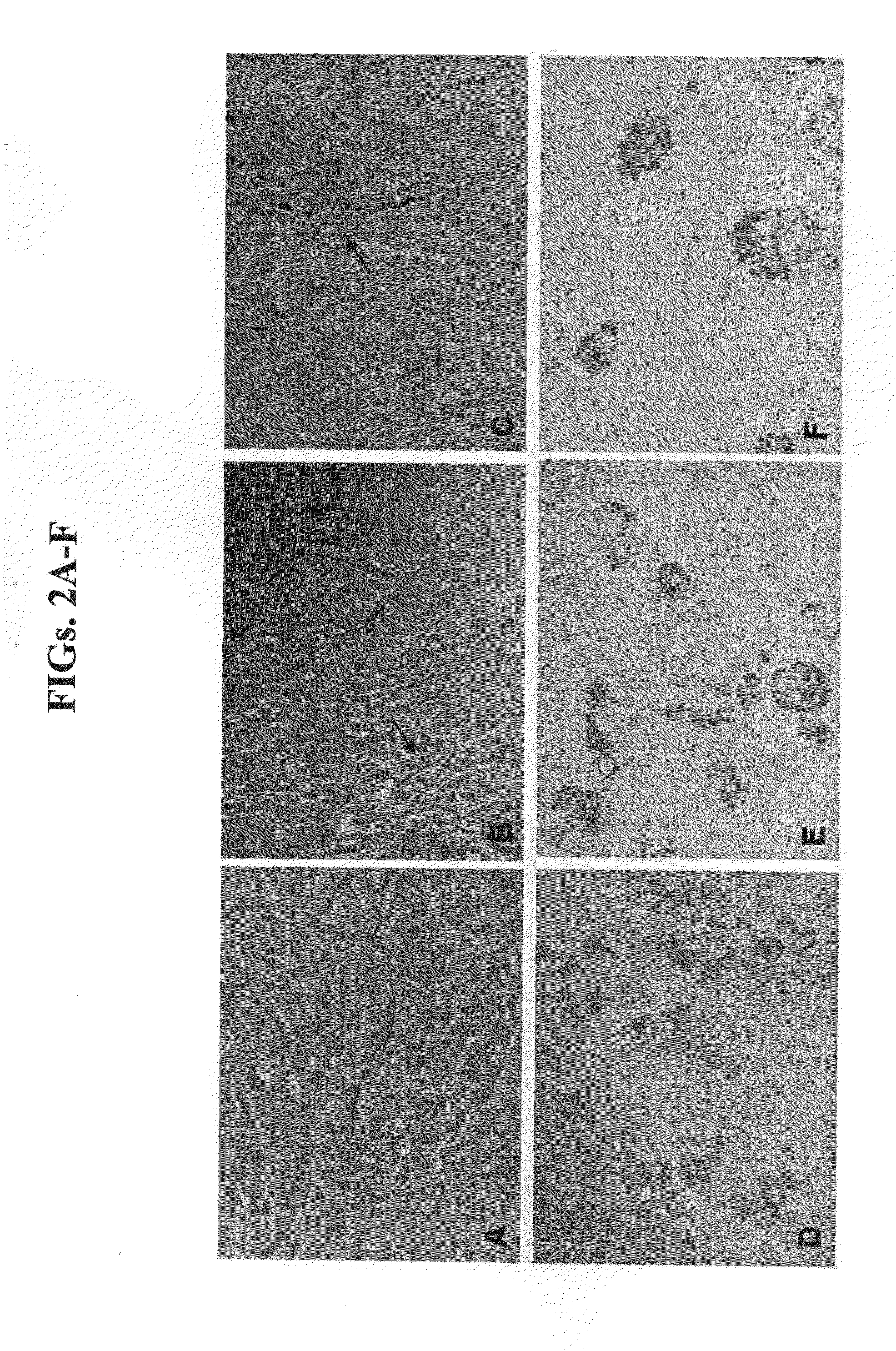
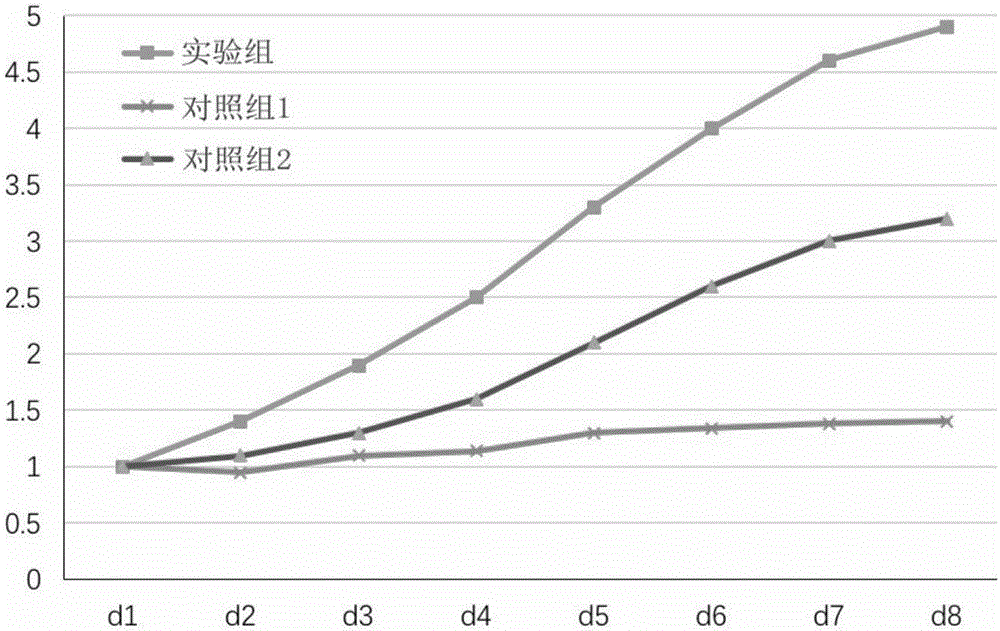
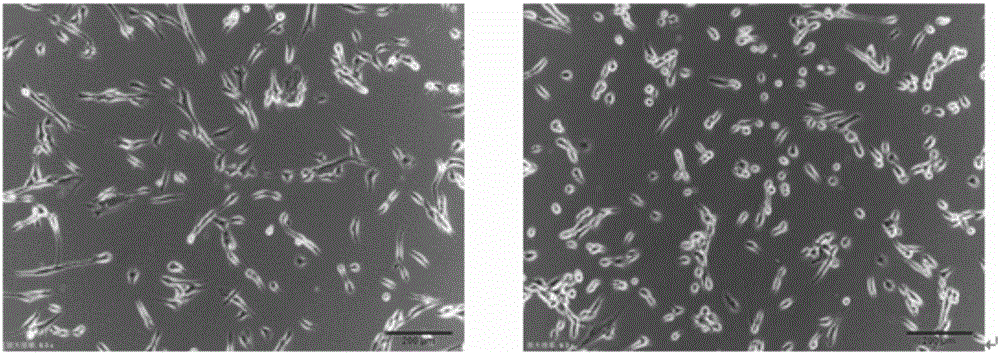
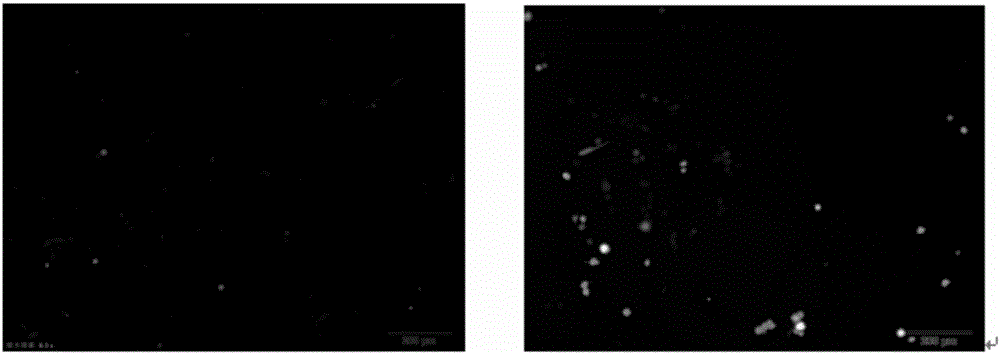
Patents
Literature
244 results about "Cell phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
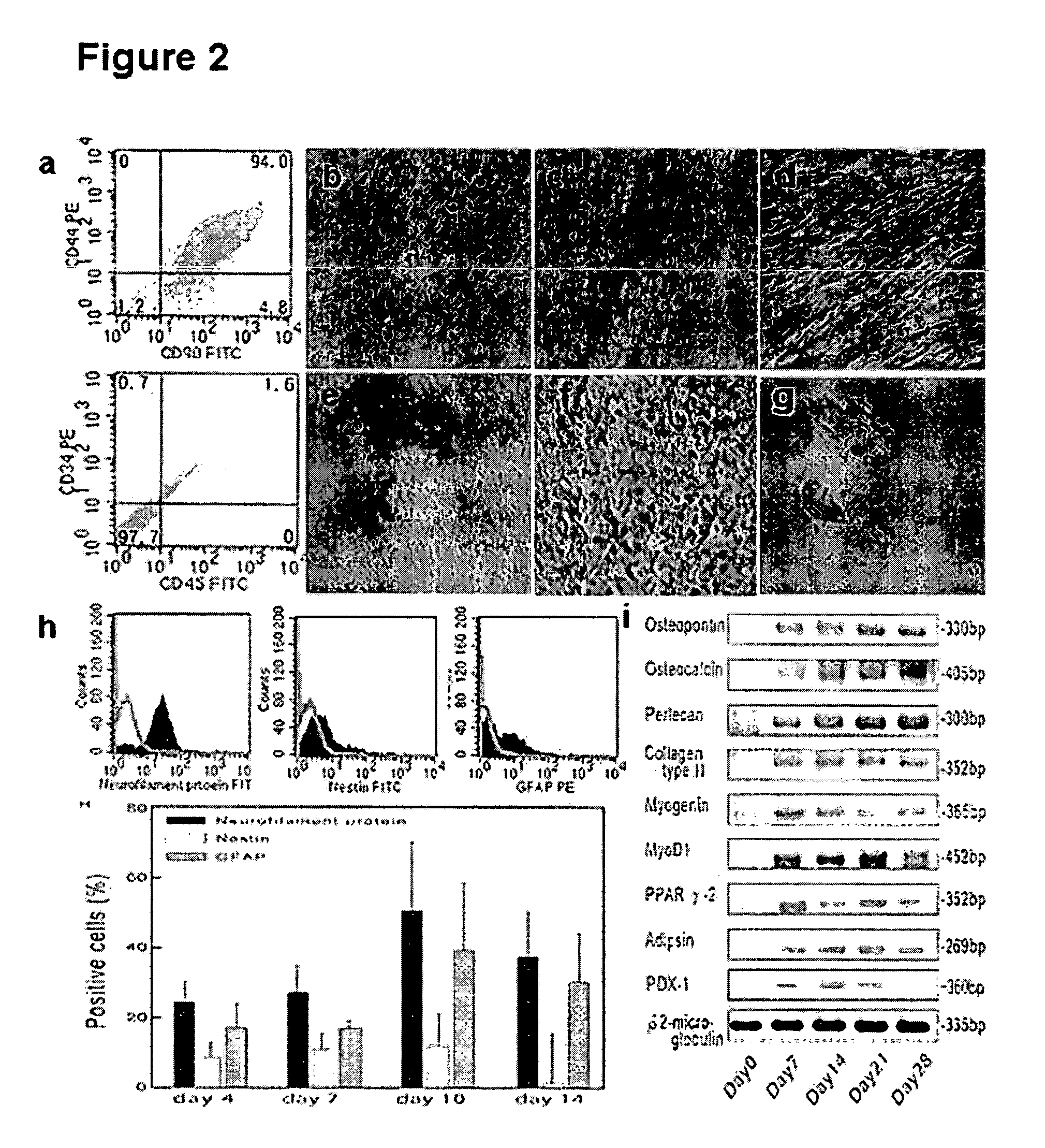
The phenotype is determined by a technique called flow cell cytometry. Briefly, this is a machine that determines which antigens (proteins) are expressed on the surface of the leukemia cell. These antigens have the names CD2, CD3, CD7, CD5, HLA-DR, etc.
Pluripotential embryonic stem cells and methods of making same
The present invention provides a non-mouse, including human, pluripotential embryonic stem cell which can:(a) be maintained on feeder layers for at least 20 passages; and(b) give rise to embryoid bodies and multiple differentiated cell phenotypes in monolayer culture.The invention further provides a method of making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell comprising culturing germ cells and germ cell progenitors in a composition comprising a growth enhancing amount of basic fibroblast growth factor, leukemia inhibitory factor, membrane associated steel factor, and soluble steel factor to primordial germ cells under cell growth conditions, thereby making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell.Also provided are compositions useful to produce the pluripotent embryonic stem cells and methods of screening associated with the method of making the embryonic stem cell.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN102827807AAvoid instabilityClear chemical compositionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeSodium bicarbonate
The invention relates to the field of biology, and discloses a serum-free culture medium which essentially comprises an IMDM (Iscove Modified Dulbecco Medium), L-glutamine, sodium bicarbonate, Hepes, recombinant human insulin, recombinant human transferrin, recombinant human albumin, 2-mercaptoethanol, protocatechuic acid, lipid, amino acid, vitamins, trace elements, Pluronic F-68, hydrocortisone, vitamin C, bonding amine or recombinant human fibronectin, progesterone, putrescine, heparin, serotonin, epidermal growth factors (EGFs), b-fibroblast growth factors (FGF), platelet derive growth factor (PDGF)-BB and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I. The serum-free culture medium is clear in chemical components, free from animal sources and serum and safe and ideal in cell cultivation and avoids the doped animal components and unstable batches, and the results of the cultured mesenchymal stem cells show that the total cellular score, the cell phenotype and the secretory cell factors are normal, so that the serum-free culture medium has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古干细胞医学工程技术研究中心
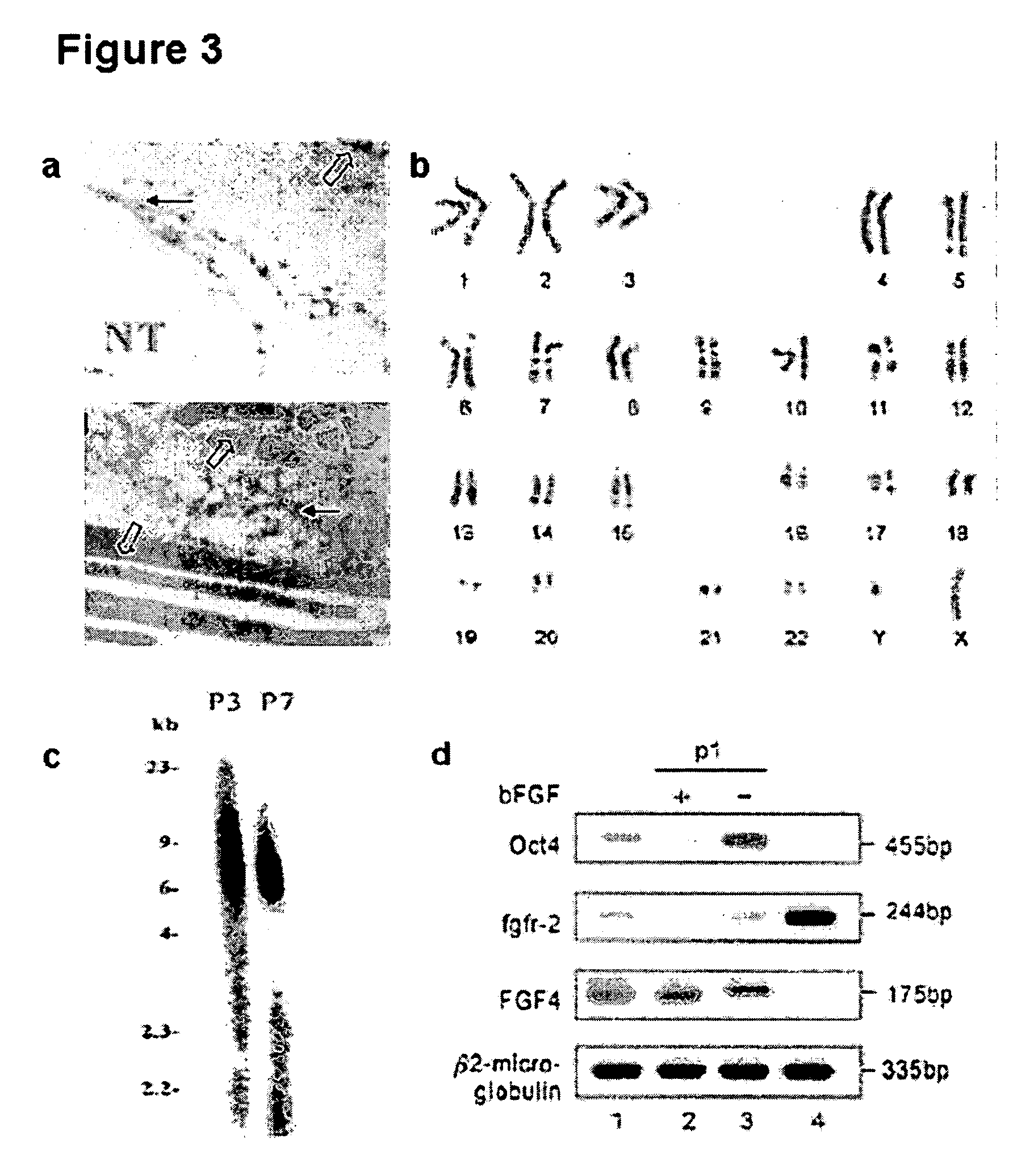
Human trophoblast stem cells and use thereof
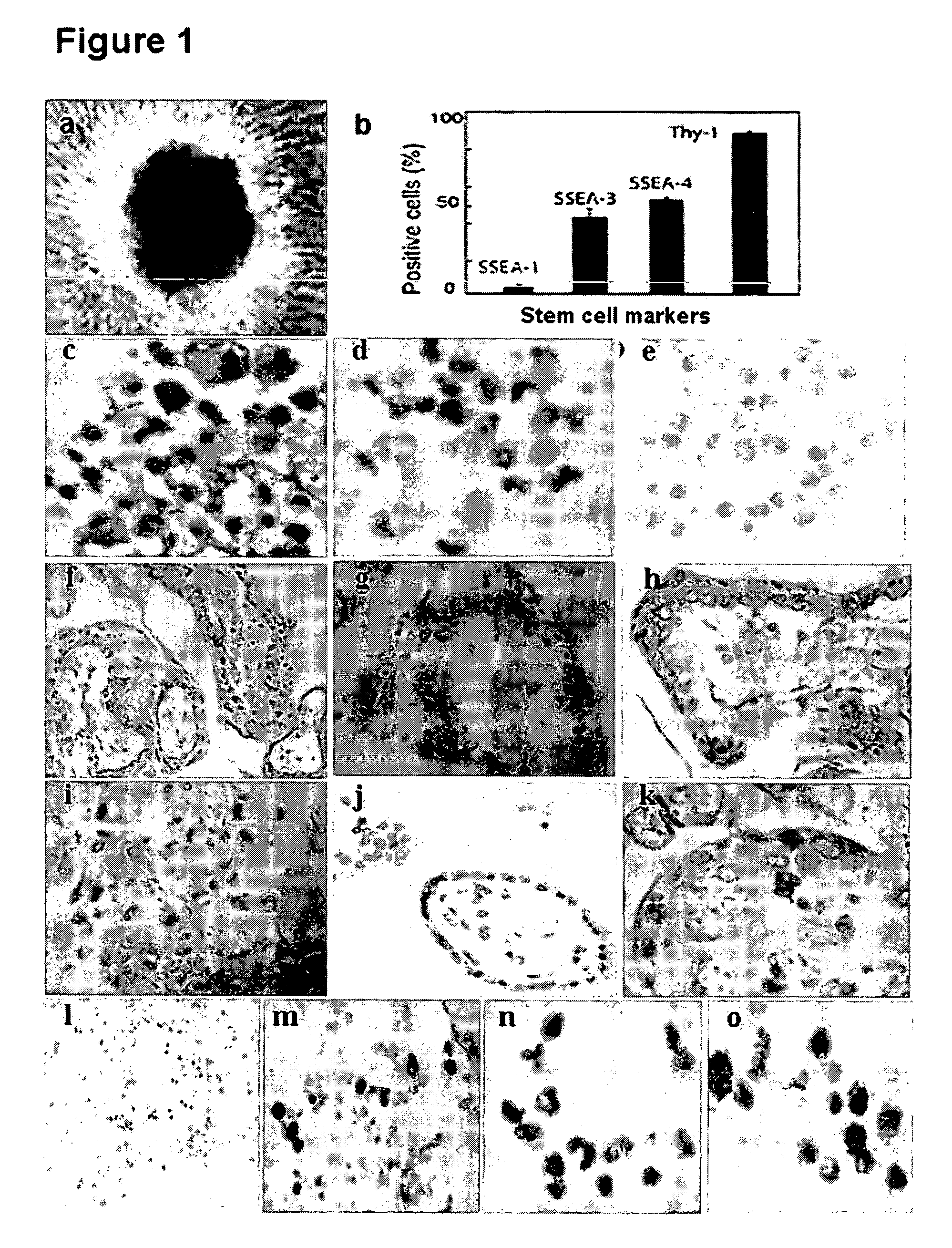
Existence of human trophoblast stem (hTS) cells has been suspected but unproved. The isolation of hTS cells is reported in the early stage of chorionic villi by expressions of FGF4, FGFR-2, Oct4, Thy-1, and stage-specific embryonic antigens distributed in different compartments of the cell. hTS cells are able to derive into specific cell phenotypes of the three primitive embryonic layers, produce chimeric reactions in mice, and retain a normal karyotype and telomere length. In hTS cells, Oct4 and fgfr-2 expressions can be knockdown by bFGF. These facts suggest that differentiation of the hTS cells play an important role in implantation and placentation. hTS cells could be apply to human cell differentiation and for gene and cell-based therapies.
Owner:ACCELERATED BIOSCI
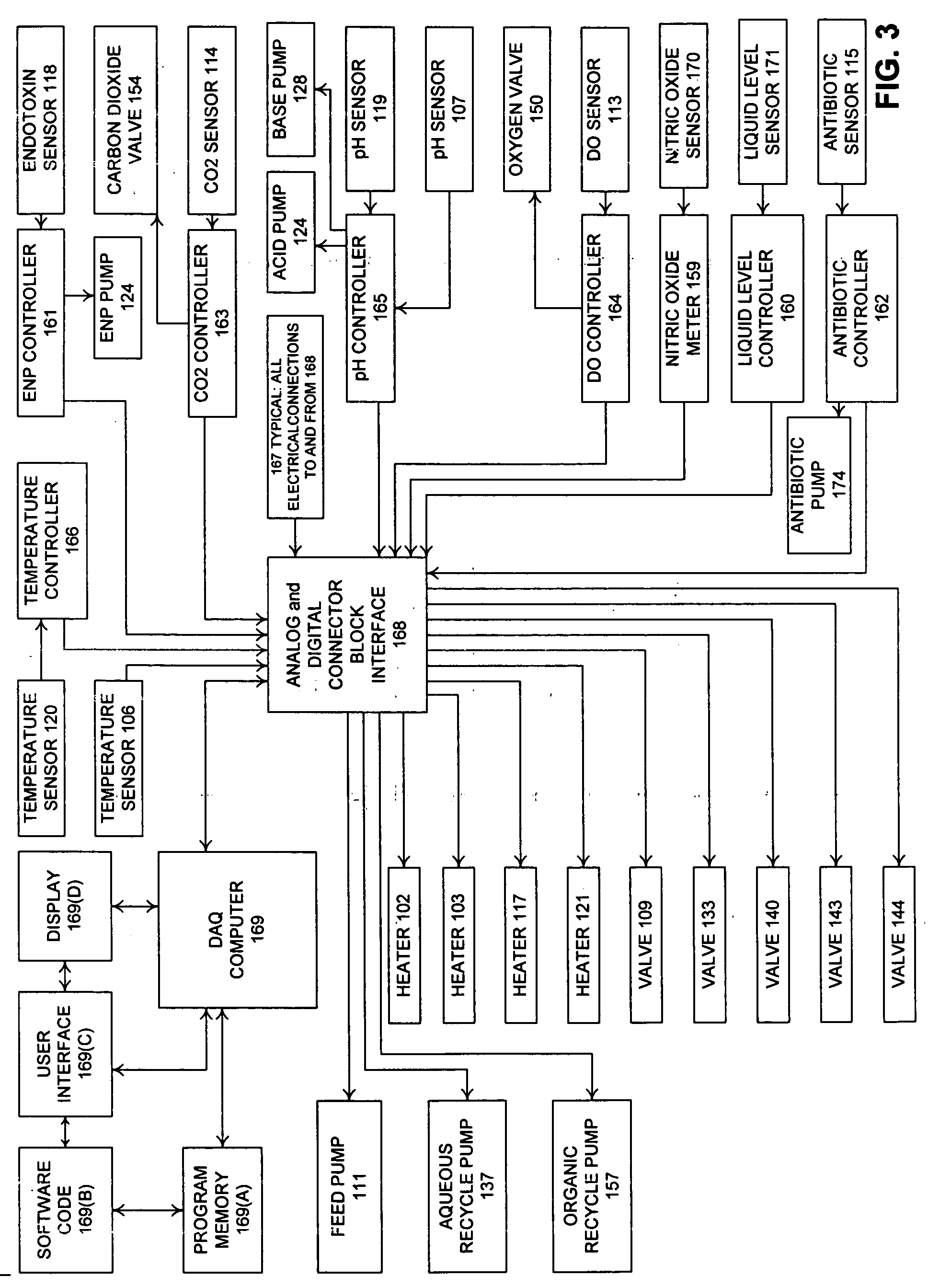
Method and apparatus for cell culture using a two liquid phase bioreactor
InactiveUS20050176140A1Maximize growthMaximize proliferationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell phenotypeEmbryo
Advanced Bioreactor Cell Culture Technology presents a method of cell culturing and bioprocessing incorporating molecular biology techniques, advanced process control methodology, and a process control interface applied to a two liquid phase cell culture bioreactors to proliferate, grow, and expand non-differentiated precursor cells, embryonic stem (ES) cells, endocrine progenitor cells, pancreatic progenitor cells, pancreatic stem cells, pancreatic duct epithelial cells, nestin-positive islet-derived progenitor cells (NIPs), or pluripotent non-embryonic stem (PNES) cells in the bioreactor, and influence, stimulate, and induce the non-differentiated precursors and progenitors into fully differentiated beta cell phenotypes; including microprocessor control of cell culture process variables and data acquisition during bioprocessing. The invention may be applied to precursors and progenitor cells either transgenic or non-transgenic derived from animals and mammals.
Owner:BENEDICT DANIEL J +1
Use of gaseous nitric oxide as an anti-cancer agent
InactiveUS20070275100A1Effectively deliver gaseous NOEfficient procedureBiocideBronchoscopesCell phenotypeAnticarcinogen
The invention relates to a method for treating, controlling, or preventing cancerous cell phenotypes and growths in an animal involving the administration of gaseous nitric oxide to one or administration sites in a body. The invention generally is capable of treating cancers found in or on the adrenal gland, bladder, bones, brain, breast, cervix, colon, colorectum, esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney, liver, large intestine, lungs, mouth, ovaries, pancreas, parathyroid, pituitary gland, prostate, salivary gland, skin, small intestine, spleen, stomach, thymus, thyroid, testicles, urinary tract, uterus, vagina, and so forth.
Owner:PULMONOX TECH
Microflow cell culture array and application thereof
InactiveCN101275114AAchieve single-cell distributionConvenient microscopic observationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiCell phenotypeMicroorganism
The present invention provides a microorganism culture array, including one or more microflow cell culture array units, the microflow cell culture array unit includes a main channel and a plurality of cell culture units connected with the main channel, each culture unit includes a diffusion channel and a cell culture room, the cell culture room is connected with the main channel. The microorganism culture array of the invention not only realizes isolation of single-cell, but also makes the cell locate in zero flow state when the culture liquid or other reagent is changed, bringing greatly convenience for the cell culture and observation especially the culture and observation of non-adherent cells, greatly fit for research work of high throughput screen based on the cell phenotype.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Human trophoblast stem cells and use thereof
Existence of human trophoblast stem (hTS) cells has been suspected but unproved. The isolation of hTS cells is reported in the early stage of chorionic villi by expressions of FGF4, fgfr-2, Oct4, Thy-1, and stage-specific embryonic antigens distributed in different compartments of the cell. hTS cells are able to derive into specific cell phenotypes of the three primitive embryonic layers, produce chimeric reactions in mice, and retain a normal karyotype and telomere length. In hTS cells, Oct4 and fgfr-2 expressions can be knockdown by bFGF. These facts suggest that differentiation of the hTS cells play an important role in implantation and placentation. hTS cells could be apply to human cell differentiation and for gene and cell-based therapies.
Owner:ACCELERATED BIOSCI
Isolated Oligodendrocyte-Like Cells and Populations Comprising Same for the Treatment of CNS Diseases
Isolated human cells and populations thereof are provided comprising at least one oligodendrocyte phenotype and at least one mesenchymal stem cell phenotype, wherein the mesenchymal stem cell phenotype is not an oligodendrocyte phenotype. Methods of generating and using same are also provided.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Serum-free medium and method for culturing mesenchymal stem cell
InactiveCN106479971AImprove stabilityIncrease success rateCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeSerum free media
The invention belongs to the technical field of stem cells, and particularly relates to a serum-free medium for culturing a mesenchymal stem cell. According to the serum-free medium, a basal culture medium L-DMEM or DMEM / F12 and multiple additives are combined in a customized manner for MSCs in vitro culture, so that ingredients in the culture medium are synergized; the stability and success rate for culturing MSCs in vitro can be greatly improved especially due to application of DKK-1; and the safety of cultured cells in clinical researches is improved by adopting a formula without animal-sourced ingredient. Compared with the prior art, the serum-free medium has the advantages of greatly improving the value adding efficiency of MSCs in vitro culture and maintaining cell growth form of MSCs and cell phenotype stability thereof, provides a novel efficient, stable and safety culture system to MSCs culture in clinical application, and has high scientific researching and medical application values.
Owner:深圳江淼医疗有限公司
Therapeutic modulation of the fas pathway
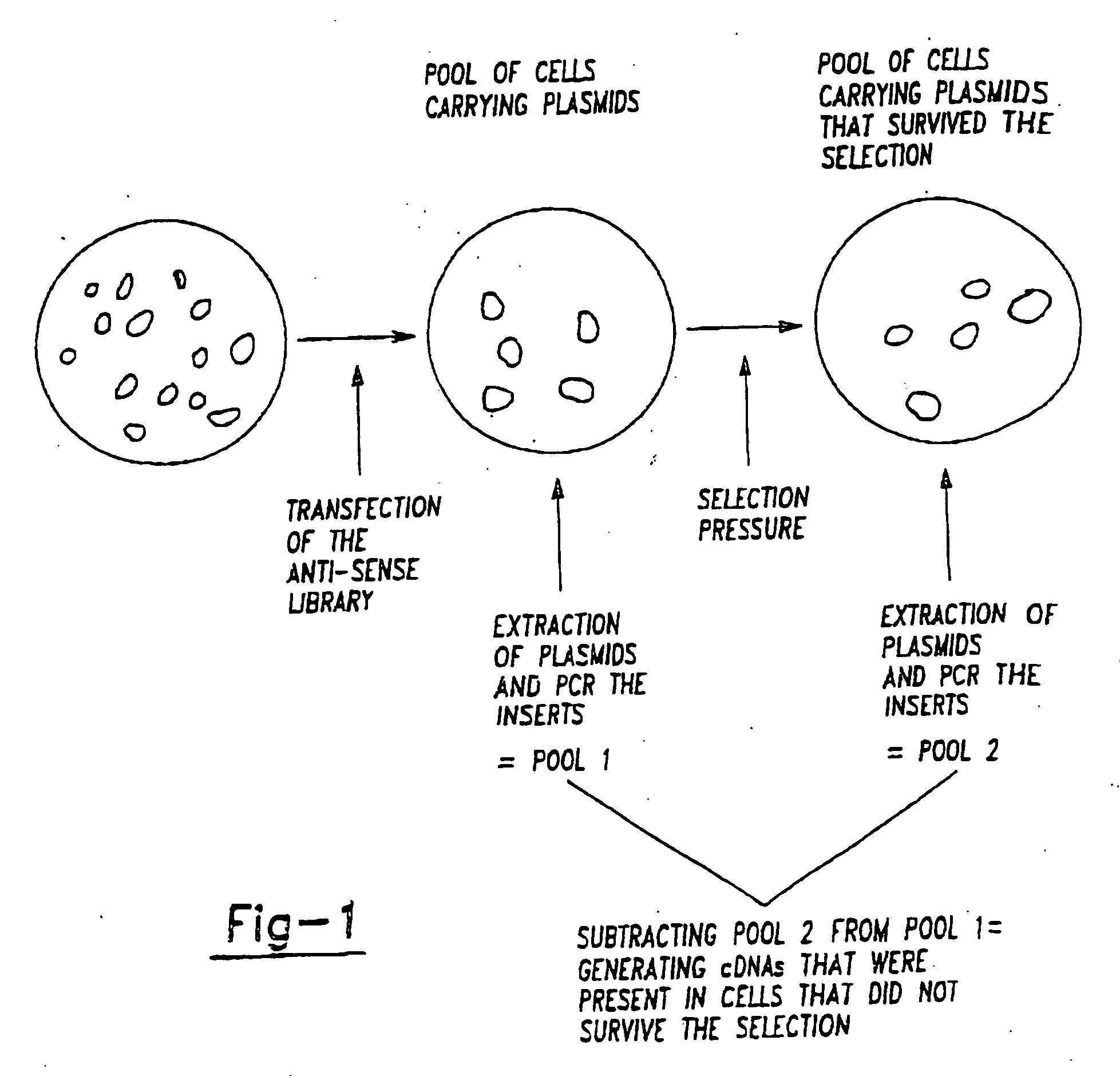
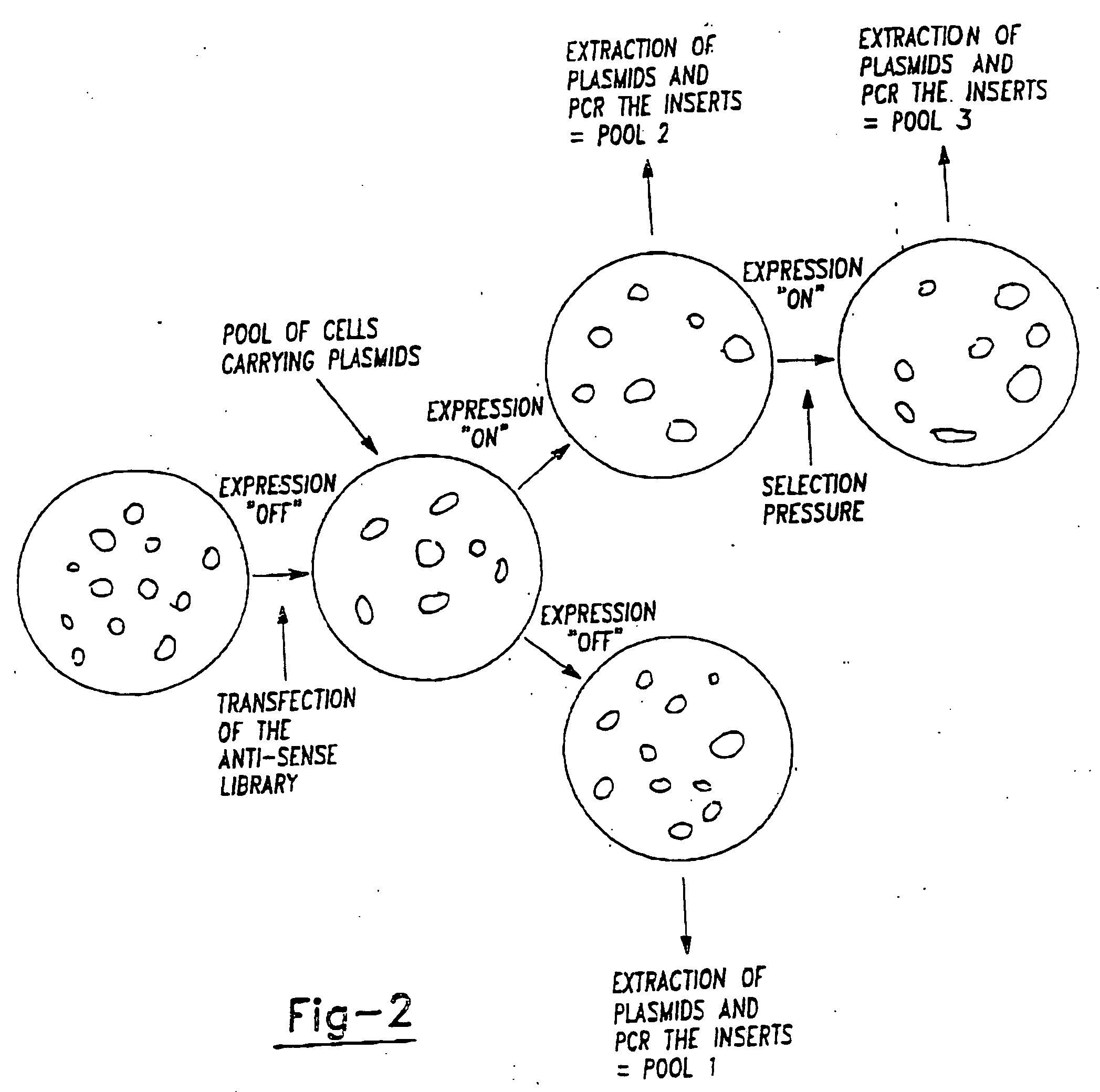
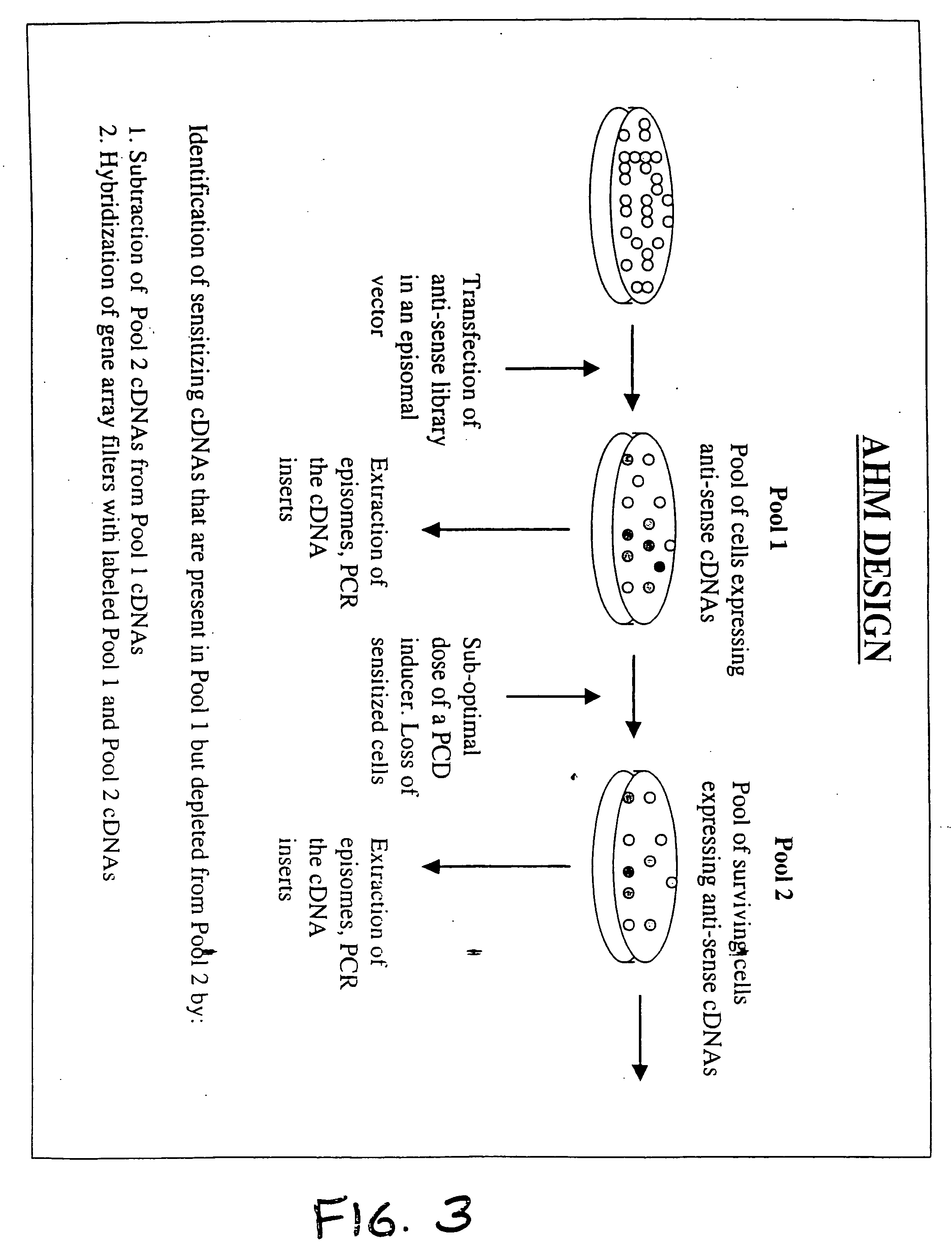
A method for the identification of genes that are essential for the maintenance of specific cell phenotypes is disclosed. The method includes the initial step of identifying a cell type with a phenotype of interest. Gene inactivation is performed on an aliquot of cells of the cell type of interest. Selection is then performed to an aliquot of the cell culture to which gene inactivation has been applied. Cells which continue to maintain the phenotype following gene inactivation have not had the gene of interest inactivated whereas cells in which genes necessary for maintaining the phenotype have been inactivated have been lost. Utilizing subtraction analysis between treated and untreated aliquots the gene in the cells which has been inactivated that affects the phenotype of interest is identified. Genes that are identified by the method are also disclosed as well as antibodies directed against the gene product of the identified genes. Further a customized kit for the practice of the gene identification method is also disclosed.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
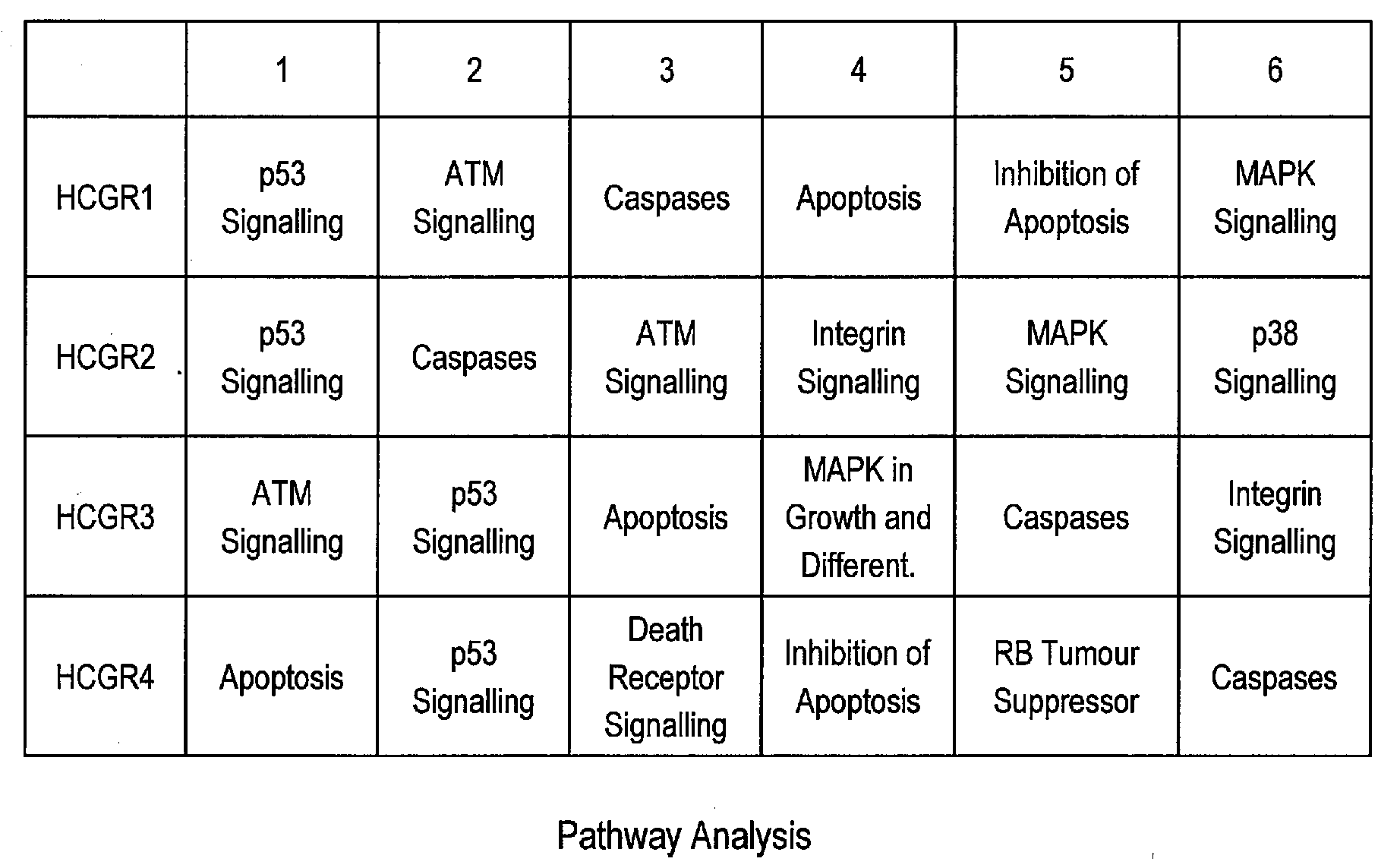
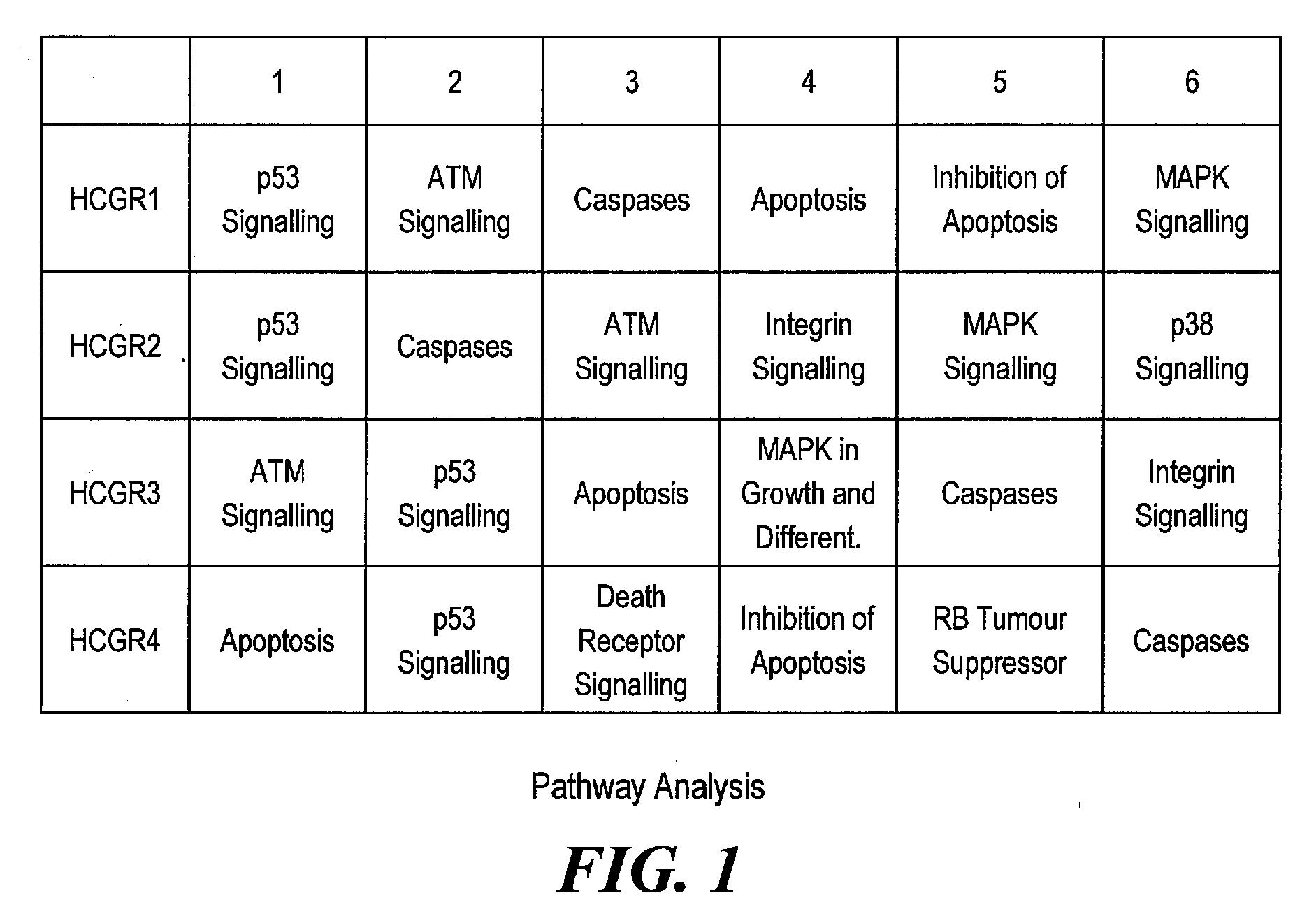
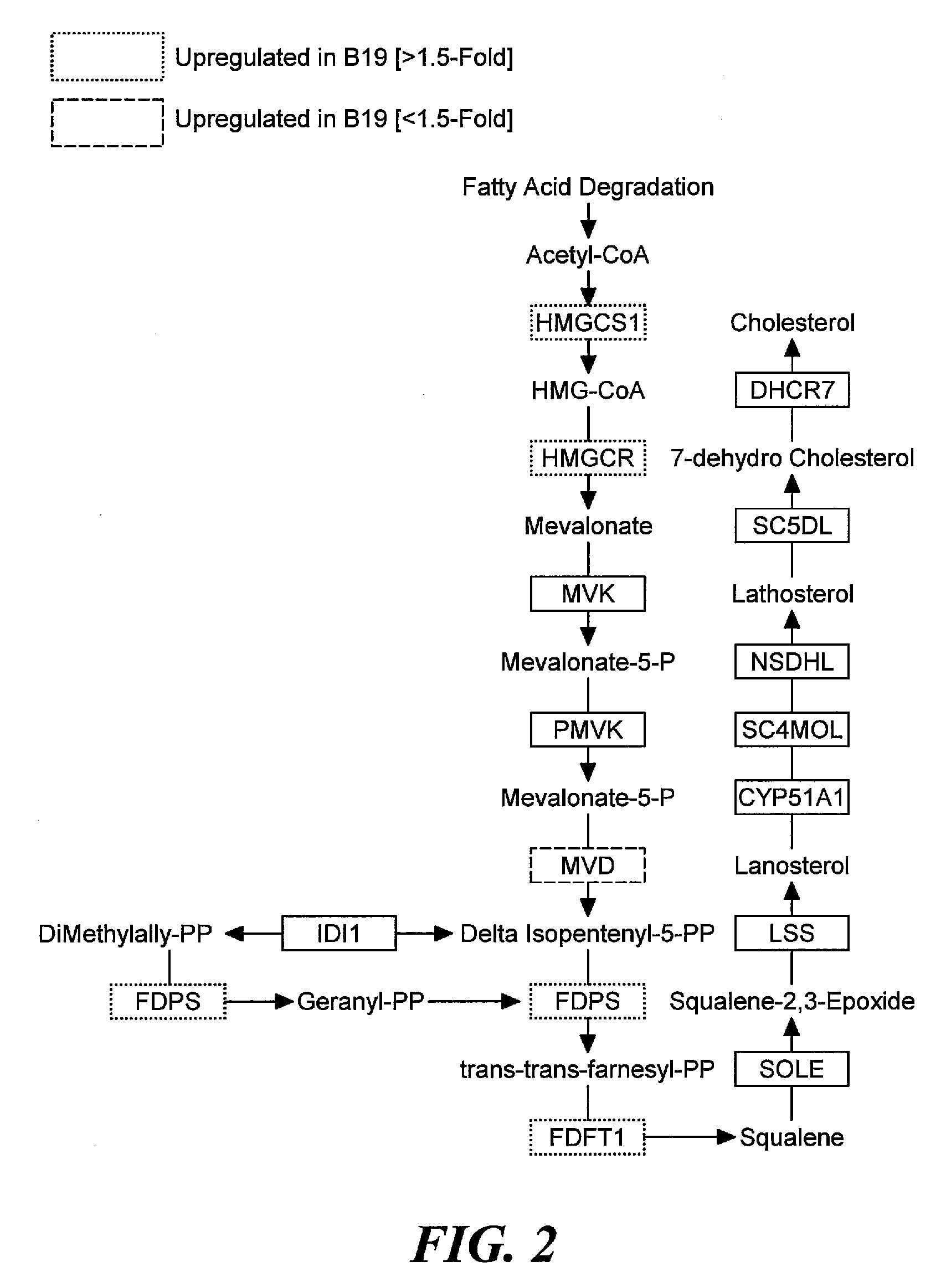
Pathway Analysis of Cell Culture Phenotypes and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090186358A1Improved sustained high cell viabilityImproved sustained high cellular productivityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCell phenotypeCultured Cell Line
The present invention provides methods for systematically identifying genes, proteins and / or related pathways that regulate or indicative of cell phenotypes. The present invention further provides methods for manipulating the identified genes, proteins and / or pathways to engineer improved cell lines and / or to evaluate or select cell lines with desirable phenotypes.
Owner:WYETH +1
Microfluidic diffusion and open intervening cell culture array chip and fabrication method and application thereof
InactiveCN102586105AGuaranteed gasGuarantee the environmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell phenotypeDiffusion network
The invention relates to a microfluidic diffusion and open intervening cell culture array chip and a fabrication method and application thereof. The cell culture array chip is suitable for cell culture, stem cell proliferation, drug screening, regenerative medicine and the like. The cell culture array chip comprises a base and a substrate fixed on the base, wherein a plurality of hole-like cell culture unit are distributed on the substrate; and a microfluidic main channel and a microfluidic diffusion channel, which are intercommunicated with each other, are arranged on the substrate and are communicated with each cell culture unit and the external environment. The cell culture array chip provided by the invention has the following advantages: (1) the required culture solution, growth factors and the like are supplied through a microfluidic diffusion network, so as to result in a zero cell shearing force and ensure the gas and moisture environment required for cell growth; (2) the in vivo microenvironment multichannel microfluidic concentration gradient of cells is simulated, and the quantitative drug release at a fixed time and other functions are realized; (3) the chip is suitable for high-throughput drug screening research on cell phenotype; and (4) the chip has a compact structure and low cost, and is suitable for batch production.
Owner:武汉介观生物科技有限责任公司
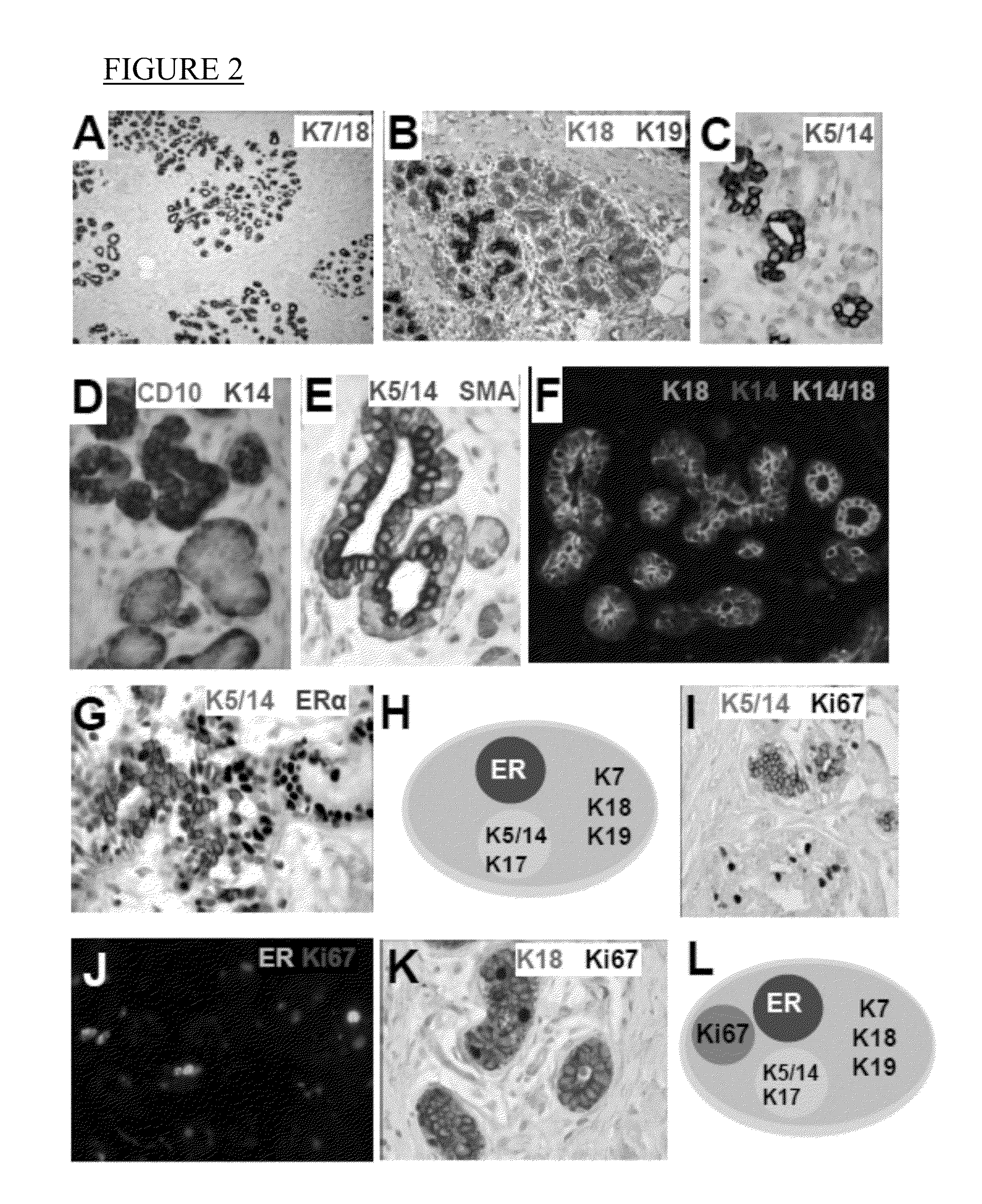
Classification system, methods and kit for classifying, predicting and treating breast cancer
InactiveUS20160146819A1Good understand and treat breast cancerSolid foundationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCell phenotypeBreast cancer classification
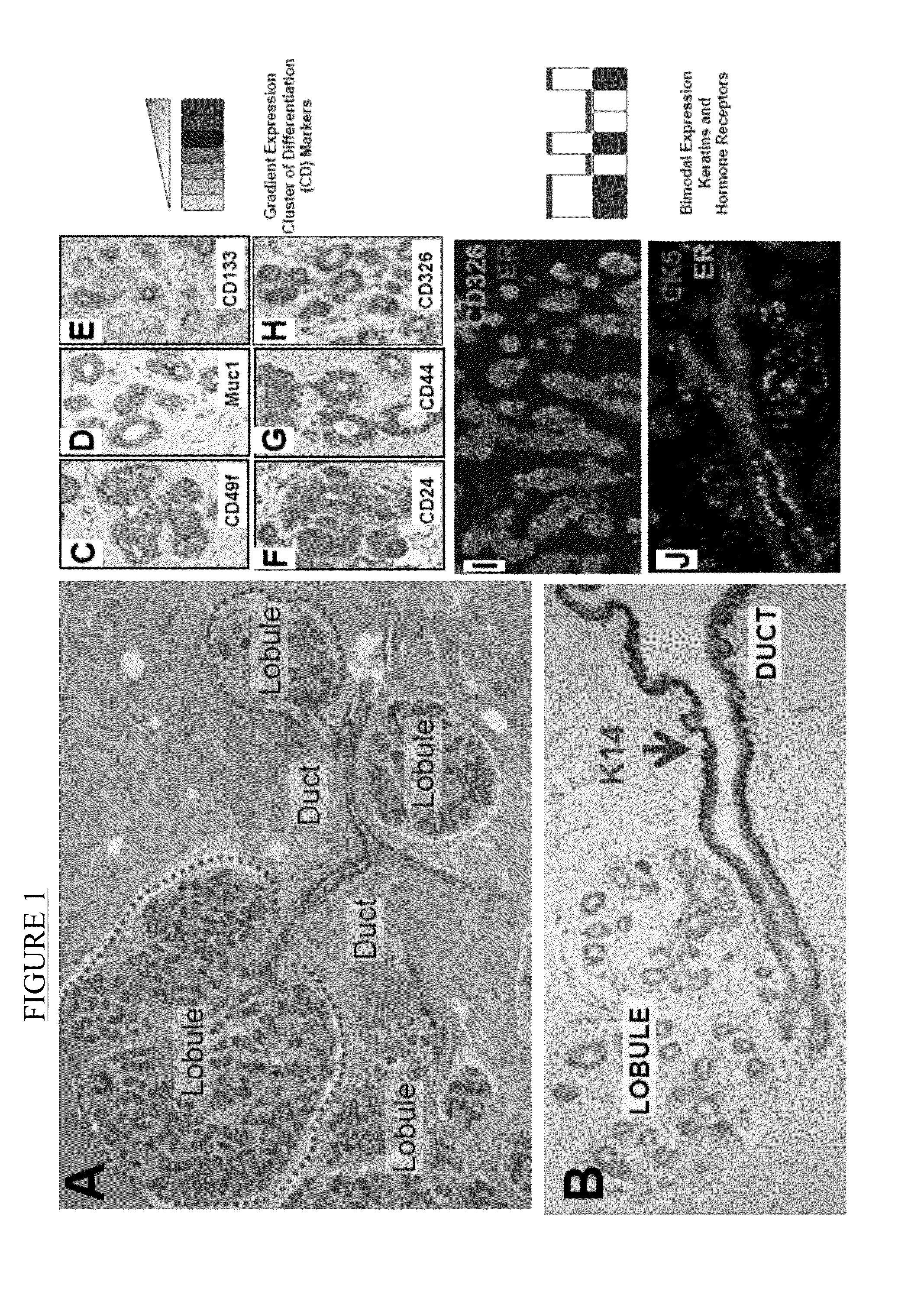
A novel classification system for breast cancer based on normal breast cell phenotypes and various expression levels of estrogen receptor (ER), androgen receptor (AR), and vitamin D receptor (VDR). The various categories of the classification system are associated with different survival rates and prognoses. The invention includes a method of classifying breast cancer comprises measuring the levels of ER, AR, and VDR in the cancerous tissue, and classifying the breast cancer into one of the above-noted categories according to expression levels. The invention includes a method of predicting the prognosis of breast cancer in a patient and a method of determining a treatment regimen for breast cancer depending on the category in which the breast cancer is classified. The invention includes a method of treating breast cancer according to the expression profile of ER, AR, and VDR detected in the cancerous tissue. Kits for detecting the same are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Animal source-free and serum-free culture medium of lymphocyte
InactiveCN103146648AGood amplification factorEnhance cell viabilityBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeSodium bicarbonate
The invention relates to the biological field and discloses an animal source-free and serum-free culture medium of lymphocyte. The culture medium disclosed by the invention essentially consists of IMDM (Iscove Modified Dulbecco Medium), L-glutamine, sodium bicarbonate, recombinant human insulin, human transferrin, human serum albumin, 2-mercaptoethanol, N-acetyl-cysteine, lipid, amino acid, vitamin, microelement, ferric citrate, hydrocortisone, cholamine and non-essential amino acid. The serum-free culture medium disclosed by the invention has the advantages of clear chemical components, no animal source, no serum, safe and ideal culture cells; the instability caused by the doping of animal components and batches is avoided; the result of culturing lymphocyte shows that the total number of the cells and the cell phenotypes are normal; and the serum-free culture medium disclosed by the invention has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING JING MENG STEM CELL TECH
Methods and systems for the identification of components of mammalian biochemical networks as targets for therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050267720A1Low costAvoid delayData processing applicationsAnalogue computers for chemical processesCellular componentCell phenotype
Systems and methods for modeling the interactions of the several genes, proteins and other components of a cell, employing mathematical techniques to represent the interrelationships between the cell components and the manipulation of the dynamics of the cell to determine which components of a cell may be targets for interaction with therapeutic agents. A first such method is based on a cell simulation approach in which a cellular biochemical network intrinsic to a phenotype of the cell is simulated by specifying its components and their interrelationships. The various interrelationships are represented with one or more mathematical equations which are solved to simulate a first state of the cell. The simulated network is then perturbed by deleting one or more components, changing the concentration of one or more components, or modifying one or more mathematical equations representing the interrelationships between one or more of the components. The equations representing the perturbed network are solved to simulate a second state of the cell which is compared to the first state to identify the effect of the perturbation on the state of the network, thereby identifying one or more components as targets. A second method for identifying components of a cell as targets for interaction with therapeutic agents is based upon an analytical approach, in which a stable phenotype of a cell is specified and correlated to the state of the cell and the role of that cellular state to its operation. A cellular biochemical network believed to be intrinsic to that phenotype is then specified by identifying its components and their interrelationships and representing those interrelationships in one or more mathematical equations. The network is then perturbed and the equations representing the perturbed network are solved to determine whether the perturbation is likely to cause the transition of the cell from one phenotype to another, thereby identifying one or more components as targets.
Owner:HILL COLIN +2
Instant, in-situ, nondestructive material differentiation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20140358447A1Improve abilitiesMaximize transmissivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalCell phenotypePrincipal component analysis
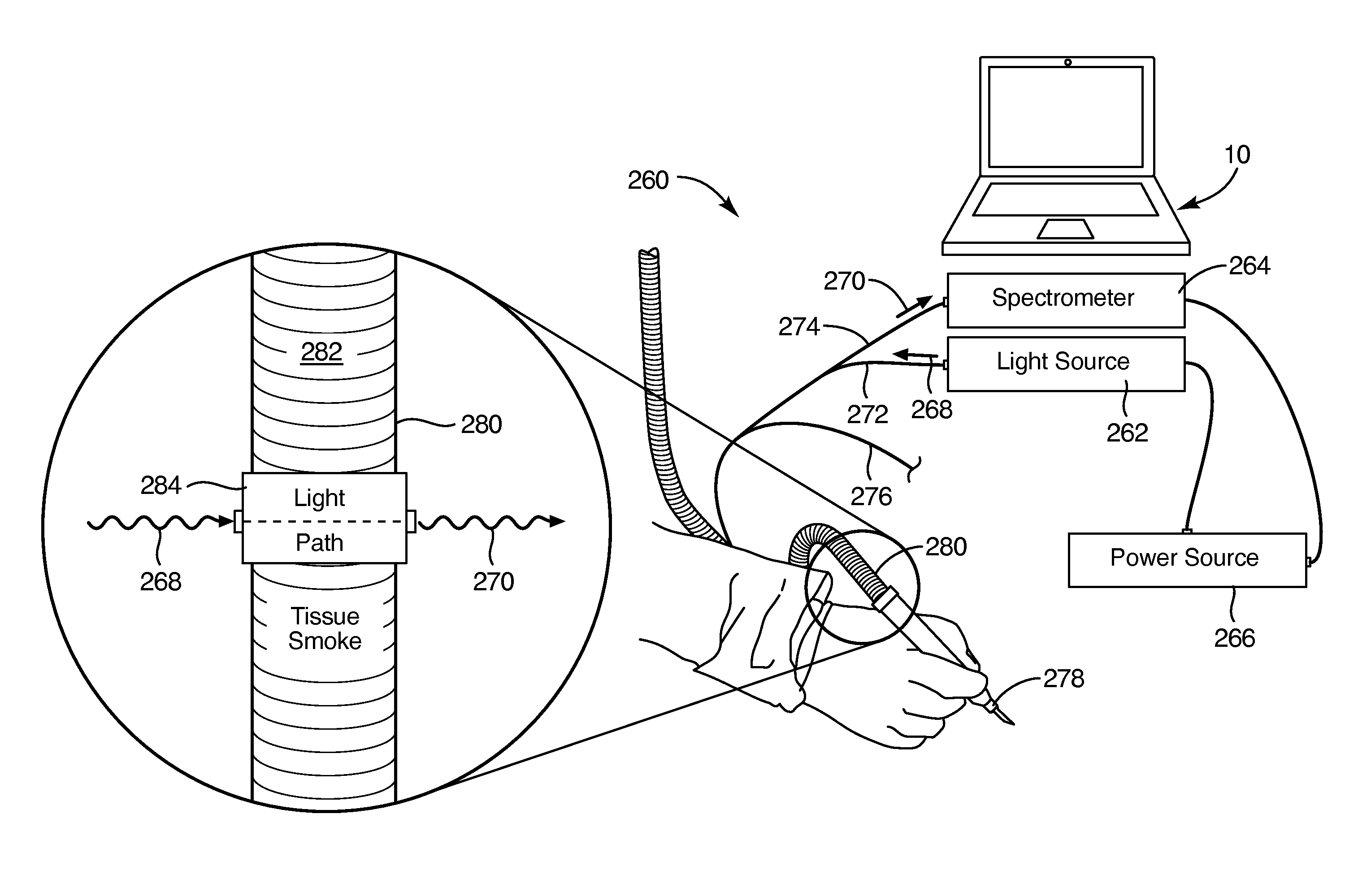
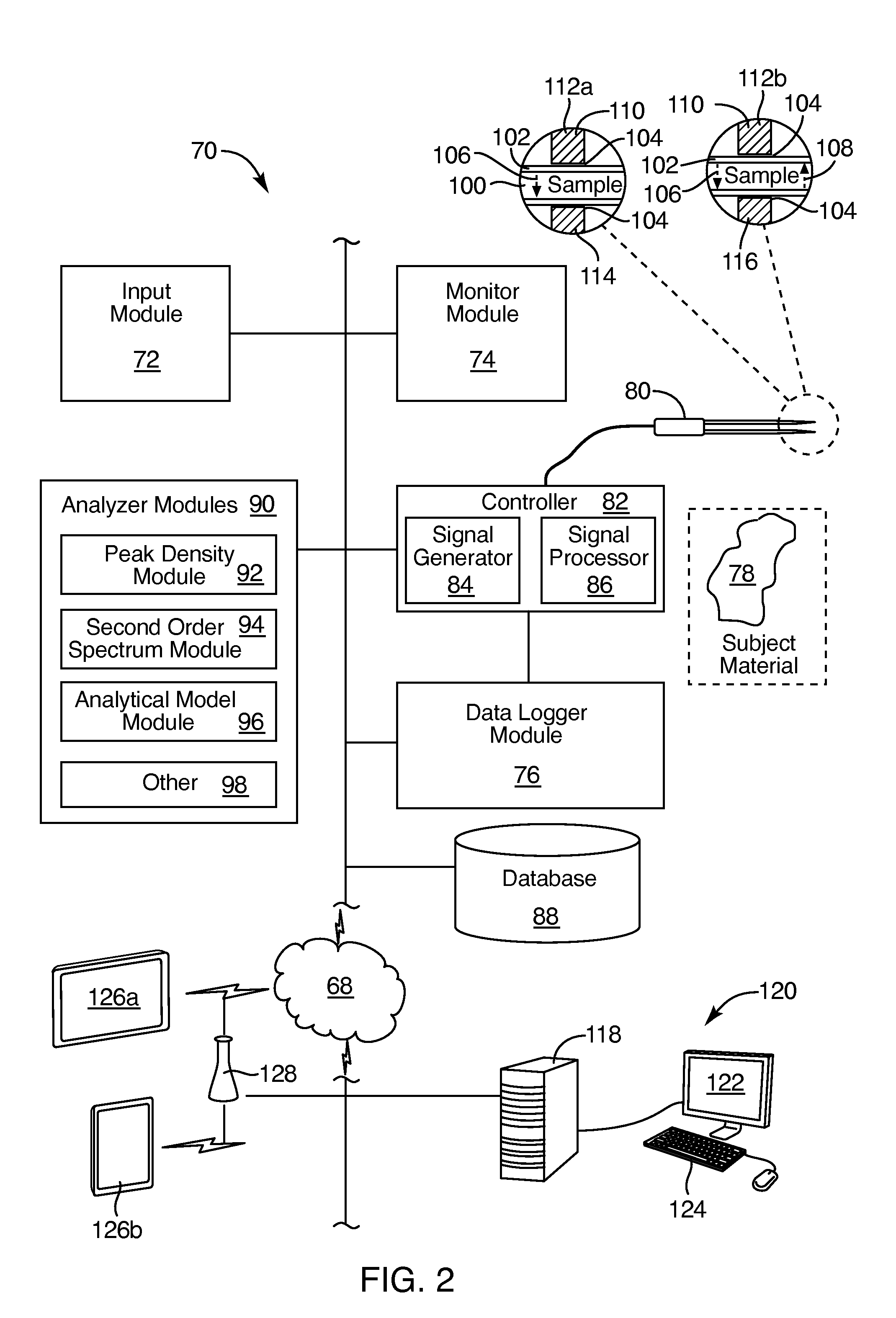
Specular, ultrasonic, piezoelectric, detection devices provide real-time, analytical, edge finding in tissues during tumor surgery. Piezoelectric probe sensors at high frequencies (e.g., 10 to 100 MHz) characterize microstructure of cells and tissues. Through-transmission or specular reflection enables nondestructive testing in real time. Peak density analysis in power spectra, second-order spectrum analysis measuring the slope of the Fourier transform of the power spectrum, artificial intelligence pattern recognition, and modeling interpret the results. Model-based data analysis may compare experimental data with a computer simulation. Such comparisons may be based upon pattern classifications, including principal component analysis (PCA). Combining the above detection devices and analytical methods provides speed, accuracy, simplicity, and nondestructive mechanisms that militate for reliable, real-time diagnosis of tumor margins, tissue pathology, cell phenotypes, and molecular subtypes.
Owner:UTAH VALLEY UNIVERSITY
Methods for in vitro expansion and transdifferentiation of human pancreatic acinar cells into insulin-producing cells
InactiveUS20060122104A1Easy to makeEasy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic cellsTransdifferentiationCell phenotype
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for expanding mammalian acinar cells, comprising culturing the cells in a cell culture system comprising a cell culture medium and a cell attachment surface, under conditions wherein the acinar cells undergo a 3-4 fold expansion together with transdifferentiation into a modified cell phenotype (IP cells) showing characteristics of acinar cells and liver cells. The invention also relates to a method for transforming these IP cells to insulin-producing cells in vitro, comprising culturing the cells in a novel, defined medium. Also disclosed are suitable culture media for performing these methods, isolated cells having the phenotype of IP cells and / or produced by these methods, and kits for performing the methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
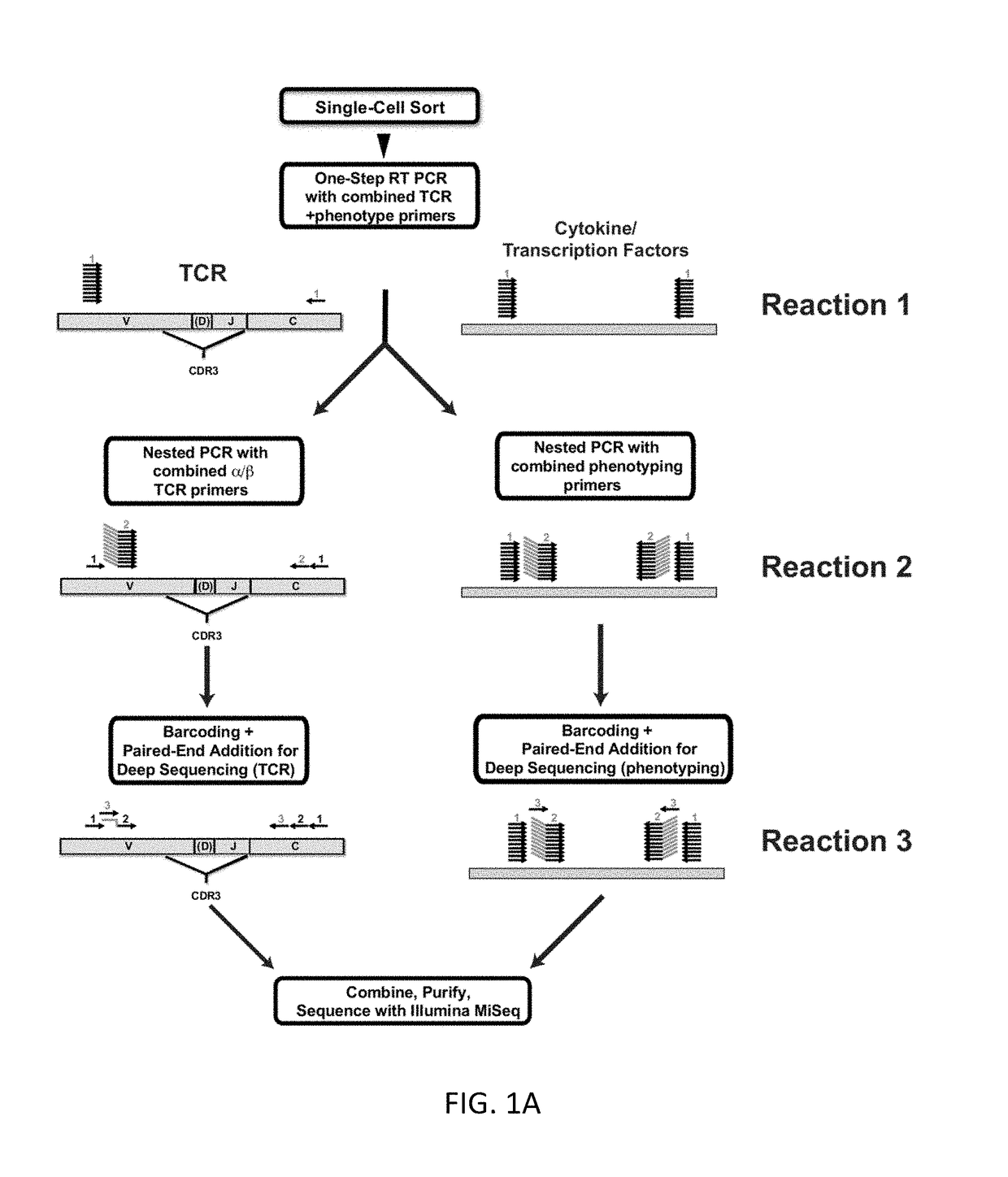
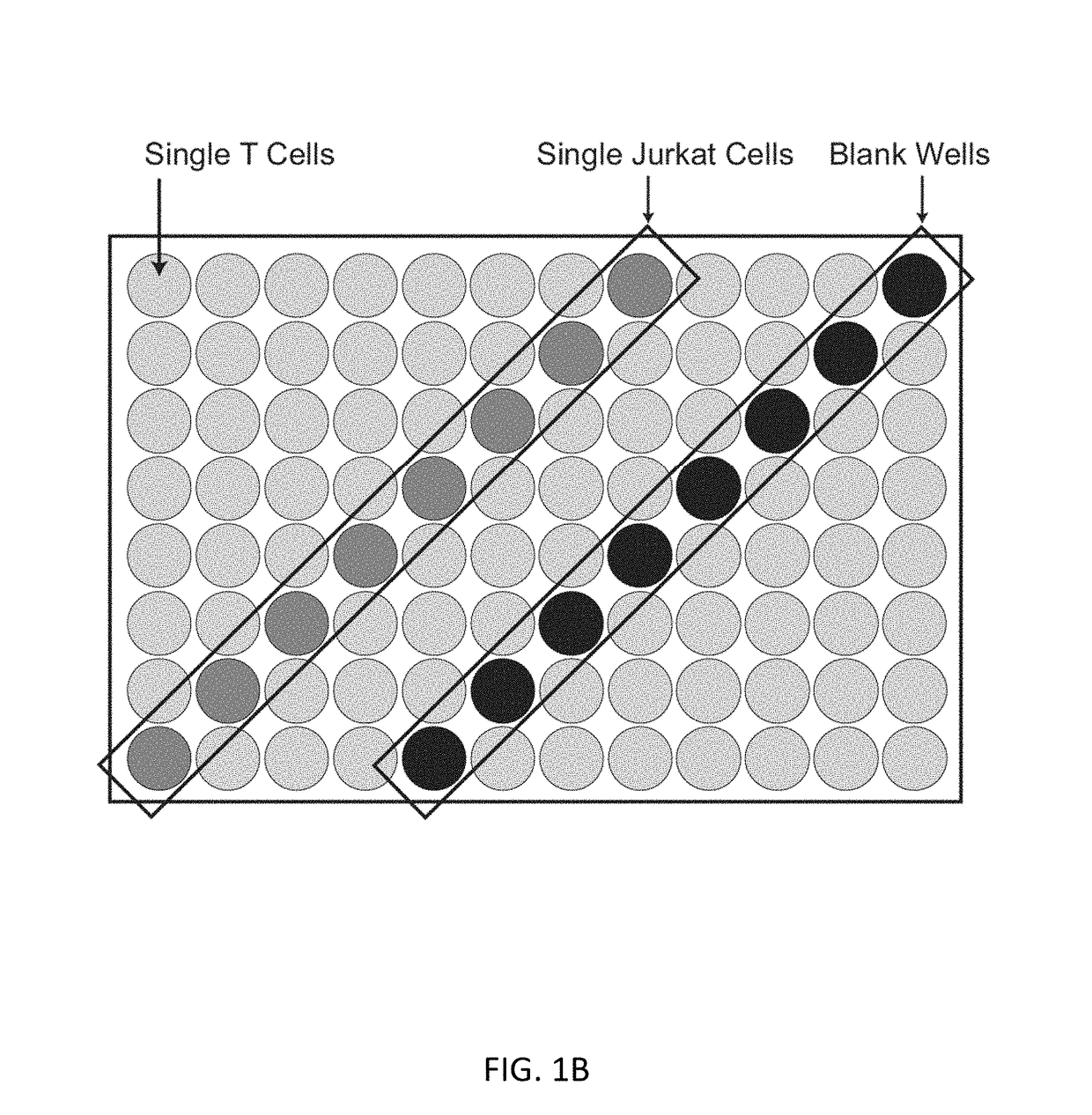
Single cell analysis of T cells using high-throughput multiplex amplification and deep sequencing
ActiveUS10202640B2Easy to produceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional studiesOligonucleotide
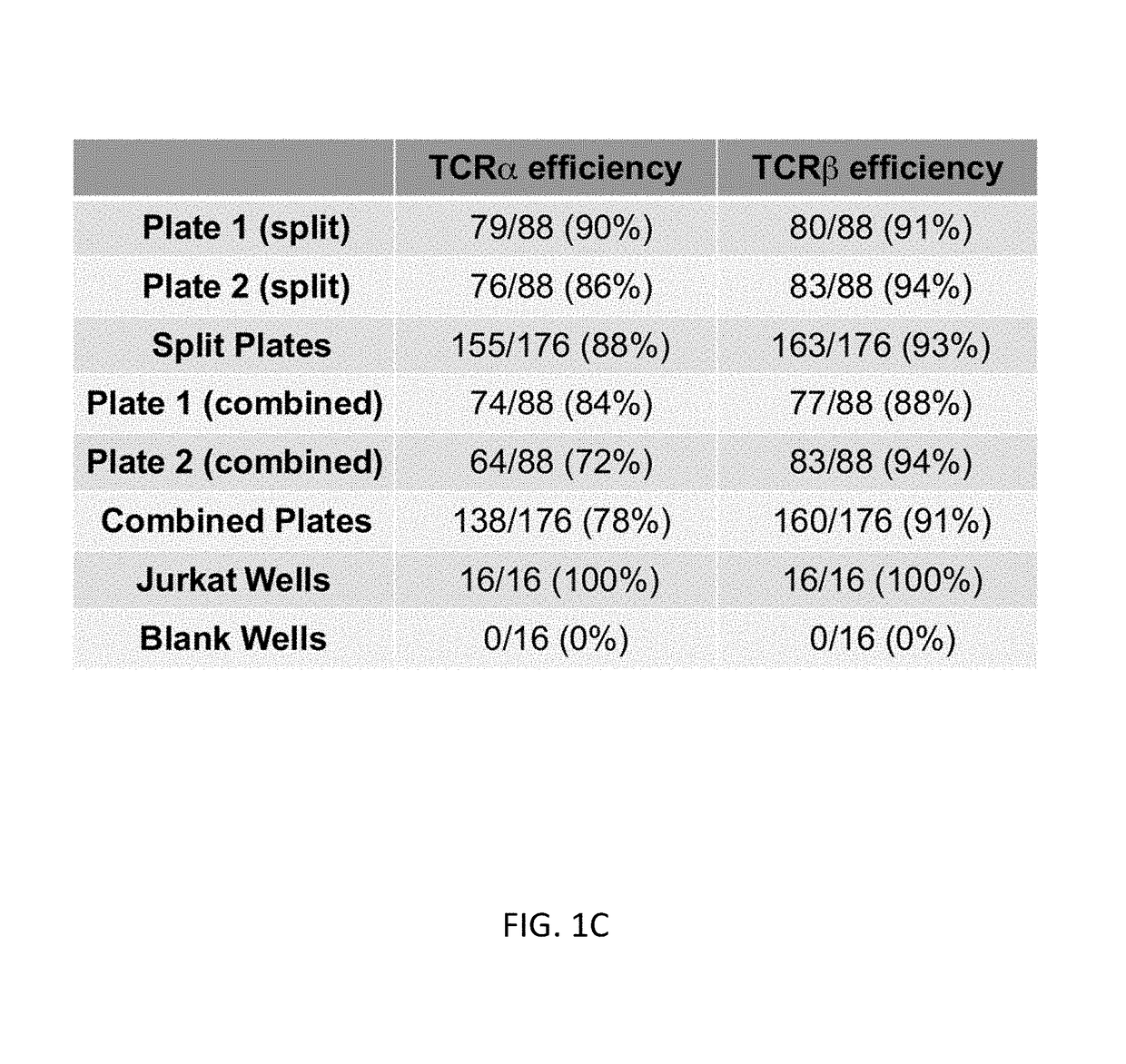
Methods and oligonucleotide reagents for analyzing individual T cells are disclosed. In particular, the present disclosure provides methods for analyzing individual T cells using high-throughput multiplex amplification and deep sequencing of nucleic acids encoding T cell receptors (TCRs) and various other T cell phenotypic markers. The present disclosure further provides methods of reconstituting TCRs from individual T cells for functional studies, ligand discovery, or screening therapeutics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Non-animal-source serum-free culture medium for umbilical cord blood stem cells
ActiveCN102827810AAvoid instabilityClear natureBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeLipid formation
The invention relates to the field of biology, and discloses a non-animal-source serum-free culture medium which essentially comprises an IMDM (Iscove Modified Dulbecco Medium), L-glutamine, sodium bicarbonate, recombinant human insulin, recombinant human transferrin, recombinant human albumin, 2-mercaptoethanol, phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), lipid, amino acid, vitamins, trace elements, interleukin-3(IL-3), stem cell factor, (SCF), Fit3-L, IL-6 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). The non-animal source serum-free culture medium is clear in chemical components, free from animal sources and serum and safe and ideal in cell cultivation, avoids the doped animal components and unstability of batches, and the results of cultured umbilical cord blood stem cells show that the total cellular score, the cell phenotype and the secretory cell factors are normal, so that the non-animal-source serum-free culture medium has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古干细胞医学工程技术研究中心
Materials from bone marrow stromal cells for use in forming blood vessels and producing angiogenic and trophic factors
InactiveUS20050158397A1Increase productionIncrease trophic factorBiocideNervous disorderCell phenotypeBone Marrow Stromal Cell
A therapeutic for use in inducing angiogenesis and vasculogenesis, the therapeutic including angiogenesis and vasculogenesis inducing factors isolated from stem cells in conjunction with a pharamaceutically acceptable cell therapy. A method of amplifying the production of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis inducing factors secreted by exposing stem cells to and co-culturing the stem cells with a compound for increasing the production of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis inducing factors. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis inducing factors isolated and purified from stem cells for use in a therapy. A process for obtaining the angiogenesis and vasculogenesis inducing factors as set forth above, the process including the steps of isolating and purifying human mesenchymal stem cells from tissue prior to differentiation and then culture expanding the mesenchymal stem cells to produce a tool for neurological and musculoskeletal therapy. Isolated and culture expanded mesenchymal stem cells under the influence of a requisite compound, that are capable of differentiating and producing a desired cell phenotype needed for tissue repair.
Owner:HENRY FORD HEALTH SYST
A mesenchymal stem cell cryoprotectant
InactiveCN106386783AKeep aliveReduce energy consumptionDead animal preservationCell phenotypeHydroxyethyl starch
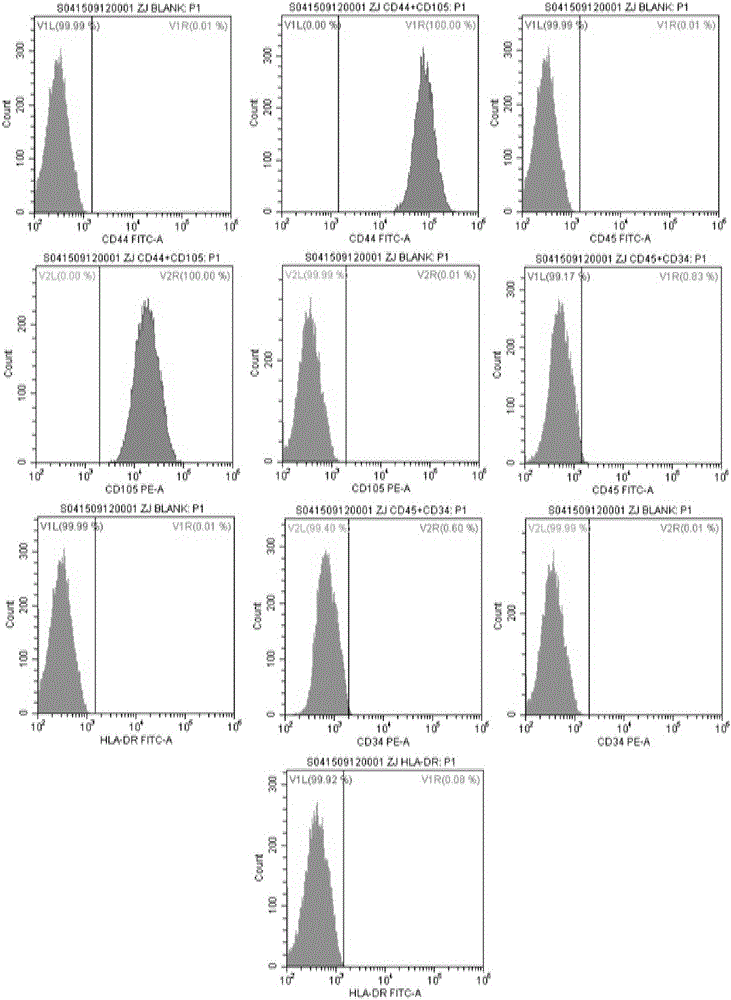
A mesenchymal stem cell cryoprotectant is disclosed. Raw materials of the cryoprotectant includes, by volume, 65.5-75.4% of 1640 culture liquid, 9.8-10.1% of dimethyl sulfoxide, 9.8-11.2% of human albumin, 9.9-10.8% of hydroxyethyl starch and 0.5-1.5% of a fibroblast growth factor. The cryoprotectant is more suitable for cryopreservation of mesenchymal stem cells, the anchoring rate of the mesenchymal stem cells after resuscitation reaches 90% or above, dead cells are few, and the quantity of cells obtained after culturing for 7 days is 2*10<7> per flask, thus greatly increasing the quantity of cells. During cell phenotype detection, CD44<+> is 99% or above and CD105<+> is 99% or above.
Owner:SINOBIOWAY CELL THERAPY CO LTD
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyalurons
InactiveUS20050058646A1Inhibit cell proliferationPrevent proliferationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCancer cell
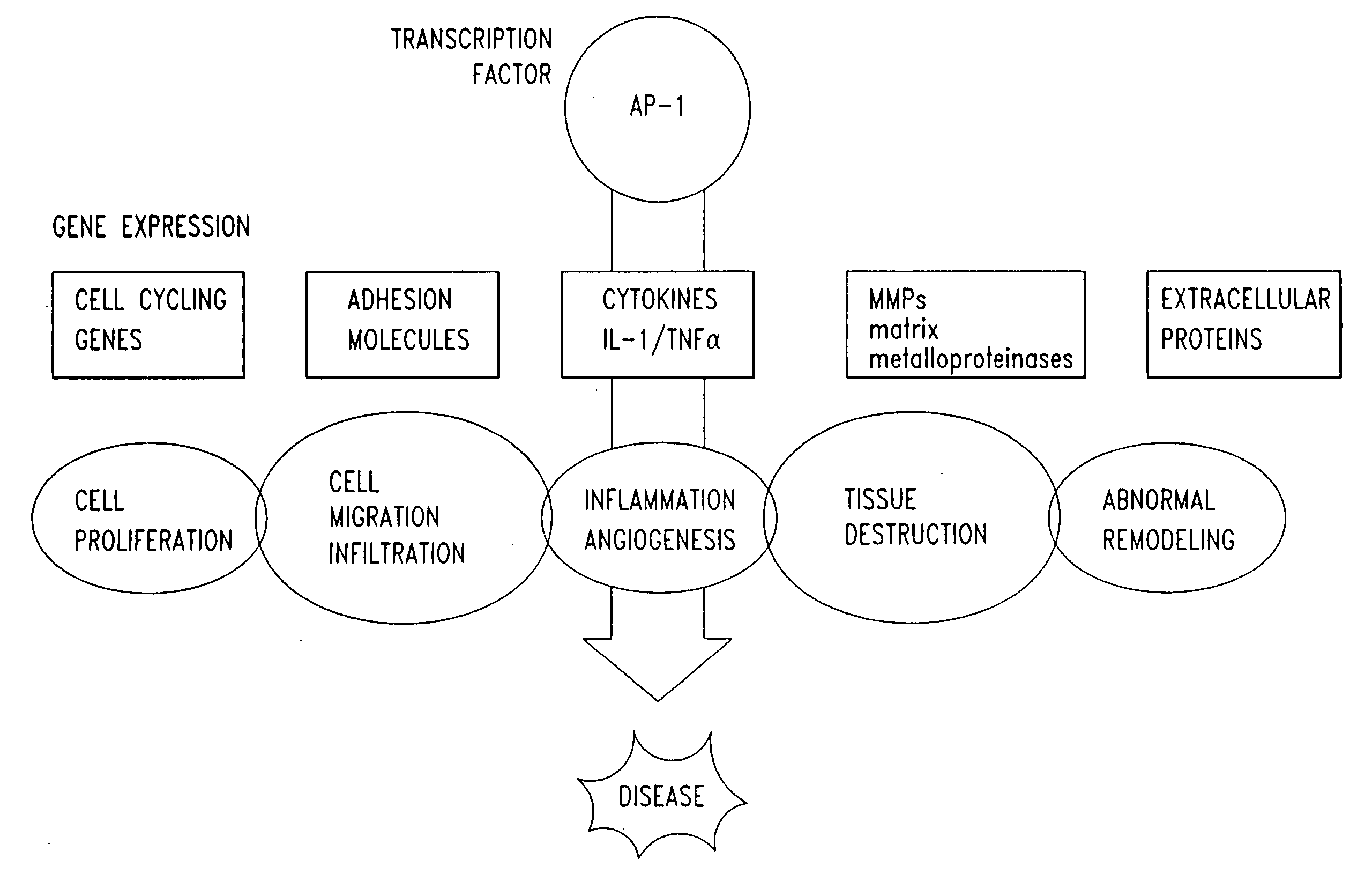
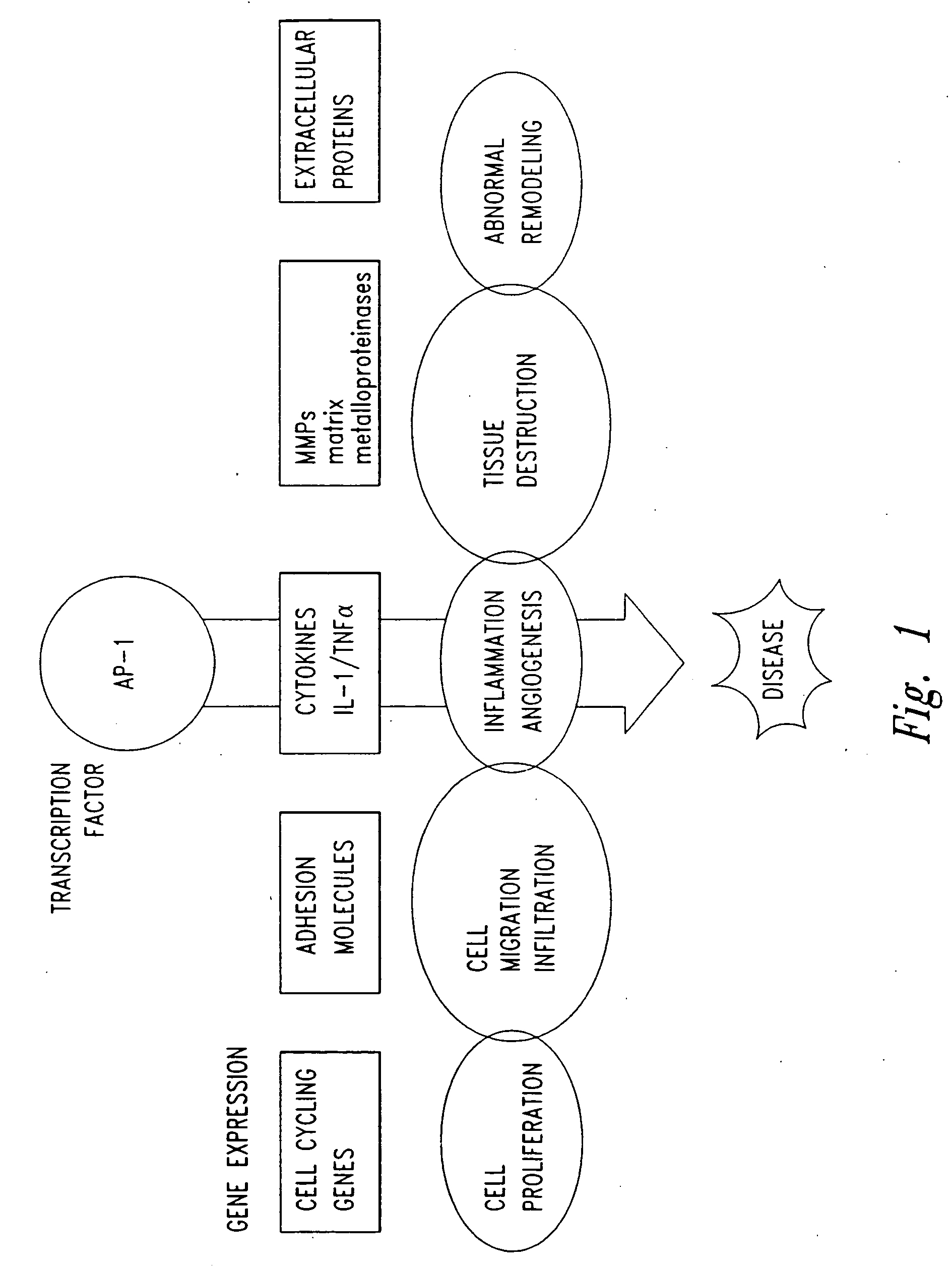
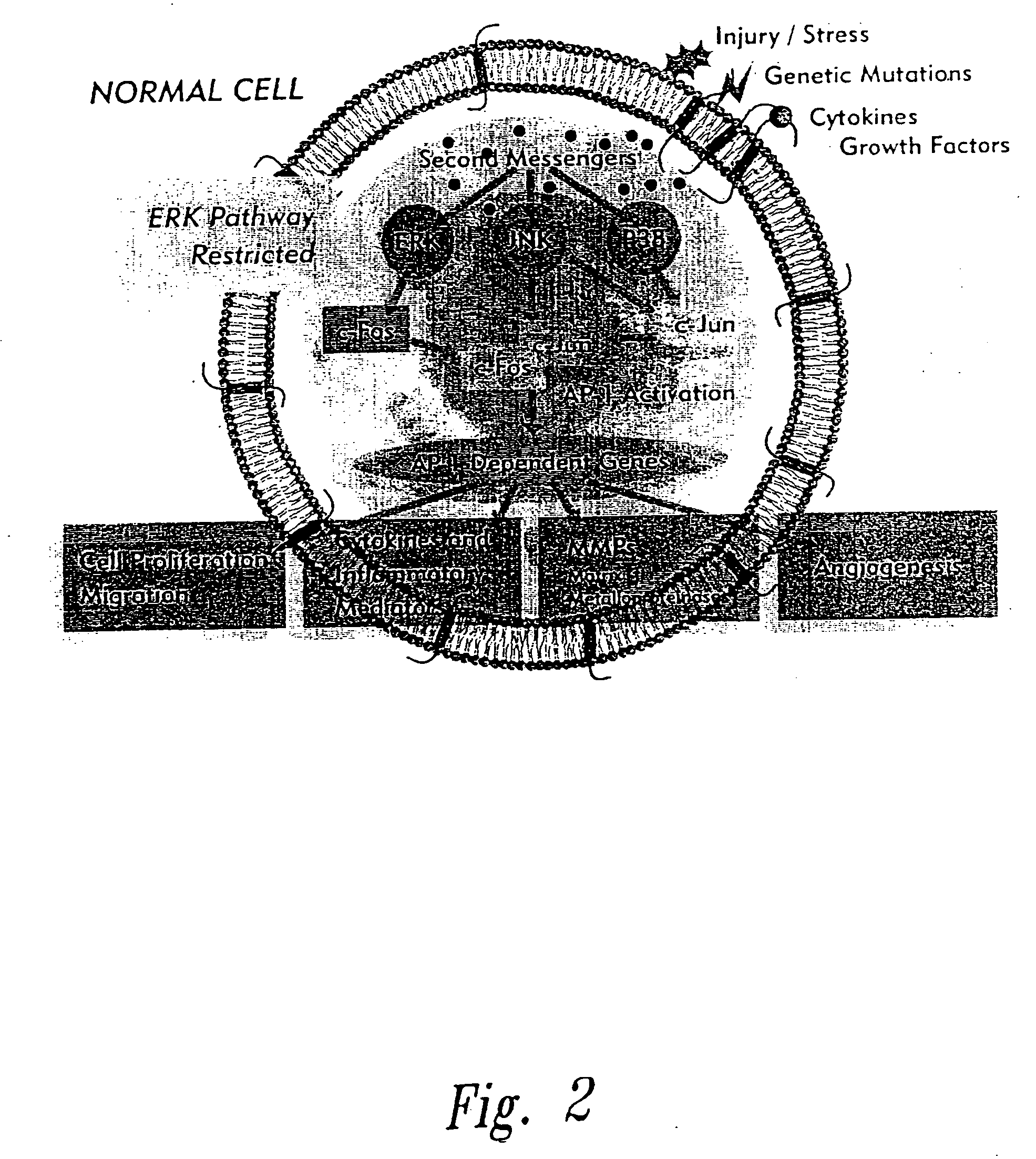
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TURLEY EVA +1
Methods and Compositions for Expanding, Identifying, Characterizing and Enhancing Potency of Mammalian-Derived Glial Restricted Progenitor Cells
Methods for producing a population of human-derived glial restricted progenitor cells (GRPs) with decreased potentially unintended or undesired cellular phenotypes and / or decreased standard deviation in the cells of the population are provided. Also provided are antibody panels and gene expression profiles to characterize GRPs and a method for its use in characterizing GRP cells. In addition methods for use of these GRP cells to generate astrocytes and / or oligodendrocytes, to re-myelinate neurons and to treat glial cell related and other neurodegenerative diseases or disorders or injuries or damage to the nervous system are provided. A method to manufacture neural cells depleted of A2B5 positive cells is also provided.
Owner:Q THERAPEUTICS
Animal derived serum-free cell freezing medium
InactiveCN105941389AAvoid unsafe ingredientsReduced Possibility of ContaminationDead animal preservationCell phenotypeHydroxyethyl starch
The invention belongs to the field of cell therapy, and especially relates to an animal derived serum-free cell freezing medium. The animal derived serum-free cell freezing medium comprises, by volume, 5-15% of human albumin, 5-15% of dimethyl sulfoxide and 70-90% of hydroxyethyl starch. The cell freezing medium contains no animal derived serum, so no exogenous proteins are introduced, and the animal pathogen pollution possibility is reduced; and the animal derived serum-free cell freezing medium is safe and effective in additional culture or clinic direct transfusion after cryopreservation resuscitation, and also has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost and good clinic application prospect. The activity of recovered cells reaches about 90%, and the cell phenotype basically has no change, so the physiologic functions and the biological functions of the recovered cells are kept. The animal derived serum-free cell freezing medium is suitable for refrigerated storage of mononuclear cells and other various cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANGECON BIOTECH
Methods for identifying and modulating co-occurant cellular phenotypes
PendingUS20200115753A1Improvement effortsOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCell phenotypeBioinformatics
The present invention provides tools and methods for the systematic analysis of genetic interactions between cells. The present invention provides tools and methods for modulating cell phenotypes and compositions, combinatorial probing of cellular circuits, for dissecting cellular circuitry, for delineating molecular pathways, and / or for identifying relevant targets for therapeutics development.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Cell-Based Methods for Coupling Protein Interactions and Binding Molecule Selection and Diversification
ActiveUS20140249044A1Improve propertiesIncrease diversityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFlow cytometryBinding properties
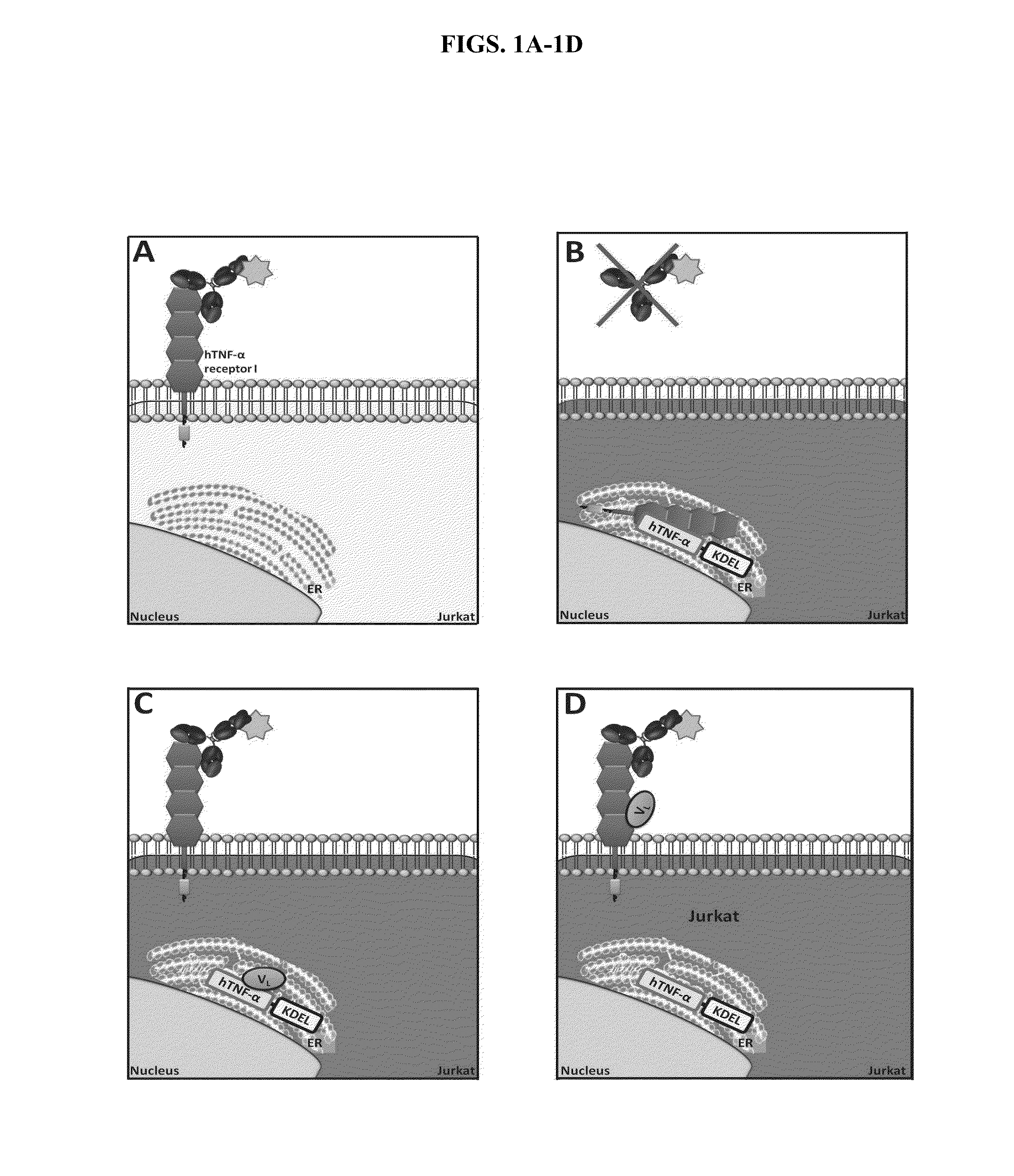
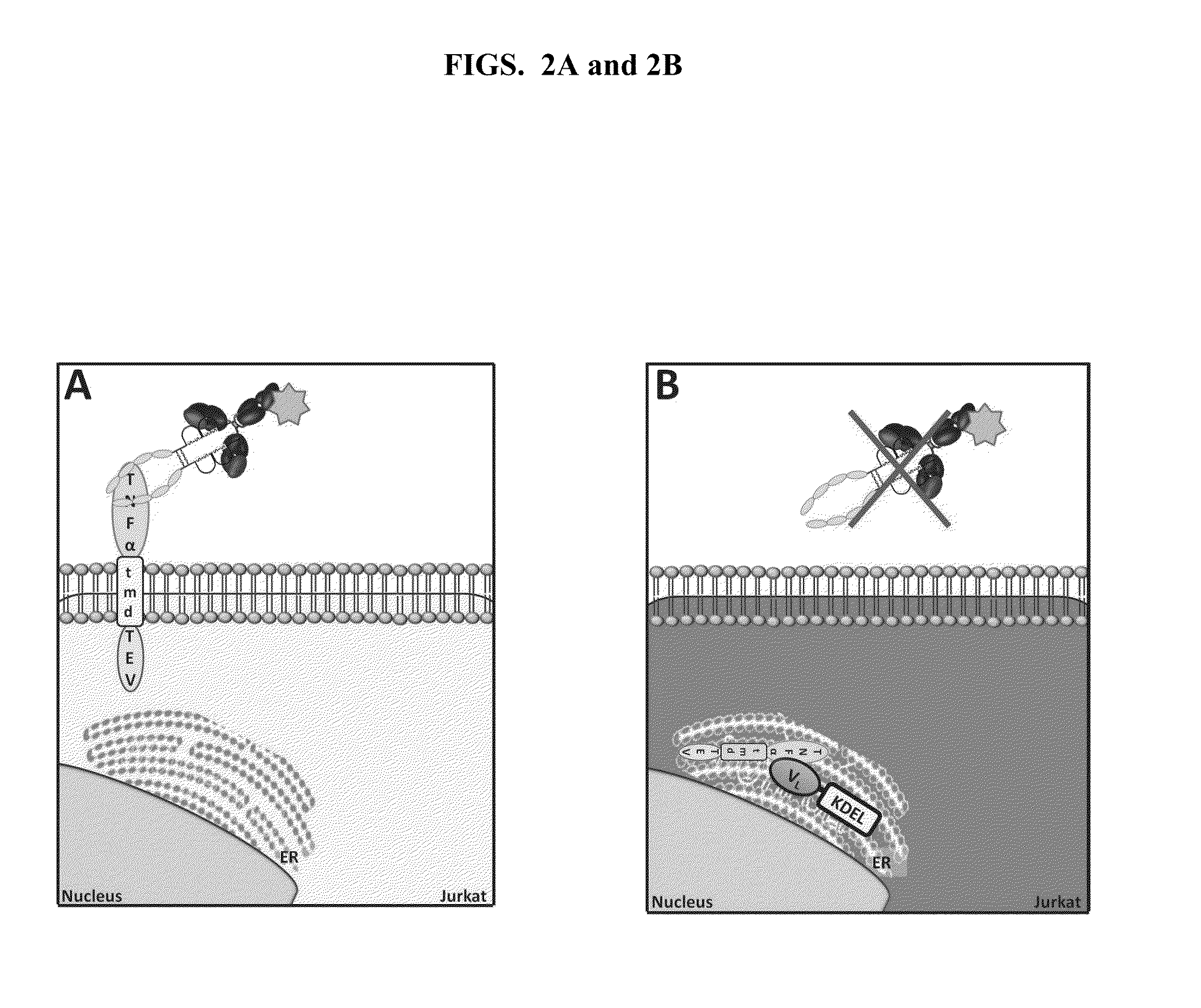
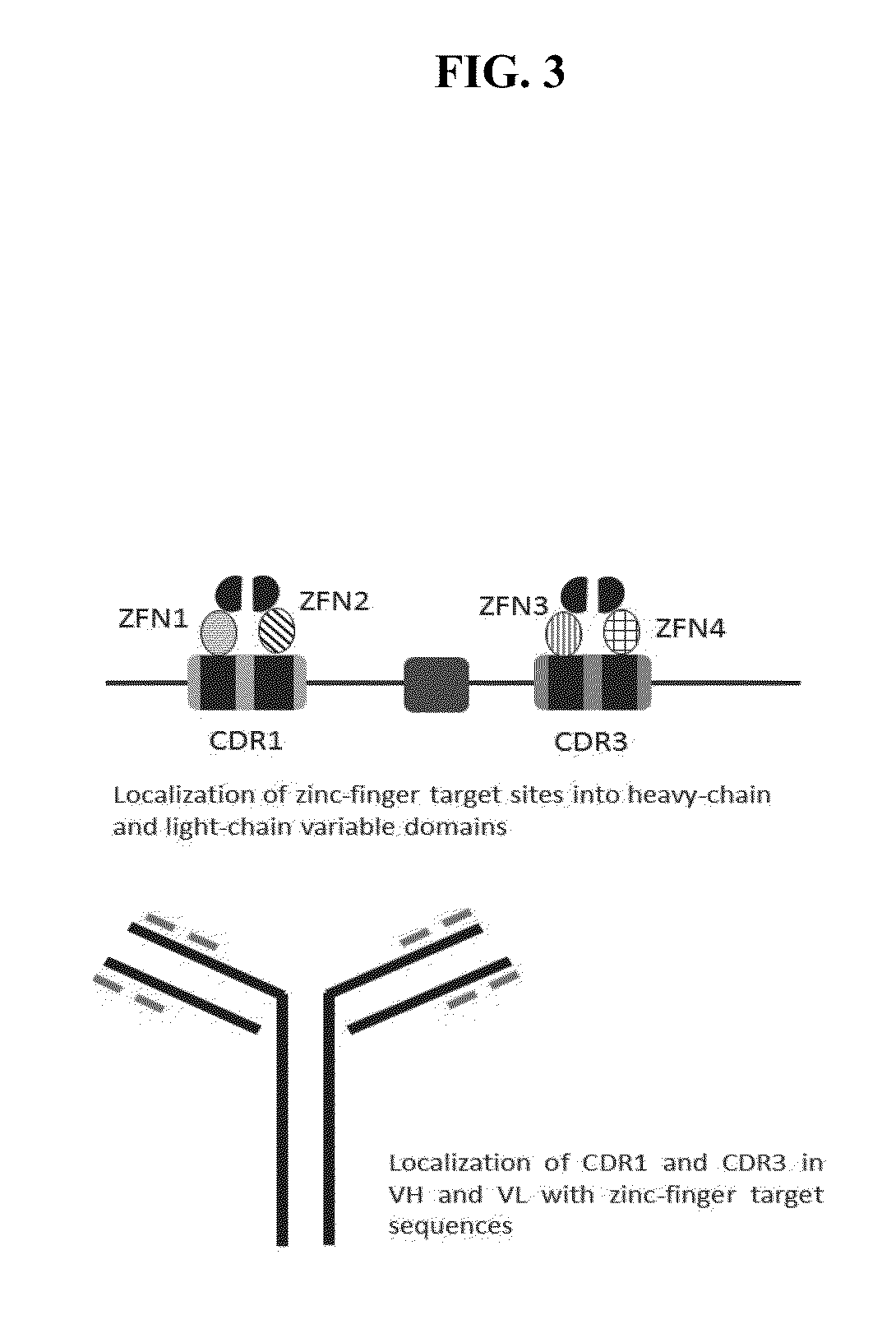
The invention relates to cell-based methods for diversifying, expressing and selecting binding molecules, e.g., antibodies, and target molecules to which they bind, all of which are expressed in the same cell. The target molecule can be a member of a ligand binding pair comprising a cell-surface expressed ligand binding receptor molecule and its cognate ligand, which interact within the cell. The methods provide retaining either the antibody or its target in a cell organelle as the site of binding and interaction. By performance of the methods, the binding or non-binding of the antibody to its target molecule within the cell produces a cell phenotype that is detectable at the cell surface via high throughput assays, e.g., flow cytometry. The methods are particularly useful for generating, recovering and providing antibodies that have optimal target molecule binding properties or activities for potential therapeutic use. Methods for generating diversity in such antibodies are also provided.
Owner:TECHNOPHAGE INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO EM BIOTECHA
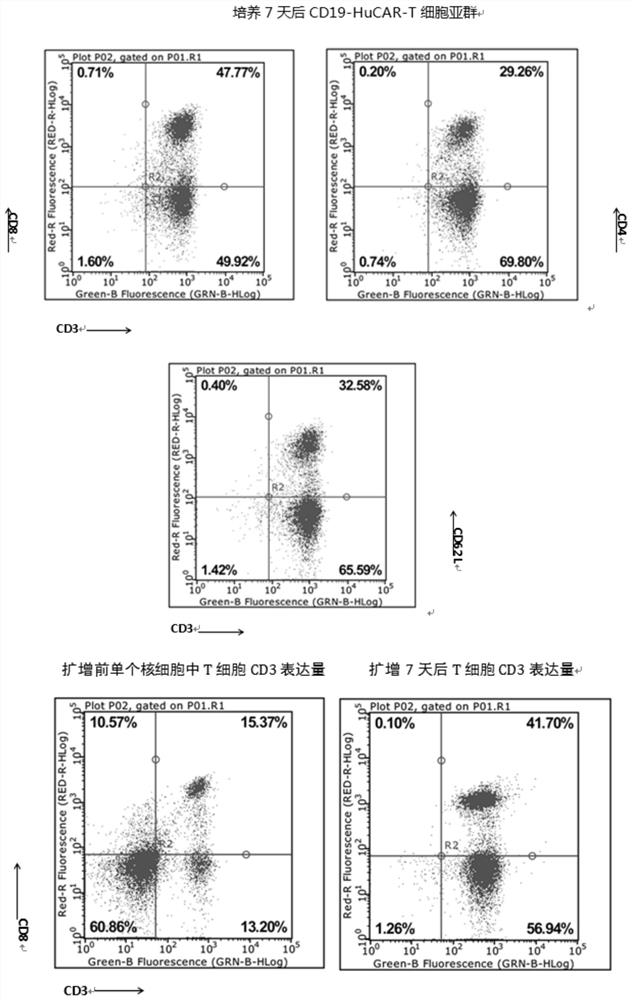
Preparation and application of CD19-targeting humanized chimeric antigen receptor
PendingCN111733186AIncrease lethalityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCell phenotypeCell kill
The invention relates to preparation and application of a CD19-targeting humanized chimeric antigen receptor, and concretely relates to construction of a human CD19-antigen-targeting humanized lentiviral vector expression plasmid. The human CD19-antigen-targeting humanized lentiviral vector expression plasmid is applied to the preparation of chimeric antigen receptor T cells; and then, the effectsare verified through the chimeric antigen receptor T cells in in-vitro proliferation tests, cell phenotype tests and cell killing tests. A CAR sequence of the invention consists of a leader peptide sequence, a human CD19-antigen-targeting single-chain scFv sequence, a hinge region, a transmembrane region structure domain and an intracellular signal conduction structure domain sequence. The chimeric antigen receptor is built into a lentivirus system expression vector, and immune cells are infected; the human CD19-antigen-targeting chimeric antigen receptor can be expressed on the surface of the immune cells; the effects of killing tumor cells can be achieved by recognizing the CD19 antigen expressed on tumor tissues; the goal of tumor treatment is achieved; and a novel measure is providedfor cancer treatment.
Owner:天津英科赛奥科技有限公司
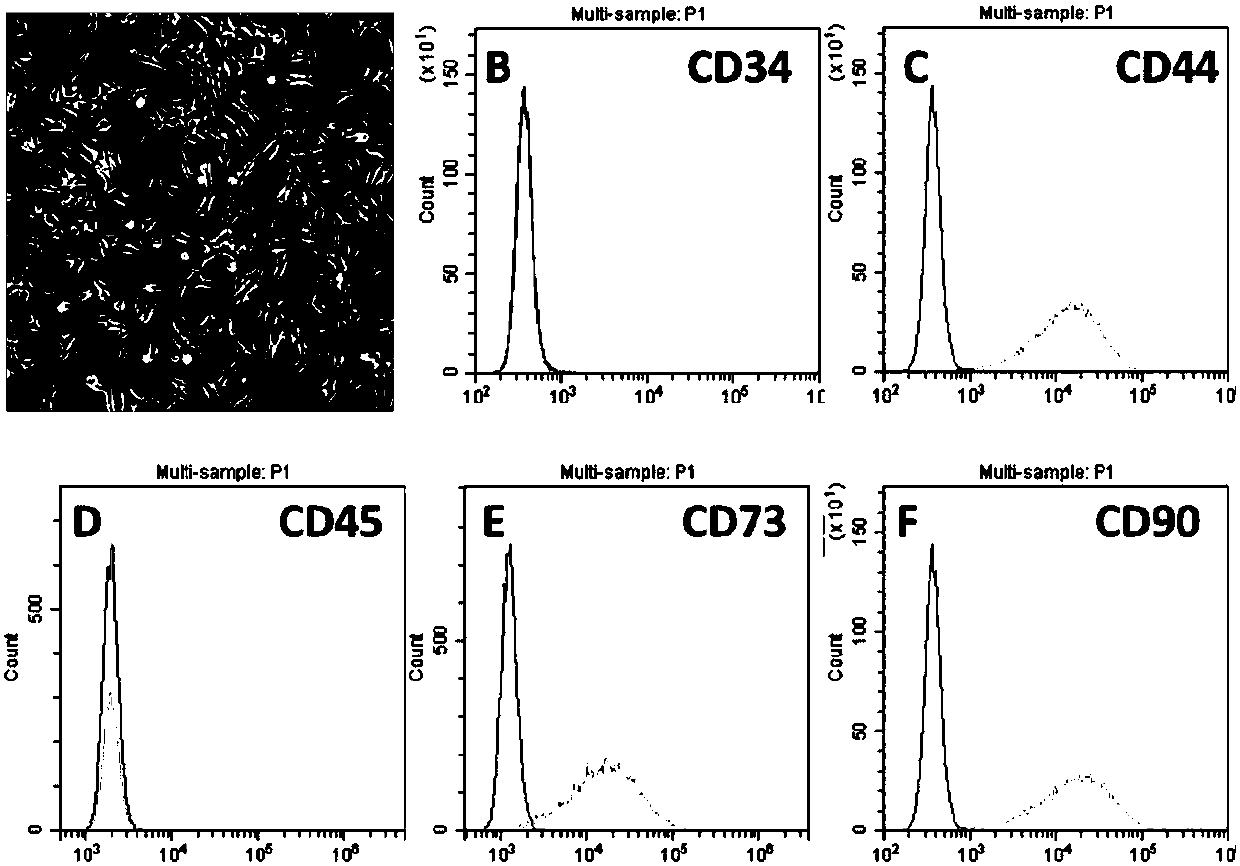
Multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107937338AIncreased therapeutic functionSolve the problem of limited sourcesCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeGerm layer
The invention discloses a multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cell and an induced differentiation method thereof. The multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigreemesenchymal stem cell is prepared by the following steps: performing in-vitro adherent culture on multipotential stem cells and maintaining the undifferentiation state of the multipotential stem cells; preparing unicellular or cell mass suspension from the cells, inoculating to a culture dish coated with matrix glue, and performing cultivation by using the multipotential stem cell culture liquid;after the cells adhere to the wall, adding GSK-3 pathway inhibitor combination into the culture liquid; after growing for 2 to 10 days, obtaining a mesoderm progenitor population; and after subculturing continuously for 2 to 6 times by using mesenchymal stem cell culture liquid, detecting the cell phenotype of mesenchyme. The defects that the human-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the mesenchymal stem cells derived from other non-finite induced way multipotential stem cells have heterogeneity and hybridity are overcome, and the obtained mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cells have higher proliferation capability and immunoregulation capability; and the standardized induced differentiation process can guarantee that the cell populations obtained from different batches have high consistency.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Tissue engineering meniscus repair sheet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103920188AProlong the action timeInduced regenerationProsthesisCell phenotypeMeniscal repair
The invention relates to a tissue engineering meniscus repair sheet and a preparation method thereof. The prepared tissue engineering meniscus repair sheet comprises an acellular meniscal thin sheet, seed cells and growth factor slow-release carriers, wherein blind micro vias are uniformly distributed on two surfaces of the acellular meniscal thin sheet, and the seed cells and the growth factor slow-release carriers are combined on two surfaces of the acellular meniscal thin sheet. The blind micro vias distributed on the acellular meniscal thin sheet increase the area of a support material, and can be used as a storage pool of the seed cells and the growth factor slow-release carriers, so that the seed cells and the growth factor slow-release carriers can be firmly attached and are not easy to fall off. Nutrition can be persistently released through the slow-release carrier by multiple growth factors, the cell amplification efficiency is improved, the cell phenotype is also maintained, cell ageing is inhibited, and fusion of the tissue engineering meniscus repair sheet and self tissue is promoted. The prepared tissue engineering meniscus repair sheet has the structure characteristic similar to the structure characteristic of natural meniscus, and is applicable to repair meniscus injure and induce regeneration of meniscus fibrous cartilage tissue.
Owner:西安博鸿生物技术有限公司
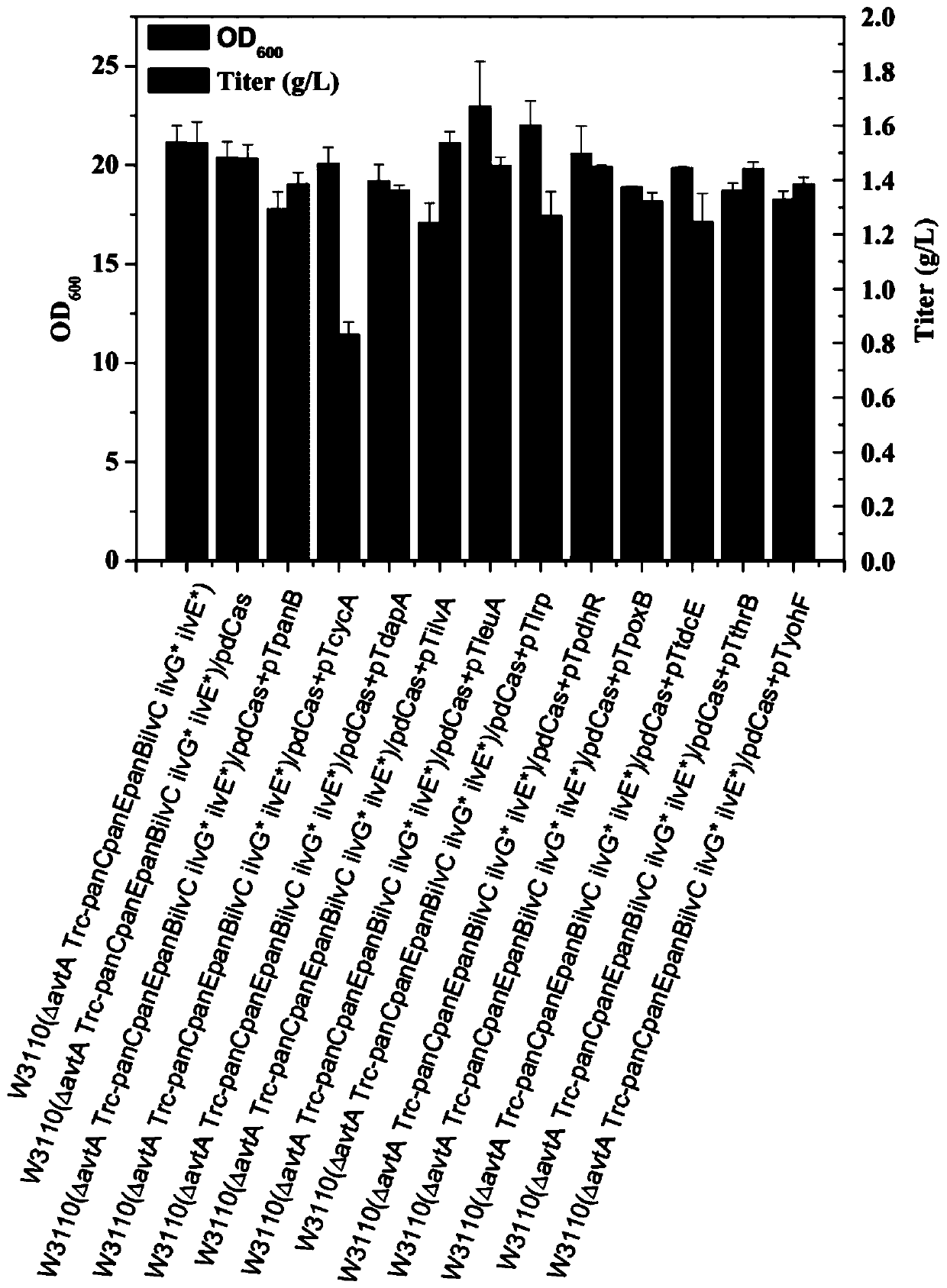
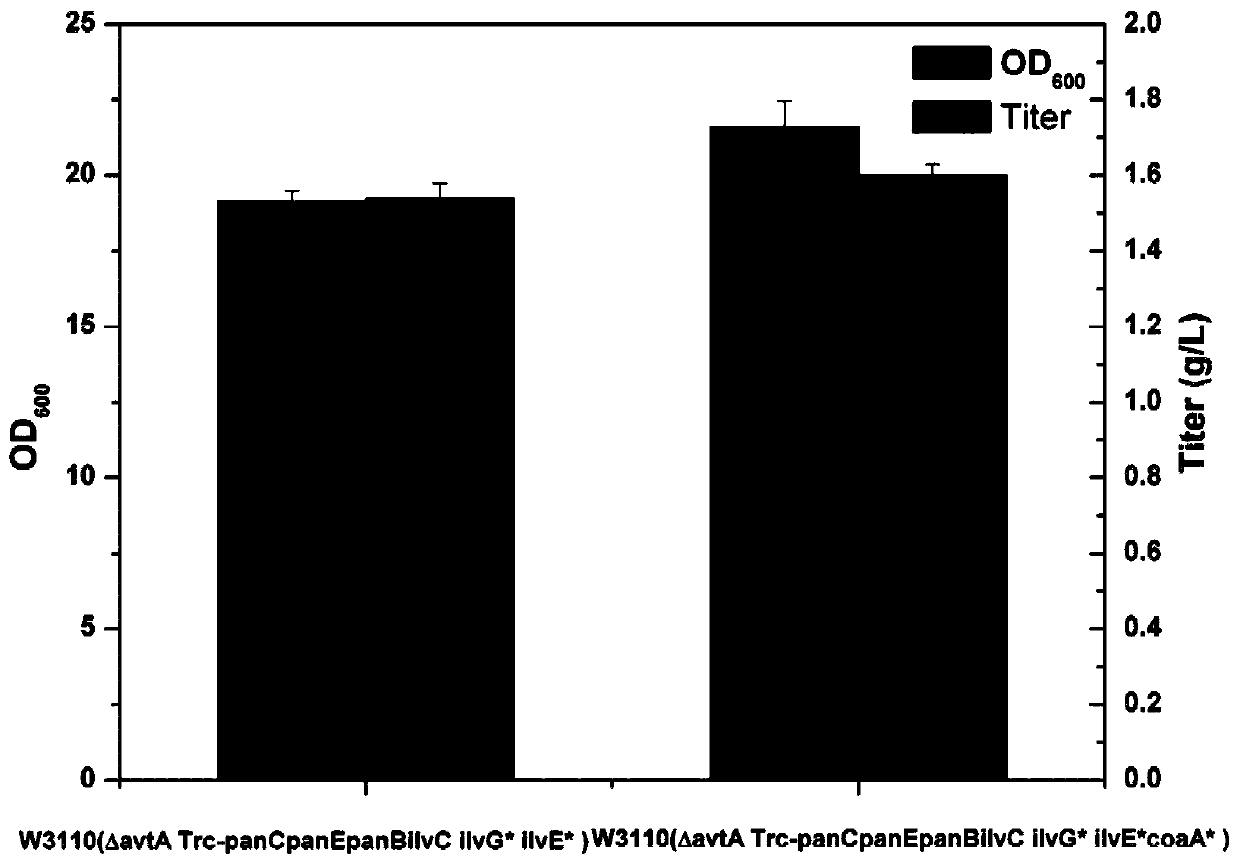
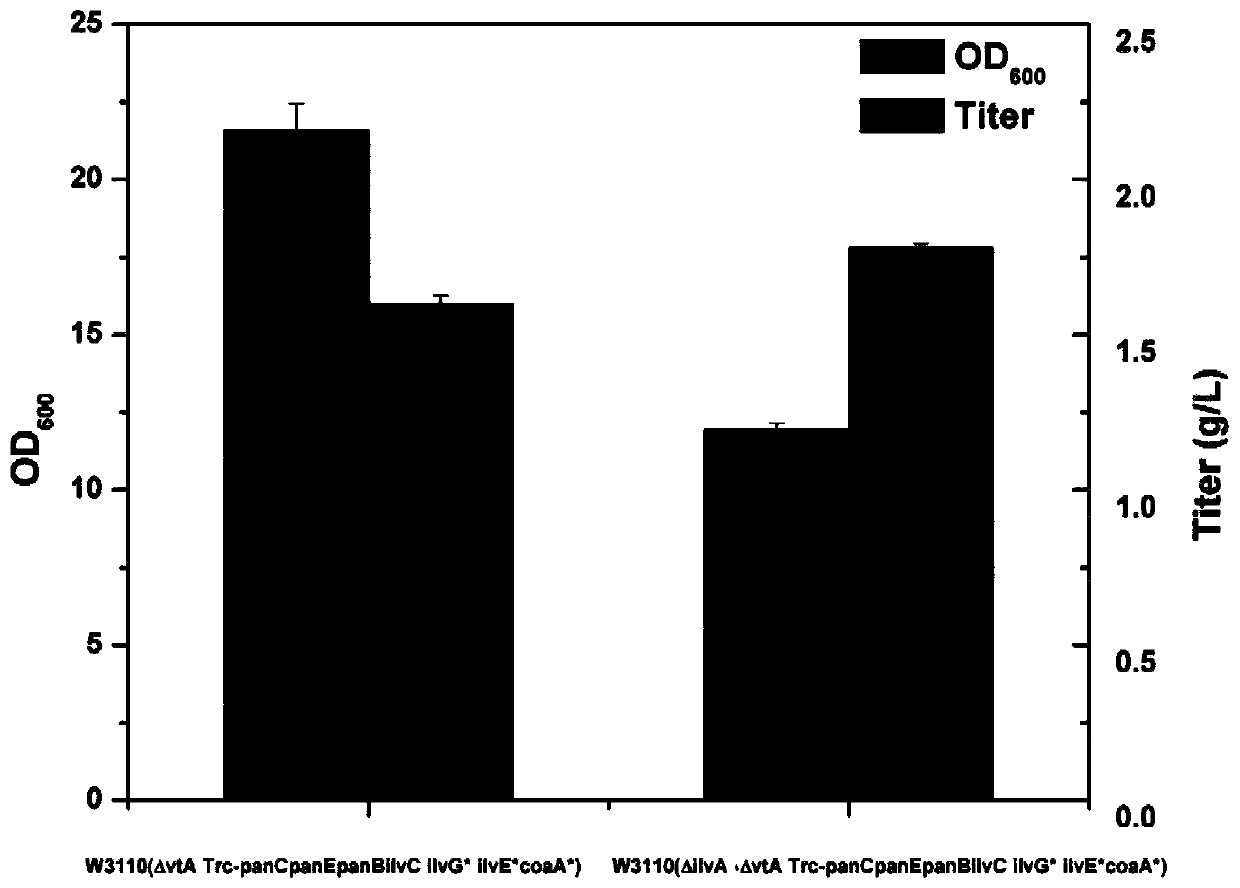
Genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, construction and application of genetic engineering bacteria
ActiveCN109913398AImprove utilizationReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaStable introduction of DNACell phenotypeEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria, and application of the genetic engineering bacteria in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. According to the invention, (1), the final step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenicacid synthesis pathway is enhanced, and the utilizing ability of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine, (2), a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is enhanced, (3), ilvG gene is repaired, and thefeedback inhibition effect of by-products on a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is weakened, (4), according to the change in cell phenotype, flux of a valine synthesis pathway is weakened, (5), a CRISPRi technique is used to screen metabolic modification sites of TCA cycle, a PPP pathway and a by-product metabolic pathway, according to the result, an isoleucine synthesis pathway is blocked, and thecompetition of 2-butanoic acid for reaction of acetolactate synthesized from pyruvic acid under catalysis of acetolactate synthase is relieved, and (6), aspartate decarboxylase from other strains is subjected to heterologous expression to obtain a genetical engineering strain capable of producing the pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of the beta-alanine. By combined expression of panB and panC which are derived from corynebacterium glutamicum and panD derived from bacillus subtilis together on pTrc99A plasmids, 1.2g / L of D- pantothenic acid is obtained without adding the beta-alanine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com