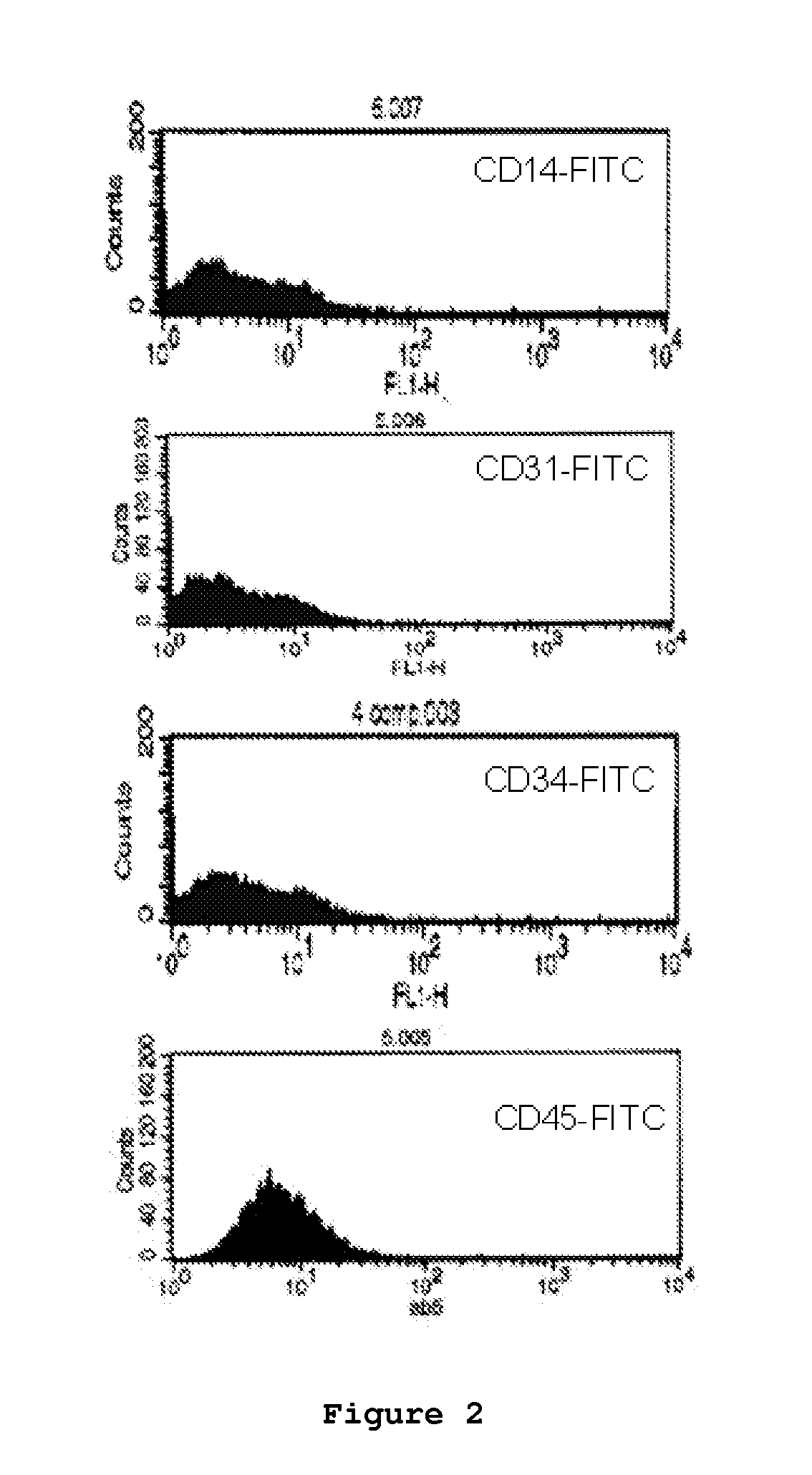
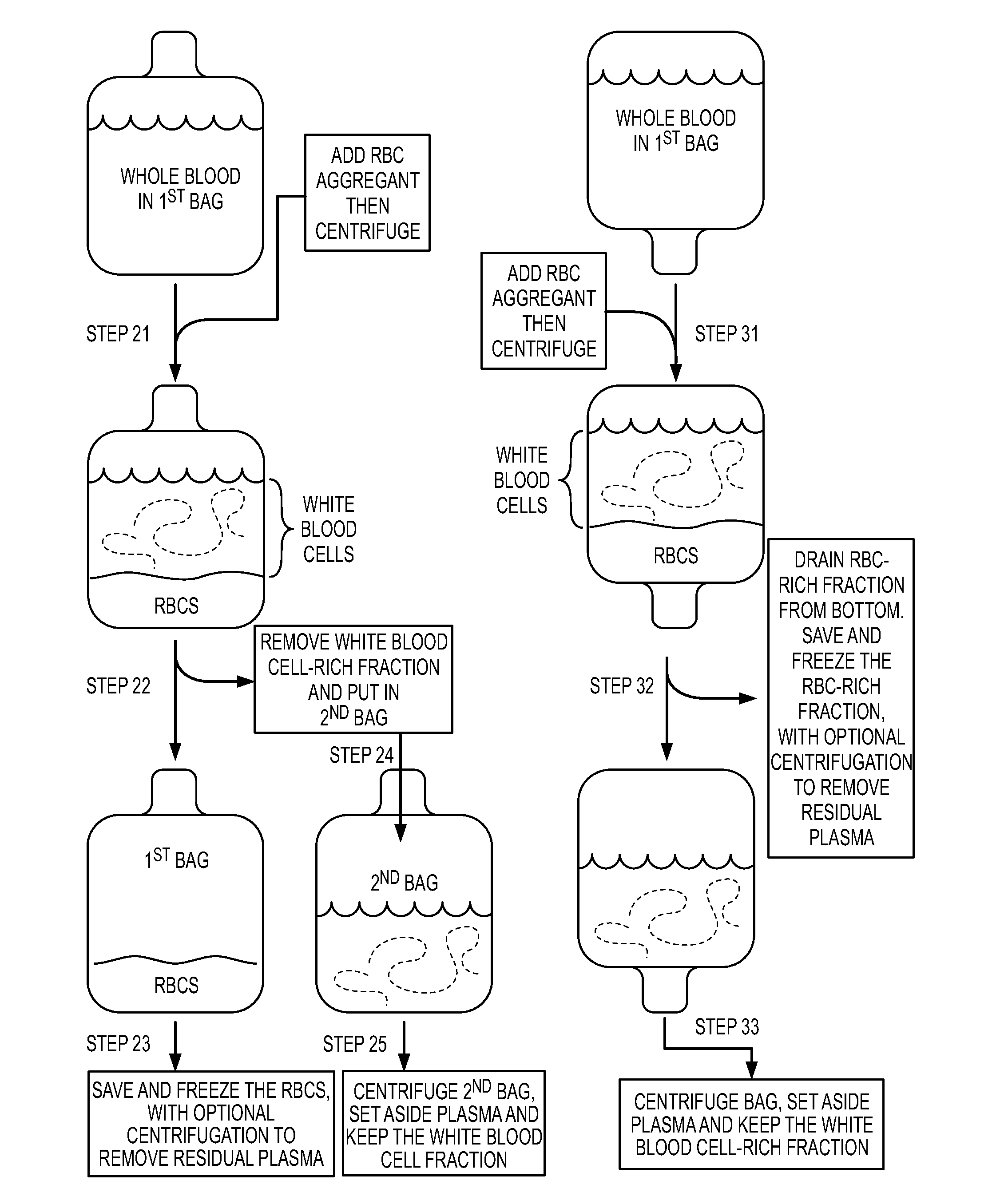
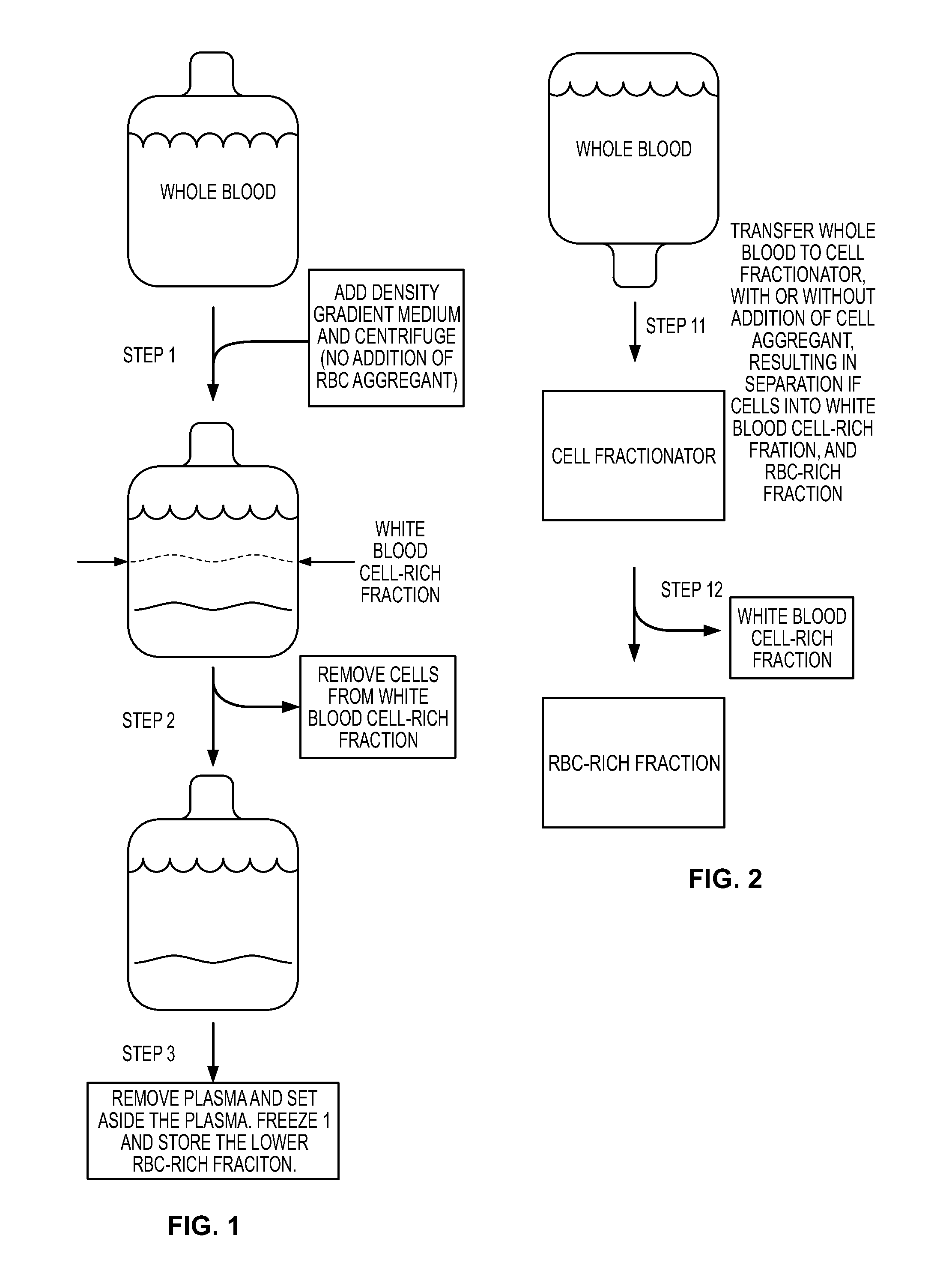
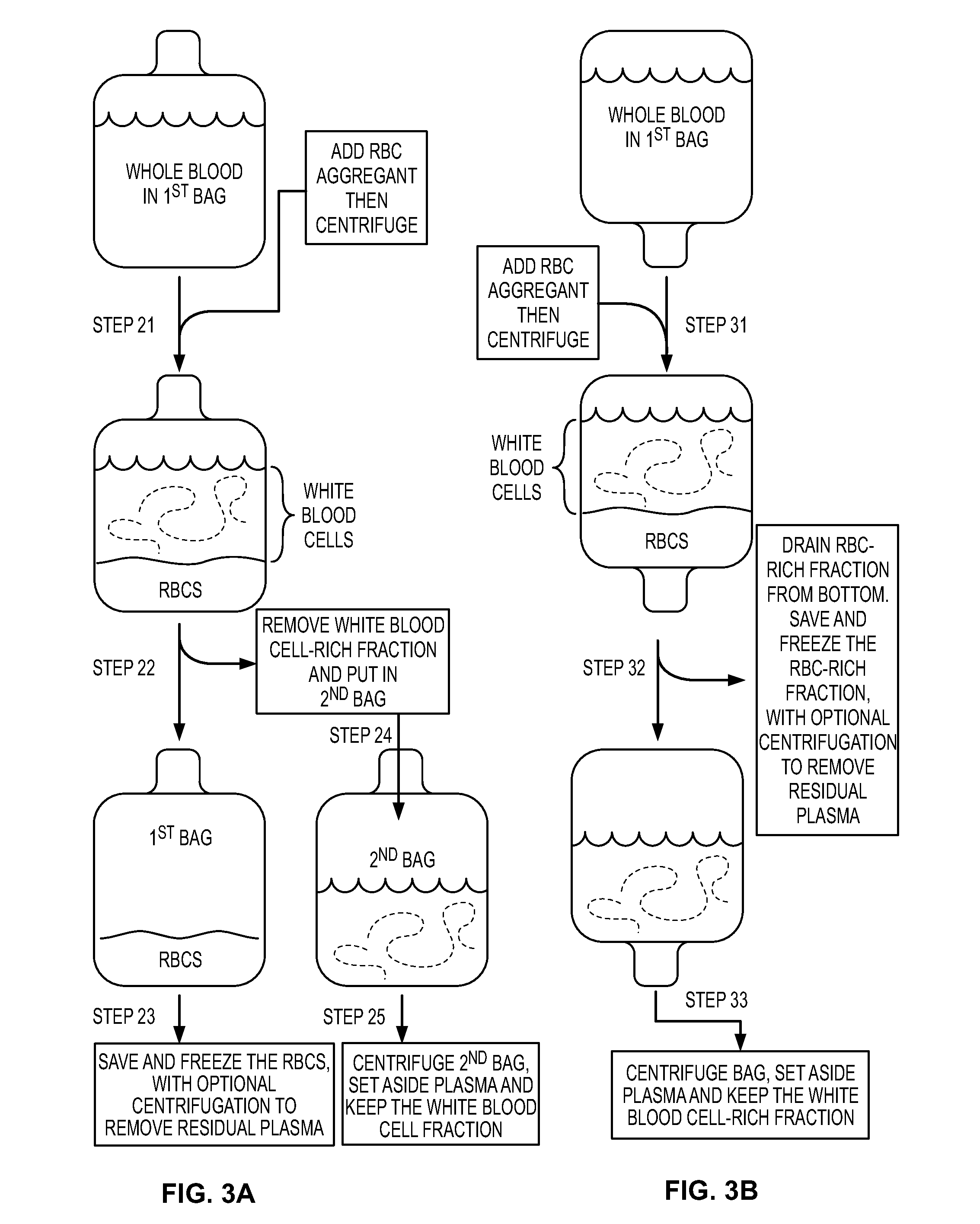
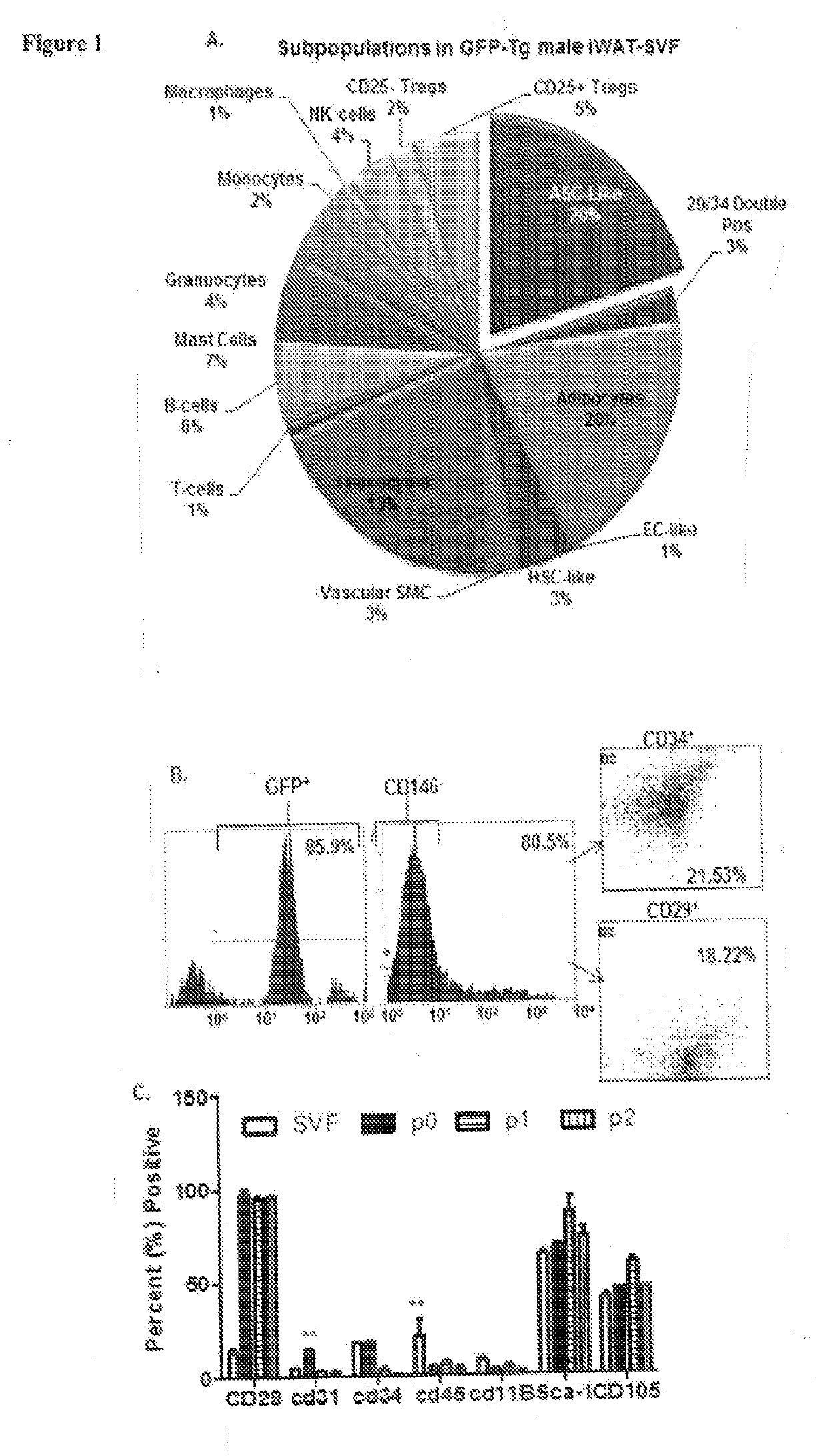
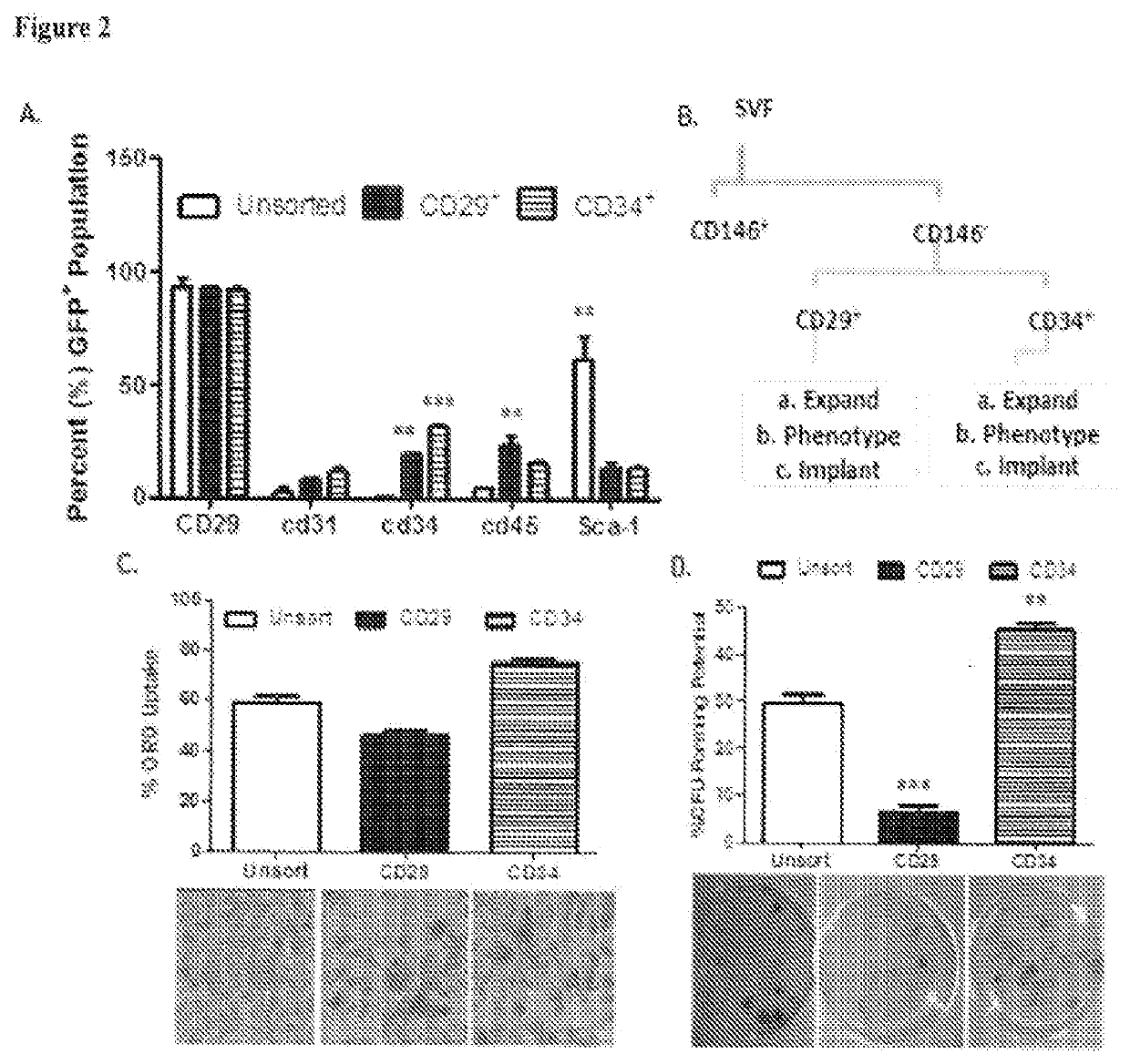
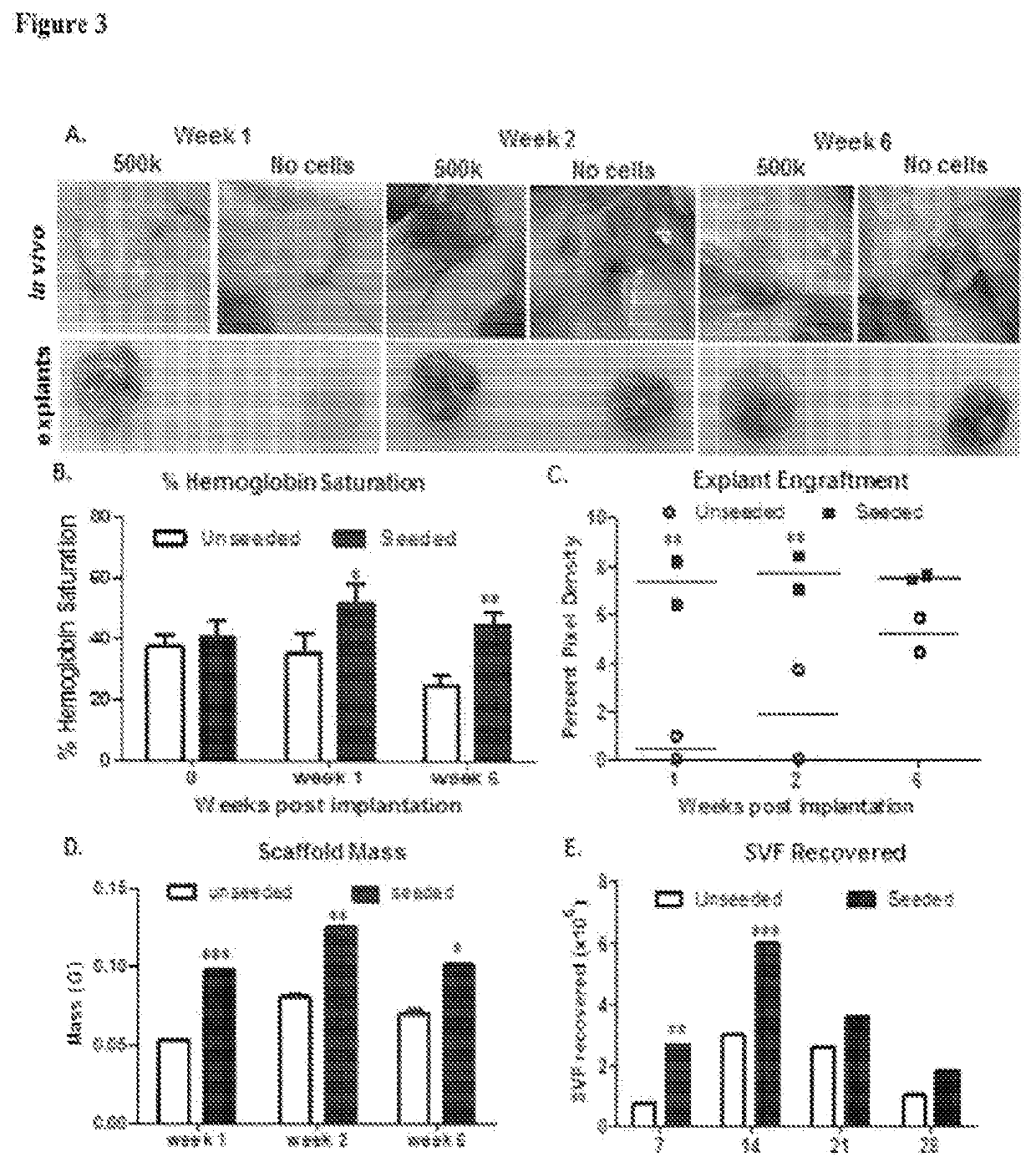
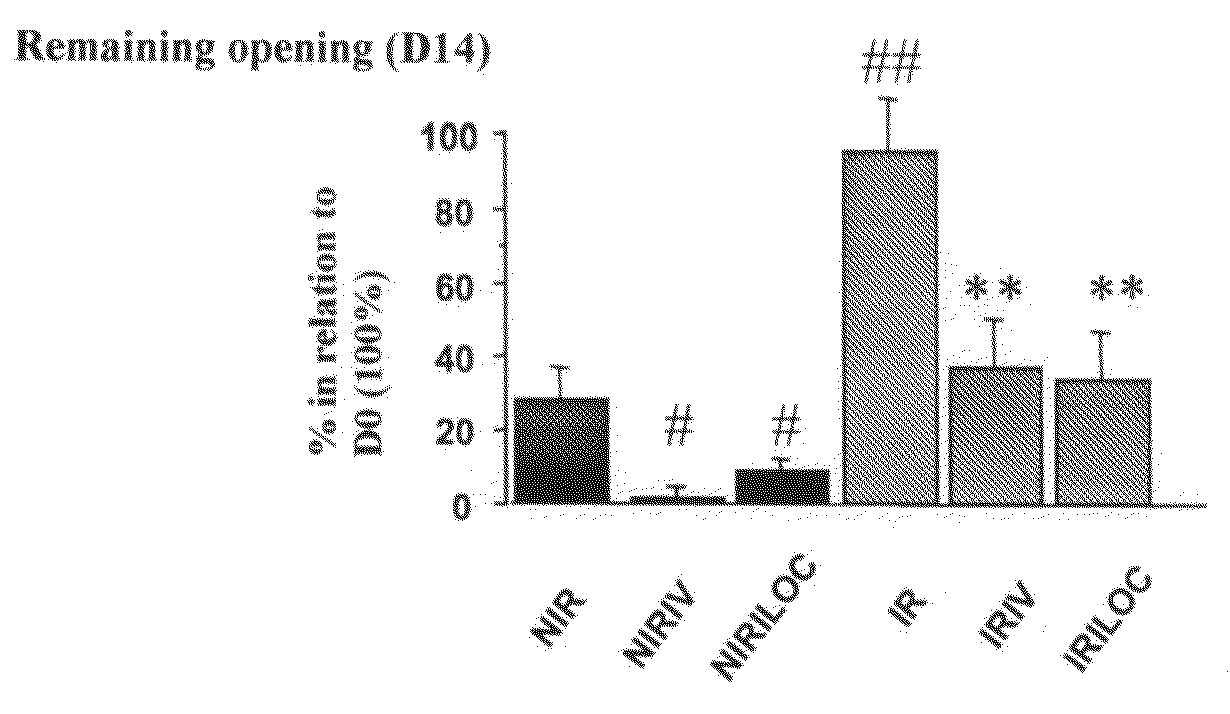
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Cell Fraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
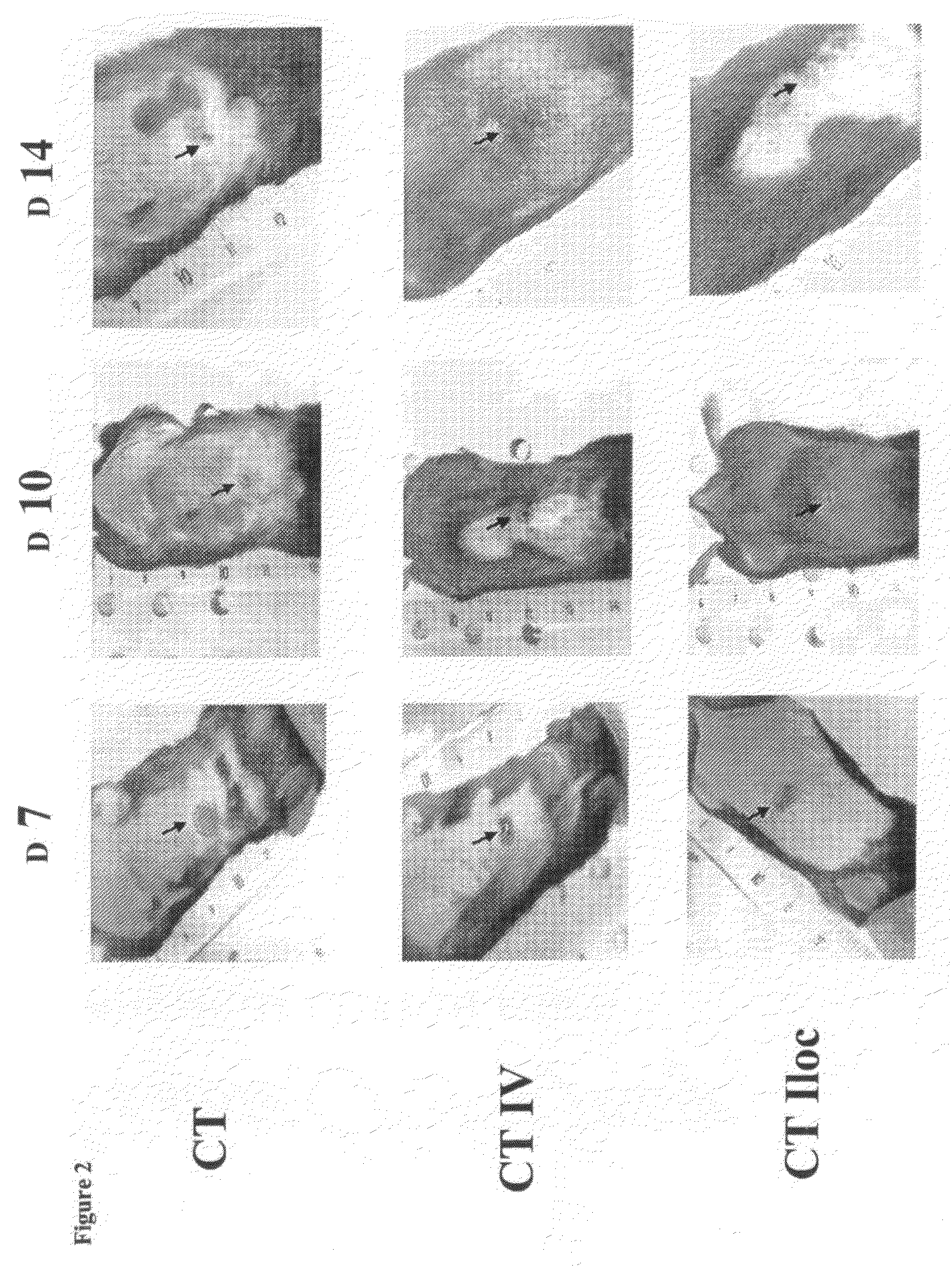
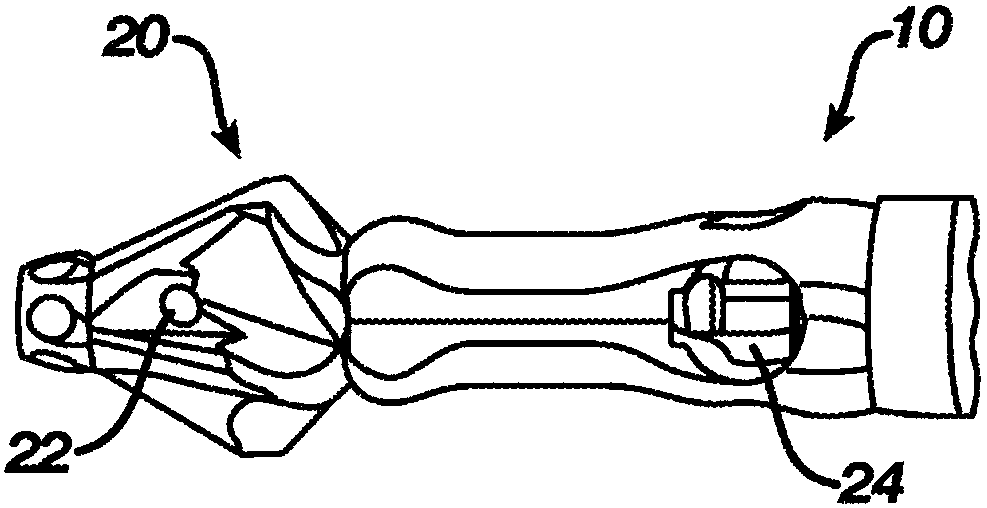
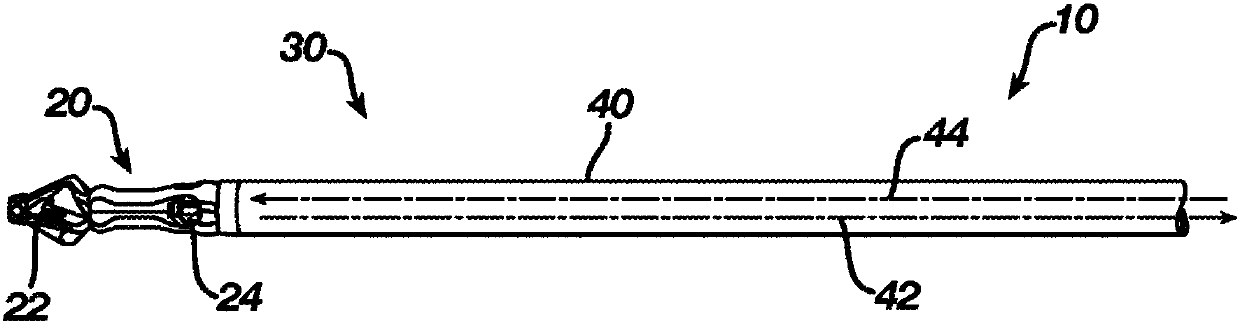
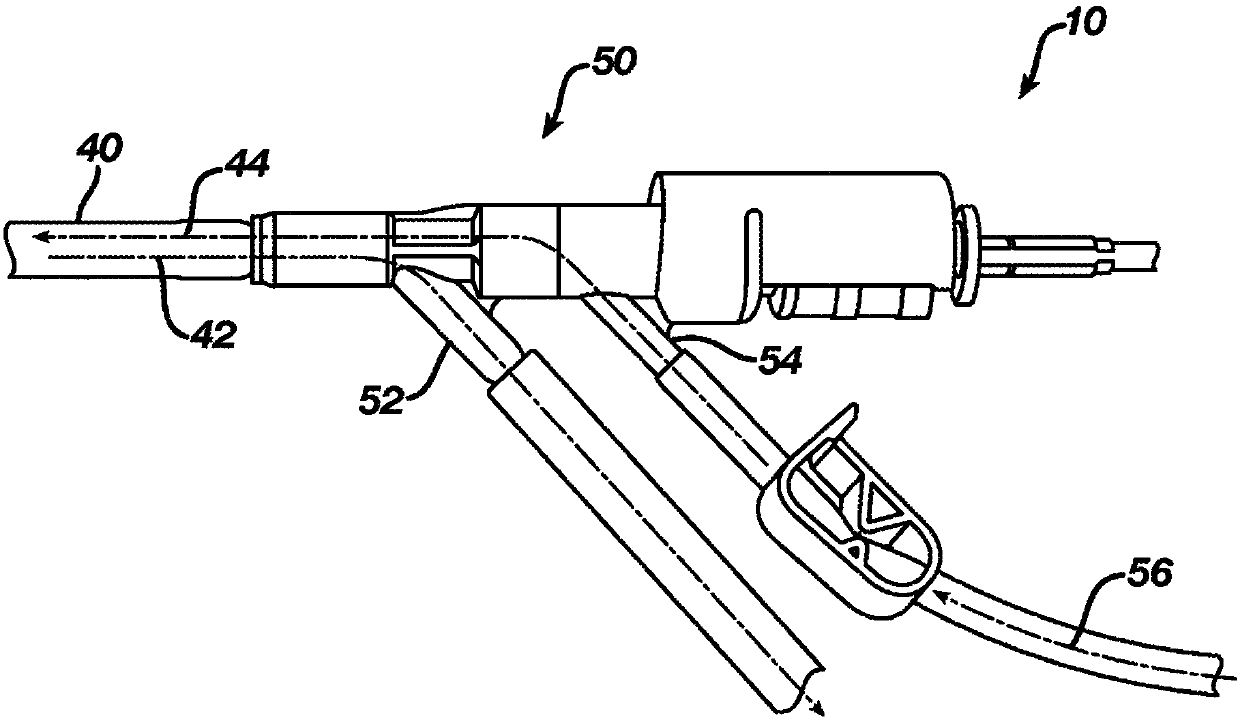
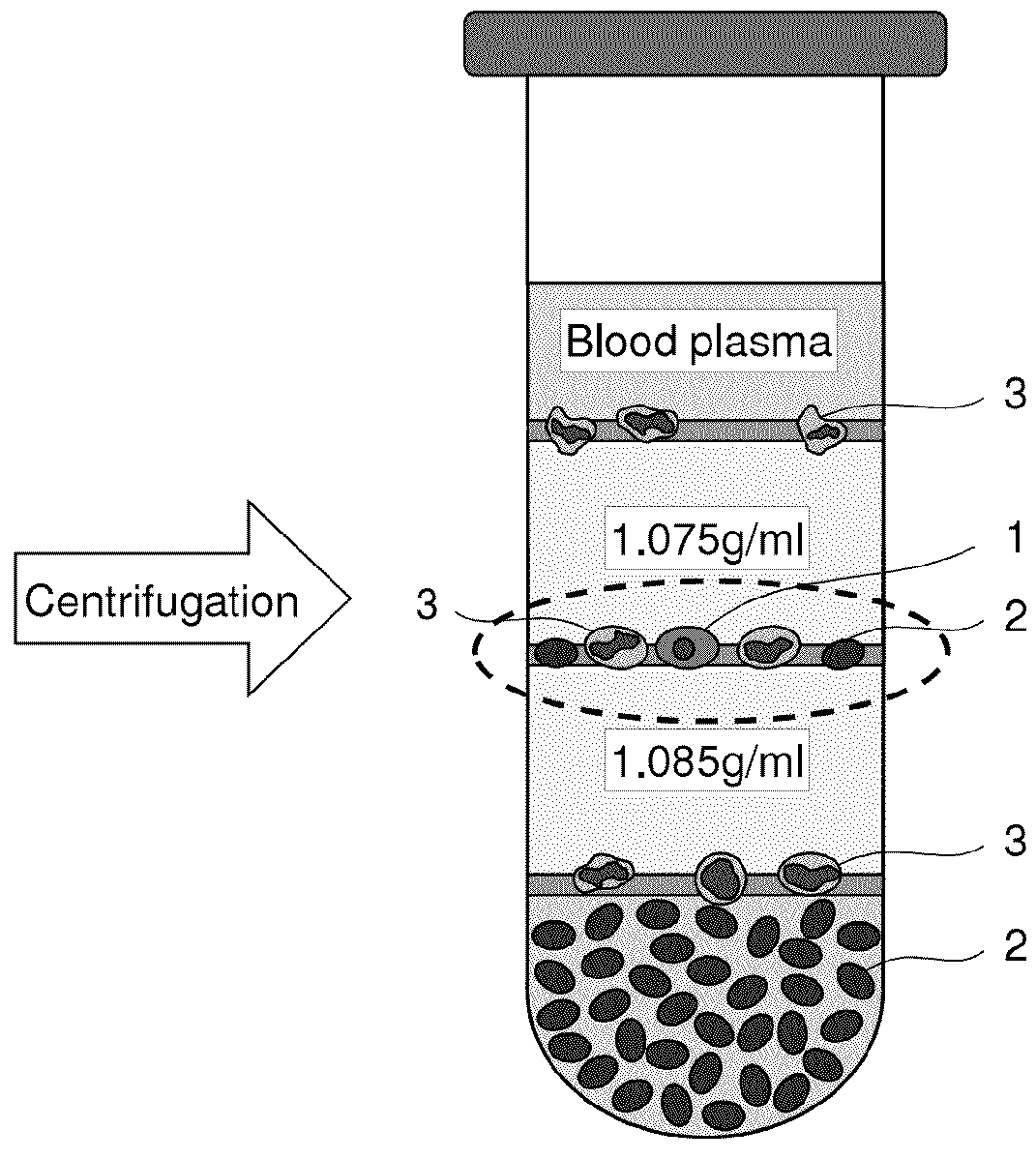
Components of a cell produced by various separation techniques which, though they disrupt the delicate anatomy of a cell, preserve the structure and physiology of its functioning constituents for biochemical and ultrastructural analysis.
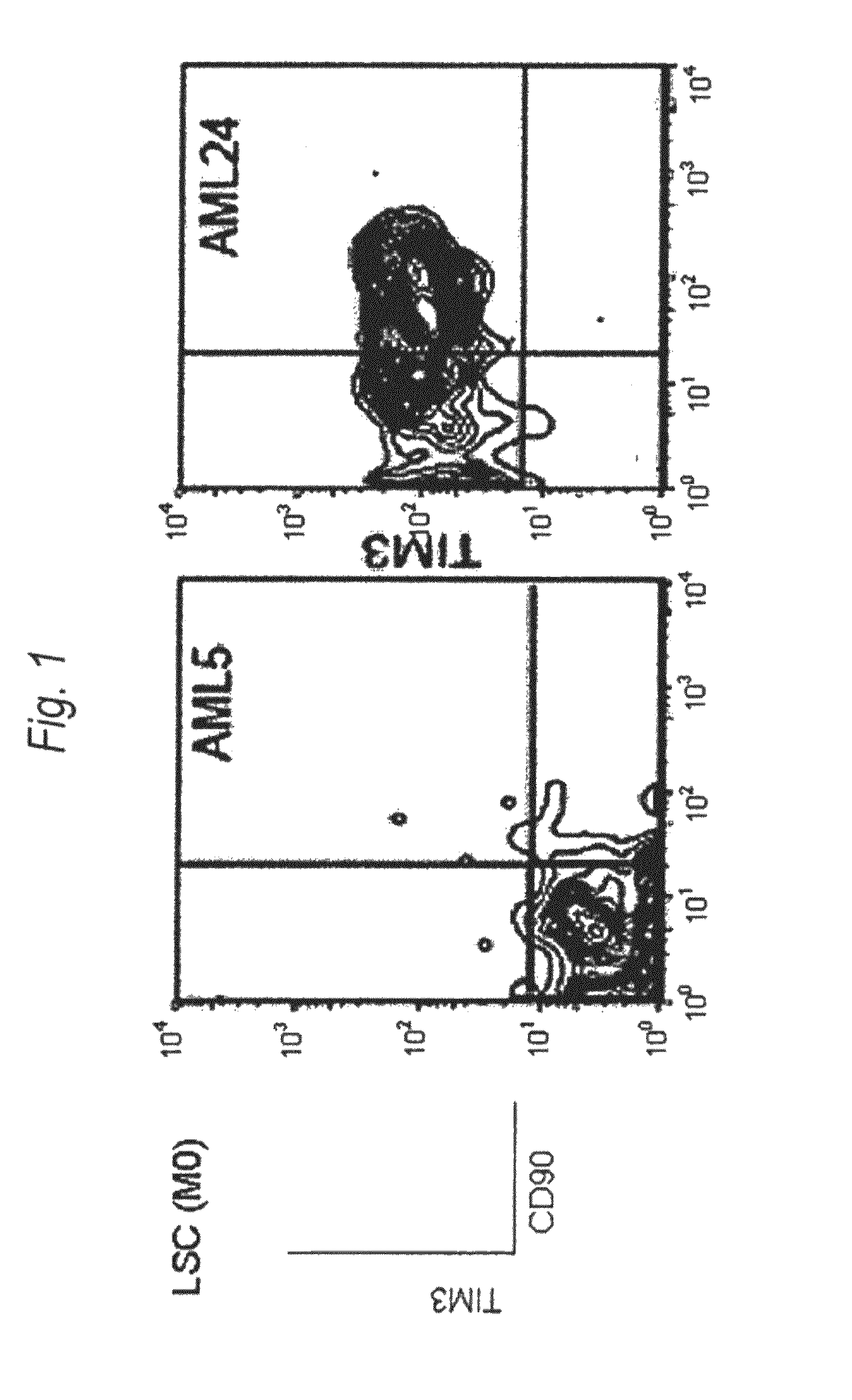
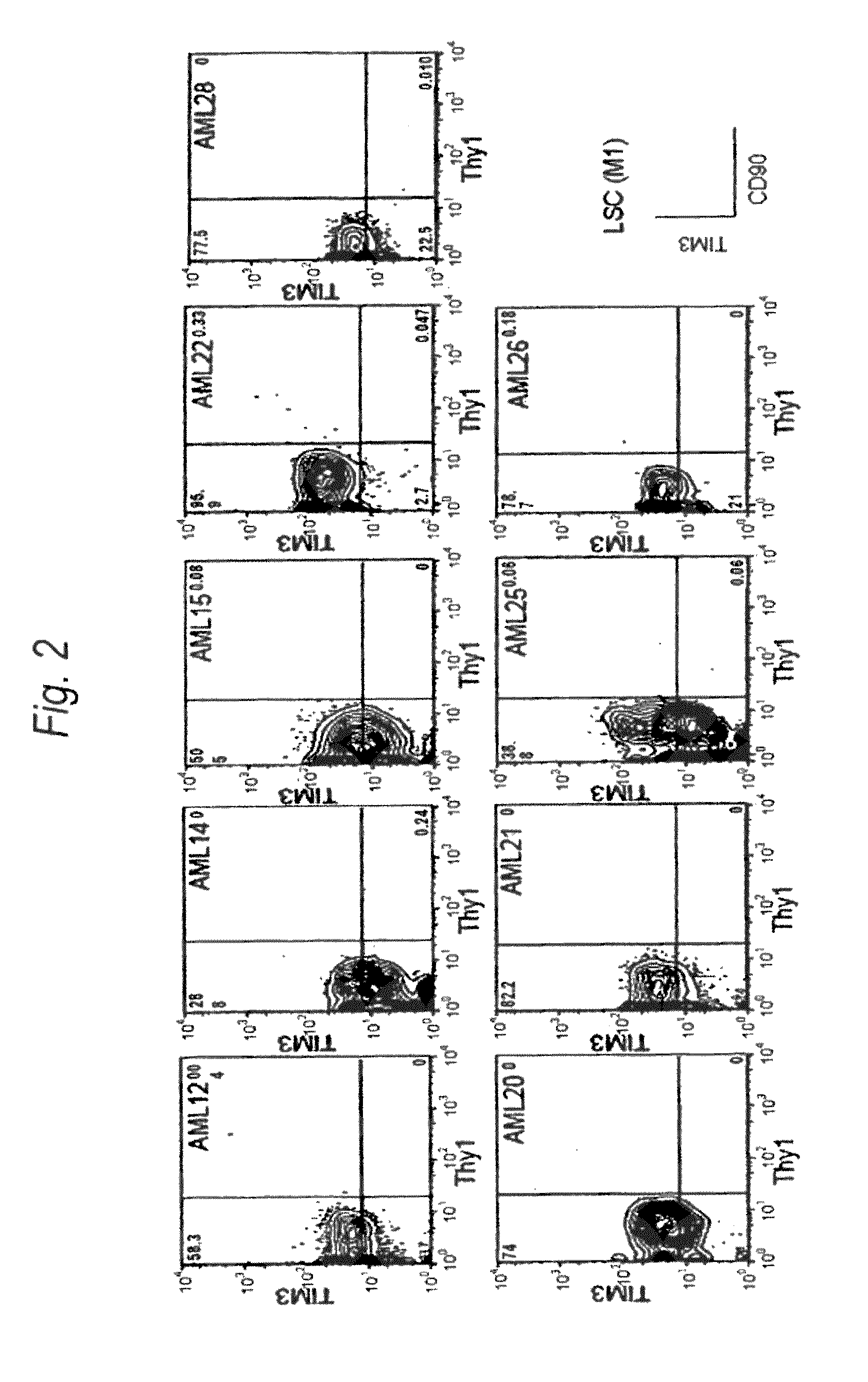
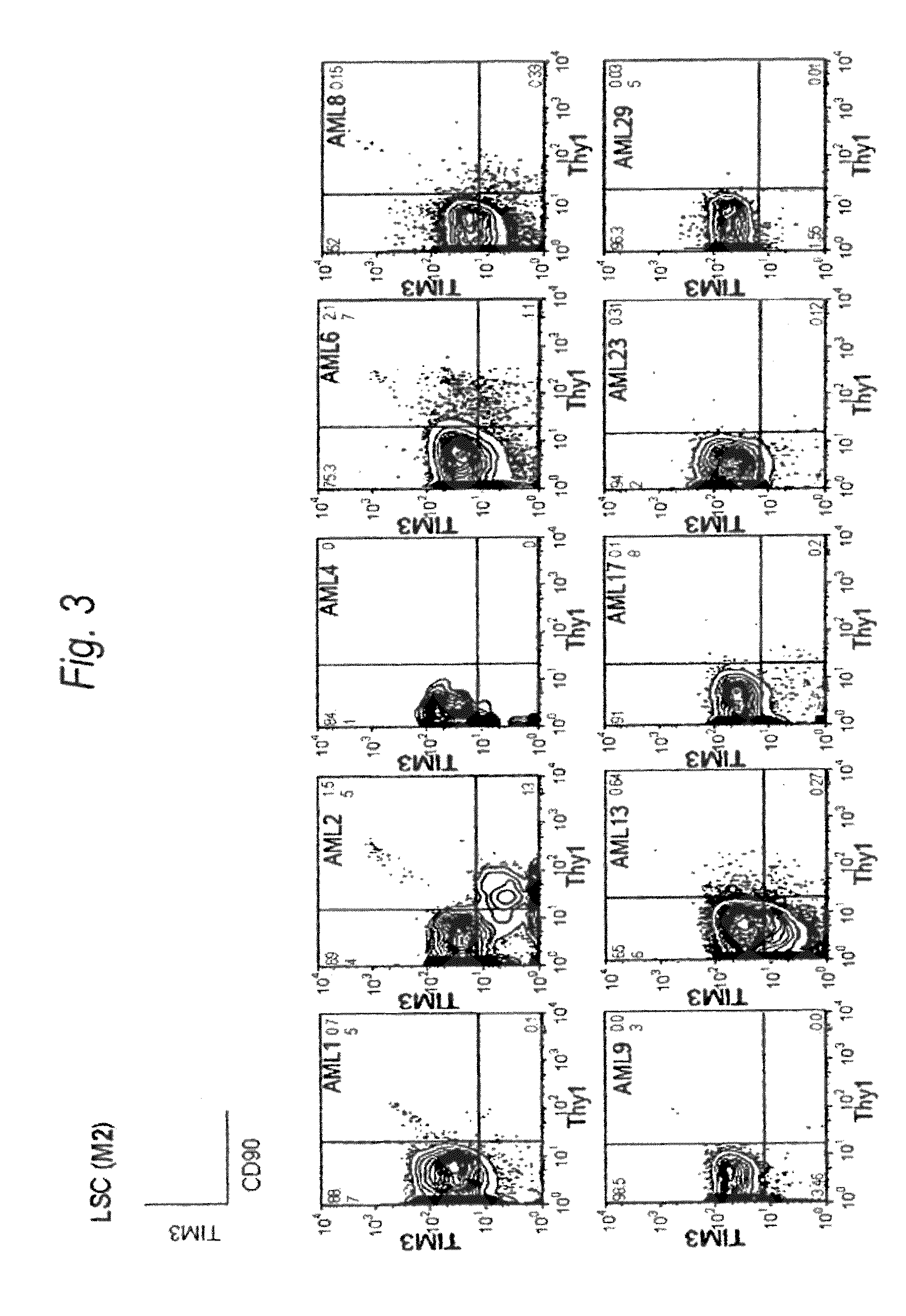
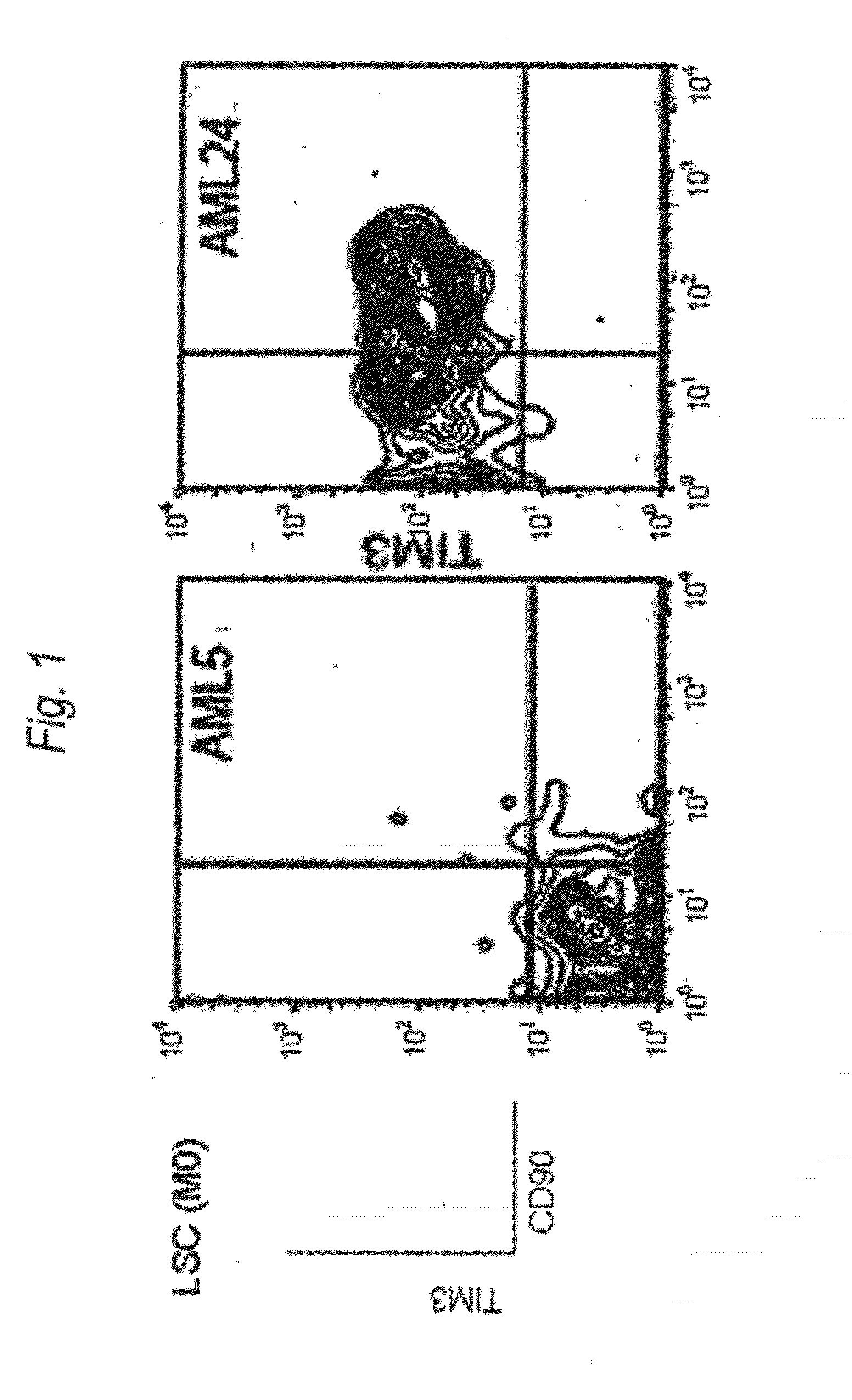
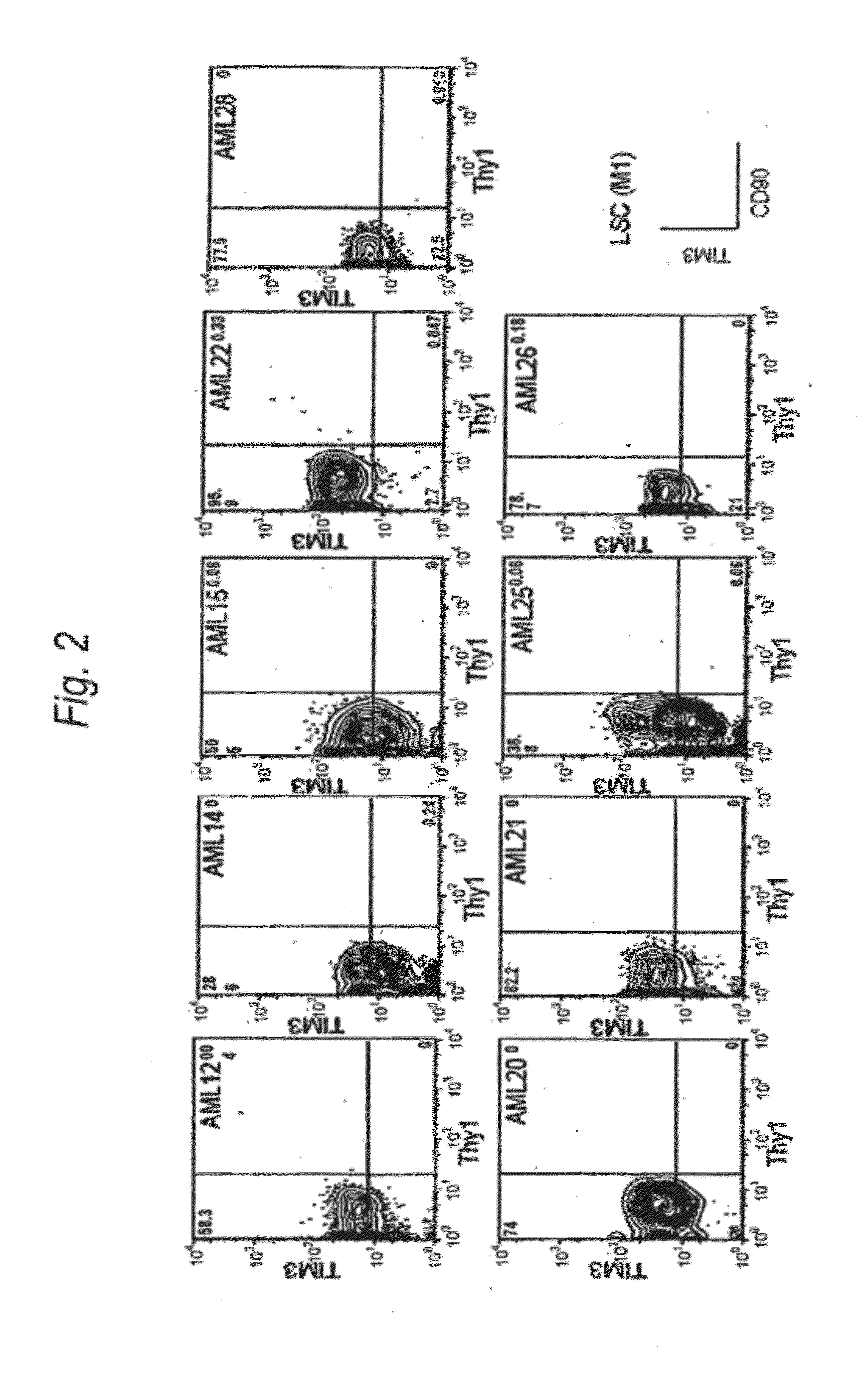
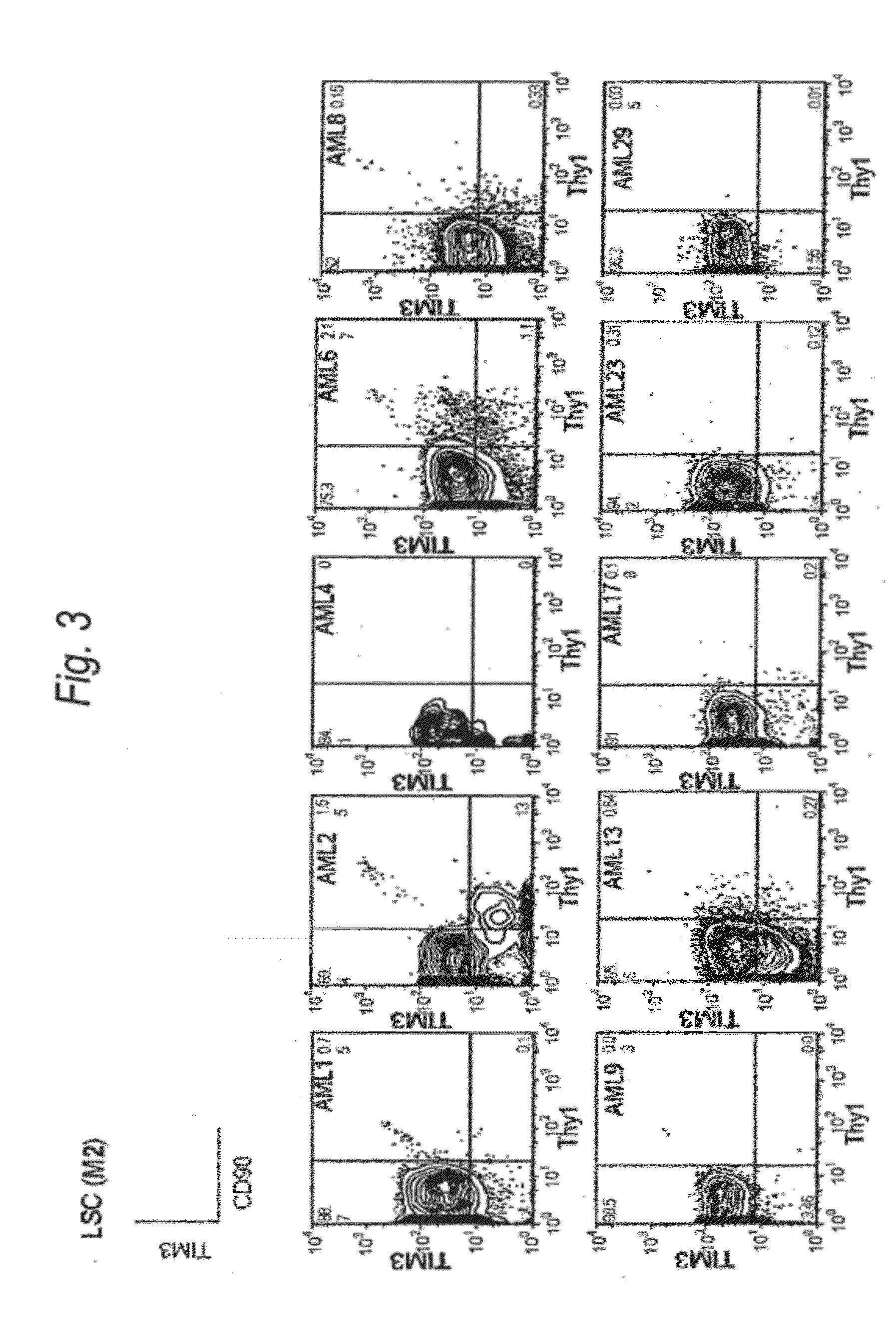
Method for treatment of blood tumor using anti-TIM-3 antibody
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
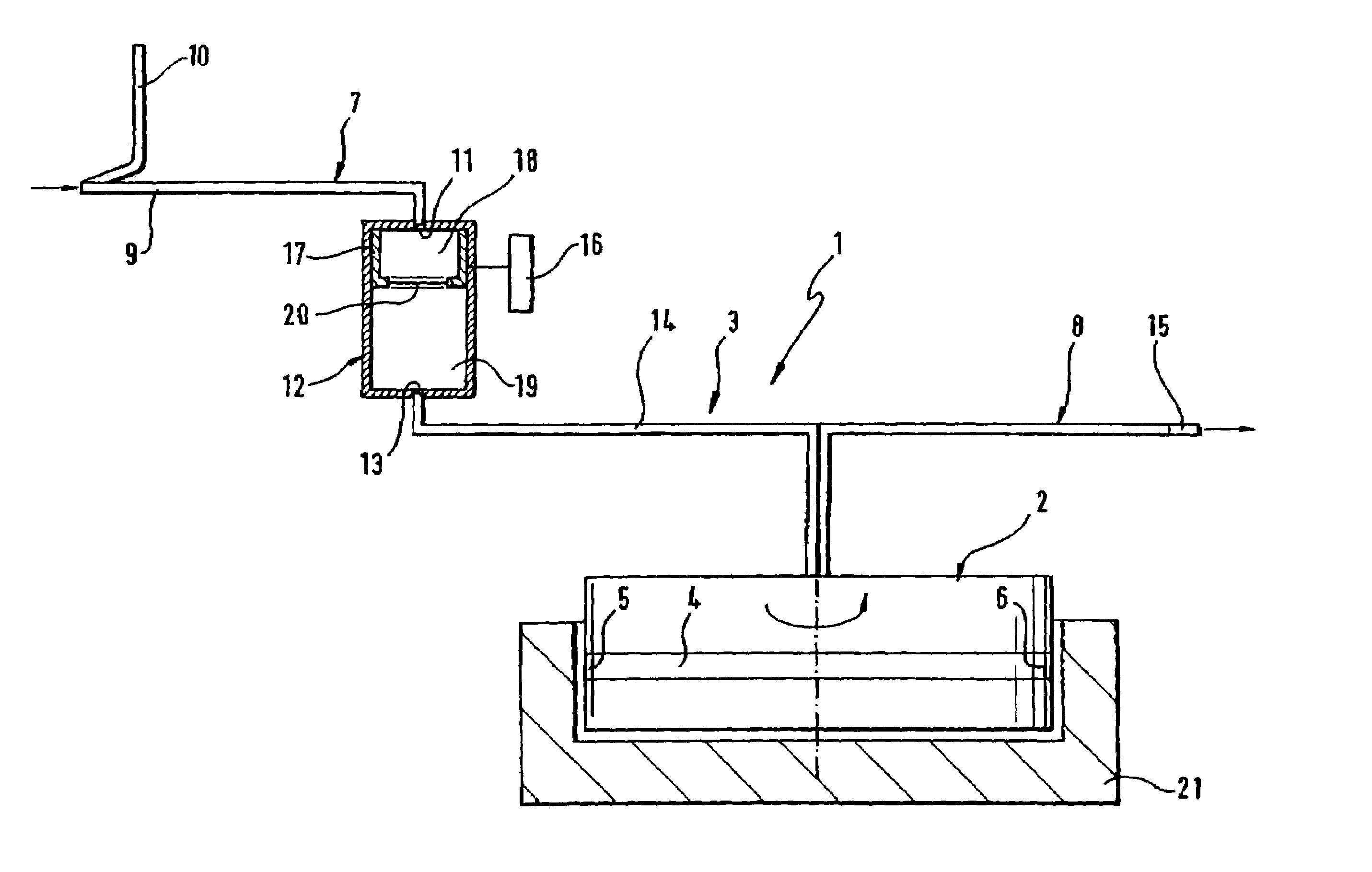
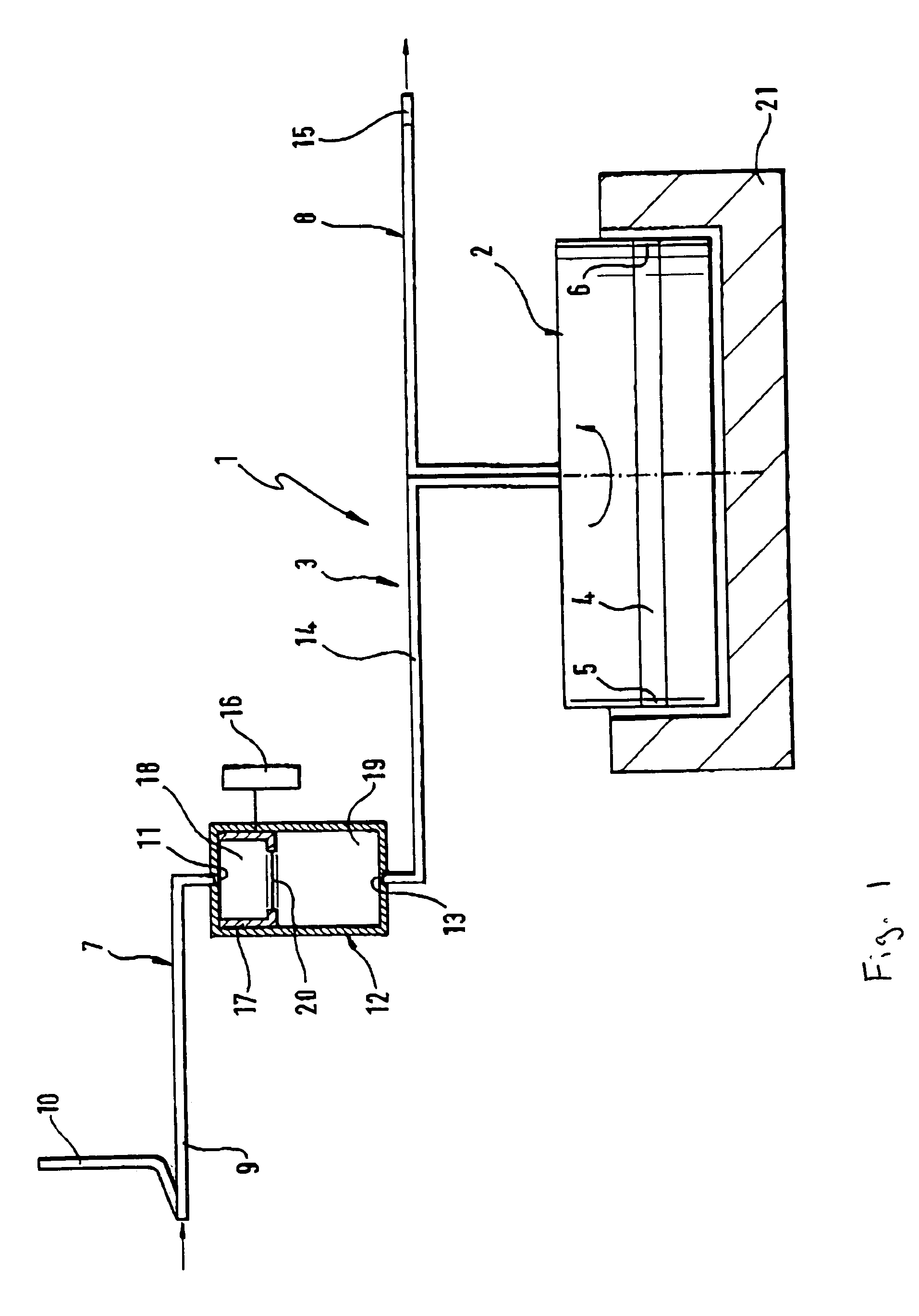
Device and method for autologous blood transfusion
InactiveUS6964646B1Avoid reactionReduce in quantityOther blood circulation devicesRotary centrifugesCell FractionLine tubing
A device for autologous blood transfusion includes a centrifuge unit with an autotransfusion set rotatably mounted thereto. The autotransfusion set includes a separation unit for concentrating a cell fraction by centrifugation and a tubing system for providing a connection to a blood supply. The tubing system includes a blood supply line leading to the separation unit for supplying blood to be processed and a return line leading away from the separation unit. A filter is integrated into the autotransfusion set in order to eliminate leukocytes and / or tumor cells, thereby yielding greater safety in autotransfusion.
Owner:FRESENIUS HEMOCARE
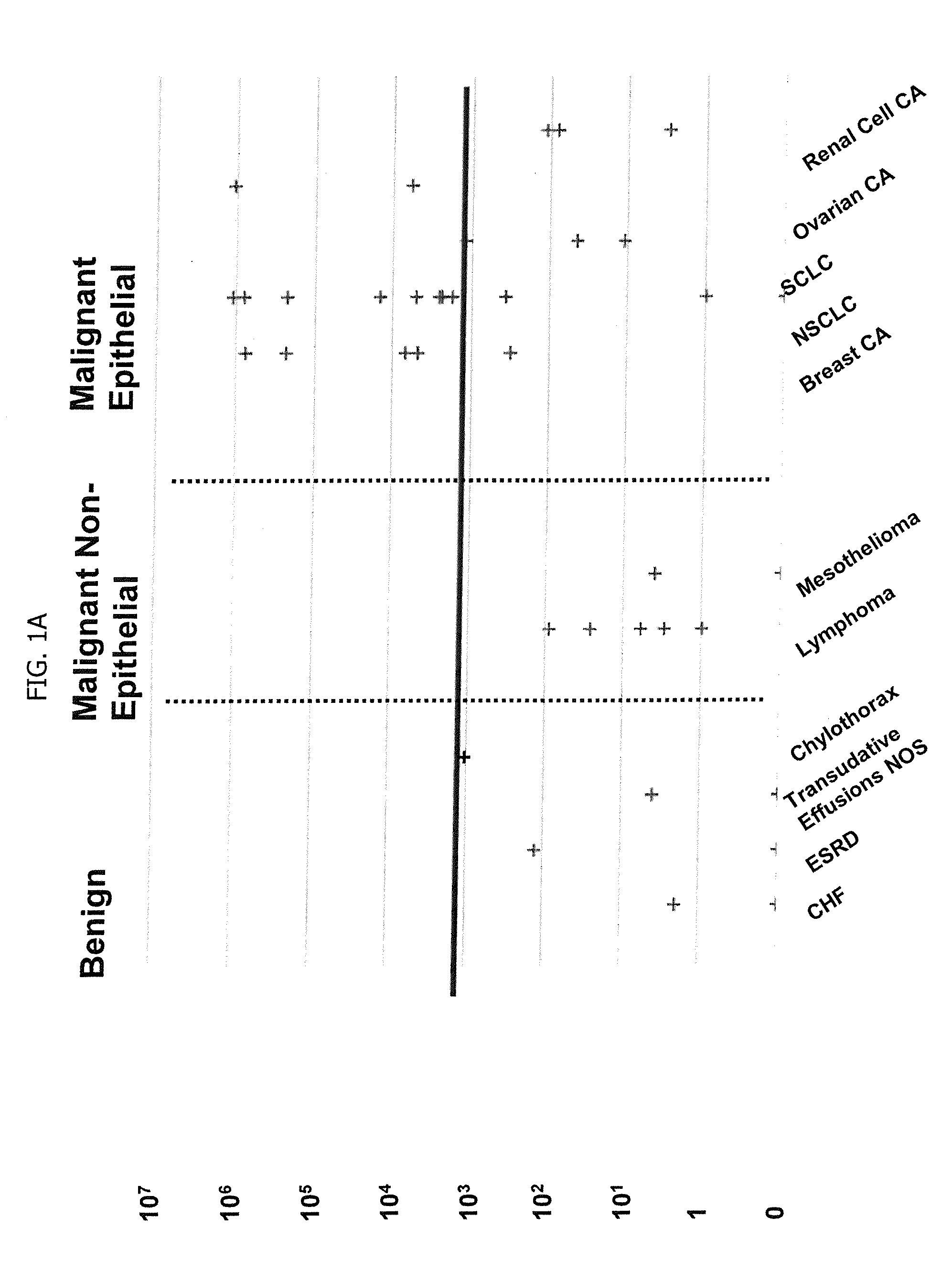
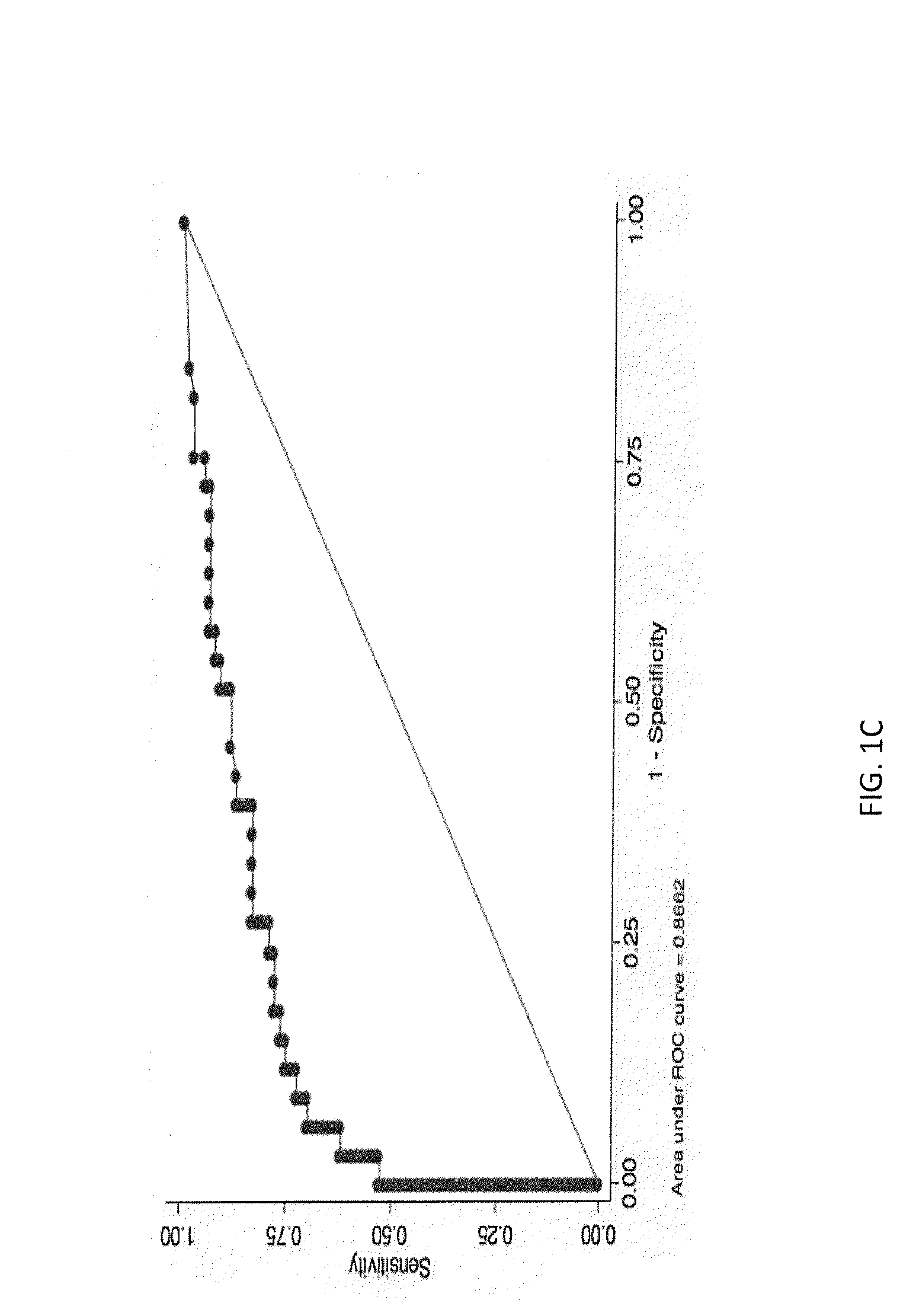
Methods for Diagnosing Cancer by Characterization of Tumor Cells Associated with Pleural or Serous Fluids
InactiveUS20140295426A1High diagnostic sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentCell Fraction
A method for diagnosing or differentially diagnosing a cancer characterized by the presence of cancer cells in the pleural fluid of a mammalian subject, the method comprising contacting a sample of pleural fluid of the subject with colloidal magnetic particles coupled to a ligand which binds to a determinant on a cancer cell, but does not bind above a baseline threshold to other cellular and non-cellular components in pleural fluid; subjecting the pleural fluid-magnetic particle mixture to a magnetic field to produce a cell fraction enriched in ligand coupled-magnetic particle-bound cancer cells, if present in the pleural fluid; and analyzing the enriched fraction for the number of cancer cells in the pleural fluid. In certain aspects, this method involves preparing the pleural fluids for the above-noted method steps by, e.g., dilution of unprocessed pleural fluid. In certain aspect, the pleural fluid is subjected to the diagnostic method within 24 hours of withdrawal from the subject. This method has advantages to present diagnostic procedures for identifying malignant pleural effusions. The tumor cells present in pleural fluid can be characterized with cellular and molecular markers to determine prognostic and predictive factors.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Method for treatment of blood tumor using Anti-tim-3 antibody
ActiveUS20120100131A1Use to establishBiological material analysisAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCell Fraction
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
Targeted-panel tumor mutational burden calculation systems and methods
PendingUS20200258601A1Adapt quicklyLarge adaptabilityBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisGenomic sequencingCell Fraction
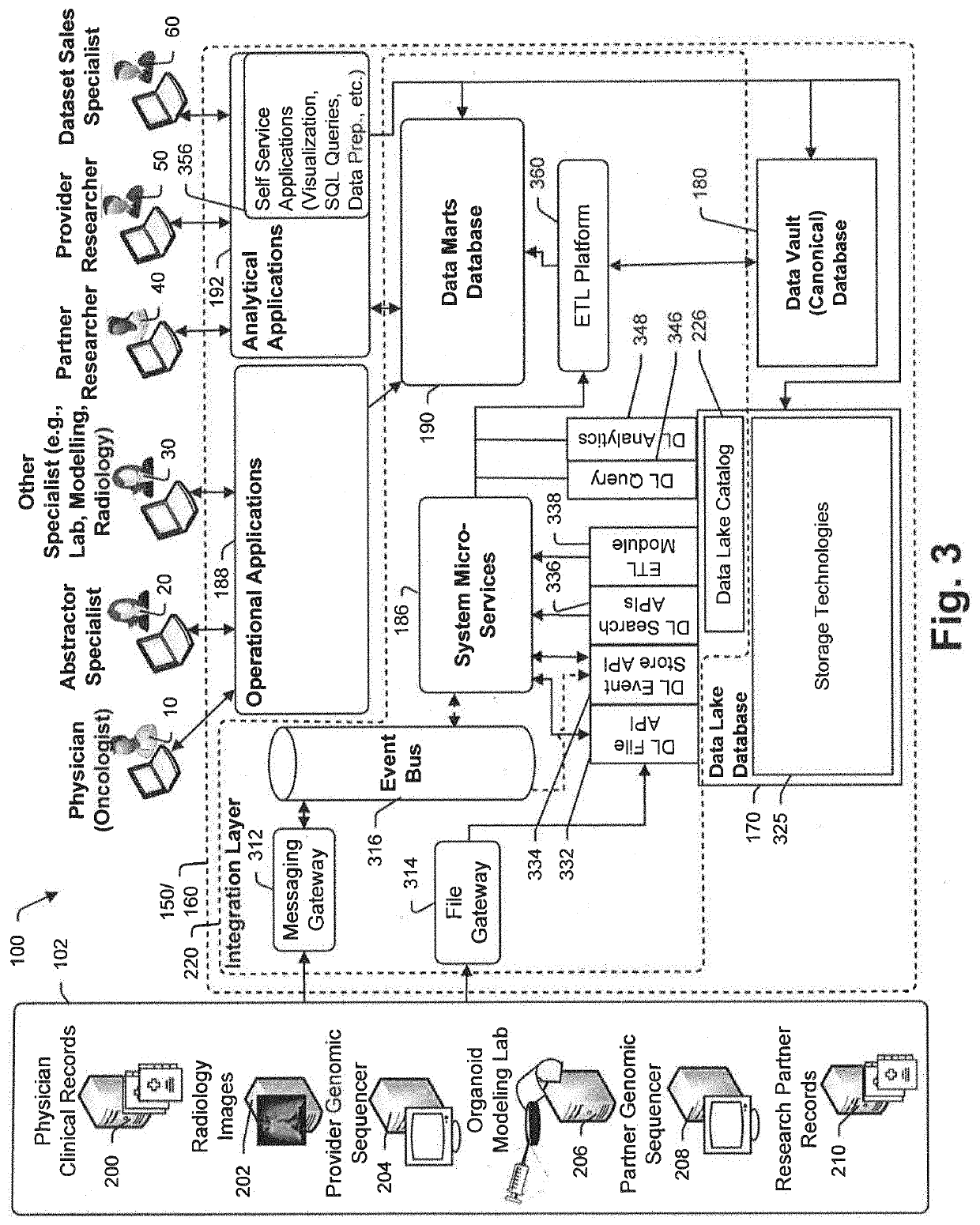
A method and system for conducting genomic sequencing, the system comprising a first microservice for receiving an order from a physician, the order to initiate an NGS of a patient's germline specimen and somatic specimen using a targeted-panel, a second microservice for executing an NGS of the patient's germline specimen to identify sequences of nucleotides in the germline specimen using the targeted-panel to generate germline sequencing results, a third microservice for executing an NGS of the patient's somatic specimen to identify sequences of nucleotides in the somatic specimen using the targeted-panel to generate somatic sequencing results, a fourth microservice for executing quality control (QC) testing on the germline sequencing results to generate a germline QC score and on the somatic sequencing results to generate a somatic QC score, a fifth microservice for generating at least one clinical report, and a sixth microservice for providing the at least one clinical report to the physician, the at least on clinical report comprising the patient's TMB status.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS
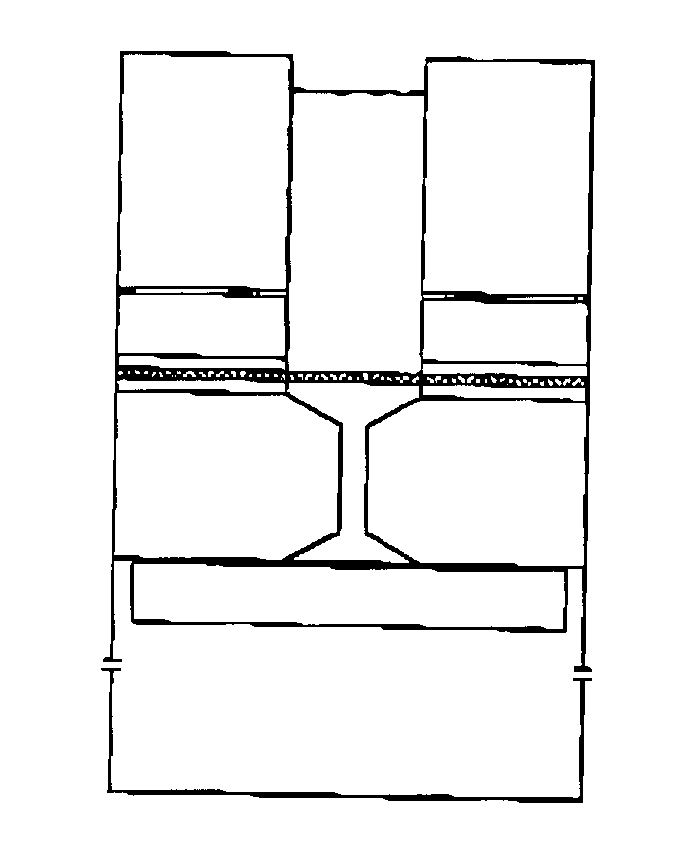
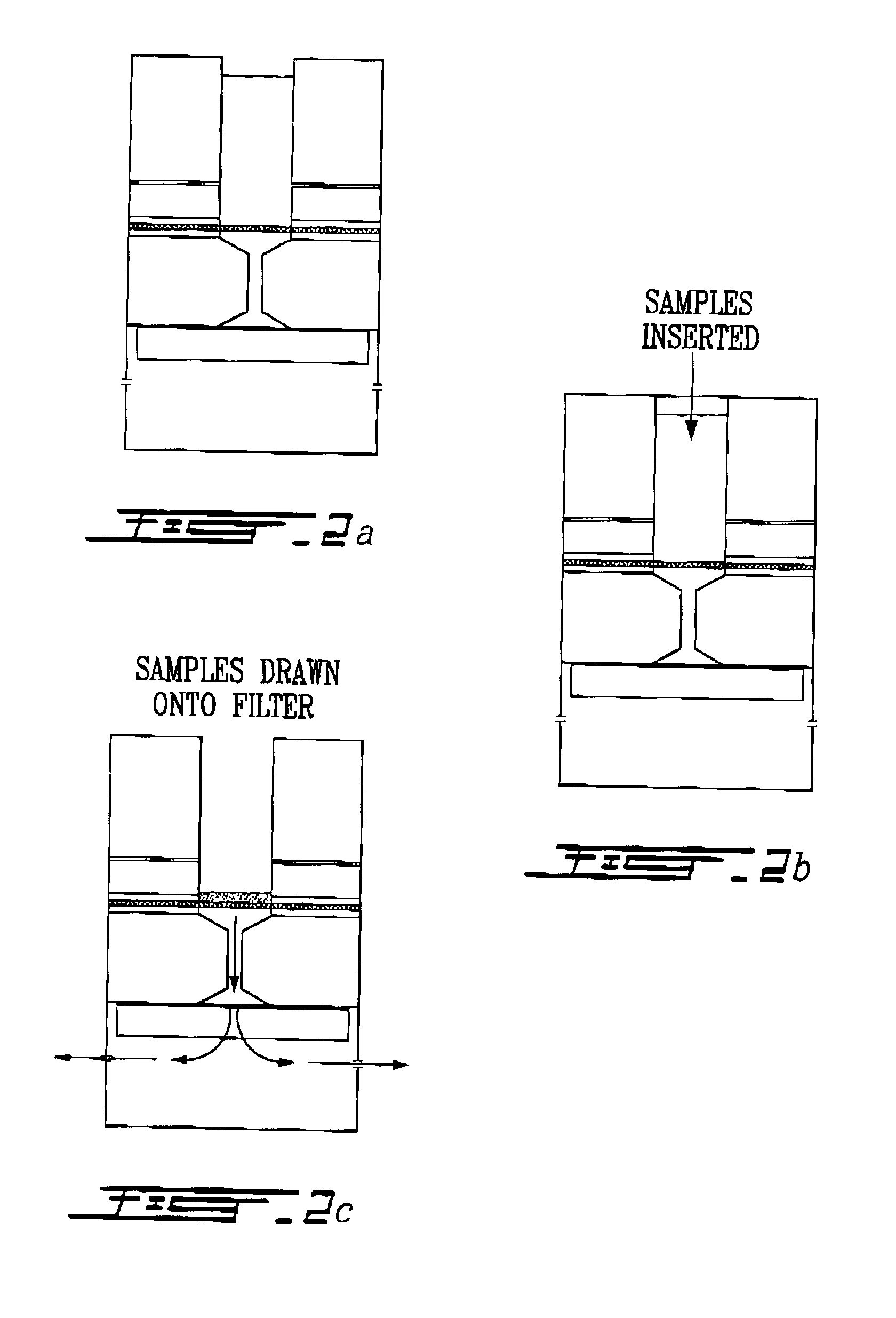
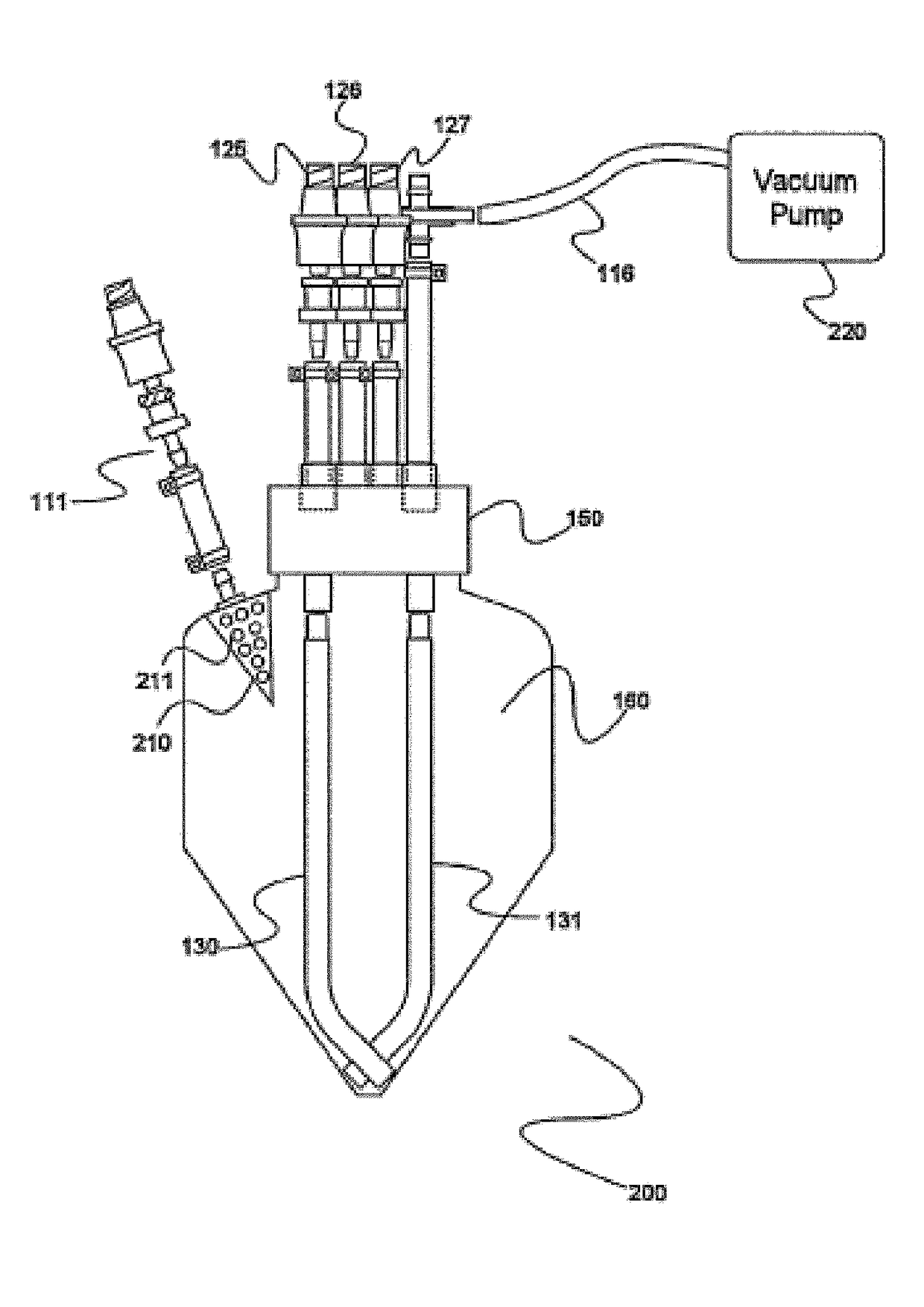
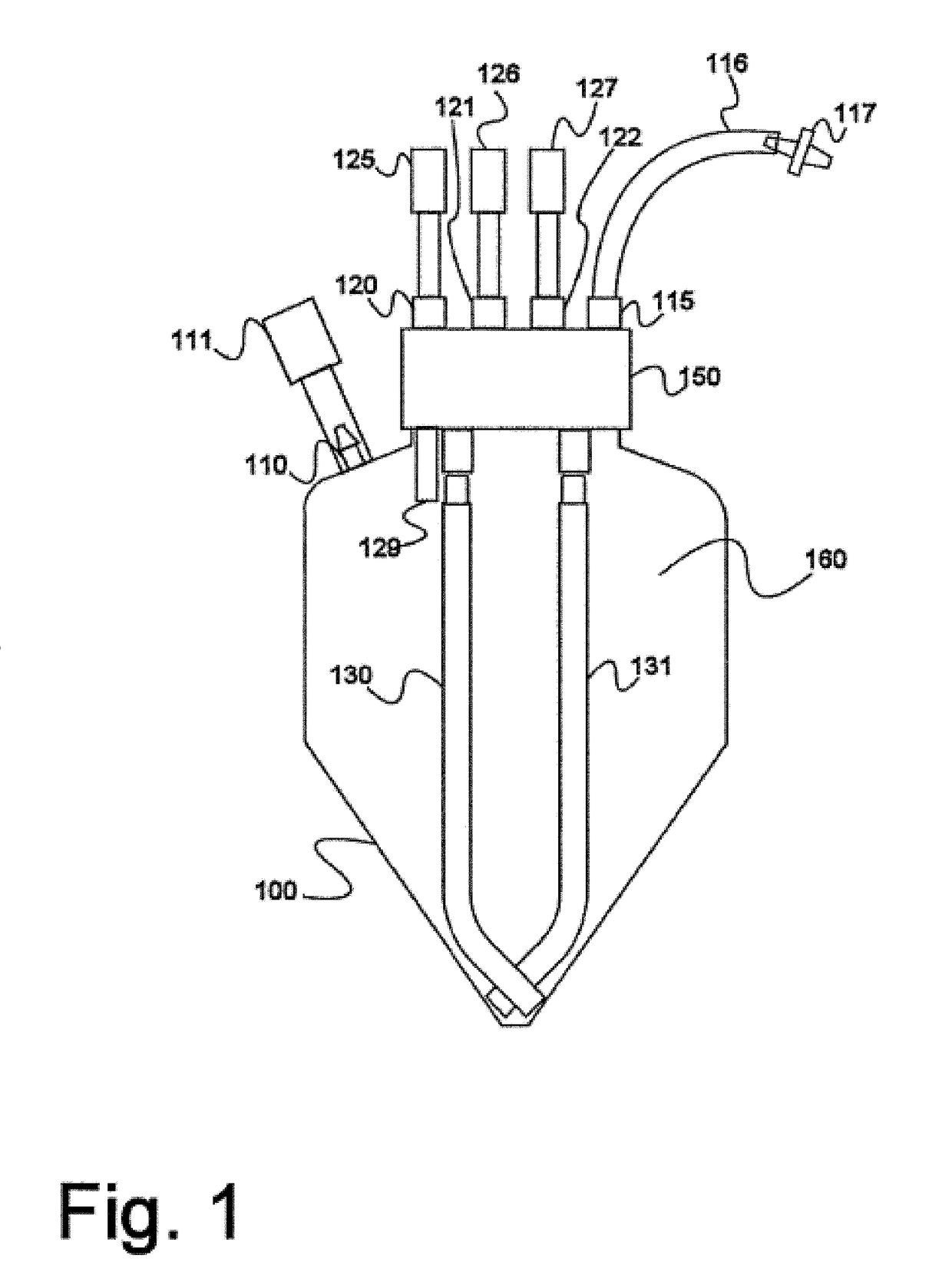
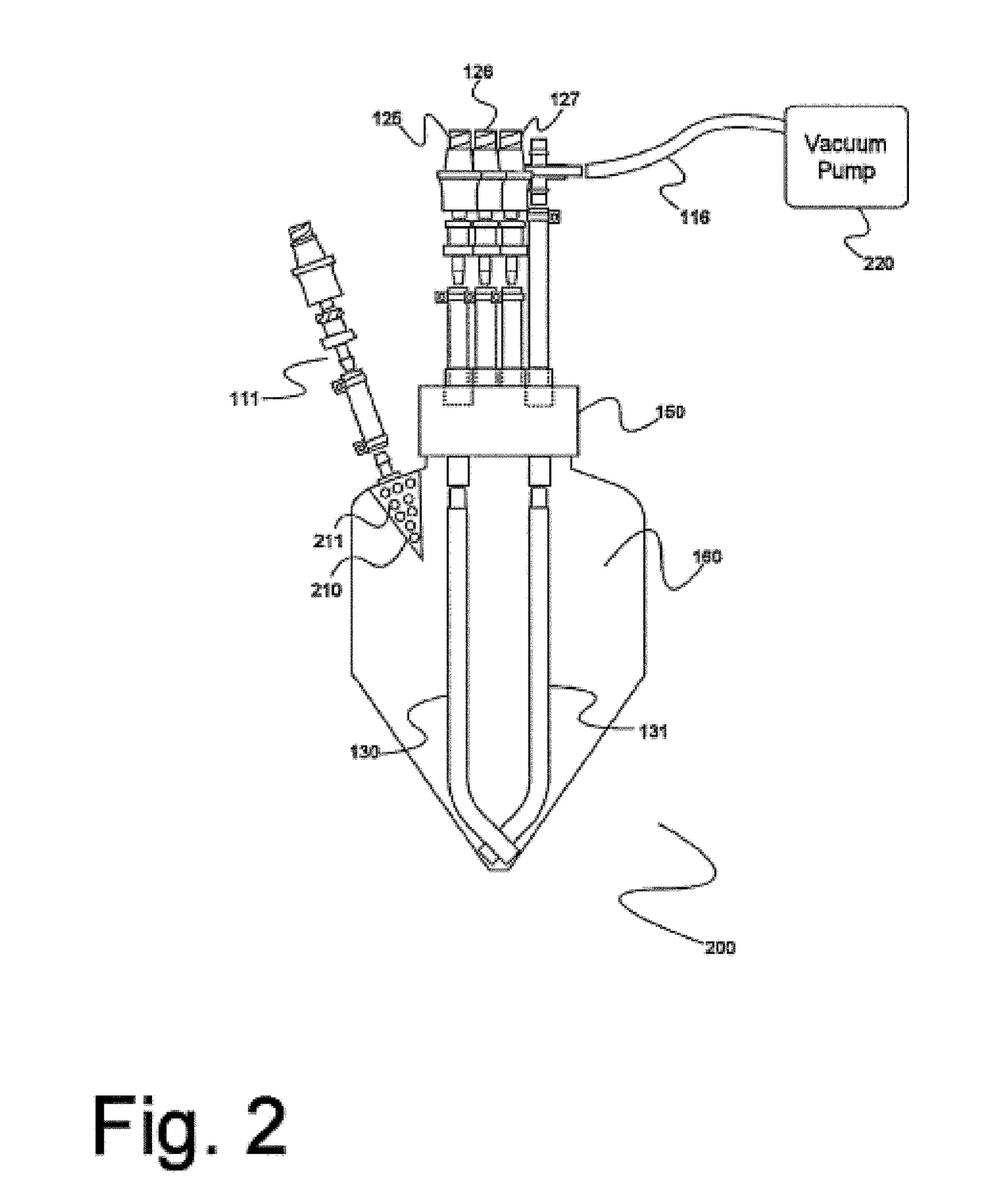
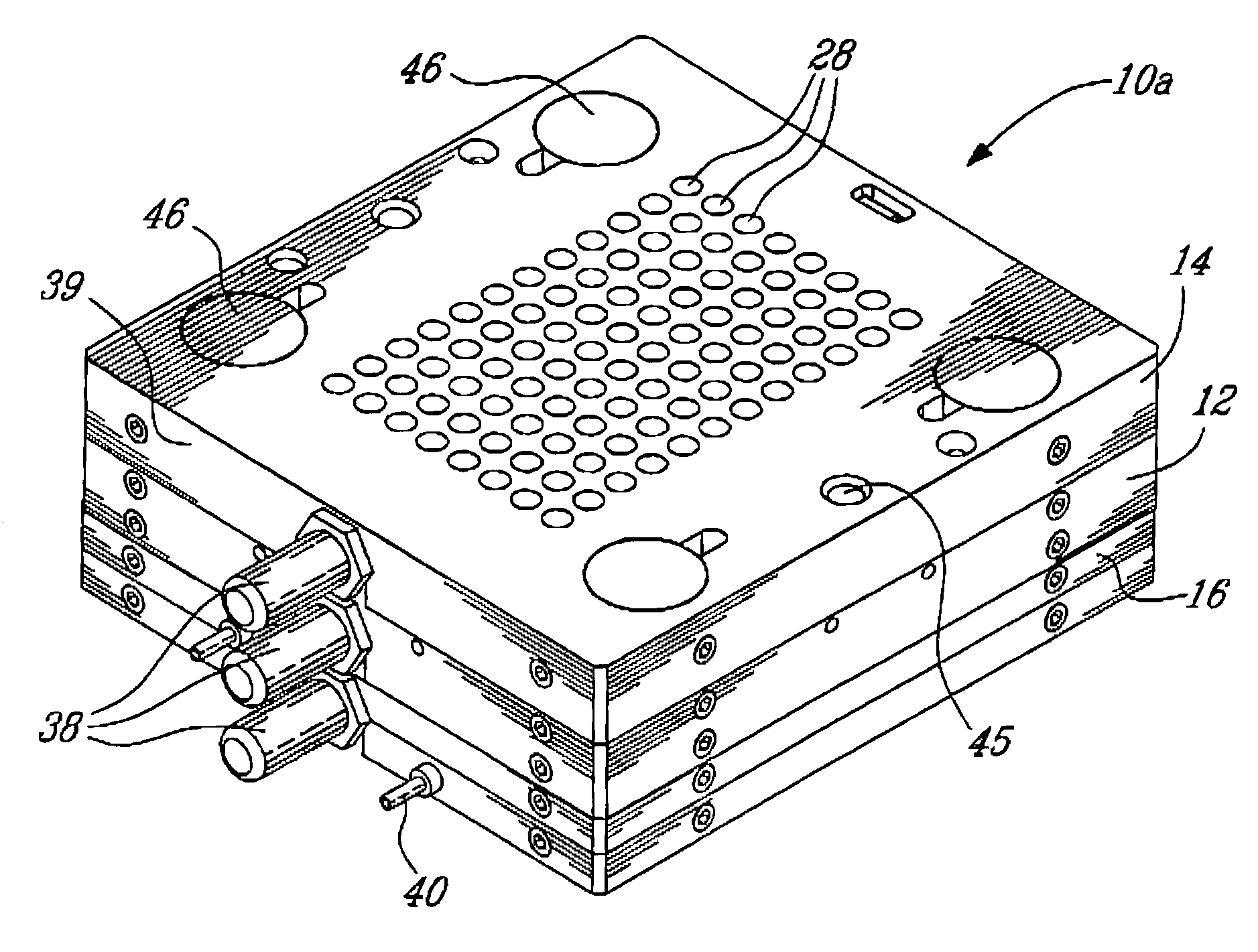
Electron microscopy cell fraction sample preparation robot
InactiveUS20060171850A1Reduce preparation timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTemperature controlCell Fraction
A parallel processing, fluid handling apparatus for concurrent temperature controlled preparation of a plurality of cell fraction samples adapted to be used for electron microscopic viewing. The apparatus comprises generally a sample receiving member, a fluid handling means, and a separation means. The sample receiving member comprises a plurality of discrete apertures each adapted to receive a biological sample therein. The fluid handling means for inserting and removing fluid to and from the plurality of apertures substantially in parallel, permits the biological samples to be processed substantially in parallel by the insertion and removal of processing fluid. The separation means permits the parallel isolated separation of the post-processing samples. The post-processing samples are adapted to be polymerized in embedding solution and removed from the sample receiving member.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
System and methods for preparation of adipose-derived stem cells
ActiveUS20180221550A1Requires environmentOut of operationBiological substance pretreatmentsRotary centrifugesInterior spaceCell Fraction
A device that allows for either fat graft preparation or cell fraction harvest is disclosed. The device includes a first centrifuge tube configured to receive and process a biological substance, the first centrifuge tube comprising an upper cylindrical portion and a lower conical portion, a sterile tissue inlet fitting, at least one sterile processing fluid inlet fitting, a sterile suction fitting, and at least one sterile extraction port connected to a first extraction tube. The first centrifuge tube further includes an internal space including a screen being positioned therein, the screen being configured to divide the internal space in half, and a filter positioned therein, the filter being positioned below the screen in the lower conical portion of the first centrifuge tube. The device may further include a second centrifuge tube configured to receive and further process the biological substance from the first centrifuge tube. The second centrifuge tube has at least one sterile fitting, wherein the second centrifuge tube is releasably connected via the at least one sterile fitting to one of the at least one sterile extraction ports of the first centrifuge tube.
Owner:JOINTECHLABS
Electron microscopy cell fraction sample preparation robot
InactiveUS7122155B2Reduce preparation timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansCell FractionTemperature control
A parallel processing, fluid handling apparatus for concurrent temperature controlled preparation of a plurality of cell fraction samples adapted to be used for electron microscopic viewing. The apparatus comprises generally a sample receiving member, a fluid handling means, and a separation means. The sample receiving member comprises a plurality of discrete apertures each adapted to receive a biological sample therein. The fluid handling means for inserting and removing fluid to and from the plurality of apertures substantially in parallel, permits the biological samples to be processed substantially in parallel by the insertion and removal of processing fluid. The separation means permits the parallel isolated separation of the post-processing samples. The post-processing samples are adapted to be polymerized in embedding solution and removed from the sample receiving member.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Kits and methods for preparing gell samples optmimized for dual staining
A method of preparing nucleated peripheral blood or bone marrow cells optimized for at least dual mode imaging. The method including: (a) isolating nucleated cells from a peripheral blood or a bone marrow sample; and (b) resuspending the nucleated cells in the presence of a morphology preserver including at least 1% serum, and recovering a cell fraction thereby preparing the nucleated peripheral blood or bone marrow cells optimized for at least dual mode imaging.
Owner:BIOVIEW
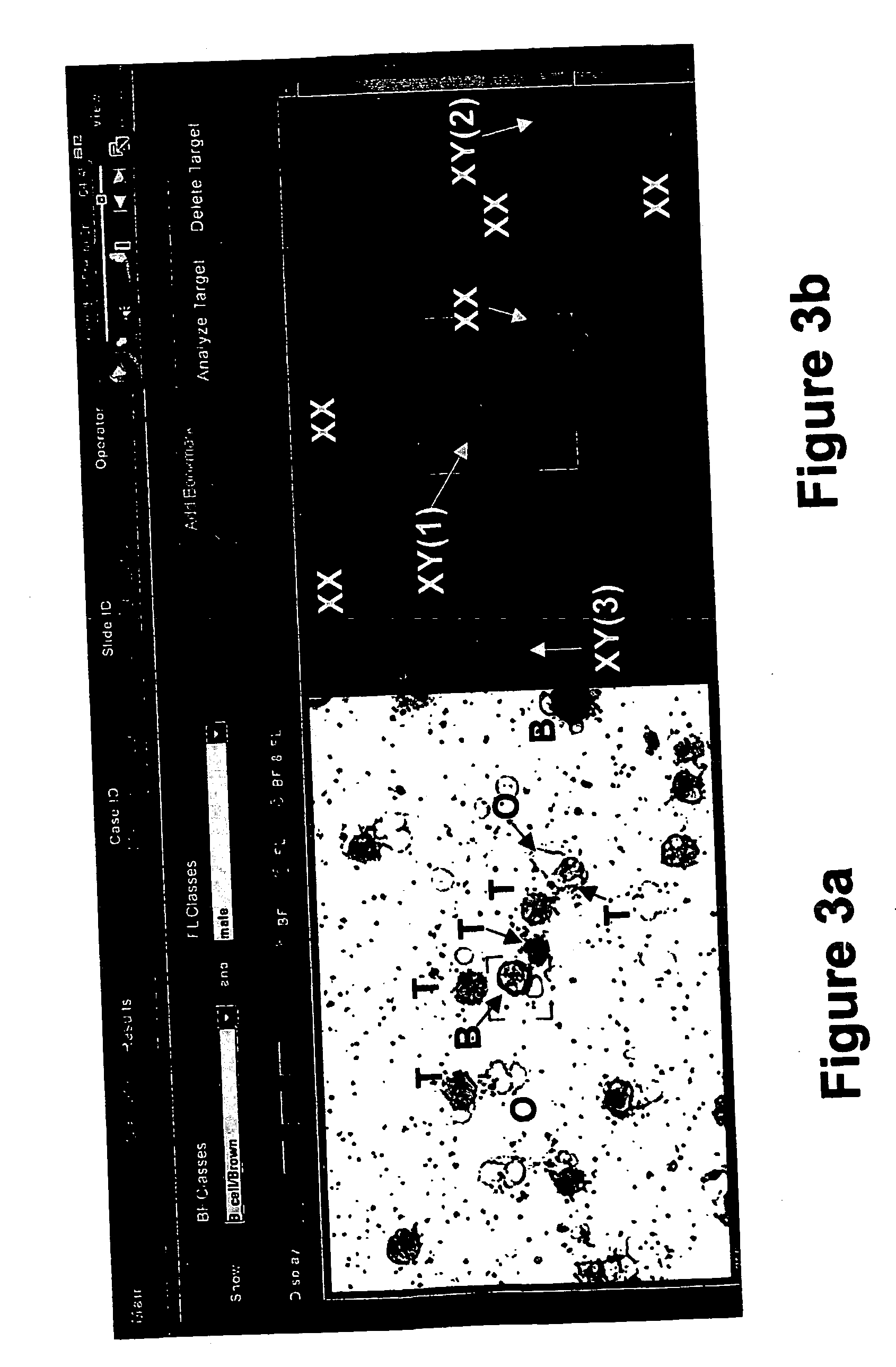
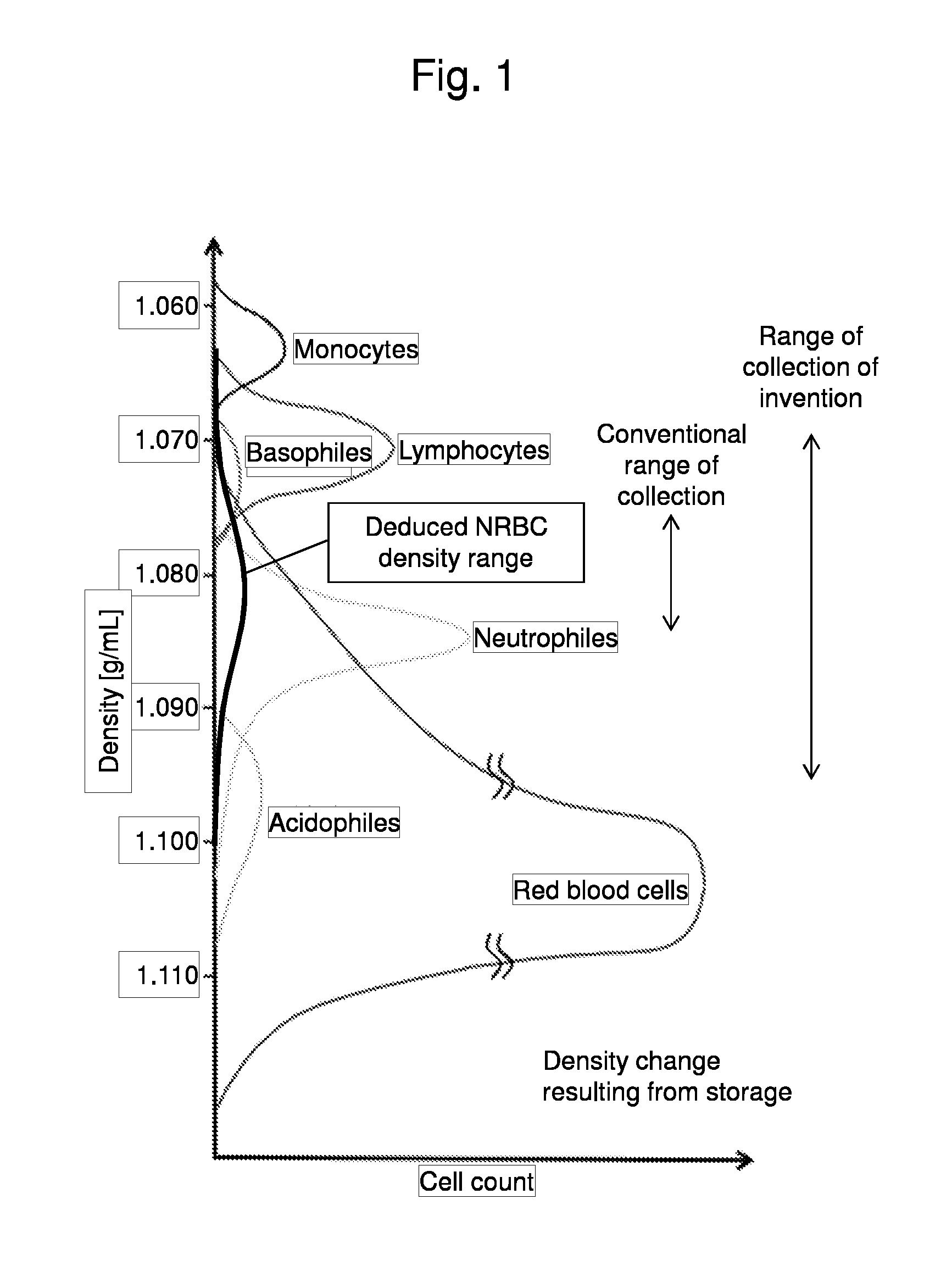
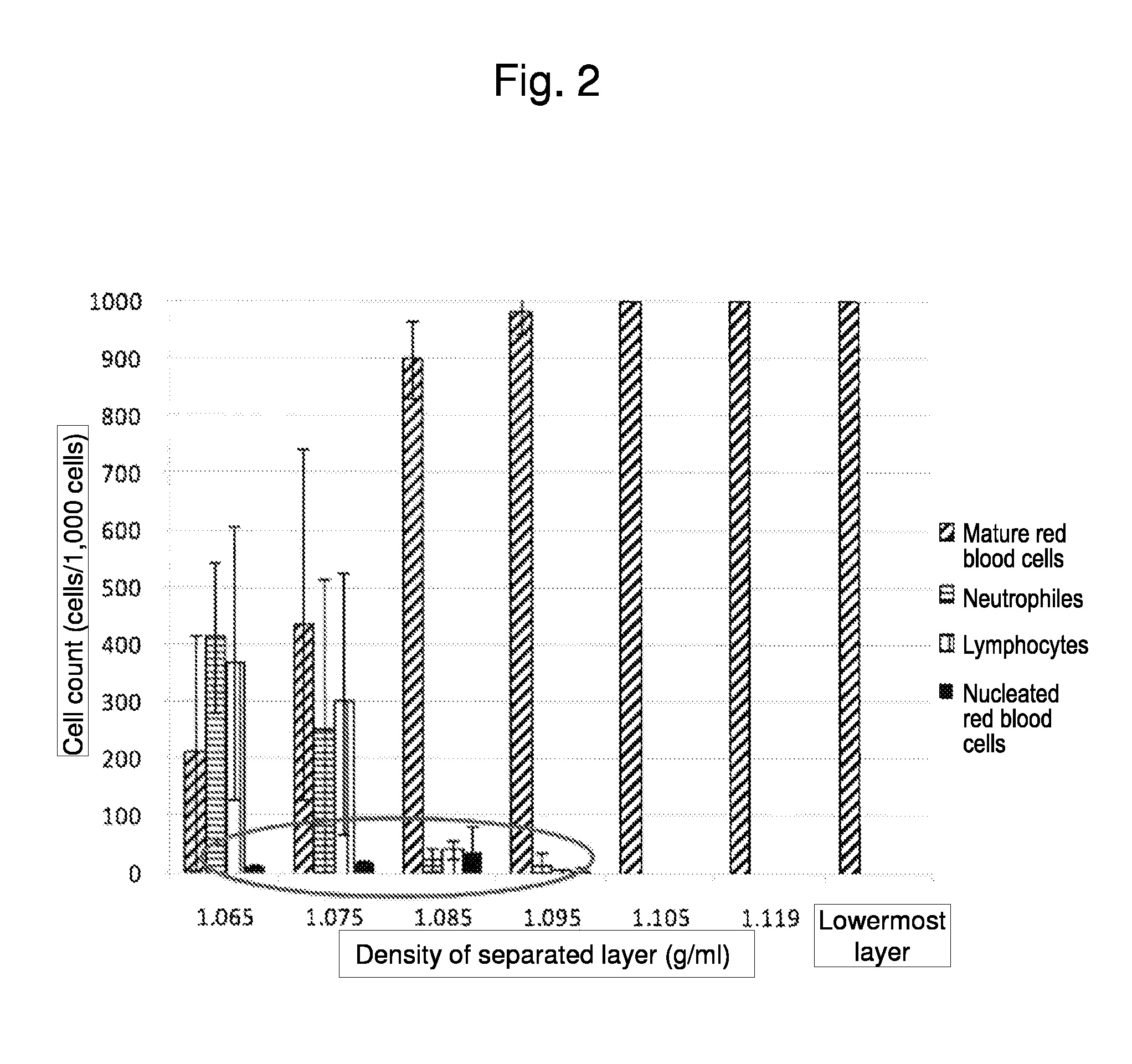
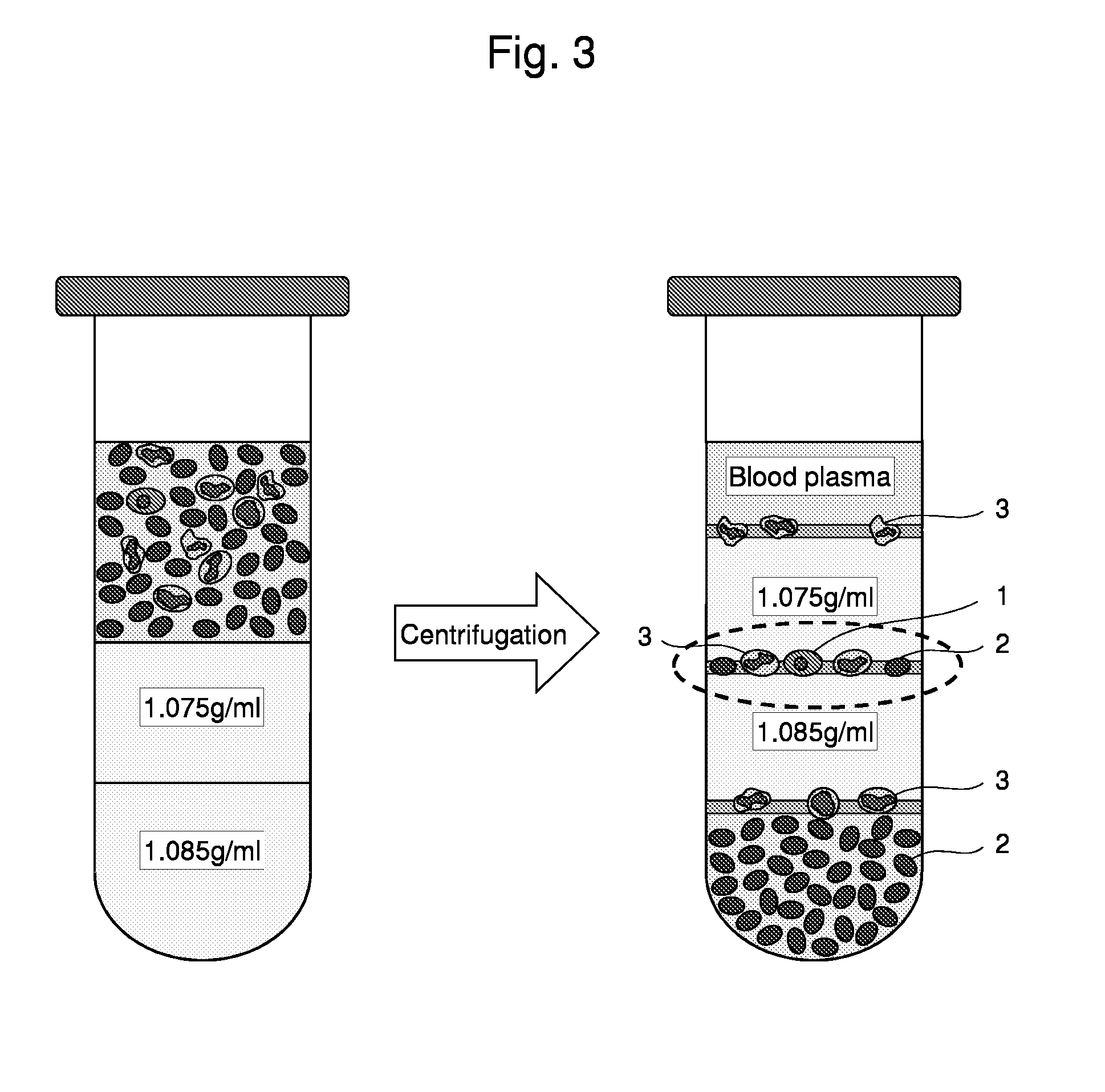
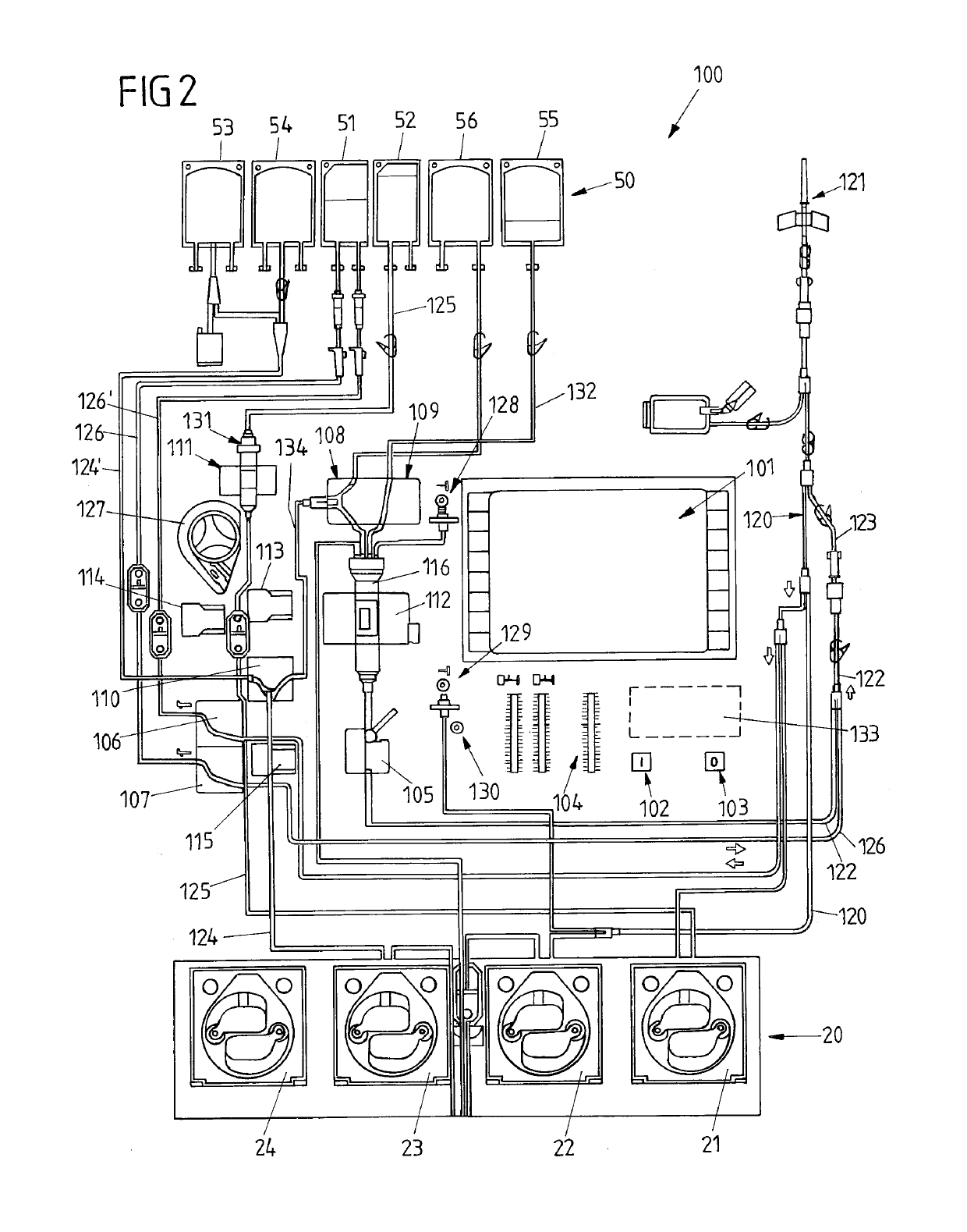
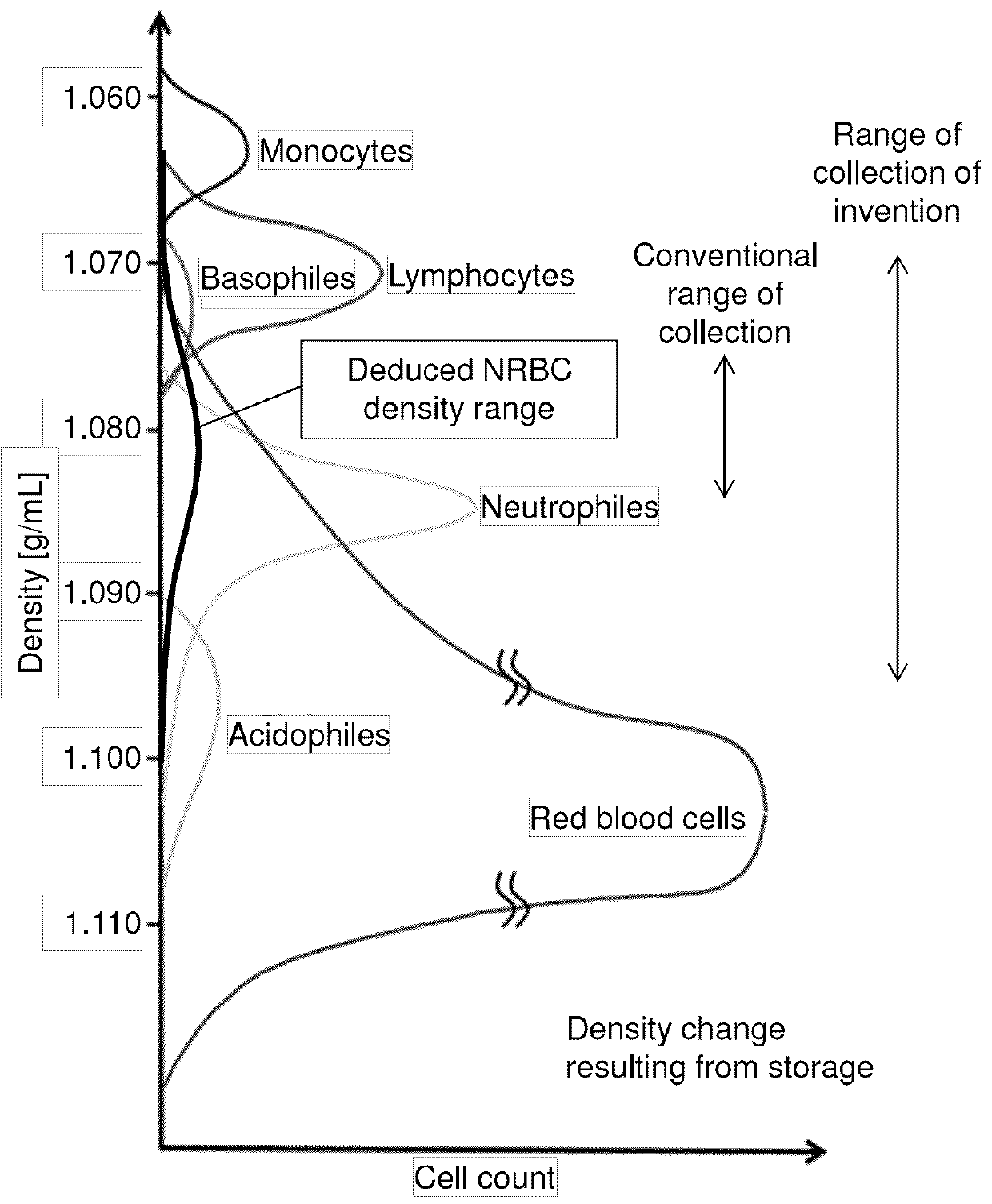
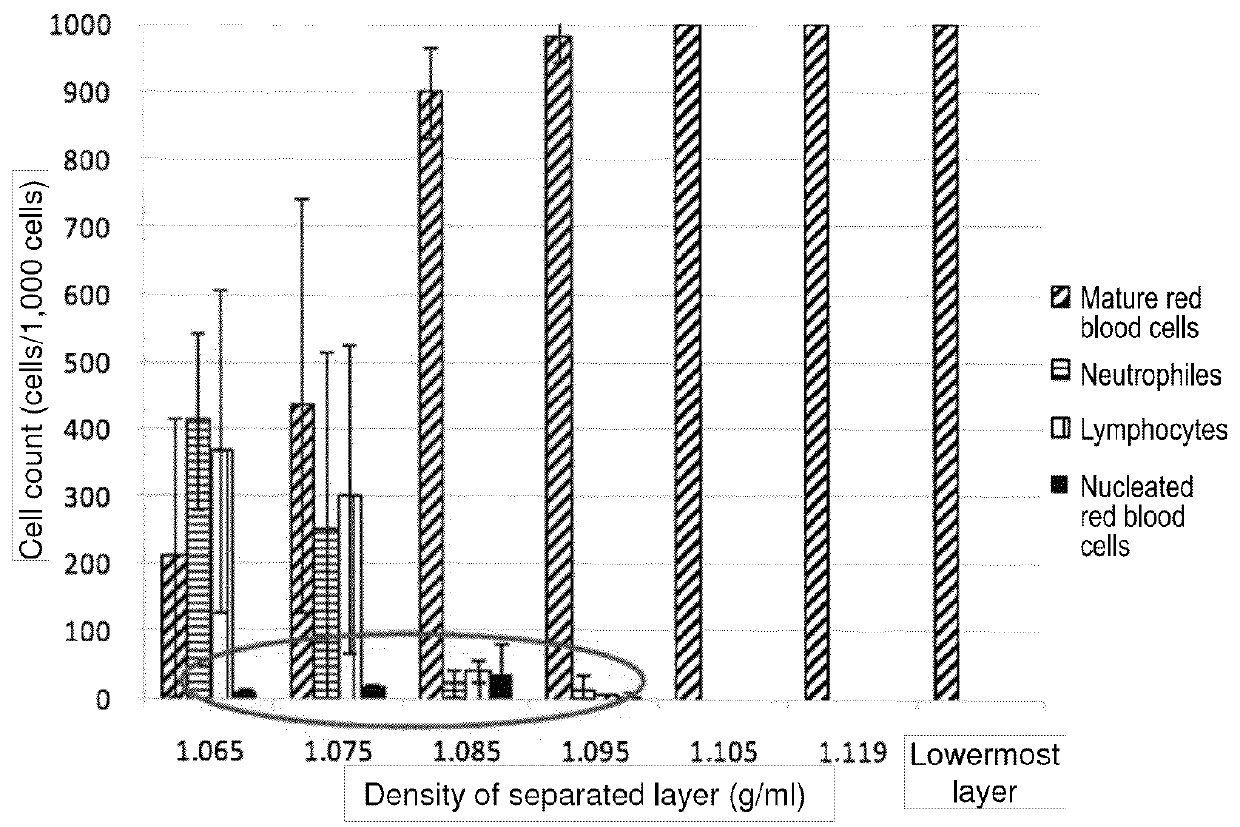
Method for collecting nucleated red blood cells via density-gradient centrifugation utilizing changes in blood cell density
ActiveUS20130072402A1Cell count is reducedIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell FractionRed blood cell
This invention provides a method for concentrating and collecting small quantities of fetal nucleated red blood cells contained in the maternal blood. The method for concentrating and collecting nucleated red blood cells from the maternal blood comprises: (i) subjecting the maternal blood to a first density-gradient centrifugation and collecting a cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells; (ii) treating the cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells so as to selectively changes the density of the nucleated red blood cells from that of the white blood cells; and (iii) subjecting the treated cell fraction containing the nucleated red blood cells to a second density-gradient centrifugation so as to collect a fraction containing nucleated red blood cells.
Owner:JAPAN ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +2
Method for the separation of cell fractions
InactiveUS20060172303A1Equal efficiencyMinimal effortMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCell FractionAbnormal tissue growth
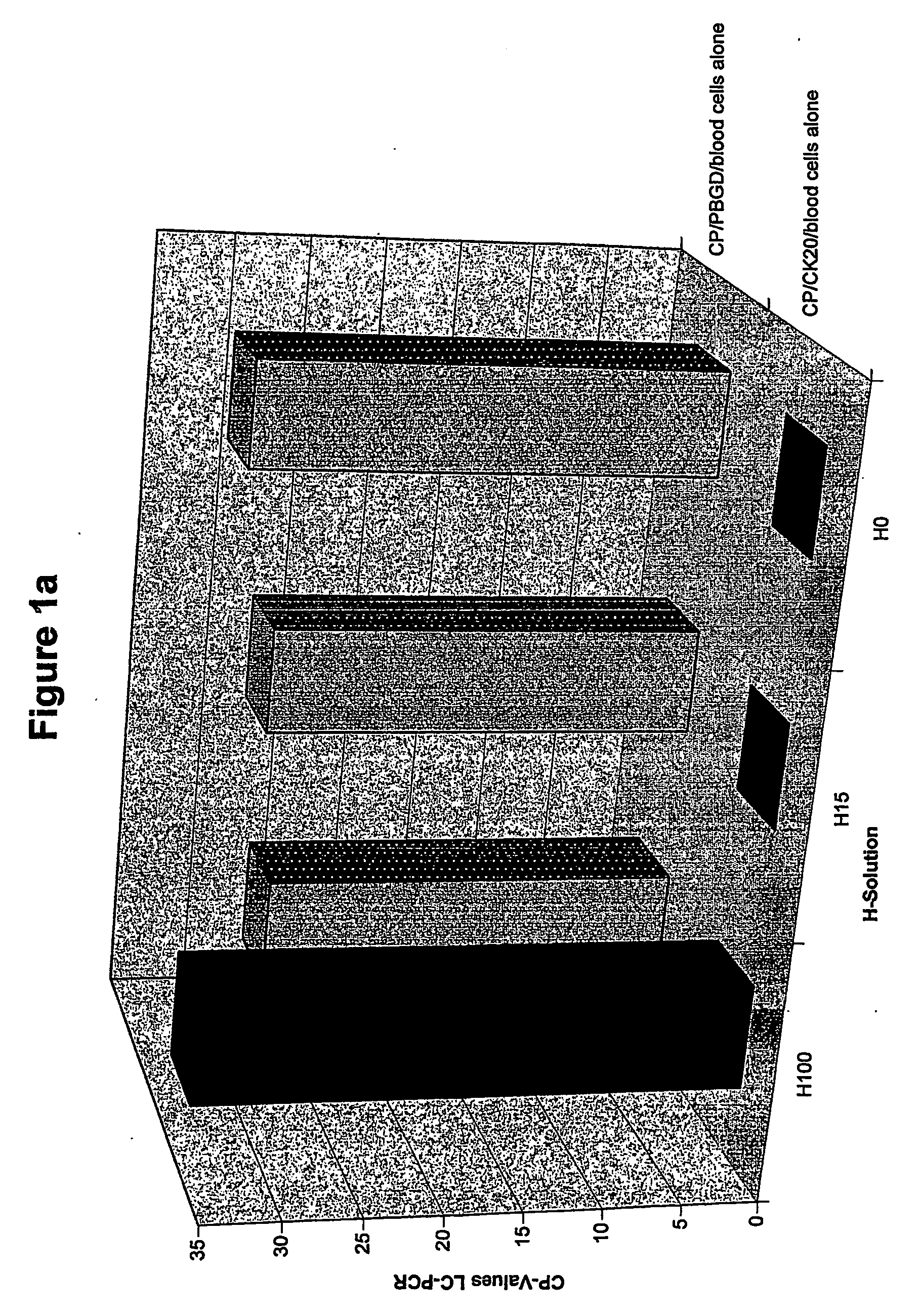
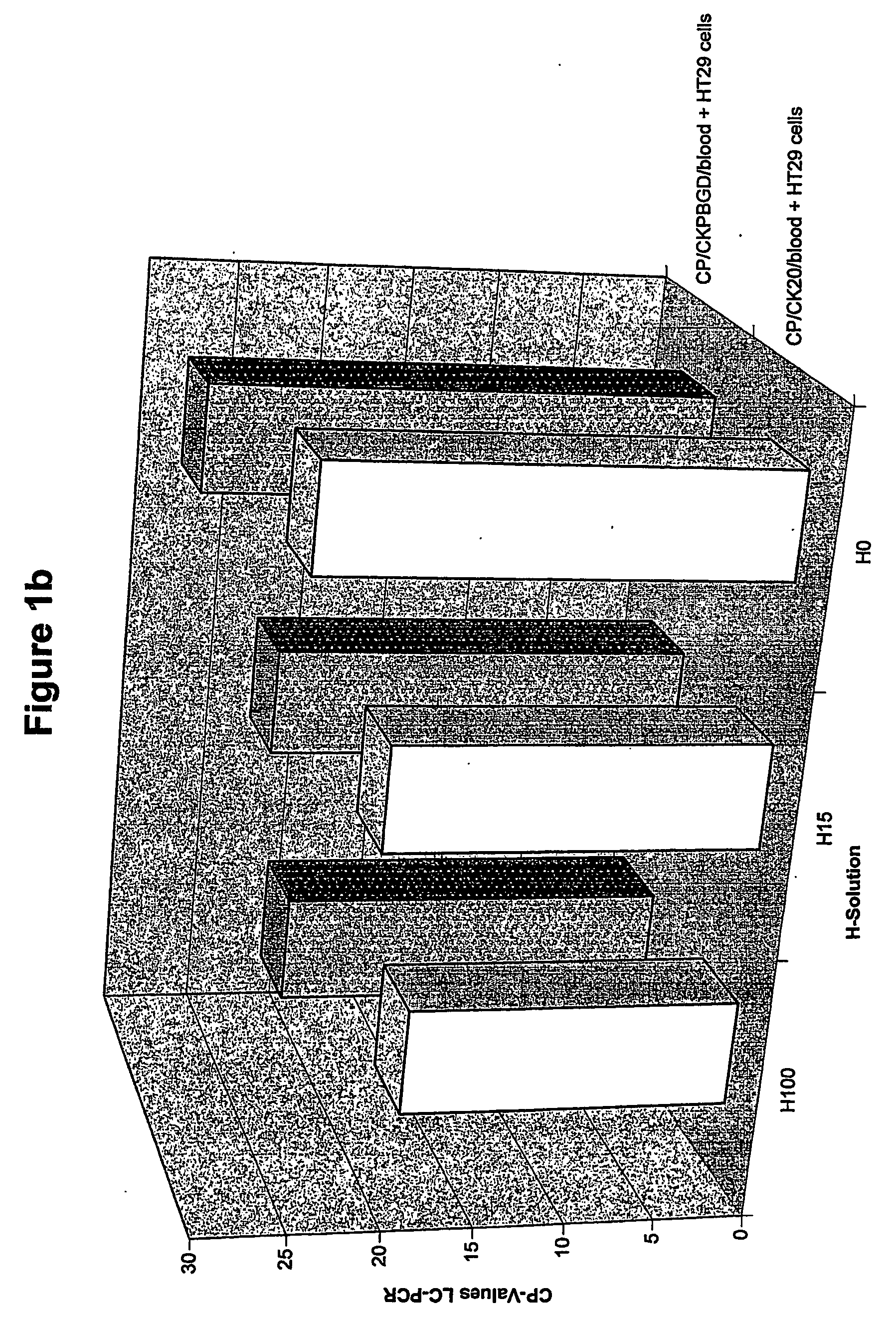
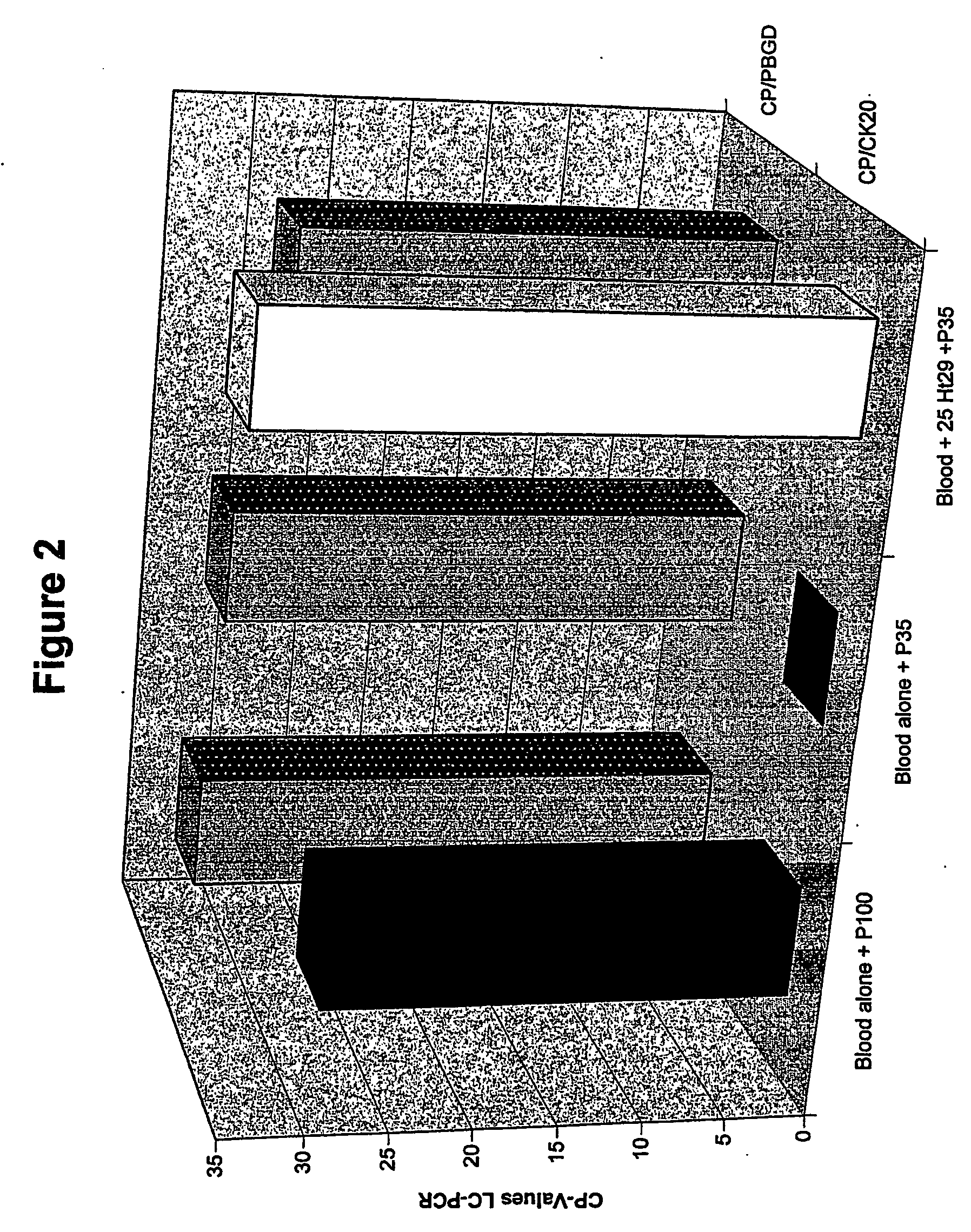
The present invention relates to a method for the separation of cells, in particular for the preparation of samples in tumor diagnostics. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for sample preparation for the detection of tumor cells of solid tumors in the course of the diagnosis for prognosis and stratification of therapy, comprising the destruction of cells that make this diagnosis more difficult or entirely impossible. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a kit for the preparation of samples and for the detection of the presence of the altered cells. Finally, the present invention relates to the use of the method and the kit in the diagnostics of altered cells such as tumor cells, and the performance of a PCR reaction to detect the tumor cells in body fluids and tissues.
Owner:LEHNERT LASSE
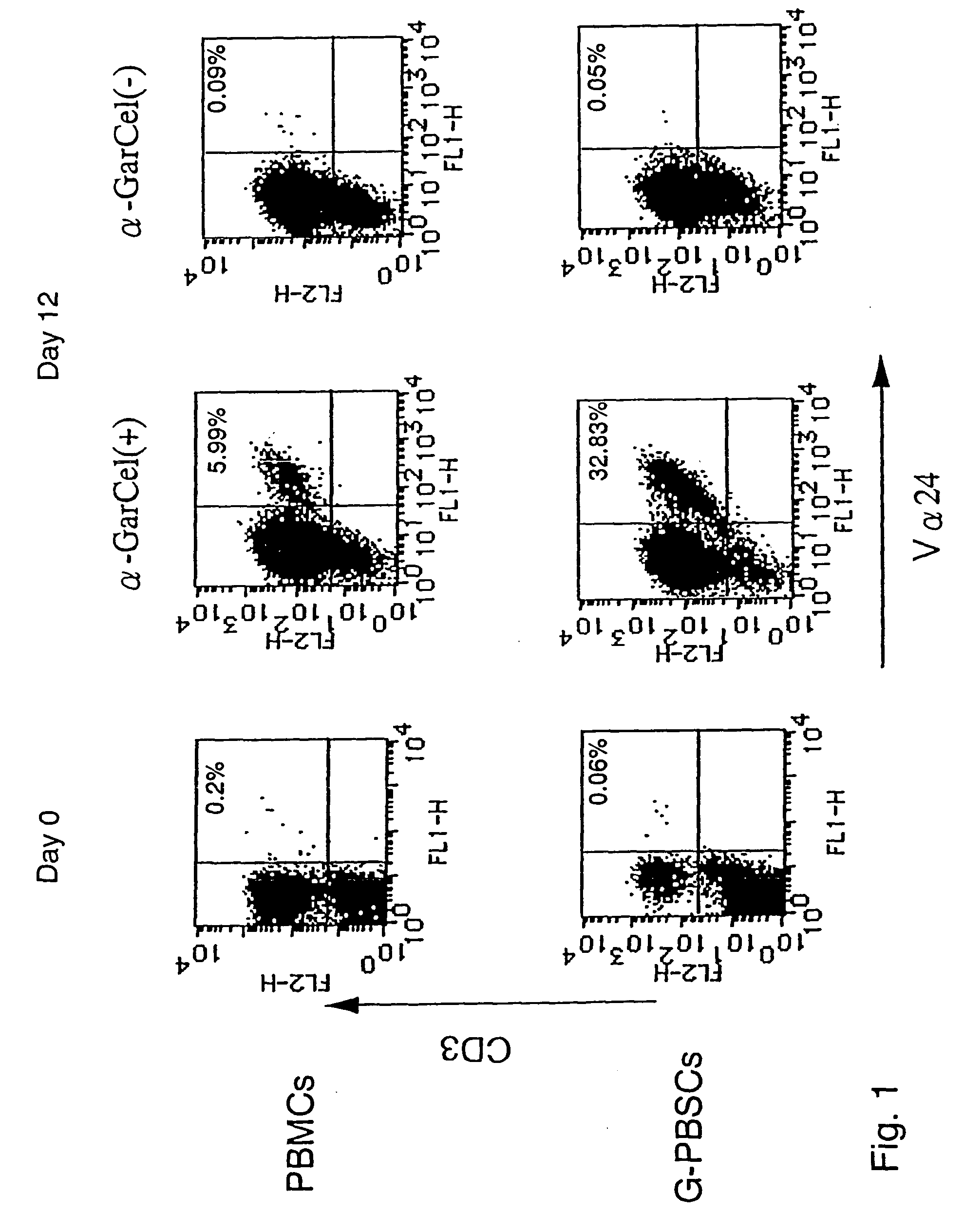
Method for amplifying natural killer t cells
InactiveUS20040009594A1Potent activityEffective in vitro expansionMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsCell FractionG-csf therapy
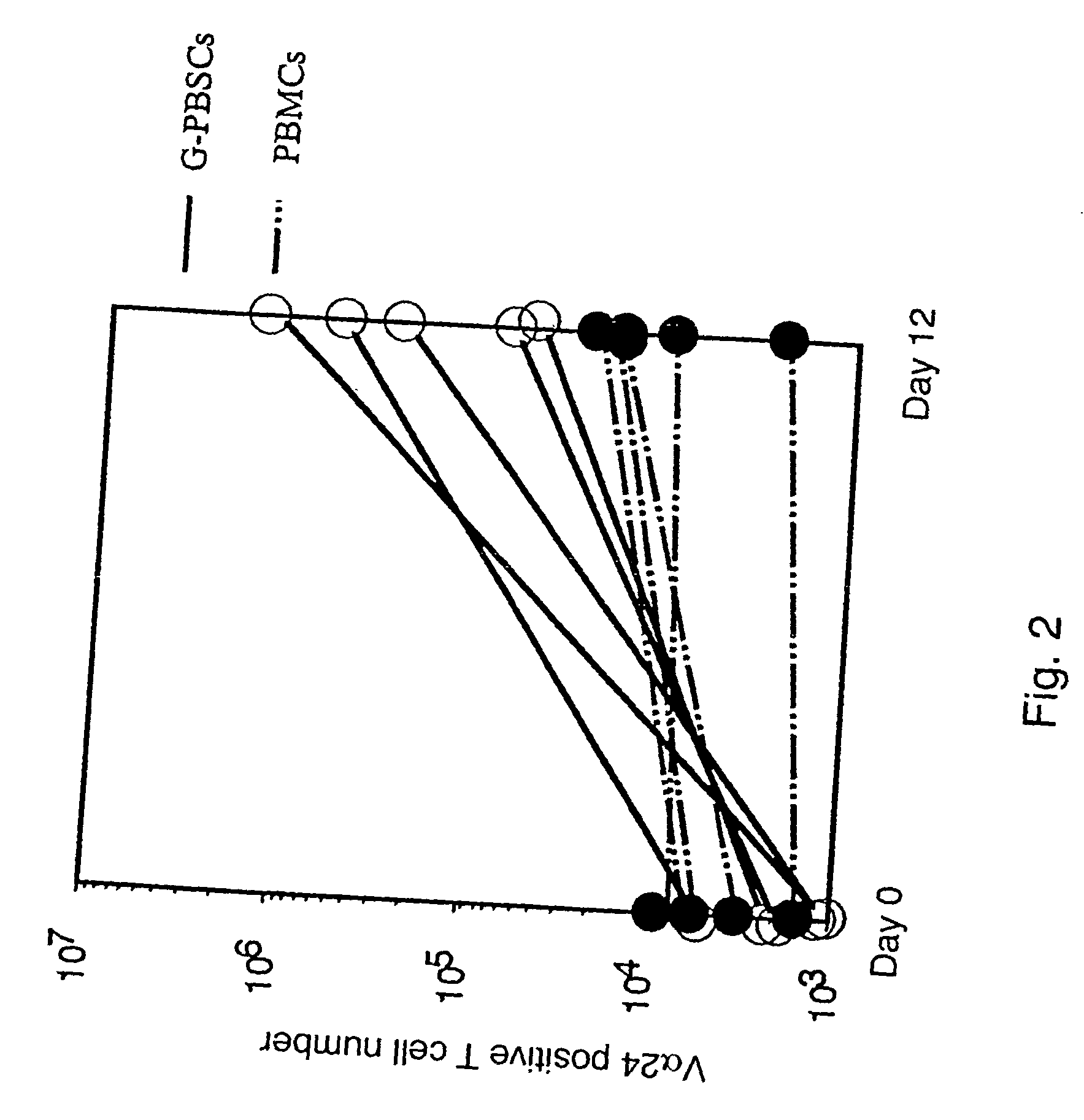
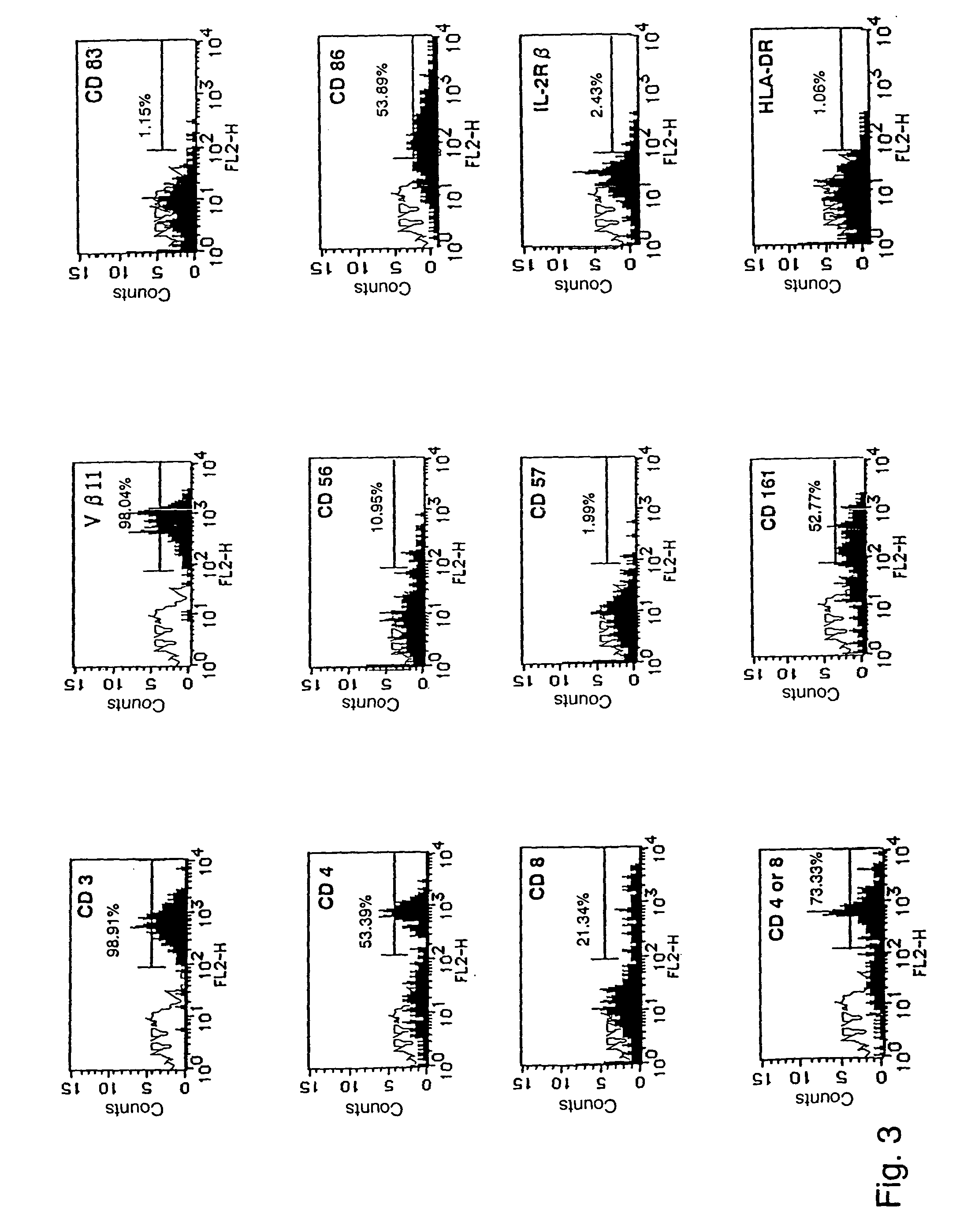
Human Valpha24<+> natural killer T cells are expanded by culturing a mononuclear cell fraction obtainable from human peripheral blood in which hemopoietic stem cells are mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, in the presence of a cytokine, such as interleukin 2, effecting proliferation and / or activation of lymphocytes and alpha-glycosylceramide. A cell fraction comprising human Valpha24<+> natural killer T cells expanded by the method, is useful as a cancer-treating agent.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Optimized and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord
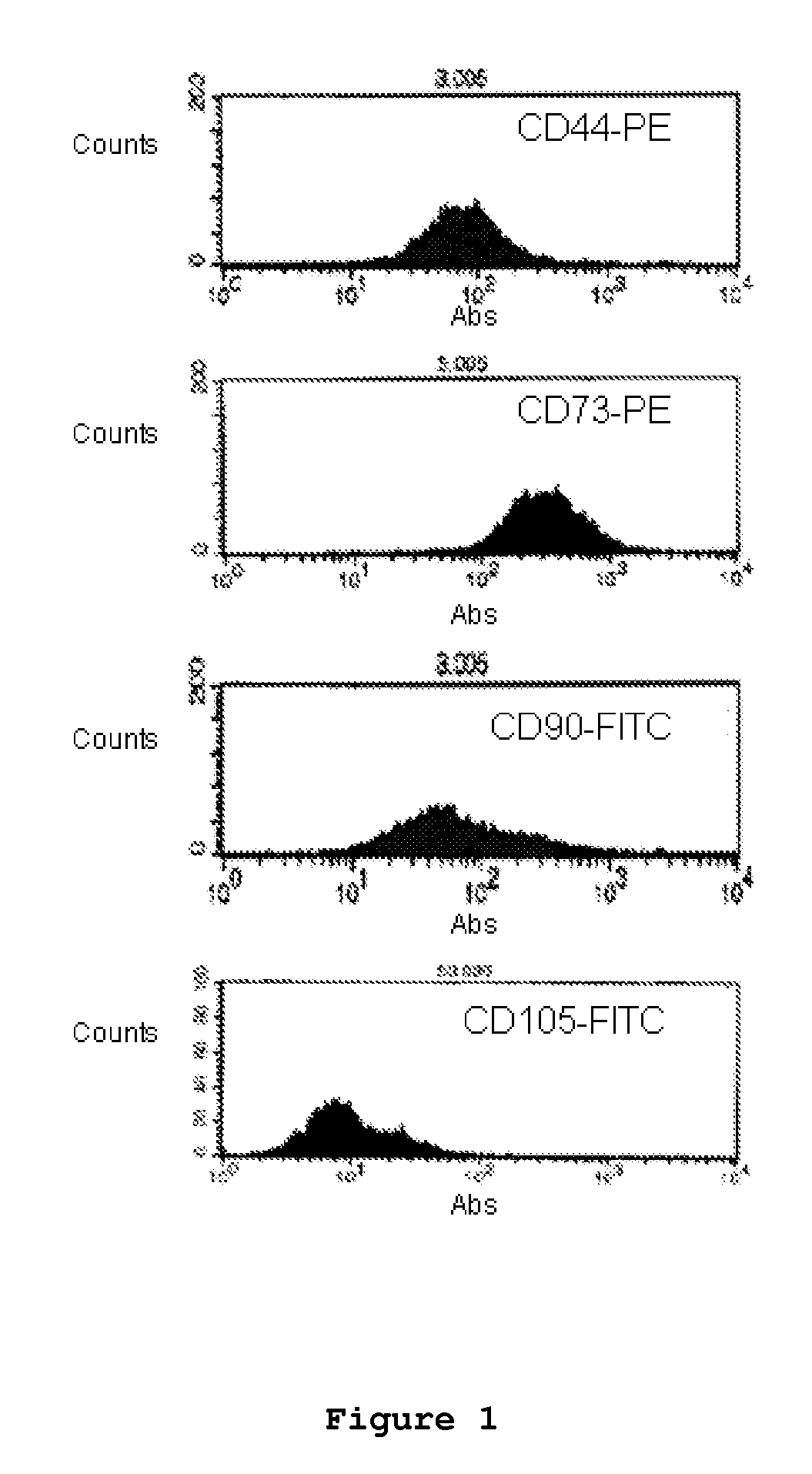
ActiveUS20100216237A1Promote resultsImprove efficiencyCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsCell FractionCell phenotype
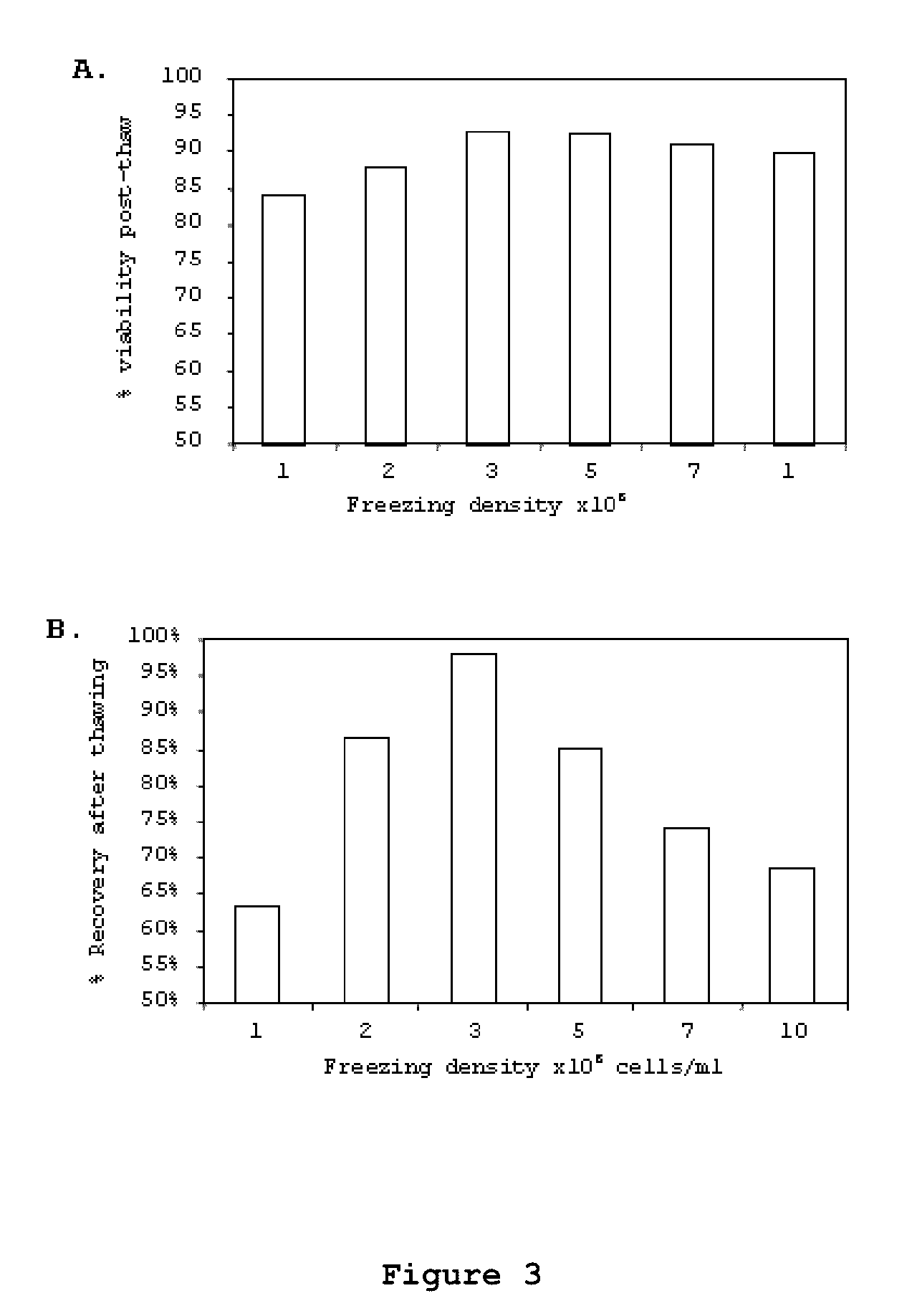
The present invention refers to an optimized and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord. Besides being reproducible and 100% reliable, in terms of the number of samples processed, the method results in a high and defined number of precursor cells, being the majority obtained after a single adhesion and expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (thus granting cell phenotype), in a shorter time frame than what was previously described in the state-of-the-art. With this method, it is possible to obtain, in 9 days, after direct freezing of a cell fraction, and after one expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (end of P0) of the majority of the cells, about 8.6(±0.1)×105 cells / gram of processed umbilical cord. In turn, the characteristics of the cells allow, for example, after 35 days, obtaining an average of 7.7×1015 cells, with precursor phenotype, from 100% of processed umbilical cord samples. The method, because it is simple, robust and 100% reliable, can be performed under good manufacturing practices (GMP) in laboratories dedicated to cell therapy in humans. Furthermore, the method has applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and biotechnology areas.
Owner:LAB MEDINFAR PROD FARMS
Optimised and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord
InactiveCN101868536ACell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeCell Fraction
The present invention refers to an optimized and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord. Besides being reproducible and 100% reliable, in terms of the number of samples processed, the method results in a high and defined number of precursor cells, being the majority obtained after a single adhesion and expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (thus granting cell phenotype), in a shorter time frame than what was previously described in the state-of-the-art. With this method, it is possible to obtain, in 9 days, after direct freezing of a cell fraction, and after one expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (end of PO) of the majority of the cells, about 8, 6, 6 (+ / -0, 1) x l05 cells / gram of processed umbilical cord. In turn, the characteristics of the cells allow, for example, after 35 days, obtaining an average of 7.7xlO15 cells, with precursor phenotype, from 100% of processed umbilical cord samples. The method, because it is simple, robust and 100% reliable, can be performed under good manufacturing practices (GMP) in laboratories dedicated to cell therapy in humans. Furthermore, the method has applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and biotechnology areas.
Owner:MEDINFAR PROD FARM
Blood cell preparations and related methods (gen 8)
InactiveUS20150328260A1Reduce spacingReduce volumeBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCell FractionWhite blood cell
The disclosure provides preparations of cells that are enriched in white blood cells, methods for separating cells into different fractions, and methods for administering the different cell fractions into a recipient subject.
Owner:HARVARDIANAMD CONSULTING
Process for obtaining dinitrogen monoxide (N20)
InactiveUS20130171711A1Improve energy balanceHighly climate-damagingWater treatment parameter controlTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesMicroorganismCell Fraction
In a method for obtaining dinitrogen monoxide by microbiological or enzymatic processes from nitrogen-containing substances, the microorganisms, bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes, fungi, parasites, phages, cells, cell fractions or membrane fractions, and / or enzymes, and / or a combination thereof to be used in this context are selected, or manipulated or partly or entirely reversibly and / or irreversibly inhibited by suitable actions, or the corresponding microbiological or enzymatic processes are controlled, for example, by way of suitable process conditions, so that, in part or entirely, dinitrogen monoxide (N2O) is formed from the nitrogen-containing compounds of the nitrogen-containing substances.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for sample preparation and storage for use with bioreaction chips
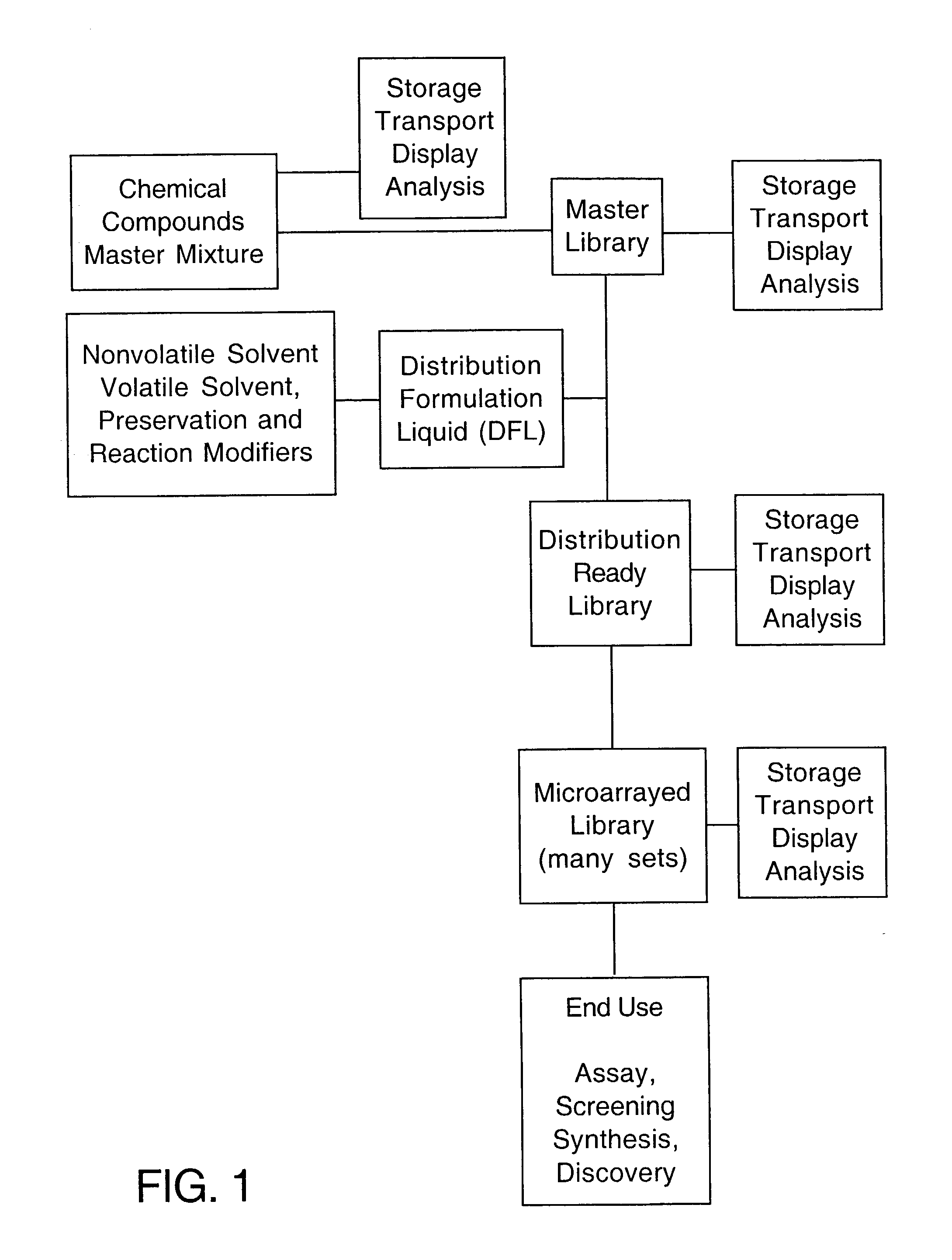
InactiveUS20030054564A1Reduce spot sizeMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesCell FractionHigh-Density Microarray
A method is defined wherein a Master Library of individual compounds, mixtures of compounds, or reaction pre-mixtures in solvent are prepared for storage and subsequent utilization in a Distribution-Ready Library by delivery of the master stock constituents into a distribution formulation liquid (DFL). The individual compounds within the Master Library can include peptides, proteins, organic chemicals, pharmaceutical compounds, RNA, DNA, or cell fractions. The Distribution-Ready Library can be maintained indefinitely in storage. At the time of manufacture or time of need, the Distribution-Ready Library is microarrayed onto substrates at high density, thereby creating numerous Library Microarrays that are identical replicates of the Master Library compound(s) in DFL at fixed and known positions on the substrate. The DFL has a defined surface tension to maintain the Master Library compound in a non-spreading, non-beading adherent microdot, or spot, at a fixed position on the substrate in a manner that is stable for extended periods of time.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA UNIV OF
Hepatocytes and hepatic non-parenchymal cells, and methods for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20180147242A1High purityEfficient mannerHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsCell FractionProgenitor
The present invention pertains to hepatocytes, liver progenitor cells, cholangiocytes, liver sinusoidal endothelial progenitor cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic stellate progenitor cells, hepatic stellate cells, and liver cellular tissue models, as well as to methods for preparing these cells. The present invention also pertains to a cell fraction comprising liver progenitor cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial progenitor cells, or hepatic stellate progenitor cells. The present invention also pertains to a pharmaceutical composition or kit comprising the above-mentioned cells, a liver cellular tissue model, or a cell fraction. The present invention also pertains to: a method for screening liver disease treatment agents; a method for evaluating the hepatotoxicity of drugs, hepatocytes for infectious disease models, and a method for preparing the same; infectious disease model tissues and a method for preparing the same; as well as a method for screening infectious liver disease treatment agents.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Biological Scaffolds, Products Containing Biological Scaffolds and Methods of Using the Same
PendingUS20200078411A1FunctionalMaintenanceSkeletal disorderMammal material medical ingredientsBiologic scaffoldCell Fraction
The present disclosure provides biological scaffolds, methods for their synthesis and methods for their use. The biological scaffolds contain at least to components, the first, a mammalian cell platelet lysate and an adipose tissue-derived cell fraction (ATDCF) cell. Products that comprise the biological scaffold(s) may be a gel, a semi-solid or a solid substrate upon which at least one surface of the substrate is contacted with the biological scaffold to form a biocompatible material. The biological scaffold and biological scaffold containing products, can find utility in a vast range of medical device technologies and may be used for therapeutic purposes or for performing experimentation to test various pharmacological agents in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:OBATALA SCI INC
Expansion and use of expanded nk cell fractions
Methods of expanding a natural killer (NK) cell fraction for transplantation into a subject are provided, and particularly, methods for providing transplantable NK cell fractions and protocols for their use, which can be employed for applications in cell transplants and infusions for treatment of cancer and other disease.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Use of adipose-tissue cell fractions for post-irradiation tissue regeneration
ActiveUS8173119B2Low elastic modulusDelayed healingBiocideSkeletal disorderCell FractionCutaneous wound
The present invention concerns the use of cells derived from the cellular fraction of the vascular stroma of the extramedullary adipose tissue to promote the regeneration of tissue following lesions caused by irradiation. More specifically, the use according to the invention aims to prepare a drug for promoting regeneration of the skin, and in particular to repair the cutaneous wounds caused by irradiation.
Owner:INSTITUT DE RADIOPROTECTION & DE SURETE NUCLEAIRE
Method of preparing an osteogenic bone graft
The present disclosure is directed to a method of preparing an osteogenic bone graft. The method includes introducing an anticoagulant compound into a volume of cellular material including a mononuclear cell population from the intramedullary canal of a long bone; collecting an effluent including the volume of cellular material containing the anticoagulant compound at a collection point; separating a concentrated cell fraction from the effluent, the concentrated cell fraction including the mononuclear cell population and the anticoagulant compound; and preparing an osteogenic bone graft from the concentrated cell fraction.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Optimized and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord
ActiveUS9546353B2Improve efficiencyReliable efficacyCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsCell phenotypeCell Fraction
The present invention refers to an optimized and defined method for isolation and preservation of precursor cells from human umbilical cord. Besides being reproducible and 100% reliable, in terms of the number of samples processed, the method results in a high and defined number of precursor cells, being the majority obtained after a single adhesion and expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (thus granting cell phenotype), in a shorter time frame than what was previously described in the state-of-the-art. With this method, it is possible to obtain, in 9 days, after direct freezing of a cell fraction, and after one expansion / multiplication phase ex vivo (end of P0) of the majority of the cells, about 8.6(±0.1)×105 cells / gram of processed umbilical cord. In turn, the characteristics of the cells allow, for example, after 35 days, obtaining an average of 7.7×1015 cells, with precursor phenotype, from 100% of processed umbilical cord samples. The method, because it is simple, robust and 100% reliable, can be performed under good manufacturing practices (GMP) in laboratories dedicated to cell therapy in humans. Furthermore, the method has applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and biotechnology areas.
Owner:LAB MEDINFAR PROD FARMS
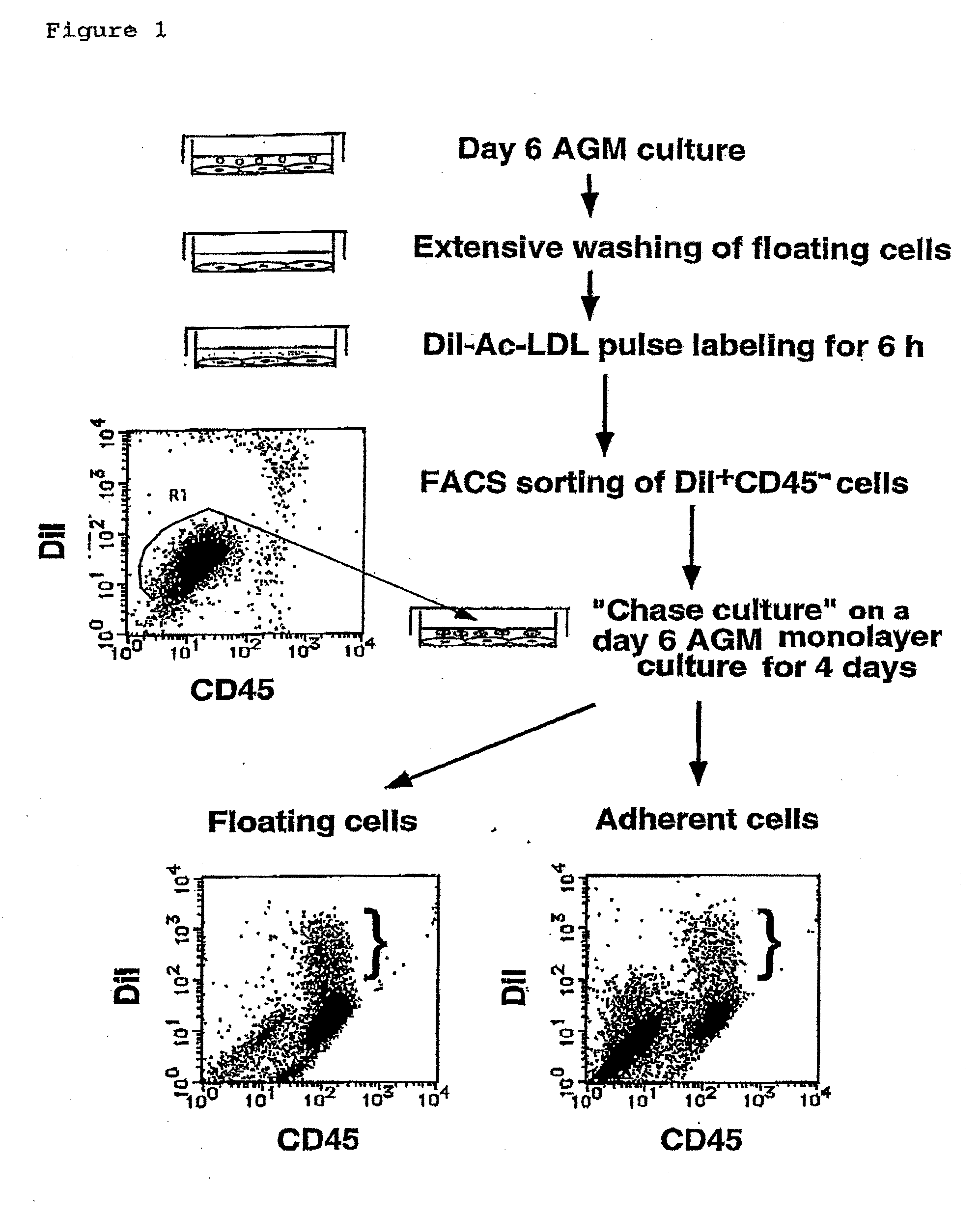
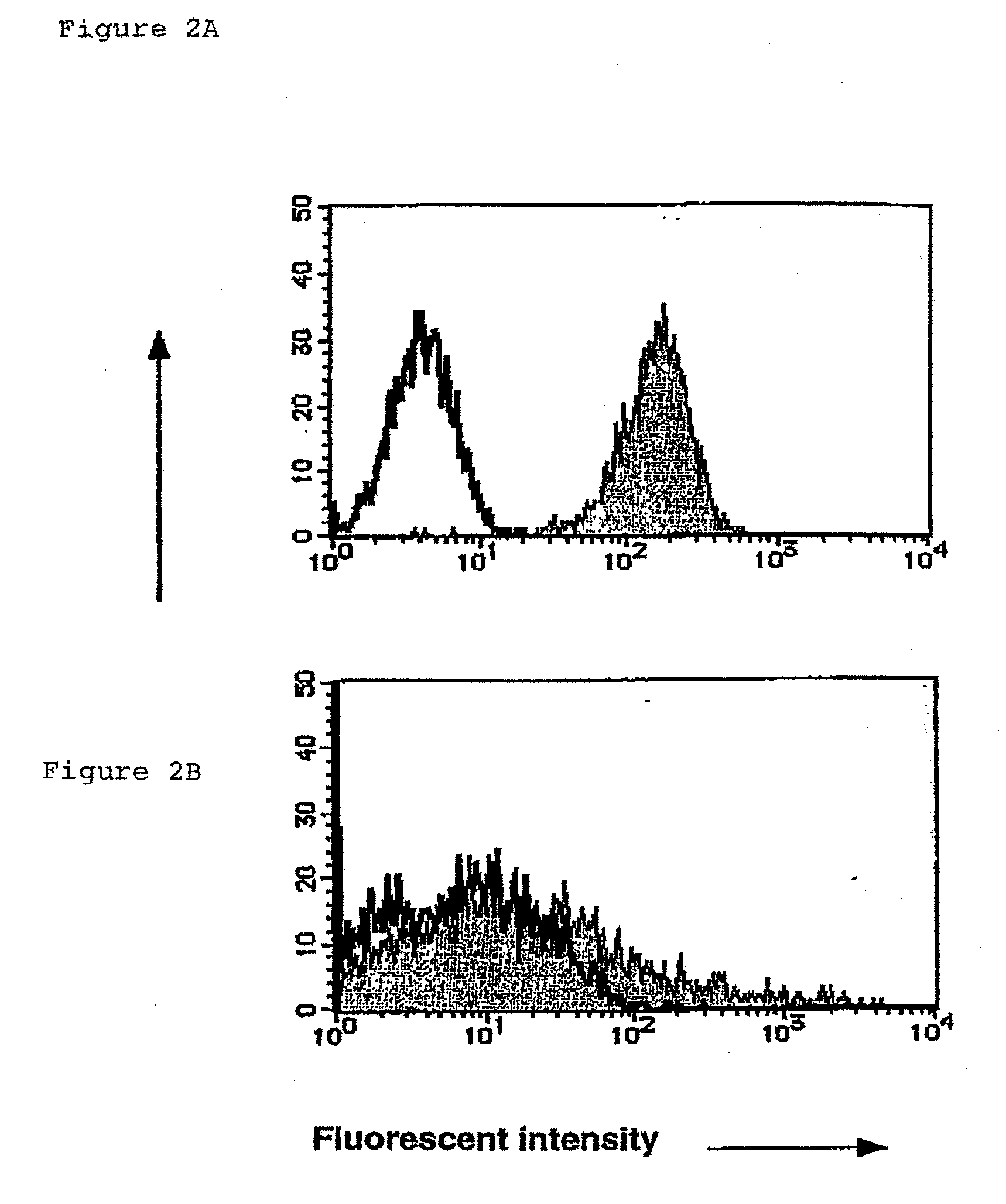
Method for Preparing Cell Fraction Containing Hemangioblasts
InactiveUS20090131634A1Facilitating purification and detectionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell FractionAntigen
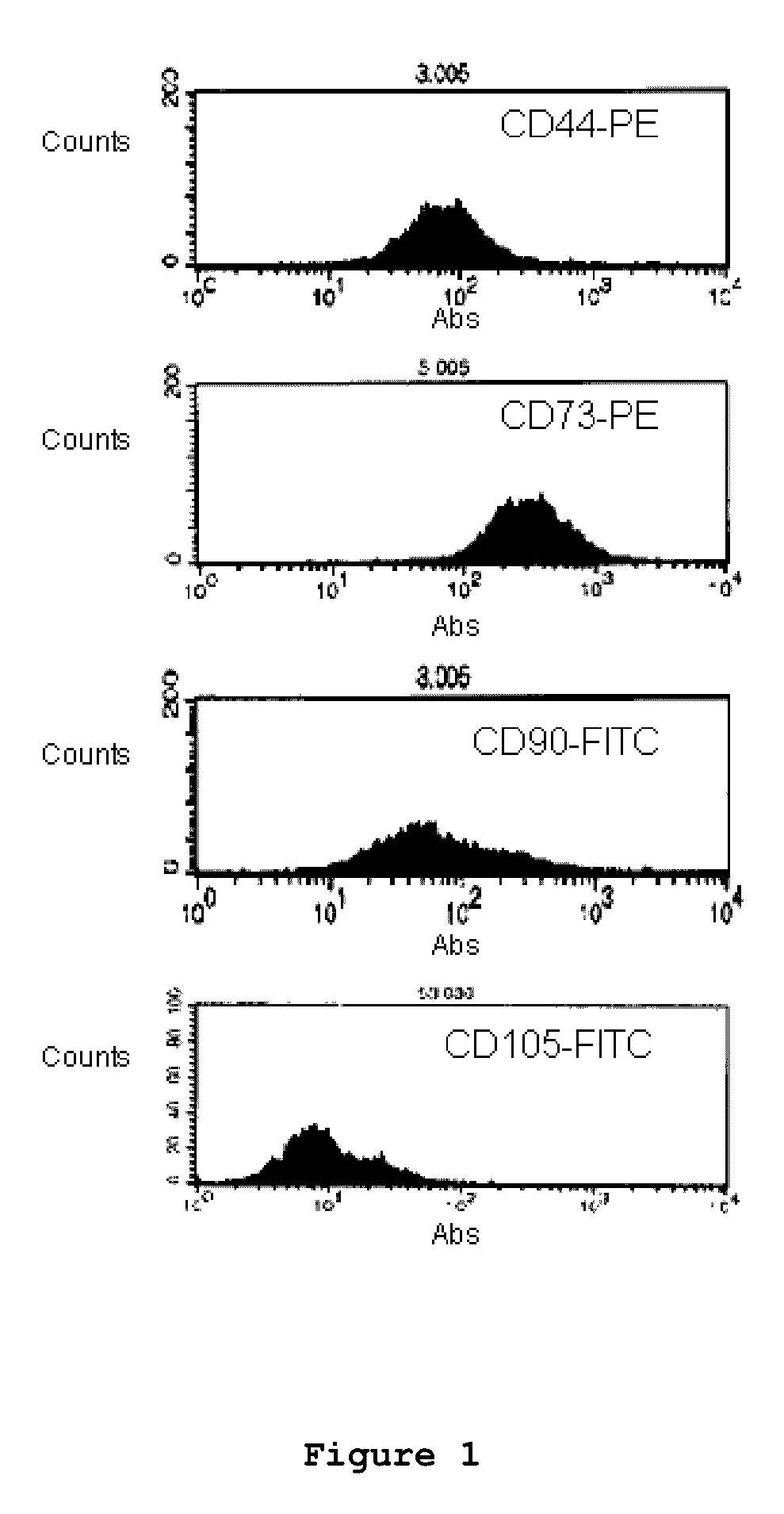
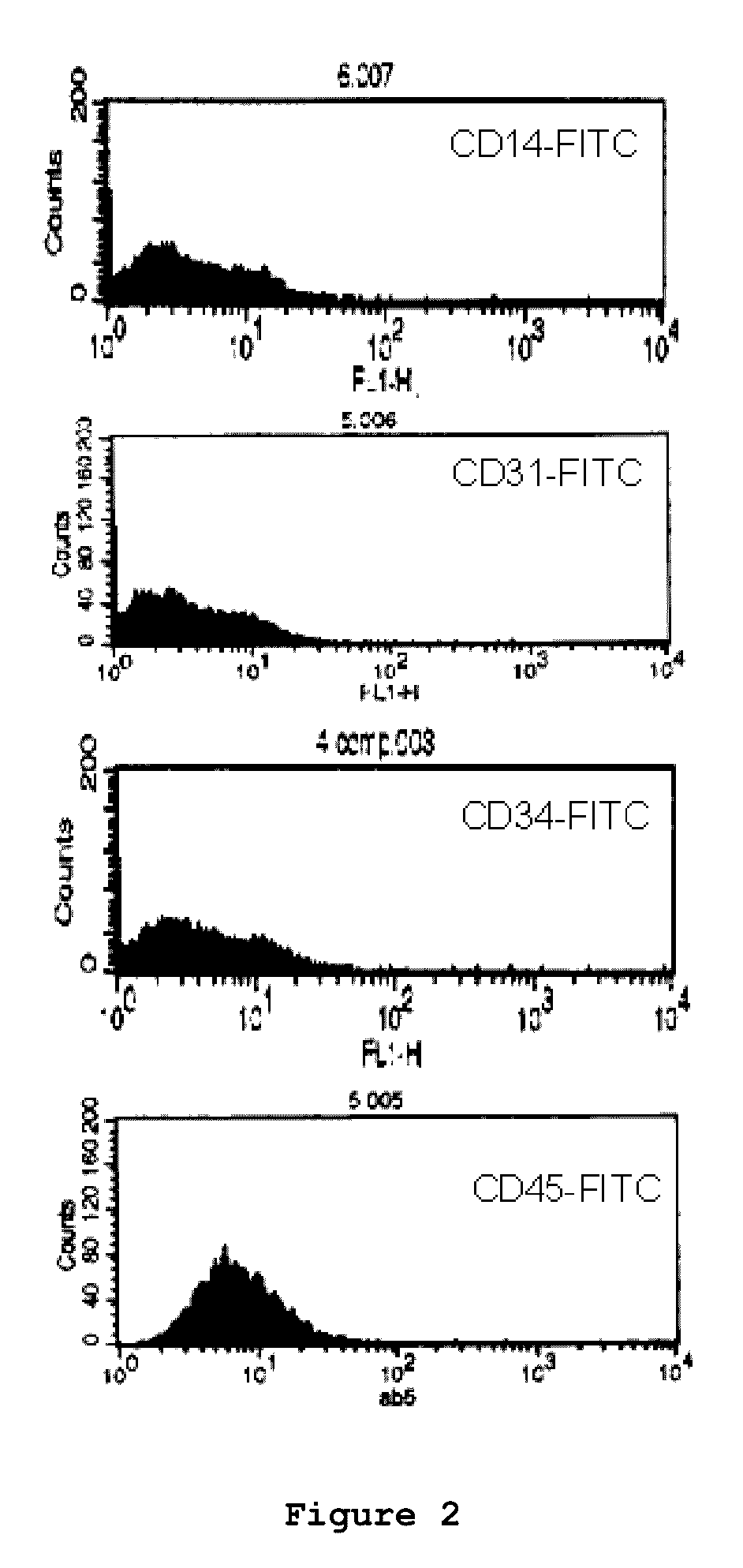
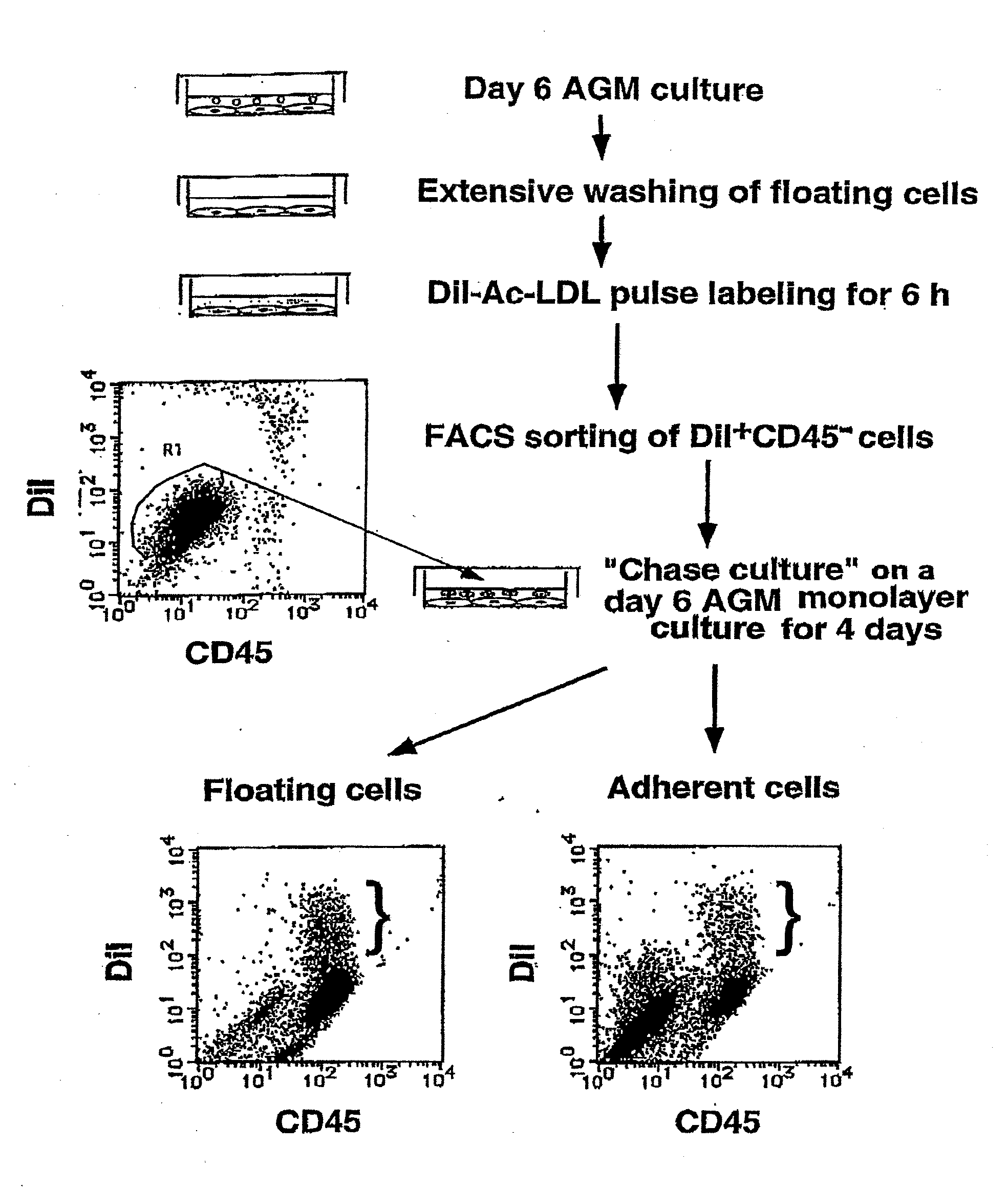
Mouse PCLP1 was identified by expression cloning with the use of a monoclonal antibody against a surface antigen of a cell line derived from mouse AGM. By fractionating PCLP1-positive / CD45-negative cells and culturing them in vitro, it was clarified that these cells differentiate into endothelial-like cells, angioblast-like cells, and hematopoietic cells. By transferring the PCLP1-positive / CD45-negative cells into a mouse defective in the hematopoietic function, the hematopoietic system was reconstructed over a long period of time. These facts indicate that the PCLP1-positive / CD45-negative cells contain mammalian hemangioblasts capable of expressing the activity as long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells (LTR-HSC). The present invention provides a method for preparing a cell fraction containing hemangioblasts, the cell fraction prepared by the method, and use of this cell fraction.
Owner:TOUDAITLO LTD
Whole blood analytic device and method therefor
Devices and methods are presented in which a plasma separation device with a first and second portion separates a blood containing fluid. Most preferably, the first portion produces a cell fraction and a plasma fraction, and the second portion captures the plasma fraction. A first actuator then fluidly isolates a portion of the plasma fraction within the second portion, and a second actuator moves the isolated portion of the plasma fraction from the second portion.
Owner:QUALIGEN INC
System for the internal qualitative and quantitative validation of marker indices
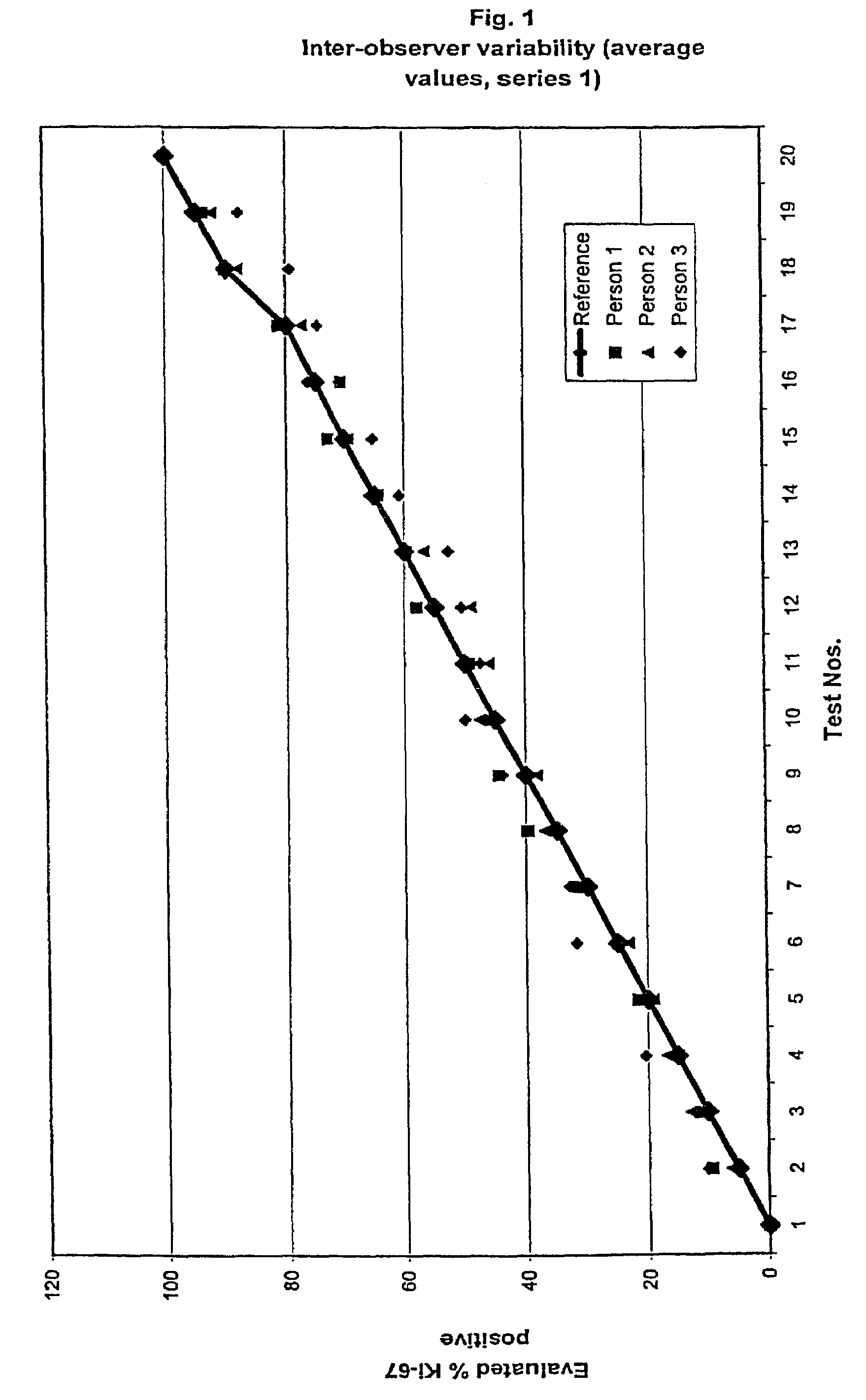
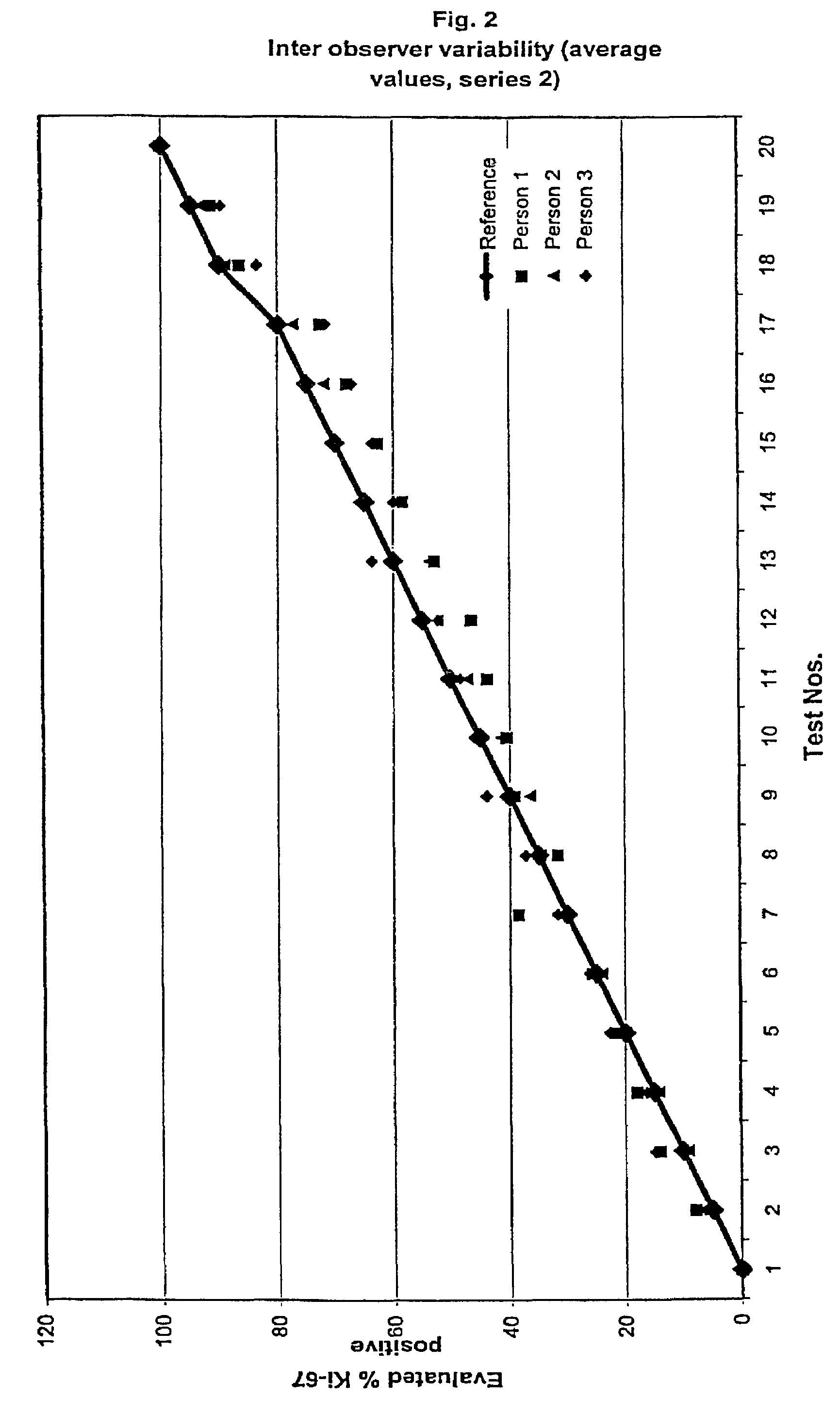
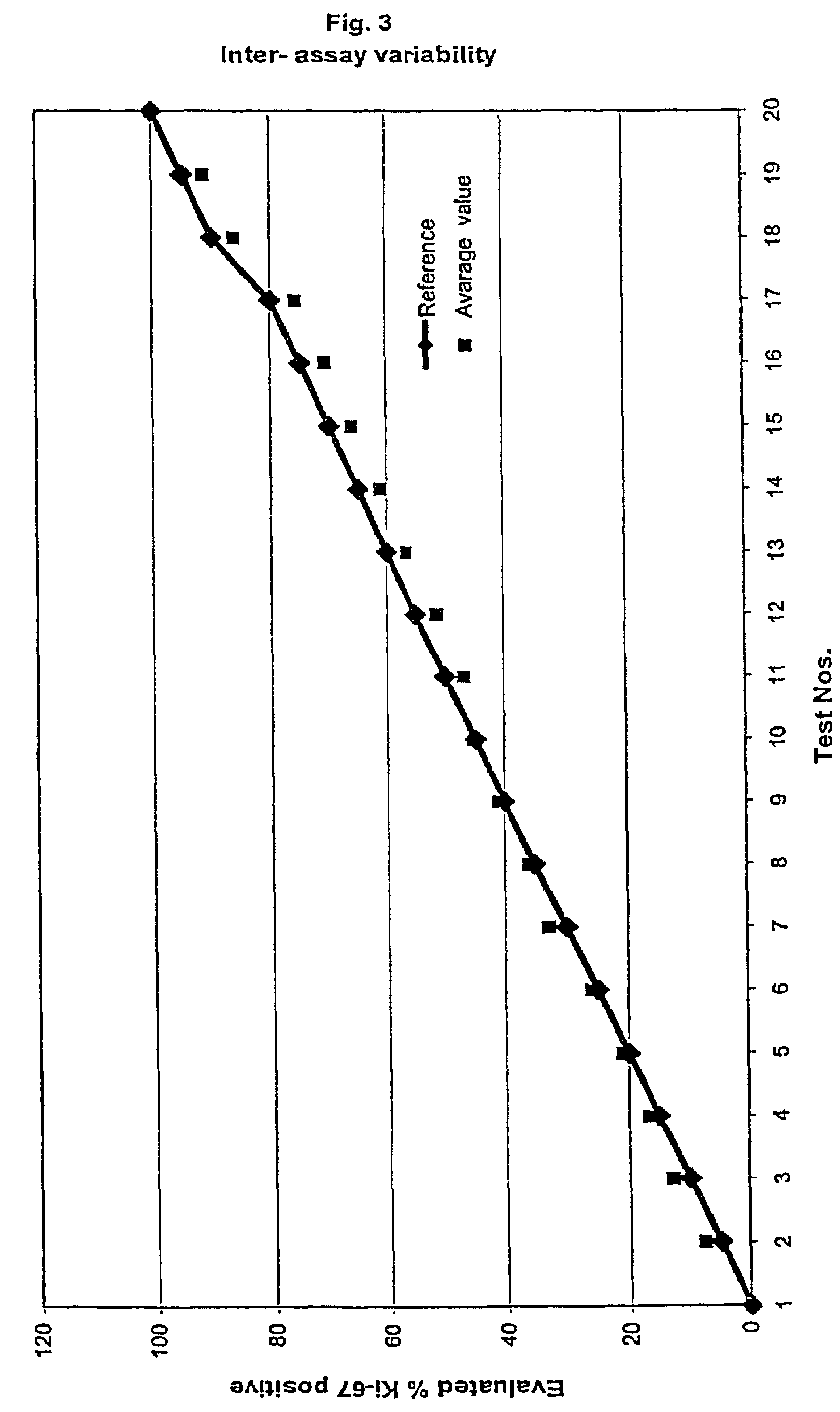
InactiveUS7560282B2Easy to useReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCell FractionMedical diagnosis
The present invention relates to the qualitative and quantitative validation of marker indices, especially for medical diagnosis and particularly for the determination of the growth fraction in a sample with antibodies against the Ki-67 protein. Diagnostic kit for the quantification of a cell fraction labeled by a marker for in vitro diagnosis, characterized in that a pseudo-tissue is used for the intra- and inter-assay standardization of the marker index.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Expansion and use of expanded nk cell fractions
Methods of expanding a natural killer (NK) cell fraction for transplantation into a subject are provided, and particularly, methods for providing transplantable NK cell fractions and protocols for their use, which can be employed for applications in cell transplants and infusions for treatment of cancer and other disease.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Automated Method For Leukocyte Collection From Whole Blood
ActiveUS20190167889A1Improve automated collection procedureOvercome disadvantagesOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesCell FractionWhite blood cell
The present invention relates to a method for separating lymphocytes and / or stem cells from whole blood in an automated blood separation system, wherein the quality of the collected lymphocytes and / or stem cells fractions is increased and the cell collection procedure is further automated by use of an optical sensor comprised in a detector device to measure turbidity and colour in the claimed method and in a cell separator, which can be used to perform the claimed method. The method of the invention is particularly useful to collect lymphocytes and / or stem cells fractions from whole blood, wherein the contamination of the collected cell fractions by platelets, red blood cells and granulocytes is reduced.
Owner:FRESENIUS KABI DEUT GMBH
Method for collecting nucleated red blood cells via density-gradient centrifugation utilizing changes in blood cell density
ActiveUS9334477B2Efficient ConcentrationReduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell FractionRed blood cell
Method for concentrating and collecting small quantities of fetal nucleated red blood cells contained in the maternal blood. The method for concentrating and collecting nucleated red blood cells from the maternal blood comprises: (i) subjecting the maternal blood to a first density-gradient centrifugation and collecting a cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells; (ii) treating the cell fraction containing nucleated red blood cells so as to selectively changes the density of the nucleated red blood cells from that of the white blood cells; and (iii) subjecting the treated cell fraction containing the nucleated red blood cells to a second density-gradient centrifugation so as to collect a fraction containing nucleated red blood cells.
Owner:JAPAN ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +2
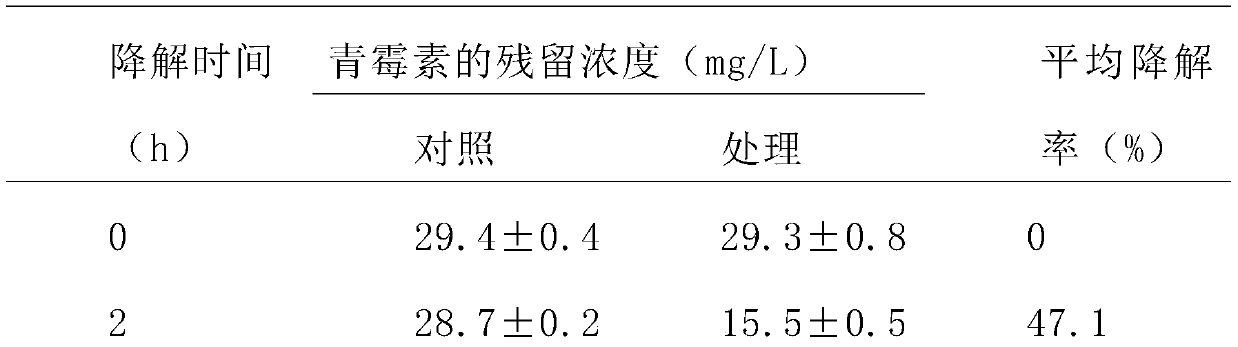
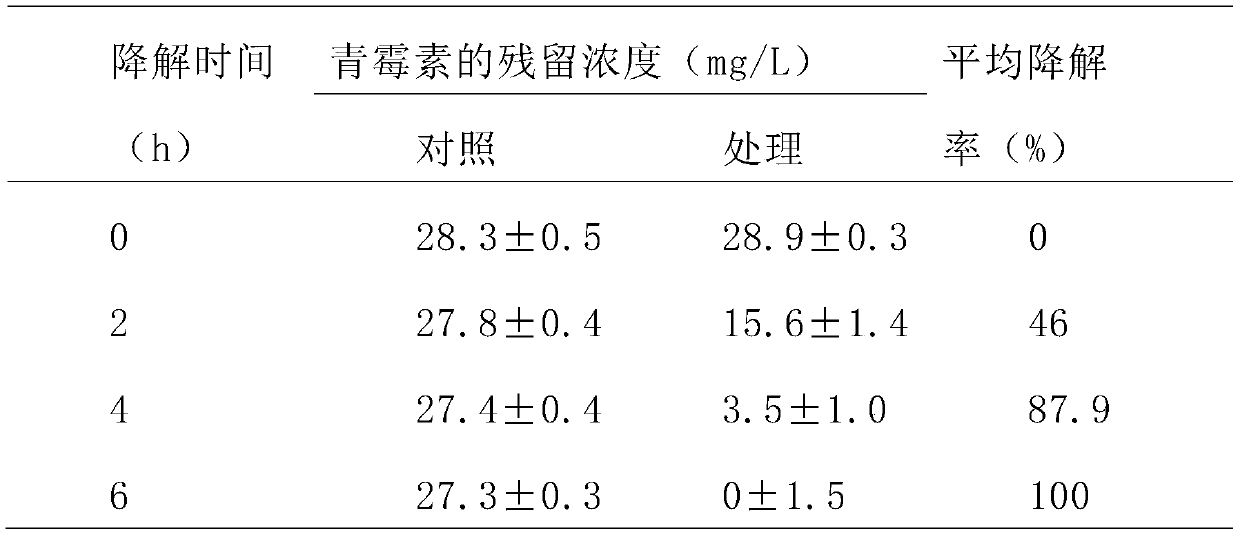
Phagocytosis capable of degrading penicillin, cell fractions and compositions thereof
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com