Sensitively detecting copy number variations (CNVs) from circulating cell-free nucleic acid
A cell nucleic acid and copy number technology, applied in genomics, instrumentation, sequence analysis, etc., can solve the problem of reduced usefulness of RC method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
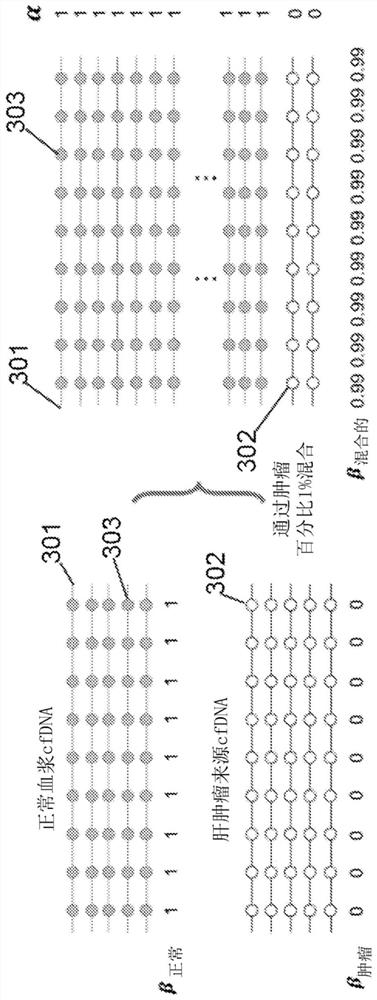
[0211] Applying the cfCNV method to liver cancer samples to deconvolute tumor cfDNA and detect cancer
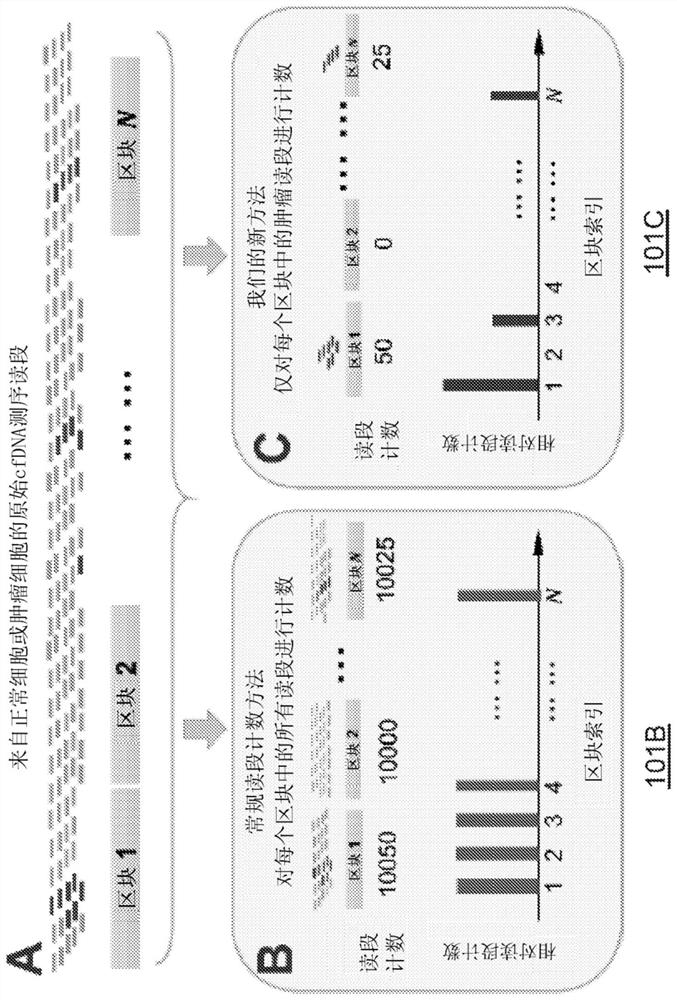
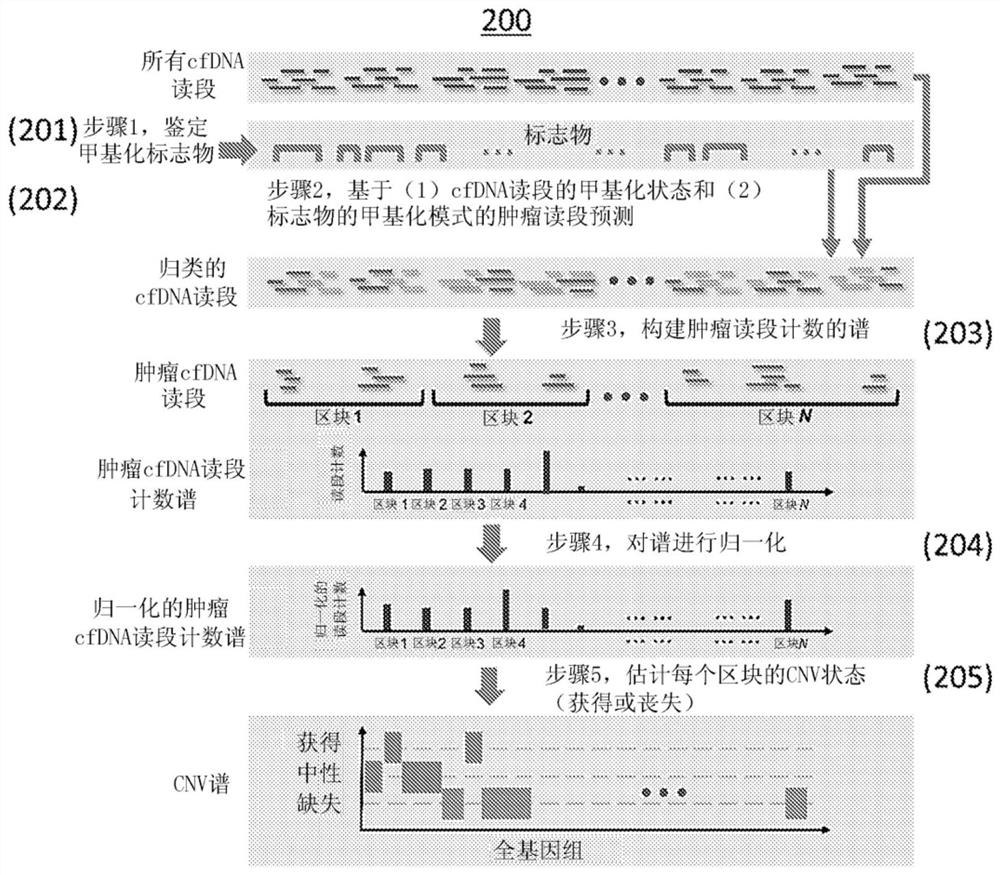
[0212] The cfCNV method is implemented as follows. In operations 1 and 2, a posterior probabilistic approach was used to classify and count tumor-derived sequencing reads among multiple sequencing reads obtained from cfDNA samples from liver cancer patients. In step 3, only leukocytes from the same blood sample were used to construct a control profile for normalization without taking into account other sources of experimental and technical bias. In step 4, the scores of blocks with abnormal log ratios were used as the final cancer indicator score.
[0213] To perform an example of a method according to a disclosed embodiment, whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) data of plasma cfDNA samples were collected from 15 liver cancer patients and 5 healthy subjects.
[0214] The performance of the cfCNV method was compared to that of a conventional sequencing read counting (RC...
Embodiment 2
[0218] Further improvements to the cfCNV method
[0219] The cfCNV method described herein can be improved by one or more of the following methods.
[0220] First, the cfCNV method can detect small CNVs. In general, using a block size of 1M base pairs ensures a sufficient number of tumor-derived sequencing reads for CNV detection, but flattens the signal of small CNVs. Therefore, advanced genome segmentation methods are suitable for automatically identifying CNV blocks with variable sizes.
[0221] Second, the cfCNV method can improve the correction of systematic bias by analyzing multiple cfDNA samples simultaneously. By modeling sequencing read counts from multiple samples per genomic region, some potential systematic biases that could not be identified in a single sample, such as poor-quality markers, were readily identified. Such a population-based strategy can fully utilize the information of multiple cfDNA samples and achieve higher performance CNV detection compared ...
Embodiment 3
[0224] Detection of prenatal disorders by inferring CNVs in placental / fetal DNA
[0225] The methods and systems described herein can be used to infer placental CNVs through methylation sequencing data analysis of maternal cfDNA to detect prenatal conditions (eg, diseases or conditions in a pregnant subject or a pregnant subject's fetus). Specifically, select its methylation pattern (see Figure 5 Three modes at different resolutions) specific genomic regions or single CpG sites that can distinguish the placenta from all other normal tissues and normal cfDNA samples as fetal methylation markers. The analysis steps remained the same (for the detection of CNVs in cancer) except that multiple placental methylation markers were used instead of cancer markers. Profiles of normalized placental read abundance were constructed and used to estimate CNV status in each genomic block. The inferred CNV status is then used to detect prenatal conditions such as fetal aneuploidy (eg Down sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com