Patents
Literature
36 results about "Fetal abnormality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Although some women are at high risk of fetal abnormalities, either because of a family history or due to exposure to teratogens such as infection and various drugs, the vast majority of fetal abnormalities occur in the low-risk group. Consequently, ultrasound examination should be offered routinely to all pregnant women.
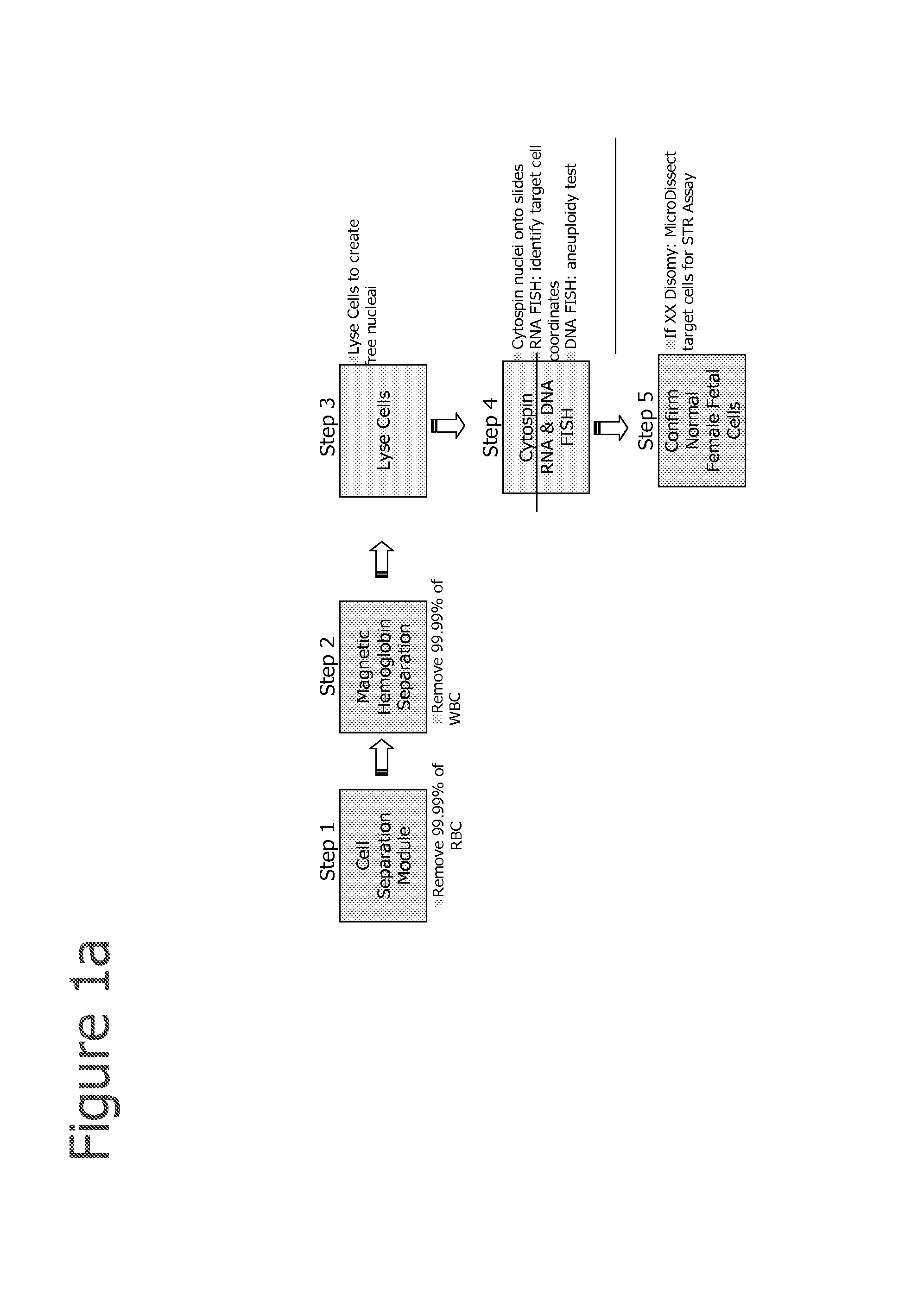
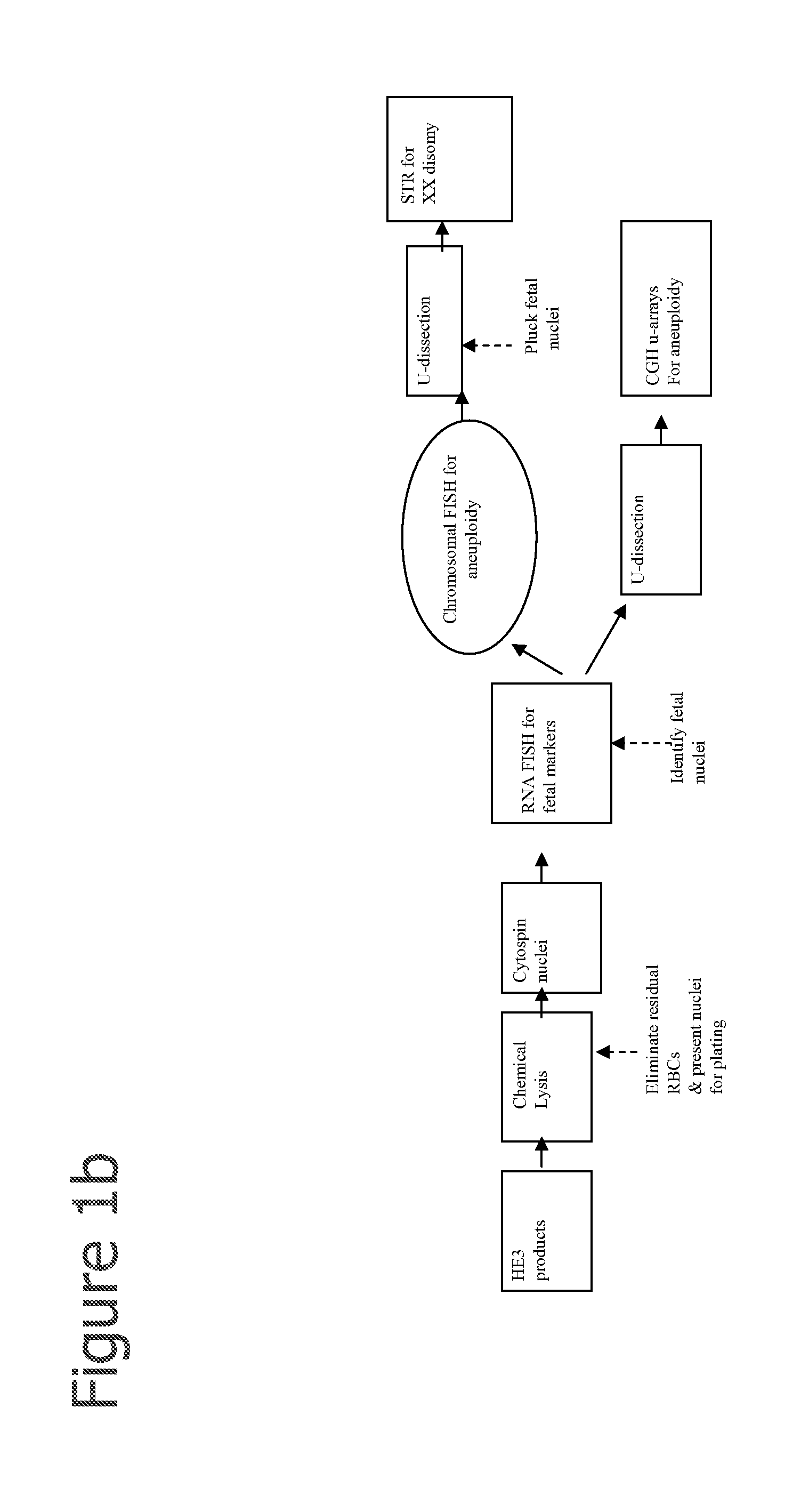
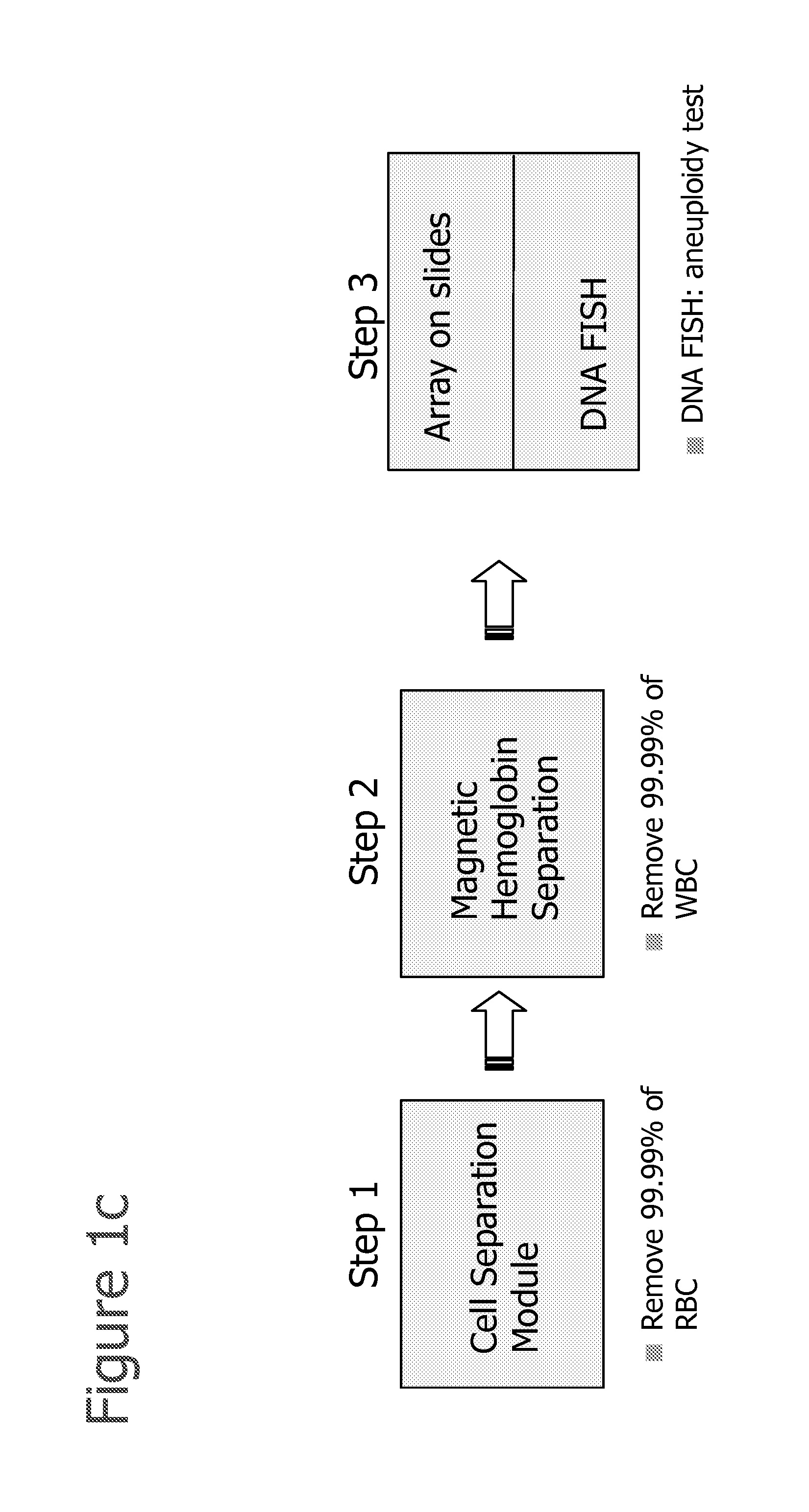
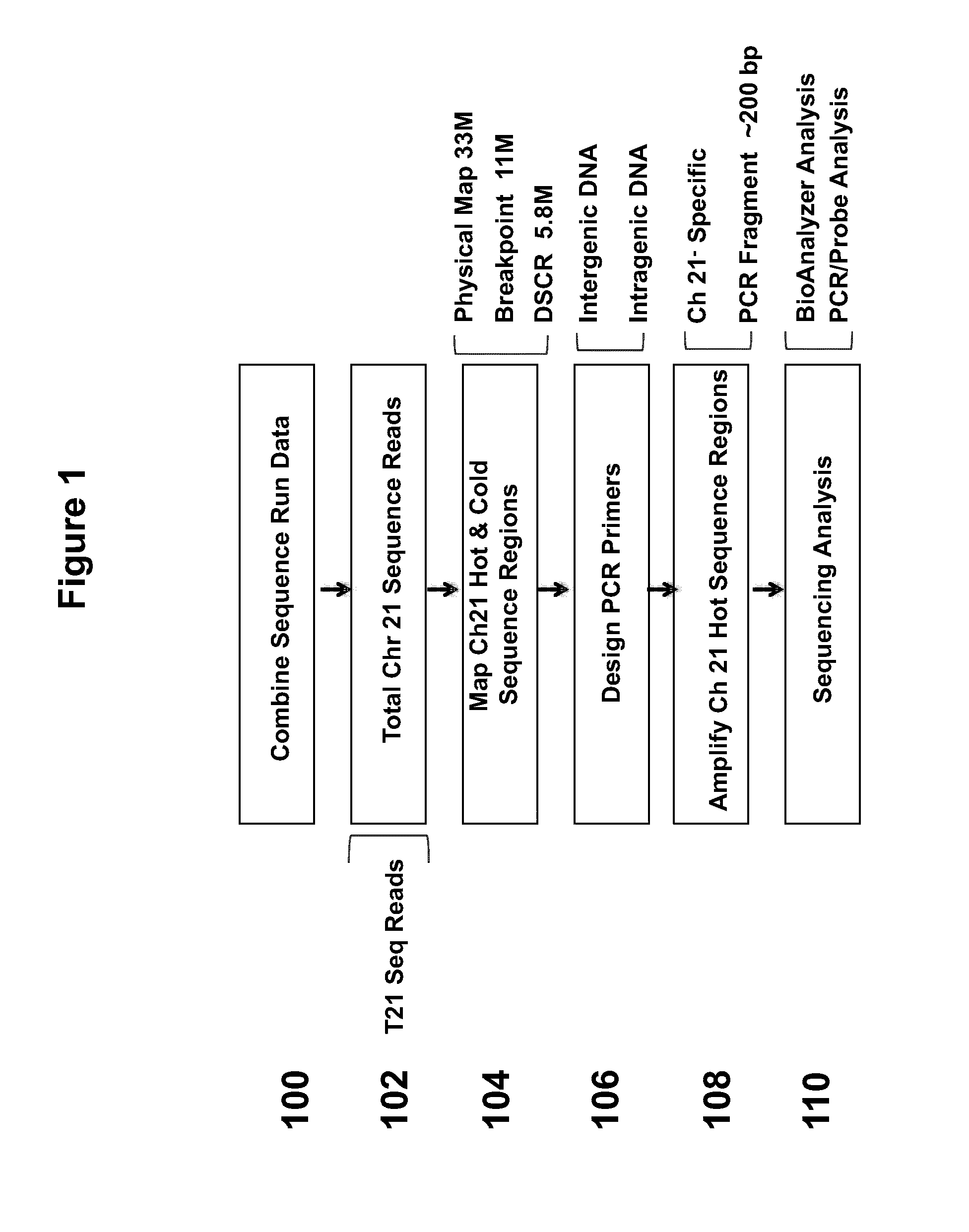
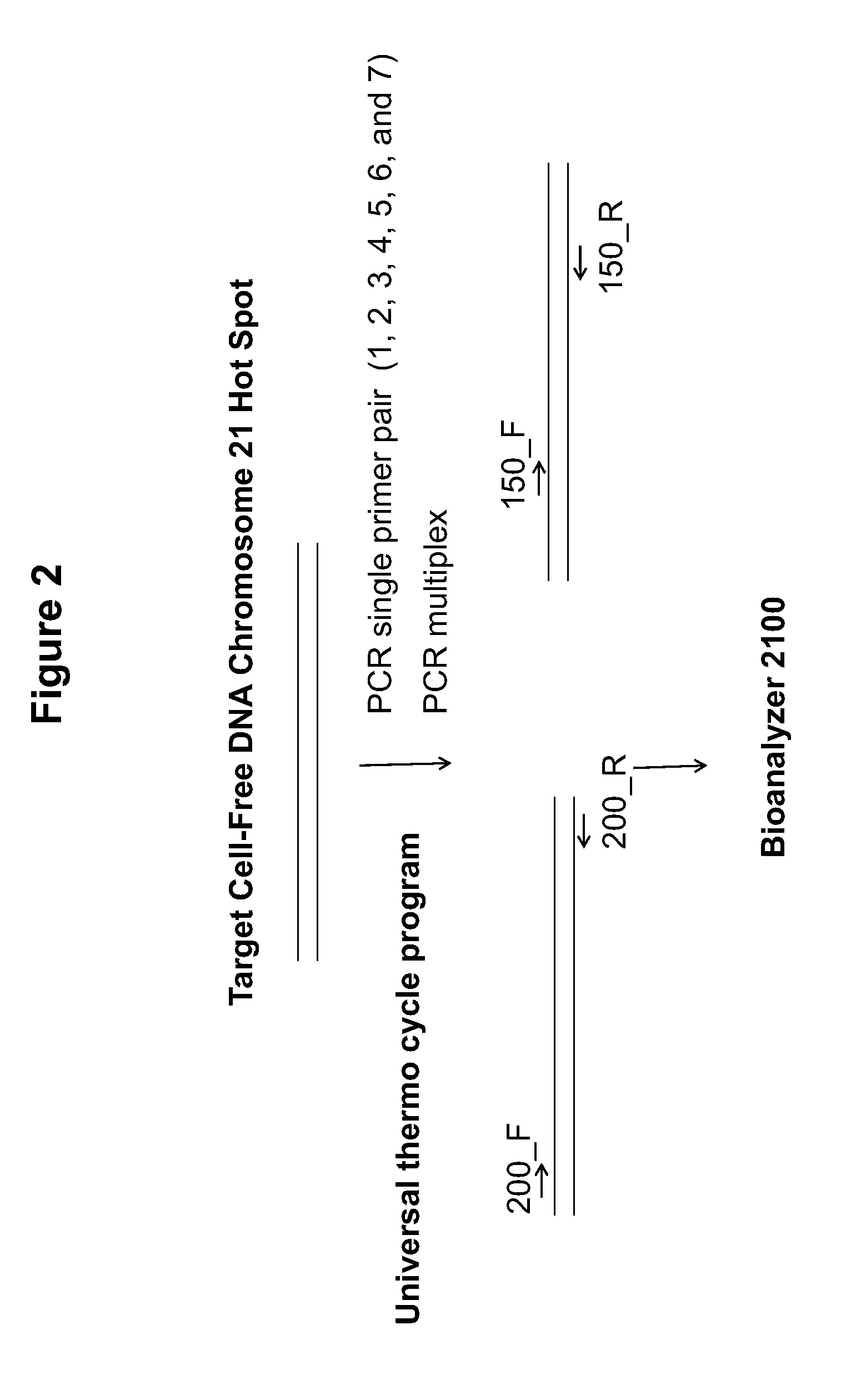
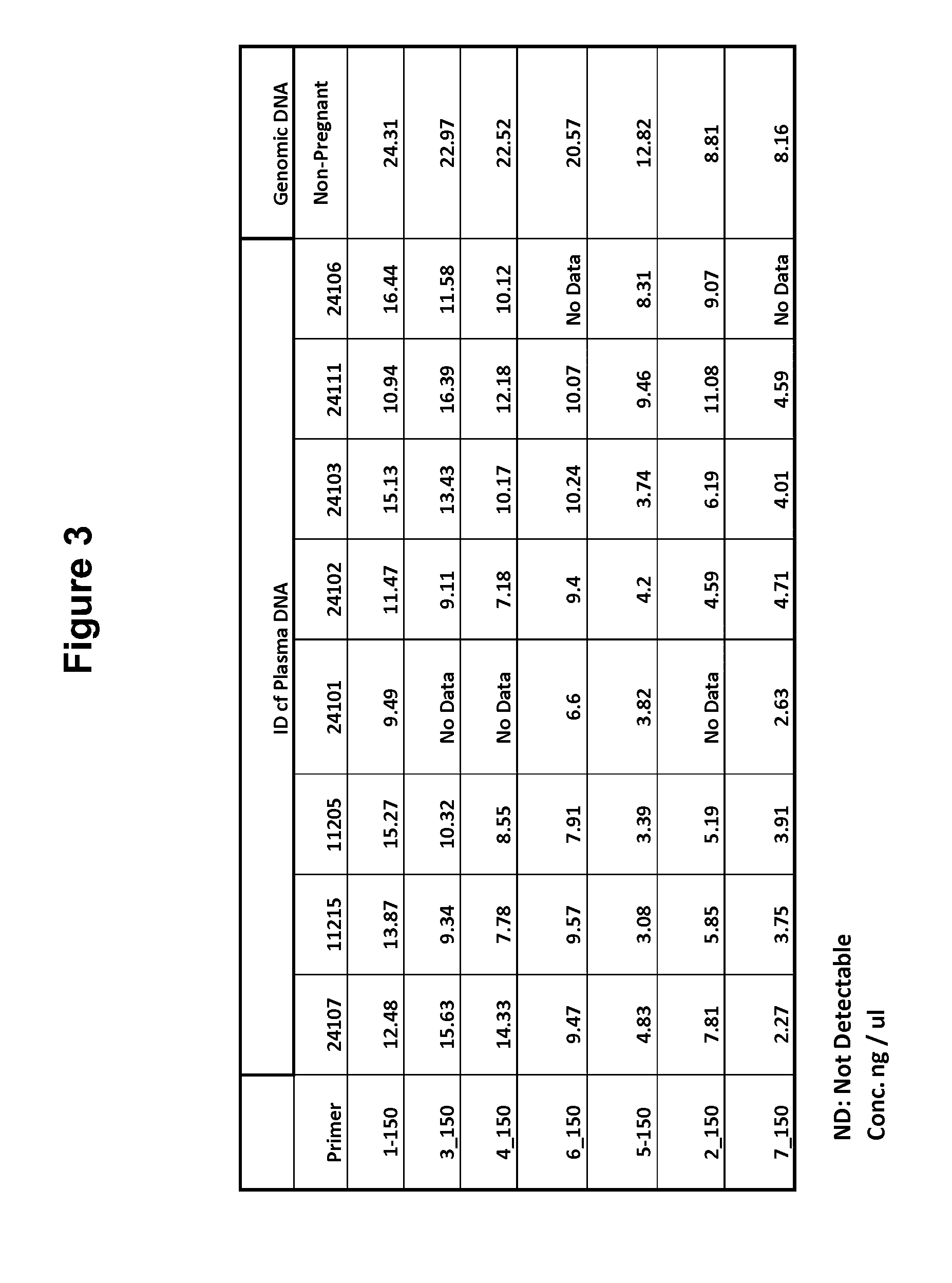
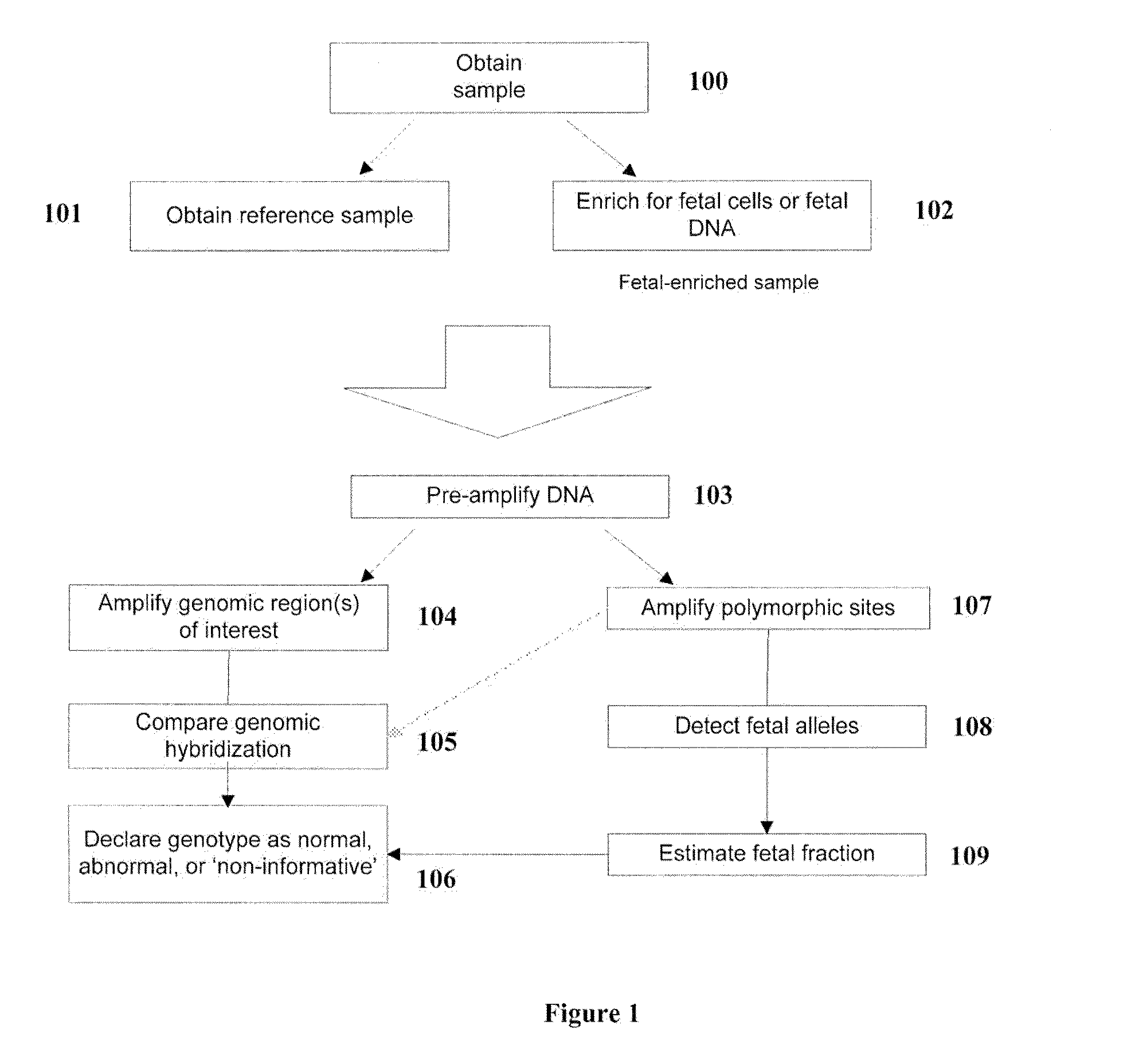
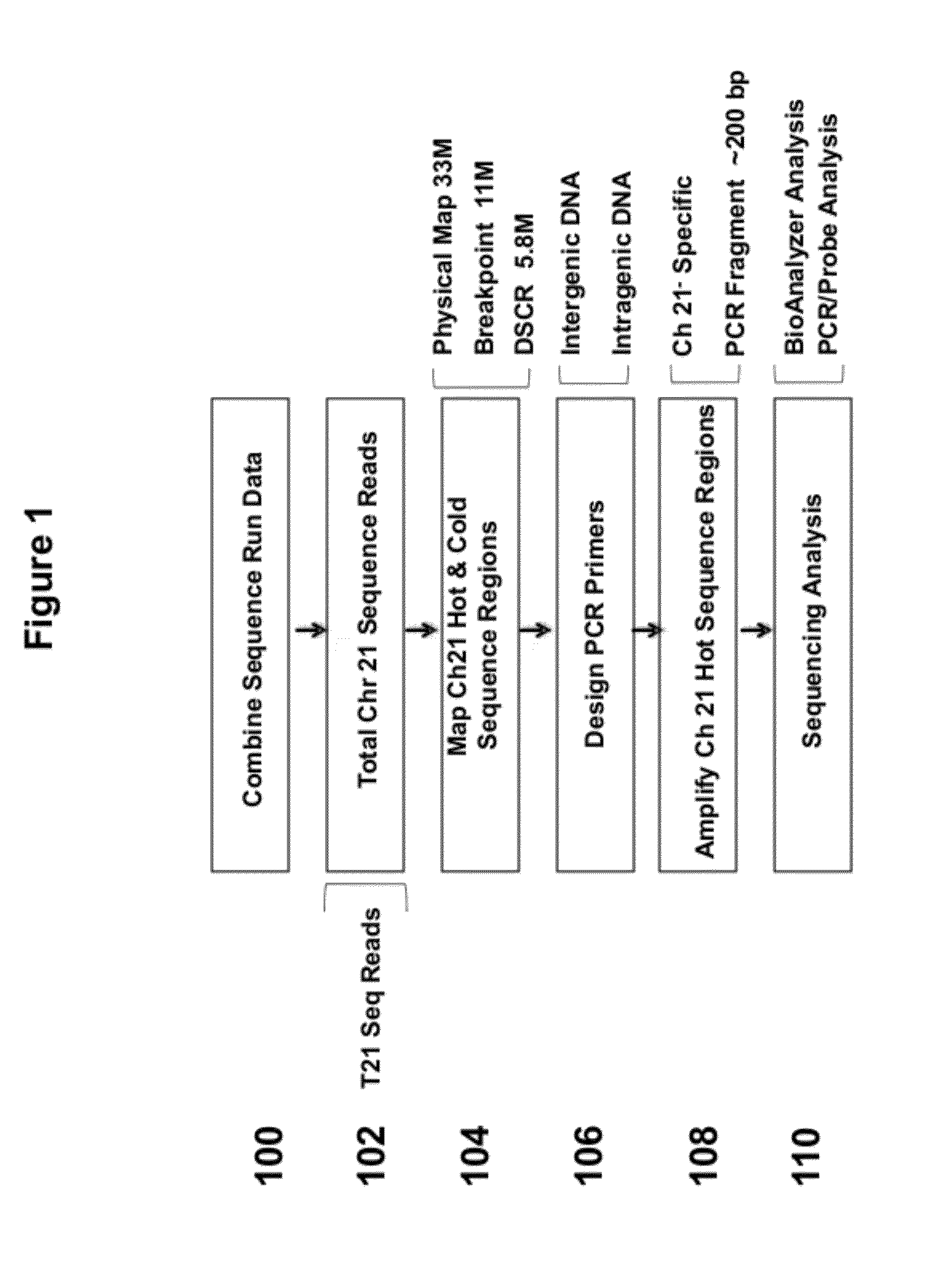
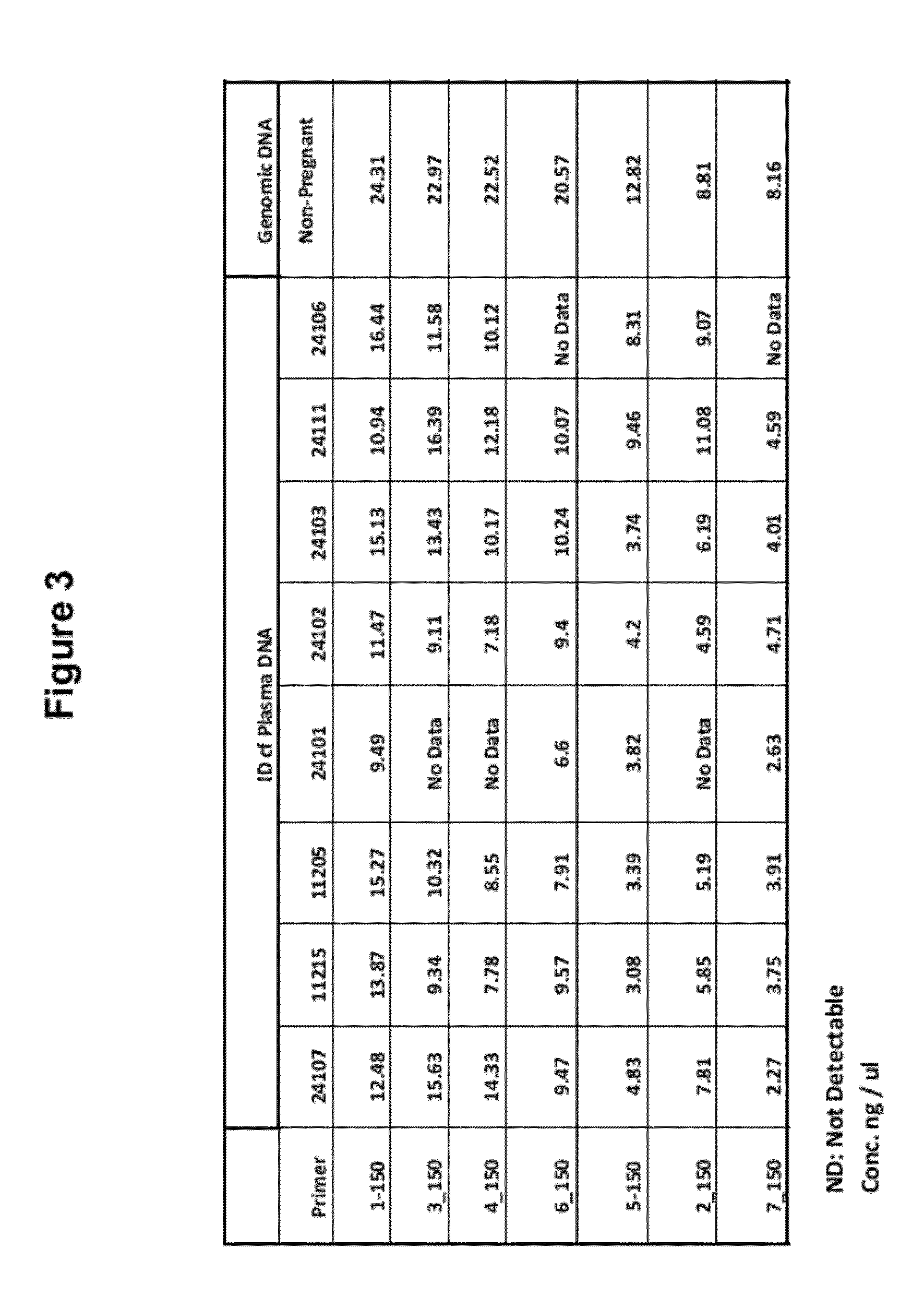
Methods for the Diagnosis of Fetal Abnormalities
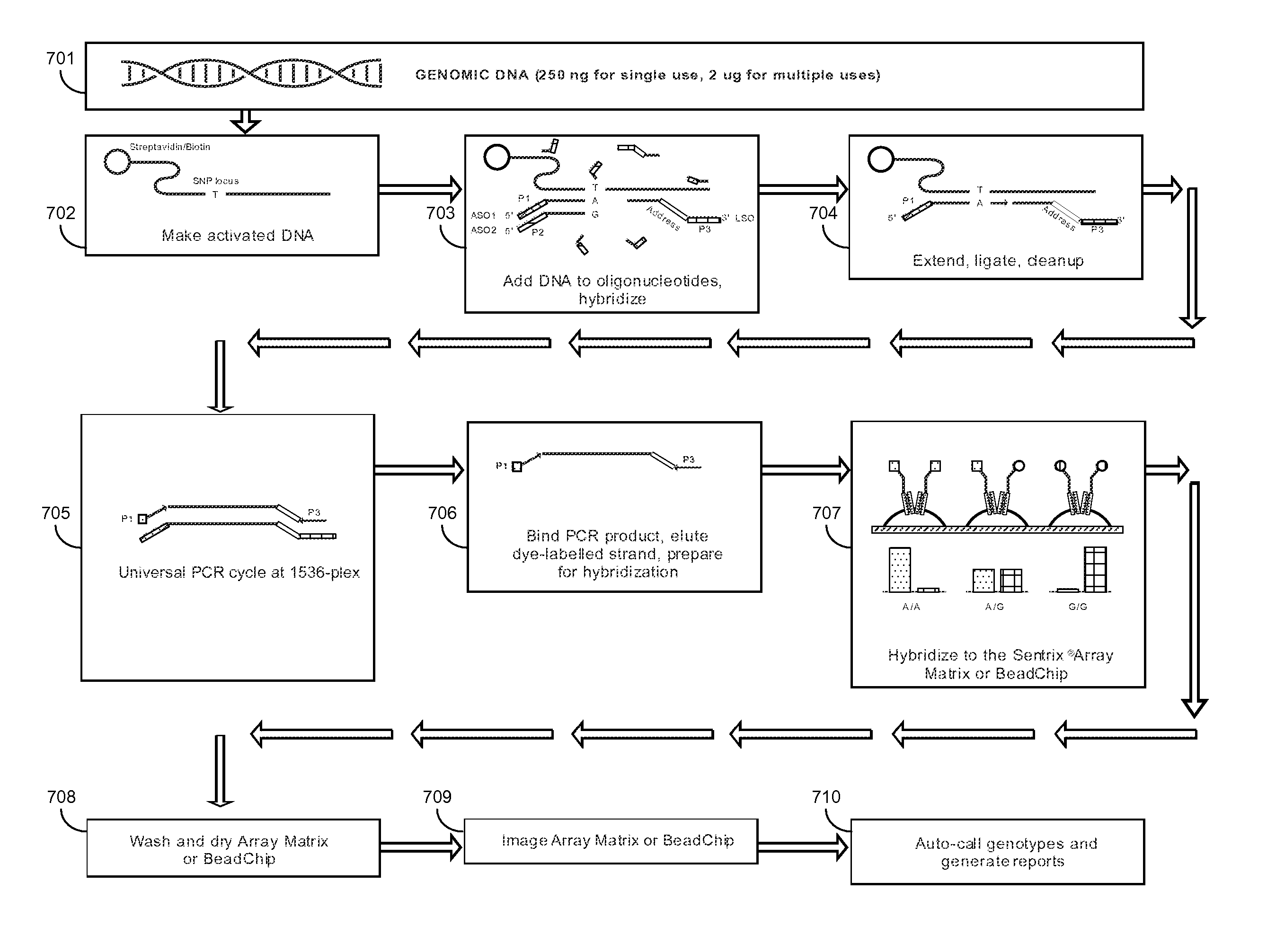
ActiveUS20080138809A1Reliable and accurate clinical diagnosisAccurate and reliable diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityRare cell
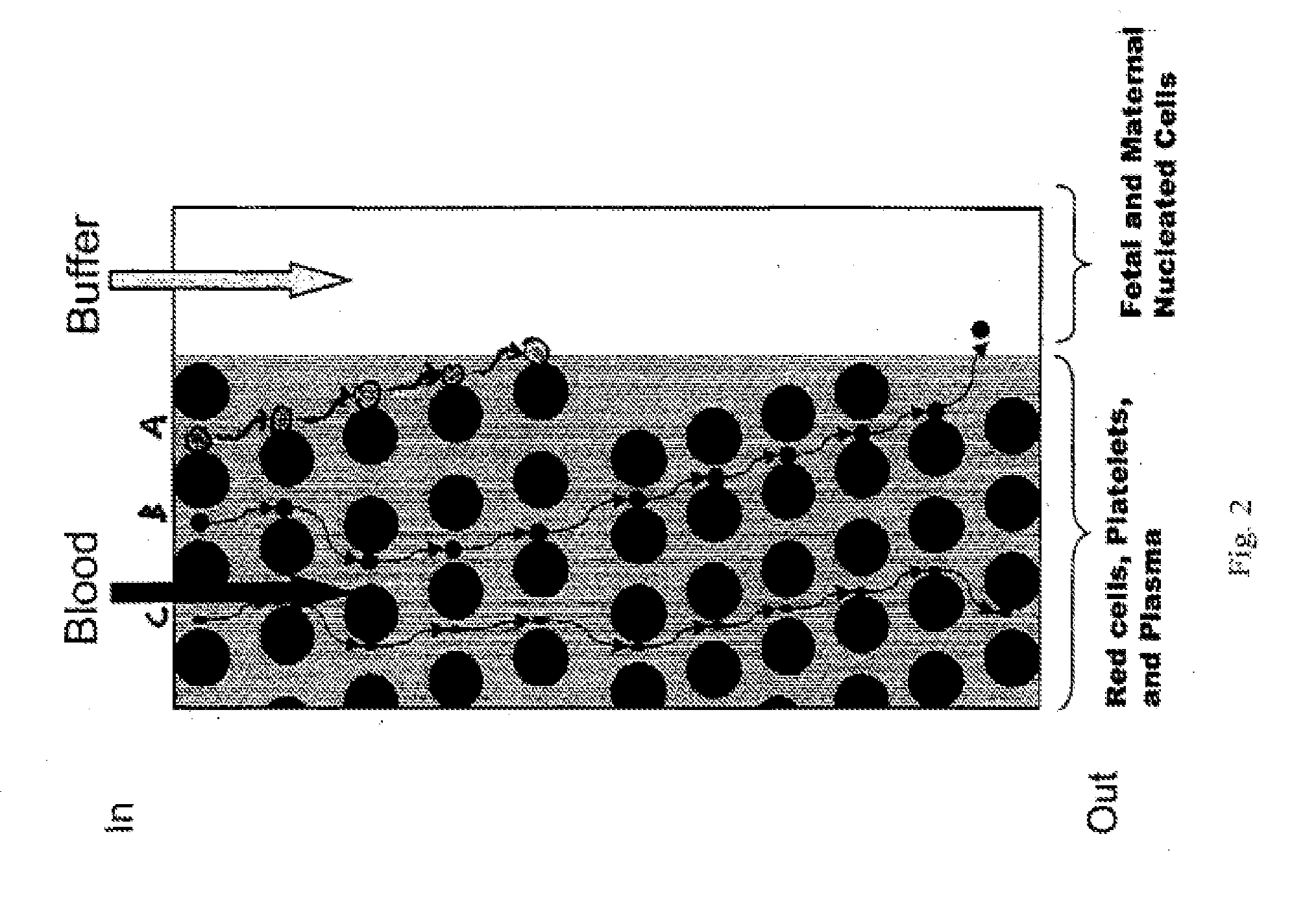
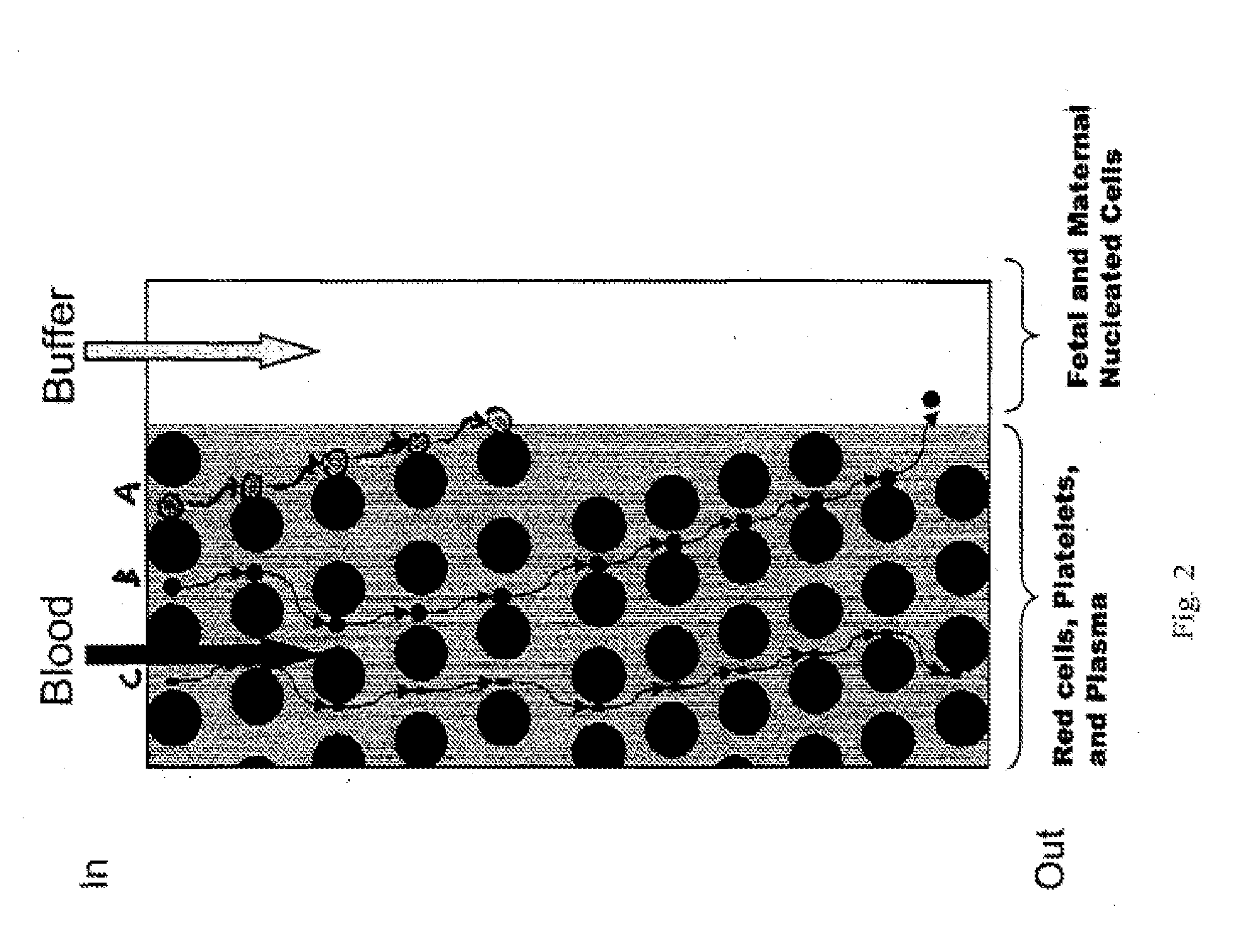
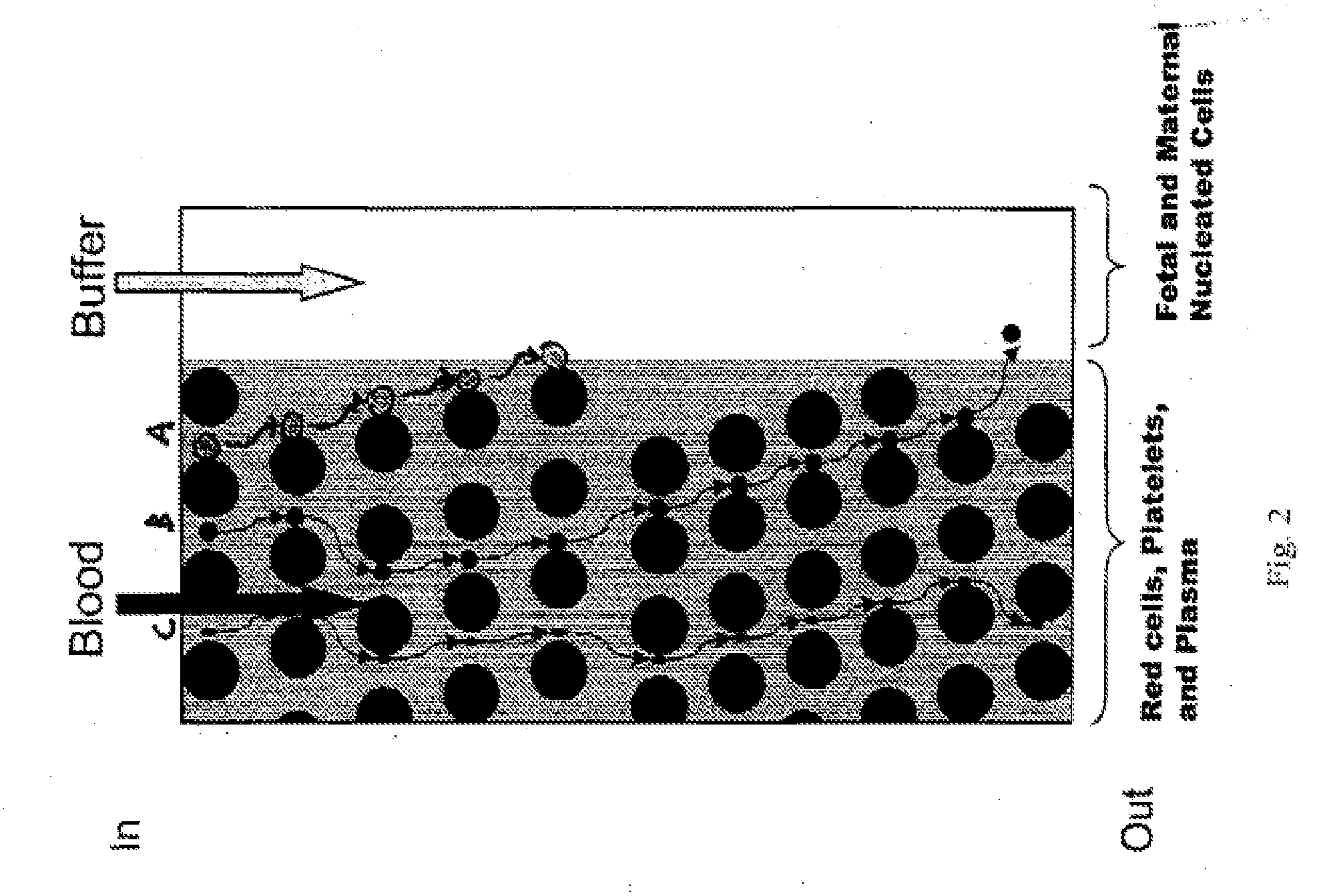
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, enriching, and analyzing rare cells that are present in the blood, e.g. fetal cells. The invention further features methods of analyzing rare cell(s) to determine the presence of an abnormality, disease or condition in a subject, e.g. a fetus by analyzing a cellular sample from the subject.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20080220422A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFetal abnormalityRare cell
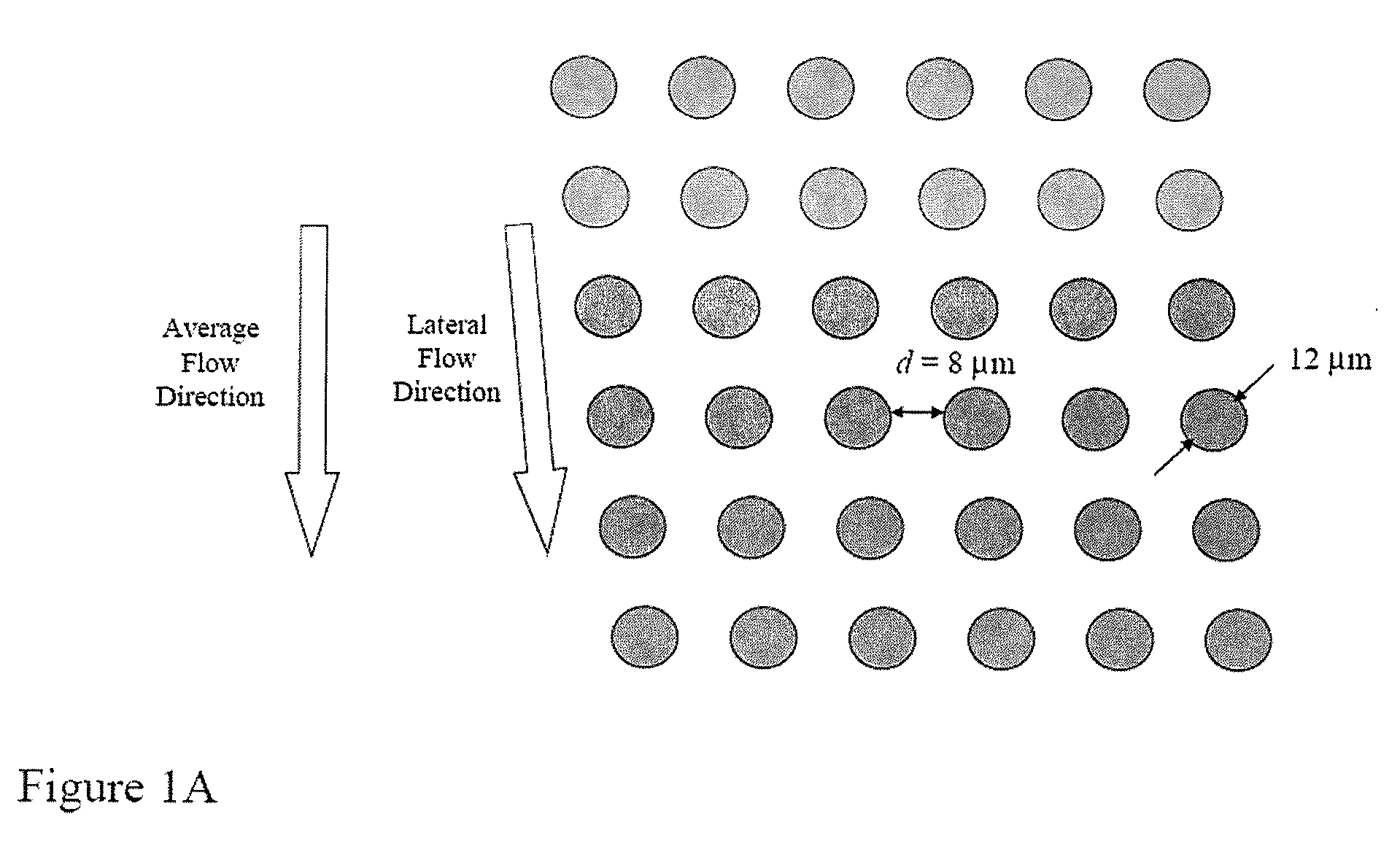
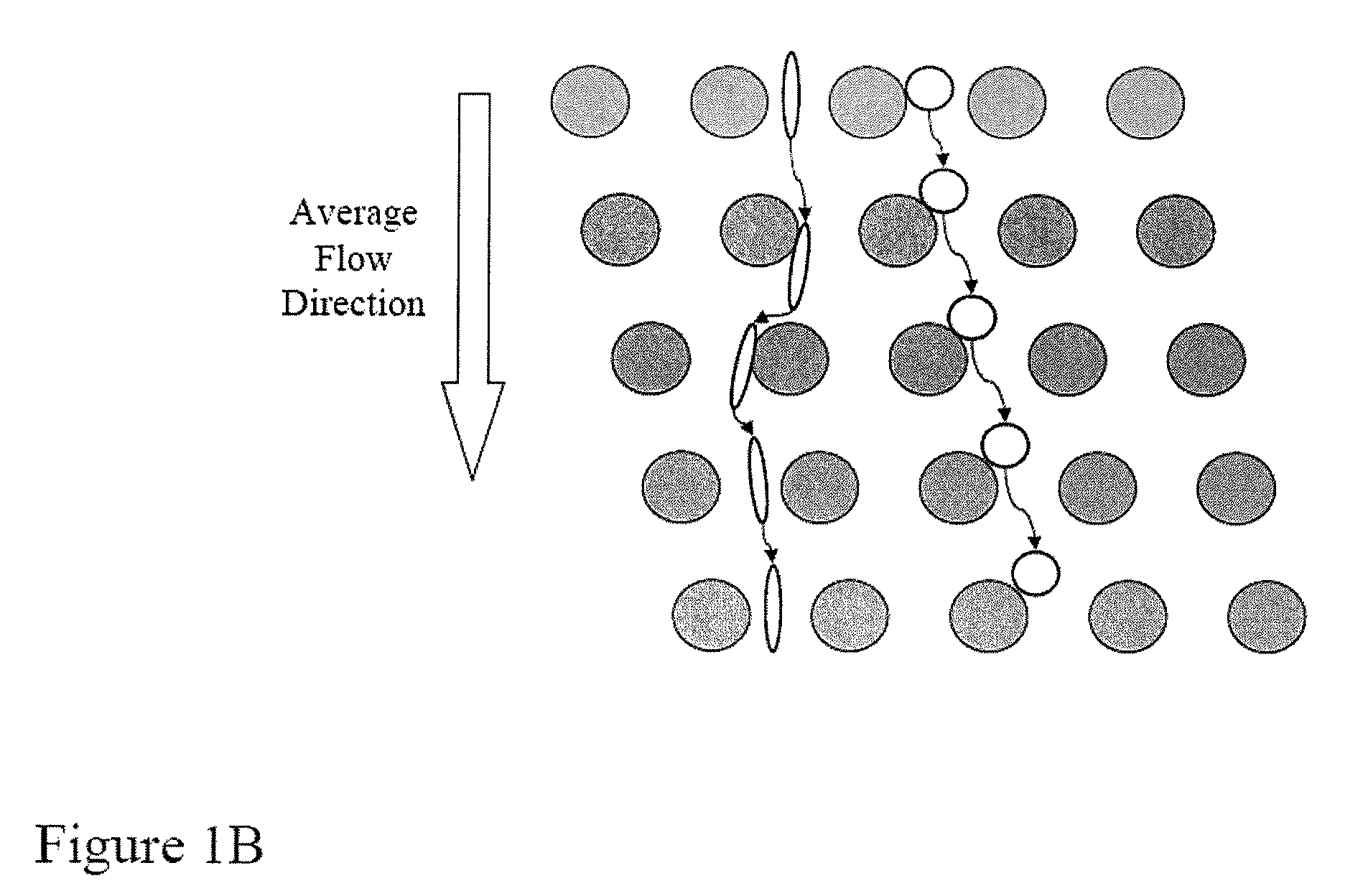
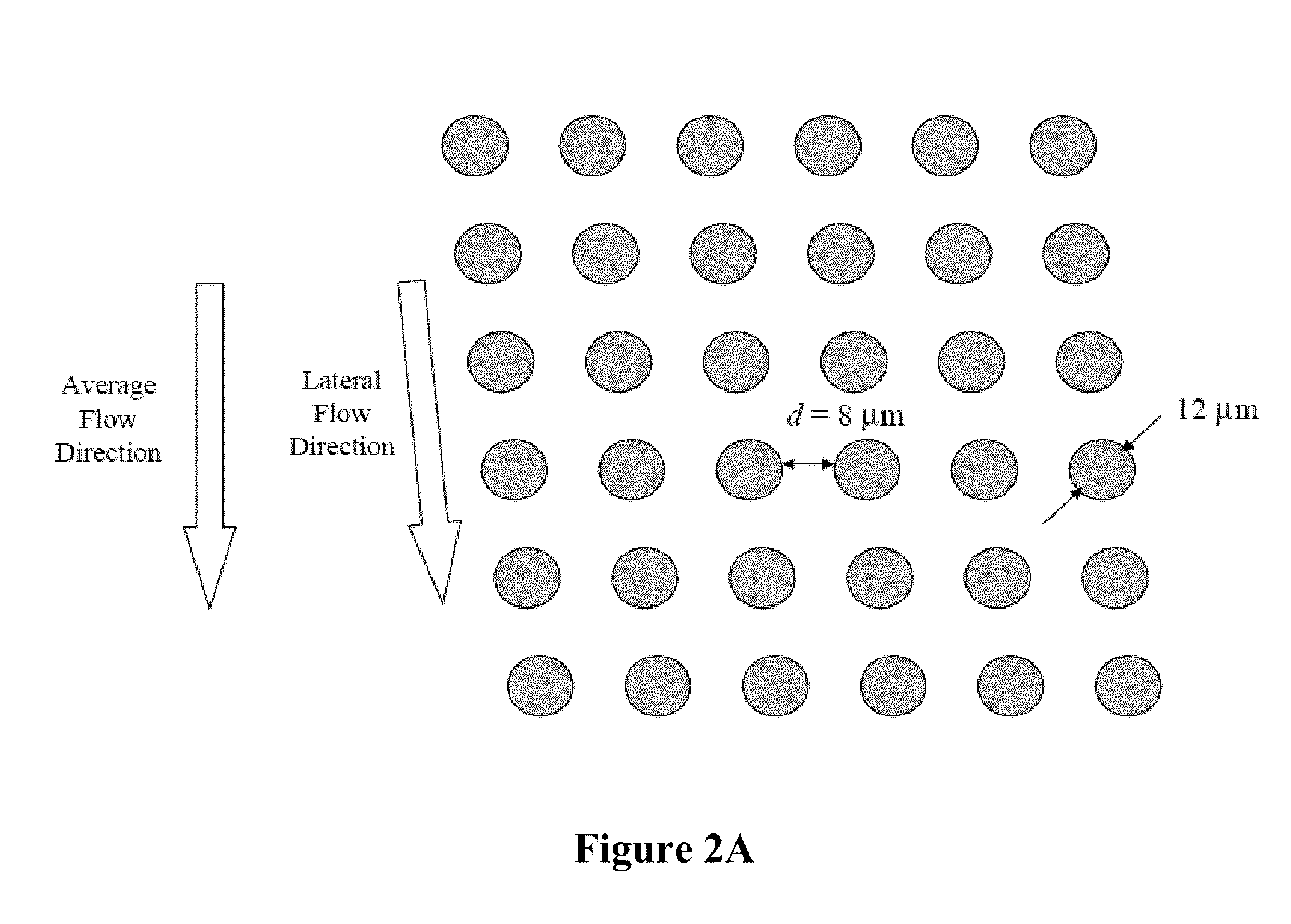
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS7166443B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
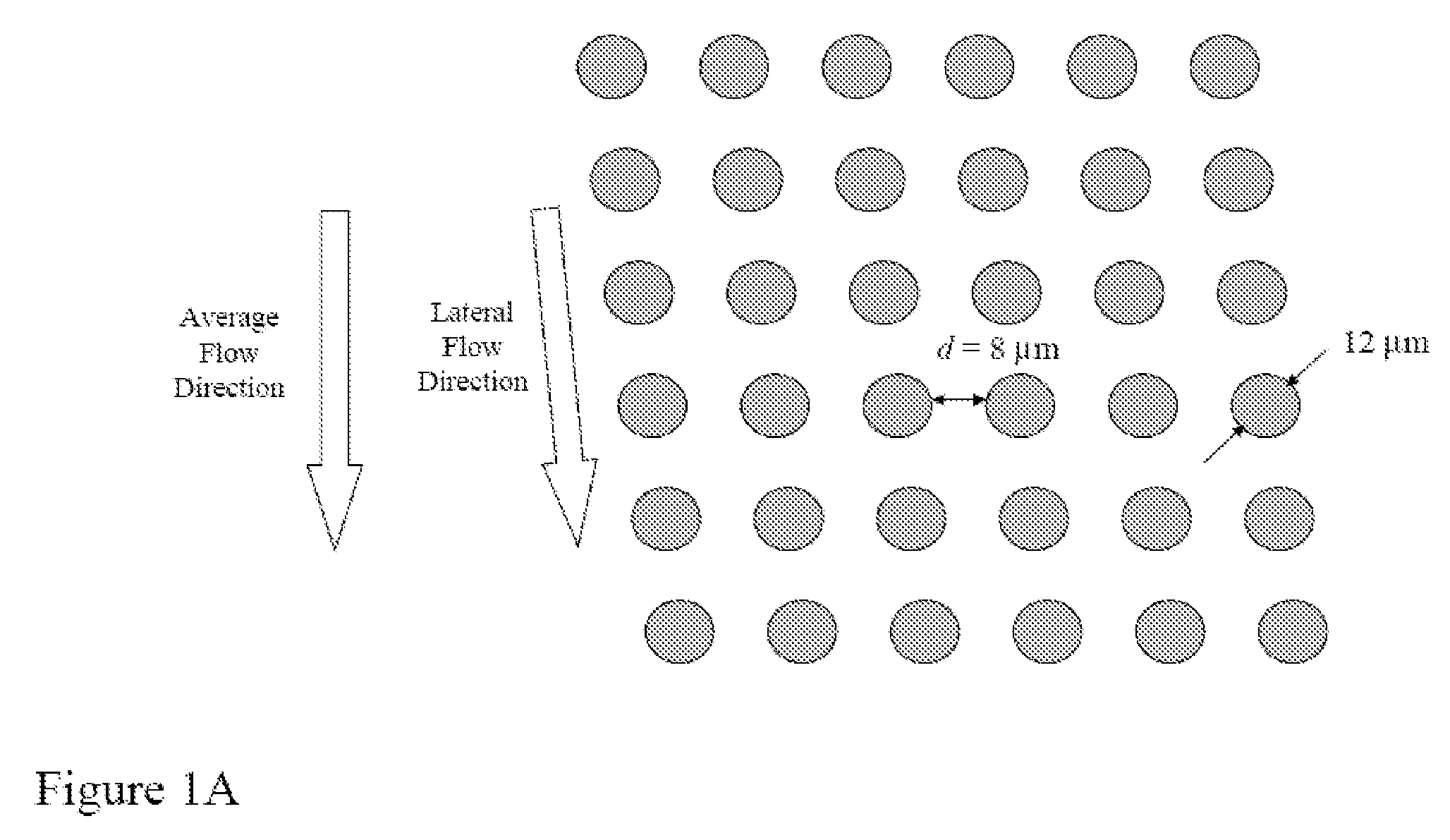
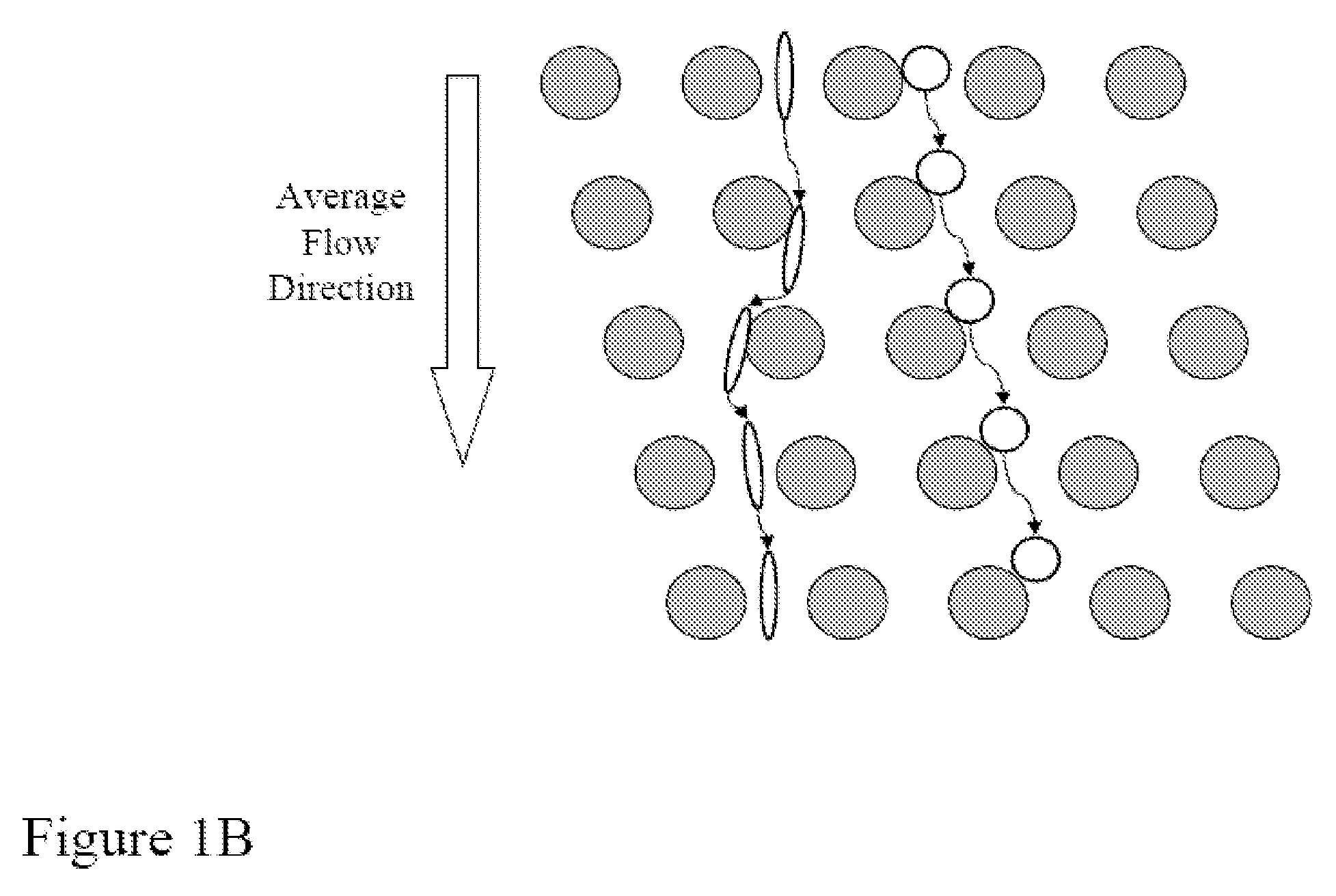
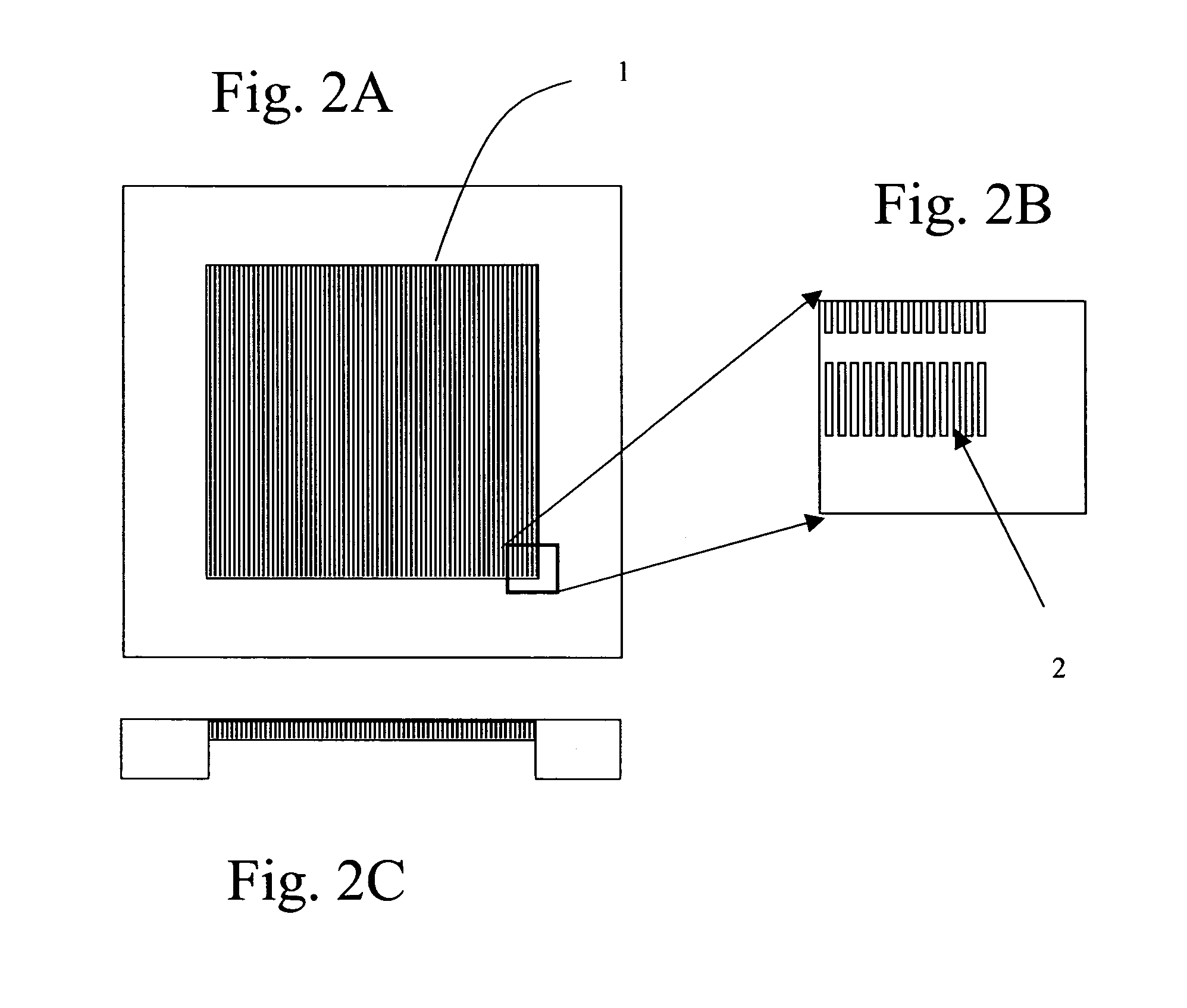
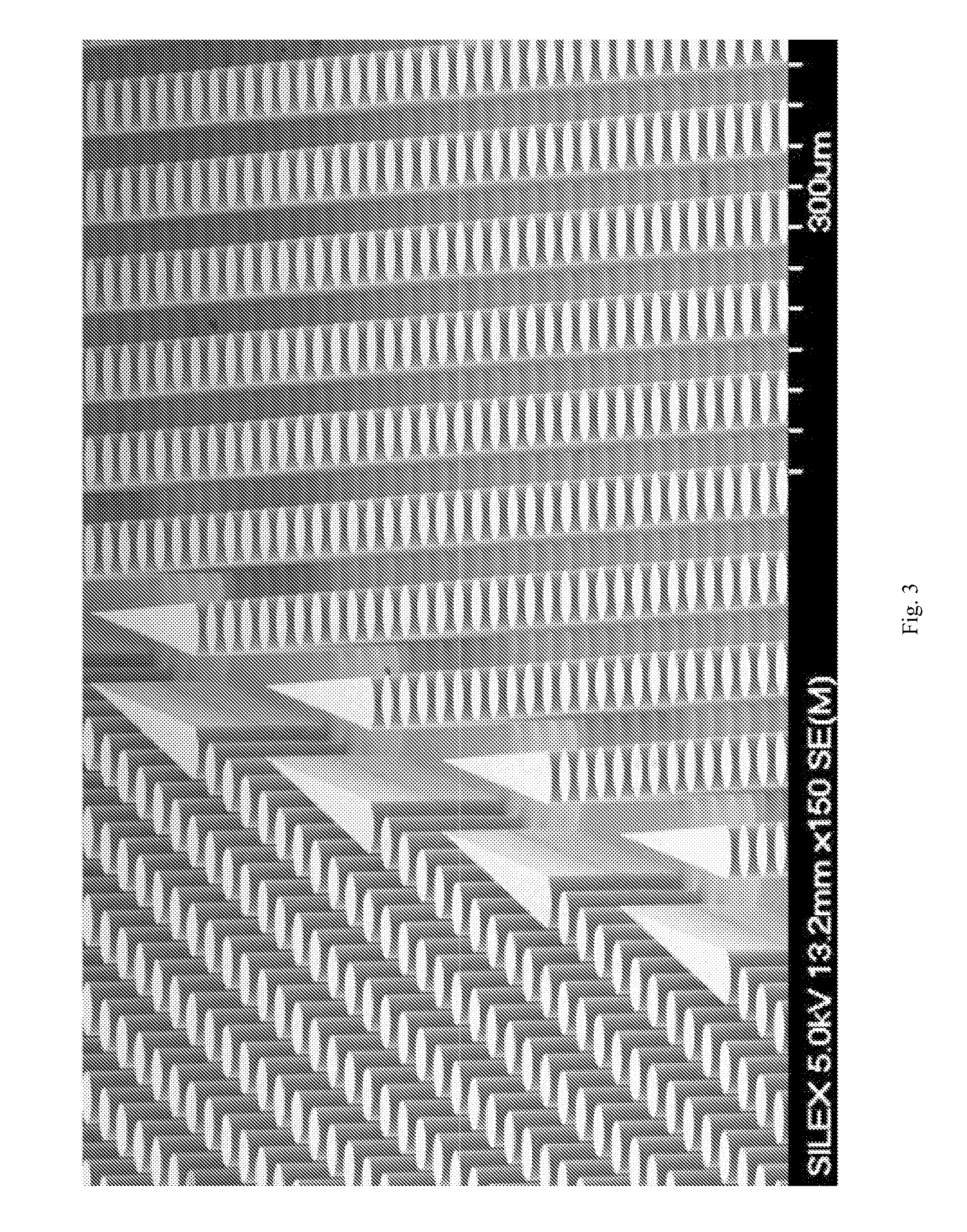
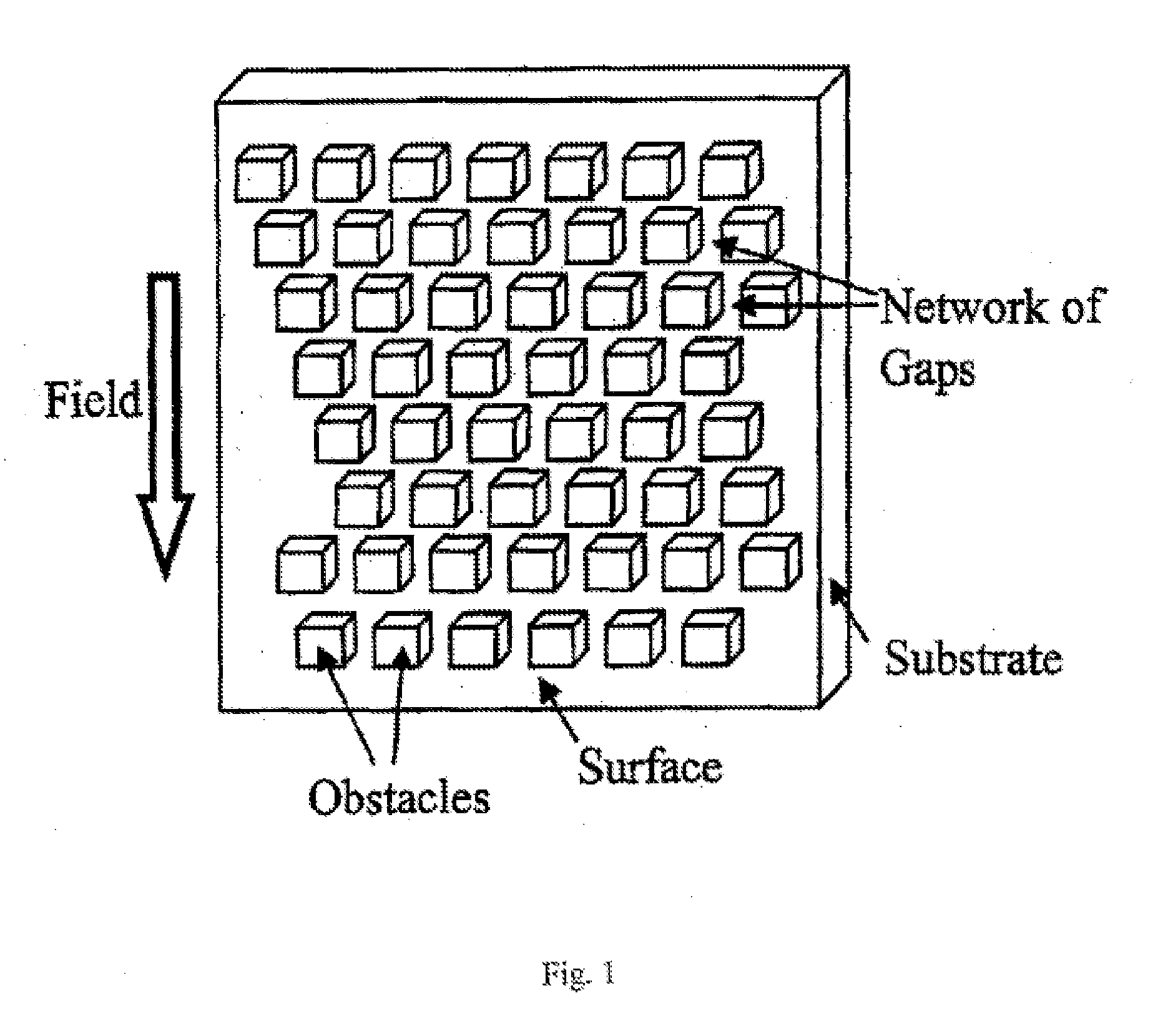
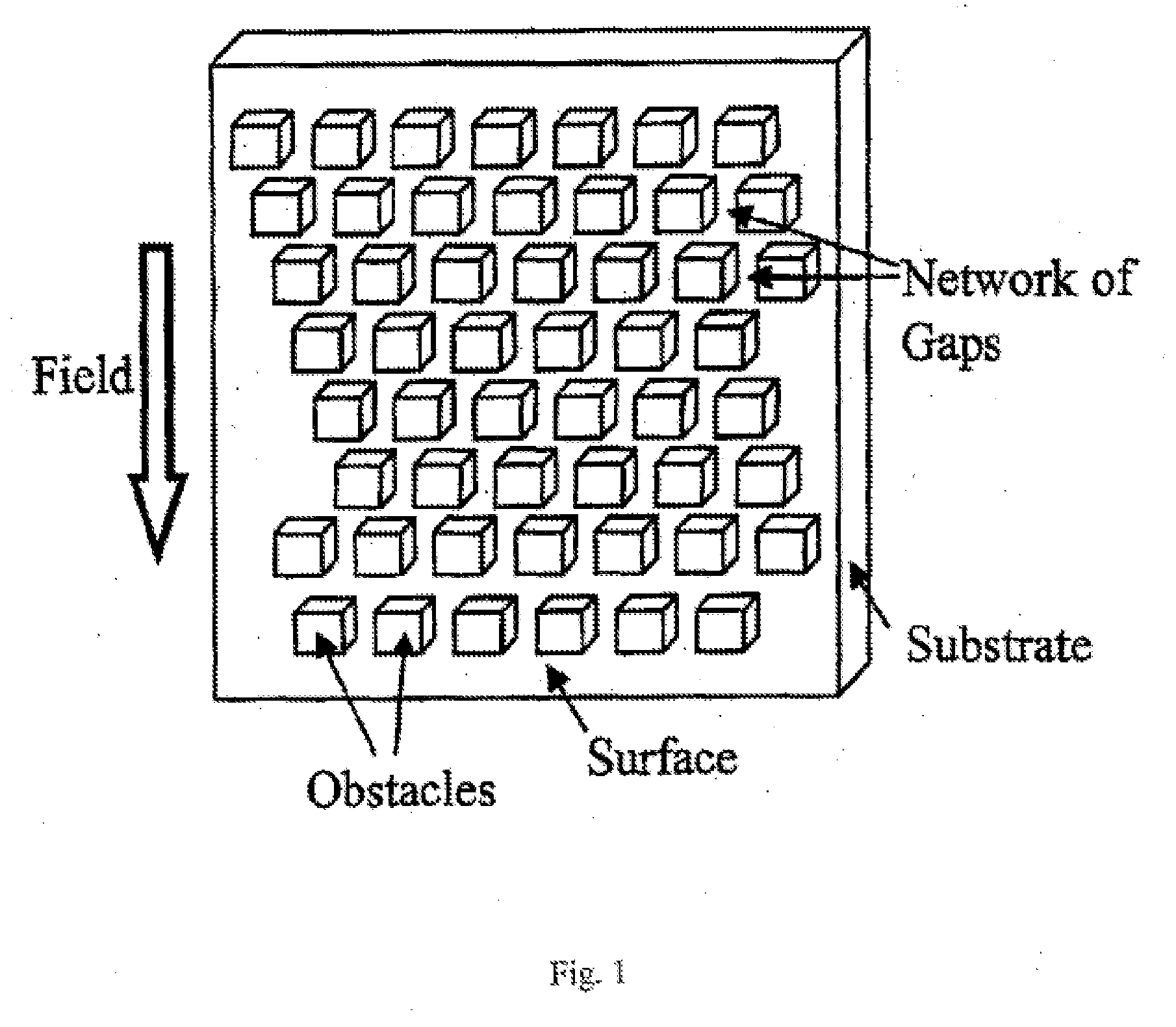
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients. The invention includes microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and methods of enriching rare cells of fluid samples using microfabricated filters of the present invention. The invention also includes solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample and methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample. Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that includes a microfabricated filter; automated means for directing fluid flow through at least one filtration chamber of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples. Preferred fluid samples are blood, effusion, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Methods for the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities
ActiveUS8137912B2Accurate and reliable diagnosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseFetal abnormality
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, enriching, and analyzing rare cells that are present in the blood, e.g. fetal cells. The invention further features methods of analyzing rare cell(s) to determine the presence of an abnormality, disease or condition in a subject, e.g. a fetus by analyzing a cellular sample from the subject.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS6949355B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients.A first aspect of the present invention is a microfabricated filter for filtering a fluid sample. A microfabricated filter of the present invention comprises at least one tapered pore, and preferably comprises at least two tapered pores whose variation in size is 20% or less. The present invention also includes a method of enriching rare cells of a fluid sample using a microfabricated filter of the present invention.Another aspect of the invention is solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample comprising a red blood cell aggregating agent and at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs. Solutions of the present invention include a combined solution for rare cell enrichment that comprise RBC aggregating agents, at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs, and at least one additional specific binding member for the removal of undesirable sample components other than RBCs. The invention also includes methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions and combined solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample.Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that comprises or engages one or more microfabricated filters of the present invention; automated means for directing fluid flow through the one or more filtration chambers of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using an automated system for separating rare cells from a fluid sample. Preferred fluid samples are effusion, blood, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Selection of cells using biomarkers
InactiveUS20080113358A1Easy to separateIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityFetal cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to isolate, select or detect the presence of a target cell (e.g., fetal cells) in a sample comprising mixed populations of cells that vastly outnumber the target cells. Target cells include fetal cells, such as nucleated red blood cells, and methods of selecting such cells include diagnosis of fetal abnormalities, i.e., aneuploidy. Furthermore, methods comprise utilizing fetal biomarkers to select fetal cells in a sample comprising fetal and adult cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Methods of fetal abnormality detection
InactiveUS20110312503A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationFetal abnormalityFetal aneuploidy
Methods and kits for selectively enriching non-random polynucleotide sequences are provided. Methods and kits for generating libraries of sequences are provided. Methods of using selectively enriched non-random polynucleotide sequences for detection of fetal aneuploidy are provided.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Business methods for prenatal Diagnosis
The present invention relates to business methods in which screening services and diagnostics for the condition of a fetus are provided. Fetal abnormalities, include chromosomal and other genetic ies, are detected through the analysis of fetal cells obtained from maternal blood samples.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
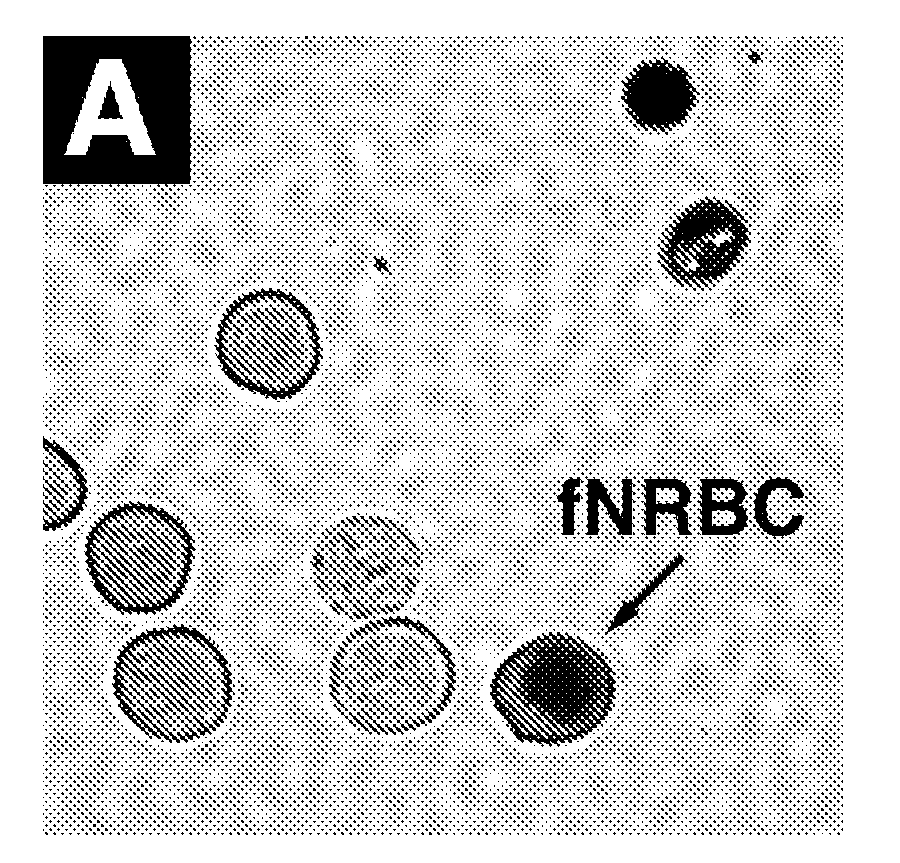
Methods for detecting fetal abnormality
InactiveUS20070059716A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal abnormalityNucleic Acid Probes
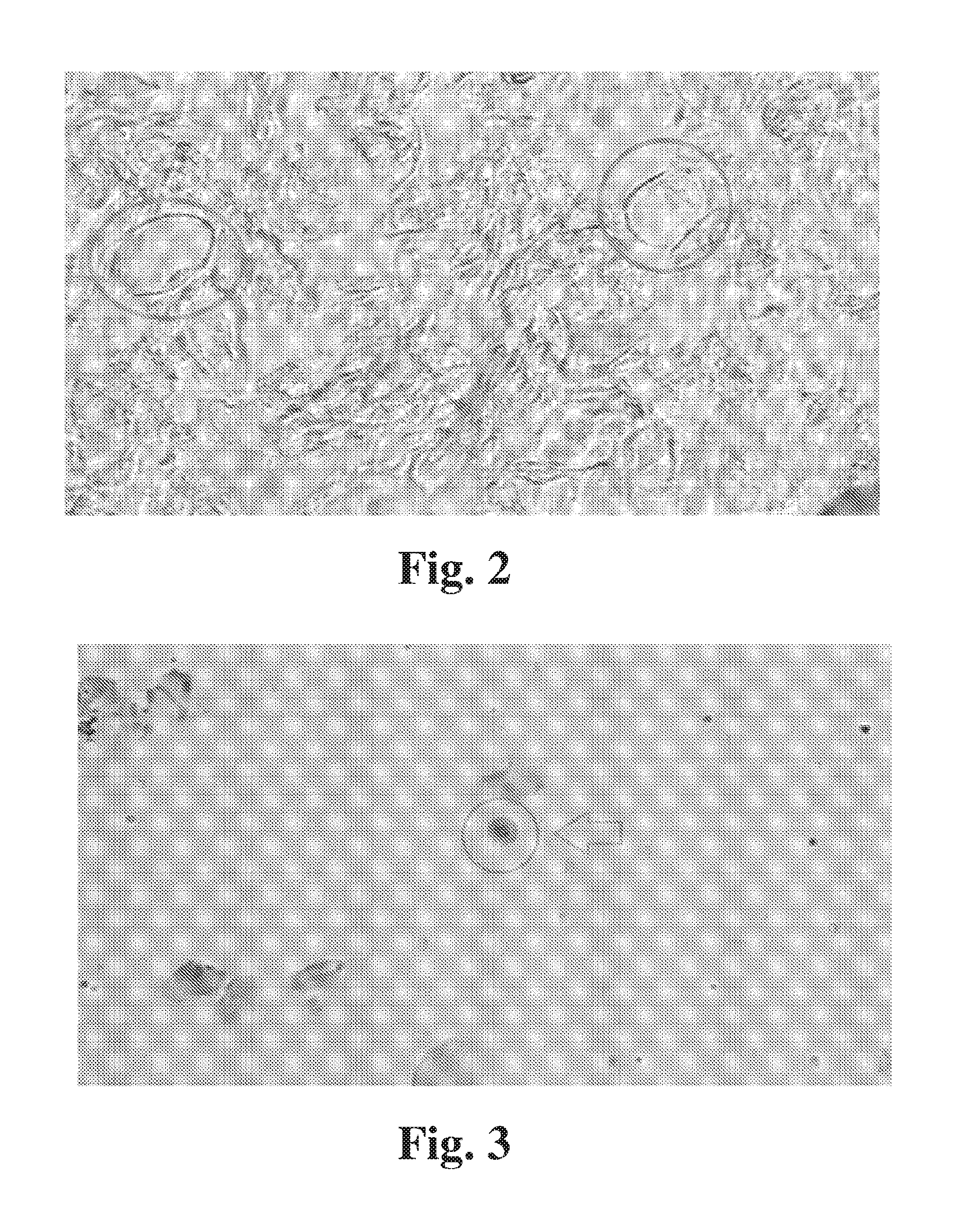
The invention relates to a method of identifying fetal abnormality from a maternal blood sample by capturing an image of a fetal nucleated red blood cell obtained from the maternal blood sample; inputting probe intensities for a plurality of nucleic acid probes that bind fetal nucleic acids of interest; analyzing the probe intensities; and generating a diagnostic output according to results of the analysis. In some embodiments, the probes are specific to a chromosome.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
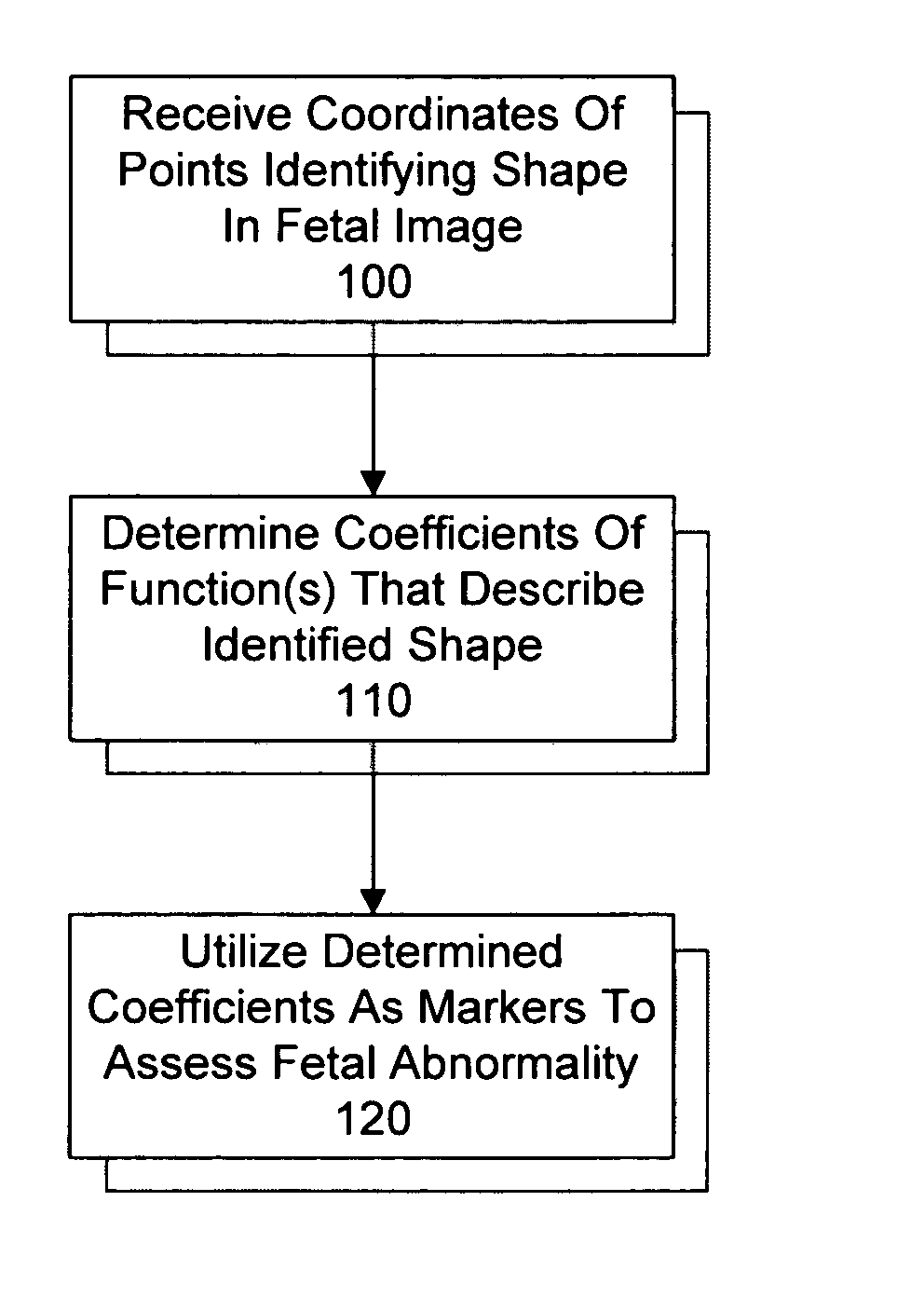
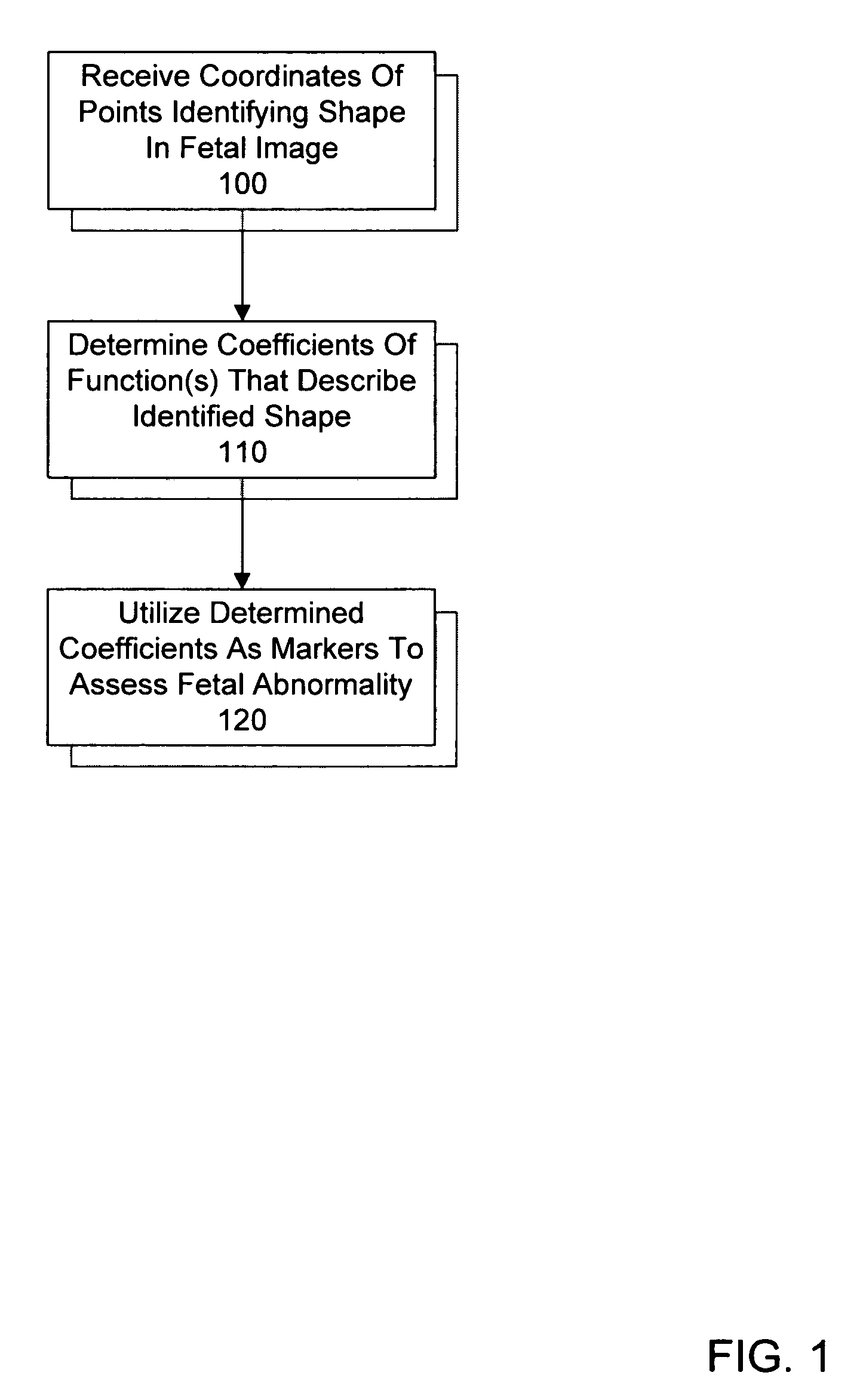
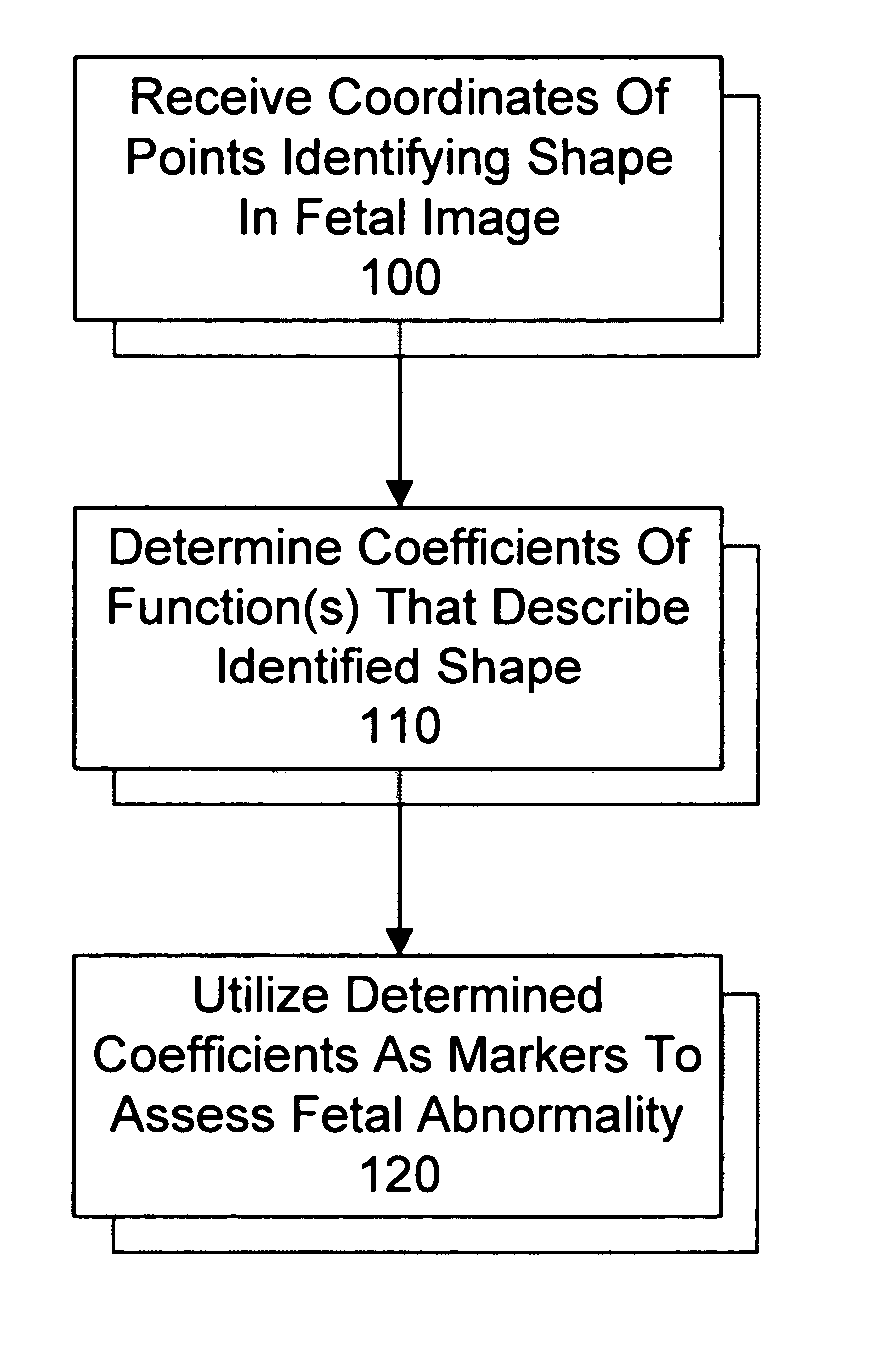
System and method for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality
InactiveUS7244233B2Medical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFetal abnormalityObstetrics
A method and system for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality. According to one embodiment, coordinates of points identifying a shape in a fetal image are received, coefficients of one or more mathematical functions that describe the identified shape are determined, and the determined coefficients are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20100136529A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresFetal abnormalityRare cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities using polymorphisms including short tandem repeats
InactiveUS20090280492A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
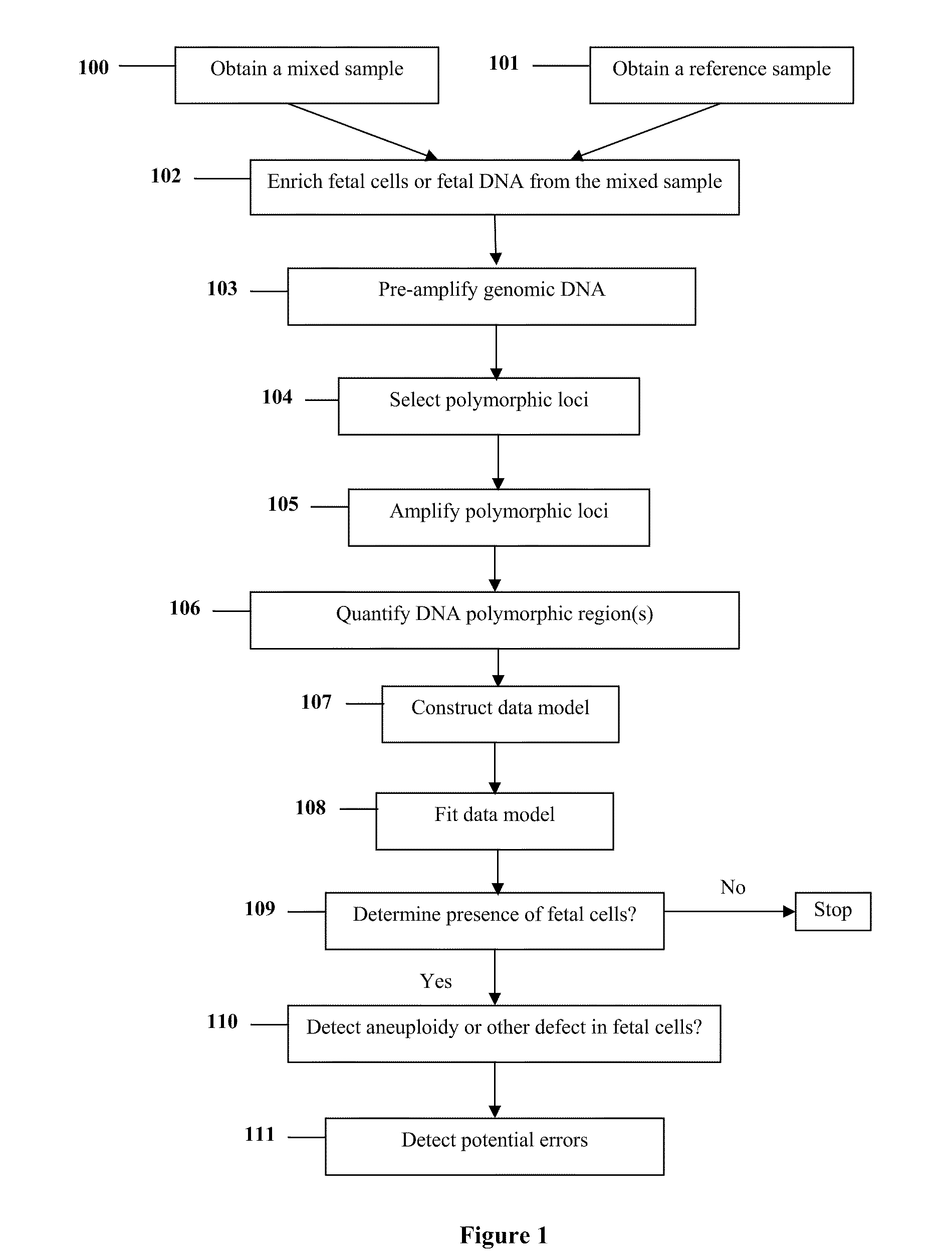
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, i.e. aneuploidy. In addition, the present invention provides methods to determine when there are insufficient fetal cells for a determination and report a non-informative case. The present invention involves quantifying regions of genomic DNA from a mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying DNA polymorphisms from the mixed sample.
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +2
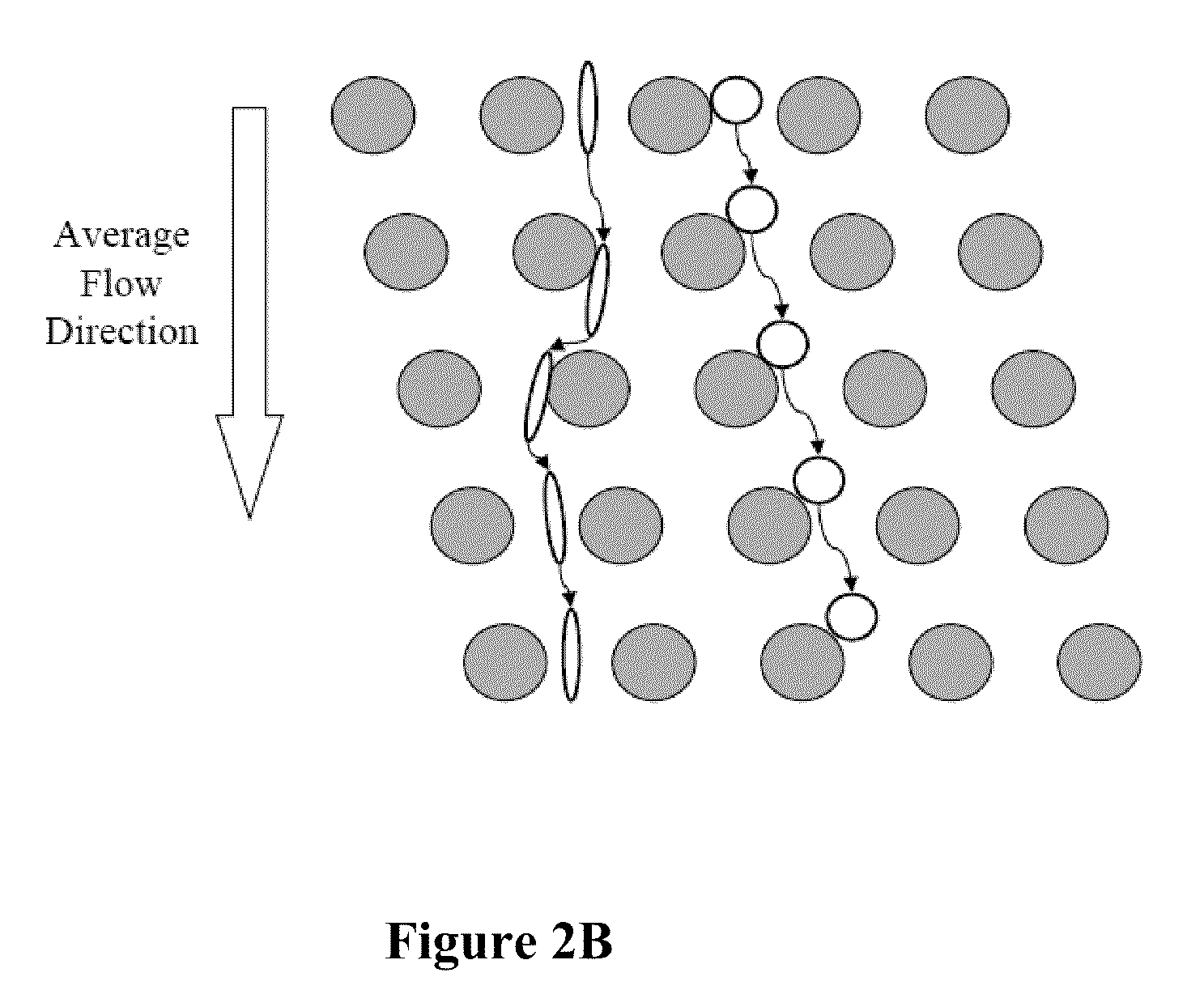
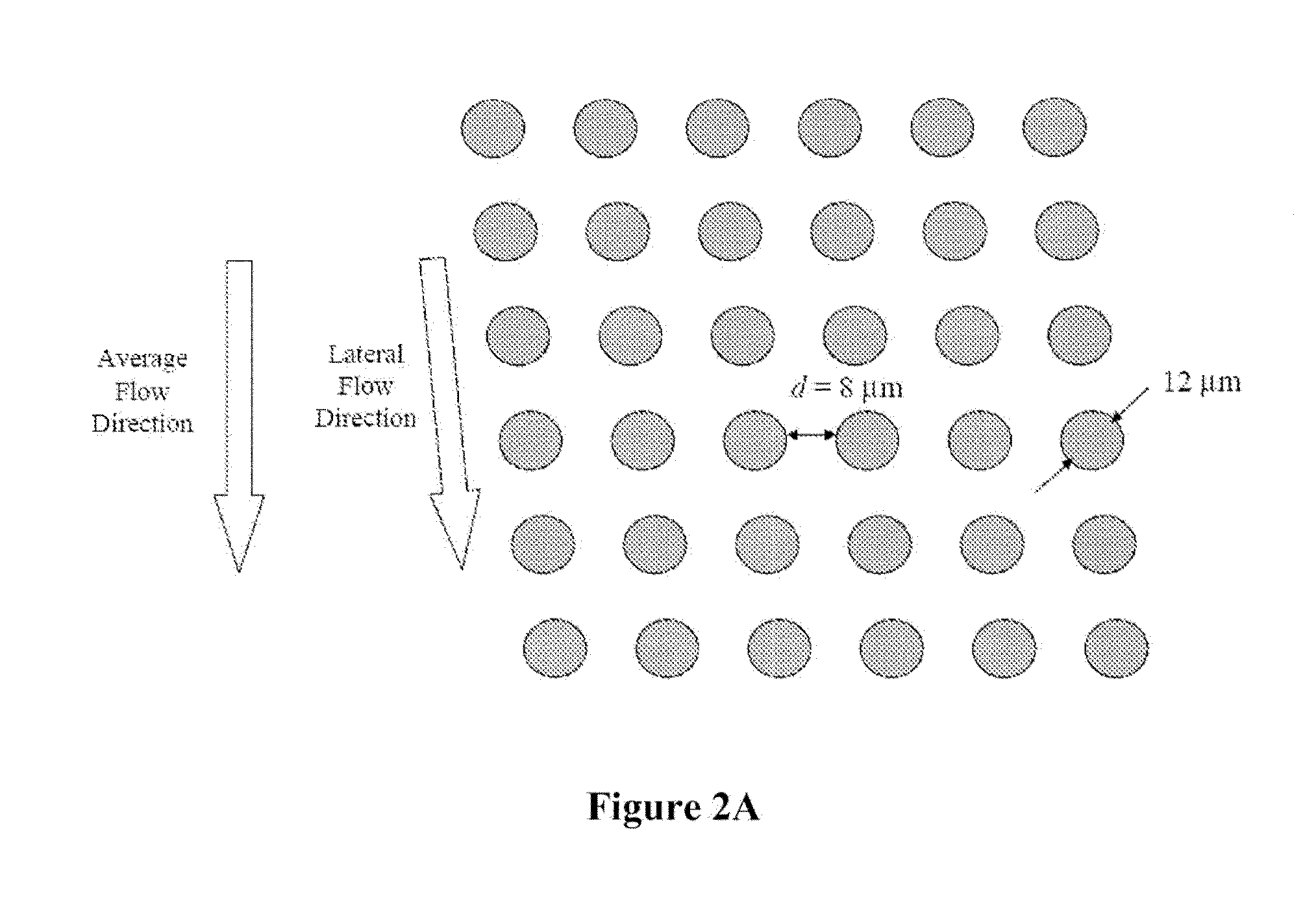
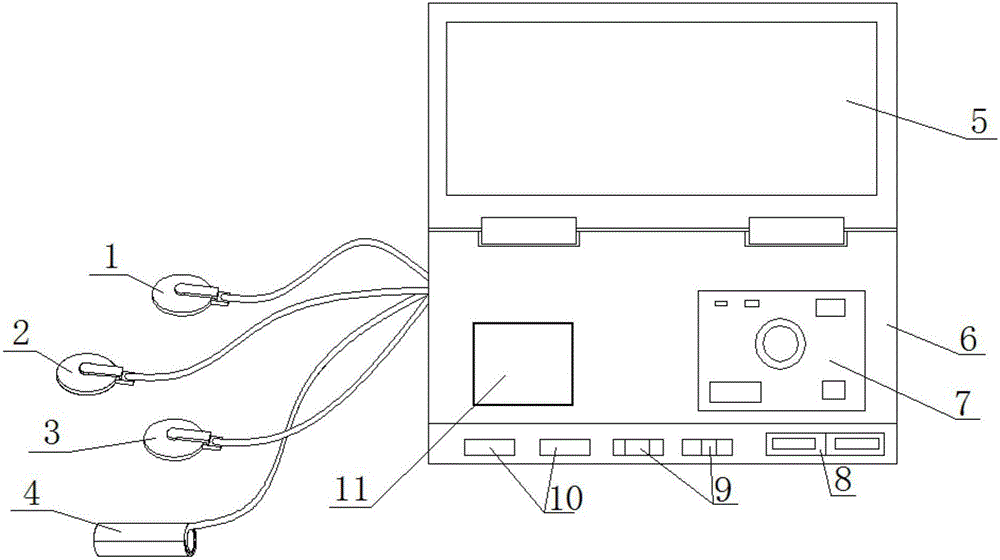
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities by comparative genomic hybridization analysis
InactiveUS20100112586A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +1
Methods of using miRNA for detection of in vivo cell death
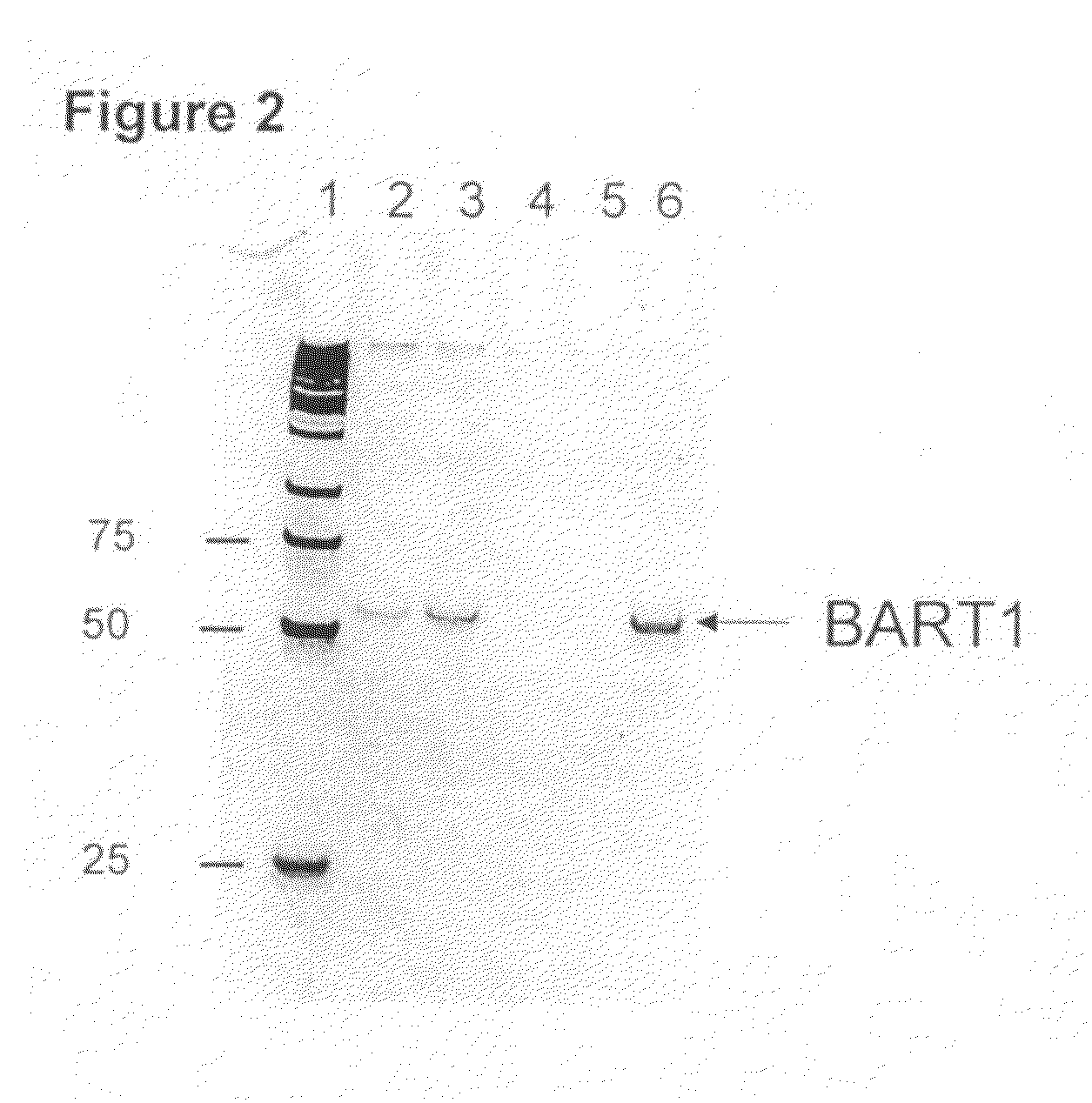
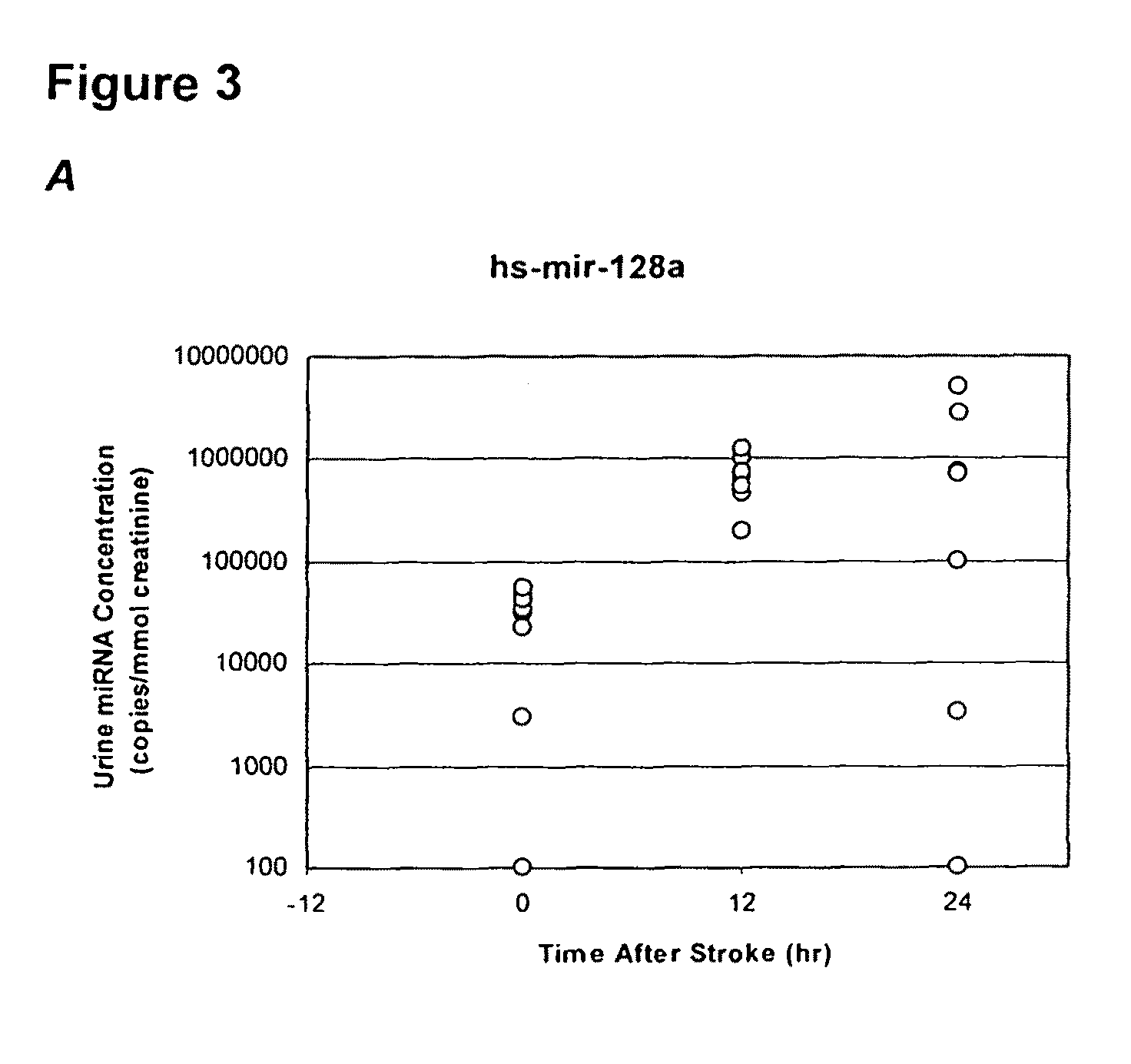
InactiveUS20090081640A1Reducing nucleic acid degradationReduce degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal abnormalityCytotoxicity
Described are non-invasive methods of detecting in vivo cell death by measuring levels of ubiquitous and tissue specific miRNA. The method can be applied for detection of pathologies caused or accompanied by cell death, as well as for diagnosis of infectious disease, cytotoxic effects induced by different chemical or physical factors, and the presence of specific fetal abnormalities.
Owner:GENSIGNIA
Method and composition for treatment of headache using magnesium
Owner:ALTURA BURTON M +2
Multi-marker screening protocol for fetal abnormalities
A method of assessing a pregnant woman's risk of having a fetus with a fetal abnormality by determining the fetus' BPD / OFD ratio and using the BPD / OFD ratio in conjunction with one or more other screening markers for the fetal abnormality. Also provided is a method of determining whether a pregnant woman is screen-positive or screen-negative by comparing the BPD / OFD ratio of the pregnant woman's fetus to a risk cut-off level.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
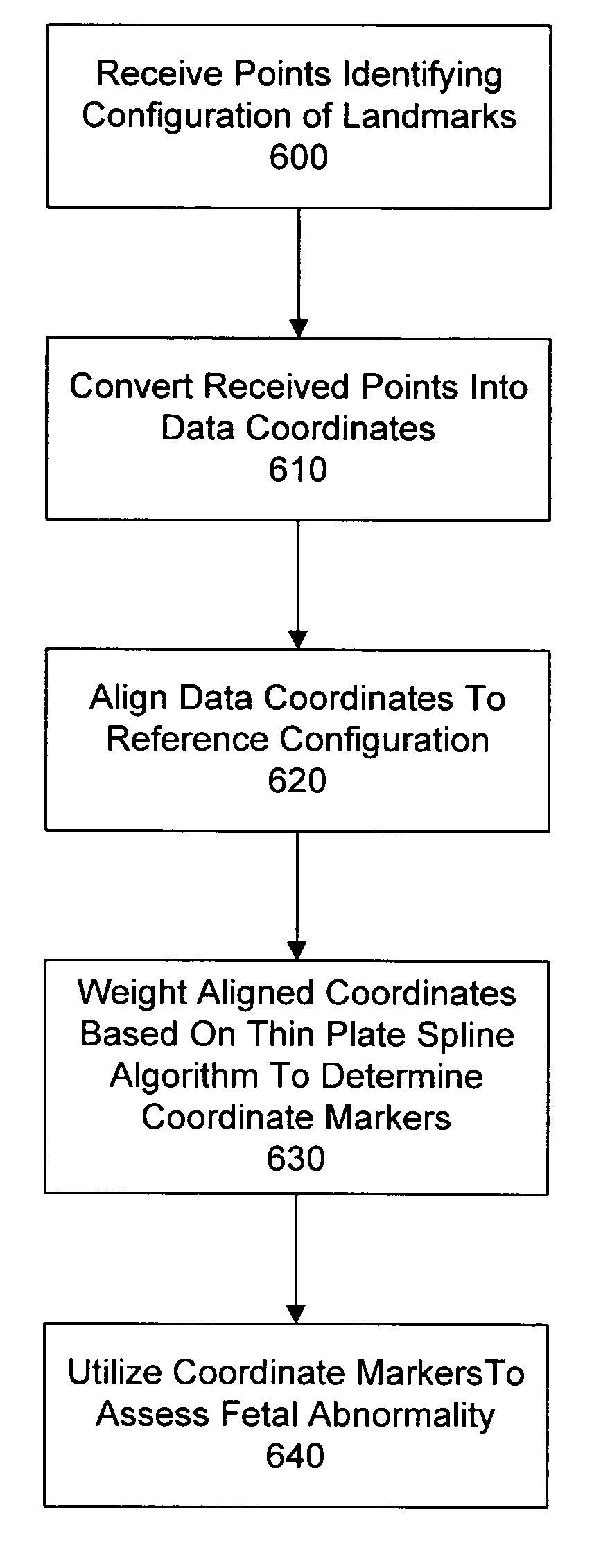
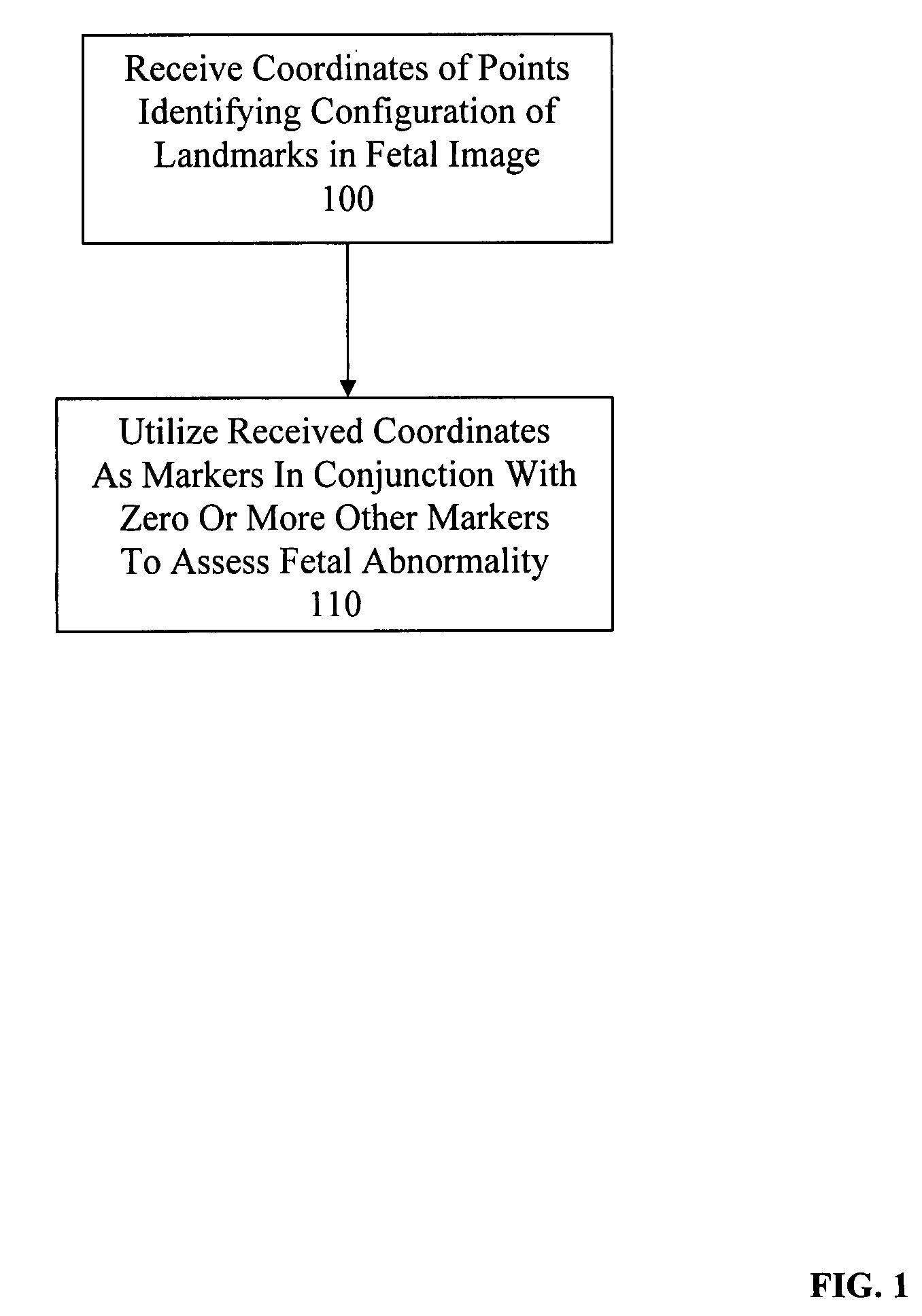
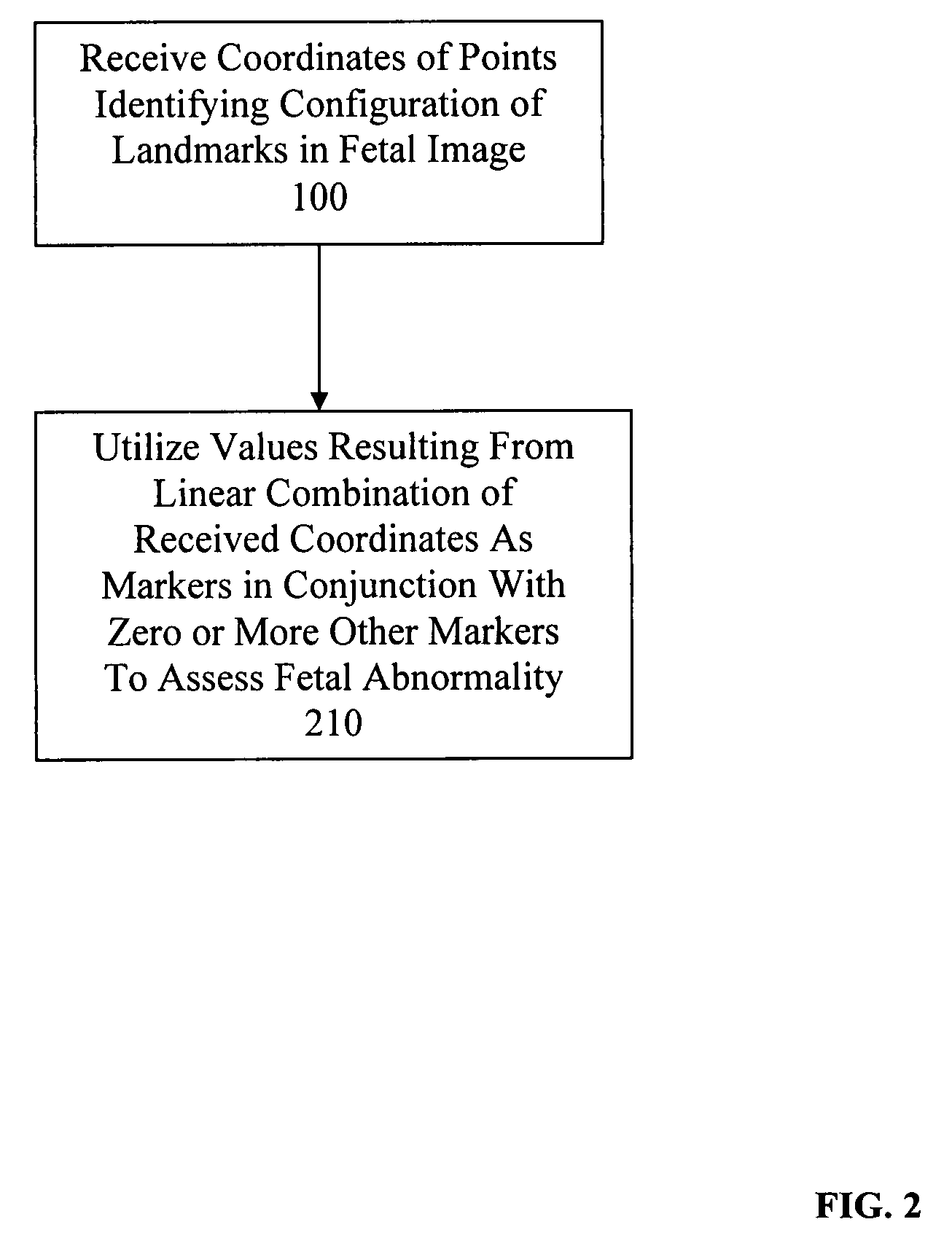
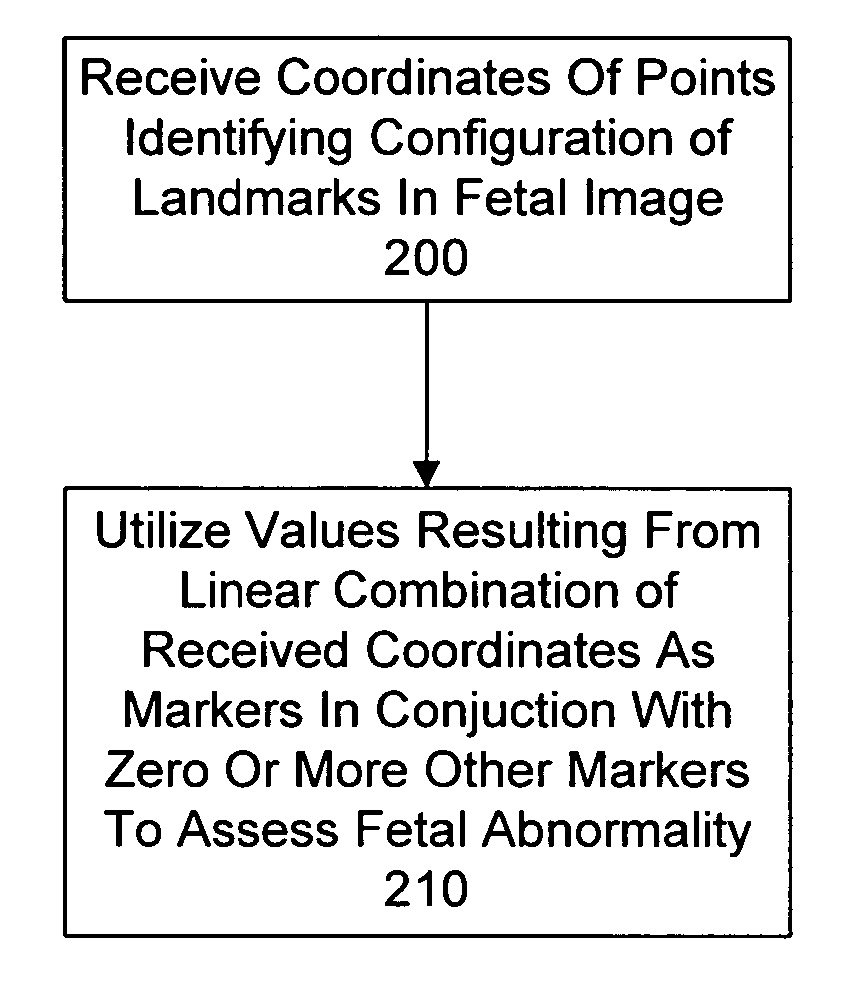
System and method for assessing fetal abnormality based on landmarks
InactiveUS7343190B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFetal abnormalityObstetrics
A method and system for assessing fetal abnormality based on landmarks. According to one embodiment, at least two coordinates are received for each of a plurality of points identifying a configuration of landmarks in a fetal image, and any of the received coordinates of any of the plurality of points are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality. According to another embodiment, at least two coordinates are received for each of a plurality of points identifying a configuration of landmarks in a fetal image, and one or more values resulting from a linear combination of any of the received coordinates of any of the plurality of points are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
Methods of detecting cell-free miRNA in urine and blood
InactiveUS8486626B2Reduce degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal abnormalityPhysical factor
Described are non-invasive methods of detecting in vivo cell death by measuring levels of ubiquitous and tissue specific miRNA. The method can be applied for detection of pathologies caused or accompanied by cell death, as well as for diagnosis of infectious disease, cytotoxic effects induced by different chemical or physical factors, and the presence of specific fetal abnormalities.
Owner:GENSIGNIA
Prenatal diagnostic methods
InactiveUS20020127616A1Blood volume expansionIncrease percentageCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsFetal abnormalityAdult liver
A method of identifying embryonic or fetal red blood cells in a sample containing maternal blood cells and embryonic or fetal red blood cells or both, the method comprising determining, which cell or cells contain or express an adult liver component. A method of isolating embryonic or fetal red blood cells from a sample containing maternal blood cells and embryonic or fetal red blood cells or both, the method comprising isolating the cells which contain or express an adult liver component. A method of determining a fetal abnormality the method comprising identifying or isolating embryonic or fetal cells according to the above methods and analysing said embryonic or early fetal cells for said abnormality. Use of a means for determining whether a cell contains or expresses an adult liver component for identifying or isolating an embryonic or fetal red blood cell.
Owner:DUNDEE UNIV OF
System and method for assessing fetal abnormality based on landmarks
InactiveUS20050245825A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFetal abnormalityObstetrics
A method and system for assessing fetal abnormality based on landmarks. According to one embodiment, at least two coordinates are received for each of a plurality of points identifying a configuration of landmarks in a fetal image, and any of the received coordinates of any of the plurality of points are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality. According to another embodiment, at least two coordinates are received for each of a plurality of points identifying a configuration of landmarks in a fetal image, and one or more values resulting from a linear combination of any of the received coordinates of any of the plurality of points are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
ADAM12, a novel marker for abnormal cell function
InactiveUS20060134654A1Improve the detection rateReduce false alarm rateMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseADAM12
The present invention provides a method, an assay and a kit for providing an indication of abnormal cell function. It was surprisingly found that the change in the serum ADAM12 concentration in individuals was useful as a prognostic tool to predict the clinical outcome, complications and mortality following an abnormal cell function. The present inventors describes ADAM12 as a overall general marker for abnormal cell function, and the present inventor for the first time demonstrate that ADAM12 is an important indicator of fetal chromosomal disease and placenta function. Specifically ADAM12 is a good marker for e.g. Downs's syndrome, trisomy 18, preeclampsia, Turner syndrome in both first and second trimester. The present inventors developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and a time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for the quantification of ADAM12 in serum. The present application demonstrates in several examples the variation of the ADAM12 level in fetal abnormality and / or adverse pregnancy outcomes correlated gestational age when compared to normal controls. It is an object of the invention to provide an improvement of the existing marker tests that exhibits a decreased false positive rate.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST +2
Methods for detecting fetal abnormality
InactiveUS20100273675A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal abnormalityNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to a method of identifying fetal abnormality from a maternal blood sample by capturing an image of a fetal nucleated red blood cell obtained from the maternal blood sample; inputting probe intensities for a plurality of nucleic acid probes that bind fetal nucleic acids of interest; analyzing the probe intensities; and generating a diagnostic output according to results of the analysis. In some embodiments, the probes are specific to a chromosome.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Prenatal Screening
ActiveUS20160054293A1Easy to calculateSmall sizeTime-of-flight spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsDiseaseFetal abnormality
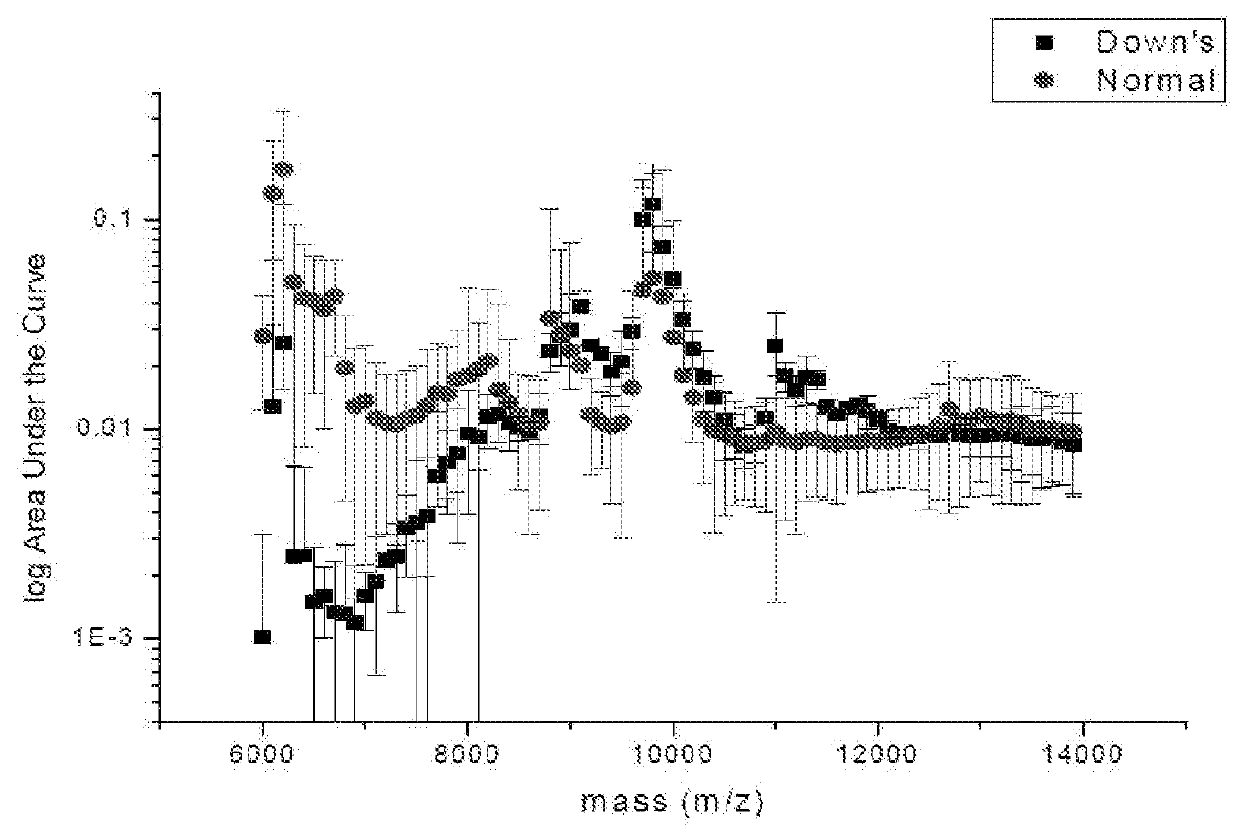
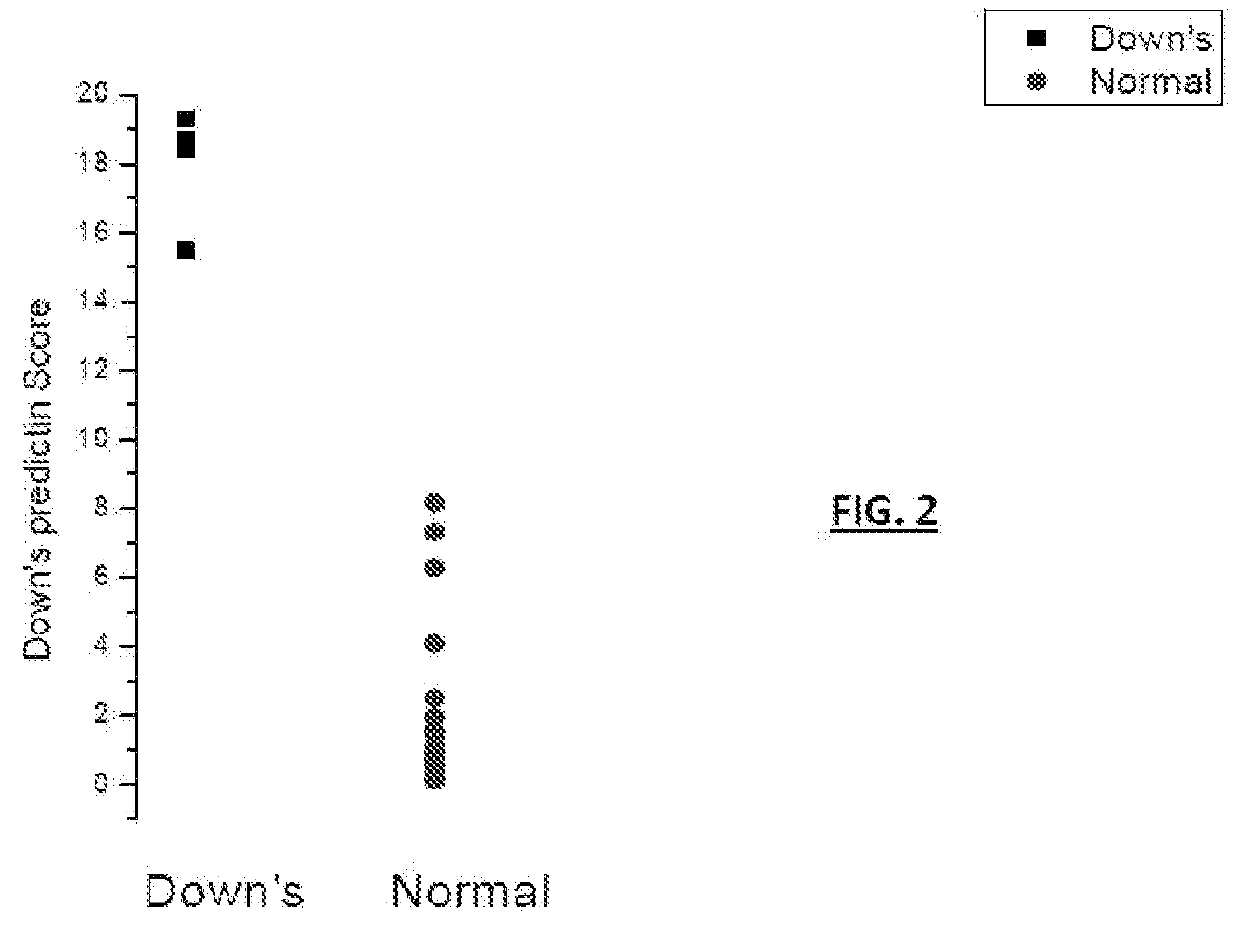
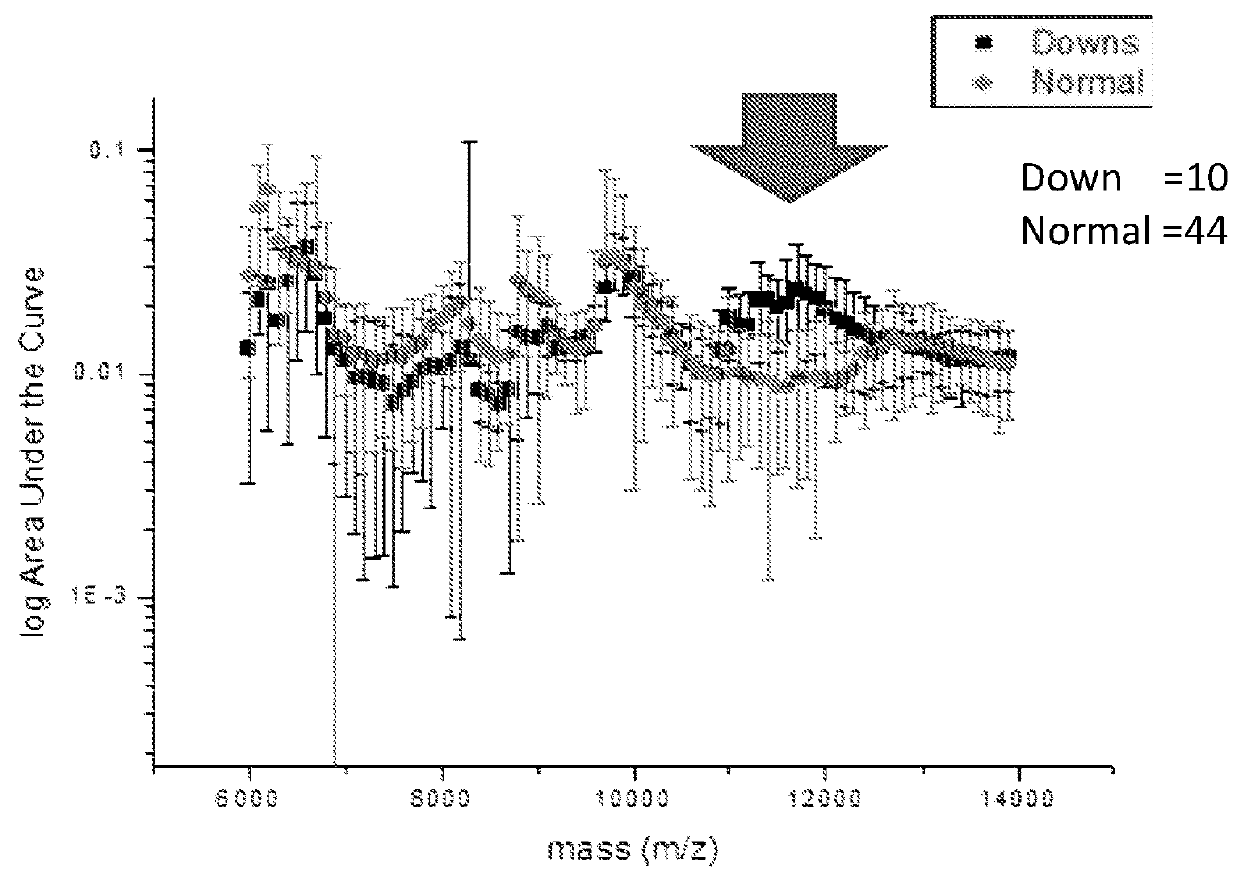
The present invention relates to a method for screening maternal urine samples for changes in the pattern of mass spectral fingerprinting which have been found to be characteristic of fetal aneuploidies such as Down's Syndrome and have application for the screening of other fetal abnormalities and disorders of pregnancy including gestational trophoblastic diseases.
Owner:MAP IP HOLDING LTD
Methods of fetal abnormality detection
ActiveUS20120135872A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFetal abnormalityPolynucleotide
Methods and kits for selectively enriching non-random polynucleotide sequences are provided. Methods and kits for generating libraries of sequences are provided. Methods of using selectively enriched non-random polynucleotide sequences for detection of fetal aneuploidy are provided.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
System and method for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality
InactiveUS20050063576A1Medical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFetal abnormalityObstetrics
A method and system for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality. According to one embodiment, coordinates of points identifying a shape in a fetal image are received, coefficients of one or more mathematical functions that describe the identified shape are determined, and the determined coefficients are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
Multi-marker screening protocol for fetal abnormalities
A method of assessing a pregnant woman's risk of having a fetus with a fetal abnormality by determining the fetus' BPD / OFD ratio and using the BPD / OFD ratio in conjunction with one or more other screening markers for the fetal abnormality. Also provided is a method of determining whether a pregnant woman is screen-positive or screen-negative by comparing the BPD / OFD ratio of the pregnant woman's fetus to a risk cut-off level.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
Methods and Systems for Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Genomic Alterations
ActiveUS20180080068A1Low rateReduce frequencyMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationReference sampleSolid tissue
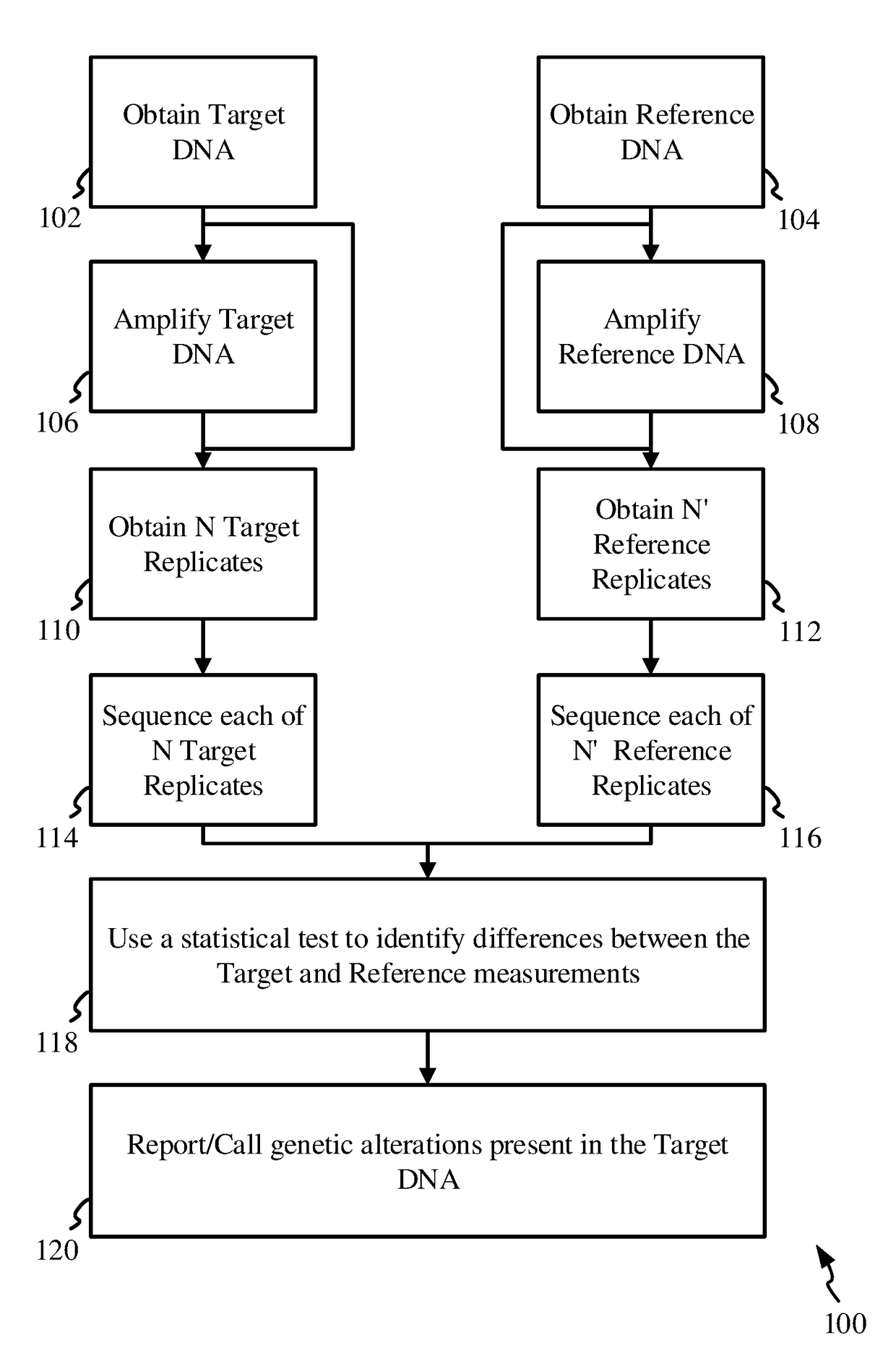
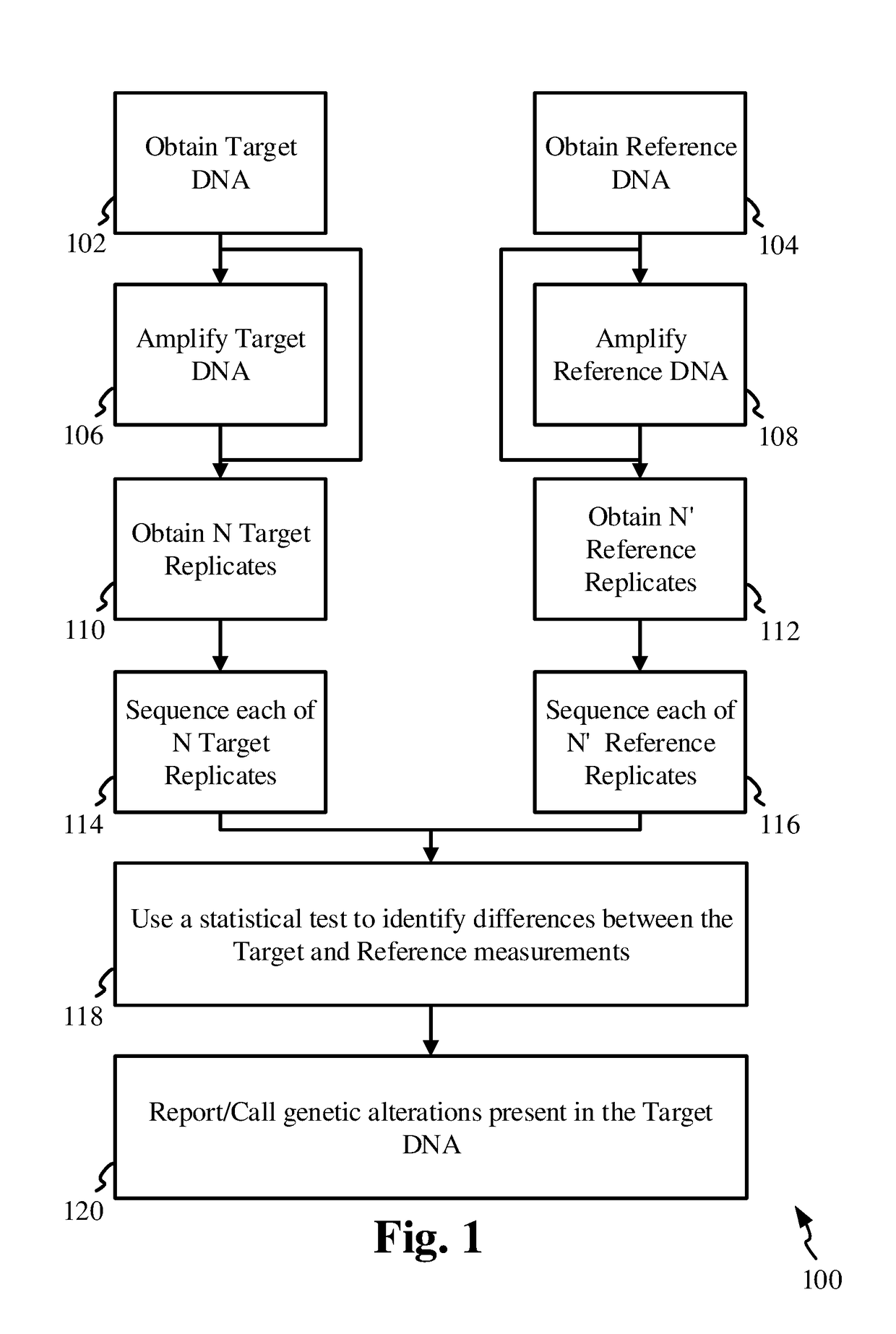
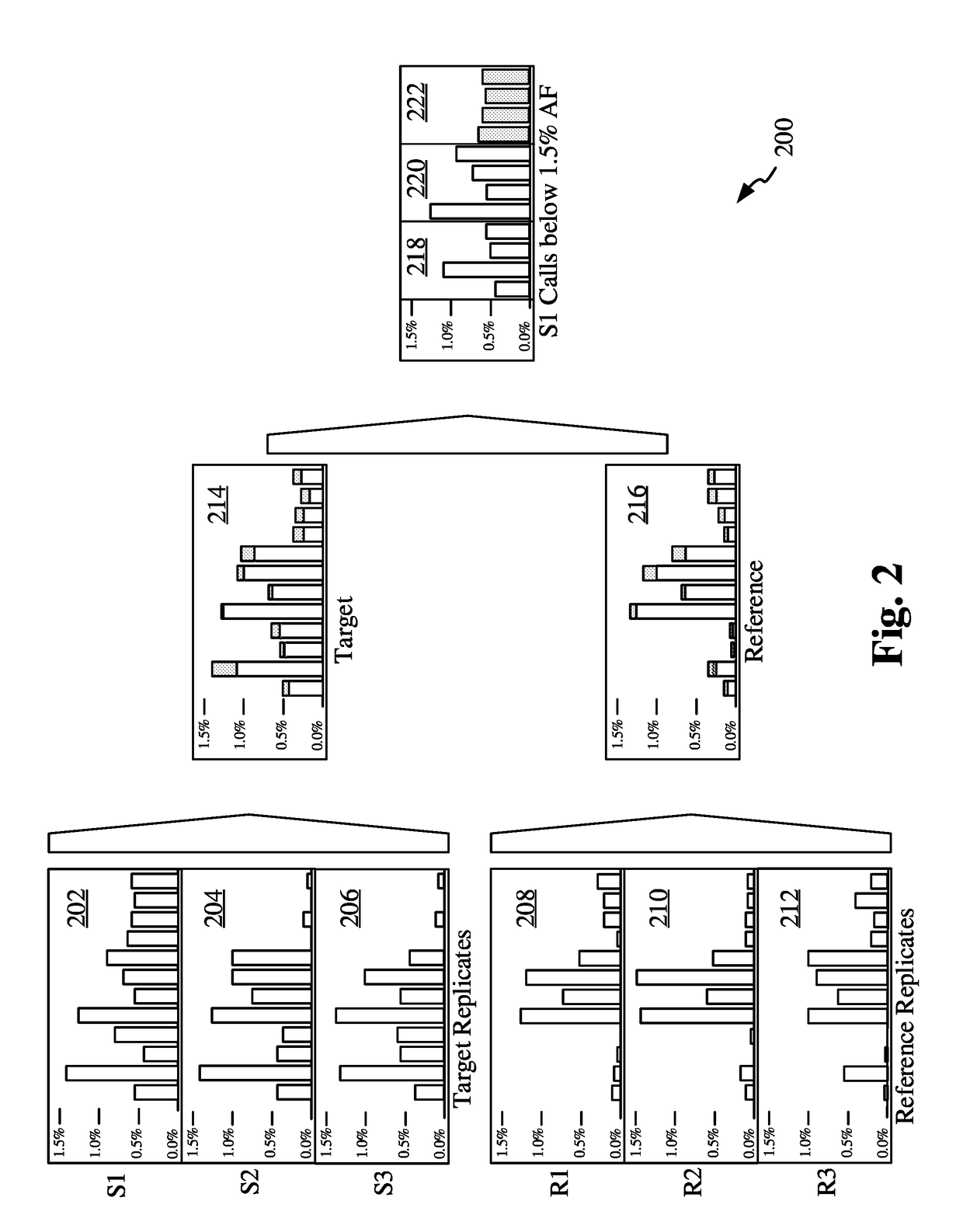
The invention discloses methods and apparatuses for the detection and diagnostics of genetic alterations / mutations in a target sample, which may be a solid tissue or a bodily fluid. A reference sample is also acquired, and the target and reference samples are replicated into multiple target and reference replicates. The replicates are sequenced, and the sequence data is analyzed based on a statistical test. The statistical test compares the measurements between the target and reference replicates at respective allelic indices. True positive calls are then made based on the results of the statistical testing, and the desired genetic alterations / mutations are identified at the base-pair level. The invention may be used for diagnostics related to cancer, auto-immune disease, organ transplant rejection, genetic fetal abnormalities and pathogens.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
Method for detection of fetal abnormalities
InactiveUS20160090631A1Convenience to workMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisFetal abnormalityTrophoblastic cell
Disclosed are methods for non-invasive fetal genetic analysis involving enrichment of trophoblast cells in a maternal cervical sample, followed by isolation and genetic analysis of the isolated trophoblasts.
Owner:STELLING JAMES R
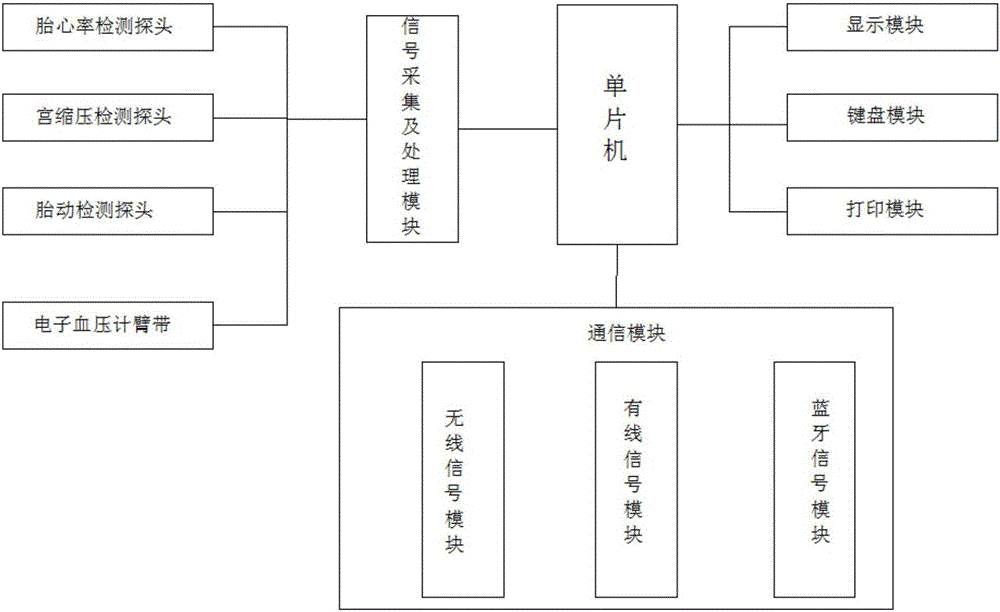
Portable fetal monitor
InactiveCN106805960AEasy to useReduce travel hassleDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFetal abnormalityControl system
The invention relates to a portable fetal monitor. The portable fetal monitor comprises a rotary display screen and a host rotationally connected with the rotary display screen. A sliding touch screen and an operation panel are arranged on the upper end face of the host, a control system is further arranged in the host, the side face of the host is connected with a fetal heart rate detection probe, a uterine pressure detection probe, a fetal movement detection probe and an electronic sphygmomanometer arm band which are independent, and the fetal heart rate detection probe, the uterine pressure detection probe, the fetal movement detection probe and the electronic sphygmomanometer arm band are all in signal connection with the control system. The portable fetal monitor can be carried portably, is conveniently used by a pregnant woman on any occasion, and is convenient to use, the pregnant woman does not need to regularly go to a hospital for examinations, the fetus condition and the condition of the pregnant woman can be detected by the pregnant woman herself, data can be exported by the monitor itself, the data is printed or directly transmitted to a doctor, the travel trouble of the pregnant woman is reduced, the diagnosis time of the pregnant woman is shortened, detection can be carried out at any time, the pregnant woman can communicate with the doctor, and the problem of fetal abnormalities is solved in time.
Owner:四川康特立医疗科技有限公司
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveCN108048549AMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g.aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com