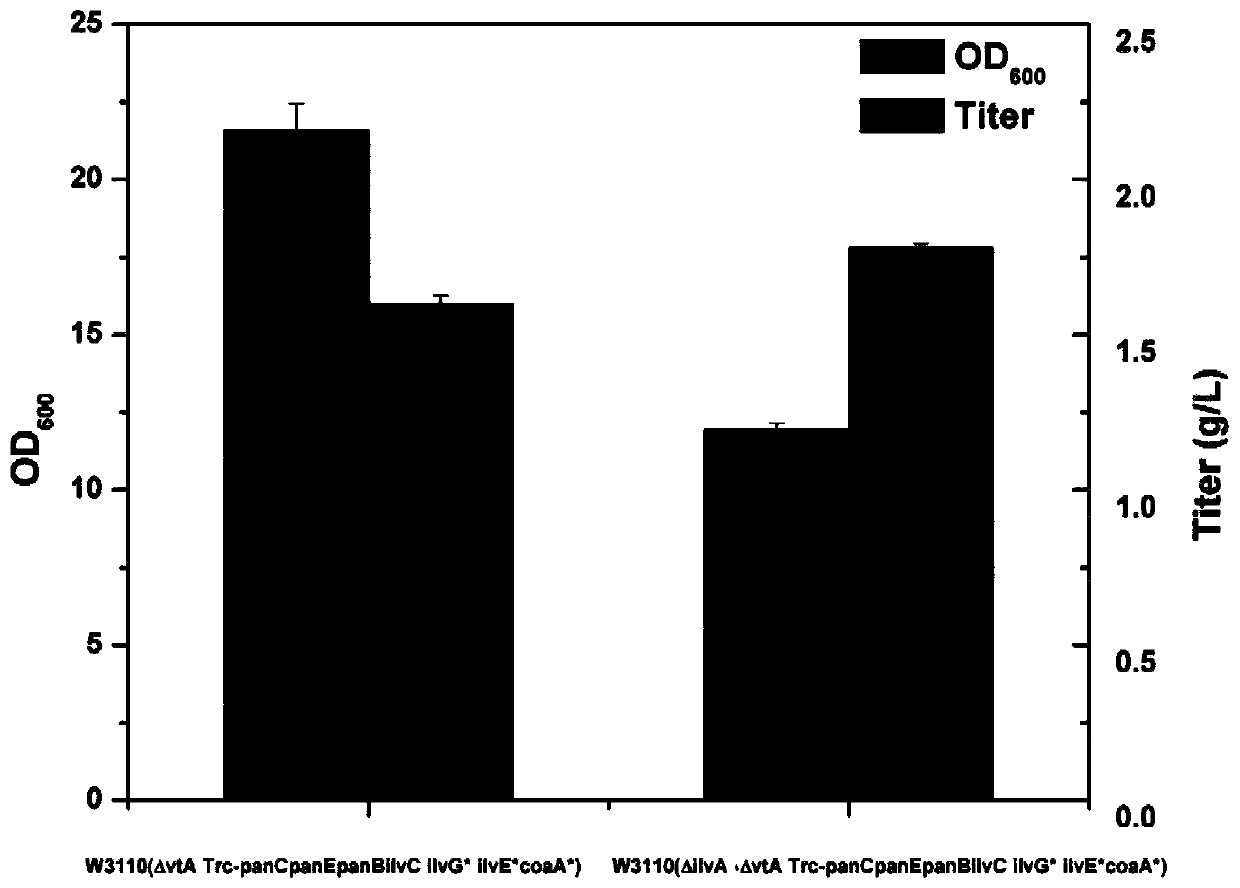
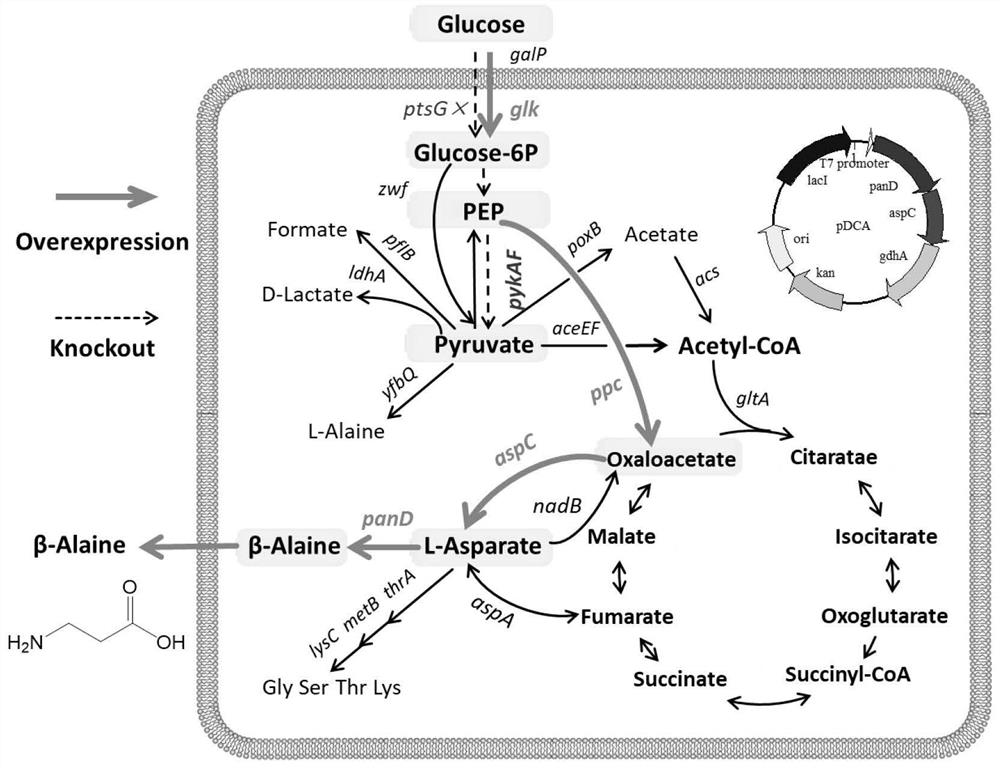
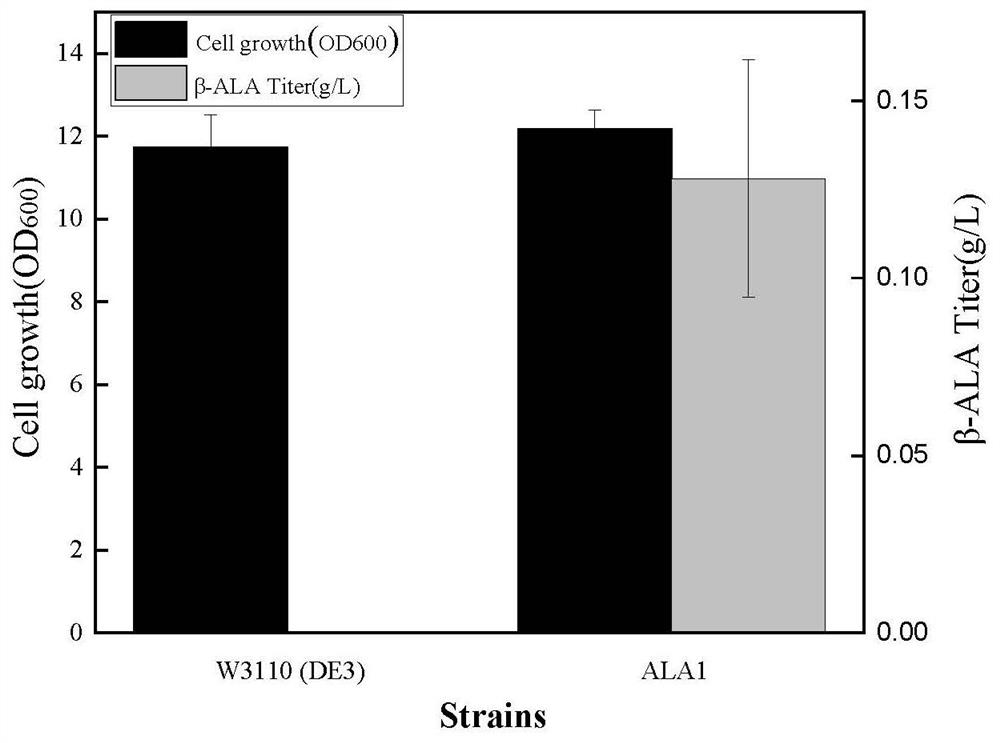
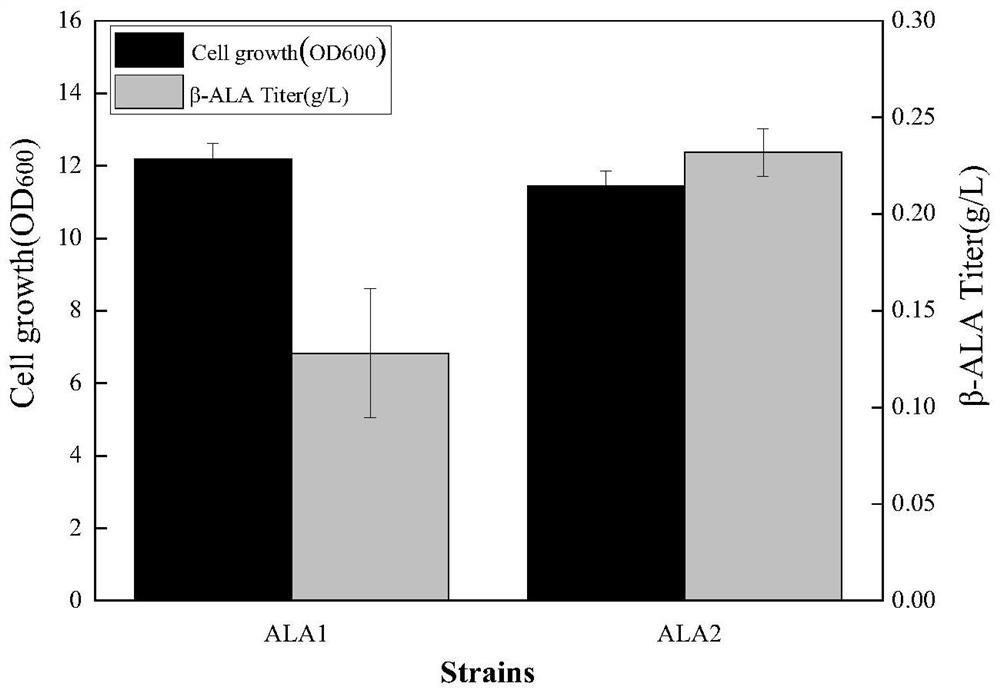
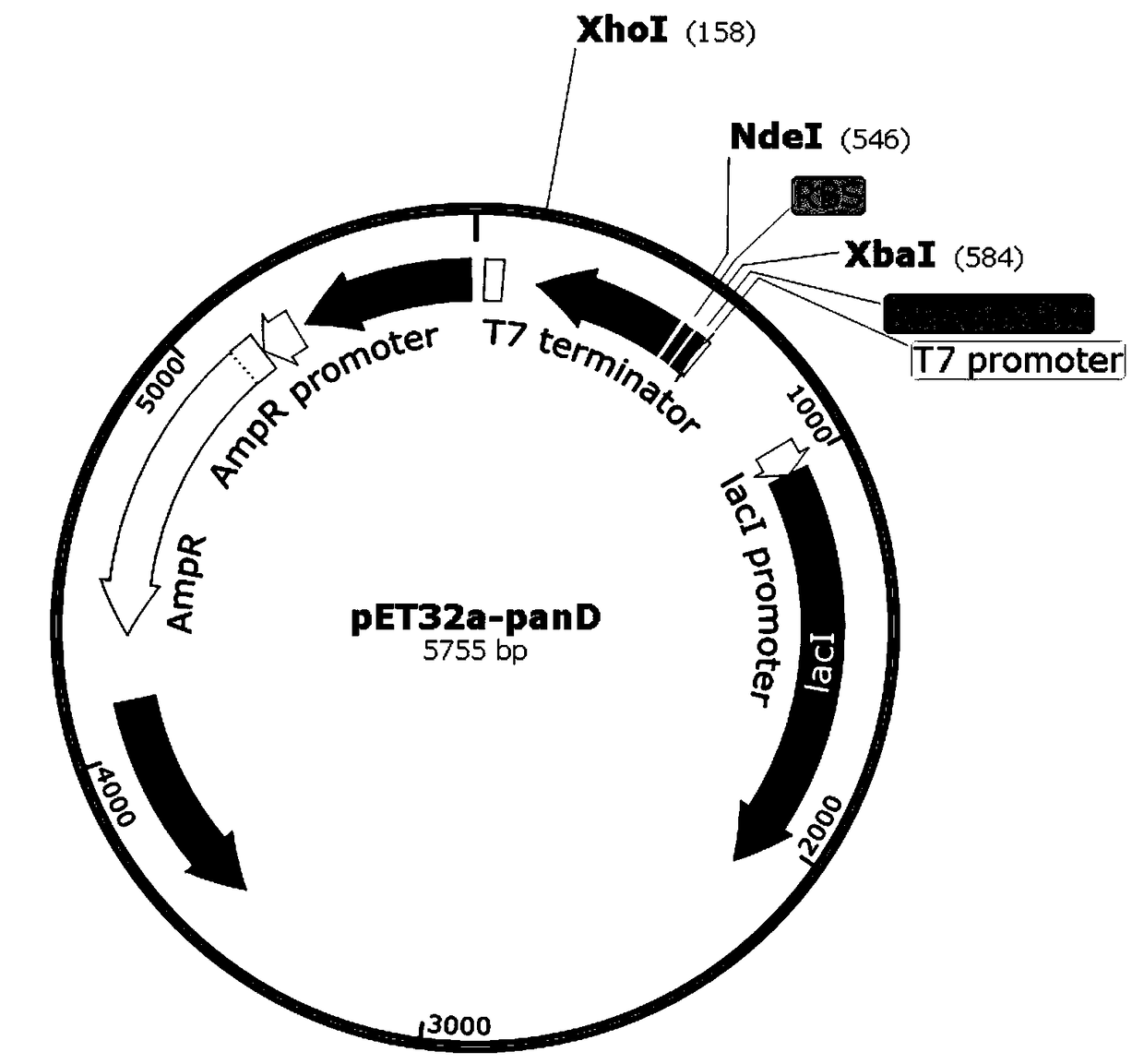
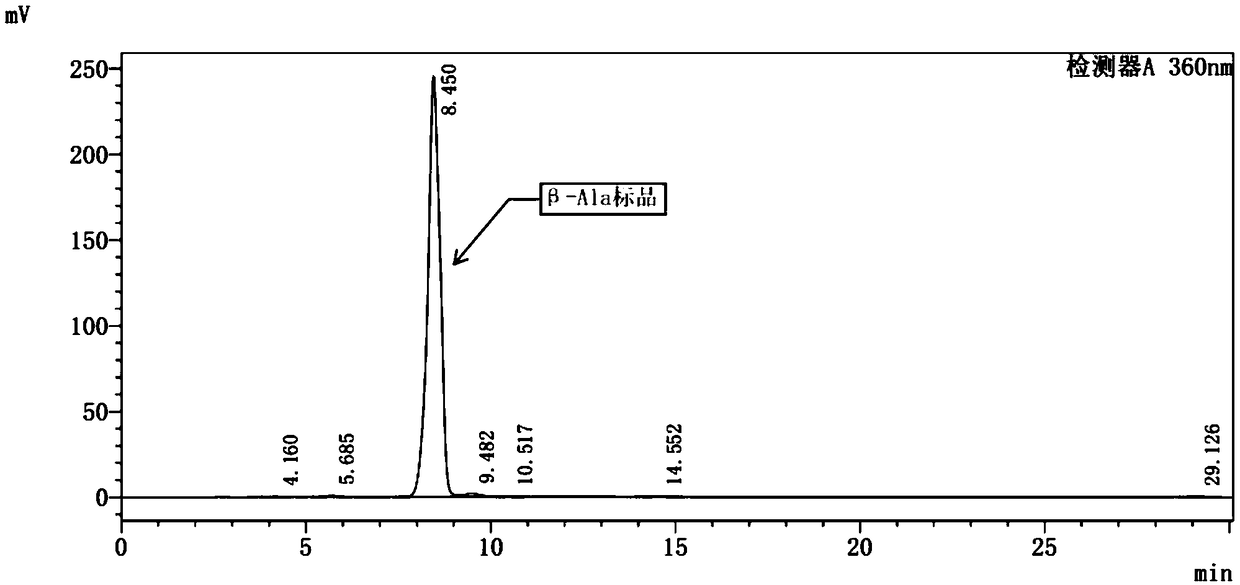
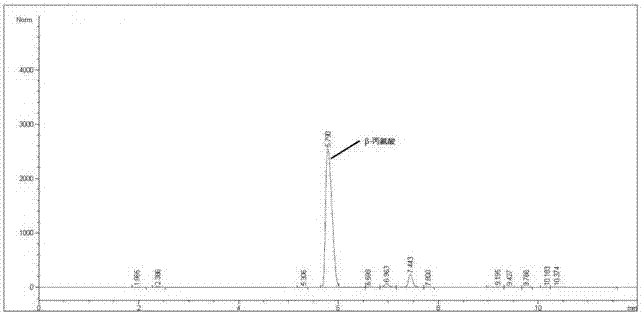
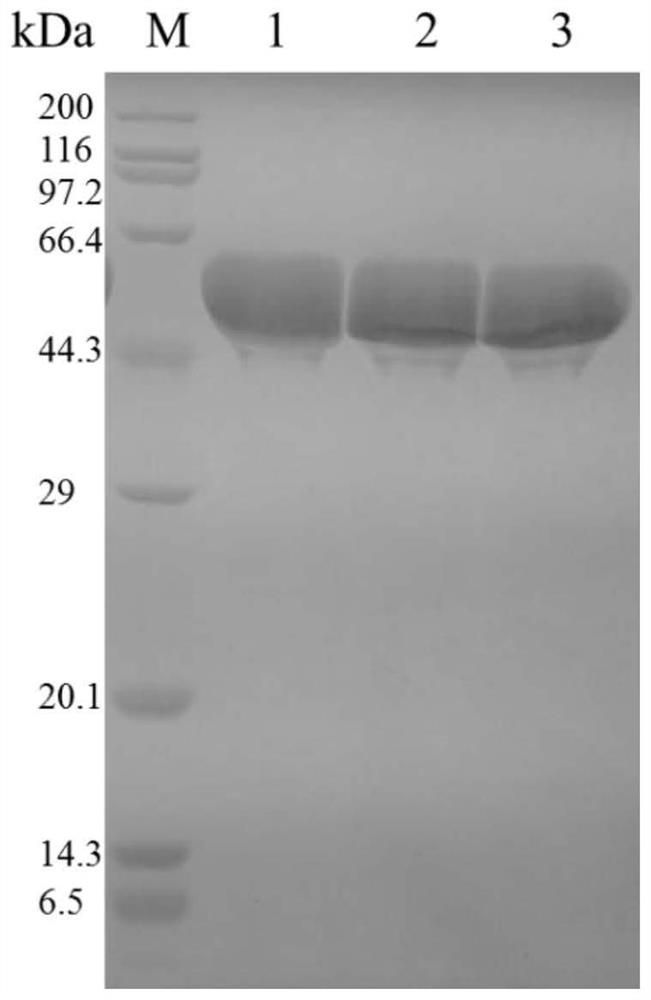
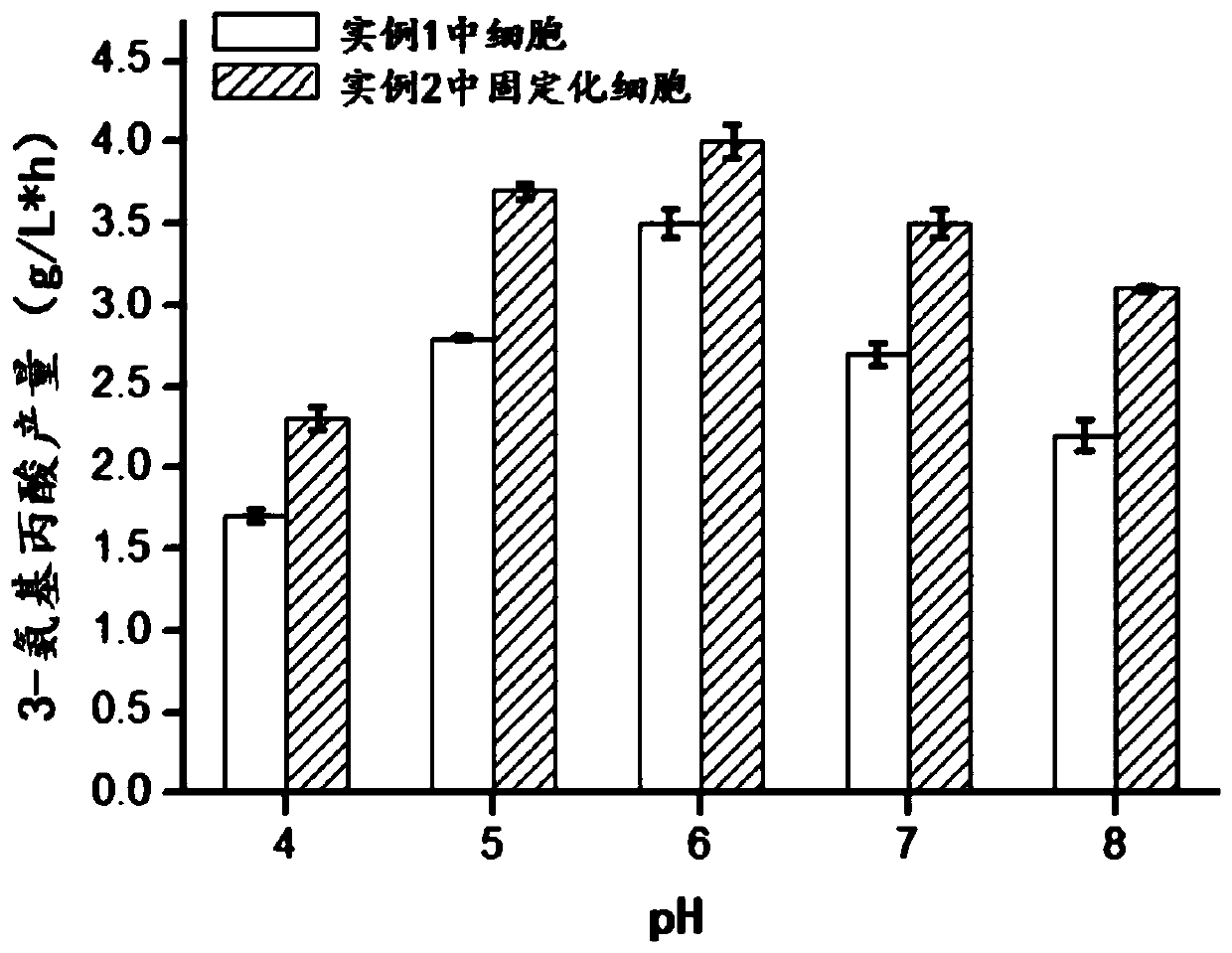
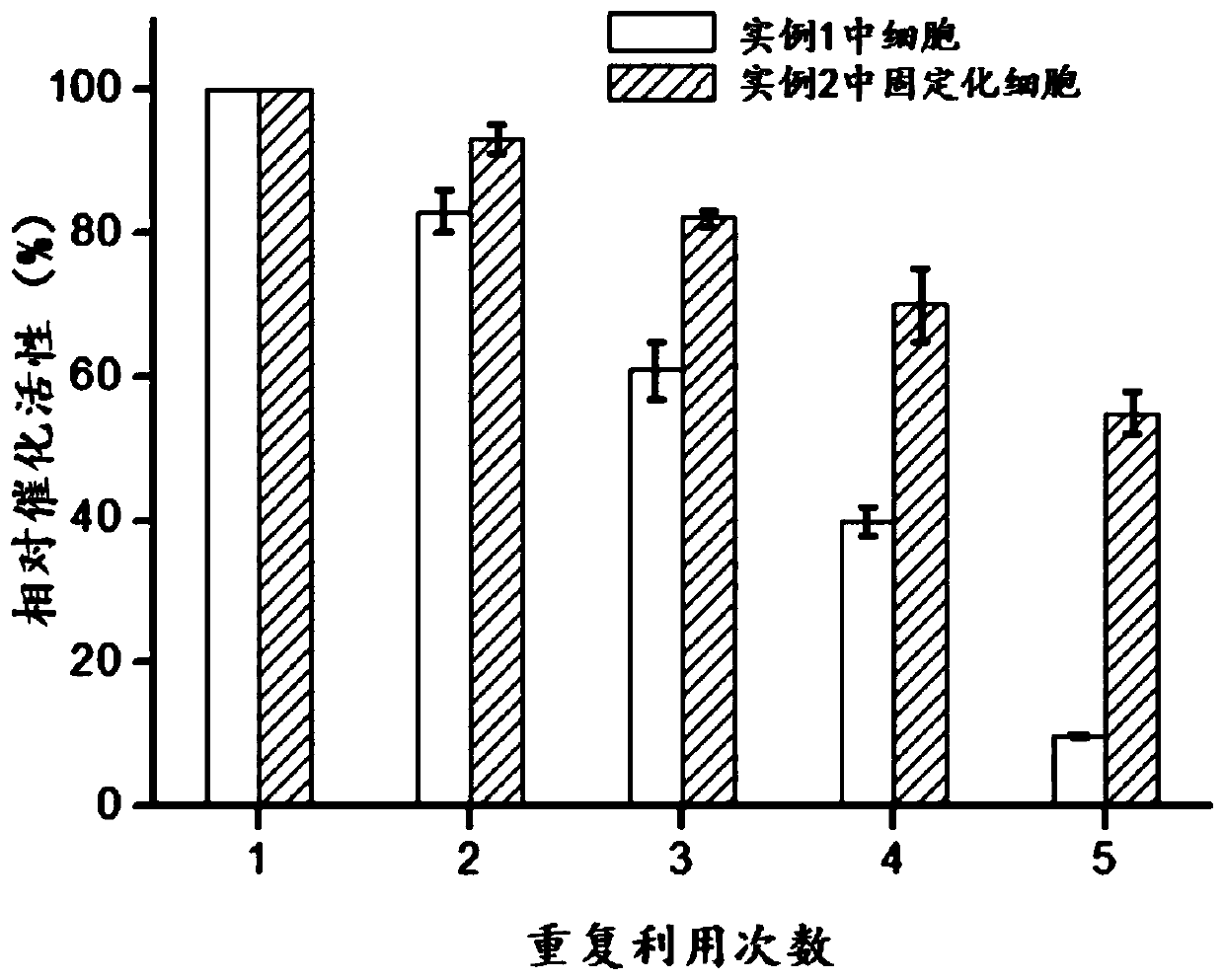
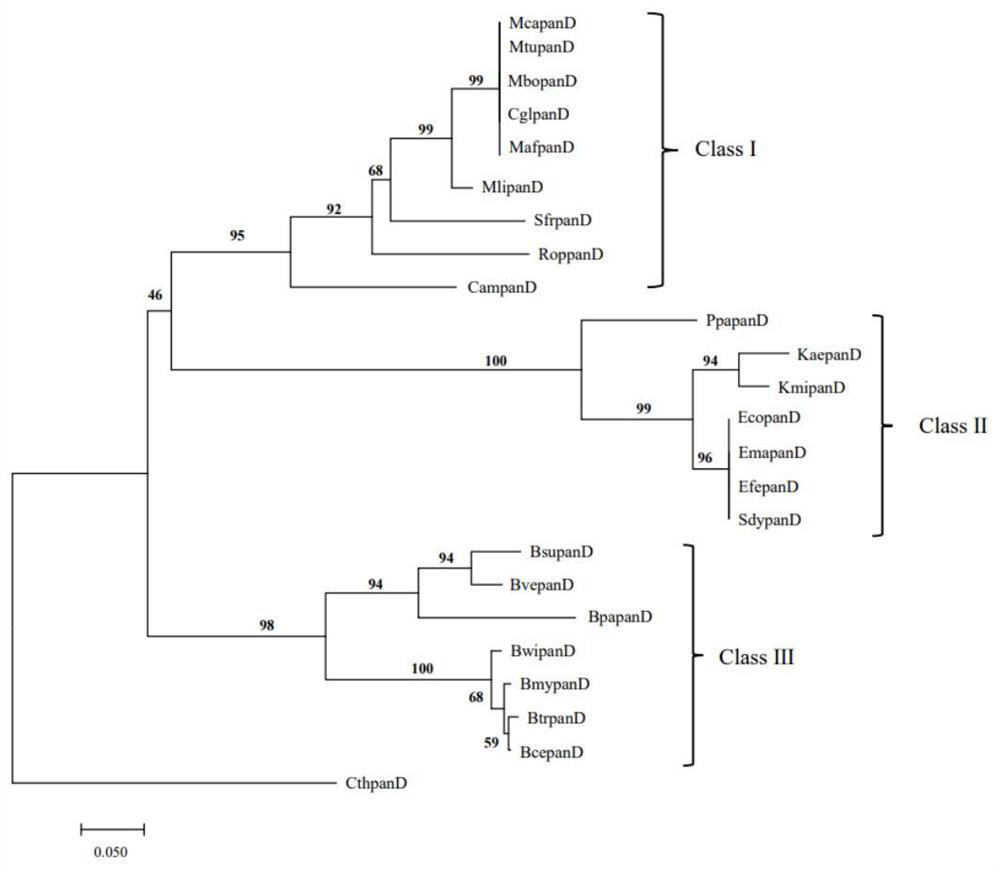
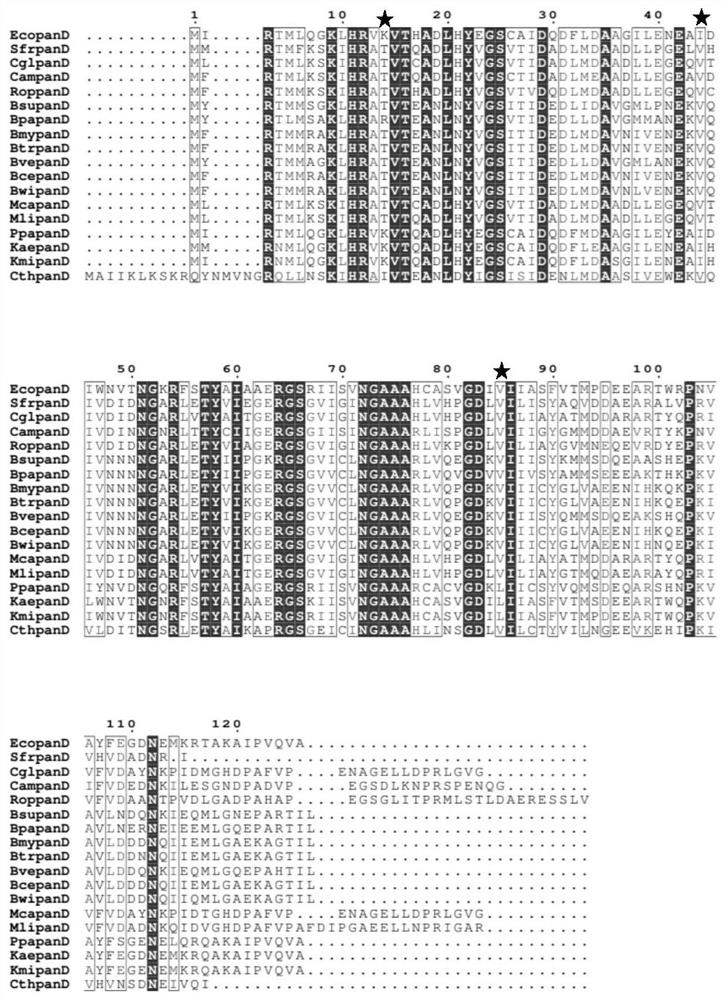
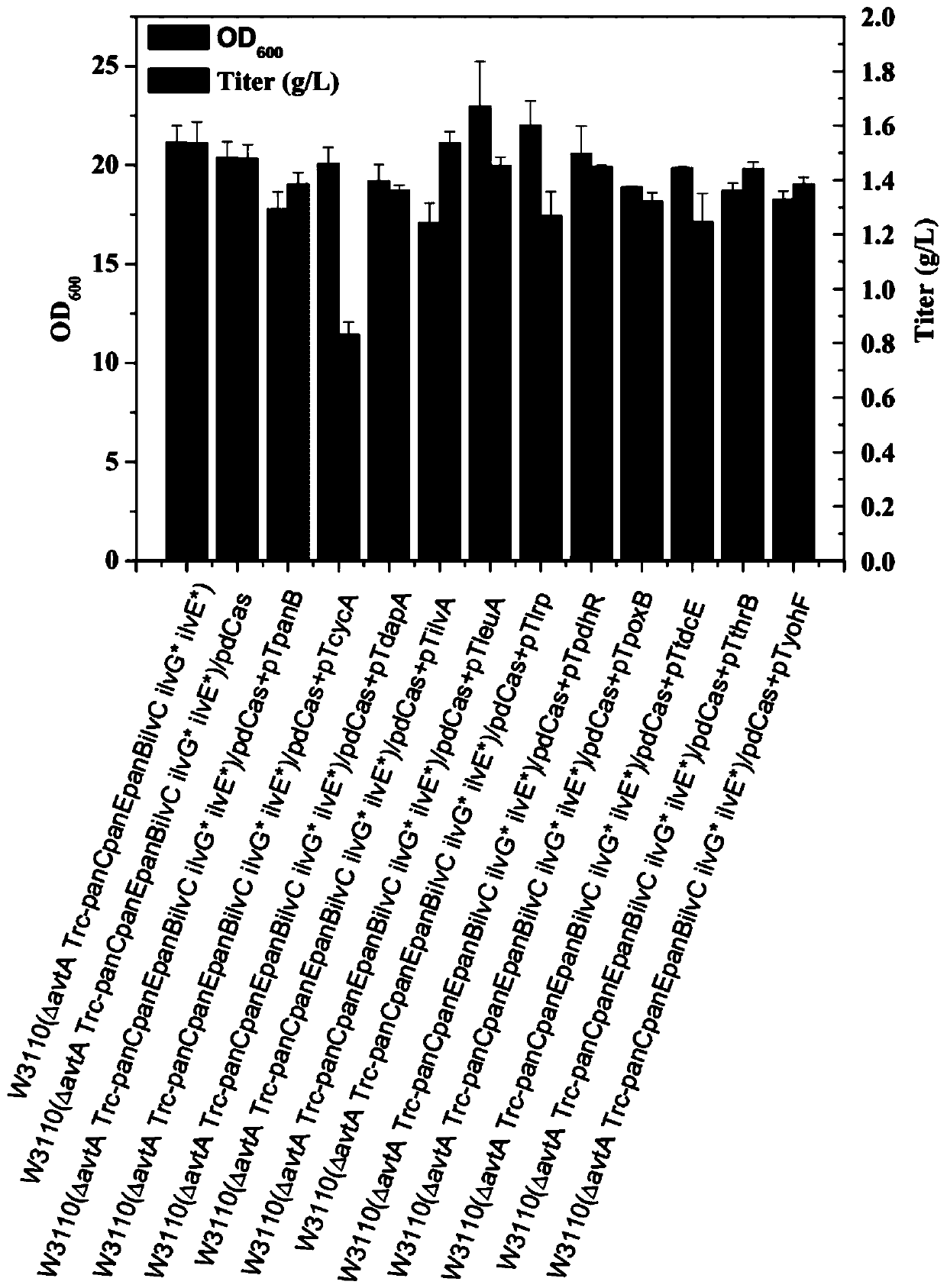
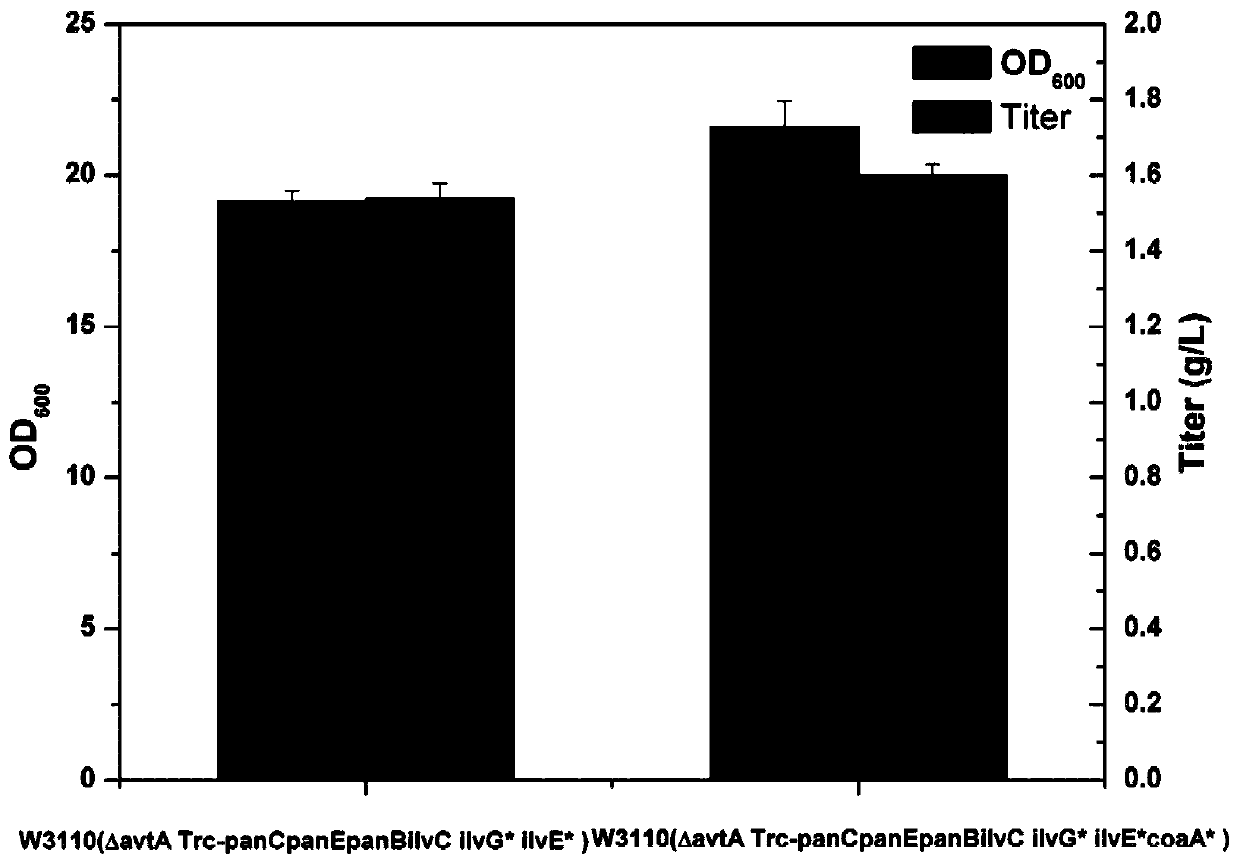
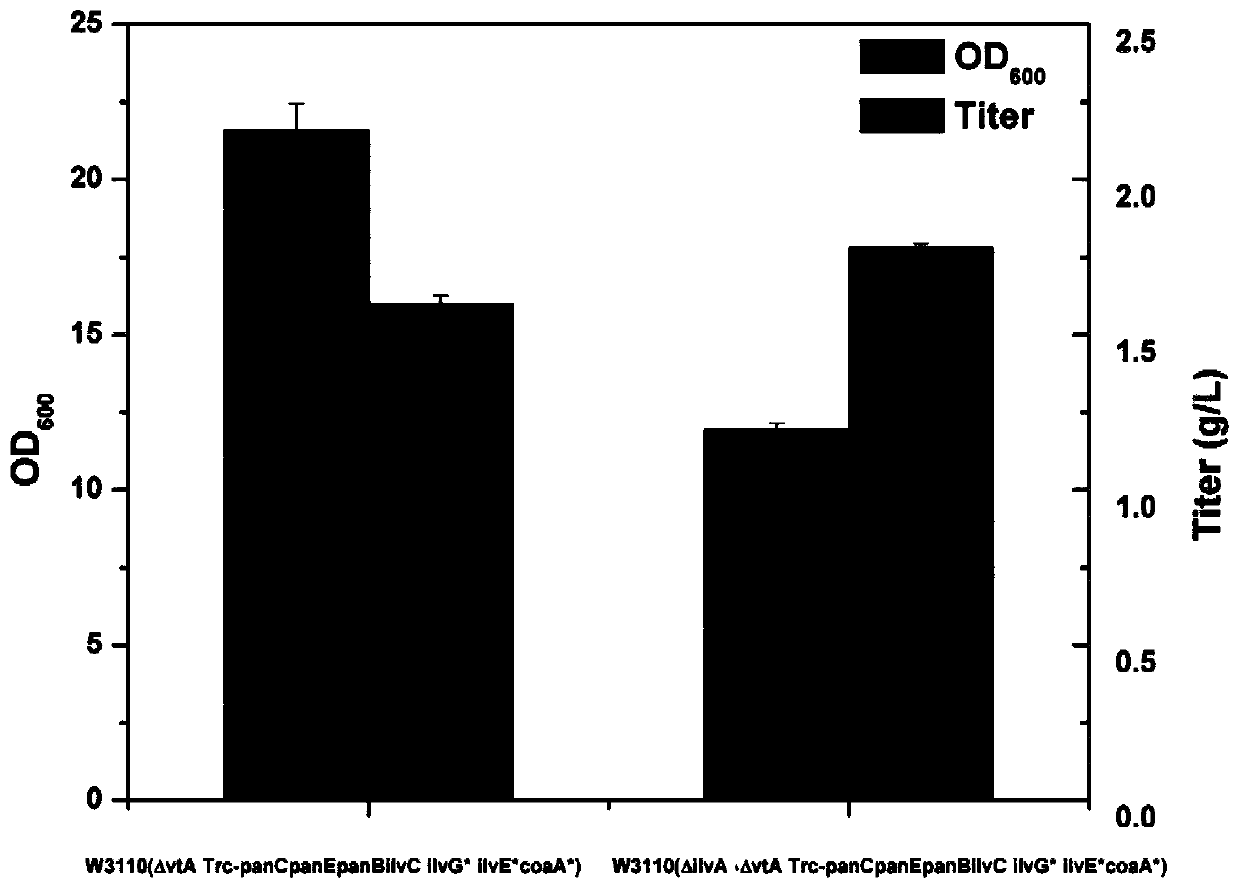
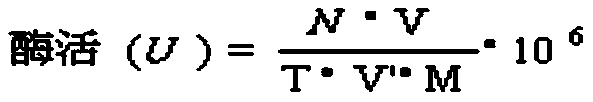Patents
Literature
31 results about "Aspartate decarboxylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recombinant escherichia coli strain for producing beta-alanine as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898035AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
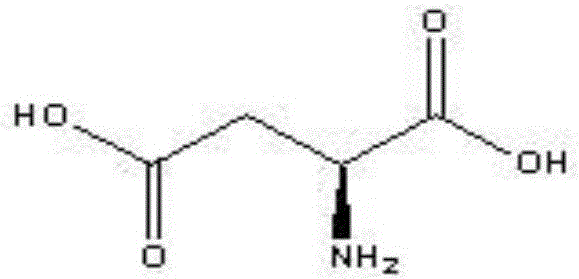
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli strain (Escheerichiacoli) AHB-36 for producing beta-alanine, the preservation number is CCTCC M 2013629, the recombinant escherichia coli strain is a deficiency aspartic acid amino lyase gene and contains an aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase gene. The invention further aims at providing a construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain. The recombinant escherichia coli strain can be used for knocking off the aspartic acid amino lyase gene and preventing the escherichia coli from pyrolyzing the aspartic acid into fumaric acid, so that the aspartic acid is completely applied to production of beta-alanine, and meanwhile aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase is expressed in the recombinant escherichia coli strain, and thus the yield of beta-alanine is further increased.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, construction and application of genetic engineering bacteria
ActiveCN109913398AImprove utilizationReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaStable introduction of DNACell phenotypeEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria, and application of the genetic engineering bacteria in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. According to the invention, (1), the final step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenicacid synthesis pathway is enhanced, and the utilizing ability of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine, (2), a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is enhanced, (3), ilvG gene is repaired, and thefeedback inhibition effect of by-products on a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is weakened, (4), according to the change in cell phenotype, flux of a valine synthesis pathway is weakened, (5), a CRISPRi technique is used to screen metabolic modification sites of TCA cycle, a PPP pathway and a by-product metabolic pathway, according to the result, an isoleucine synthesis pathway is blocked, and thecompetition of 2-butanoic acid for reaction of acetolactate synthesized from pyruvic acid under catalysis of acetolactate synthase is relieved, and (6), aspartate decarboxylase from other strains is subjected to heterologous expression to obtain a genetical engineering strain capable of producing the pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of the beta-alanine. By combined expression of panB and panC which are derived from corynebacterium glutamicum and panD derived from bacillus subtilis together on pTrc99A plasmids, 1.2g / L of D- pantothenic acid is obtained without adding the beta-alanine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for high producing beta-alanine and co-culture preparation of D-pantothenic acid
ActiveCN112625985AIncrease intakePromote accumulationBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousAspartate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for high producing beta-alanine, co-culture preparation of D-pantothenic acid, a construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium and application of the genetically engineered bacterium to co-culture preparation of the D-pantothenic acid. According to the invention, original promoters of panD, aspC and ppc genes on a genome are replaced with a pTrc99A-derived Trc promoter and a ribosomebinding site (RBS) sequence so as to enhance synthesis of the beta-alanine, and genes pykA and pykF are knocked out to block consumption of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and modify a glucose uptake path of escherichia coli, and thus, a non-phosphotransferase system (non-PTS) transport system is enhanced to block a PTS transport system, and synthesized precursor PEP is accumulated; on the basis, heterologous aspartate decarboxylase genes panD and aspC of E.coli W3110 are introduced to enhance the enzyme activity of key enzymes, so that supply and conversion of beta-alanine precursors are enhanced; gdhA genes of E.coli W3110 are introduced to enhance cyclic regeneration of coenzymes NADP / DNAPH, and finally, the titer of the beta-alanine is increased from 0 to 2.48g / L. The strain and a previous D-pantothenic acid producing strain DPA 21 / pBCST3 undergo construction of a primary co-culture system; the inoculation ratio is optimized; and when the inoculation ratio of the two strains is 1: 1, the co-culture strain can produce 3.08 g / L of D-pantothenic acid in a same fermentation medium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing L-aspartic acid and L-alanine by using maleic anhydride
InactiveCN106755157ASimple processRealize circular productionFermentationHydration reactionMaleopimaric acid
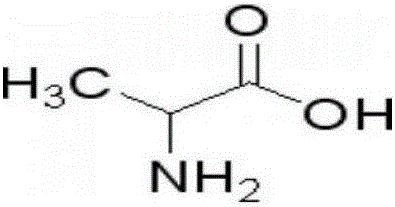
The invention provides a method for preparing L-aspartic acid and L-alanine by using maleic anhydride. The method comprises the following steps: heating the maleic anhydride as the raw material to obtain a maleic acid solution through hydration reaction; adding maleate isomerase and L-aspartase; after filtering and concentrating obtained liquid of enzymatic reaction to deaminize, regulating the pH value until the isoelectric point of the L-aspartic acid is equal to 2.8 by using the maleic acid solution as an acidifying agent; crystallizing to separate out the L-aspartic acid; and converting the L-aspartic acid into the L-alanine by further using aspartate decarboxylase. The L-aspartic acid is prepared through one-step reaction by a two-enzyme method, the process is simple and convenient, the conversion ratio is high, production of malic acid as a by-product can be controlled effectively, and the quality of the product is good; and maleic acid is used as the acidifying agent to prepare the L-aspartic acid in an isoelectric point crystallization manner, crystallization mother liquor can be used as an enzyme reaction substrate and then is recycled, the discharge amount of waste water is greatly reduced, and the method conforms to the idea of environmental protection. In addition, the L-aspartic acid is further converted into the L-alanine by an enzymic method, so that products obtained by a whole process are diversified; and the market competitiveness is high.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Enzymatic preparation of beta alanine
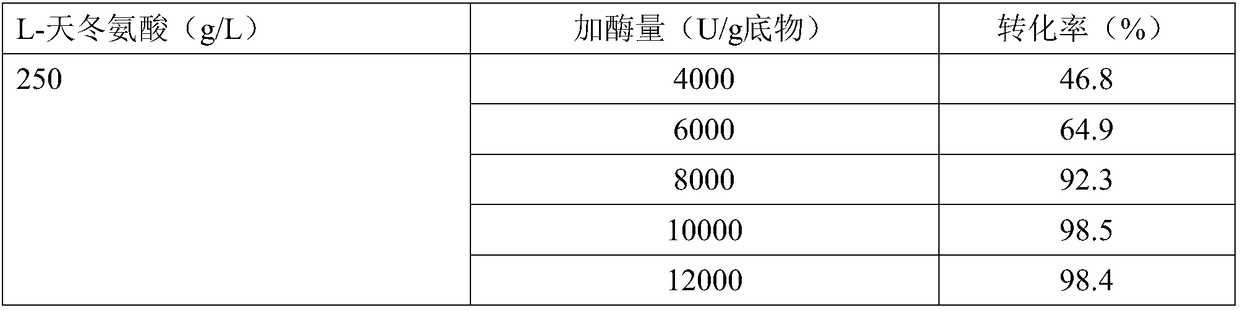
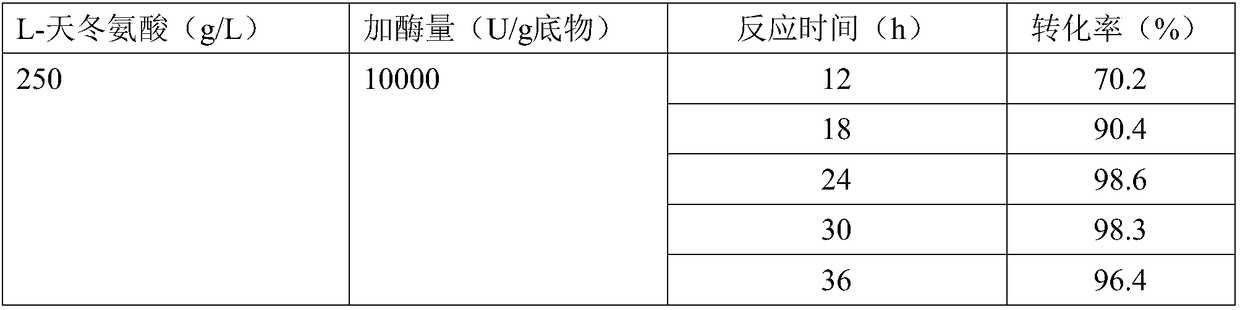
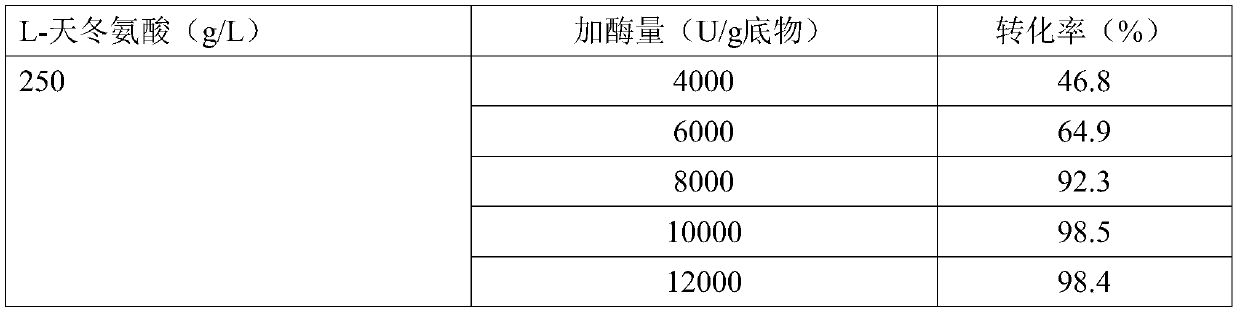
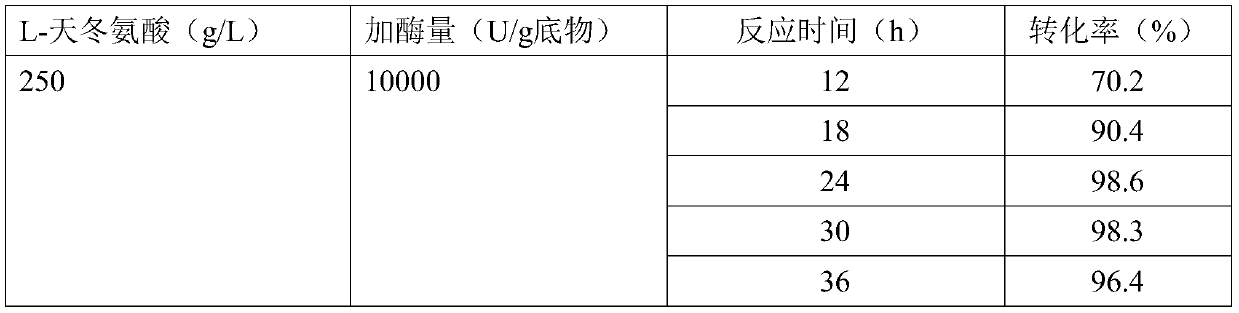
A high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant can be obtained by a directed evolution method, the high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant can efficiently catalyze decarboxylation of aspartic acid to produce beta-alanine, and by optimization of the reaction process, the aspartic acid substrate concentration can reach 250g / L. After 24 hours of conversion, the conversion rate canreach above 98.3%, and the high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant has industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for producing beta-alanine and D-aspartic acid through conversion with biological enzyme method
InactiveCN108841883AEasy to operateEasy to controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAspartate decarboxylase
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme catalysis, particularly relates to a method for producing beta-alanine and D-aspartic acid through conversion with a biological enzyme method, and aims to solve the problem that existing methods for synthetizing the beta-alanine and the D-aspartic acid with the biological enzyme method are not suitable for industrialization due to the fact that the existing methods are too low in yield or solid substrates are required to be manually and uninterruptedly added in biological conversion processes. According to the technical scheme, the methodcomprises steps as follows: [1] engineered Escherichia coli for overexpression of L-aspartate decarboxylase is obtained through high-density fermentation; [2] biological conversion is performed by theaid of the engineered Escherichia coli by using DL-aspartic acid as a substrate, a DL-sodium aspartate solution is fed for substrate addition during conversion, meanwhile, the pH of the conversion system is controlled through feeding of a DL-aspartate hydrochloride solution, and the beta-alanine and the D-aspartic acid are obtained. The beta-alanine can be synthetized separately by replacing thesubstrate with L-aspartic acid. The method is applicable to synthesis of the beta-alanine and D-aspartic acid.
Owner:SICHUAN TONGSHENG BIOTECH
Immobilized L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107164361AImprove biological activityWide range of optimumChemical industryMicroorganism based processesEpsilon-PolylysineBio engineering
The invention discloses an immobilizing method of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, TiO2 modified by a poly amino acid is used as a carrier, the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase is bonded onto the surface of the carrier, and the poly amino acid is gamma-polyglutamic acid or epsilon-polylysine. Immobilization studies on the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase by respective use of the modified carrier and an unmodified carrier find that the enzyme carrier content of the modified carrier is about 8 times of that of the unmodified carrier.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering strain of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and application
InactiveCN109402097AIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyL-Aspartate
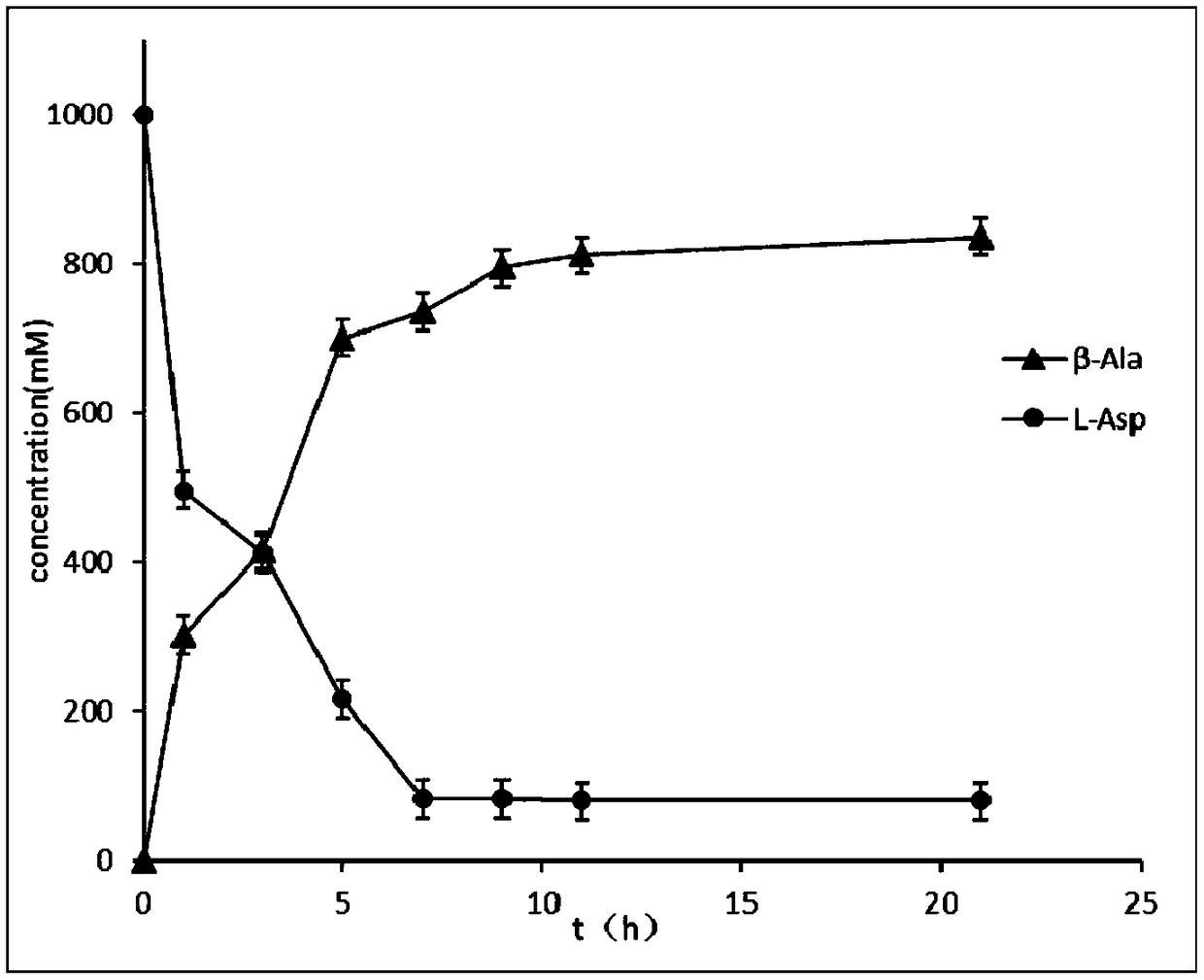
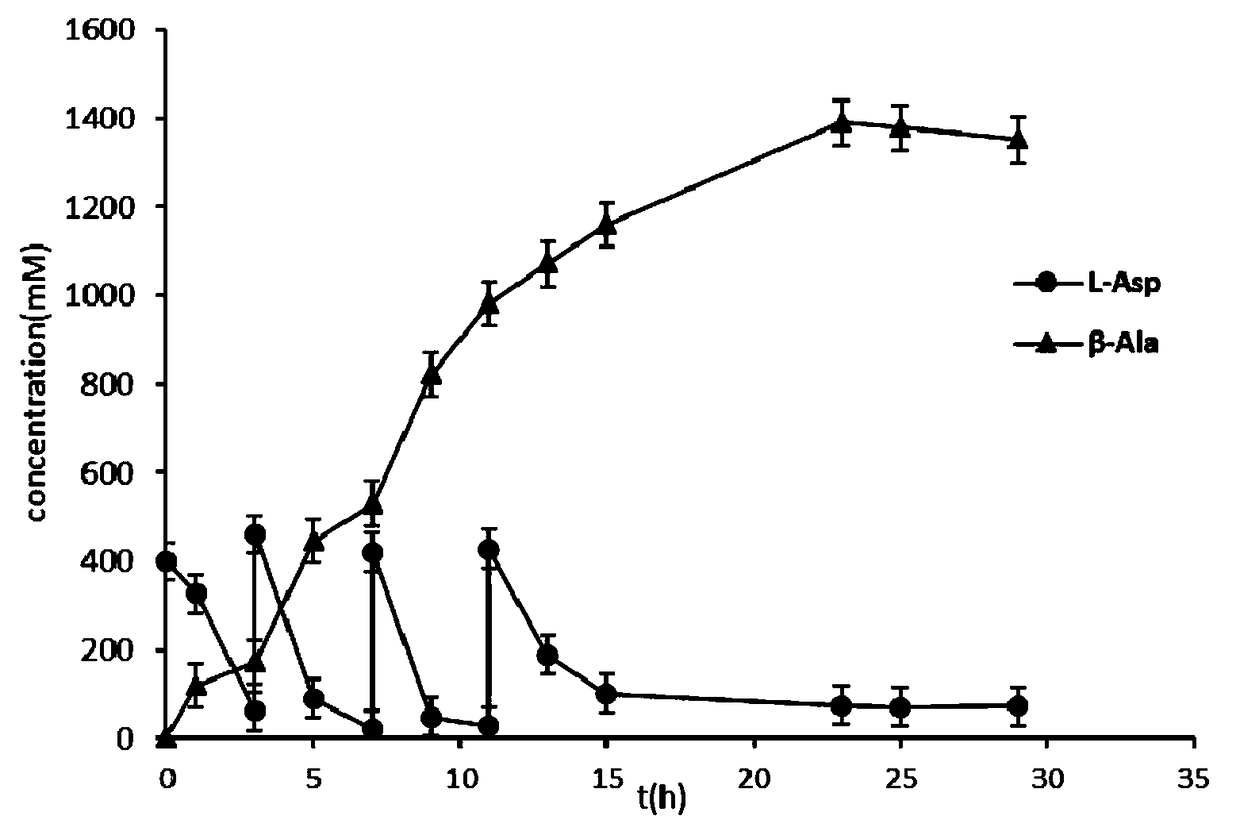
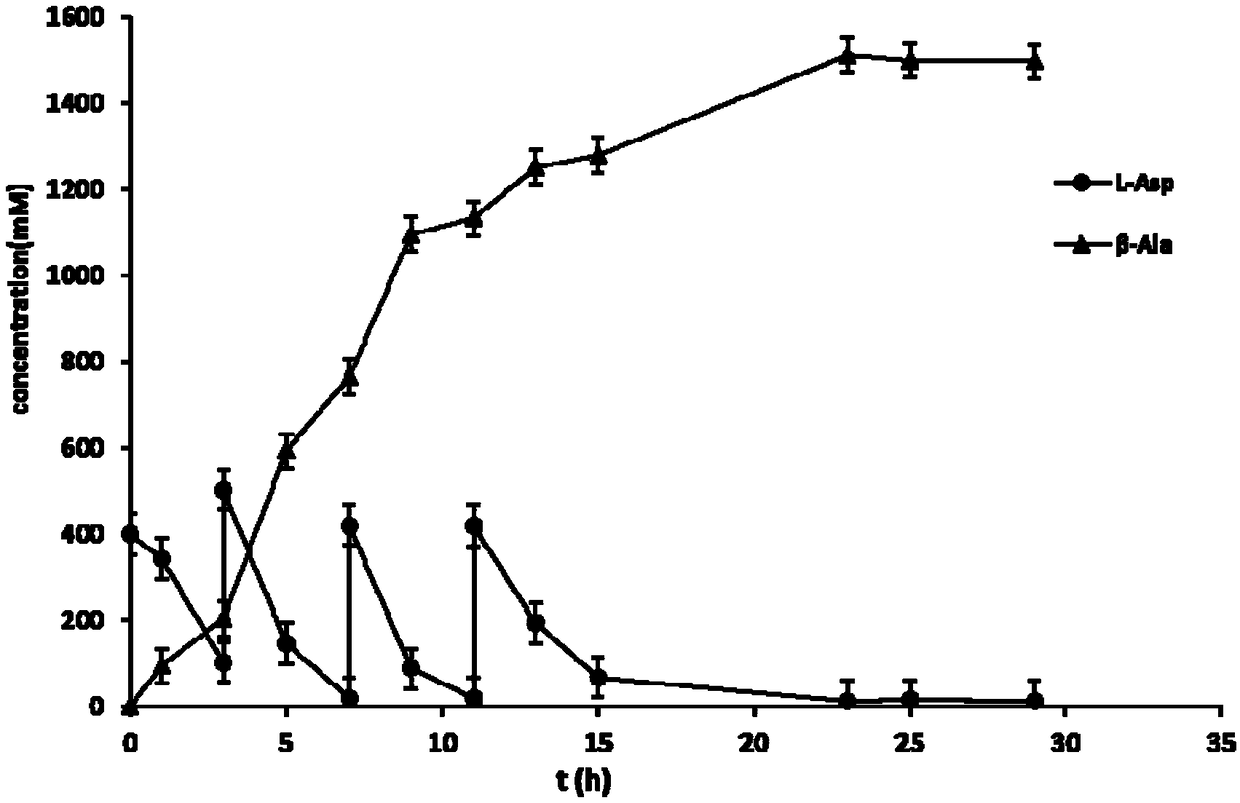
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and an application, particularly relates to a method for catalytically synthesizing beta-alanine by the genetic engineering strain of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and application and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the method, through establishing and optimizing awhole-cell catalysis process and adopting a substrate batched-adding mode, after a substrate is added in four times, about 123.81g / L of beta-alanine is produced through 23h of conversion of wild typerecombinant strains; the concentration of the product, i.e., beta-alanine can reach 134.72g / L through 23h of conversion of mutant strains K221R; the concentration of the product, i.e., beta-alanine can reach 136.33 g / L through 23h of conversion of mutant strains G369A. By the method, the yield of beta-alanine is increased relatively greatly, and this discovery has an important application value inindustrialized preparation of beta-alanine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase mutants and application thereof
ActiveCN110804602AImprove stabilityGood enzymatic propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAspartate decarboxylaseBio engineering
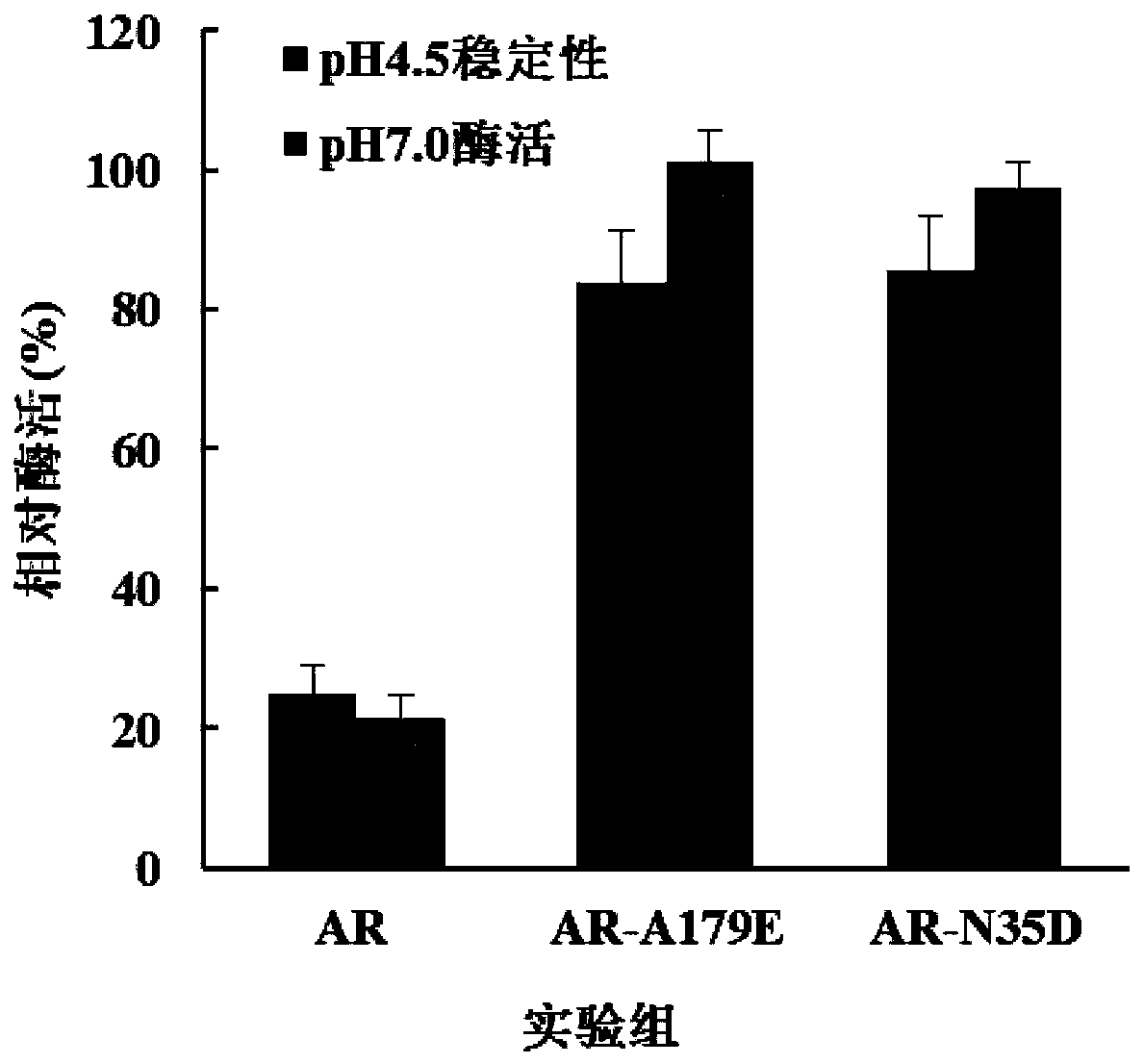
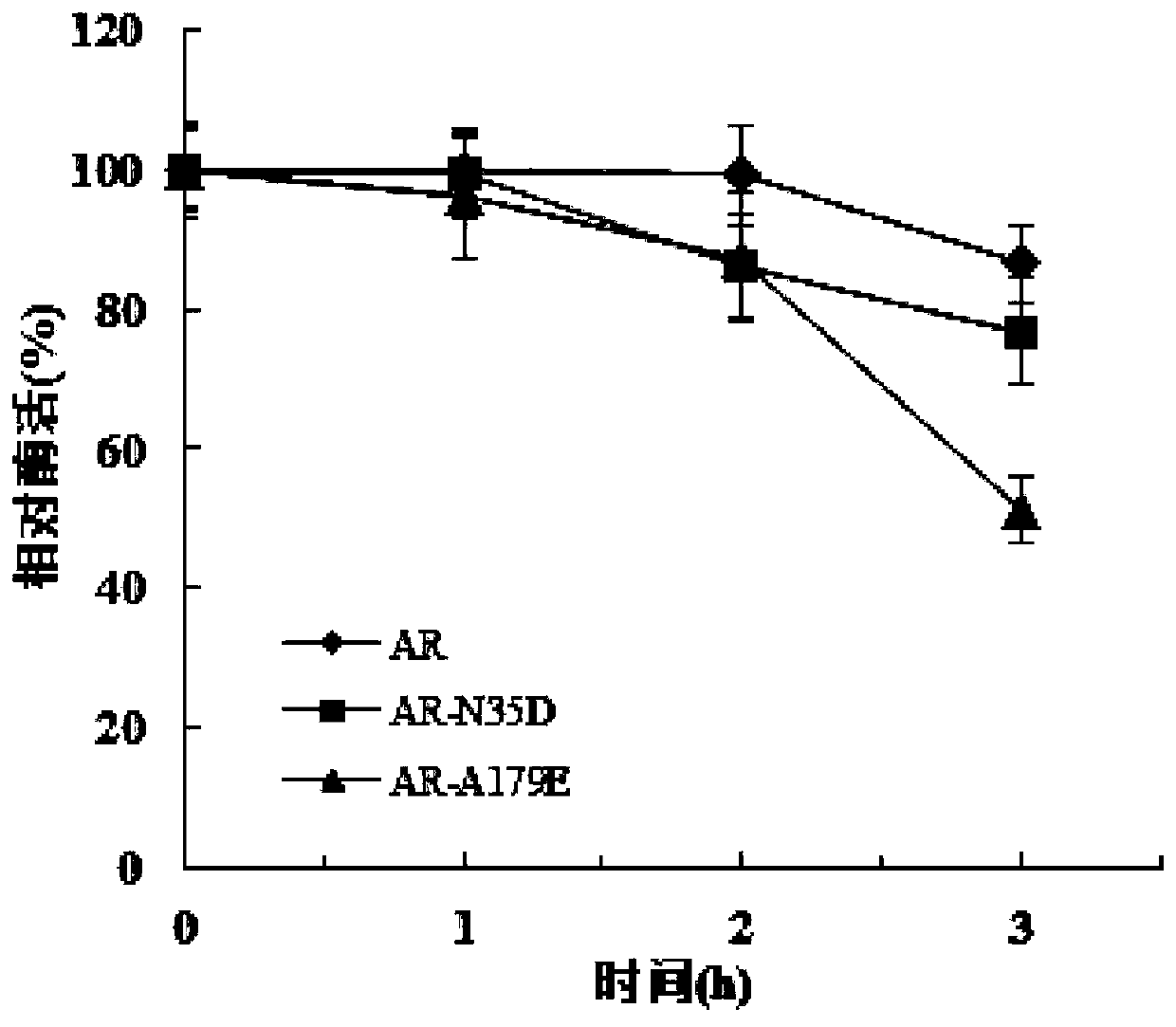
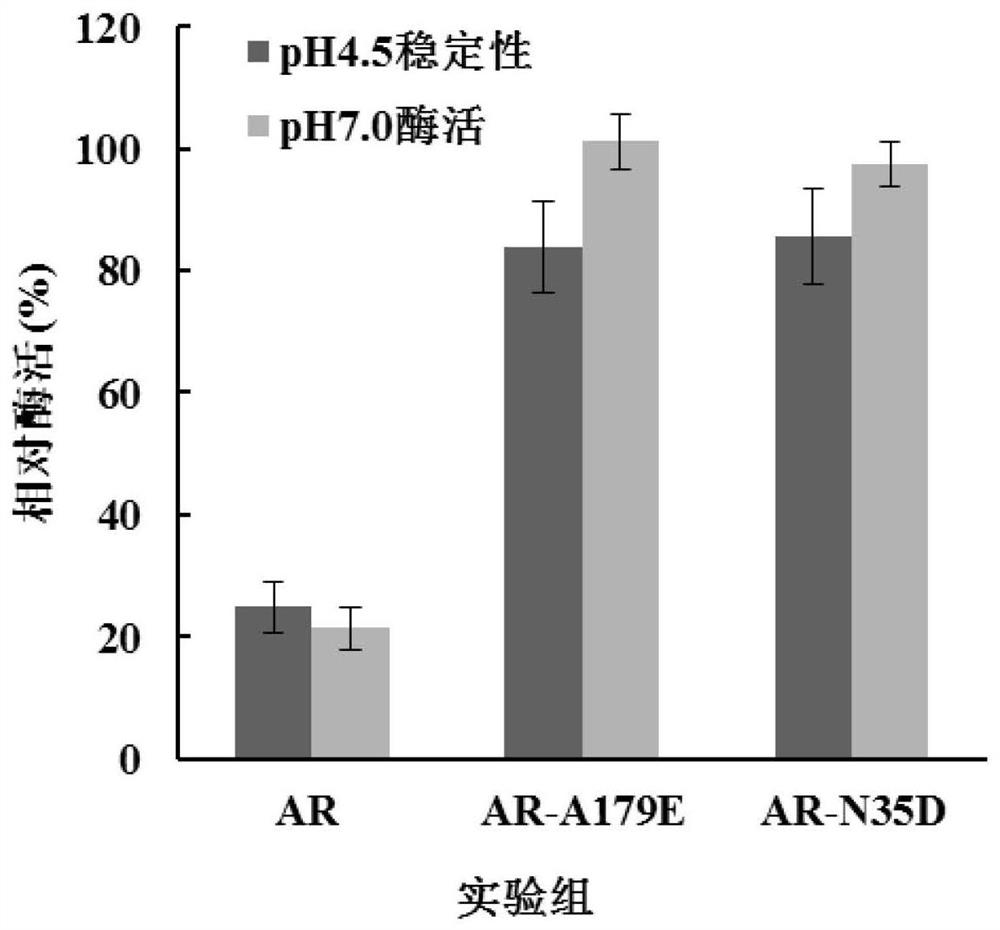
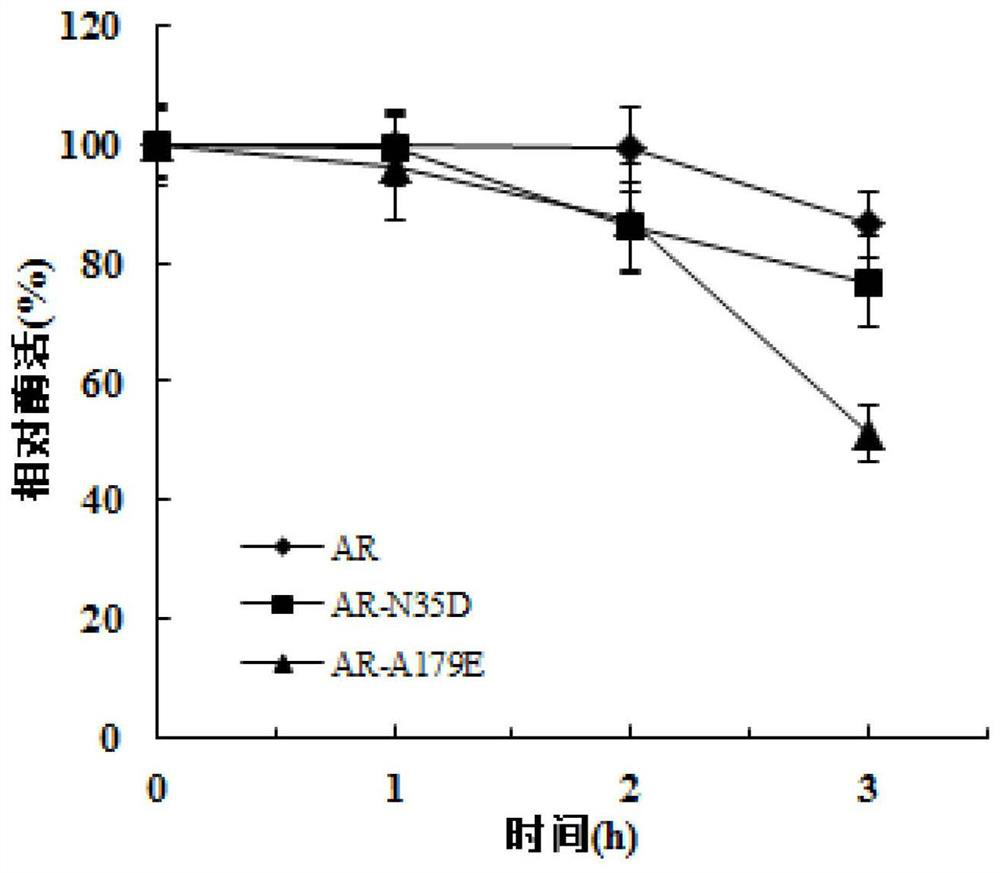
The invention discloses L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase mutants and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The catalytic enzyme activity of the L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase mutants N35D and A179E provided by the invention are improved by 238% and 244% respectively under the pH of 7.0, the remaining enzyme activity of the mutants N35D and A179E treated for 12 h under the pH of 4.5 is 83.9% and 85.5%, respectively, and compared with a control wild-type enzyme having residual enzyme activity of 24.8%, the mutants provided by the invention have significantly-improved acid stability, and therefore the L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase mutants N35D and A179E provided by the invention have better enzymatic properties.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing L-alanine by catalyzing maleic acid through double-enzyme coupled whole cells
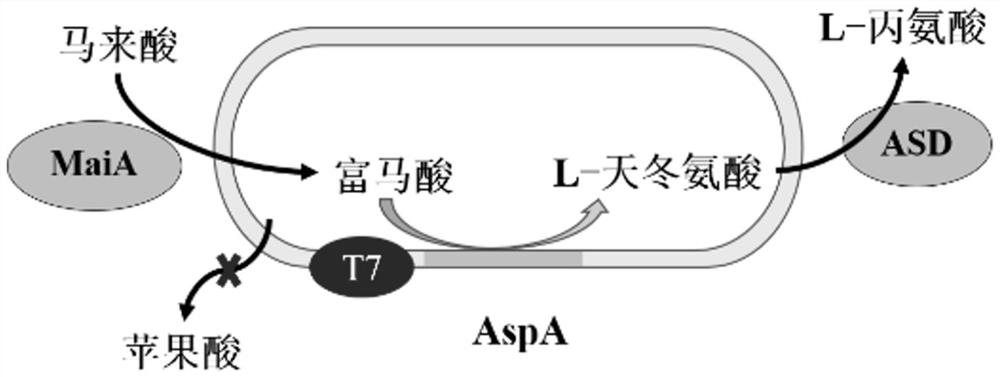
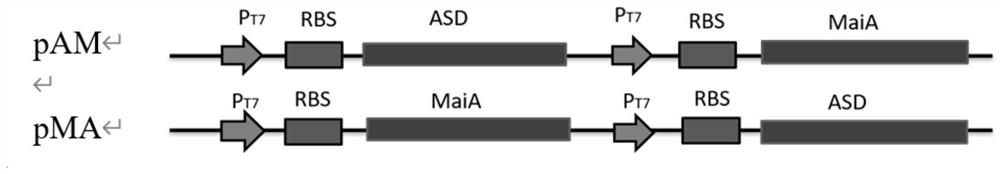
PendingCN112941003ASimple processLow costCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaAspartate decarboxylaseIsomerase
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-alanine by catalyzing maleic acid through double-enzyme coupled whole cells, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a recombinant strain for coupling expression of maleic acid cis-trans isomerase and L-aspartic acid beta decarboxylase is established, and host bacterium modification and optimization are carried out on the recombinant strain, so that a recombinant bacterium capable of catalyzing maleic acid to generate L-alanine in a whole-cell high-conversion-rate manner is obtained. The recombinant strain can generate L-alanine by using relatively cheap maleic acid, almost no intermediate products fumaric acid and L-aspartic acid are accumulated, the conversion rate reaches 96% or above, the highest production rate reaches 28.43 g / (L.h), and the highest yield reaches 261.2 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase and application thereof
PendingCN112779243AReduce dosageRapid responseBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCysteinesulfinate decarboxylase
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering, in particular to L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase. The L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase has an amino acid sequence and a gene sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3 in SEQUENCE LISTING. The gene is synthesized in vitro after codon optimization based on a gene sequence encoding cysteinesulfinate decarboxylase in genome of Myzus persicae. The gene is cloned into an expression vector and transformed into Escherichia coli to construct a high-expression engineering strain. After the engineering strain is cultured and induced, it is found that the enzyme has activity of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase, and the enzyme can convert L-aspartic acid into beta-alanine under proper conditions, overcome a defect that prokaryotic-derived L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase in the prior art is easy to inactivate, and can be used for industrial production of beta-alanine under conditions of small enzyme dosage and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Strain capable of highly producing aspartate decarboxylase and method for producing alanine
ActiveCN105368758ABroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAspartate decarboxylaseActive agent
The invention relates to a strain capable of highly producing aspartate decarboxylase and a method for producing alanine and belongs to the technical field of biology. The class name of the strain is bacillus tequilensis PanD37 and the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preservation number of CGMCC No.10506 on February 2, 2015. The bacillus tequilensis PanD37 capable of producing L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase, provided by the invention, is reported for the first time, the strain PanD37 is good in genetic stability, and low in culture cost, the produced L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase is high in enzyme activity, the strain fermentation liquor can be directly converted into beta-alanine, and a surfactant, an organic solvent and other membrane permeable agents are not required to be added during catalytic synthesis, so that exogenous impurities are prevented from being introduced, the extraction separation operation is facilitated and an advantage in industrial application is realized.
Owner:山东中酶生物科技有限公司
Enzyme catalyst and preparation method and application thereof in production of 3-aminopropionic acid
InactiveCN111304184AHigh catalytic activityImprove toleranceFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesPtru catalystAspartate decarboxylase
The invention discloses an enzyme catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof in production of 3-aminopropionic acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) culturingan L-aspartate decarboxylase strain, and performing centrifuging to obtain thalli; (2) re-suspending the thalli obtained in the step (1) with water to obtain a resuspension, adding a surfactant into the resuspension, and performing stirring and centrifuging to obtain a supernatant; and (3) adding metal ions into the supernatant obtained in the step (2), performing mixing, adding a ligand solution,and performing stirring, washing and centrifuging to obtain a precipitate, namely the enzyme catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the method simplifies the operation process of extracting enzyme from cells, prepares the nano-material immobilized enzyme catalyst in a two-step rapid synthesis form, is simple and convenient in preparation process, and has low requirement on equipment; and the method realizes recycling and good repeated utilization rate of L-aspartate decarboxylase.
Owner:南京凯诺生物科技有限公司
A high-throughput screening method for l-aspartate β-decarboxylase-producing bacteria
ActiveCN105648036BSolve the problem that the pH value keeps rising and the enzyme activity decreasesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A high-throughput screening method for an L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase producing strain is disclosed. The method includes 1) subjecting microorganisms in a sample to enrichment culture and primary separation by adopting an enrichment culture medium, 2) inoculating single colonies obtained through separation from a plane plate to a 96-micropore plate primary screening semisolid medium and performing primary screening to obtain L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase producing strains, 3) inoculating the strains obtained through primary screening to a 24-prore plate, performing liquid culturing, and performing secondary screening to obtain the L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase producing strain with high yield by combining paper chromatography, and 4) subjecting the high-yield strain obtained through secondary screening to fermentation in a shake flask, and determining enzyme activity by combining an oxidation coloration process. The method is suitable for high-throughput screening of the L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase producing strain. The strain obtained through screening is alkali-resistant, thus avoiding tedious pH value controlling steps in a cell production processes. References are provided for high-throughput screening of producing strains bio-enzymes of the same kind.
Owner:SHANDONG INT BIOTECH PARK DEV
A kind of immobilized l-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107164361BImprove biological activityWide range of optimumChemical industryMicroorganism based processesAspartate decarboxylasePolylysine
The invention discloses an immobilizing method of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, TiO2 modified by a poly amino acid is used as a carrier, the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase is bonded onto the surface of the carrier, and the poly amino acid is gamma-polyglutamic acid or epsilon-polylysine. Immobilization studies on the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase by respective use of the modified carrier and an unmodified carrier find that the enzyme carrier content of the modified carrier is about 8 times of that of the unmodified carrier.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A kind of pand mutant gene, encoded protein, carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN106754845BImprove efficiencyBreeding goals are clearFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBase JAspartate decarboxylase
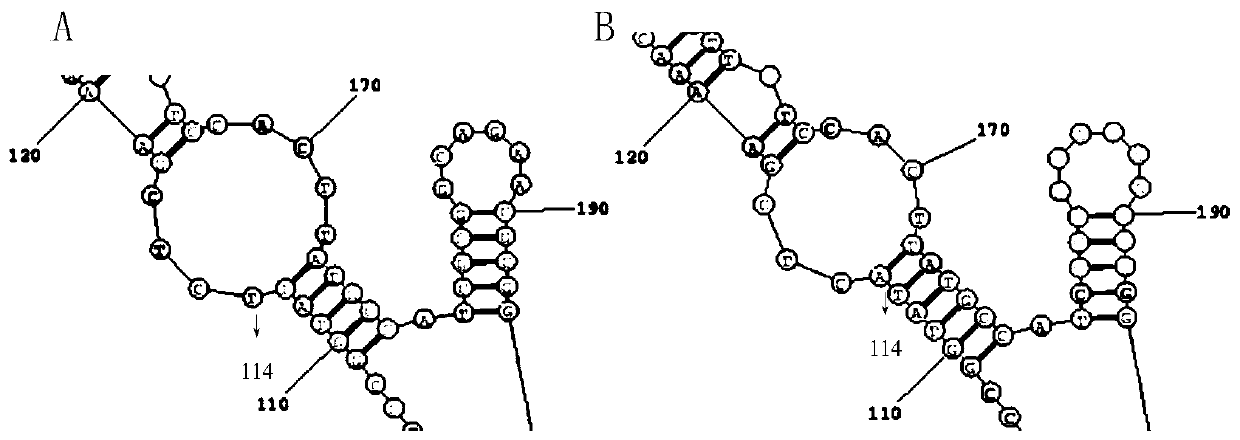
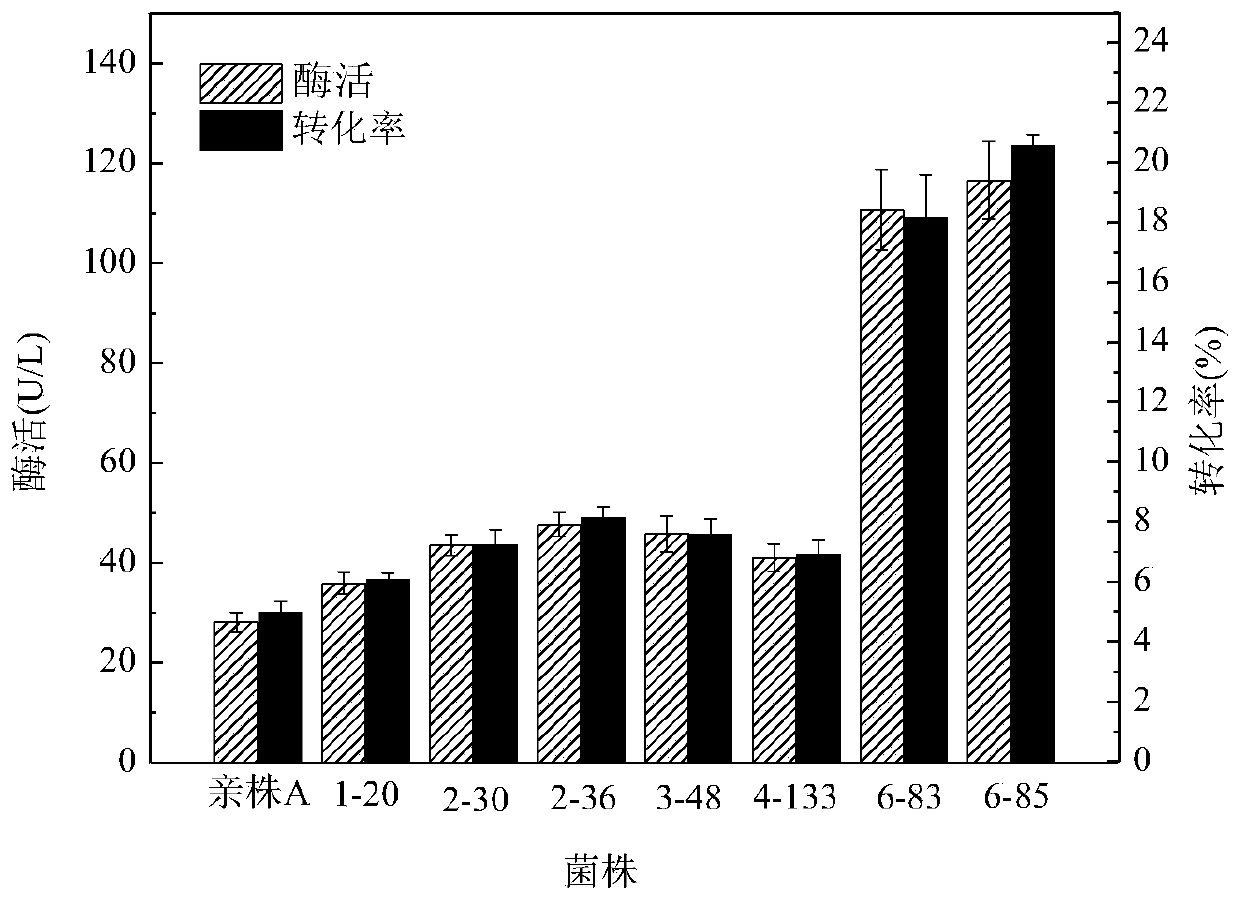
The invention relates to a panD mutant gene, encoded protein, a vector, an engineering bacterium and an application of the encoded protein. Series recombinant escherichia coli, for high-yield production of L-aspartate-[alpha]-decarboxylase (PanD), is obtained by changing codon base of the panD gene through random mutation of error-prone PCR. With the application of gene engineering bacterium for high-yield production of the PanD, the efficient transformation of the L-aspartate is achieved, so that [beta]-alanine can be prepared by virtue of a biological method, wherein PanD enzyme activity of recombinant escherichia coli numbered as 6-85 can reach 250U / L or above and [beta]-Ala yield can reach about 8.5g / L, nearly 4 times and 3 times above that of a parent strain.
Owner:浙江科峰生物技术有限公司
Platform bacterium for producing L-aspartate, recombinant bacterium constructed based on platform bacterium for producing beta-alanine and construction method of recombinant bacterium
ActiveCN111778200AImprove conversion rateEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAspartate decarboxylase
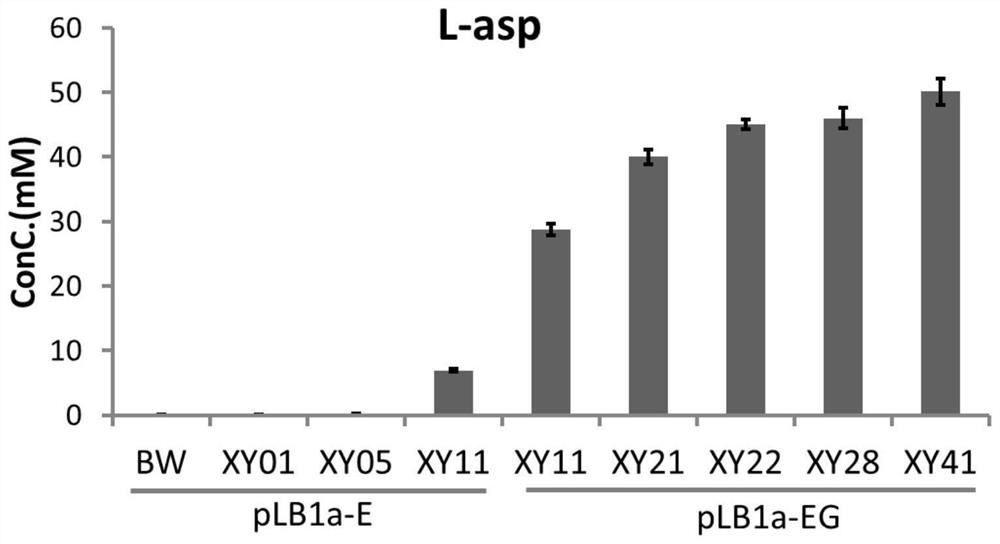
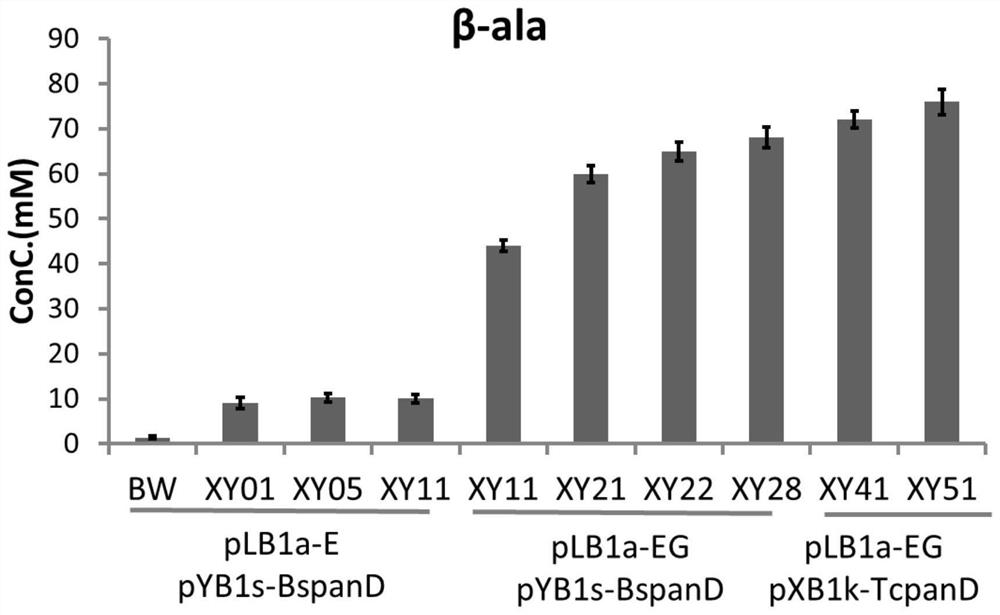
The invention discloses a platform bacterium for producing L-aspartate, a recombinant bacterium constructed based on the platform bacterium for producing beta-alanine and a construction method of therecombinant bacterium. By changing a glucose intake pathway and a glycolysis pathway of escherichia coli, phosphoenolpyruvic acid is accumulated in a large amount, so that a carbon fixation pathway isenhanced to obtain a large amount of precursor substance oxaloacetic acid, and related gene targets of an L-aspartate synthesis pathway are enhanced; by introducing a cofactor circulating system, theproblem of insufficient co-substrates is solved, and a central metabolic pathway tricarboxylic acid cycle is transformed and a byproduct competitive bypass is knocked out, so that the platform bacterium is obtained; and based on the platform bacterium, expression of aspartate decarboxylase is enhanced to obtain the recombinant bacterium. The platform bacterium can synthesize 50.10+ / -2.10 mM L-asp, and the conversion rate reaches 1.00 M / M glucose; and the recombinant bacterium can synthesize 76.01+ / -2.80 mM beta-alanine, and the conversion rate is 1.52 M / M glucose. The platform bacterium for producing the L-aspartate, the recombinant bacterium constructed based on the platform bacterium for producing the beta-alanine and the construction method of the recombinant bacterium have important application value.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of beta-alanine
PendingCN111718969ASimple production processReduce manufacturing costFermentationPtru catalystAspartate decarboxylase
The invention provides a preparation method of beta-alanine. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a beta-alanine product from a reactant containing fumaric acid and ammonia water inthe presence of a catalyst, wherein the catalyst comprises a catalytic composition comprising aspartase and L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase, and fumaric acid is added during the reaction, and the total molar amount of the added fumaric acid is equal to the amount obtained by subtracting the initial molar amount of fumaric acid in the reactant from the initial molar amount of ammonia water in the reactant.
Owner:GUANG AN MOJIA BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A high-yielding aspartate decarboxylase strain and its method for producing alanine
ActiveCN105368758BBroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to a strain with high production of aspartate decarboxylase and a method for producing alanine, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is classified and named as Bacillus tequila PanD37, which was published on February 2, 2015. Preserved in China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, preservation number: CGMCC No.10506. The Bacillus tequila producing L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase provided by the present invention is reported for the first time. The bacterial strain PanD37 has good genetic stability and low cultivation cost, and the produced L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase enzyme With high activity, the fermentation broth of this strain can be used to directly convert β-alanine. No need to add surfactants, organic solvents and other membrane-permeable agents during the catalytic synthesis, avoiding the introduction of exogenous impurities, which is conducive to extraction and separation operations, and has advantages in industrial applications .
Owner:山东中酶生物科技有限公司
A kind of l-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase mutant and its application
ActiveCN110804602BImprove stabilityGood enzymatic propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAspartate decarboxylaseBio engineering
The invention discloses a L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase mutant and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. For the L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase mutants N35D and A179E provided by the present invention, the catalytic enzyme activity is increased by 238% and 244% respectively under the condition of pH 7.0. After 12 hours of treatment at pH 4.5, 83.9% and 85.5% of the remaining enzyme activity remained, compared with 24.8% of the remaining enzyme activity of the wild-type enzyme in the control, the acid stability of the mutant was significantly improved. Therefore, the L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase mutants N35D and A179E provided by the present invention have better enzymatic properties.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Immobilized whole-cells, preparation method of immobilized whole-cells, and application in production of 3-aminopropionic acid
PendingCN111321161AEasy to synthesizeImprove controllabilityOn/in organic carrierFermentationAspartate decarboxylaseBiochemistry
The invention discloses immobilized whole-cells, a preparation method of the immobilized whole-cells, and application in production of 3-aminopropionic acid. The preparation method of the immobilizedwhole-cells comprises the steps of: (1), culturing an L-aspartate decarboxylase strain, and centrifuging, so that thallus is obtained; (2), re-suspending the thallus obtained in the step (1) by usingwater, so that cell re-suspension solution is obtained; and (3), mixing the cell re-suspension solution obtained in the step (2) with ion solution, adding ligand solution, stirring, washing, and precipitating the solid part after being washed, so that precipitates, namely immobilized whole-cells, are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method in the invention has the advantages that: the catalytic activity, the tolerance and the repeated utilization rate of cells in a catalytic system are improved.
Owner:南京凯诺生物科技有限公司
L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN113444712AIncreased self-shear levelsIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAspartate decarboxylase
The invention provides an L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and an application of the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant in synthesis of beta-alanine. According to the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and the application thereof, L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase is modified by whole plasmid site-directed mutagenesis, and amino acid sites at the 14th site, the 44th site and the 85th site of the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase which has an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.1 and is derived from Escherichia coli are replaced, so that a mutant strain influencing the self-shearing of the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase is obtained. According to the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and the application thereof, by comparing mutants EcoPanDK14T, EcoPanDI44V and EcoPanDV85L with a wild type, it is found that compared with the wild type, the self-shearing level of the mutant is remarkably increased, and the yield of beta-alanine is remarkably increased after fermentation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A l-aspartate-α-decarboxylase with improved thermostability
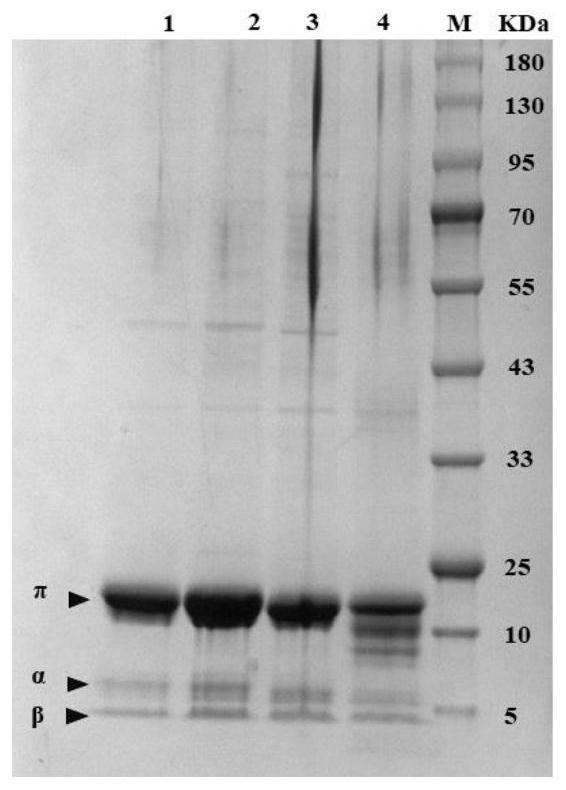
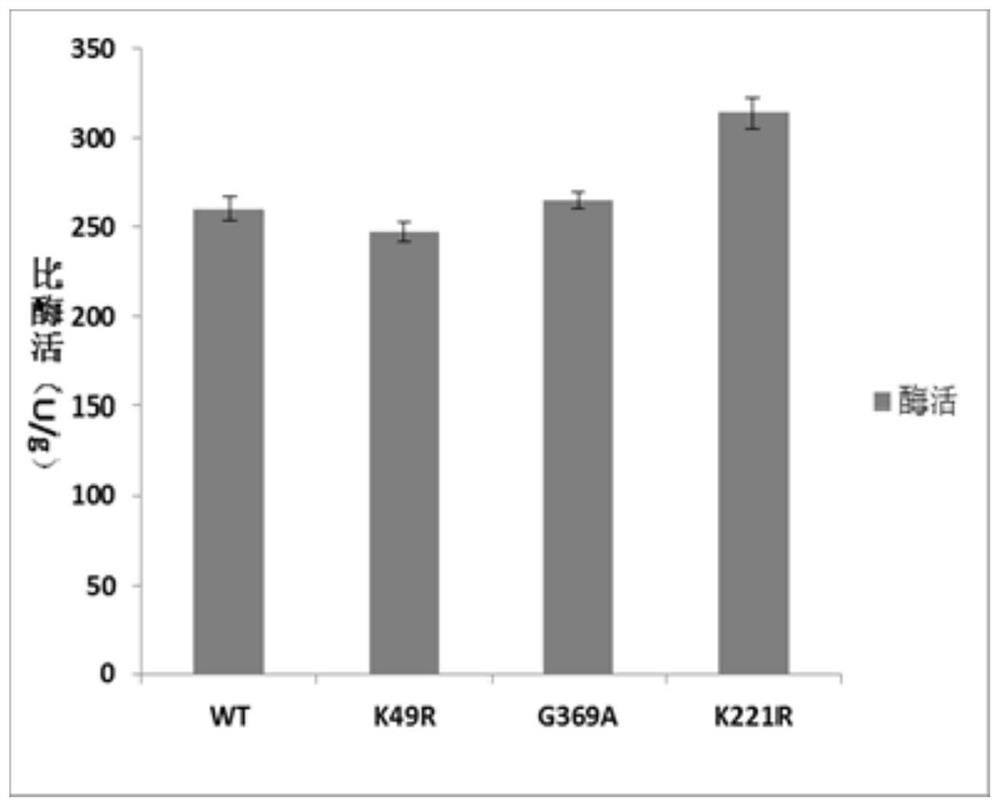
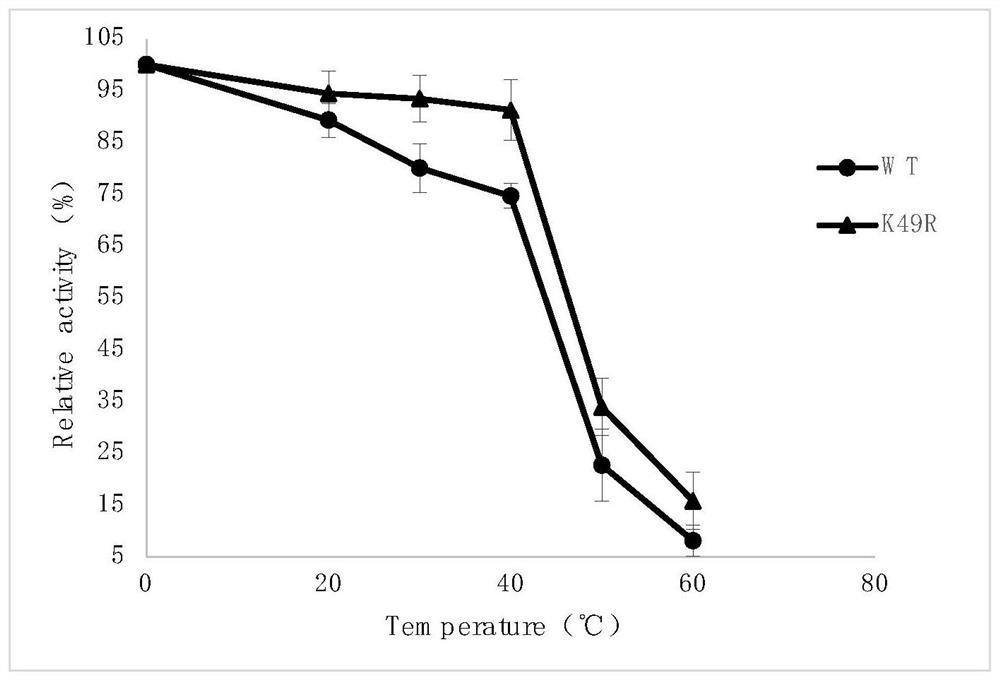
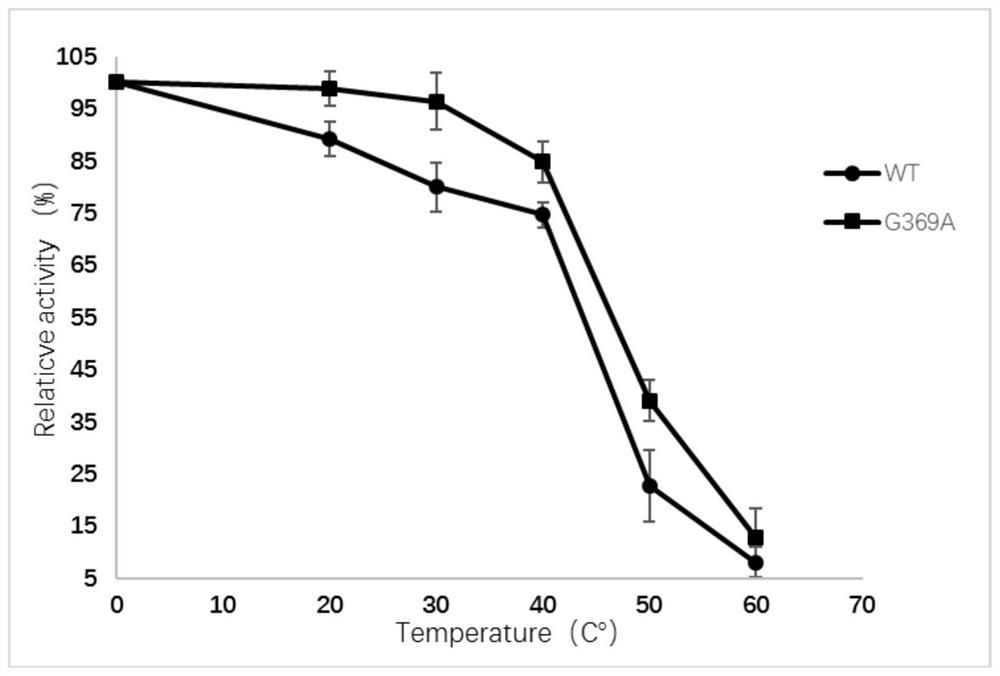
ActiveCN109055346BImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAspartate decarboxylase
The invention discloses L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase with improved thermal stability and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. Three enzyme mutants including K49R, G369A and K221R areobtained through site-directed mutation of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase from tribolium castaneum, recombinant plasmid of the mutants is transformed into escherichia coli BL21, and a substrate L-aspartic acid is catalyzed to produce beta-alanine after expression separation and purification. At the treatment temperature of 50 DEG C, K49R can improve the thermal stability by 14% as compared withwild enzyme, G369A can improve the thermal stability by 20% as compared with wild enzyme, and K221R can improve the thermal stability by 23% as compared with wild enzyme, wherein K221 can make the enzyme activity reach about 320 U / g and has the enzyme activity improved by 23% as compared with the wild enzyme, and the discovery has important study value for industrial preparation of beta-alanine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production method of D-aspartic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of amino acid production, and particularly discloses a production method of D-aspartic acid. The production method of the D-aspartic acid comprises the following steps of: mixing a reaction base material DL-aspartic acid solution with fermentation liquor containing L-aspartic acid-beta decarboxylase for conversion reaction, and performing conversion in a manner of feeding DL-aspartic acid solid and the DL-aspartic acid solution reaction base material in the reaction process. The concentration of the D-aspartic acid in a conversion liquid system obtained by reaction is high, and the yield and purity of a D-aspartic acid product are remarkably improved.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA BIOCHEMICAL CO LTD
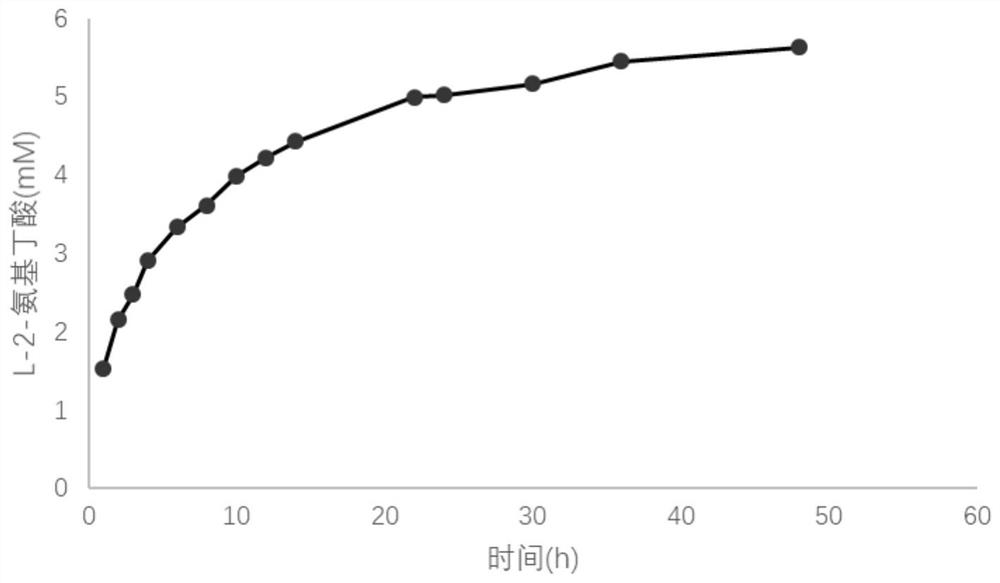
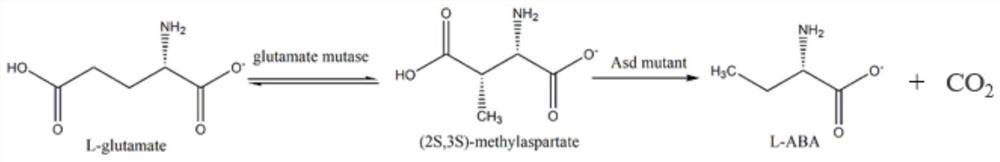
A kind of method for preparing l-2-aminobutyric acid with double enzymes in series
ActiveCN111172213BLow priceReduce manufacturing costTransferasesMicroorganism based processesAspartate decarboxylaseRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-2-aminobutyric acid in tandem with two enzymes, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The present invention obtains L-glutamic acid mutase and L-aspartic acid-β-decarboxylase by respectively cultivating recombinant Escherichia coli expressing L-glutamic acid mutase and L-aspartic acid-β-decarboxylase decarboxylase. The two enzymes are added to the reaction system with a certain mass ratio, and L-glutamic acid is used as a substrate to carry out an enzyme reaction to prepare L-2-aminobutyric acid. When the amount of L-aspartic acid-β-decarboxylase 2mg / mL, reacted for 24h, converted into 8.5mmol / L L-2 aminobutyric acid, and the molar conversion rate was 85.00%. Compared with the chemical production method, this method has a safe production process and no environmental pollution. Compared with the multi-enzyme synthesis system using threonine as the substrate, the substrate is cheaper and the process is simpler.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzymatic preparation of beta alanine
A high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant can be obtained by a directed evolution method, the high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant can efficiently catalyze decarboxylation of aspartic acid to produce beta-alanine, and by optimization of the reaction process, the aspartic acid substrate concentration can reach 250g / L. After 24 hours of conversion, the conversion rate canreach above 98.3%, and the high enzyme activity aspartate decarboxylase mutant has industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetically engineered bacteria, construction and application of high-yielding pantothenic acid without the addition of β-alanine
ActiveCN109913398BEasy to synthesizeD-pantothenic acid potency boostBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliCell phenotype
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria, and application of the genetic engineering bacteria in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. According to the invention, (1), the final step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenicacid synthesis pathway is enhanced, and the utilizing ability of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine, (2), a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is enhanced, (3), ilvG gene is repaired, and thefeedback inhibition effect of by-products on a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is weakened, (4), according to the change in cell phenotype, flux of a valine synthesis pathway is weakened, (5), a CRISPRi technique is used to screen metabolic modification sites of TCA cycle, a PPP pathway and a by-product metabolic pathway, according to the result, an isoleucine synthesis pathway is blocked, and thecompetition of 2-butanoic acid for reaction of acetolactate synthesized from pyruvic acid under catalysis of acetolactate synthase is relieved, and (6), aspartate decarboxylase from other strains is subjected to heterologous expression to obtain a genetical engineering strain capable of producing the pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of the beta-alanine. By combined expression of panB and panC which are derived from corynebacterium glutamicum and panD derived from bacillus subtilis together on pTrc99A plasmids, 1.2g / L of D- pantothenic acid is obtained without adding the beta-alanine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Mixed bacteria secondary fermentation technology and application thereof in industrial production of L-alanine
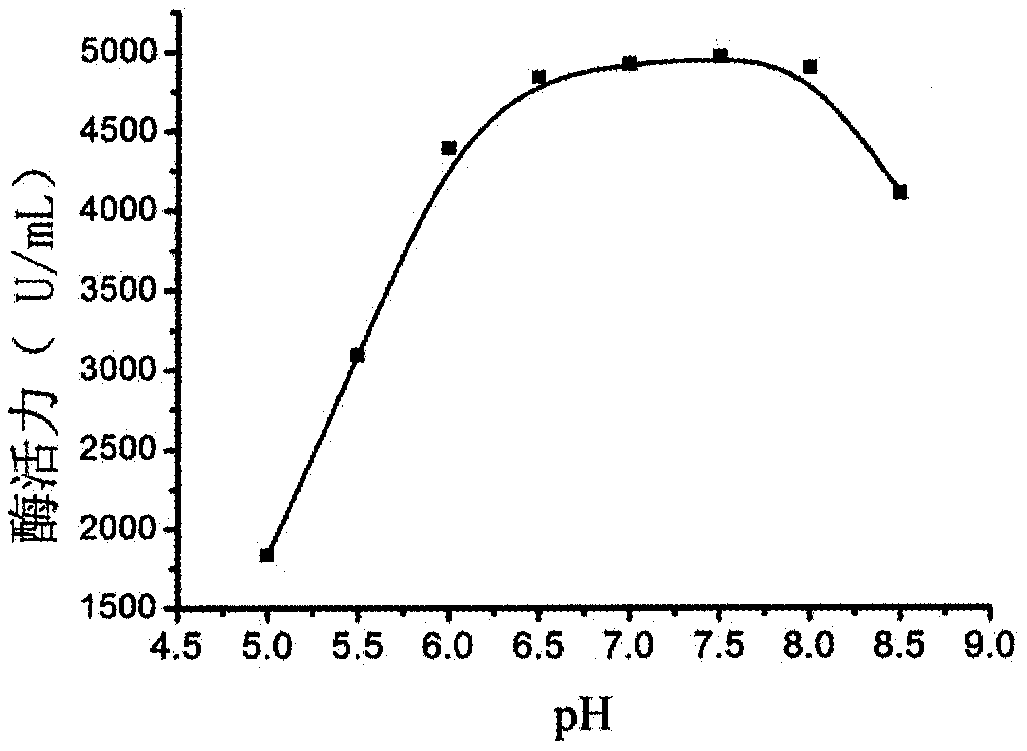
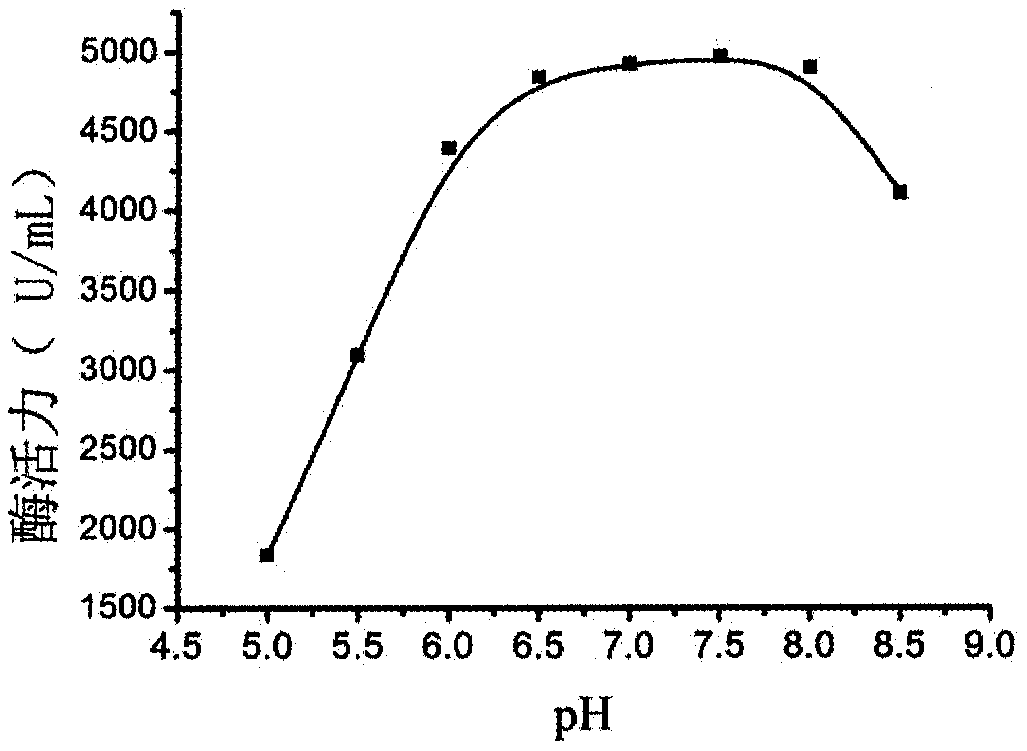
The invention discloses a mixed bacteria secondary fermentation technology and an application thereof in industrial production of L-alanine, and belongs to the field of microbial fermentation engineering. Escherichia coli and comamonas testosterone are used as starting strains, the composition of a mixed fermentation medium and a fermentation process are optimized, and then the mixed secondary fermentation method is established successfully. Under optimum fermentation conditions, enzyme activity of L-aspartase in a fermentation broth reaches 4900 U / mL, the pH tolerance and application range ofL-aspartase is 6.0-8.0, and activity of aspartase decarboxylase reaches 26000 U / mL. The fermentation broth is taken as an enzyme source to catalyze fumaric acid and ammonia water, double enzyme catalysis can be realized, and L-alanine can be obtained in one step, wherein the molar conversion rate reaches 98.6%, the catalytic time is 8 h, and catalytic efficiency is increased by 300%. The mixed bacteria secondary fermentation technology has an industrial application value.
Owner:BEIJING CITY UNIVERSITY +1
Method for preventing moss biological weathering on sandstone by using alcaligenes
ActiveCN114315415AAchieving preventive effectRestrict growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineAspartate decarboxylase
The invention belongs to the fields of cultural relic protection and environmental science and engineering application, and discloses a method for preventing moss biological weathering on sandstone by using alcaligenes, which comprises the following steps: screening autogenous alcaligenes of red sandstone stone cultural relics, extracting an extracellular enzyme preparation, uniformly spraying on the rock surface of the stone cultural relics without moss growth, and carrying out fermentation for 1-2 hours. The method is used for regulating and controlling acid-producing weathering bacteria growing in moss, and the effect of preventing moss biological weathering is achieved from the microenvironment. Wherein the alkali-producing strain achromobacter xylosoxidans contains various decarboxylase genes such as aspartic acid decarboxylase and arginine decarboxylase, biological enzymes can be synthesized, biogenic amines can be generated by utilizing amino acids, the biogenic amines and organic acids at the roots of moss can be subjected to dehydration condensation reaction to generate near-neutral amide and water, and then the moss can be subjected to hydrolysis reaction to generate the xylosoxidans. Further, the acidic weathering environment on the sandstone surface is neutralized. According to the method, a green biological method is adopted, the method is friendly to cultural relics and the environment, and moss biological weathering on the gravel cultural relics can be prevented.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli as well as preparation method and application thereof
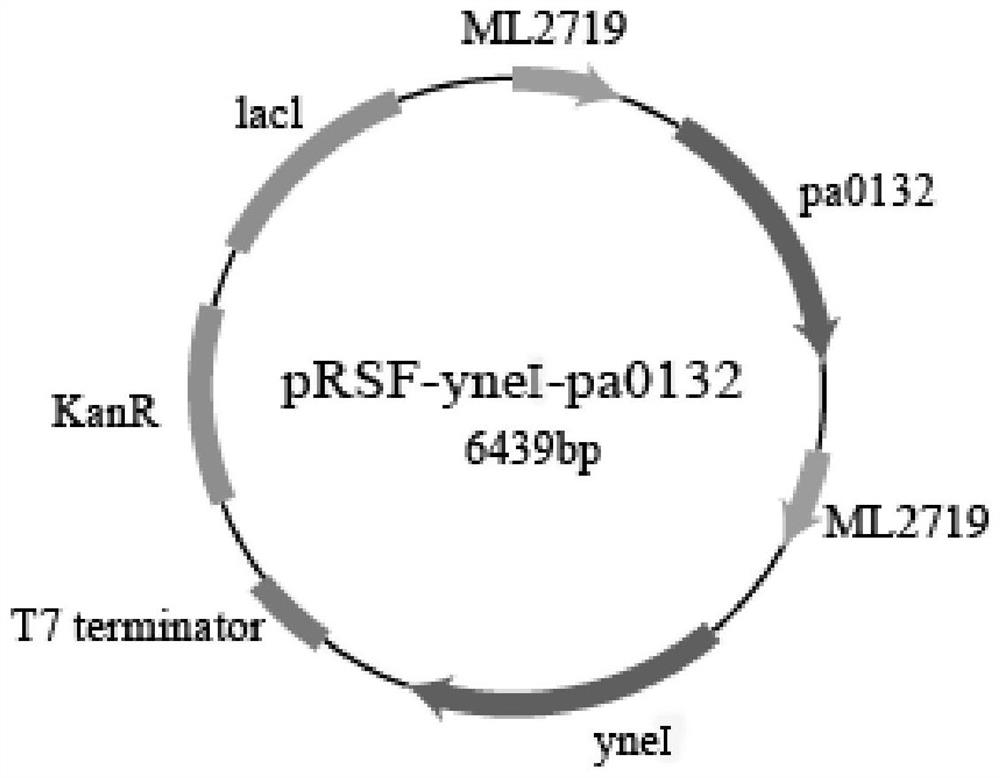
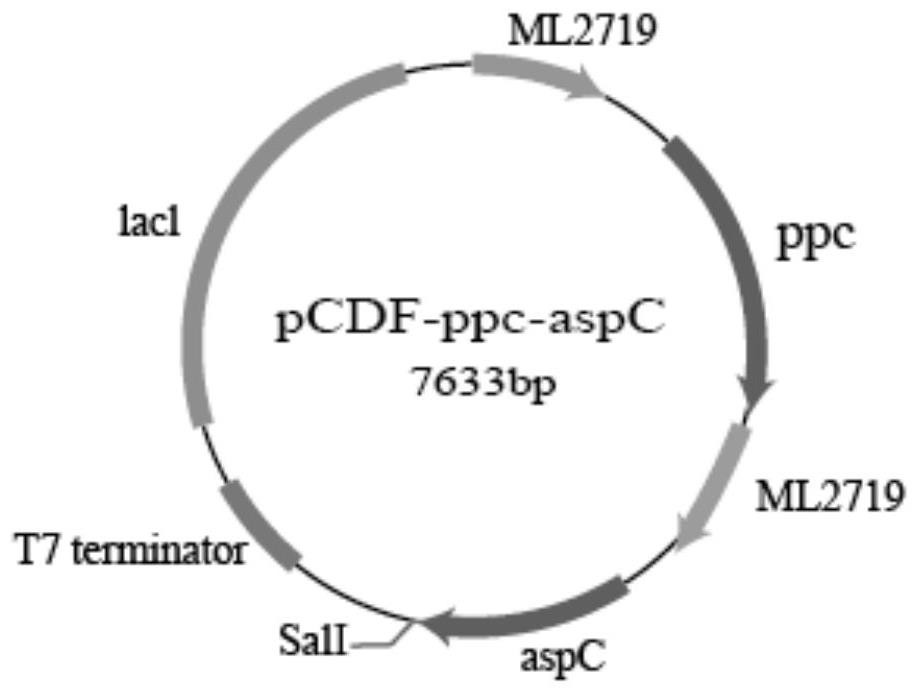
PendingCN114736841AReduce manufacturing costReduce lossesBacteriaTransferasesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
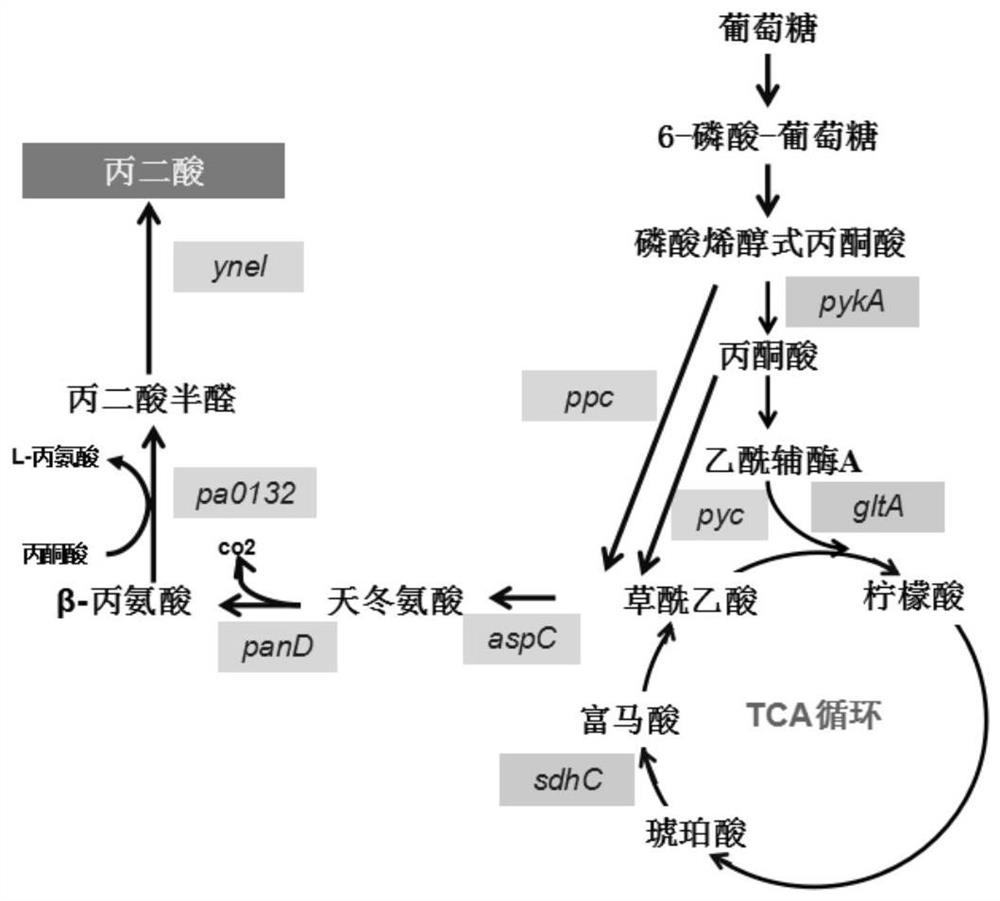
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant escherichia coli disclosed by the invention can be used for synthesizing malonic acid by taking glucose as a raw material through an oxaloacetic acid-aspartic acid way; according to the invention, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, aspartic acid transaminase and aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase which are derived from escherichia coli and beta-alanine pyruvate transaminase which is derived from pseudomonas aeruginosa are subjected to constitutive overexpression according to modules; the succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase is derived from escherichia coli; and the pyruvate carboxylase is derived from corynebacterium glutamicum. According to the method, the malonic acid can be synthesized by using the escherichia coli through a whole biological method, and the method is simple to operate, low in cost and capable of being used for industrial production.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com