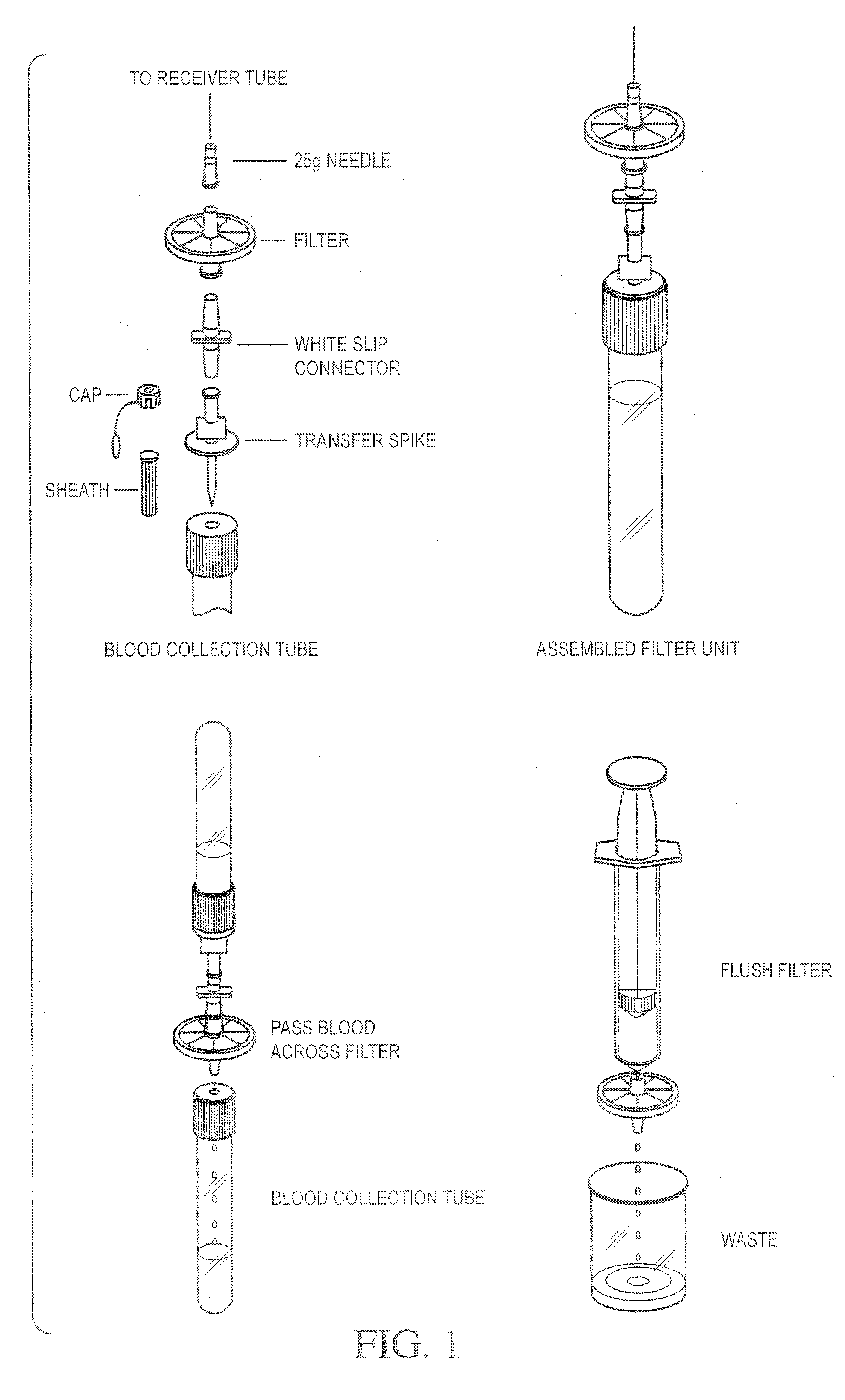
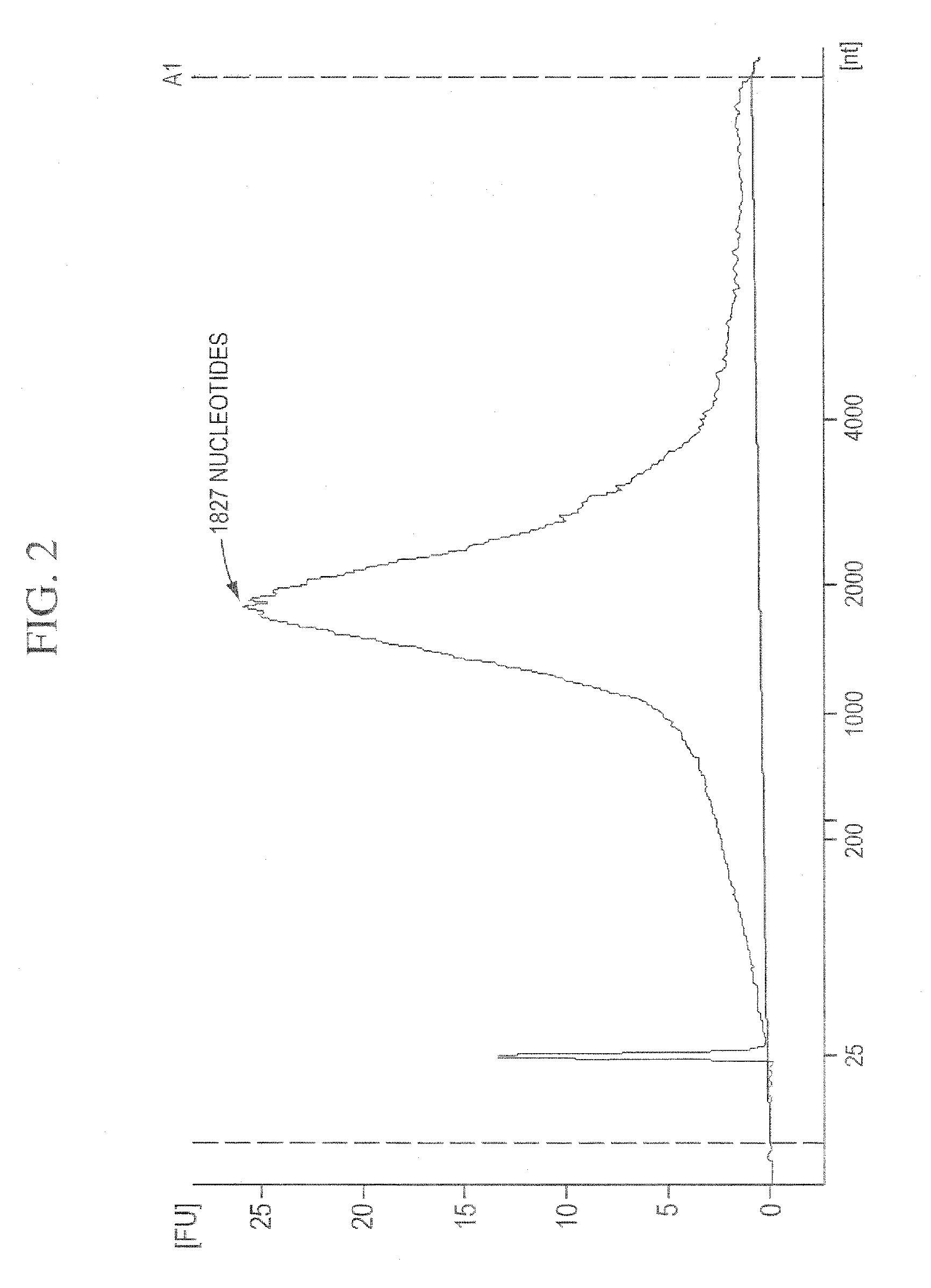
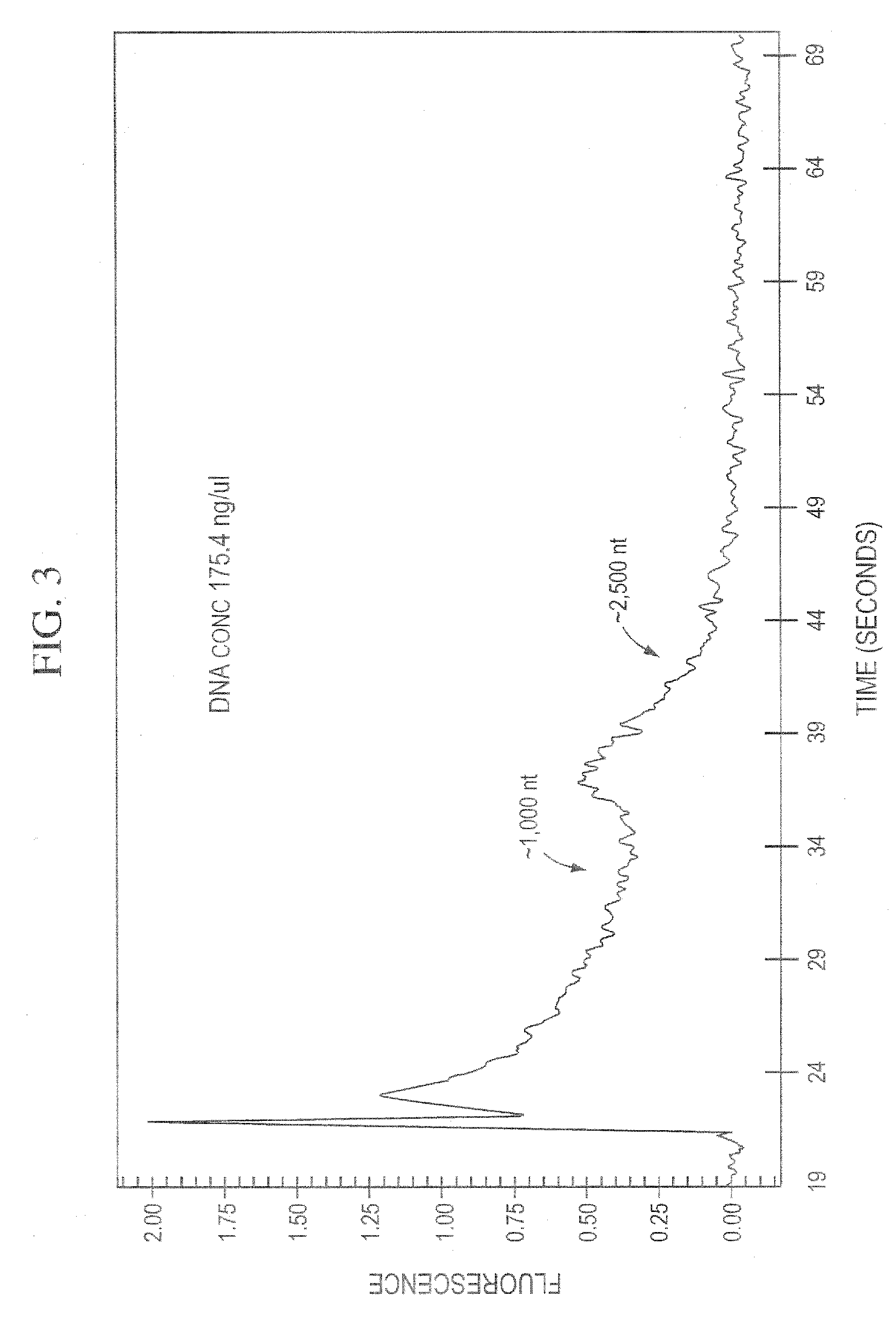
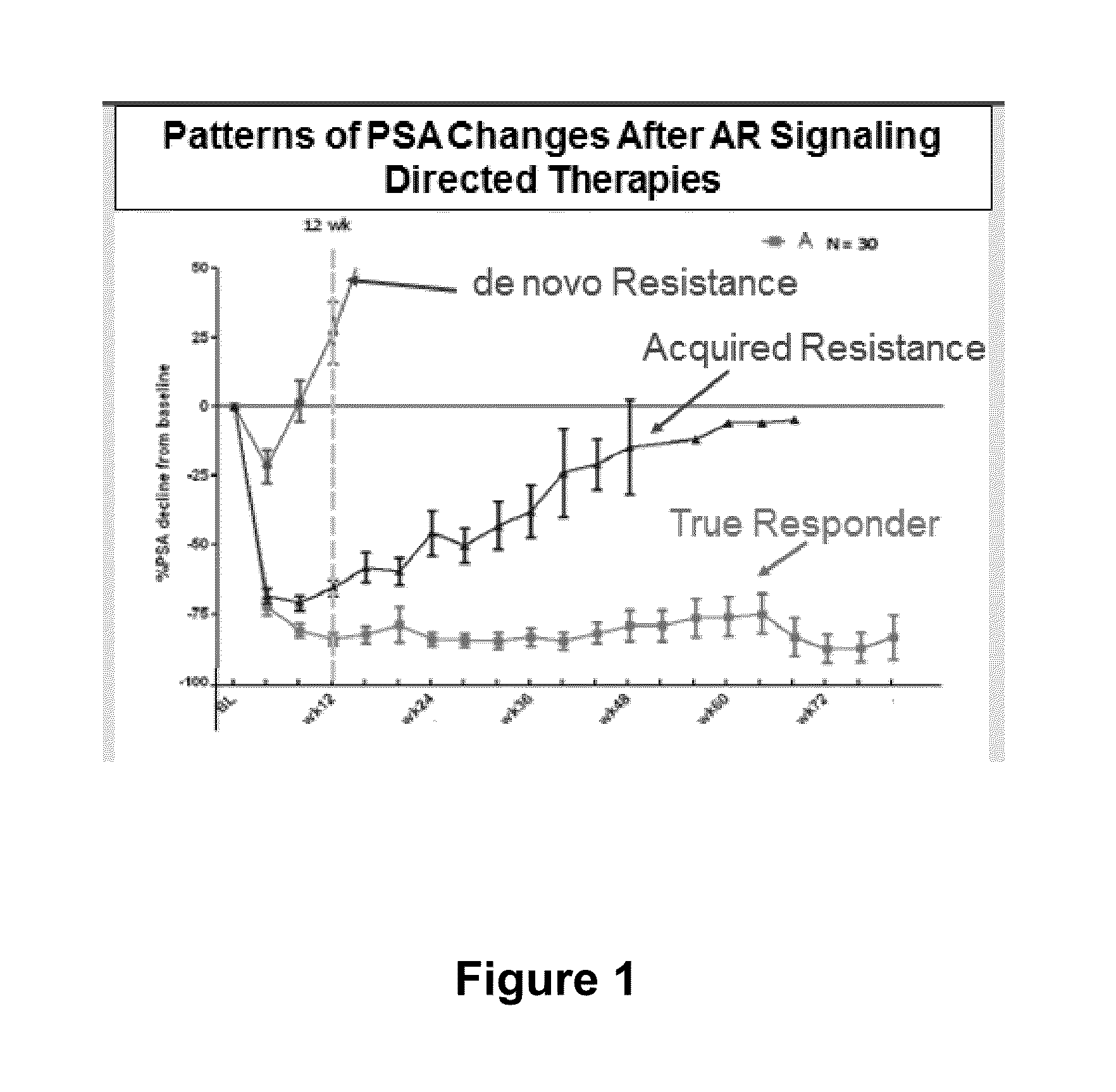
Patents
Literature
187 results about "Nucleated cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell that consists of protoplasm surrounded by a plasma membrane; together with other cells and intercellular matrix, it constitutes tissues. Examples: lymphocyte, fibroblast, neuron.
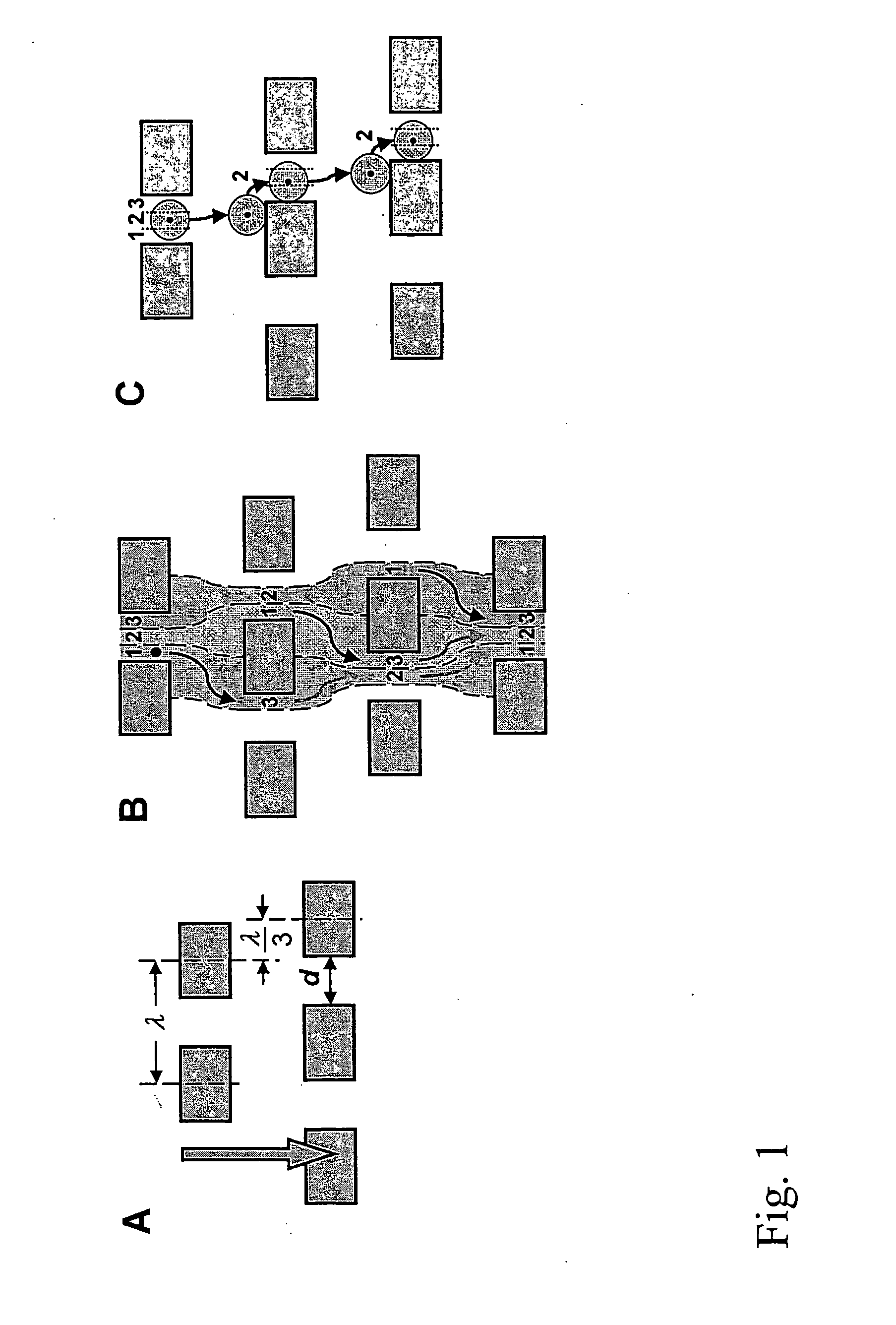
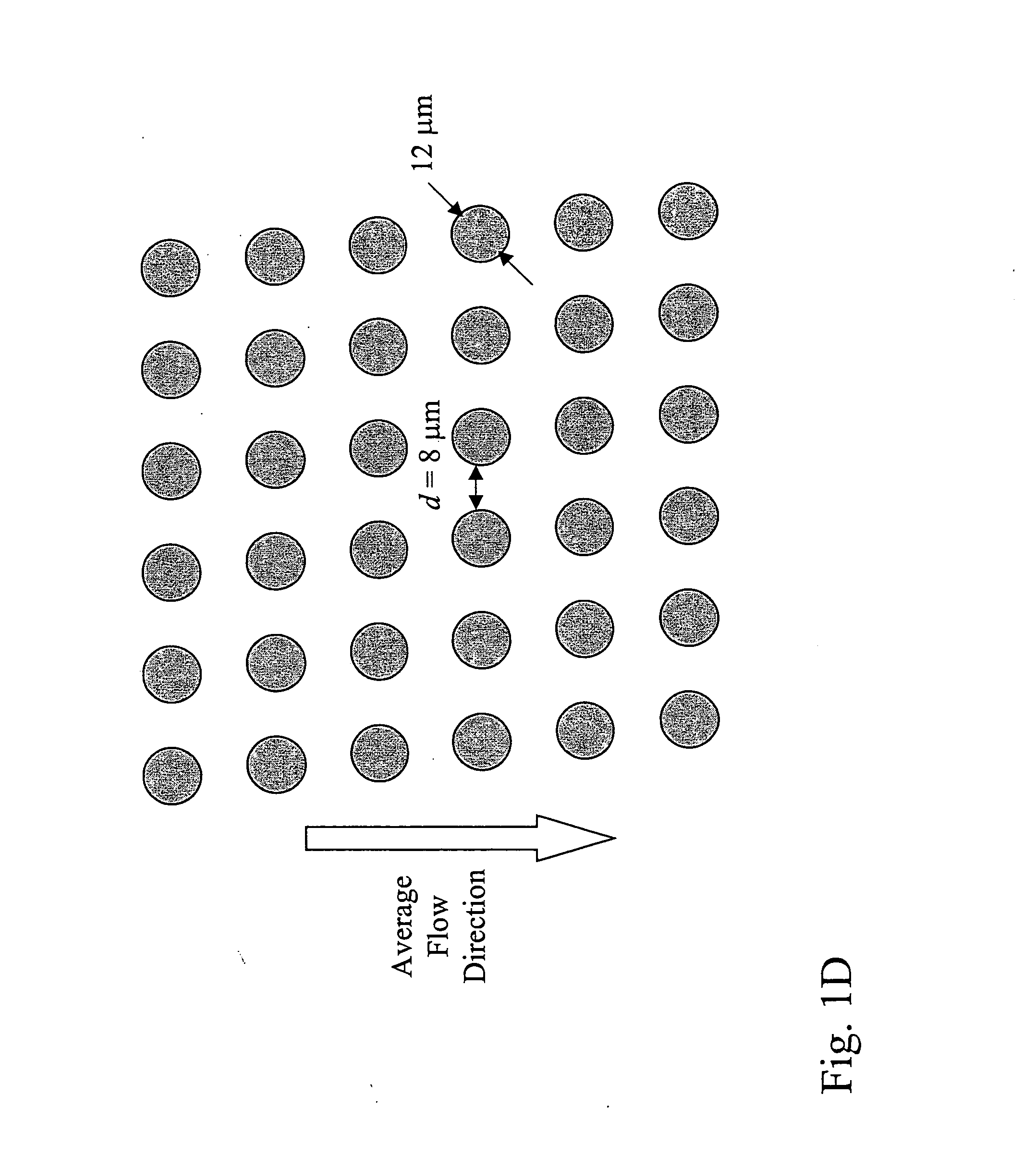
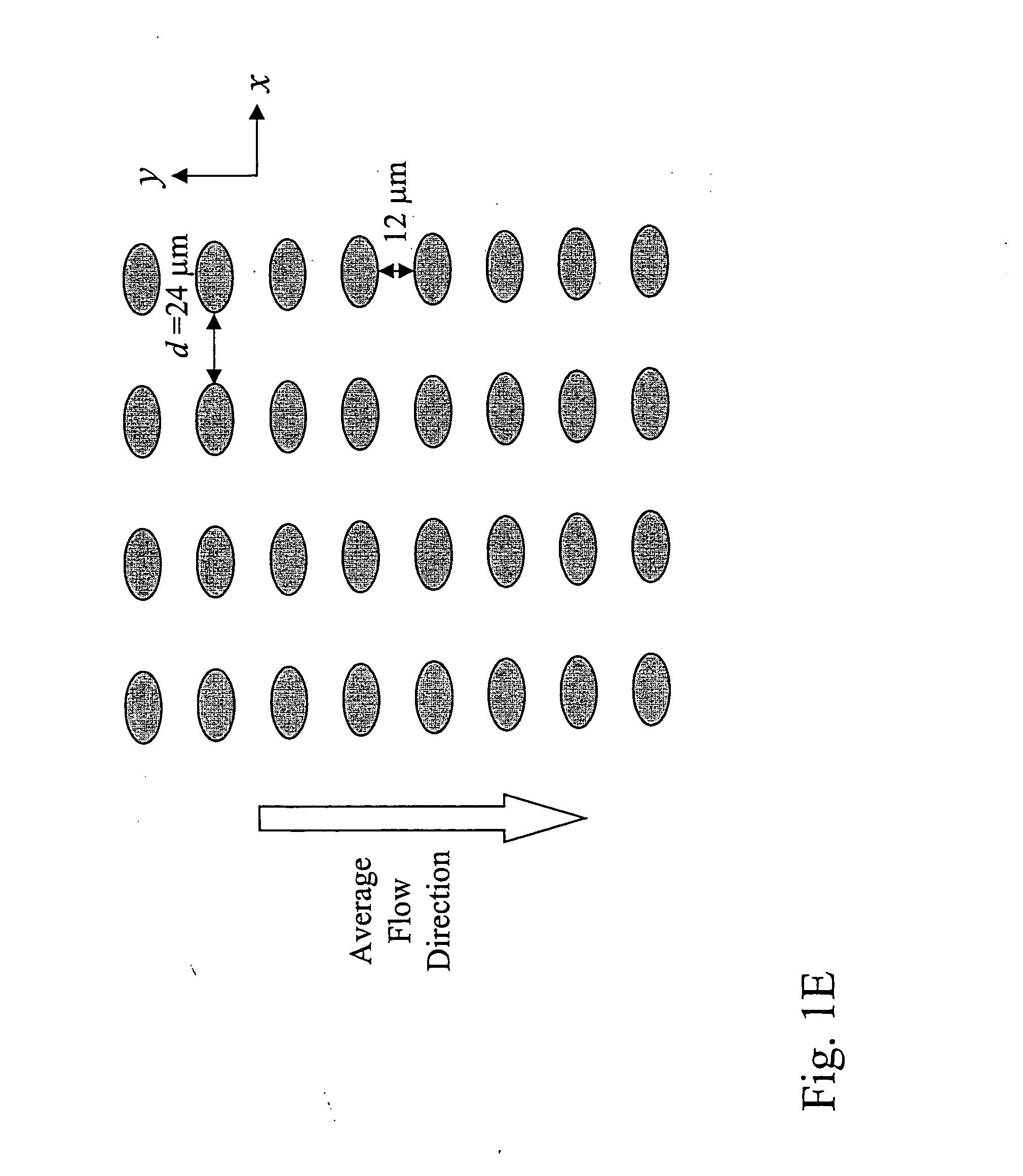
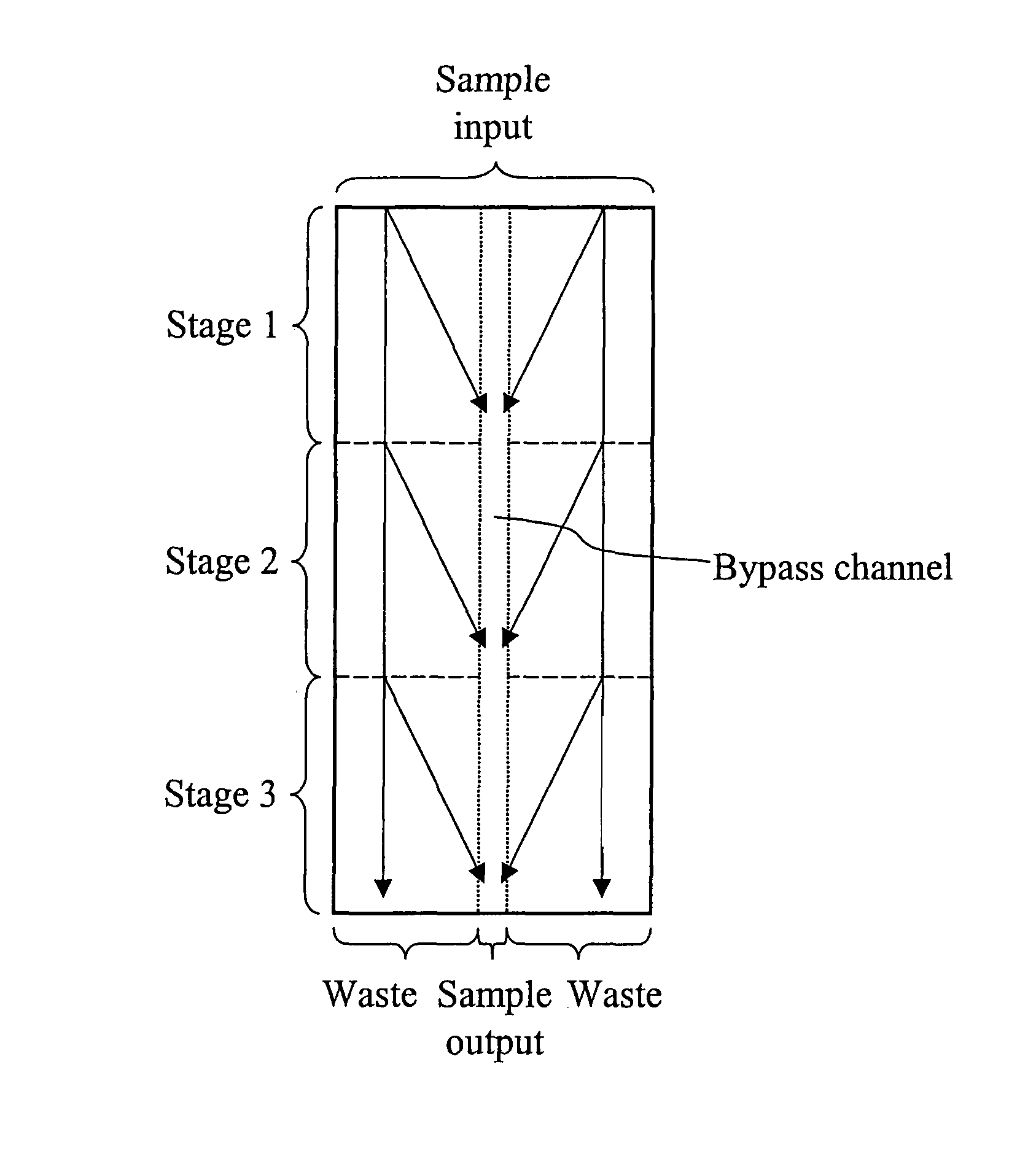
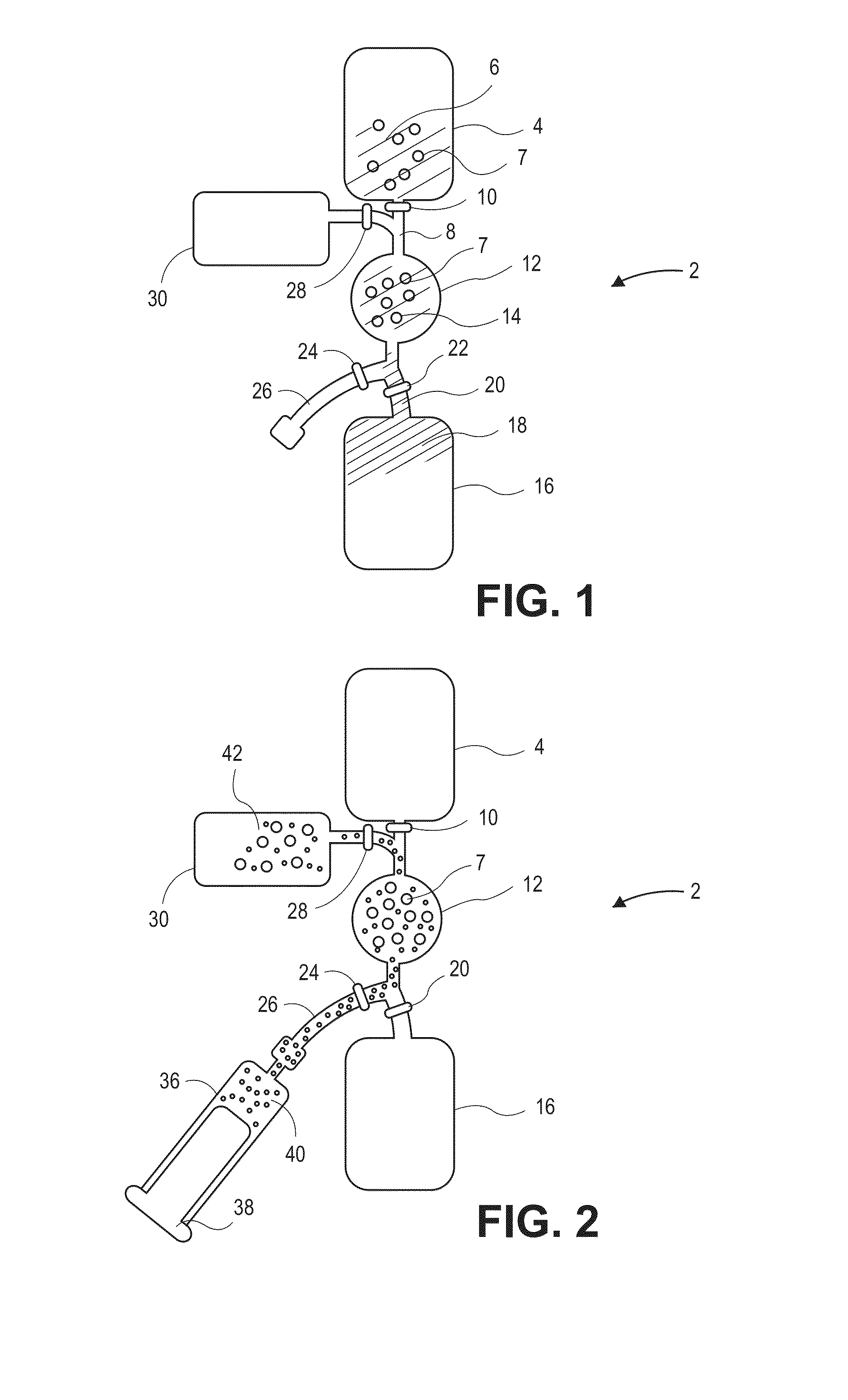
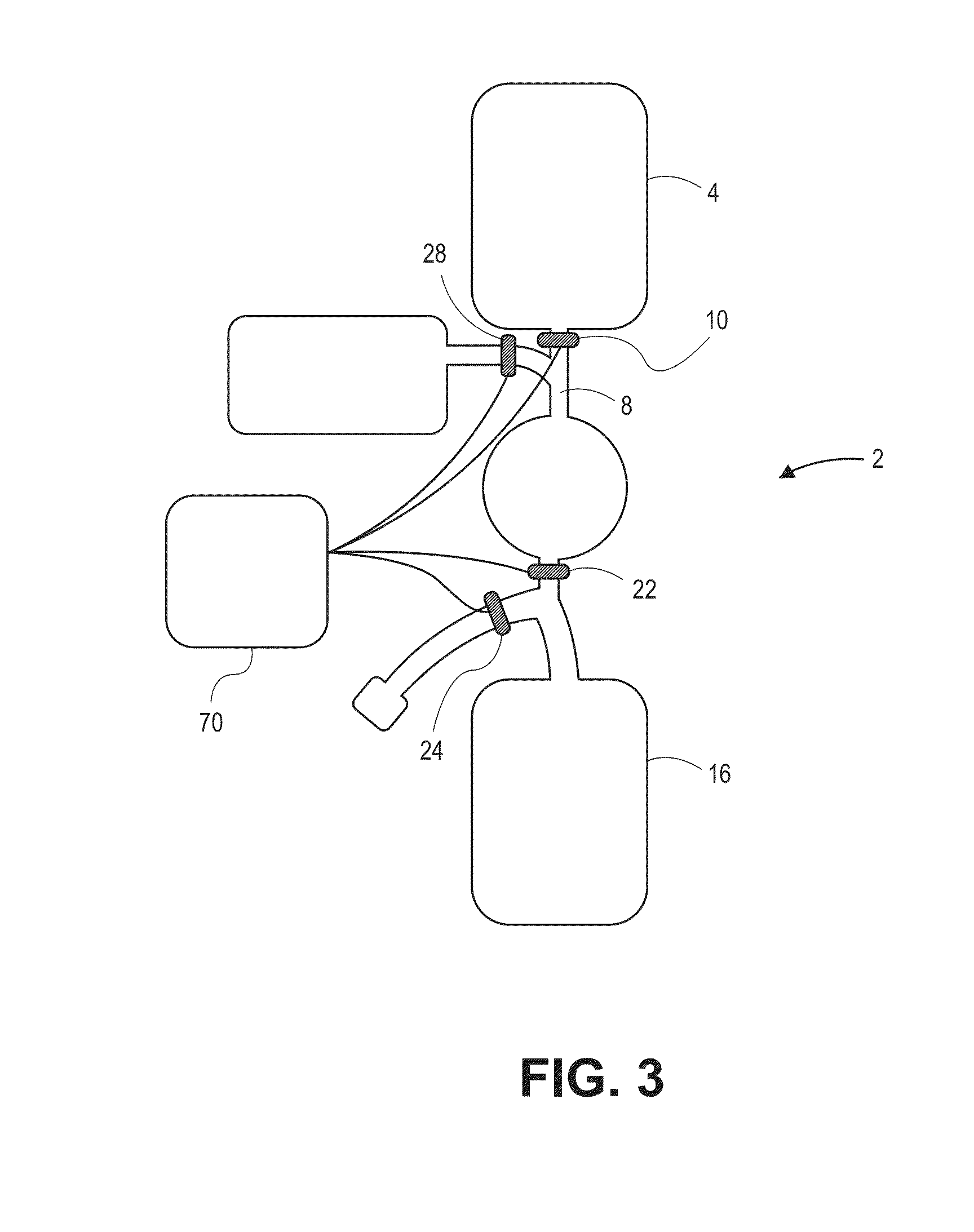
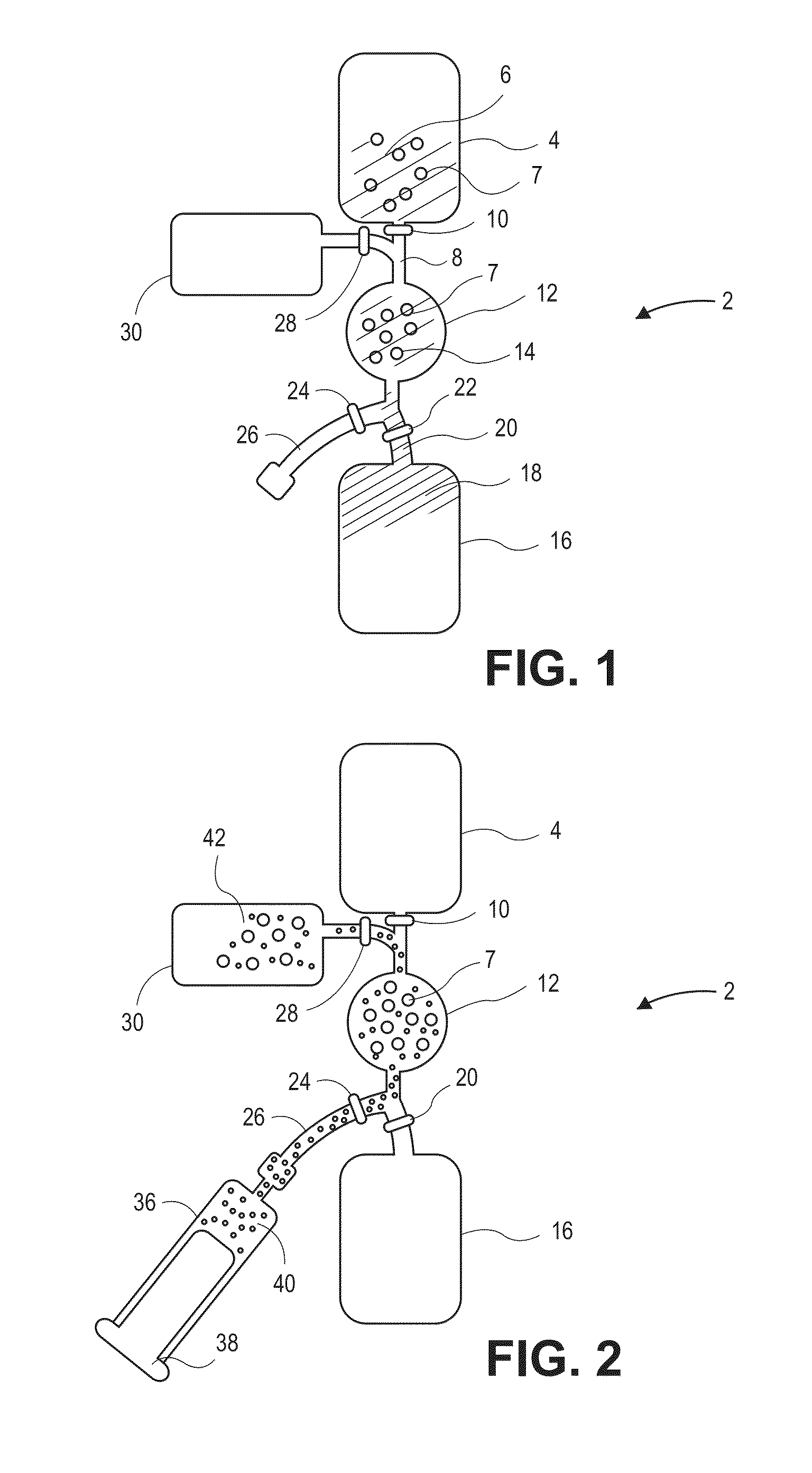
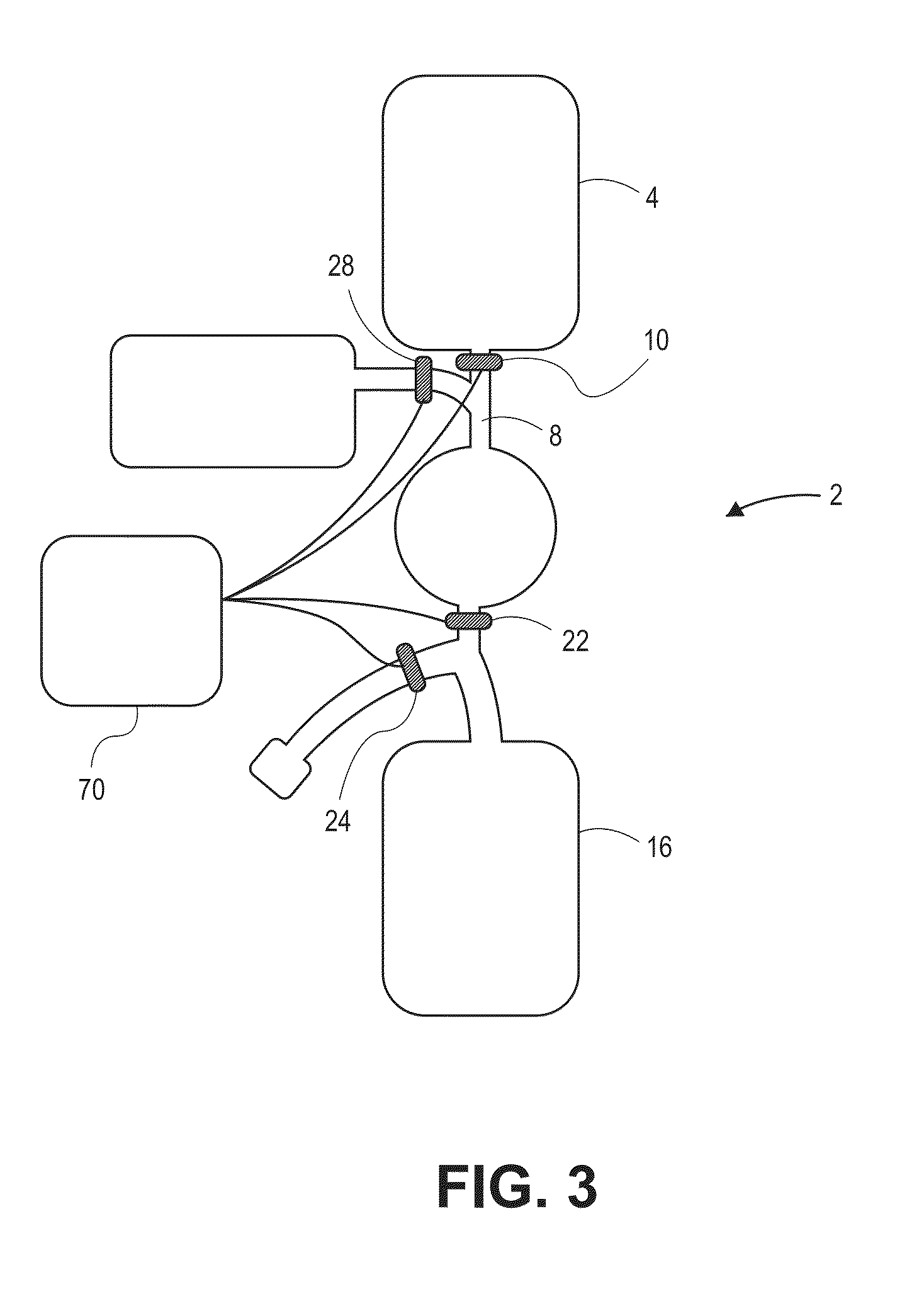
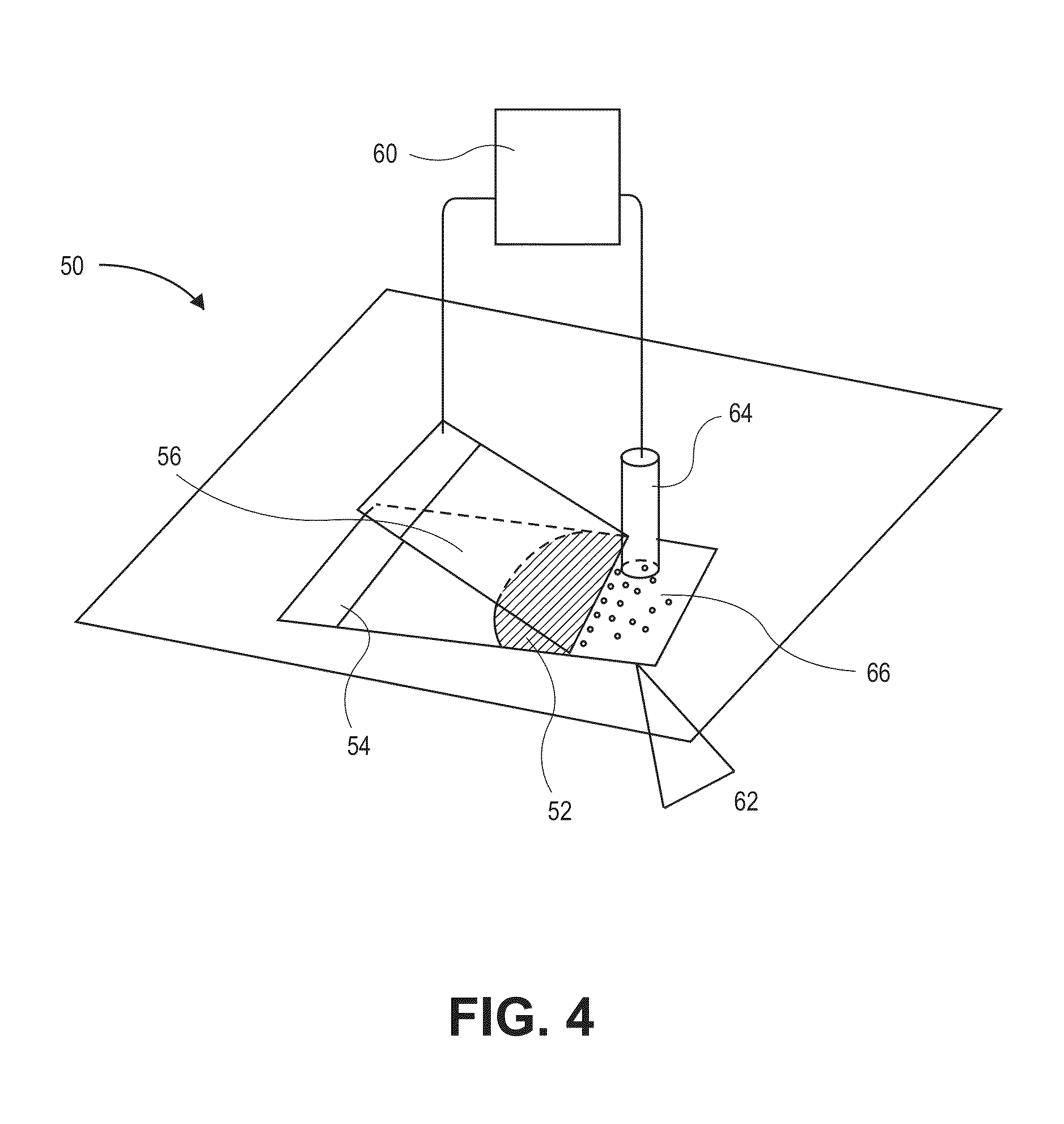
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
ActiveUS20070026381A1Increase volumeReduced deformabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentLysis
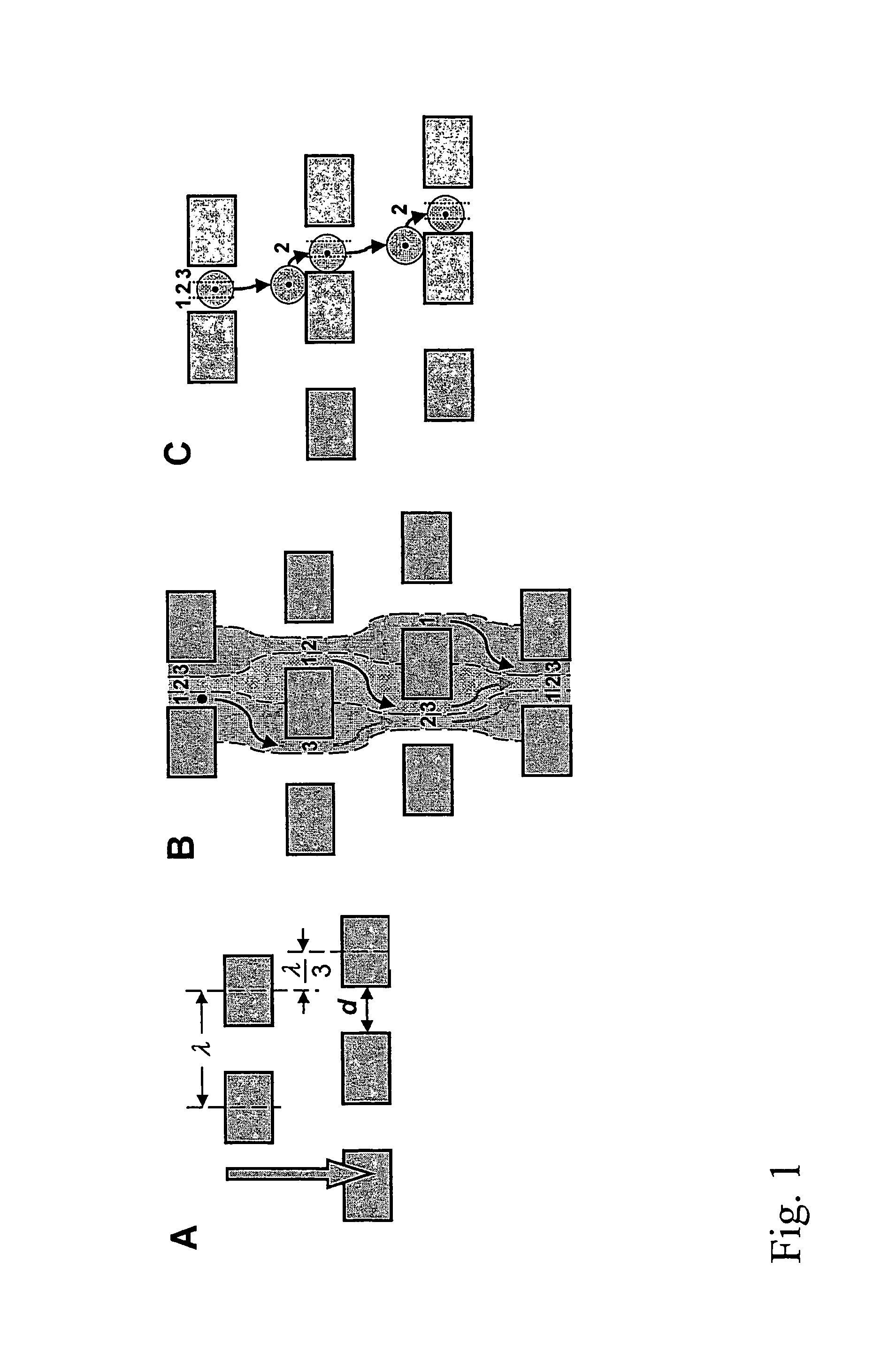
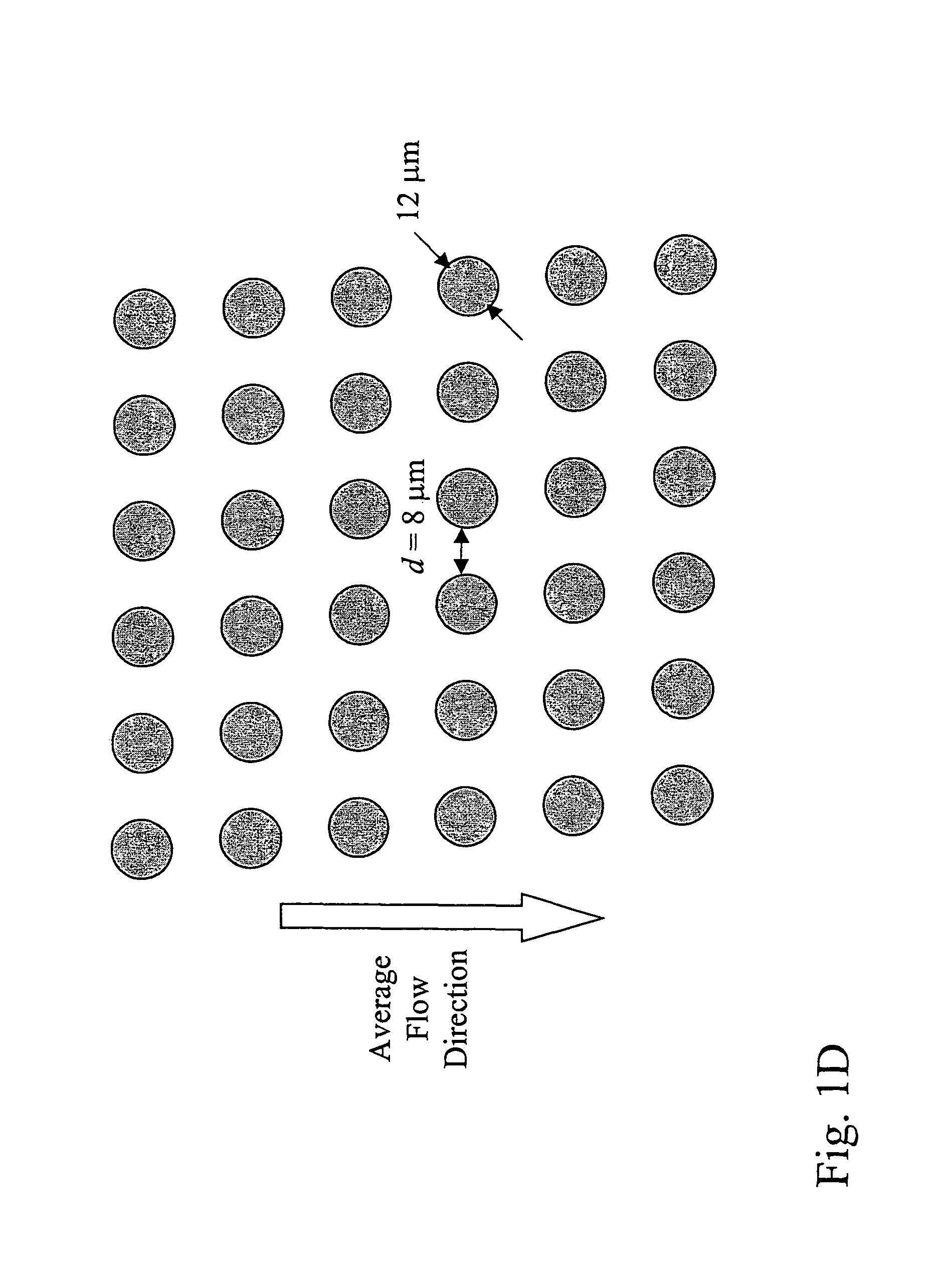
The invention features devices and methods for the deterministic separation of particles. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired particle or the alteration of a desired particle in the device. The devices and methods are advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood and rare cell components, e.g., fetal cell nuclei. The invention further provides a method for preferentially lysing cells of interest in a sample, e.g., to extract clinical information from a cellular component, e.g., a nucleus, of the cells of interest. In general, the method employs differential lysis between the cells of interest and other cells (e.g., other nucleated cells) in the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
ActiveUS8021614B2Increases the hydrodynamic radius of a particleIncrease volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentClinical information
The invention features devices and methods for the deterministic separation of particles. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired particle or the alteration of a desired particle in the device. The devices and methods are advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood and rare cell components, e.g., fetal cell nuclei. The invention further provides a method for preferentially lysing cells of interest in a sample, e.g., to extract clinical information from a cellular component, e.g., a nucleus, of the cells of interest. In general, the method employs differential lysis between the cells of interest and other cells (e.g., other nucleated cells) in the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Use of umbilical cord blood to treat individuals having a disease, disorder or condition
The present invention provides methods of using cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells in high doses to treat various conditions, diseases and disorders. The high-dose cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells have a multitude of uses and applications, including but not limited to, therapeutic uses for transplantation and treatment and prevention of disease, and diagnostic and research uses. In particular, the cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells are delivered in high doses, e.g., at least 3 billion nucleated cells per treatment, where treatment may comprise a single or multiple infusions. The invention also provides for the use of cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells from multiple donors without the need for HLA typing.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Non-invasive method for isolation and detection of fetal DNA
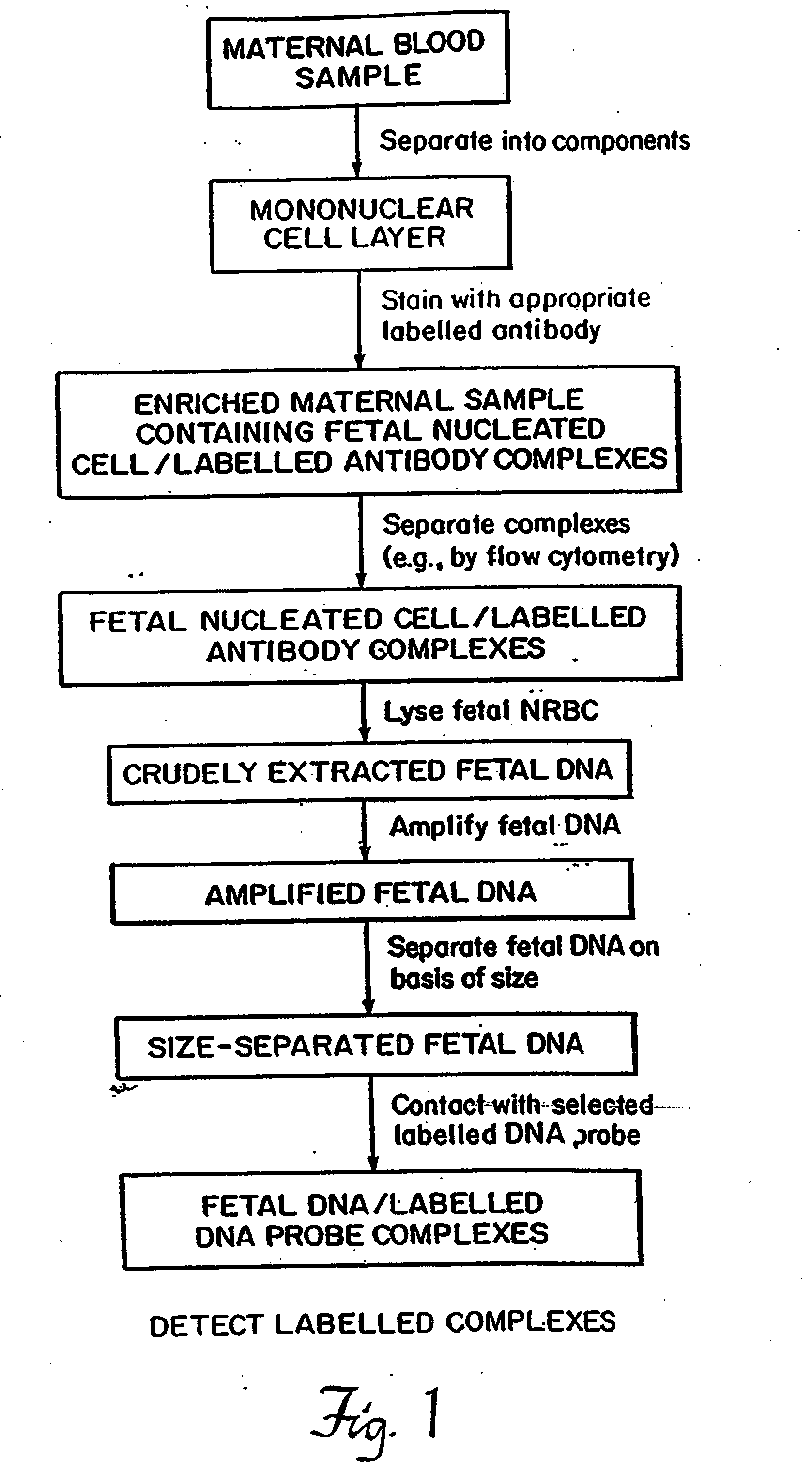
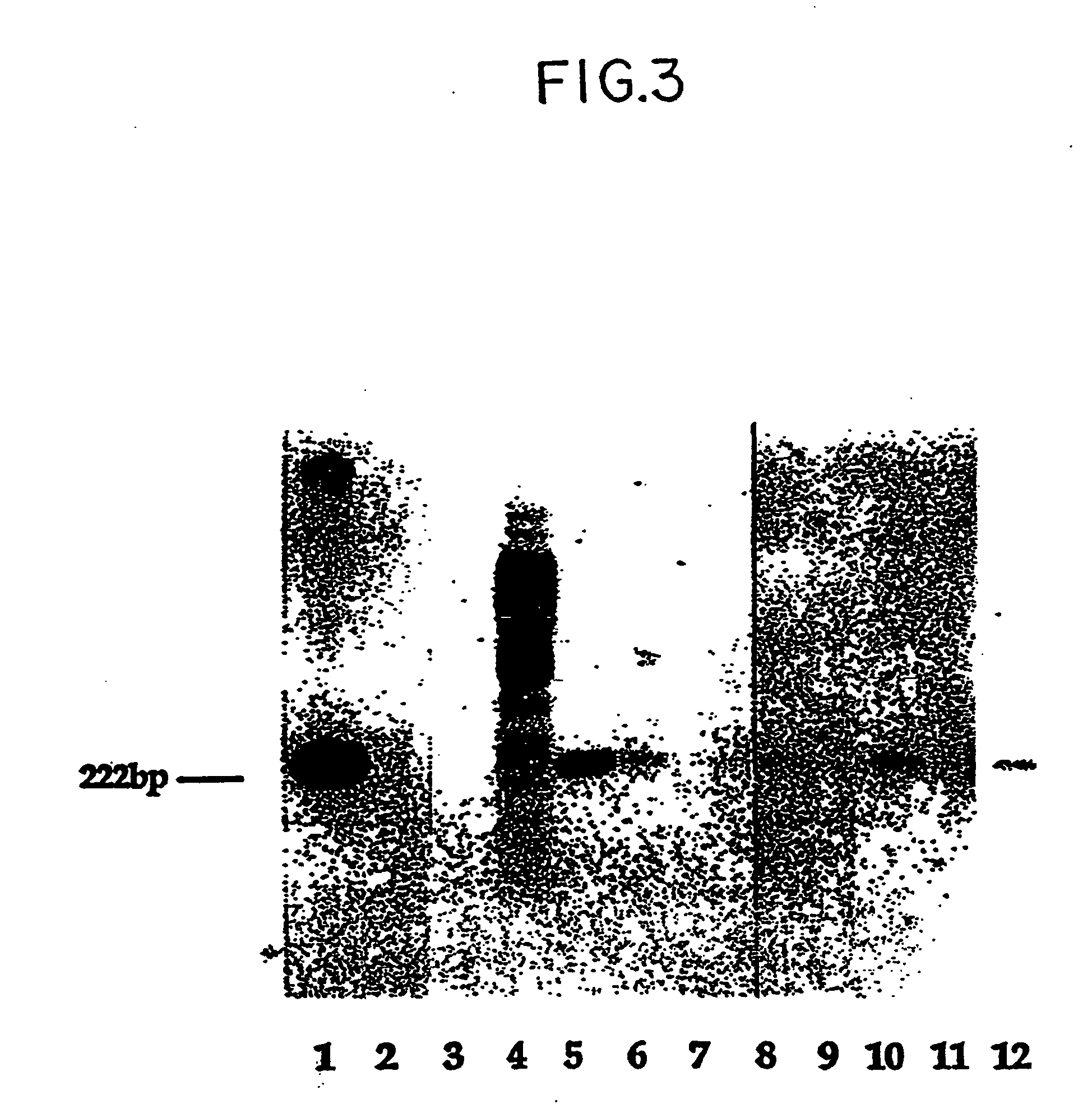
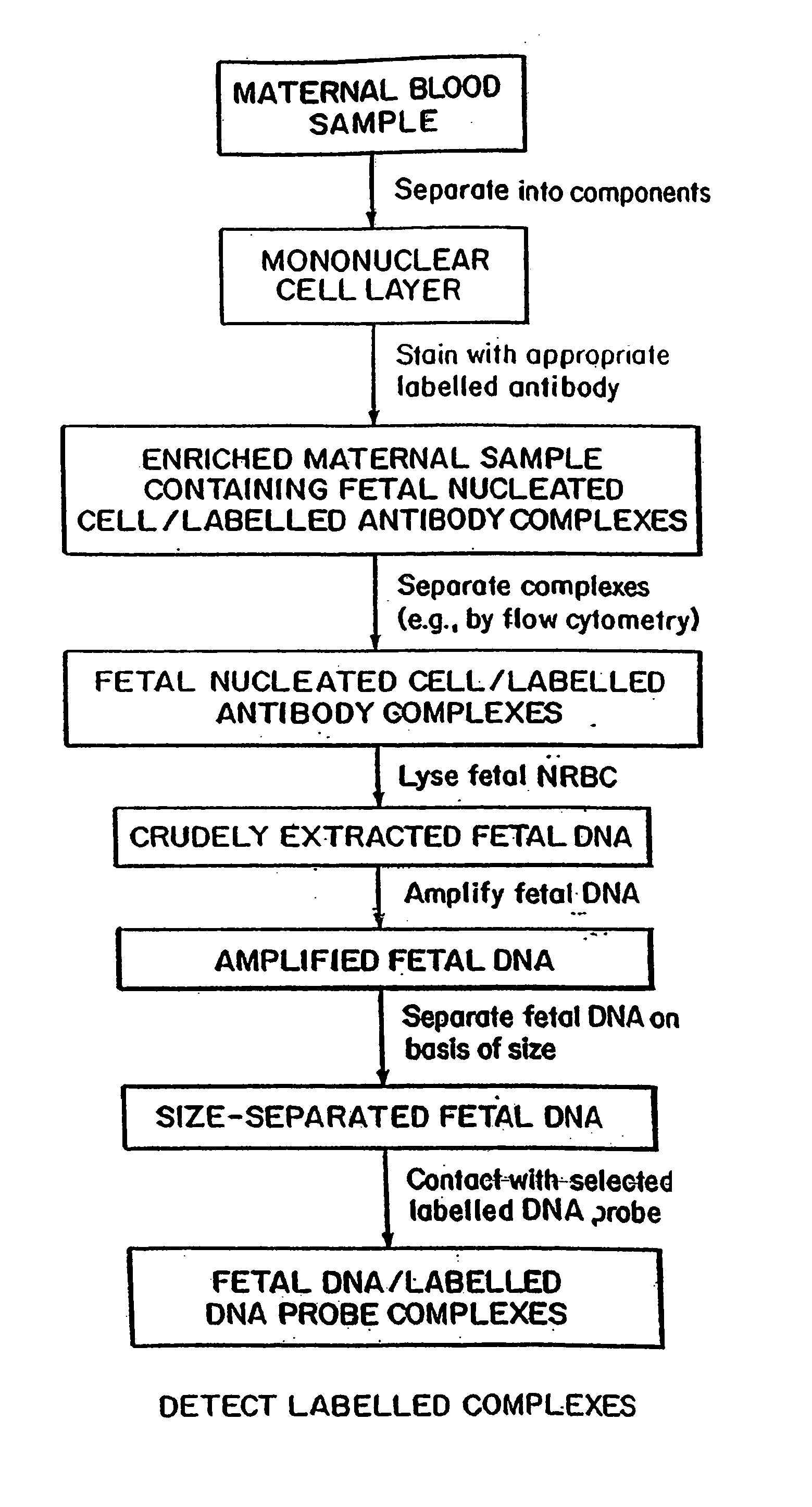
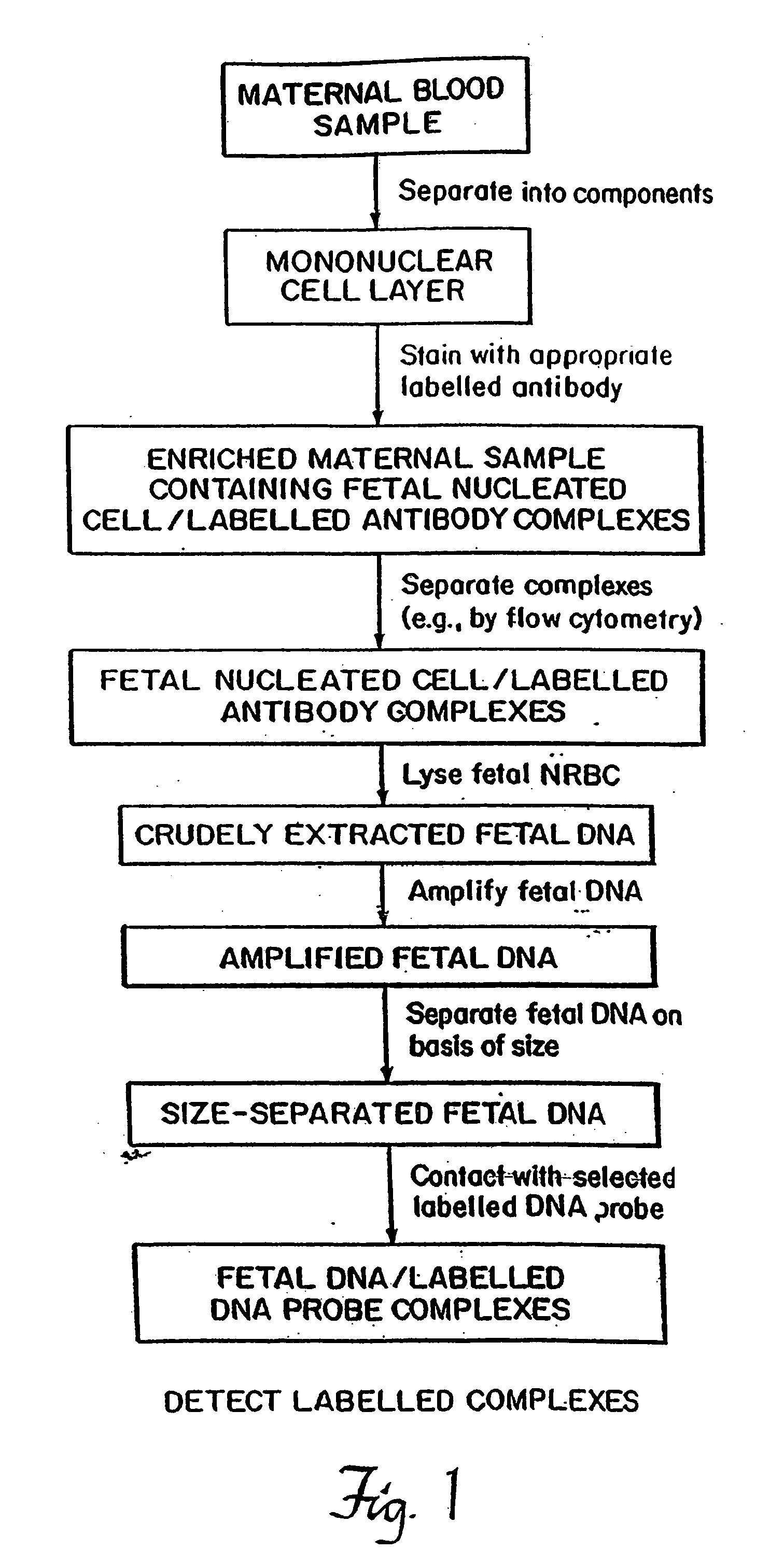
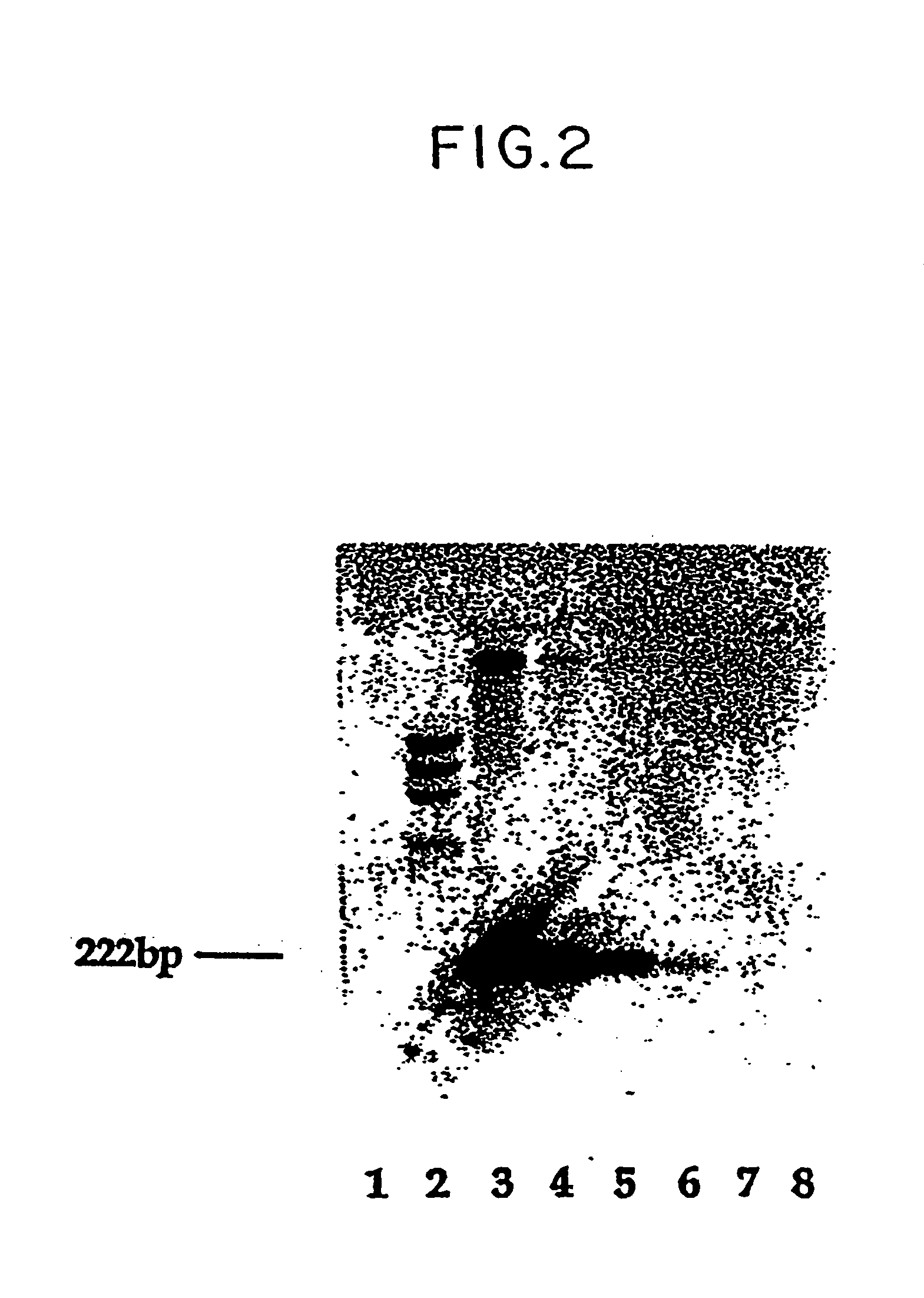
A method of detecting the presence or absence of the fetal DNA sequence of interest in fetal DNA derived from a sample of peripheral blood obtained from a pregnant woman is described. The method involves obtaining a sample peripheral blood from a pregnant woman, treating the sample of peripheral blood such that the fetal DNA present in the fetal nucleated cells is made available for detection and detecting the presence or absence of the fetal DNA sequence of interest in the available fetal DNA. The proportion of fetal nucleated cells present in the sample of peripheral blood can be increased forming a sample enriched in fetal nucleated cells prior to the detection step. The fetal DNA sequence of interest can be detected by treating the peripheral blood sample such that fetal DNA present in the sample is made available for hybridization with a DNA probe and subsequently contacting the available fetal DNA with a DNA probe hybridizable to fetal DNA of interest under hybridization conditions. The presence or absence of hybridization between the DNA probe and the fetal DNA of interest is detected as an indication of the presence or absence of the fetal DNA of interest.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Use of umbilical cord blood to treat individuals having a disease, disorder or condition
The present invention provides methods of using cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells in high doses to treat various conditions, diseases and disorders. The high-dose cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells have a multitude of uses and applications, including but not limited to, therapeutic uses for transplantation and treatment and prevention of disease, and diagnostic and research uses. In particular, the cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells are delivered in high doses, e.g., at least 3 billion nucleated cells per treatment, where treatment may comprise a single or multiple infusions. The invention also provides for the use of cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells from multiple donors without the need for HLA typing.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Non-invasive method for isolation and detection of fetal DNA
A method of detecting the presence or absence of the fetal DNA sequence of interest in fetal DNA derived from a sample of peripheral blood obtained from a pregnant woman is described. The method involves obtaining a sample peripheral blood from a pregnant woman, treating the sample of peripheral blood such that the fetal DNA present in the fetal nucleated cells is made available for detection and detecting the presence or absence of the fetal DNA sequence of interest in the available fetal DNA. The proportion of fetal nucleated cells present in the sample of peripheral blood can be increased forming a sample enriched in fetal nucleated cells prior to the detection step. The fetal DNA sequence of interest can be detected by treating the peripheral blood sample such that fetal DNA present in the sample is made available for hybridization with a DNA probe and subsequently contacting the available fetal DNA with a DNA probe hybridizable to fetal DNA of interest under hybridization conditions. The presence or absence of hybridization between the DNA probe and the fetal DNA of interest is detected as an indication of the presence or absence of the fetal DNA of interest.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
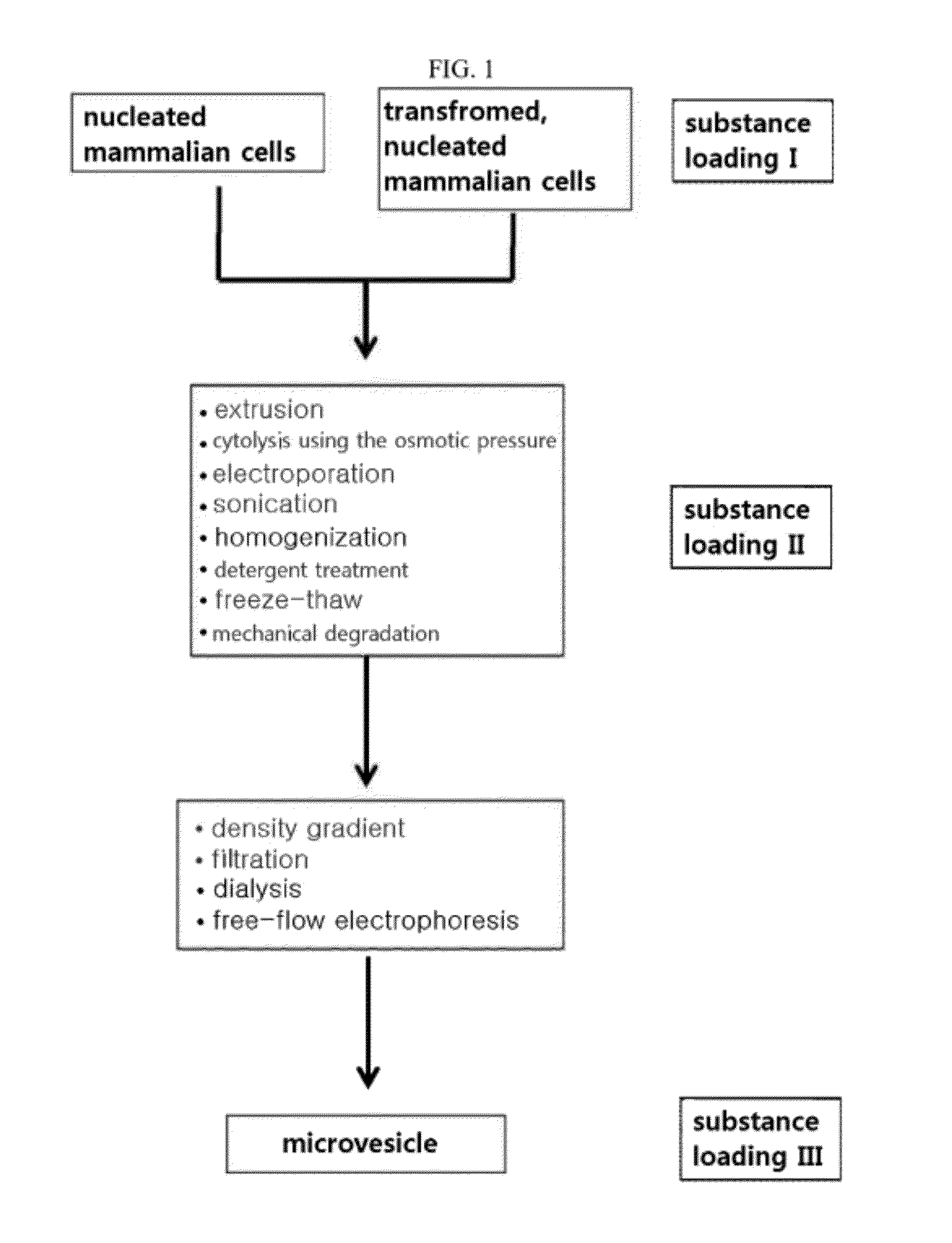
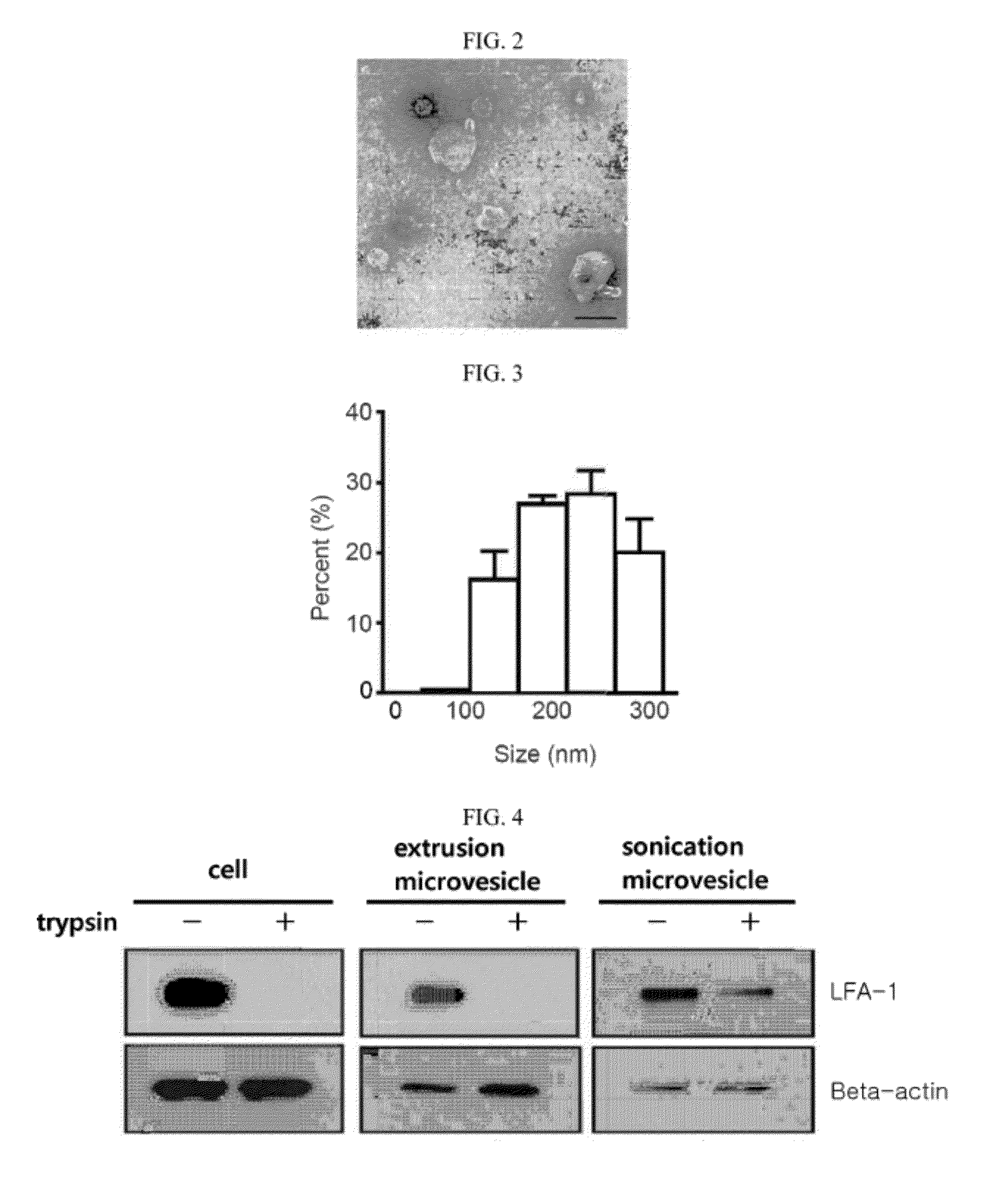
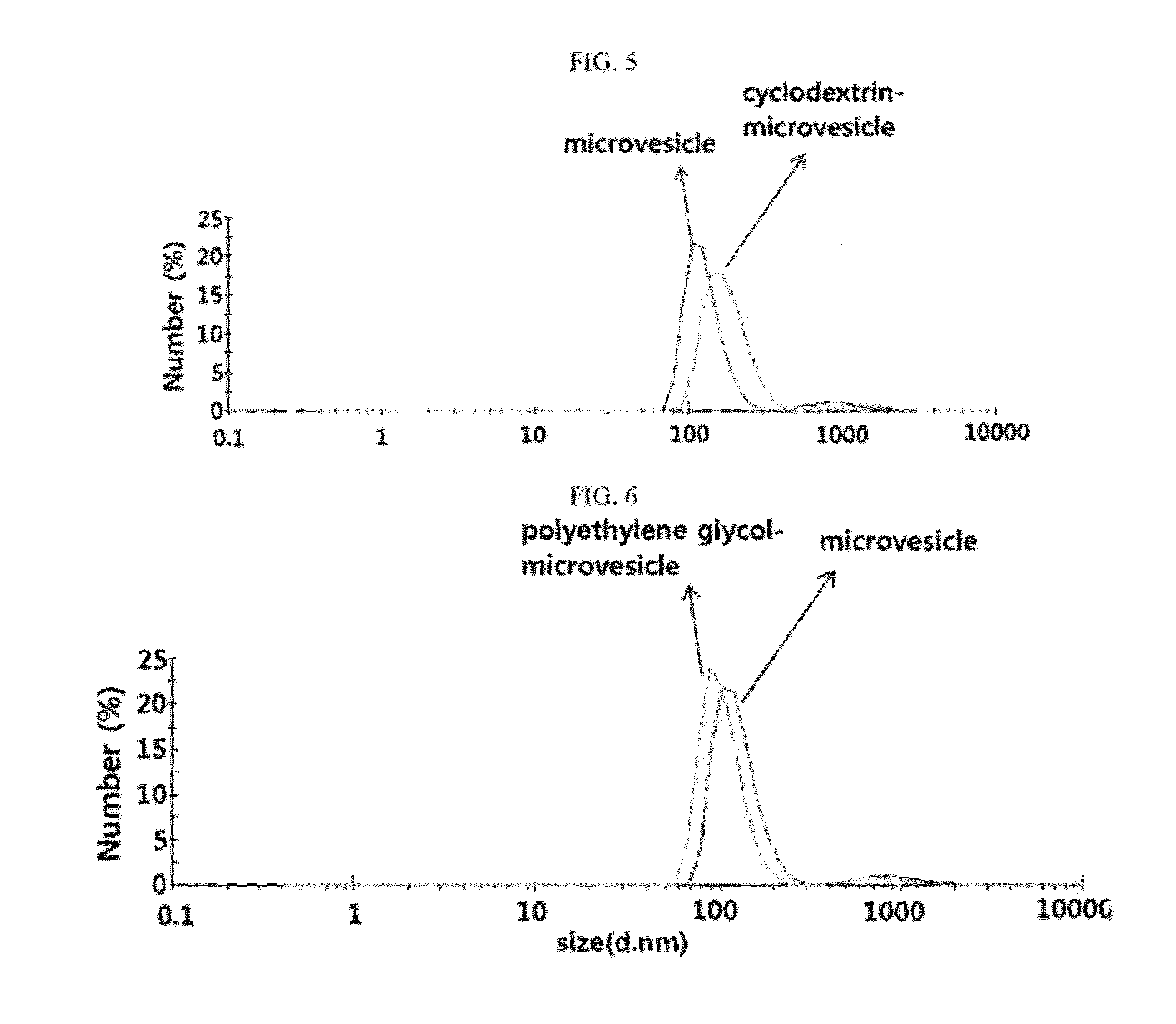
Microvesicles derived from nucleated, mammalian cells and use thereof
InactiveUS20120177574A1Reducing agonyReduce inconvenienceMammal material medical ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsDendritic cellMonocyte
The present invention relates to a microvesicle that is derived from nucleated mammalian cells, which are smaller than the nucleated cells. The microvesicles of the present invention can be used in the delivery of a therapeutic or diagnostic substance to specific tissues or cells, and more particularly, relates to microvesicles derived from monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, stem cells or the like, which can be used to deliver specific therapeutic or diagnostic substances for treating and / or diagnosing tissue associated with cancer, diseased blood vessels, inflammation, or the like.
Owner:AEON MEDIX
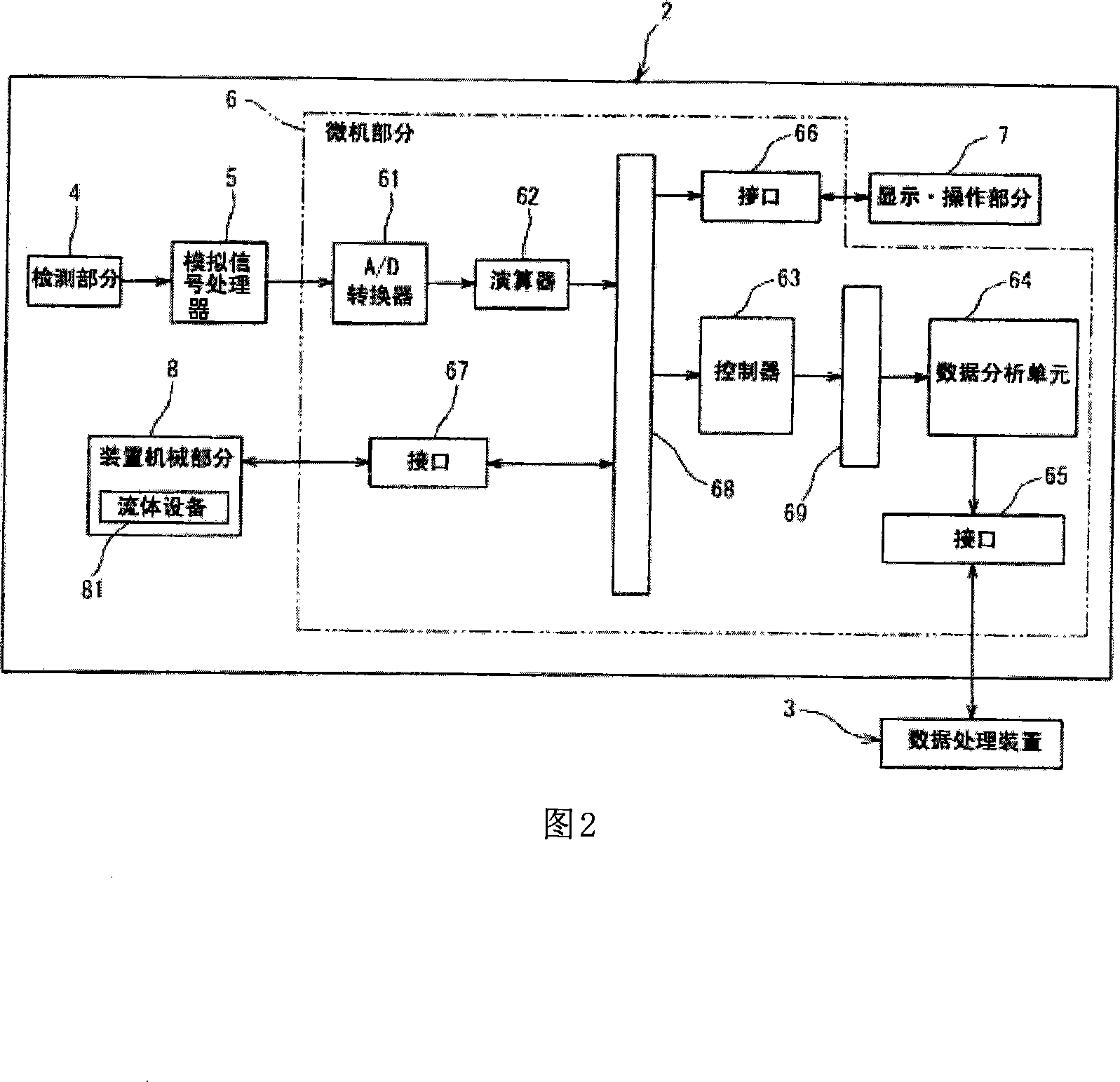
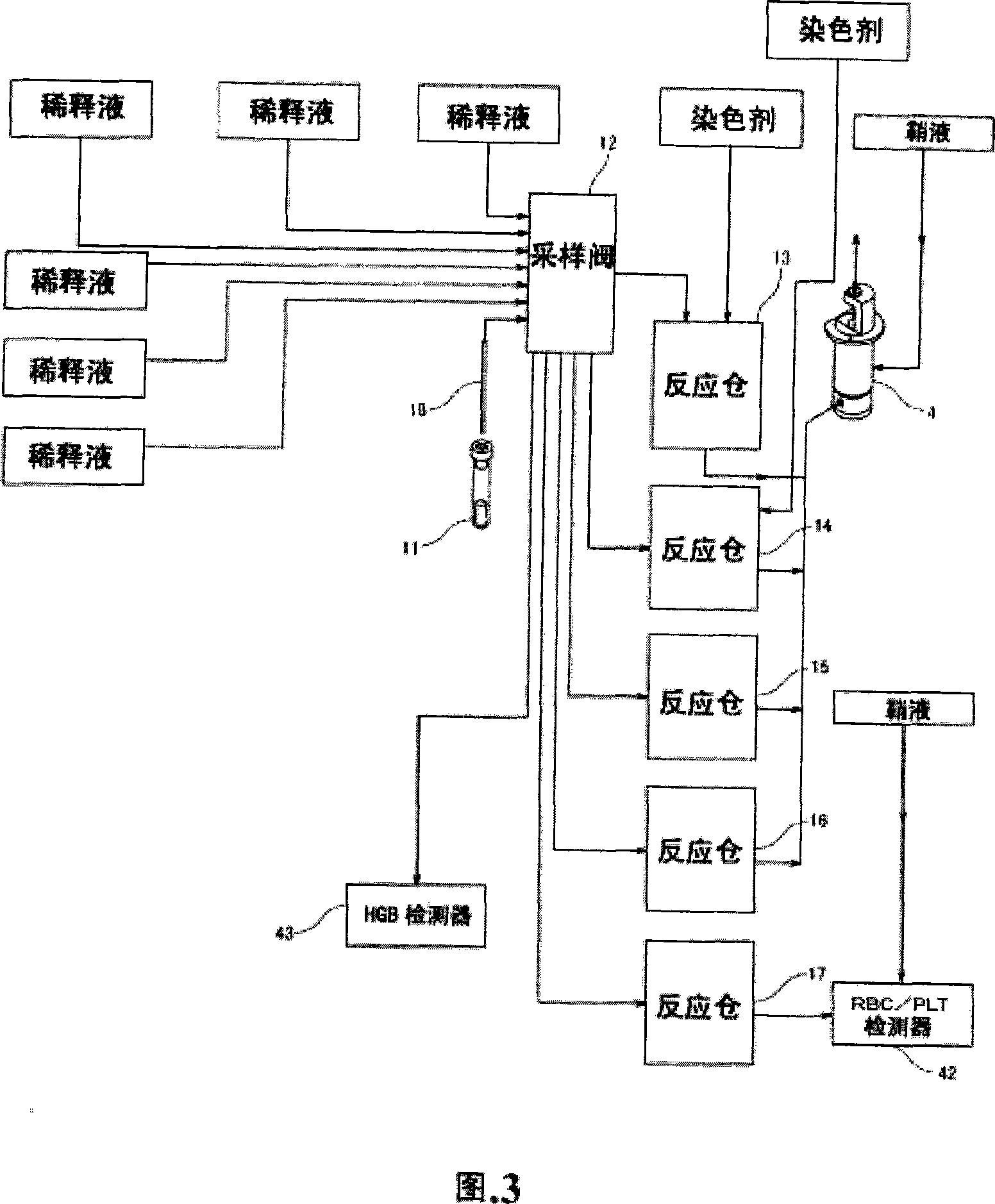
Hematological analyzer, method for analyzing body fluid and control system thereof
ActiveCN101236195AMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisMeasurement testWhite blood cell
The present invention provides a blood cell analyzer, comprising: a measurement mode setting unit for setting the body fluid measurement mode; a measurement start indicating unit for receiving an instruction to start the measurement; an optical information acquisition unit for illuminating the measurement sample, from which The optical information is obtained from the cells contained in the measurement sample; the analysis unit, after the above-mentioned body fluid measurement mode is set, when the above-mentioned measurement start instruction unit receives an instruction to start the measurement, according to the above-mentioned measurement test prepared from the body fluid sample and the reagent for leukocyte measurement, The optical information obtained in the sample is used to classify the cells contained in the measurement sample into at least leukocytes and nucleated cells other than leukocytes, and count the nucleated cells other than leukocytes. The invention also provides a body fluid analysis method and a control system.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
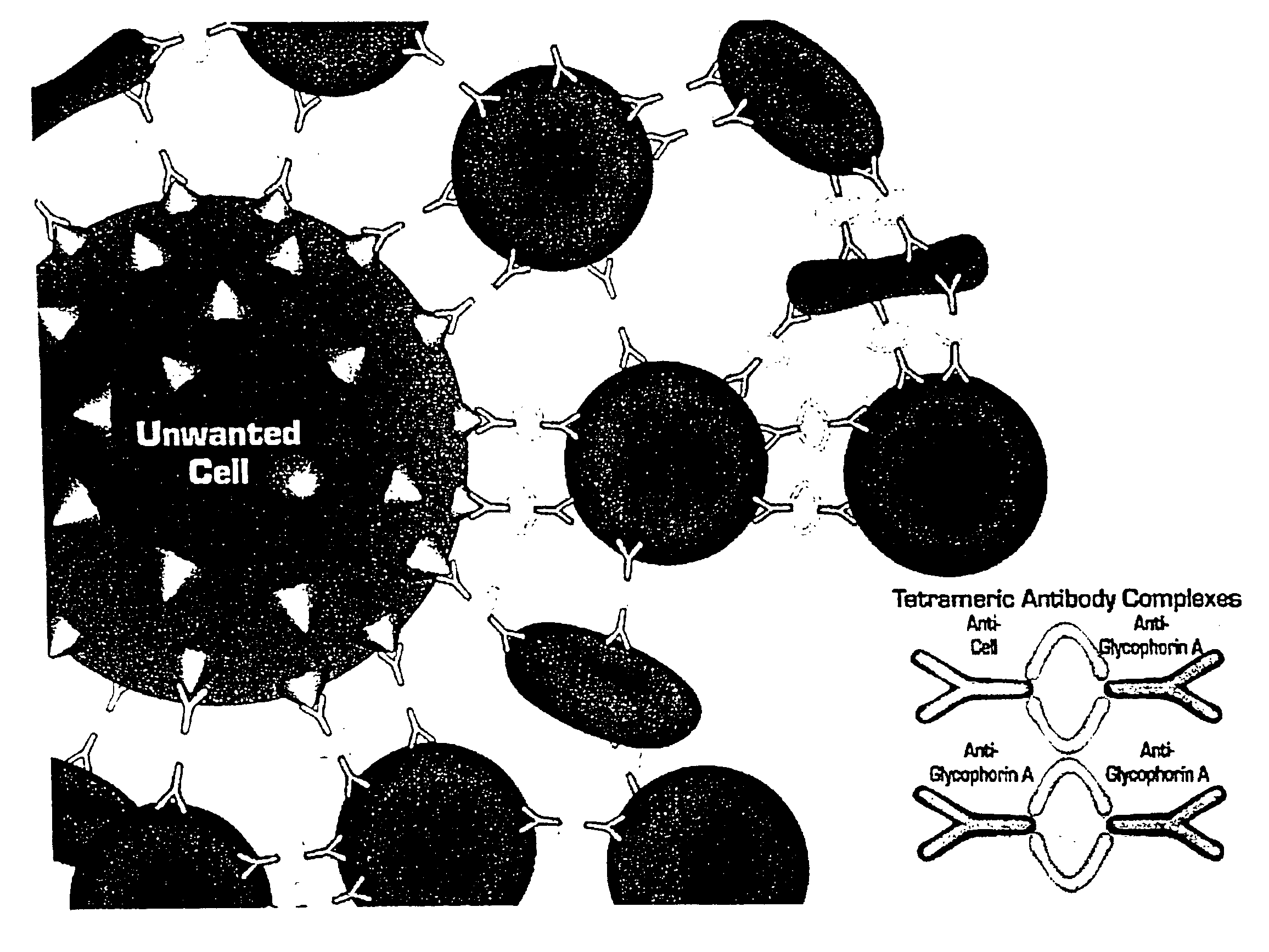
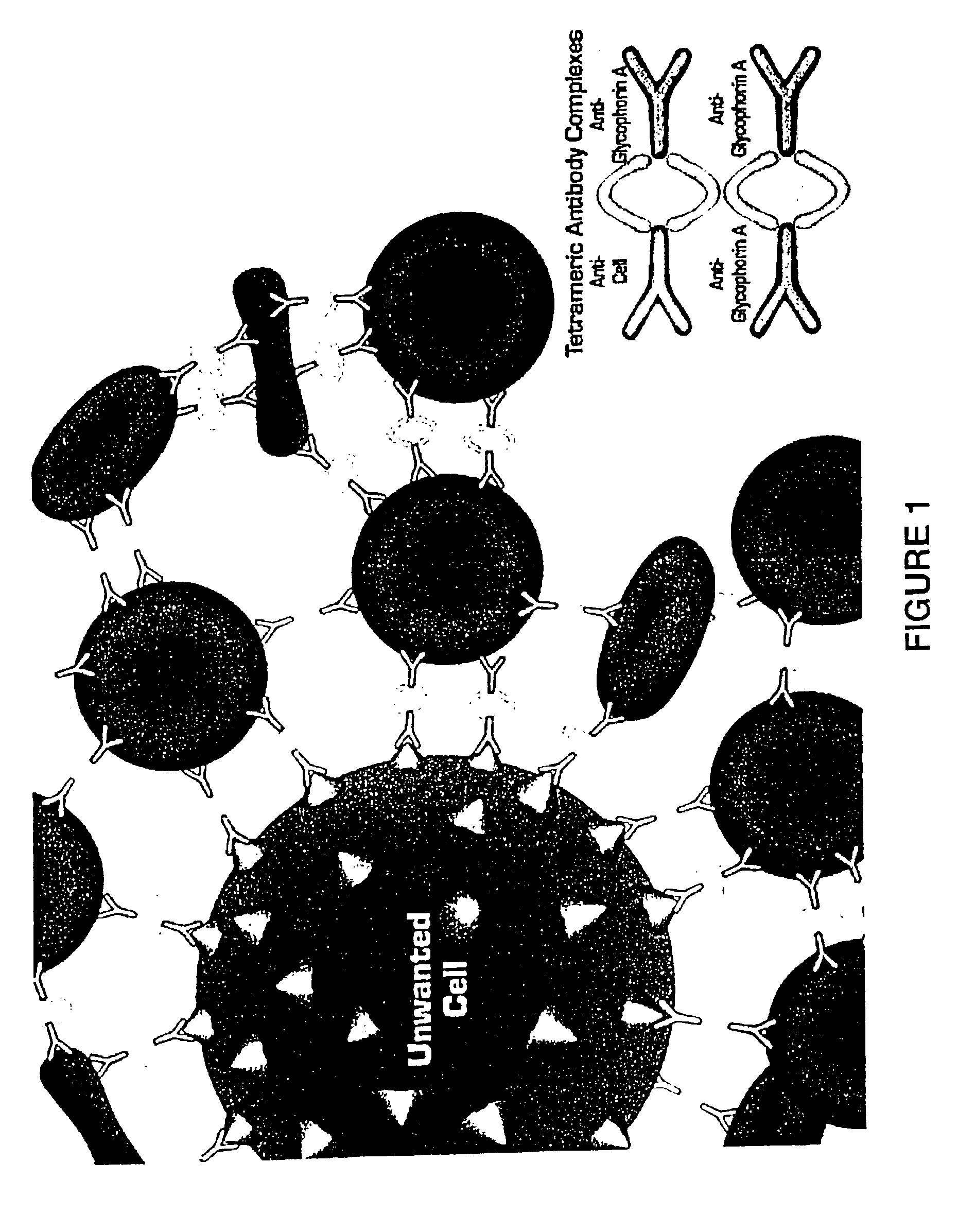
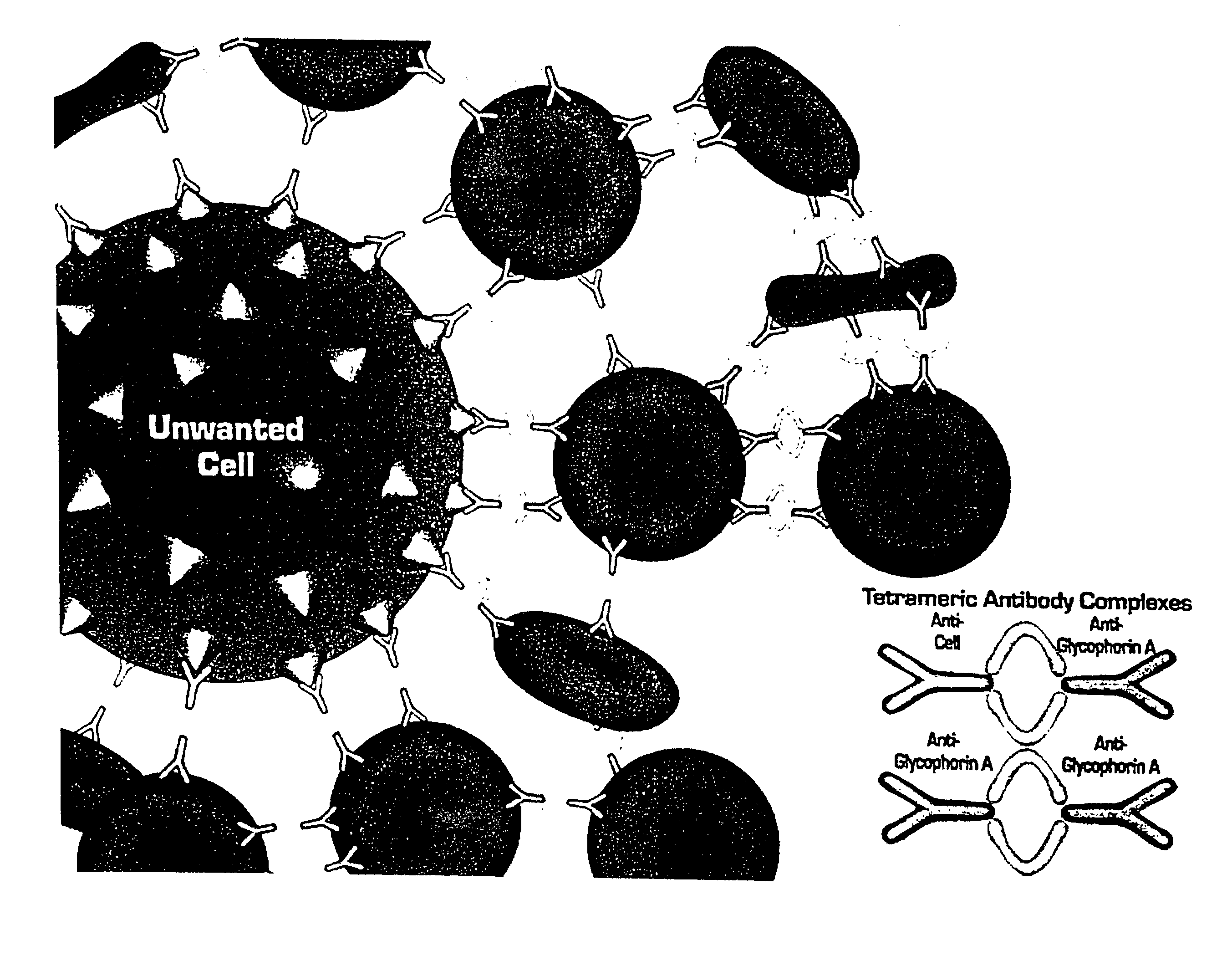
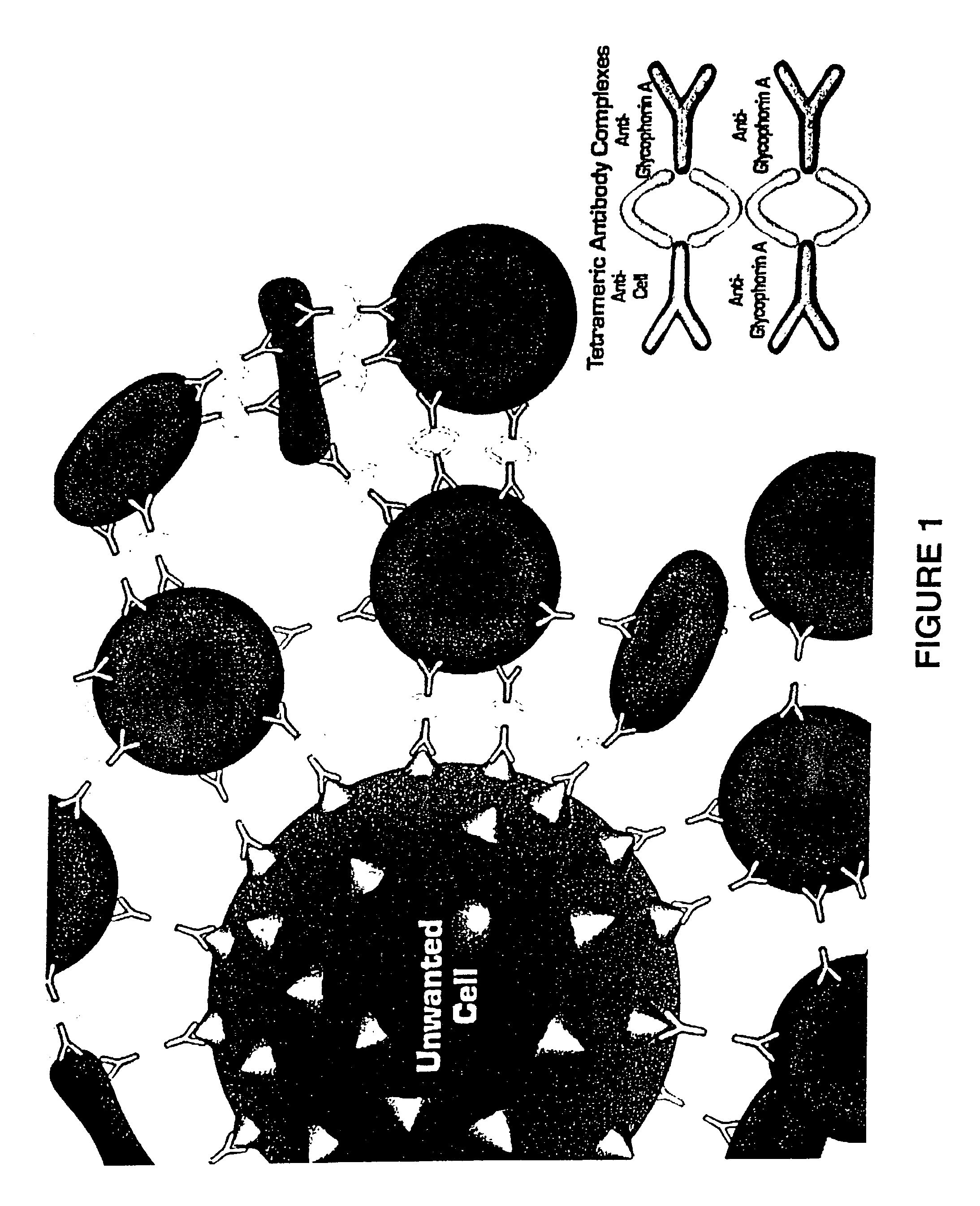
Method for separating cells using immunorosettes
The present invention relates to methods for separating cells using immunorosettes. The method involves contacting a sample containing nucleated cells and red blood cells with an antibody composition which allows immunorosettes of the nucleated cells and the red blood cells to form. The antibody composition preferably contains bifunctional antibodies or tetrameric antibody complexes.
Owner:STEMCELL TECHNOLOGIES
Methods and kits for sequentially isolating RNA and genomic DNA from cells
InactiveUS20070238118A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWhite blood cellGenomic DNA
Methods for obtaining nucleic acid from nucleated cells are disclosed, wherein RNA and fragmented genomic DNA can be sequentially obtained from the same starting material are disclosed. In some embodiments, protein can also be obtained from the same starting material as the RNA and DNA are obtained. According to certain methods, whole blood or a blood fraction comprising nucleated cells is combined with a capture surface and at least some of the leukocytes are retained on the surface. The RNA is released from the retained leukocytes, then the capture surface is treated with a suitable nuclease or other DNA fragmenting agent to release DNA fragments. In certain embodiments, either the released RNA, the released DNA, or both the released RNA and the released DNA are employed in one or more molecular biology application.
Owner:AMBION INC
Circulating tumor cell diagnostics for biomarkers predictive of resistance to androgen receptor (AR) targeted therapies
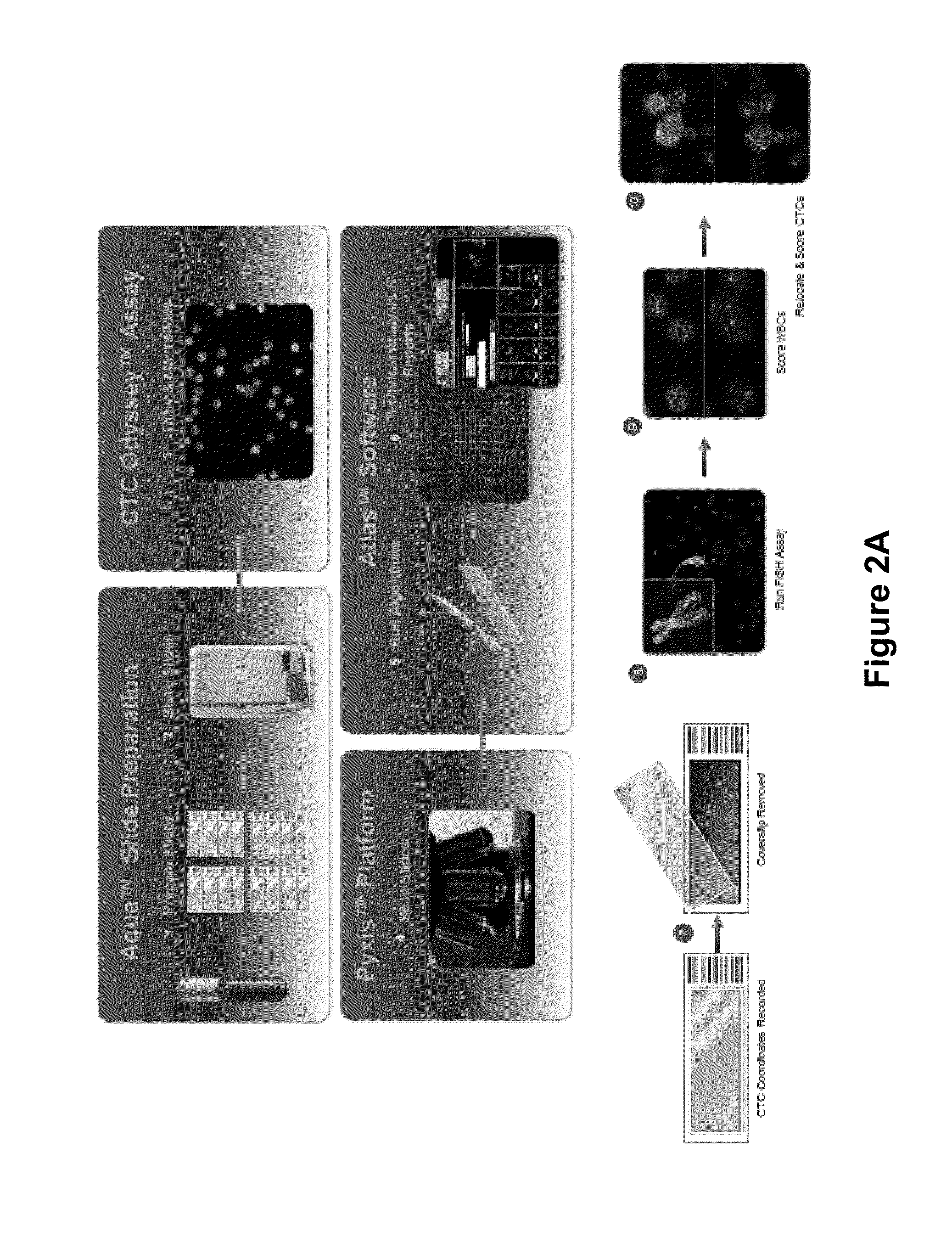
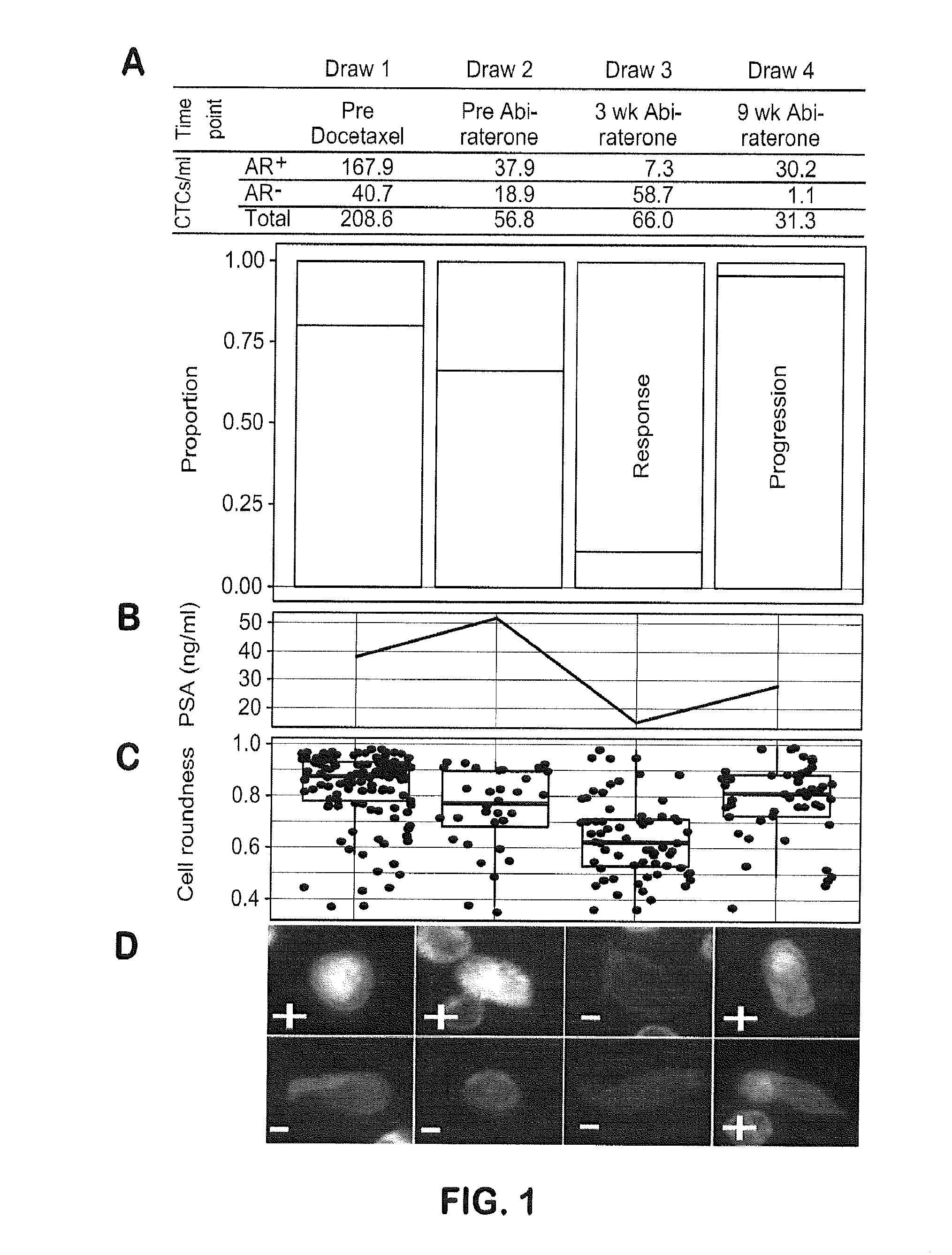
The disclosure provides a method of predicting resistance to androgen receptor (AR) targeted therapy in a prostate cancer patient comprising (a) performing a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characterization of nucleated cells in a blood sample obtained from the patient to identify circulating tumor cells (CTCs), and (b) based on said direct analysis further determining the presence of a biomarker signature that is predictive of resistance to AR targeted therapy in the prostate cancer patient, wherein the biomarker signature comprises CK+, AR+, nucleoli+ CTCs in a subpopulation of said CTCs. The present disclosure also provides a method of predicting resistance to taxane-based chemotherapy in a prostate cancer patient comprising (a) performing a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characterization of nucleated cells in a blood sample obtained from the patient to identify circulating tumor cells (CTCs), and (b) based on said direct analysis further determining the presence of a biomarker signature that is predictive of resistance to taxane-based chemotherapy in the prostate cancer patient, wherein the biomarker signature comprises CK+, AR−, nucleoli+, small size in a subpopulation of said CTCs.
Owner:EPIC SCIENCES
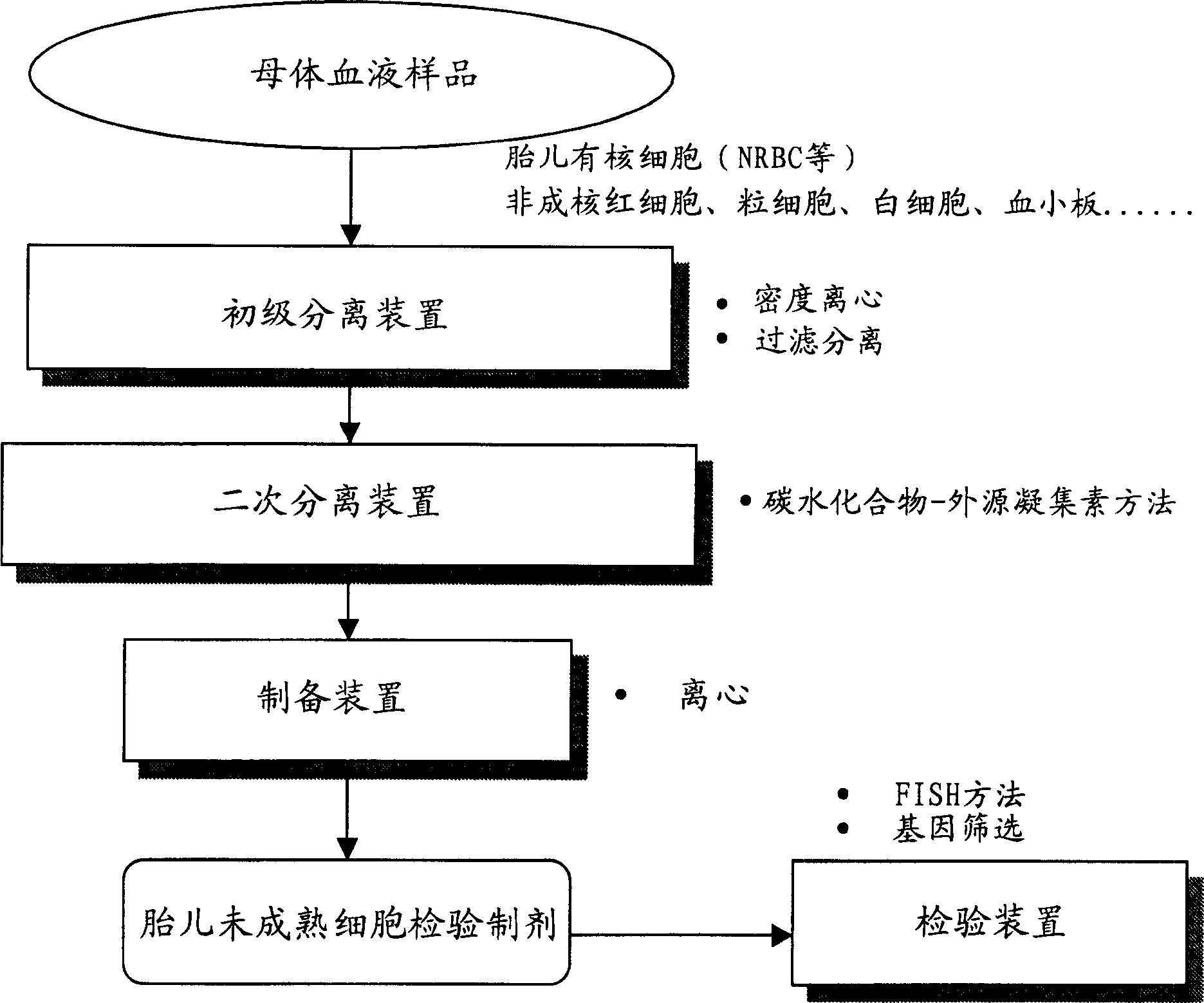
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130265A1Microbiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
Cell Preservation Method
The present invention provides a method for freezing a stem cell or a cell derived therefrom, the method including the steps of providing a cell suspension, performing ice nucleation on the cell suspension, and lowering the temperature of the ice nucleated cell suspension to a temperature sufficiently low to allow long term storage of the stem cell. The method is preferably used for the cryopreservation of human embryonic stem cells.
Owner:ES CELL INT
Method for discriminating non-blood-borne nucleated cells enriched from human or animal biological fluid
ActiveCN103091491AHigh recovery rateAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationHuman bodyStaining
Owner:有限会社林平
Composition and kit for rapid extraction of circulating unrelated nucleated cell from peripheral blood and application thereof
ActiveCN101880650AHigh recovery rateShorten centrifugation timeMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureSurface markerNon magnetic
The invention provides a composition and a kit for rapid and efficient extraction of a circulating unrelated nucleated cell from peripheral blood. The composition for rapid extraction of the circulating unrelated nucleated rare cell from the blood comprises buffer solution, hypotonic erythrocyte breaking solution, magnetic or non-magnetic immune micro-spheres coated with an anti-blood nucleated cell surface marker antibody and a cell separation medium with a certain density. Compared with the common commercial centrifugation medium on the market at present, the composition of the invention can greatly reduce the centrifugation time, and stably improve the cell recovery rate from original 60 plus or minus 20 percent to above 95 percent. When combined with the agent to remove leukocytes andhypotonic erythrocyte breaking means, the composition can be used for effectively and rapidly concentrating and extracting circulating unrelated nucleated rare cells in the peripheral blood, such as epithelial tumor cells and vascular endothelial cells. Therefore, the invention has great practical clinical significance for early diagnosis of tumors and heart diseases.
Owner:有限会社林平
Method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units
InactiveUS6852534B2Accurate assessmentAutomatically performBiocideDead animal preservationCord blood stem cellCell dose
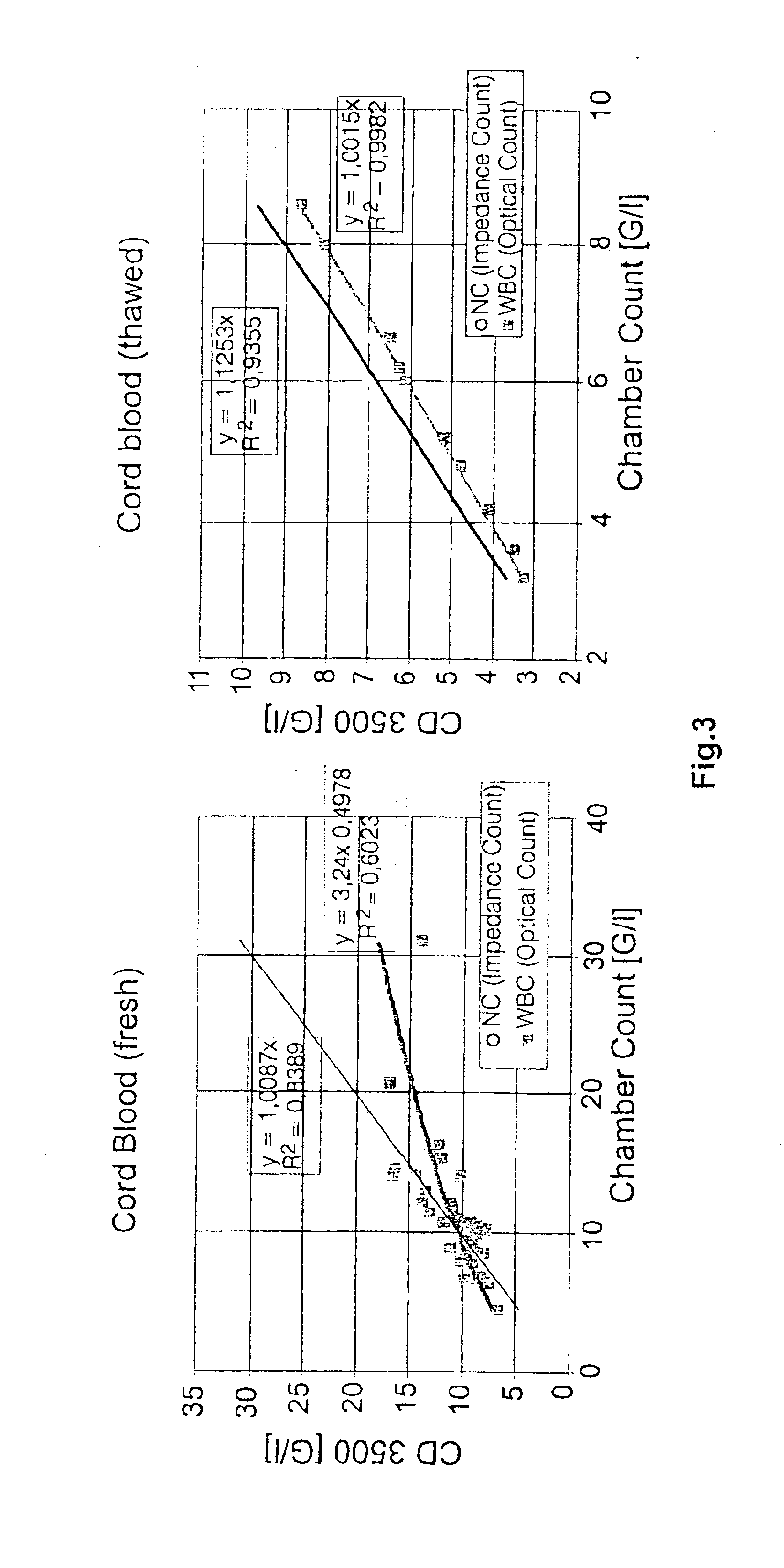
A method to determine an engrafting cell dose of hematopoietic stem cell transplant units from transplant sources having nucleated cells selected from the group consisting of cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood comprising the steps of[0002]subjecting the source to a substantially complete erythrocyte lysis,[0003]measuring in a cell counter a signal corresponding selectively to white blood cells,[0004]assessing essentially quantitatively nucleated red blood cell (NRBC) count as part of the total nucleated cell (NC) count,[0005]and determining the number of white blood cells (WBCs) as transplant relevant cells.
Owner:KOURION THERAPEUTICS
Genotypic and Phenotypic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells to Monitor Tumor Evolution in Prostate Cancer Patients
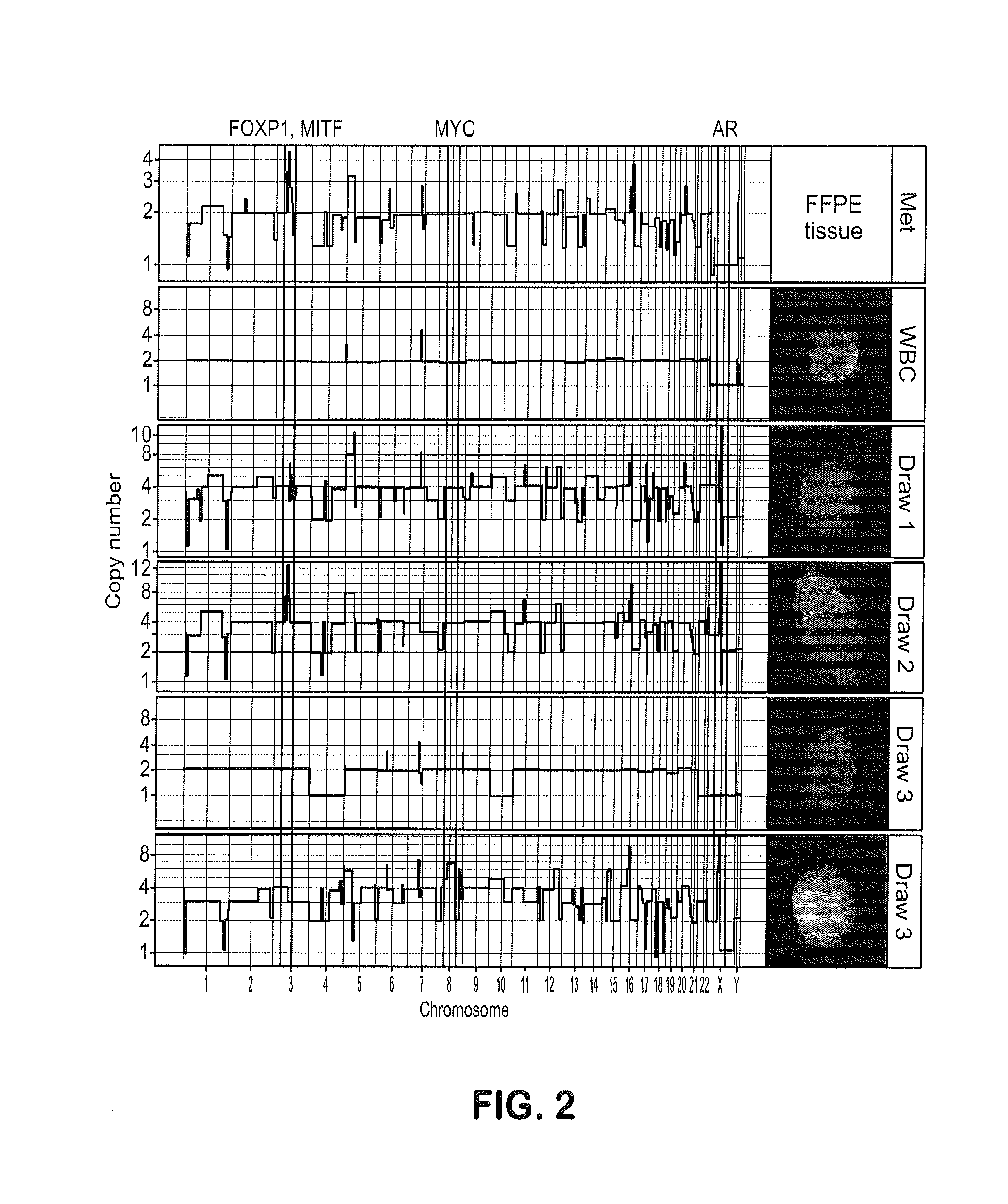
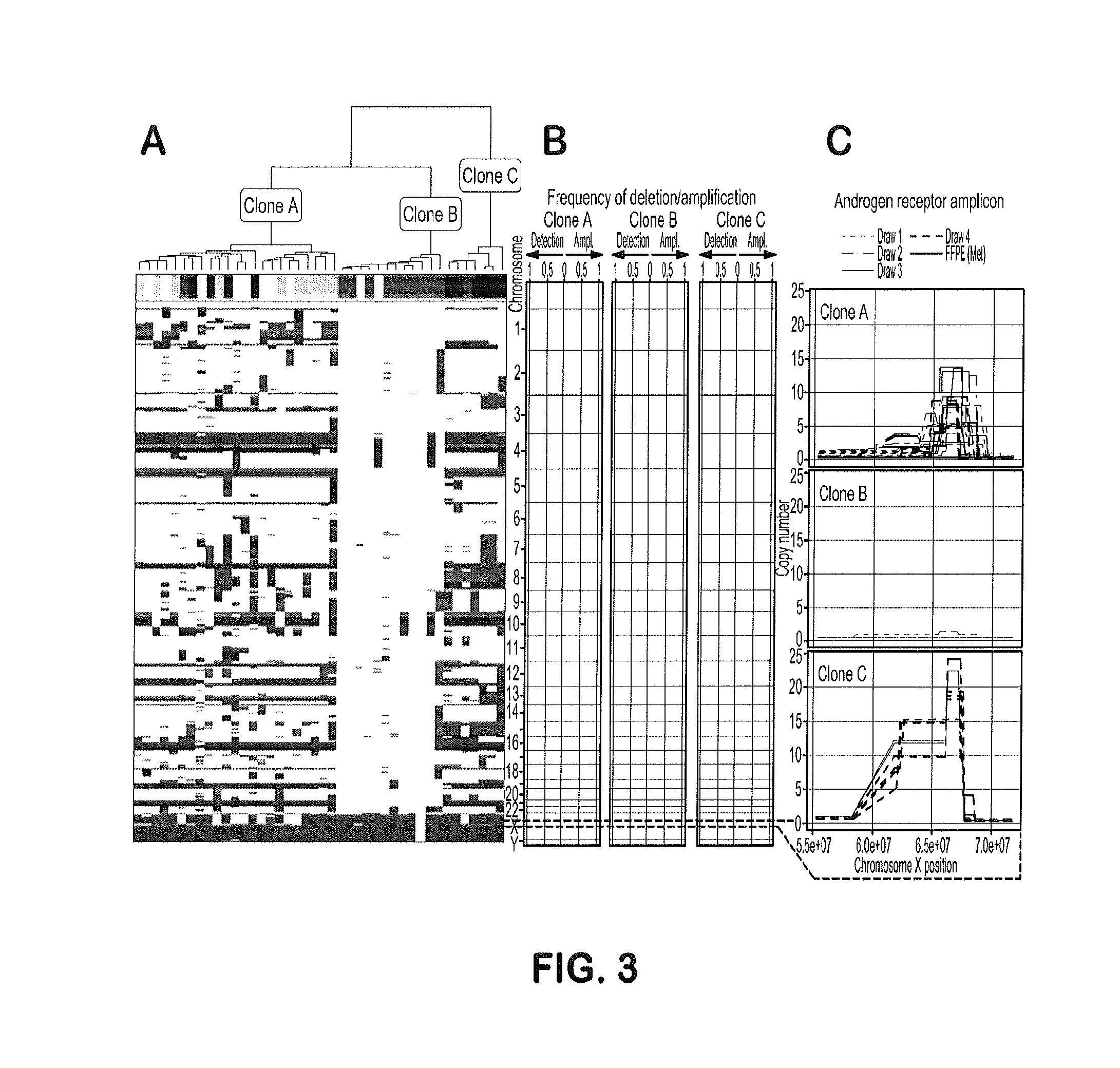
The present invention provides methods for predicting response to a hormone-directed therapy or chemotherapy in a prostate cancer (PCa) patient comprising (a) performing a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characterization of nucleated cells in a blood sample obtained from the patient to identify and enumerate circulating tumor cells (CTC); (b) individually characterizing genotypic, morphometric and protein expression parameters to generate a profile for each of the CTCs, and (c) predicting response to hormone-directed therapy in the prostate cancer PCa patient based on said profile. In some embodiments, the methods comprise repeating steps (a) through (c) at one or more timepoints after initial diagnosis of prostate cancer to sequentially monitor said genotypic, morphometric and protein expression parameters.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
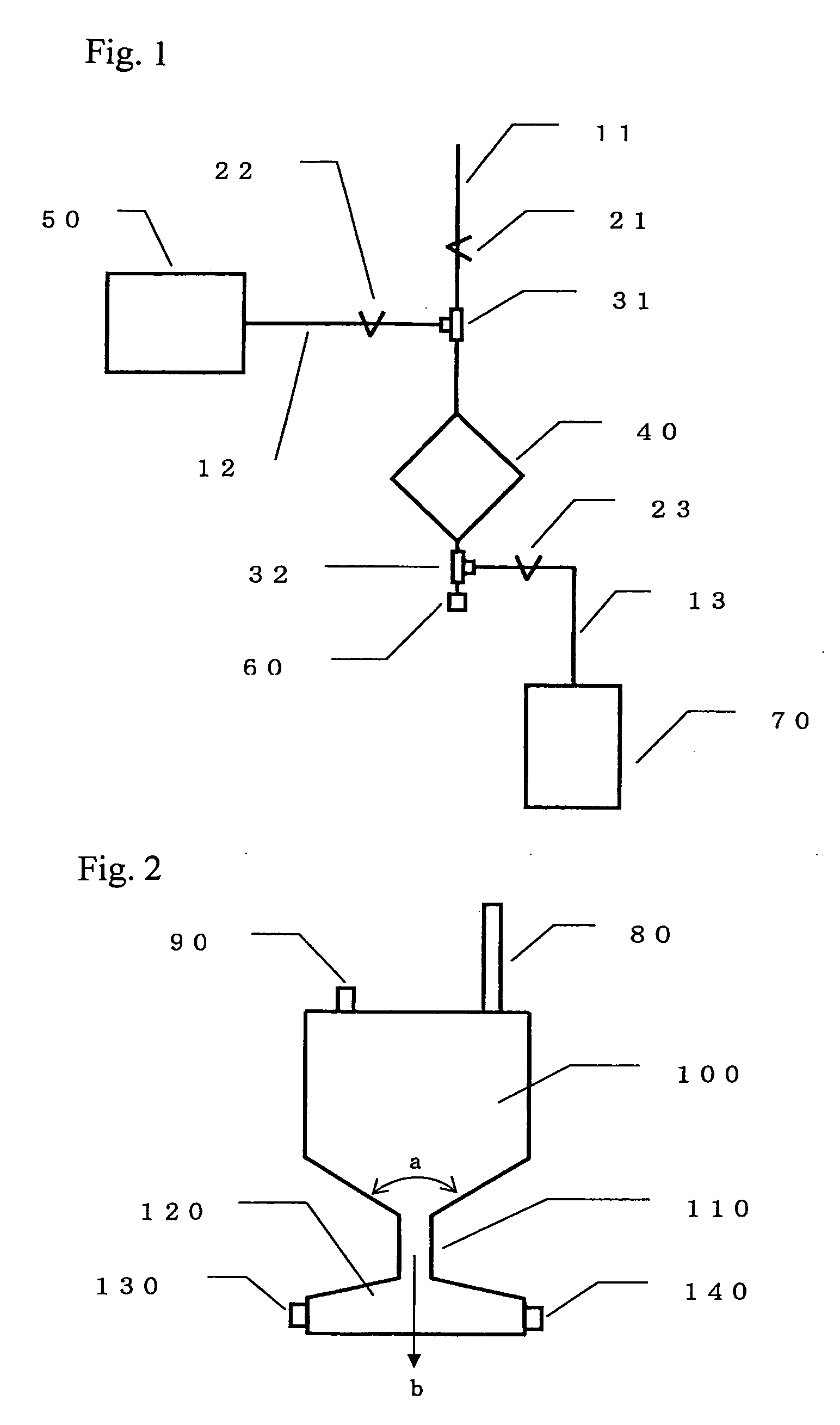
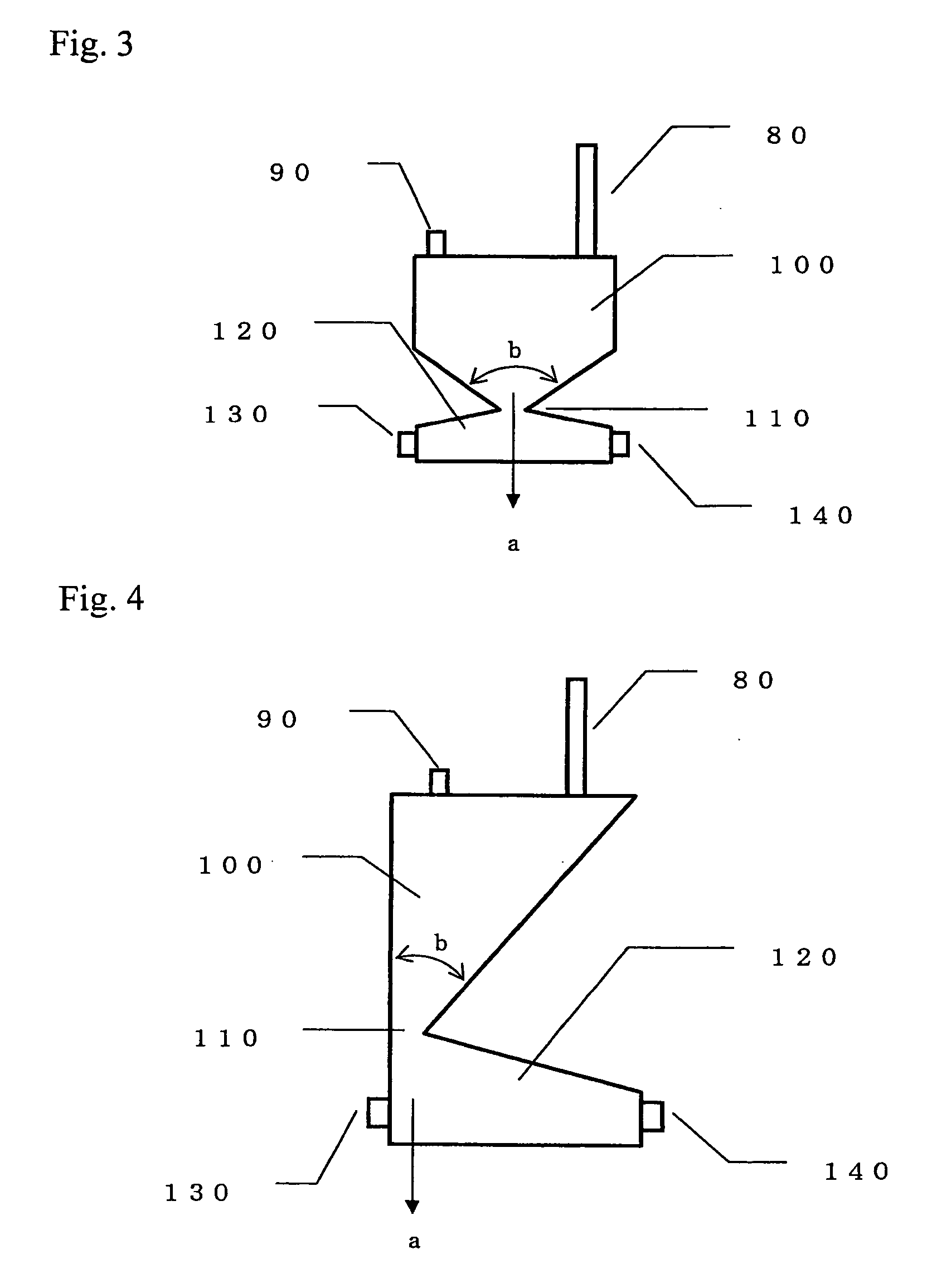
Method for Preparing Cell Concentrate and Cell Composition
InactiveUS20070275459A1Stable recoveryHigh yieldDead animal preservationSedimentation separationCryopreservationCell separation
It is an object of the present invention to provide: a method for preparing a cell concentrate which efficiently separates nucleated cells from unnecessary cells contained in a cell-containing solution by simple operations, thereby reducing the volume of a solution used for cryopreservation that contains the nucleated cells, when the cell-containing solution that contains the nucleated cells and the unnecessary cells has been filtrated with a filter device and when a recovery solution is then introduced into the filter device to recover the nucleated cells captured by a filter material; and a cell composition. The present invention provides a method for preparing a cell concentrate, which comprises: introducing a cell-containing solution that contains nucleated cells and unnecessary cells into a filter device comprising a filter material for substantially capturing the nucleated cells and for substantially giving passage to the unnecessary cells, so as to capture the nucleated cells by the above-described filter material and to discharge the unnecessary cells from the above device; and introducing a recovery solution into the above-described filter device, so as to recover the nucleated cells captured by the above-described filter material, wherein the above-described method is characterized in that the cell-containing solution that contains nucleated cells and unnecessary cells are separated into a layer that is rich in nucleated cells and a layer that is rich in unnecessary cells, the layer rich in unnecessary cells is first introduced into the above-described filter device, and the layer rich in nucleated cells is then introduced therein, so as to discharge the unnecessary cells remaining in the above-described filter device while capturing the nucleated cells by the above-described filter material, and a recovery solution is then introduced into the above-described filter device, so as to recover the nucleated cells captured by the above-described filter material.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
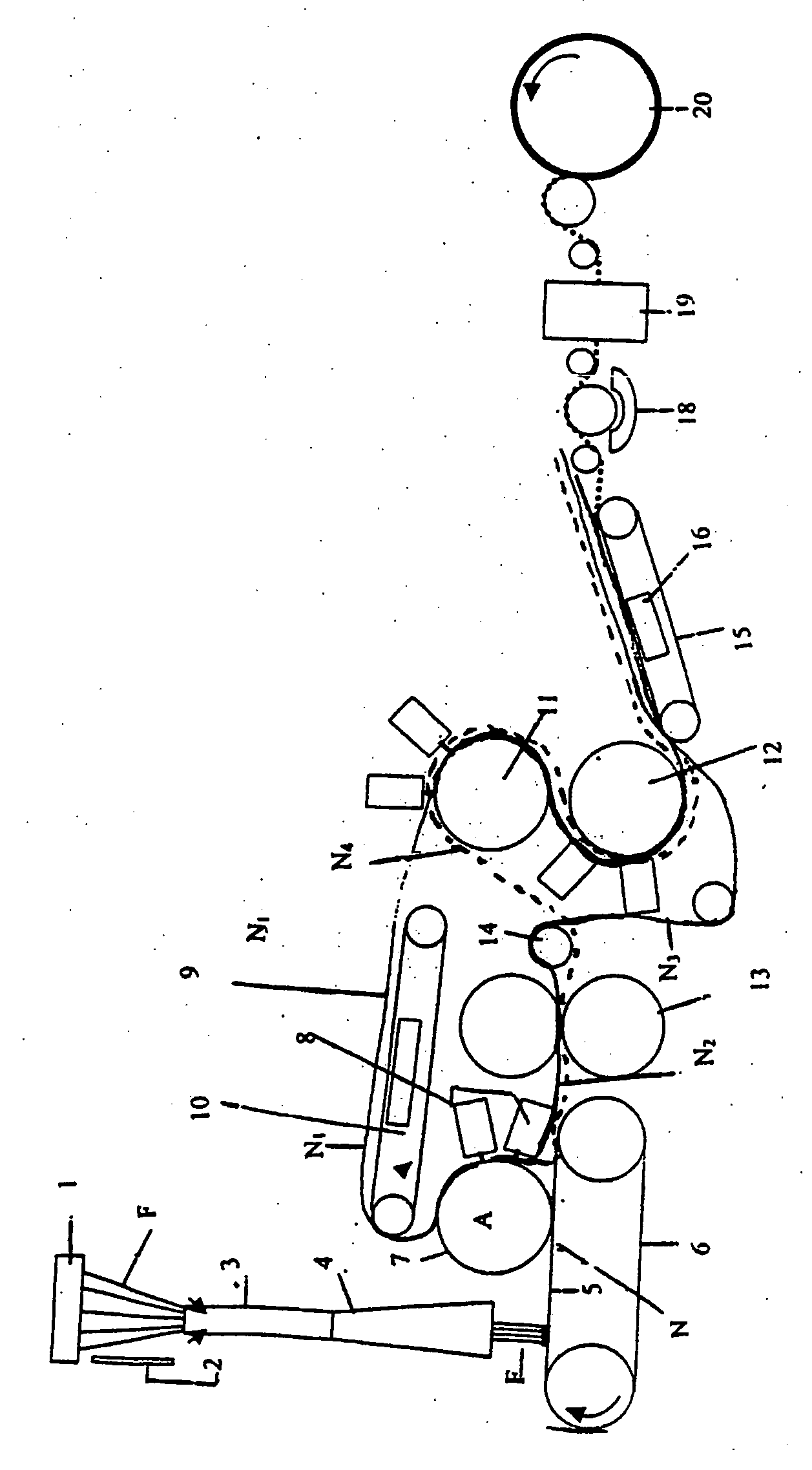
Blood cell separation system
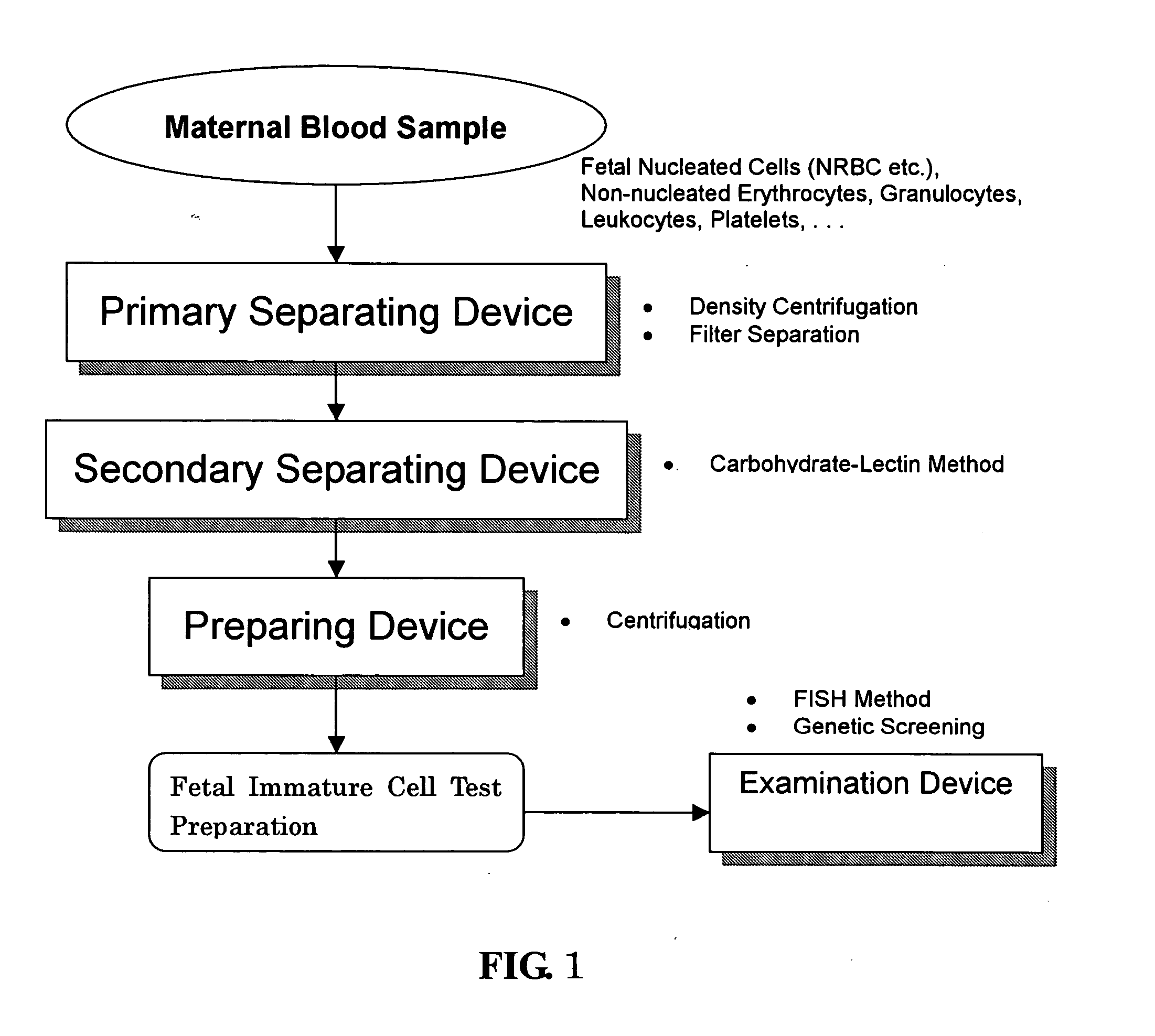
The invention provides a blood cell separation system, which is used for the precise separation and concentration of rare fetal nucleated cells mixed in the blood of pregnant women, so as to facilitate the obtaining of test preparations that can be used for prenatal chromosome / gene diagnosis. The blood cell separation system is characterized in that it includes (1) a primary separation device, which is used to mainly remove non-nucleated red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman to obtain a primary separation sample, (2) a secondary separation device , for the removal of residual non-nucleated erythrocytes and leukocytes from a primary fraction obtained using the primary fractionation device using the carbohydrate-lectin method to obtain a secondary fraction containing concentrated fetal nucleated cells, and (3) A preparation device for preparing the secondary separation sample obtained by the secondary separation device.
Owner:NETECH
Circulating tumor cell diagnostics for lung cancer
InactiveUS20150185204A1High riskMicrobiological testing/measurementRadioactive preparation carriersStainingCirculating cancer cell
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing lung cancer in a subject comprising (a) generating circulating tumor cell (CTC) data from a blood sample obtained from the subject based on a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characteristics of nucleated cells in the sample, wherein CTCs are identified in context of surrounding nucleated cells based on a combination of the immunofluorescent staining and morphological characteristics; (b) obtaining clinical data for the subject; (c) combining the CTC data with the clinical data to diagnose lung cancer in the subject.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Blood cell separating system
InactiveUS20050214758A1Prevent loss of fetalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed blood cellWhite blood cell
A blood cell separating system is offered for precisely separating and concentrating rare fetal nucleated cells intermixed in the blood of a pregnant woman, to conveniently obtain test preparations capable of being used for prenatal chromosomal / genetic diagnosis. A blood cell separating system is characterized by comprising (1) a primary separating device for removing mainly non-nucleated erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets from blood samples taken from a pregnant woman to obtain a primary separated sample, (2) a secondary separating device for using a carbohydrate-lectin method to remove residual non-nucleated erythrocytes and leukocytes from the primary separated sample obtained by the primary separating device to obtain a secondary separated sample with concentrated fetal nucleated cells, and (3) preparing device for preparing the secondary separated sample obtained by the secondary separating device.
Owner:NETECH
Kits and methods for preparing gell samples optmimized for dual staining
A method of preparing nucleated peripheral blood or bone marrow cells optimized for at least dual mode imaging. The method including: (a) isolating nucleated cells from a peripheral blood or a bone marrow sample; and (b) resuspending the nucleated cells in the presence of a morphology preserver including at least 1% serum, and recovering a cell fraction thereby preparing the nucleated peripheral blood or bone marrow cells optimized for at least dual mode imaging.
Owner:BIOVIEW
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130930A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
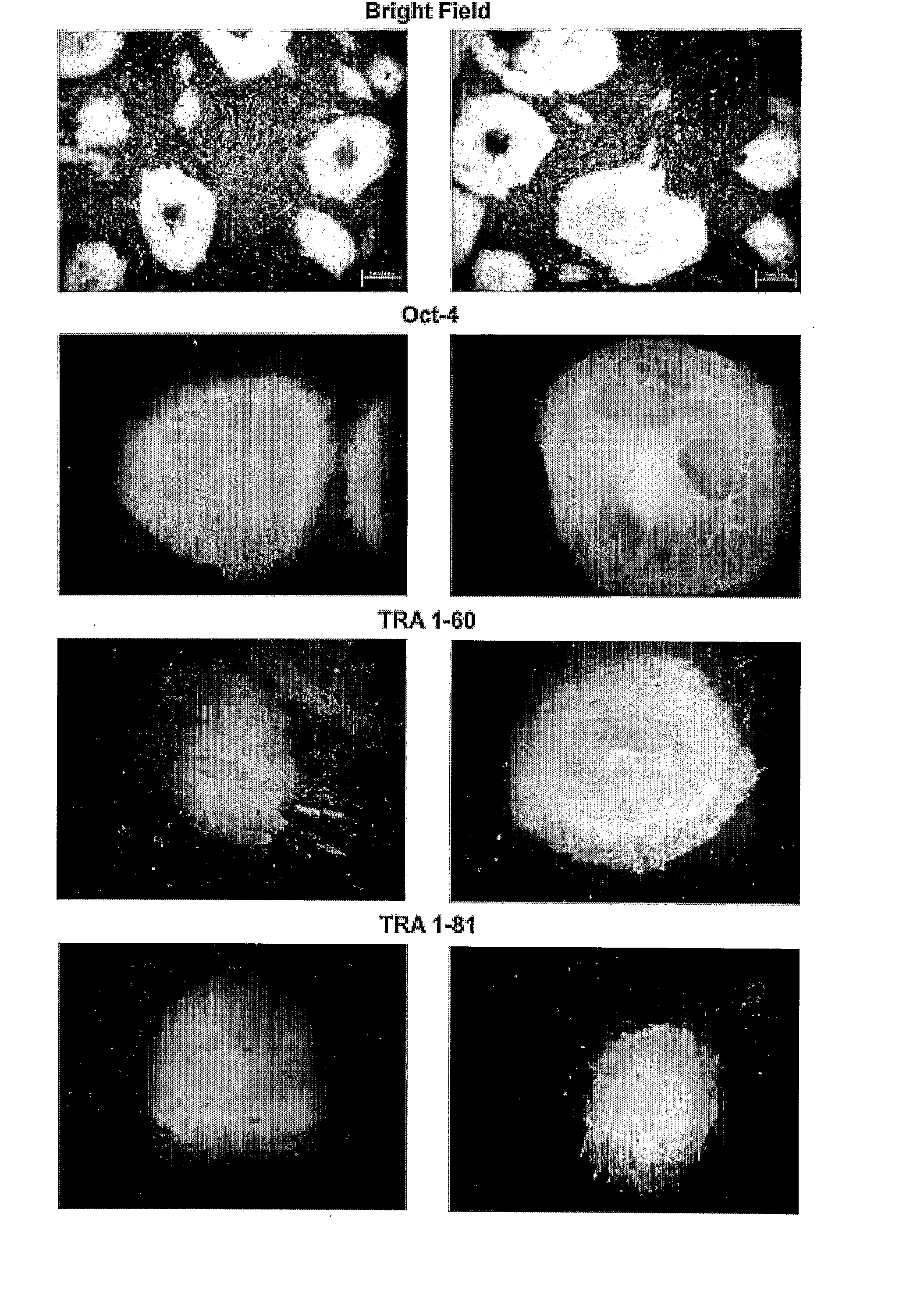
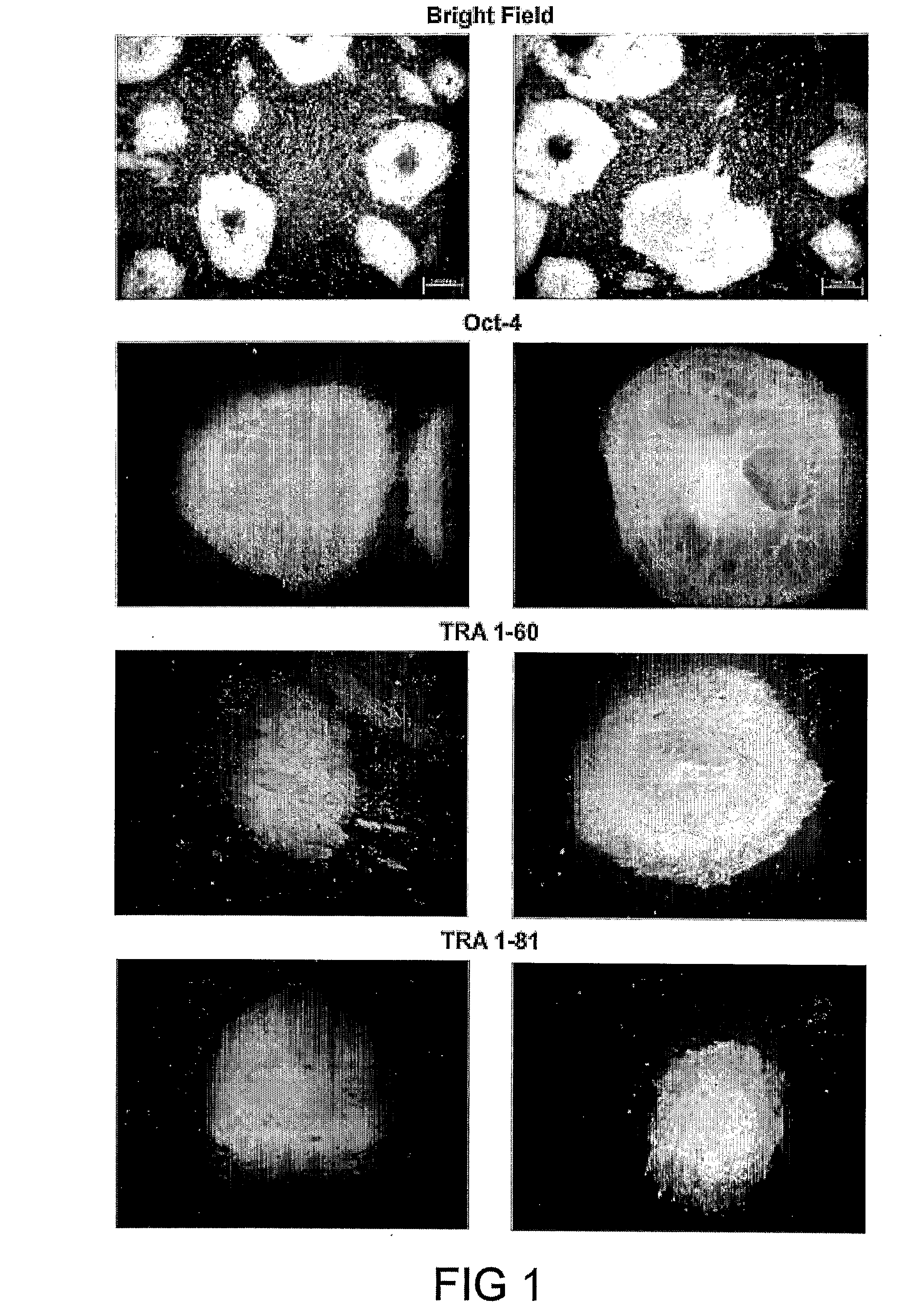
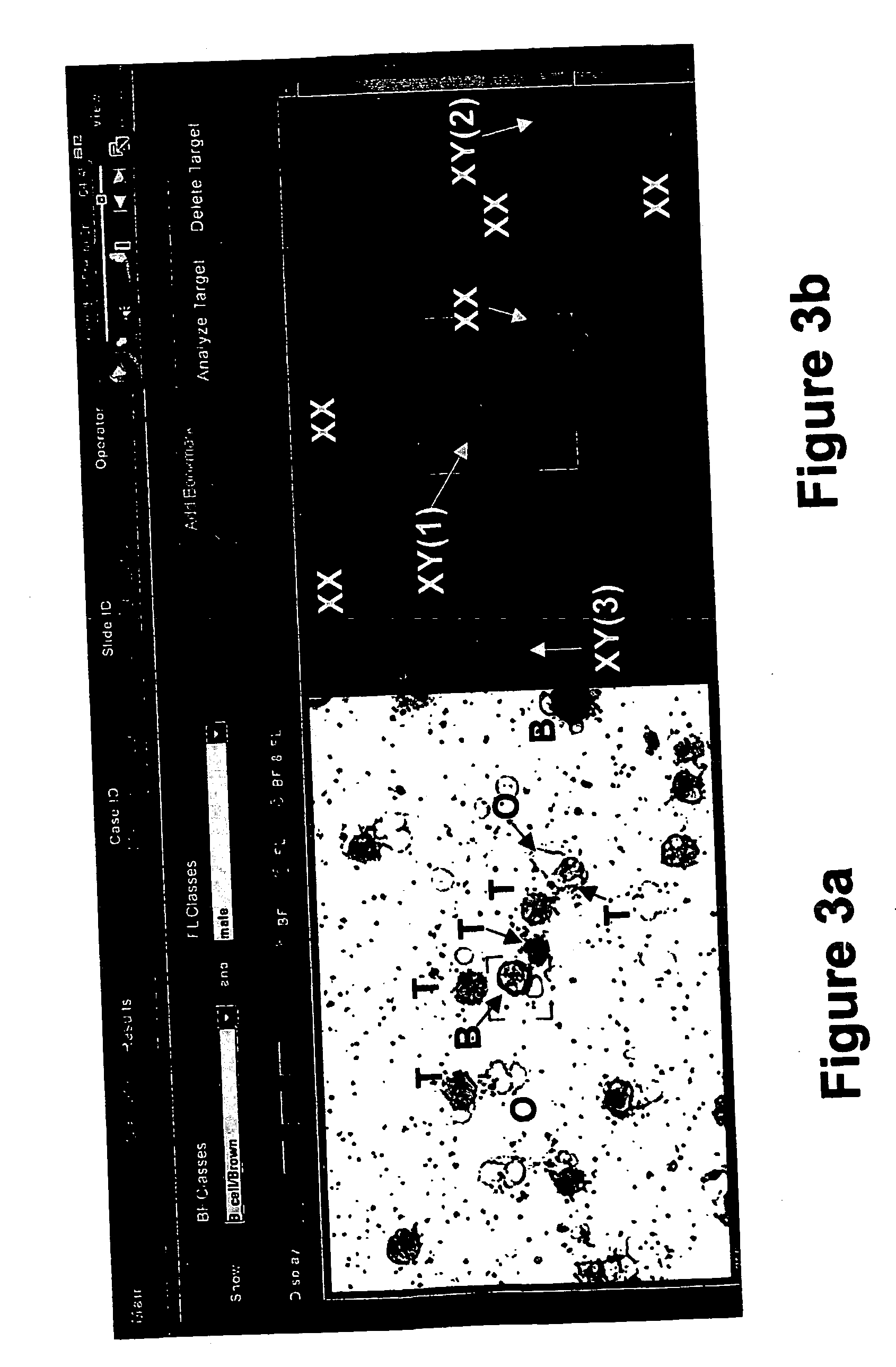
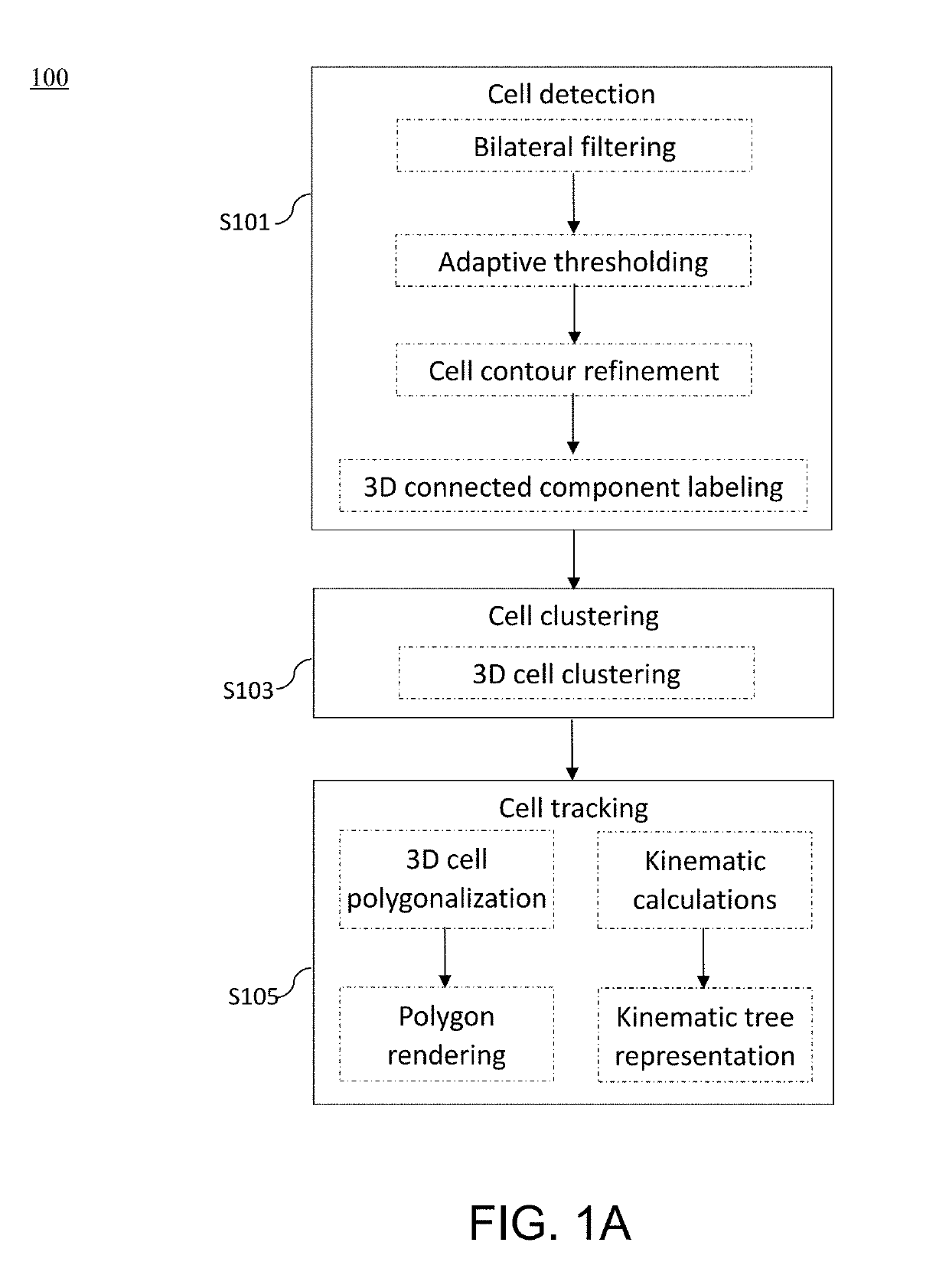
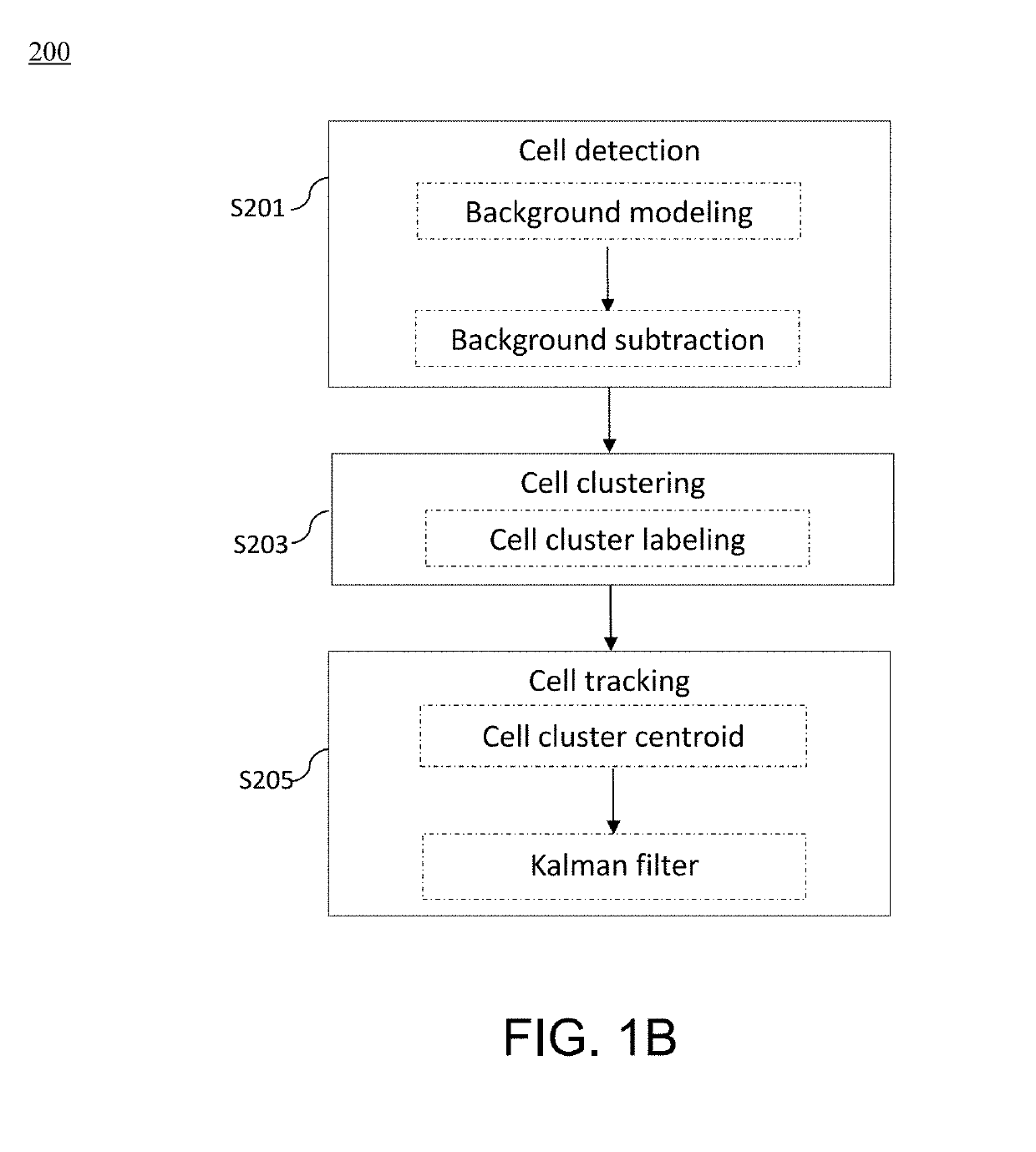
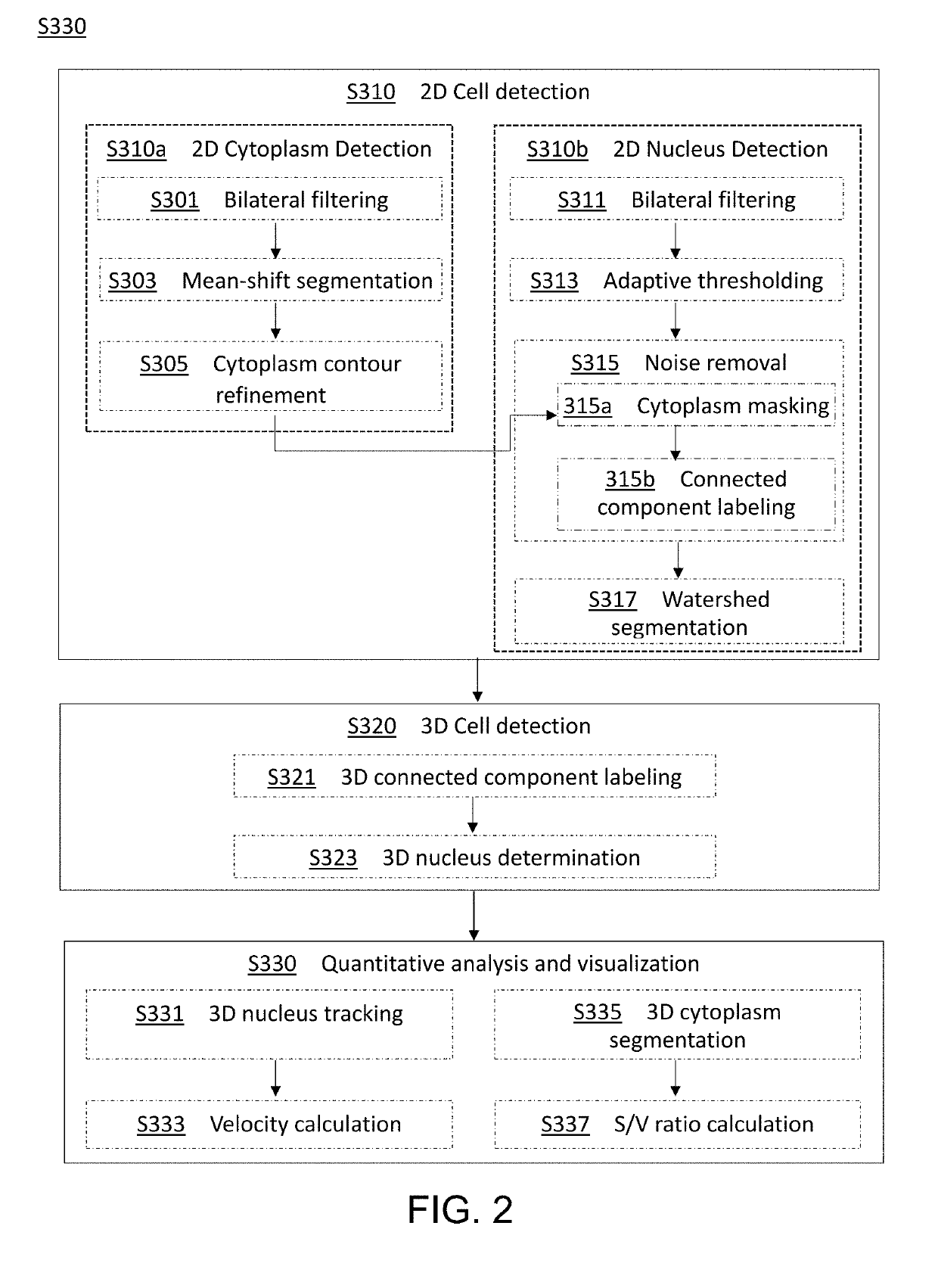
Method and apparatus for image processing and visualization for analyzing cell kinematics in cell culture
Disclosed herein are methods for analyzing cell kinematics in a nucleated cell culture from a time-series sequence of multiple fluorescence microscopic images of the nucleated cell culture. The method includes the steps of, (a) identifying every cell nucleus in each fluorescence microscopic image; (b) identifying every cell cluster using the cell nuclei identified in the step (a); and (c) tracking the cells and / or cell clusters using the cell nuclei and cell clusters identified for the fluorescence microscopic images in steps (a) and (b) respectively.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Method for separating cells using immunorosettes
InactiveUS7135335B2Improved T cell enrichmentHigh purityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed CellBiology
The present invention relates to methods for separating cells using immunorosettes. The method involves contacting a sample containing nucleated cells and red blood cells with an antibody composition which allows immunorosettes of the nucleated cells and the red blood cells to form. The antibody composition preferably contains bifunctional antibodies or tetrameric antibody complexes.
Owner:STEMCELL TECHNOLOGIES
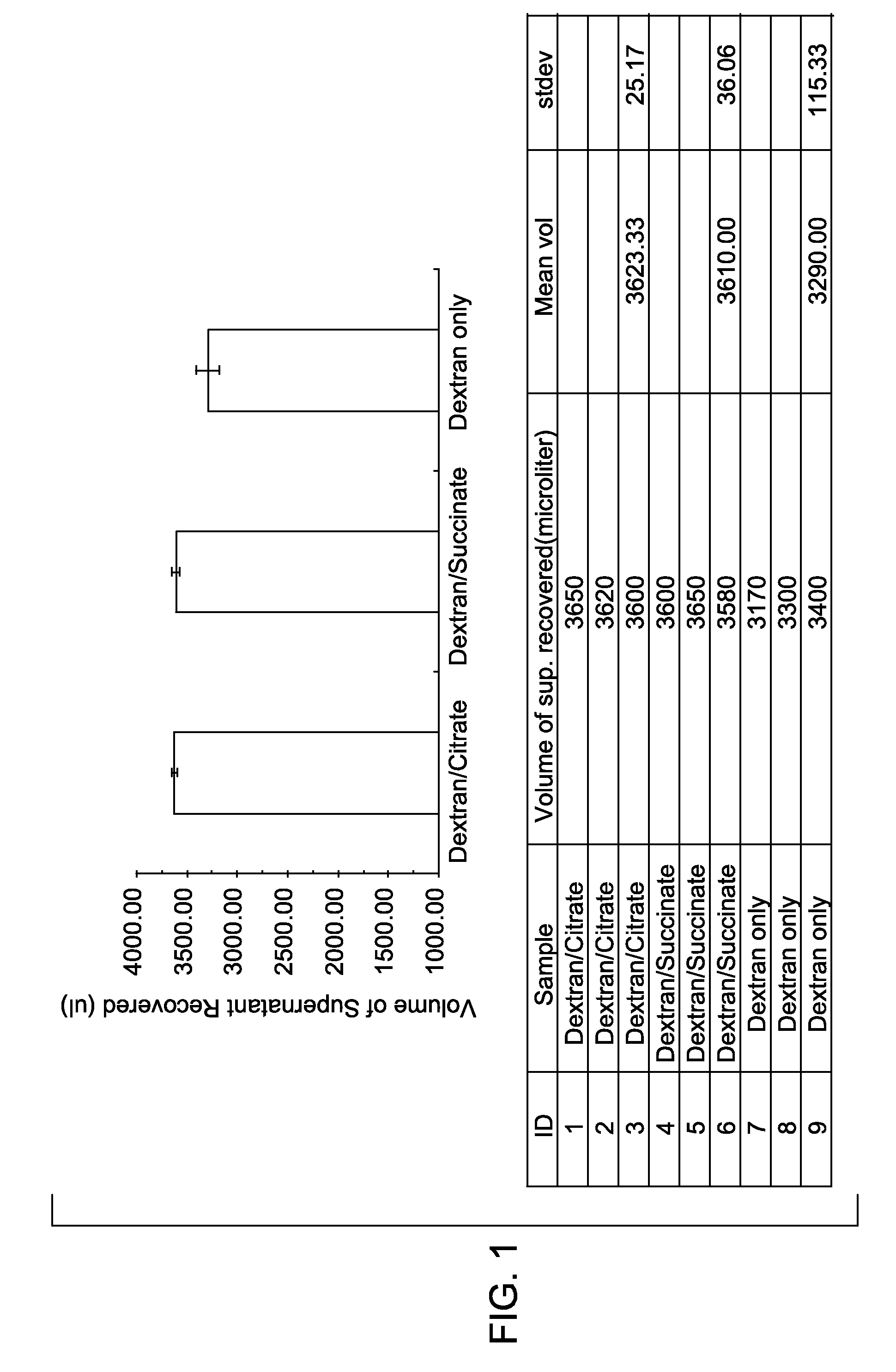
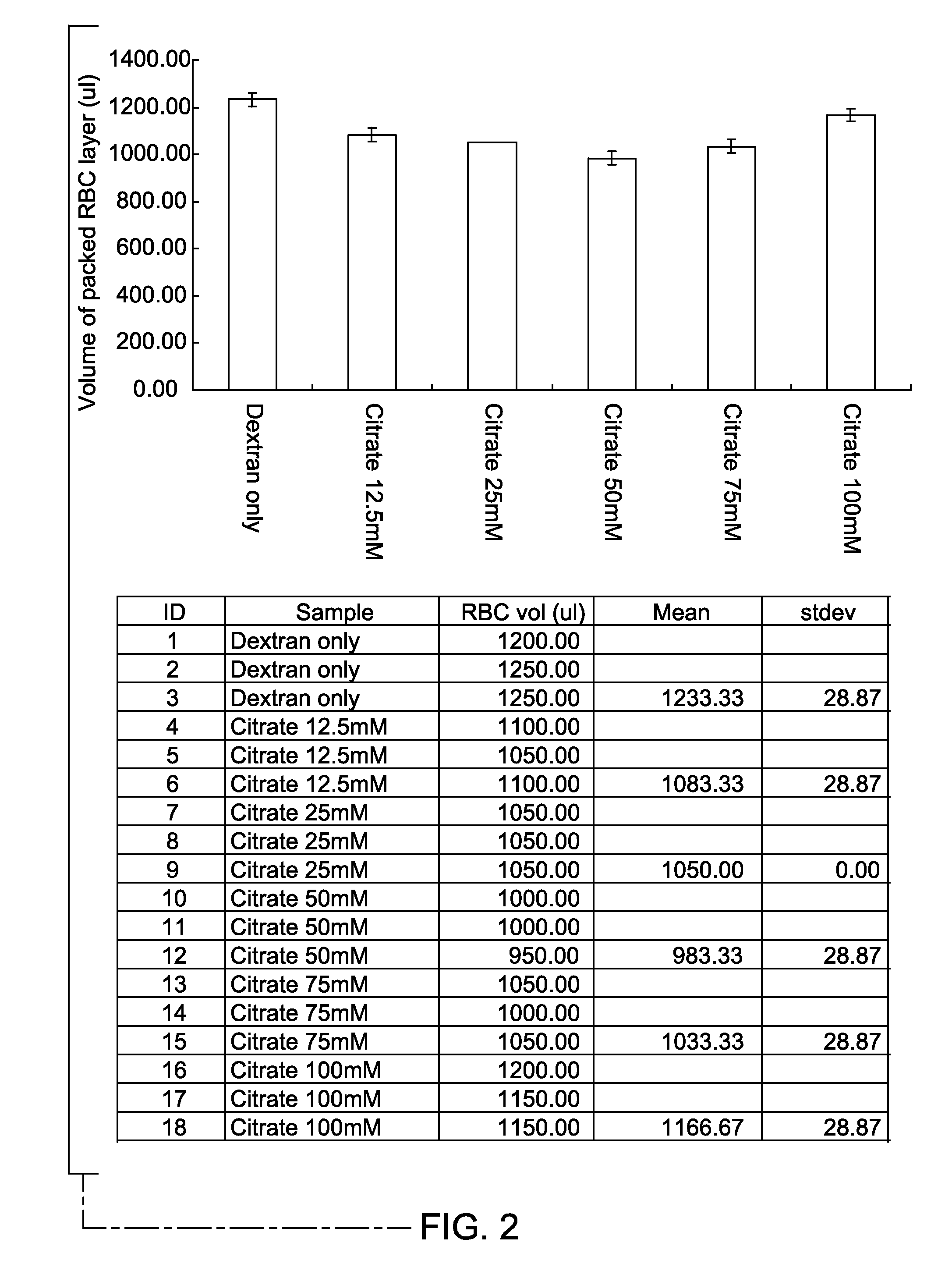
Methods and kits for enhancing sedimentation and recovery of cells in a sample
InactiveUS20100151438A1Improve efficiencyPromote recoveryDead animal preservationMaterial analysisBiologyNucleated cell
The methods and kits provide sedimentation-enhancing agents that significantly increase the efficiency of cell-sedimentation. They also increase the efficiency of blood cell separation methods and thereby increase the recovery of total nucleated cells.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
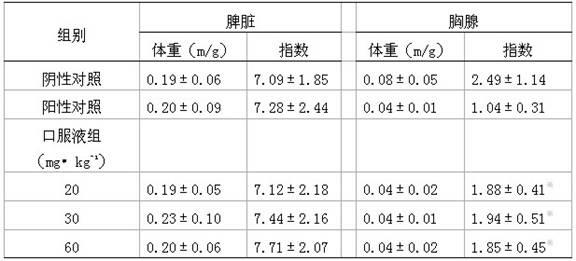
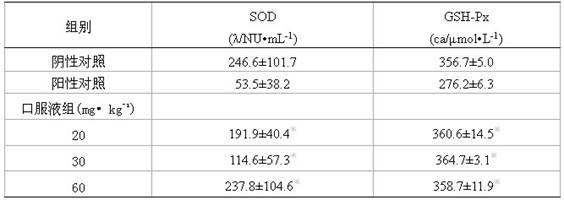
Chinese medicinal preparation for preventing and treating radiation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102139021ASimple processing technologyReasonable processing technologyAntinoxious agentsDermatological disorderWhite mouseBarbed Skullcap Herb
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal preparation for preventing and treating radiation and a preparation method thereof and relates to the Chinese medicinal preparation for treating and preventing radiation injury and the preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicinal preparation is specifically prepared from heterophylly falsestarwort root, indian buead, bighead atractylodes rhizome, liquorice, Szechuan lovage rhizome, Chinese angelica, red paeony root, rehmannia root, barbed skullcap herb, honeysuckle, mulberry leaf, hairyvein agrimonia herb, medlar and green tea in a certain proportion. Pharmacodynamic experiments carried out by adopting an animal model with reduced tangible hemocytes and nucleated cells in bone marrow of a white mouse due to 60Co-gamma rays show that the preparation has a good effect on hemocytes and hemopoietic tissues injured by nuclear radiation.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for separating fetal nucleated red blood cells in maternal peripheral blood
InactiveCN103602632AEfficient removalPromote enrichmentBlood/immune system cellsEmbryonic cellsCell layerCell culture media
The invention discloses a method for separating fetal nucleated red blood cells in maternal peripheral blood. The method comprises the following steps: (a) enriching nucleated cells, namely, (1) collecting whole blood, (2) centrifuging, and collecting cell precipitates, (3) preparing cell suspension, namely adding a cell culture medium to the cell precipitates, and uniformly mixing so as to prepare the dilute cell suspension, (4) putting a cell separating medium in a centrifugal tube in advance, and adding the dilute cell suspension to a layering liquid surface, (5) centrifuging so as to obtain a cell layer, and (6) sucking up the cell layer, adding Hank, s liquid, uniformly mixing, centrifuging at a room temperature, and washing cells, and (7) resuspending the cells; and (b) screening the fetal nucleated cells in the maternal blood, to be specific, (9) separating out the fetal nucleated red cells, and (10) carrying out quadruple morphology identification on nucleated red cell pictures obtained by sorting, and collecting the nucleated red cells meeting the standards for extracting the fetal whole genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). According to the method, the purity and the recovery rate of the fetal nucleated red blood cells obtained by the separation and purification of the maternal peripheral blood are high.
Owner:邯郸市康业生物科技有限公司
Single cell genomic profiling of circulating tumor cells (CTCS) in metastatic disease to characterize disease heterogeneity
InactiveUS20190025312A1High LST scoreMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseStaining
The disclosure provides a method of detecting heterogeneity of disease in a cancer patient comprising (a) performing a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characteristization of nucleated cells in a blood sample obtained from the patient to identify and enumerate circulating tumor cells (CTC); (b) isolating the CTCs from the sample; (c) individually characterizing genomic parameters to generate a genomic profile for each of the CTCs, and (d) determining heterogeneity of disease in the cancer patient based on the profile. In some embodiments, the cancer is prostate cancer. In some embodiments, the prostate cancer is hormone refractory.
Owner:EPIC SCIENCES
Universal cell processing kit and application method thereof
The invention provides a universal cell processing kit and an application method thereof, and relates to a kit for separating stem cells from human cord blood, bone marrow and peripheral blood and an application method of the kit. The kit contains a reagent A (cell diluent), a reagent B (high-molecular-weight cell precipitant) and a reagent C (medium-density layering agent). The application method of the kit comprises the steps of: firstly, uniformly mixing the cord blood, bone marrow or peripheral blood with the cell diluent, adding the high-molecular-weight cell precipitant, standing for 30 minutes, collecting the supernatant, centrifuging, collecting the concentrated solution, adding the medium-density layering agent to the concentrated solution, centrifuging for 20 minutes, collecting a karyocyte layer and washing with saline for injection 3 times. In the invention, a cell precipitant with a molecular weight of 450000-700000 is used, the survival rate of the separated karyocytes is not lower than 98%, the collection rate of karyocytes is not lower than 85%, and the method provided by the invention is simple, safe and practical, has low cost, can realize industrialized production, and is easy to popularize.
Owner:崔慧斐 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com