Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
一种细胞、胎儿细胞的技术,应用在检测或诊断癌症,测定胎儿异常领域,能够解决生存率低、不能及时检测到等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0299] Example 1. Isolation of fetal umbilical cord blood
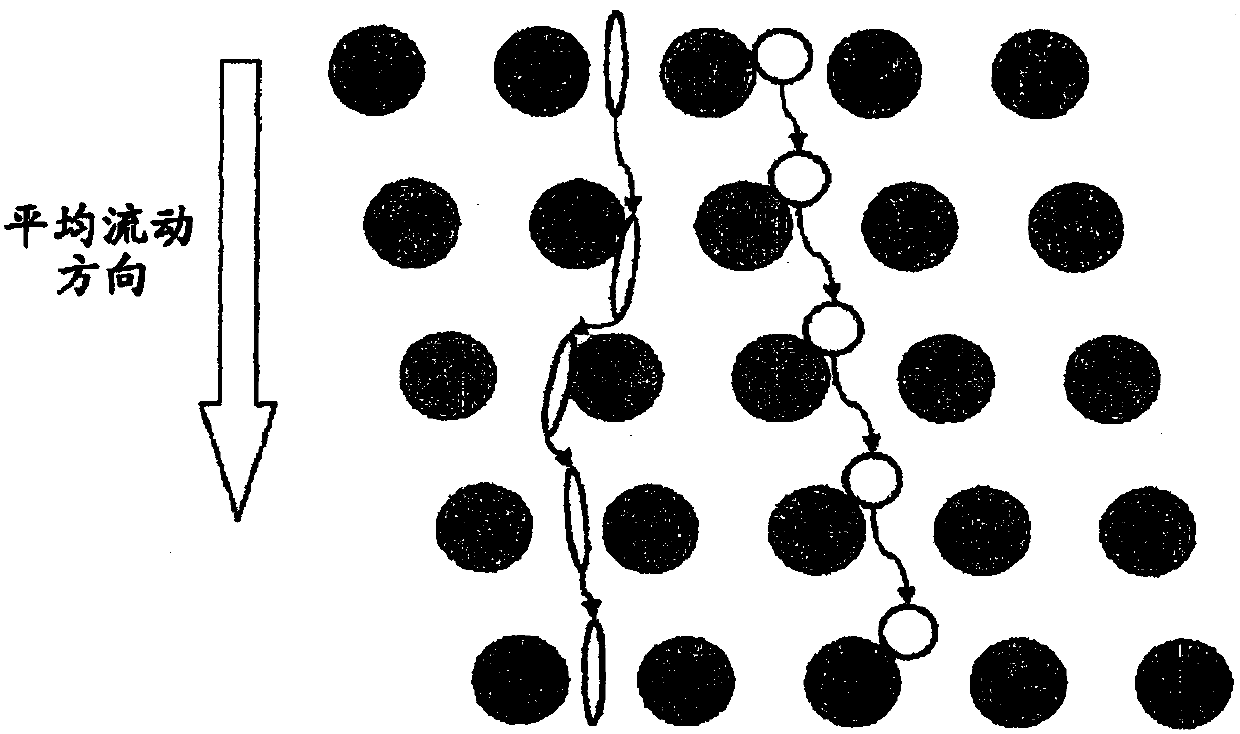
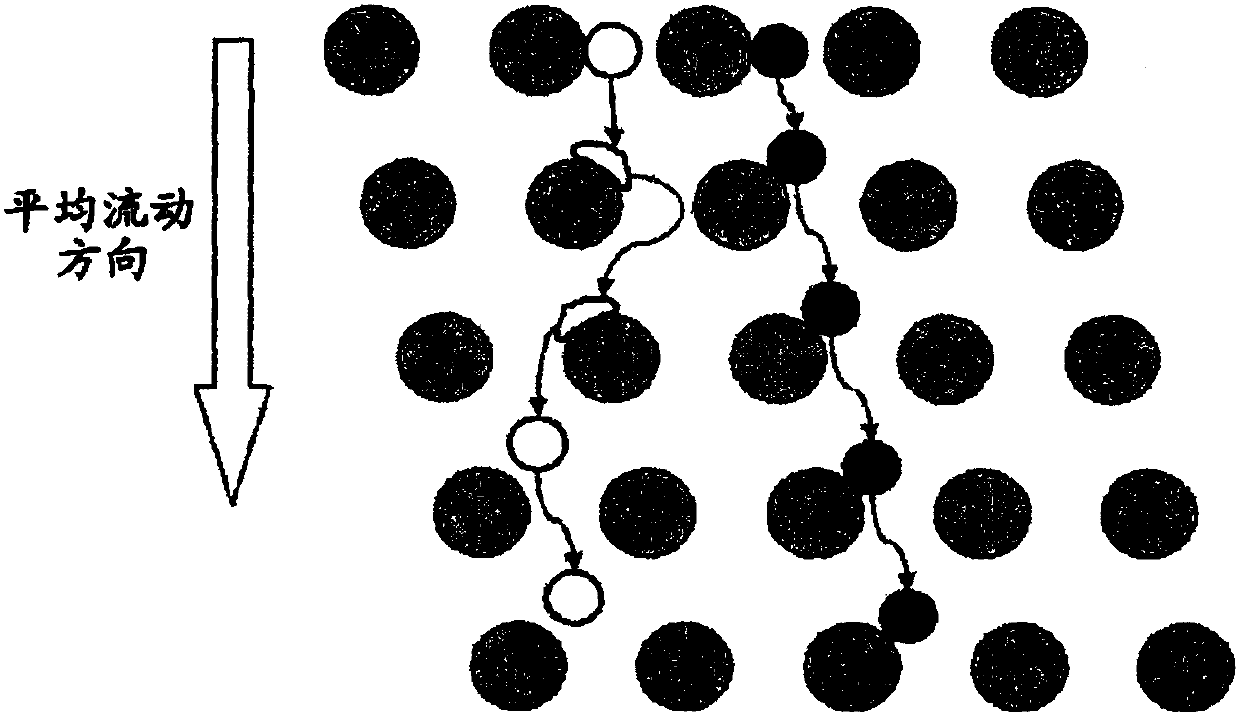
[0300] Figure IE shows a schematic diagram of an apparatus for isolating nucleated cells from fetal cord blood.
[0301] Size: 100mm×28mm×1mm
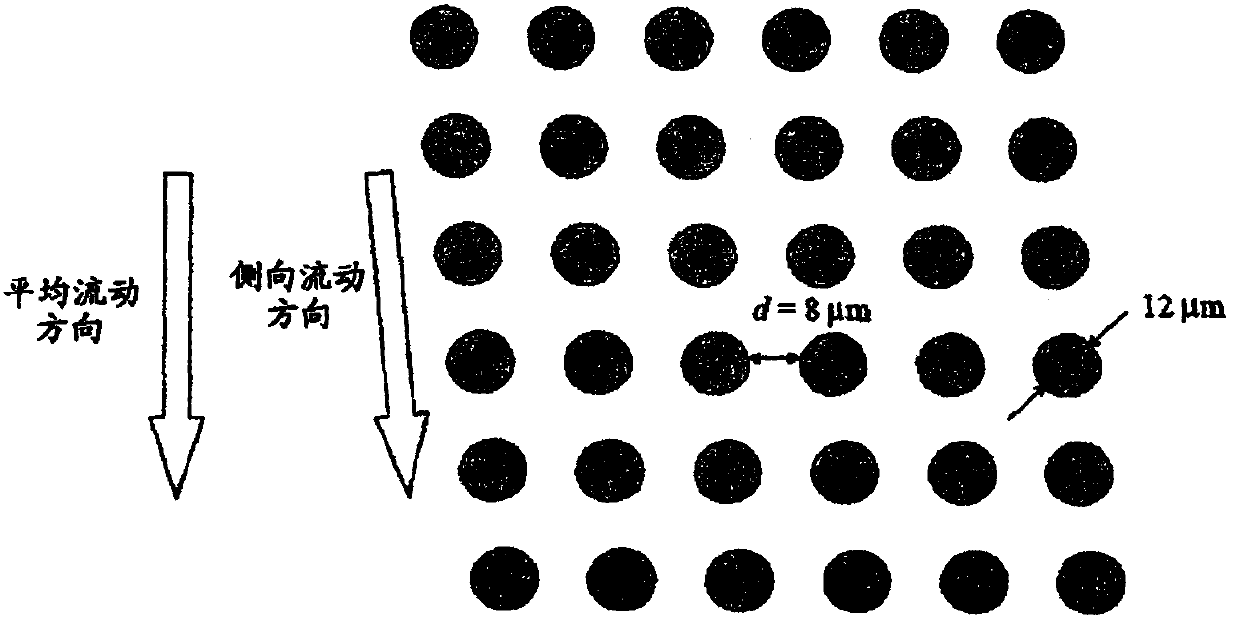
[0302] Array design: 3 segments, gap size = 18, 12 and 8 μm for the first, second and third segments, respectively.
[0303] Device Fabrication: Arrays and channels are fabricated in silicon using standard photolithography and deep silicon reactive etch techniques. The etching depth is 140 μm. Vias for fluid entry were made using KOH wet etching. The silicon substrate was sealed on the etched surface using a blood-compatible pressure-sensitive adhesive (9795, 3M, St Paul, MN) to create an airtight fluid channel.
[0304] Device Assembly: The device is mechanically coupled to a plastic manifold with external fluid reservoirs to deliver blood and buffer to the device and extract the resulting fractions.
[0305] (00217] Device Operation: An external pressure source was us...
Embodiment 2
[0309] Example 2. Isolation of fetal cells from maternal blood
[0310] The apparatus and methods detailed in Example 1 were used in combination with immunomagnetic affinity enrichment techniques to demonstrate the feasibility of isolating fetal cells from maternal blood.
[0311] Experimental Conditions: Blood was collected from a consenting maternal donor carrying a male fetus into K 2 EDTA vacutainer tubes (366643, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) followed by elective termination of pregnancy immediately thereafter. Undiluted blood was processed using the apparatus described in Example 1 at room temperature and within 9 hours of drawing. The nucleated and non-nucleated cells (erythrocytes and platelets) of the blood were separated, and the plasma was passed into a calcium-free and Magnesium Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (14190-144, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was in the buffer stream. Subsequently, the nucleated cell fraction was labeled with anti-CD71 microbea...
Embodiment 3
[0314] Example 3. Confirmation of the presence of male fetal cells in enriched samples
[0315] Confirmation of the presence of male fetal cells in the enriched samples was performed using qPCR with primers specific for DYZ, a marker repeated in high copy number on the Y chromosome. Following enrichment of fnRBCs by any of the methods described herein, the resulting enriched fnRBCs were partitioned by splitting the sample into 100 PCR wells. Enriched samples can be screened by FISH for the presence of any fnRBCs containing aneuploidy of interest prior to partitioning. Because of the low number of fnRBCs in maternal blood, only a fraction of wells contained a single fnRBC (other wells were expected to be negative for fnRBC). Cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde and stored at 4°C. Cells in each partition were pelleted and resuspended in 5 μl PBS plus 1 μl 20 mg / ml proteinase K (Sigma #P-2308). Cells were lysed by incubation at 65°C for 60 minutes, followed by inactivatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com