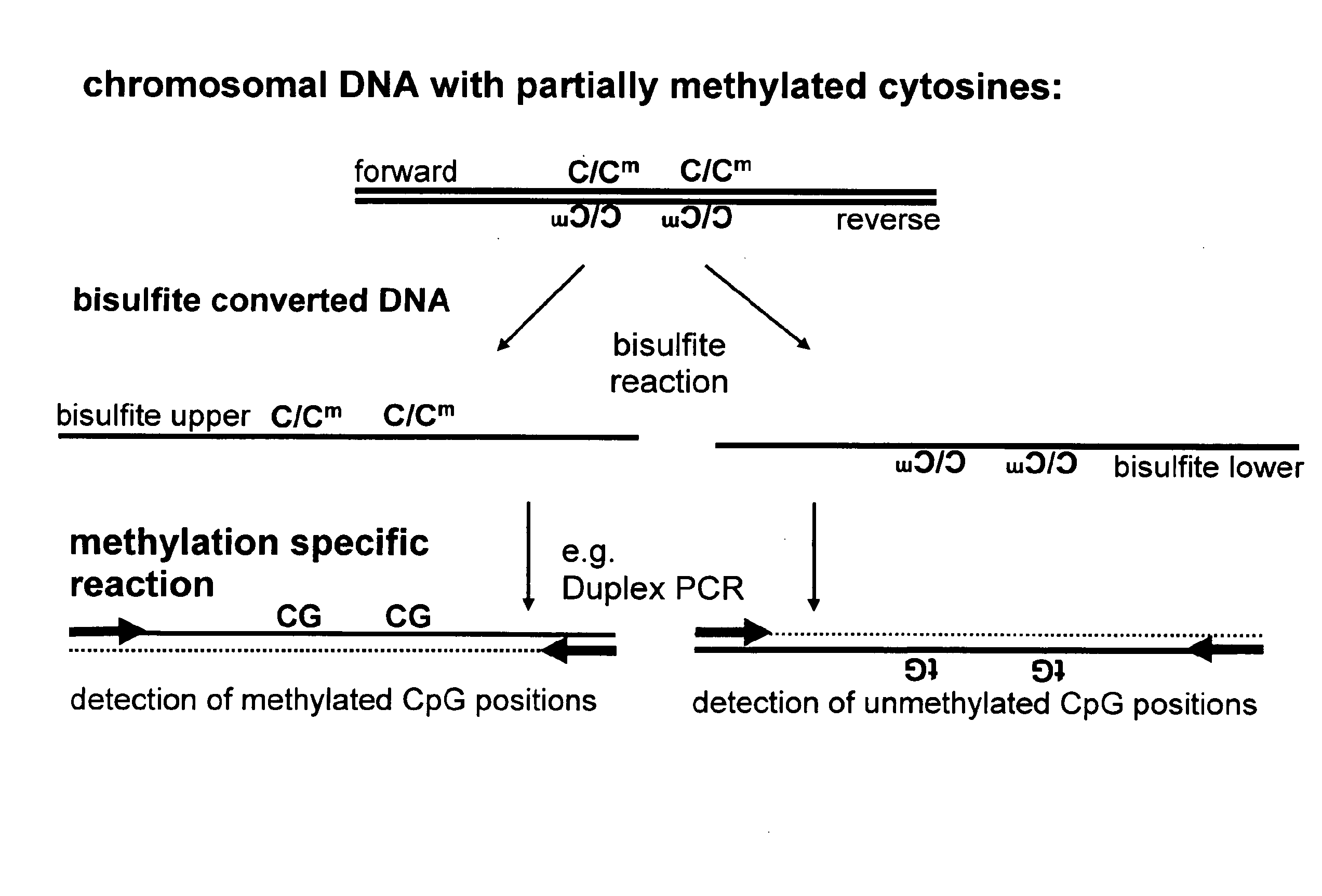
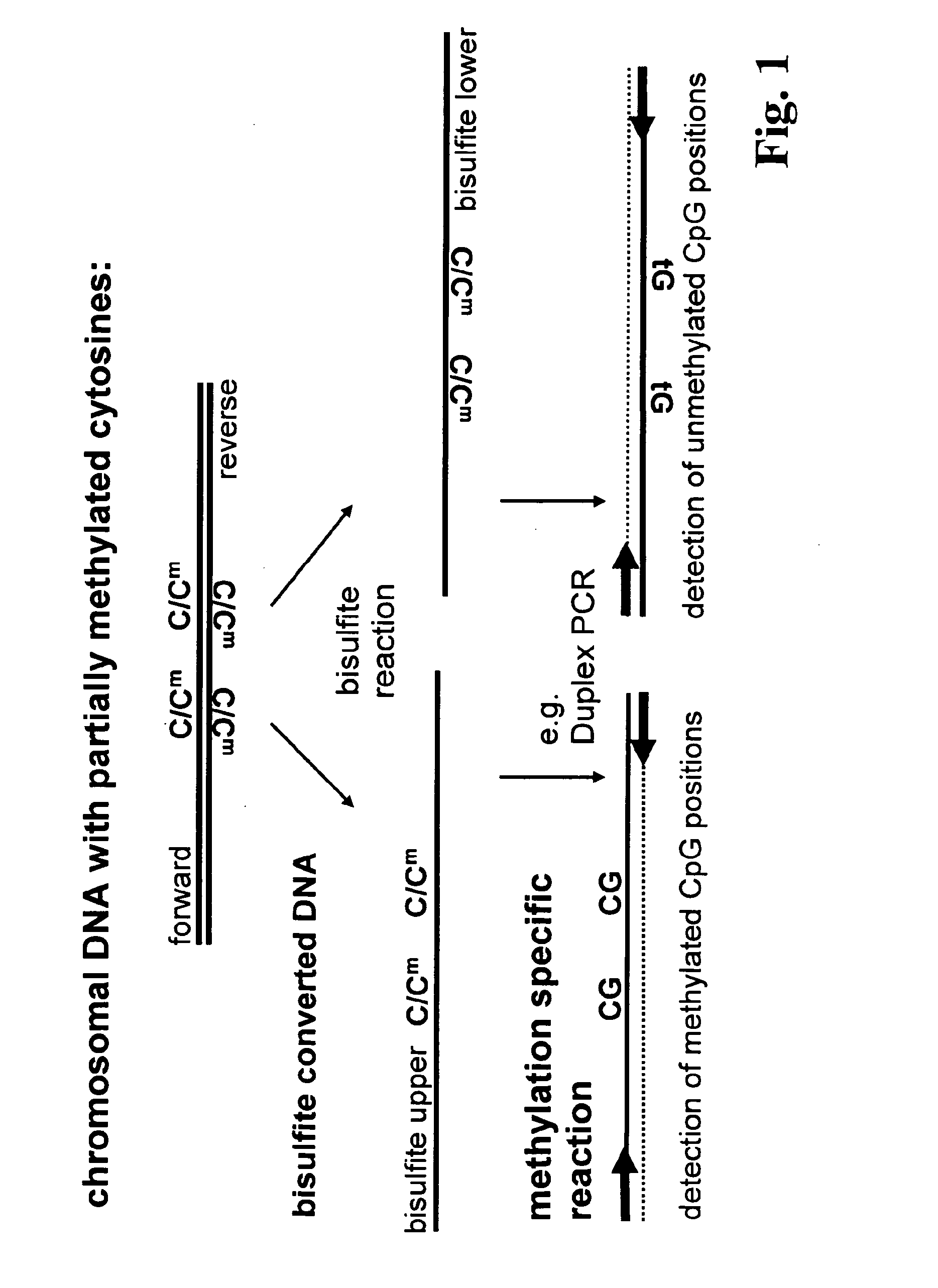
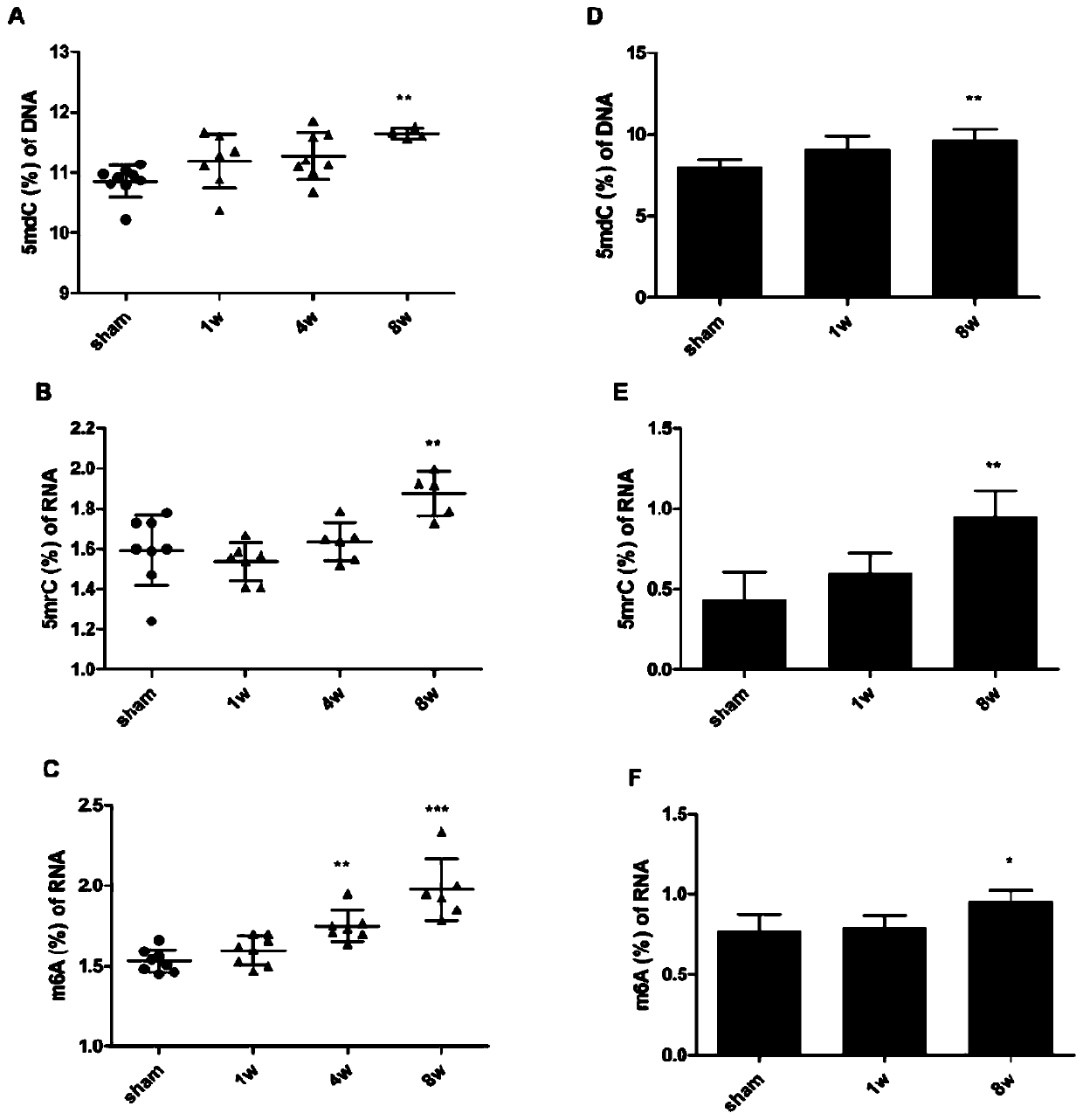
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Nucleic acid methylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
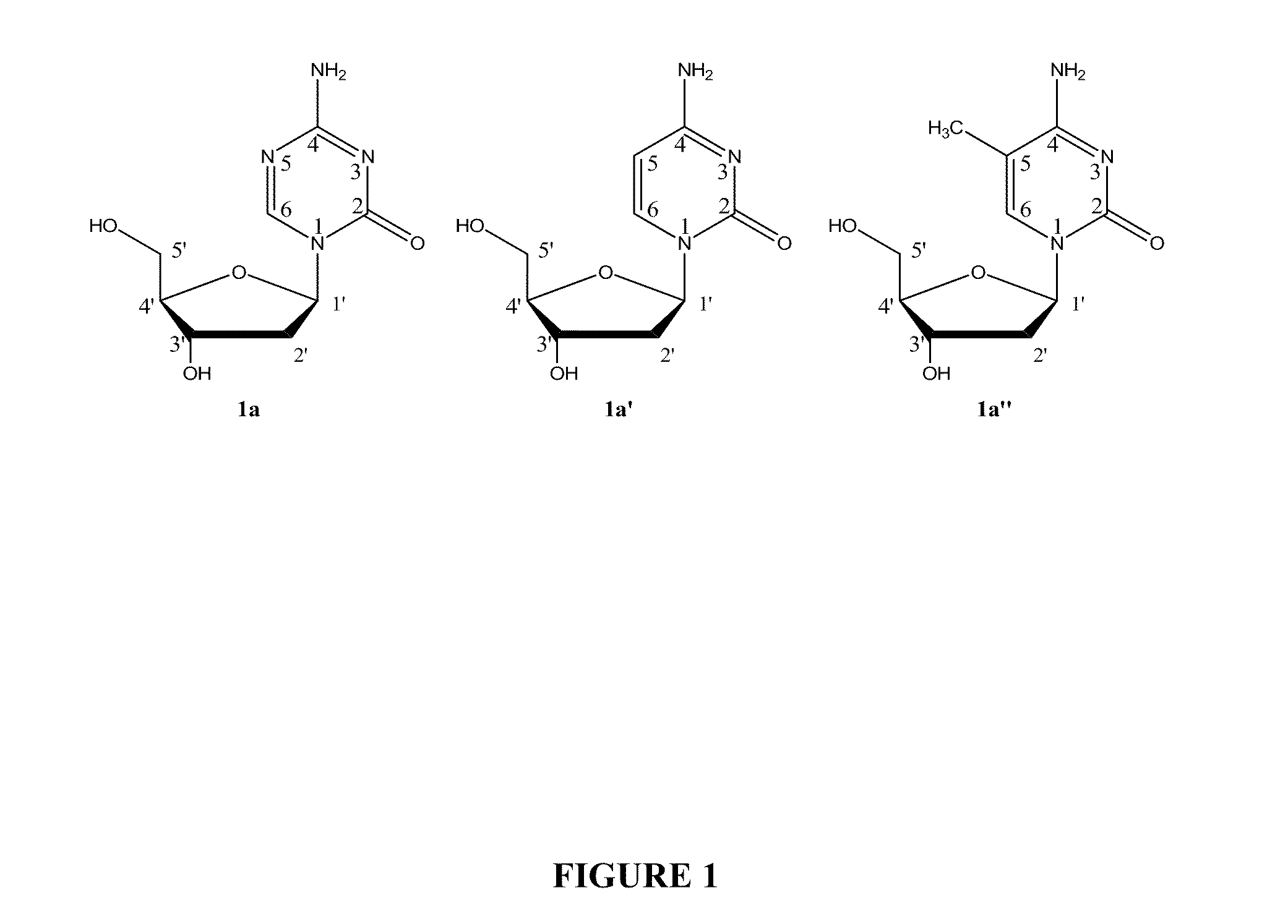
Addition of methyl groups to nucleic acid.
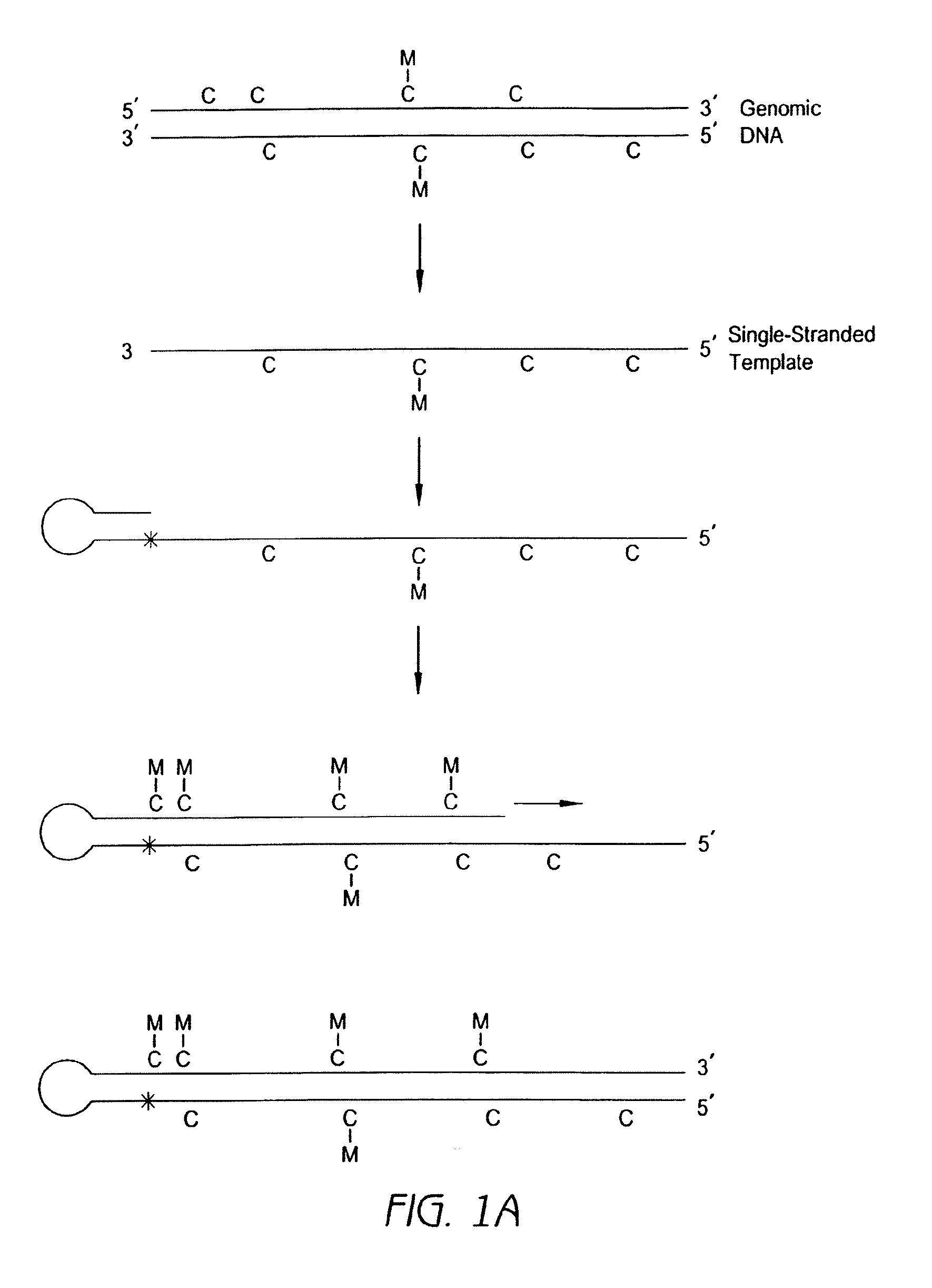
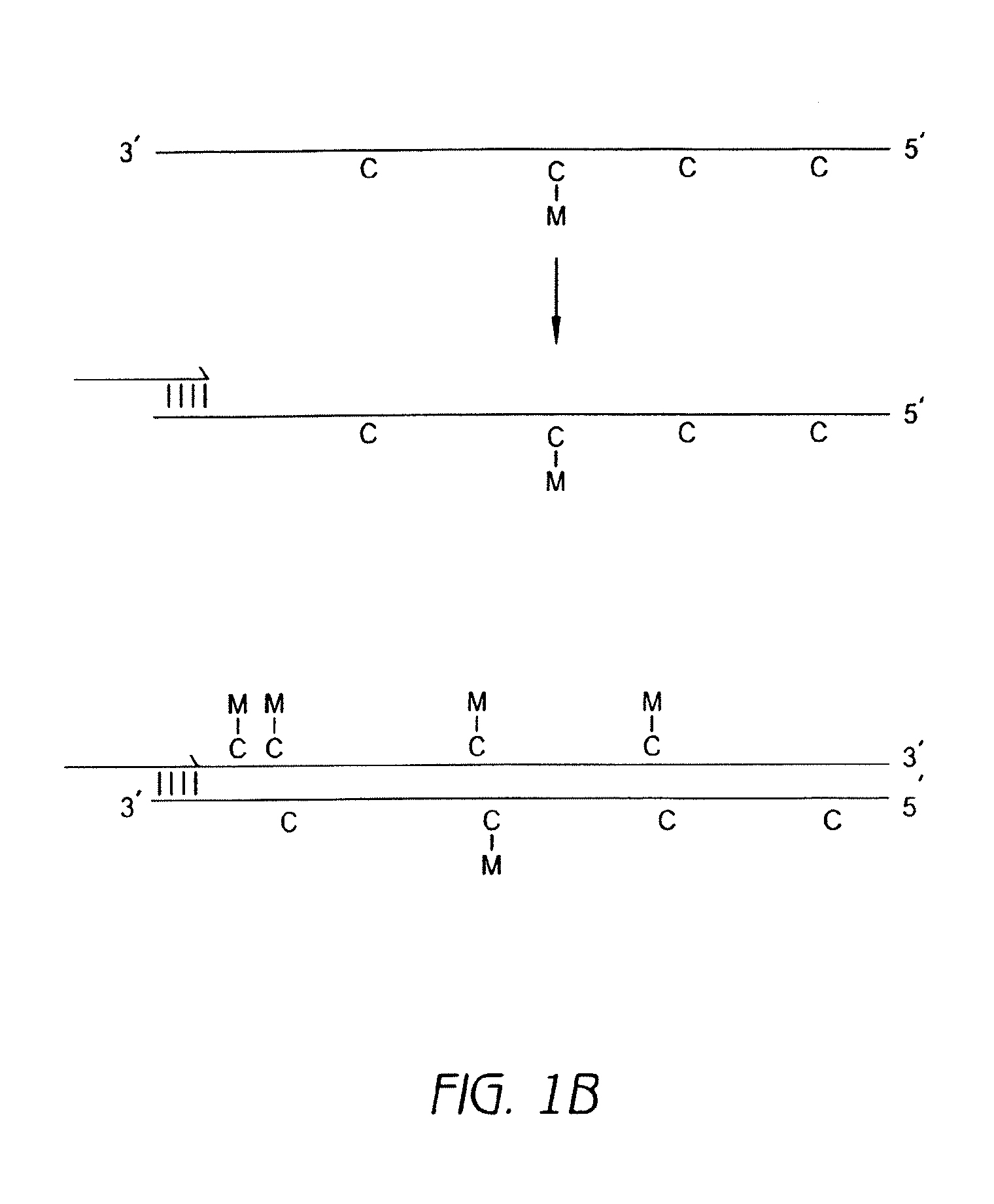
Methods for analysis of nucleic acid methylation status and methods for fragmentation, labeling and immobilization of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050208538A1Reduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOrganic chemistryNucleic acid methylation
The invention relates to methods for analysis of nucleic acid methylation status, and fragmentation and / or labeling and / or immobilization of nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for fragmentation and / or labeling and / or immobilization of nucleic acids comprising labeling and / or cleavage and / or immobilization at abasic sites.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
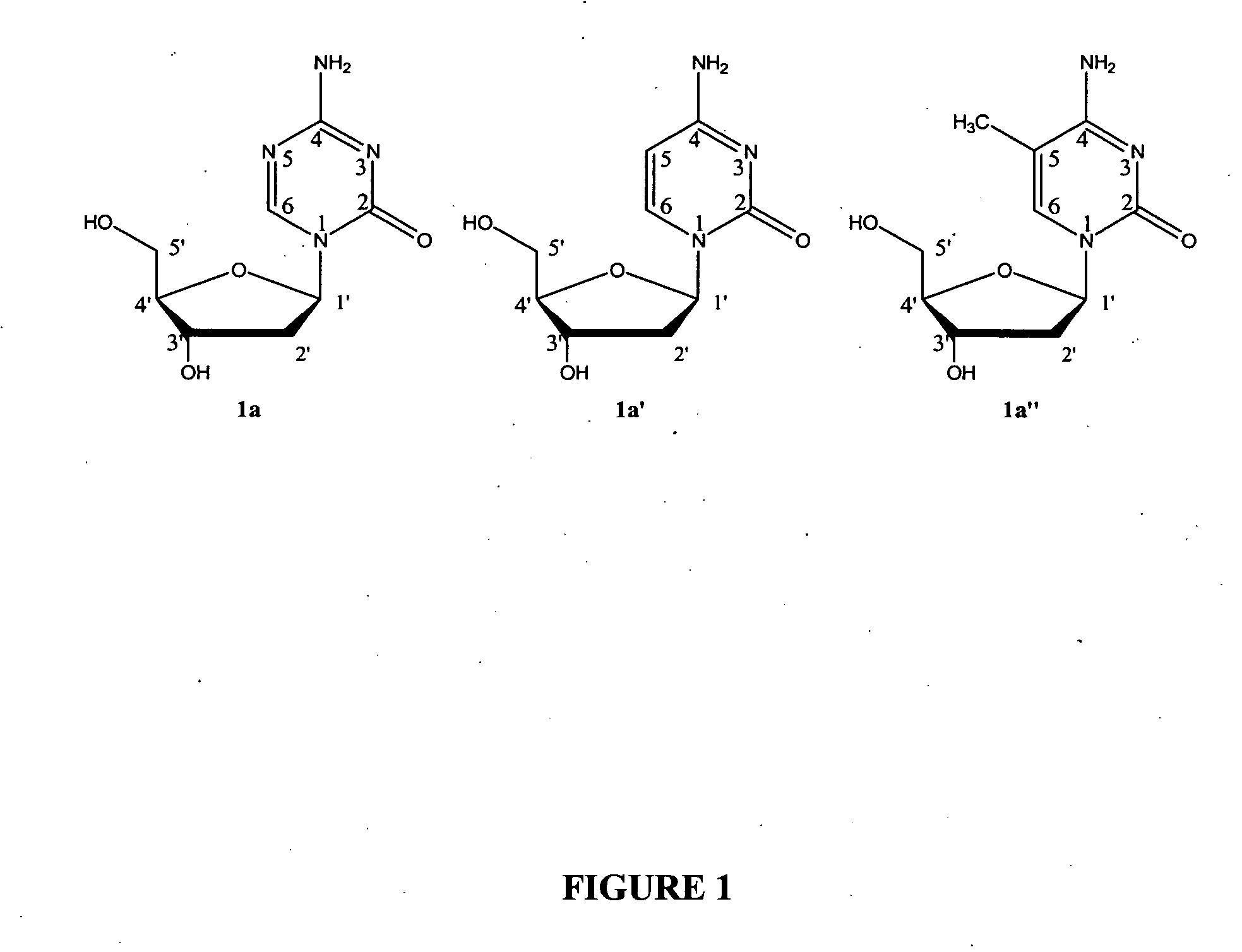
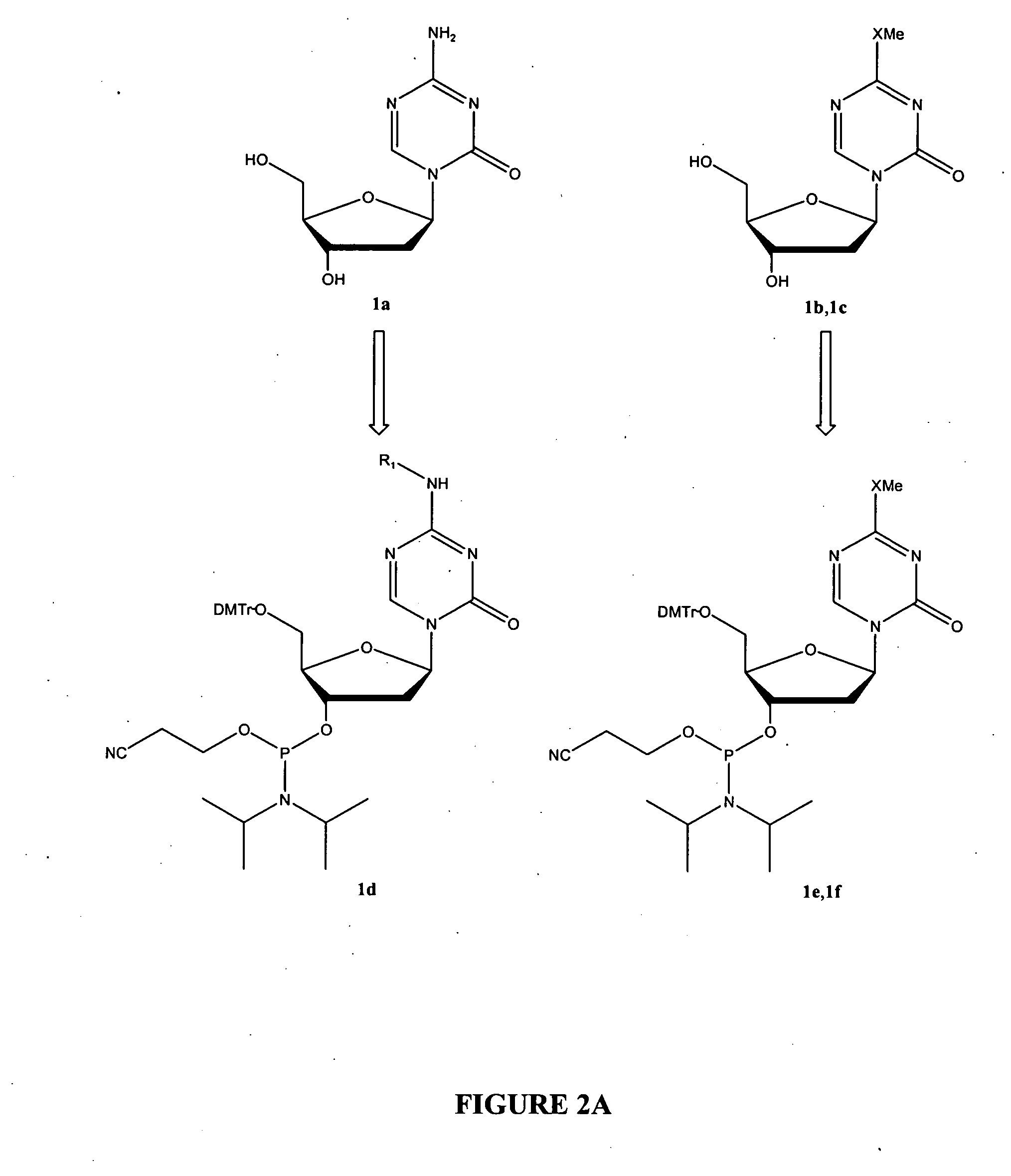
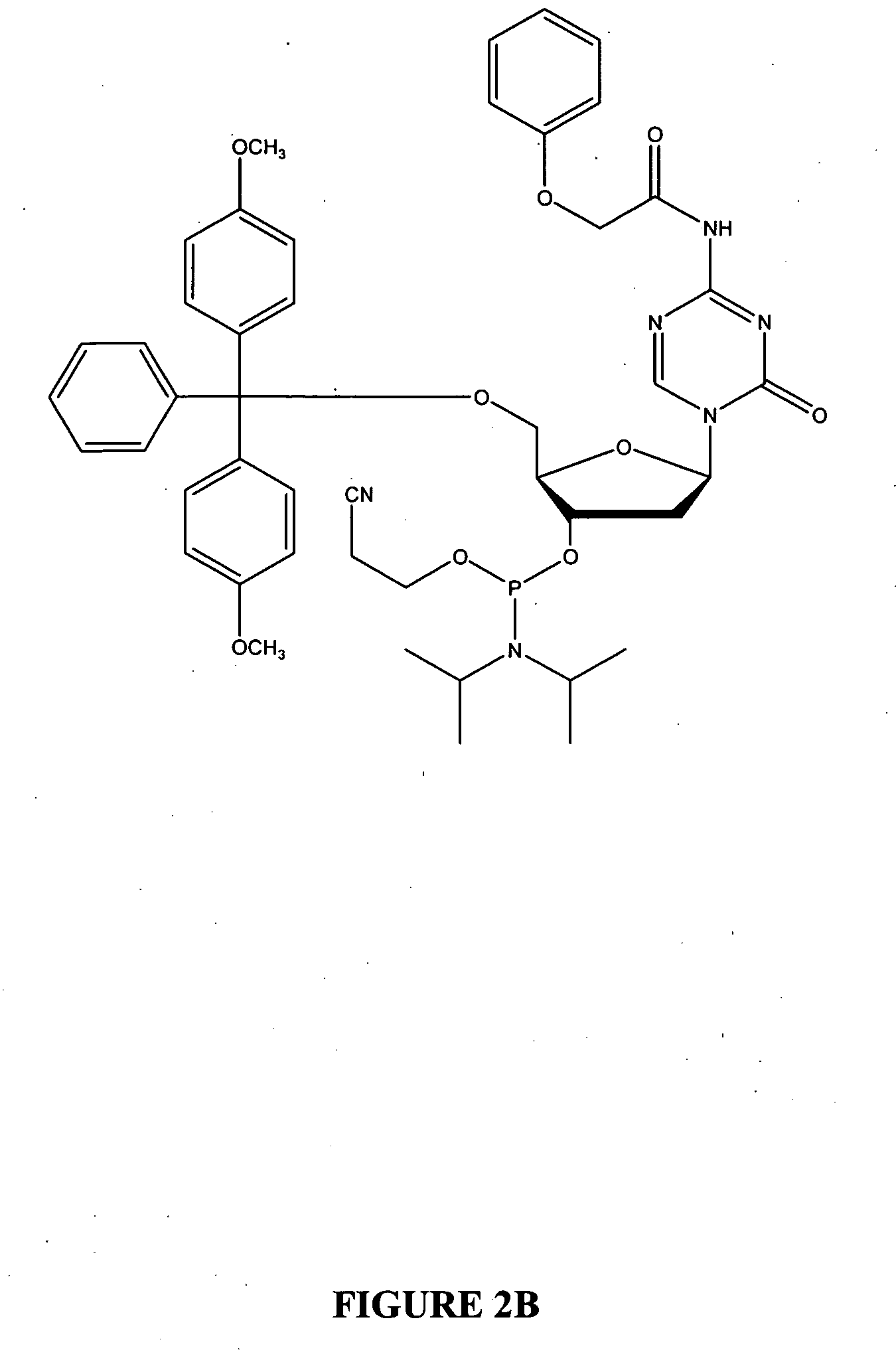
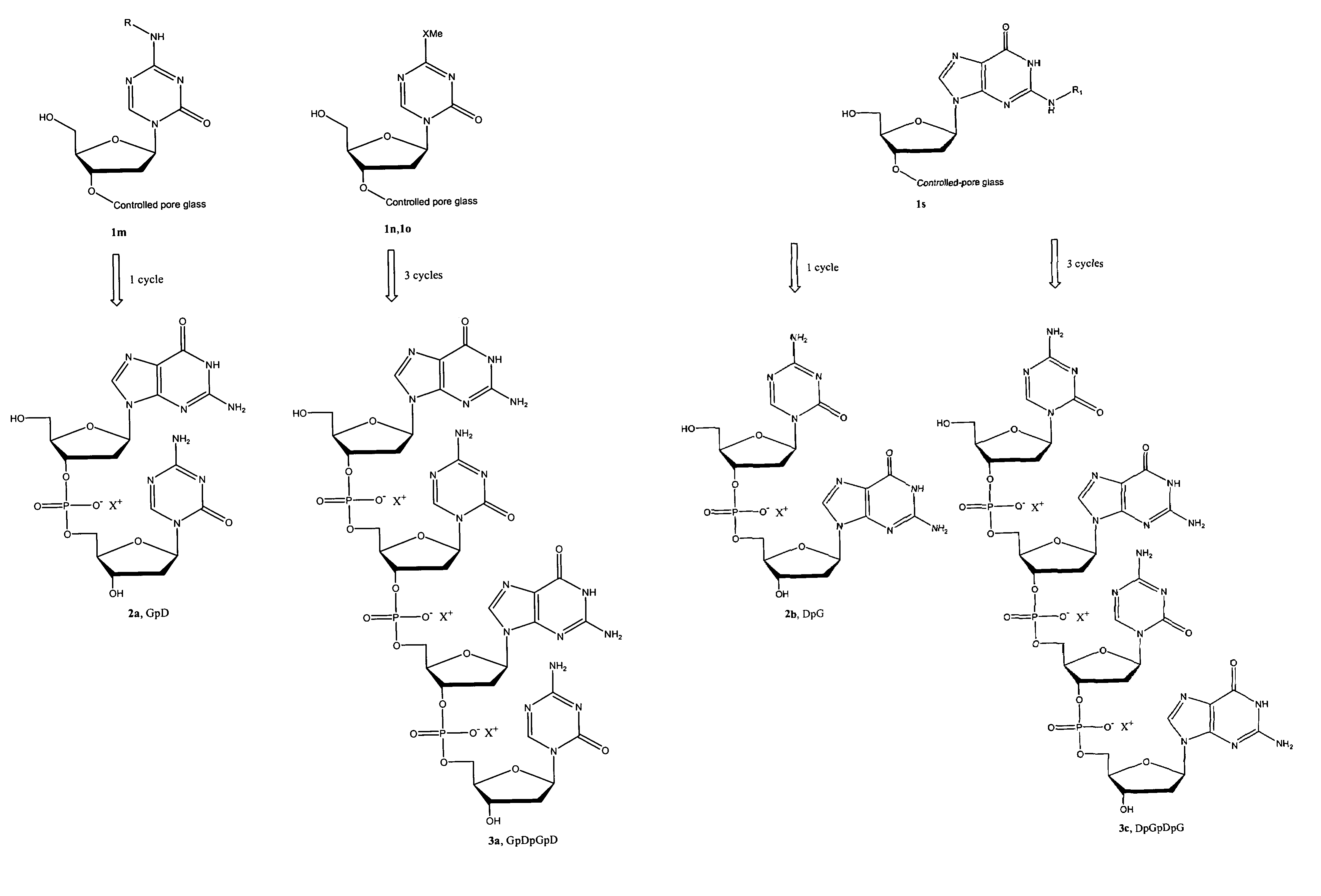
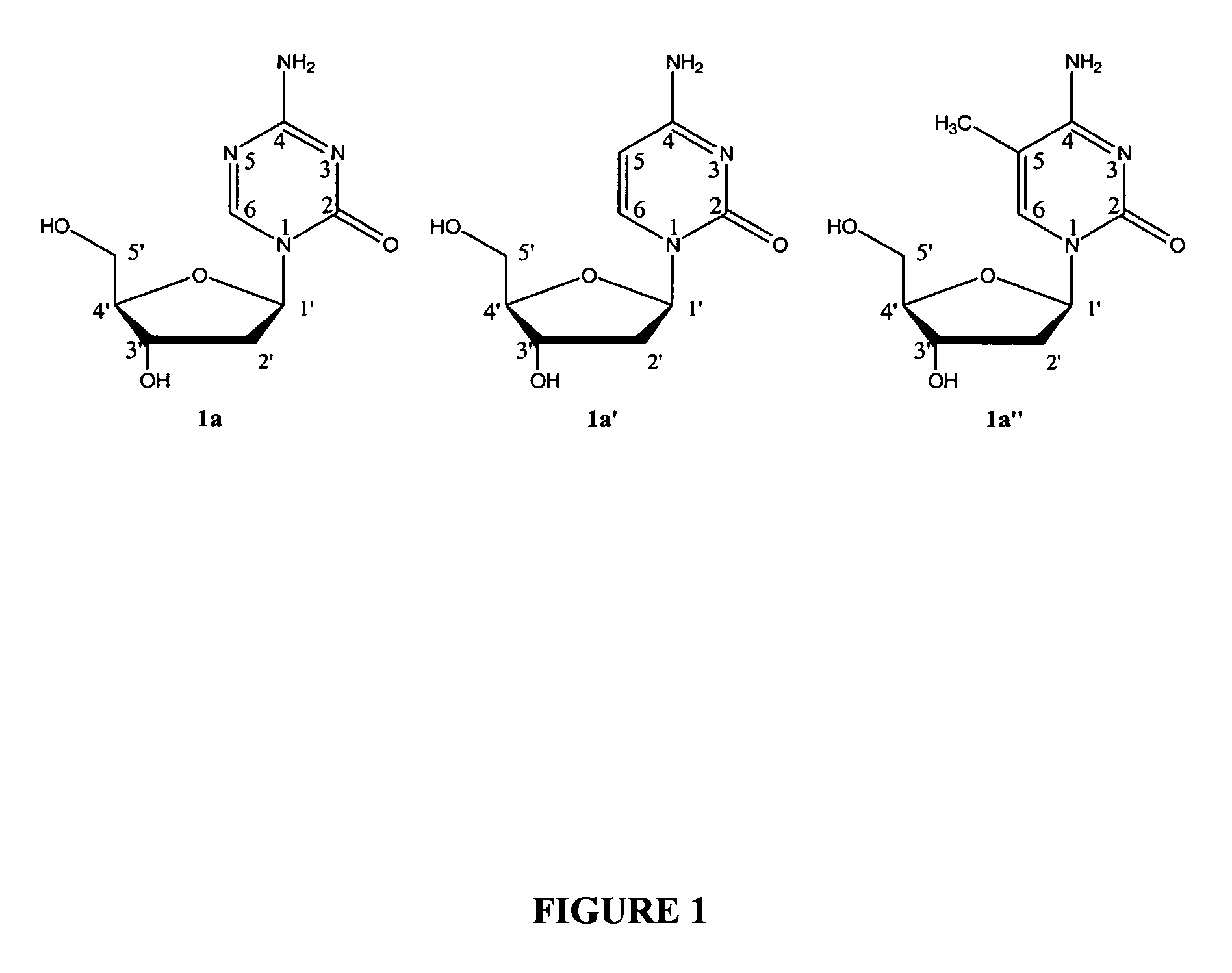
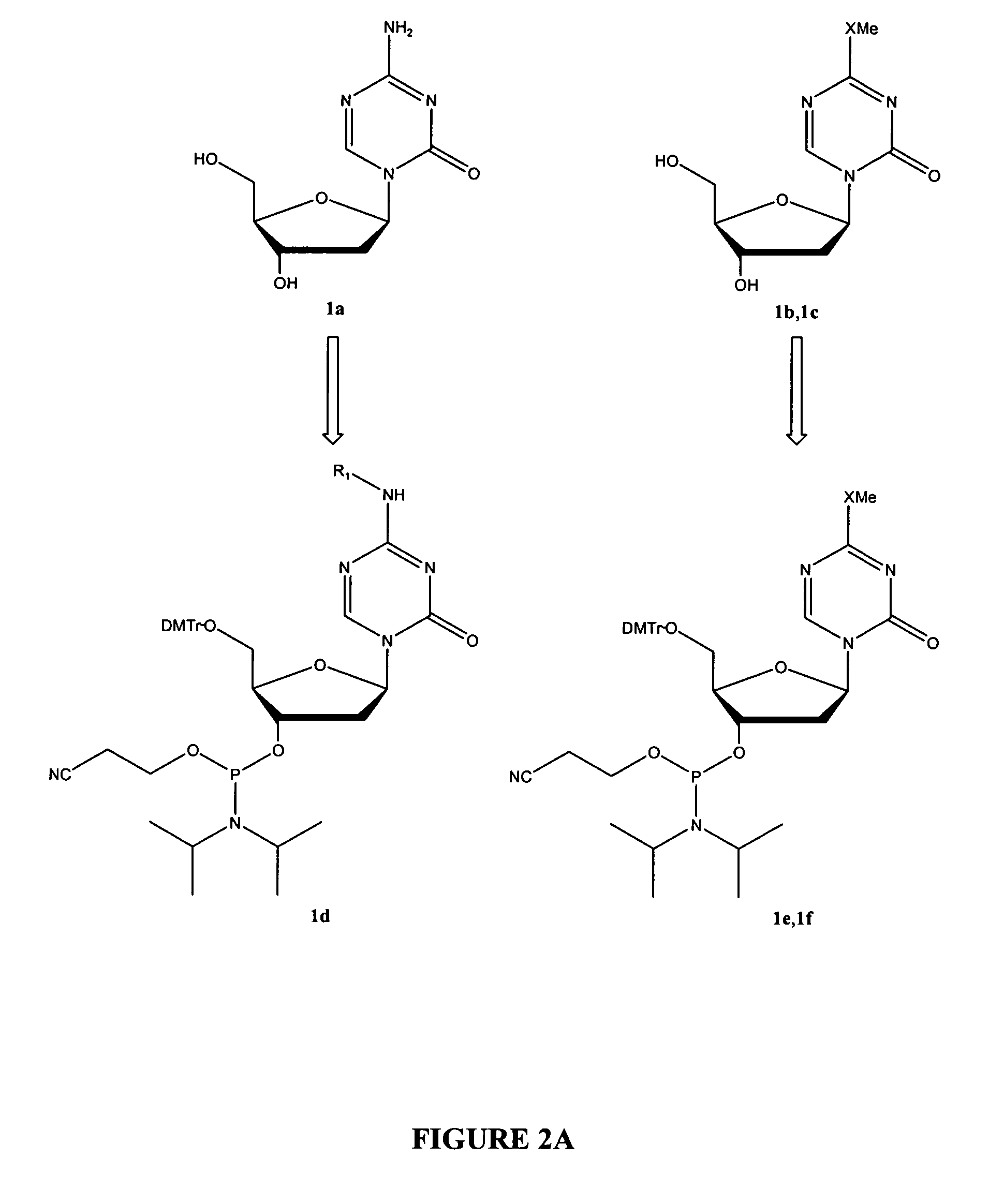
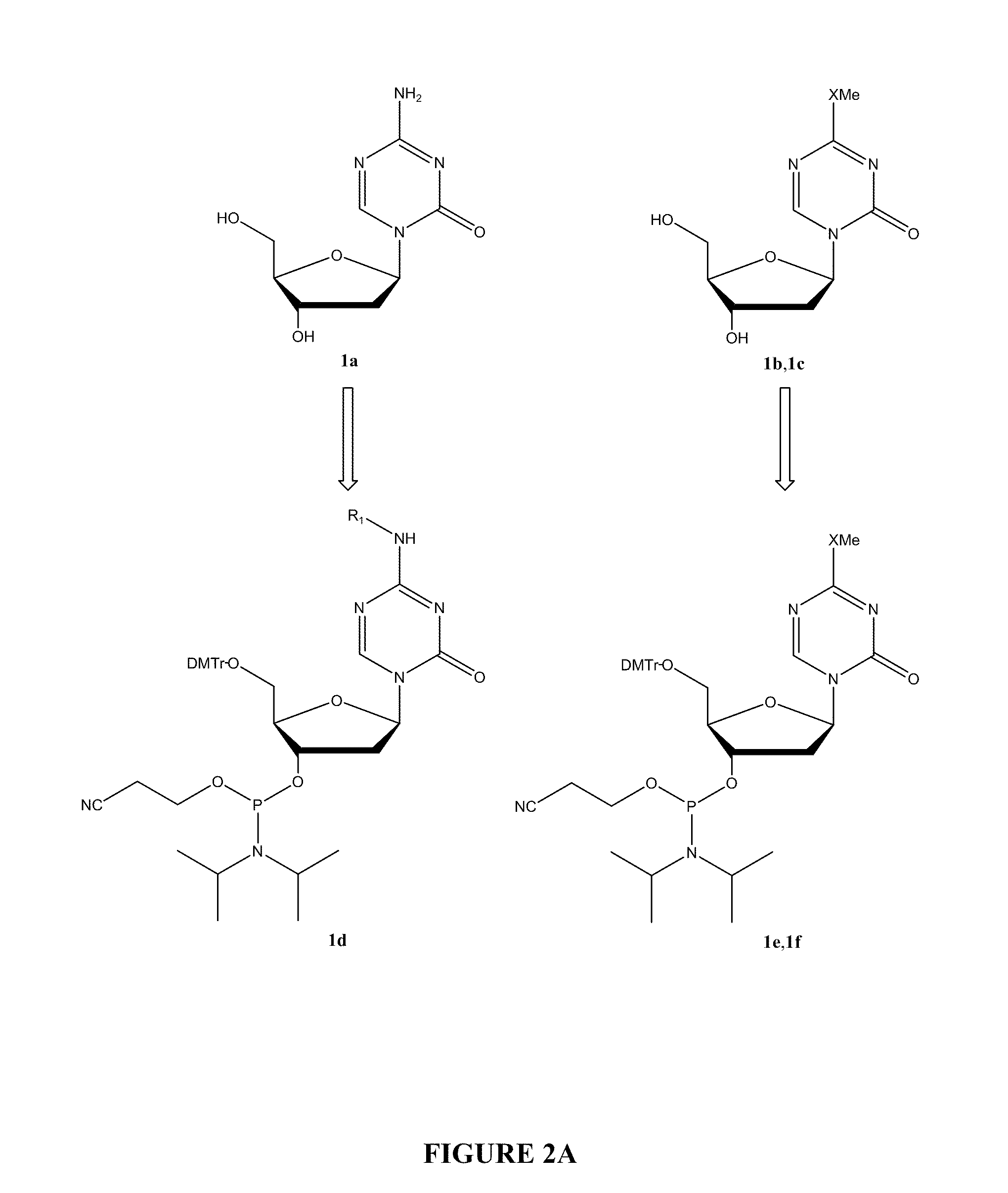
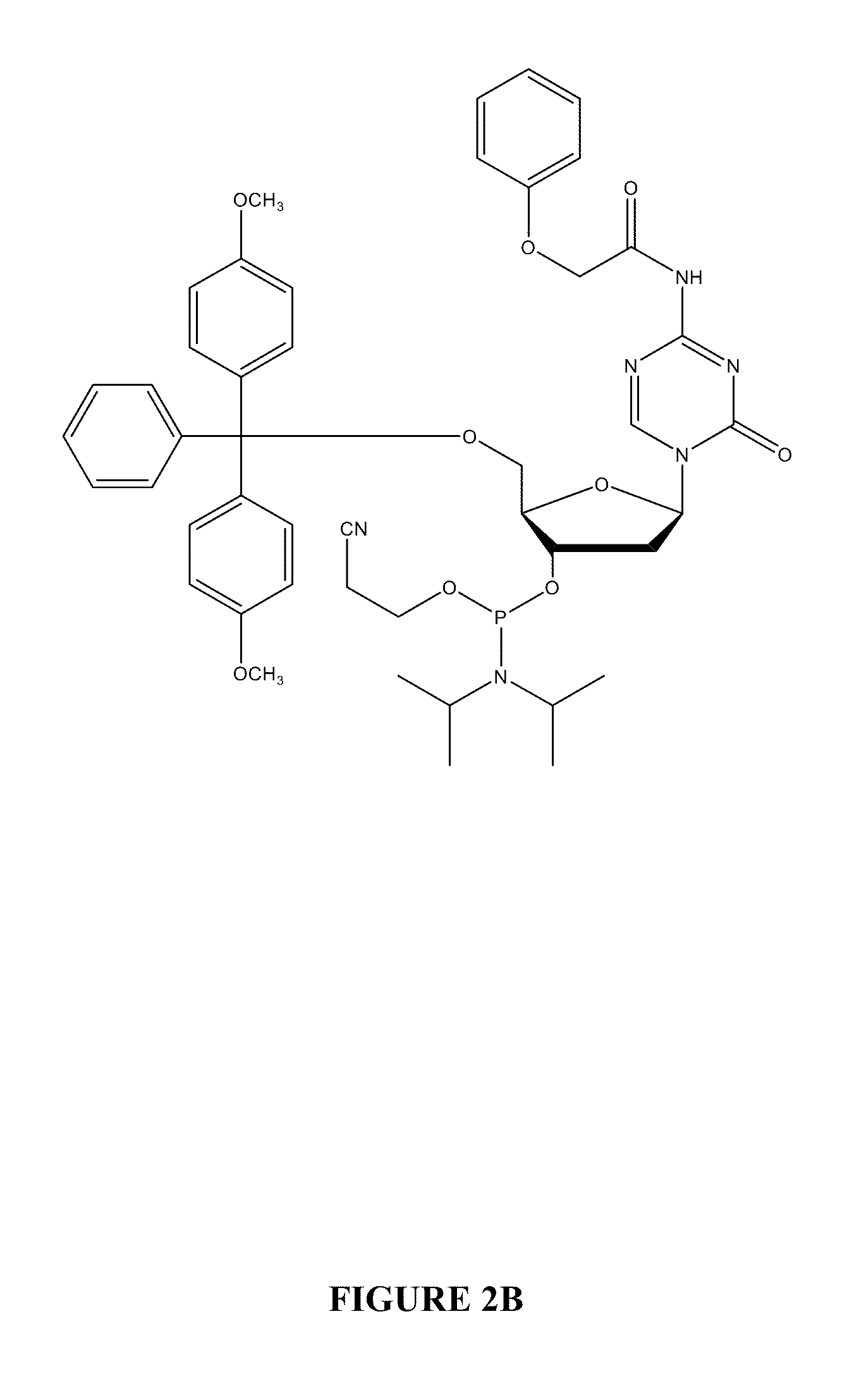
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Methods for analysis of nucleic acid methylation status and methods for fragmentation, labeling and immobilization of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090233804A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistryNucleic acid methylation
Owner:NUGEN TECH
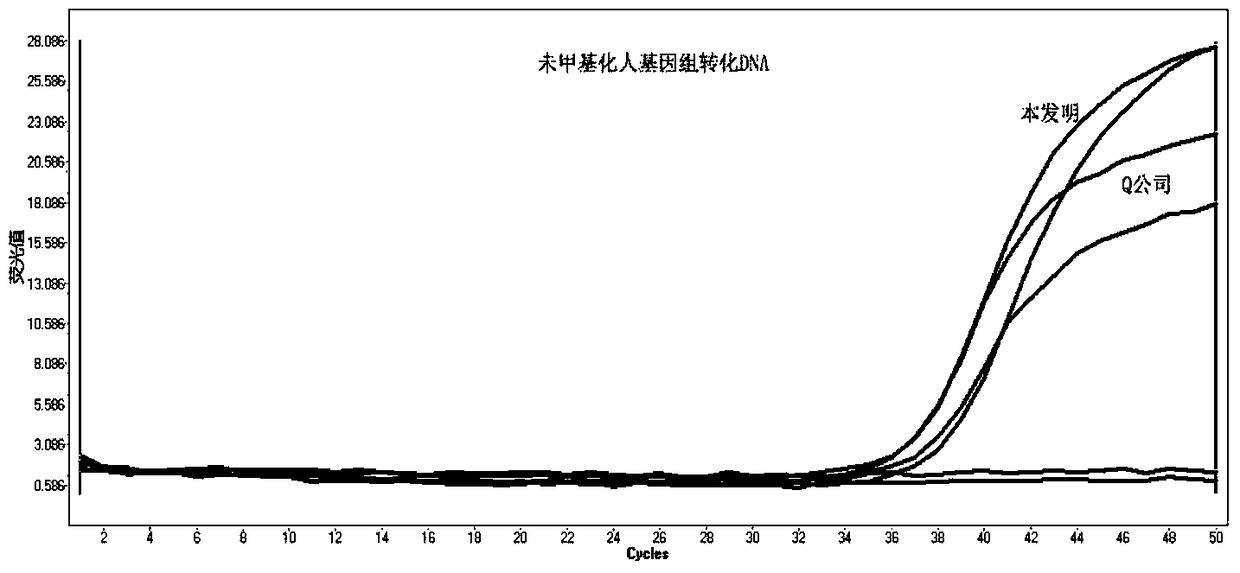
DNA sulfite conversion and purification method
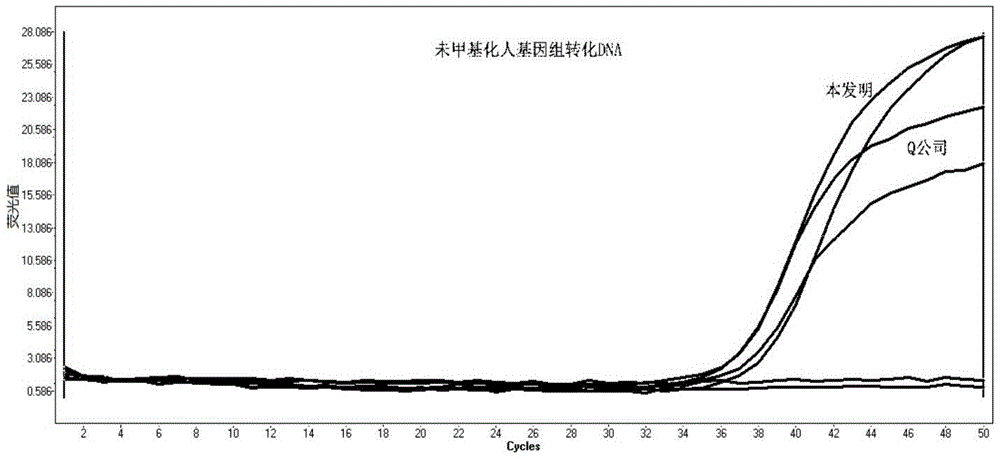
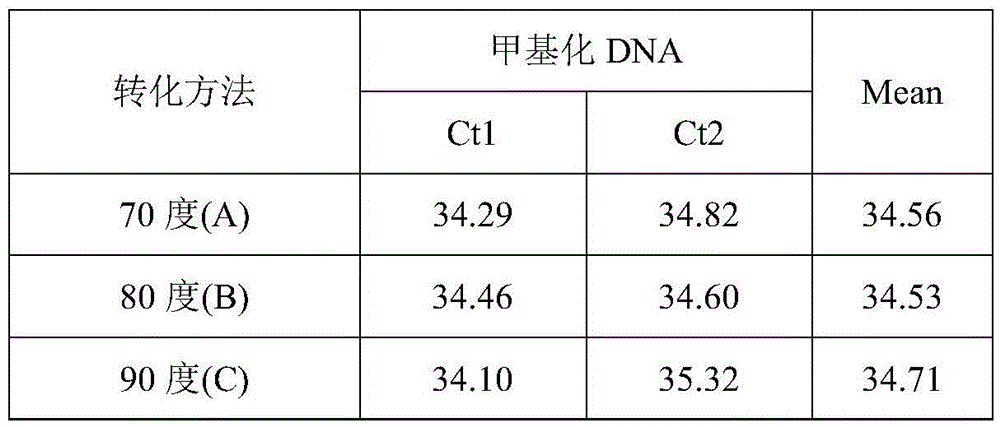
ActiveCN105462960AShort conversion timeSimple equipmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPurification methodsMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a DNA sulfite conversion and purification method. The method does need early sodium hydroxide denaturating treatment conducted on nucleic acid, adopts varying-temperature conversion conditions different from a commercialized reagent on the market and can perform a conversion experiment under the constant temperature condition. A magnetic bead method is adopted to perform nucleic acid purification after nucleic acid methylation conversion, a high-salt low pH value is utilized to perform nucleic acid separation and purification, then a low-salt high pH value is utilized to perform elution, the step of performing desulfonating by adopting sodium hydroxide on the market at present is omitted in the purification process, and meanwhile high-conversion-rate, high-quality and high-purity DNA can be obtained only by adopting a one-step washing step. The DNA sulfite conversion and purification method has the advantages of being quick, simple and convenient to operate and improving the conversion efficiency, the extraction efficiency and the extraction purity.
Owner:杭州千基生物科技有限公司 +1
Rapid methods for detecting methylation of a nucleic acid molecule
InactiveUS20050260630A1Rapid and inexpensiveAccurate and easily reproducible resultMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMammalian genomeCapillary electrophoresis
Disclosed are methods for determining the methylation status of a target double-stranded nucleic acid molecule using PCR amplification and capillary electrophoresis. The methods are generally useful in measuring the methylation status of a nucleic acid sample, including a mammalian genomic DNA sample, and may be further specifically applied to detecting changes in methylation status of a nucleic acid that are associated with exposure to a toxic compound or treatment, or that are associate with a disease or disorder.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
ActiveUS20100215729A1Heavy metal active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseHuman DNA sequencing
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
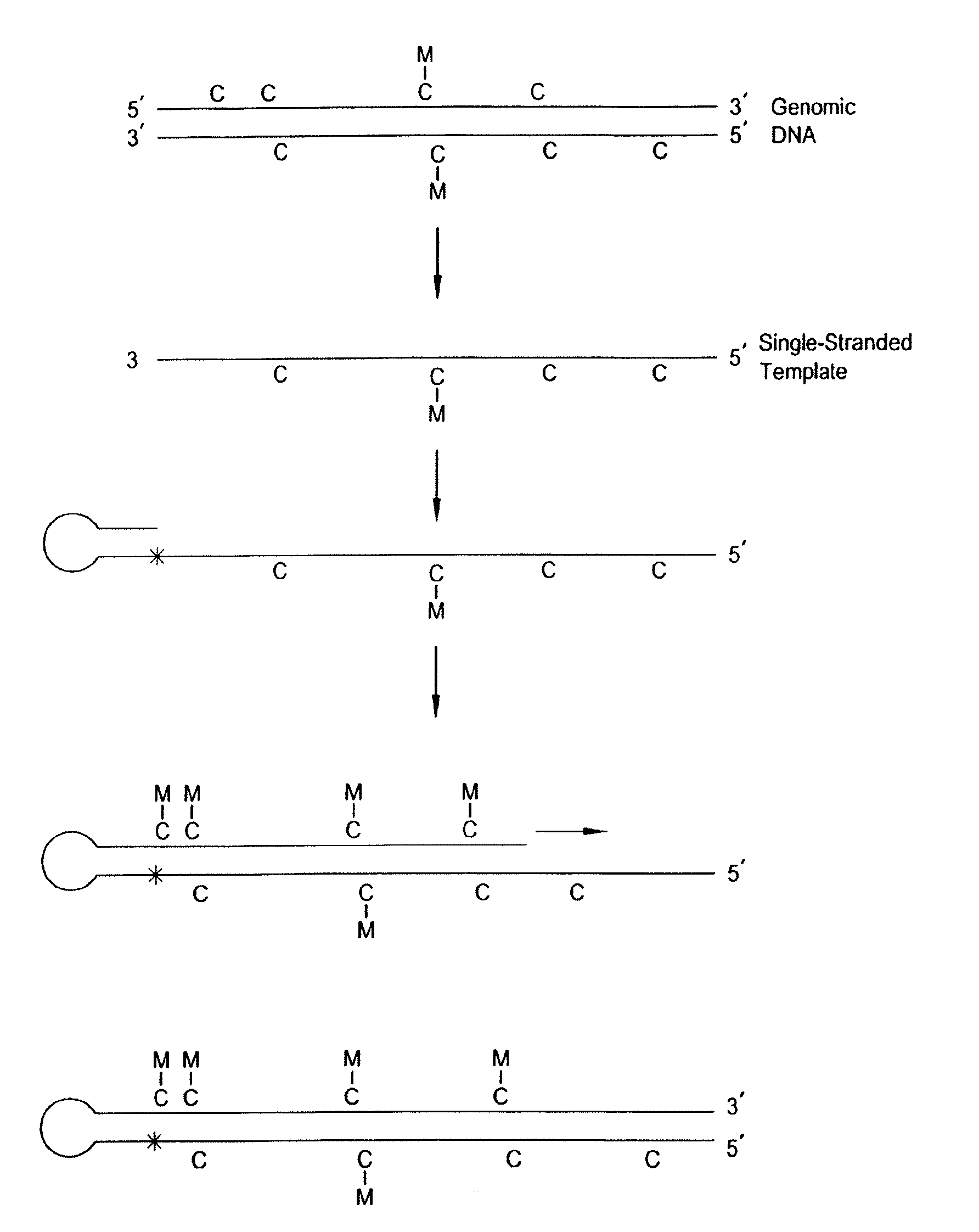
Preservation of information related to genomic DNA methylation
The present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for analyzing the methylation state of nucleic acids. Some embodiments relate to a compositions, methods and systems for analyzing the methylation state of DNA with a gene array.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
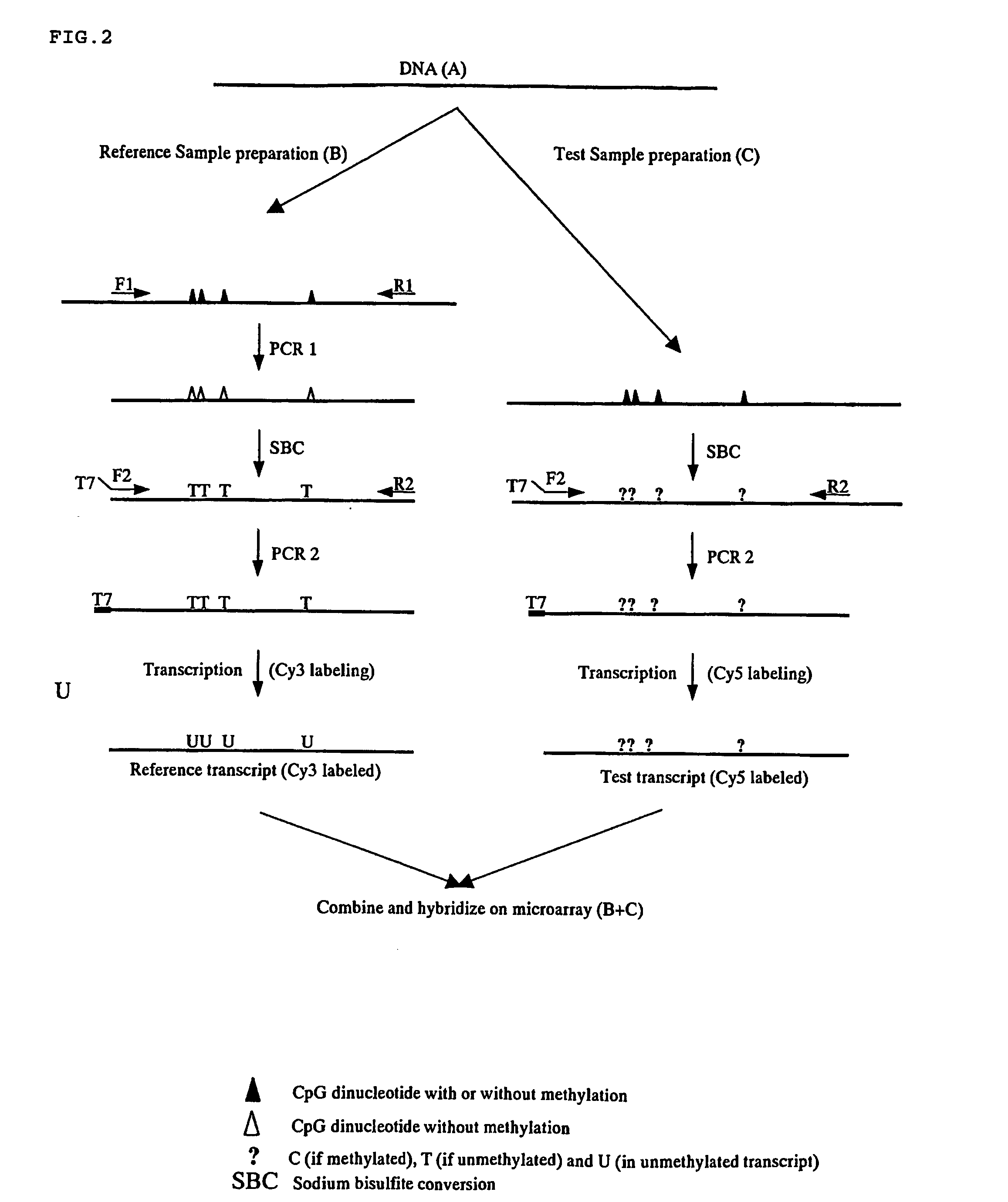
Nucleic acid methylation detection process using an internal reference sample
InactiveUS20060110741A1Rapidly and effectively screenNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference sampleFluorescence
There is disclosed a process for detection of DNA methylation at CpG sites using nucleic acid arrays and preferably microarrays. Specifically, there is disclosed a process for directly generating a reference sample from the sample to be tested and detecting methylation at large numbers of CpG island sites simultaneously. More specifically, the inventive process comprises dividing a DNA sample into two samples (a first sample and a second sample), amplifying the first DNA sample by a nucleic acid amplification process such that any methylcytosine residues are amplified as unmethylated cytosine residues, treating the amplified first sample and the (unamplified) second sample with bisulfite to convert unmethylated cytosine residues in both samples to deoxyuracil residues, labeling the bisulfite-converted second sample with a second fluorescent marker and the bisulfite-converted first sample with a first fluorescent marker, wherein the first and second fluorescent markers have non-overlapping fluorescent excitation and emission spectra; and hybridizing the first sample and the second sample onto a microarray device having a plurality of oligonucleotide capture probes designed to hybridize to CpG island sites of the DNA sample as converted and non-converted by bisulfite.
Owner:COMBIMATRIX CORP +1
Method for methylation analysis of nucleic acid
ActiveUS20100092951A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiochemistryMethylation analysis
The present invention relates to a method for methylation analysis. It comprises the providing of a double stranded nucleic acid; its conversion, whereby unmethylated bases become distinguishable in their base-pairing behavior from methylated bases, and the analysis of both of the converted nucleic acid strands.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for methylation analysis of nucleic acid
ActiveUS8771939B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethylation analysisAnalysis method
The present invention relates to a method for methylation analysis. It comprises the providing of a double stranded nucleic acid; its conversion, whereby unmethylated bases become distinguishable in their base-pairing behavior from methylated bases, and the analysis of both of the converted nucleic acid strands.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Methylation markers for prostate cancer and methods of use
InactiveUS20100297067A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProstate cancerBiology
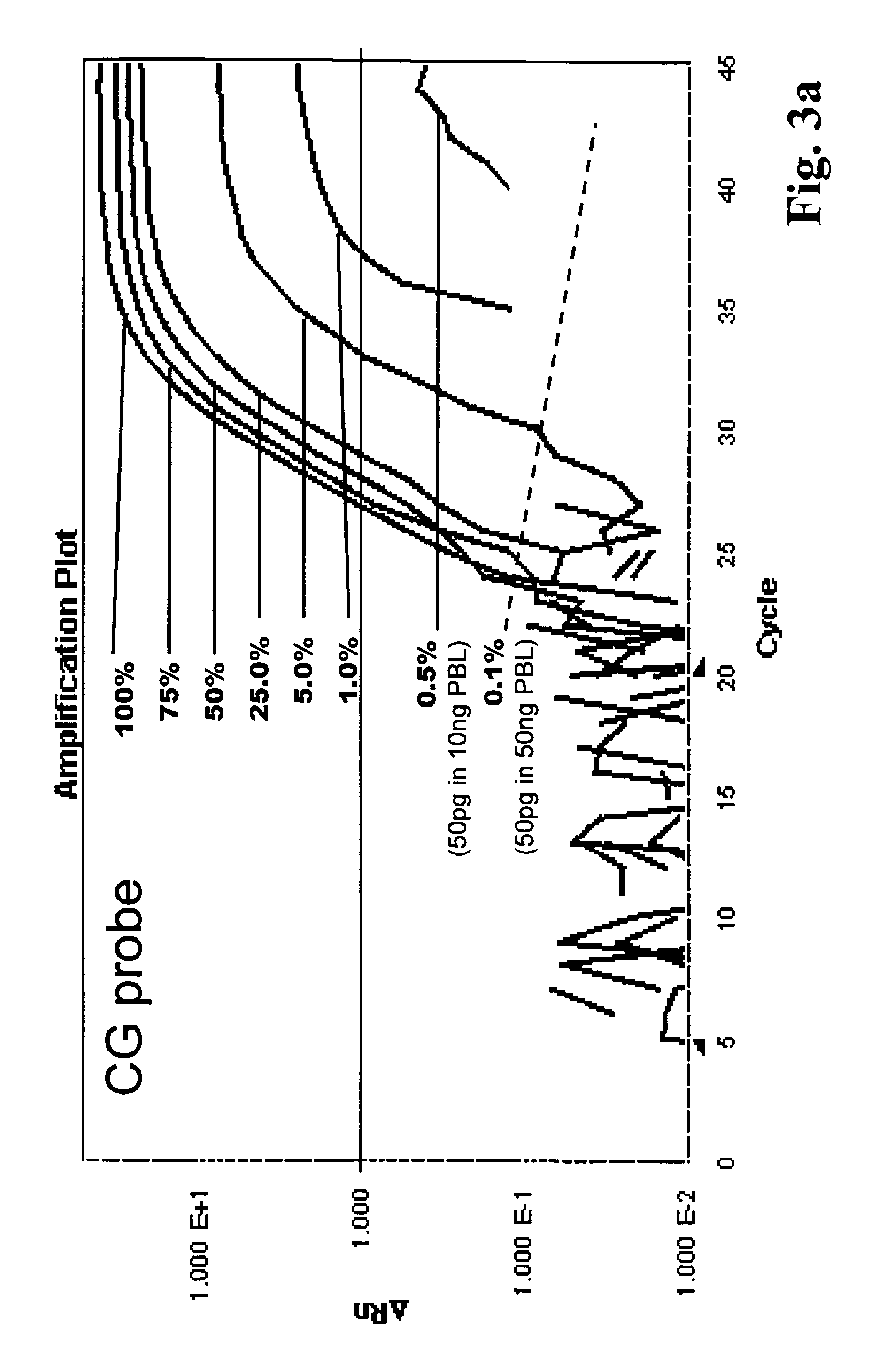
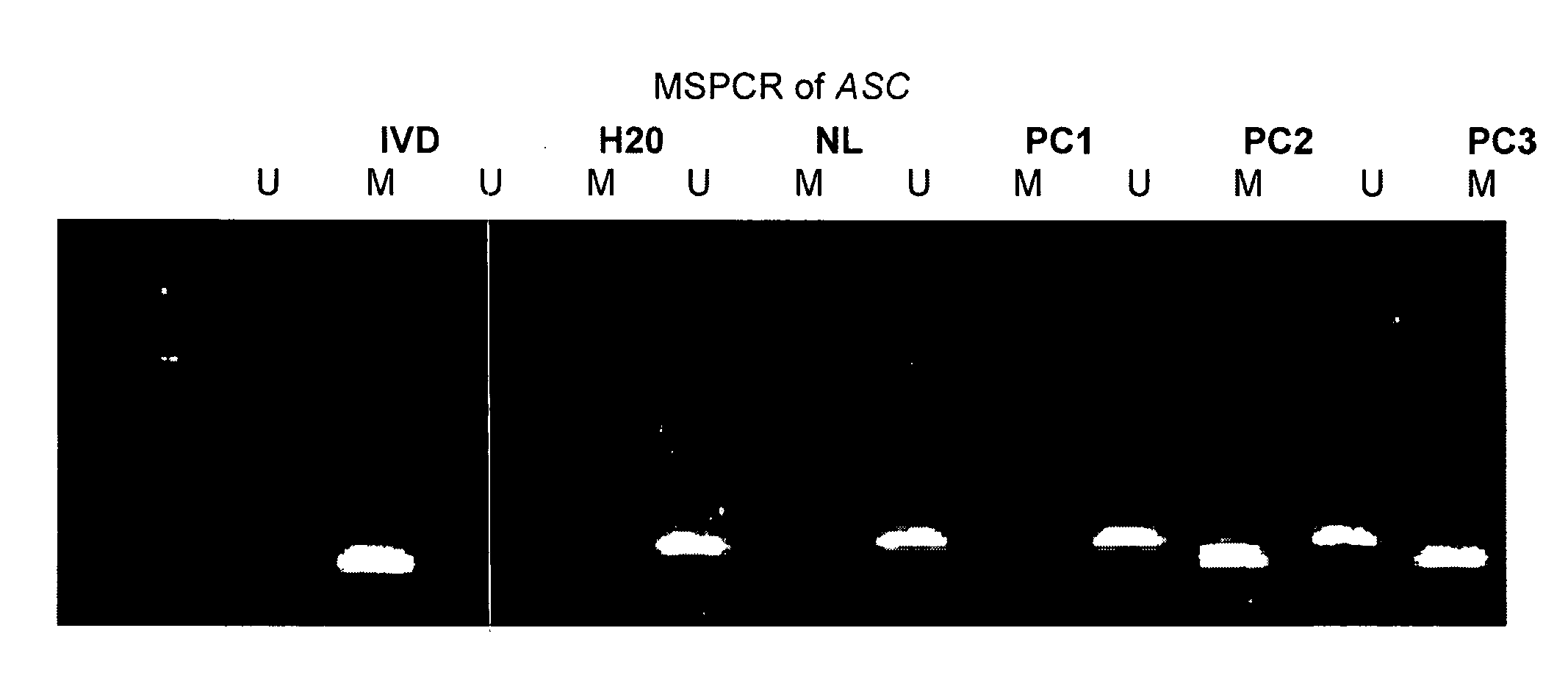
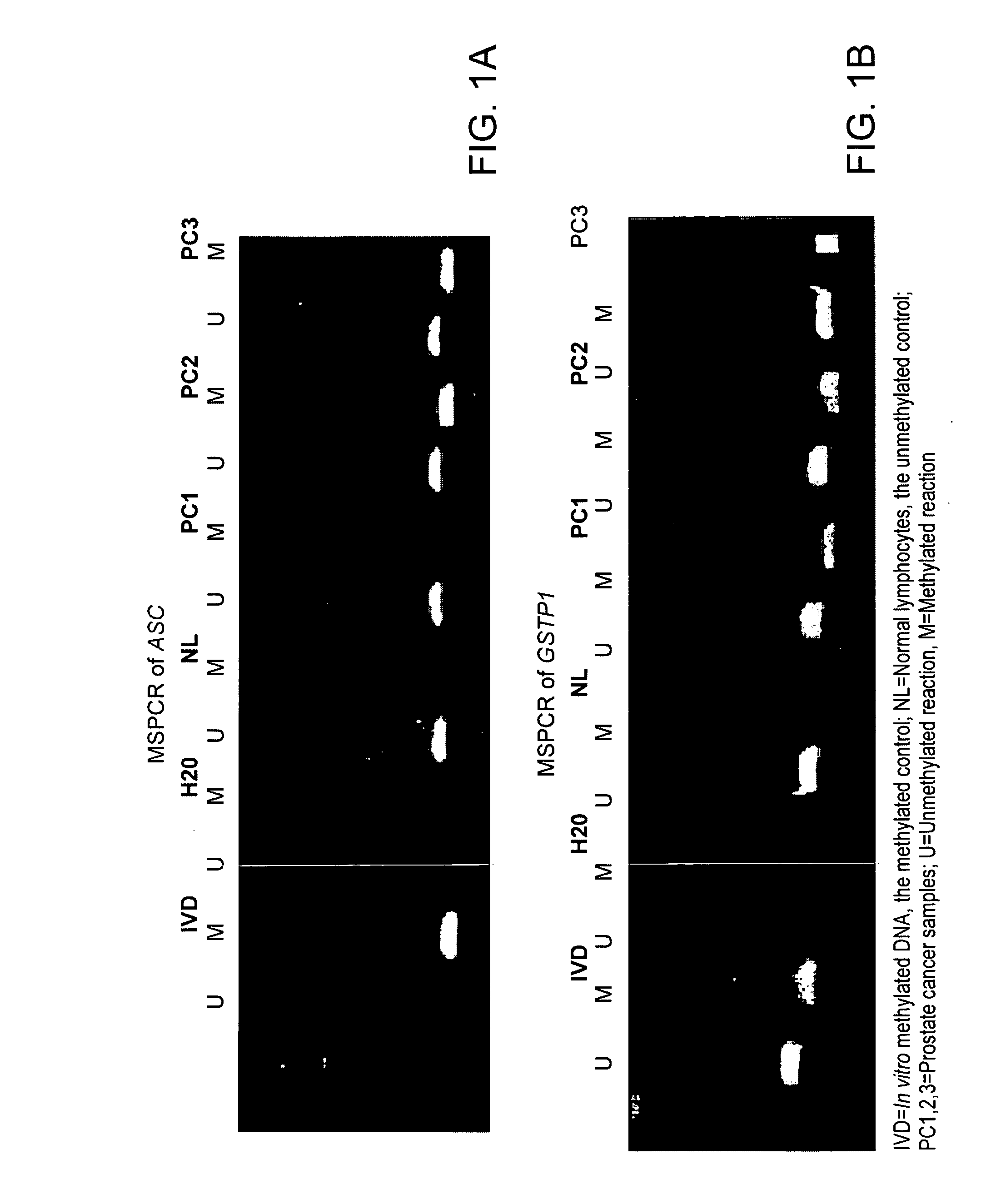
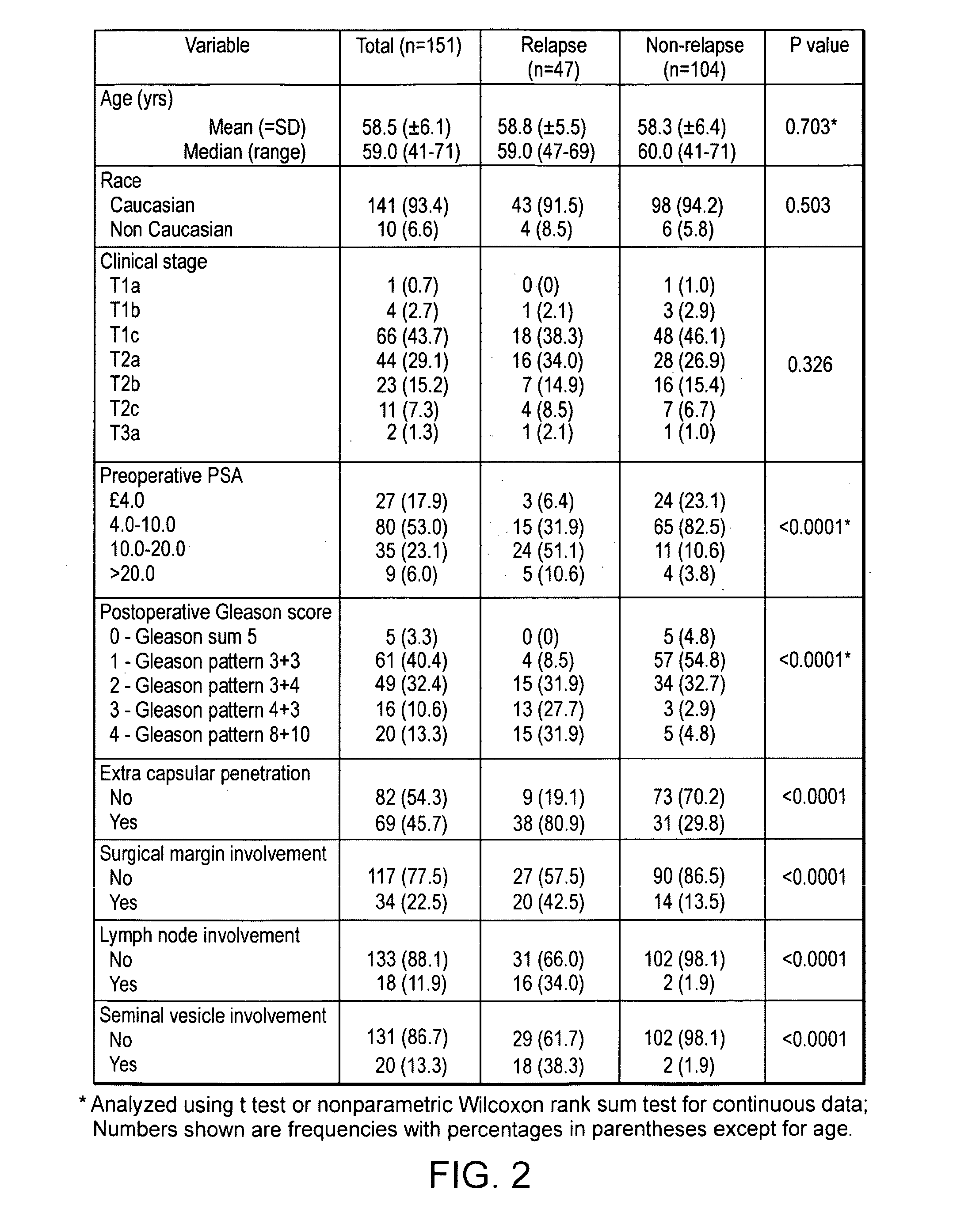
The present invention provides methods for identifying prostate cancer by detecting nucleic acid methylation of one or more genes in one or more samples. The invention further relates to DNA methylation as a predictor of prostate cancer recurrence and patient prognosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Quantitative analysis method for epigenetic modification of high-throughput nucleic acid
ActiveCN109182465AReduce usageShort analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method for epigenetic modification of a high-throughput nucleic acid. The quantitative analysis of methylated modification is realized by utilizing thedifference of pause time when a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase passes different methylated modification object loca; an epigenetic modified basic group to be tested is specifically marked witha group which has relatively large steric hindrance or relatively strong polarity to reduce the amplification efficiency and further amplify a detection signal. The quantitative analysis method can avoid the shortcomings such as complication, time consumption, large dosage of samples and the like in a conventional nucleic acid methylation detection method; through simple and intuitive steps, thedosage of the detection sample is reduced, and the analysis time is shortened; the resolution ratio of the single basis group is achieved; and the rapid, sensitive, high-throughput quantitative detection of epigenetic modification in a genome under mild conditions is realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Age-modified cells and methods for making age-modified cells
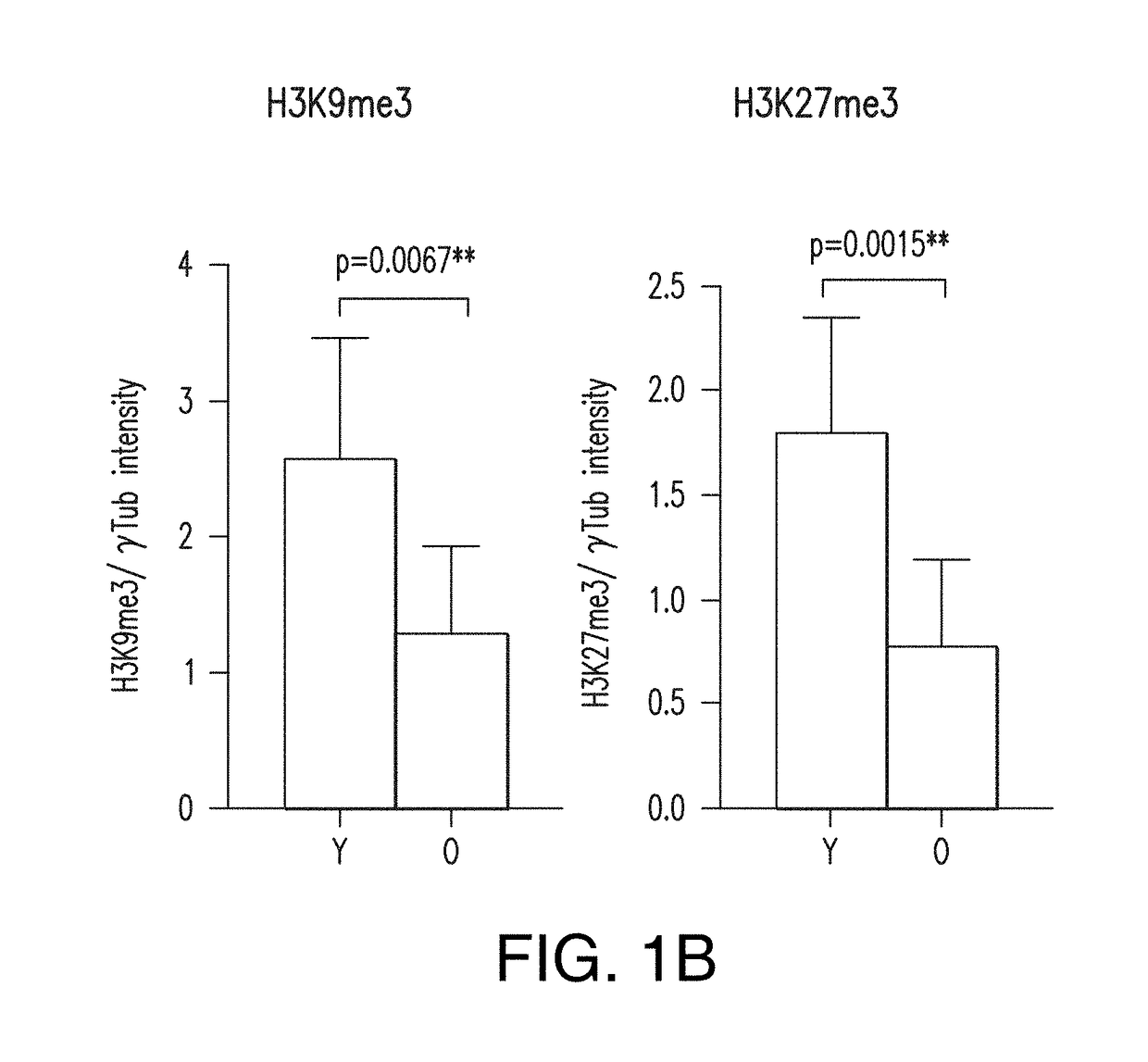
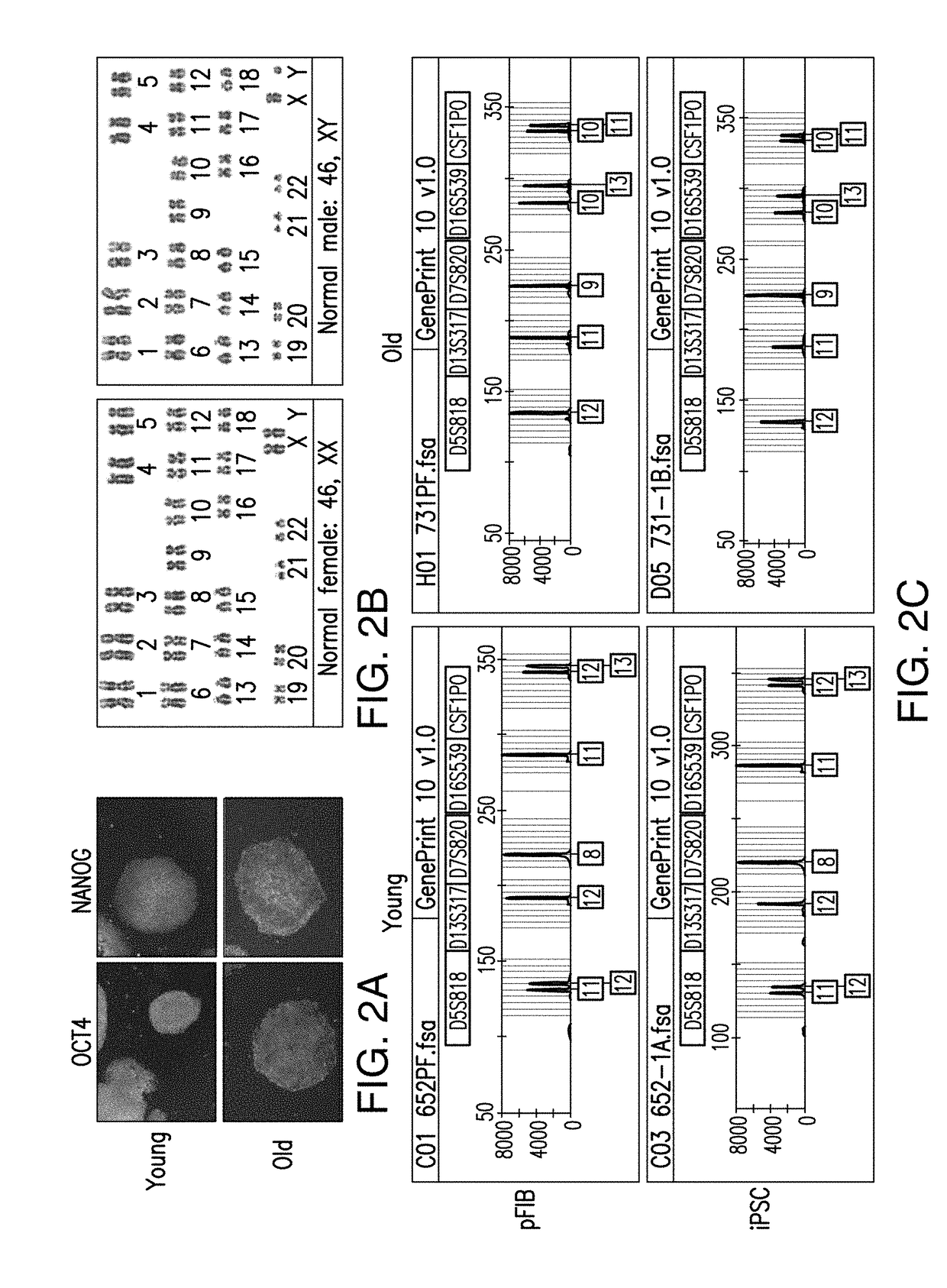
InactiveUS20170363618A1Elevated methylation levelLower methylation levelsMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsImmature cellsModel system
Provided are age-modified cells and method for making age modified cells by reducing or increasing the level of genomic nucleic acid methylation in the cells. The aging and / or maturation process can be accelerated or reduced and controlled for young, aged, mature and / or immature cells, such as a somatic cell, a stem cell, a stem cell-derived somatic cell, including an induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cell, by reducing or increasing the level of genomic nucleic acid methylation in the cells. Methods described by the present disclosure can produce age-appropriate cells from a somatic cell or a stem cell, such as an old cell, young cell, immature cell, and / or a mature cell. Such age-modified cells constitute model systems for the study of late-onset diseases and / or disorders.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Excrement nucleic acid methylation purification method
InactiveCN106047858AFewer extraction stepsImprove purification efficiencyDNA preparationPurification methodsMagnetic bead
The invention provides an excrement nucleic acid methylation purification method. The method includes the following steps that 100 ul of an excrement solution is provided into a centrifugal tube; 1 mL of lysate is added into the centrifugal tube, wherein the lysate is prepared from 0.3N sodium hydroxide, 0.4M potassium chloride, 0.025%N sodium lauroyl sarcosine, 2mM EDTA, 0.4M Tris HCL and 1.5% triton X-100; 100 ul of a conversion solution with the ph value being 5.5 is added into the centrifugal tube, and the centrifugal tube is put in an environment at the constant temperature of 75 DEG C for 90 Min; after the material is cooled to room temperature, 10 ul of a magnetic bead solution is added, and the material is mixed to be uniform and put for 15 Min; the centrifugal tube is put on a magnetic frame for 5 Min, and clean liquid is removed; the second step to the six step are repeated till magnetic beads are separated, and supernate is transferred into another centrifugal tube.
Owner:SUZHOU HAIMIAO BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods and systems for high-depth sequencing of methylated nucleic acid
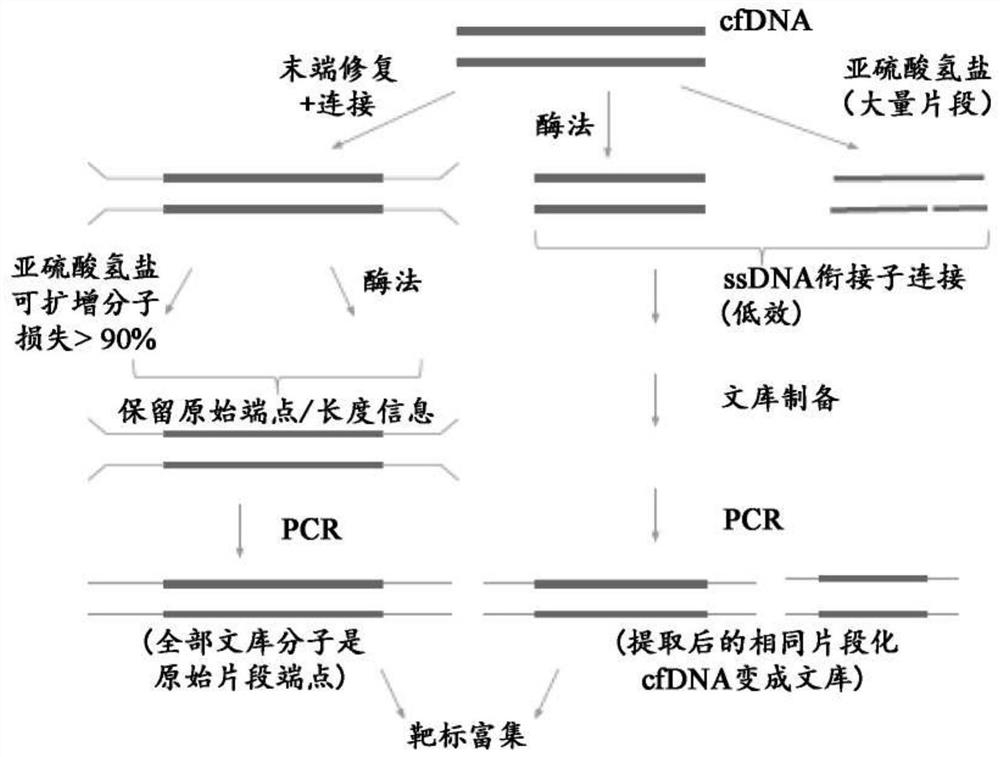
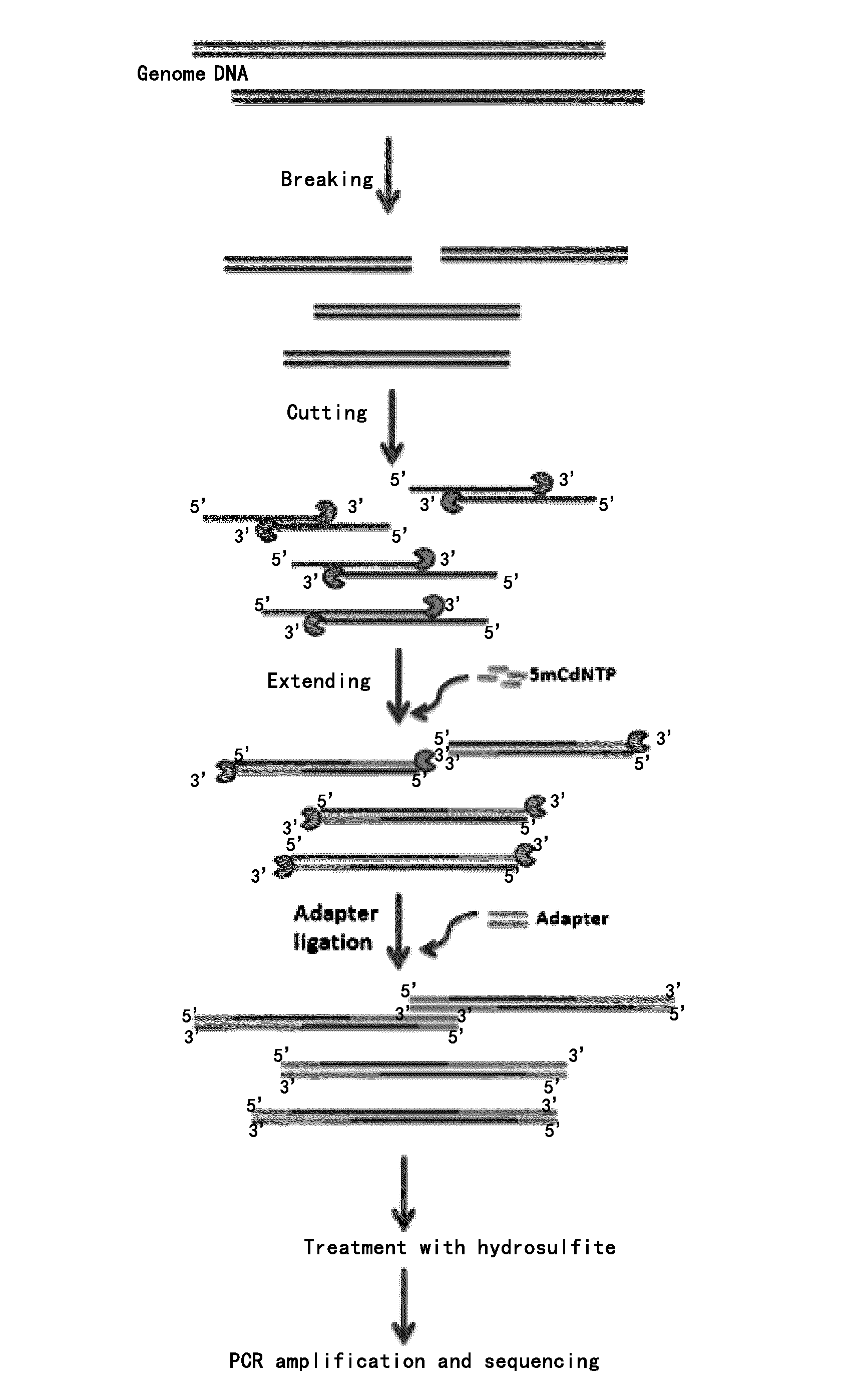
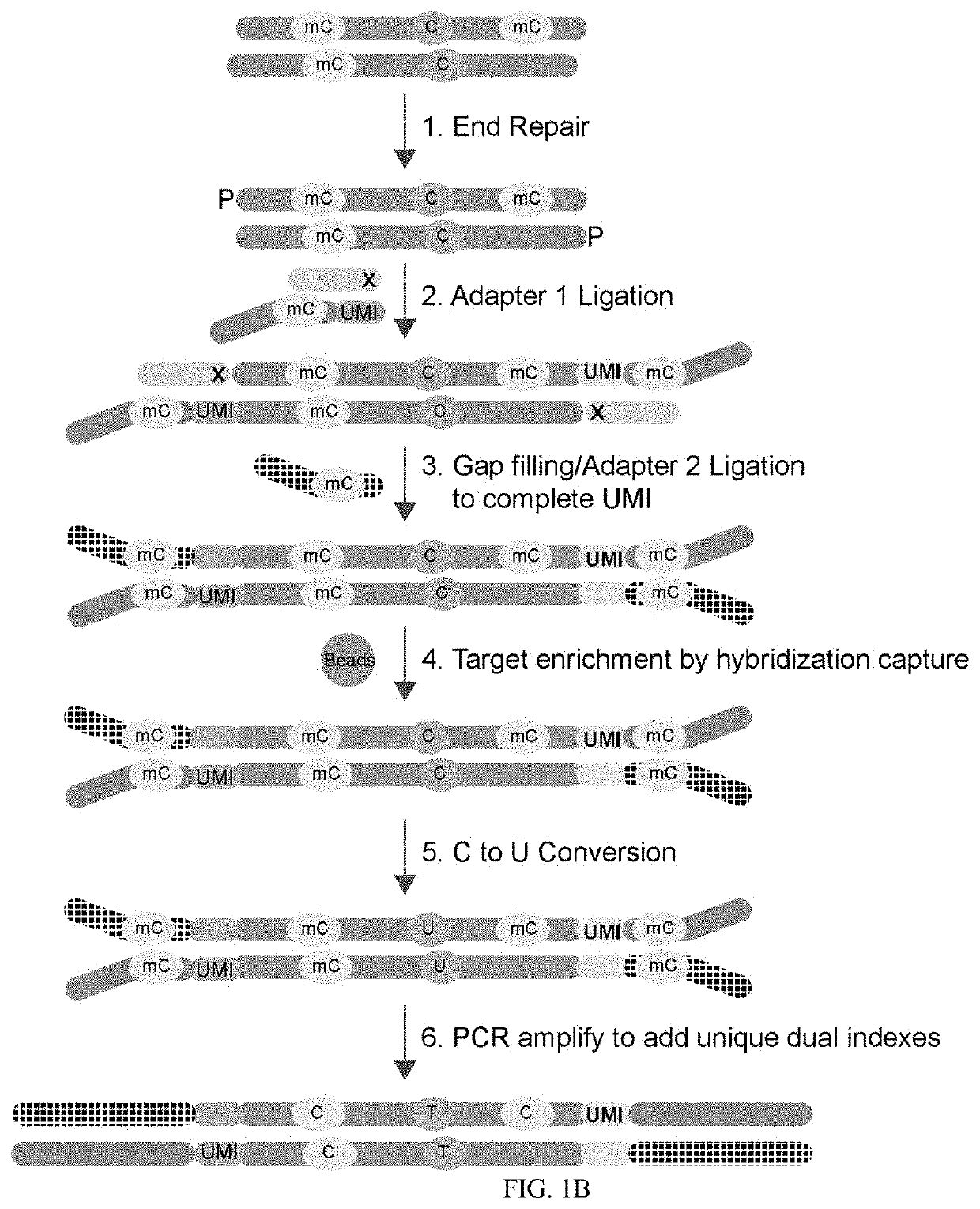
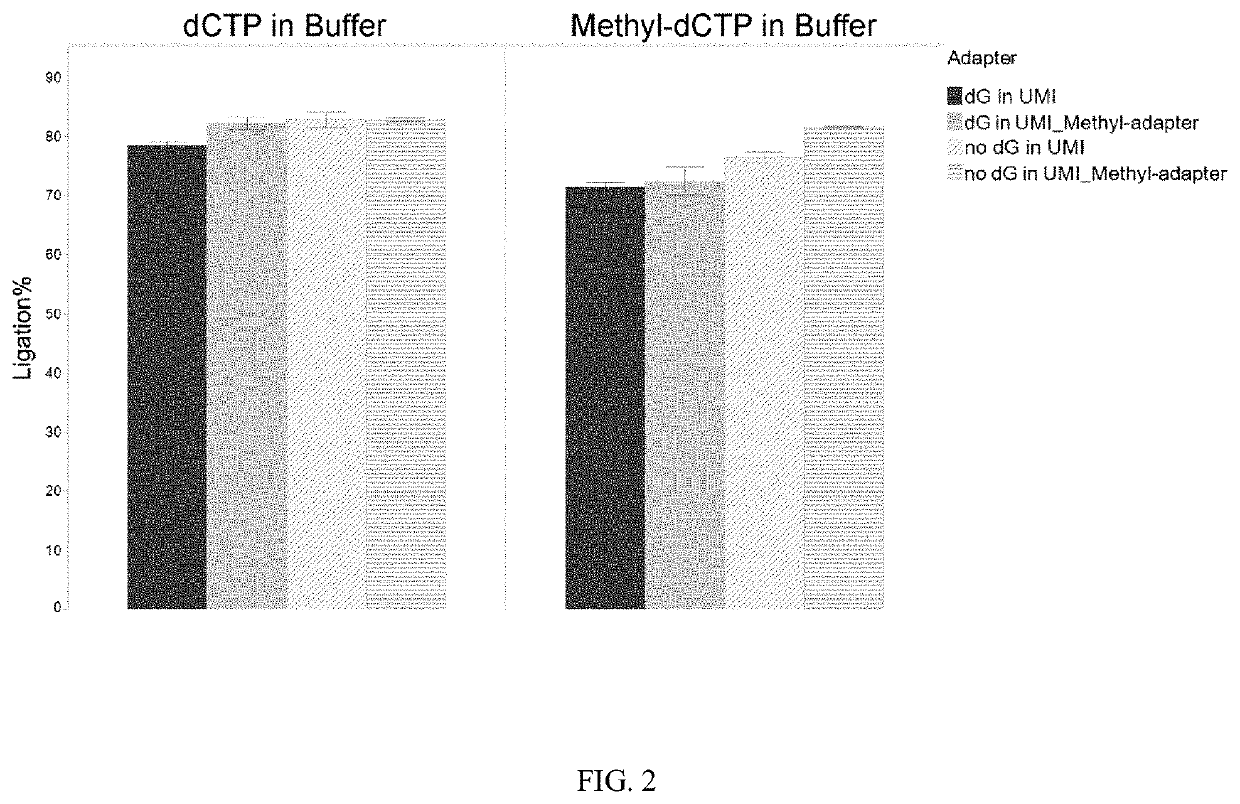
Methods and systems provided herein address current limitations of bisulfite-based methylation sequencing by improving the quality and accuracy of nucleic acid methylation sequencing and uses thereof for detection of disease. Methods that include minimally-destructive conversion methods for methylation sequencing as well as specialized UMI adapters provide for improved quality of sequencing libraries and sequencing information. Greater accuracy and more complete methylation-state information permits higher quality feature generation for use in machine learning models and classifier generation.
Owner:フリーノム ホールディングスインク
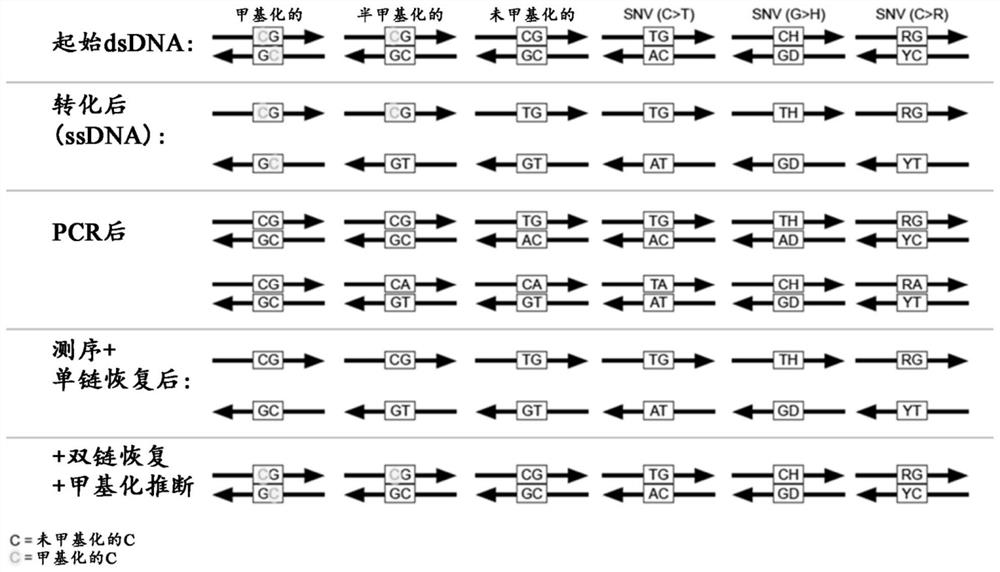
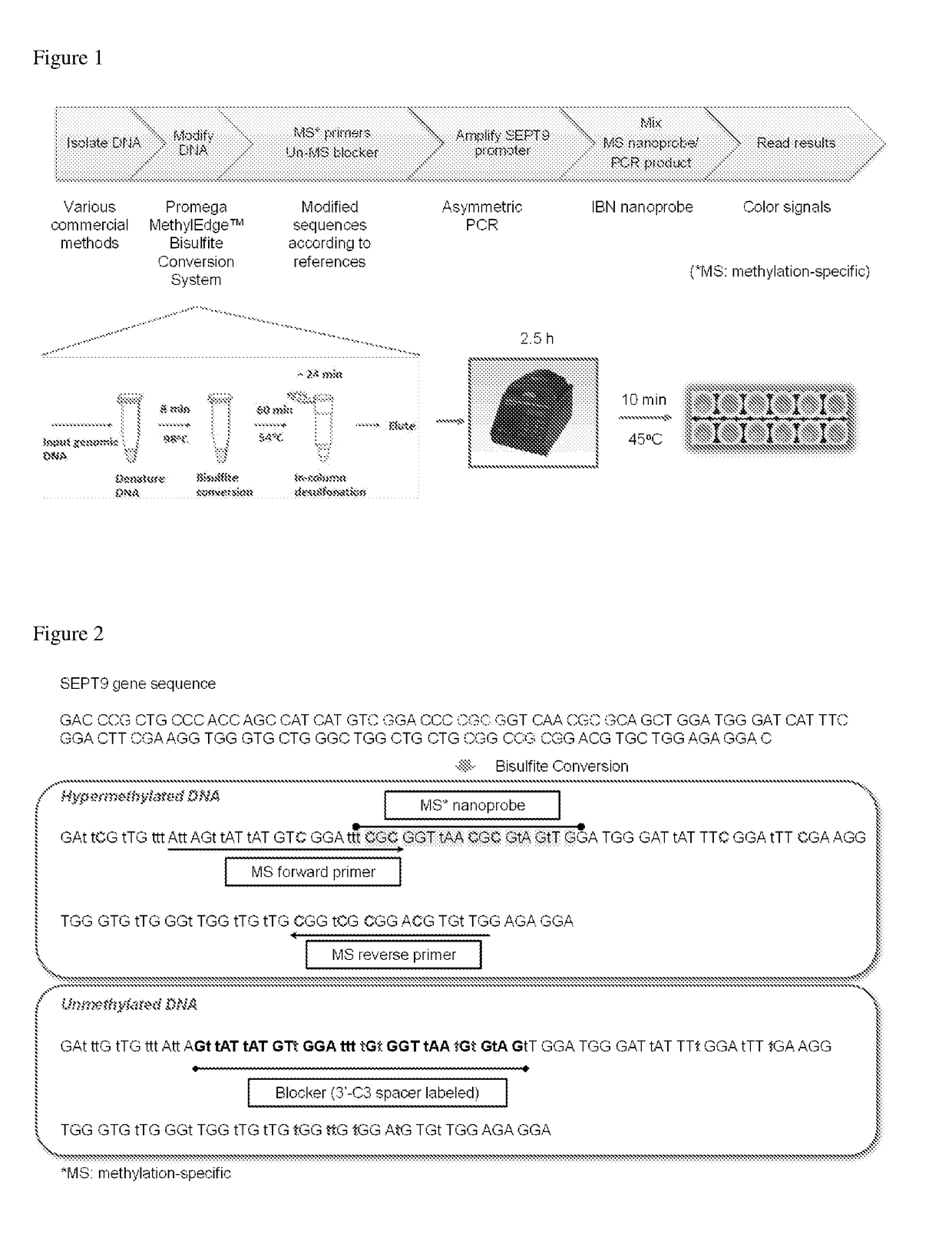
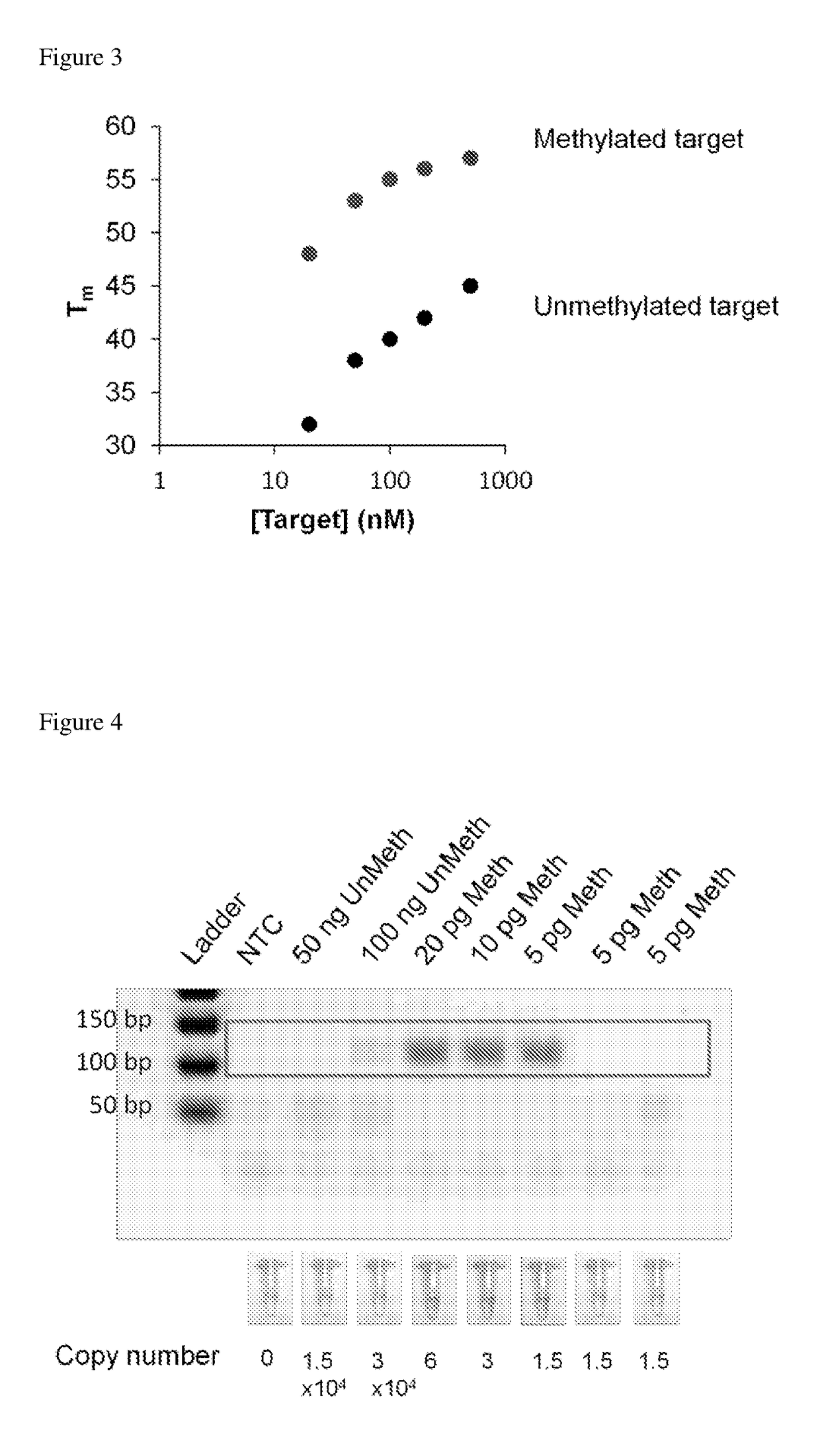
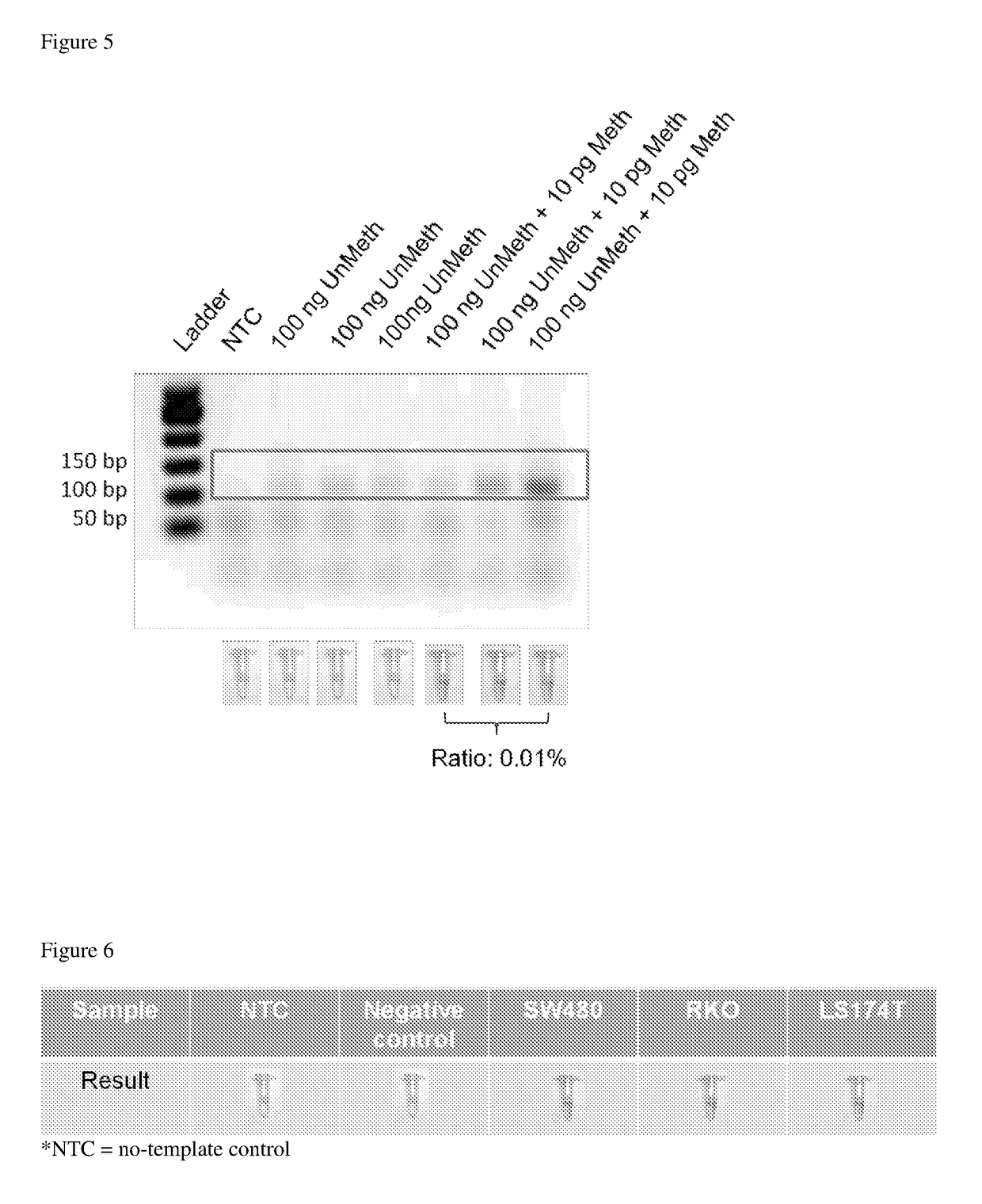
Determination of nucleic acid methylation
ActiveUS20190017110A1Easy to adaptMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeNanoparticle
The invention relates to methods and kits for determining the methylation status of a target nucleic acid molecule in a sample comprising (a) bisulfite treatment of the target nucleic acid, (b) amplifying the treated target nucleic acid with methylation-specific primers, (c) contacting the amplicons with a methylation-specific plasmonic nanoprobe and (d) determining the methylation status based on melting temperature Tm of the hybrid probe and the target nucleic acid. In particular, a plasmonic gold nanoparticle covalently coupled to a morpholino oligonucleotide probe. Also claimed are methods and kits for determining methylation status of the Septin 9 (SEPT9) gene promoter.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Targeted sequencing technique for whole genome DNA methylation
ActiveUS20160376644A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomeNucleic acid methylation
This invention is directed to a guide positioning sequencing technology of whole-genome DNA methylation. The invention provides a new detection method of nucleic acid methylation. In particular, a concept of “positioning” in the detection of nucleic acid methylation is provided. Specifically, a portion of a sequence is used for genome wide positioning and the other portion of the sequence is used for methylation detection in sequencing, thereby solving / defeating previously existing challenges in methylation detection and bioinformatics analysis of a genome.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for detecting and diagnosing neoplasia
InactiveUS20190048422A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementZFP42 GeneLung cancer
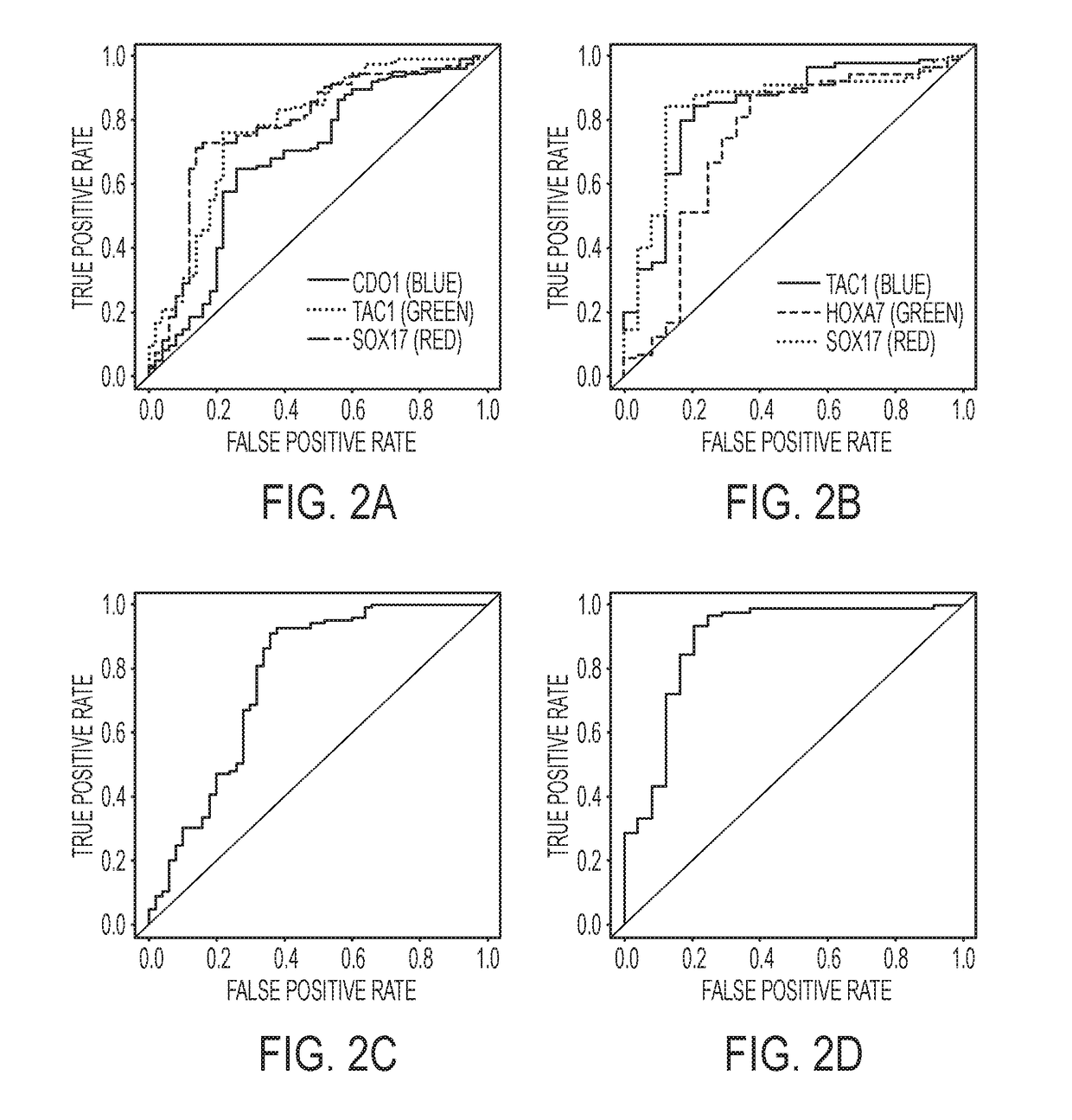
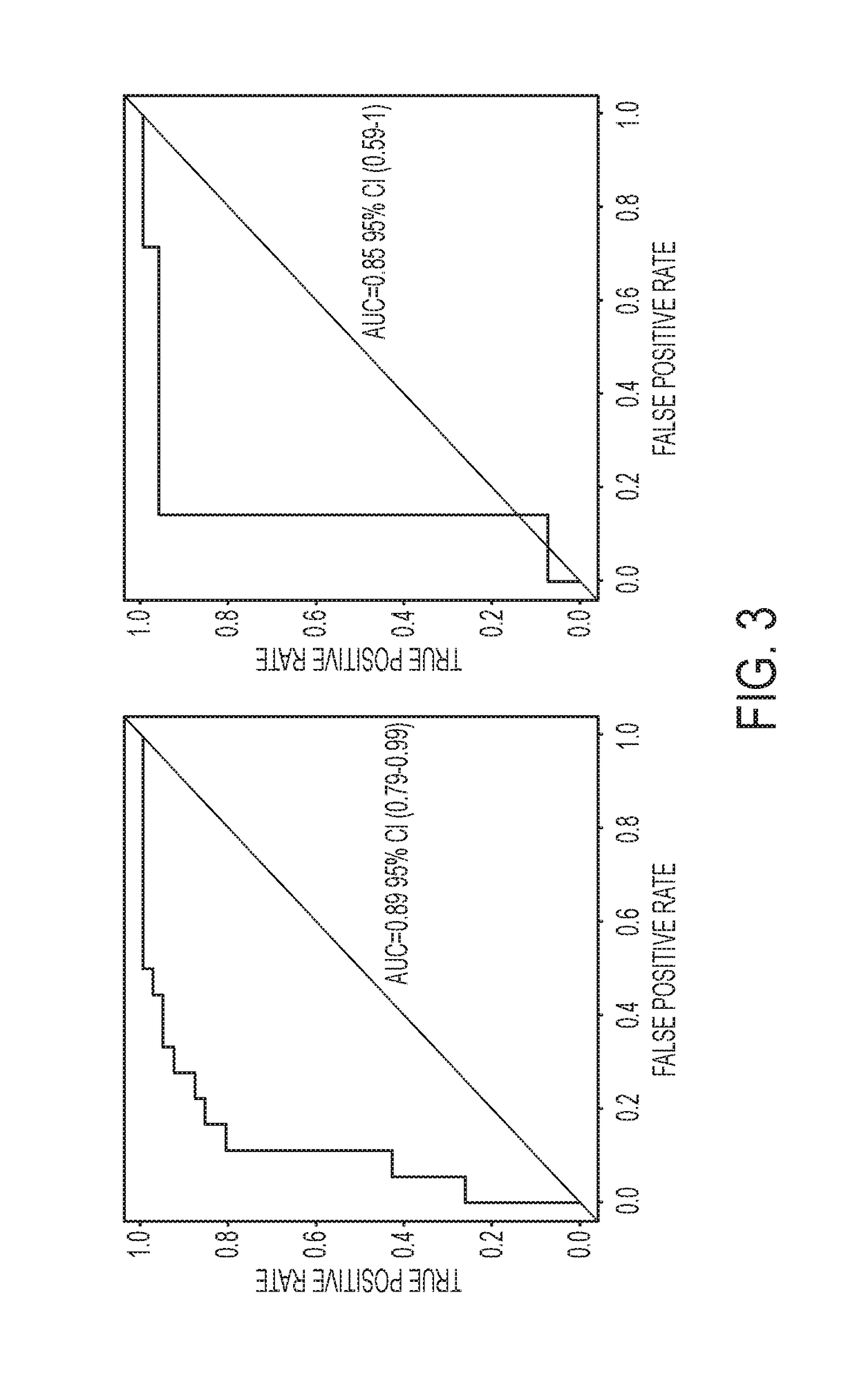
The present invention relates to the use of nucleic acid methylation and methylation profiles to detect risk of developing neoplasia and in particular, lung cancer. The invention relates to methods for identifying a methylation profile of the CDO1, SOOX17, HOXA7, HOXA9, TAC1, and ZFP42 genes from plasma and sputum samples.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Nucleic acid methylation cytosine conversion method
PendingCN114085894AImprove conversion efficiencySimplify the difficulty of operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCytosine
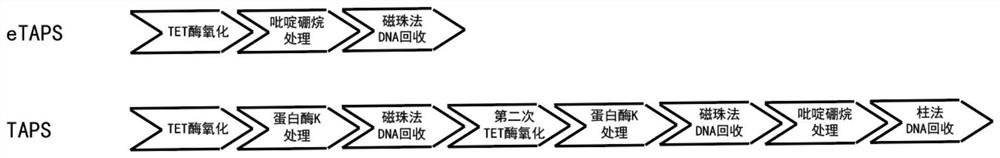
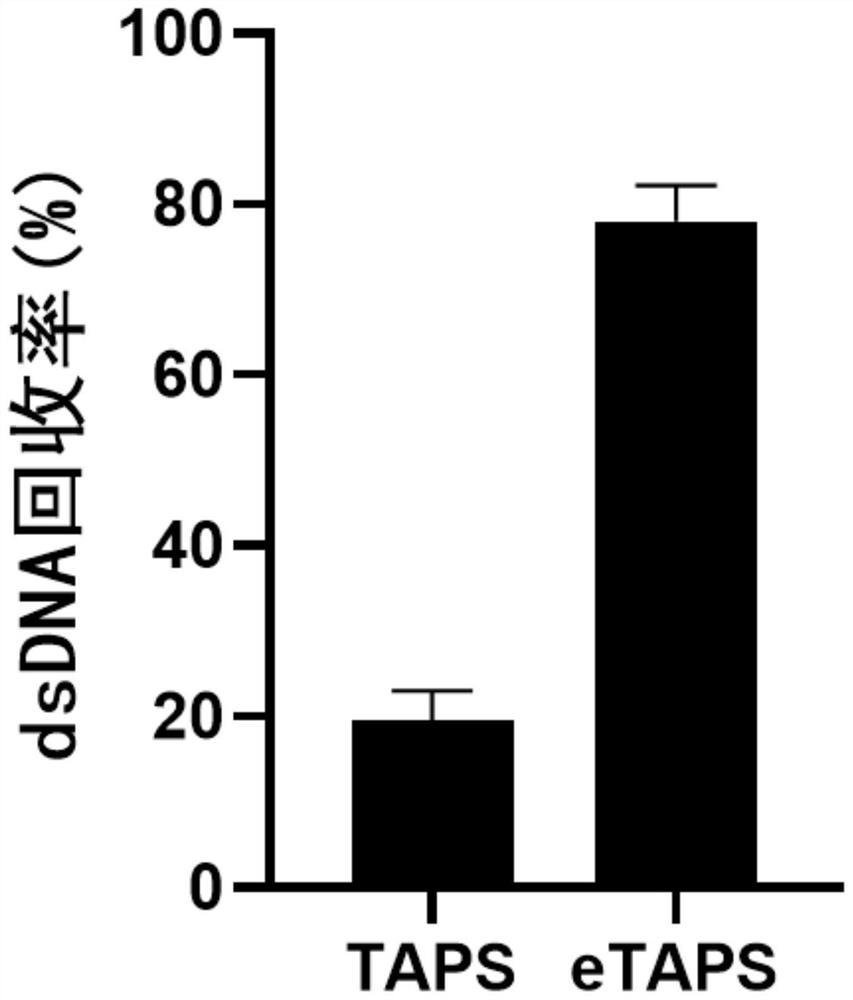
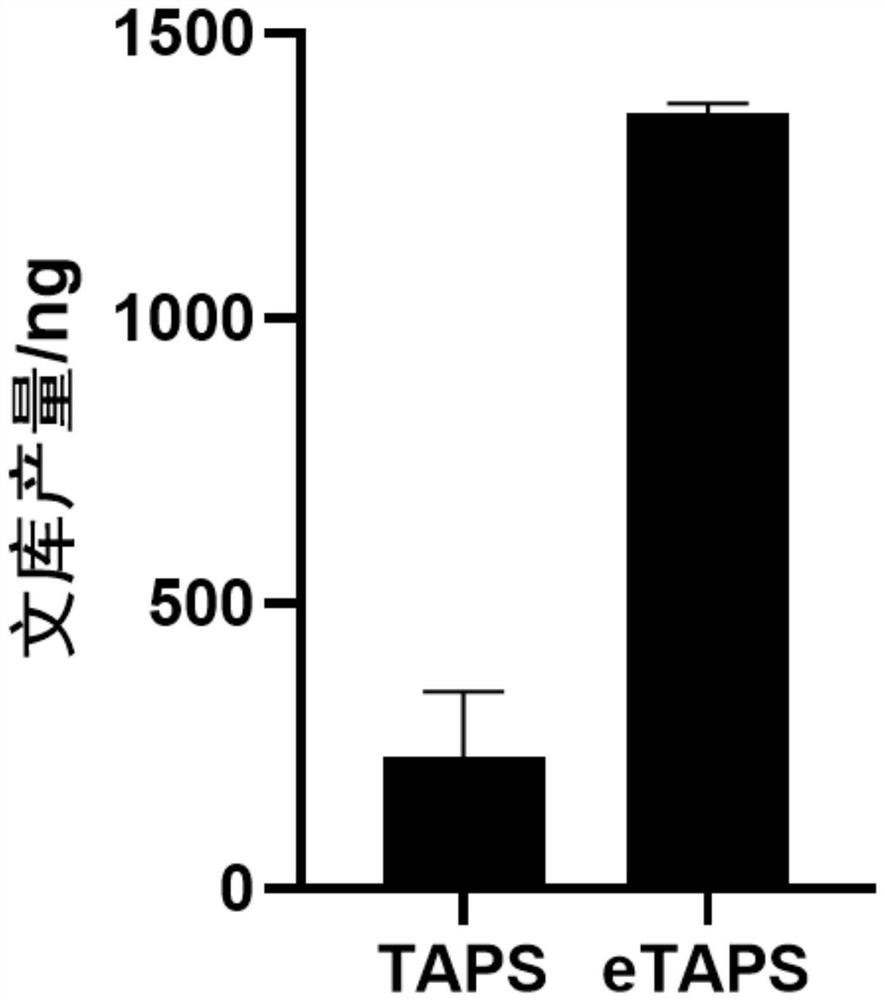
The invention provides a nucleic acid methylation cytosine conversion method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out TET enzyme oxidation treatment on a DNA or RNA sample; (2) adding pyridine borane into a reaction system for treatment; and (3) recovering DNA or RNA in the reaction system by magnetic beads. According to the present invention, the whole process of the nucleic acid methylation cytosine conversion method only comprises three steps such as TET enzyme oxidation, pyridine borane treatment and DNA magnetic bead recovery, such that the conversion efficiency of the TAPS is improved, the operation difficulty and the operation flow of the TAPS are simplified, and the nucleic acid methylation cytosine conversion method is named as Enhanced TET-assisted pyridine borane sequencing (eTAPS), the eTAPS has the advantages of high conversion rate, small DNA damage, simplicity in operation, convenience in automation and the like, and in addition, we find that the eTAPS also has efficient and sensitive detection efficiency in RNA cytosine methylation. Therefore, the eTAPS technology has an important value in nucleic acid methylation detection, especially in the fields of tumor early screening and disease diagnosis.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
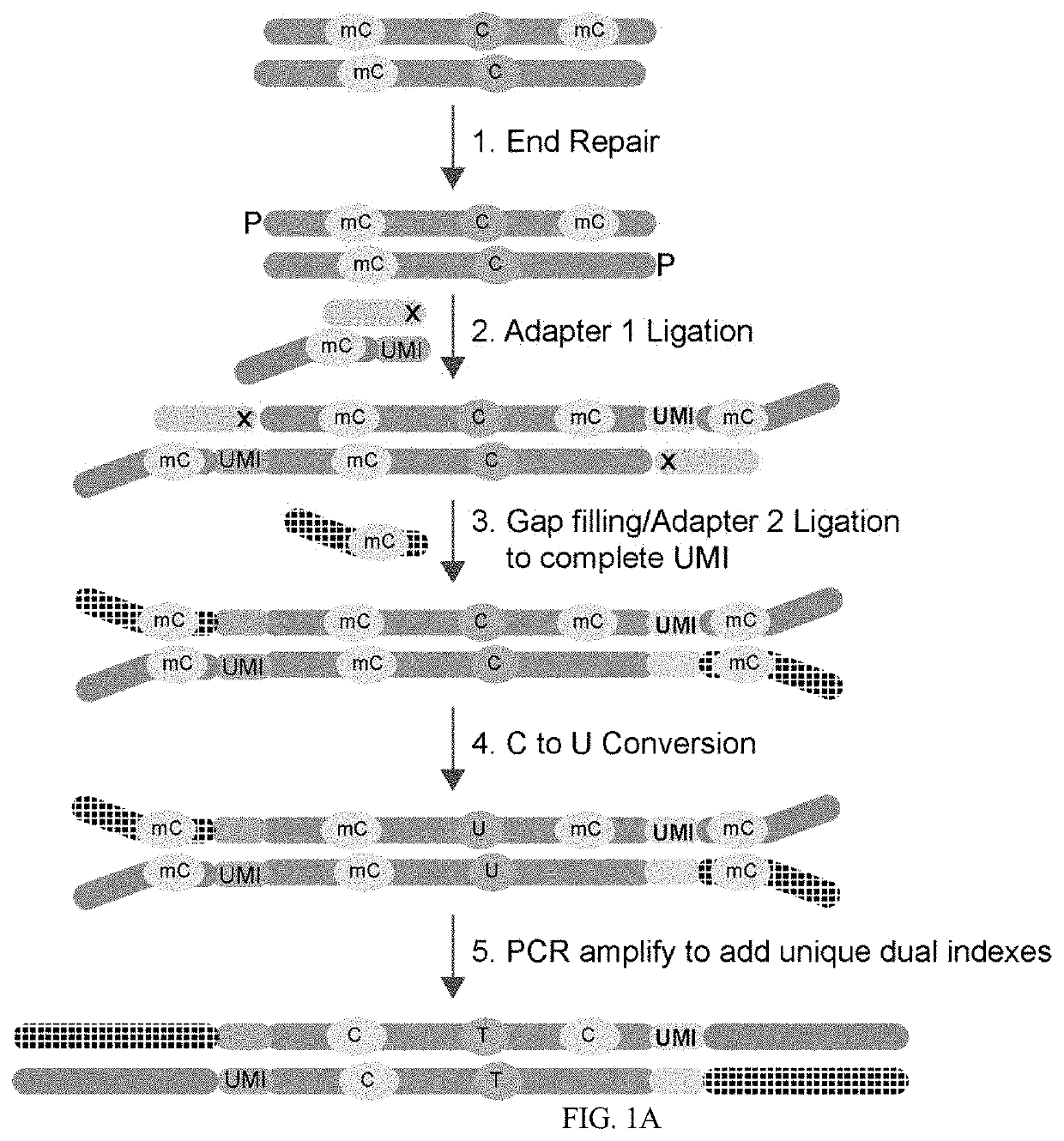
Methods of Preparing Dual Indexed Methyl-Seq Libraries
PendingUS20210095351A1Improve accuracyOptimization orderMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWhole genome sequencingMethylC-Seq
The invention pertains the methods and compositions for generating methyl-seq NGS libraries, for whole genome sequencing or targeted resequencing. Additionally, the invention pertains the methods and compositions for determining methylation profiles of target nucleic acids.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Amplification of bisulfite-reacted nucleic acids
ActiveUS10087482B2Speed up the conversion processHigh magnificationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesSulfationCytosine
The present invention relates to a reaction mixture for the amplification of nucleic acids, the non-methylated cytosine bases of which have been converted to uracil bases by means of a bisulfition reaction. The invention also discloses methods for amplifying bisulfited nucleic acid and for determining the nucleic acid methylation state, and also kits based on the reaction mixture according to the invention.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
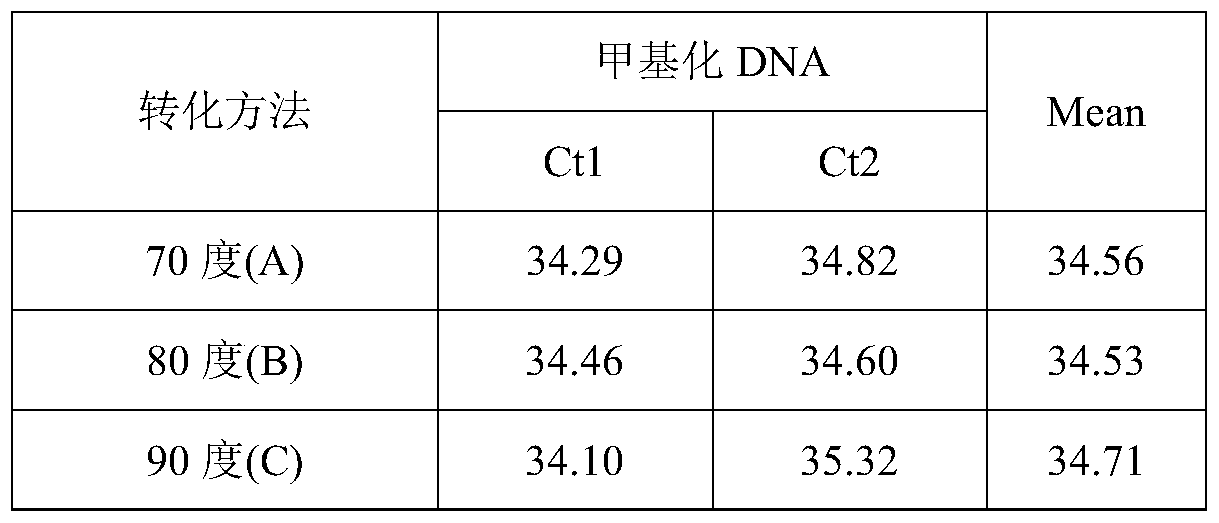
A method for dna sulfite conversion and purification
ActiveCN105462960BShort conversion timeSimple equipmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadSulfite salt
The invention discloses a DNA sulfite conversion and purification method. The method does need early sodium hydroxide denaturating treatment conducted on nucleic acid, adopts varying-temperature conversion conditions different from a commercialized reagent on the market and can perform a conversion experiment under the constant temperature condition. A magnetic bead method is adopted to perform nucleic acid purification after nucleic acid methylation conversion, a high-salt low pH value is utilized to perform nucleic acid separation and purification, then a low-salt high pH value is utilized to perform elution, the step of performing desulfonating by adopting sodium hydroxide on the market at present is omitted in the purification process, and meanwhile high-conversion-rate, high-quality and high-purity DNA can be obtained only by adopting a one-step washing step. The DNA sulfite conversion and purification method has the advantages of being quick, simple and convenient to operate and improving the conversion efficiency, the extraction efficiency and the extraction purity.
Owner:杭州千基生物科技有限公司 +1
Methods for Detecting and Treating Esophageal Cancer
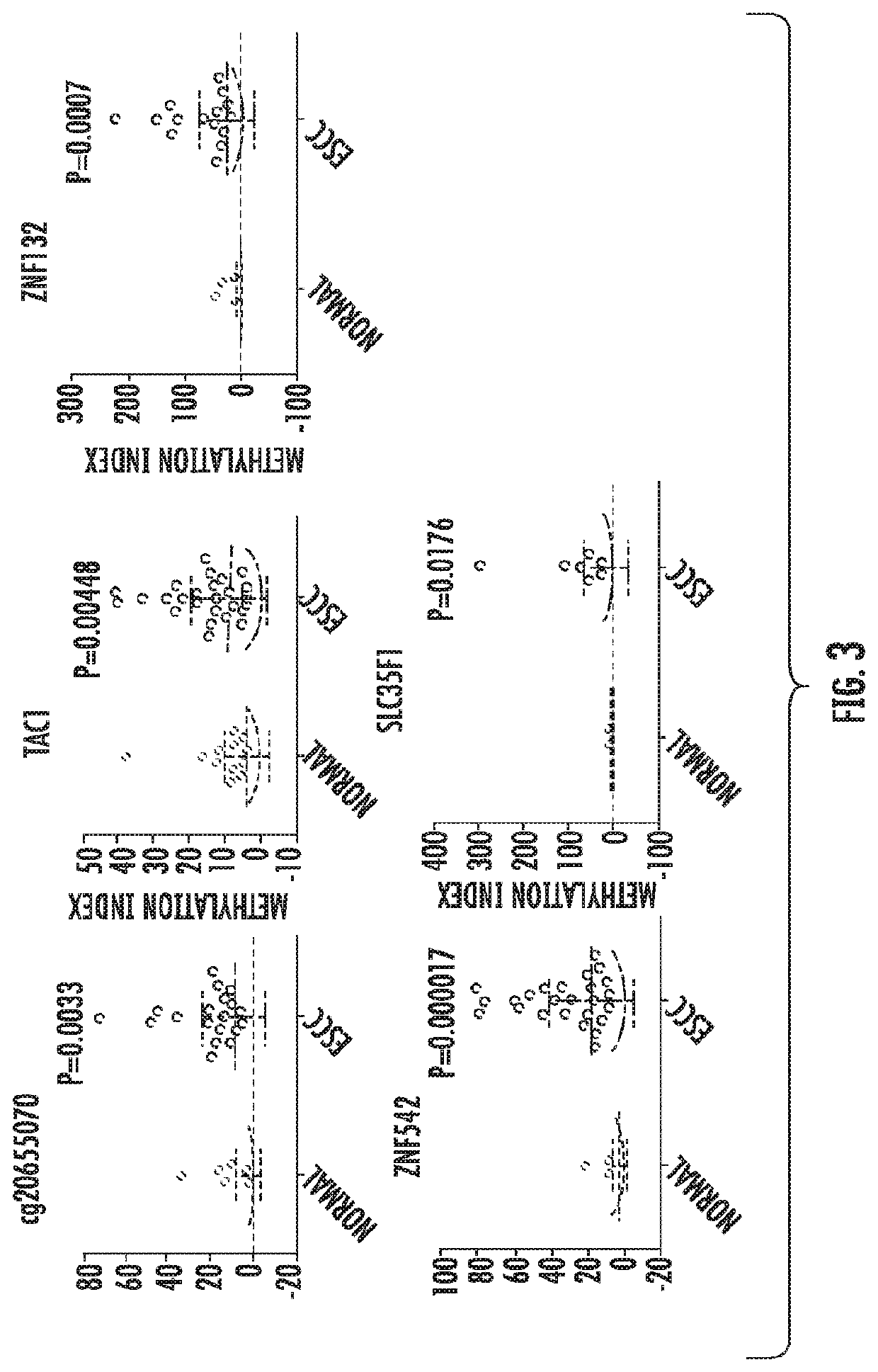
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides compositionsand methods useful for detecting and treating esophageal cancer. In a specific embodiment, a method for identifying a subject having esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) comprises (a) extracting genomic DNA from a sample obtained from the subject; (b)performing a conversion reaction on the genomic DNA in vitro to convert unmethylated cytosine to uracil by deamination; and (c)detecting nucleic acid methylation of one or more genes in the converted genomic DNA, wherein detecting nucleic acid methylation e identifies the subject as having ESCC. The one or more genes can comprise ZNF542, ZNF132, cg20655070, TAC1 and SLC35F1. In amore specific embodiment, the one or more genes comprise ZNF542 and ZNF132 and can further comprise detecting the nucleic acid N methylation of one or more of cg20655070, TAC1 and SLC35F1.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Full-automatic nucleic acid methylation amplification detection equipment
ActiveCN112608829AImprove throughputHigh-throughput detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringNucleic acid methylation
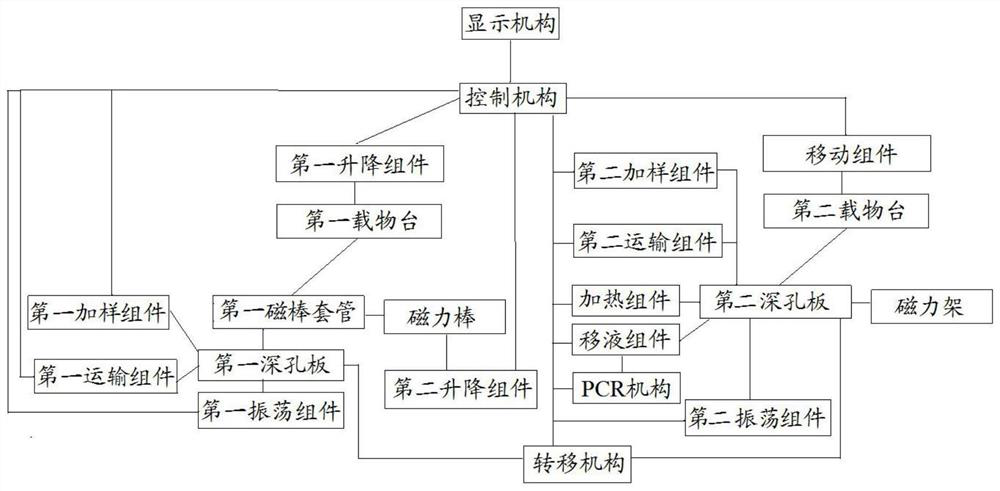
The invention discloses full-automatic nucleic acid methylation amplification detection equipment. The equipment comprises a control mechanism, a pre-treatment mechanism, a post-treatment mechanism, a transfer mechanism and a detector; the control mechanism is communicated with the pre-treatment mechanism, the post-treatment mechanism and the transfer mechanism; the pre-treatment mechanism is communicated with the post-treatment mechanism through the transfer mechanism; the pre-treatment mechanism comprises a first magnetic bar sleeve, a first deep hole plate, a first oscillation assembly and a first magnetic attraction assembly; the first deep hole plate is used for containing a to-be-treated liquid; the first oscillation assembly is connected with the first deep hole plate; the first oscillation assembly is located below the first deep hole plate and used for oscillating liquid in the first deep hole plate; the first magnetic attraction assembly is used for primarily separating a to-be-treated detection sample in the to-be-treated liquid; and the post-treatment mechanism comprises a second deep hole plate, a second oscillation assembly and a second magnetic attraction assembly and is used for realizing sulfite conversion and purification of DNA.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH
Sensitively detecting copy number variations (CNVs) from circulating cell-free nucleic acid
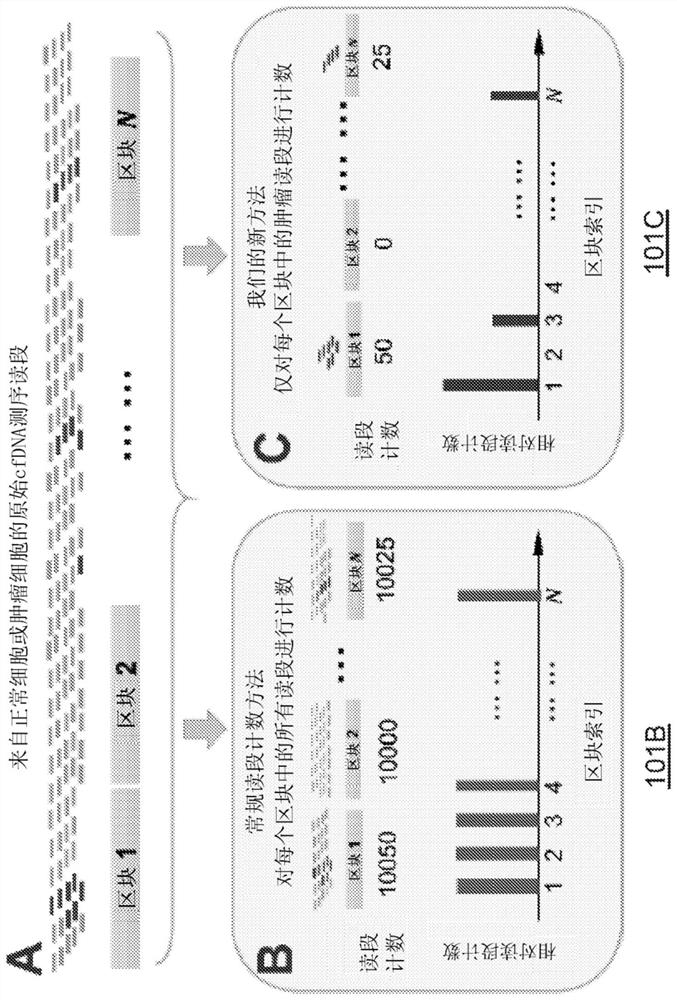
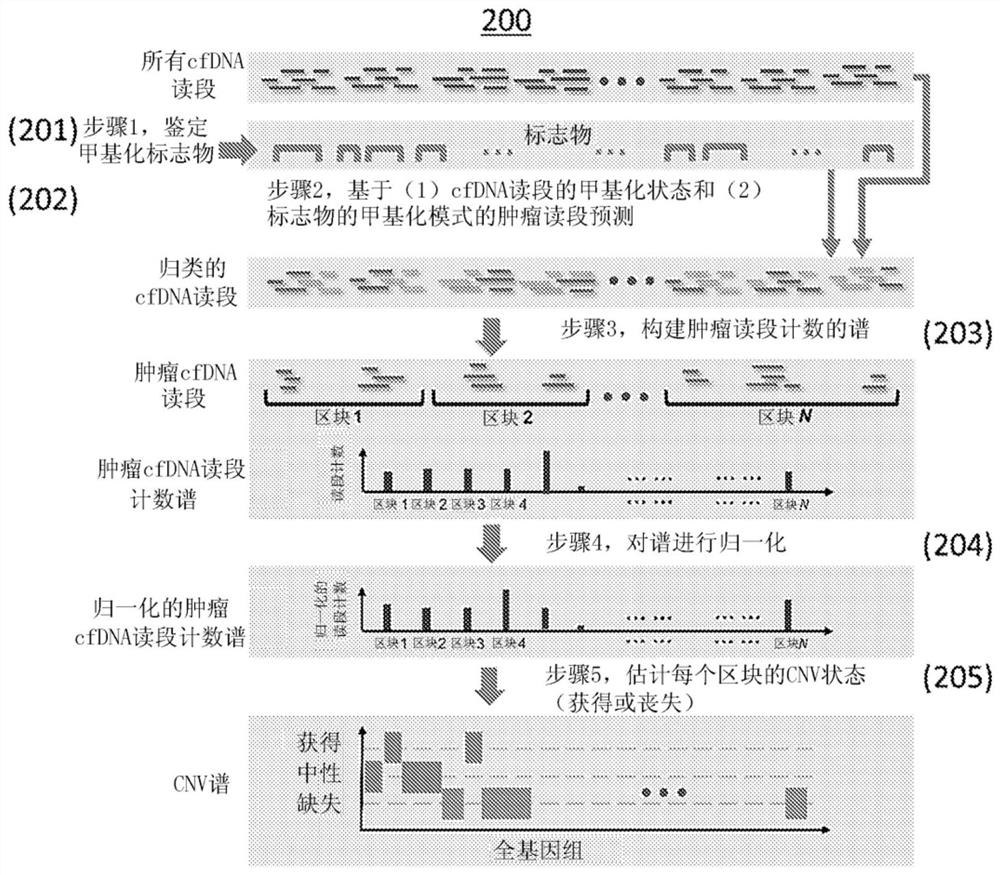
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for detecting or inferring levels of Copy Number Variants (CNVs) in cell-free nucleic acid samples to detect or assess cancer and prenatal diseases. Cell-free nucleic acid methylation sequencing data may be utilized to distinguish tumor-derived or fetal-derived sequencing reads from normal cfDNA sequencing reads. Each cell-free nucleic acid sequencing read (e.g., containing tumor or fetal methylation markers) may be classified as corresponding to a tumor / fetal-derived or a normal-plasma cell-free nucleic acid, based on the methylation cfDNA sequencing data (e.g., obtained using Bisulfite sequencing or bisulfite-free sequencing methods) and tumor / fetal methylation markers. Next, a profile of the tumor / fetal-derived sequencing read counts may be constructed and then normalized. The CNV status (e.g., gain or loss) of each genomic region may be inferred, and a diagnosis or prognosis can be made based on a subject's inferred CNV profile.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for methylation analysis
ActiveUS20170145485A1Monitor efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineMethylation analysis
The present invention relates generally to a method for assessing nucleic acid methylation, in particular DNA and methylation. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of either qualitatively or quantitatively assessing, with improved sensitivity, the cytosine methylation of partially methylated DNA or RNA. The method of the present invention is useful in a range of applications including, but not limited to, the diagnosis of conditions or monitoring of developmental phenotypes which are characterised by DNA or RNA methylation changes.
Owner:CLINICAL GENOMICS PTY LTD
Heart failure detection device based on nucleic acid methylation change and application
InactiveCN111411040AIncreased methylation rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCardiac muscleDNA extraction
The invention provides a heart failure detection device based on nucleic acid methylation change and application. The device comprises an RNA and DNA extraction mechanism, an RNA and DNA enzymolysis mechanism and a methylated RNA and DNA determination mechanism. The invention finds that the methylation rates in myocardial tissues and peripheral blood of a myocardial infarction mouse both have an increasing trend, and the trends are consistent, so that peripheral blood lymphocytes are prompted to possibly become good substitutes for the myocardial tissues, and the methylation rates are positively correlated with the severity of myocardial infarction. The invention preliminarily shows that DNA and RNA methylation may have a certain potential effect in the occurrence and development of heartfailure, and may be used as a reference index for clinical heart failure diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
Amplification of bisulfite-reacted nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110045542A1Speed up the conversion processHigh magnificationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesSulfationCytosine
The present invention relates to a reaction mixture for the amplification of nucleic acids, the non-methylated cytosine bases of which have been converted to uracil bases by means of a bisulfition reaction. The invention also discloses methods for amplifying bisulfited nucleic acid and for determining the nucleic acid methylation state, and also kits based on the reaction mixture according to the invention.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Early detection of liver cancer based on F12 gene methylation
InactiveCN114438211AAccurate detectionNo painMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTissue sampleBlood plasma
The invention discloses a nucleic acid methylation detection method for early screening of liver cancer and a corresponding kit for liver cancer detection. A methylation gene detected by the kit contains an F12 (Coagation factor XII) gene, and a detected sample comprises a tissue sample and a plasma sample.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEW HORIZON HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com