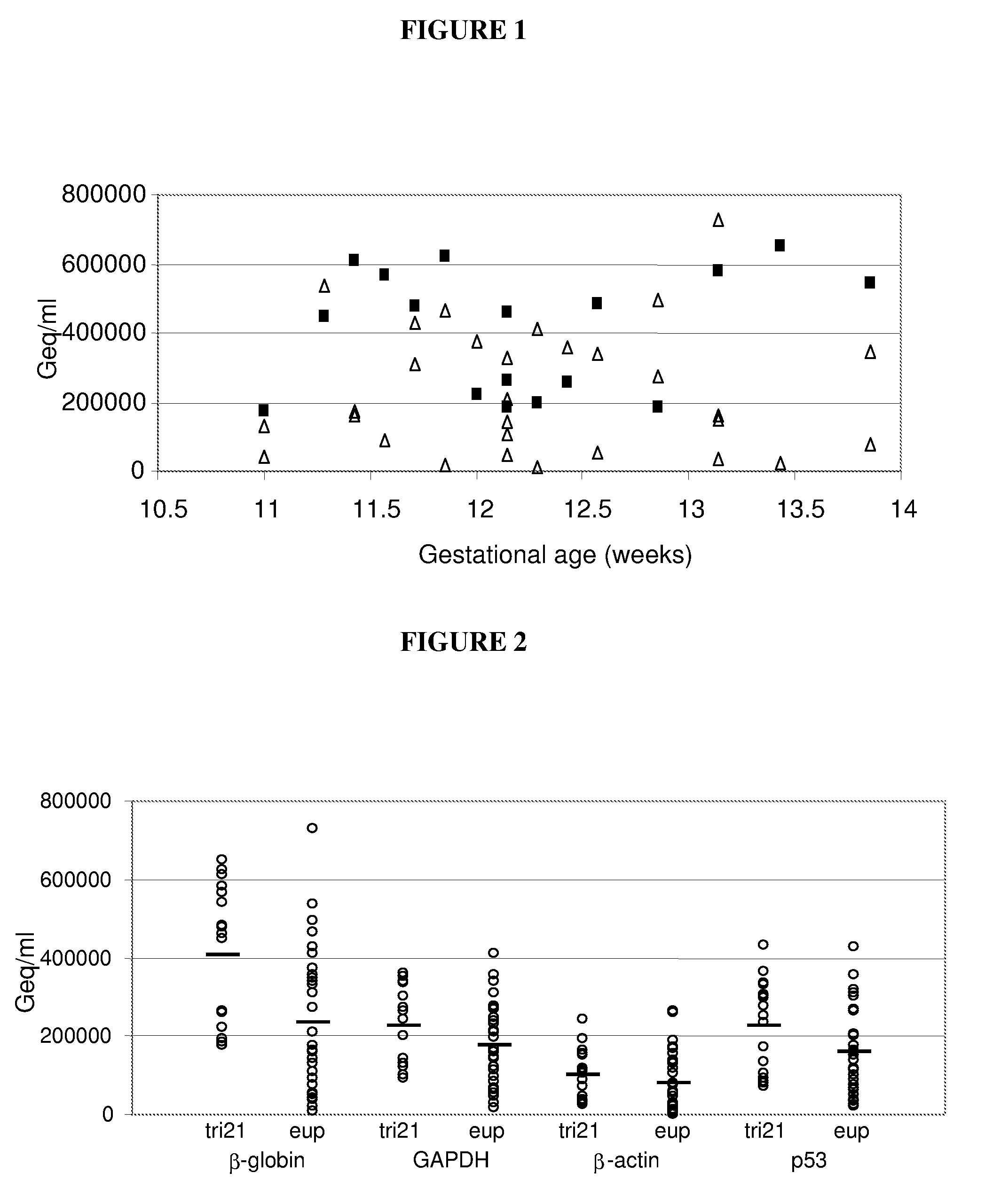
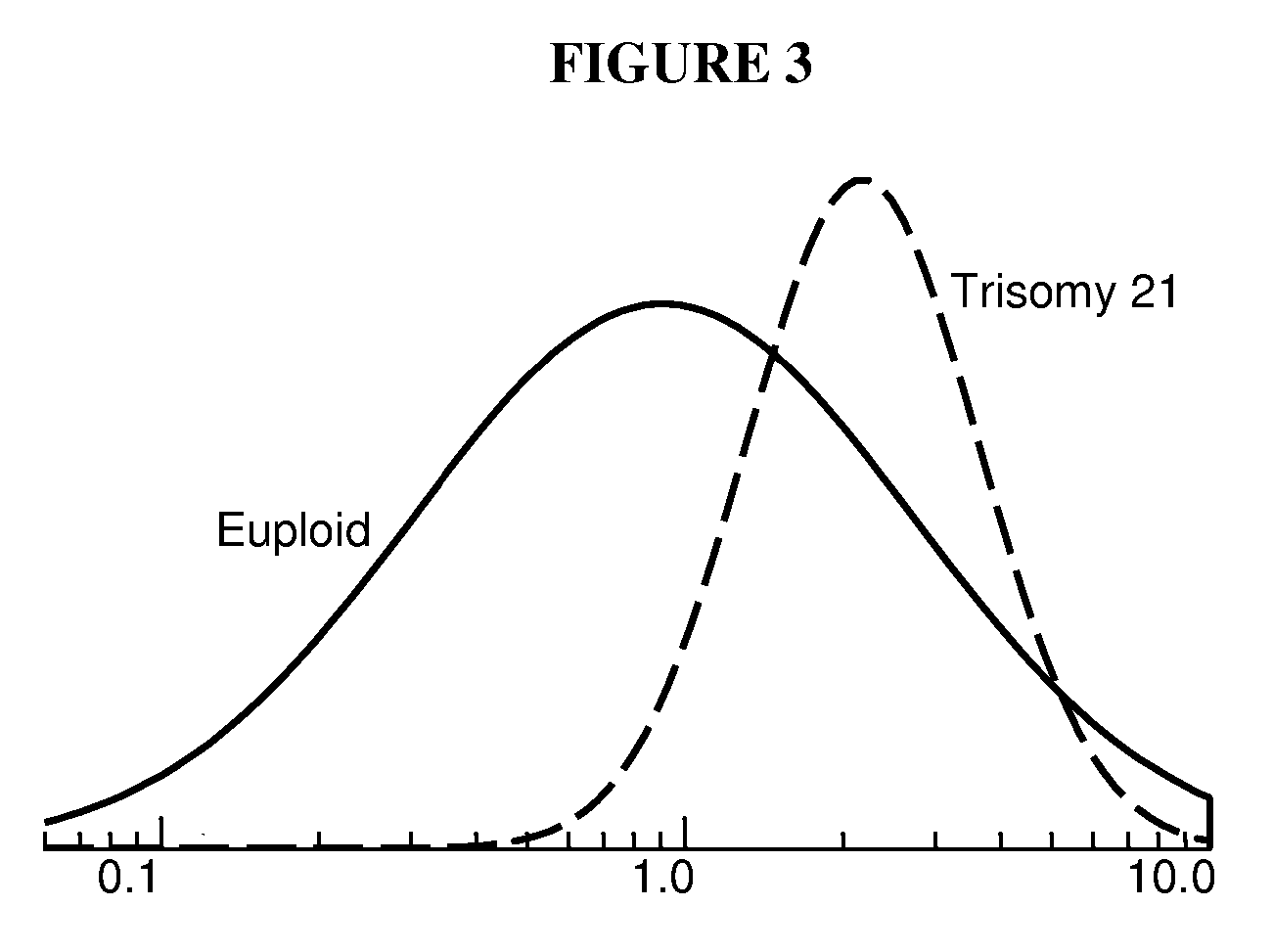
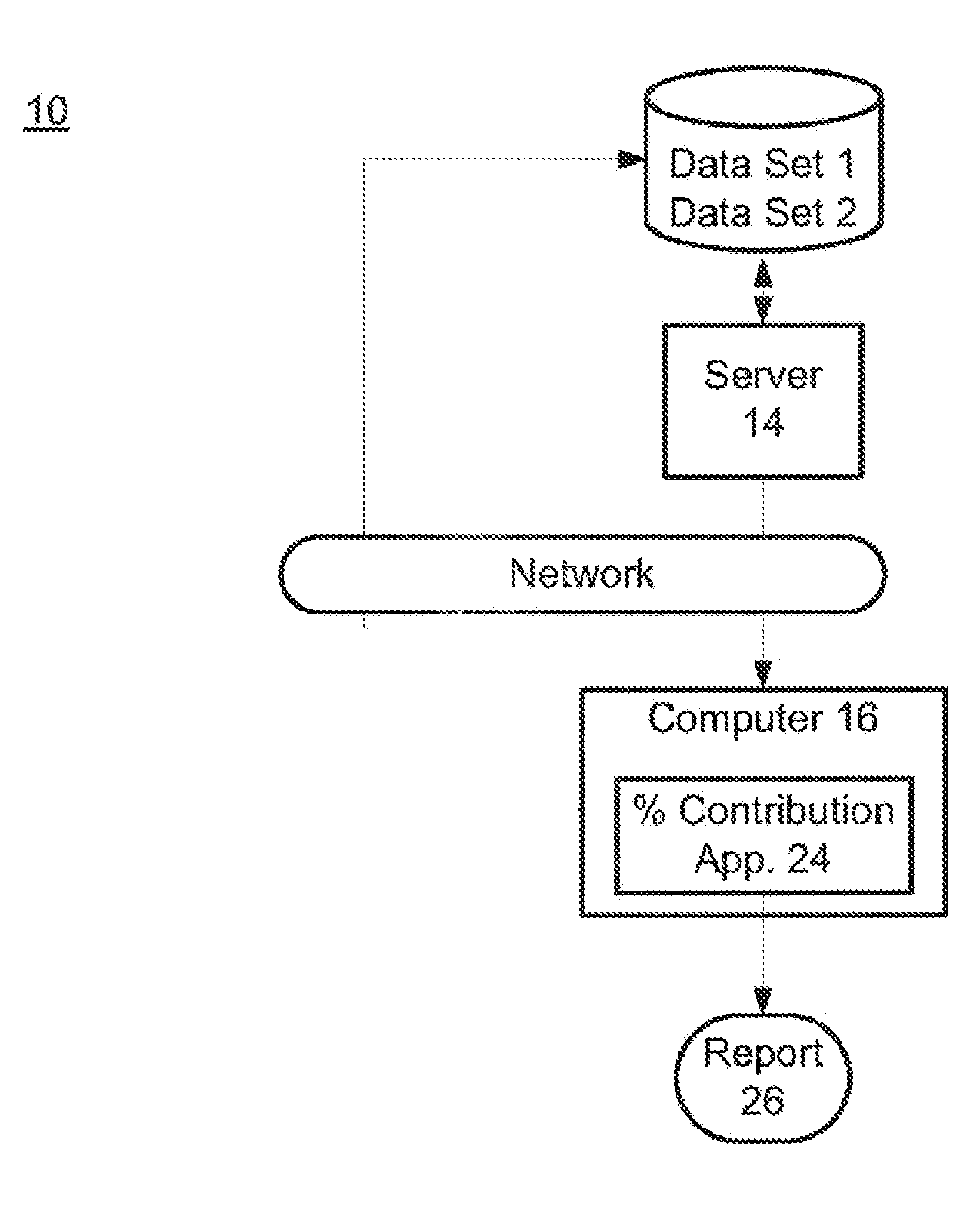
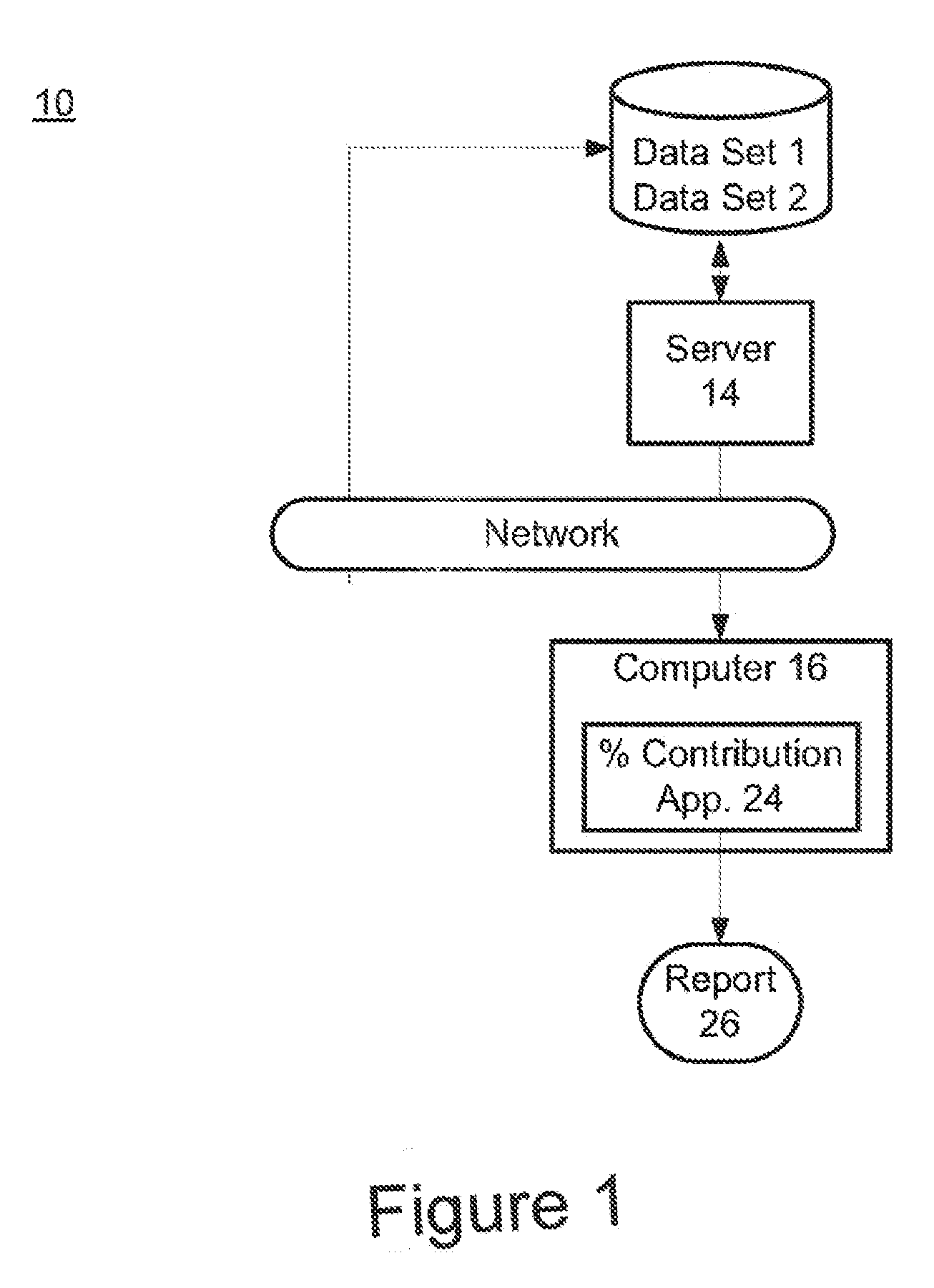
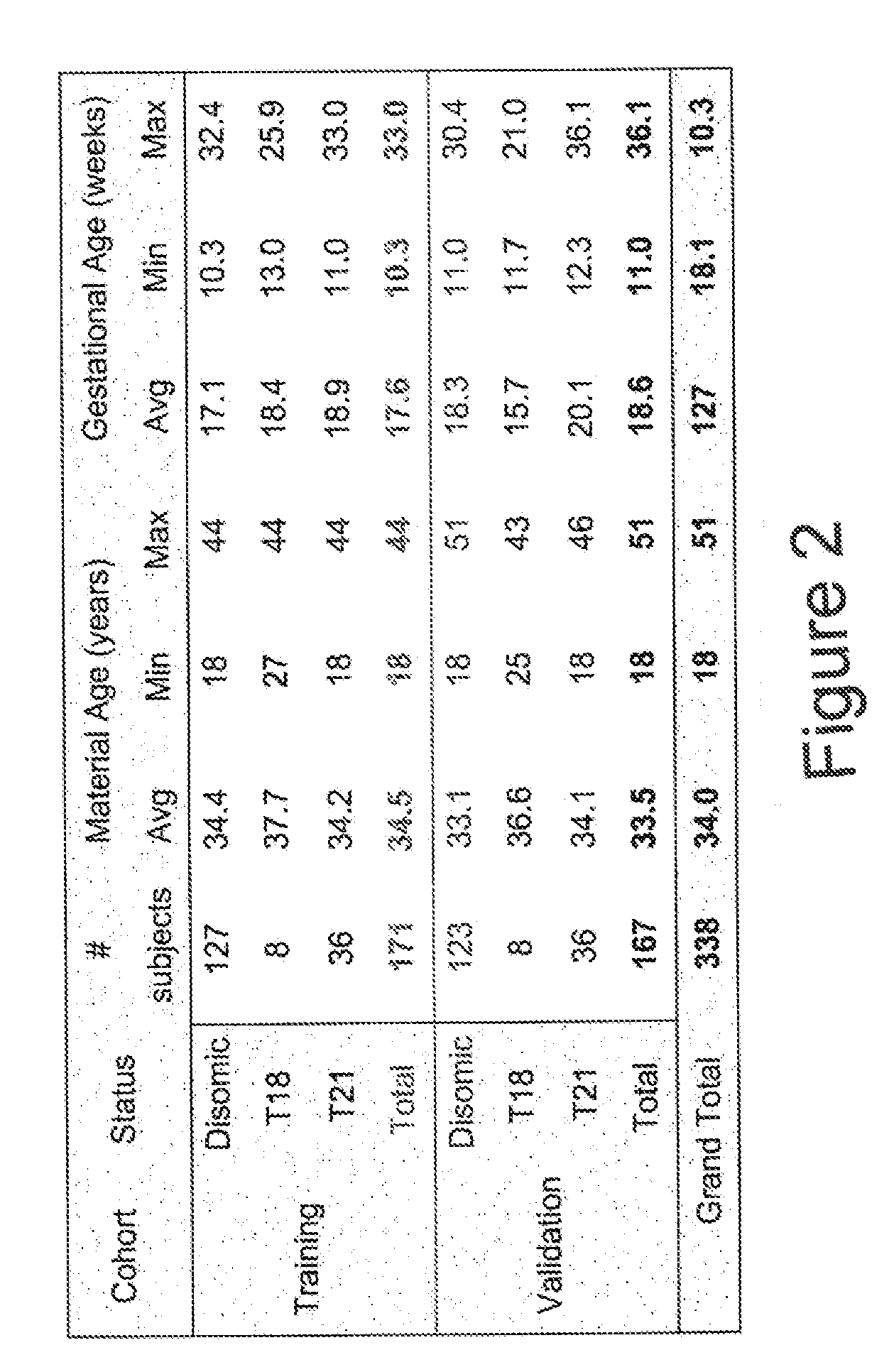
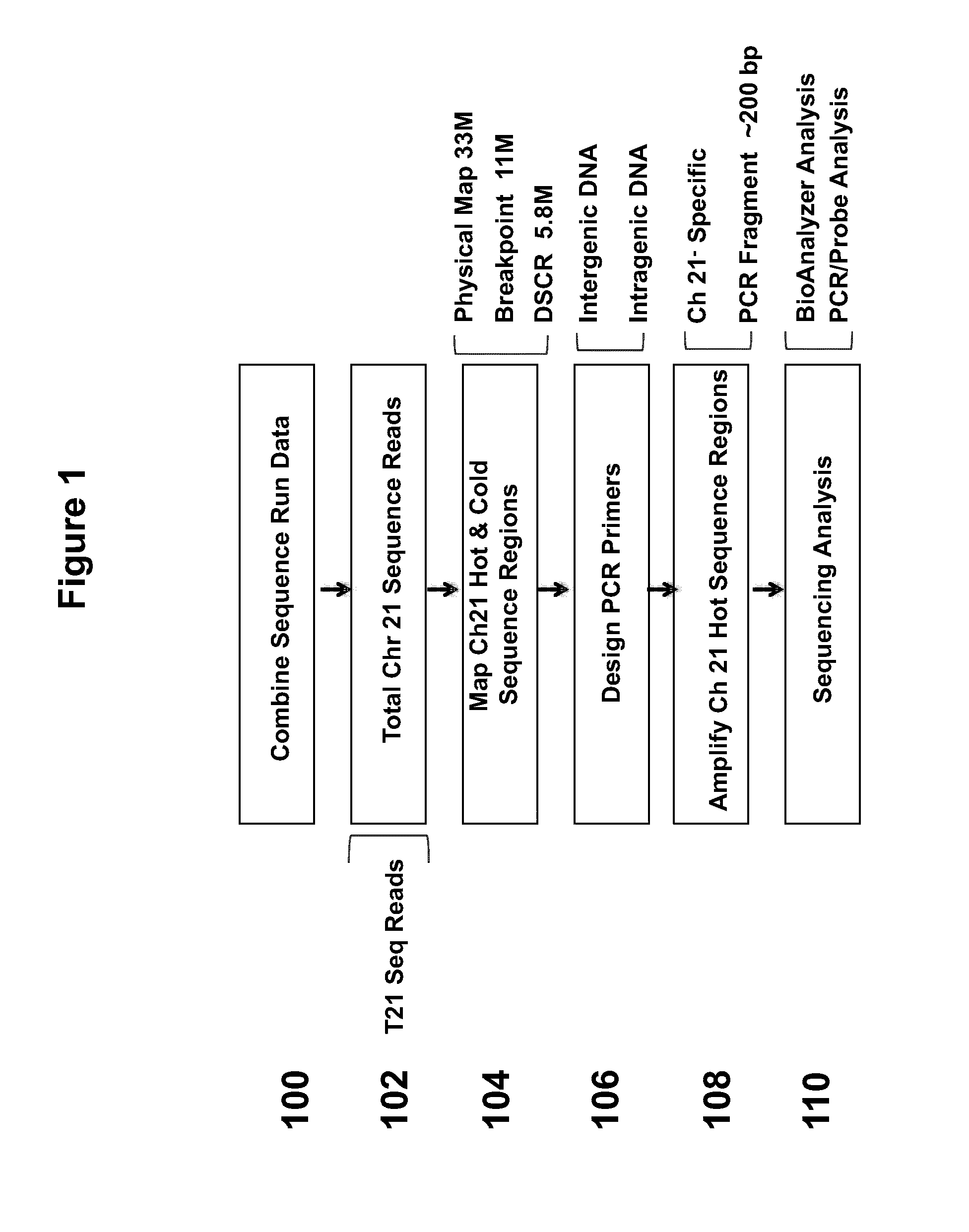
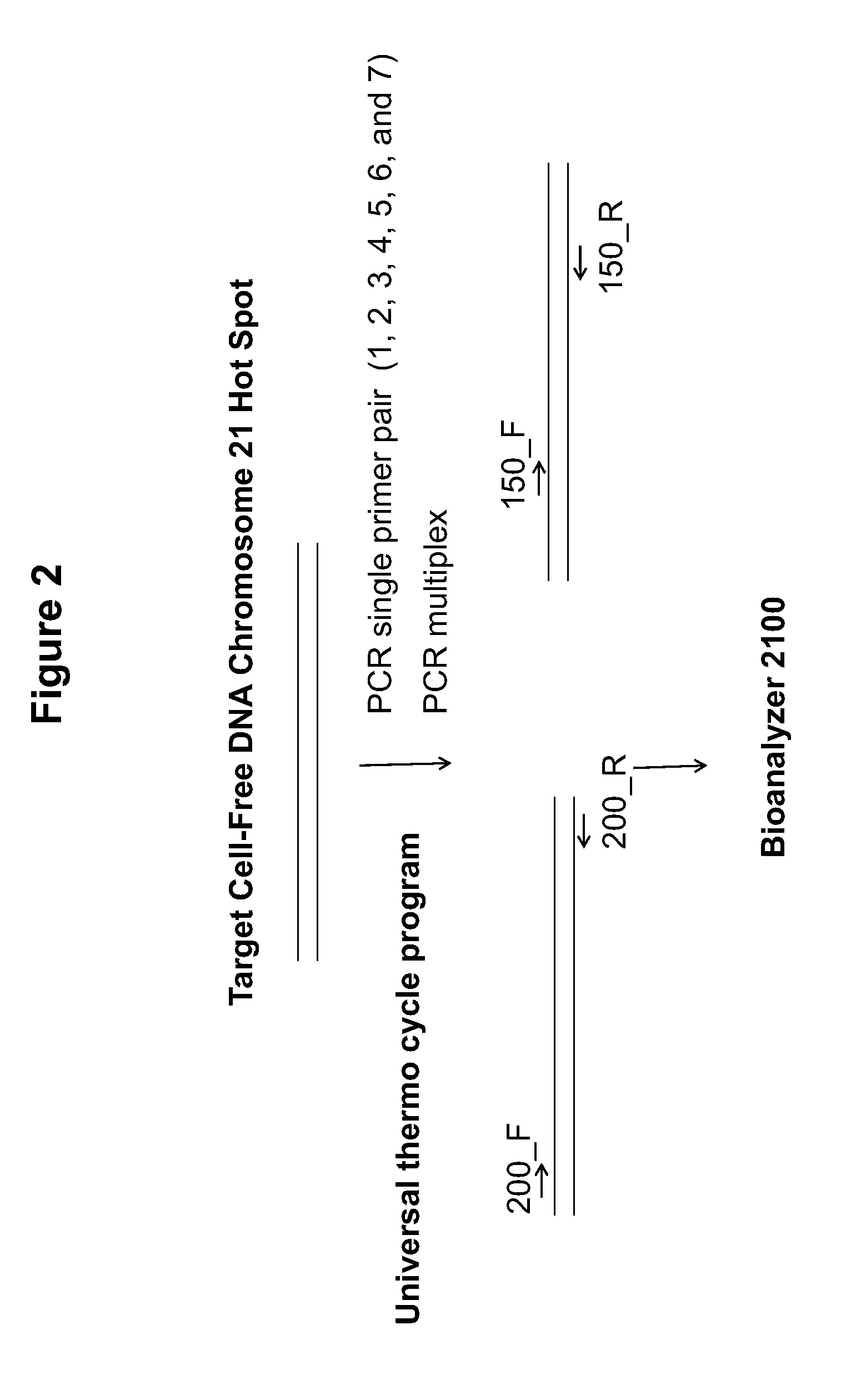
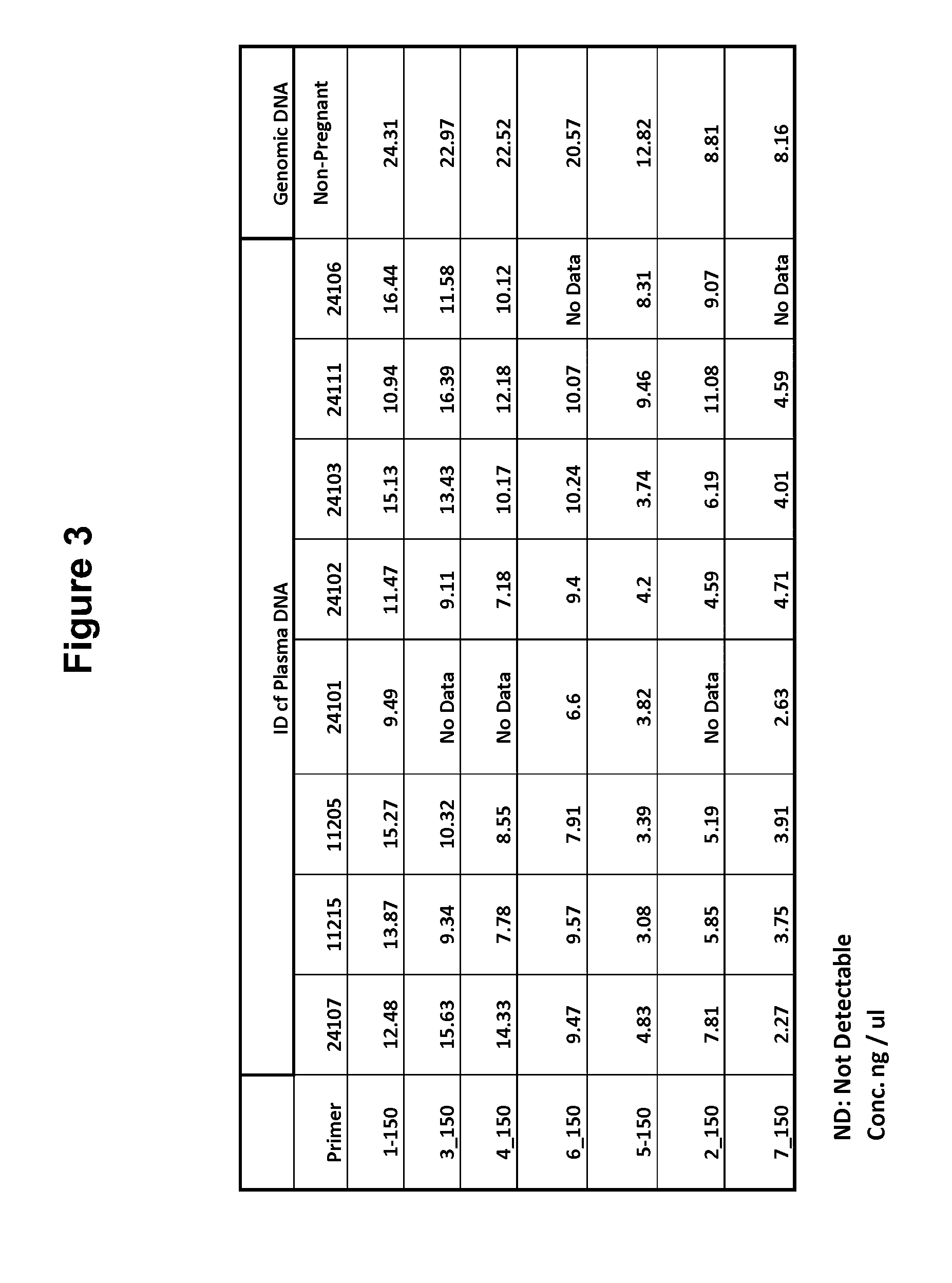
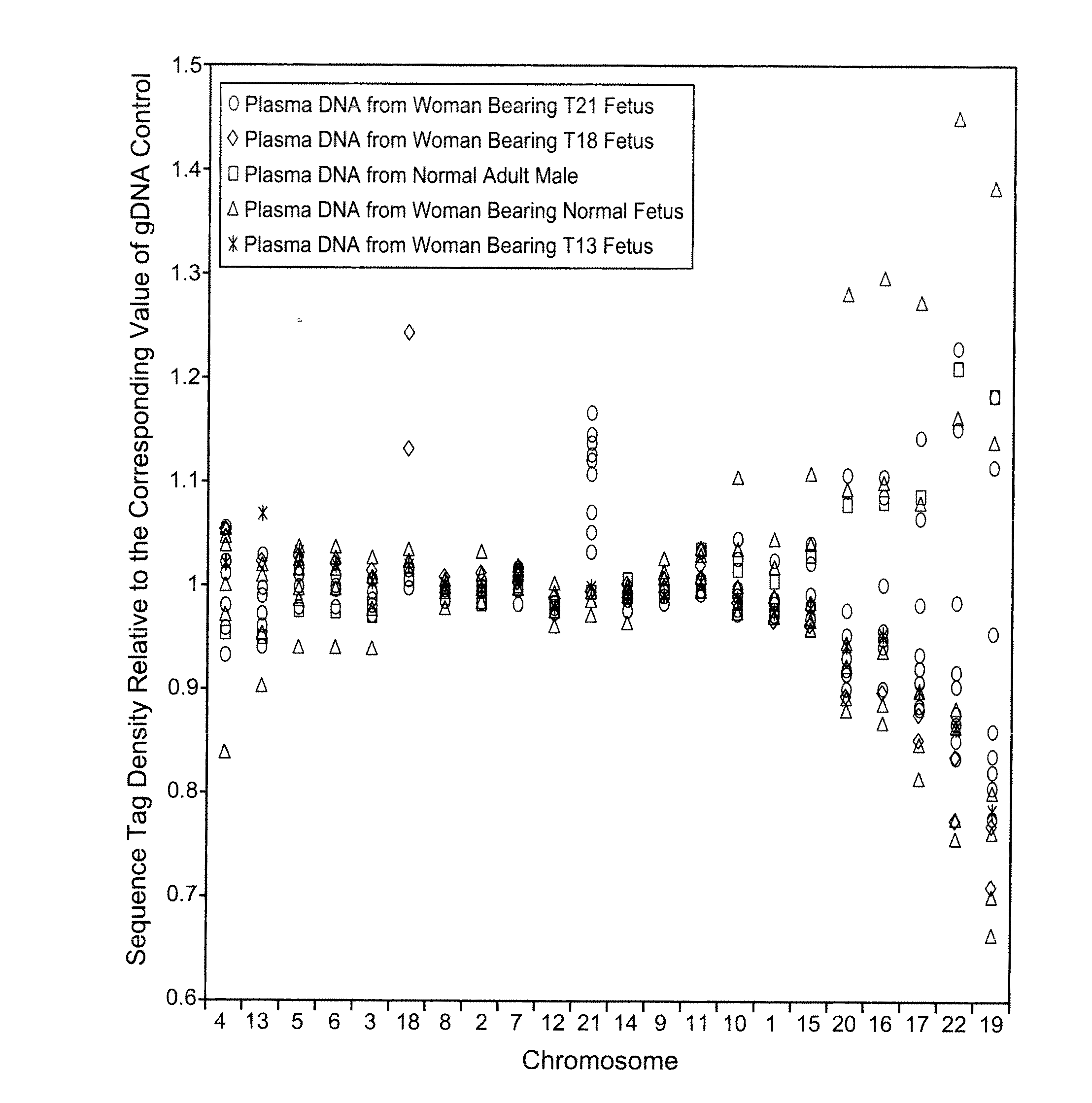
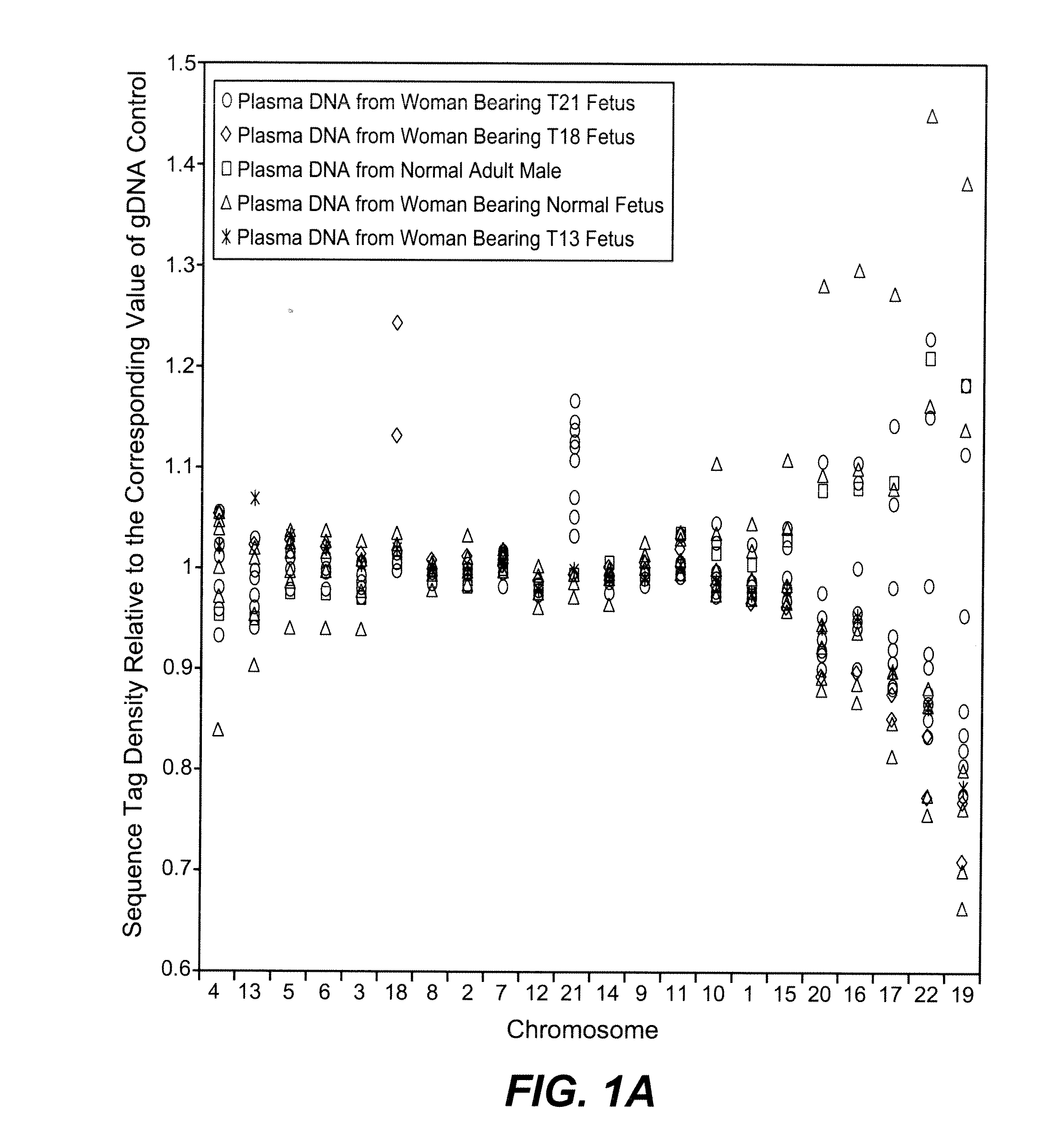
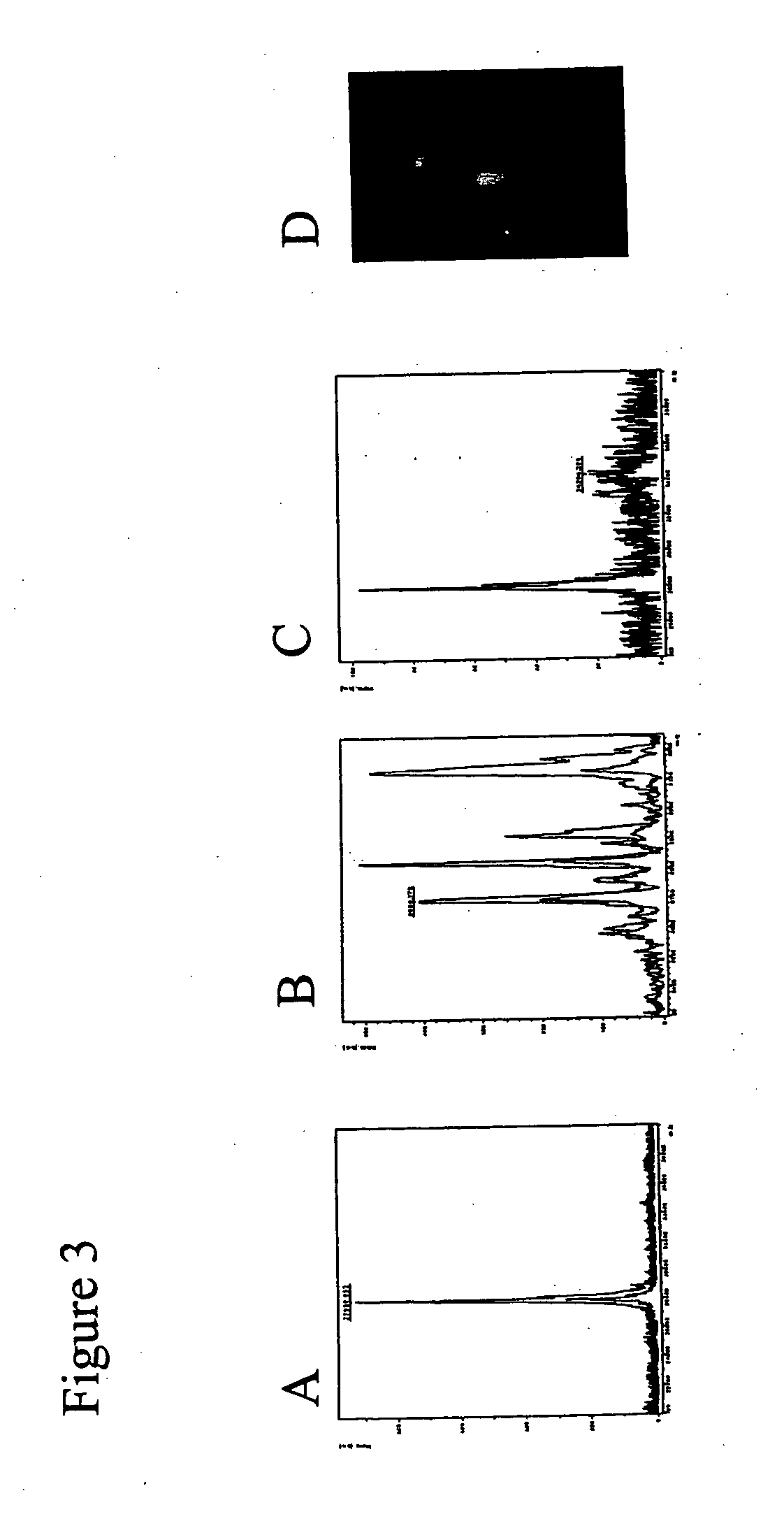
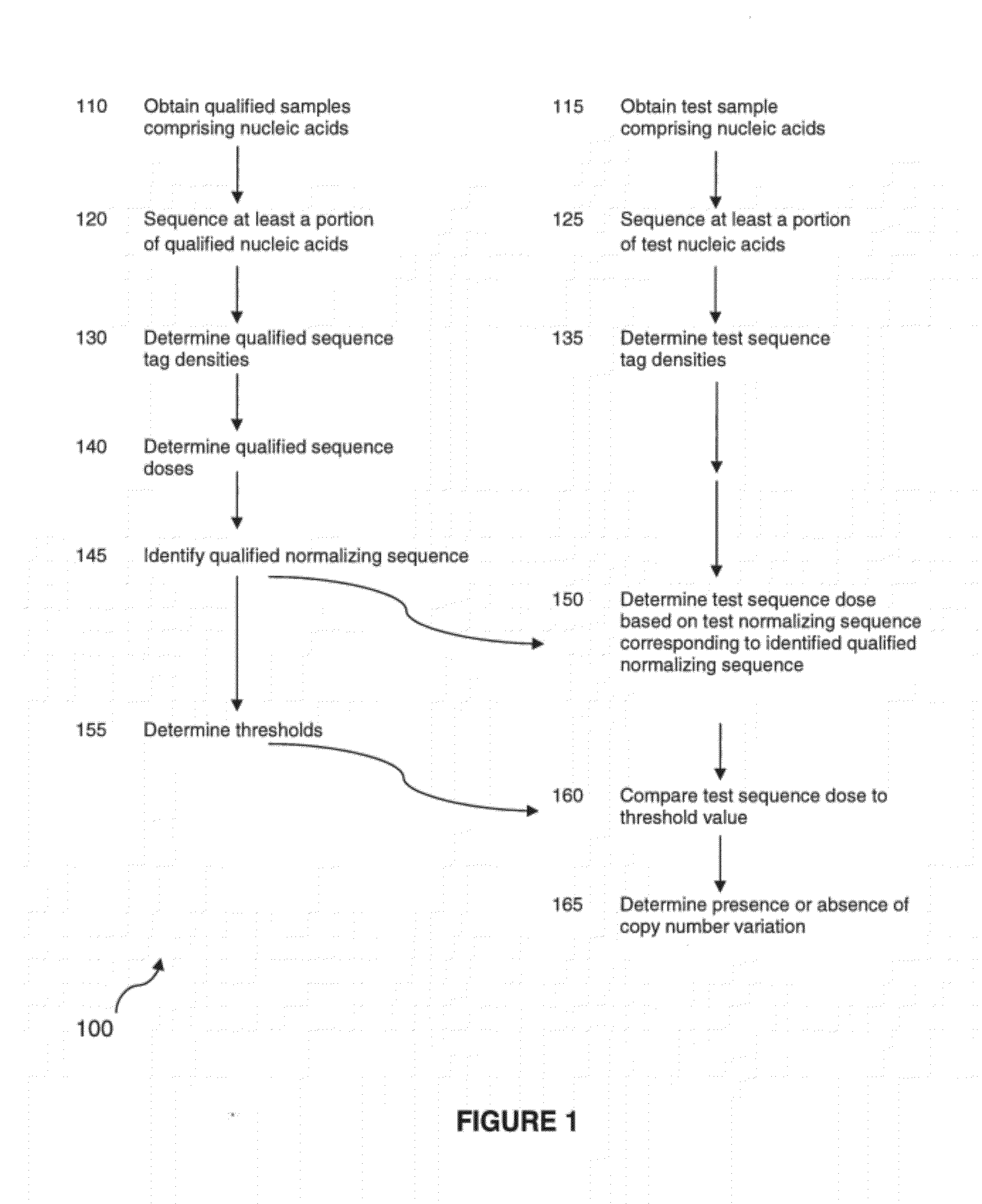
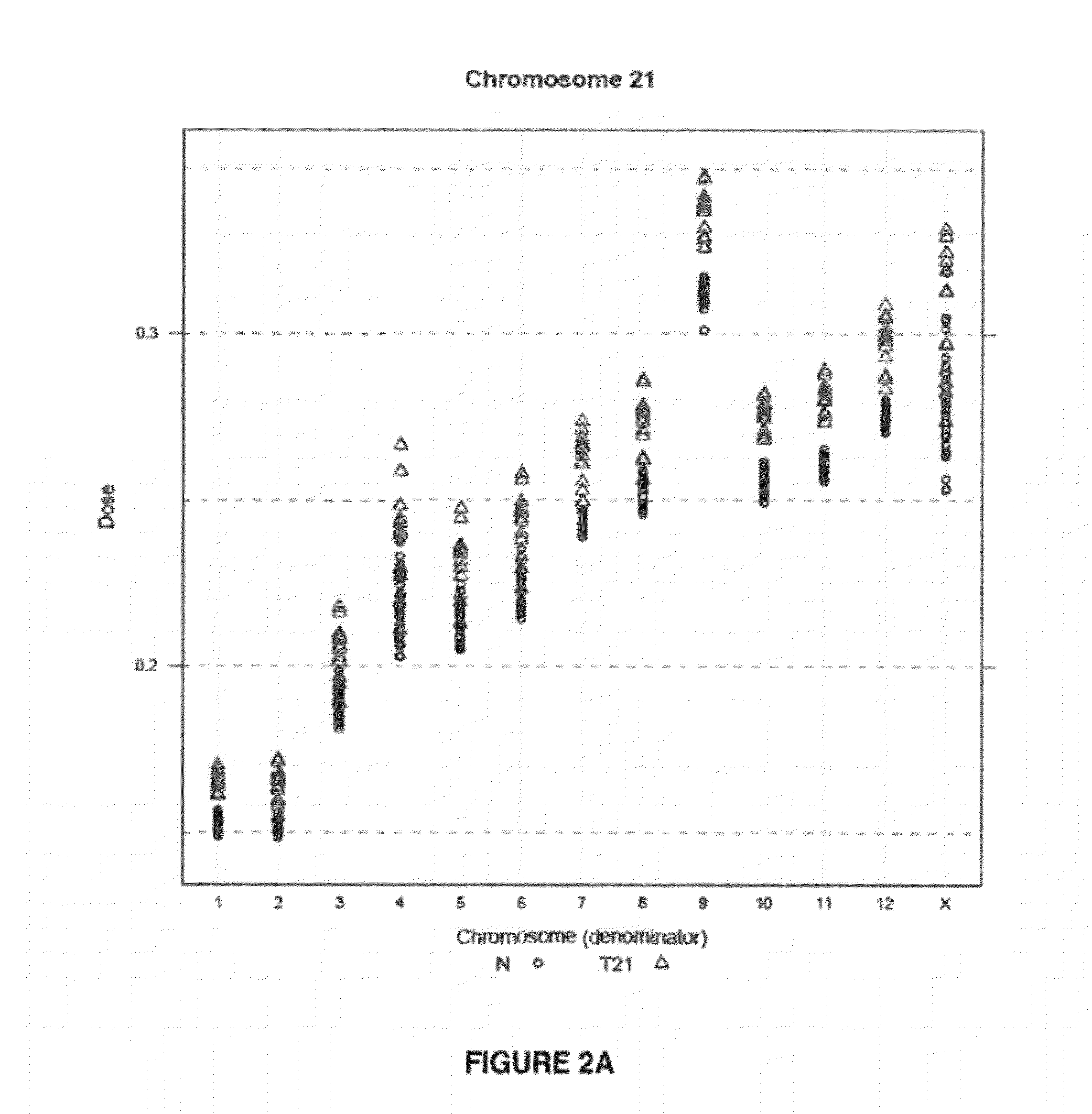
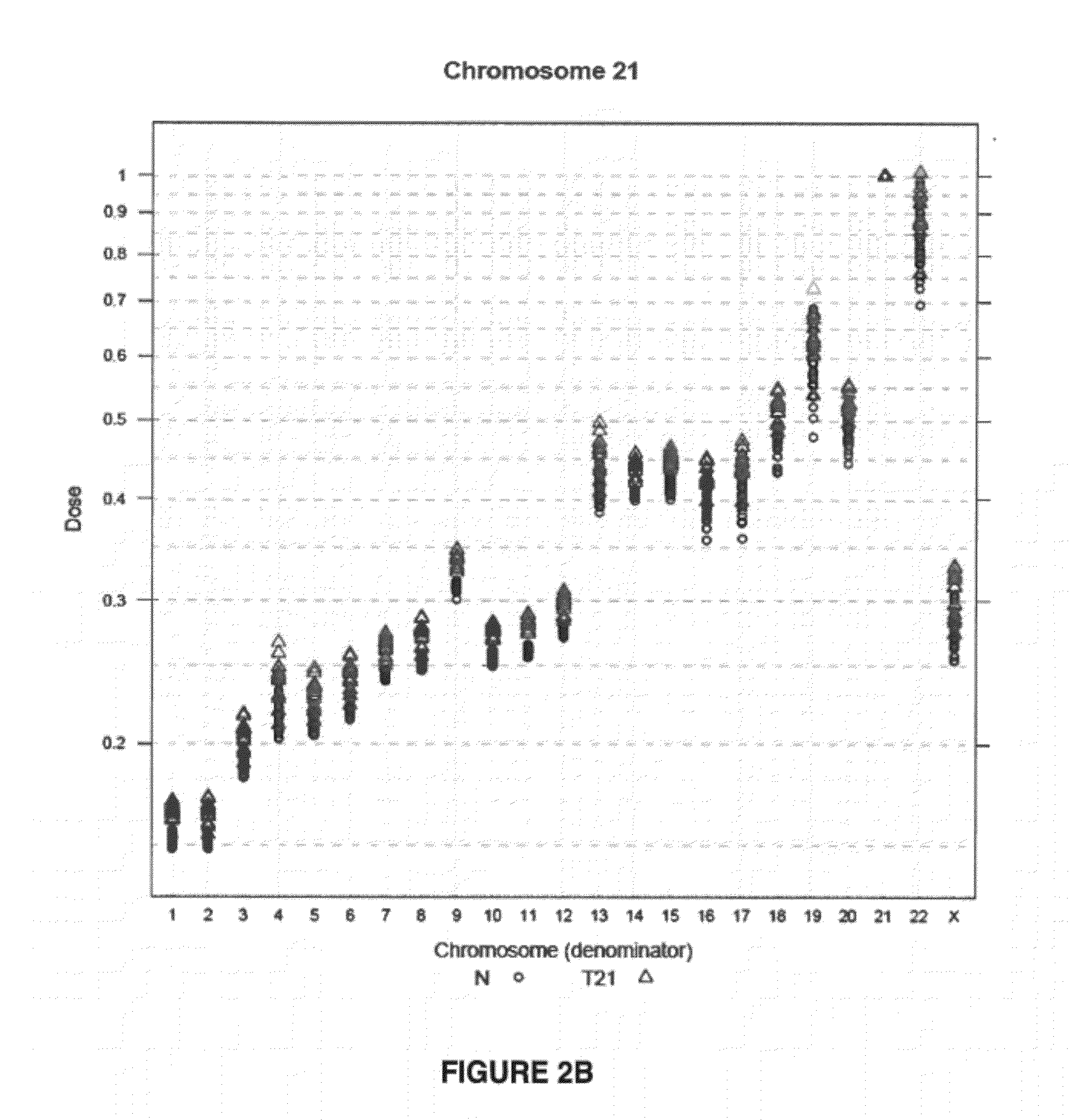
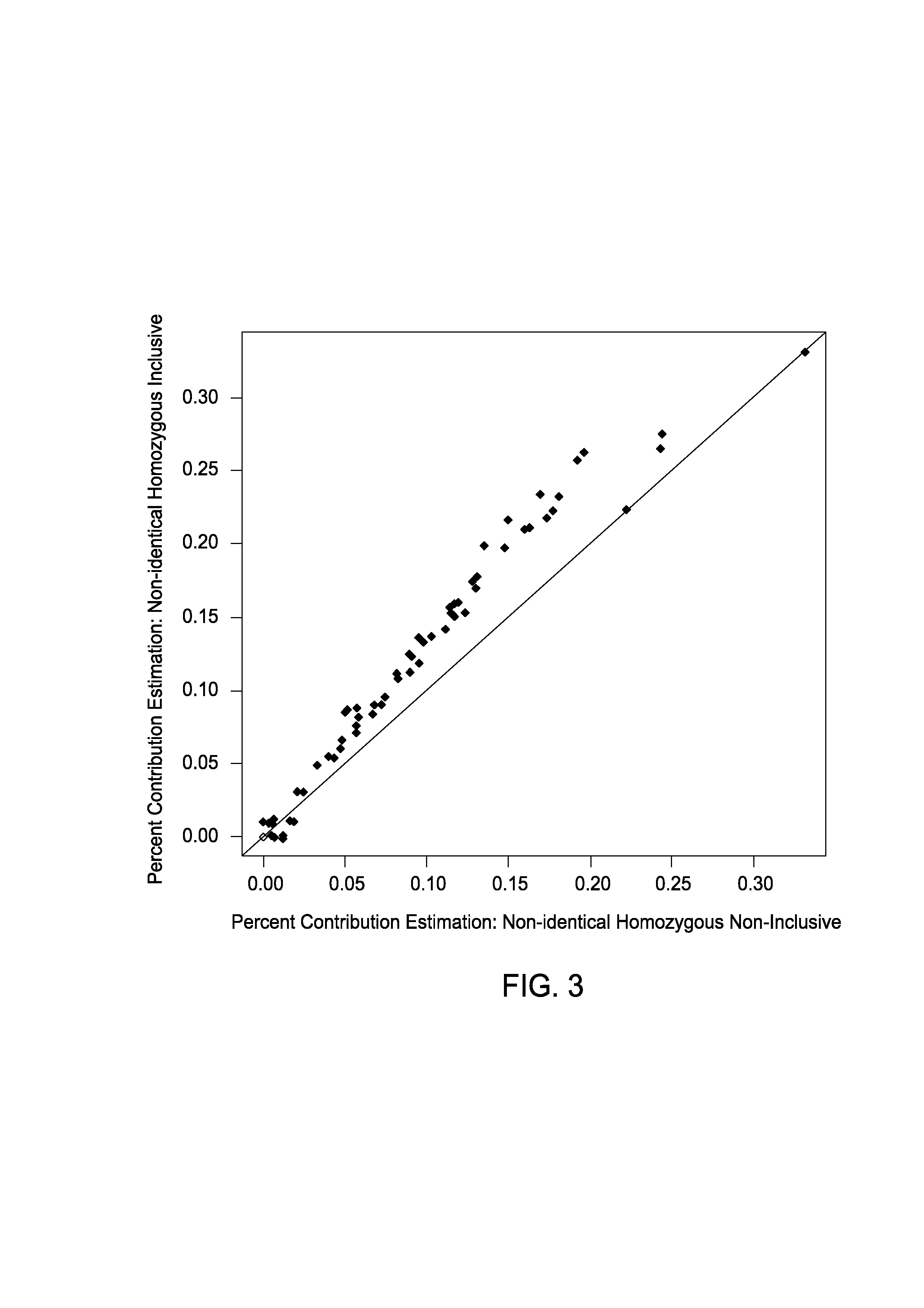
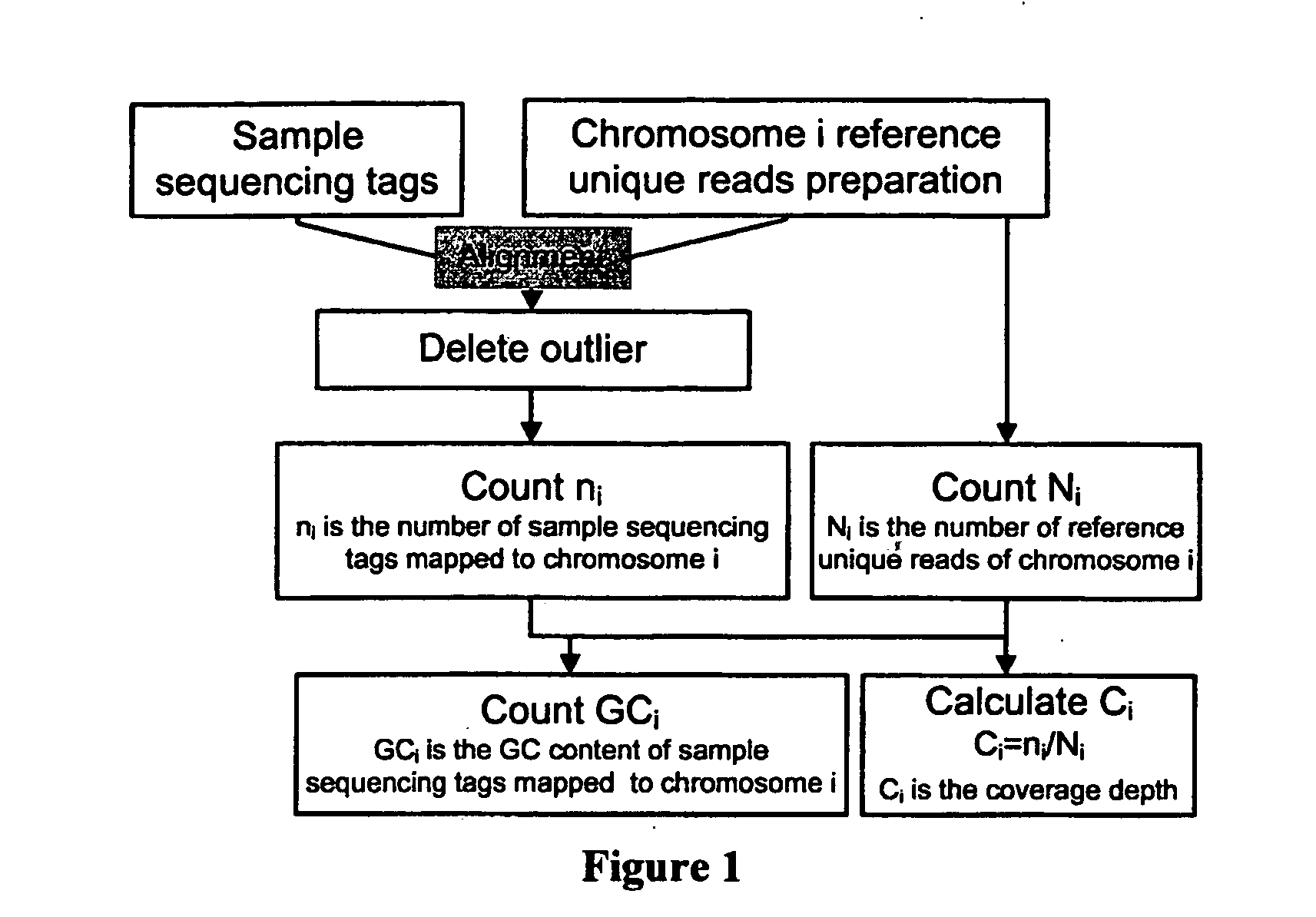
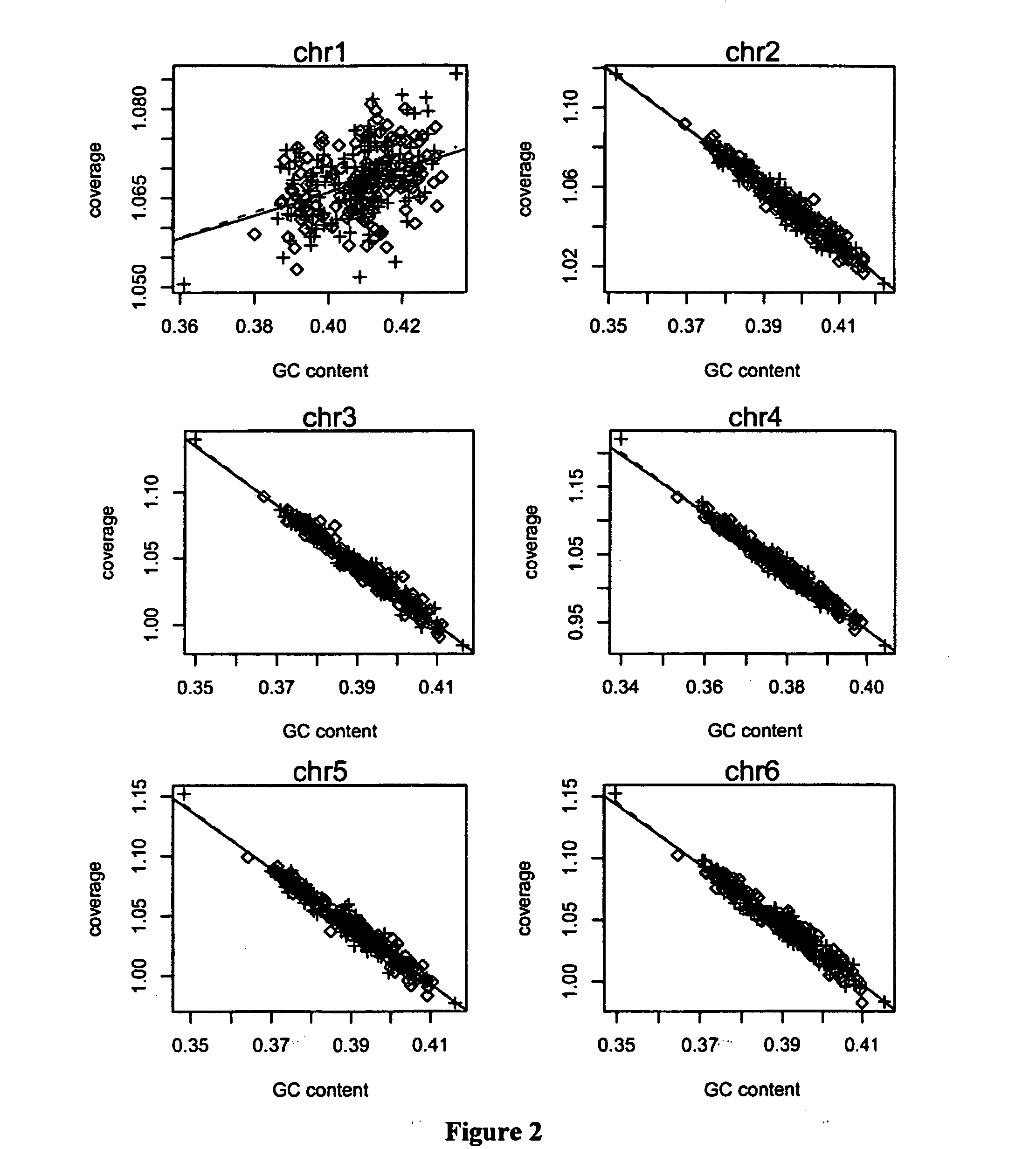
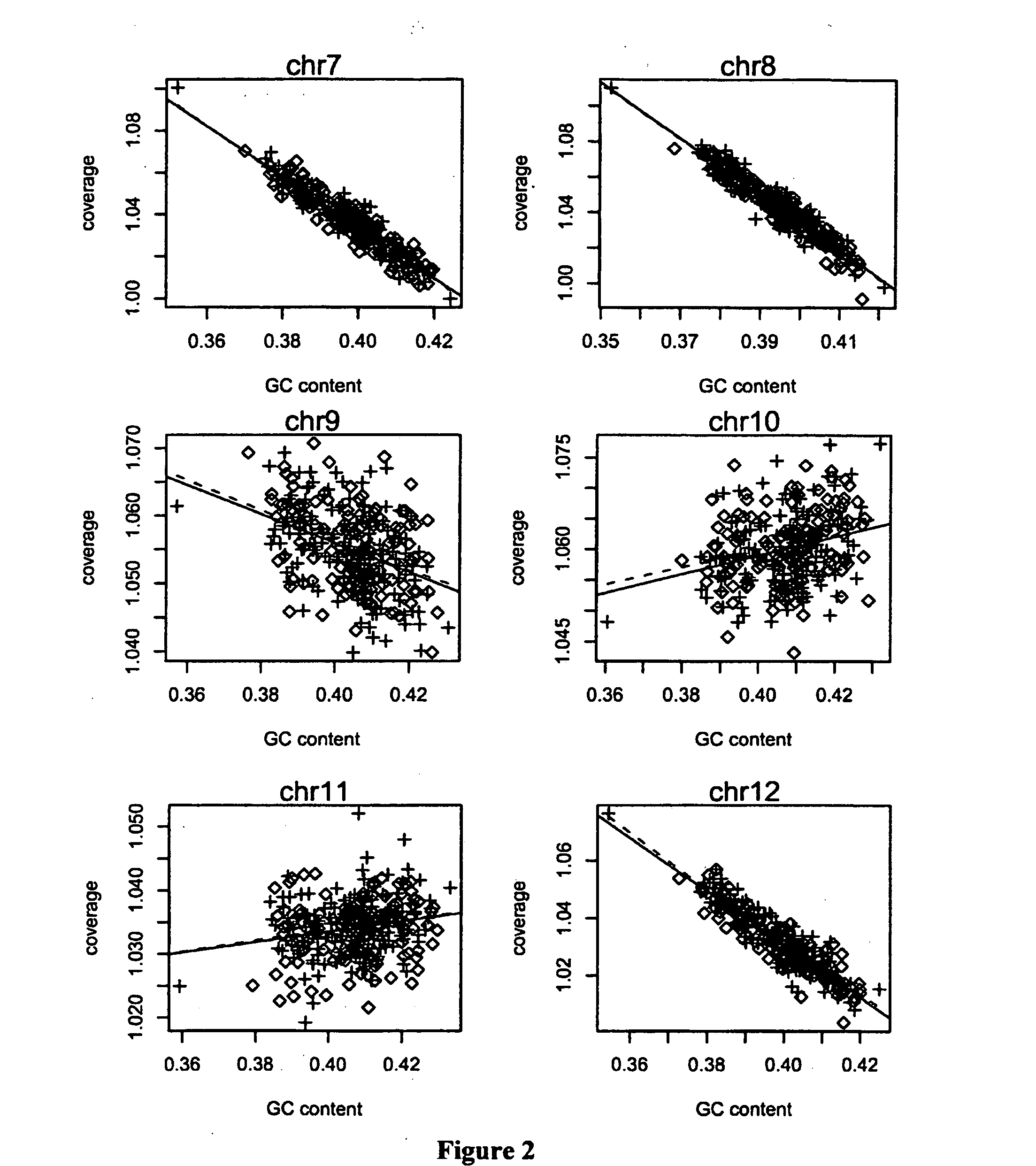
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Fetal aneuploidy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aneuploidy is the loss or gain of a chromosome. Instead of pairs being formed, a single chromosome ends up alone or with multiple partners. ... Aneuploidy also alters cell division and growth, and therefore fetal development, often resulting in miscarriage or severe birth defects. When germ cells exhibit aneuploidy, they give rise to certain disorders, depending on if a chromosome is missing, monosomy, or if there is an extra chromosome, trisomy.
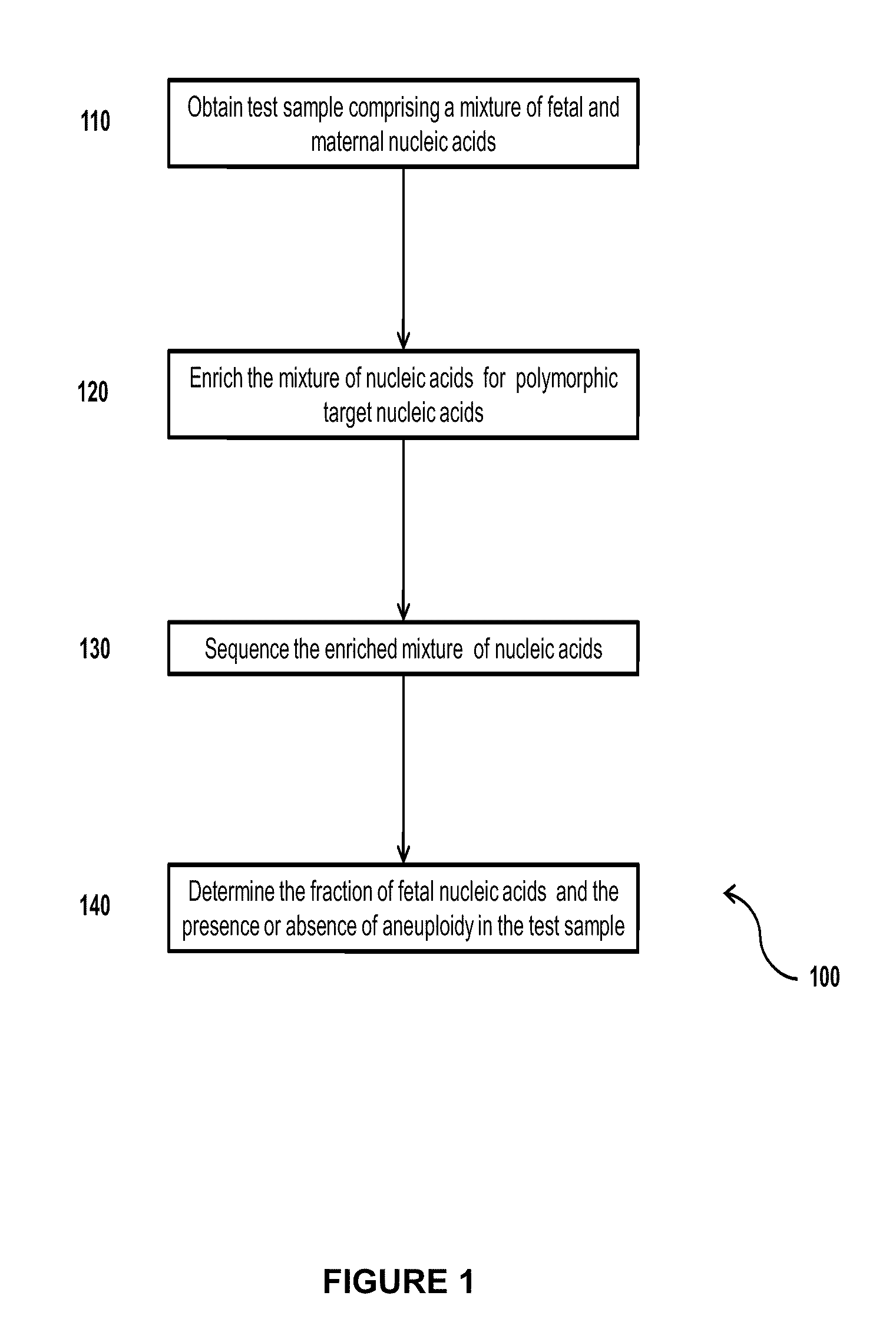
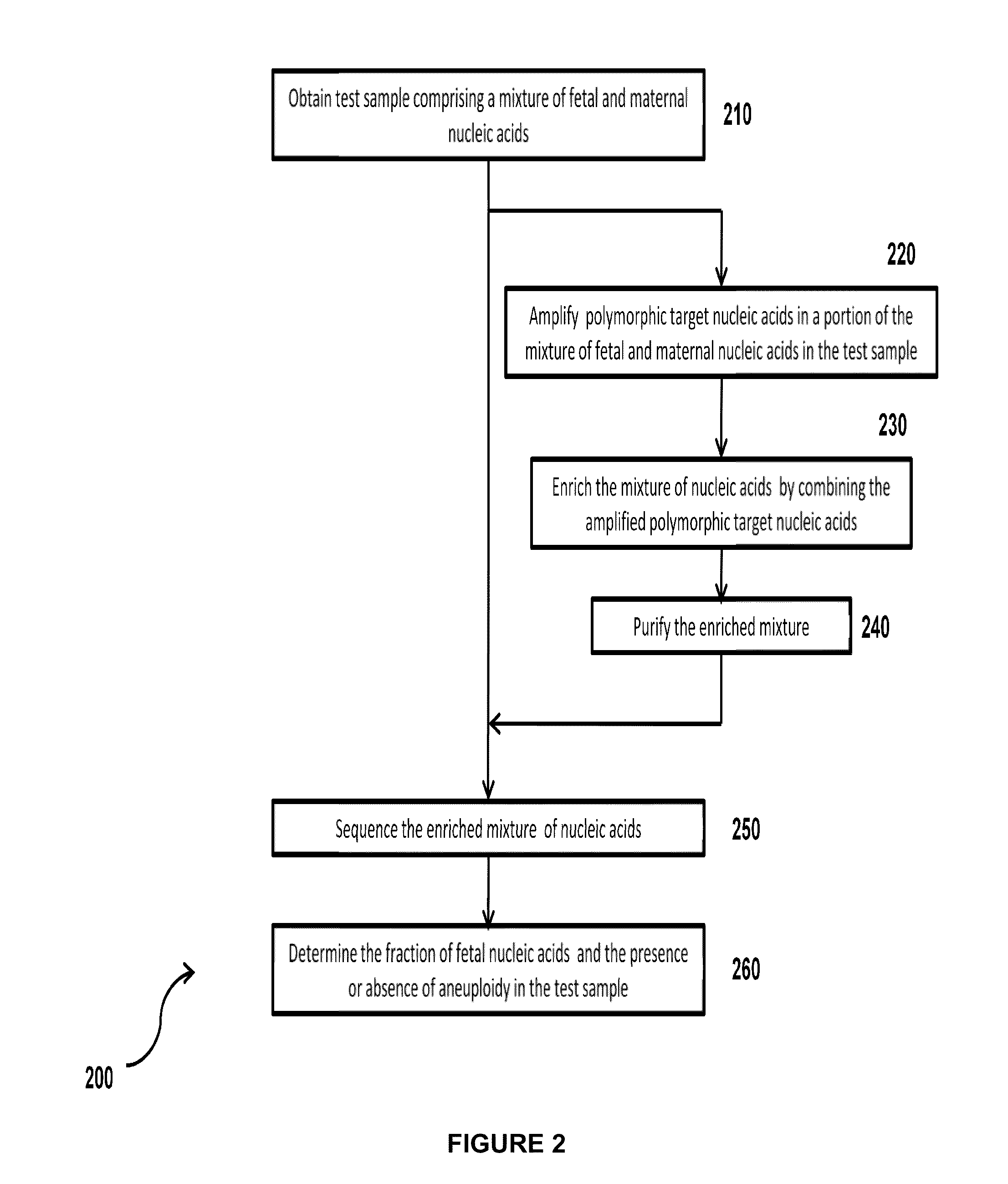
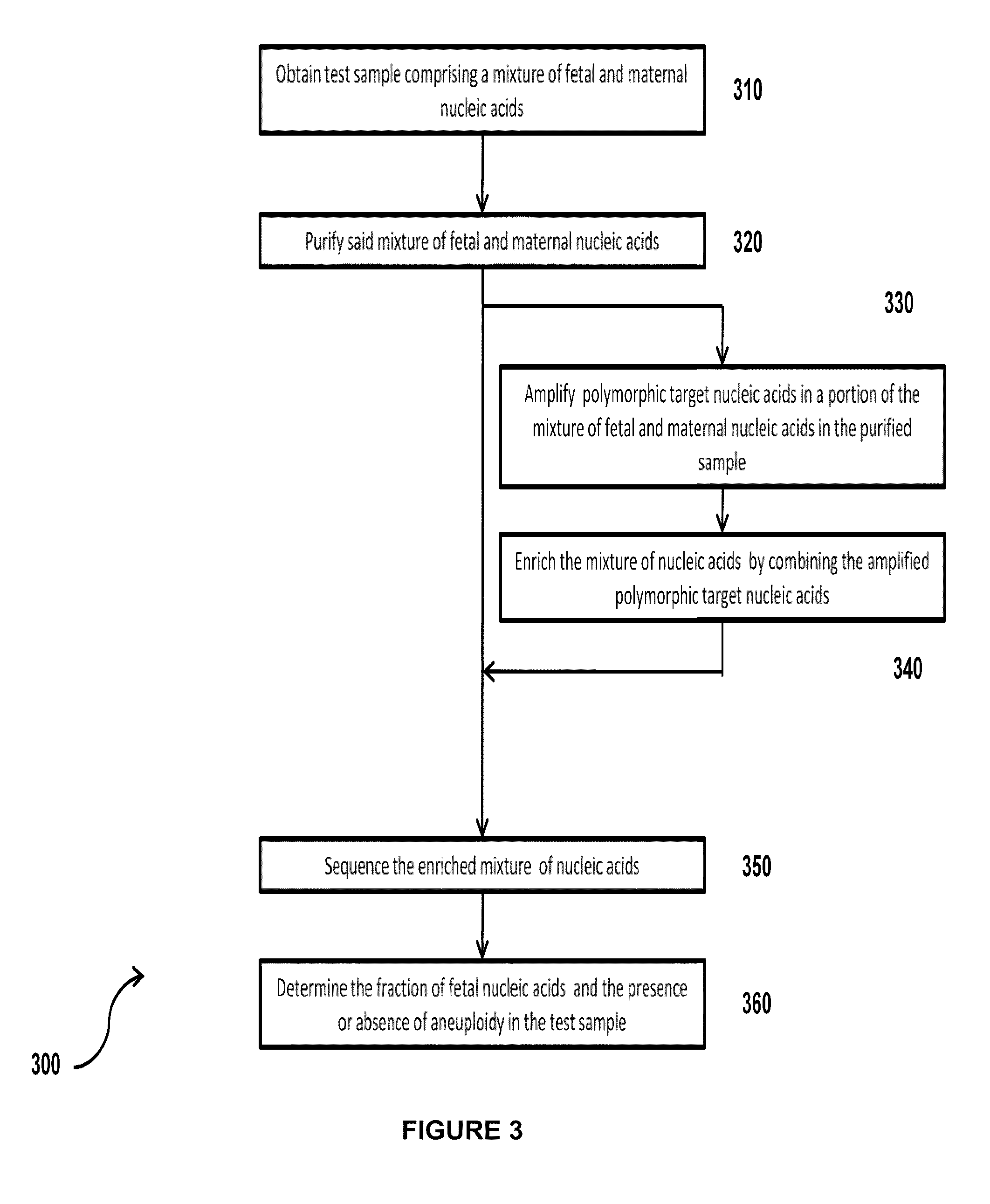
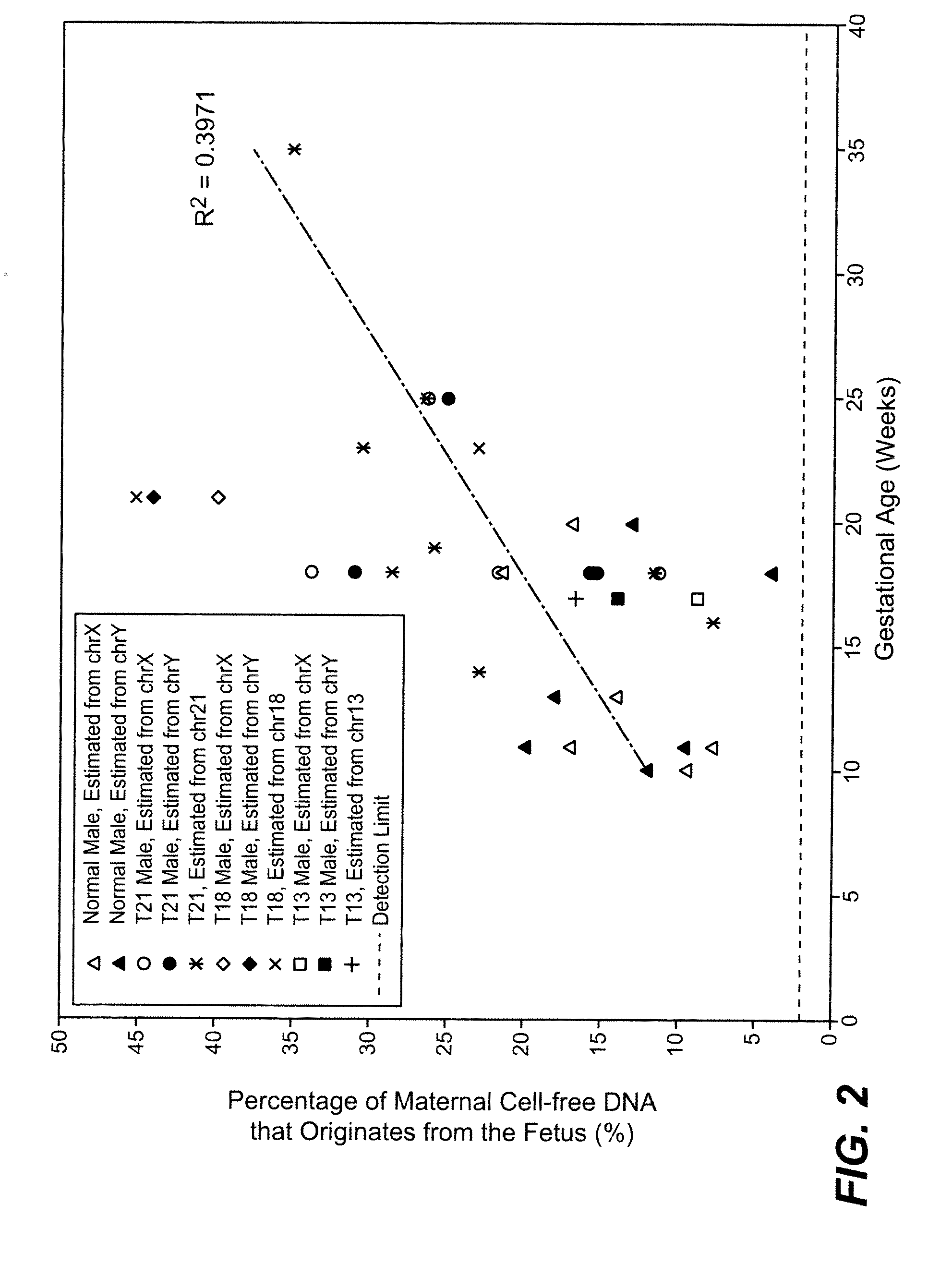
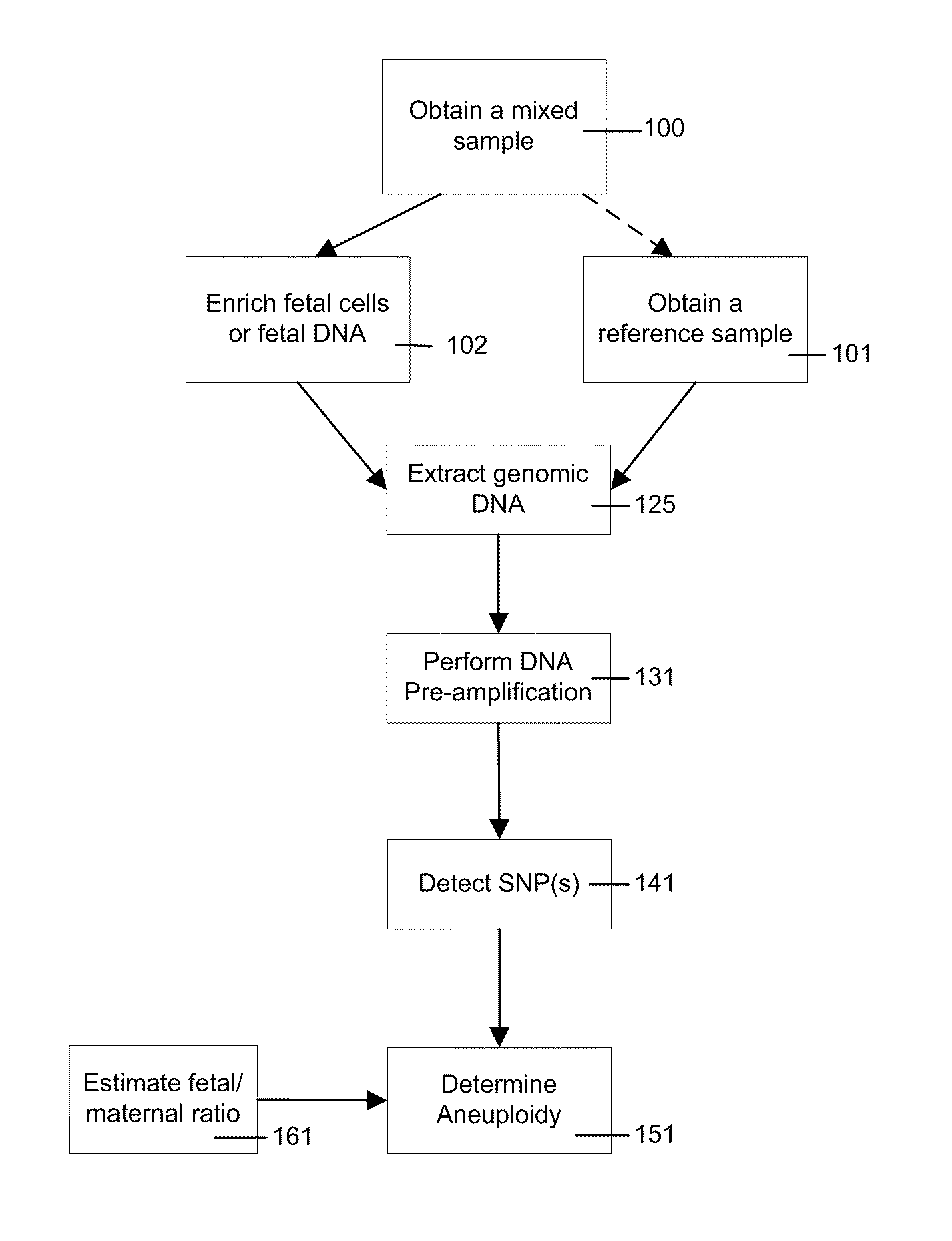
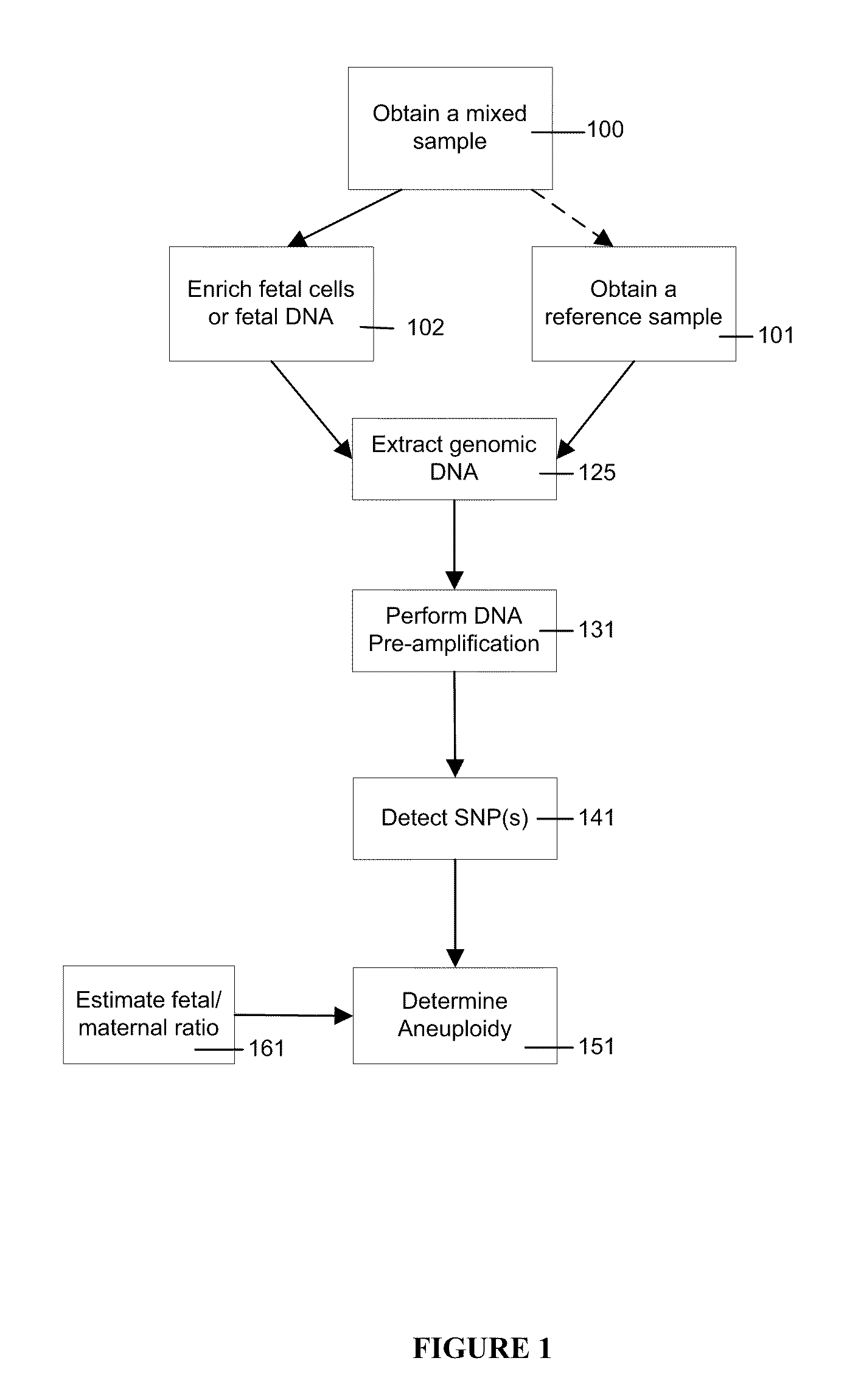
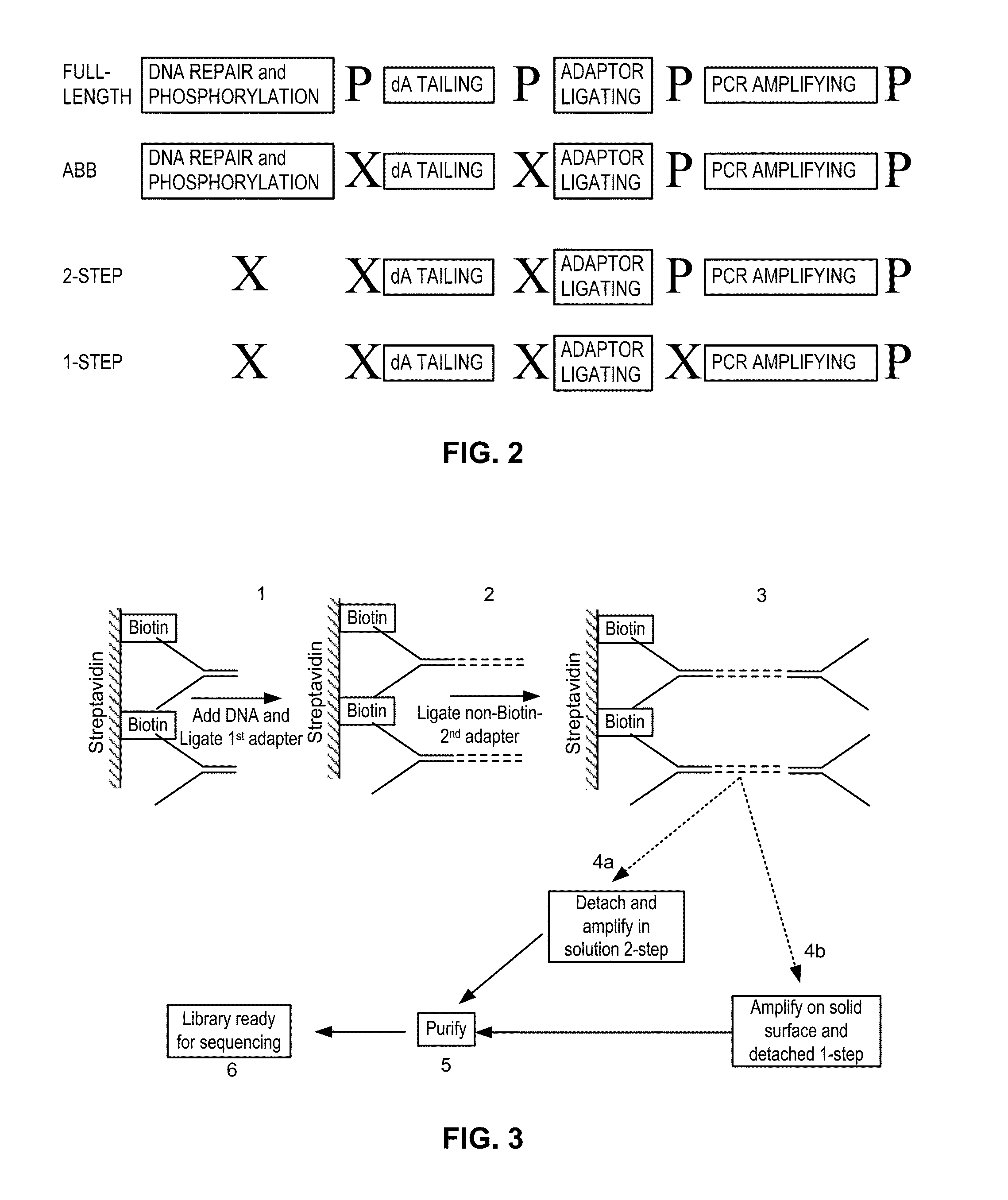
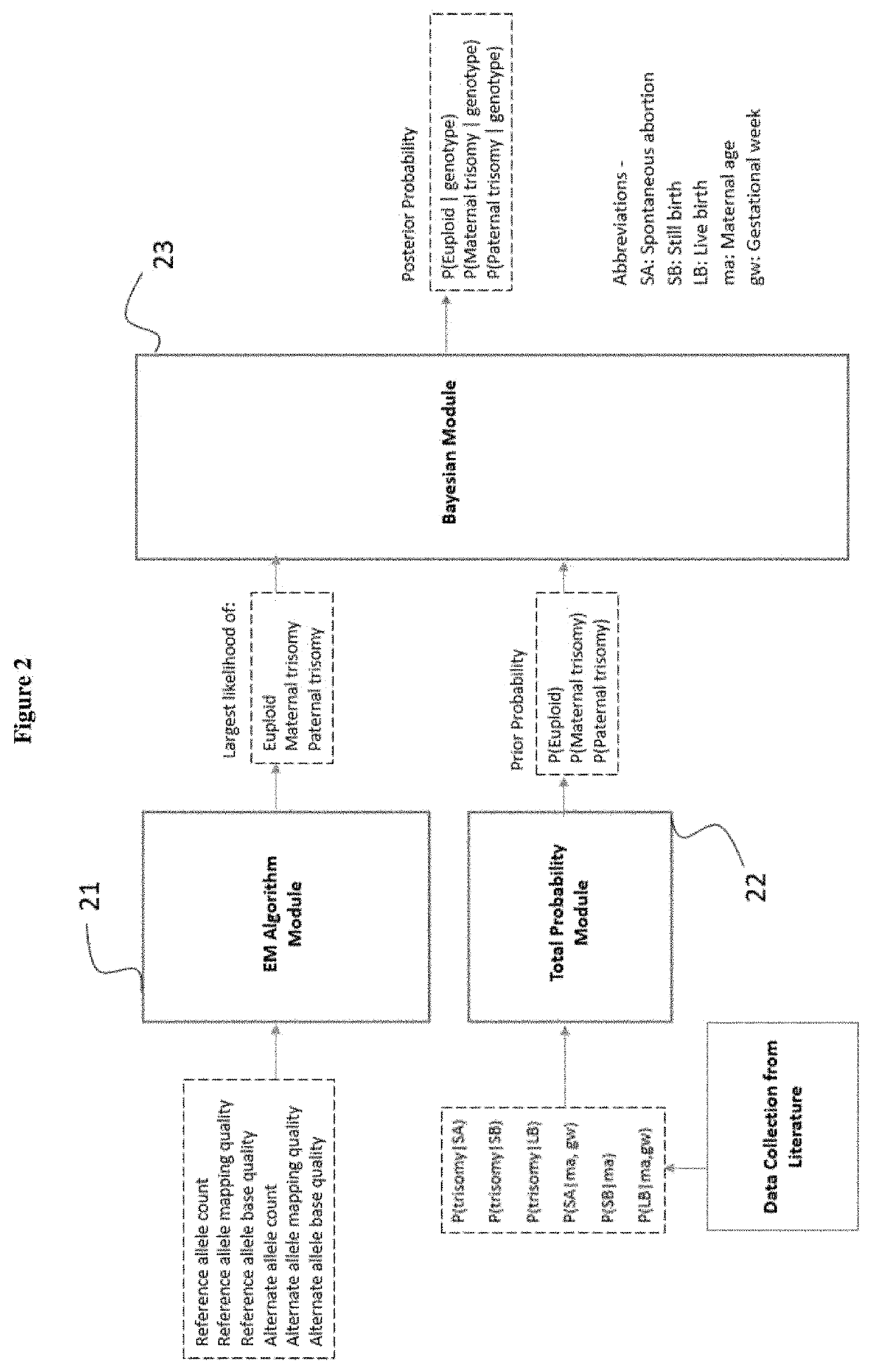
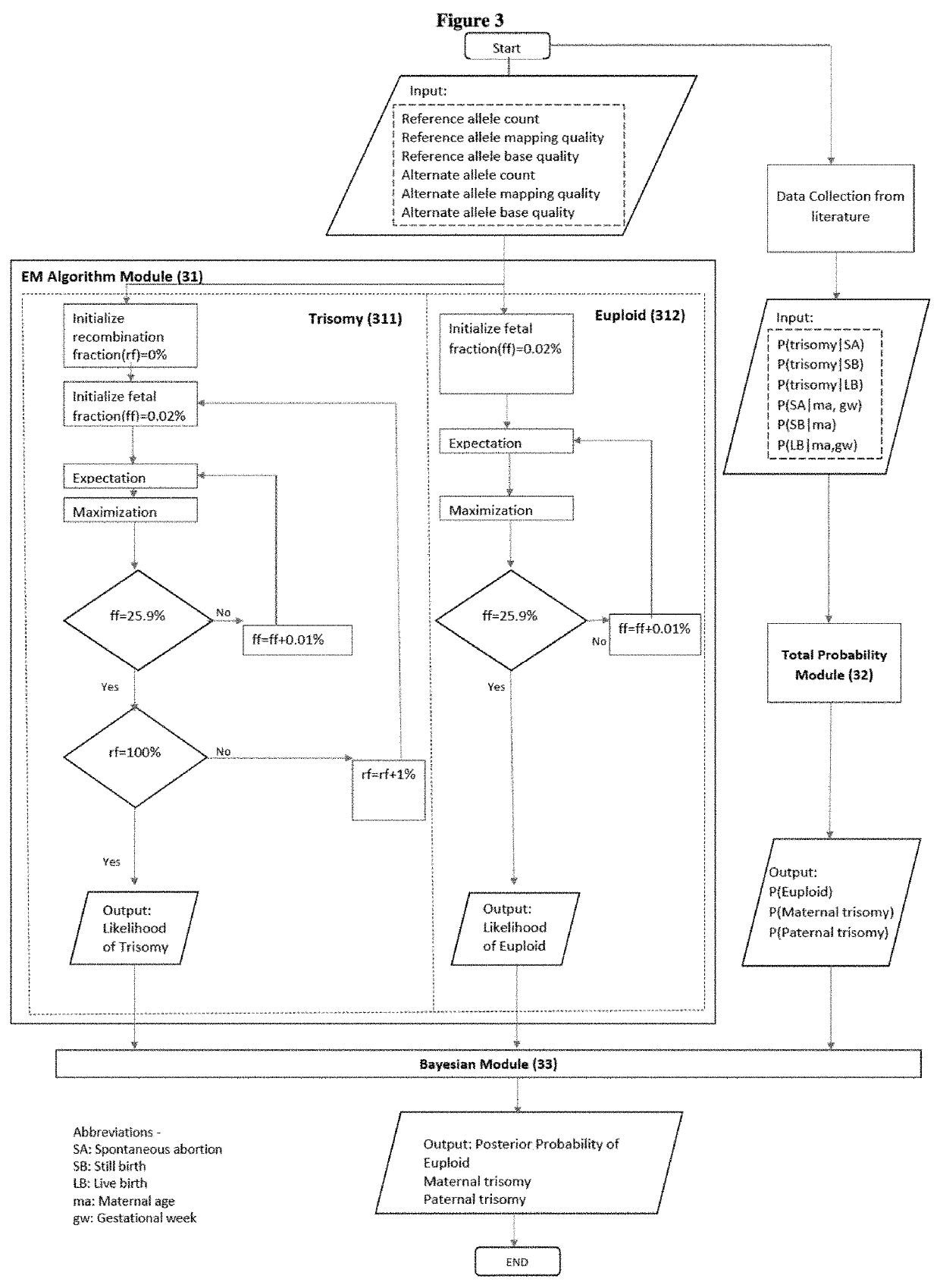
Simultaneous determination of aneuploidy and fetal fraction
InactiveUS20110224087A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal aneuploidyBiology
The invention provides compositions and methods for simultaneously determining the presence or absence of fetal aneuploidy and the relative amount of fetal nucleic acids in a sample obtained form a pregnant female. The method encompasses the use of sequencing technologies and exploits the occurrence of polymorphisms to provide a streamlined noninvasive process applicable to the practice of prenatal diagnostics.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
InactiveUS20100112575A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
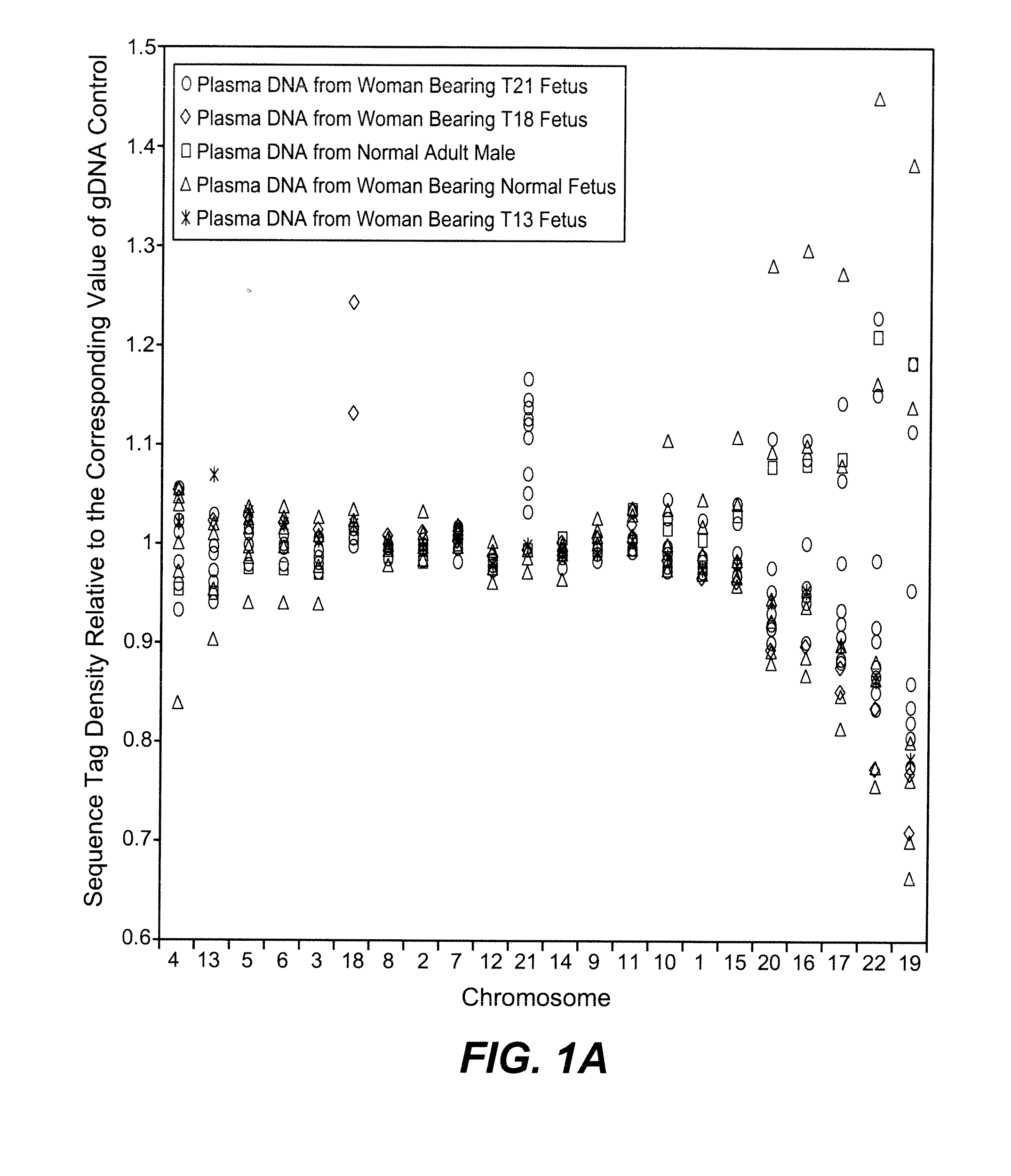
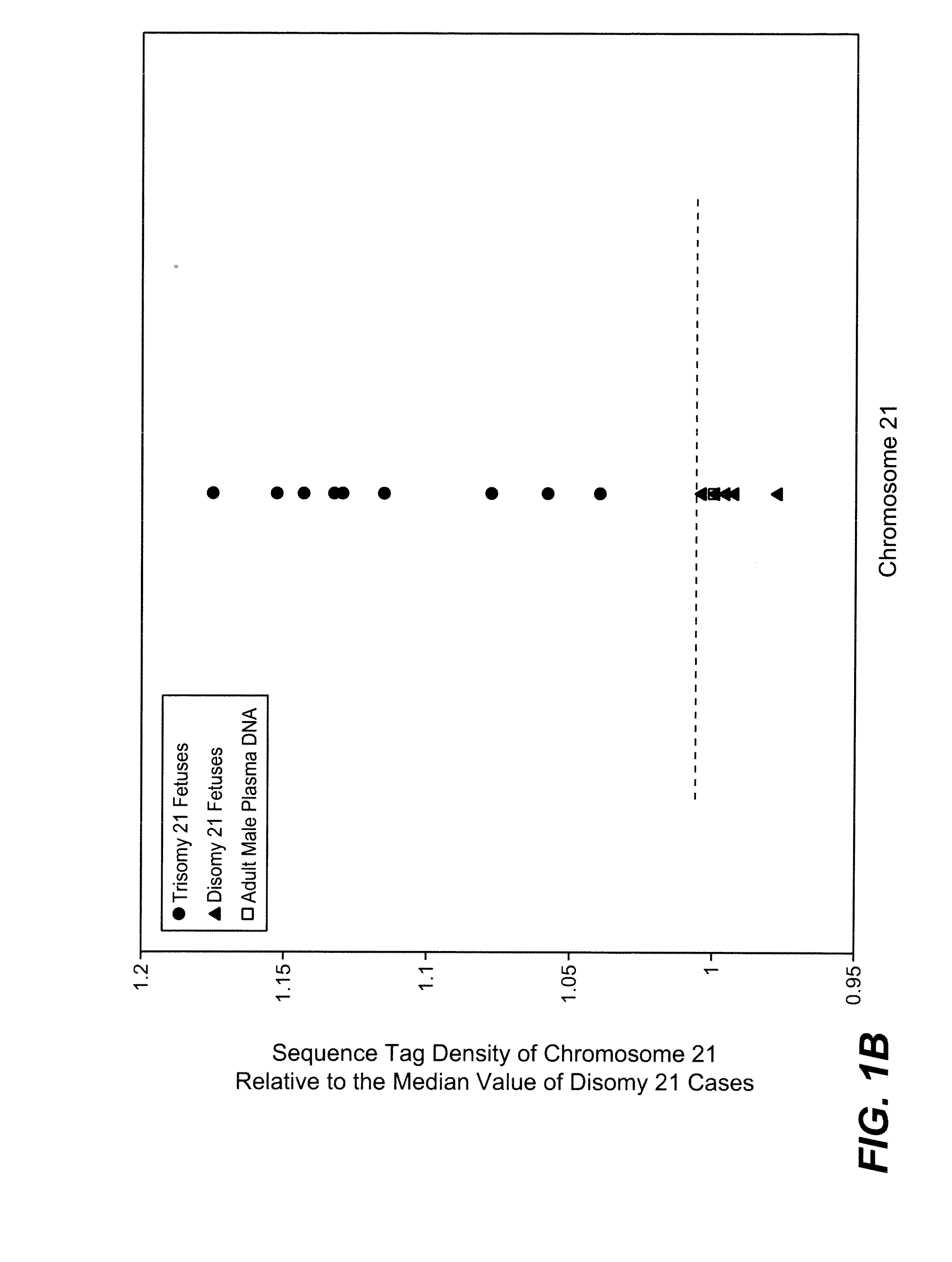
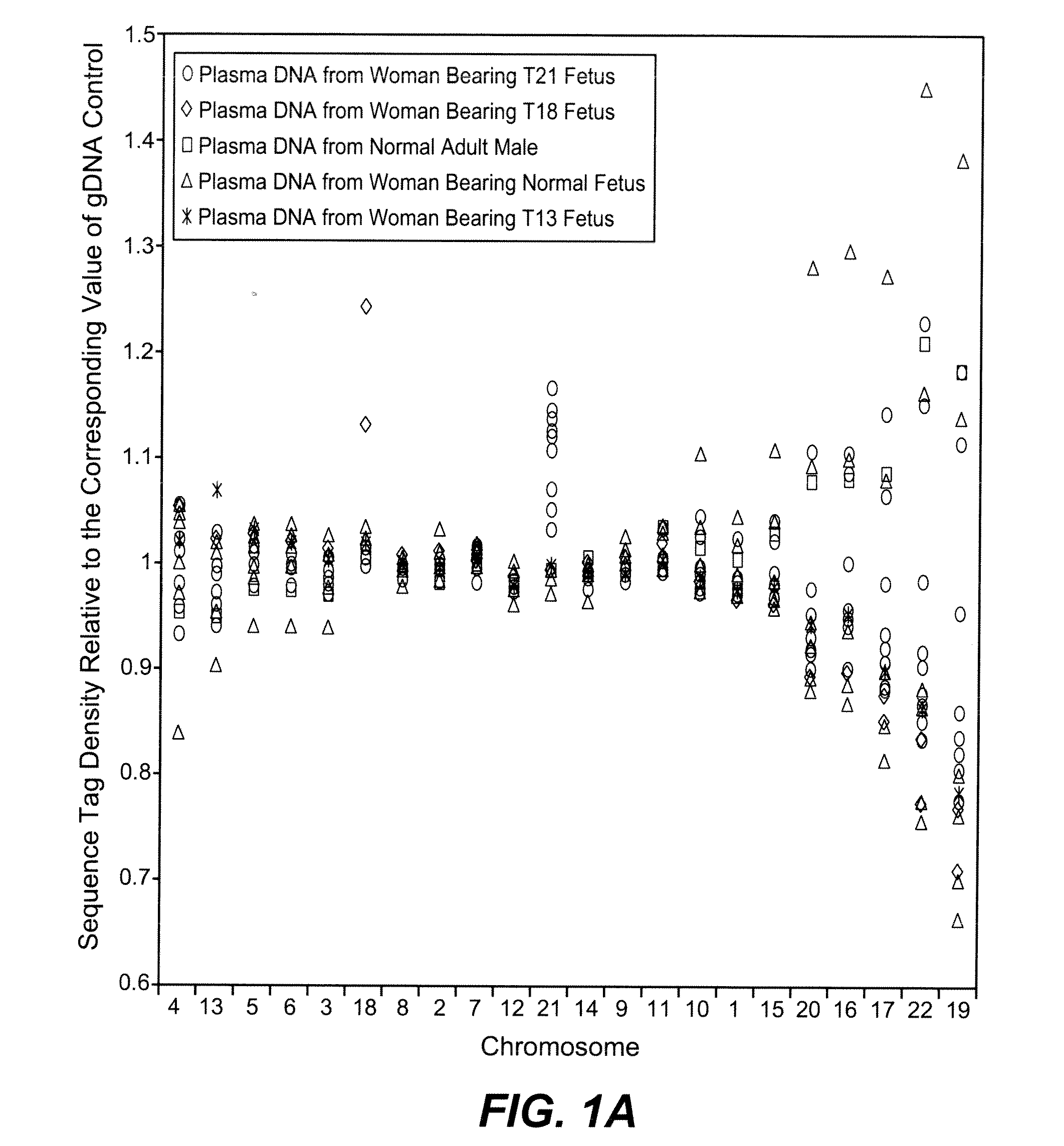
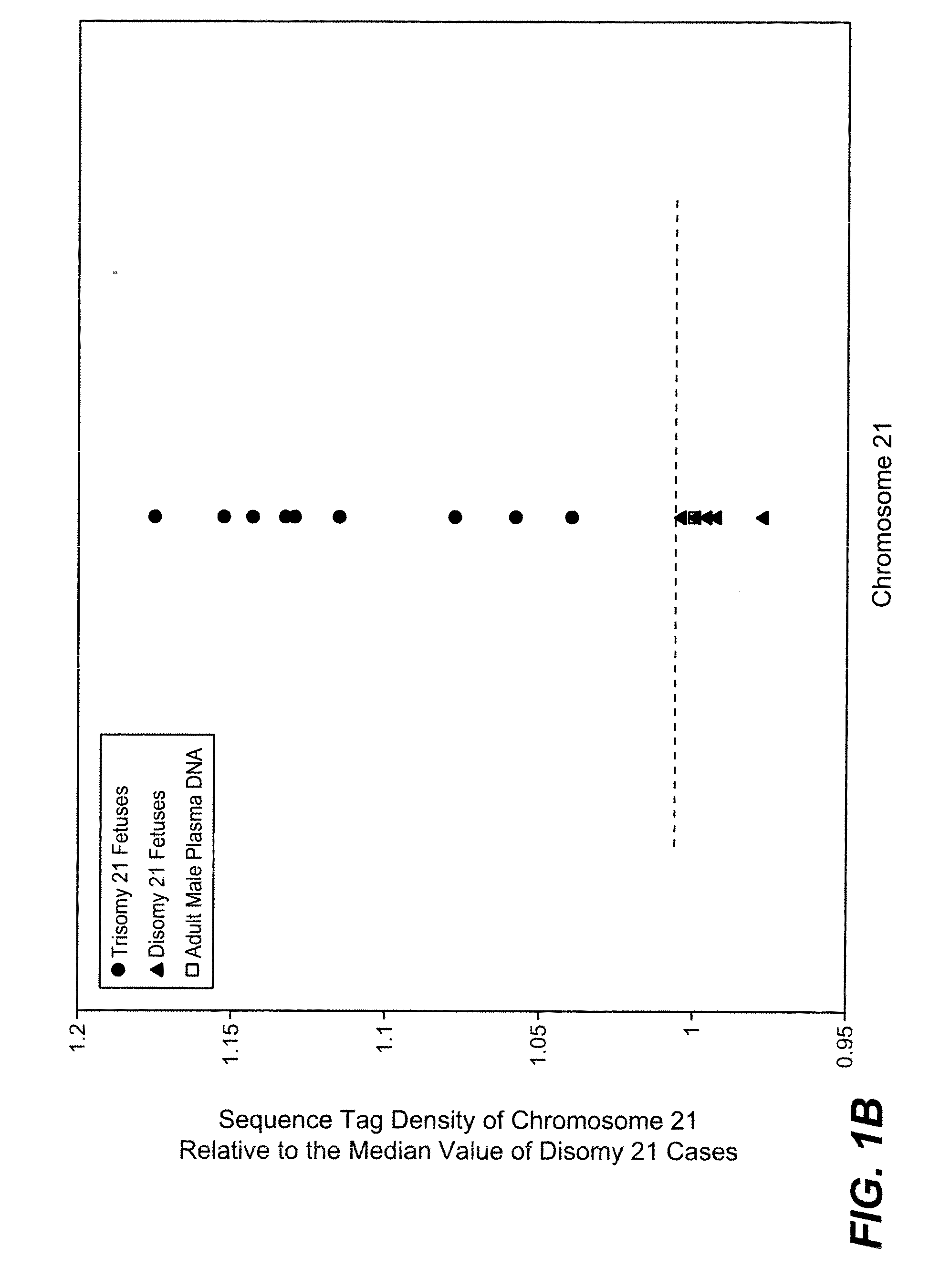
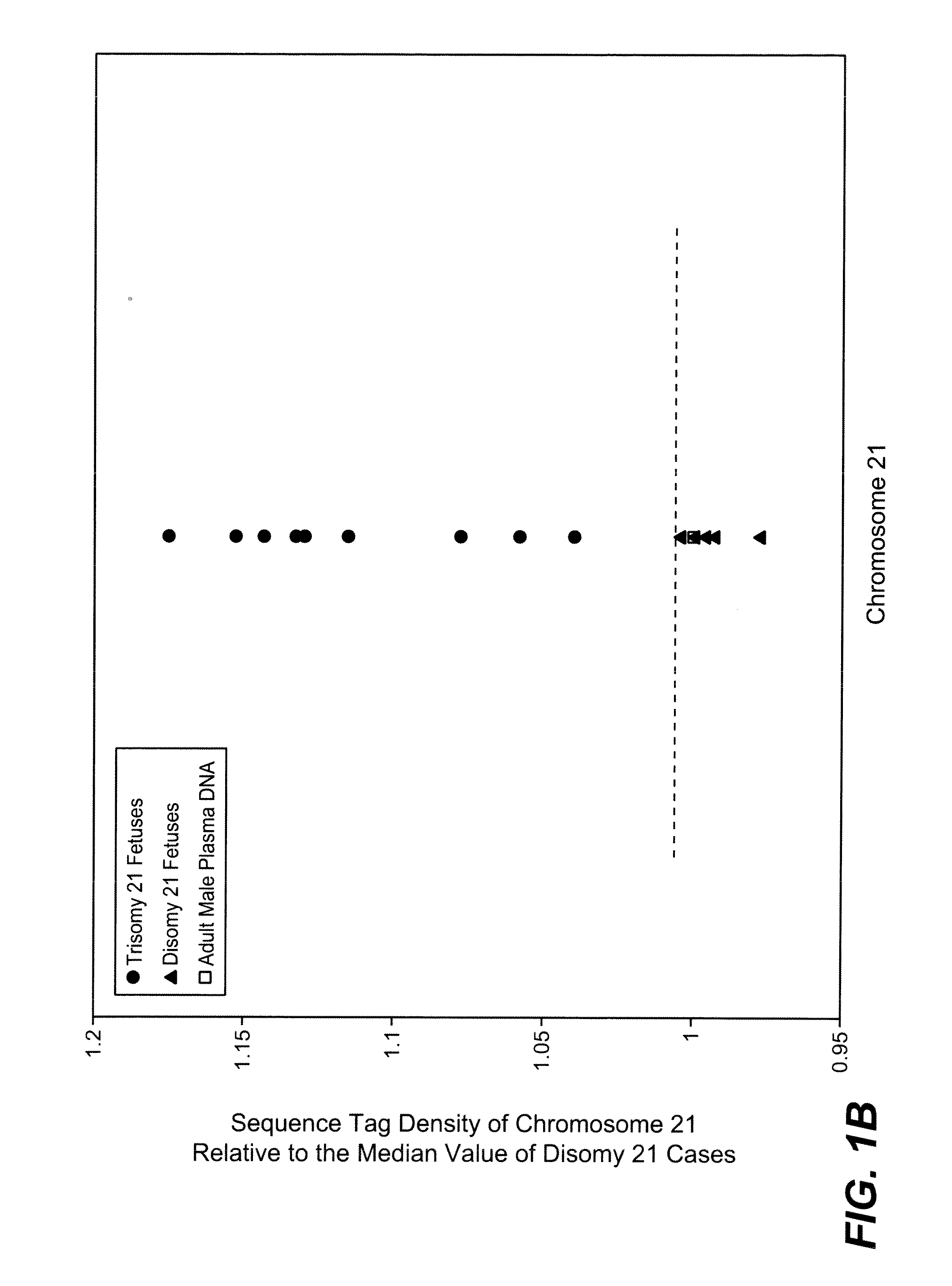
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20100138165A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Fetal aneuploidy detection by sequencing
InactiveUS20100291572A1Eliminate riskAnalysis time-consume and proneMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal aneuploidyBiology
Owner:ARTEMIS HEALTH INC
Screening for down syndrome
The present disclosure describes methods for screening and identifying genomic sequences useful in estimating the risk of fetal aneuploidy, particularly trisomy 21. This disclosure also describes methods for utilizing such genomic sequences alone or to augment existing non-invasive diagnostics for Trisomy 21 and other aneuploidies.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Direct Molecular Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy
ActiveUS20110151442A1Addressing slow performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific chromosomeFetal tissues
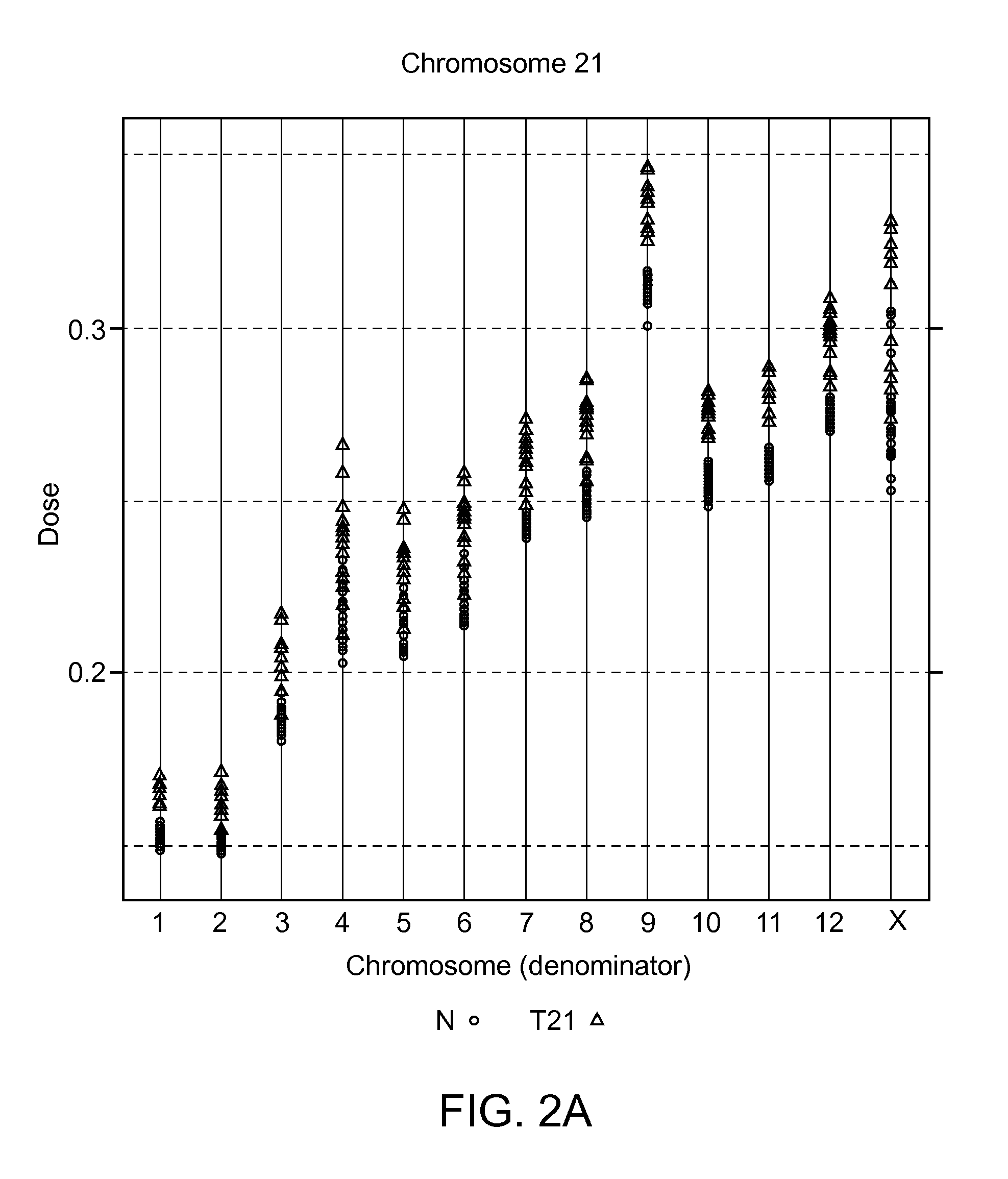
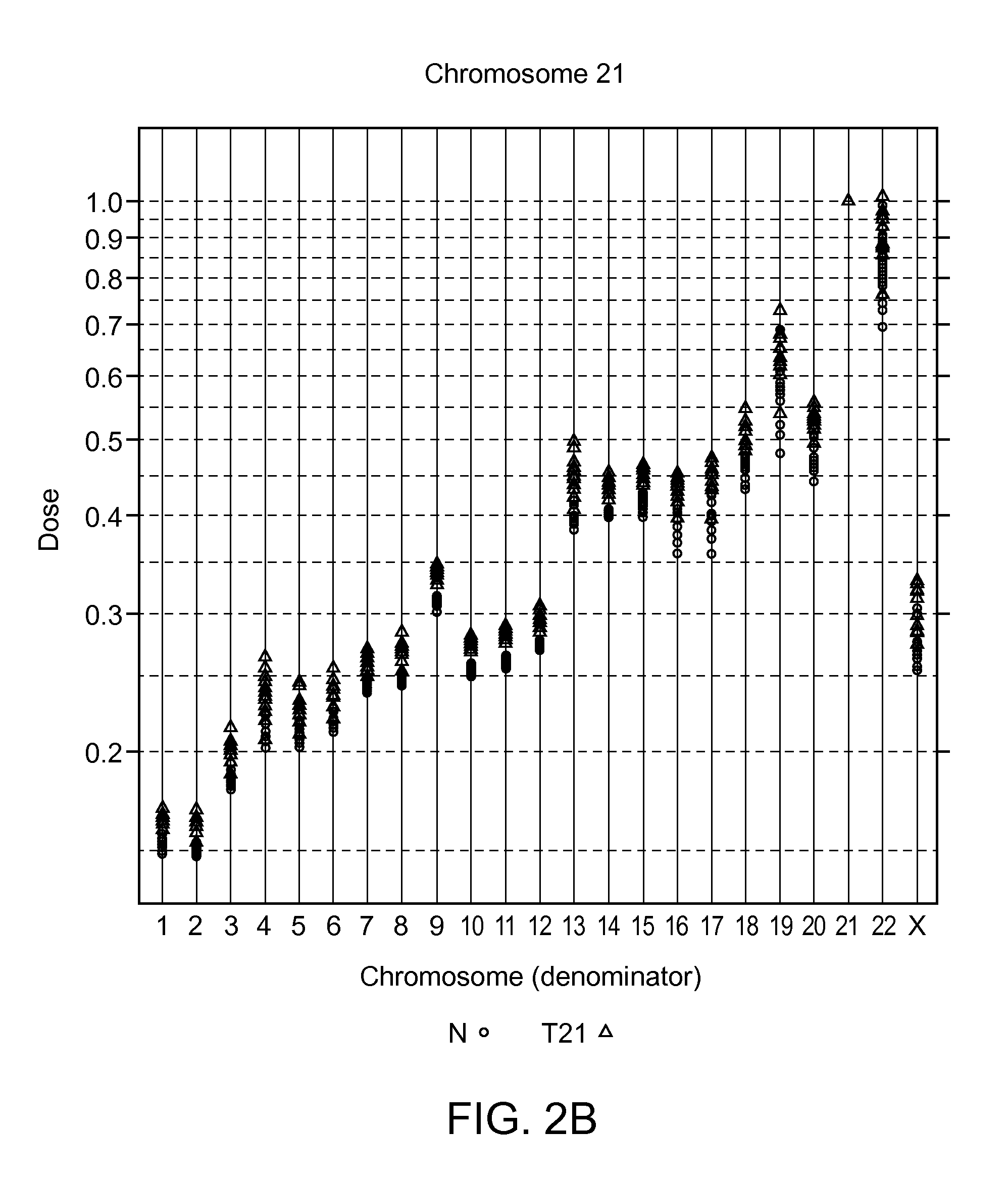
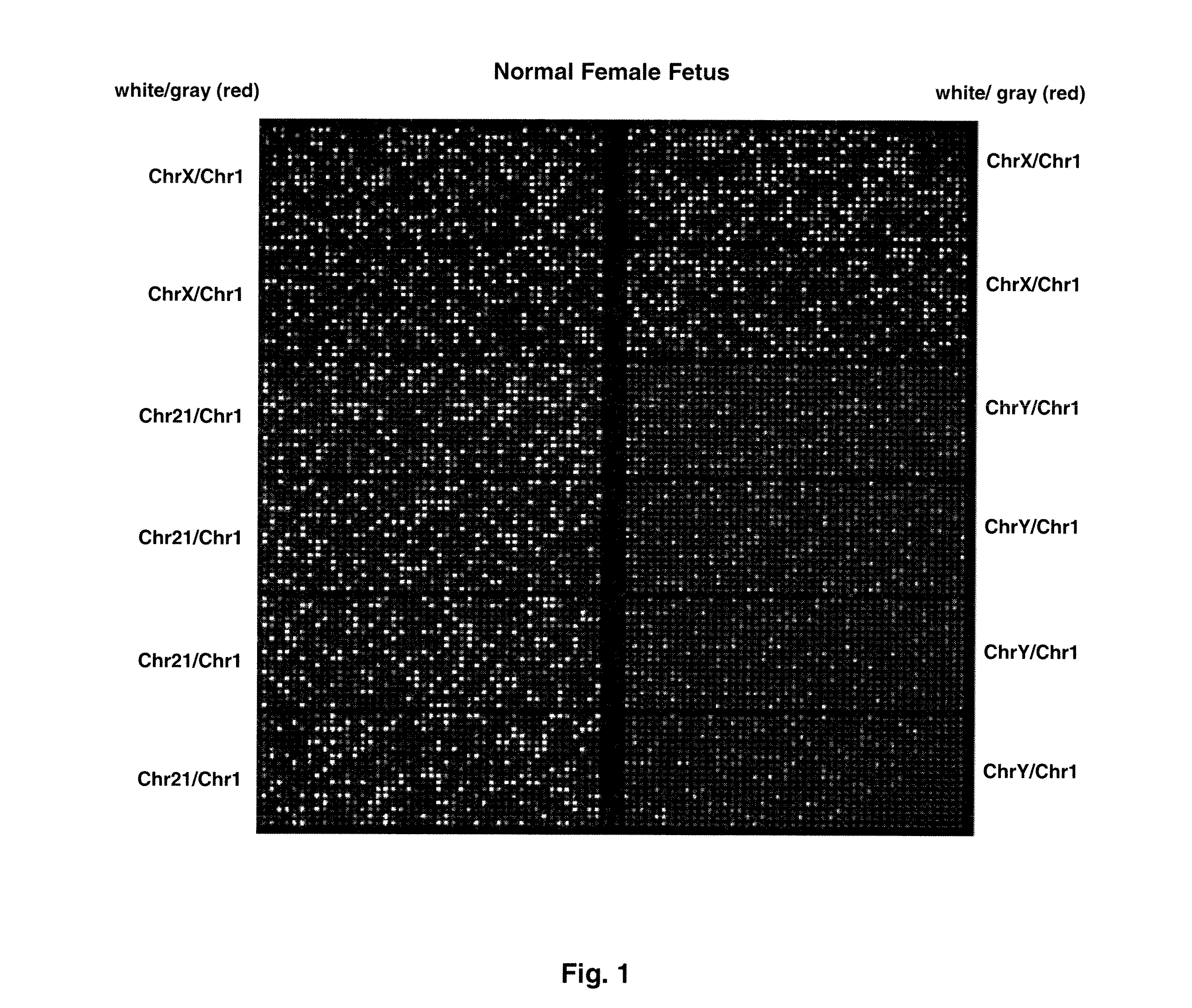
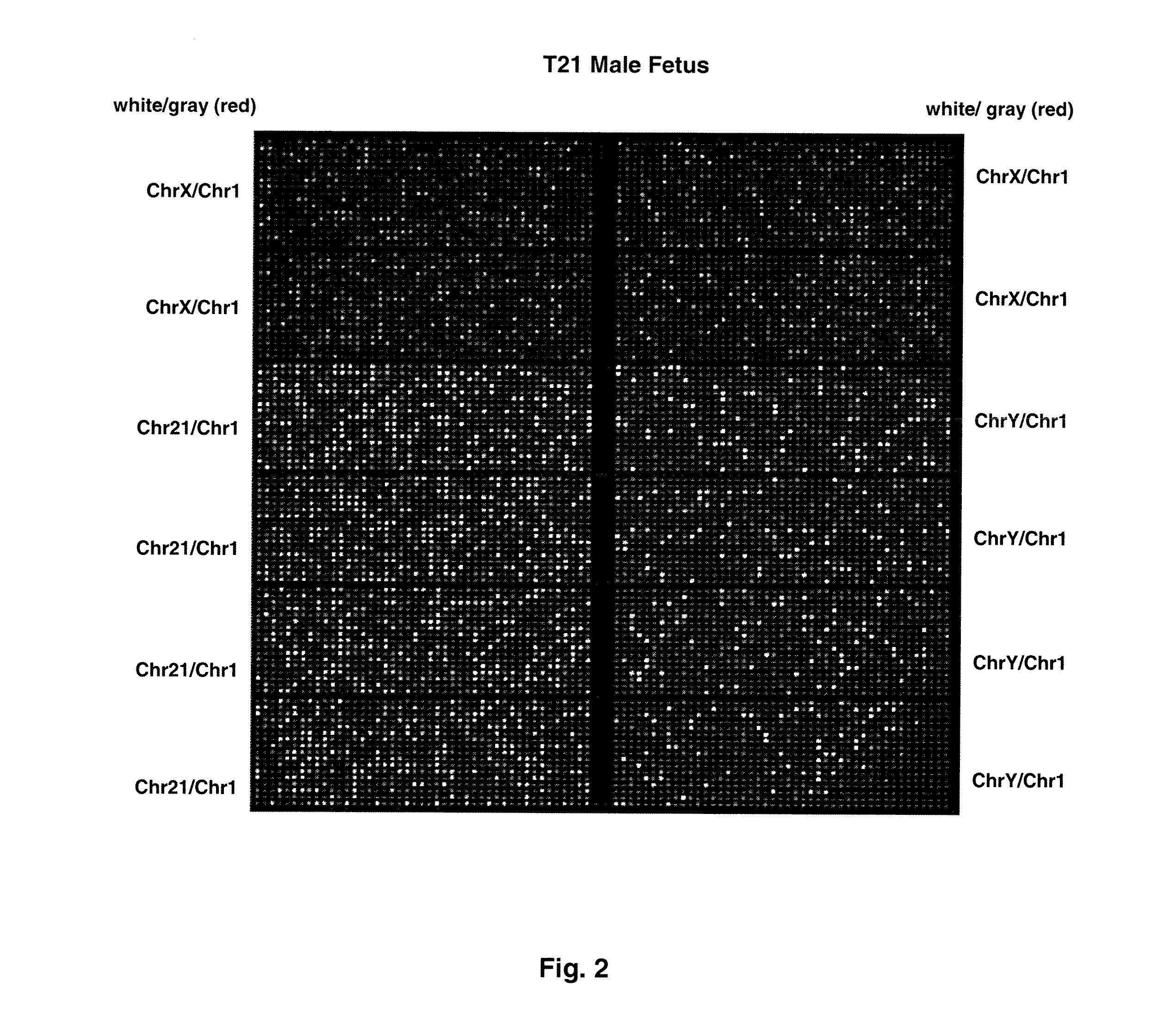
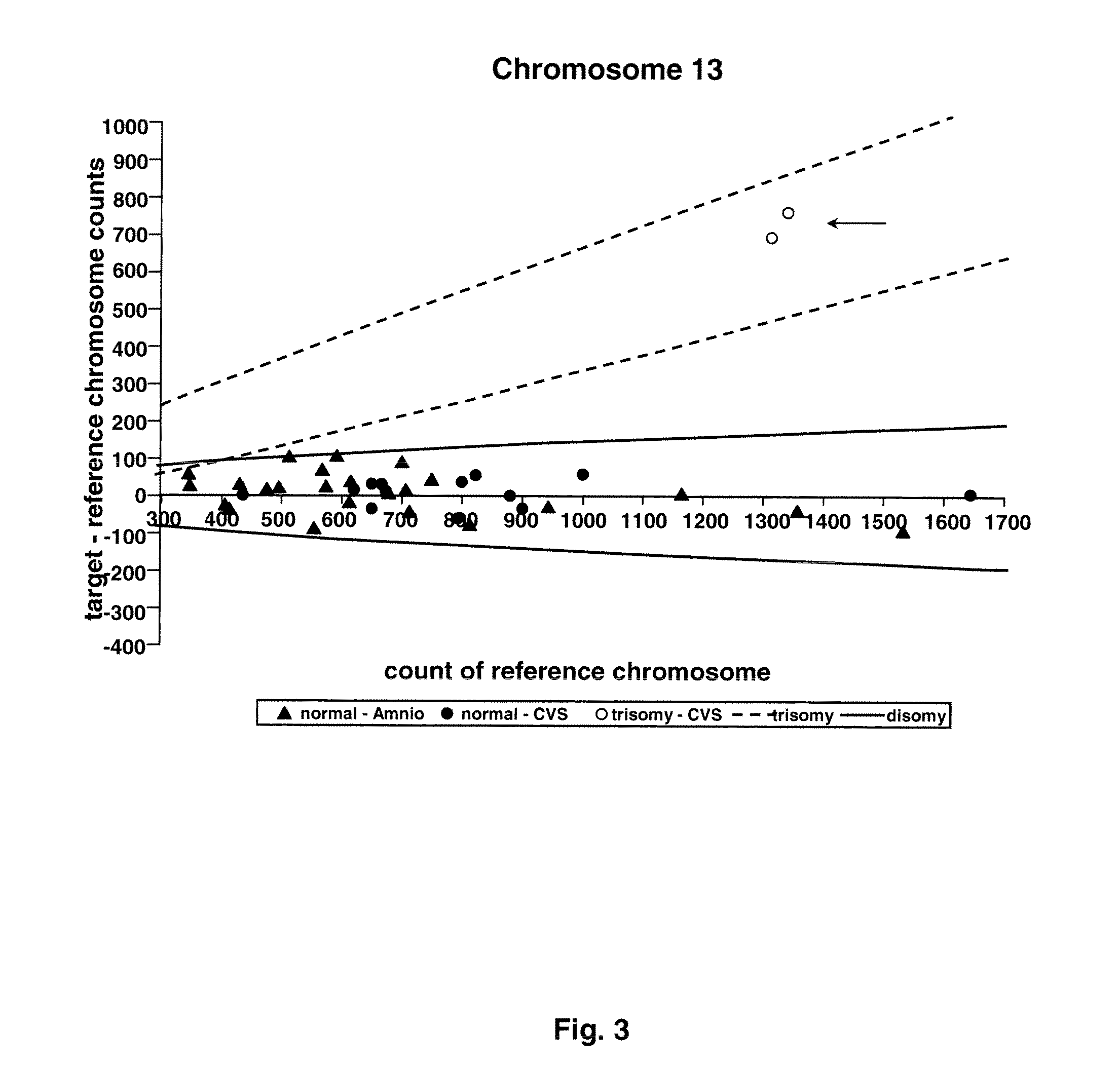
Methods and materials for detection of aneuploidy and other chromosomal abnormalities using fetal tissue are disclosed. Results can be obtained rapidly, without cell culture. The method uses digital PCR for amplification and detection of single target sequences, allowing an accurate count of a specific chromosome or chromosomal region. Specific polynucleic acid primers and probes are disclosed for chromosomes 1, 13, 18, 21, X and Y. These polynucleic acid sequences are chosen to be essentially invariant between individuals, so the test is not dependent on sequence differences between fetus and mother.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
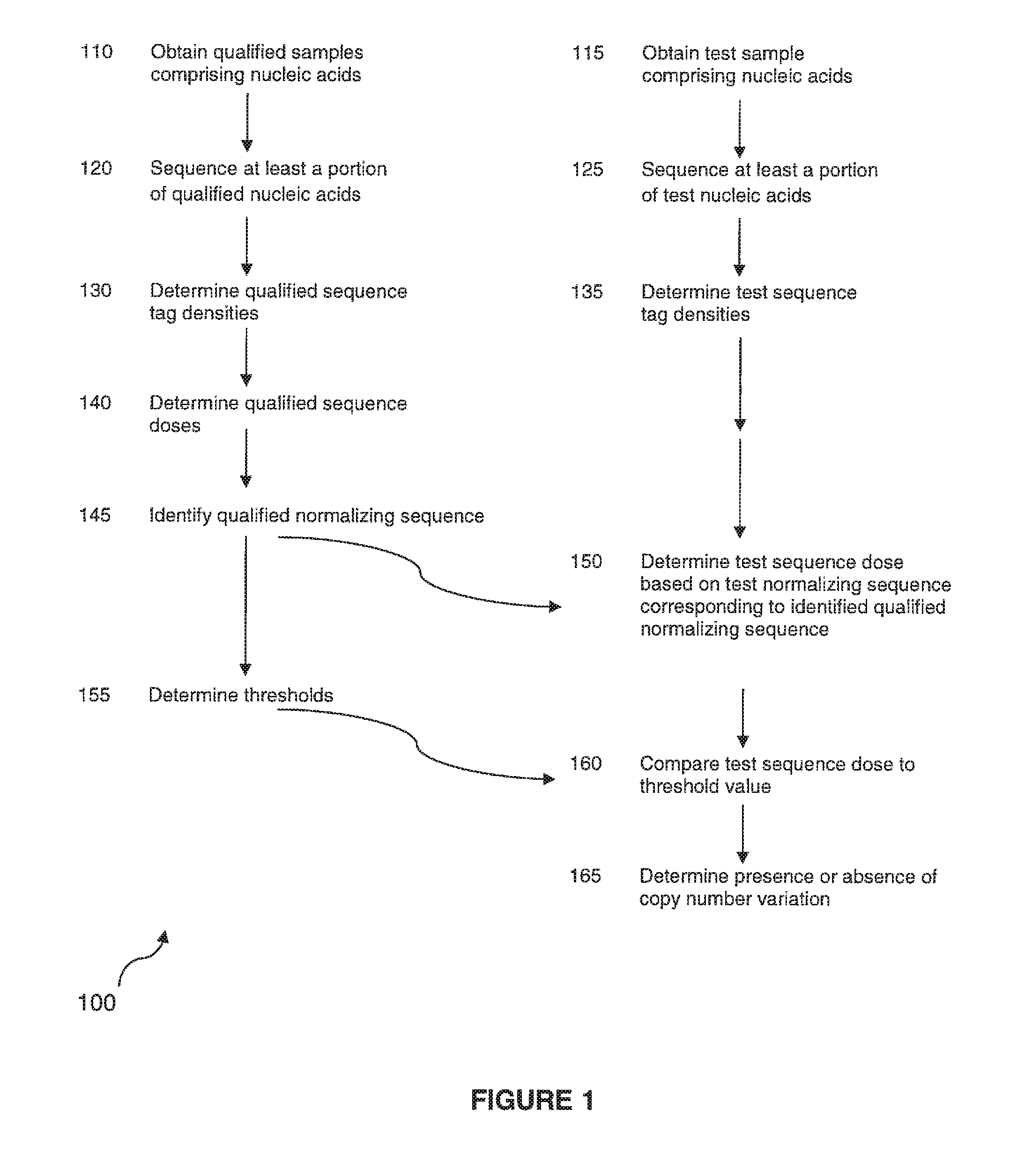
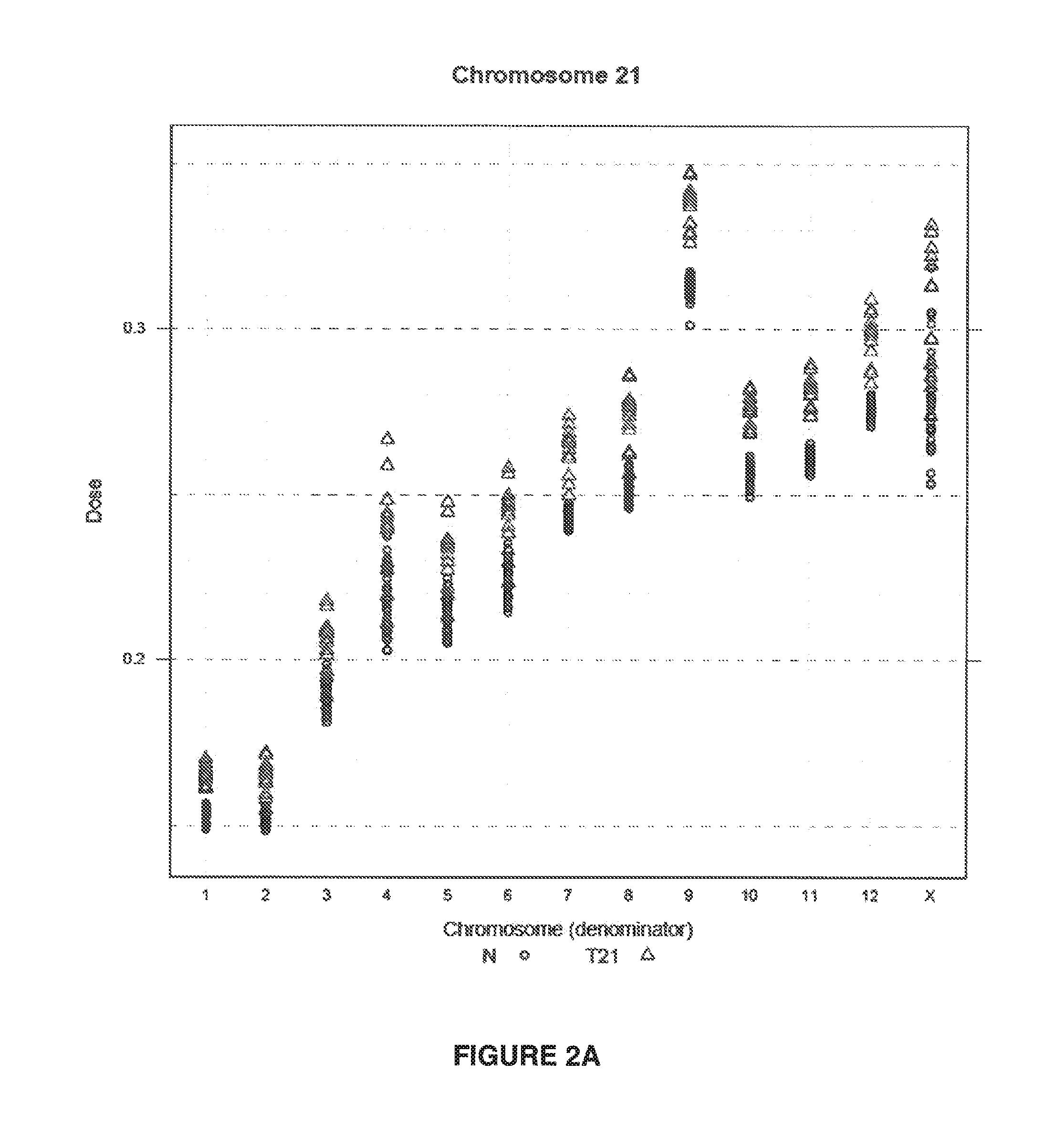
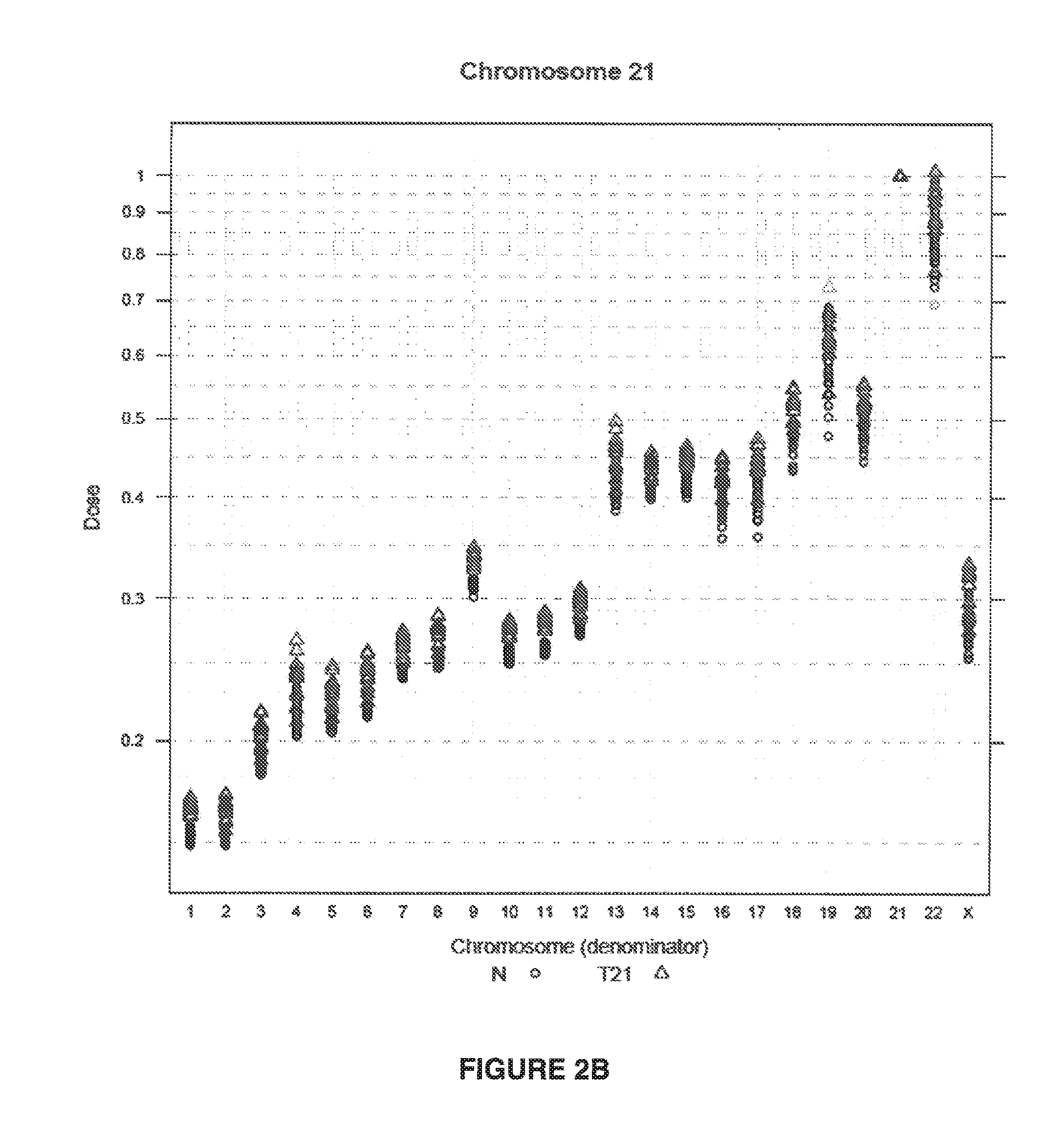
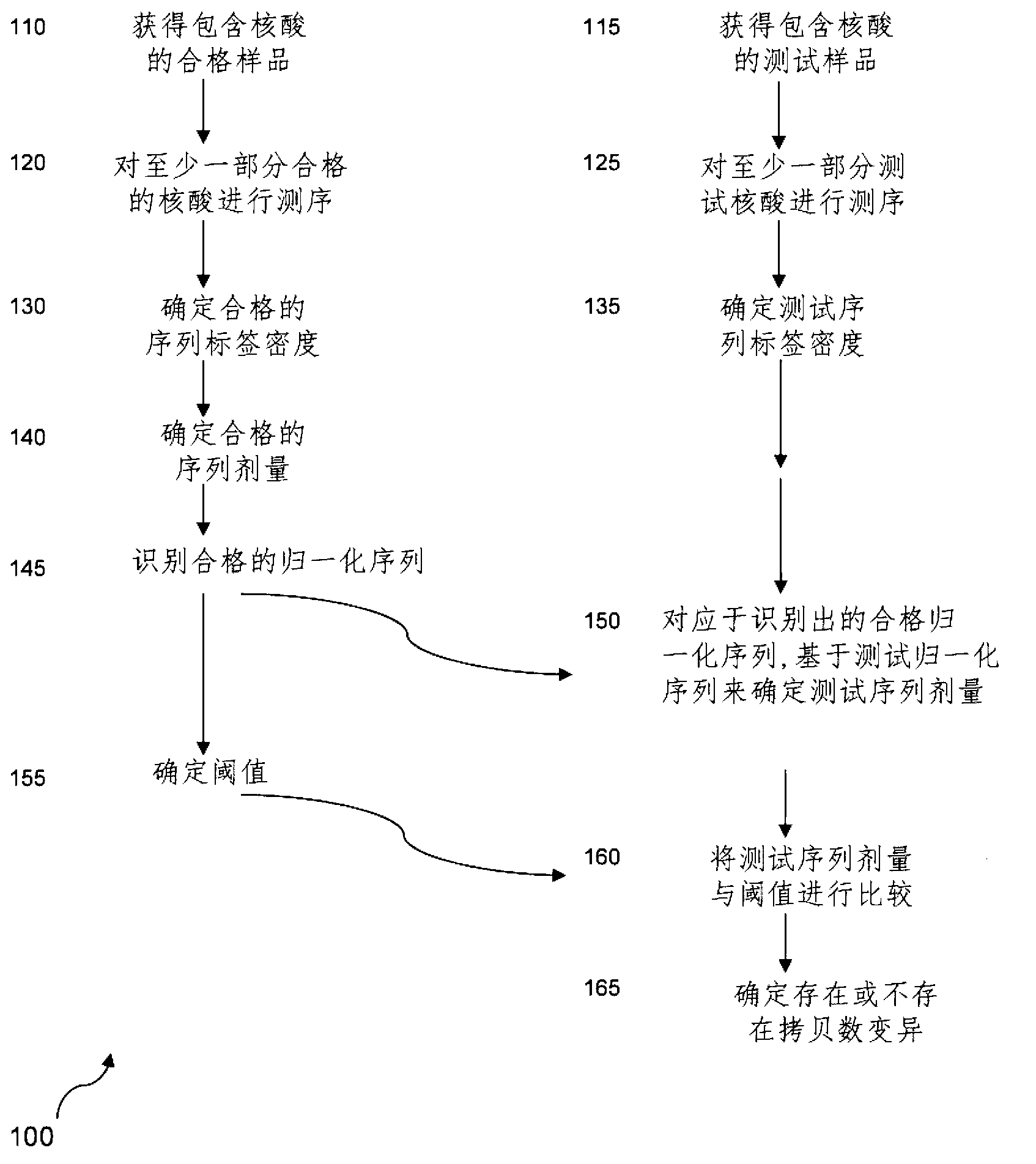
Method for determining copy number variations
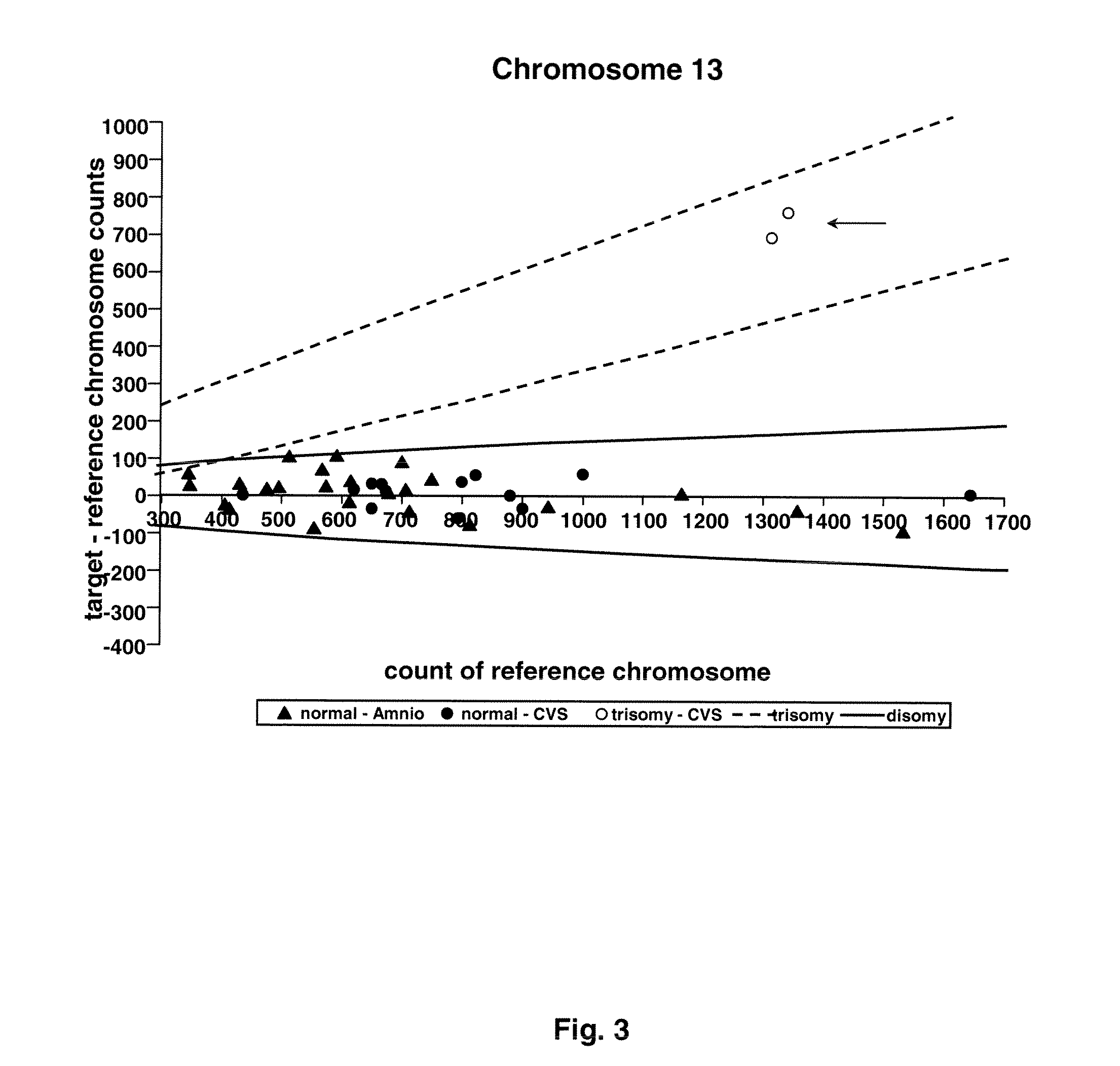
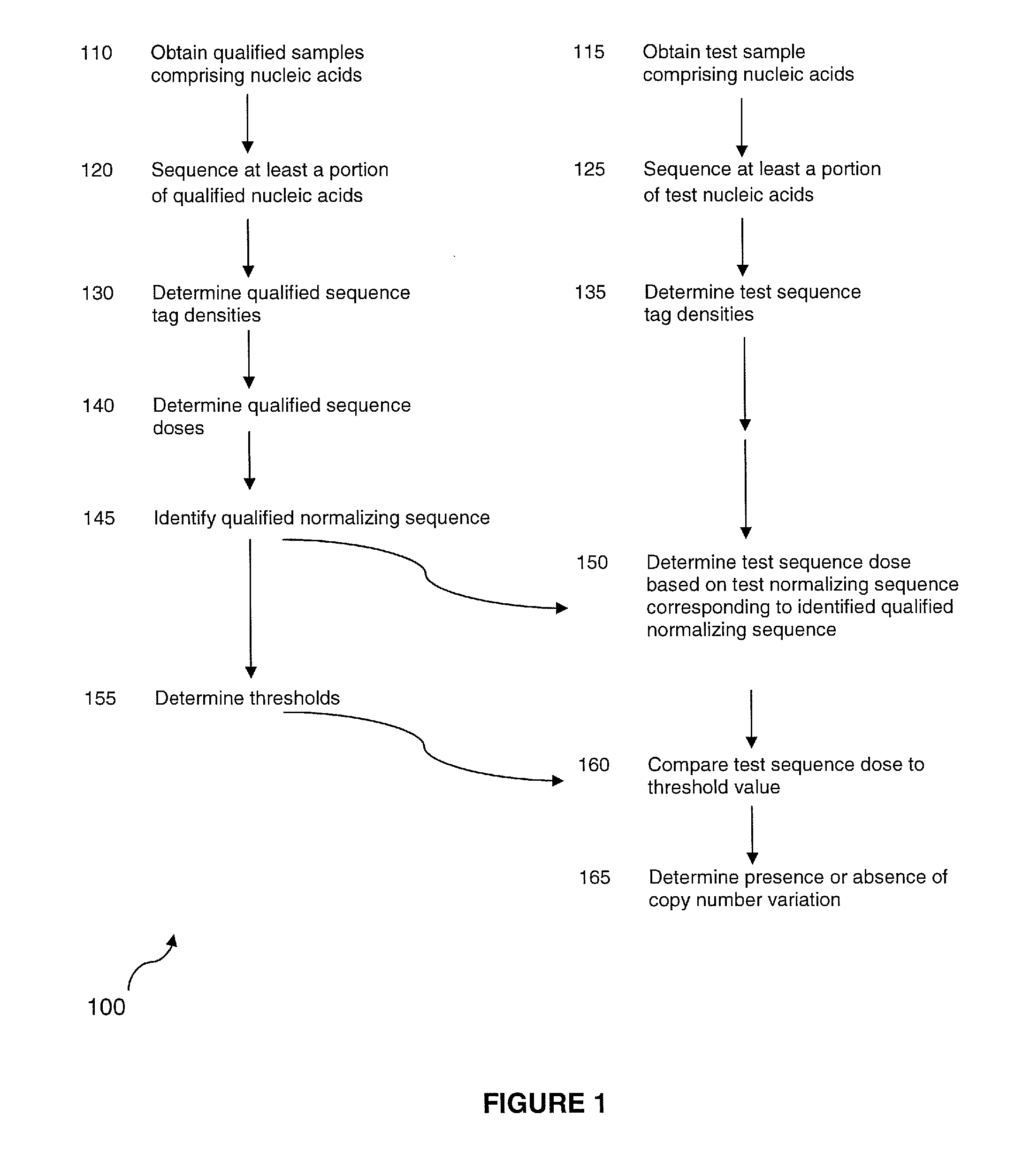
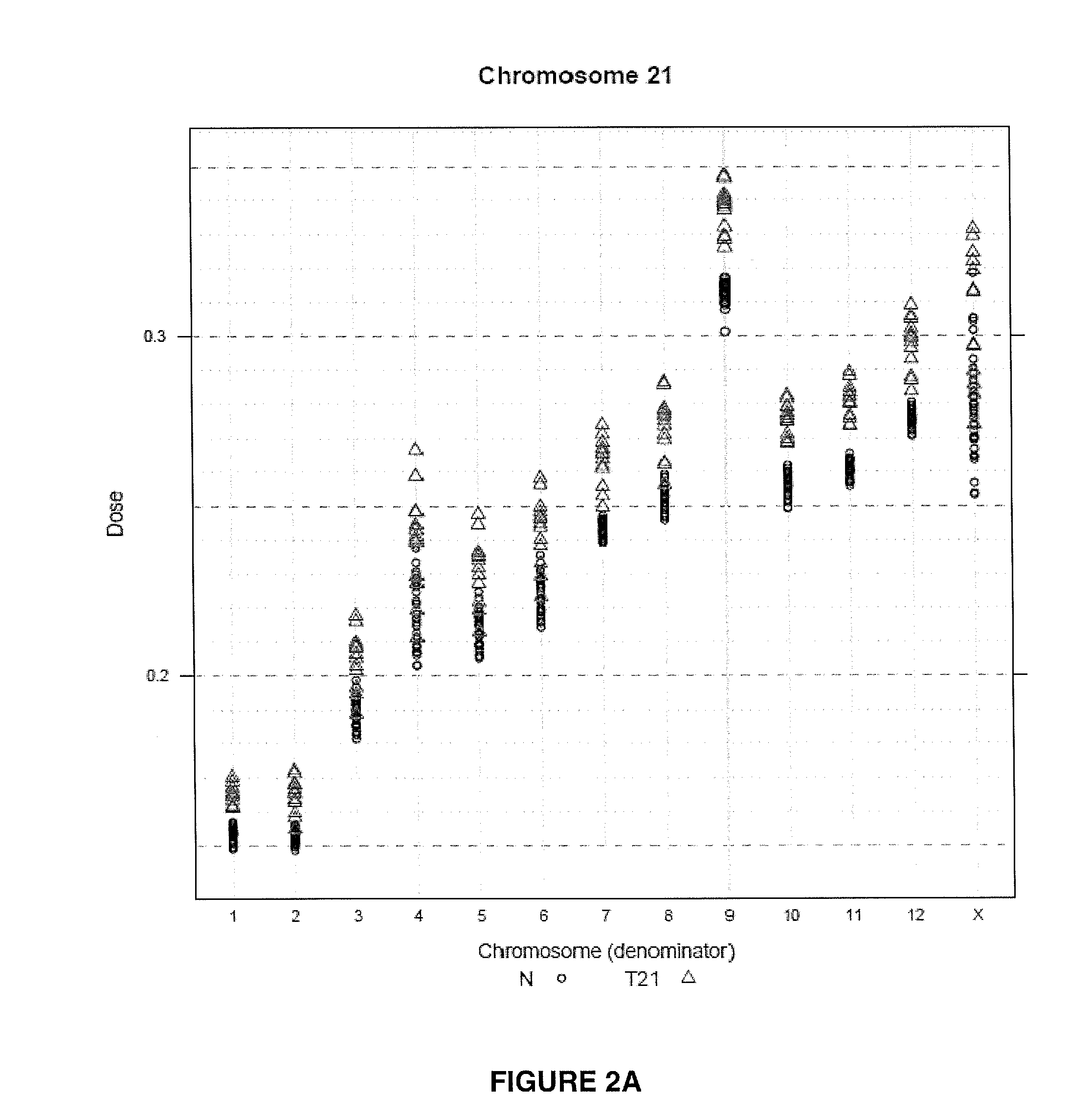
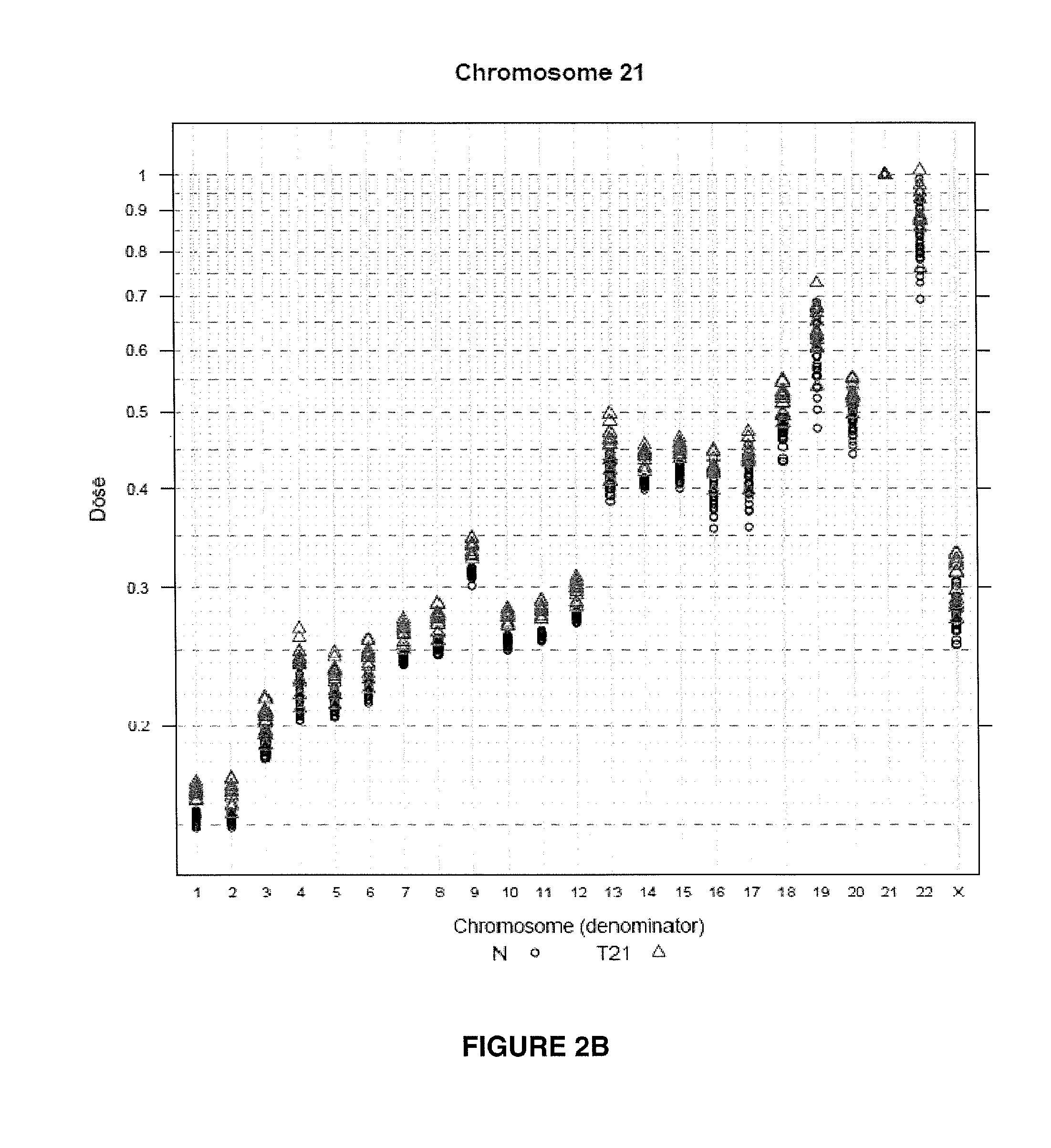
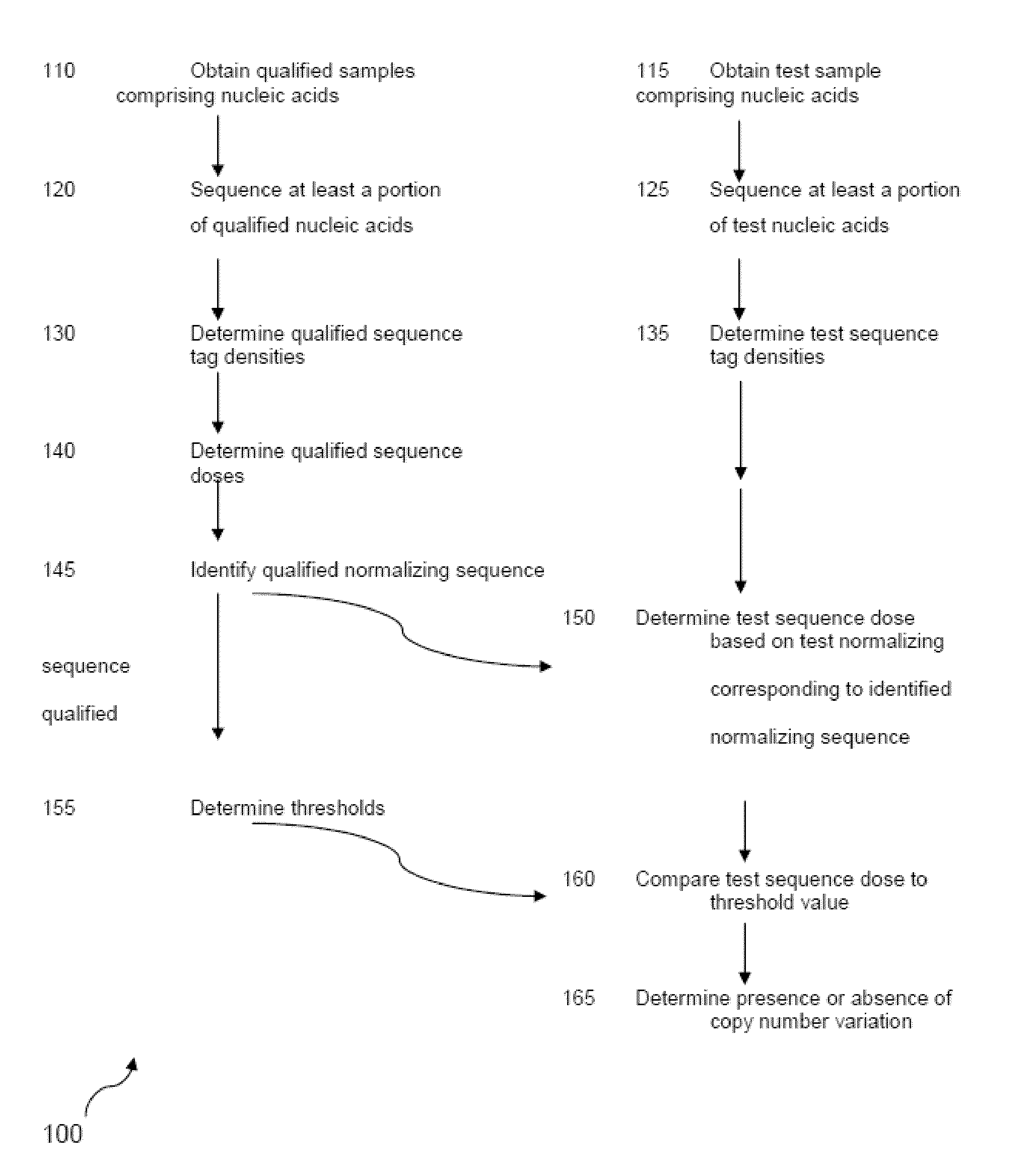
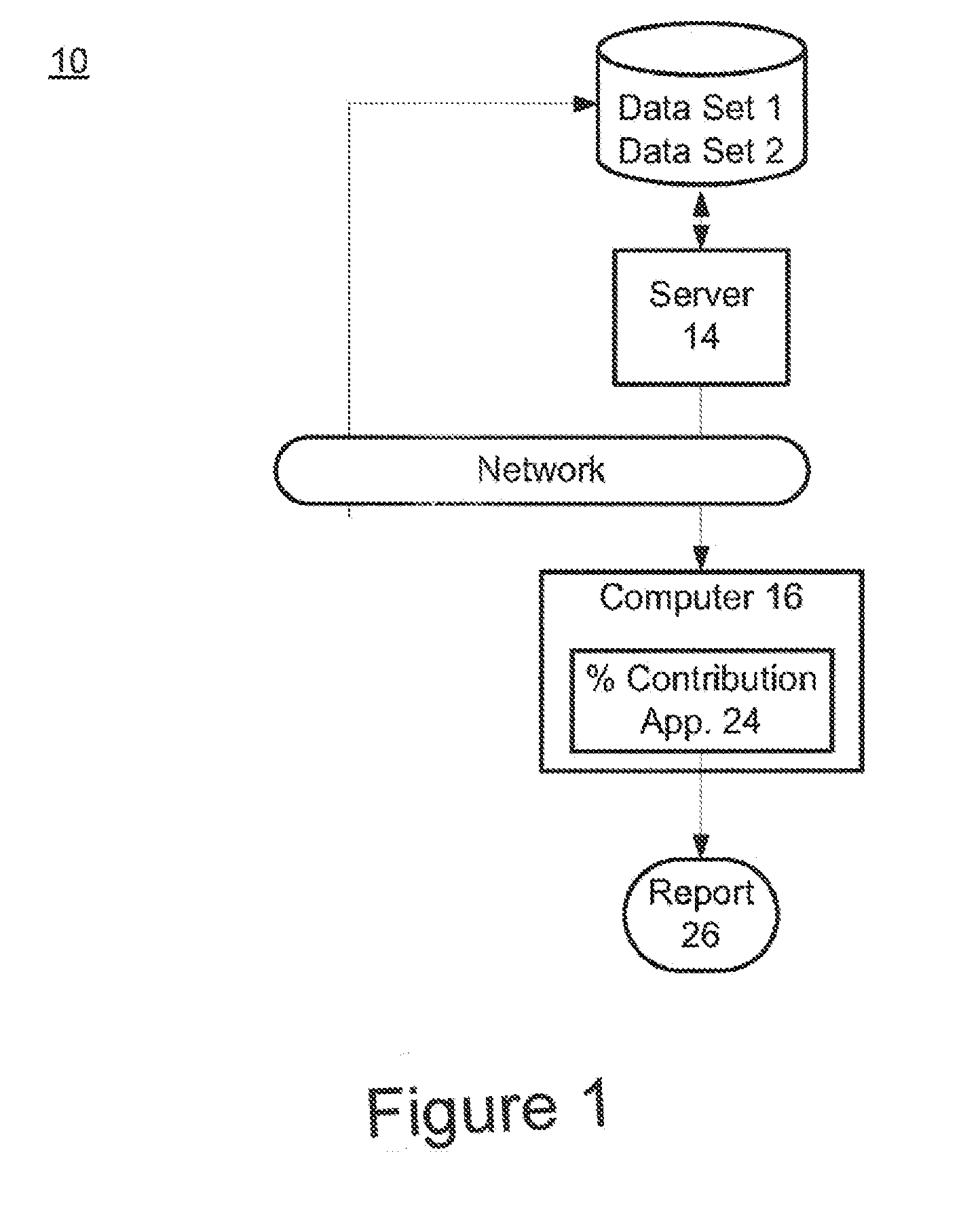
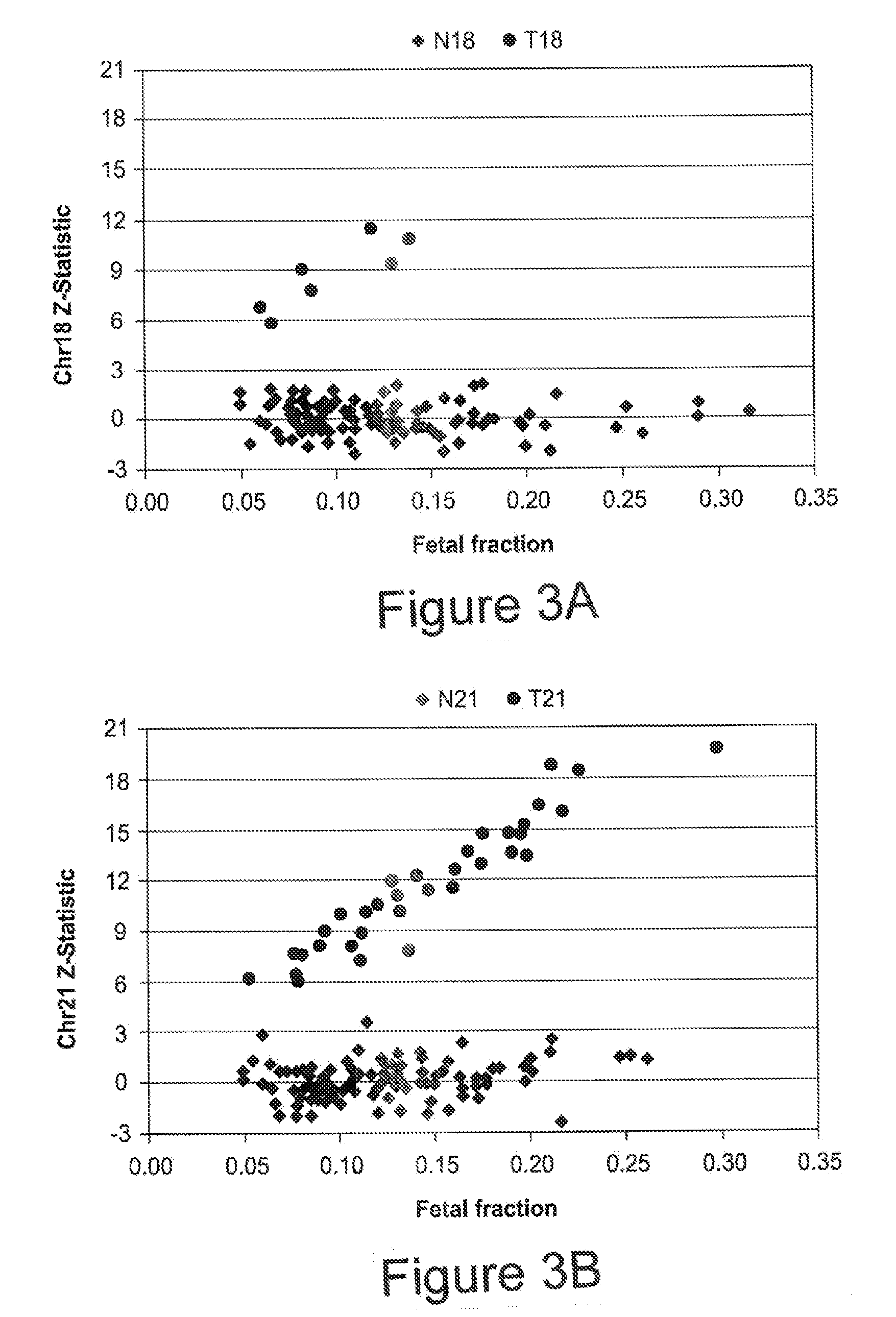
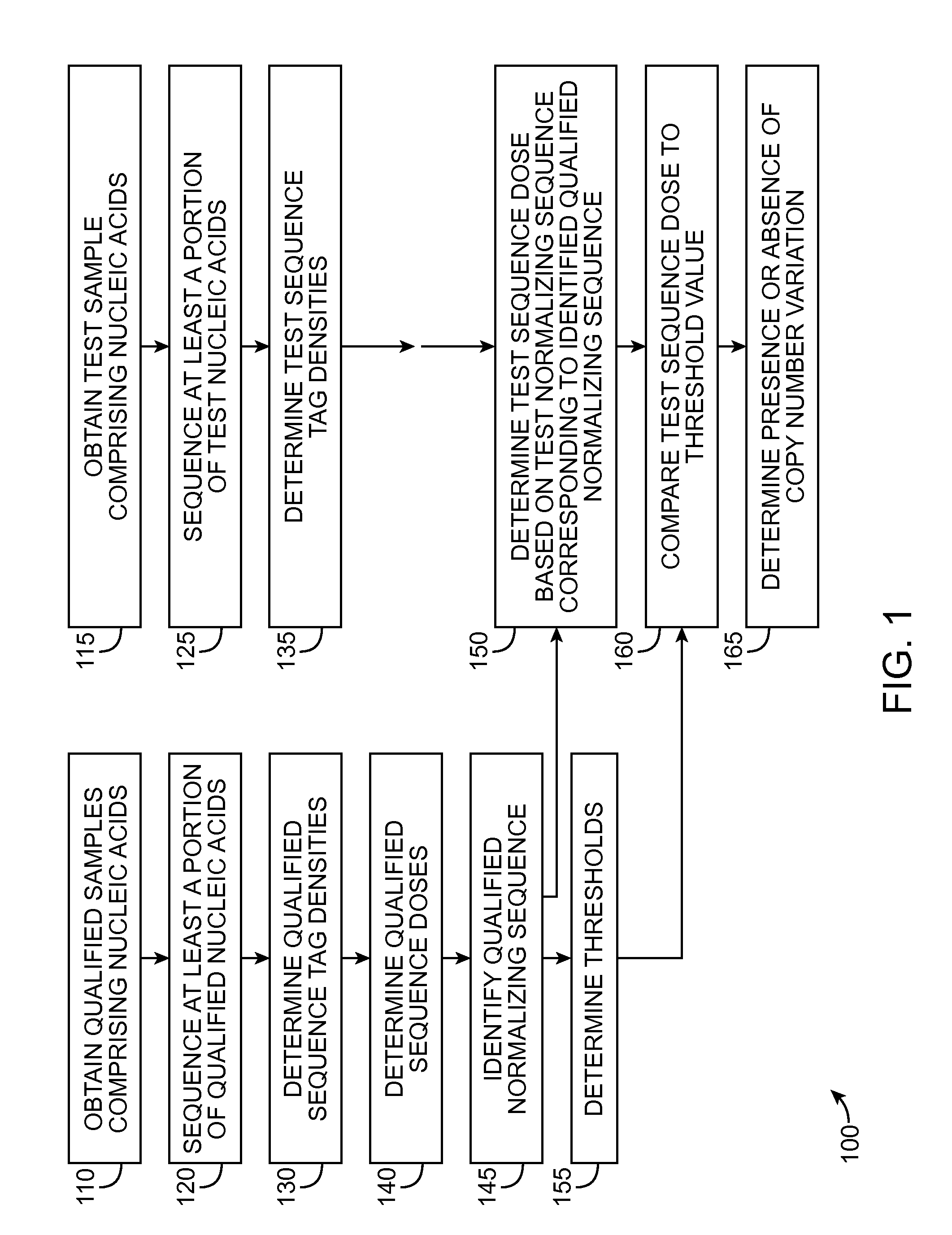
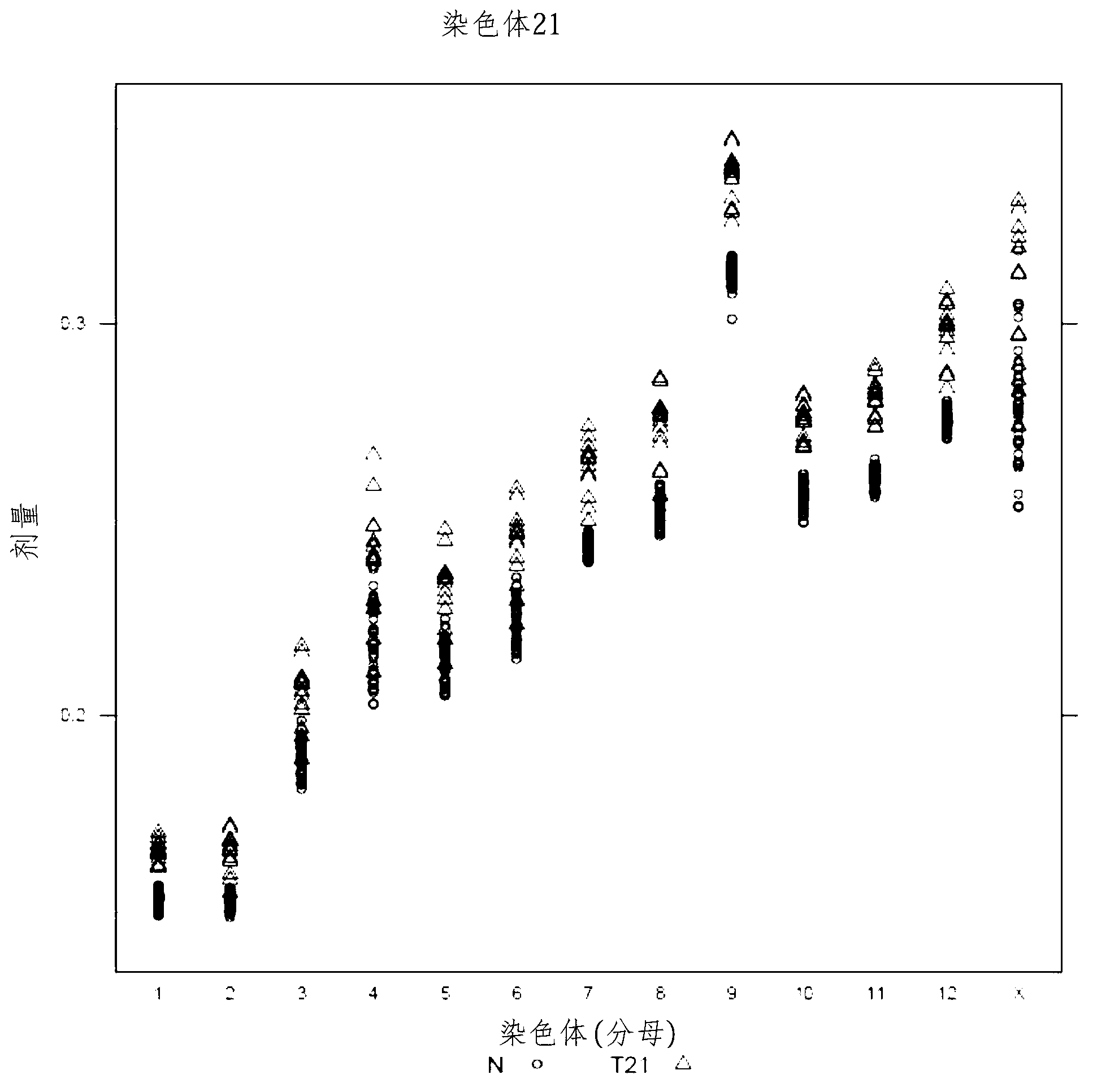
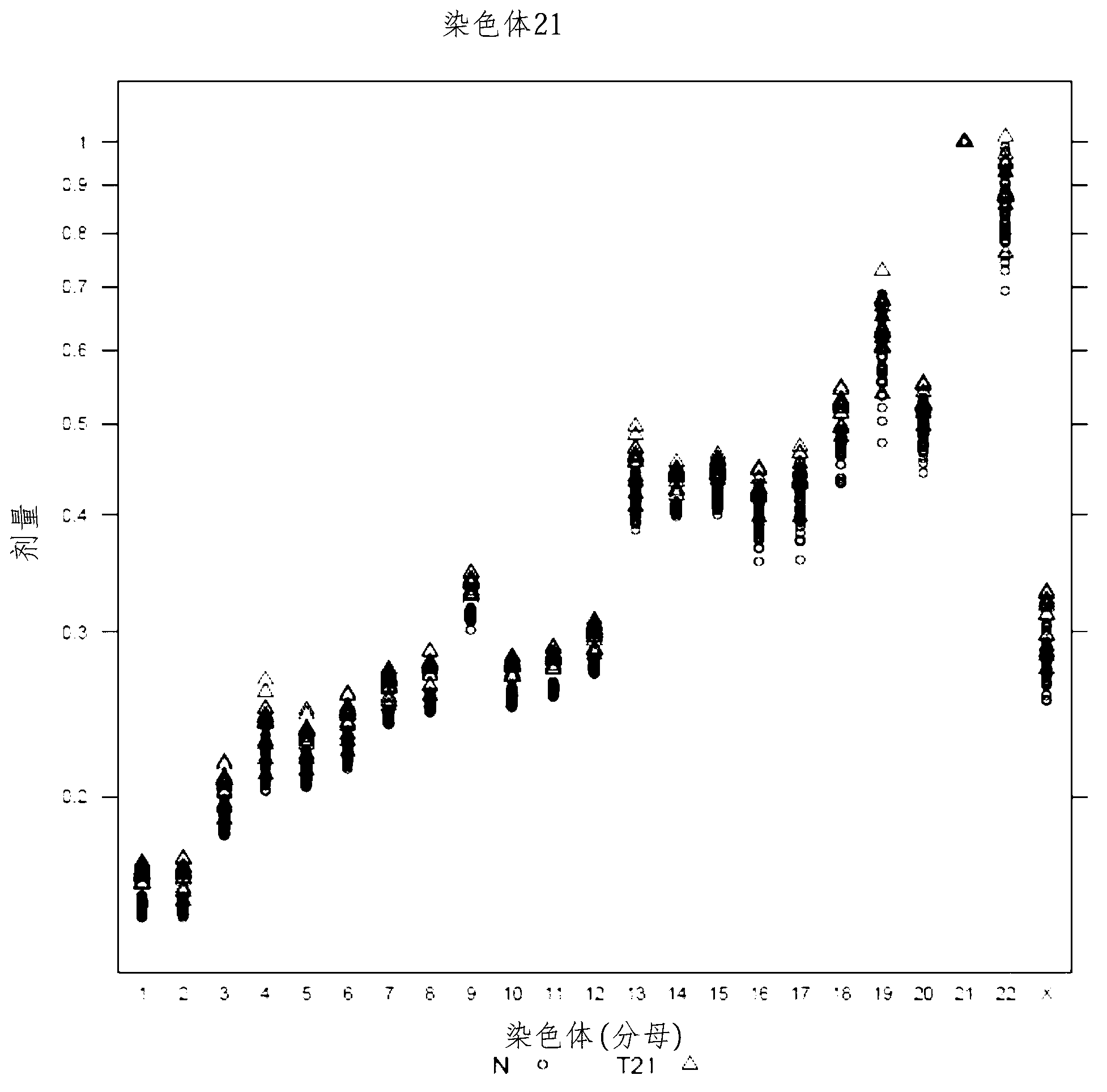
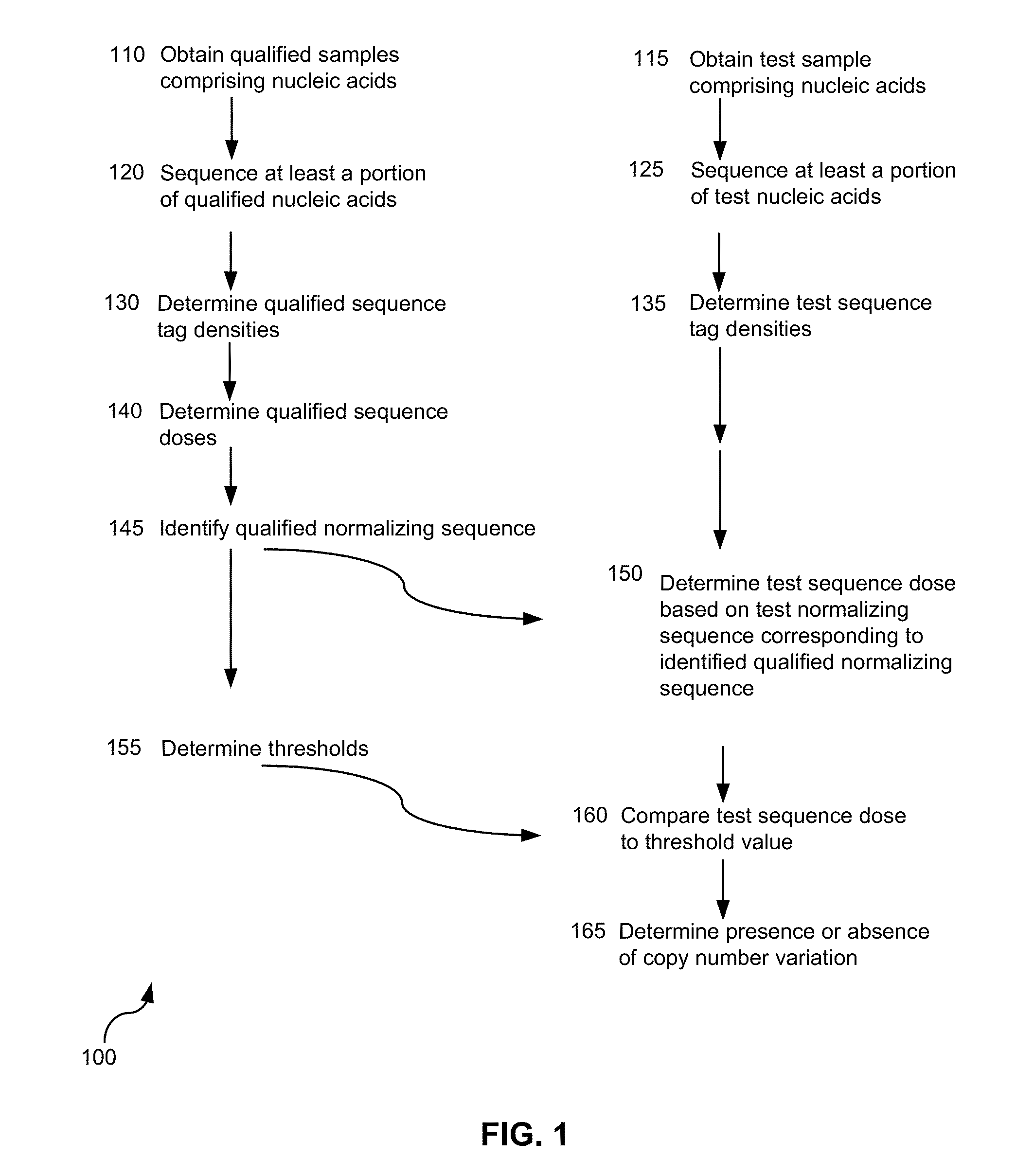
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the present method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample. Any aneuploidy can be determined from sequencing information that is obtained by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for fetal aneuploidies. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods of fetal abnormality detection
InactiveUS20110312503A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationFetal abnormalityFetal aneuploidy
Methods and kits for selectively enriching non-random polynucleotide sequences are provided. Methods and kits for generating libraries of sequences are provided. Methods of using selectively enriched non-random polynucleotide sequences for detection of fetal aneuploidy are provided.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20110246083A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Detecting and classifying copy number variation
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
InactiveUS20120190557A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNon invasiveFetal aneuploidy
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for chromosome dosage abnormalities. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for determining copy number variations
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy
The invention relates to a method for the early non-invasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy. In particular, the invention concerns the diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by identifying protein expression patterns characteristics of fetal aneuploidy in a maternal biological fluid, such as maternal serum or amniotic fluid.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Method for determining copy number variations
InactiveUS20120149582A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPresent methodTest sample
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Method for determining copy number variations
InactiveUS20120149583A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPresent methodTest sample
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the present method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Method for determining the presence or absence of different aneuploidies in a sample
ActiveCN103003447ADiagnose and monitor metastatic progressionMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationPresent methodTest sample
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the present method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample. Any aneuploidy can be determined from sequencing information that is obtained by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Analyzing copy number variation in the detection of cancer
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
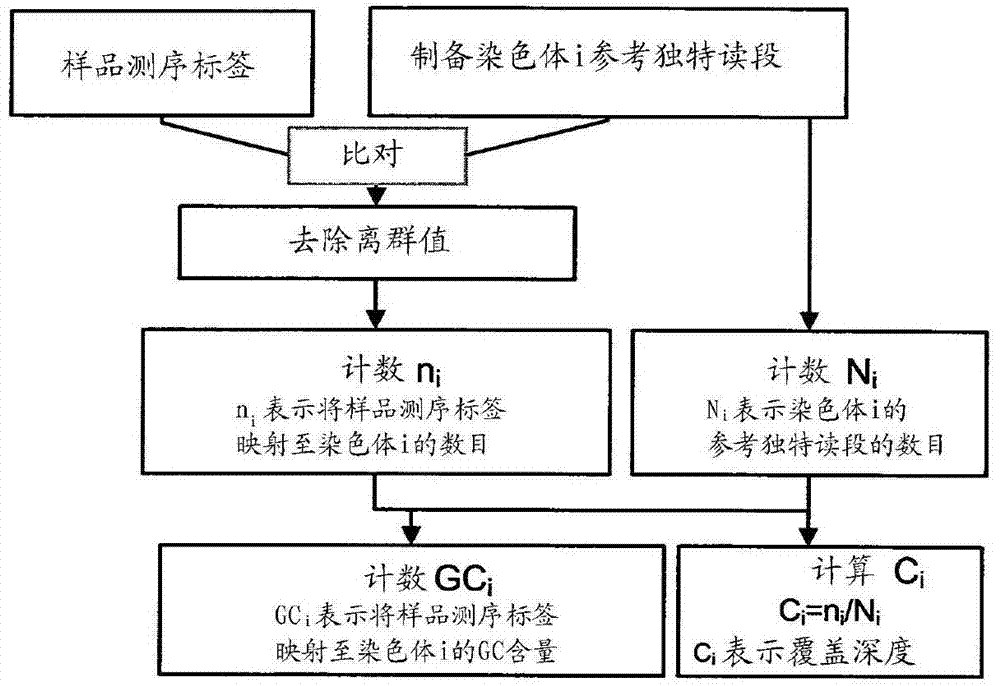
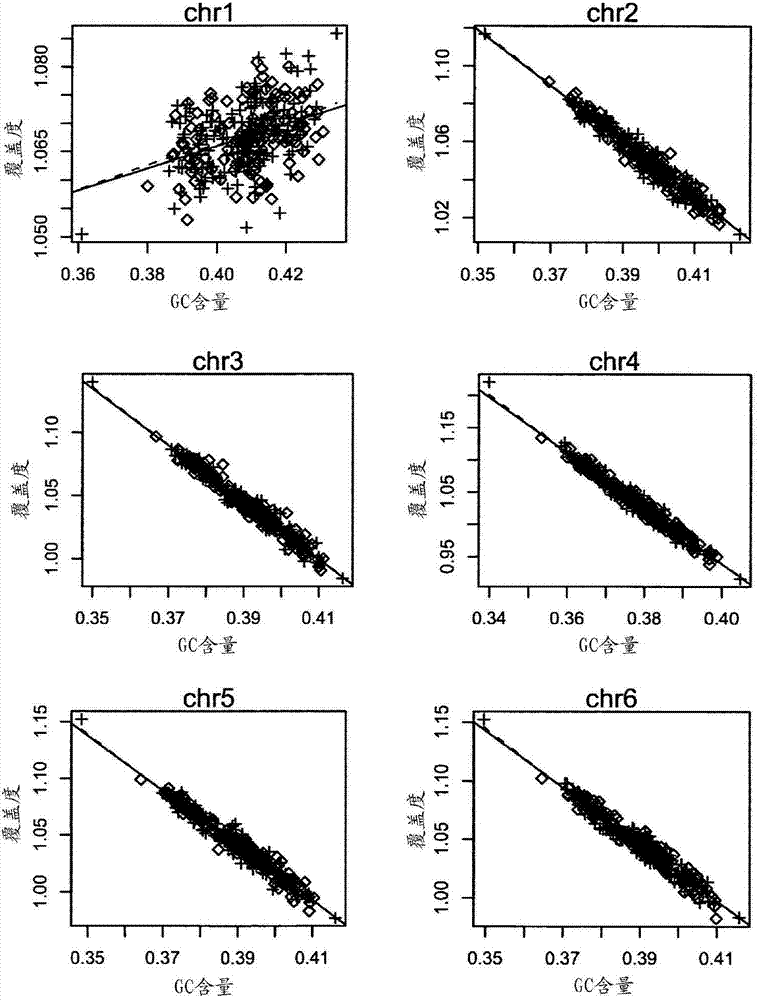
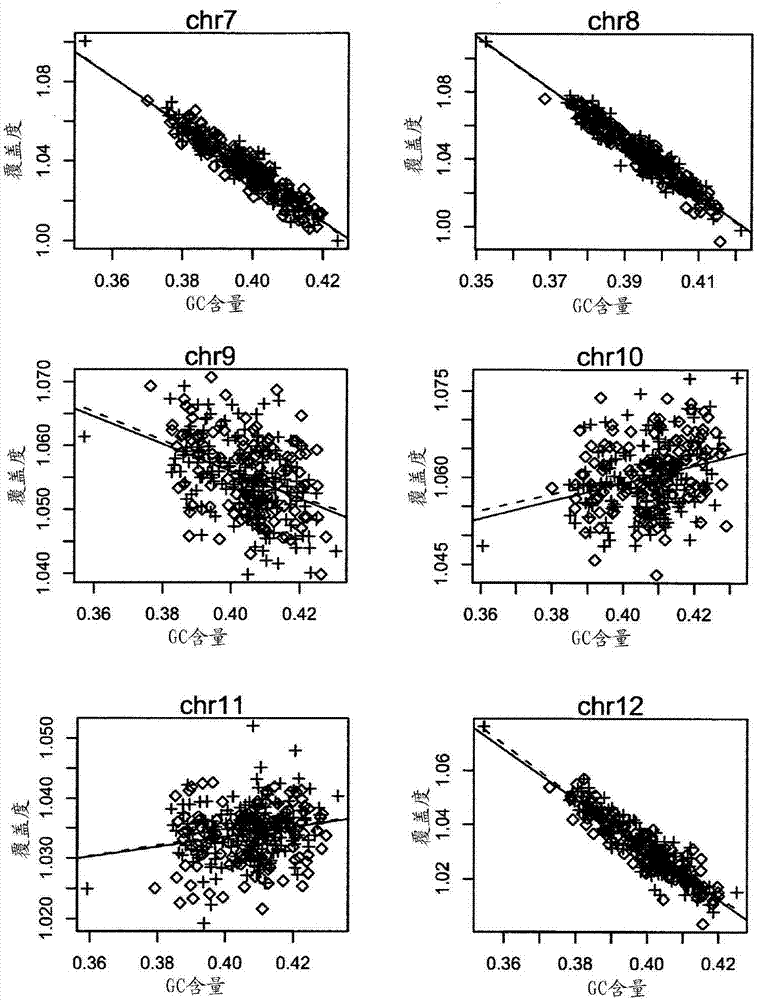
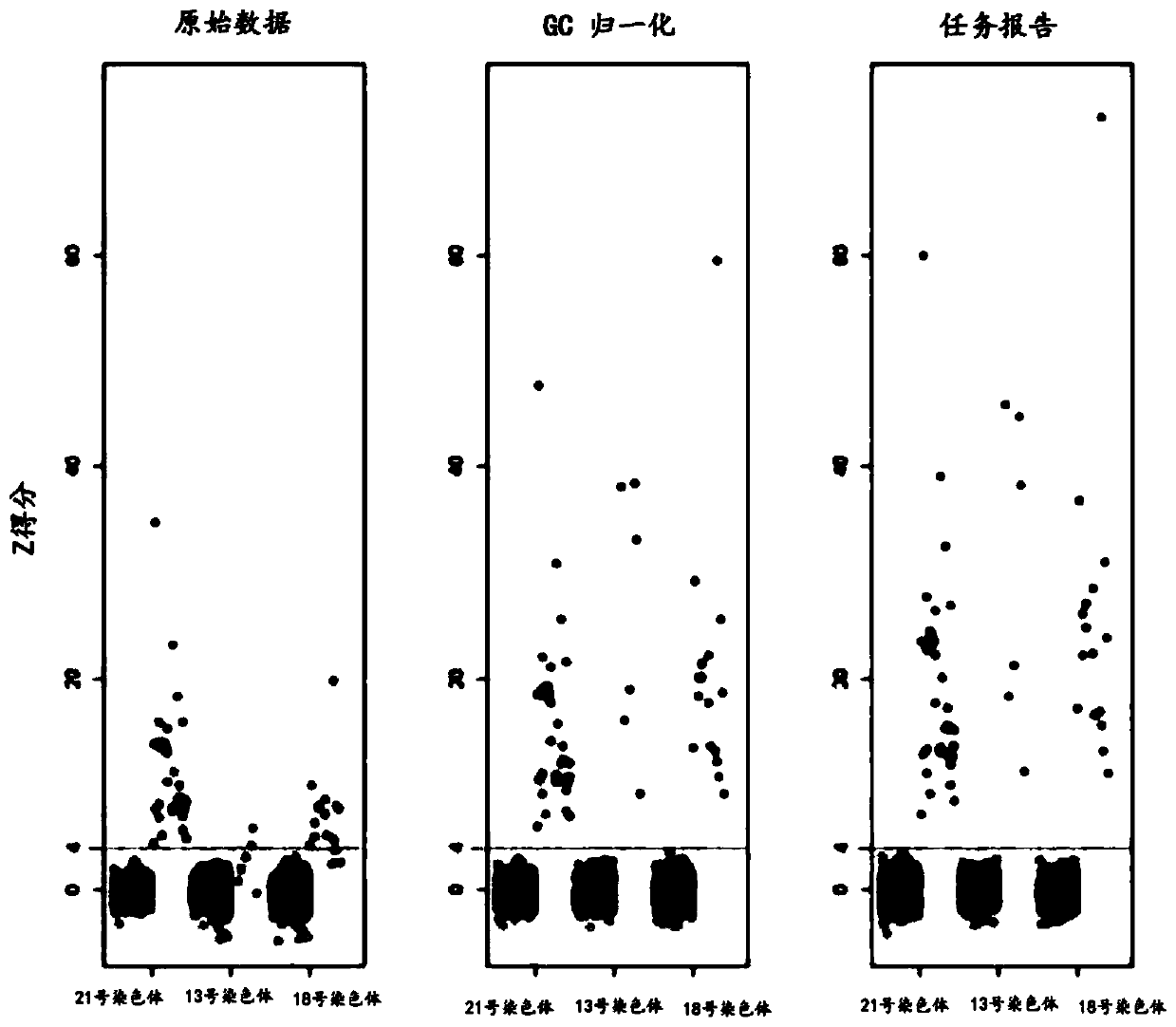
Method and device for carrying out GC correction on chromosome sequencing results
ActiveCN104120181ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHereditary disordersLarge-Scale Sequencing
The invention relates to a non-diagnostic method for noninvasively detecting fetal hereditary disorder by sequencing nucleotides from a maternal biological sample on a large scale, and further provides a method for eliminating sequencing result GC bias caused by chromosome GC content difference. The method disclosed by the invention not only enables detection to be more accurate, but also provides a non-diagnostic comprehensive method for detecting fatal aneuploidy including sex chromosomal disease cases, for example, XO, XXX, XXY, XYY, and the like.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies
ActiveUS20120282613A1Accurate predictionDiagnosing fetal aneuploidiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethylated DNA immunoprecipitationAdult female
The invention provides methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies. A large panel of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) have been identified. Certain of these DMRs are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA, whereas others are hypermethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypomethylated in fetal DNA. Moreover, DMRs that are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA have been shown to accurately predict a fetal aneuploidy in fetal DNA present in a maternal blood sample during pregnancy. In the methods of the invention, hypermethylated DNA is physically separated from hypomethylated DNA, preferably by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
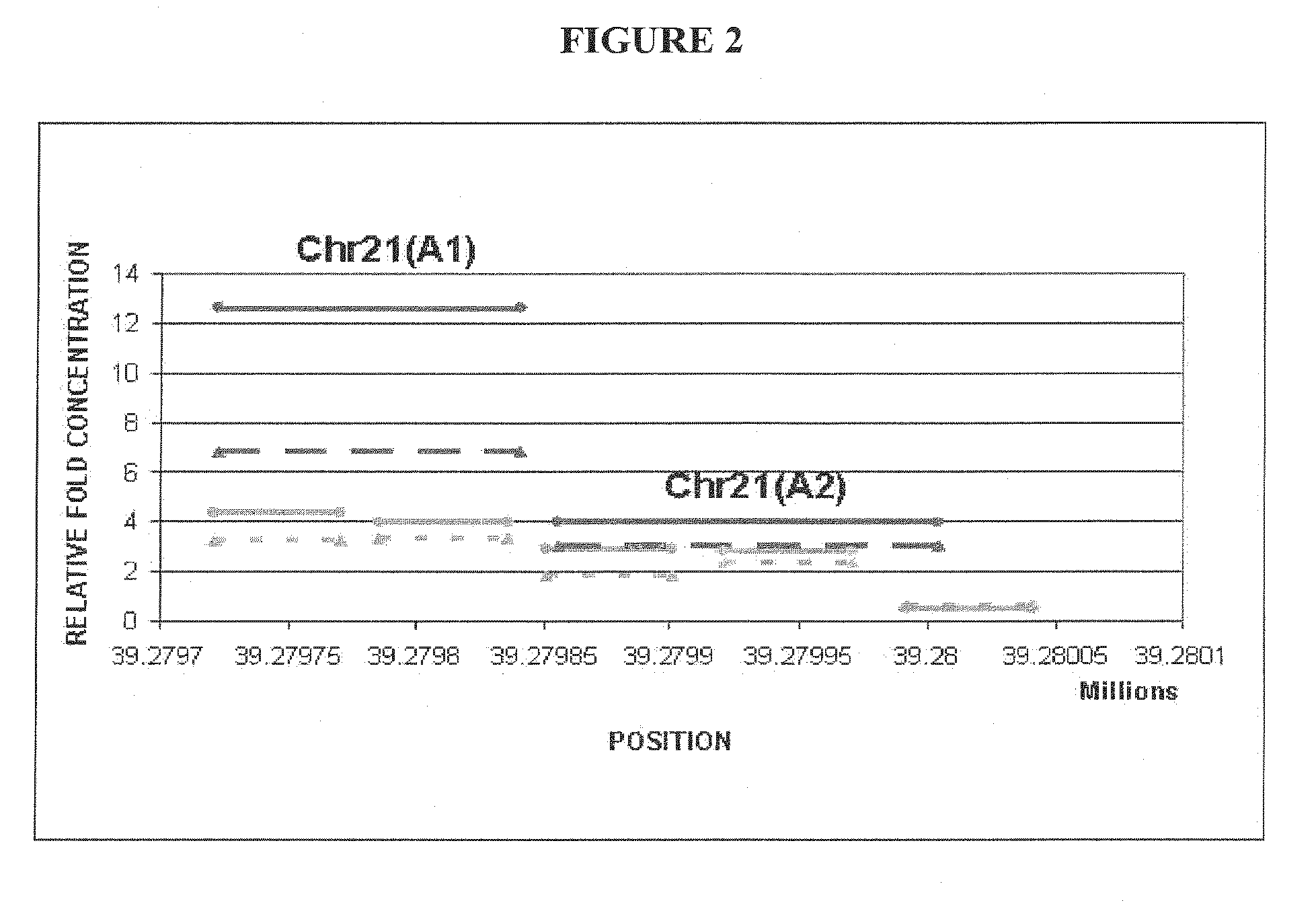
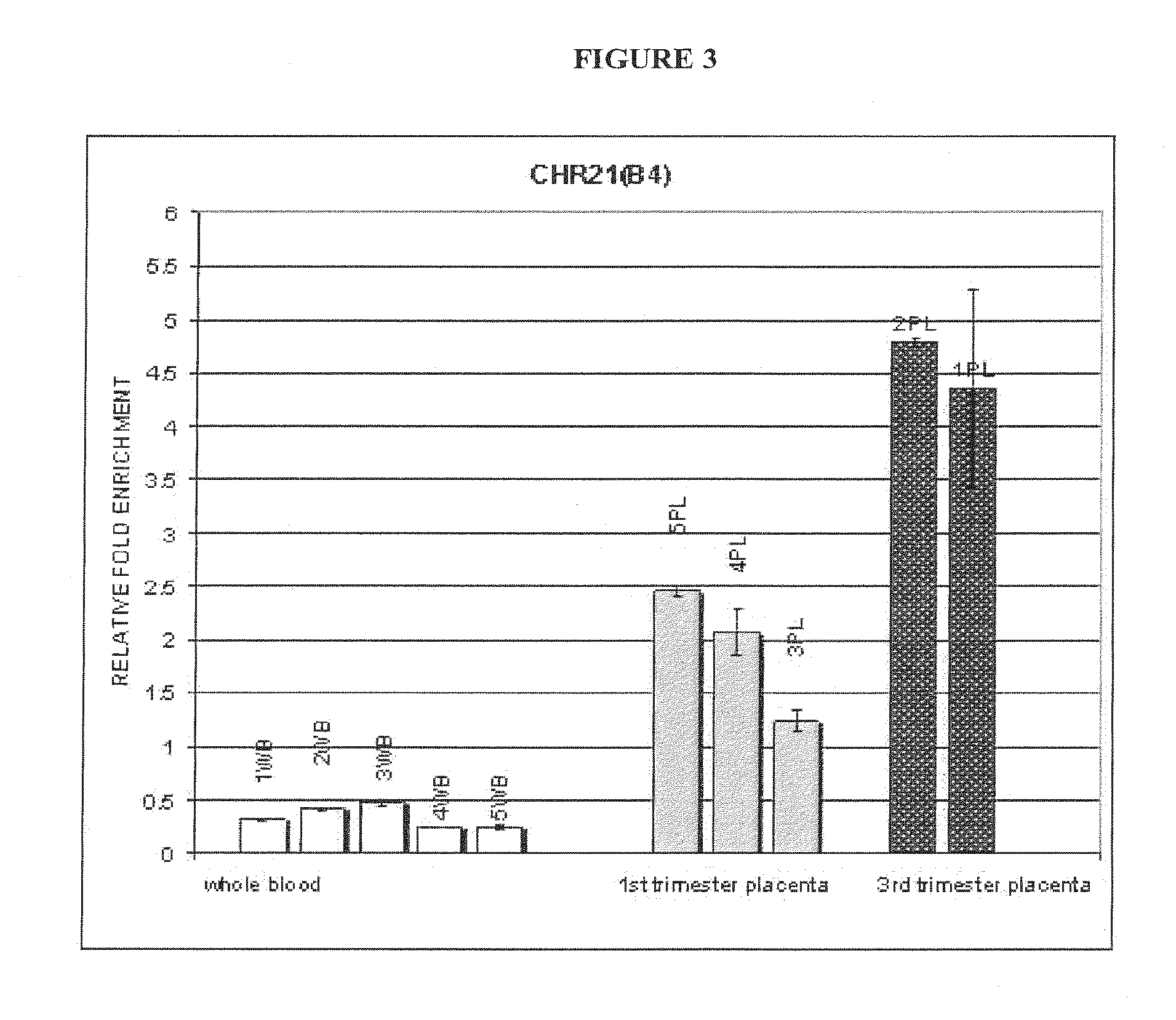
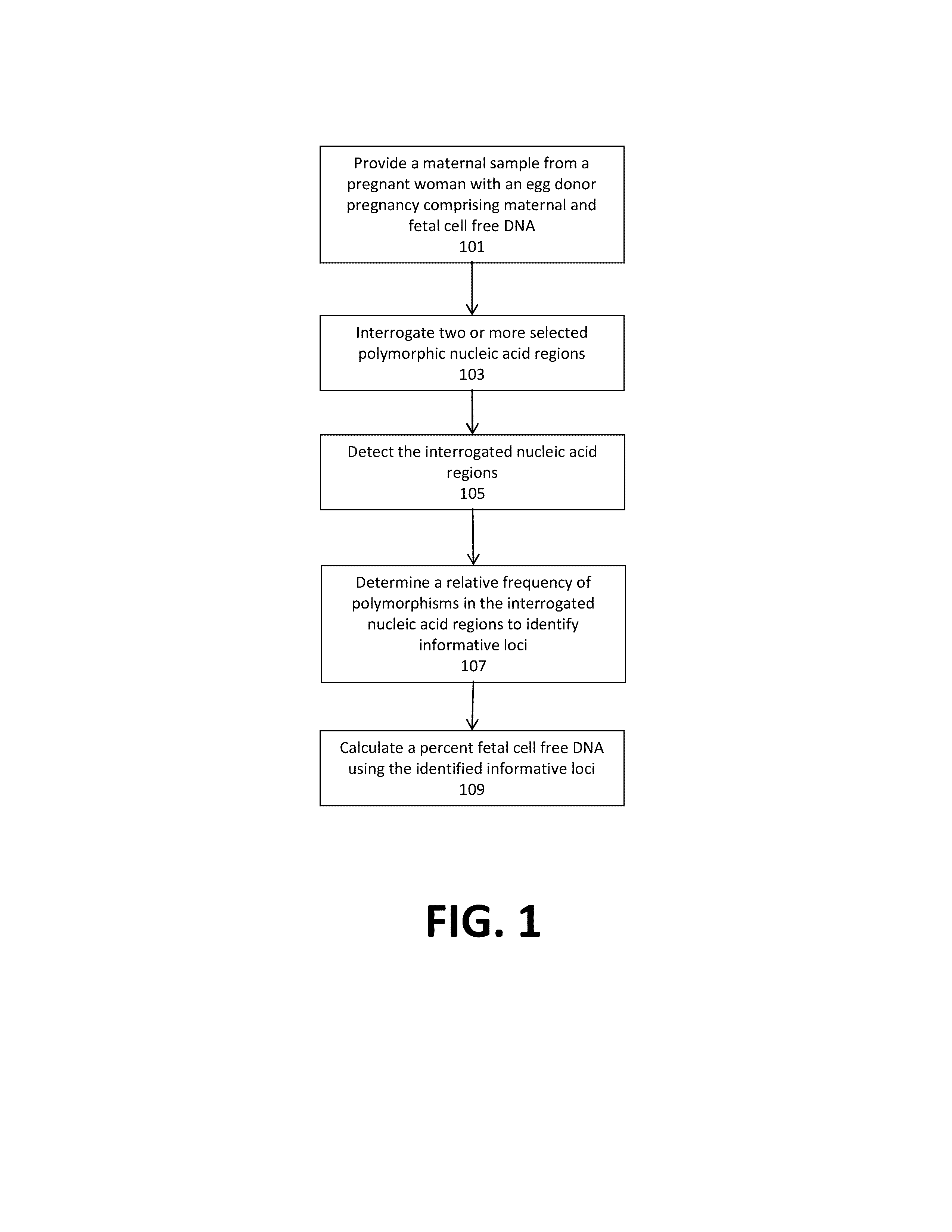
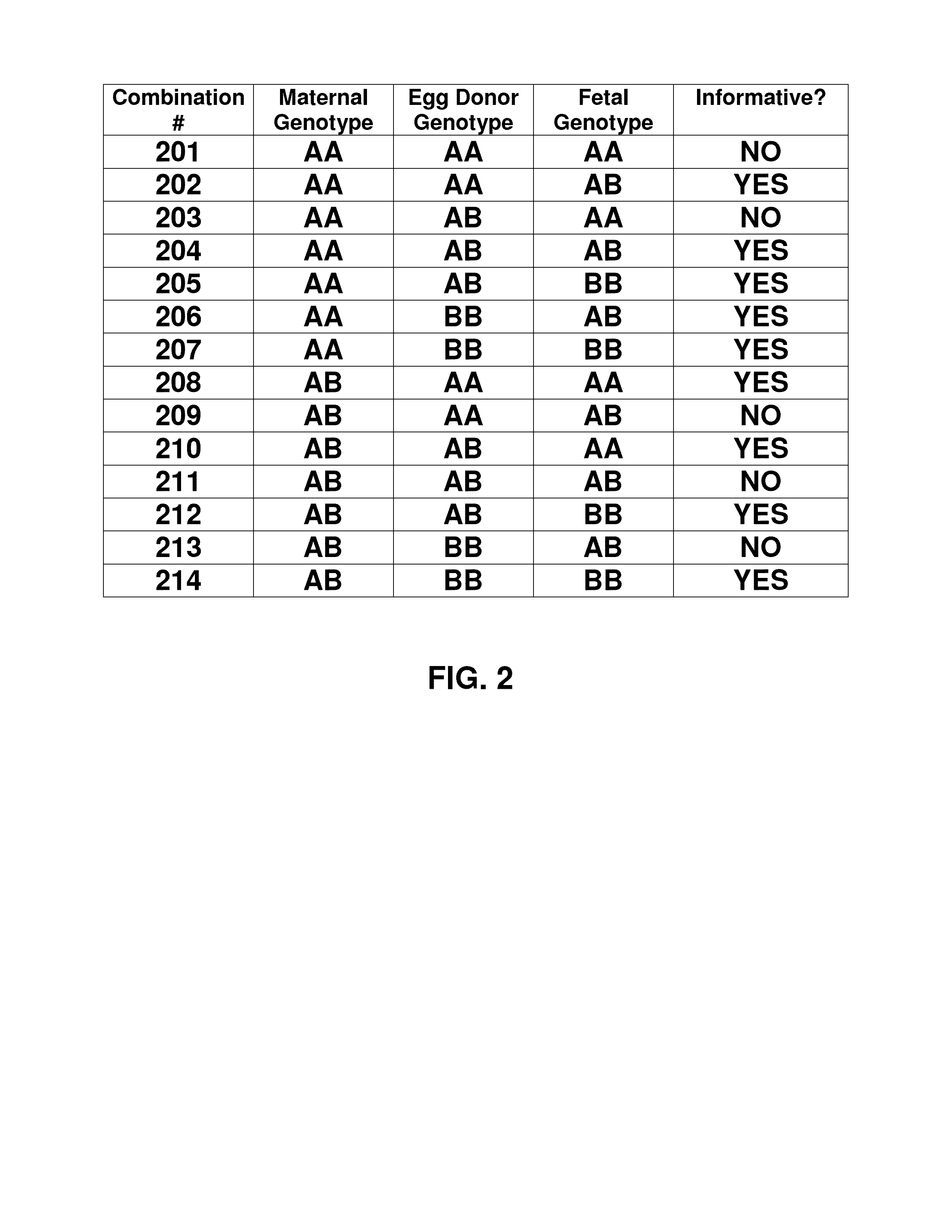
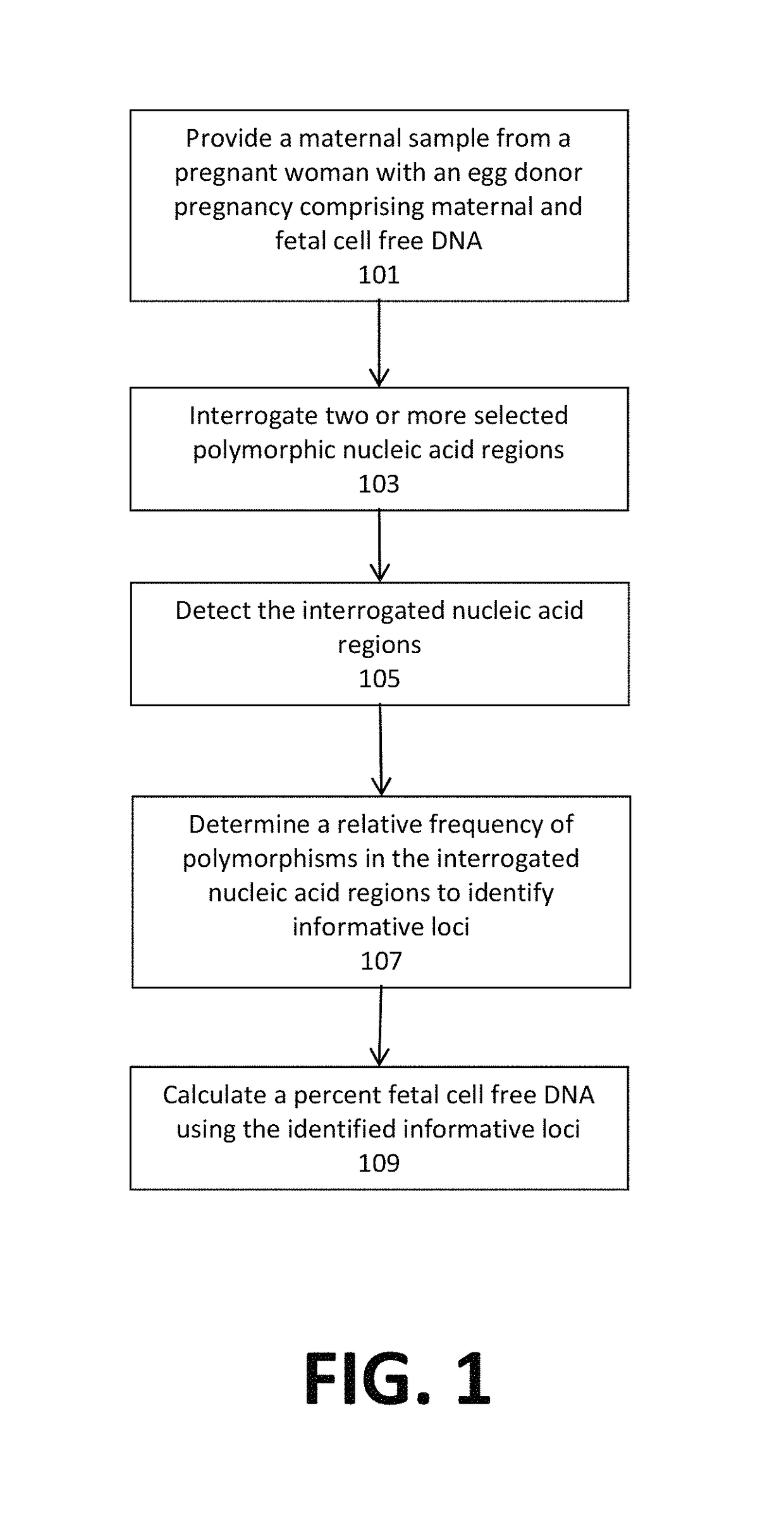
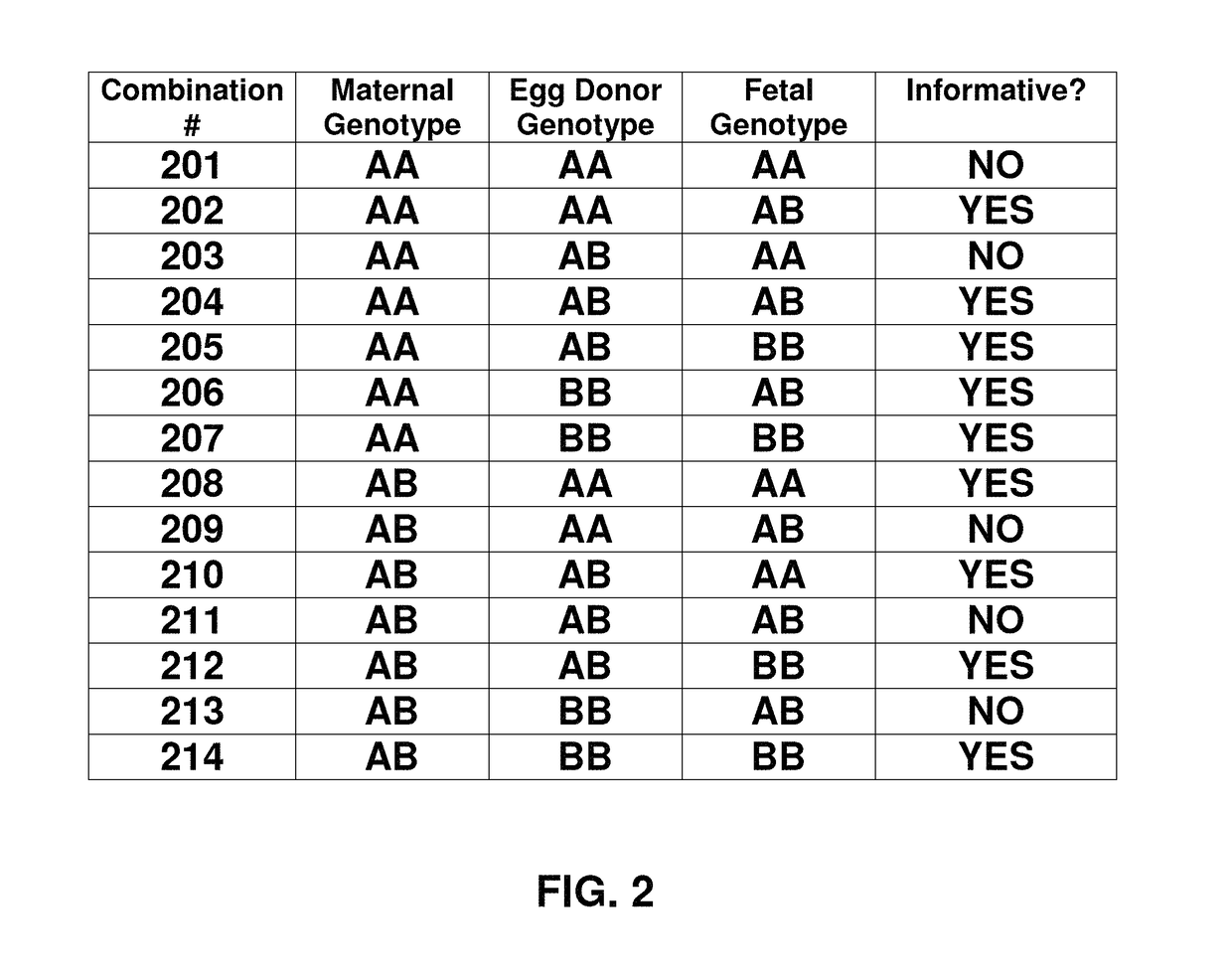
Noninvasive detection of fetal aneuploidy in egg donor pregnancies
ActiveUS20130178371A1Quick sortingBeneficialMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationCell freeFetal aneuploidy
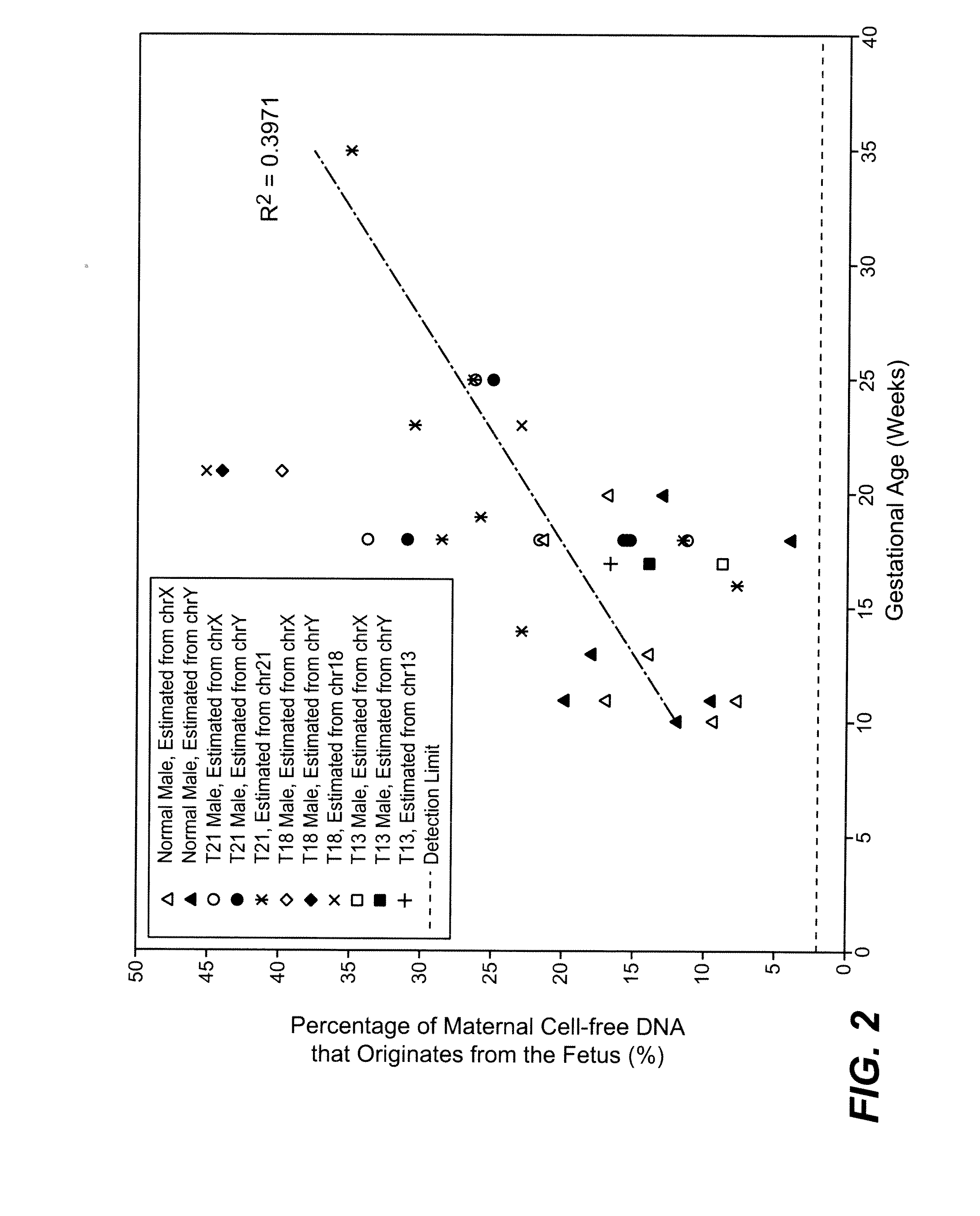
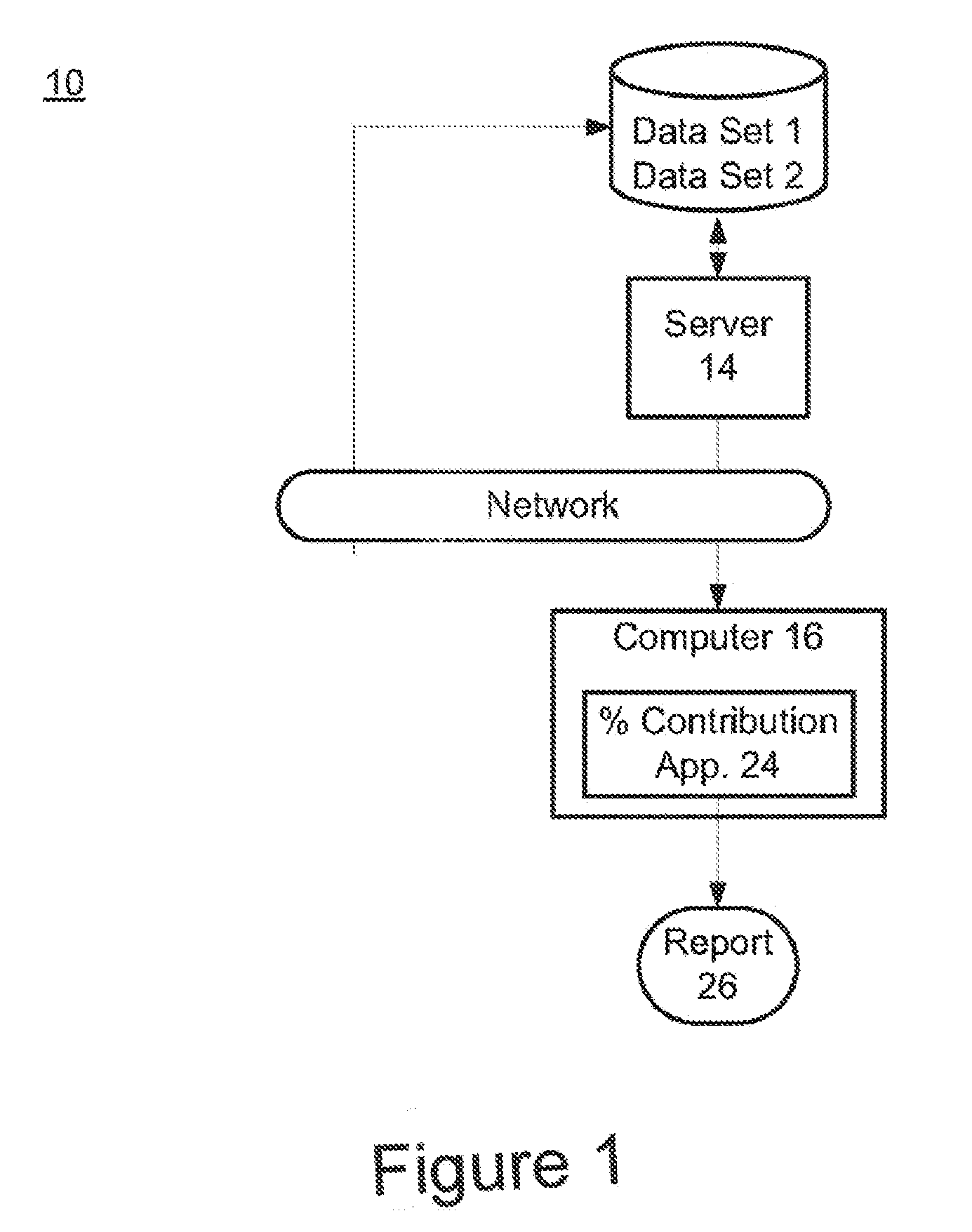
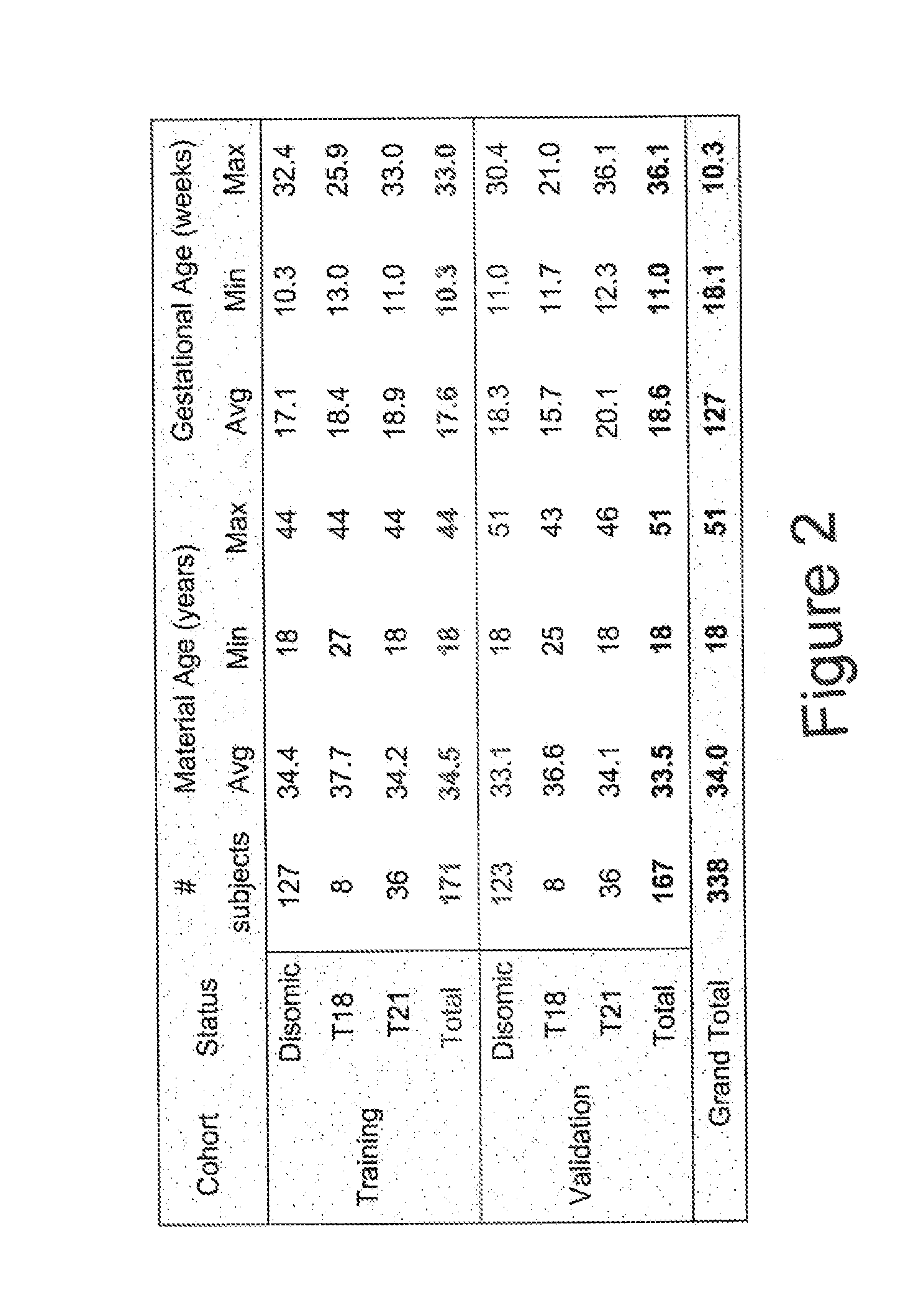
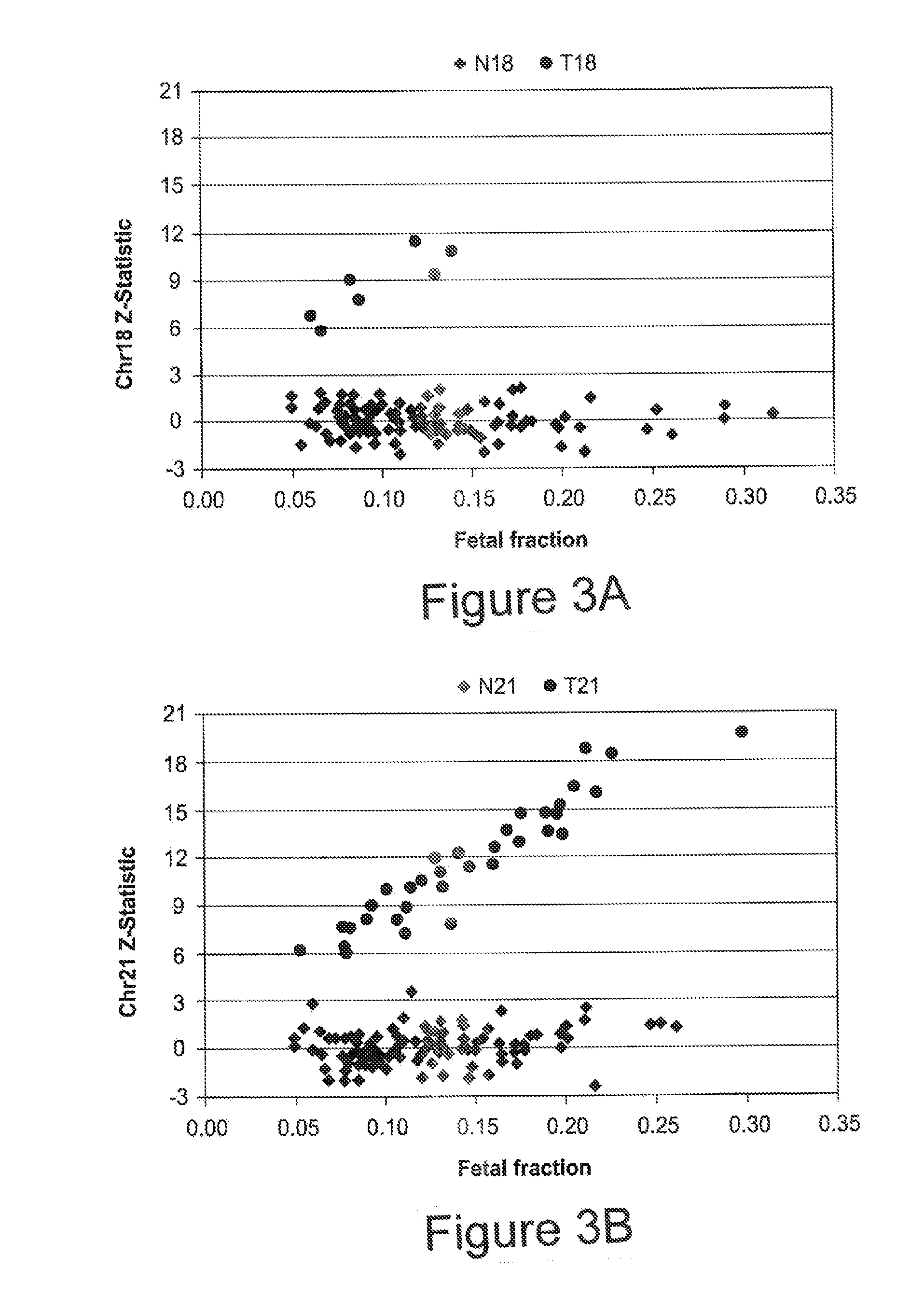
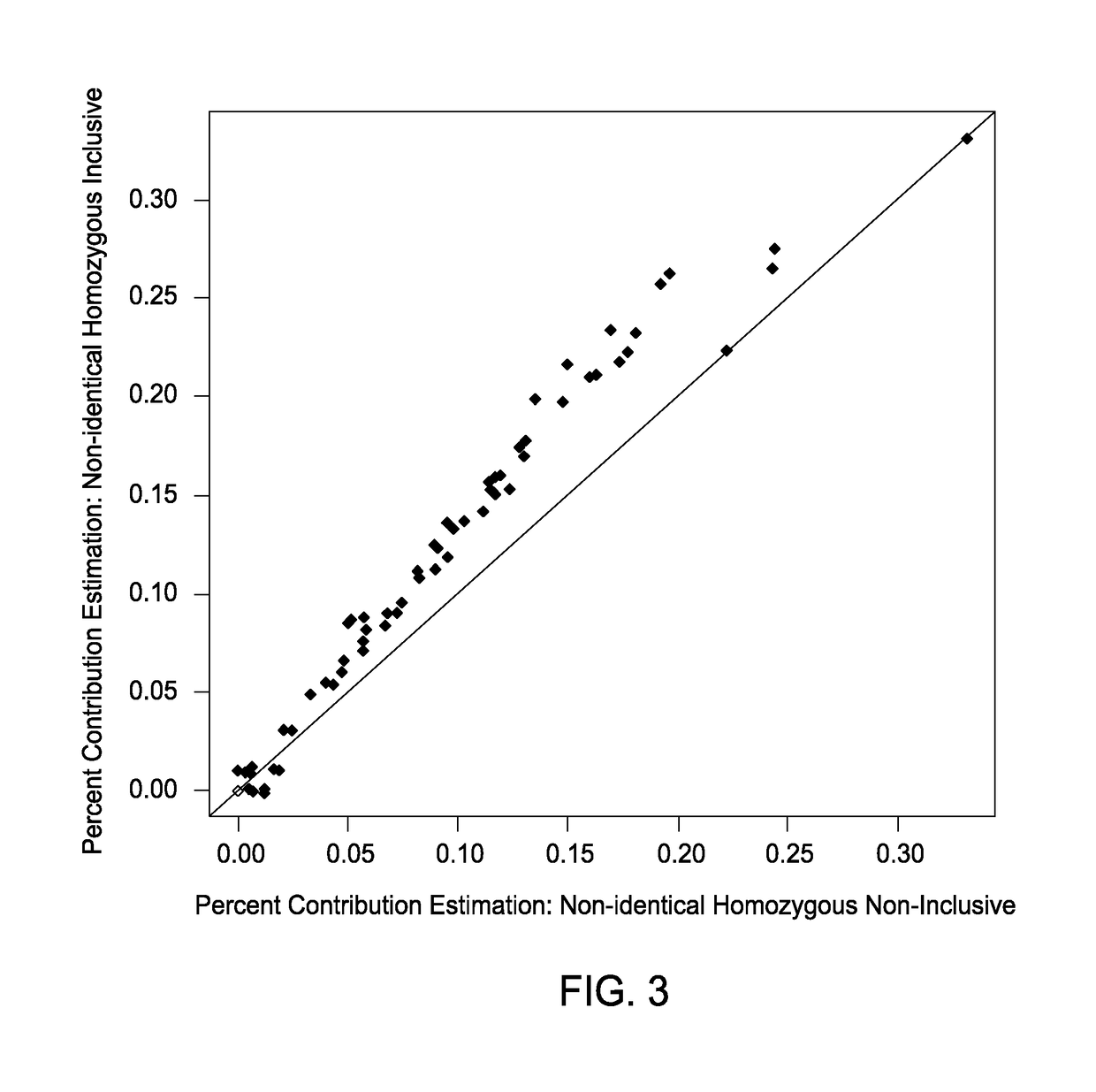
The present invention provides assay systems and methods for determining the percent fetal contribution of cell-free DNA in a maternal sample from a pregnant female with an egg donor pregnancy. Further provided, are assay systems and methods for determining a statistical likelihood of the presence or absence of a fetal aneuploidy in a maternal sample using a determined percent fetal cell-free DNA in the sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormality
ActiveUS20140099642A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLarge-Scale SequencingFetal aneuploidy
The current invention is directed to methods for noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormalities by large-scale sequencing of nucleotides from maternal biological sample. Further provided are methods to remove GC bias from the sequencing results according to the difference in GC content of a chromosome. The current invention not only makes the detection much more accurate but also represents a comprehensive method for fetal aneuploidy detection including sex chromosome disorders such as XO, XXX, XXY, and XYY, etc.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Prenatal Screening
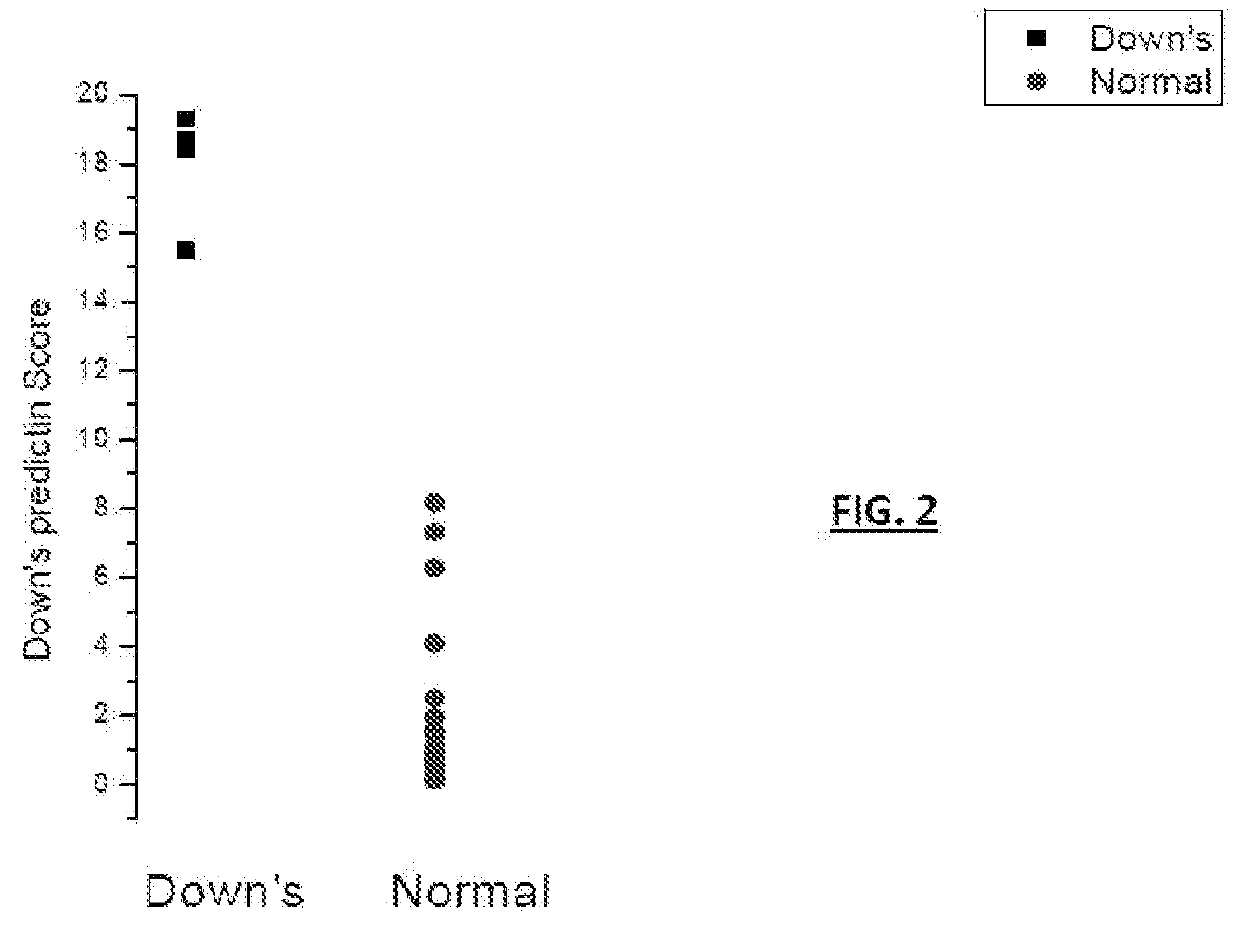
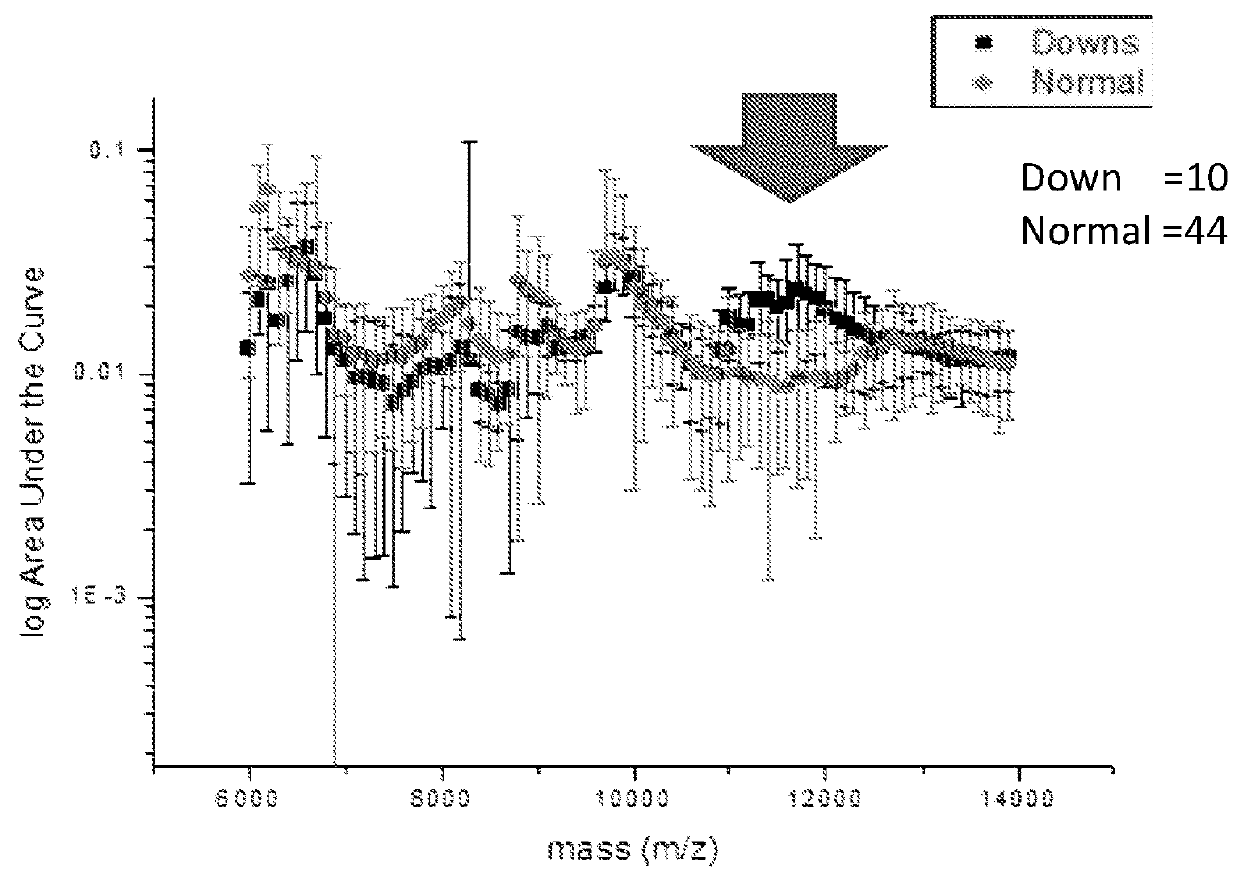
ActiveUS20160054293A1Easy to calculateSmall sizeTime-of-flight spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsDiseaseFetal abnormality
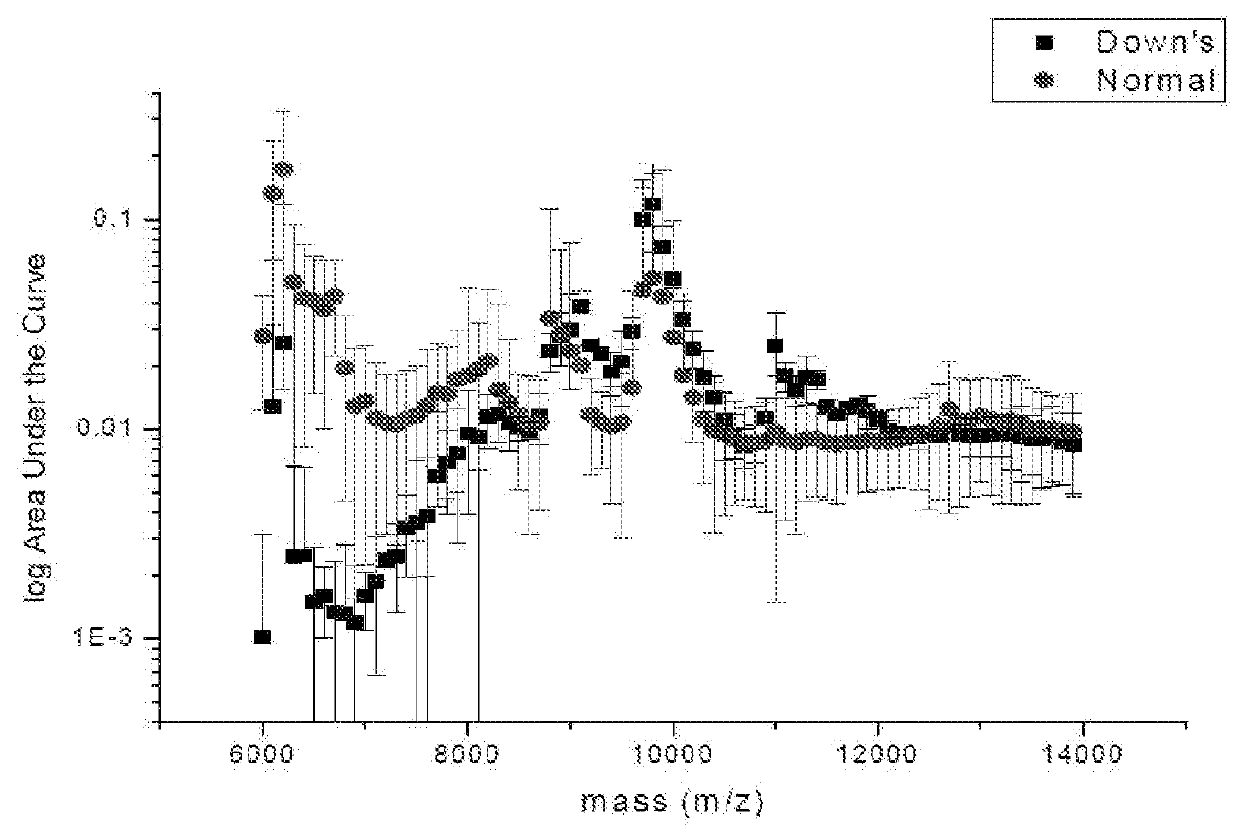
The present invention relates to a method for screening maternal urine samples for changes in the pattern of mass spectral fingerprinting which have been found to be characteristic of fetal aneuploidies such as Down's Syndrome and have application for the screening of other fetal abnormalities and disorders of pregnancy including gestational trophoblastic diseases.
Owner:MAP IP HOLDING LTD
Methods of fetal abnormality detection
ActiveUS20120135872A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFetal abnormalityPolynucleotide
Methods and kits for selectively enriching non-random polynucleotide sequences are provided. Methods and kits for generating libraries of sequences are provided. Methods of using selectively enriched non-random polynucleotide sequences for detection of fetal aneuploidy are provided.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method for non-invasive antenatal determination of aneuploidy by targeting next generation sequencing with biallelic SNP
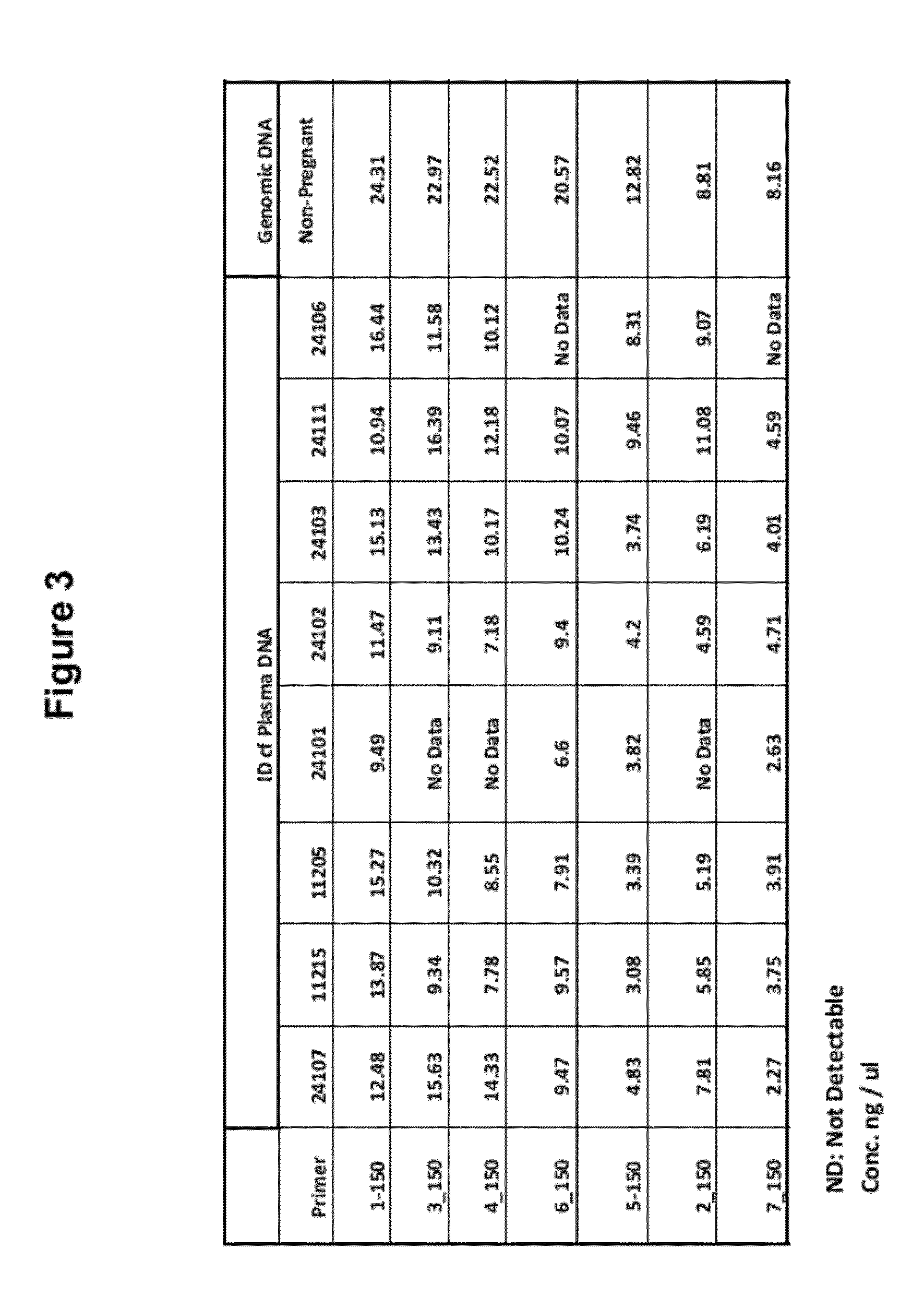
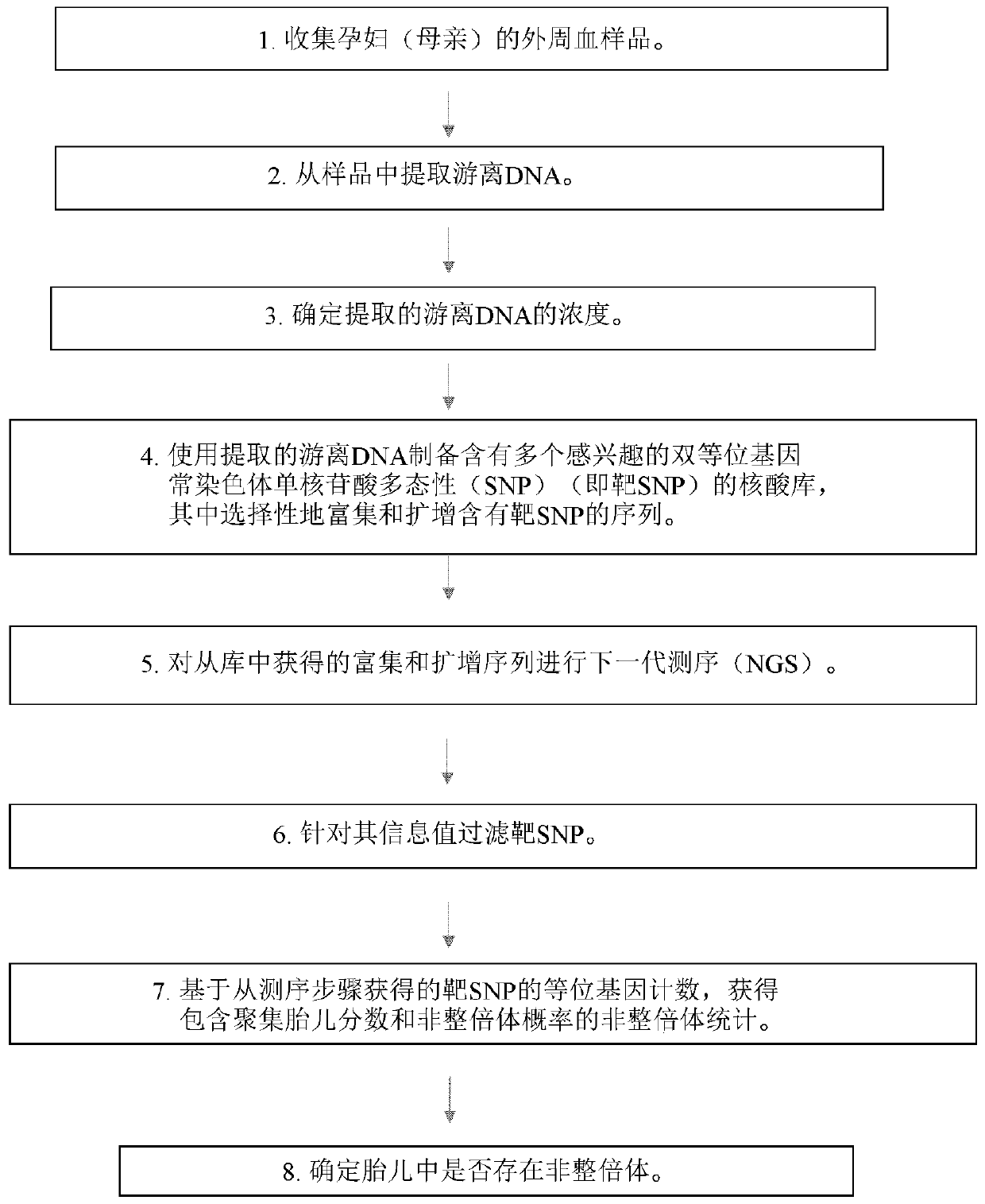
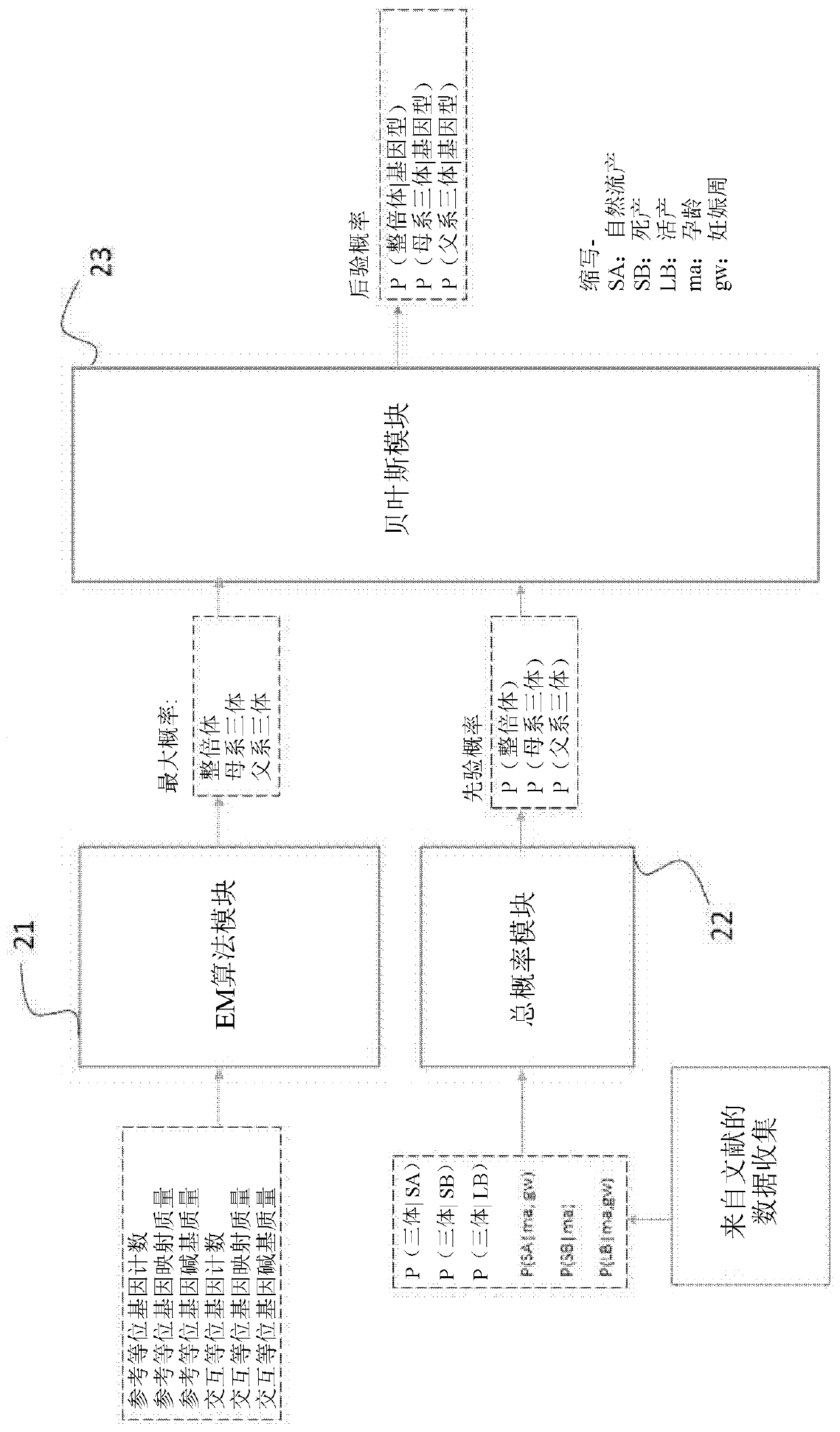
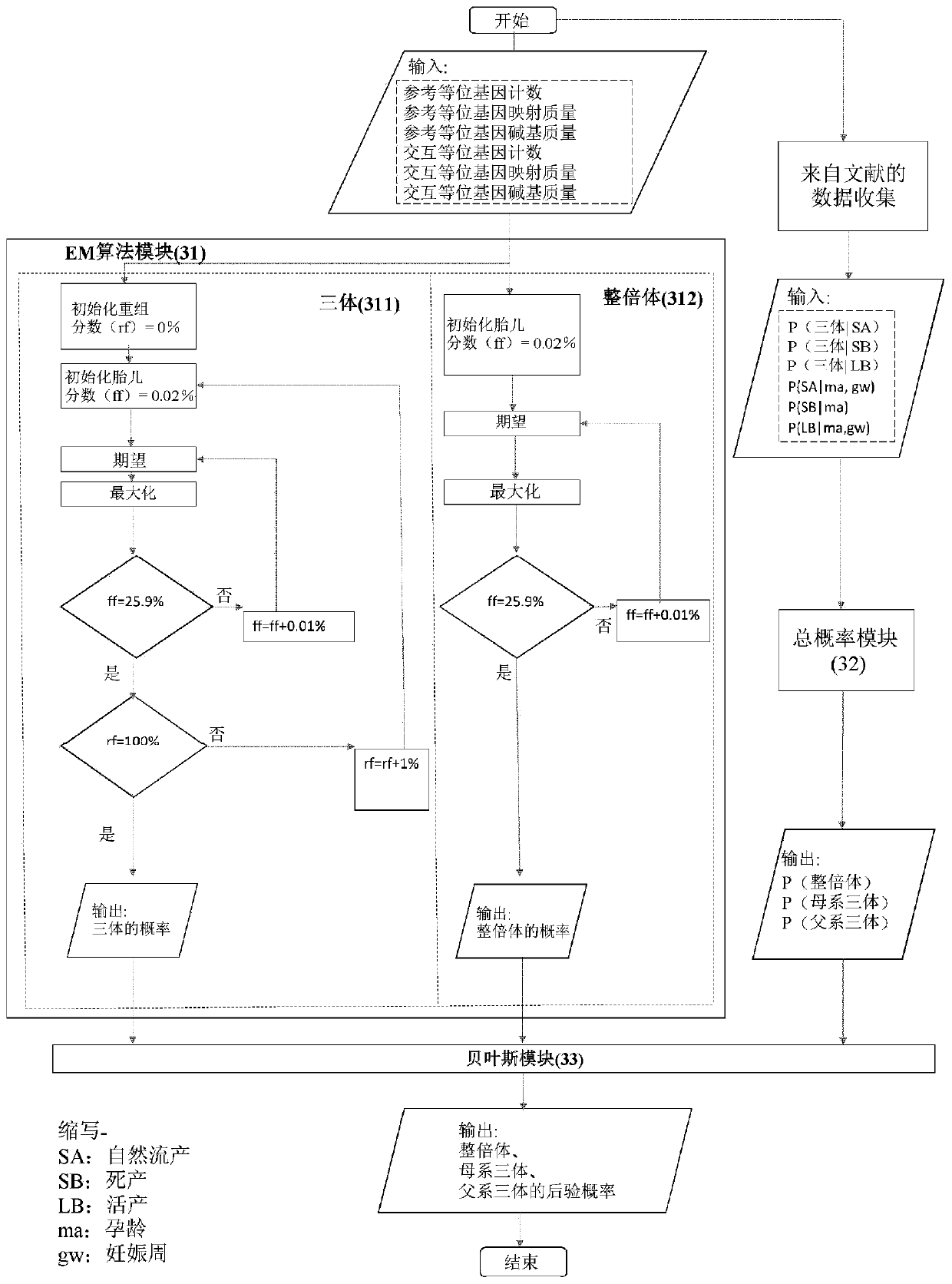
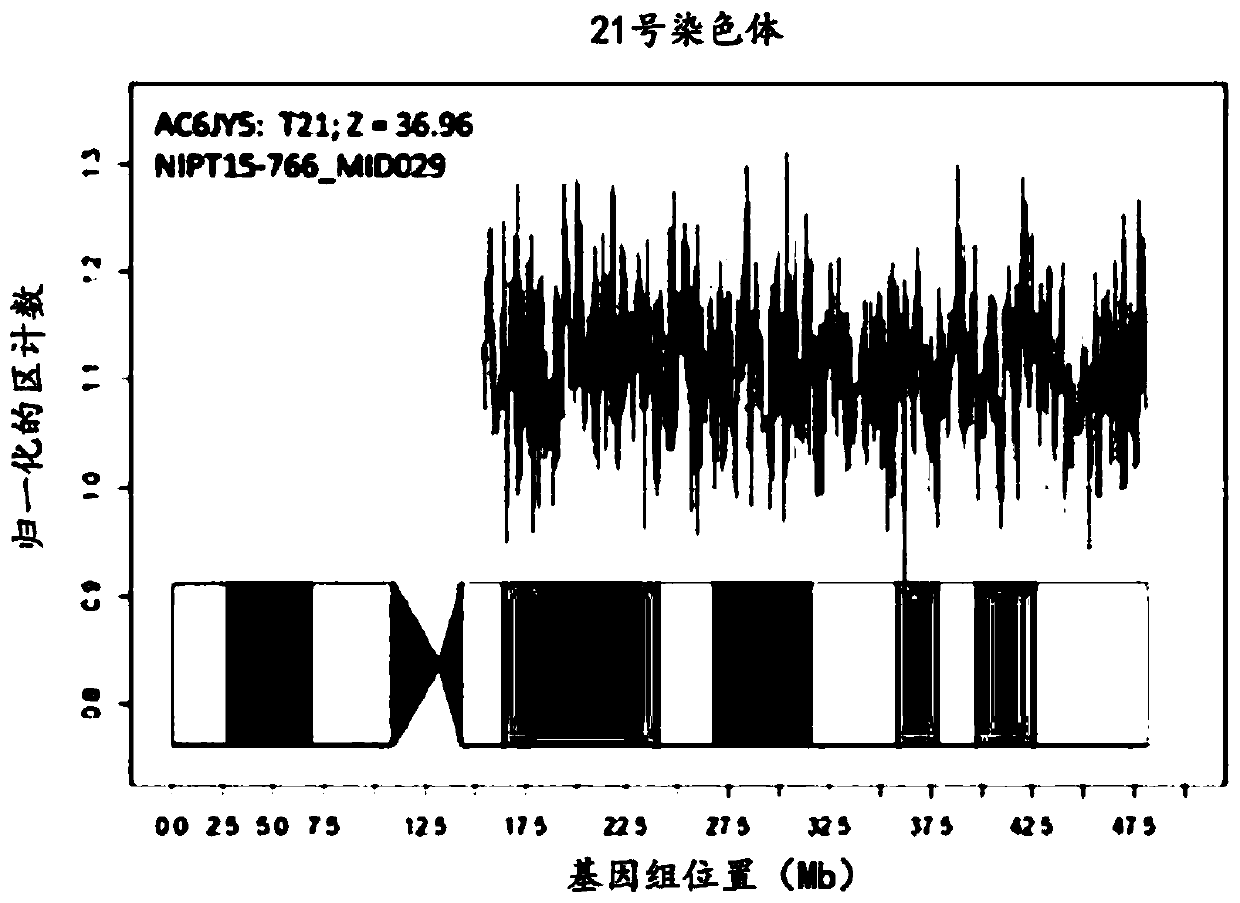
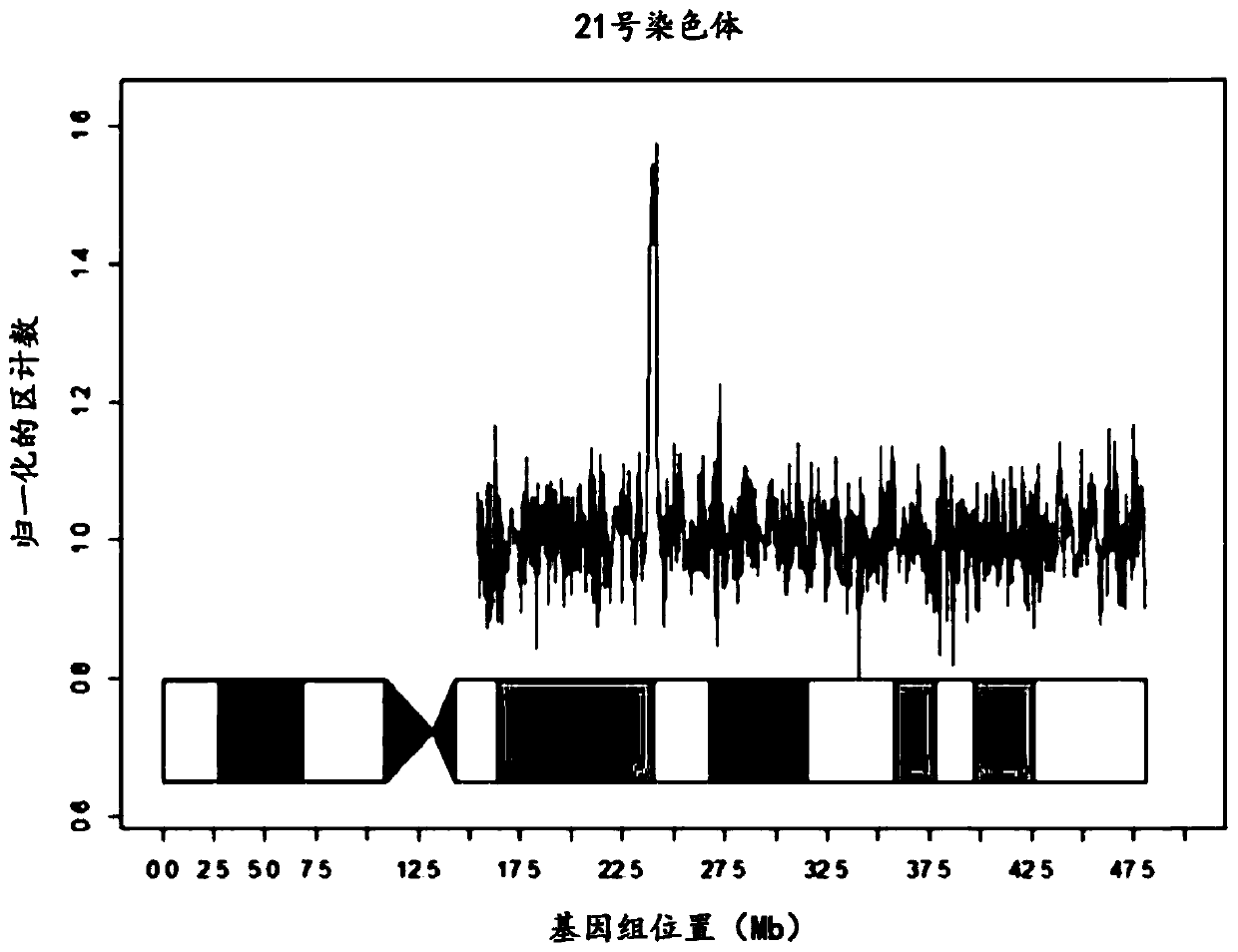
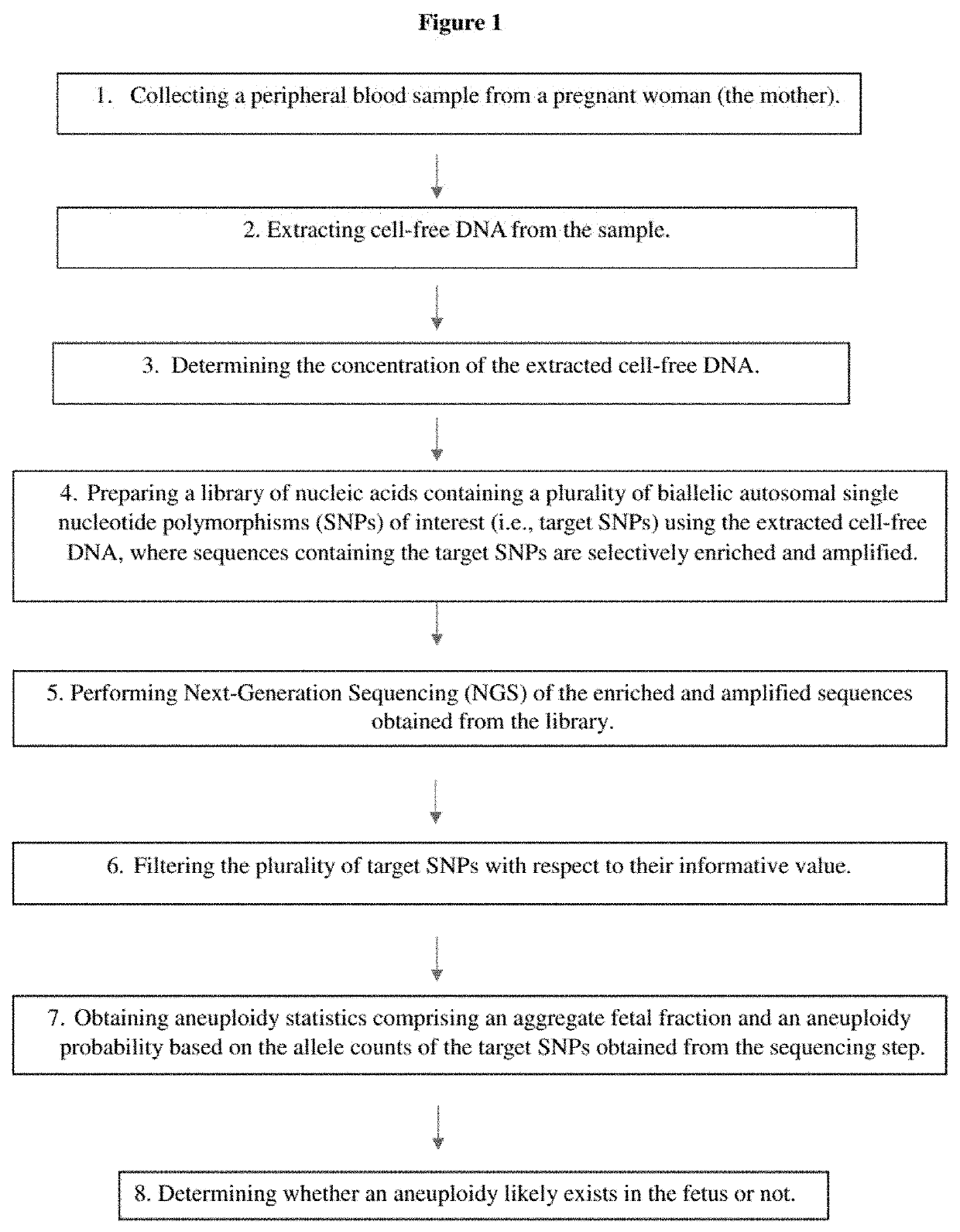
The present invention provides a method for non-invasive pre-natal test (NIPT) for determining the probability of aneuploidy in a fetus. The method includes a step of carrying out absolute or relativequantification platform quantification and analysis of the autosomal single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) to determine the probability of fetal aneuploidy. In one embodiment, the method comprises thefollowing steps: obtaining a blood sample containing free DNA (cfDNA) from a pregnant woman; using the extracted DNA to prepare a nucleic acid library containing a plurality of target biallele autosomal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) (i.e., target SNPs) by using a target enrichment method; carrying out targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) by using the prepared library, obtaining allele counting of a target SNP in the free DNA, and determining the probability of fetal aneuploidy.
Owner:MEDTIMES MOLECULAR LAB LTD
Method for non-invasive prenatal screening for aneuploidy
The present disclosure provides methods for non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS) of fetal aneuploidies. The present methods are based on analyzing cell-free fetal DNA (cff DNA) found in a pregnant woman's circulation through the next generation sequencing (NGS) technology. Particularly, the present methods analyze the relative abundance of different fetal genomic fragments present in the maternal sample, where the fragments can be aligned to particular chromosomal locations of the fetal genome. The relative abundance information is indicative as to whether a particular chromosome is overrepresented or underrepresented in a fetal genome as compared to normal individuals, and thus can be used to detect fetal aneuploidy. Additionally, methods for increasing the positive predictive values (PPV) of NIPS by excluding false-positive detections are also provided.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Methods for non-invasive prenatal determination of aneuploidy using targeted next generation sequencing of biallelic snps
This invention provides methods for non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) for determining the probability of aneuploidy in a fetus. The present invention comprises quantification and analysis of autosomal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) using platforms capable of absolute or relative quantification to determine the probability of aneuploidy in the fetus. In one embodiment, the present methods comprise obtaining a blood sample containing cell-free DNA from a pregnant woman, using the extracted DNA to prepare a library of nucleic acids encompassing a plurality of biallelic autosomal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of interest (i.e., target SNPs) using a target enrichment approach, performing targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) using the library prepared, obtaining the allele counts of the target SNPs in the cell-free DNA and determining the probability of aneuploidy in a fetus.
Owner:MEDTIMES MOLECULAR LAB LTD
Noninvasive detection of fetal aneuploidy in egg donor pregnancies
ActiveUS10131947B2Quick sortingBeneficialMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCell freeFetal aneuploidy
The present invention provides assay systems and methods for determining the percent fetal contribution of cell-free DNA in a maternal sample from a pregnant female with an egg donor pregnancy. Further provided, are assay systems and methods for determining a statistical likelihood of the presence or absence of a fetal aneuploidy in a maternal sample using a determined percent fetal cell-free DNA in the sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Direct molecular diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy
ActiveUS8574842B2Addressing slow performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific chromosomeChromosomal region
Methods and materials for detection of aneuploidy and other chromosomal abnormalities using fetal tissue are disclosed. Results can be obtained rapidly, without cell culture. The method uses digital PCR for amplification and detection of single target sequences, allowing an accurate count of a specific chromosome or chromosomal region. Specific polynucleic acid primers and probes are disclosed for chromosomes 1, 13, 18, 21, X and Y. These polynucleic acid sequences are chosen to be essentially invariant between individuals, so the test is not dependent on sequence differences between fetus and mother.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com