Method for self-locating sensor network node within sparseness measuring set base on shortest path
A sensor network, shortest path technology, applied in positioning, measuring devices, data exchange networks, etc., can solve the problem that the positioning result deviates from the real position of the node
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
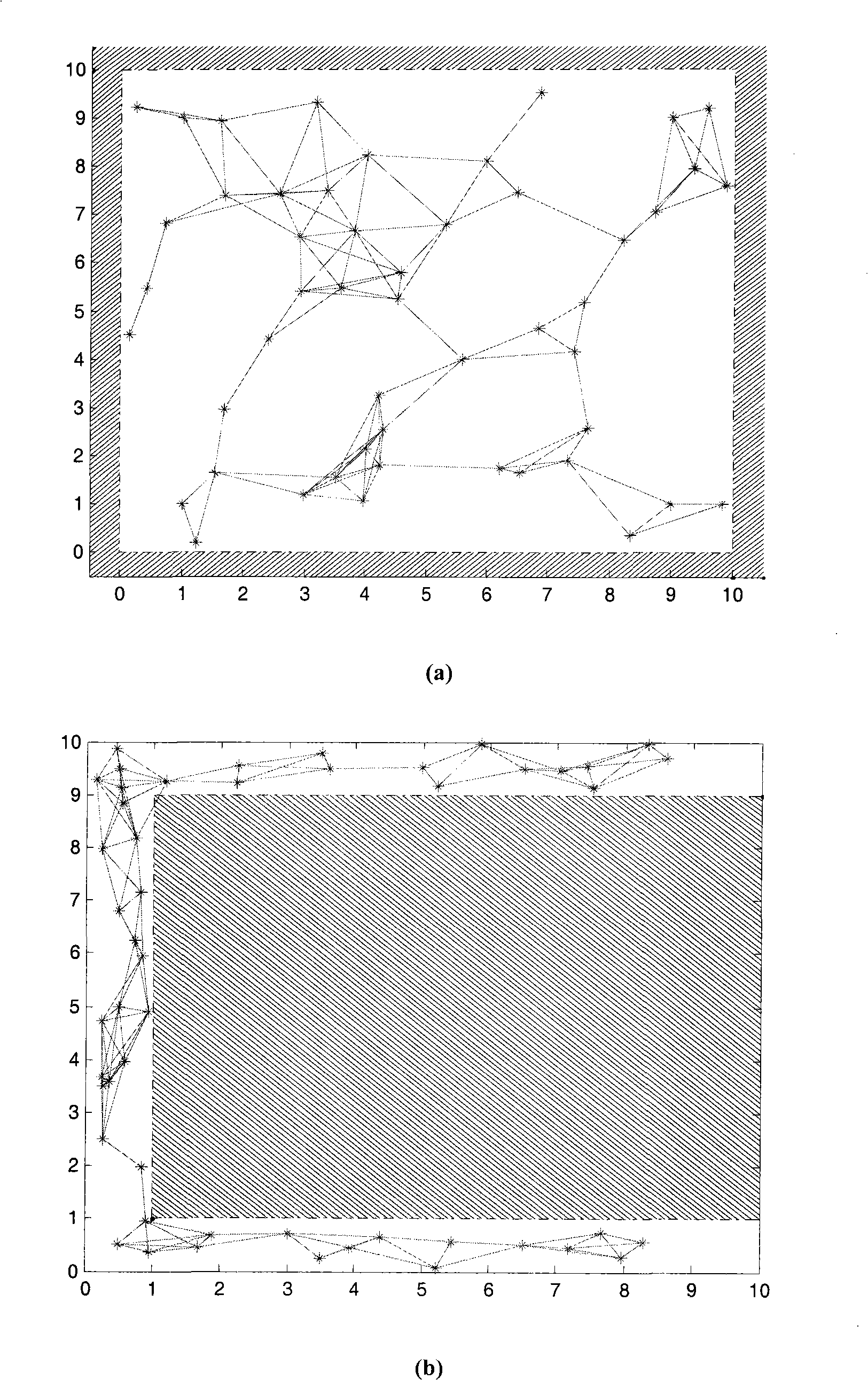
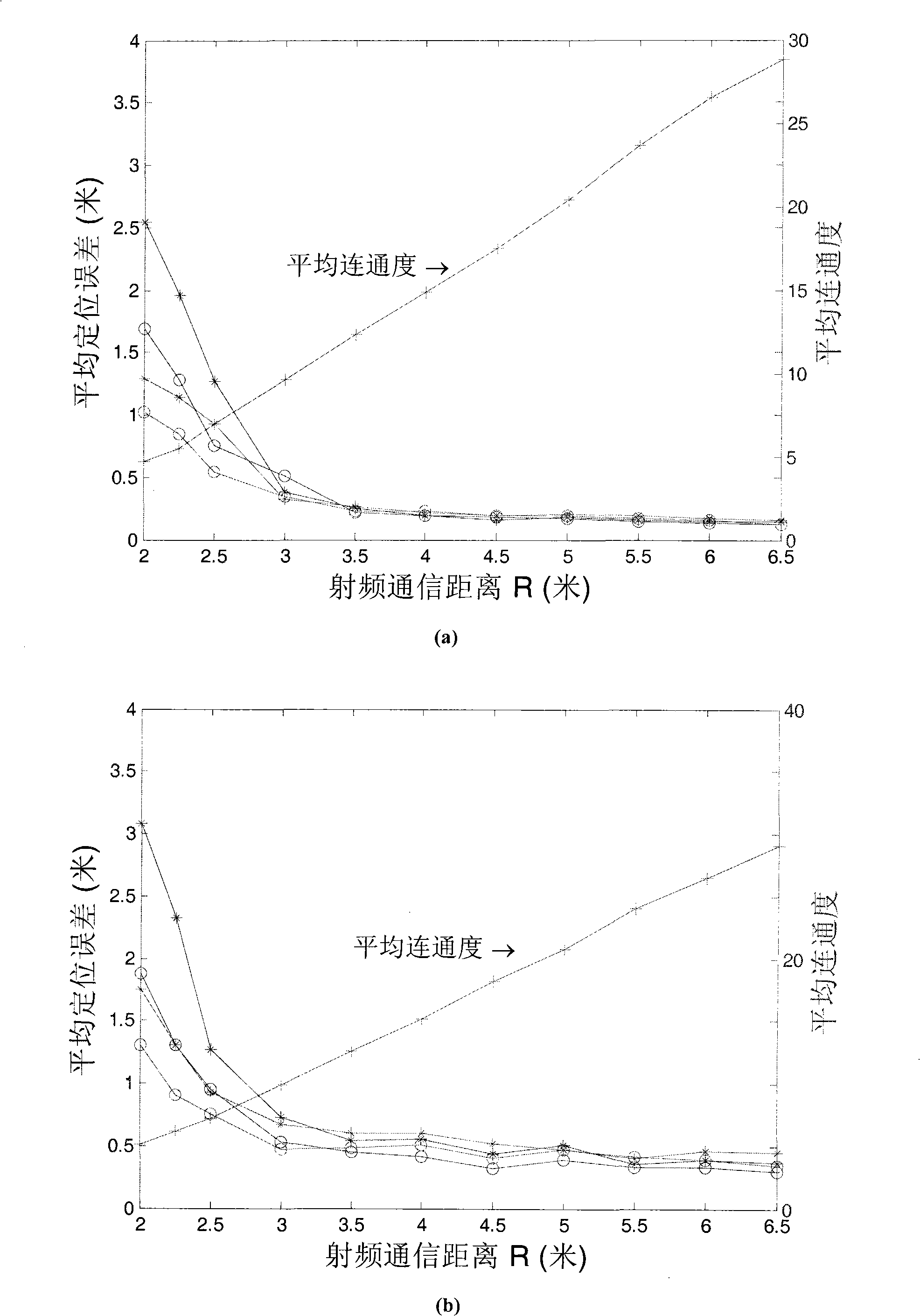
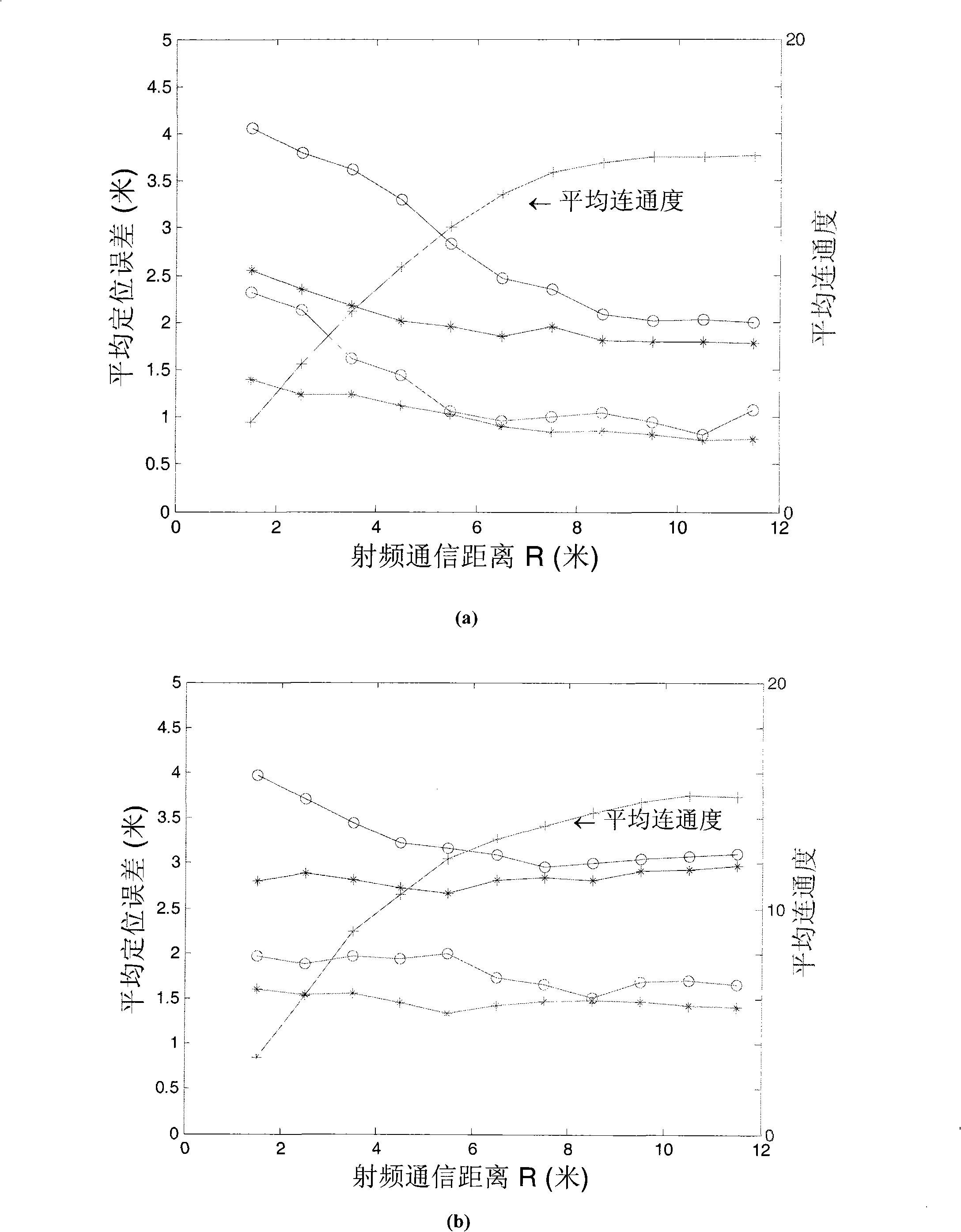
[0075] To complement the unmeasured distance, in addition to the existing distance measurements, we also need to use other observation information in the network. In the following, these are collectively referred to as network constraints.
[0076] By observing the empty items in the distance measurement set D, it can be found that the absence of these empty items is not random in wireless sensor networks. For example, the distance d between node i and node j ij has not been observed, although the information provided by this fact itself cannot allow us to infer a specific value, we can still conclude that d ij The RF signal transmission distance of the node is exceeded, or there is occlusion between nodes i and j, and there is no direct line-of-sight communication path. The above assertion can be regarded as a network constraint obtained by observation, which is used to limit the relative positional relationship between nodes i and j; in positioning, we not only make the res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com