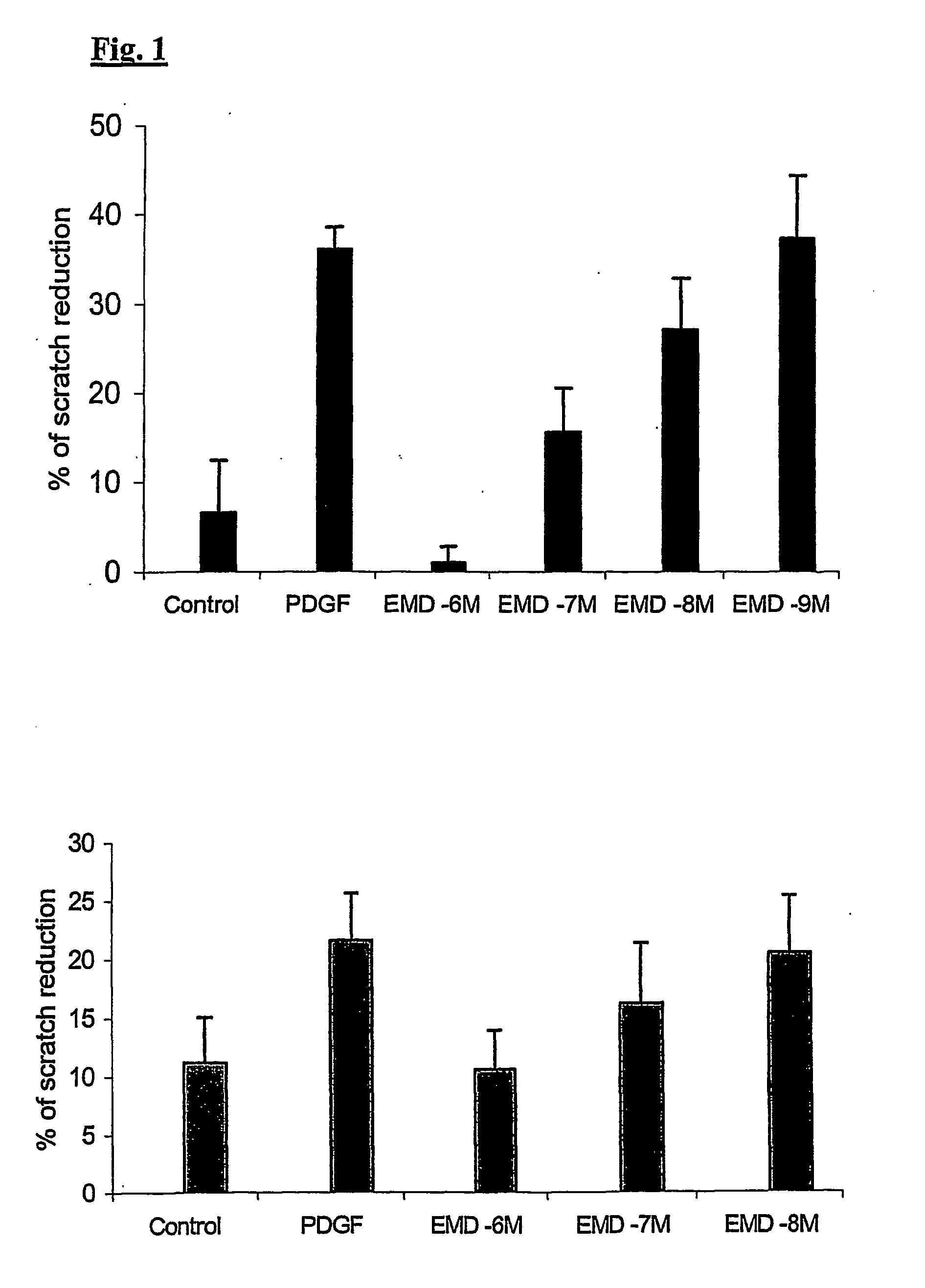
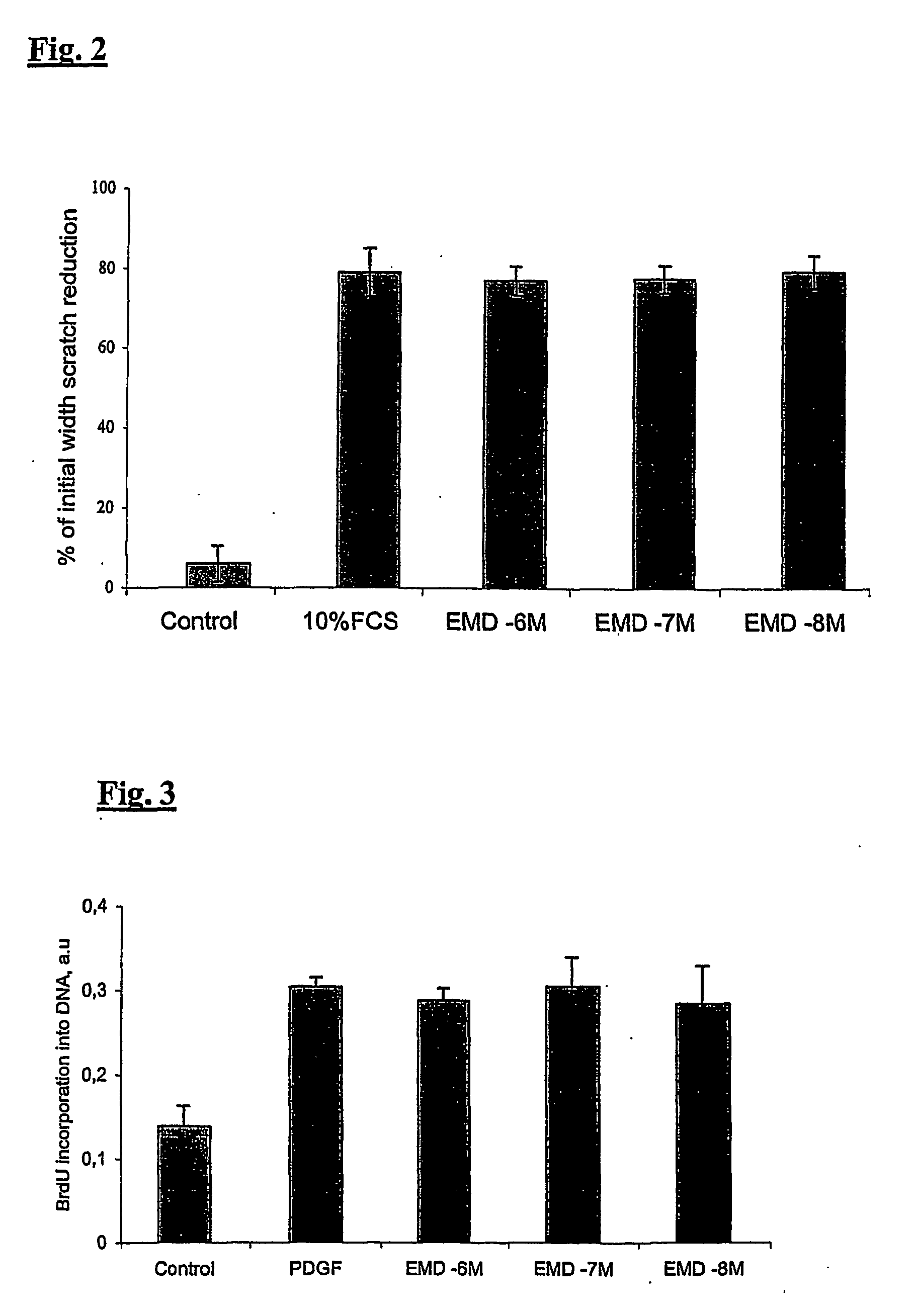
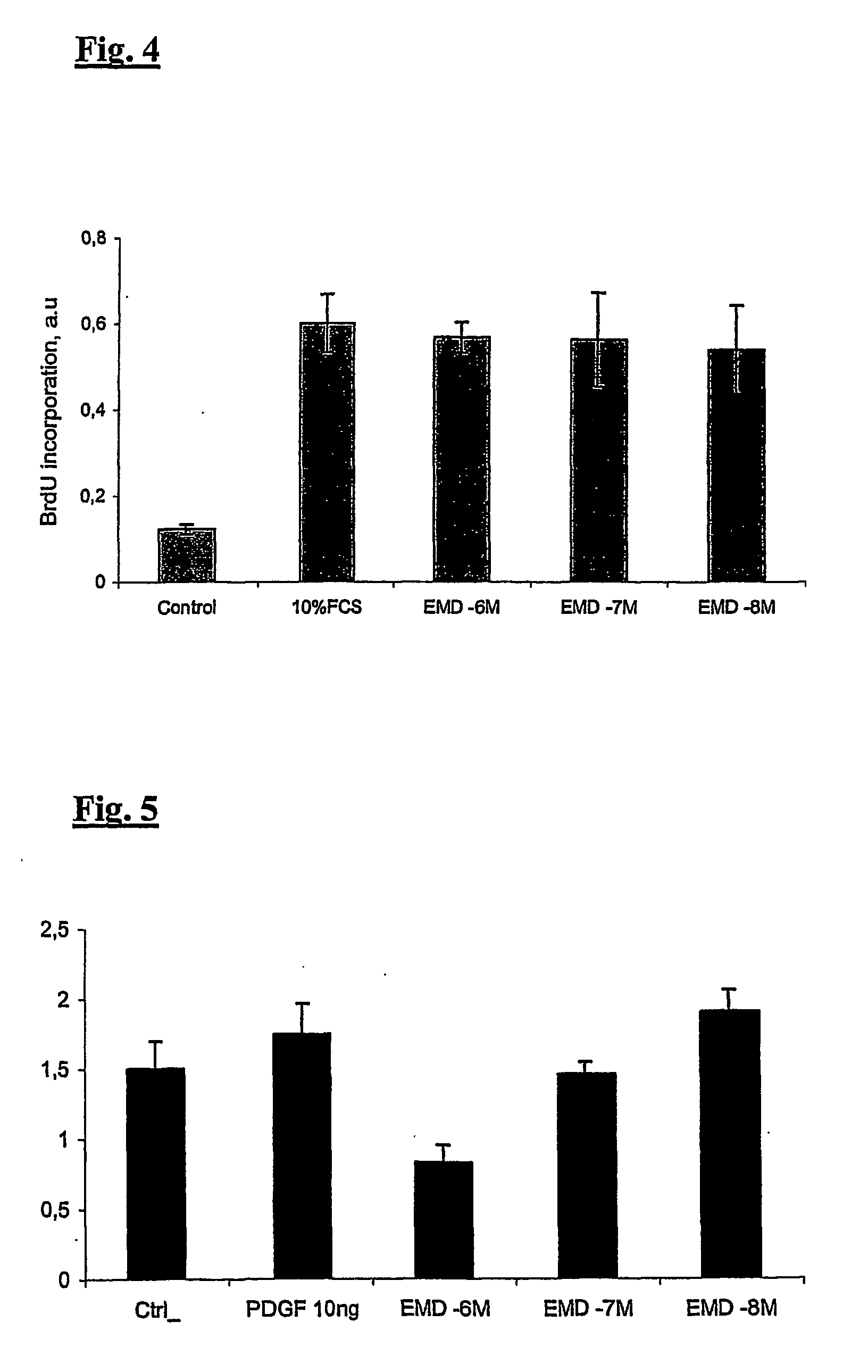
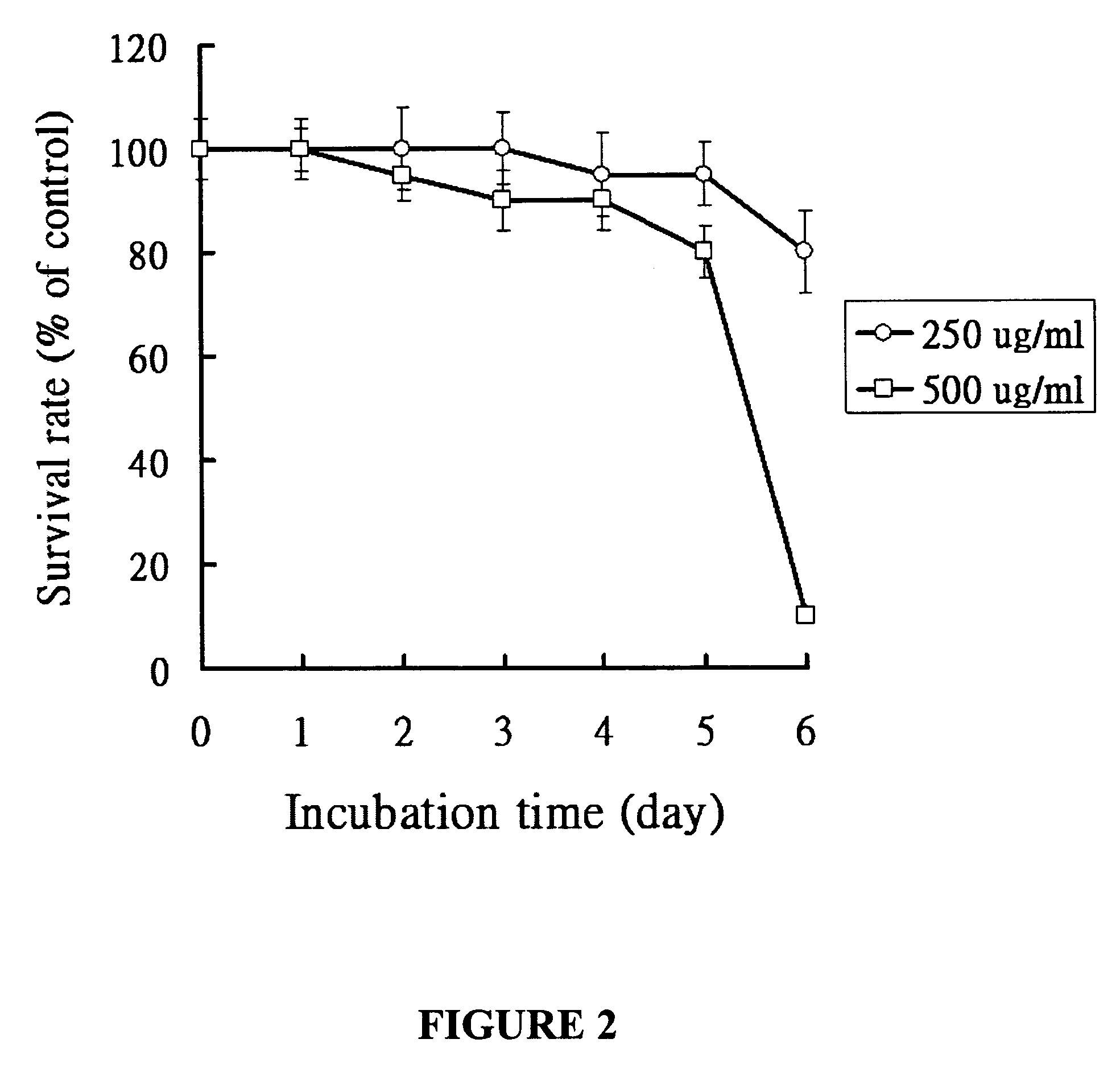
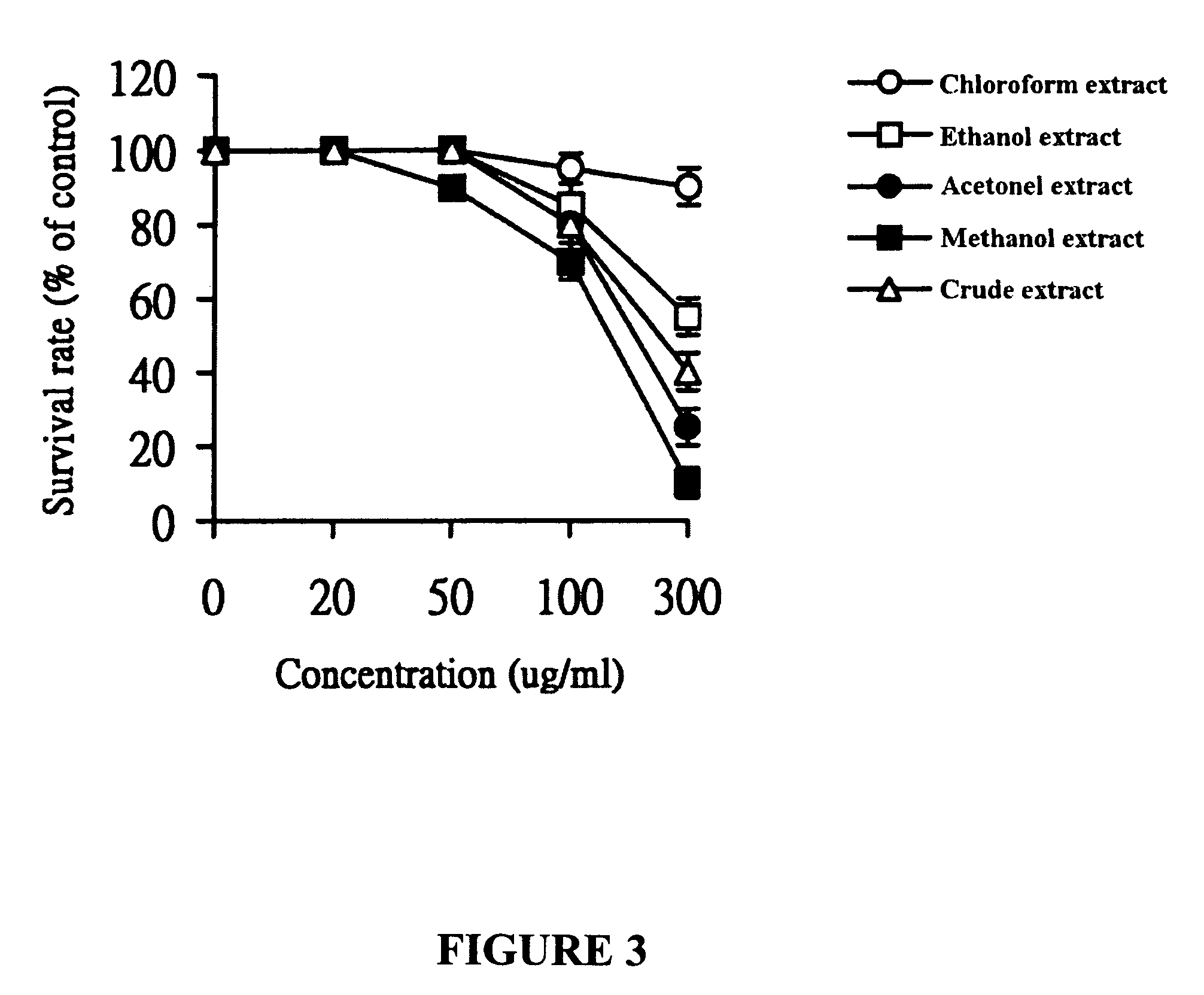
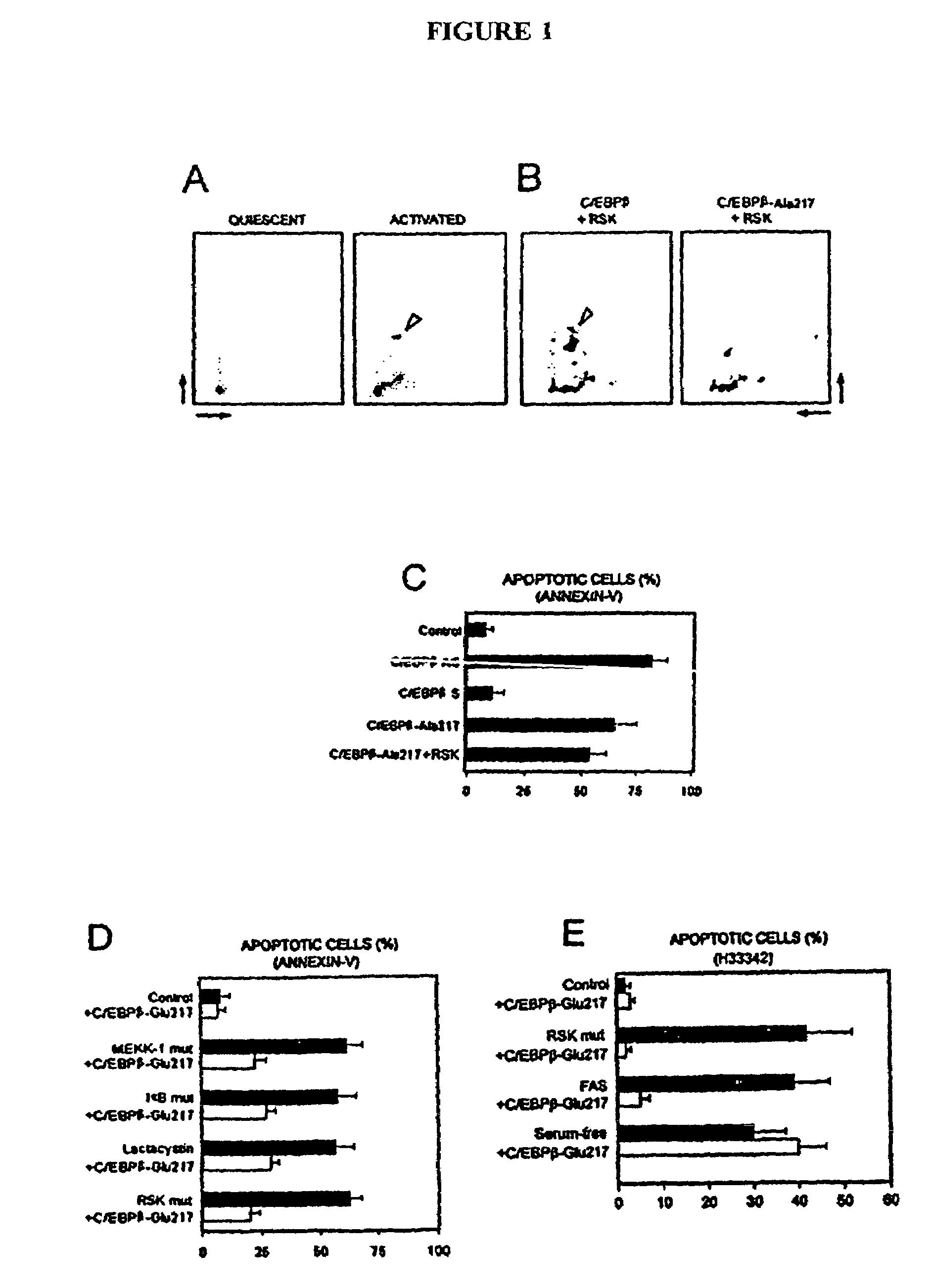
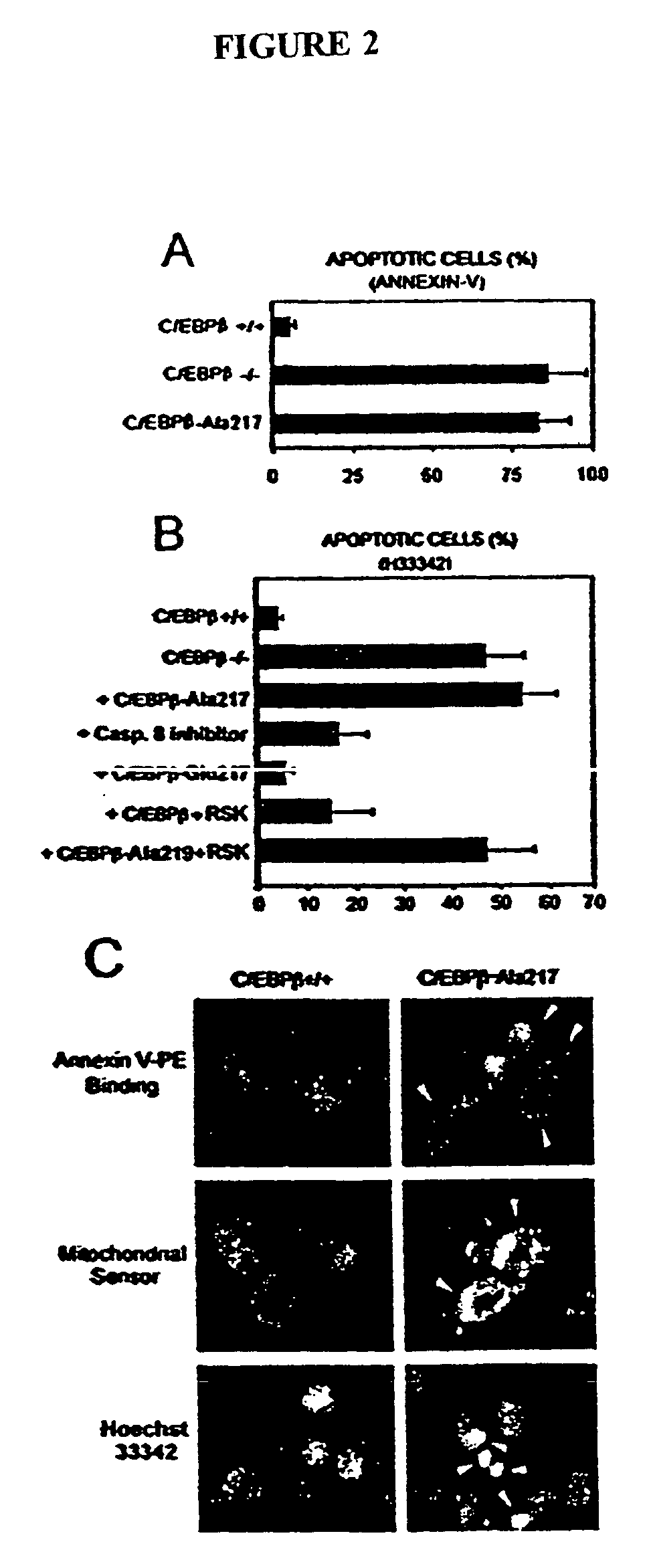
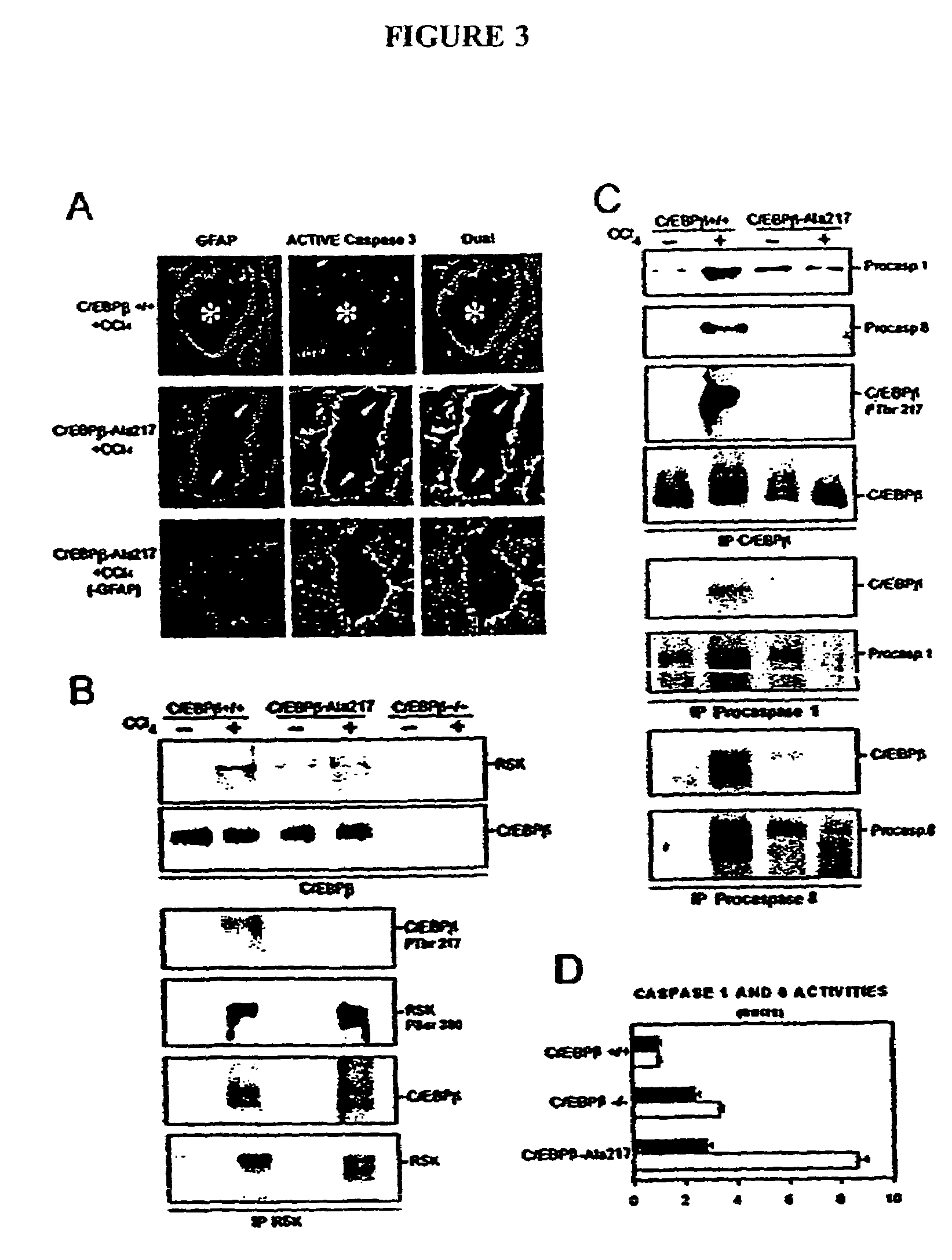
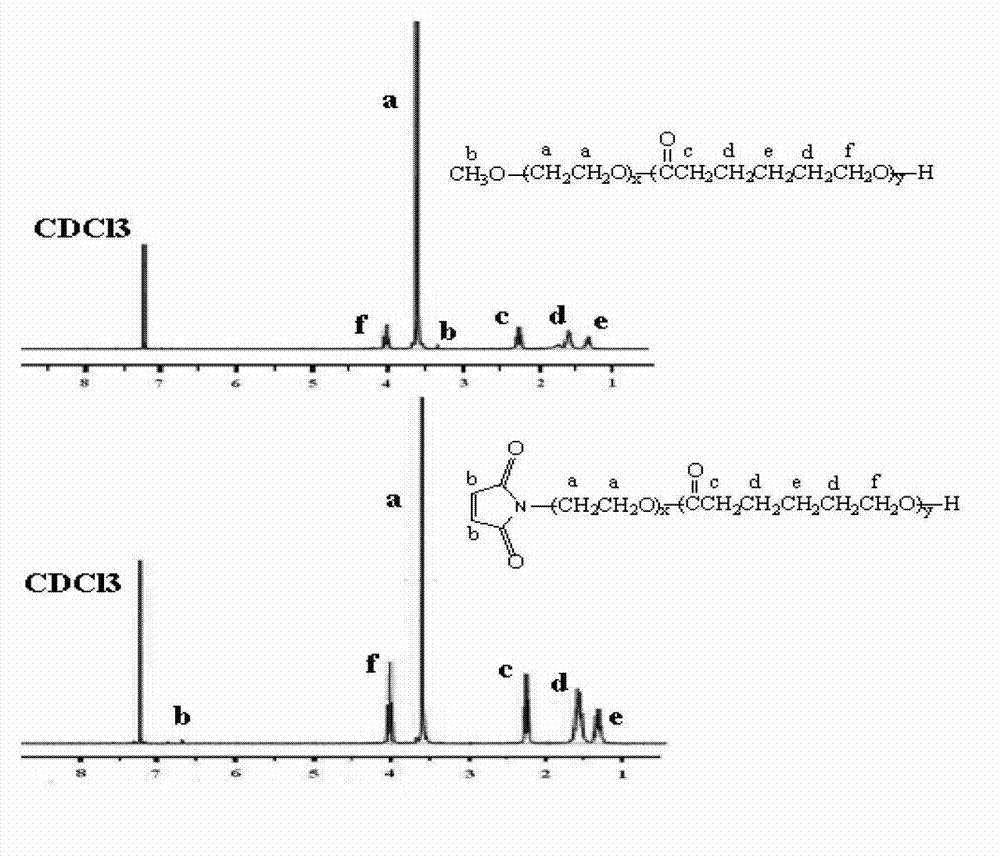
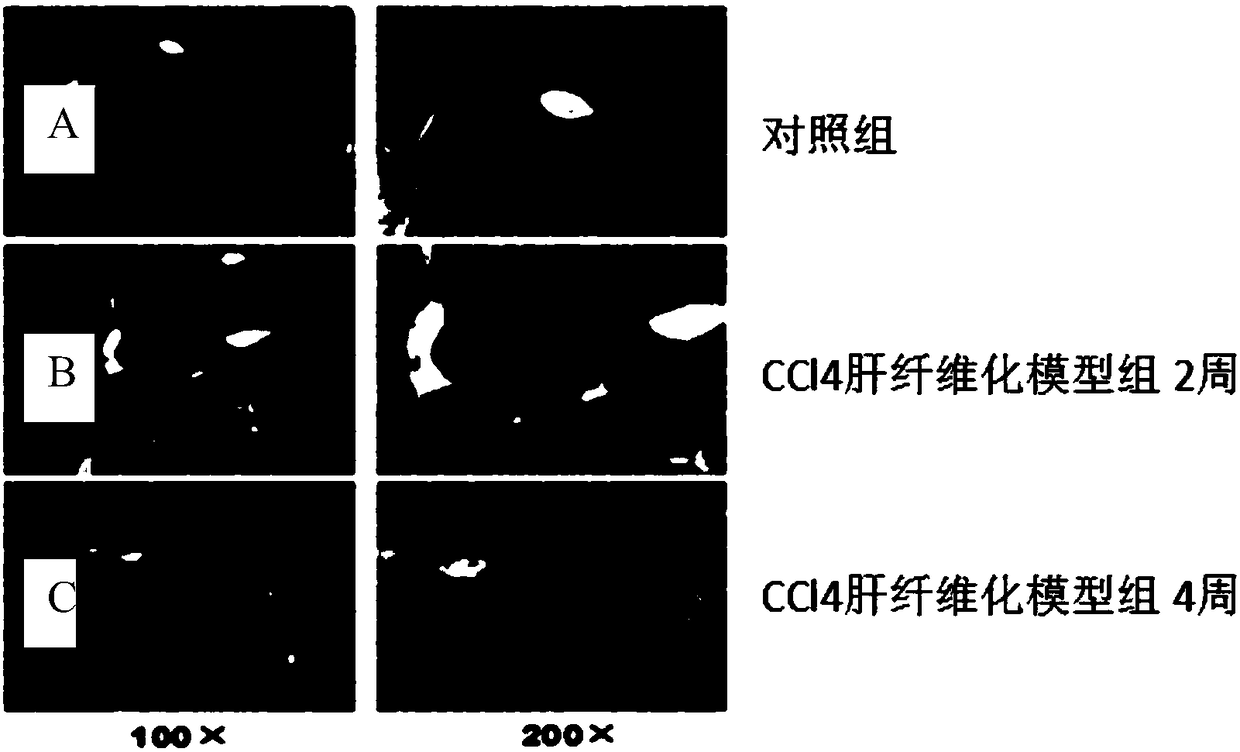
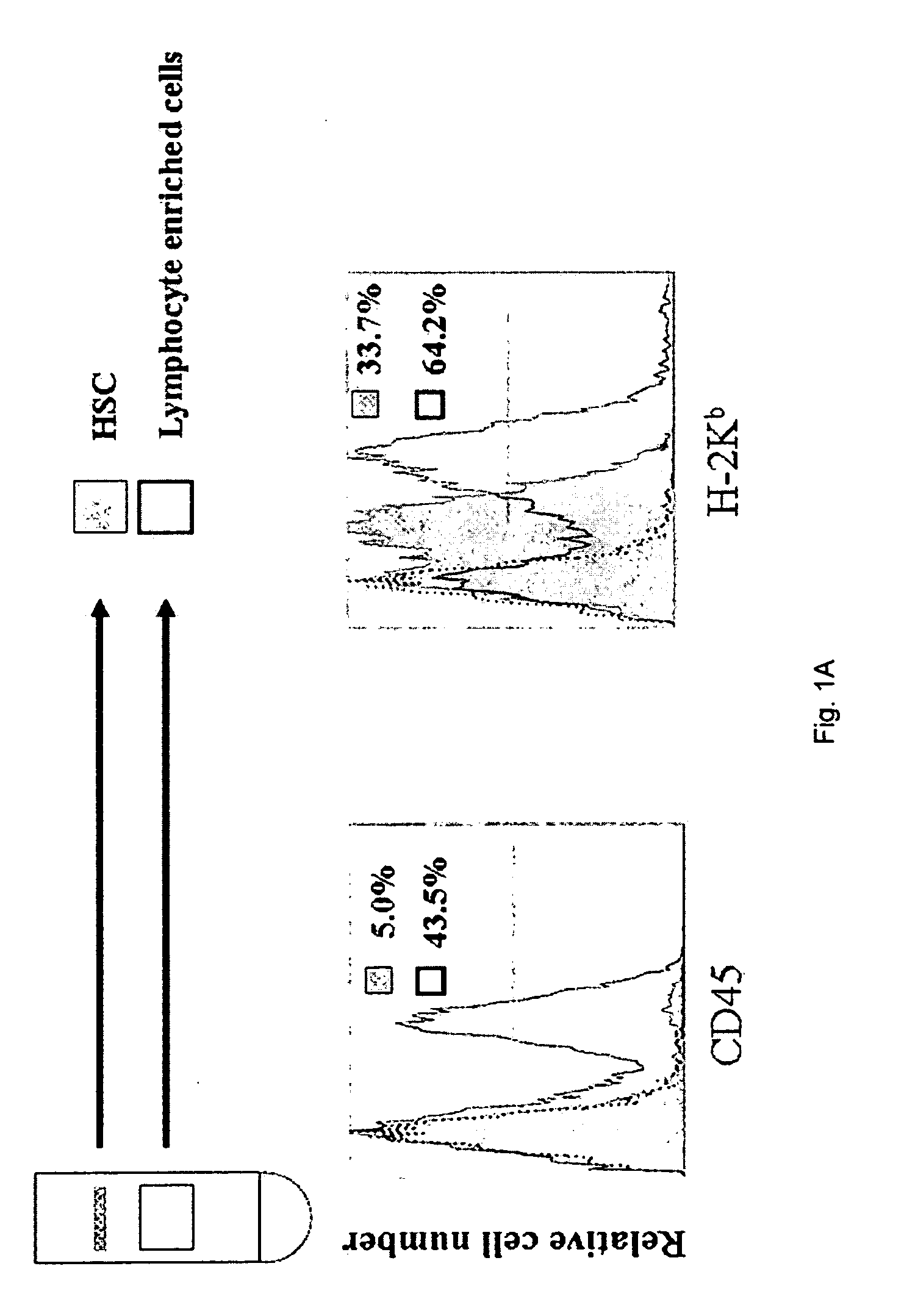
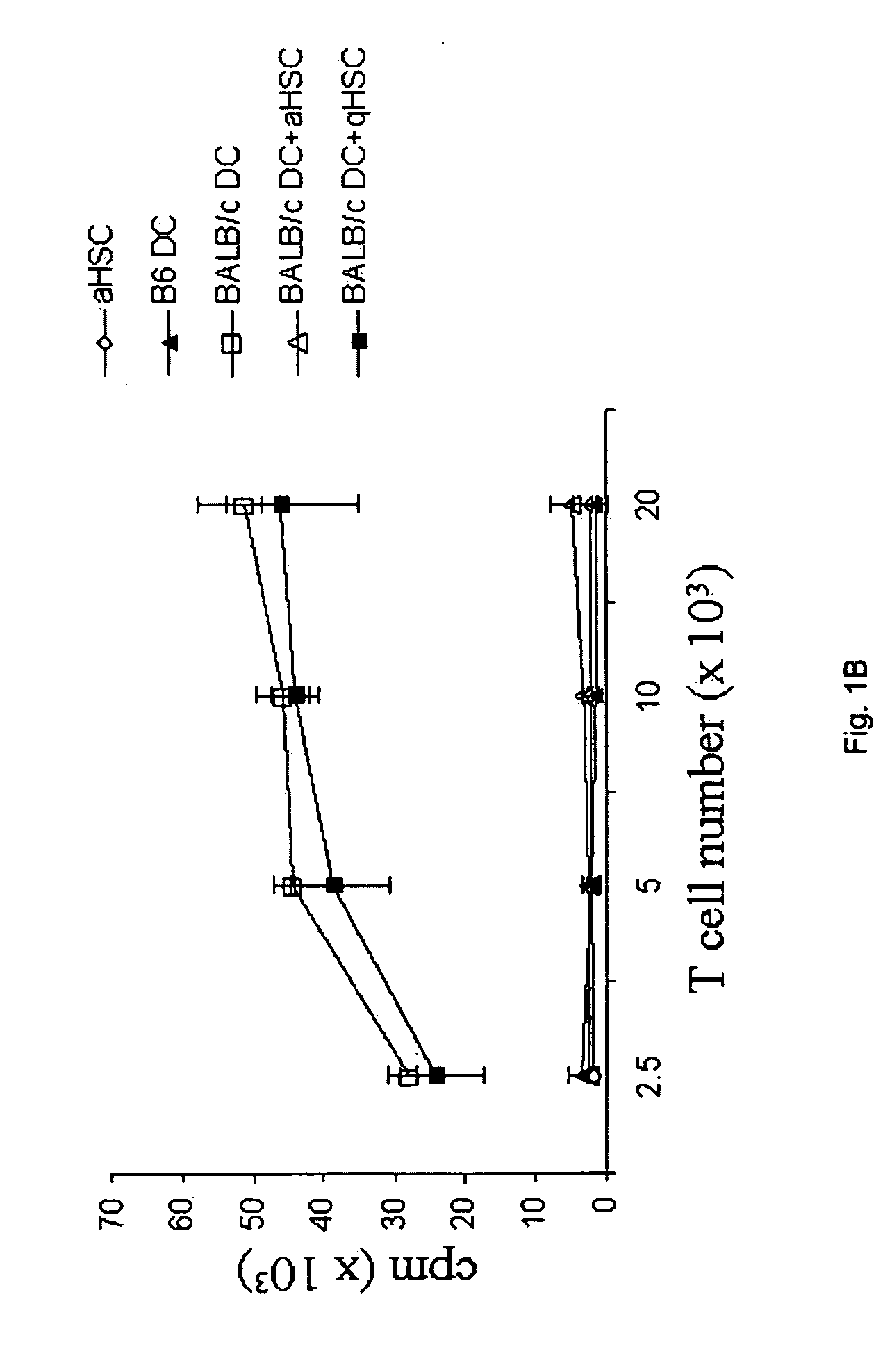
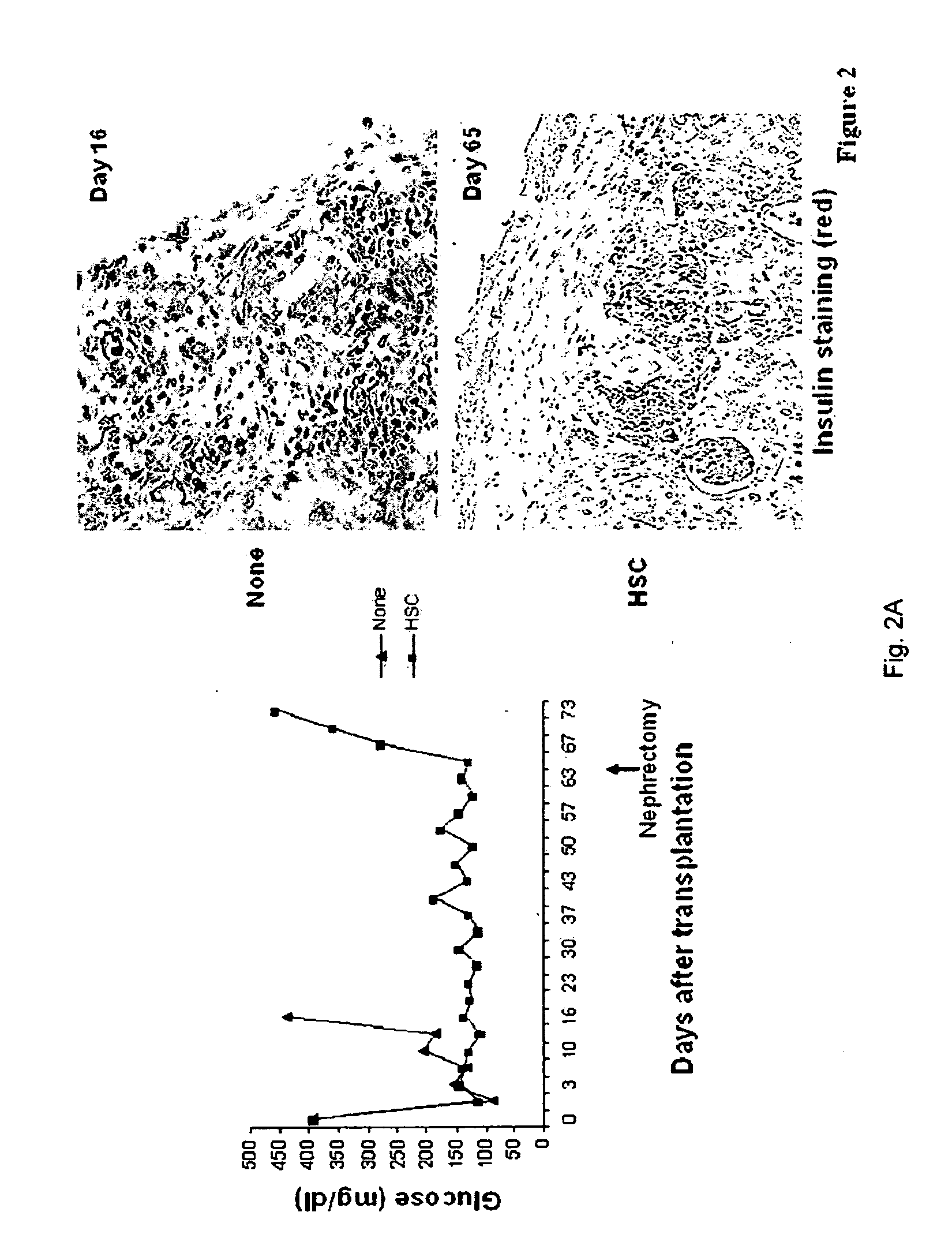
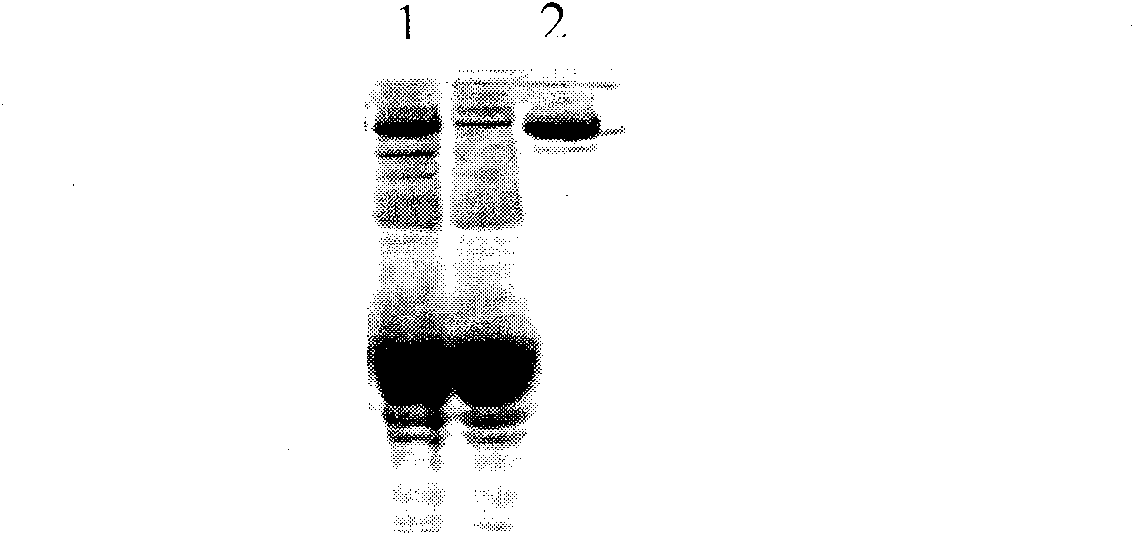
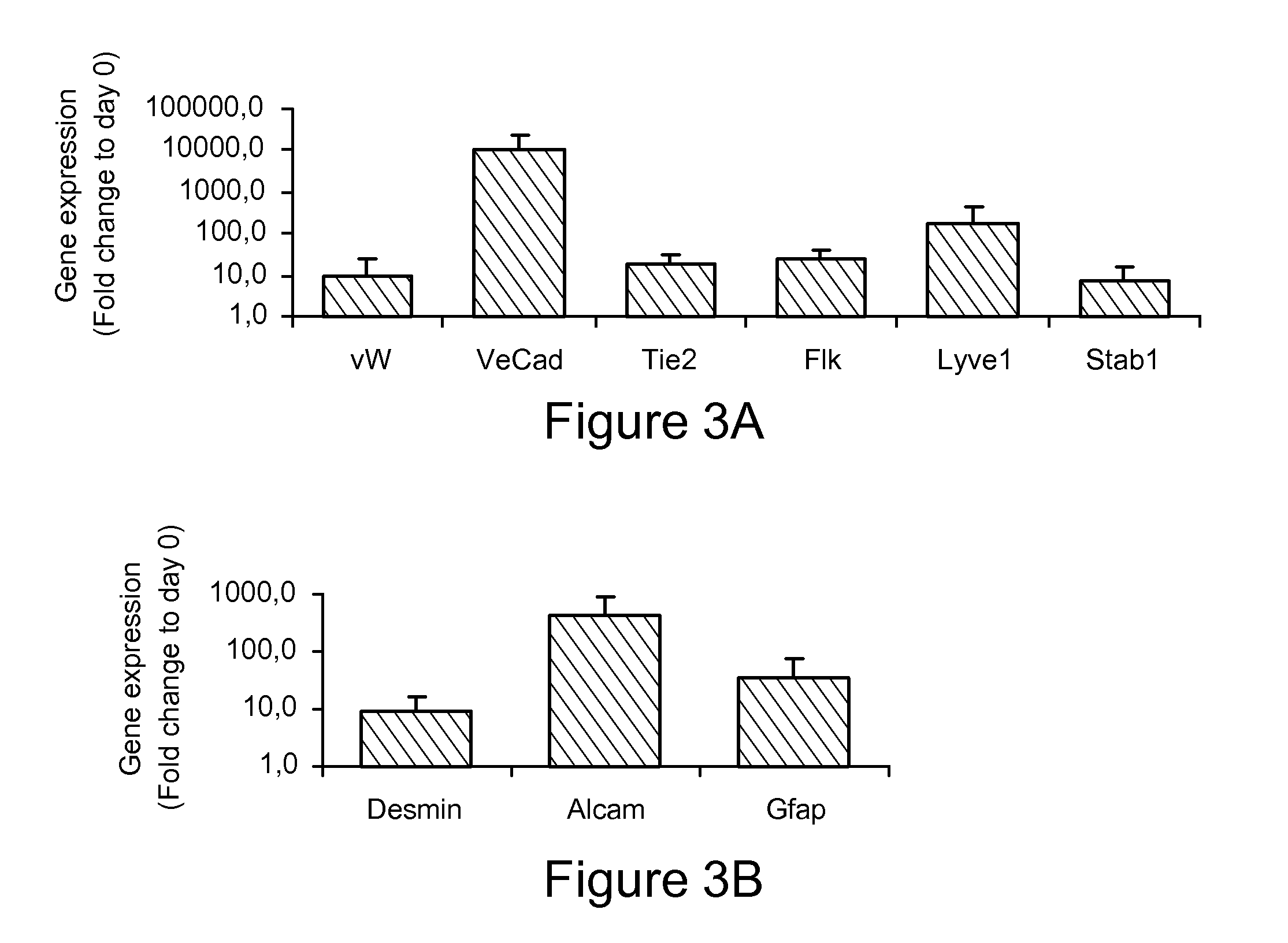
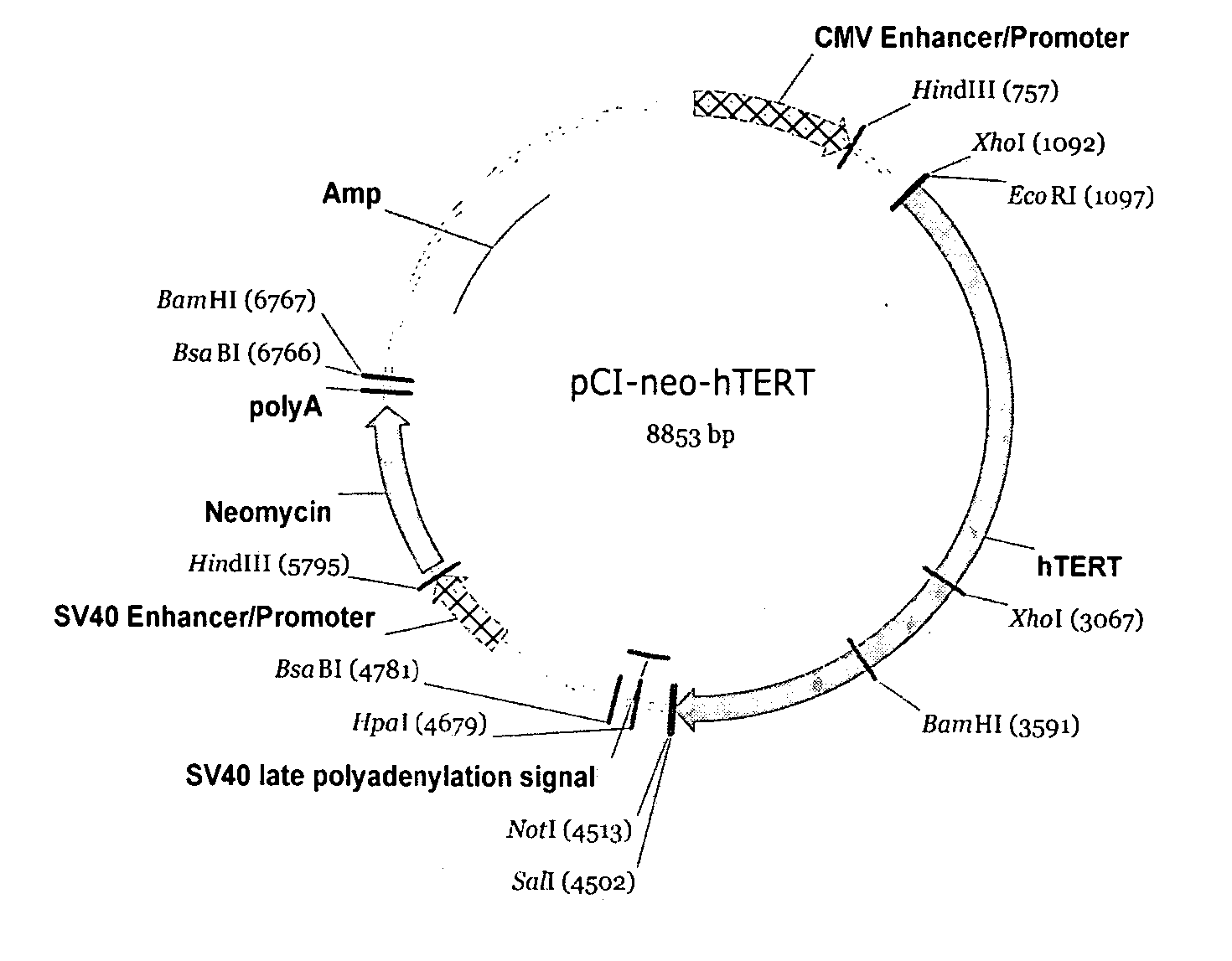
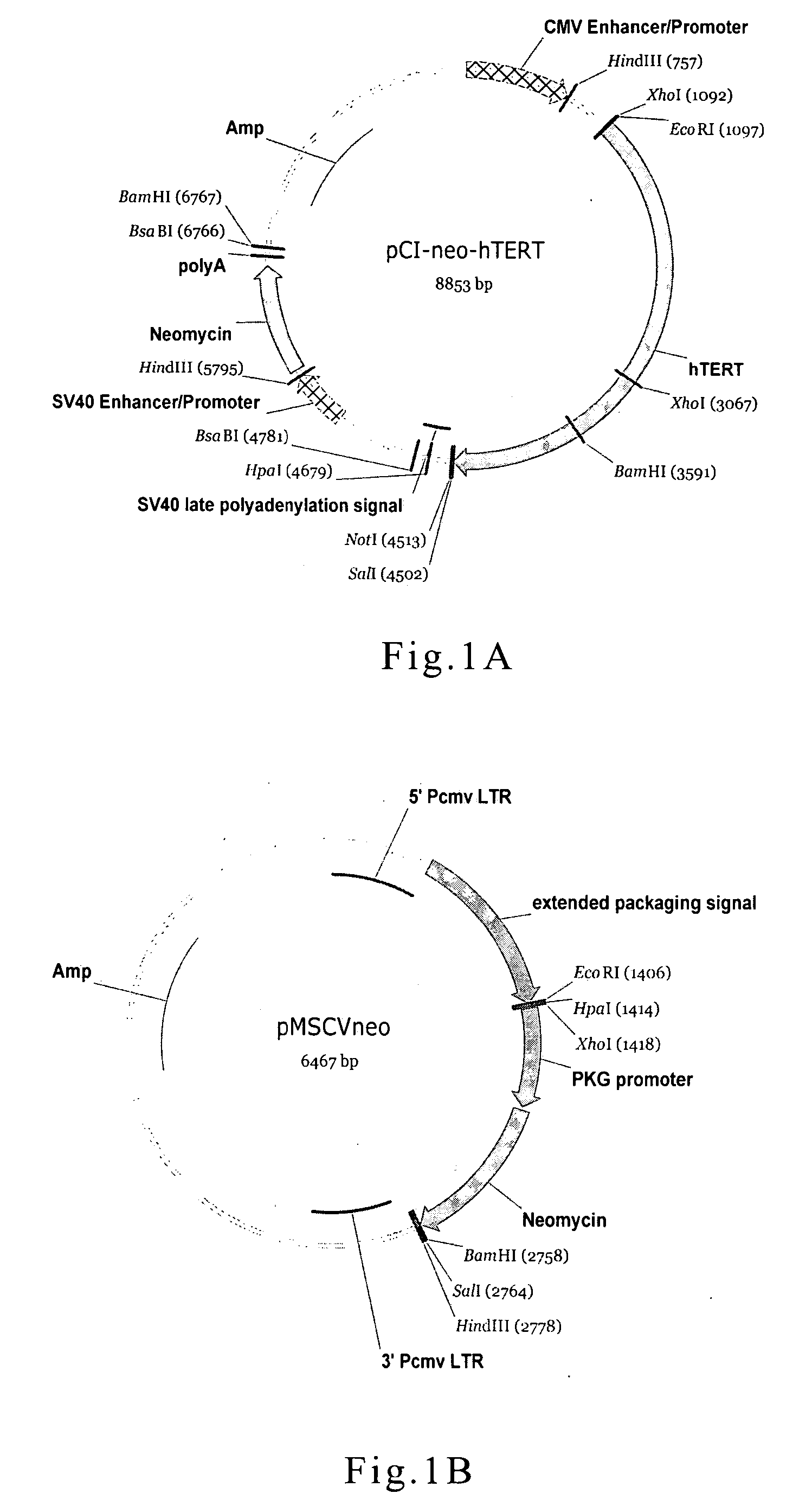
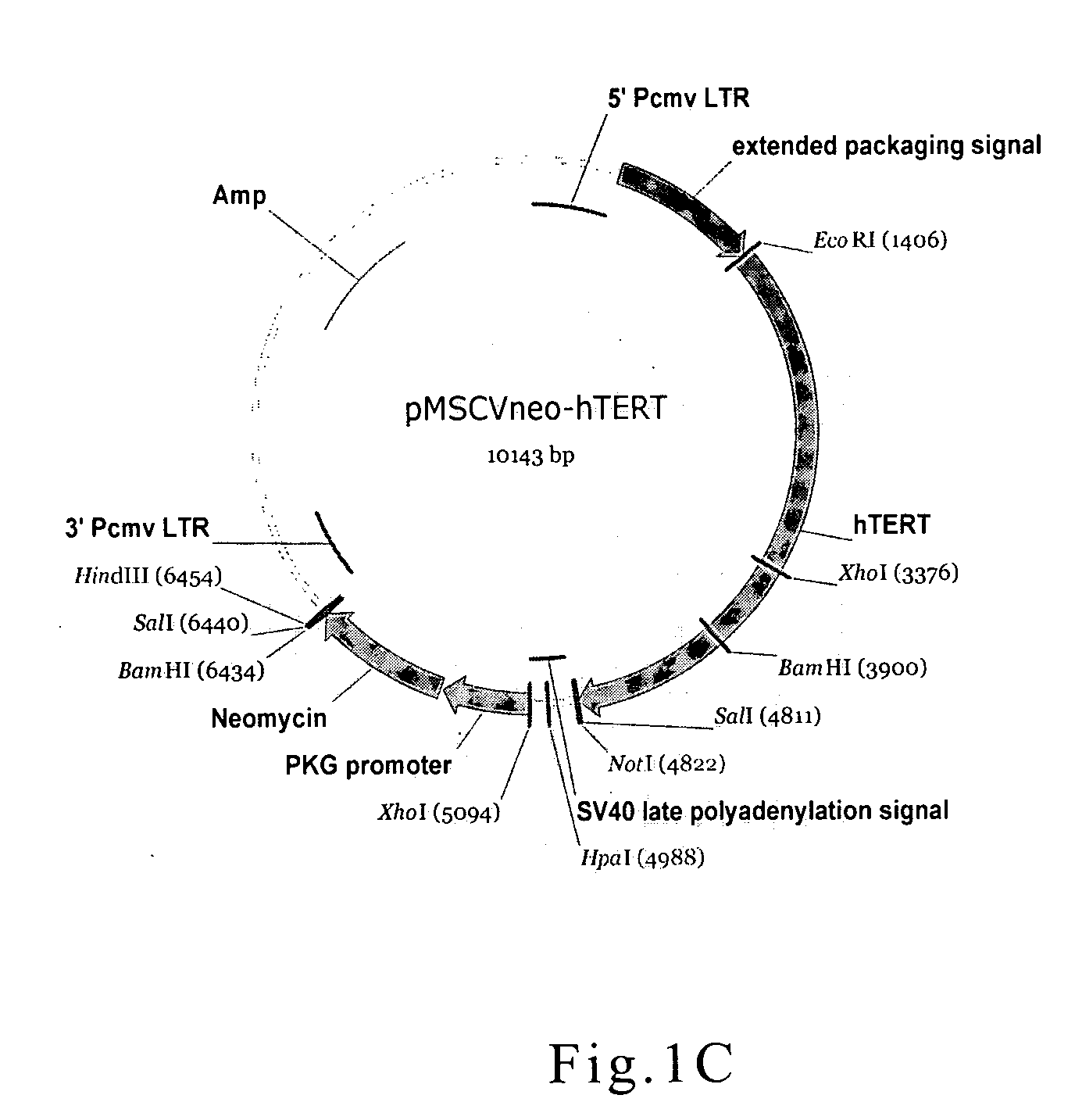
Patents
Literature
250 results about "Hepatic stellate cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hepatic stellate cells (here HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier lipocytes or fat-storing cells), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between the sinusoids and hepatocytes). The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis, which is the formation of scar tissue in response to liver damage.
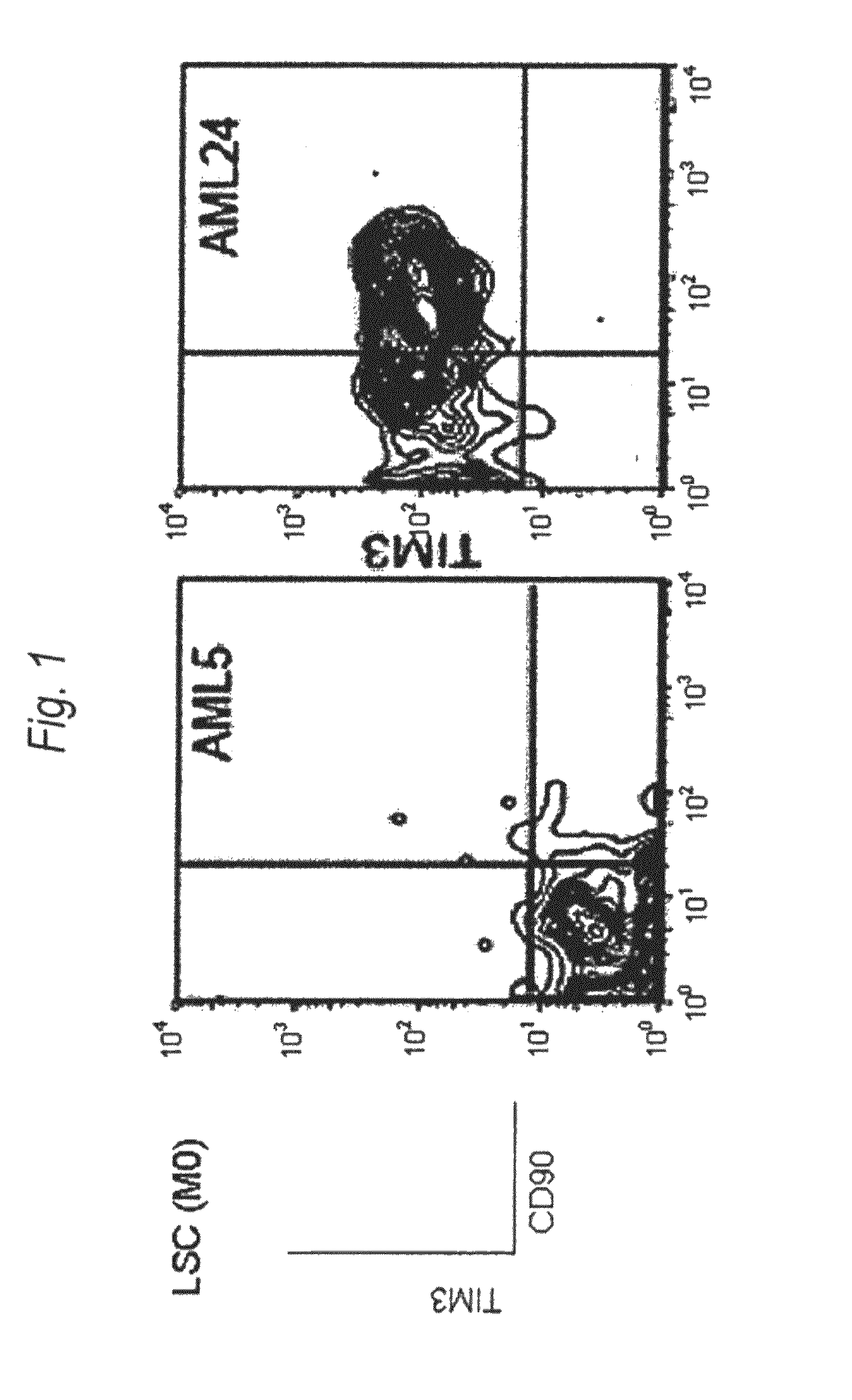
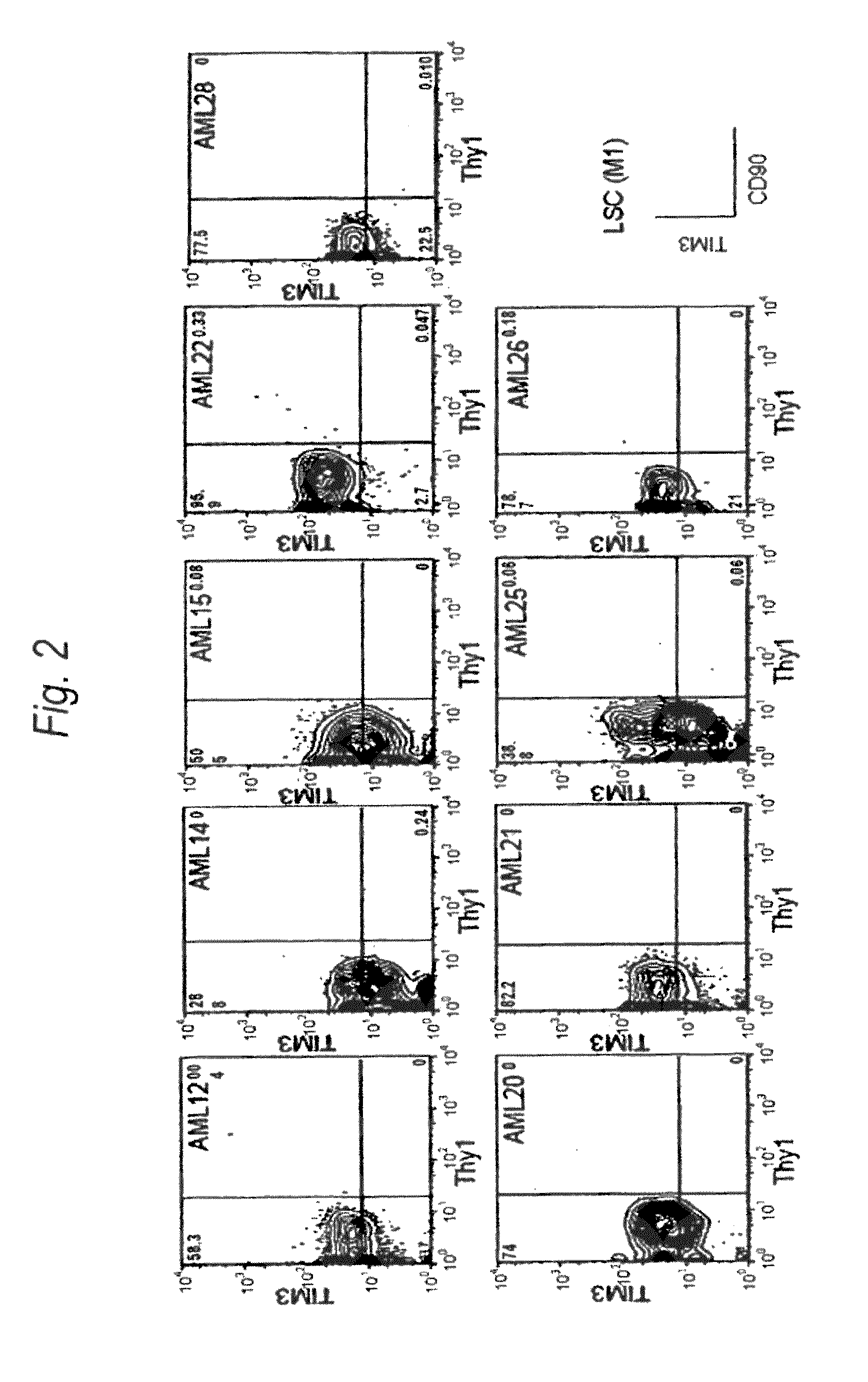
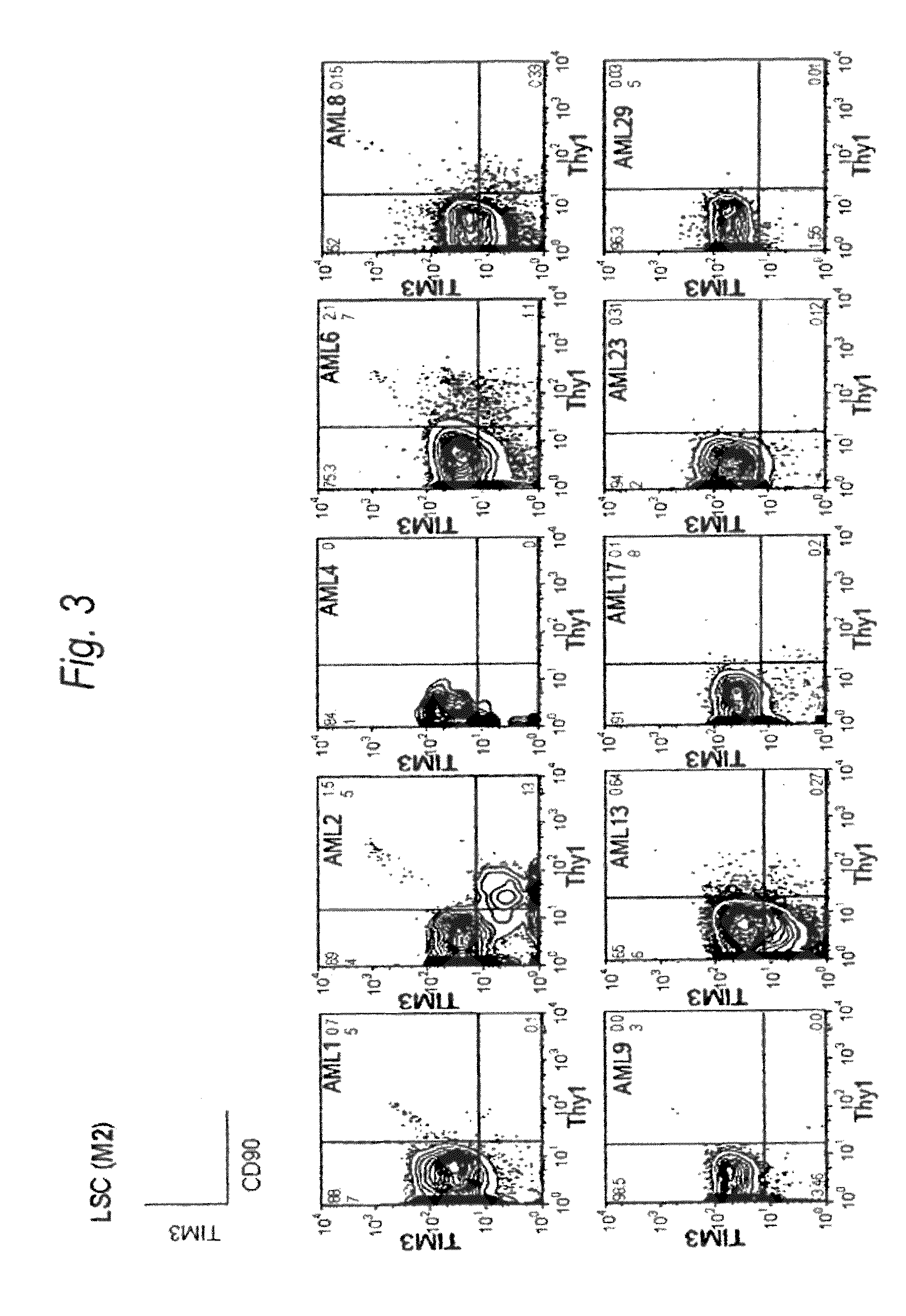
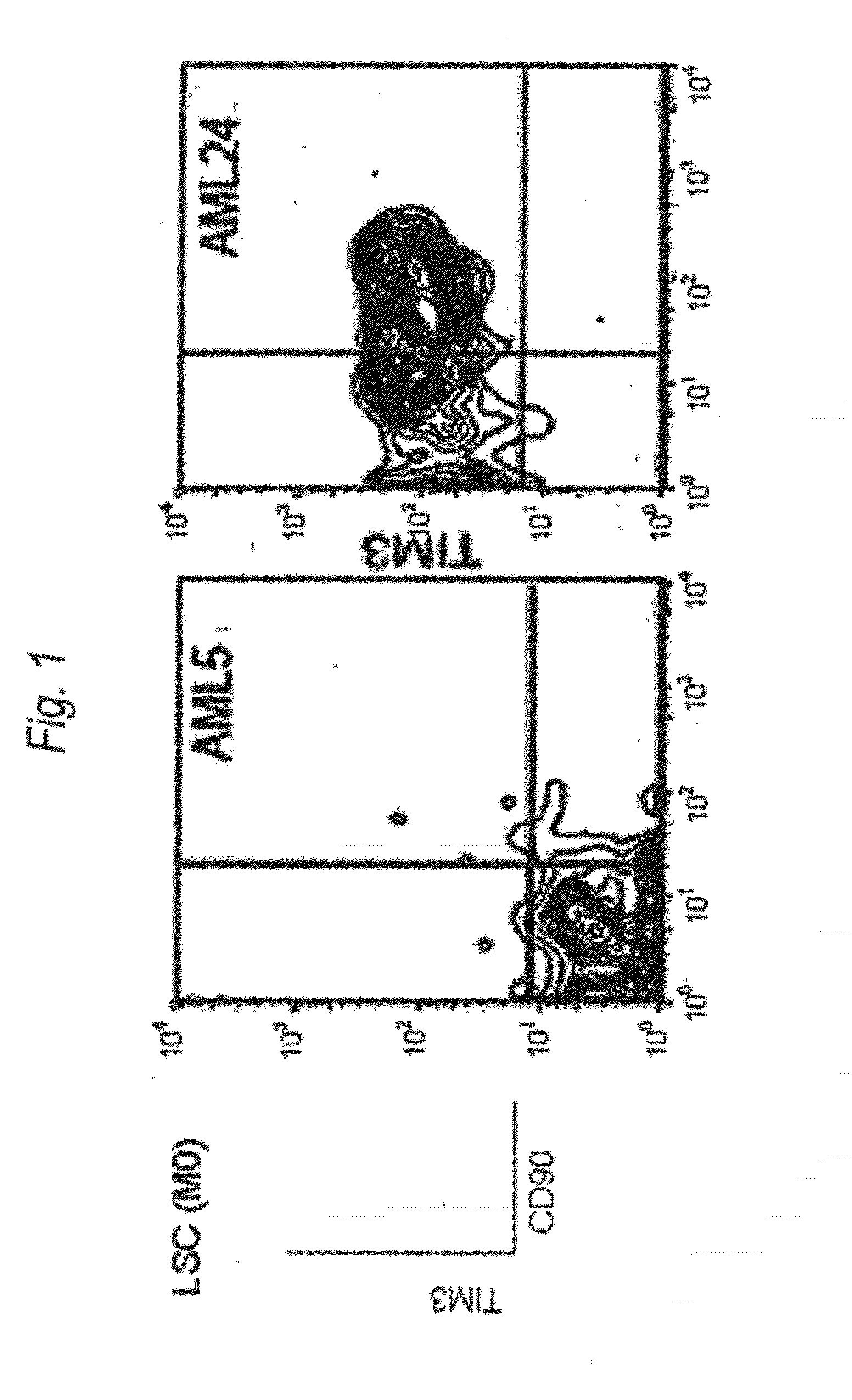
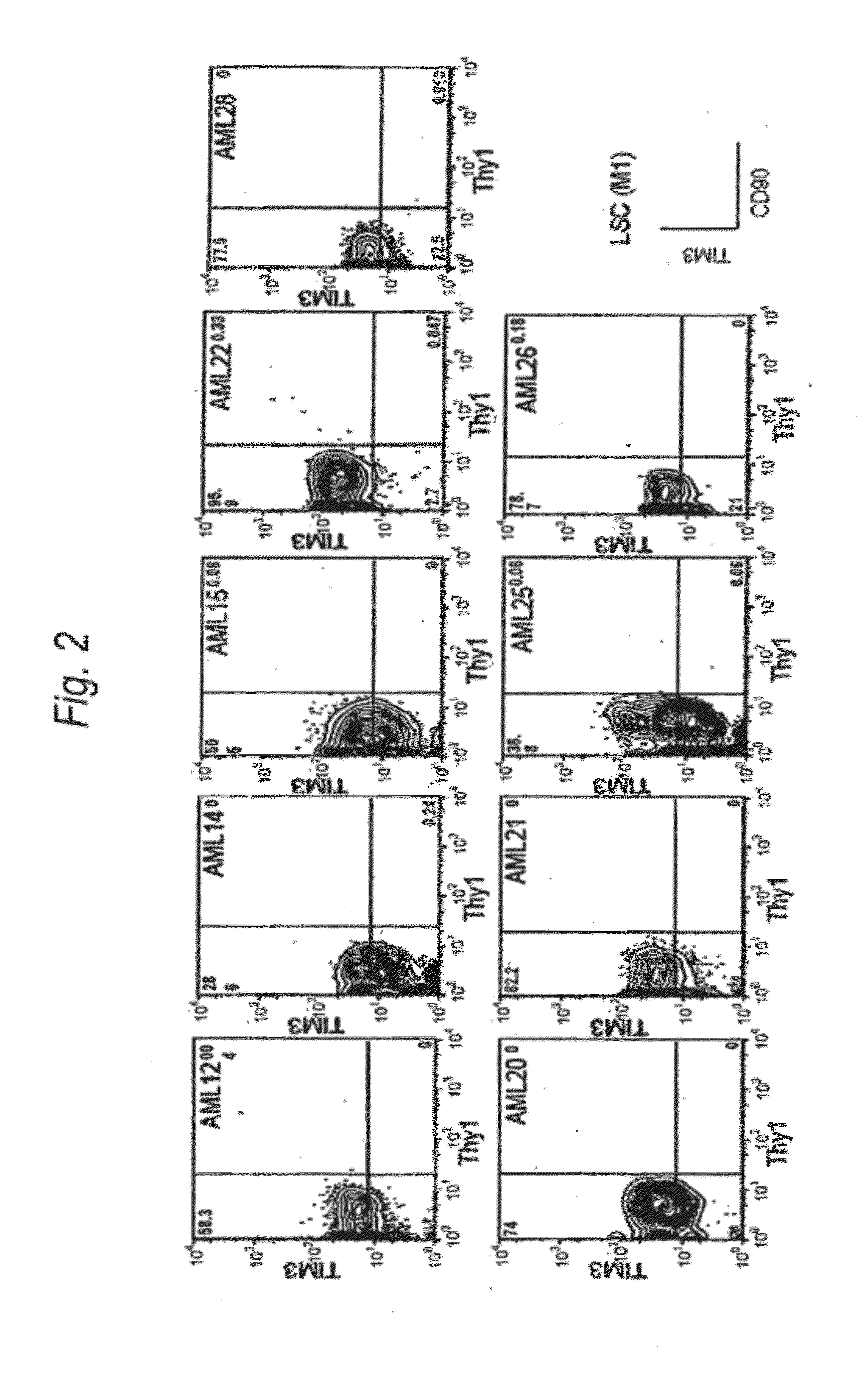
Method for treatment of blood tumor using anti-TIM-3 antibody
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
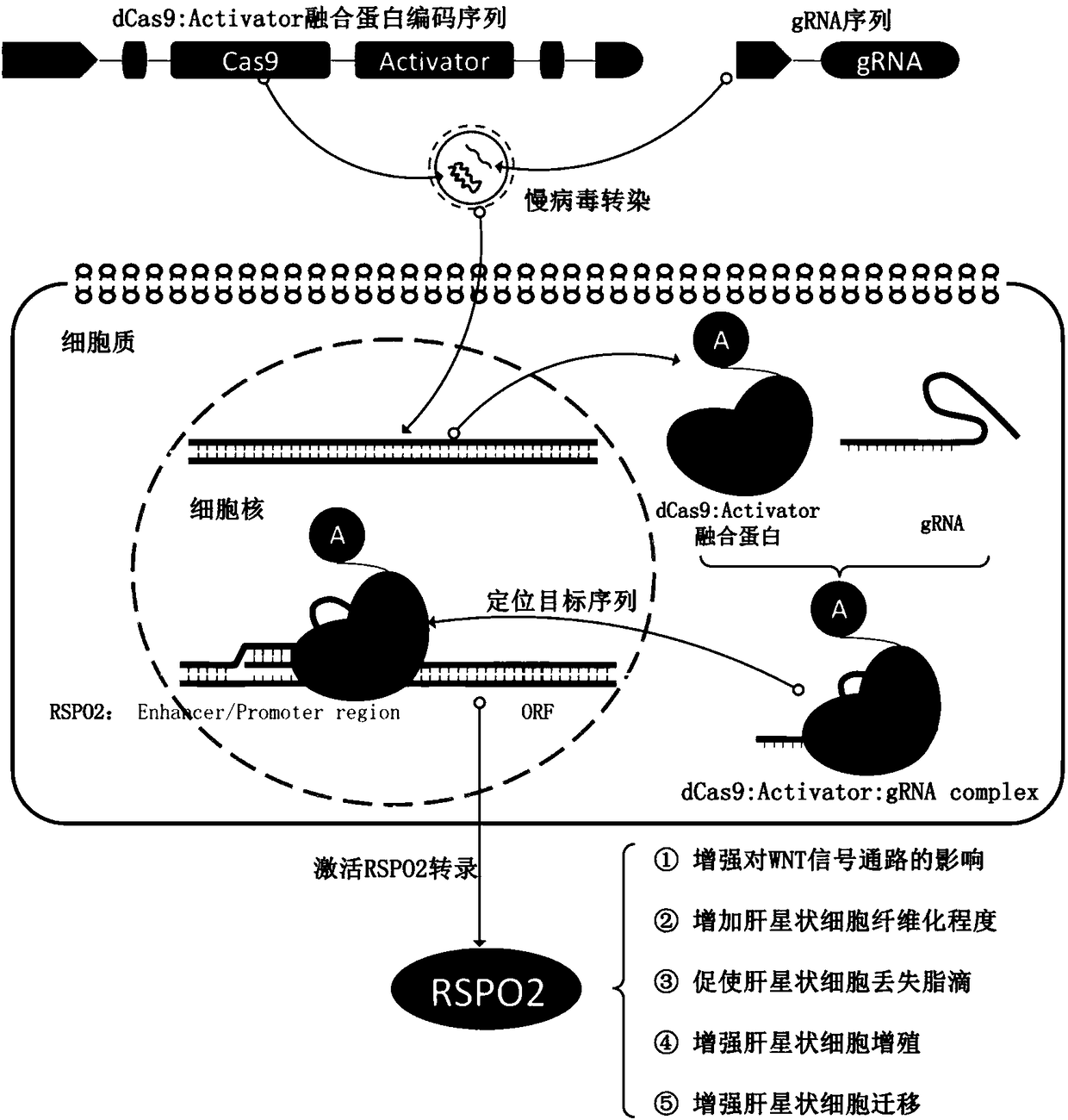
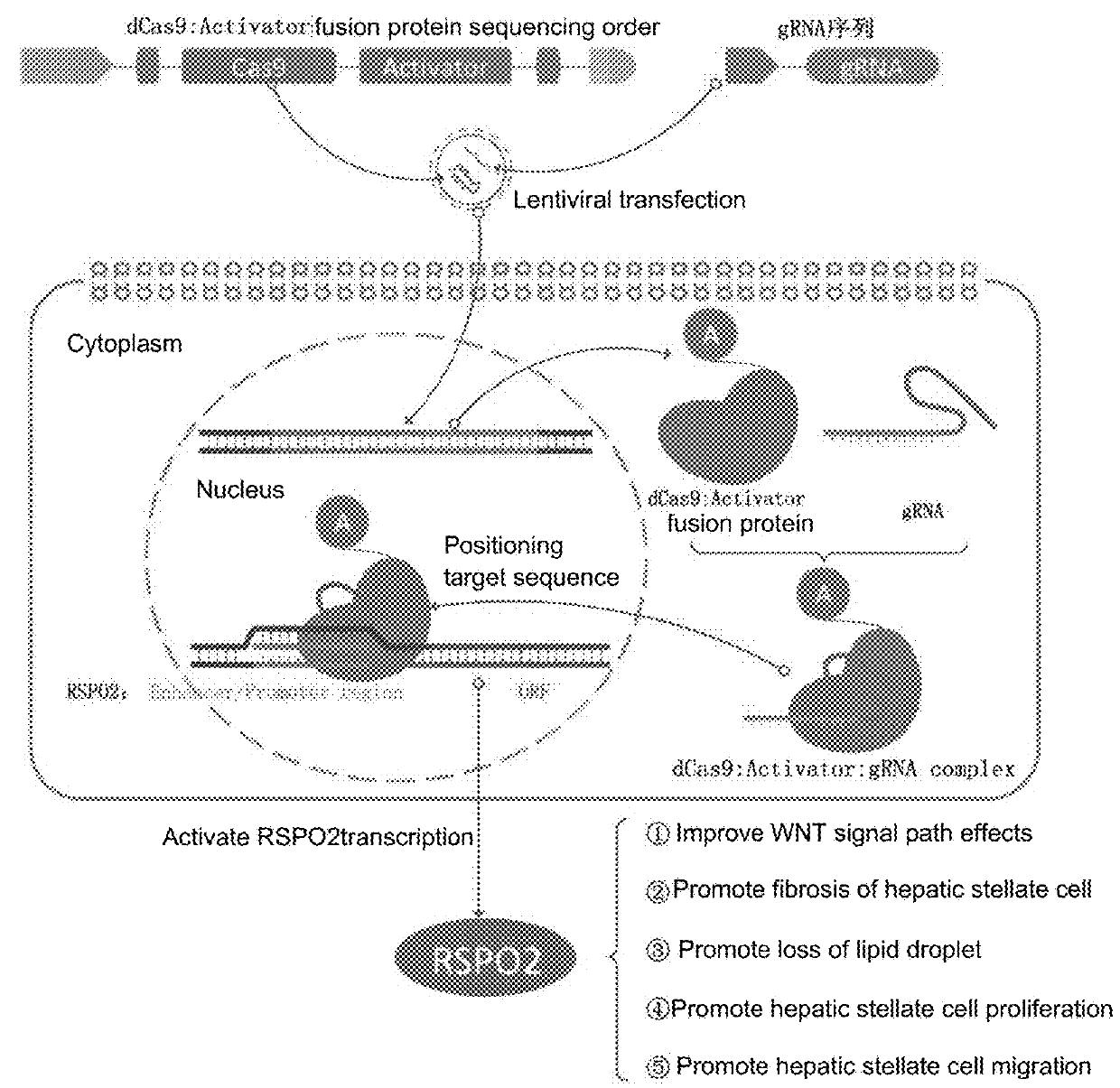
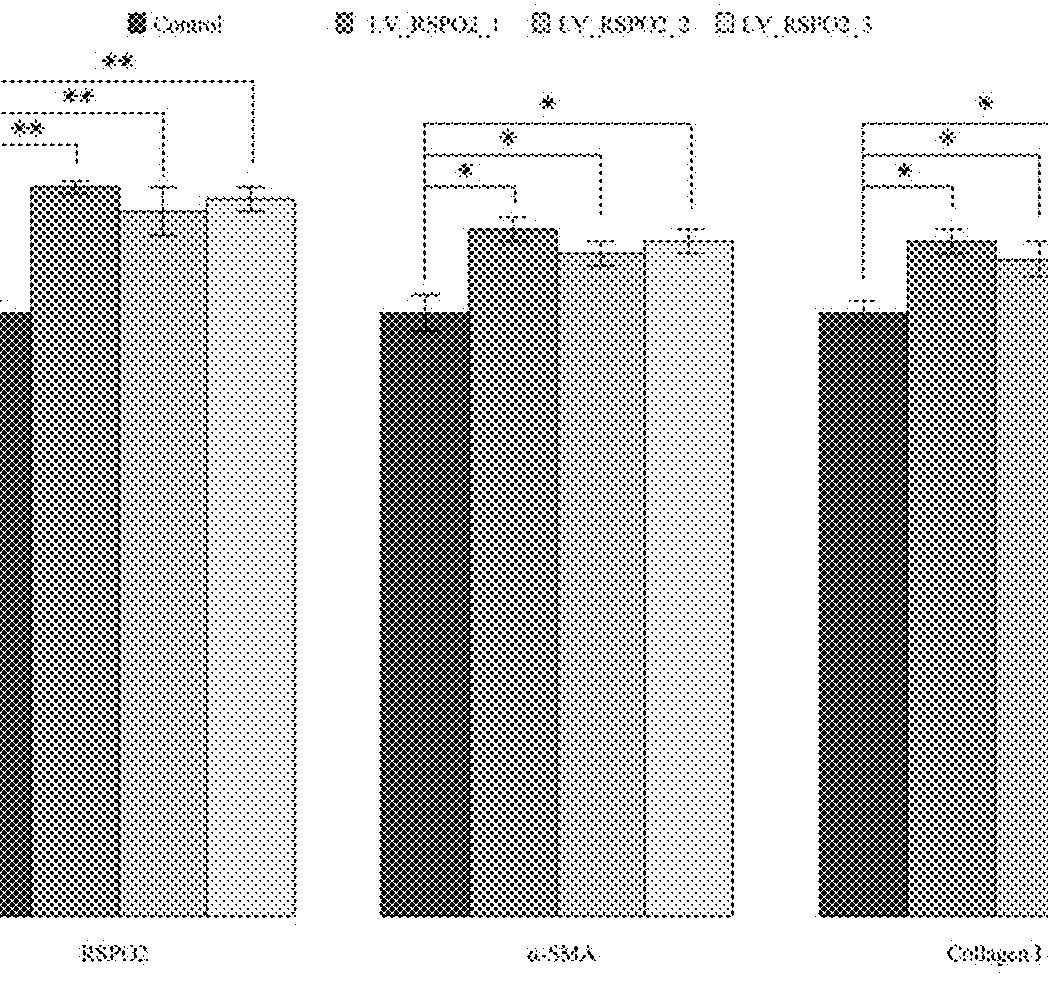
SgRNA specifically targeting human RSPO2 gene in CRISPR-Cas9 system and activation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a sgRNA specifically targeting human RSPO2 gene in a CRISPR-Cas9 system and an activation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The CRISPR-Cas9 system specifically activates the expression of the human RSPO2 gene, and introduces the activity of human hepatic stellate cells to activate Wnt signaling pathway so as to significantly upregulate the expression of liver fibrosis markers alpha-SMA and Collagen I. The CRISPR-Cas9 system designed for RSPO2 gene targets can effectively activate the hepatic stellate cells, thereby providing an effective way for liver fibrosis research.
Owner:JIAXING NO 1 HOSPITAL
Alfavbeta3 and alfavbet6 integrin antagonists as antifibrotic agents
InactiveUS20070117849A1Prevent and mitigate and even reverse developmentEasy to prepareBiocideDigestive systemIntestinal structureCTGF
This invention relates to inhibition of αv integrins, especially αvβ3 and αvβ6 integrins, by specific antagonists, preferably non-peptidic antagonists, related compounds and compounds with comparable specificity, that downregulate fibrogenesis by inhibiting cell migration and production of pro-fibrogenic molecules (e.g., collagens, TIMP-1) and cytokines (e.g., CTGF) by activated hepatic stellate cells / myofibroblasts, activated epithelia and endothelia. These antagonists alone or in combination with other agents can effectively prevent, mitigate or even reverse development of advanced fibrosis, such as fibrosis / cirrhosis of the liver and fibrosis of other organs, such as lungs, kidneys, intestine, pancreas, skin and arteries.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
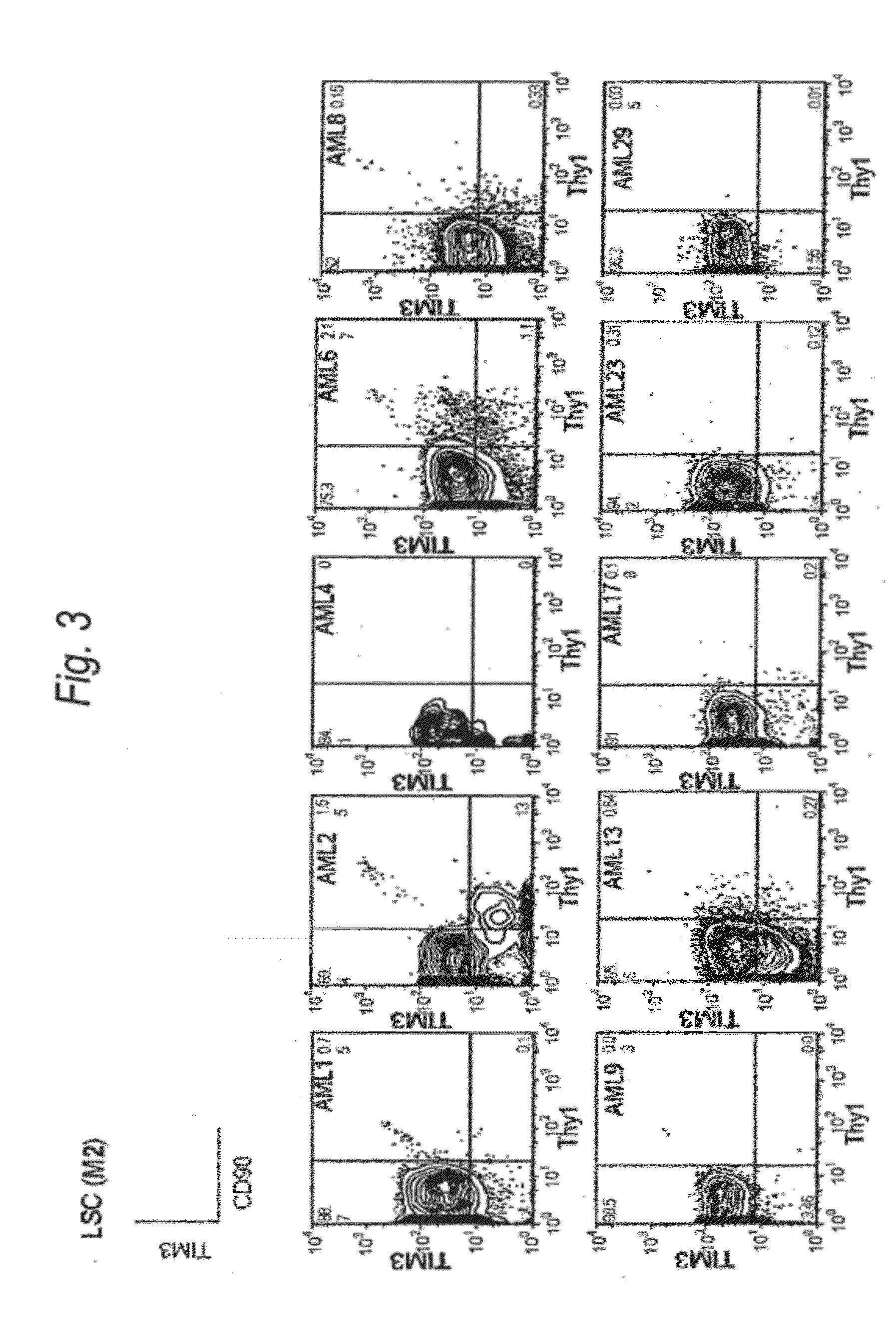
Method for treatment of blood tumor using Anti-tim-3 antibody
ActiveUS20120100131A1Use to establishBiological material analysisAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCell Fraction
Disclosed is a therapeutic method comprising administering a TIM-3 antibody to a subject who is suspected to be suffering from blood tumor and in whom TIM-3 has been expressed in a Lin(−)CD34(+)CD38(−) cell fraction of bone marrow or peripheral blood or a subject who has been received any treatment for blood tumor. Also disclosed is a composition for preventing or treating blood tumor, which comprises a TIM-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Conceived diseases include those diseases which can be treated through the binding or targeting of the TIM-3 antibody to blood tumor cells (AML cells, CML cells, MDS cells, ALL cells, CLL cells, multiple myeloma cells, etc.), helper T cell (e.g., Th1 cells, Th17 cells), and antigen-presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and cells resembling to the aforementioned cells (hepatic stellate cells, osteoclasts, microglial cells, intraepidermal macrophages, dust cells (alveolar macrophages), etc)), all of which are capable of expressing TIM-3. The diseases for which the therapeutic use is to be examined include blood diseases in which the expression of TIM-3 is observed in bone marrow or peripheral blood, particularly blood tumor.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +1
sgRNA and method for specifically activating human RSPO2 gene with CRISPR-Cas9 and application thereof
A method of constructing a specific CRISPR-Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats associated) to activate a RSPO2 (R-spondin 2) gene is disclosed in the present invention. The method comprises the following steps: designing a sgRNA (single guide RNA) of a specifically targeted human RSPO2 gene; constructing a CRISPR-Cas9 recombinant lentivirus vector of a specifically activated RSPO2 gene; and lentiviral packaging a CRISPR-Cas9 system of the specifically activated RSPO2 gene. The CRISPR-Cas9 system designed by the present invention activates the RSPO2 target gene expression and promotes the activation of the hepatic stellate cell.
Owner:JIAXING NO 1 HOSPITAL
Methods of Treating Portal Hypertension
ActiveUS20150313871A1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationSubcellular localization
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
HAb18GC2 monoclonal antibody and its light and heavy chain variable area genes, coding polypeptide and use
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 and its variable area gene of its heavy chain and light chain and polypeptide, and their uses in preparing therapeutic agent for reversing hepatic fibrosis etc. matrix deposition disease. The present monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 can bind specificly with antibody HAb18G / CD147 highly expressed in human liver fibrosis tissue and with liver astrocyte and possesses function of facilitating MMPs secretion and reducing the extracellular matrix. The antibody light, heavy chain variable area genes are successfully cloned in the present invention and small molecule gene engineered antibodies of all kinds are constructed and expressed based on the gene for preparing drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease. The polypeptide coded by the present gene can crosslink with multiple effector molecule and prepare drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
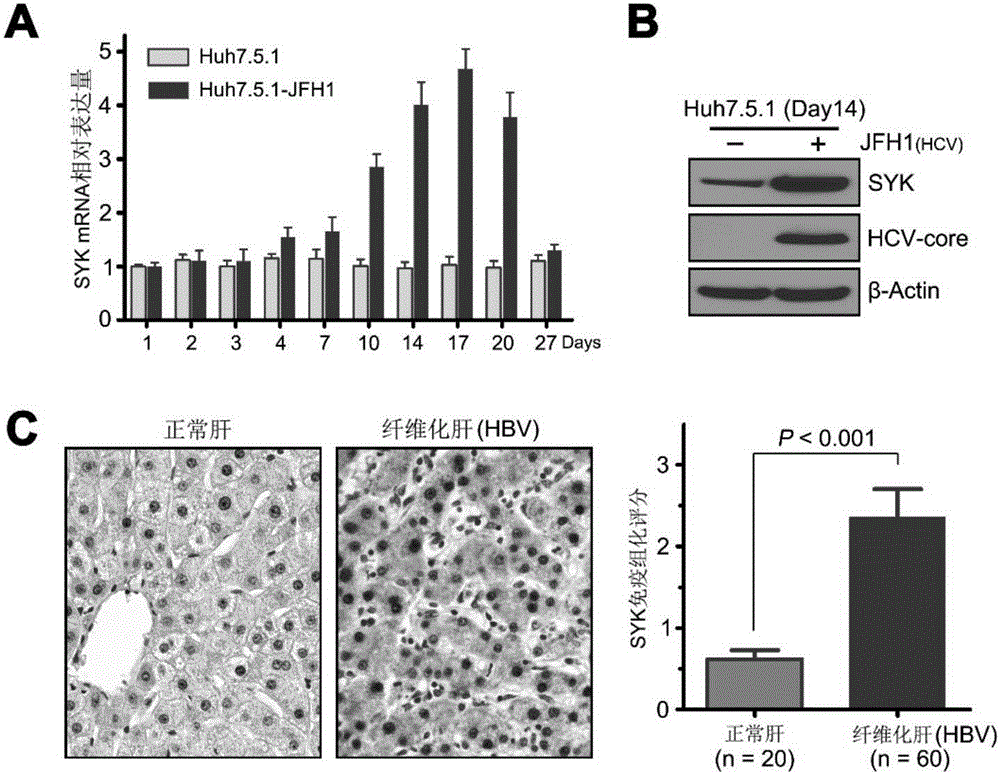
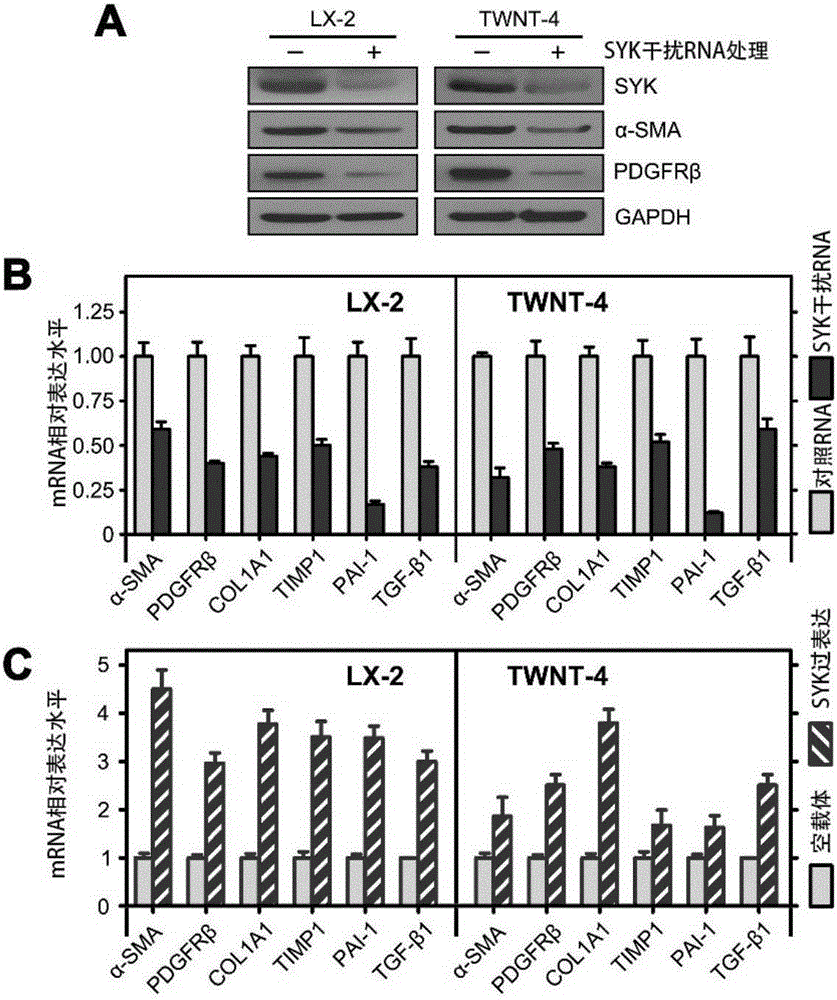
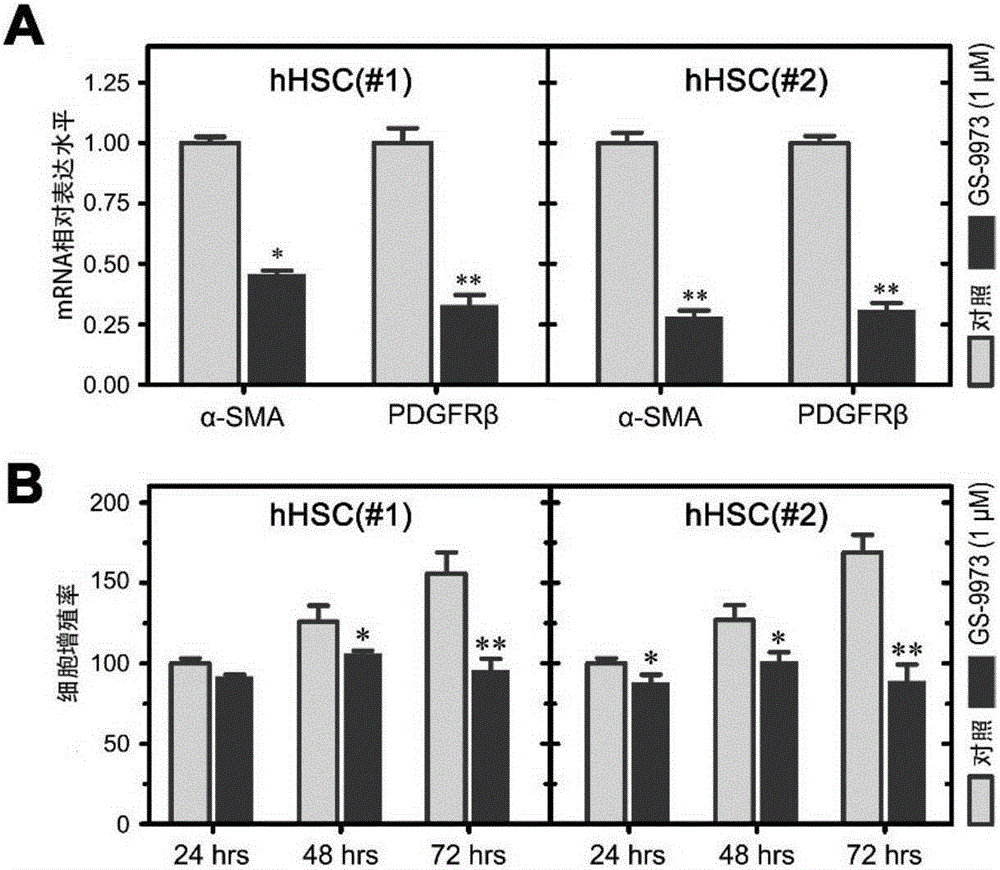
Application of SYK as hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis therapeutic target
ActiveCN105664178APromote activationSpeed up the processOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHepatic fibrosisTherapeutic effect
Owner:洪健
Applications of andrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof in preparation of anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines
ActiveCN106946821ADefinitive anti-hepatic fibrosis activityInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCell-Extracellular MatrixHepatic stellate cell activation
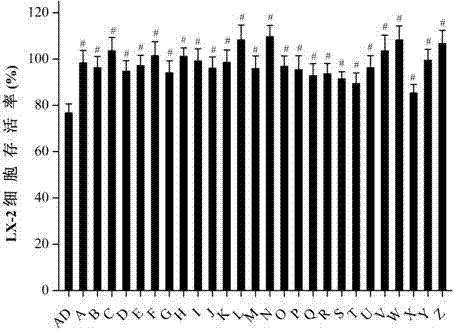
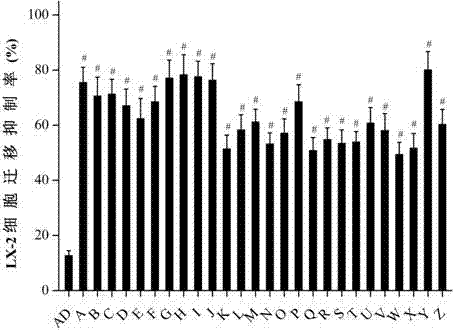
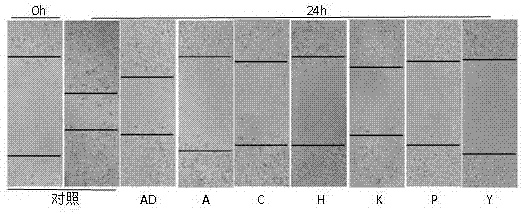
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, discloses applications of andrographolide derivatives in preparation of medicines preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis, and relates to 15-benzylidene-14-deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide derivatives and 3,19 esterified compounds thereof. Experiments prove that the compounds significantly inhibit human hepatic stellate cell LX-2 metastasis and activation, significantly reduce the fibrosis level of hepatic tissues of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, reduce contents of extracellular matrix protein (ECM) related components, significantly reduce the level of immune inflammation correlation factors of rats affected with hepatic fibrosis, effectively inhibit immuno-inflammatory responses, inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation in hepatic tissues, and promote collagen degradation. The compounds are used as active components for preparing the anti-hepatic fibrosis medicines, and are efficient and low in toxicity, thus providing a novel medicine route for hepatic fibrosis treatment and prevention, and expanding the optional range of clinical medicine application. The compounds and the applications have good development prospects.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Pharmaceutical use of Graptopetalum and related plants
ActiveUS7364758B2No detectable side effectImprove survival rateBiocideAntipyreticDiseaseLiver fibrosis
The present invention relates to compositions comprising Graptopetalum and uses thereof Graptopetalum can protect animals from liver diseases and medical conditions, such as inflammation, steatosis, and fibrosis. In particular, Graptopetalum inhibits proliferation of activated hepatic stellate cells, which play a pivotal role in liver fibrosis. Graptopetalum also has anti-fibrosis activities as well as inhibits proliferation of lung fibroblasts. Therefore, in addition to being a prophylactic and therapeutic agent for the liver, Graptopetalum is useful against fibrosis or inflammation of tissues or organs other than the liver, in particular lung, kidney, and bladder. Other plants in the family of Crassulaceae, particularly Echeveria, have similar effects as Graptopetalum.
Owner:TAICHUNG VETERANS GENERAL HOSPITAL +1
Small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) lipid nanometer vesicles with targeted hepatic stellate cells, and application of siRNA lipid nanometer vesicles
InactiveCN105688229AAchieve targetedAchieve deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to the technical field of gene therapy drugs, and in particular discloses small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) lipid nanometer vesicles with targeted hepatic stellate cells, and the application of the siRNA lipid nanometer vesicles. The nanometer vesicles respectively comprise a treatment component and a delivery component, wherein the treatment component is siRNA having a targeted gene inhibition effect, and the delivery component is a lipid carrier. The nanometer vesicles formed by encapsulating the treatment component by the delivery component are prepared by an ethanol dilution method; a gene delivery system existing in a form of nanometer vesicles is capable of effectively overcoming the obstacles preventing the delivery of the gene therapy drugs in the body.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Treatment for liver disease
InactiveUS20050191302A1Promote and enhance resolutionPrevent buildupOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseApoptosis
The present invention is based on the finding that the artificial induction of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) apoptosis in vivo can promote the resolution of liver fibrosis. Thus, the present invention provides methods for treating liver disease in a subject involving administration of an inducer of apoptosis which is capable of selectively inducing hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in the liver of the subject or of an agent which is capable of giving rise to such an inducer in the subject. In addition, the invention provides methods for treating liver fibrosis in a subject comprising the selective delivery of an inducer of apoptosis specifically to the hepatic stellate cells of the subject or of an agent which is capable of giving rise to an inducer of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
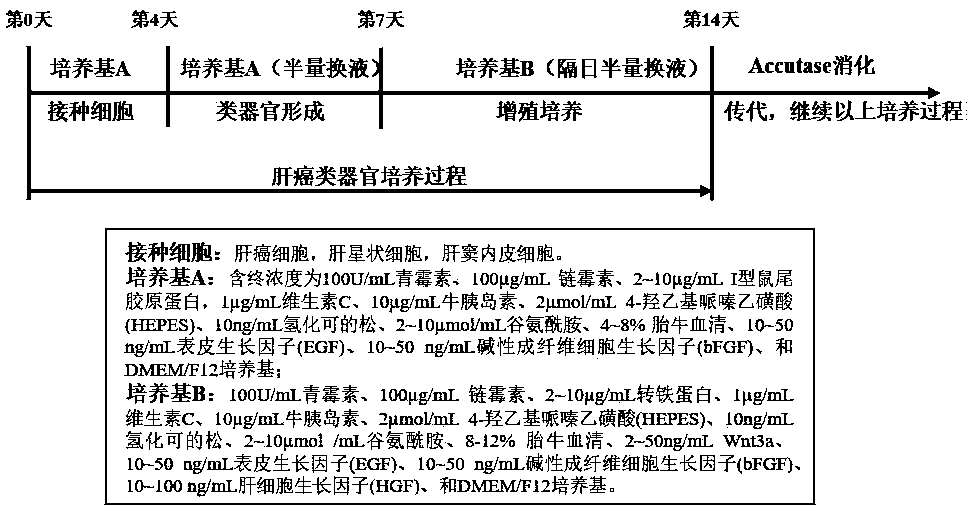
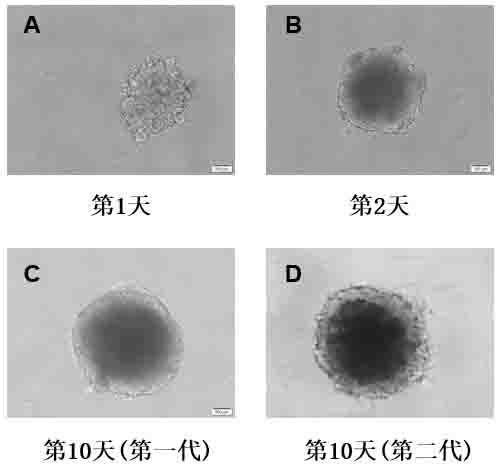
In-vitro construction method of liver cancer organ model
ActiveCN110004109AEasy constructionDetectable validityHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsOperability
The invention discloses an in-vitro construction method of a liver cancer organ model. Liver cancer cells, hepatic stellate cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are suspended in a culture medium A in a specific proportion; on the fourth day of culture, half of culture liquid is replaced, and culture is maintained; from the seventh day, the culture medium A is replaced with a culture mediumB, and then culture is continuously conducted for seven days; amplification subculture is conducted on the fourteenth day. On the basis of complex cellularity in a tumor microenvironment, the 3D liver cancer organ in-vitro model which is uniform in size, stable in structure, capable of being used for detecting the effectiveness of anticancer drugs and capable of achieving multiplication culture is quickly constructed. The constructed liver cancer organ model is simple in method, quick to construct, high in operability and suitable for researching a liver cancer generation and development mechanism, high-throughput screening of liver cancer drugs and the like, and has industrialization significance.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
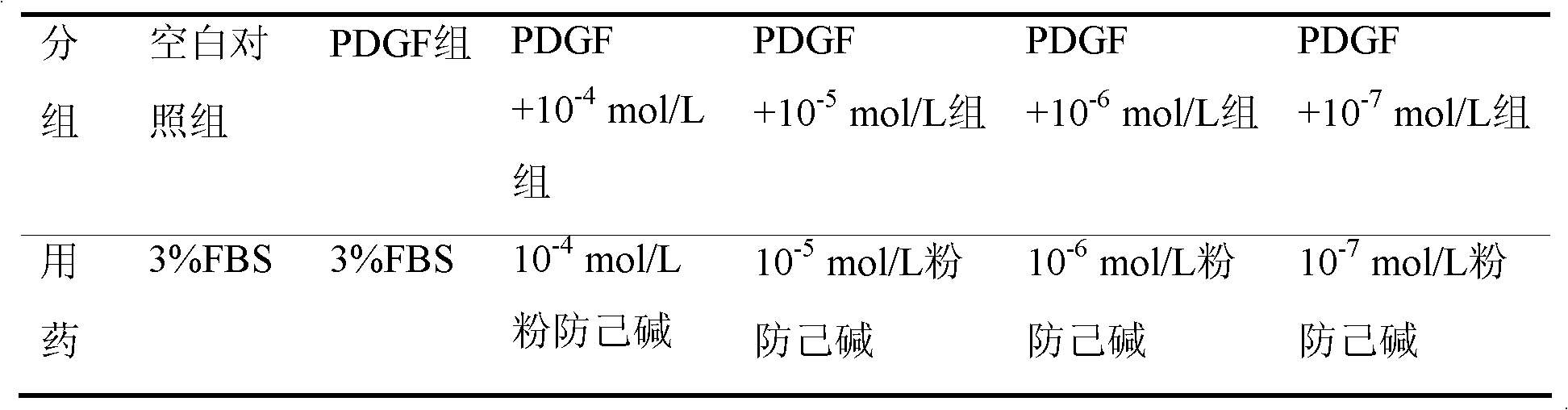
Application of tetrandrine in hepatic stellate cell migration inhibition drug preparation
InactiveCN102988367AInhibit migrationOptimal working concentrationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDrugs preparationsTetrandrine
The present invention discloses an application of tetrandrine in hepatic stellate cell migration inhibition drug preparation. According to the present invention, a PDGF-induced human hepatic stellate cell line (LX-2) migration screening platform is designed, and results show that PDGF-induced hepatic stellate cell (HSC) migration can be inhibited with 10<-4>-10<-7> mol / L tetrandrine.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Treatment of disease by inducing cell apoptosis
InactiveUS7402567B2Decreased and complete cessationInhibition of activationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal growthsDisease
The present invention relates generally to the treatment and prevention of diseases characterized by excess cell proliferation and / or activation. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods to suppress the activation and / or proliferation of various cells. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods to suppress the activation and / or proliferation of mesenchymally derived cells (including, but not limited to hepatic stellate cells), as well as cells with abnormal growth characteristics. In particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods to induce fibrosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
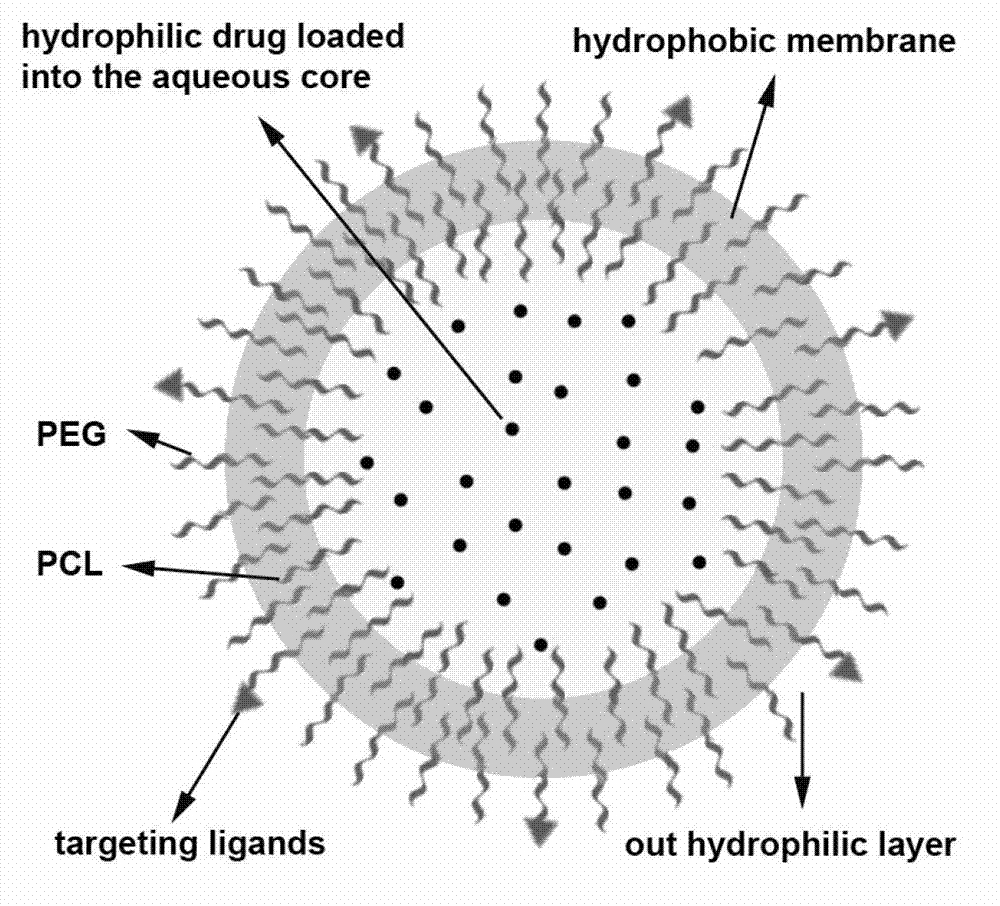
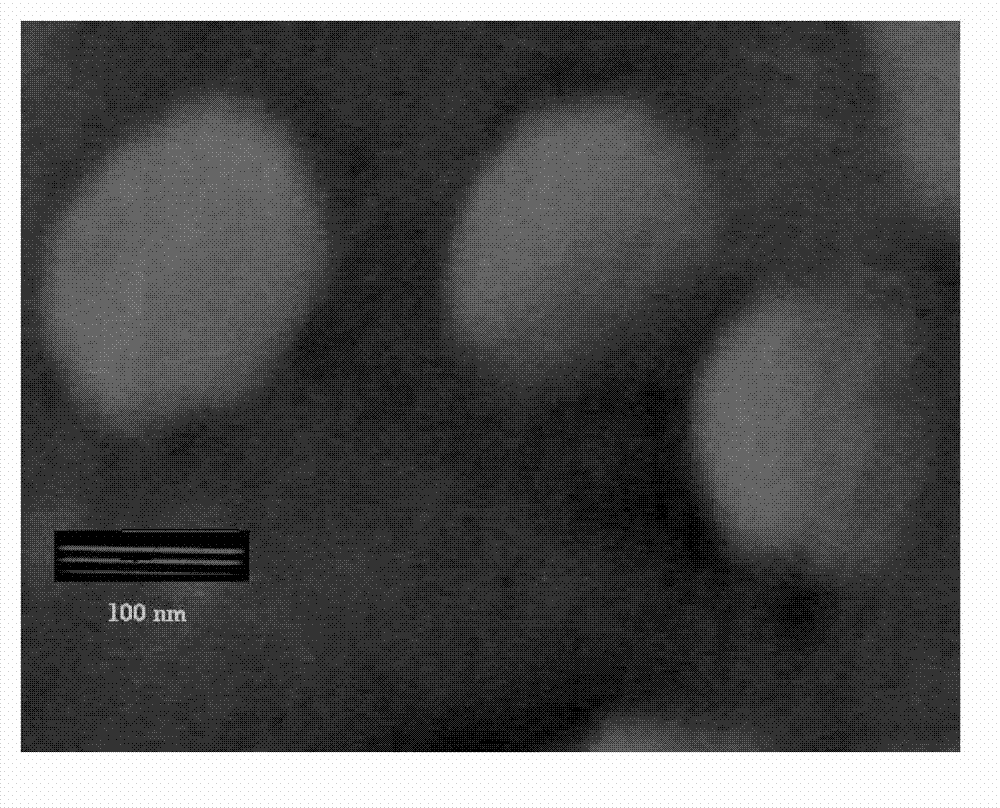
Oxymatrine hepatic targeting nano drug delivery system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102961360AReduce intakeSpeed up entryOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPolyethylene glycolEvaporation
The invention relates to an oxymatrine hepatic targeting nano drug delivery system and a preparation method thereof. The oxymatrine hepatic targeting nano drug delivery system is prepared by the following steps of: with polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone block polymer as a carrier, preparing polymer nanoparticles by adopting a film dispersion method, a reverse evaporation method or an organic solvent injection method, encapsulating oxymatrine into the polymer nanoparticles, then modifying a new glycoprotein or cyclic octapeptide ligand to be taken as a ligand on the surfaces of the nanoparticles, and constructing an anti-hepatic fibrosis nano targeting drug delivery system for hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The nano drug delivery system has the advantages that particle size is 50-260nm, encapsulation efficiency is 18-42%, drug loading capacity is 2-12% and the surface of the nano drug delivery system is rich in new glycoprotein M6PHSA (mannose-6-phosphate human serum albumin) or cyclic octapeptide RGD (arg gly asp). The oxymatrine hepatic targeting nano drug delivery system provided by the invention can increase opportunities that nanoparticles enter the liver through blood circulation, is beneficial to targeting distribution of drugs at focus parts of the liver and is beneficial to absorption of drug-carrying nanoparticles at lesion parts of the liver and ingestion of HSCs, so that hepatic fibrosis treatment is enhanced.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Medicine and treatment method for treating hepatic fibrosis
InactiveCN108686211AImprove expression levelPromote apoptosisCompounds screening/testingSsRNA viruses negative-senseCell-Extracellular MatrixPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a screening method for a medicine for targeting NS5ATP9 (HCV NS5A-transactivated protein 9) prevention or treatment of tissue fibrosis and tissue sclerosis, and the medicine obtained by screening using the method. NS5ATP9 significantly regulates the expression of extracellular matrix collagen and non-collagen glycoprotein and affects the occurrence and development of tissue fibrosis by regulating a TGFbeta1 / Smad3 signaling pathway; and the NS5ATP9 promotes the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells, inhibits the proliferation of the hepatic stellate cells and regulates extracellular matrix deposition by regulating the phosphorylation level and the intracellular translocation condition of a Smad3 protein. TDF / TAF can effectively regulate the expression of NS5ATP9 gene,and is verified in CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis model, and the TDF / TAF achieves significant effects in the prevention or treatment of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice.
Owner:北京泛亚同泽生物医学研究院有限公司
Co-transplantation of hepatic stellate cells and graft
InactiveUS20080145342A1Prevent graft rejectionPrevent rejectionBiocideHepatocytesCo transplantationMAMMAL LIVER
A method of inhibiting graft rejection includes isolating Hepatic Stellate Cells from a mammal liver, activating the isolated Hepatic Stellate Cells, and administering a combination of Hepatic Stellate cells and a graft to a mammal.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
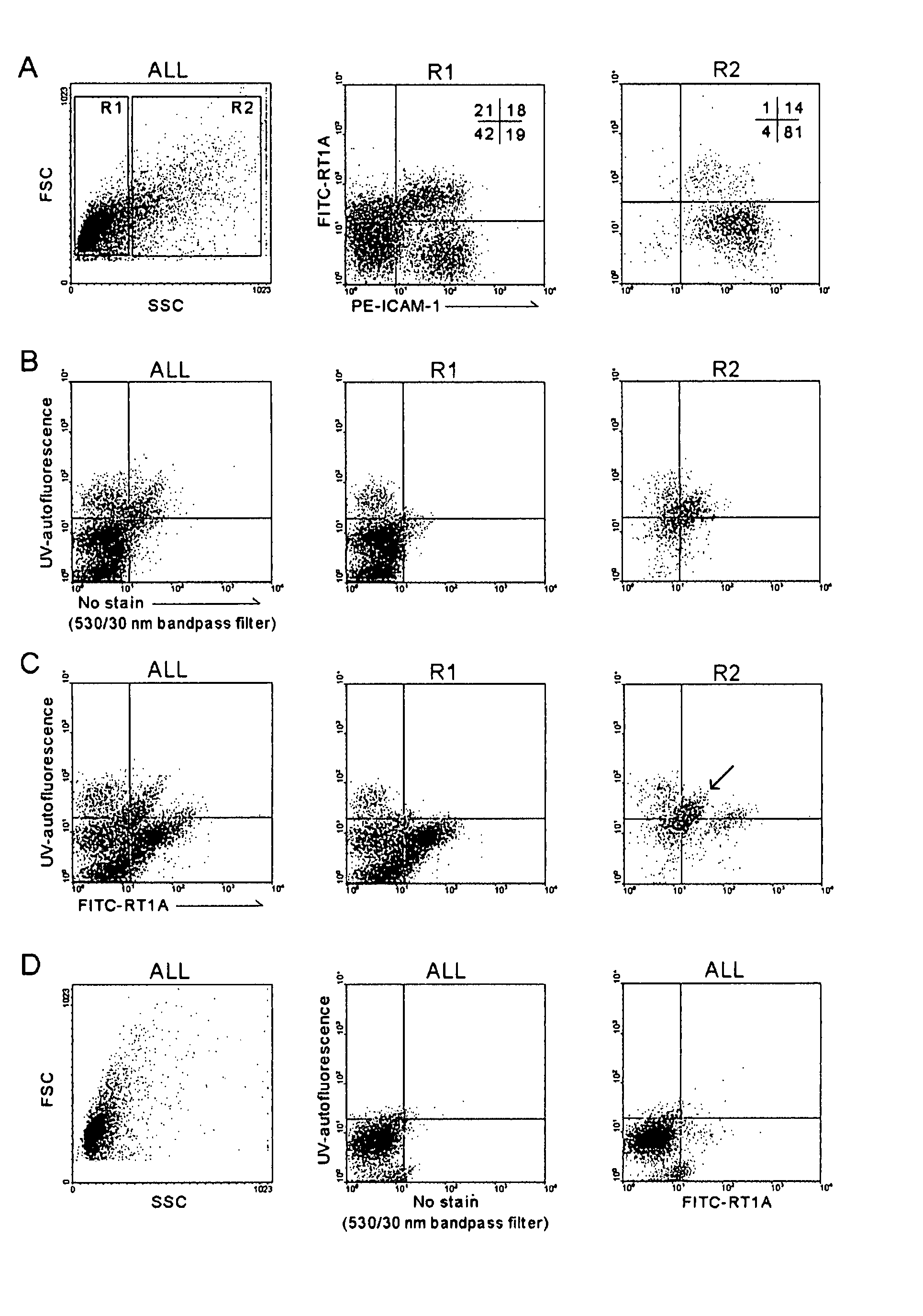
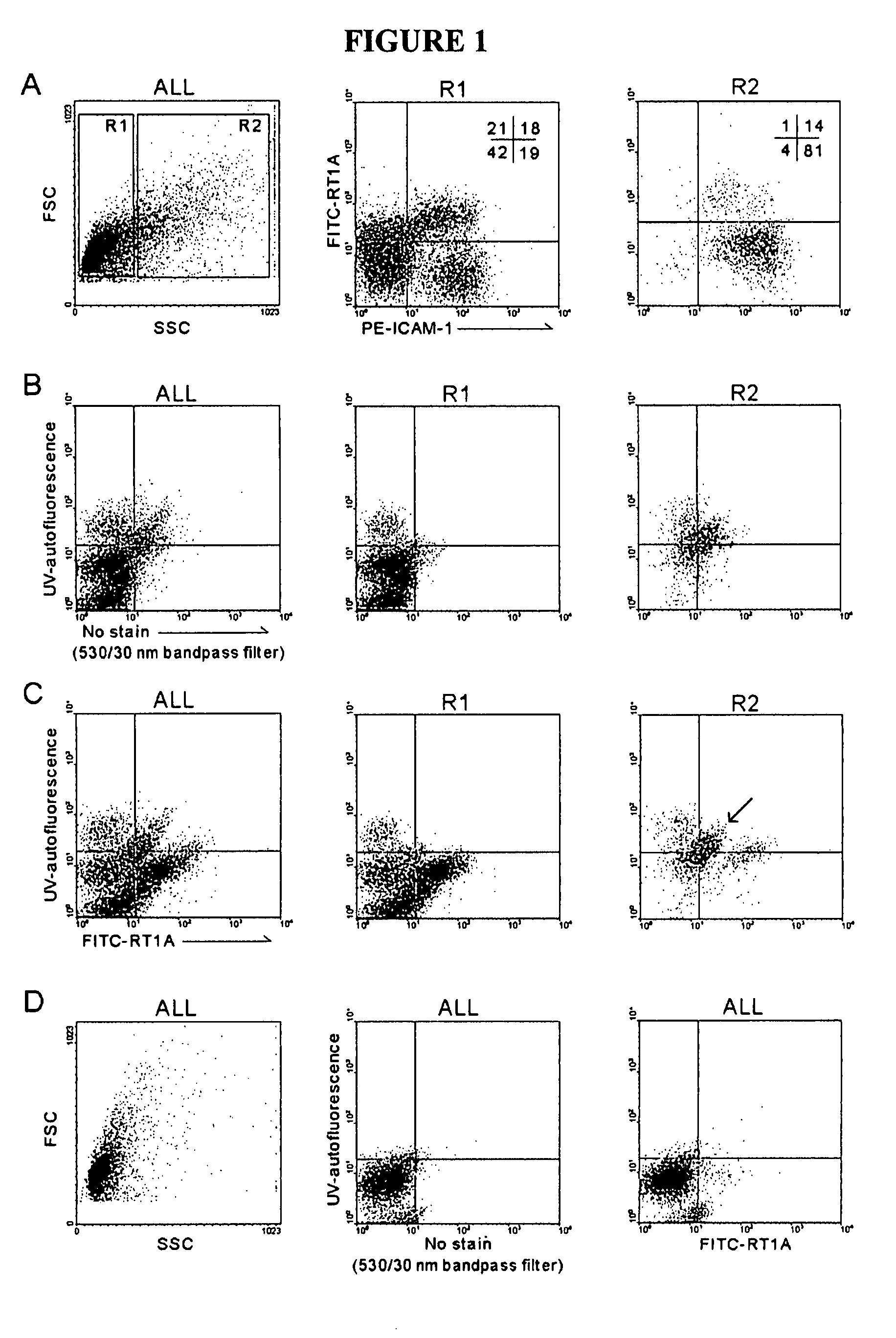
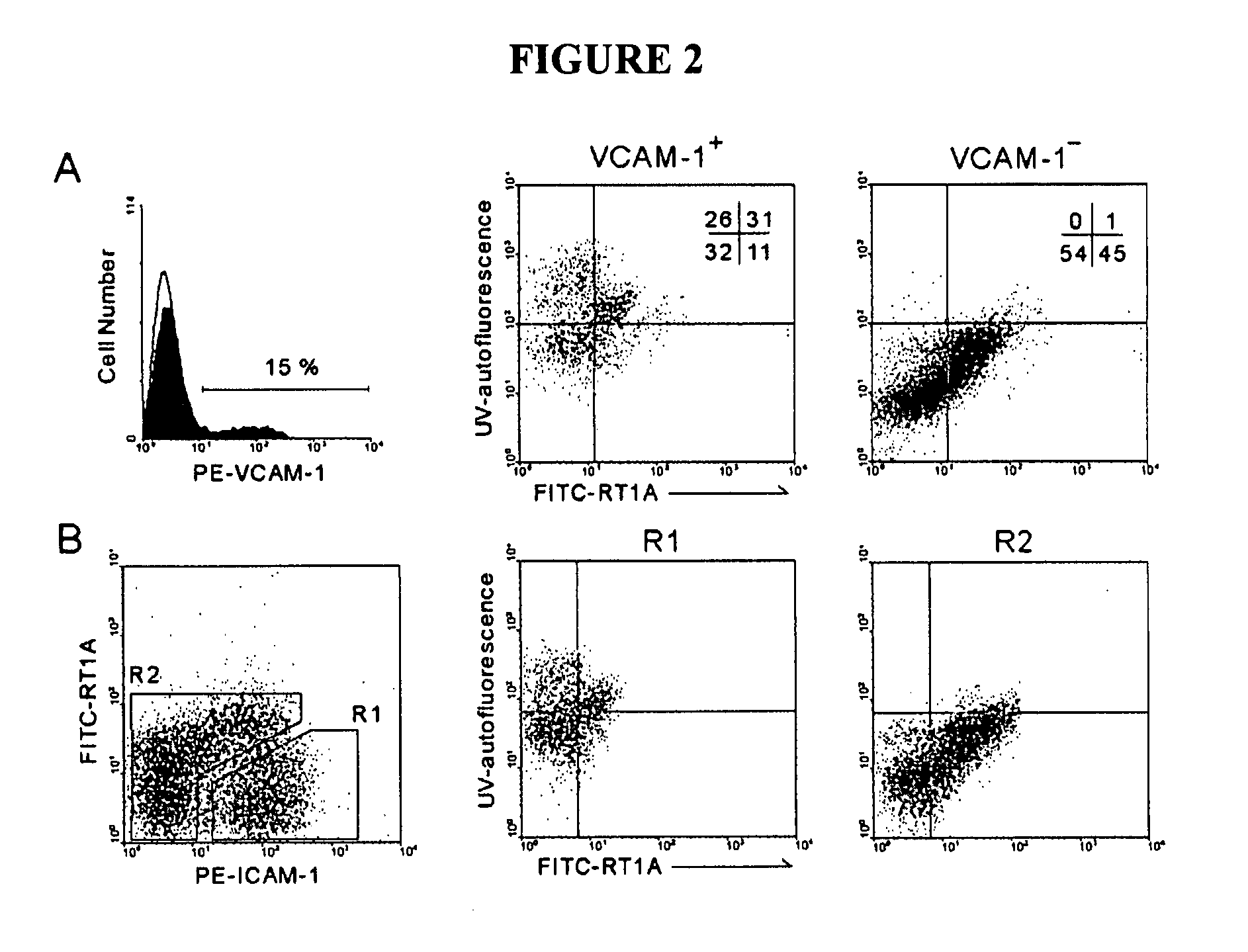
Hepatic stellate cell precursors and methods of isolating same
The present invention relates to precursor cells to hepatic stellate cells, compositions comprising same and methods of isolating same. The surface antigenic profile of the precursors is MHC class Ia negative, ICAM-1+, VCAM-1+, β3-integrin+. In addition to expression of these surface markers, the cells also express the intracellular markers desmin, vimentin, smooth muscle α-actin, nestin, hepatocyte growth factor, stromal derived factor-1α and H1x homeobox transcriptional factor.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
HAb18GC2 monoclonal antibody and its light and heavy chain variable area genes, and application
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 and its variable area gene of its heavy chain and light chain and polypeptide, and their uses in preparing therapeutic agent for reversinghepatic fibrosis etc. matrix deposition disease. The present monoclonal antibody HAb18GC2 can bind specificly with antibody HAb18G / CD147 highly expressed in human liver fibrosis tissue and with liverastrocyte and possesses function of facilitating MMPs secretion and reducing the extracellular matrix. The antibody light, heavy chain variable area genes are successfully cloned in the present invention and small molecule gene engineered antibodies of all kinds are constructed and expressed based on the gene for preparing drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease. The polypeptide coded by the present gene can crosslink with multiple effector molecule and prepare drug for reversing liver fibrosis matrix deposition-related disease.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-fibrosis medicine nanometer preparation and preparation method thereof
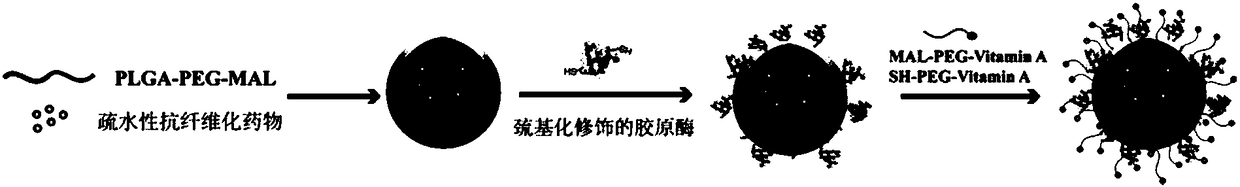
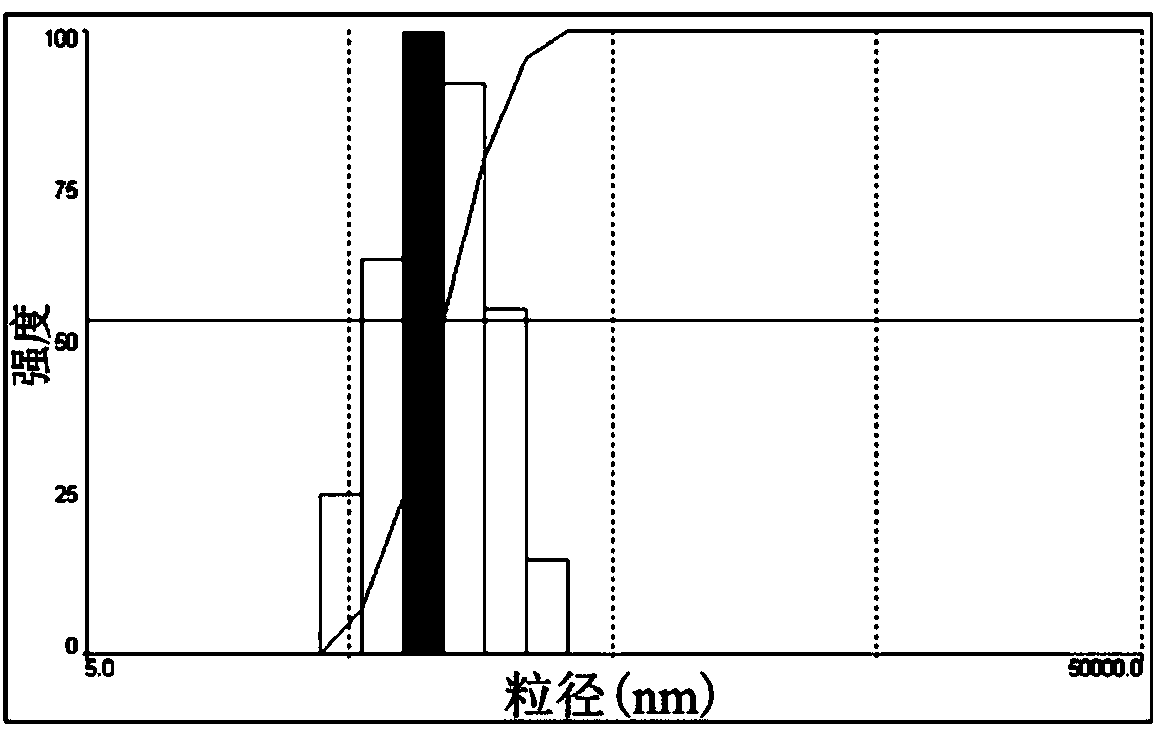
ActiveCN108273061AHigh activityImprove utilizationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemMedicineAnti fibrosis
The invention discloses a high-efficiency targeted type anti-fibrosis medicine nanometer preparation and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a collagenase and / or vitamin A-modified nanometerpreparation or a carrier thereof. The high-efficiency targeted type anti-fibrosis medicine nanometer preparation is characterized in that firstly, collagenase penetrates through a fibrosis collagen carrier; hepatic stellate cells are specifically targeted by the vitamin A, so that an anti-hepatic fibrosis medicine can be transferred in a targeted way at high efficiency, thereby reaching the purpose of high-efficiency hepatic fibrosis therapy. The high-efficiency targeted type anti-fibrosis medicine nanometer preparation has the advantage that the substance exchange barrier caused by accumulation of excessive collagen in the hepatic fibrosis process is overcome by the collagenase-modified nanometer preparation for the first time, so as to provide a novel way and strategy for the high-efficient transfer of the anti-hepatic fibrosis medicine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
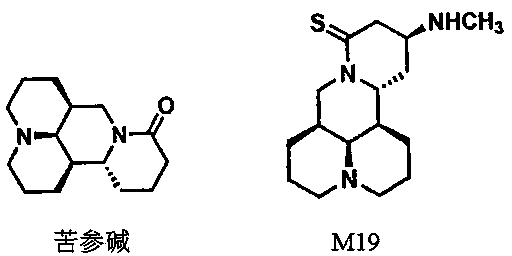
Application of matrine compounds in preparing anti-hepatic fibrosis and anti-liver cancer medicaments
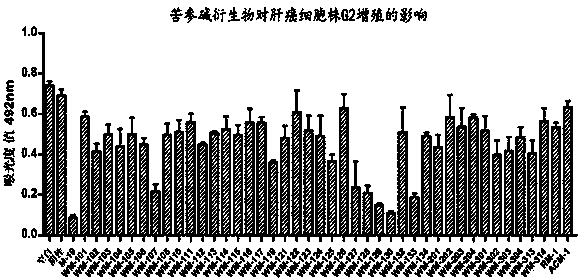
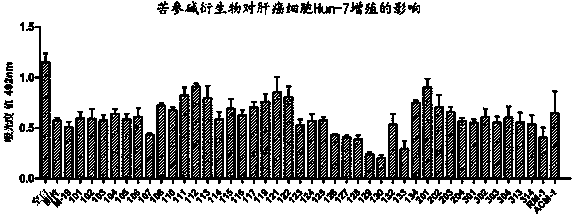
InactiveCN103933038AAntiproliferative activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer cellHepatic fibrosis
The invention relates to application of compounds and salt thereof, and particularly relates to application of matrine compounds and salt thereof in preparation of anti-hepatic fibrosis and anti-liver cancer medicaments. The compounds have the advantages of remarkably inhibiting the proliferation of hepatoma cell lines Hep-G2, Hun-7, MHCC-97L, SMMC-7721 and Hep-3B and proliferation activities of fibroblast BJ, human hepatic stellate cells LX-2 and hepatic stellate cells HSC-T6, and can be used for preparing medicaments for treating hepatic fibrosis and liver cancer.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
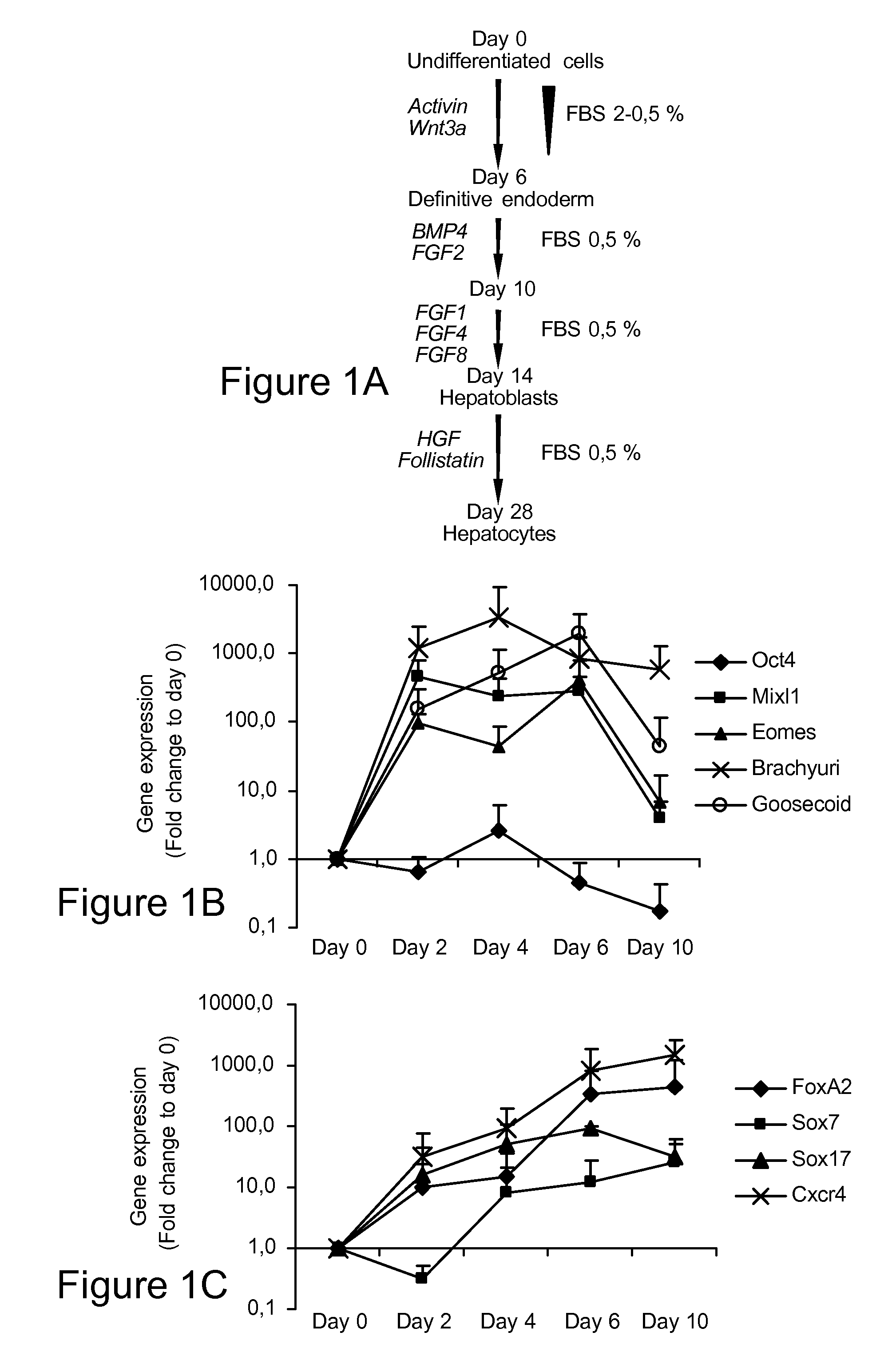
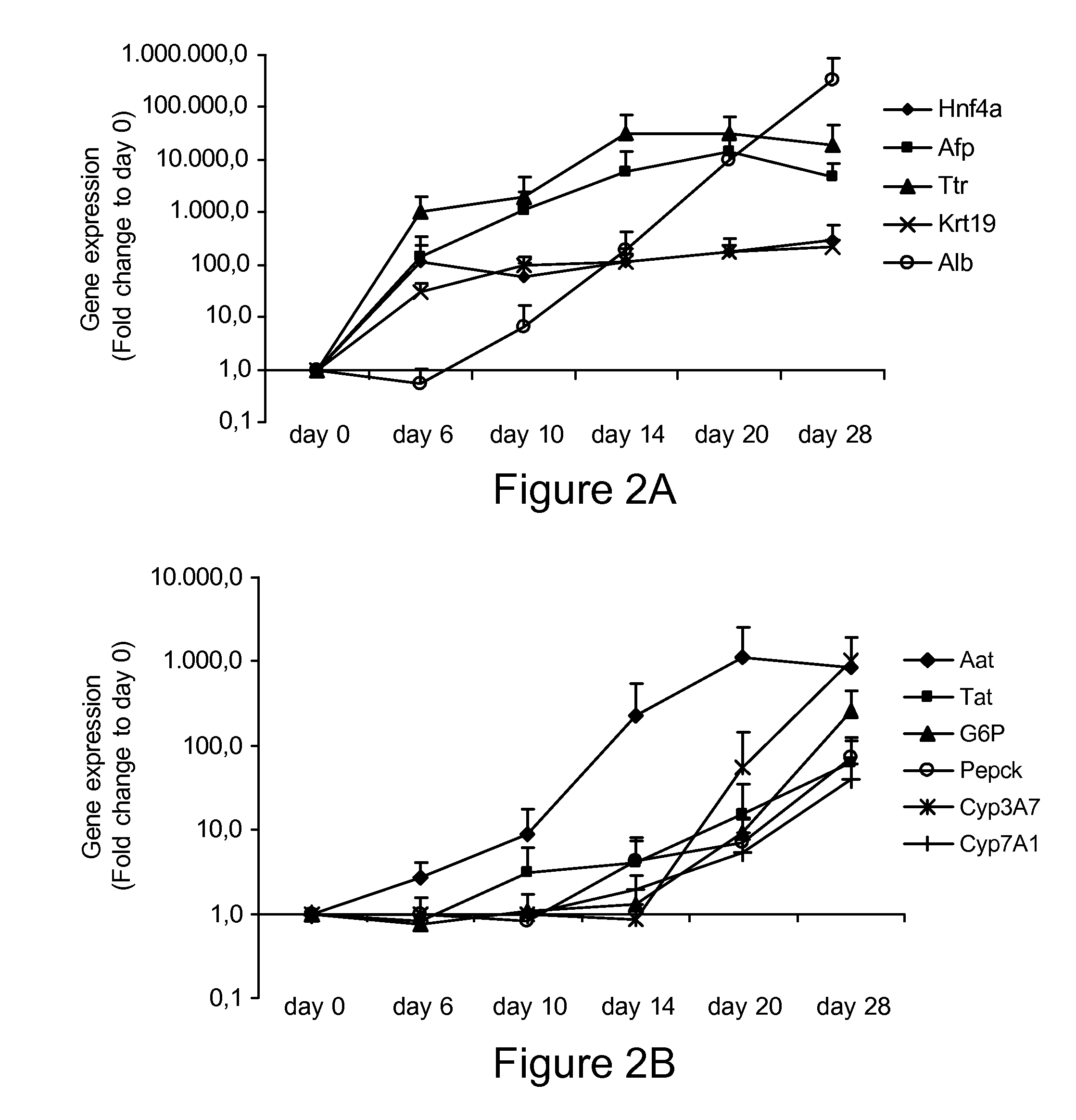
Methods for Differentiating Cells into Hepatic Stellate Cells and Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells, Cells Produced by the Methods, and Methods for Using the Cells
ActiveUS20120009672A1Artificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCulture cellLiver metabolism
The invention is directed to methods for culturing cells so that the cells are induced to differentiate into cells that express a hepatic stellate phenotype and cells that express a hepatic sinusoidal endothelial phenotype. The invention is also directed to cells produced by the methods of the invention. The cells are useful, among other things, for treatment of liver deficiency, liver metabolism studies, and liver toxicity studies.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Cell culture and method for screening for a compound useful in the treatment or prevention of hepatic cirrhosis
InactiveUS20060172416A1Simple structureMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCell specificHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention provides a cell-culturing model and a method for screening compounds which can be applied in treating or preventing hepatic cirrhosis. The cell culturing model comprises a population of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) derived from co-culturing, and at least one population of the cells comprises a nucleotide sequence fragment of a reporter gene and a cell specific regulatory sequence. The cell-culturing model of the present invention can be applied in high throughput screening for effective compounds of medication, and also in understanding the functional mechanism of the effective compounds.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of hepatic stem cell and application thereof
InactiveCN104531611AImprove proliferative abilityCapable of reproductionDigestive systemArtificial cell constructsDiseaseCD63
The invention relates to the technical field of medical bioengineering, and provided with a specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of a hepatic stem cell. The invention further provided with application of the specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of the hepatic stem cell. A method that the molecule marker is used for quickly separating, culturing and amplifying the hepatic stem cell from a liver specifically comprises the steps that the specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of the hepatic stem cell is used to quickly separate the hepatic stem cell from prepared liver cell suspension through a flow cytometer. The hepatic stem cell of the CD63+ has the characters of self-renewing and bilateral differentiation out of a body, and has therapeutical effects on a damaged mouse liver. According to the specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of the hepatic stem cell and the application of the specificity surface molecule marker CD63 of the hepatic stem cell, the hepatic stem cell obtained by separation can be served as a seed cell for liver drug screening, systematization projection liver and hepatic disease cell therapy, and provides an ideal cell model for liver development and the cell biological property research of the hepatic stem cell.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Cyclic peptide containing arginine, glycine, asparagicacid-sequence and active target liposome
InactiveCN1687118ASmall molecular weightEasy to retouchDigestive systemPeptidesArginineTherapeutic effect
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical technology and clinical pharmacy, relates to a cyclopeptide containing arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) sequence and its active liposome targeting, its preparation and application. The described cyclopeptide structure meets the requirements as ligand, and is cyclized by amido bond, its spatial conformation is stable, and is not easily degraded, its one end contains active sulphydryl group, and is convenient for modifying artificially-synthetic function peptide, its molecular weight is small, so that it is not easy to result in immune reaction, and can be used as ligand, and can be combined with hepatic stellate cell (HSC) surface integrator acceptor to construct active liposome targeting and implement target therapy for experimental hepatic fibroid cell. Said invention can obtain good therapeutic effect for curing hepatitis fibrosis.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
Treatment Of Disease By Inducing Cell Apoptosis
InactiveUS20100035825A1Promote cell proliferationPromote gene expressionTetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsAbnormal growthsDisease
The present invention relates generally to the treatment and prevention of diseases characterized by excess cell proliferation and / or activation. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods to suppress the activation and / or proliferation of various cells. In some preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods to suppress the activation and / or proliferation of mesenchymally derived cells (including, but not limited to hepatic stellate cells), as well as cells with abnormal growth characteristics. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods to inhibit or eliminate fibrosis. In alternative preferred embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods to induce fibrosis. In still further embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions to treat and / or prevent cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
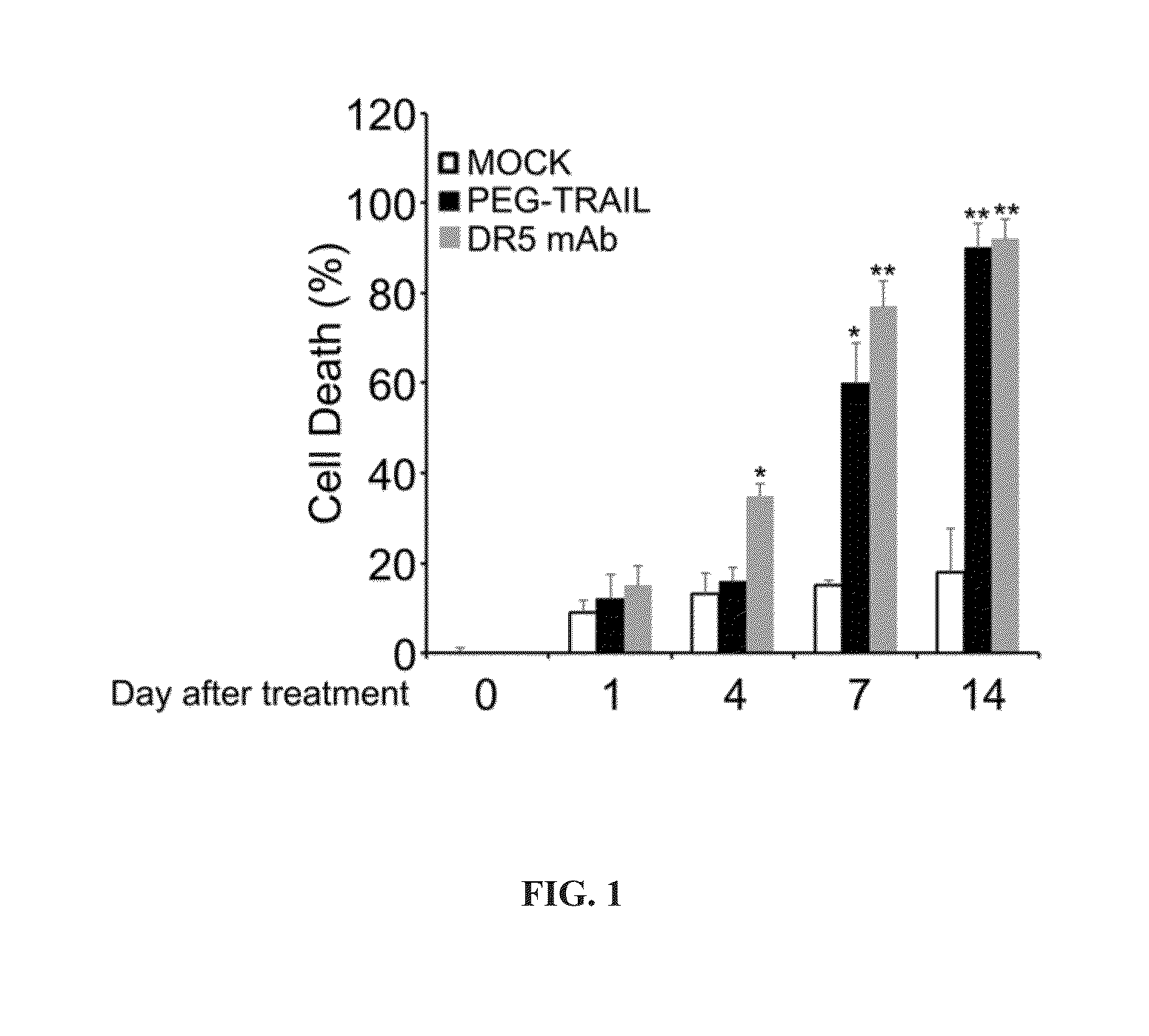
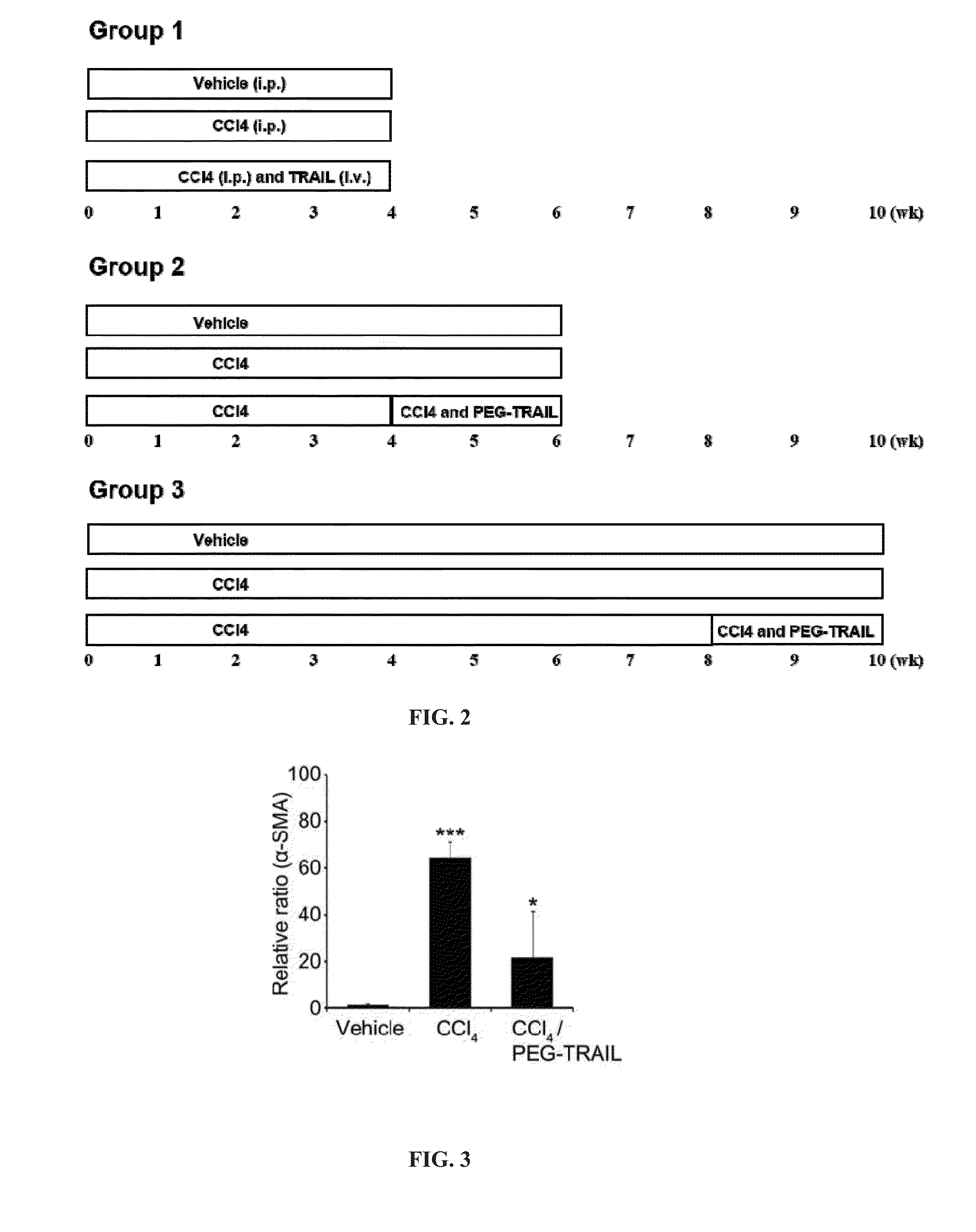
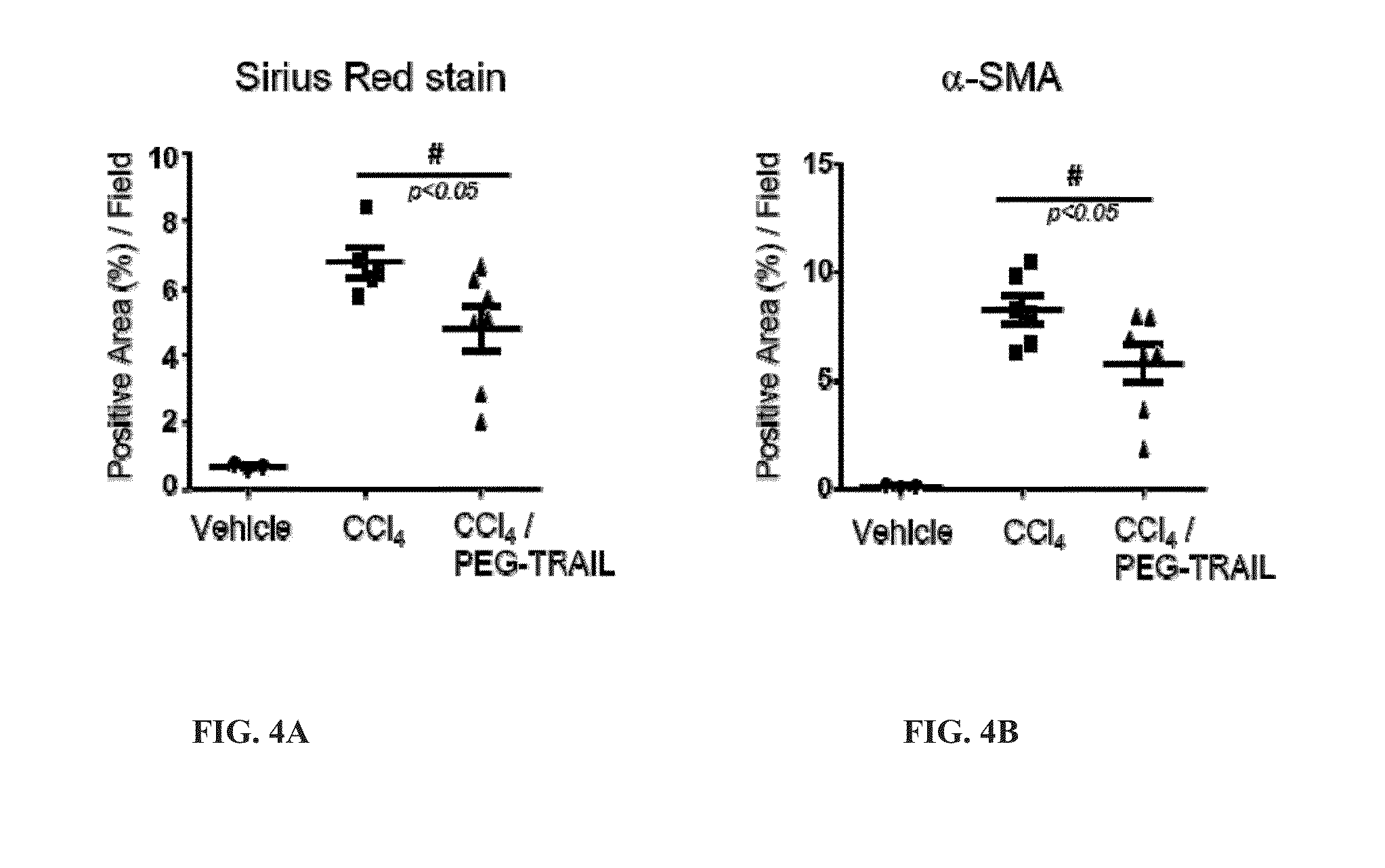
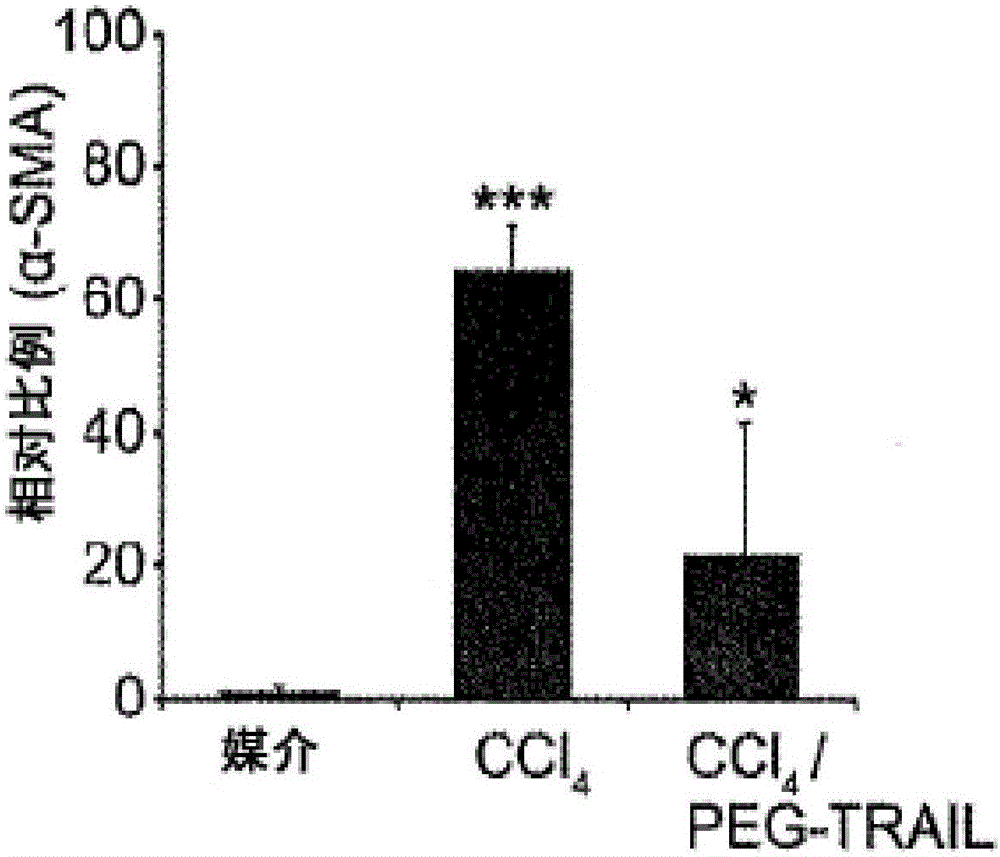
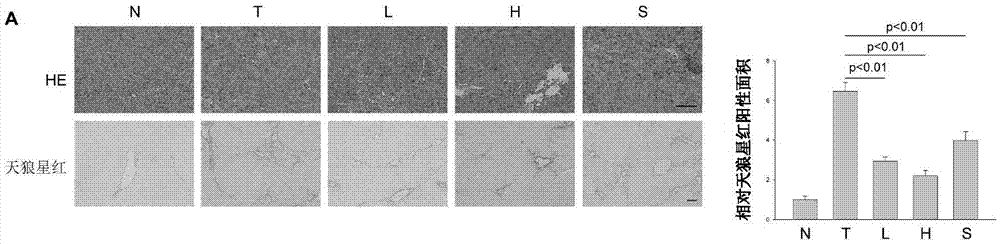
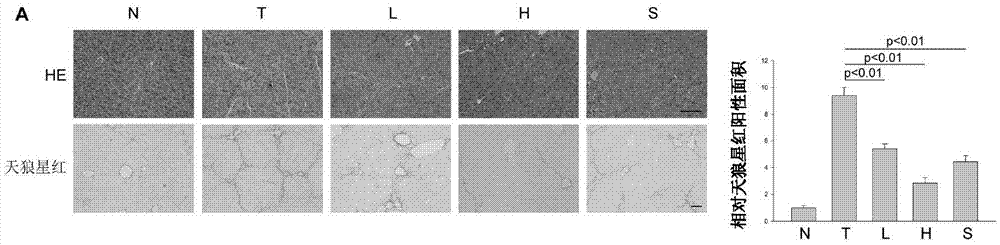
Trail receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic disease
ActiveUS20160022776A1Reduce the amount requiredUnwanted scarringPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTrail r1
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:D&D PHARMATECH INC
TRAIL receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic diseases
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:B&L DELIPHARM CORP
Application of O-GlcNAc glycosylation modification in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis
The invention provides an application of O-GlcNAc glycosylation modification in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis. In the invention, excessive activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells as well as the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and I-type collagen and the formation of fibrous septum can be inhibited by enhancing O-GlcNAc glycosylation modification, and the O-GlcNAc glycosylation modification has a good application prospect in preventing and / or treating hepatic fibrosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com