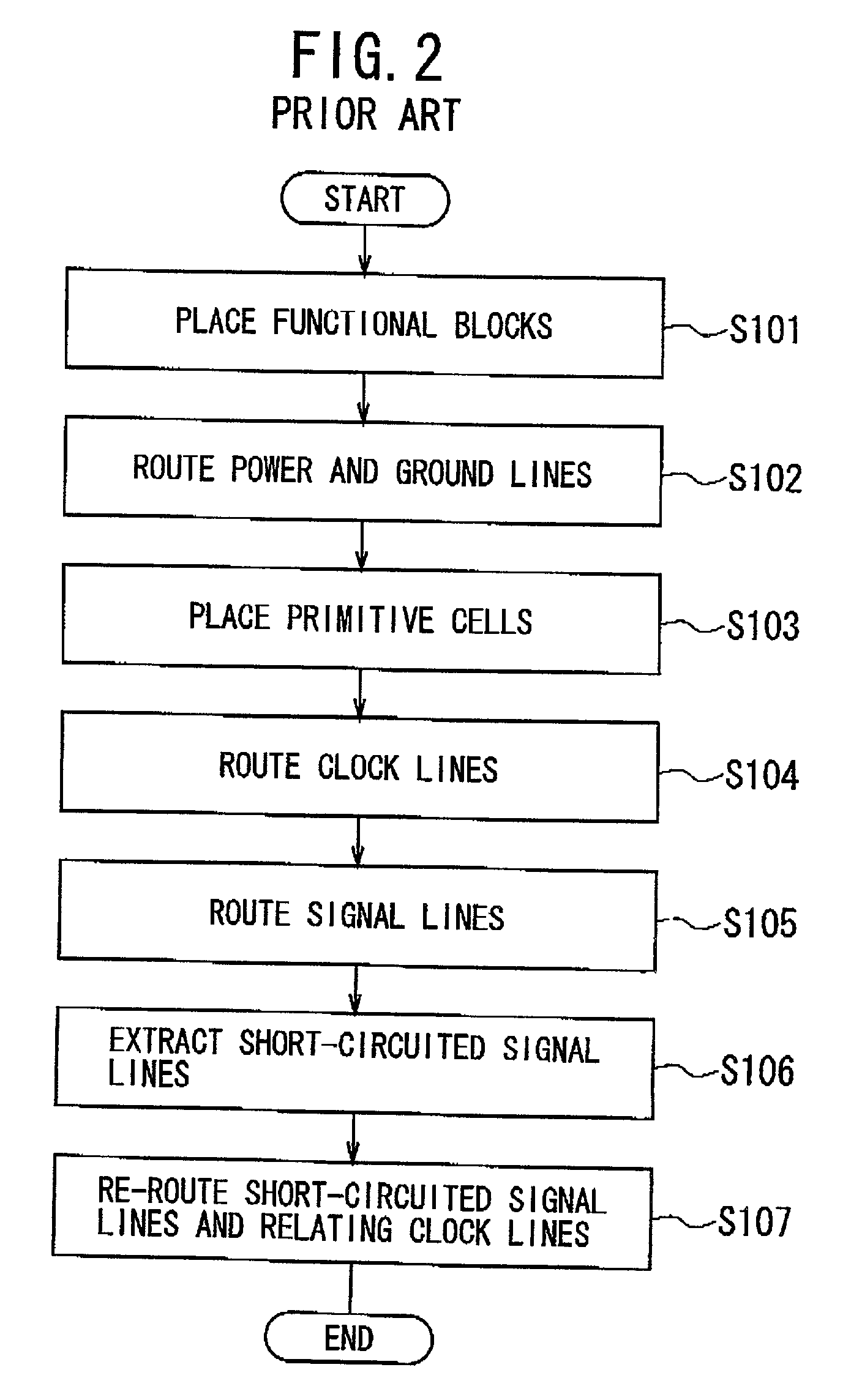
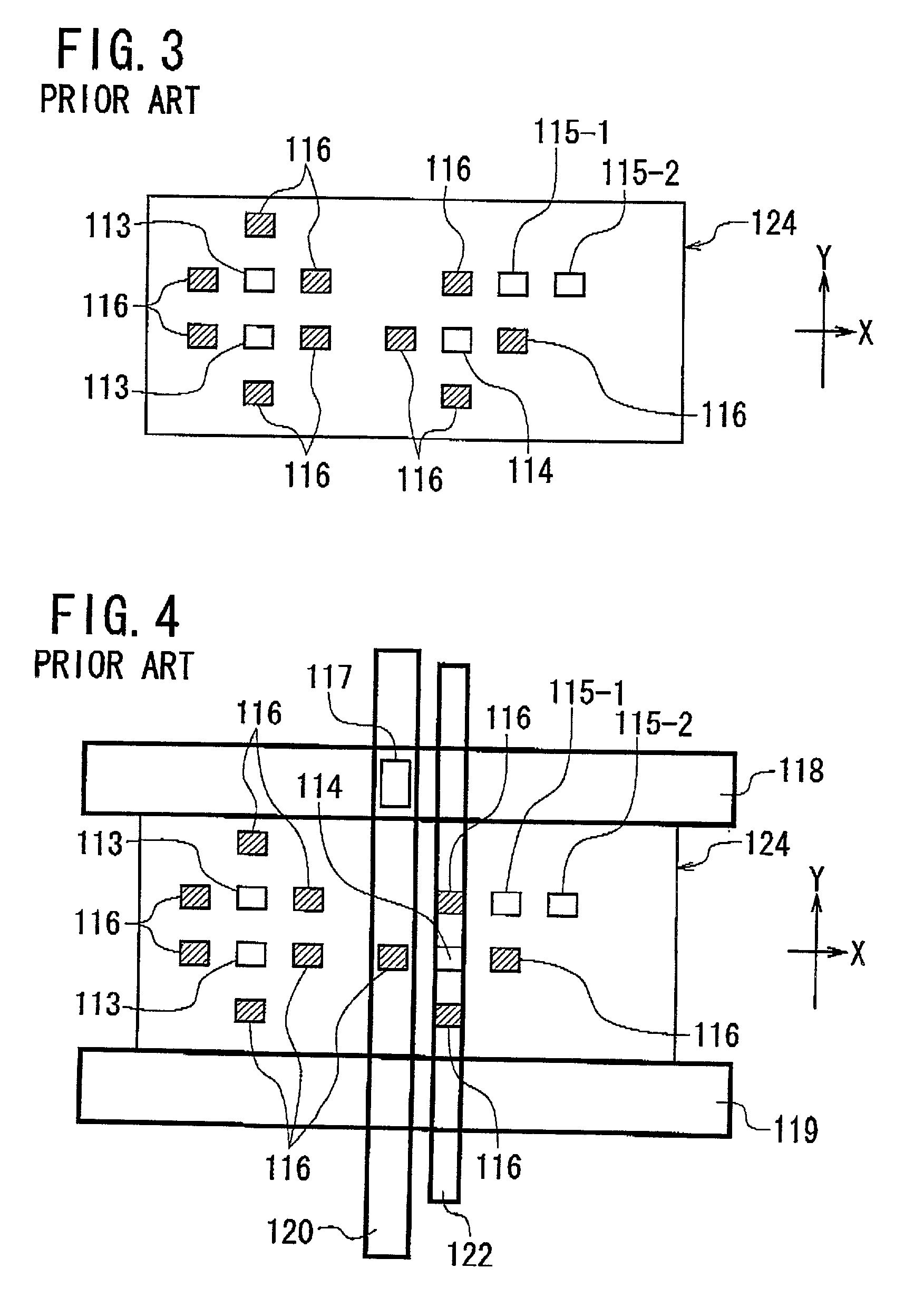
A method of designing the layout for an IC is provided, which eliminates the signal line re-routing process and which optimizes the relative skew of the clock signal. This method comprises the steps of: (a) determining prohibited areas in each of stacked wiring layers; the prohibited areas causing an obstacle to determine layout of signal lines in each of the wiring layers if clock lines are defined to intersect the prohibited areas; (b) defining layout of clock lines in each of wiring layers through a Clock Tree Synthesis process in such a way that none of the clock lines intersects the prohibited areas; and (c) defining layout of signal lines in each of the wiring layers after the step (b). Preferably, prohibited area information about a primitive cell including at least one of the prohibited areas is provided, where the prohibited area information is used in the CTS process in the step (b).
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS7122868B2Reduce power consumptionEasy to handleTransistorEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingClock tree synthesisEngineering
To provide a semiconductor integrated circuit device that reduces charging and discharging currents flowing through clock tree synthesis, thereby reducing current consumption of entire circuits of the semiconductor integrated circuit device.In a semiconductor integrated circuit device including a clock synchronous type circuit that operates in synchronization with either of rising and falling edges flank of a reference clock and a plurality of clock buffer circuits for distributing the reference clock to the clock synchronous type circuit, each clock buffer circuit is constituted from a first transistor that drives a load at one of the edges flank of the reference clock with which the clock synchronous type circuit does not operate in synchronization and a second transistor that drives the load at the other edge flank of the reference clock. A gate width of the first transistor is set so that a change in the edge flank is slowed down, provided that a pulse waveform of the reference clock is not destroyed. A carrier type of the second transistor is different from the carrier type of the first transistor, and the second transistor is formed to have the gate width larger than the first transistor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for rapidly selecting types of buffers which are inserted into the clock tree for high-speed very-large-scale-integration
InactiveUS20060010414A1Quick selectionComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsClock tree synthesisComputer science
A method and apparatus for rapidly selecting types of buffers which are inserted in the clock tree for high-speed VLSI design is disclosed. The developed tool can be embedded in the existing clock tree synthesis design flow to ensure minimizing the clock delay and satisfying the clock skew constrains. Given the clock tree netlist, inserted buffers locations information, wires electrical parameters and buffers timing library, the components delay (buffer delay and wire delay) of the clock tree can be calculated first. Then, for each I / O pin, the path delay, clock delay and clock skew can be obtained. Finally using the proposed method, a modified clock tree netlist which satisfying the timing specifications can be constructed.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Integrated circuit back end design system and method
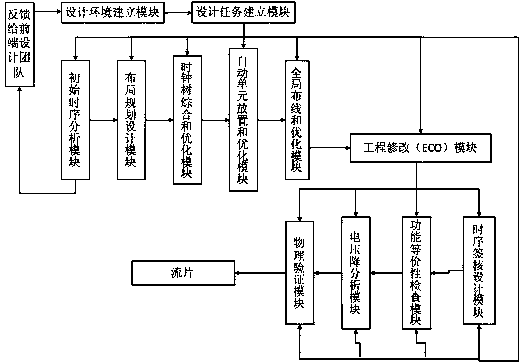
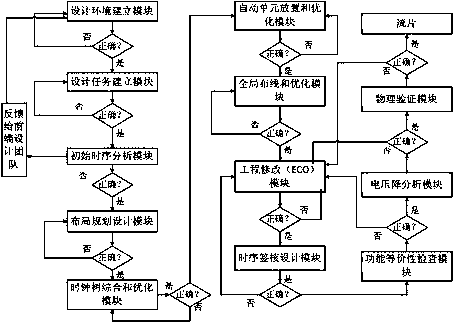
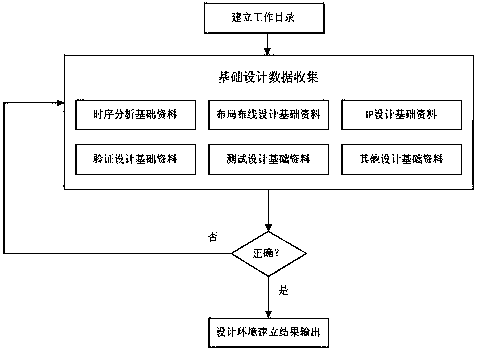
InactiveCN108133069AVersatileLower Design BarriersSpecial data processing applicationsLayout planningUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses an integrated circuit back end design system. The system comprises an environment building module, a design task module, a layout planning design module, an automatic unit placement optimization module, a clock tree synthesis optimization module, a global routing optimization module, a functional equivalence checking module, a timing sign-off design module, a voltage attenuation design module and a physical verification module. According to the integrated circuit back end design system, design sequence standardization is carried out on the main design links of the backend design, so that the design has good universality, thus the design threshold of the back end design is greatly reduced, the labor cost is reduced, the design efficiency is improved, and the designquality is ensured.
Owner:嘉兴倚韦电子科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com