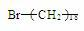Patents
Literature
144 results about "Primitive cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometry, biology, mineralogy, and solid state physics, a primitive cell is a minimum-volume cell (a unit cell) corresponding to a single lattice point of a structure with discrete translational symmetry. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its primitive cell.
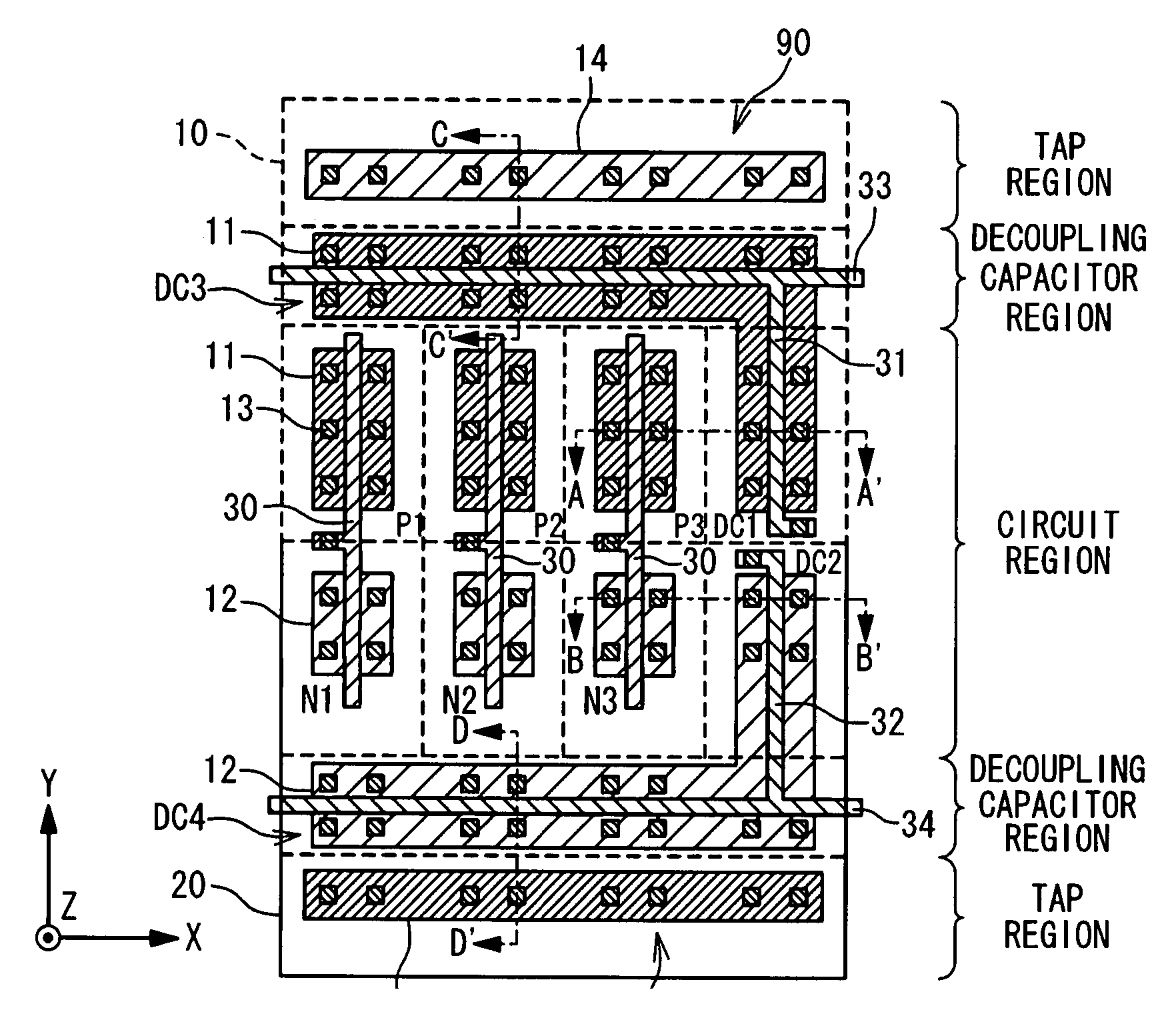
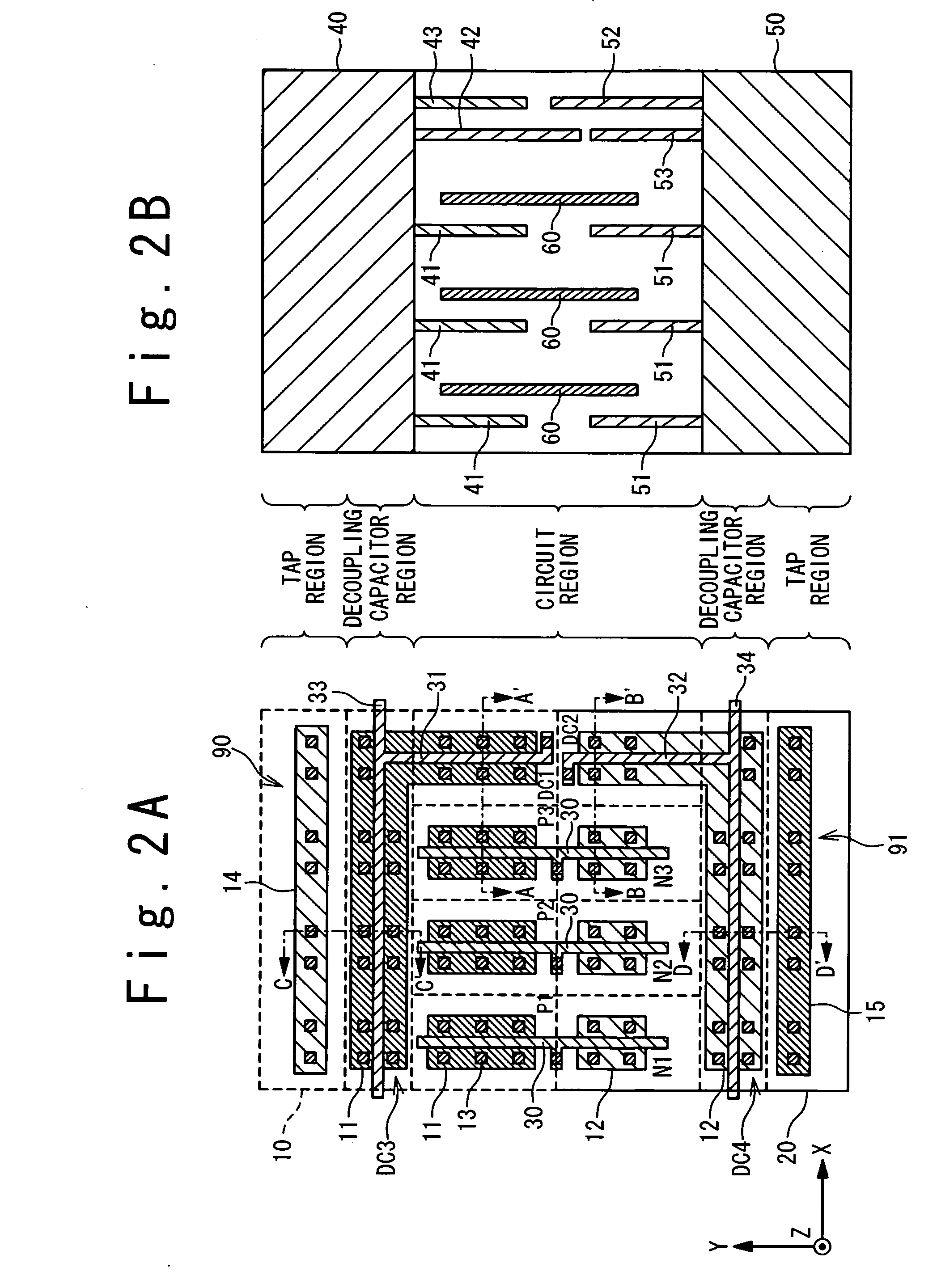
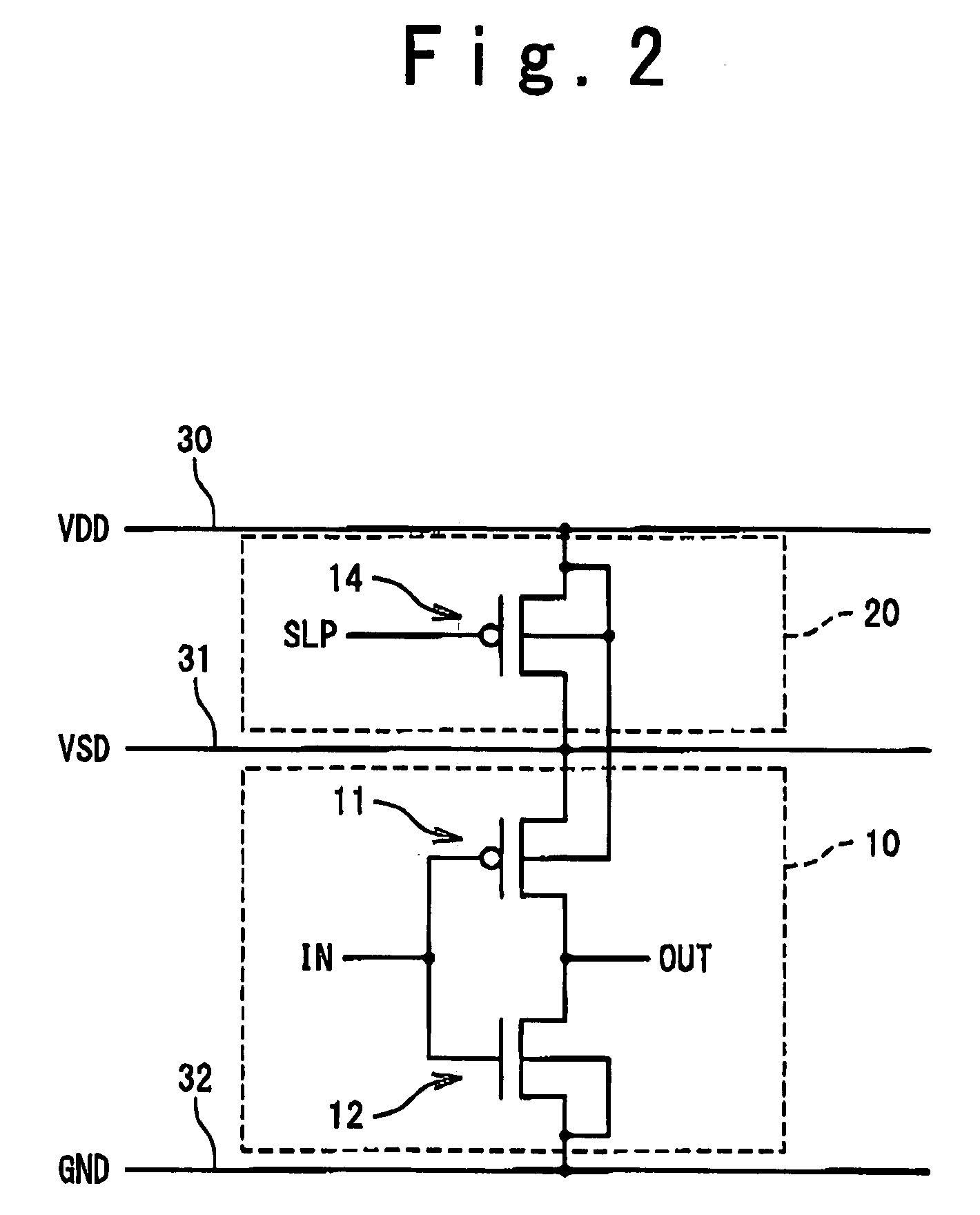
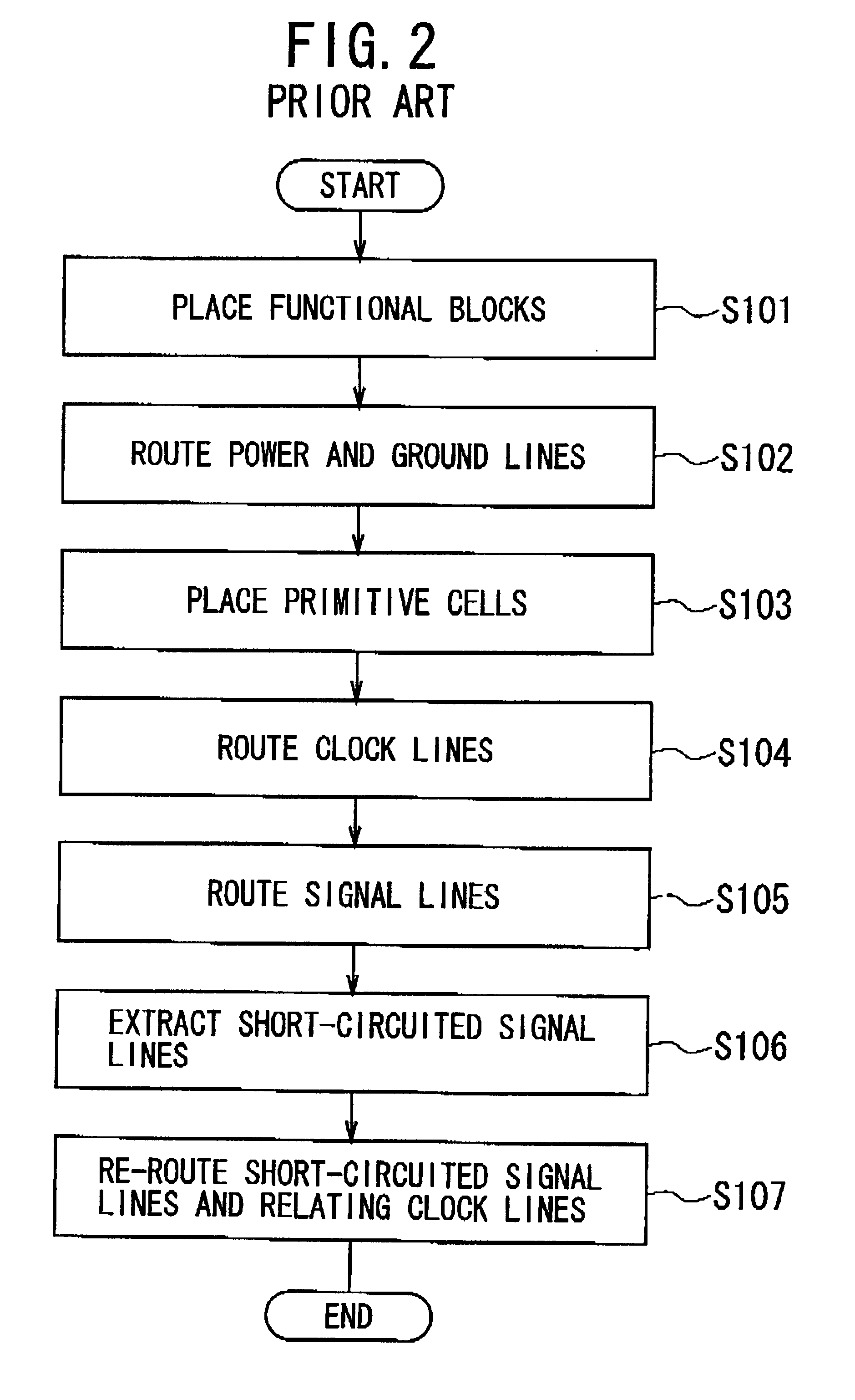
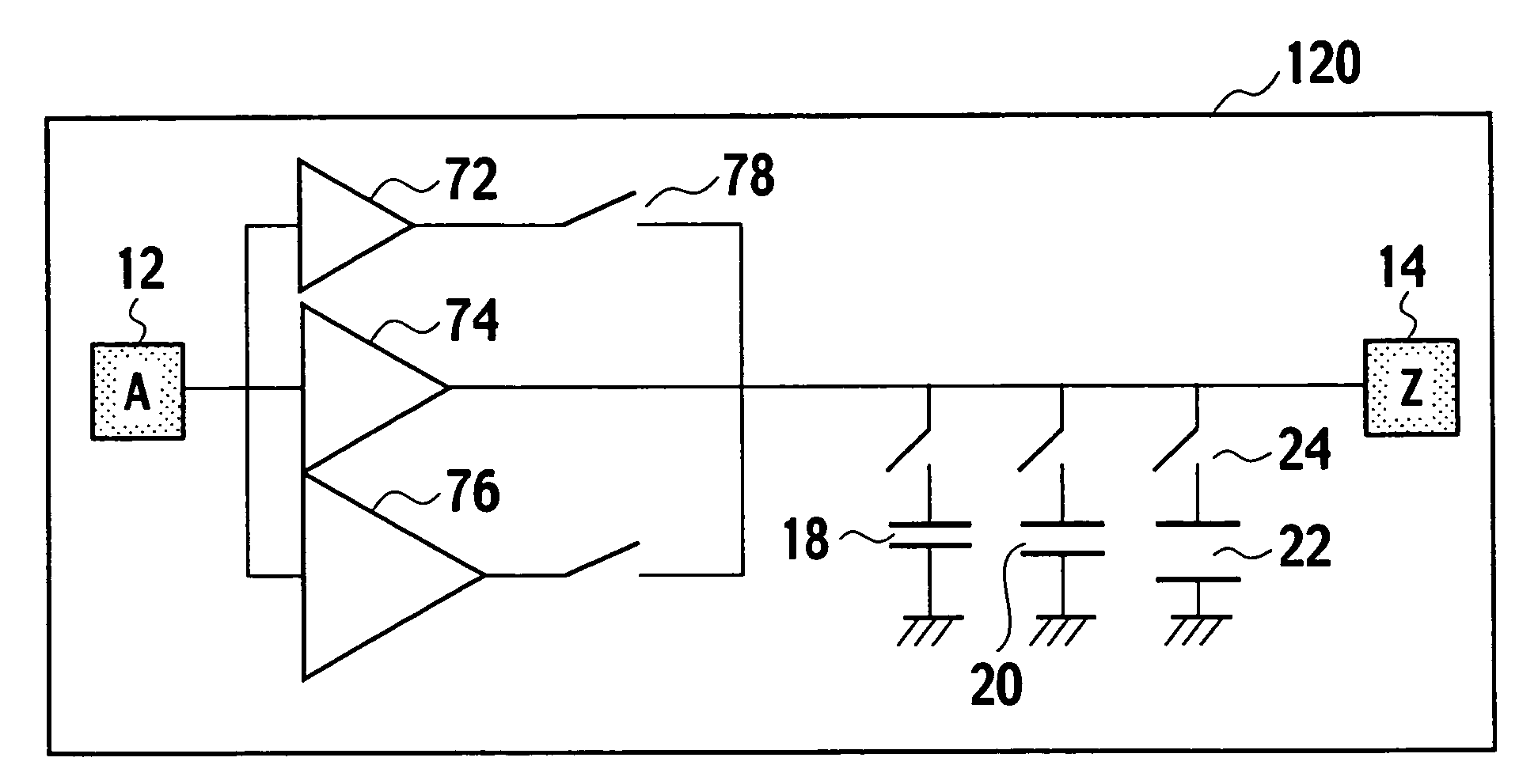
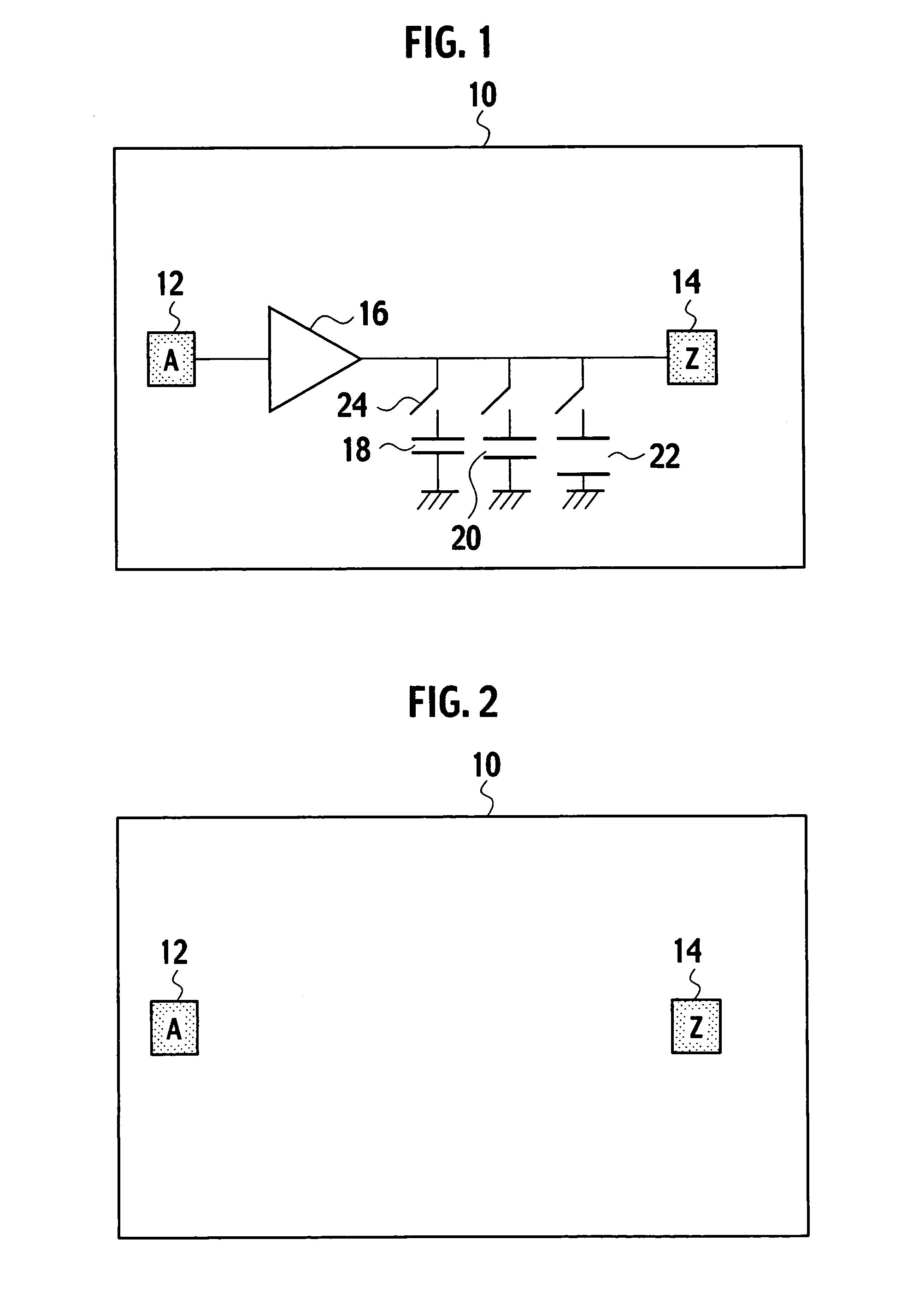
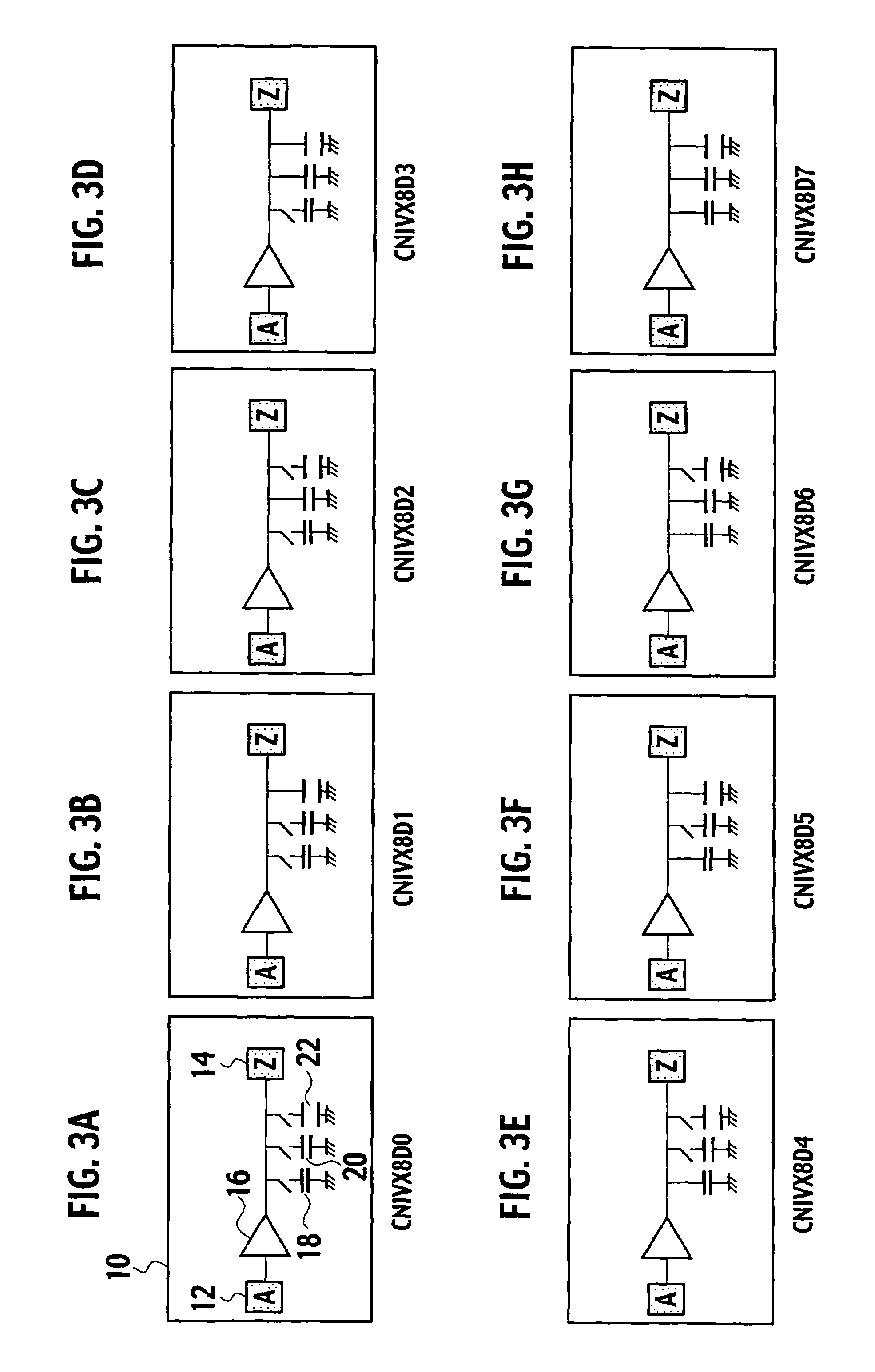
Integrated circuit incorporating decoupling capacitor under power and ground lines
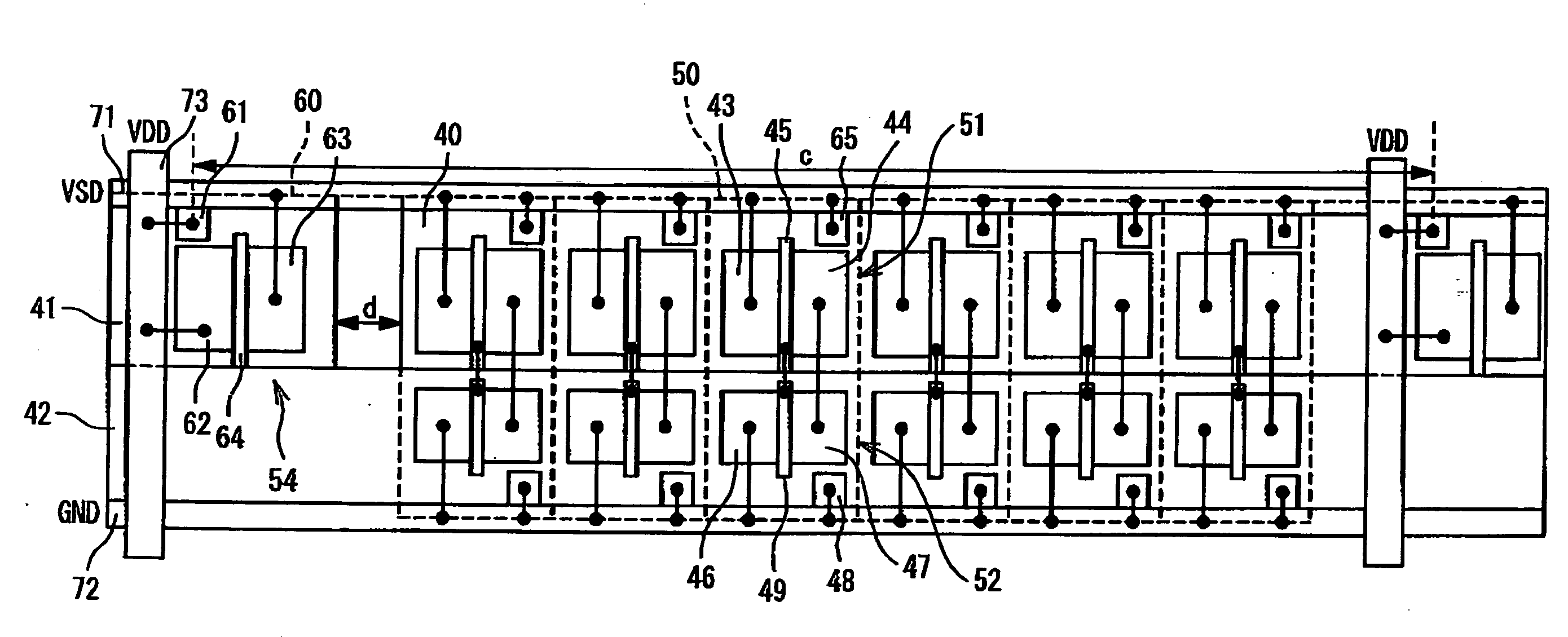
A semiconductor device is composed of: an array of CMOS primitive cells provided in a circuit region; a power supply line extended along the array of the CMOS primitive cells and connected to the CMOS primitive cells; a ground line extended along the array of the CMOS primitive cells and connected to the CMOS primitive cells; a first decoupling capacitor provided under the power supply line; a second decoupling capacitor provided under the ground line. The first decoupling capacitor is formed of a PMOS transistor having a gate connected to the ground line. At least one of the source and drain of the PMOS transistor is connected to the power supply line. The second decoupling capacitor is formed of an NMOS transistor having a gate connected to the power supply line. At least one of the source and drain of the NMOS transistor is connected to the ground line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
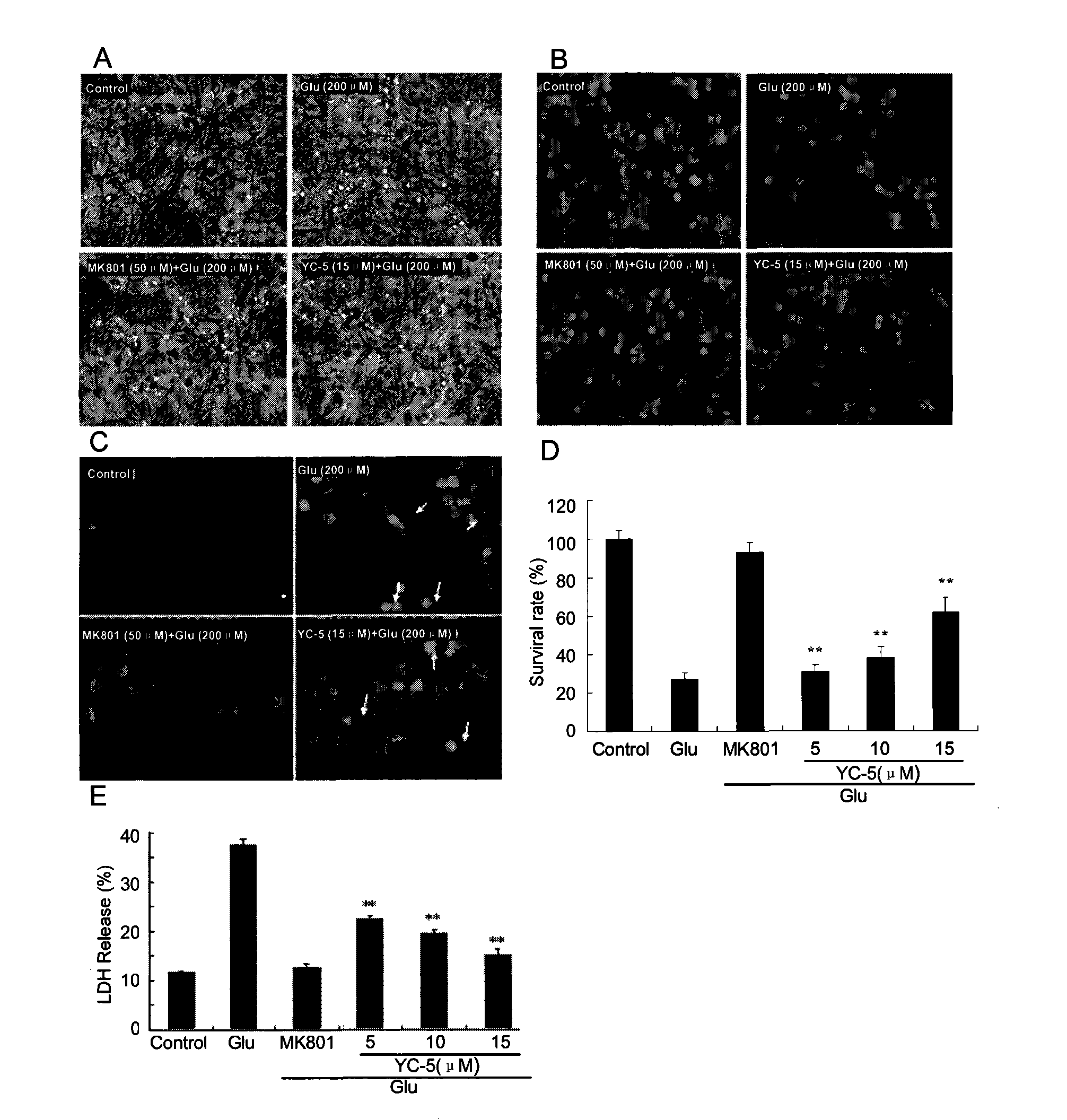
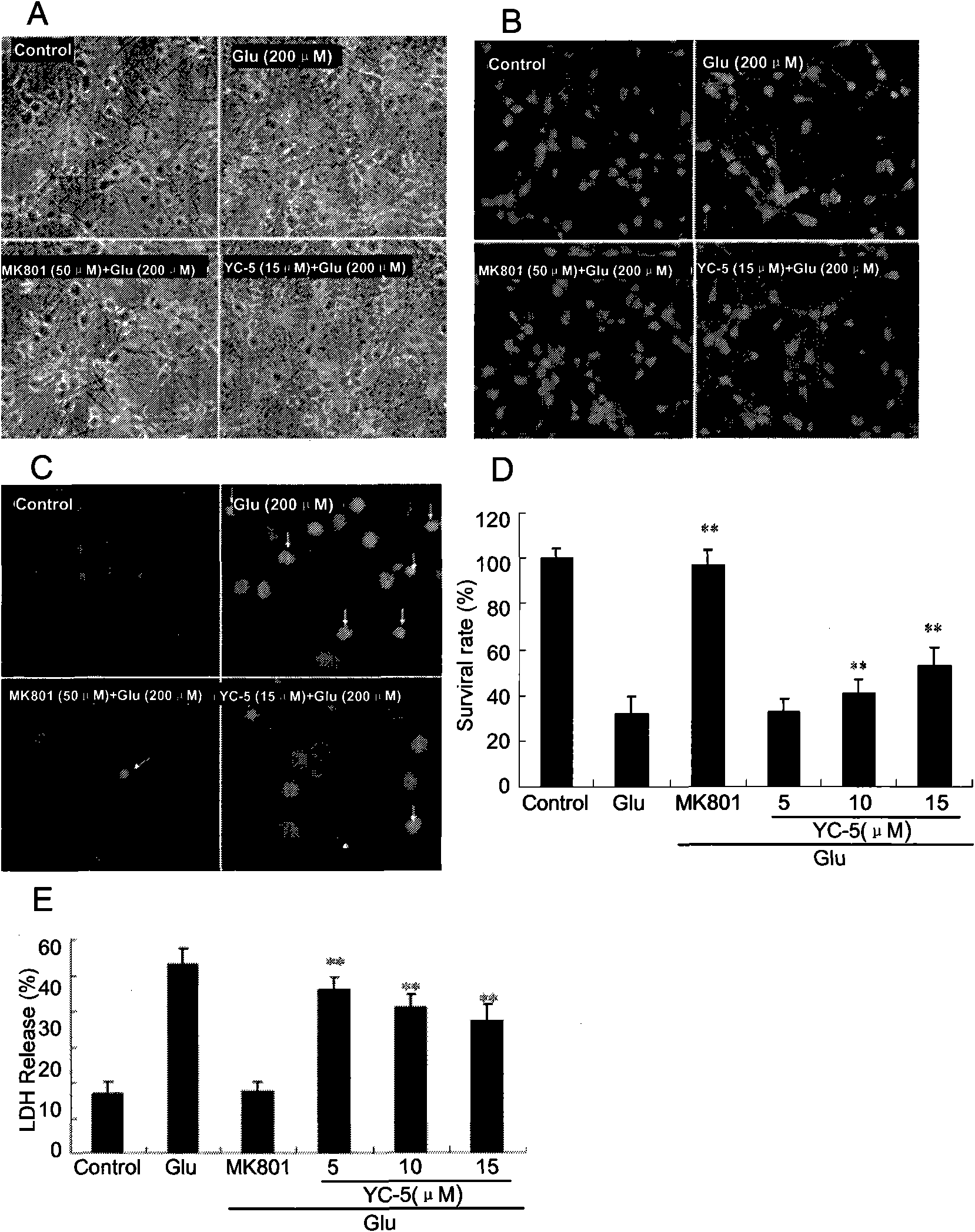
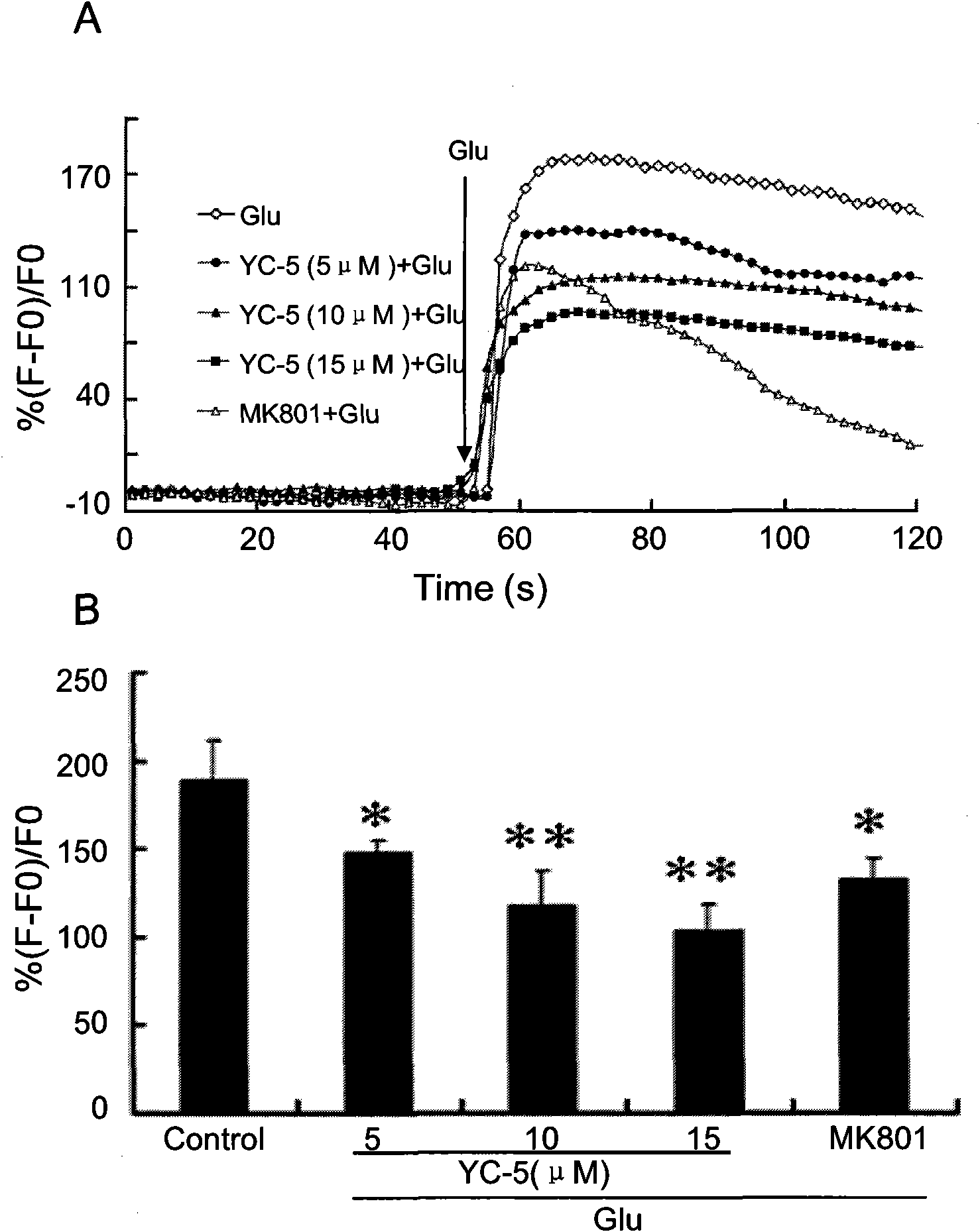
Application of cholestane-3 beta, 5 alpha, 6 beta-triol in preparation of neuronal protection medicine
The invention reveals that endogenous cholesterol metabolic product cholestane-3 beta, 5 alpha, 6 beta-triol (YC-5) has protection function for neuronal damage caused by cerebral ischemia, ischemia ofspinal cord, epileptic seizure and convulsion and relates to an application of YC-5 in preparation of neuronal protection medicine. The YC-5 can be prepared from cholesterol through two steps. The primitive cell culture in vitro and spinal cord ischemia animal model proves that YC-5 has protection function for neuronal damage caused by cerebral ischemia, ischemia of spinal cord, epileptic seizureand convulsion. YC-5 in effective dose has no toxic and side reactions. YC-5 is an effective neural protectant which aims to multiple molecular mechanism and cures cerebral ischemia damage, spinal cord ischemia damage, epileptic seizure and convulsion.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CELLPROTEK PHARMA
Method for determining unknown crystal Bravais lattice by electric back scattering diffraction
InactiveCN101413906ARealize analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBravais latticeReal time analysis
The invention provides a method used for determining Bravais lattice of unknown crystal by electron backscatter diffraction. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the steps as follows: 1) an electron backscatter diffraction spectrum is obtained and the crystal diffraction information in the diffraction spectrum is measured; 2) a two-dimensional reciprocal surface of the crystal is obtained; 3) a three-dimensional reciprocal primitive cell is reconstructed by the two-dimensional reciprocal surface; 4) the cell parameter of the three-dimensional reciprocal primitive cell s worked out according to the width of the Kikuchi band and the angle between the Kikuchi bands in the same Kikuchi electrode; 5) a reciprocal reduced cell of the crystal is solved; 6) the Bravais lattice of the crystal is determined in the reciprocal space; 7) the Bravais lattice of the crystal is determined. In the method, only a scanning electron microscope and an electron backscatter diffraction accessory are used to realize the analysis on unknown lattice of bulk crystals, and the exponential of the Kikuchi band and the Kikuchi electrode in the electron backscatter diffraction spectrum is marked at the same time. The method has no special requirement on the samples to be analyzed, is suitable for quickly analyzing bulk samples, and can be used for analyzing the microstructure morphologies and crystal structure in the buck samples.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Shield grid trench MOSFET device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105702739AIncrease the doping concentrationLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetEngineering
The invention discloses a shield grid trench MOSFET device.In grid electrode structures of primitive cells, shield electrodes are formed after epitaxial layers filling trenches are etched back, and trench grids are formed at the tops of the shield electrodes; the shield electrodes and adjacent drift regions make direct contact, carrier balance is achieved, the shield electrodes of the primitive cells and the drift regions form alternately-arranged structures in the transverse direction, and the shield electrodes carry out transverse exhausting on the adjacent drift regions in reverse bias of the device.The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the shield grid trench MOSFET device.According to the shield grid trench MOSFET device and the manufacturing method, it is unnecessary to arrange dielectric films at the bottoms of the shield electrodes, stepping of device units can be reduced, the specific on-resistance of the device can be reduced, manufacturing difficulty can be lowered, and the uniformity of device performance can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SANRISE TECH CO LTD
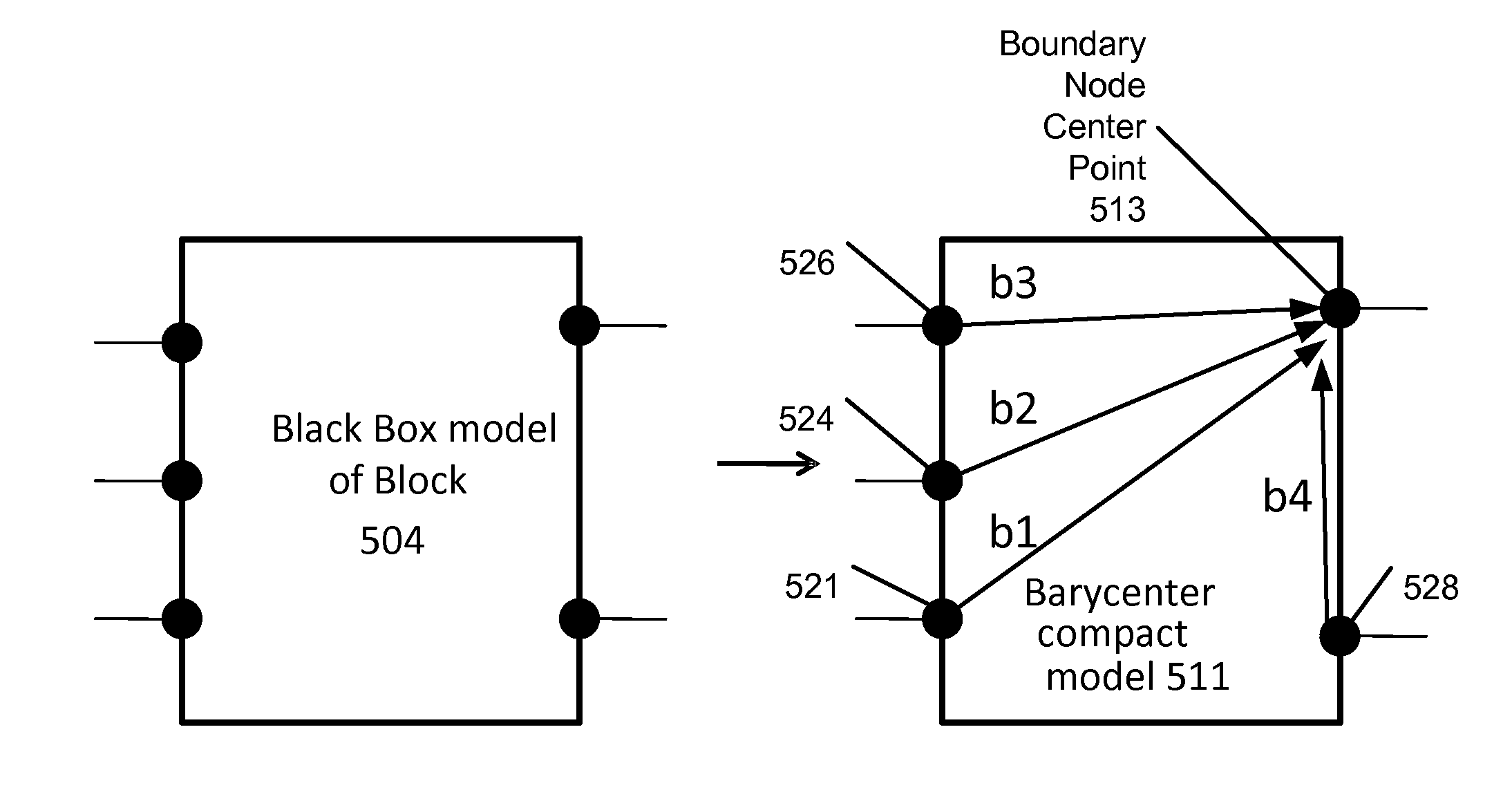
Solving a hierarchical circuit network using a Barycenter compact model
ActiveUS8694302B1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer architectureDirichlet boundary condition
Any primitive cells or blocks can be represented physically by a Barycenter compact model (or Barycenter model), and any black box model can also be physically represented by a Barycenter compact model physically. A hierarchical boundary condition between blocks is formulated by the Barycenter compact model. Hierarchical boundary condition problems between blocks can be limited within two levels only if using the Barycenter compact model.
Owner:WORLDWIDE PRO
Size-reduced layout of cell-based integrated circuit with power switch
InactiveUS20080093632A1Reduce circuit sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower switchingCell based
An integrated circuit is provided with a first power line, a plurality of additional power lines intersecting with the first power line, a plurality of power switch transistors each having a drain connected with the first power line and a source connected with one of the additional power lines, a well provided to extend along the first power line; and a plurality of primitive cells each including a first transistor prepared within the well, the first transistor having a source connected with the first power line. The plurality of additional power lines includes first and second additional power lines The plurality of primitive cells are provided between the first and second additional power lines along the first power line. A bias voltage is fed to the well through both of first and second well contacts, the first well contact providing a connection between the first additional power line and the well, and the second well contact providing a connection between the second additional power line and the well.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Unilateral MOS-type device manufacturing method integrated with SBD structure
InactiveCN108183131AImprove conduction performanceLow application costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeMOSFETReverse recovery
The invention discloses a unilateral MOS-type device manufacturing method integrated with an SBD structure. Through introducing a special angle groove manufacturing process, an inclination angle unilateral ion implantation process and a schottky metal process compatible with an ohm process, manufacturing of an SiC groove MOSFET device integrated with an SBD structure is realized. The silicon carbide SBD structure is integrated in the silicon carbide groove-type MOSFET device, a reverse follow current function can be realized well, the reverse recovery time of the MOSFET device can be reduced,and the application cost of a silicon carbide power electronic device can be effectively reduced. In combination of a unilateral high-mobility groove structure with special crystal face etching, whilethe groove mobility is improved, the size of a primitive cell is narrowed, and the device conduction ability is improved.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Semiconductor tube of hyperconjugation longitudinal double diffusion metal oxide with N channels
InactiveCN101552291AIncrease working currentGuaranteed withstand voltage levelSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionHyperconjugation
The invention relates to a semiconductor tube of hyperconjugation longitudinal double diffusion metal oxide with N channels, comprising an N-type doped silicon substrate which is also used as a drain region, an N-type doped silicon epitaxial layer, a primitive cell region and a terminal region arranged at the periphery of the primitive cell region; the N-type doped silicon epitaxial layer is arranged on the N-type doped silicon substrate; the primitive cell region and the terminal region are arranged on the N-type doped silicon epitaxial layer; the terminal region comprises a first hyperconjugation structure and an N-type silicon doped semiconductor region, wherein the first hyperconjugation structure comprises a P-type column and a N-type column; an N-type heavily doped semiconductor region is arranged in the N-type silicon doped semiconductor region; the first hyperconjugation structure and the N-type silicon doped semiconductor region are respectively provided with a field oxidation layer; and the N-type heavily doped semiconductor region is connected with a metal layer. The semiconductor tube is characterized in that the first hyperconjugation structure and the N-type silicon doped semiconductor region are respectively provided with the field oxidation layer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
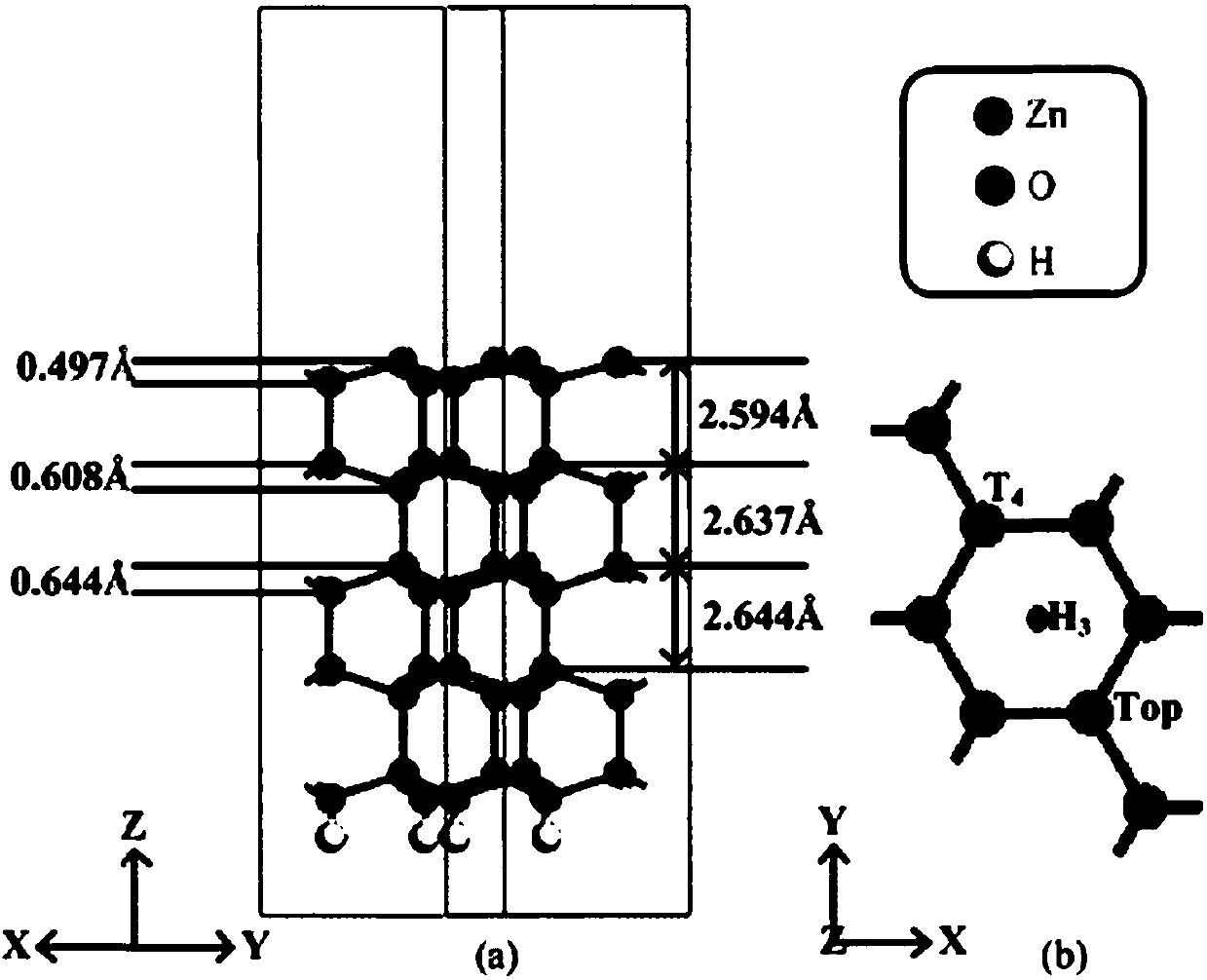
Calculation method for improving photocatalytic properties of ZnO (0001) surface through Fe atom doping and adsorption
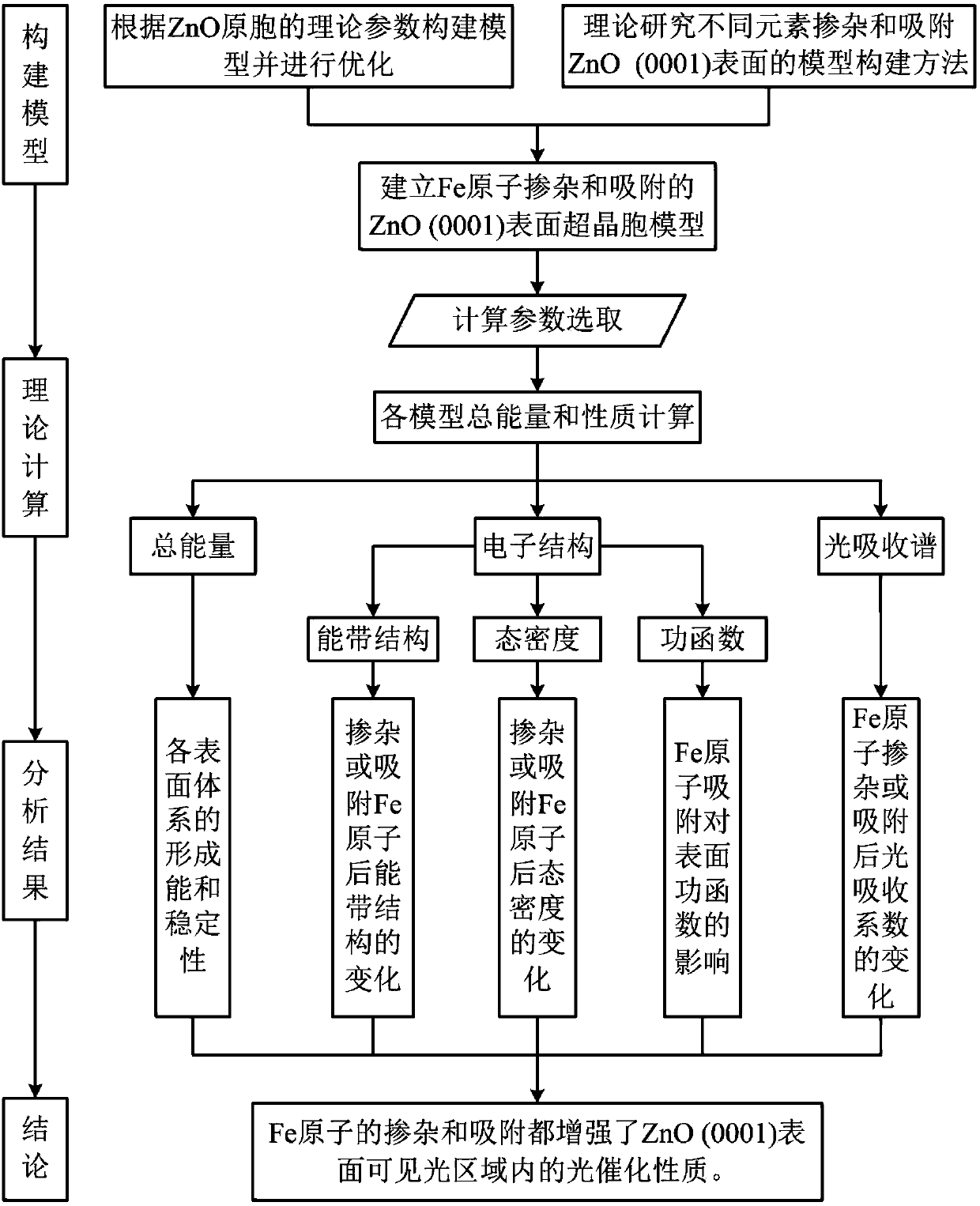
ActiveCN108256287AImprove photocatalytic propertiesThe result is accurateChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic structureOptical property
The invention discloses a calculation method for improving the photocatalytic properties of the ZnO (0001) surface through Fe atom doping and adsorption. The method includes the steps of constructingthe primitive cells of ZnO body material in MS software, optimizing the structure, and constructing ZnO (0001) surface supercells and doping and adsorption models of Fe atoms at different loci on thepure ZnO (0001) surface; conducting structural optimization and GGA+U method calculation on the surface, selecting the energy band structure, the state density, the optical properties and the accuracycorresponding separately, and conducting calculation on each model; analyzing each model through a CASTEP module, obtaining the formation energy, optical property constant and work function of the ZnO (0001) surface doped and adsorbed by the Fe atoms, and obtaining the electronic structure and the optical property corresponding to each model. Therefore, the photocatalytic activity of the ZnO (0001) surface in the visible light range is improved, and certain reference is provided for the practical application of ZnO photocatalysis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method of designing layout for integrated circuit
InactiveUS6519750B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designIntegrated circuit layoutEngineering
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
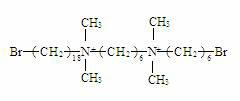
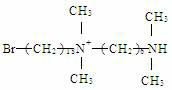
Gemini cationic surfactant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102351718AImprove bindingImprove surface activityOrganic compound preparationTransportation and packagingStructural formulaAlkylation
The invention discloses a gemini cationic surfactant and a preparation method thereof. The method is as follows: after a quaternization reaction and an alkylation addition reaction, two electropositive hydrophilic groups and two asymmetric hydrophobic chains are respectively introduced on both sides of a long-chain aliphatic hydrocarbon to prepare the gemini cationic surfactant of which structural formula is shown as below. The prepared gemini cationic surfactant can be used as the template agent to synthesize primitive cell nano-layer MFI nanometer thin-layer zeolite of which the thickness is only 2nm, the zeolite can be used to increase the activity and selectivity of the catalytic reaction; and the chemical bonding in a polar head group area inhibits a separation force between the original head groups of the single-chain single-head group surfactant, which is an important breakthrough for the increase of the surface activity and is also a new way for practical applications. By revealing the relation between the new molecular structure and the self-organizing behavior, the amphiphilic molecule self-organizing mechanism can be understood deeply.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor circuit, operating method for the same, and delay time control system circuit
A semiconductor circuit allows a timing adjustment after detailed routing without rearrangement and rerouting, an adjustment of delay variance due to process variation, and a delay adjustment even after chip formation using a primitive cell with a built-in means for adjusting delay time. The circuit connected between an input pad and an output pad, an operating method for the same, and a delay time control system circuit, which externally adjusts delay time of a plurality of control terminal-equipped / variable capacitance embedded buffers configures a semiconductor circuit. The structure includes: a first buffer connected between the input pad and the output pad; and a plurality of capacitances connectable in parallel between a fixed potential and a current flowing path, which is positioned between the first buffer and the output pad, and that controls connection between each of the plurality of capacitances and the output pad.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
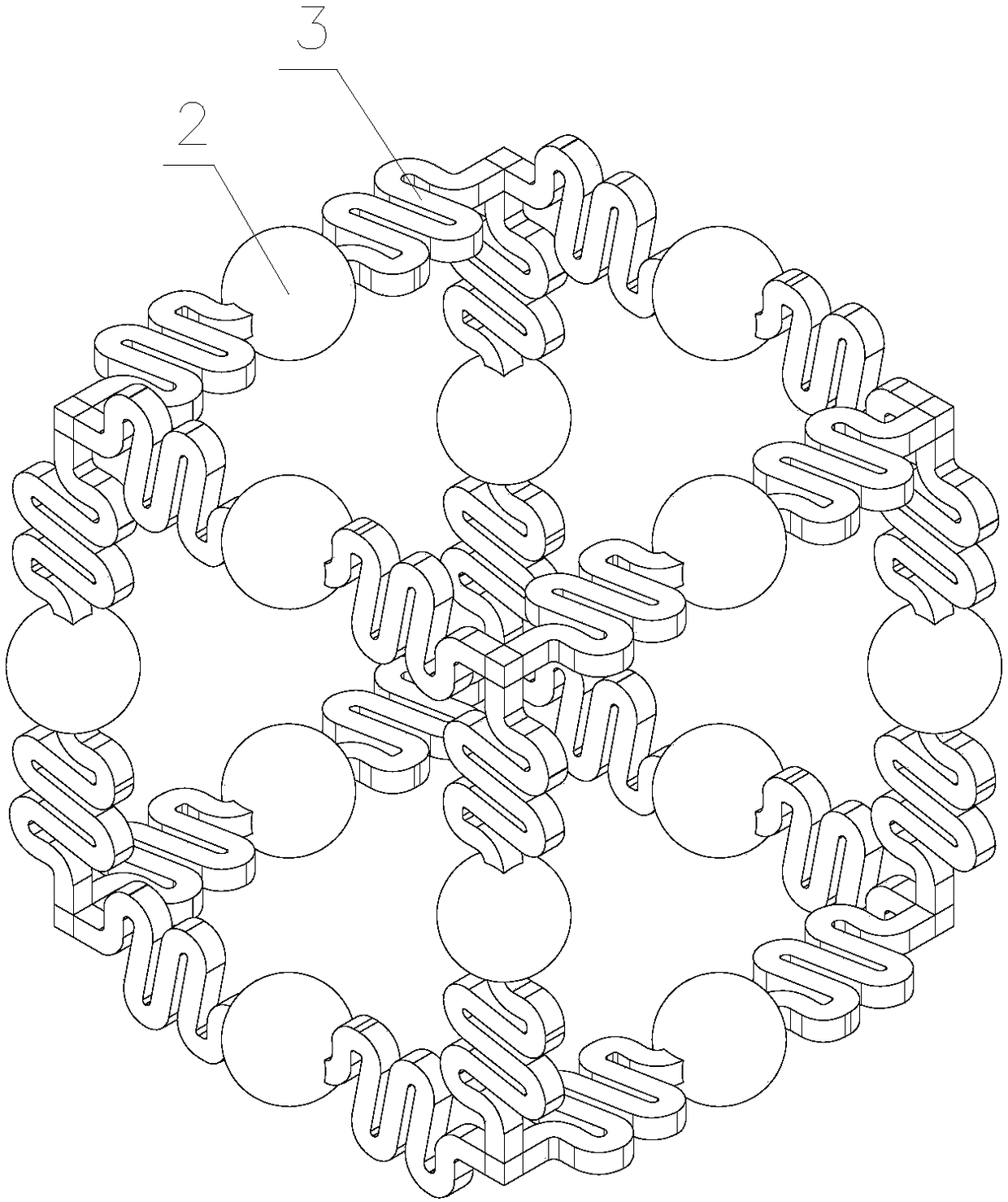
Folded beam type sonic crystal with wide amplitude and low frequency band gap characteristics
ActiveCN108492815AReduce connection stiffnessEasy to moveSound producing devicesResonanceLow frequency band
The invention discloses a folded beam type sonic crystal with wide amplitude and low frequency band gap characteristics. The folded beam type sonic crystal comprises multiple primitive cells, whereinmultiple primitive cells are distributed in a three-dimensional cube array and form the sonic crystal; each primitive cell comprises 12 borders, the 12 borders are connected to form a cubic frame structure, each border comprises two folded beams and mass blocks, first ends of the two folded beams are respectively fixedly connected with the outer side surface of the mass blocks, and axes of the twofolded beams are coincided and pass through the center of the mass blocks. The folded beam type sonic crystal with the wide amplitude and low frequency band gap characteristics has the advantages that the mass blocks are connected by virtue of the folded beams, connection stiffness among the mass blocks is reduced, based on a local resonance mechanism, an energy band gap can beneficially move tolow frequency, and a wider energy band gap is formed.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS +1
Low frequency broad-band gap 3D phonon crystal for vibration damping noise reduction
ActiveCN109036367AReduce quality problemsSmall sizeSound producing devicesEngineeringElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a low frequency broad-band gap 3D phonon crystal for vibration damping noise reduction; the phonon crystal comprises a plurality of primitive cells that are periodically arranged; the primitive cell comprises 6 same 2D chiral structures; the chiral structure comprises a disc and four connecting rods; the axis of the connecting rod is orthogonal to that of the disc; one endof the connecting rod is connected with the disc periphery; the 4 connecting rods encloses the disc and are symmetrically arranged in a rotary mode; the 6 2D chiral structures are connected via the connecting rod end portions so as to form a hexahedron; the rotary directions of the chiral structures on two mutually parallel surfaces are opposite to each other; two adjacent chiral structures are mutually vertical to each other. The phonon crystal not only has a low frequency broad-band gap property energy zone structure, and is simple in preparation, thus reducing the structure complexity, improving the structure vibration damping stability, and providing a new path for the vibration damping noise reduction.
Owner:南京光声超构材料研究院有限公司
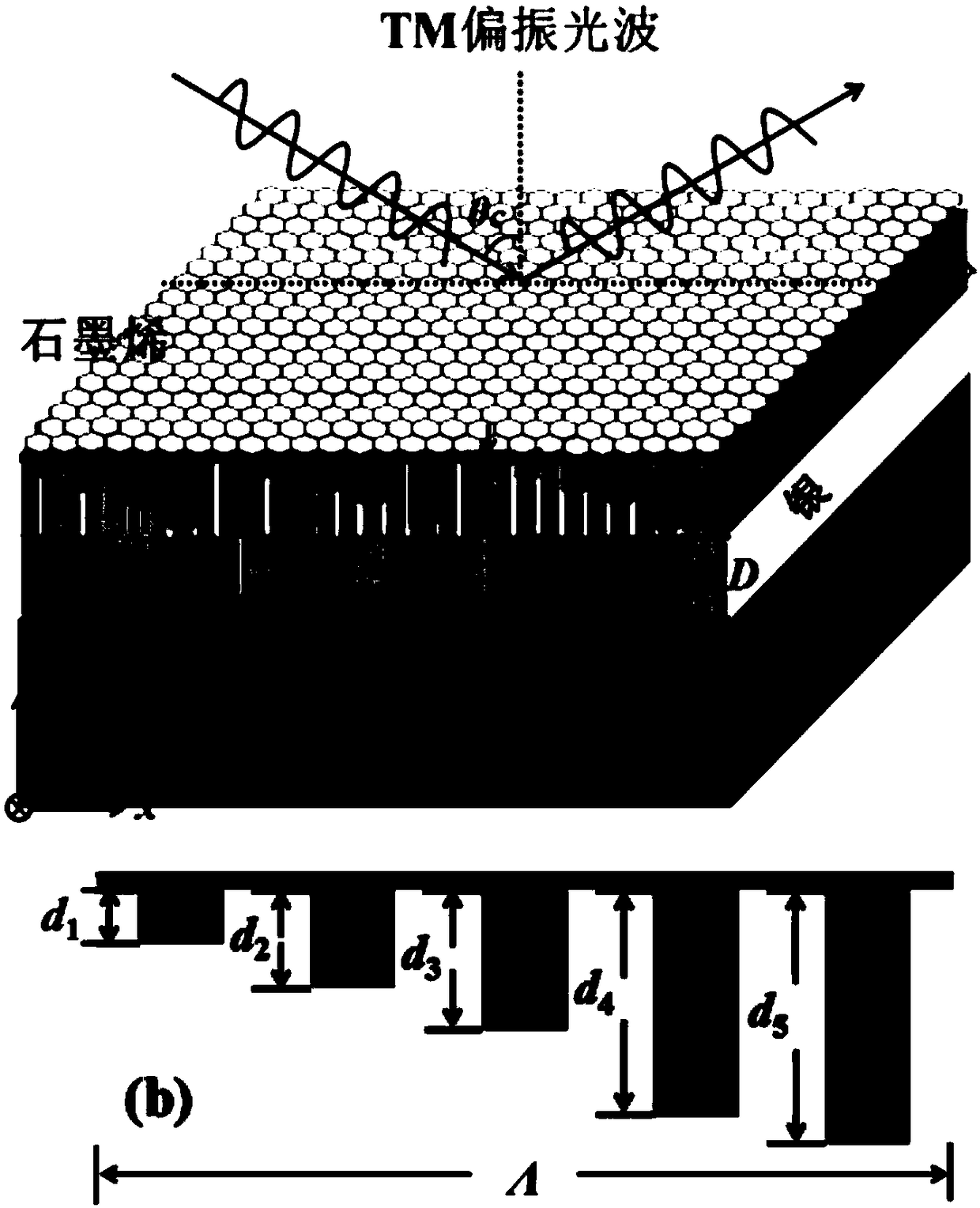
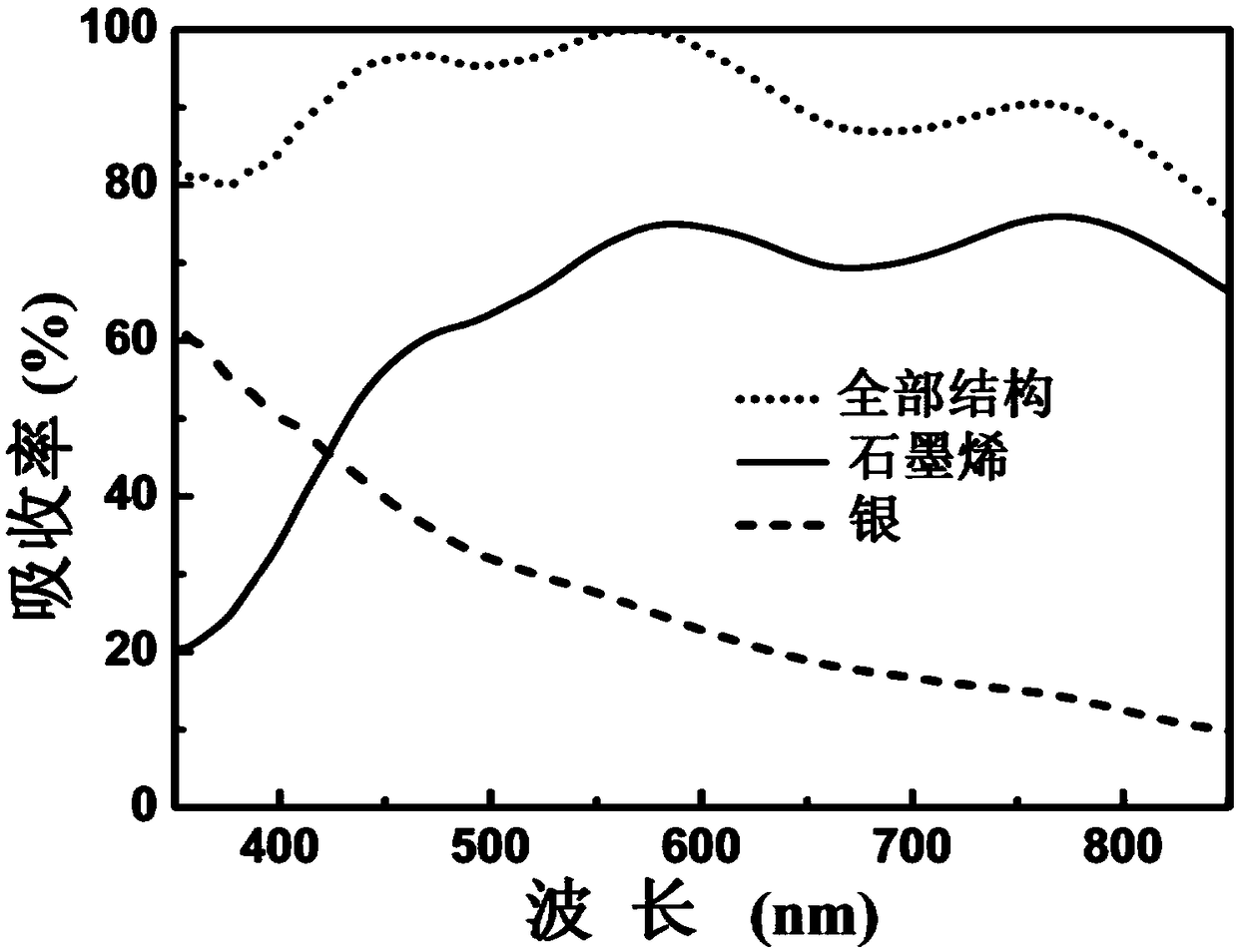
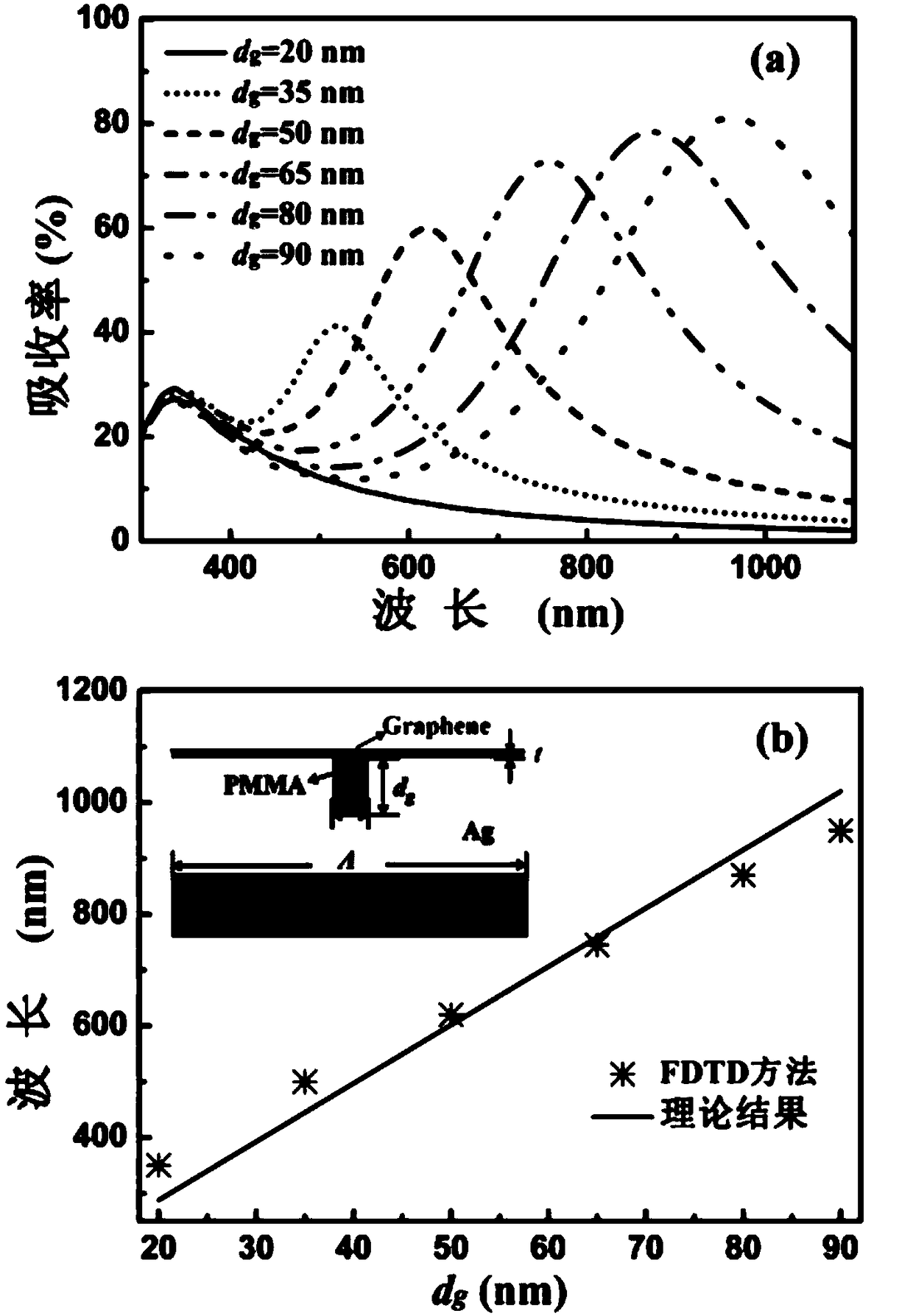
Method and device for realizing wave absorbing of graphene at visible light waveband
ActiveCN109188579AImprove performanceExcellent broadband light absorption effectOptical elementsMicro nanoMicro structure
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing wave absorbing of graphene at a visible light waveband, and belongs to the field of photoelectric detection and micro-nano optical, mechanical and electrical systems. A multi-groove structure provided by the invention is a periodic micro-structure, a primitive cell (a basic unit of the structure) of the periodic micro-structure is formedby a plurality of narrow metal grooves with the same width and different depths, a dielectric coating layer is filled into the grooves and above the grooves, and the graphene is deposited above the dielectric coating layer. For TM polar incident light waves, due to a cavity resonance effect of the grooves, the grooves with different depths correspond to different graphene light absorption wavelengths, and broadband absorption of the graphene at the visible light waveband can be realized through combination of the grooves with the different depths. In addition, an absorption spectrum of a waveabsorber is insensitive to the change of an incident angle, and even the incident angle is obviously changed, the graphene still has excellent broadband light absorption performance; and the method and the device have an application prospect in the fields such as light modulators, solar cells, touch screens, biological sensing and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
LED chip and production method thereof
ActiveCN107689407AReduce leakage currentImprove stabilitySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyElectricity
The invention discloses an LED chip and a production method thereof. The LED chip comprises a substrate and an extension structure arranged on the substrate, wherein the extension structure is dividedinto a plurality of LED primitive cells; peripheral side walls of the extension structure are provided with a side wall groove, and the side wall groove is used for reducing the total emission of thelight in the LED primitive cells; a primitive cell groove is formed between two adjacent LED primitive cells, the substrate is exposed by virtue of the bottom of the primitive cell groove, and the primitive cell groove reduces the total emission of the light in the LED primitive cells as well as the leak current; an insulation layer is arranged in the primitive cell groove; and a connection electrode covers the insulation layer, and the connection electrode electrically connects two adjacent LED primitive cells. In the technical scheme of the invention, the total emission of the light in theLED primitive cells is reduced by virtue of the side wall groove, the total emission of the light in the LED primitive cells and the leak current can be reduced by virtue of the primitive cell groove,so that the light emitting efficiency can be improved, the current leakage rate is reduced, and the external quantum efficiency can be improved.
Owner:XIAMEN CHANGELIGHT CO LTD
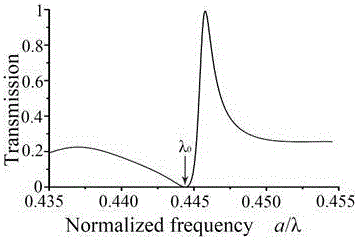
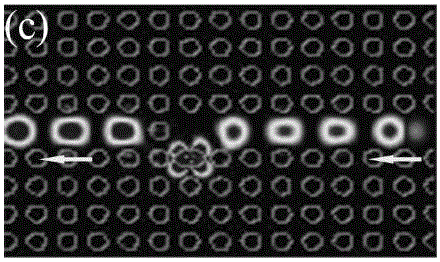
Method for realizing all-optical diode
InactiveCN106405977AAdjust the forbidden band rangeEasy to integrateOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsPicosecondLattice constant
The invention discloses a method for realizing an all-optical diode. In a two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide, a micro-cavity is designed on the side; and a dielectric column primitive cell is additionally arranged as a reflective layer in the photonic crystal waveguide near the micro-cavity, and the position of the reflective layer is a lattice constant deviated from the position where the waveguide is over against the micro-cavity. When the incident light intensity increases all along, the forward incident light first reaches a power threshold for exciting the nonlinear Kerr effect of the micro-cavity material, and the backward incident light is in a cut-off state under the light intensity, so as to realize the forward conduction / backward cut-off function of the all-optical diode. The working band of the all-optical diode can be adjusted by adjusting the lattice constant, and the all-optical diode is easy to be integrated in an all-optical network, so that the all-optical diode has a great application value. The all-optical diode has a response time on the order of picosecond, and the photonic crystal has the characteristic of adjusting the forbidden band range according to the lattice constant of the photonic crystal.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
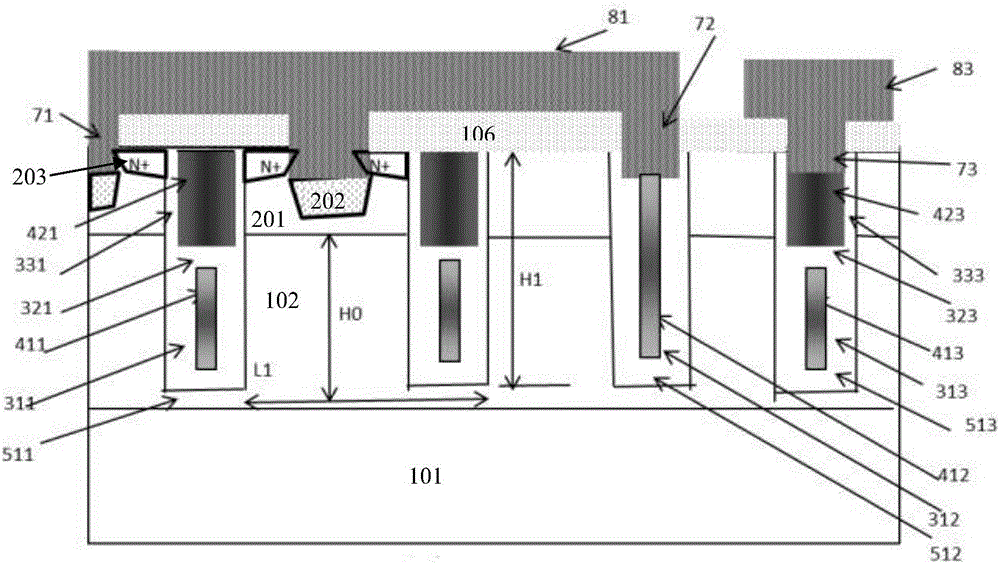
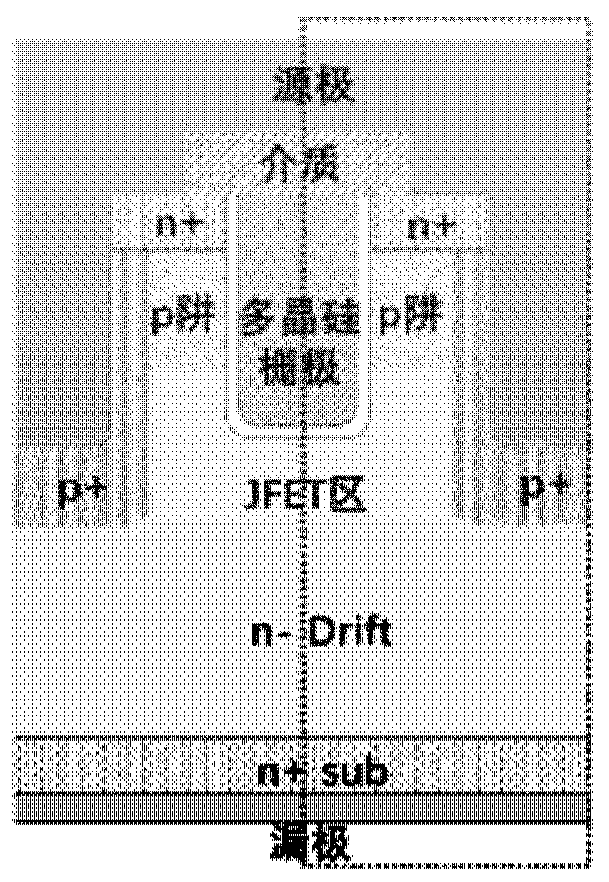
Semiconductor device with super junction structure
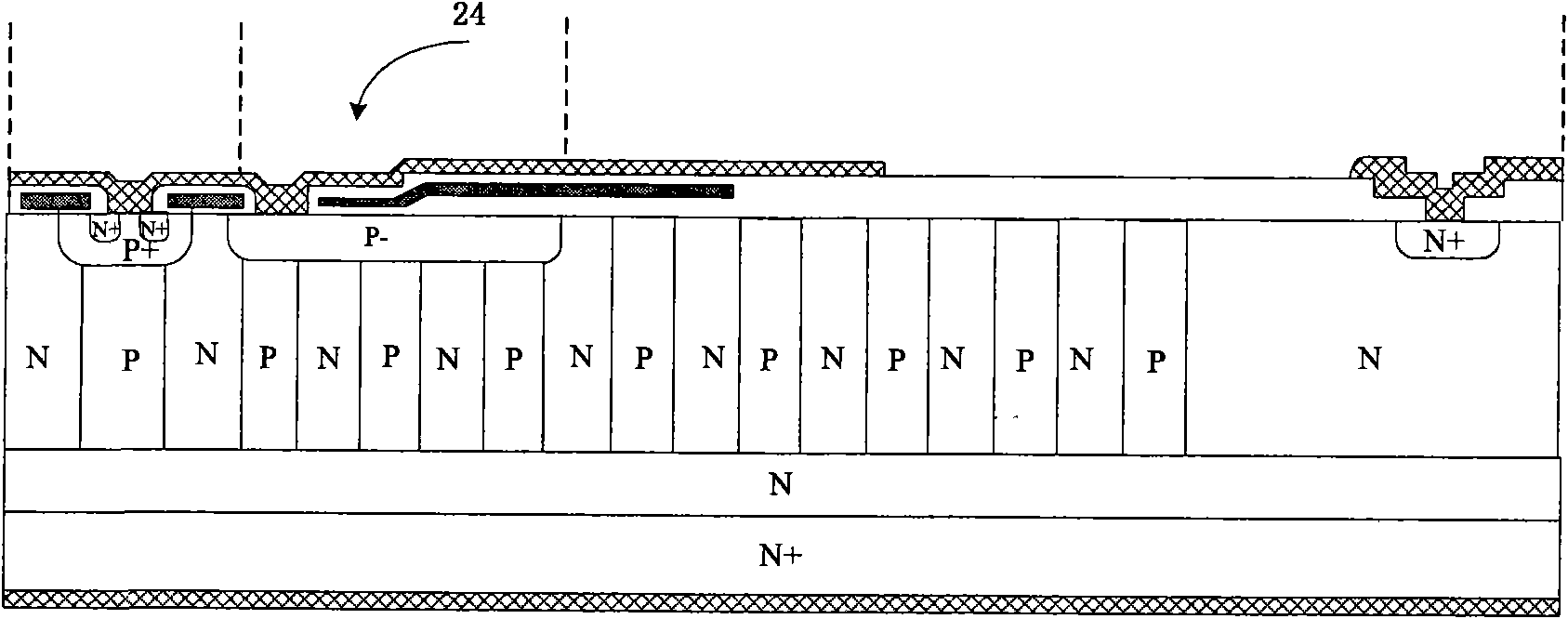
InactiveCN103779399AManufacturing process will not increaseImprove reliabilitySemiconductor devicesGate oxideDielectric layer
The invention provides a semiconductor device with a super junction structure. The semiconductor device comprises an N-type doped semiconductor substrate and an N-type doped epitaxial layer, wherein the N-type doped semiconductor substrate and the N-type doped epitaxial layer are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, and a first P-type filling well region, a second P-type filling well region and a third P-type filling well region are arranged inside the N-type doped epitaxial layer. A first P-type doping region is arranged on the upper side of the first P-type filling well region and provided with an N-type doping region, and a second P-type doping region is arranged on the upper side of the second P-type filling well region. A terminal pressure-withstanding structure T is arranged on the periphery of a primitive cell source electrode region C, wherein the terminal pressure-withstanding structure T comprises the second P-type filling well region, the second P-type doping region, the third P-type filling well region and the corresponding part of the N-type doped epitaxial layer, and the primitive cell source electrode region C comprises the first P-type filling well region, the first P-type doping region, the N-type doping region and the corresponding part of the N-type doped epitaxial layer. The parts, corresponding to polycrystalline silicon arranged in a part of dielectric layer above a gate oxide layer, of the terminal pressure-withstanding structure T and the primitive cell source electrode region C form a gate electrode structure and a polycrystalline silicon field plate structure respectively.
Owner:XIAN SEMIPOWER ELECTRONICS TECH
SiC MOSFET component of slant channel and making method
ActiveCN106847879AQuality improvementImprove channel mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETGrating
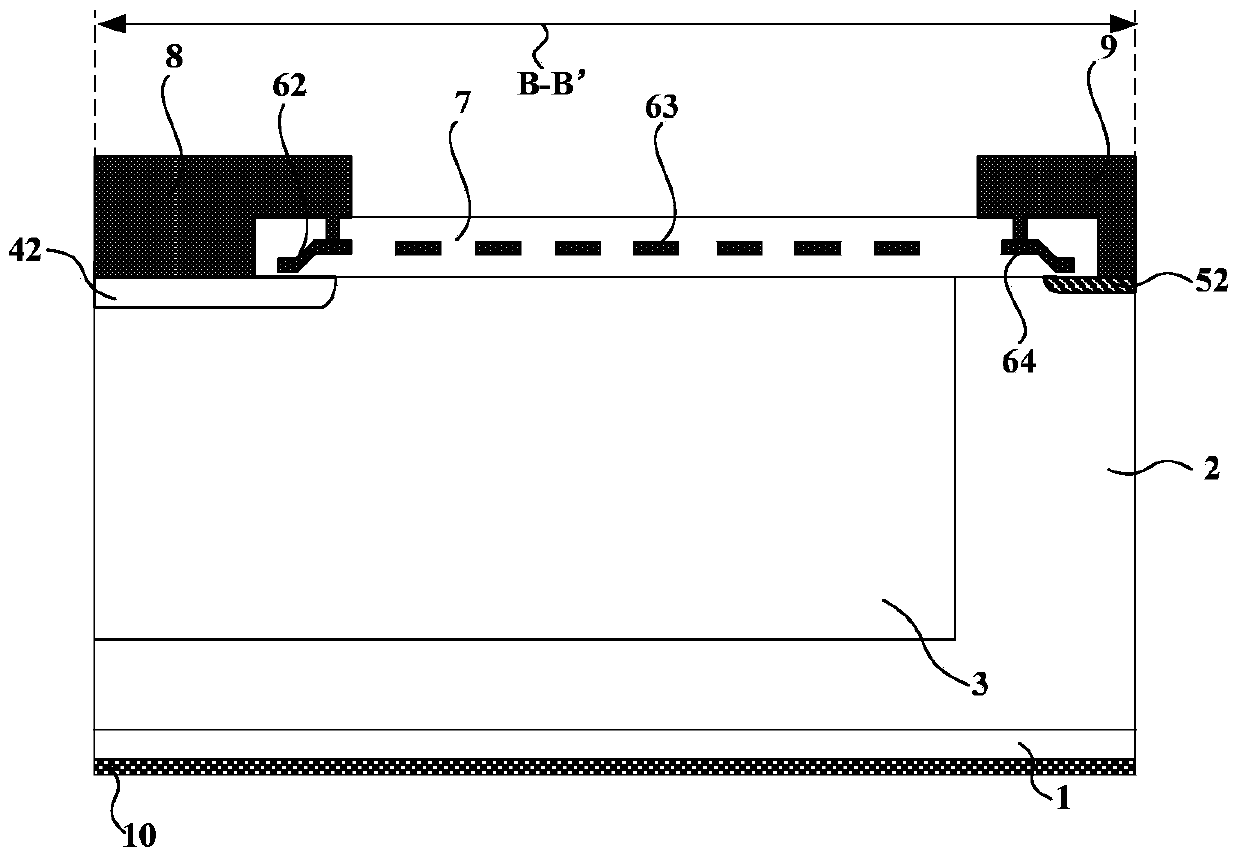
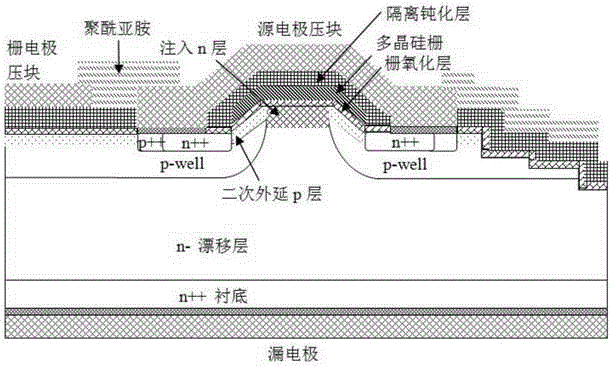
The invention discloses an SiC MOSFET component of a slant channel. A primitive cell structure of an active region of the SiC MOSFET component sequentially comprises a drain electrode, an n++ substrate, an n-drifting layer, two p-well layers arranged in left and right symmetry, a p++ region, an n++ region and a source electrode from bottom to top; the opposite side of the p-well layer is in an arc shape inclined upwards, secondary epitaxy p-type layers which incline toward the vertical central axis of the primitive cell structure are arranged above the arc part of the p-well layer, an injected n layer is arranged between the two secondary epitaxy p-type layers, and an arch-shaped gate oxide layer, an arch-shaped polycrystalline silicone layer and an arch-shaped isolated passivation layer are sequentially arranged above the secondary epitaxy p-type layer and the injected n layer. The invention provides a making method of the SiC MOSFET component of the slant channel. A crystal face with high electron mobility serves as the plane of the channel, the channel is formed in a high-quality secondary-epitaxy SiC surface, the quality of an MOS grating can be effectively improved, the channel mobility can be effectively improved, and on-resistance of the component can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING CENTURY GOLDRAY SEMICON CO LTD
Photonic crystal of two-dimensional graphene-like duplex structure
InactiveCN103901513ALarge TE bandgap ratioIncrease band gapOptical elementsPhotonic crystalDielectric cylinder
A photonic crystal of a two-dimensional graphene-like duplex structure comprises a tabulate base part. Primitive cell units are periodically arranged on the tabulate base part, and each primitive cell unit comprises a first dielectric medium and a second dielectric medium. Each primitive cell unit comprises a hexagon prism-shaped hollow structure which is formed by one first dielectric medium and a cylindrical dielectric cylinder which is axially arranged in each hexagon prism-shaped hollow structure, each hexagon prism-shaped hollow structure is filled with one second dielectric medium, and each second dielectric medium is filled into the gap between the corresponding hexagon prism-shaped hollow structure and the cylindrical dielectric cylinder. The cylindrical dielectric cylinders are arranged between the adjacent primitive cell units, and the cylindrical dielectric cylinders are made of the first dielectric media. The structure parameter is optimized, so that the maximal TE band gap rate of 55.89% is obtained so far. According to the photonic crystal of the two-dimensional graphene-like duplex structure, the duplex structure is introduced, compared with a simple periodic structure, forbidden band modulating controllability is higher, and it is of great significance to designing and manufacturing two-dimensional photonic crystals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for determining crystal reciprocity primitive cell basis vector based on EBSD pattern
InactiveCN105021637AEfficient exclusionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAlgorithmCrystal cell
The invention discloses a method for determining a crystal reciprocity primitive cell basis vector based on an EBSD pattern. A pattern center PC and a probe distance DD are utilized for geometrically correcting a chrysanthemum pool zone to obtain a reciprocal vector corresponding to the chrysanthemum pool zone, the component of the reciprocal vector corresponding to the chrysanthemum pool zone in the three-dimensional reciprocal space is determined, and therefore the reciprocal primitive cell basis vector is guided out; by the adoption of the method, false crystal cell information can be effectively removed; on the condition that the width error of the chrysanthemum pool zone is large, the size of the primitive cell is accurately recognized, and the basis vector of the primitive cell is determined.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
X-ray diffraction in-situ characterization method of film orientation crystal growth
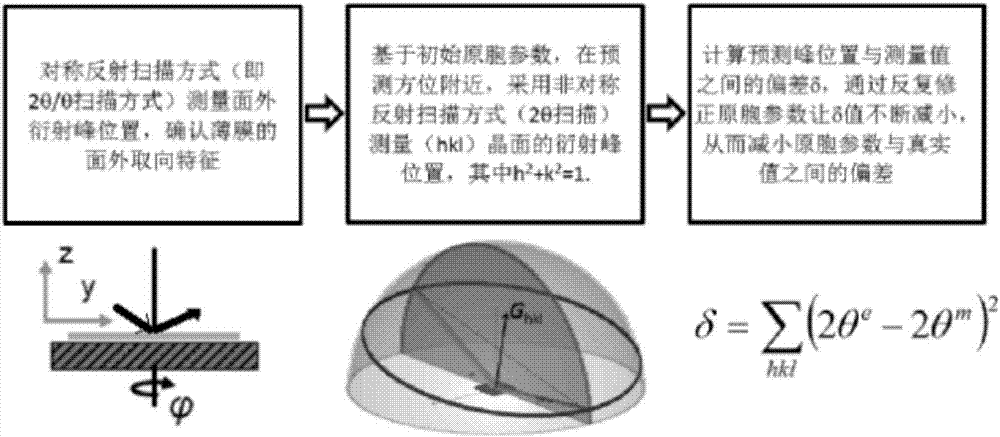
ActiveCN107085003AEnables in situ characterizationSuitable for analysisMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayComputer-aided
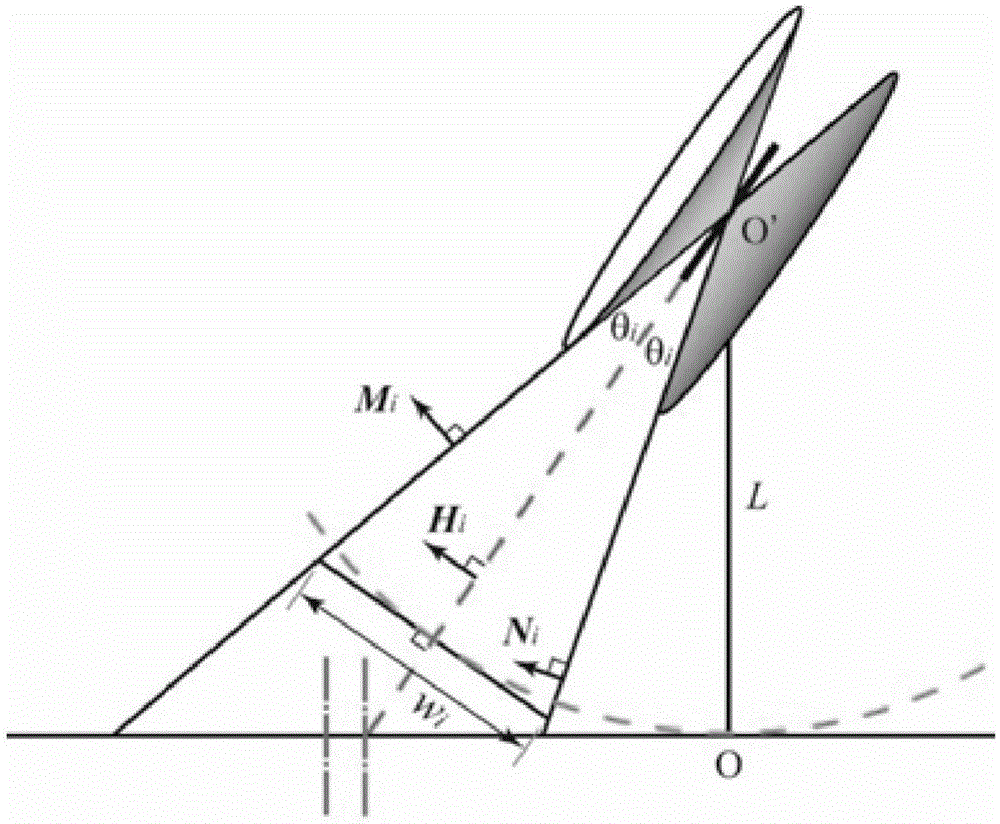
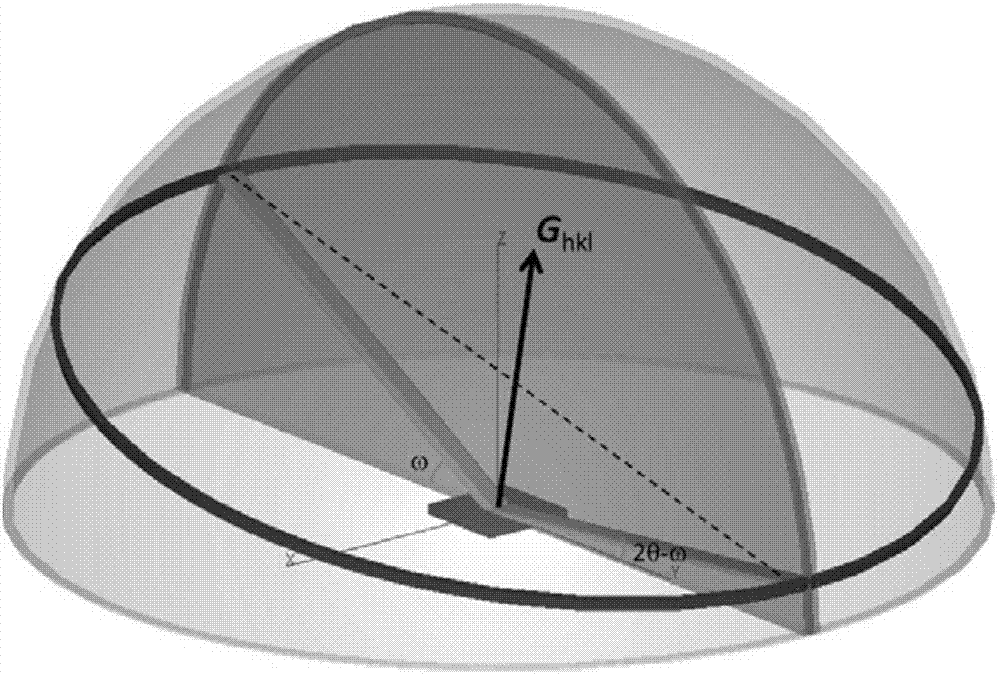
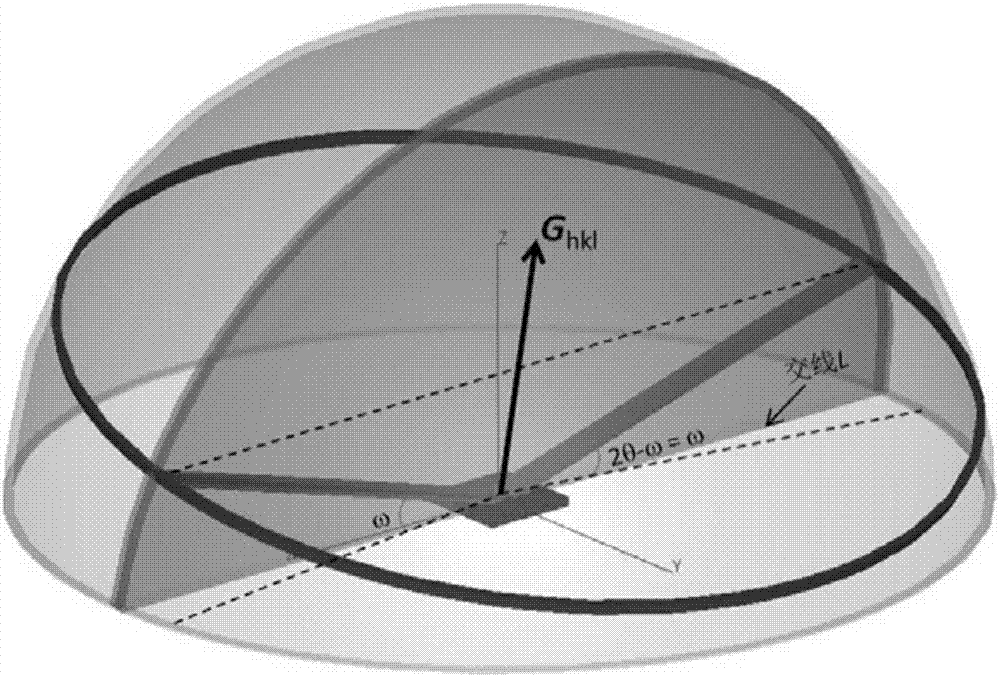
The invention discloses an X-ray diffraction in-situ characterization method of film orientation crystal growth. The in-situ characterization method comprises the steps of firstly utilizing a symmetrical reflective scanning method to measure out-plane diffraction peak position of a film and determining an out-plane orientation characteristic of the film; then utilizing an asymmetrical reflective scanning method to obtain the diffraction peak position of a crystal face set near a predicted orientation based on initial primitive cell parameters, wherein crystal faces of the crystal face set form inclined included angles with a substrate; calculating out the difference delta between the diffraction peak position obtained by measurement and a prediction value based on the initial primitive cell parameters and continuously reducing the delta through lattic parameter correction and loop iteration calculation until the delta is small enough to obtain more accurate lattic parameter information. According to the X-ray diffraction in-situ characterization method disclosed by the invention, a computer-assisted calculating method is utilized, high enough analysis accuracy can be obtained within several seconds, and output data can be directly utilized as an input value of the next measuring period; thus, a high-speed dynamic measuring and analyzing system is formed.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
High-voltage LED chip structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109817779AHigh light efficiencyReduce areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerEngineering
The invention provides a high-voltage LED chip structure and a manufacturing method thereof. The high-voltage LED chip structure comprises a plurality of LED chip particles and primitive cell isolation grooves formed between every two adjacent LED chip particles, wherein each primitive cell isolation groove comprises a connecting area primitive cell isolation groove and a non-connecting area primitive cell isolation groove, and the width of the non-connecting area primitive cell isolation groove is smaller than that of the connecting area primitive cell isolation groove in the direction of a connecting line of centers of two adjacent LED chip particles; and the inclination of the side wall of the non-connection area primitive cell isolation groove is greater than that of the side wall of the connection area primitive cell isolation groove. Therefore, the area of the non-connecting area primitive cell isolation groove is reduced, the area of the light-emitting area is increased, and thelighting effect of the high-voltage LED chip is improved. Due to the fact that the side wall of the connection area primitive cell isolation groove is slow, effective coverage of a bridge connectioninsulation isolation layer and a bridge connection electrode is guaranteed, and the product reliability of the high-voltage LED chip structure is guaranteed.
Owner:XIAMEN CHANGELIGHT CO LTD
Flip light emitting diode (LED) with ODR structure and preparation method, and flip high-voltage LED
InactiveCN106169531AImprove reflectivityIncrease brightnessSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactReflective layer
The invention discloses a flip light emitting diode (LED) with an ODR structure and a preparation method, and a flip high-voltage LED. According to the flip LED, an N type layer, an active layer and a P type layer are arranged on a substrate in sequence; a stage is formed through etching to expose a part of the N type layer; a current expansion layer is formed on the P type layer and the exposed N type layer; a DBR layer is formed on the current expansion layer; the DBR layer is etched to expose a part of the current expansion layer; an Ag reflection layer is formed on the DBR layer and the part of the exposed current expansion layer; and the Ag reflection layer is stripped to form a P contact metal layer and an N contact metal layer which are in ohmic contact with the current expansion layer on the P type layer and N type layer respectively. By adoption of the flip LED, the luminance of a chip is improved; extra metal evaporation is not required to form ohmic contact with an N-GaN layer, so that the technological steps and material are reduced, and the cost is low; and in addition, for the flip high-voltage LED, the Ag reflection layer can be used as high-reflection metal for forming the ODR structure, and also can be used as interconnecting metal between primitive cells, so that the technological steps are reduced, and the luminance of the chip is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN CHANGELIGHT CO LTD
Two-dimensional liquid-liquid phononic crystal topology optimization method
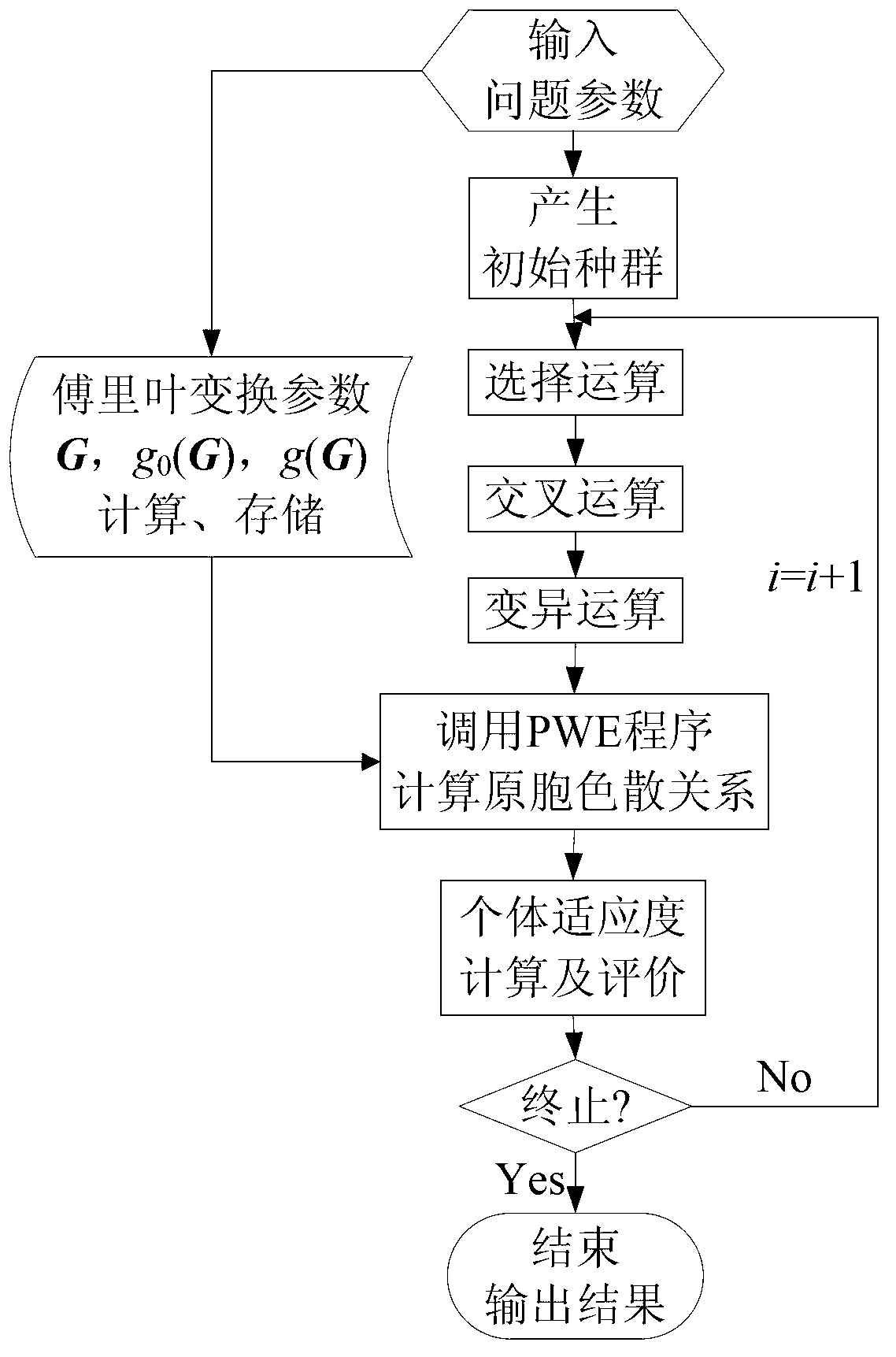
InactiveCN103218488ANovel structureStrong designabilityGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsPlane wave expansion methodTopology optimization
The invention relates to a two-dimensional liquid-liquid phononic crystal topology optimization method, which comprises the following steps of dividing a phononic crystal primitive cell into an N*N square pixel structure; developing a plane wave expansion method program for quickly calculating a two-dimensional liquid-liquid pixel phononic crystal energy band laid by any material according to an acoustic wave equation satisfied by a two-dimensional liquid-liquid phononic crystal dispersion relationship, and calculating a band gap; and finally, searching the optimal material layout of the two-dimensional liquid-liquid phononic crystal primitive cell according to the requirements on the band gap by utilizing a genetic optimization algorithm. The process comprises the following steps of inputting a parameter to be solved, and initializing; calculating individual fitness; sequentially performing the genetic operations of selection, crossover and mutation to generate the next generation of genus group, so that the genus group evolutes forwards; and checking whether the genus group meets a stop condition. Through the topology optimization method, the designability of phononic crystals is enhanced, and the novel phononic crystal structure with optimal band gap characteristics is obtained; and meanwhile, the calculating time is reduced, and the calculating efficiency is improved, so that the designed phononic crystal has the best technical and economic performances.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
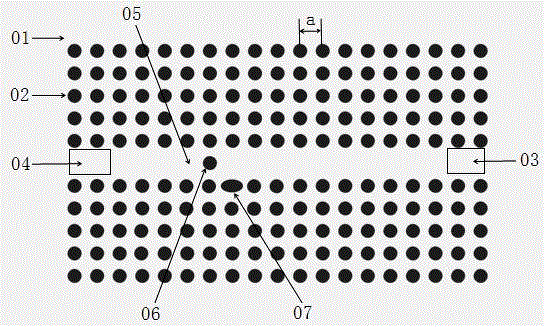
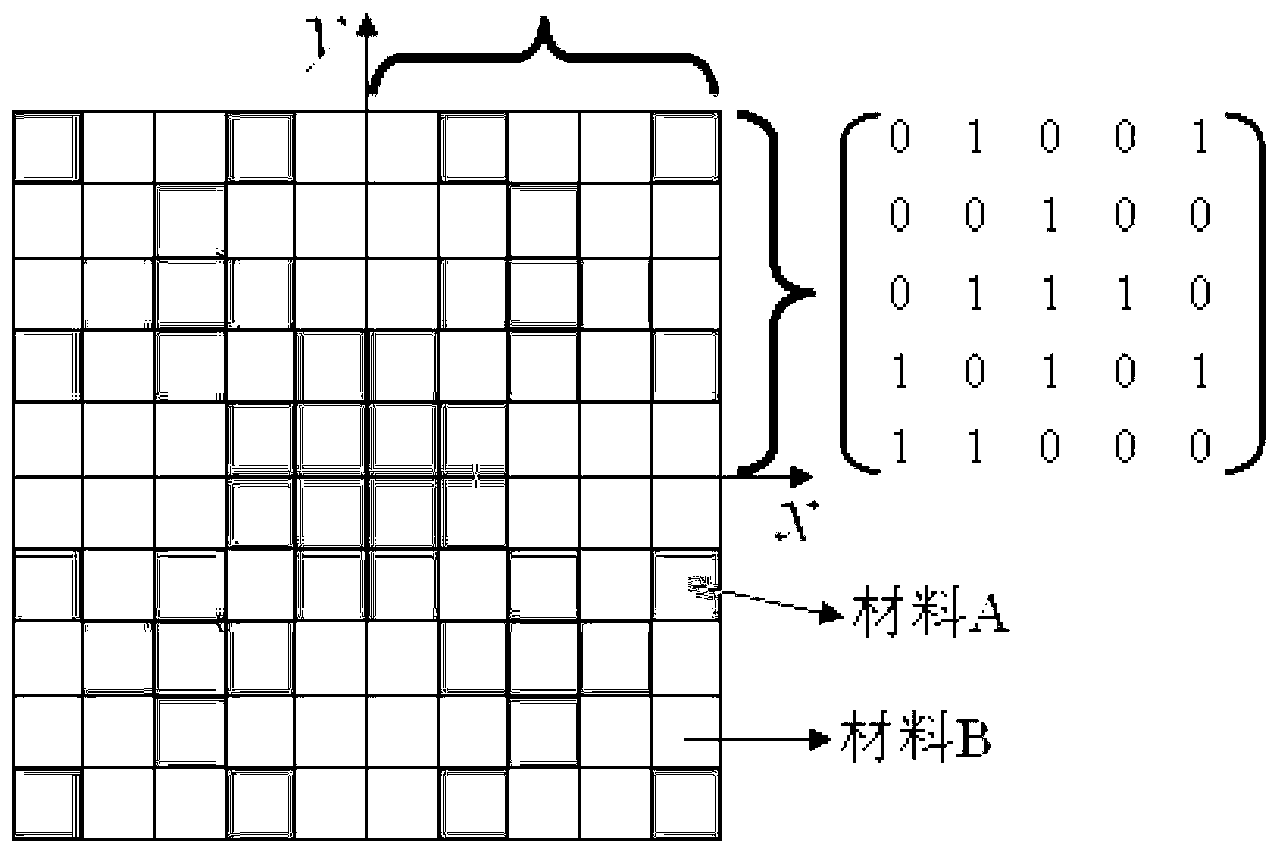
Two-dimensional photonic crystal with large absolute band gap
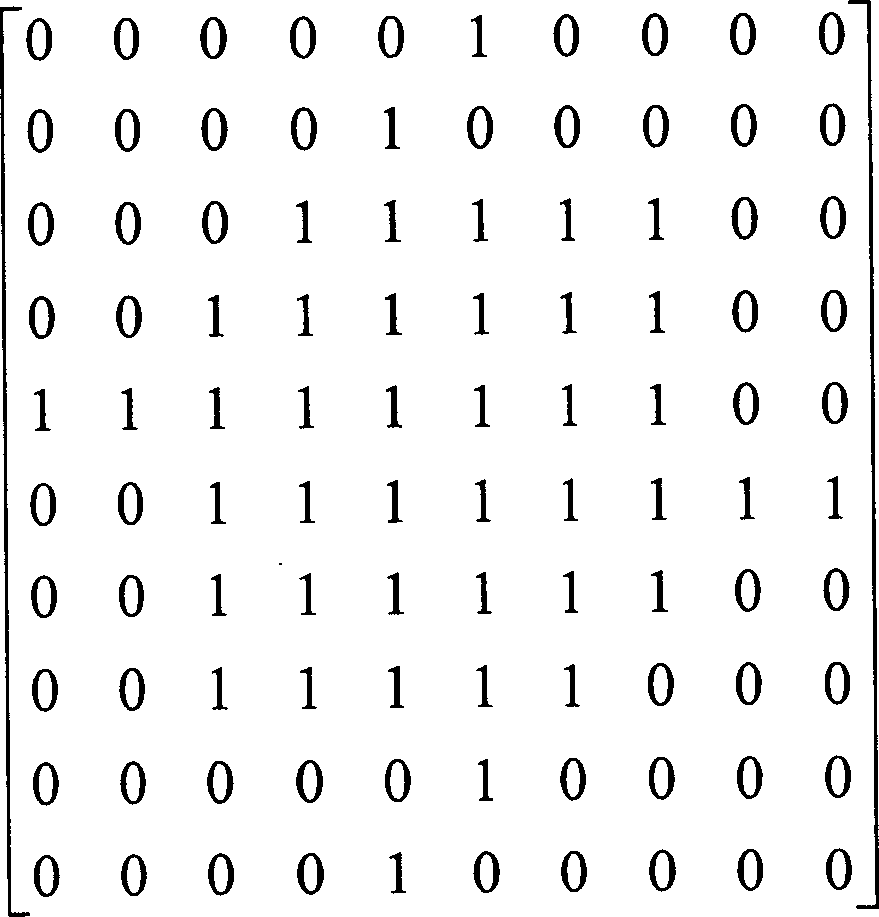
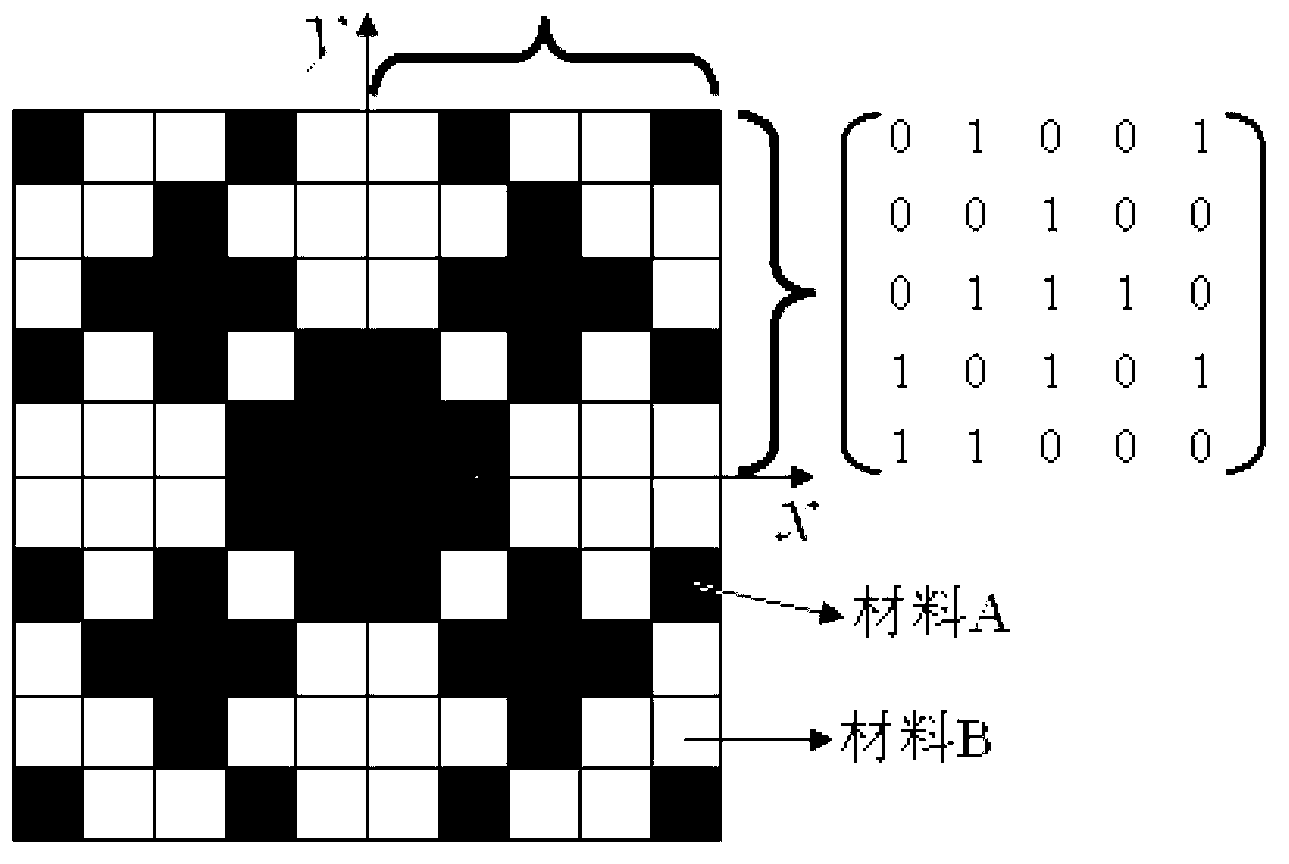
The invention discloses regular crystal lattice two-dimension photon crystal with absolute forbidden band at low frequency area under fifth energy level. Primitive cell is divided into square pixel structure with 10*10 high and low refractive index dielectric material distributed in the primitive cell pixel of which 1 represents high refractive index dielectric material; 0 represents low one. The primitive cell structure of the invention satisfies inversion symmetry. When a lattice constant is 1mum, the relative value of the forbidden band under the fifth energy level for silicon / air material is 10.28%.
Owner:HENAN SHIJIA PHOTONS TECH
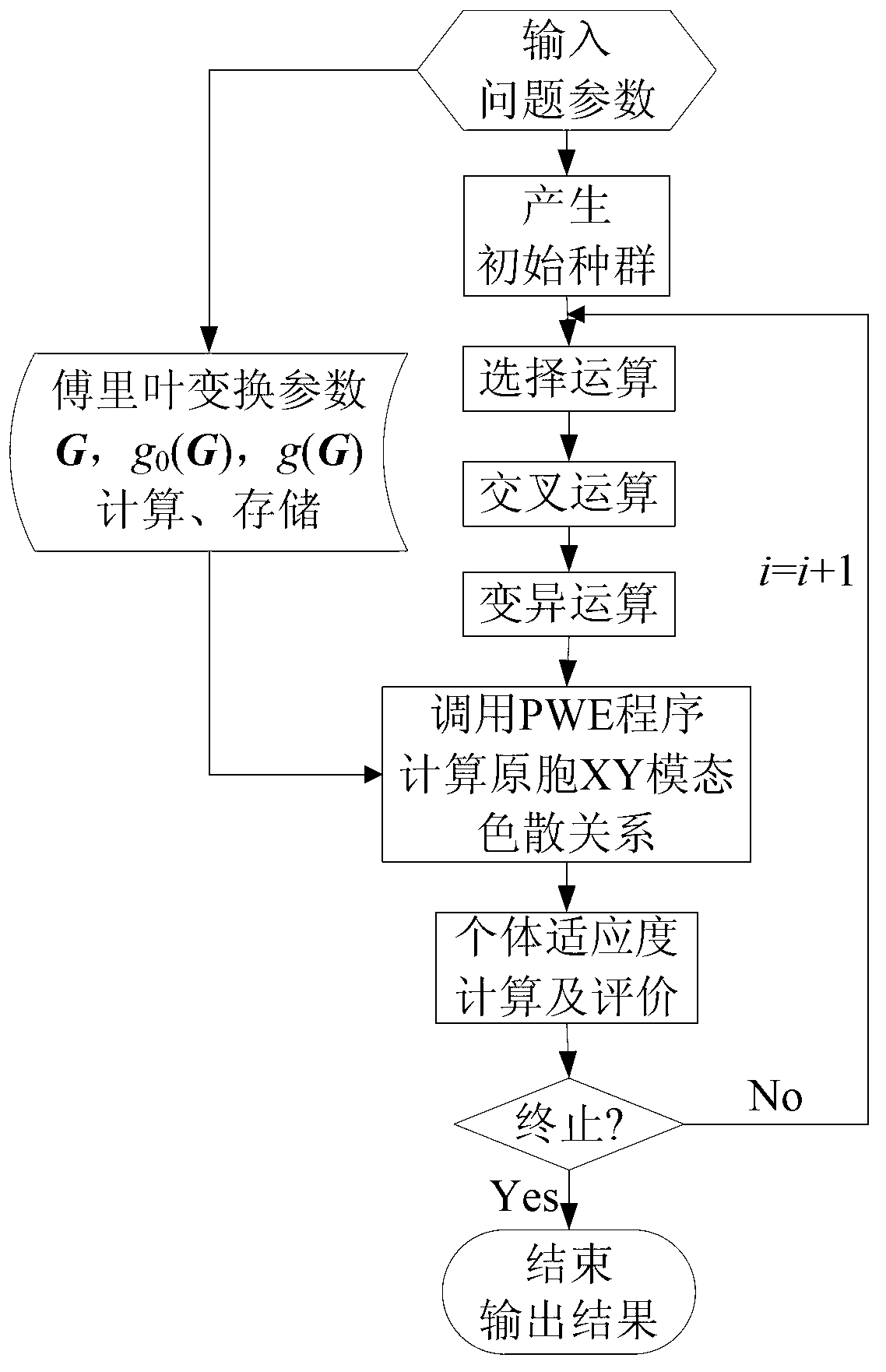
Two-dimensional solid-solid phononic crystal XY mode topological optimization method
InactiveCN103218529ANovel structureStrong designabilitySpecial data processing applicationsPlane wave expansion methodTopology optimization
The invention relates to a two-dimensional solid-solid phononic crystal XY mode topological optimization method, which comprises the following steps of inputting a problem parameter to be solved, and initializing; calculating a dispersion relationship of a phononic crystal primitive cell XY mode corresponding to each genetic individual to obtain a corresponding forbidden band value by using an improved fast plane wave expansion method; according to an optimized goal, using phononic crystal forbidden bands to build an objective function, and then using the value of the objective function to measure the fitness of the genetic individuals; sequentially performing the genetic operations of selection, crossover and mutation to generate the next generation of genus group, so that the genus group evolutes forwards; and checking whether the genus group meets a stop condition. The traditional experience design idea is eliminated, and the goal of actively designing a phononic crystal structure according to the band gap needs is achieved, so that the designability of phononic crystals is enhanced, and the novel phononic crystal structure with optimal band gap characteristics is obtained; and meanwhile, the calculating time is reduced, and the calculating efficiency is improved, so that the designed phononic crystal has the best technical and economic performances.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
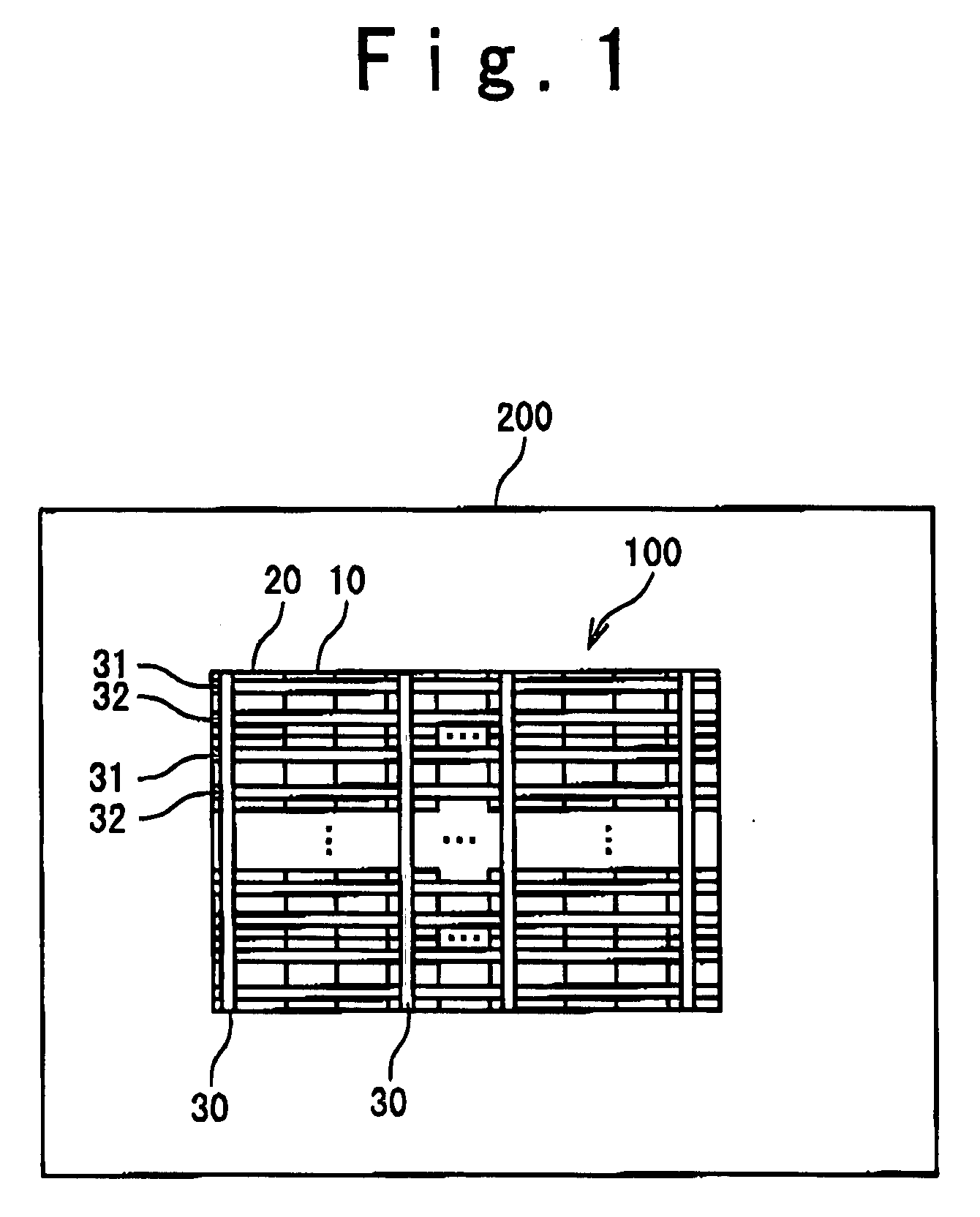
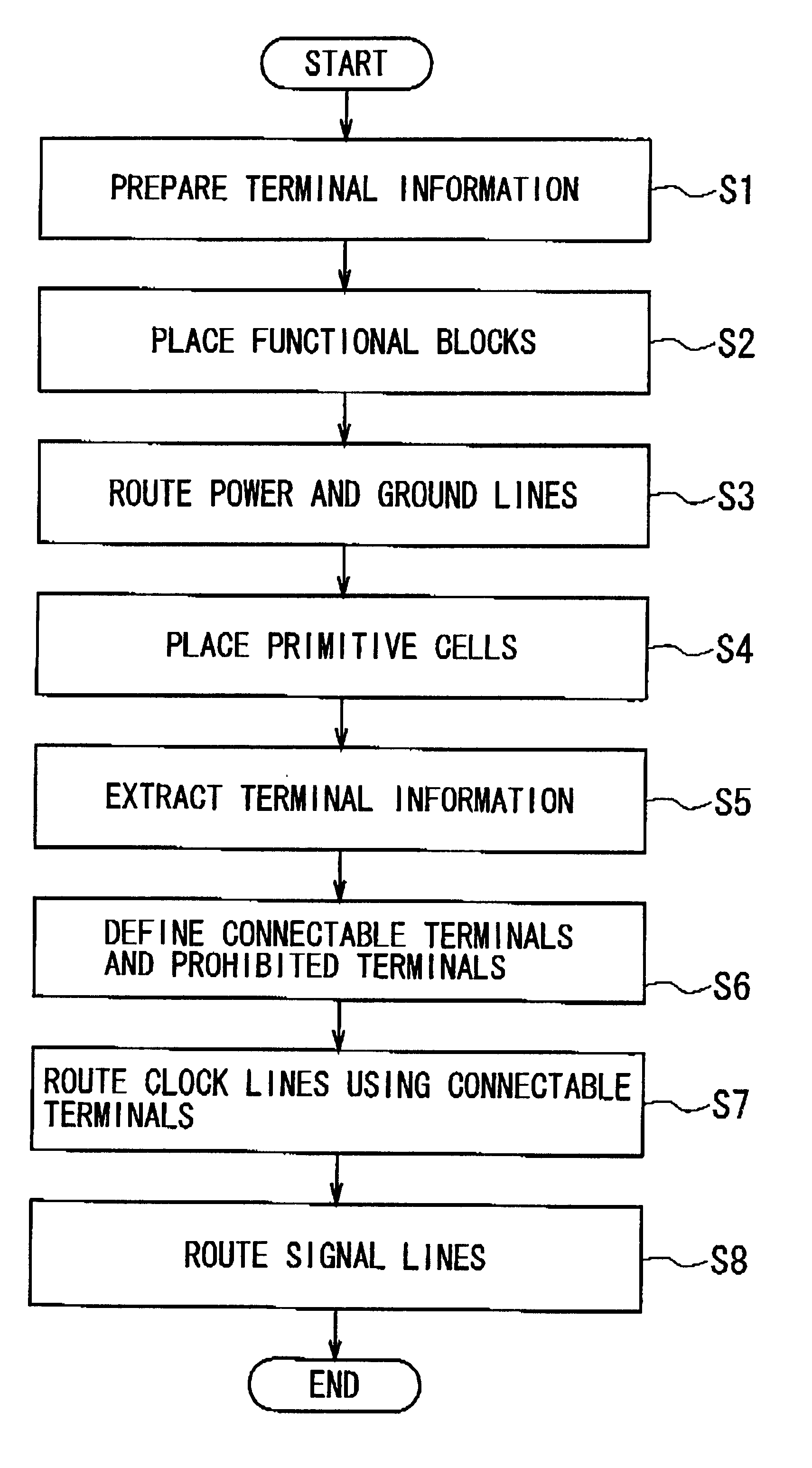
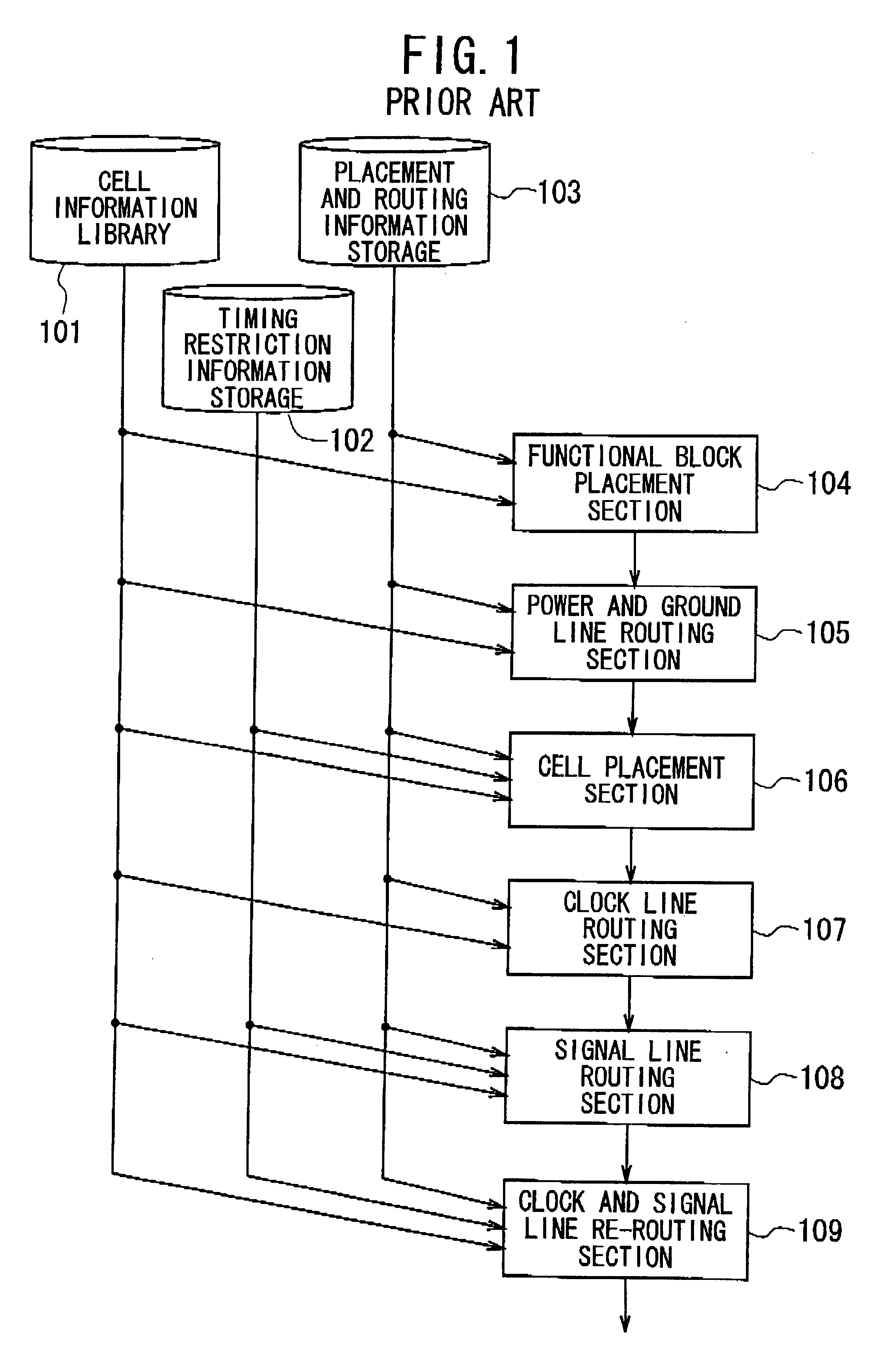
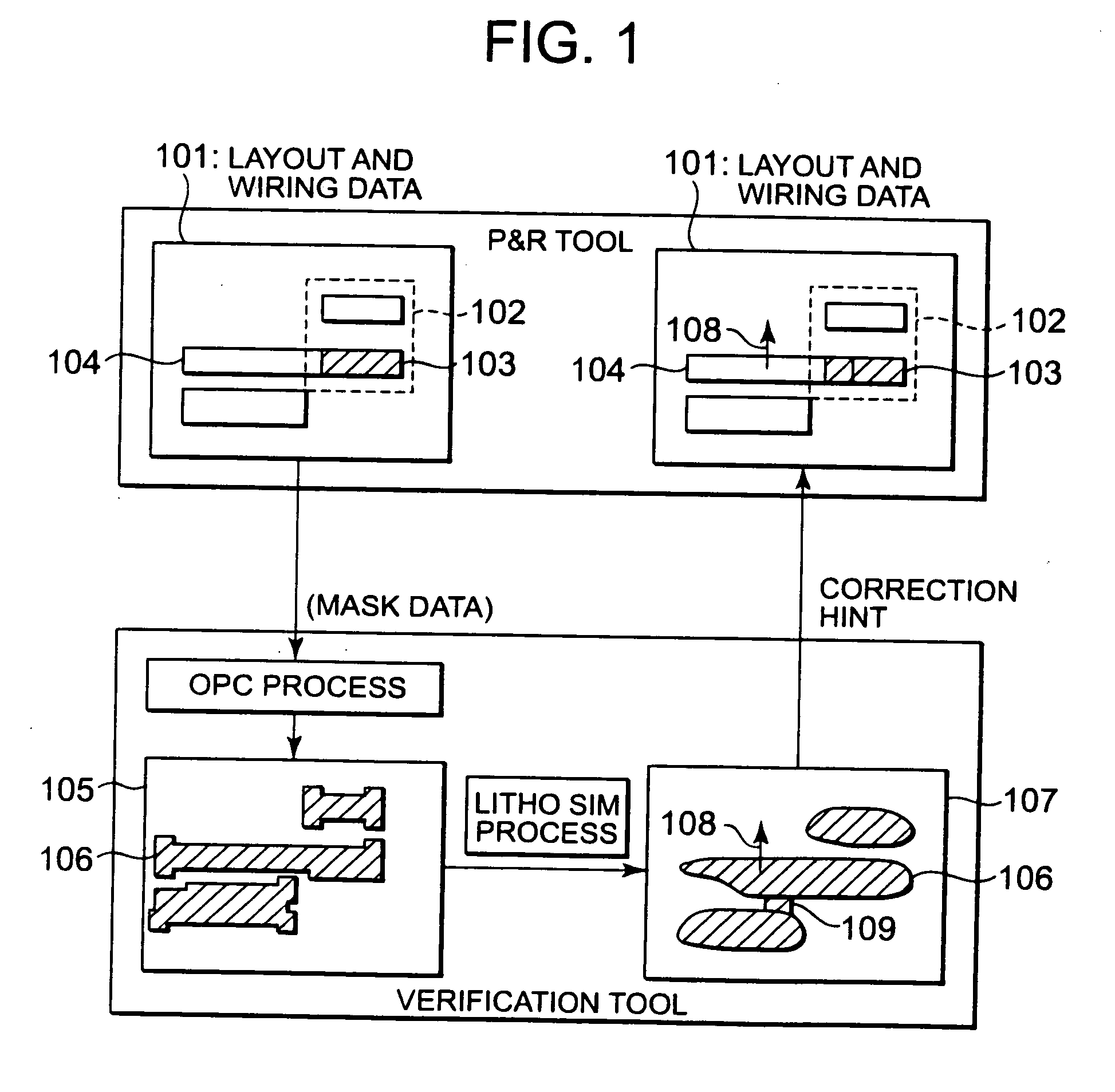
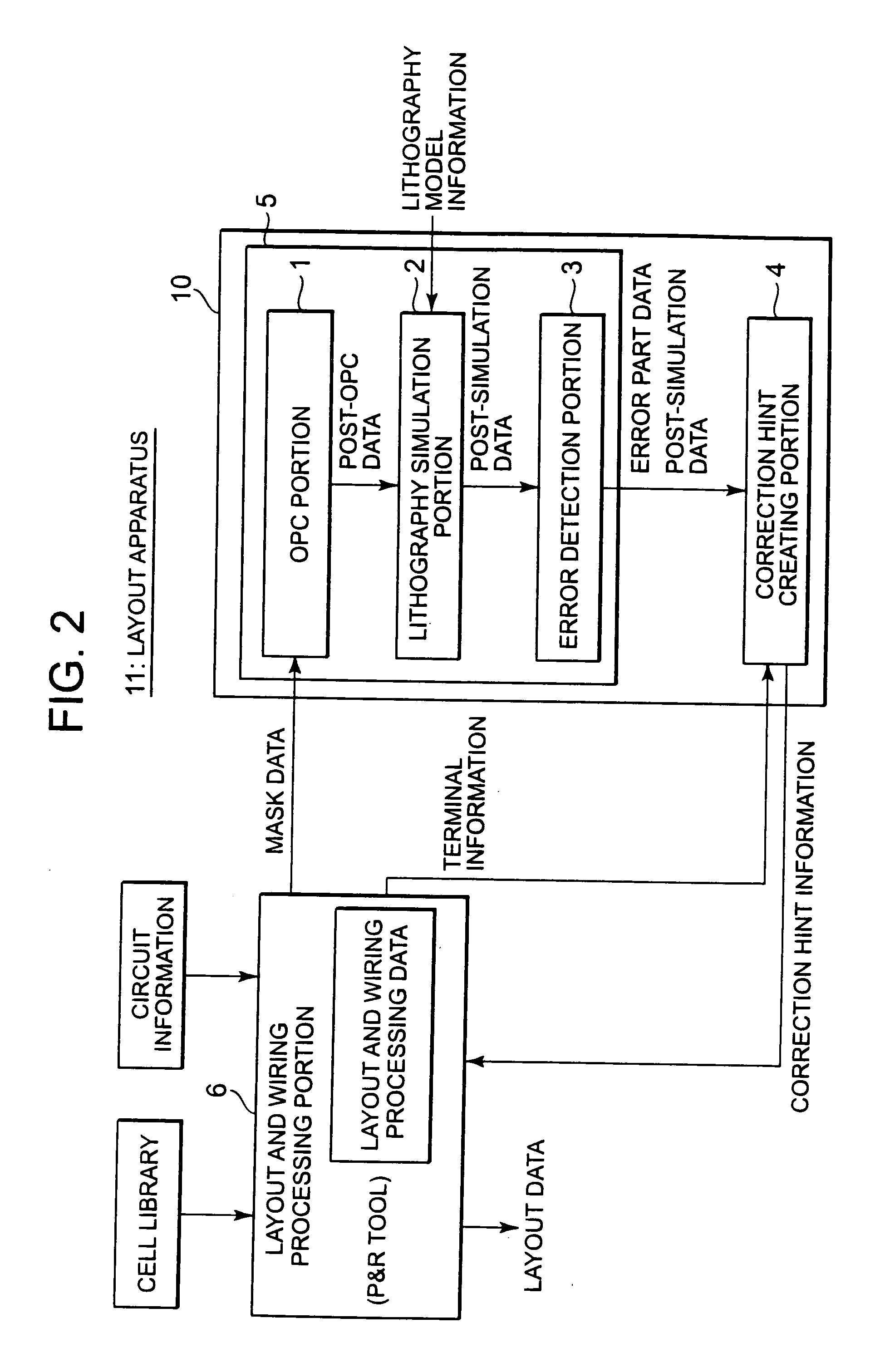
Layout verification apparatus, layout apparatus, layout verification method, layout verification program, and wiring forming method
InactiveUS20100115765A1Line/current collector detailsComputer aided designData validationValidation methods
The layout verification apparatus includes: a verification unit for obtaining mask data indicating a mask pattern to be drawn on a mask based on layout and wiring data indicating positions of a group of primitive cells and positions of connection wires connected to the group of primitive cells, and for verifying a position of the mask pattern based on the mask data, so as to detect an error part; and a correction hint creating unit for creating correction hint information based on the error part, and for sending the correction hint information to a layout and wiring unit for correcting the layout and wiring data. The correction hint creating unit obtains terminal information indicating positions of a group of terminals included in the group of primitive cells and creates the correction hint information based on the terminal information so that the positions of the group of terminals are not changed by the layout and wiring unit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
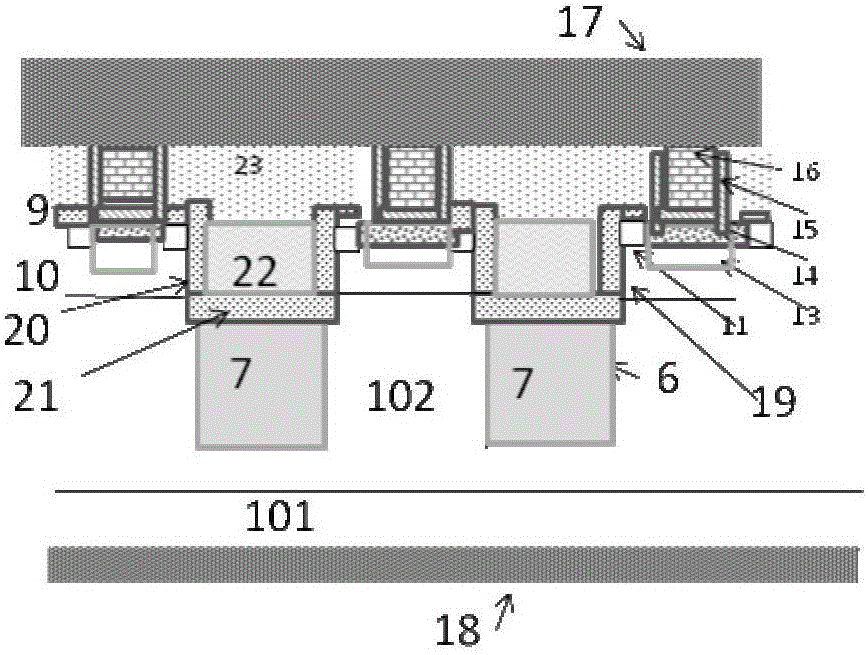
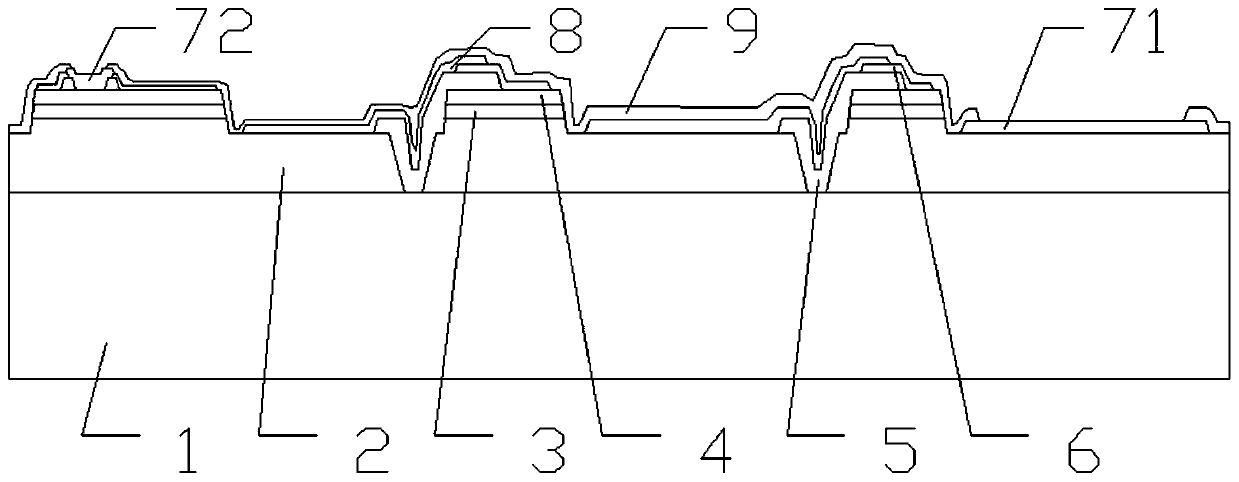
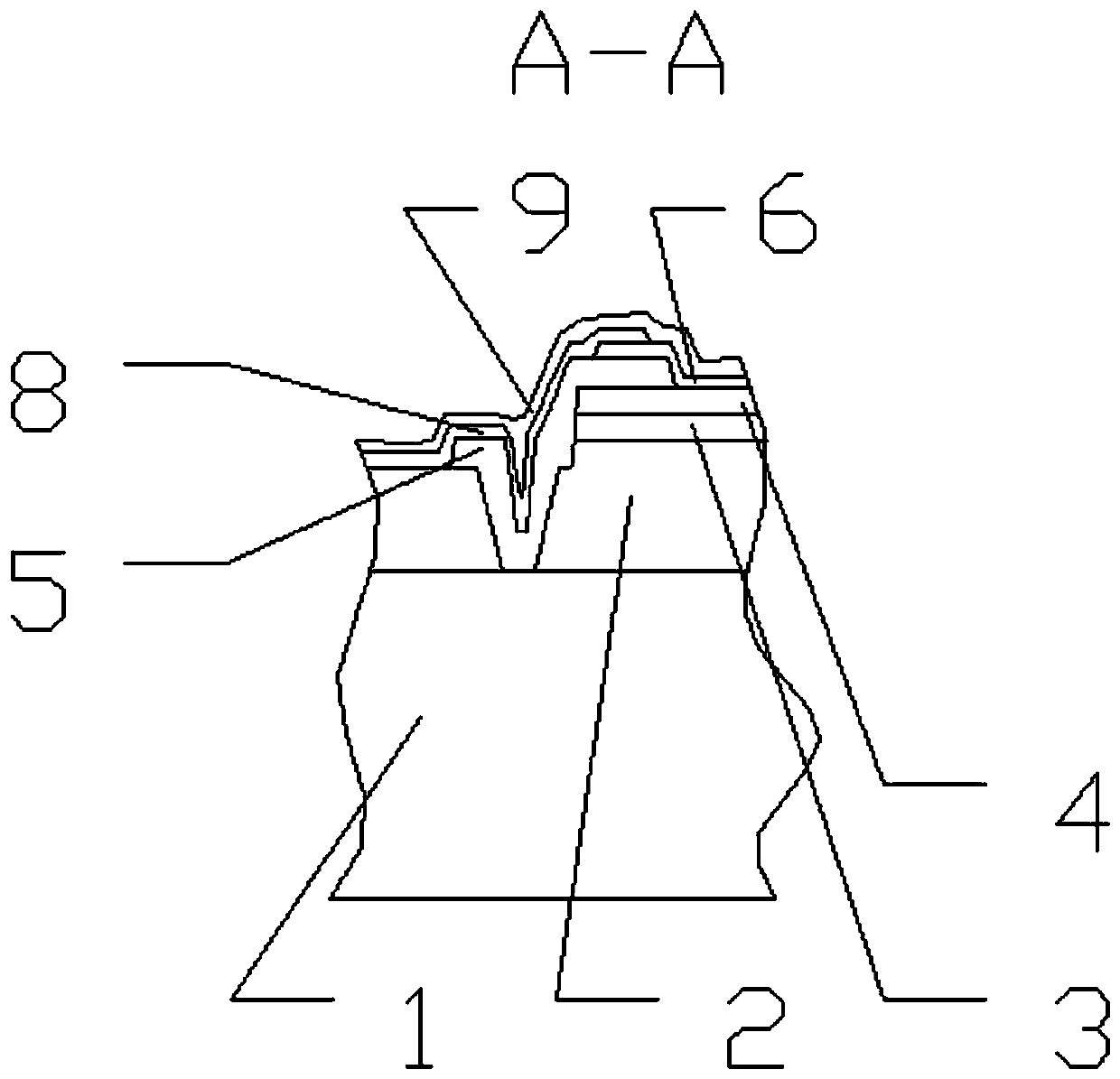
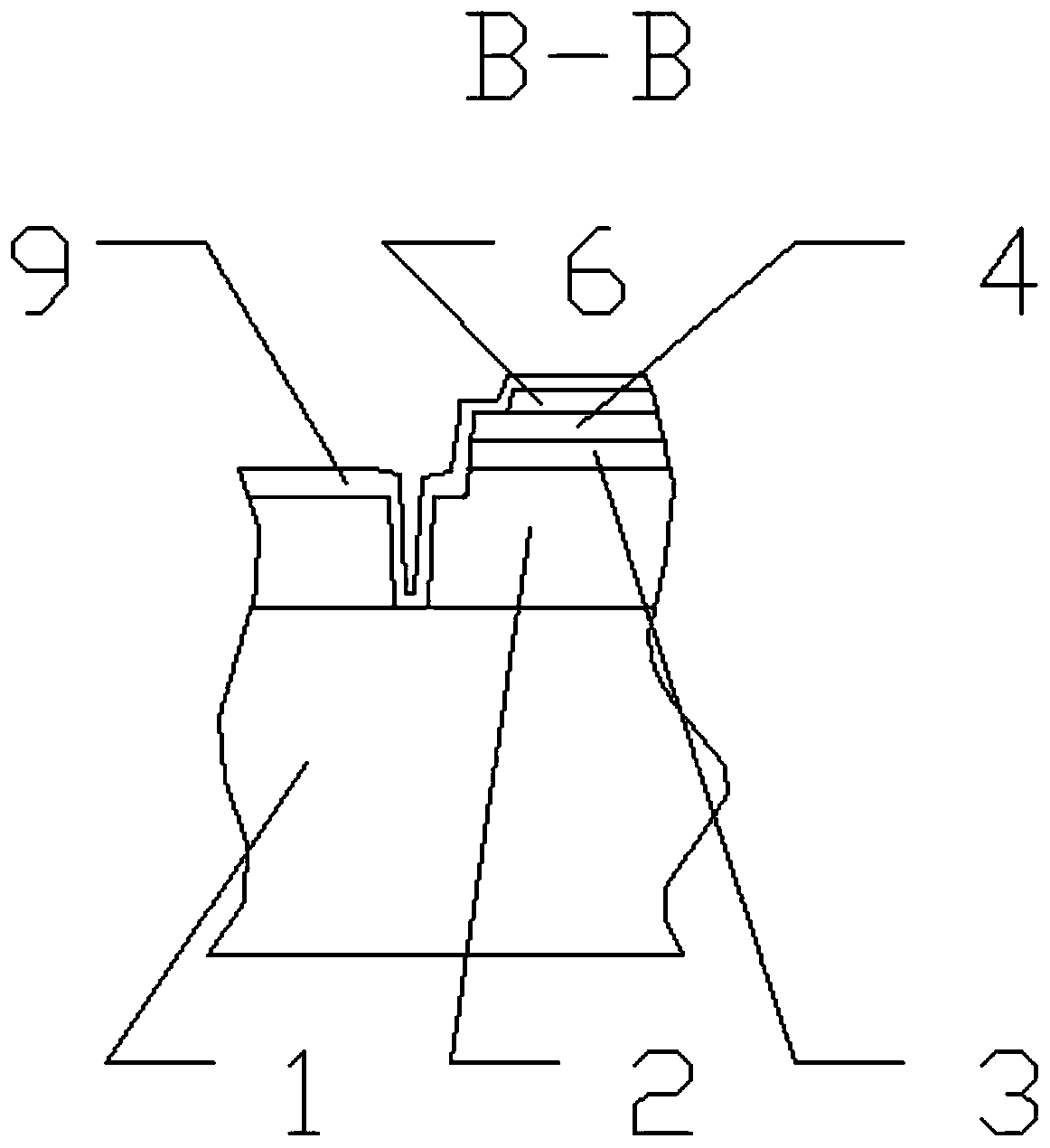
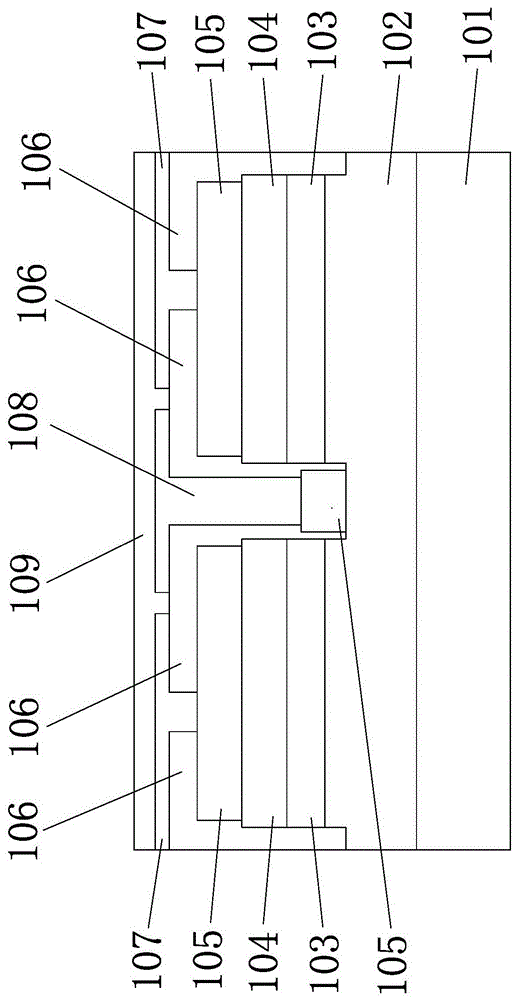
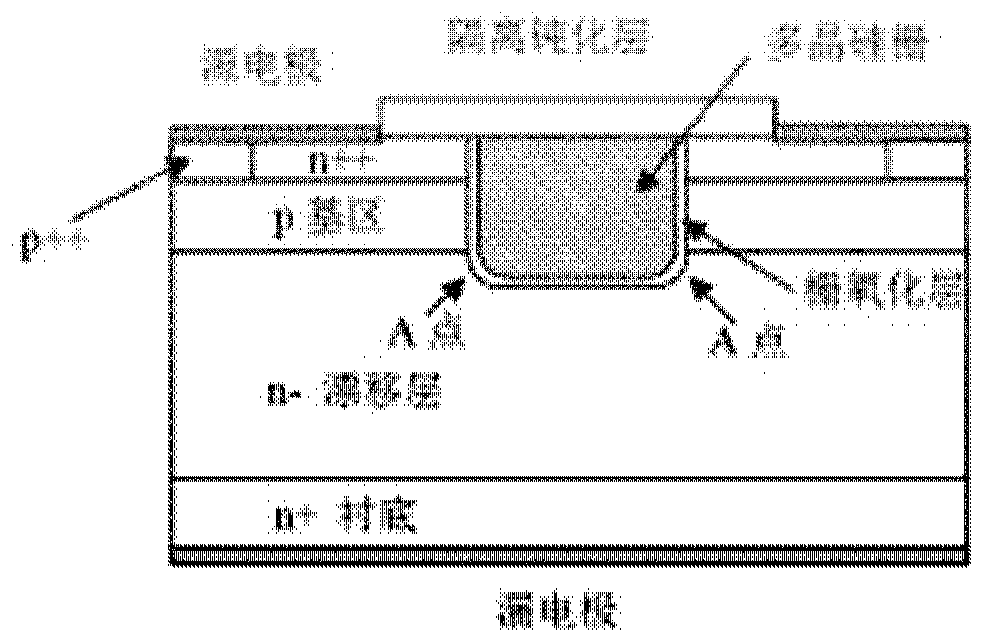
MOSFET device
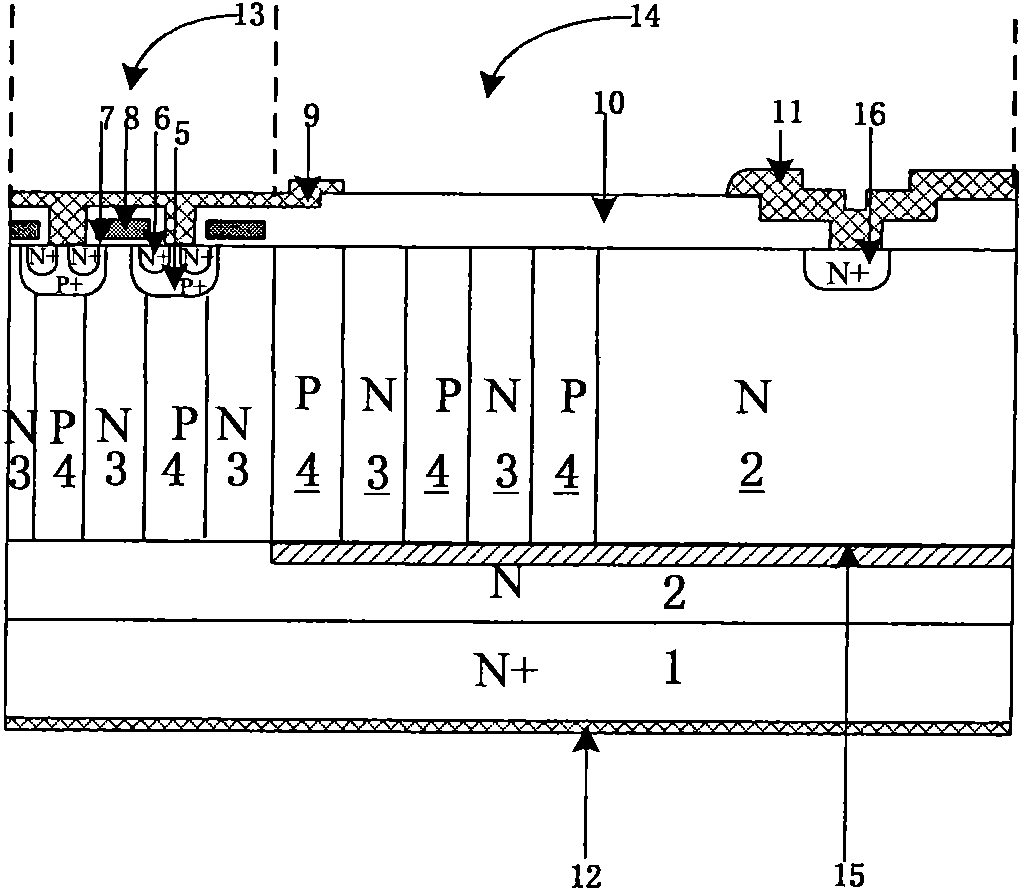
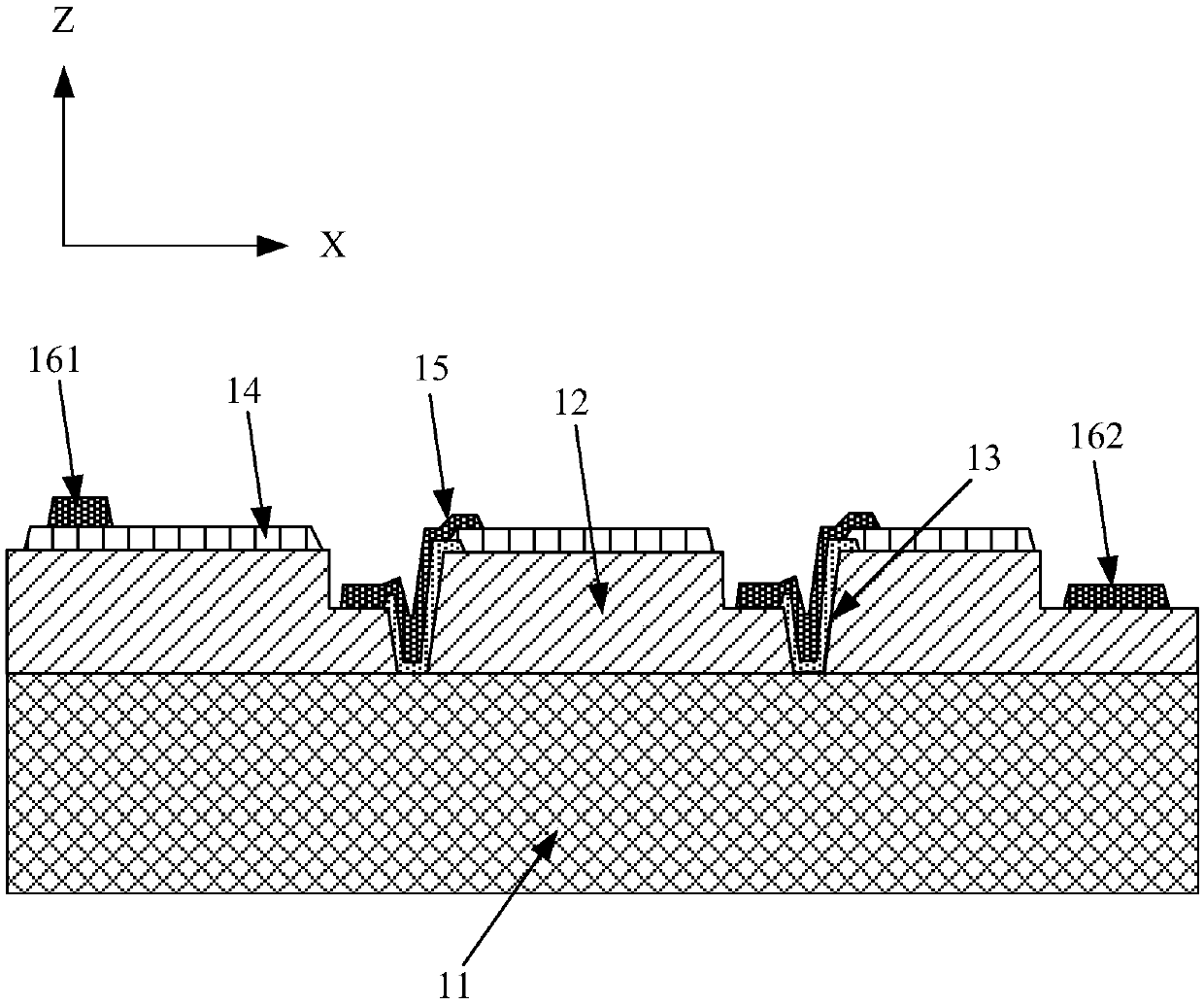
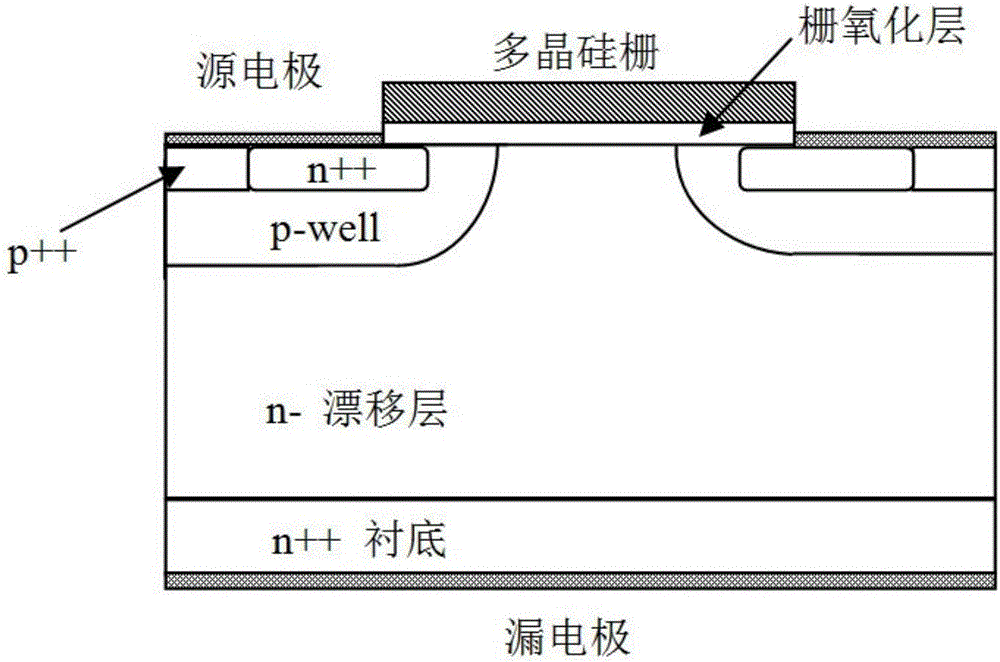
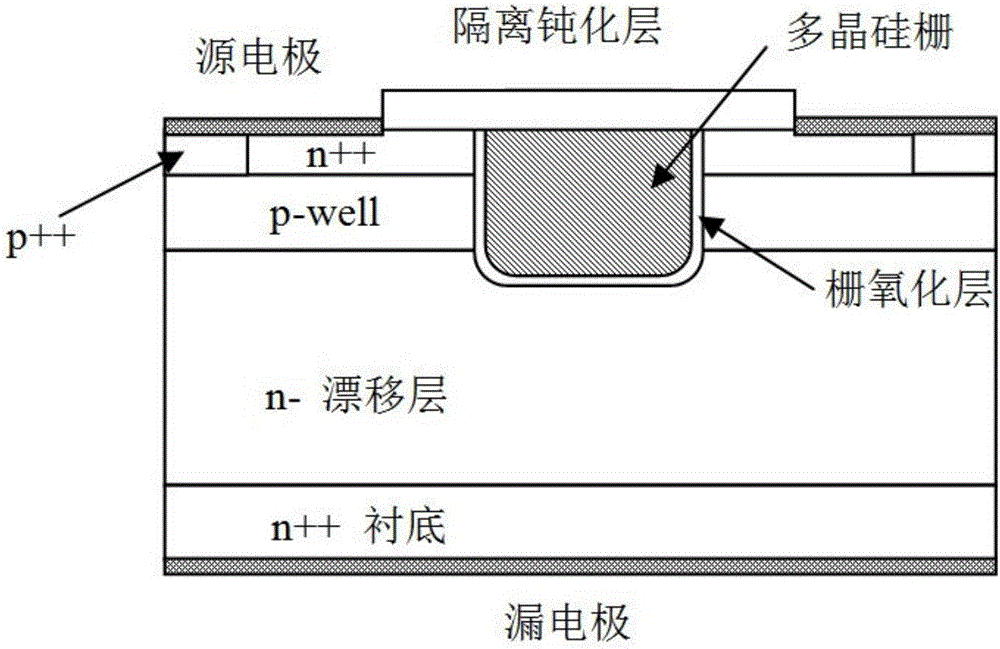
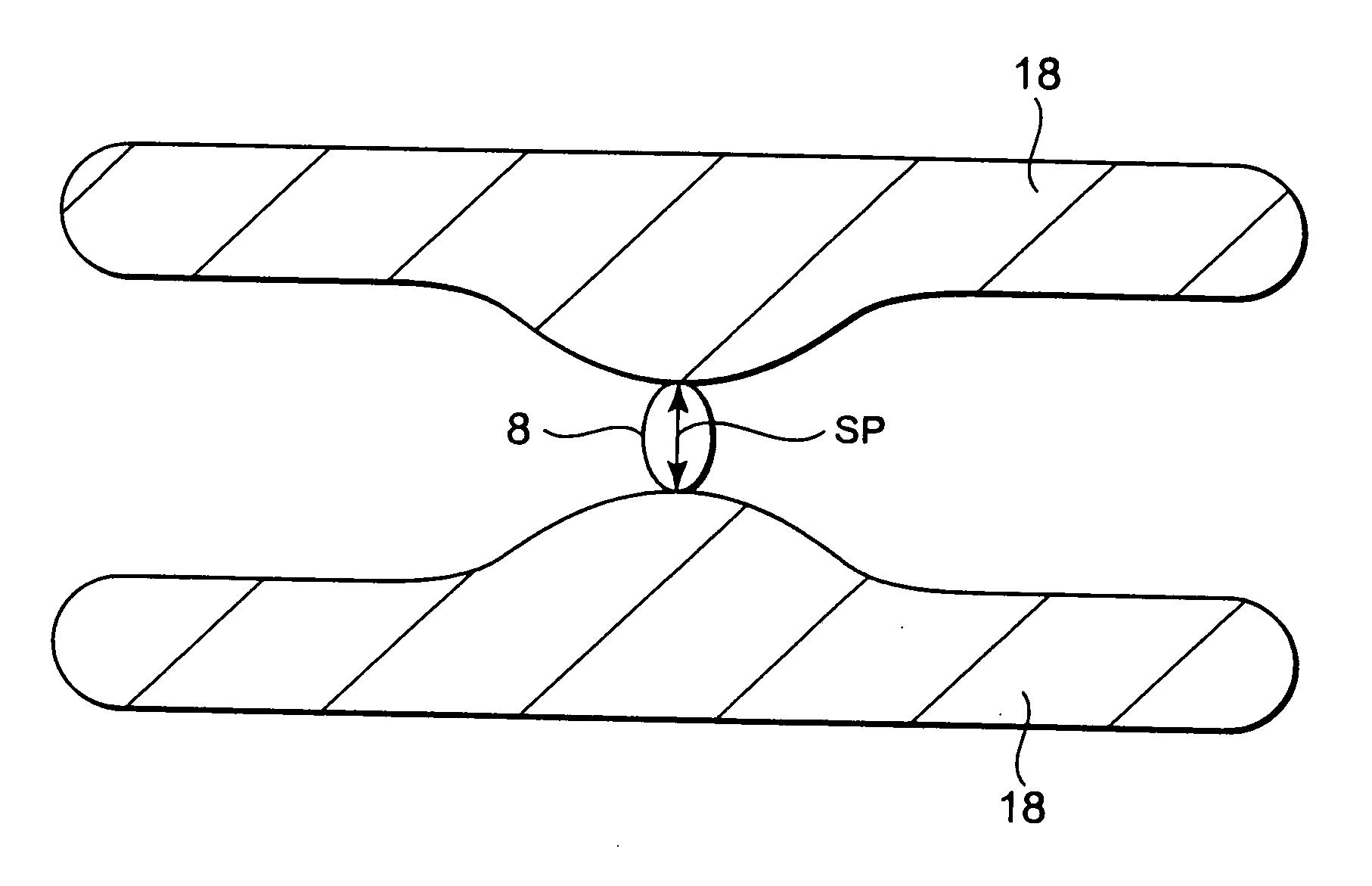
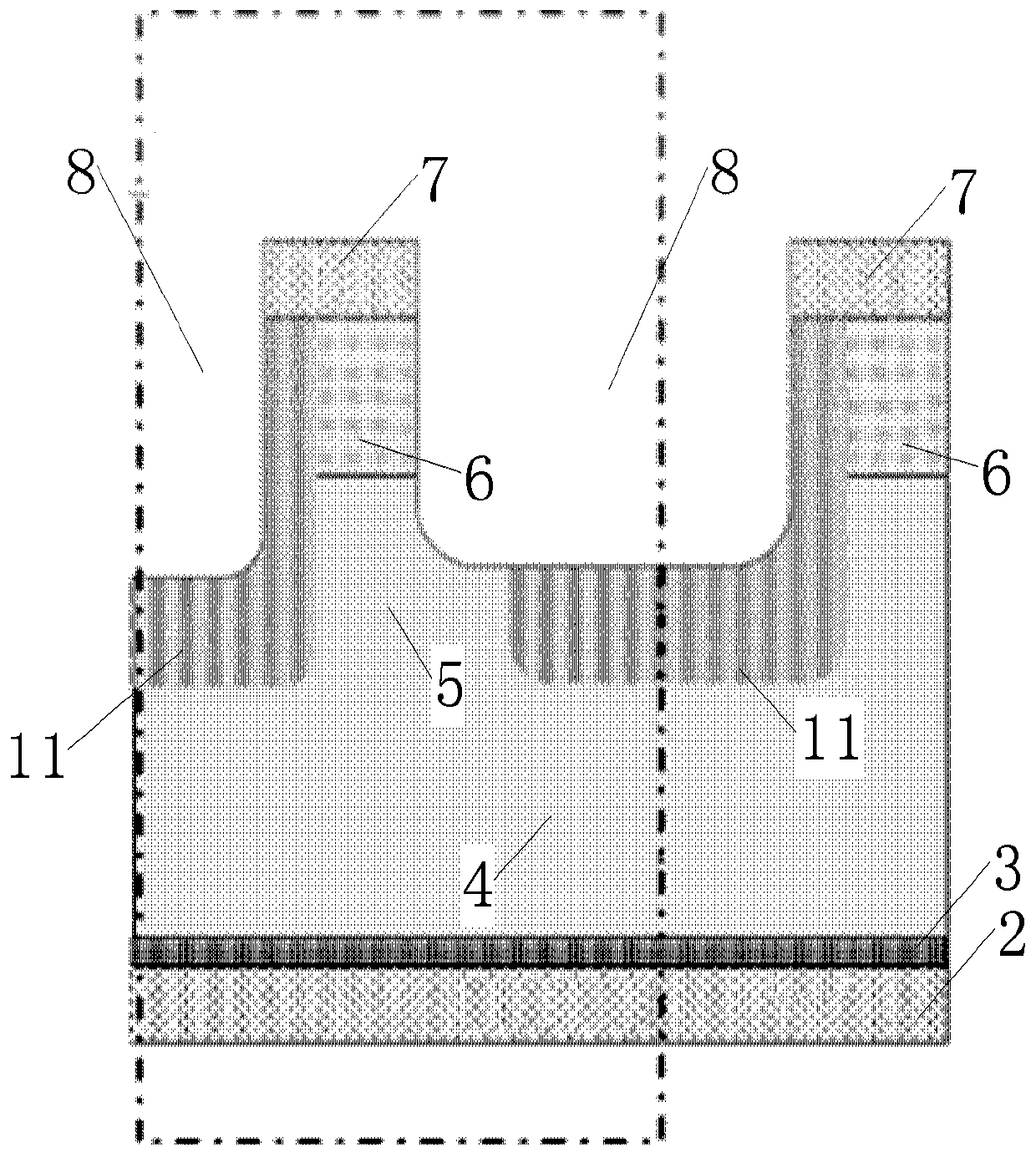
The invention discloses an MOSFET device, which is applied to the technical field of semiconductors. A primitive cell structure of an active region of the MOSFET device comprises a drain electrode (1), an n+ substrate (2), an n-type buffer layer (3), an n-drift region (4), an n-type JFET region (5), a P base region (6) and an n+ layer (7) in sequence from bottom to top; the primitive cell structure of the active region of the MOSFET device is an asymmetric structure; a groove (8) is formed in the primitive cell structure; one side of the groove (8) is provided with a gate dielectric (9) and apolysilicon gate electrode (10), and the other side of the groove (8) is provided with a P+ region (11) and a source electrode (12); and the polysilicon gate electrode (10) and the source electrode (12) are isolated by a dielectric layer (13). The structure of the device can effectively shield an electric field of the gate dielectric at the bottom of the groove (8), so that the reliability and theservice life of the device are improved and prolonged, and meanwhile, low on resistance and gate-drain capacitance are obtained.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN107425056AReduced Miller CapacitanceReduce energy consumptionSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceDielectric layer
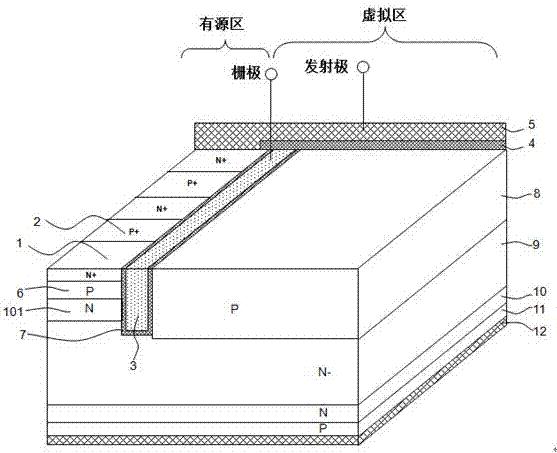
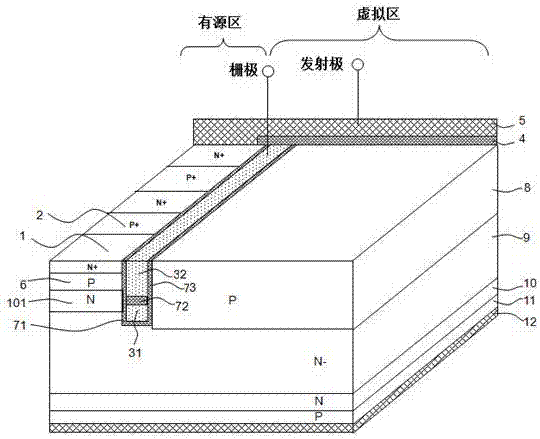
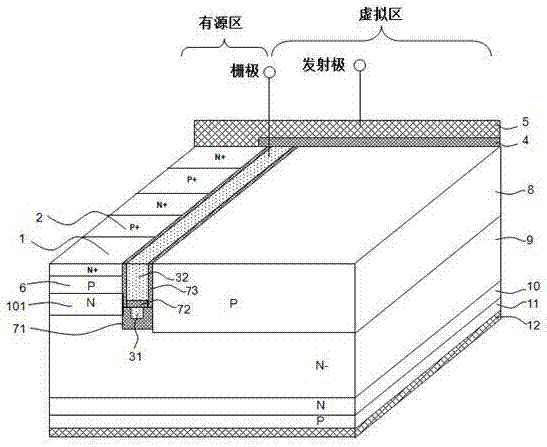
The invention discloses an insulated gate bipolar transistor. Compared with the prior art, polycrystalline silicon filled in a trench is separated by a dielectric layer into an upper polycrystalline silicon layer and a lower polycrystalline silicon layer, the upper polycrystalline silicon layer and the lower polycrystalline silicon layer are mutually contacted with an oxide layer at the upper part of the trench and an oxide layer at the lower part of the trench respectively, the upper polycrystalline silicon layer is connected with a gate electrode, and the lower polycrystalline silicon layer is connected with an emitting electrode; and bottom part of the upper polycrystalline silicon layer in the trench is deeper than a P-type well region of an active primitive cell. The structure disclosed by the invention reduces the Miller capacitance and the turn-on power consumption of the device.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ZHONGMING SEMICON TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com