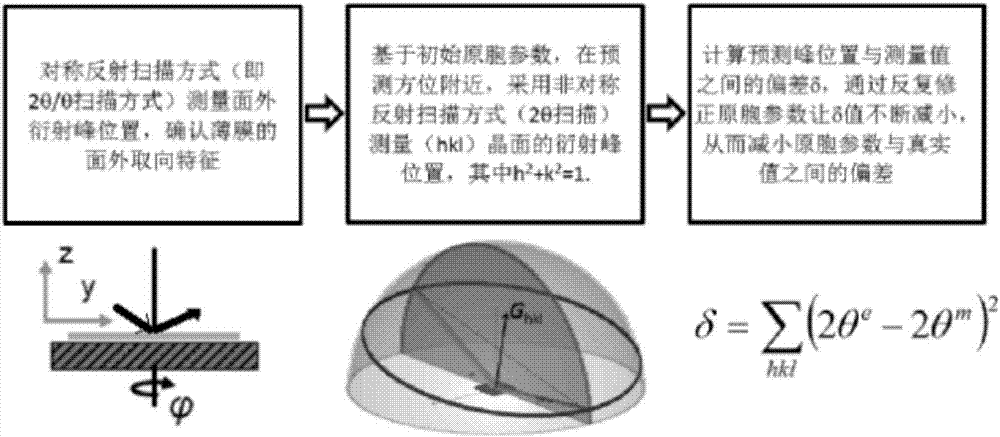
X-ray diffraction in-situ characterization method of film orientation crystal growth
A thin film orientation and X-ray technology, which is applied in the field of thin film crystal phase structure characterization, can solve the problems of in-situ characterization, long characterization time, and insufficient detection depth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Analysis of lattice constants of oriented thin films prepared by pulling TIPS pentacene with different solvents:
[0070] The initial input lattice parameters here come from references, and δ can be a number greater than 1 and less than 10.
[0071] Initial input (a b c α β γ δ) = [7.75 7.96 17.02 104.3 87.4 99.6 1.85].
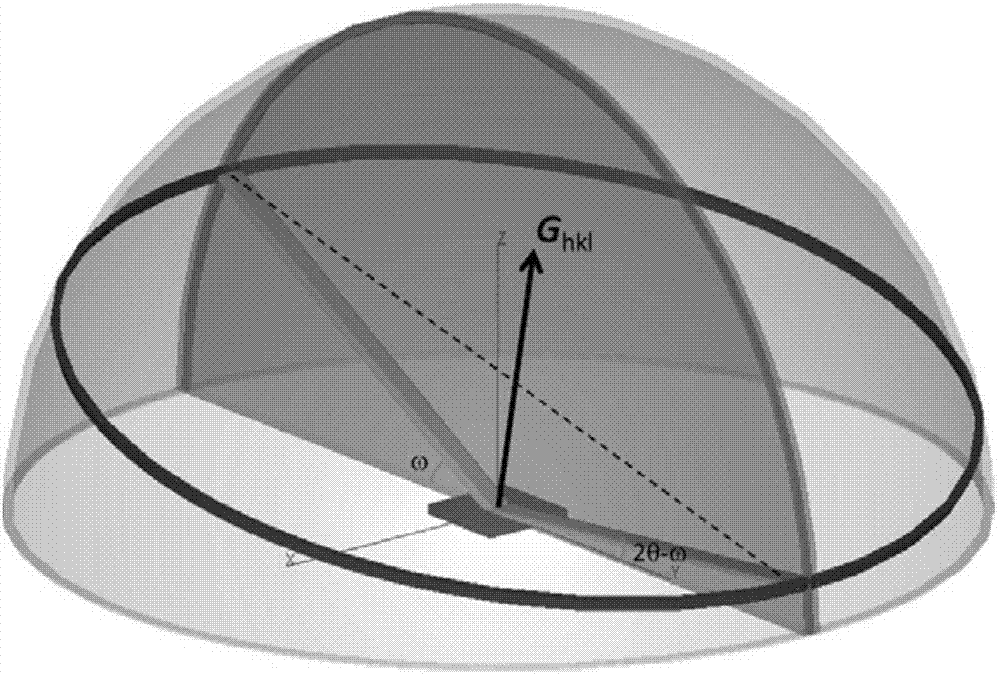
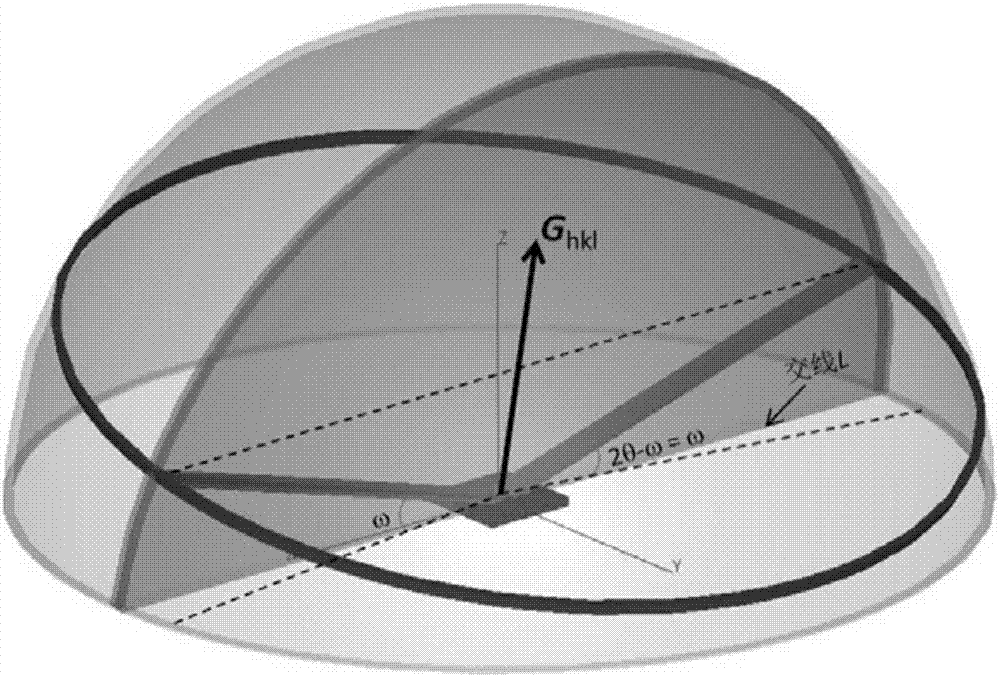
[0072] Under the coplanar constraint, calculate a series of (hkl) predicted test orientation data such as Image 6 , where h 2 +k 2 =1, l=7, 8, 9; the crystal plane index (Miller index) and its predicted deflection angle 2θ in line with the asymmetric reflection test conditions e Such as Figure 7 Shown; measured l = 8 crystal plane diffraction deflection angle 2θ m Such as Image 6 As shown, according to the out-of-plane diffraction peak positions and Image 6 In the asymmetric diffraction measurement, the continuously optimized lattice parameters and the deviation δ between the predicted peak position and the measured peak position are calcula...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Lattice constant analysis of C8-BTBT oriented film prepared by solution method:
[0075] The initial input lattice parameters here come from references, and δ can be a number greater than 1 and less than 10.
[0076] Initial input (a b c α β γ δ) = [5.91 7.88 29.12 90 91 90 1.85].
[0077] The lattice parameter analysis process and output results of C8-BTBT film are as follows Figure 9 As shown, the deviation δ is still greater than 1 after multiple cycles of calculation, and the deviation is relatively large. The in-plane texture of the film can be further finely analyzed based on the condition of asymmetric reflection scanning by making a pole figure, and the measurement orientation can be corrected based on the corresponding results. Measurement accuracy can be improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com