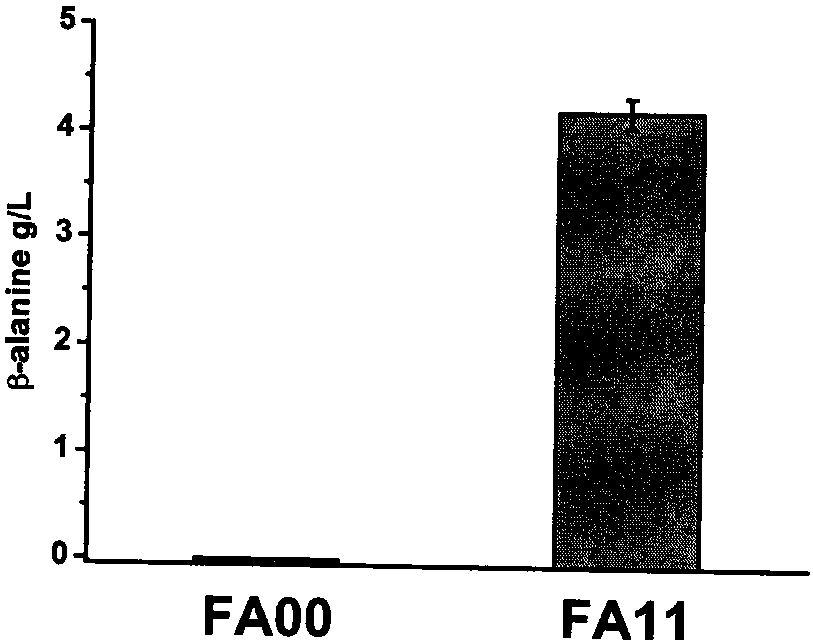
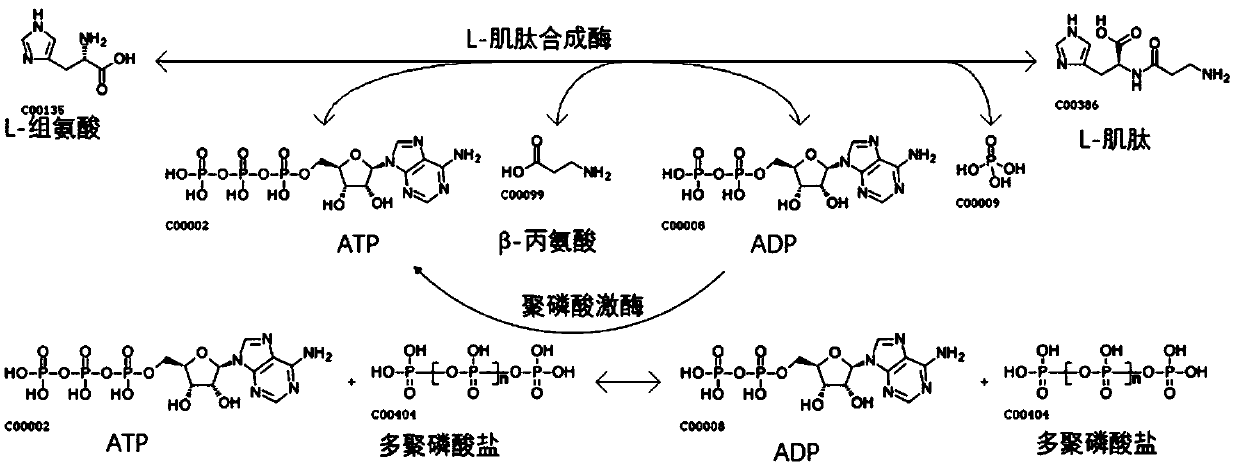
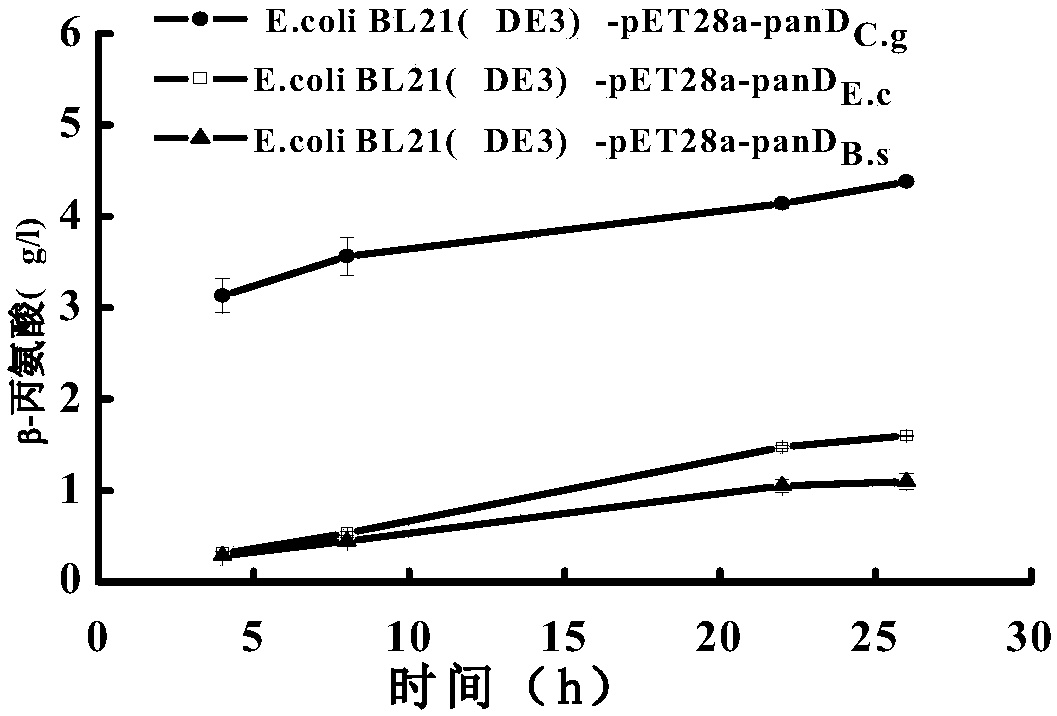
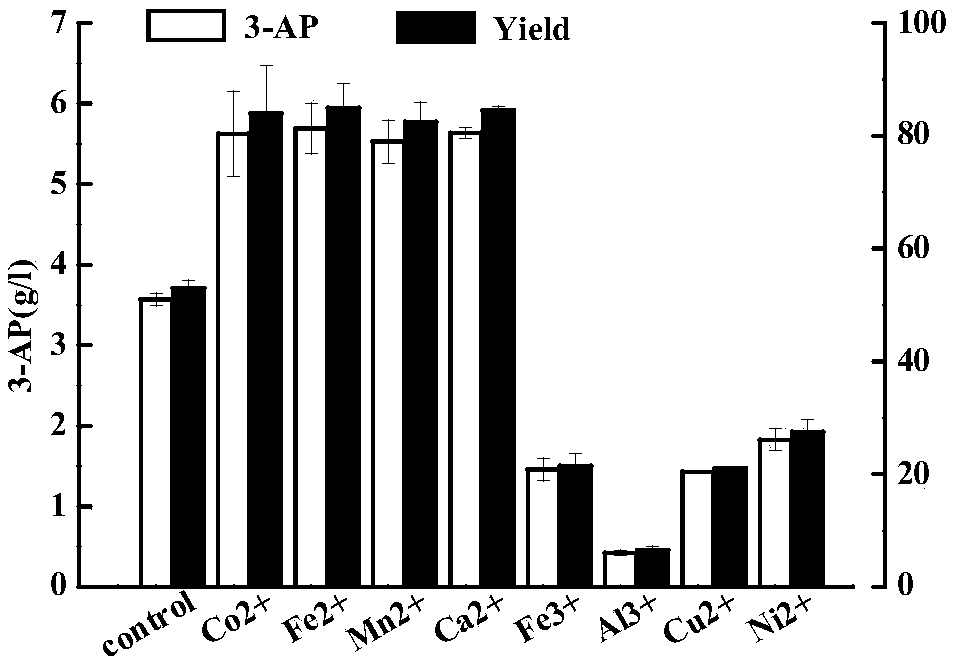
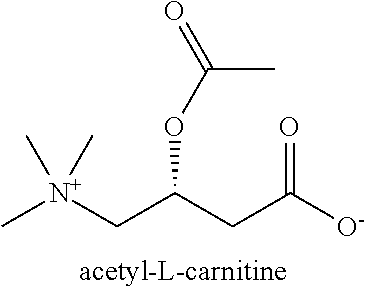Patents
Literature
156 results about "Beta-Alanine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
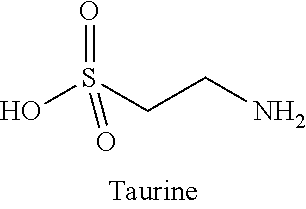
Β-Alanine (or beta-alanine) is a naturally occurring beta amino acid, which is an amino acid in which the amino group is at the β-position from the carboxylate group (i.e., two atoms away, see Figure 1). The IUPAC name for β-alanine is 3-aminopropanoic acid. Unlike its counterpart α-alanine, β-alanine has no stereocenter.
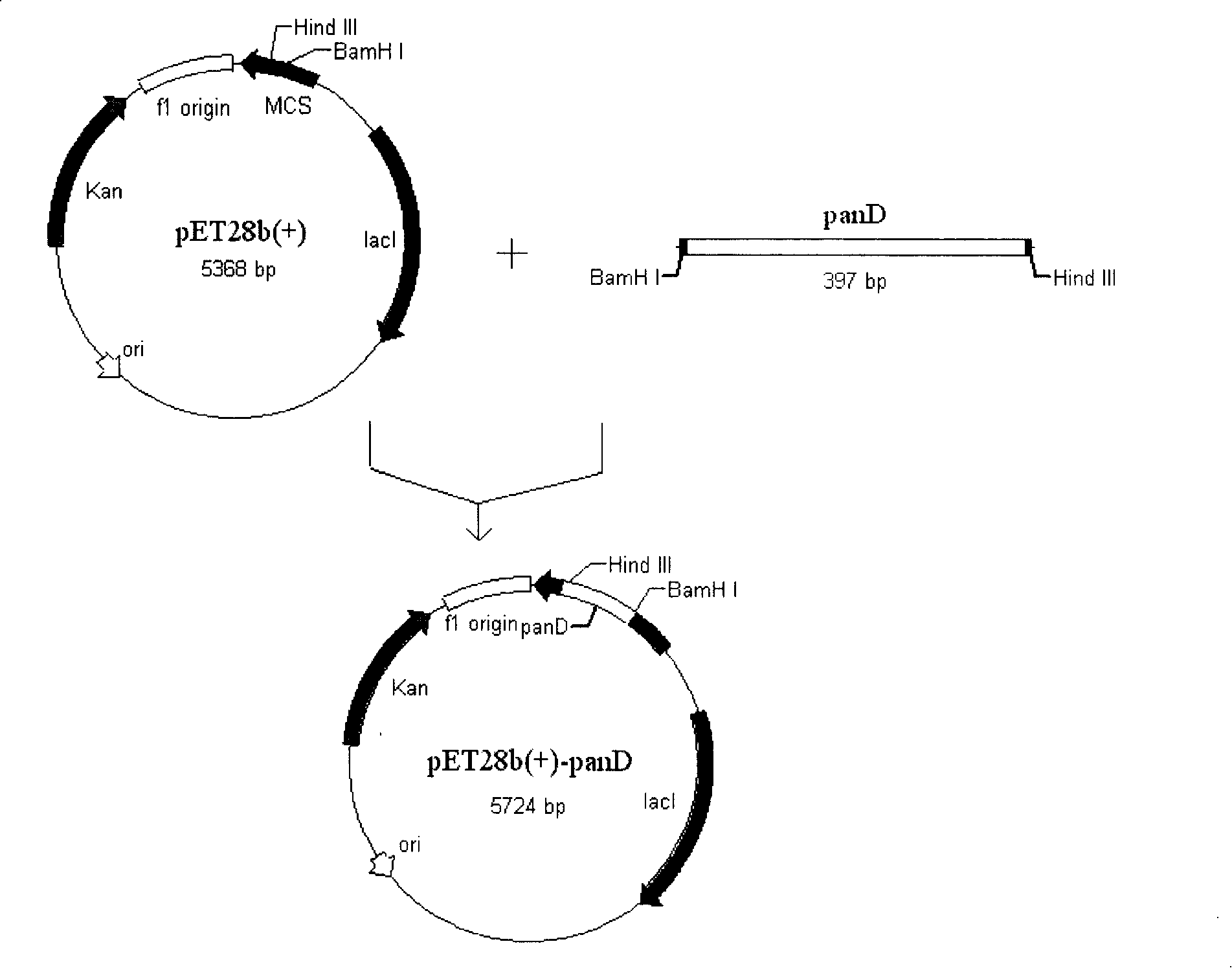
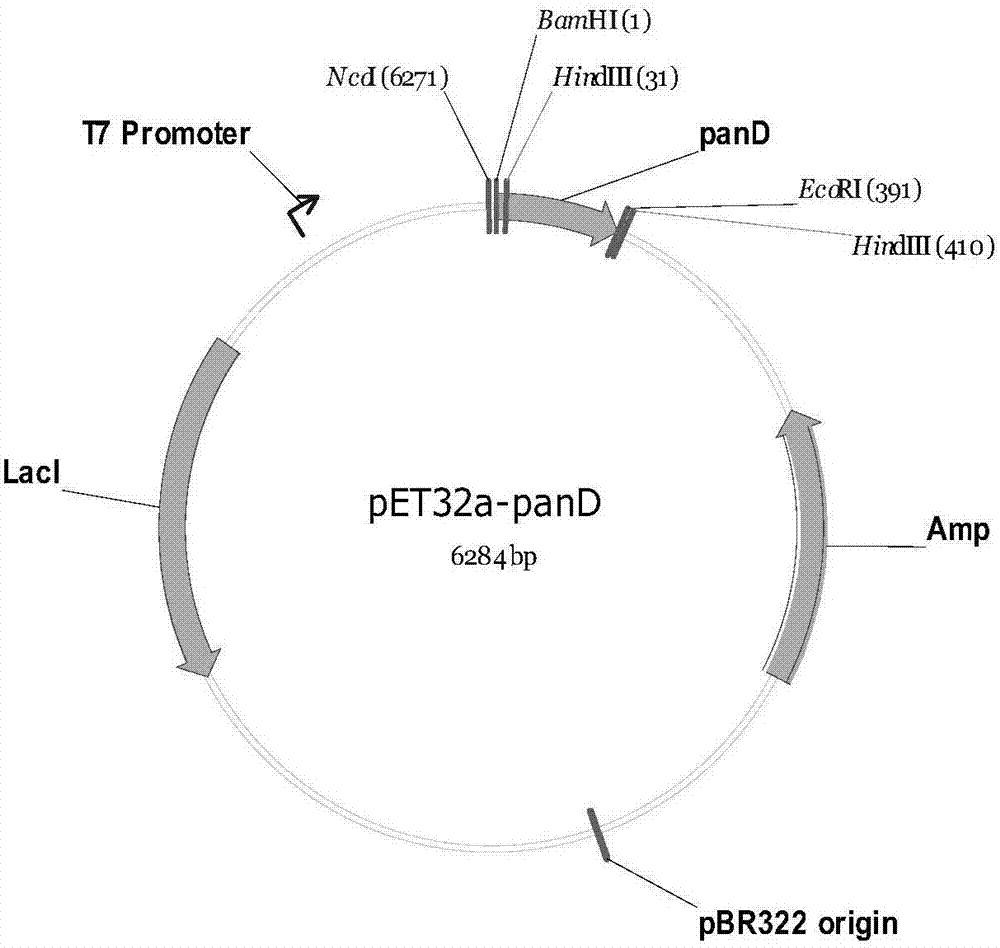
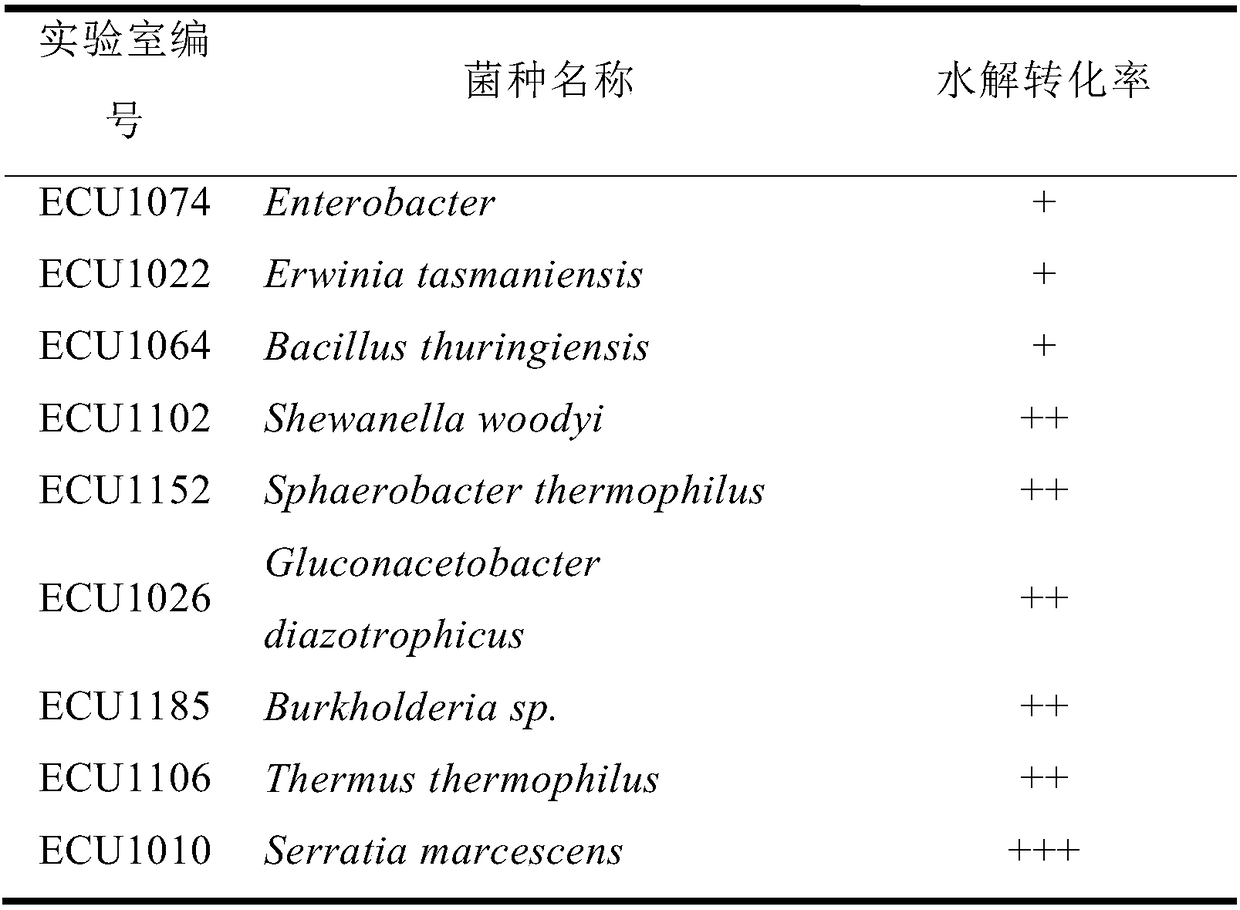
Gene engineering bacterium for producing beta-alanine and its preparation and application
InactiveCN101210230ABreeding goals are clearImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGene engineering
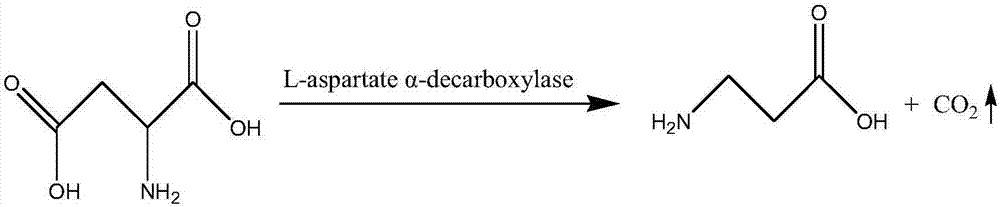
The invention provides genetic engineering bacteria for producing beta-alanine. The genetic engineering bacteria are obtained by the following method of amplifying L-aspartic acid alpha-decarboxylase gene panD of a donor containing panD gene by PCY, cloning the panD to a plasmid capable of expressing a foreign gene at high efficiency to obtain a vector for abundant expression of the panD gene, and transforming the vector into a receiver to obtain the genetic engineering bacteria for producing beta-alanine. The genetic engineering bacteria and preparation and application thereof have the main advantages that (1) the engineering bacteria of beta-alanine can be synthesized by the preparation of Escherichia coli; (2) the engineering bacteria has high ability in synthesizing beta-alanine, and the primary study determines that the synthesis ability is up to 2.94 g / l and that the beta-alanine is unlikely be determined by an identical method using a starting strain; and (3) the Escherichia coli is improved by using genetic engineering technology to achieve definite breeding target and high efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Synthetic method of L-carnosine
ActiveCN101284862AAvoid formingReduce consumptionPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionHydrazine compoundOrganic synthesis
A method for synthesizing L-carnosine belongs to the organic synthesis technical field. The method is as follows: beta-alanine is dissolved in non-polar solvent to be reacted with phthalic anhydride under the catalysis of organic amine, and then phthaloyl-beta-alanine is obtained through water recrystallization; the phthaloyl-beta-alanine is dissolved in solvent to synthesize phthaloyl-beta-alanyl chloride through the chlorinated reagent of acyl chloride phthaloyl-beta-alanine; L-histidine is reacted with hexamethyl disilazane or trimethylchlorosilane to obtain L-histidine trimethylsilane protector; the protector is reacted with the phthaloyl-beta-alanyl chloride to obtain hydrochloride product with the protecting group divested by water, and then neutralization product is obtained by the hydrochloride product obtained through the neutralization condensation reaction of alkaline reagent, thereby obtaining L-carnosine crude product through the hydrazinolysis of the neutralization product by hydrazine hydrate; and the crude product is purified to obtain L-carnosine finished product. The method has low raw material consumption, short reaction procedure and high yield; moreover, the quality of synthesized L-carnosine can meet the requirements of industrial production.
Owner:SUZHOU FUSHILAI PHARMA CO LTD
Genetically engineered bacterium with high pantothenic acid yield as well as construction method and application
ActiveCN109868254AReduce feedback inhibitionImprove utilizationBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliMicroorganism
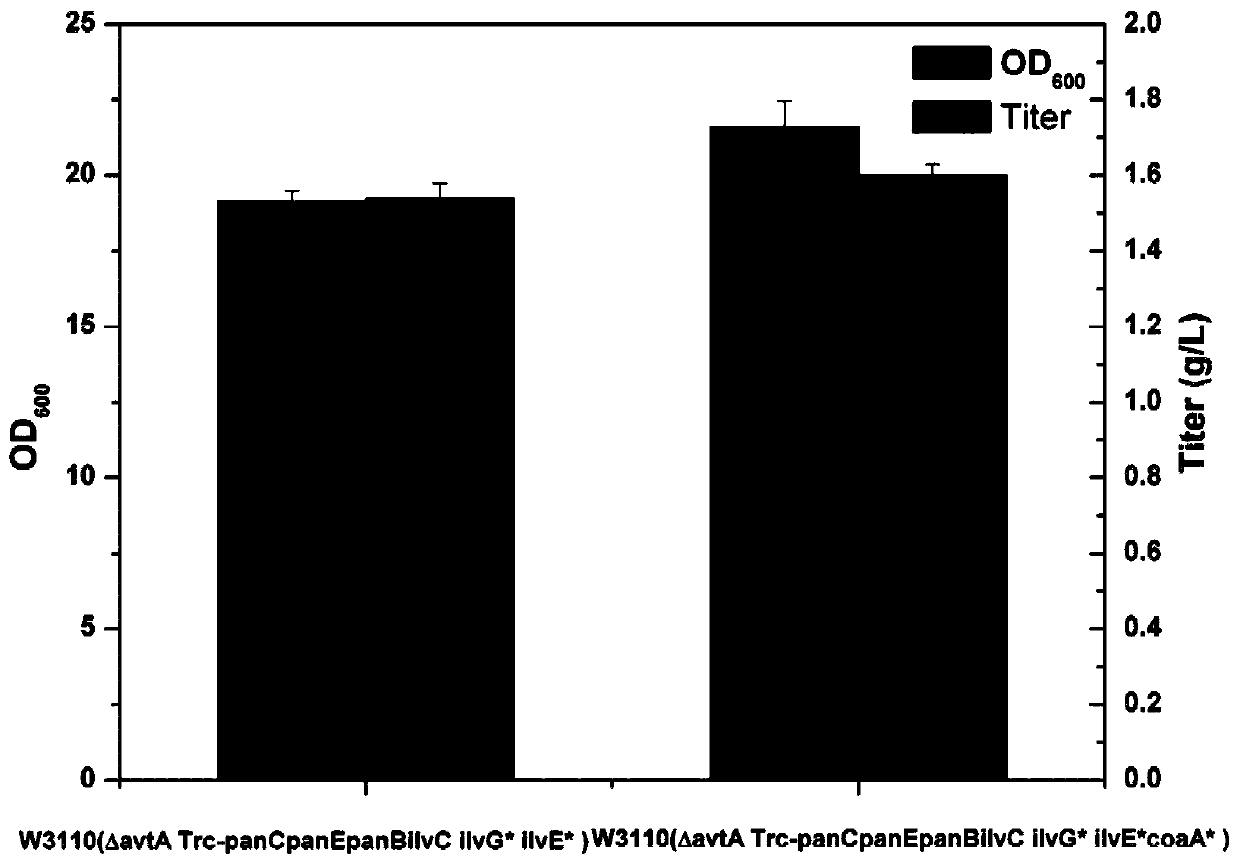
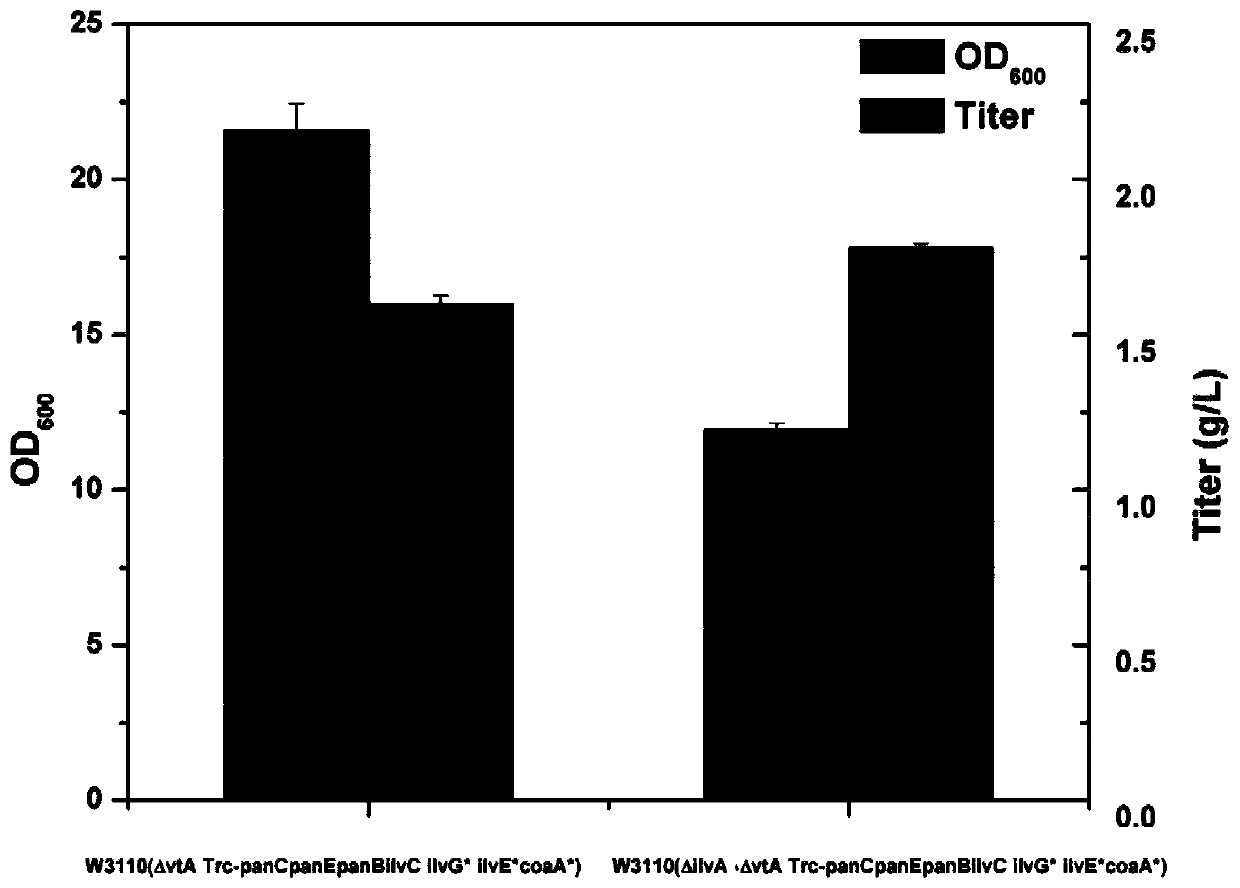
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium with a high pantothenic acid yield, a construction method of the bacterium, and application of the genetically engineered bacterium to preparation of D-pantothenic acid through microbial fermentation. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) reinforcing a last step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenic acid synthesis wayto reinforce the utilization capacity of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine; (2) reinforcing a pantoic acid synthetic way; (3) repairing an ilvG gene and weakening the feedback inhibitioneffect of byproducts on the pantoic acid synthetic way; and (4) weakening the flux of a valine synthetic way according to the phenotypic change of cells to obtain an escherichia coli genetically engineered strain with high yield of D-pantothenic acid. According to the invention, the expression of key enzymes PanB, PanC, PanE and IlvC in the D-pantothenic acid biogenic way is enhanced; the ilvG gene is repaired to weaken feedback regulation and control and reinforce the pantoic acid synthesis path, so that the extracellular accumulation of D-pantothenic acid and valine reaches 0.48 g / L and 0.51g / L respectively, a competitive branch is weakened by knocking out avtA and knocking down ilvE to obtain a plasmid-free high-yield bacterium, and the titer of D-pantothenic acid is increased from 0.48 g / L to 1.54 g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing beta-alanine by biological catalysis
InactiveCN102851333AImprove qualityLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-AspartateGenus Catellibacterium
The invention provides a method for synthesizing beta-alanine by biological catalysis, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The method comprises the following steps: culturing escherichia coli microbe to obtain aspartase and L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase, mixing the enzyme-containing escherichia coli cells with an ammonium fumarate aqueous solution, performing an enzyme reaction to generate beta-alanine. The method of the invention is cheap and easily available in raw materials, simple in production process, safe, environment-friendly, mild in reaction condition, high in efficiency, low in production cost, and high in product quality, and has significant economic benefits and environmental protection benefits when compared with traditional methods.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
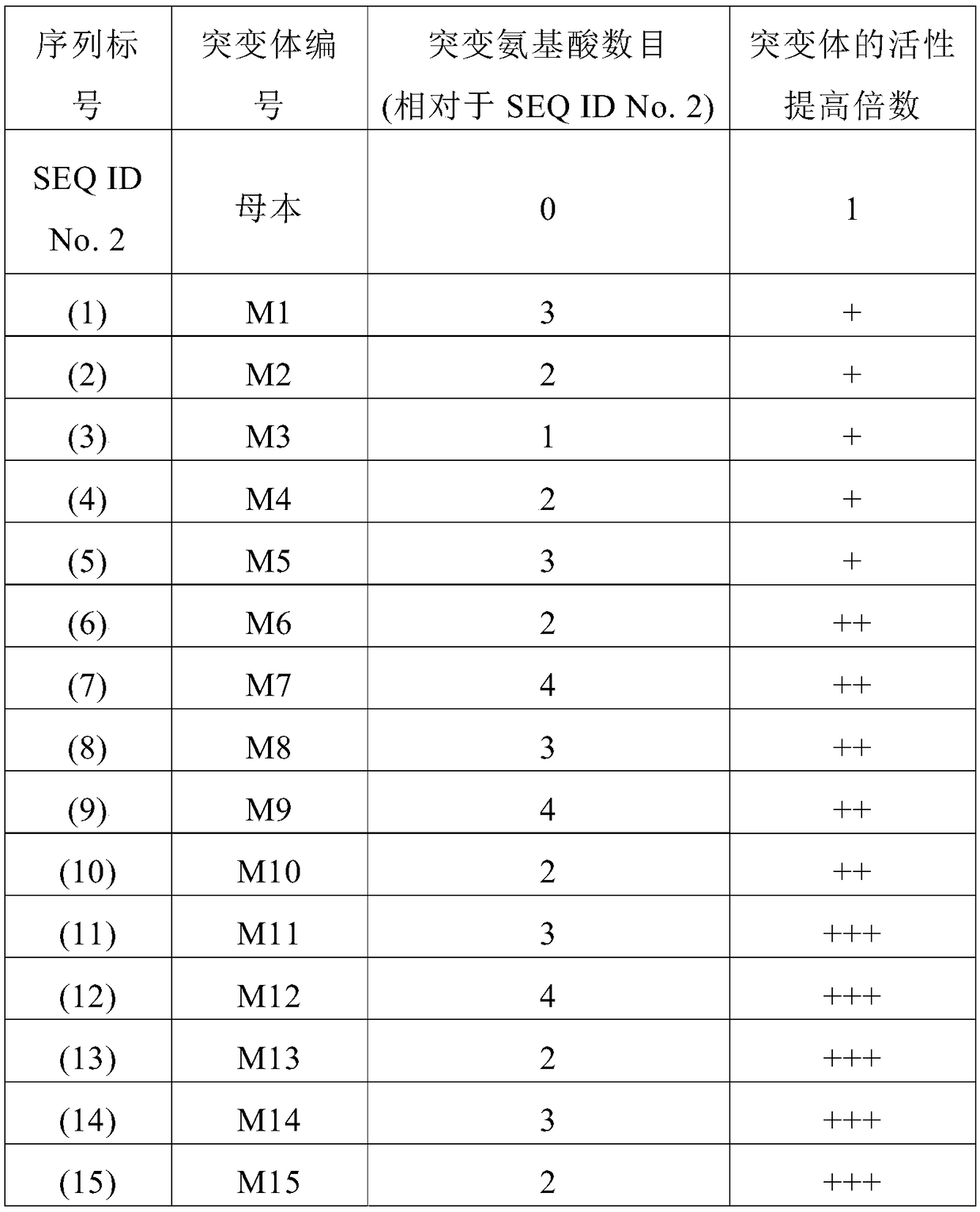
Aminopeptidase for catalytic synthesis of carnosine, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107217048ALow cost of industrializationHigh reaction rateHydrolasesGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneUltrafiltration
The invention provides aminopeptidase for catalytic synthesis of carnosine, and a preparation method and application thereof. The aminopeptidase has the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2. For the preparation of biological enzymes, firstly, a gene engineering strain of the biological enzymes is built; the biological enzyme gene fragment obtained through full gene synthesis is subjected to linearized plasmid recombination by using restriction enzymes SalI. The built gene-engineered strain is suitable for high-density culture; the exoenzyme is biologically synthesized; solid-liquid separation is performed; ultrafiltration concentration is performed to obtain enzyme liquid; histidine and beta-alanine can be catalyzed in normal-temperature and normal-pressure water solution to efficiently synthesize carnosine; the reaction environment is friendly; the production cost is low; the conversion time is short; the process operation is simple; the reaction system impurity content is low; the post treatment is easy; the wide prospects of large-scale industrial application are realized.
Owner:JIANGSU CHENGXIN PHARMA
D-calcium pantothenate synthesis method
InactiveCN1765877AReduce usageSolve environmental problemsCarboxylic acid amides optical isomer preparationSynthesis methodsDiethyl oxalate
The invention discloses a synthesis method for D-calcium pantothenate, which comprises: synthesizing keto lactone pantothenate with diethyl oxalate, isobutanal and formaldehyde, reducing said product, using carbamidine carbonate to resolution out D-pantothenic carbonate and L- pantothenic carbonate; preparing the product with D-pantoic lactone, beta-alanine both from D-pantothenic carbonate and calcium metal. This invention avoids the application of hypertoxic sodium cyanide, stabilizes product quality, and increases material utilization ratio.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Peptoid and preparation method as well as application thereof
ActiveCN106854233AImprove bindingRapid diagnosisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEthylenediamine1-Naphthylamine
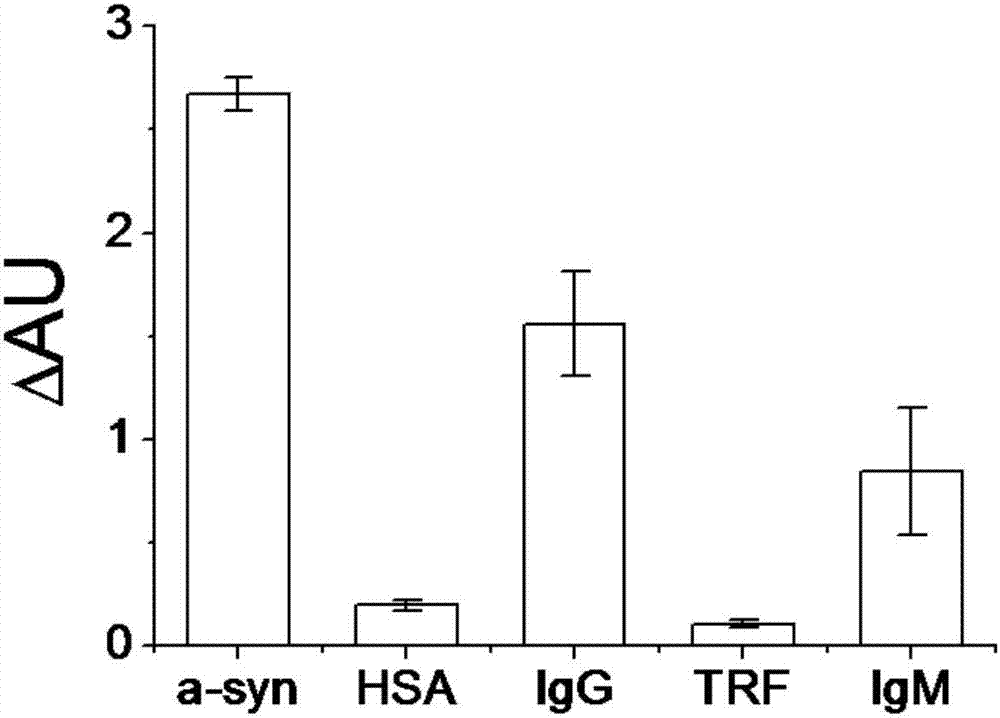
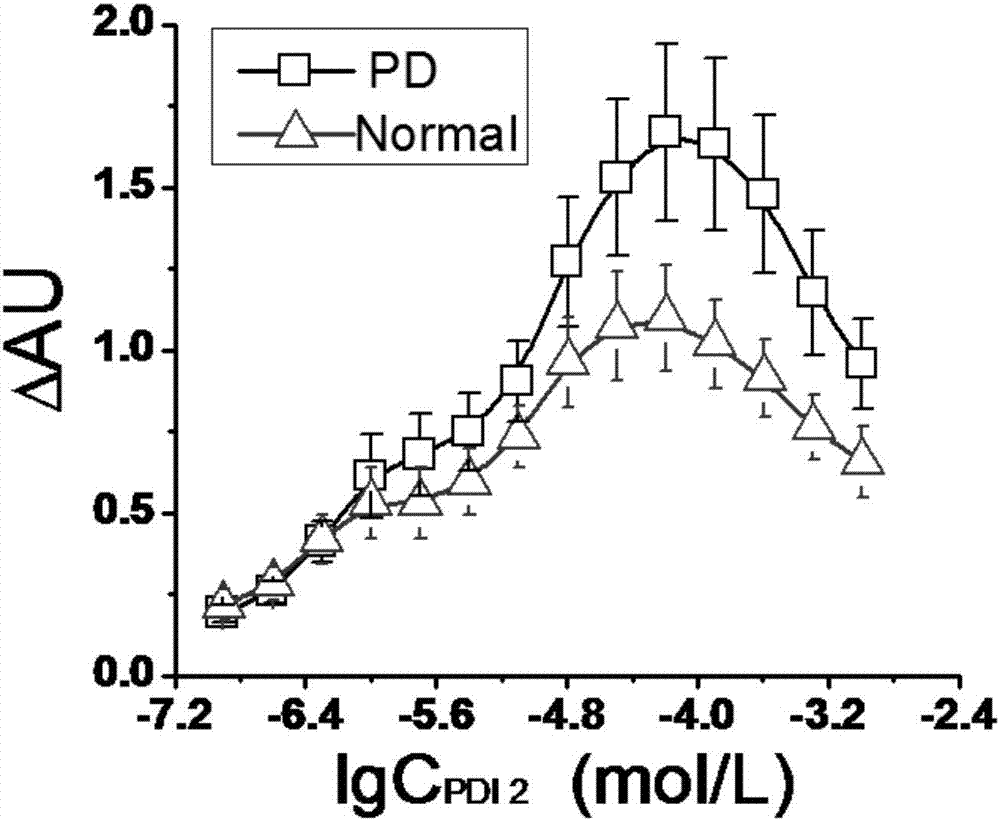
The invention provides a peptoid as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The peptoid comprises the following subunits: ethylenediamine (I), piperonylamine (II), beta-alanine (III), 1-naphthylamine (IV) and cysteine (V). The peptoid is simple in synthesis, has strong combining capacity with alpha-synuclein, can effectively screen the serum of PD patients and able-bodied persons through alpha-synuclein in the serum, and provides a novel liquid biopsy method and concept for diagnosis and monitoring of the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method for preparing beta-alanine by coupled enzymatic reaction
InactiveCN103320480ALow costReduce equipment investmentFermentationEnzyme catalysisIon-exchange resin
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, and in particular relates to a method for preparing beta-alanine by a coupled enzymatic reaction. The method comprises the following steps: by using ammonium fumarate as a raw material, mixing bacterial cells respectively comprising aspartase and aspartic acid-alpah-decarboxylase or a crude enzyme liquor of the two enzymes with an ammonium fumarate aqueous liquor, wherein pH of the ammonium fumarate aqueous liquor is 7.0-7.5; performing enzymatic reaction at 25-55 DEG C; obtaining high purity beta-alanine by separating converted products by isoelectric point crystallization or a method combining isoelectric point crystallization or ion exchange resin. The beta-alanine is prepared by coupled enzymatic reaction, and the method has the advantages of wide source of raw materials, low cost, simplicity and convenience in operation, short enzymatic conversion time, low production cost and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli strain for producing beta-alanine as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898035AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli strain (Escheerichiacoli) AHB-36 for producing beta-alanine, the preservation number is CCTCC M 2013629, the recombinant escherichia coli strain is a deficiency aspartic acid amino lyase gene and contains an aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase gene. The invention further aims at providing a construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain. The recombinant escherichia coli strain can be used for knocking off the aspartic acid amino lyase gene and preventing the escherichia coli from pyrolyzing the aspartic acid into fumaric acid, so that the aspartic acid is completely applied to production of beta-alanine, and meanwhile aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase is expressed in the recombinant escherichia coli strain, and thus the yield of beta-alanine is further increased.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Health base flavoring for hotpot
The invention relates to a hotpot base flavoring, in particular relates to a health base flavoring for hotpot, and belongs to the field of food processing. The health base flavoring contains balsam pear which contains balsam pear glycosides, amino acids (such as glutamic acid, alanine, beta-alanine, phenylalanine, proline, alpha-aminobutyric acid, citrulline, galacturonic acid) and pectin. Accordingly, the base flavoring is nutritious and beneficial to health.
Owner:DALIAN CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Construction, expression and application of genetic engineering bacteria for high-production of beta-alanine
InactiveCN103898033AImprove synthesis abilityIndustrial Application AdvantagesBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyL-Aspartate
The invention provides new genetic engineering bacteria used for producing beta-alanine, having strong synthetic ability and having higher enzyme activity, construction, expression and purification of the high-production engineering bacteria, and methods for synthesis of beta-alanine respectively through whole cell transformation and fermentation liquid direct transformation. A synthetic method comprises the steps: an L-aspartic-alpha-alanine decarboxylase (PanD) gene of lactobacillus plantarum is obtained by a gene engineering method and has the gene sequence number of NC-004567.2, the gene is constructed into a high-efficiency expression vector, then the high-efficiency expression vector is transformed into recipient bacteria, and thus the genetic engineering bacteria for producing beta-alanine are obtained. The genetic engineering bacteria are subjected to fermentation culture, 80 g / L of a substrate can be transformed by whole cells, and the beta-alanine content reaches 59.7 g / L; and the substrate is directly added into a fermentation liquid, the transformation concentration can reach 10 g / L, the beta-alanine content reaches 6.8 g / L, and the synthetic ability is higher than that of conventional reported genetic engineering bacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Synthetic method of beta-alanine
InactiveCN104531796AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease production capacityFermentationFiltrationL-Aspartate
The invention discloses a synthetic method of beta-alanine. The method comprises the steps: a) preparation of a substrate: filling 5g / L-80g / L L-aspartic acid substrate solutions into an enzyme reactor, and regulating pH into 5.0-8.5 by using alkalizers; b) enzymic catalytic reaction: adding enzyme-containing bacterium solutions into the substrate solutions for performing catalytic reaction, adding a proper amount of L-aspartic acid in batch during reaction to regulate pH of a reactant to 5.0-9.0, and performing fermentation culture, condensation and pulverization on the enzyme-containing bacterium solutions by utilizing engineering bacteria of high-yield L-aspartic acid alpha-decarboxylase; and c) filtration, decoloring and crystallizing treatment of the reactant in the enzyme reactor to obtain beta-alanine. L-aspartic acid is further catalyzed by using the enzyme-containing bacterium solutions and converted into beta-alanine, and the beta-alanine is mild in production condition, simple in process, low in environment pollution, high in quality of products and convenient to extract at the downstream; the purity reaches 99.0 percent, and the conversion rate of beta-alanine reaches 99.5 percent.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, construction and application of genetic engineering bacteria
ActiveCN109913398AImprove utilizationReduce feedback inhibitionBacteriaStable introduction of DNACell phenotypeEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria capable of producing pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of beta-alanine, a construction method of the genetic engineering bacteria, and application of the genetic engineering bacteria in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. According to the invention, (1), the final step of an escherichia coli D-pantothenicacid synthesis pathway is enhanced, and the utilizing ability of escherichia coli to extracellular beta-alanine, (2), a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is enhanced, (3), ilvG gene is repaired, and thefeedback inhibition effect of by-products on a pantoic acid synthesis pathway is weakened, (4), according to the change in cell phenotype, flux of a valine synthesis pathway is weakened, (5), a CRISPRi technique is used to screen metabolic modification sites of TCA cycle, a PPP pathway and a by-product metabolic pathway, according to the result, an isoleucine synthesis pathway is blocked, and thecompetition of 2-butanoic acid for reaction of acetolactate synthesized from pyruvic acid under catalysis of acetolactate synthase is relieved, and (6), aspartate decarboxylase from other strains is subjected to heterologous expression to obtain a genetical engineering strain capable of producing the pantothenic acid at high yield without addition of the beta-alanine. By combined expression of panB and panC which are derived from corynebacterium glutamicum and panD derived from bacillus subtilis together on pTrc99A plasmids, 1.2g / L of D- pantothenic acid is obtained without adding the beta-alanine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
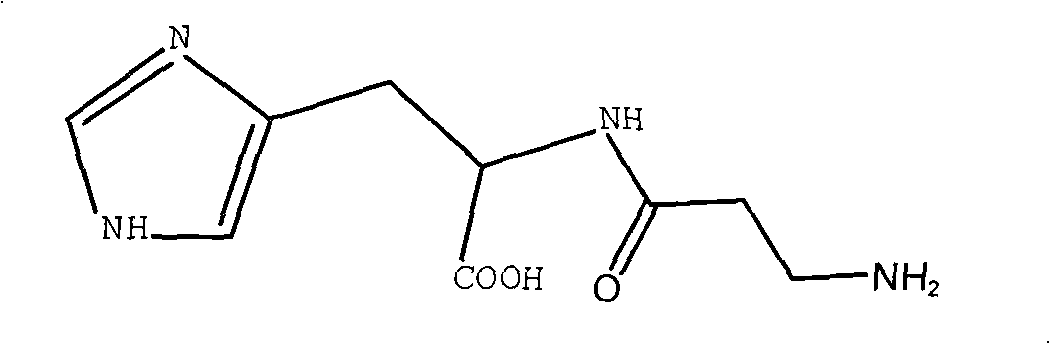
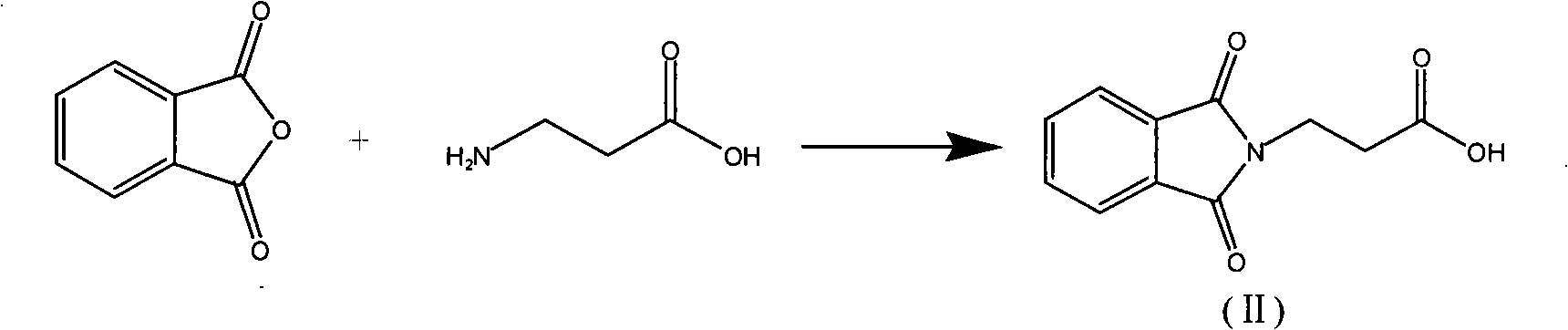
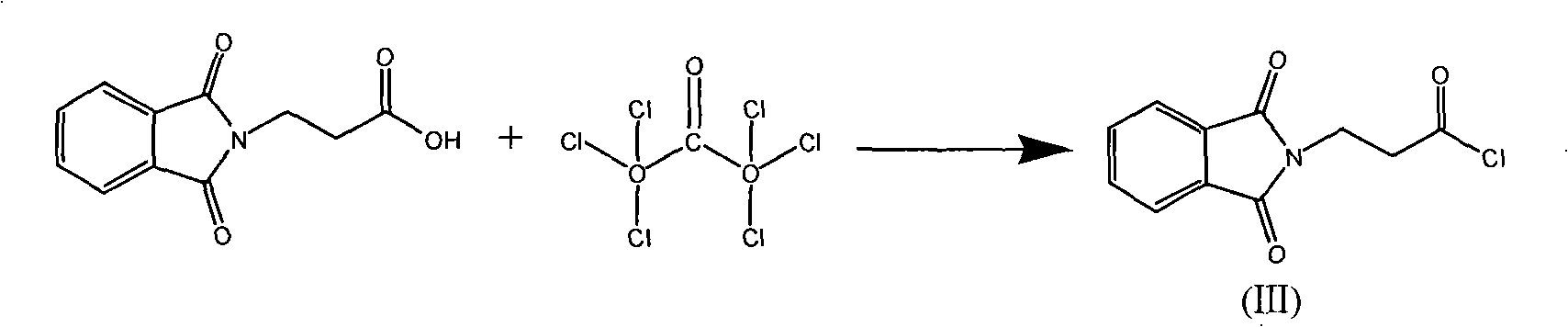
Novel method for synthesizing L-carnosine
InactiveCN101117334AInhibit side effectsHigh optical purityPeptides with abnormal peptide linkSilanesL-Carnosine
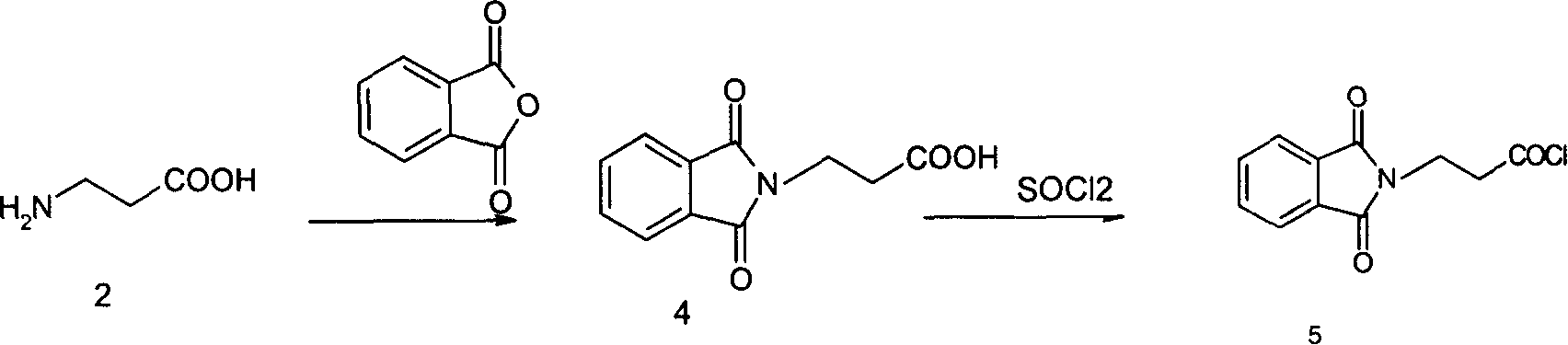
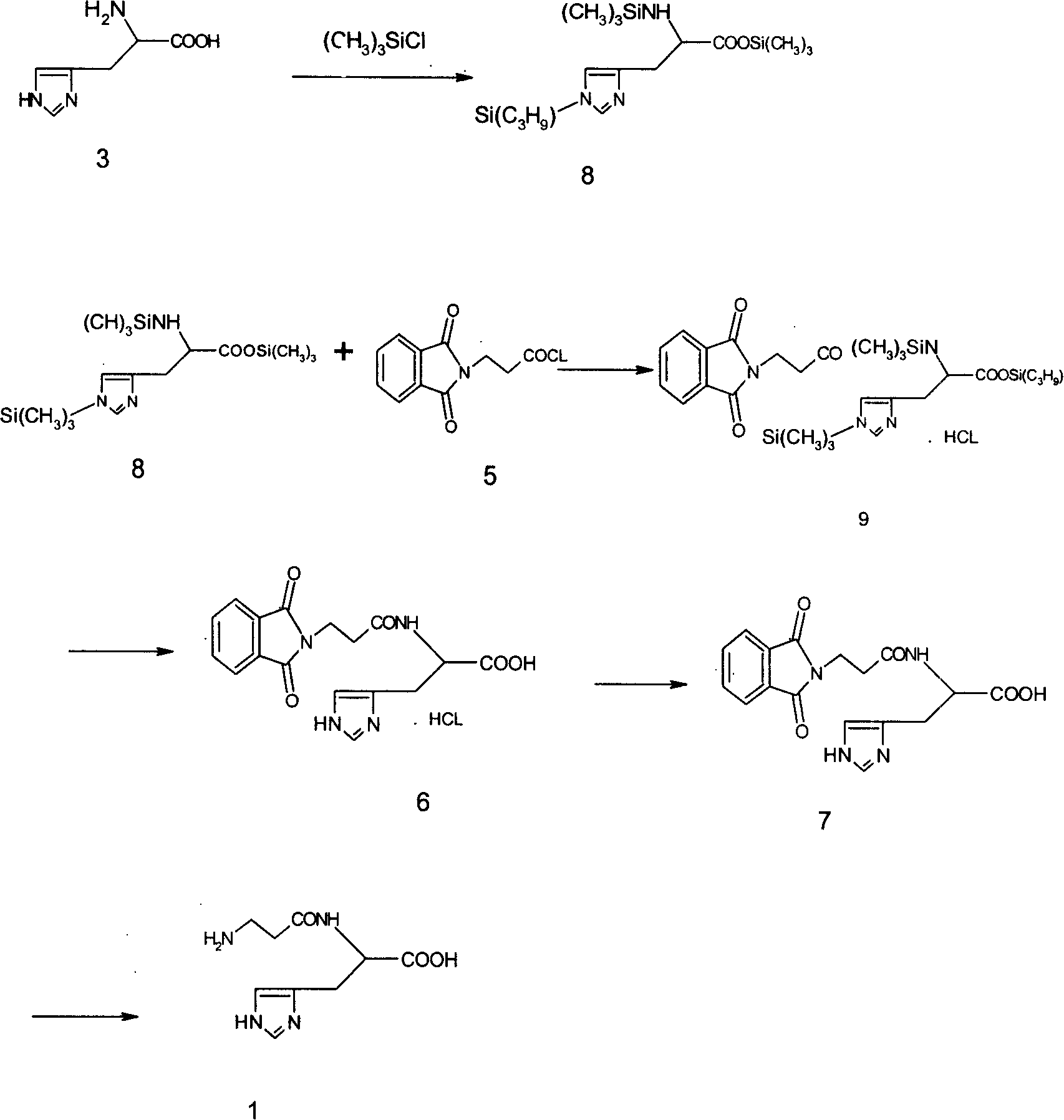
The invention discloses a synthesis method for L-Carnosine. In the prior art, the imidazole ring of the L-Histidine can take part in the reaction and has side-reactions, which decreases the yields of the products and makes the L-Carnosine assume the toxicity at the same time. In this invention, the o-phthalic anhydride is reacted with beta-alanine to produce the o-phthalic beta-alanine, the o-phthalic beta-alanine is made an acyl chlorination by the chloro-substitution reagent to synthesize into the o-phthalic beta-alanyl chloride; L-Carnosine is reacted with the edittrialkyl chlorosilane or hexamethyldisilazane to produce the trialky silane protection compound which is condensed with the o-phthalic beta-alanyl chloride to produce the hydrochloride; the hydrochloride is made a de-protection by the absolute alcohol, and then is neutralized by the basic solution to produce a product of neutralization; the hydrazine hydrate is used for a hydrazinolysis to the product of neutralization, then the L-Carnosine is precipitated from the absolute alcohol. The invention protects the imidazole ring on the L-Carnosine, avoids that the imidazole ring on the L-Carnosine makes side-reactions with other substances so as to obtain the pure L-Histidine, has low side-effects and high total yields as well as contents.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast medium based on metal fullerene and its prepn process
InactiveCN1810293AEasy to operateEasy to achieve large-scale productionNanosensorsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsCarboxyl radicalChelation
The magnetic resonance imaging contrast medium based on metal fullerene has the molecular expression of Gd@C82OHx(NH2CH2CH2COOH)y.Gd@C82OHx(HNCH2CH2SO3H)y, where x=16-22 and yú¢6-8. The preparation process is the neucleophilic addition reaction between metal fullerene material Gd@C82 and the alkali solution of beta-alanine or amino ethyl sulfuric acid to form the water- soluble metal fullerene derivative with decorating carboxyl radical or sulfo radical. The preparation process is simple and mild, and may be used in industrial production. The water- soluble derivative of the present invention has magnetic resonance imaging efficiency obviously higher than available Gd-divinyl triamino penta acetic acid chelate.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for constructing engineering bacterium capable of producing beta-alanine and method for producing beta-alanine by adopting engineering bacterium
InactiveCN107338258AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliL-Aspartate
The invention discloses a method for constructing an engineering bacterium capable of producing beta-alanine and a method for producing beta-alanine by adopting the engineering bacterium, belonging to the field of biotechnologies. The invention provides L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase gene of a bacillus tequilensis strain, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the engineering bacterium comprising the PanD gene. The invention further provides a constructing method of the engineering bacterium capable of producing the L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase, L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase obtained through expression and secretion is adopted for transforming L-aspartic acid, and thus beta-alanine is produced. According to the invention, L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase derived from bacillus tequilensis is adopted for transforming L-aspartic acid for producing beta-alanine for the first time at home and abroad, after the enzyme is expressed in escherichia coli, the generated L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase has high enzyme activity, the thallus does not need to be crushed and can be directly used for carrying out transformation, L-aspartic acid of 180g / L can be transformed to the maximum, the yield of beta-alanine can achieve 119.8g / L, and the industrial application has the advantages.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Synthetic method of urethane artificial antigen
InactiveCN102718861AReduced shieldingAccurate dosageOvalbuminSerum albuminEthyl chloroformateChemical synthesis
The invention provides a synthetic method of urethane artificial antigen. The urethane artificial antigen is prepared by the following steps of: 1, preparation of beta-alanine and ethyl chloroformate; 2, synthesis of hapten; 3, purification of hapten; 4, preparation of 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide solution; 5, synthesis of artificial antigen; 6, dialysis and detection of artificial antigen; and 7, calculation of quantity of different used carrier proteins. According to the synthetic method, the shielding effect of the protein to the hapten obtained by chemical synthesis is low, therefore, high-titer polyclonal antibody can be generated in an immune animal, and the molecular weight can be detected during synthesizing the artificial antigen, and the coupling ratio can be calculated, and the quantity of used raw materials for synthesizing is precise.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase with improved thermal stability
ActiveCN109055346AImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Aspartate
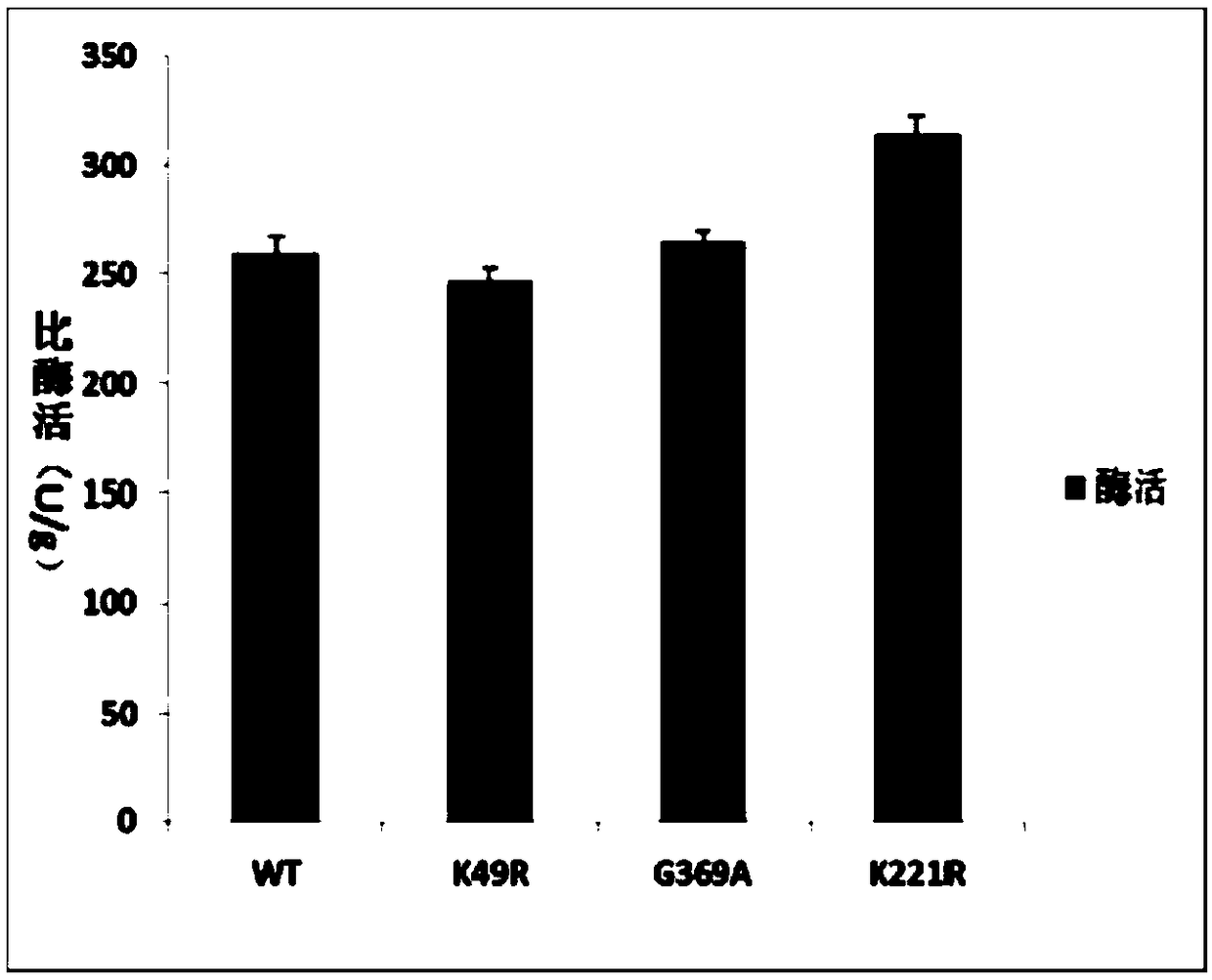
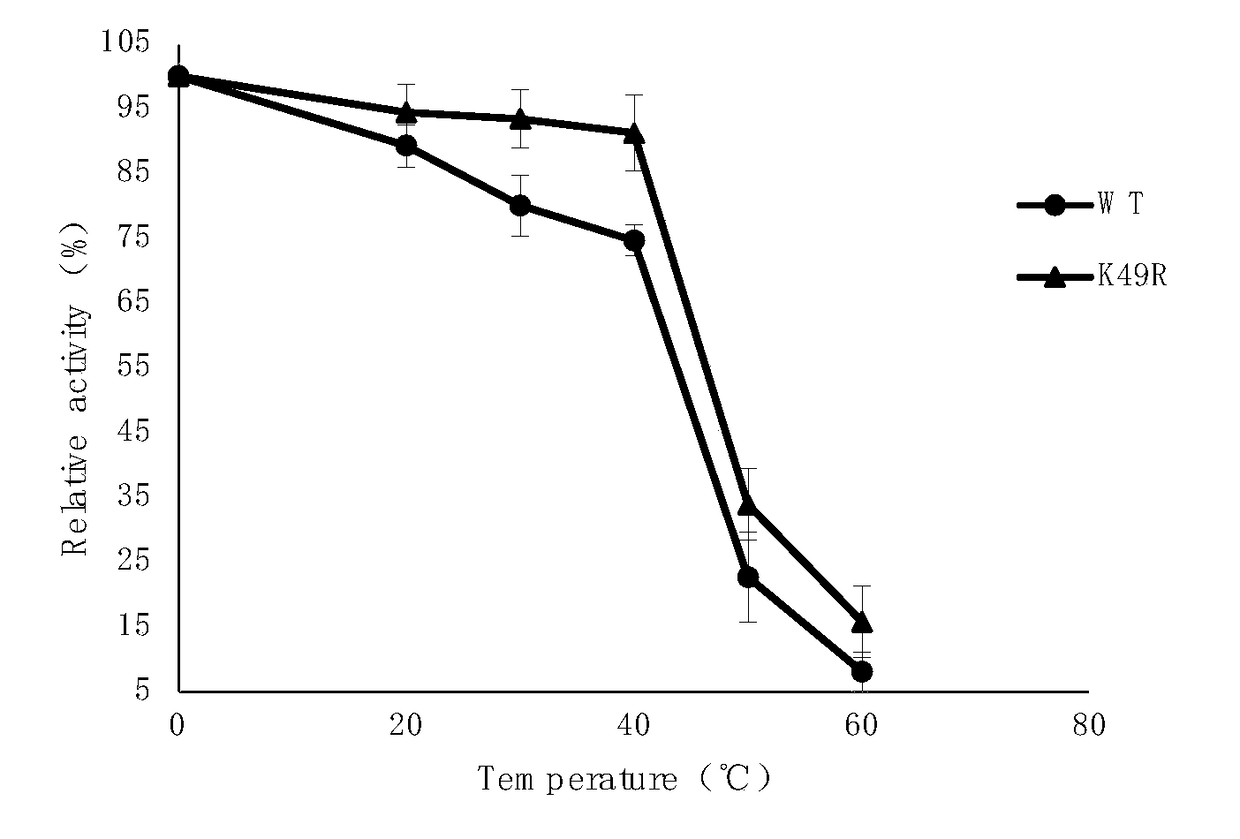
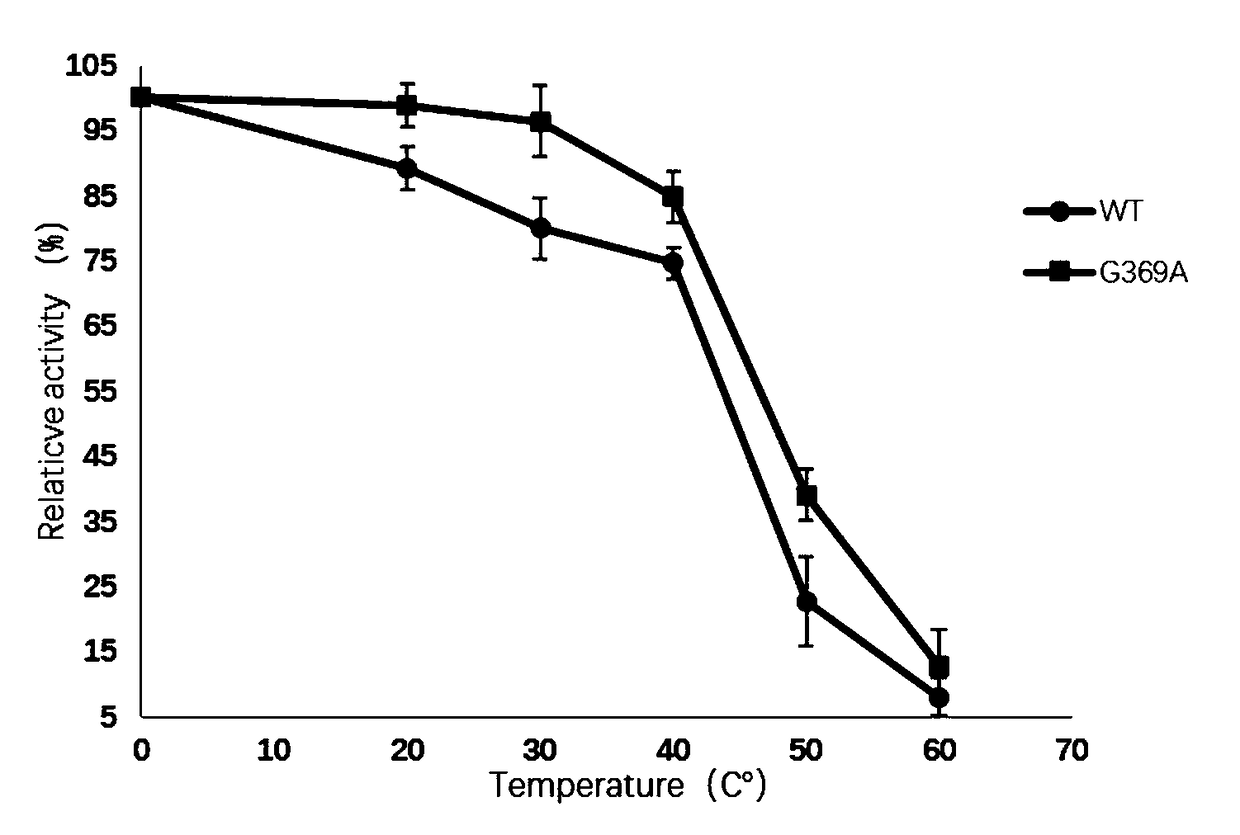
The invention discloses L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase with improved thermal stability and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. Three enzyme mutants including K49R, G369A and K221R areobtained through site-directed mutation of L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase from tribolium castaneum, recombinant plasmid of the mutants is transformed into escherichia coli BL21, and a substrate L-aspartic acid is catalyzed to produce beta-alanine after expression separation and purification. At the treatment temperature of 50 DEG C, K49R can improve the thermal stability by 14% as compared withwild enzyme, G369A can improve the thermal stability by 20% as compared with wild enzyme, and K221R can improve the thermal stability by 23% as compared with wild enzyme, wherein K221 can make the enzyme activity reach about 320 U / g and has the enzyme activity improved by 23% as compared with the wild enzyme, and the discovery has important study value for industrial preparation of beta-alanine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Caffeine-free dietary supplements for increasing energy and methods of administering the same
Disclosed herein are caffeine-free dietary supplements for increasing energy in a subject and methods of administering the same. The method comprises administering to a subject a caffeine-free dietary supplement comprising omega-3 fatty acids, resveratrol, beta-alanine, gamma aminobutyric acid, and valerian root extract product, in amounts such that the supplement is effective for increasing energy and mental focus and relieving stress in the subject.
Owner:RELIV INT
Carnosine hydrolase, gene, mutant and application thereof
PendingCN109468303AHigh activityImprove thermal stabilityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringL-CarnosineThermal stability
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to carnosine hydrolase and a mutant thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing the enzyme and a mutant gene, and arecombinant expression transformant, a preparation method of the recombinant enzyme, a method for immobilizing the recombinant enzyme, and a method for preparing levo form L-carnosine by using the recombinant enzyme through reverse hydrolysis reaction. Compared with the prior art, the carnosine hydrolase disclosed by the invention is high in activity and high in thermal stability, and the enzyme is used for catalyzing beta-alanine and L-histidine to prepare L-carnosine through direct condensation, so that the steps of protection and deprotection in a conventional chemical method of synthesizing peptides are avoided; the process is simple, and the conditions are mild and environmentally friendly. Therefore, the carnosine hydrolase has an extremely good application prospect in industrial production of the L-carnosine.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
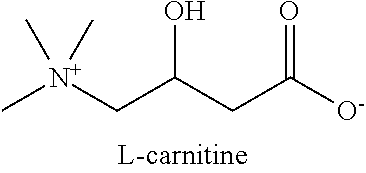
Compositions and Methods for Pain Relief
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions having improved effects and synergistic efficacy against pain, and provides methods for their use to treat pain, wherein the composition comprises: a sulfur-containing amino acid; a carnitine compound; and at least one compound that is a L-citrulline compound or a beta-alanine compound.
Owner:CROSS III WILLIAM H
Preparation method of indium tin oxide composite powder
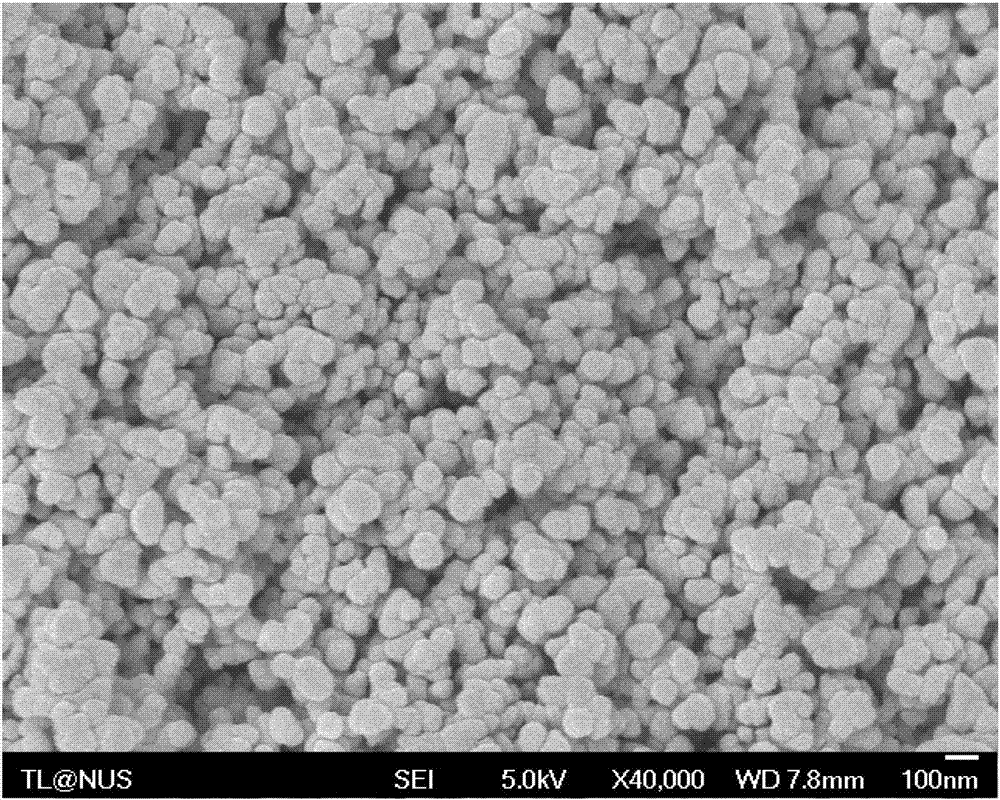
ActiveCN106882835AReduce agglomerationReduce hard agglomeratesMaterial nanotechnologyGallium/indium/thallium compoundsIndiumIndium tin oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of indium tin oxide composite powder, belonging to the technical field of preparation of indium tin oxide composite powder. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of mixed salt liquid: putting an InCl3 liquid and an SnCl4 liquid into a reaction kettle according to the In2O3:SnO2 weight ratio of 9:1, and uniformly mixing; addition of dispersing agents: adding polyvinylpyrrolidone, beta-alanine and ethanediol according to the weight ratio of 2:1:3, and adding more than 20% excessive of urea; coprecipitation reaction: gradually heating to 60-90 DEG C, keeping the temperature while continuously stirring until the In<3+> in the reaction solution is completely precipitated, carrying out ultrasonic treatment for 1 hour, continuing stirring, and aging to obtain an indium tin precipitate; and washing, drying, grinding, screening and carrying out high-temperature calcination to obtain the high-sintering-activity nano indium tin oxide composite powder. The indium tin oxide composite powder prepared by the method has the advantages of less hard aggregation and favorable flowability, and is easy for pressure molding.
Owner:ANHUI TUOJITAI NOVEL CERAMIC TECH
Beta-alanine producing strain and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110272857AEfficient productionReduce manufacturing costCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliAspartic acid
The invention discloses a beta-alanine producing strain and a preparation method and application thereof. The beta-alanine producing strain (Escherichia coli) has a preservation number of CGMCC NO: 17830. The beta-alanine producing strain constructed by the invention can realize the effective accumulation of the beta-alanine in the fermentation liquor in the fermentation process without adding aspartic acid in the fermentation process, and improves the yield of the beta-alanine and the sugar conversion rate. The yield of the beta-alanine is up to 50g / L, the sugar-acid conversion rate is up to 40%, and the producing strain has the application potential of large-scale production.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Biology method for synthesizing beta alanine
A biologic synthesis method for beta-alanine includes providing the microbes able to generate aminating enzyme, adding them to the seed culture medium containing acrylic acid and the fermenting culture medium containing acrylic acid to culture relative aminating enzyme, adding them to the aqueous solution of ammonia containing acrylic acid, synthesizing beta-alanine under the action of enzyme, removing ammonia, and purifying. Its advantages are high efficiency, no pollution and high purity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
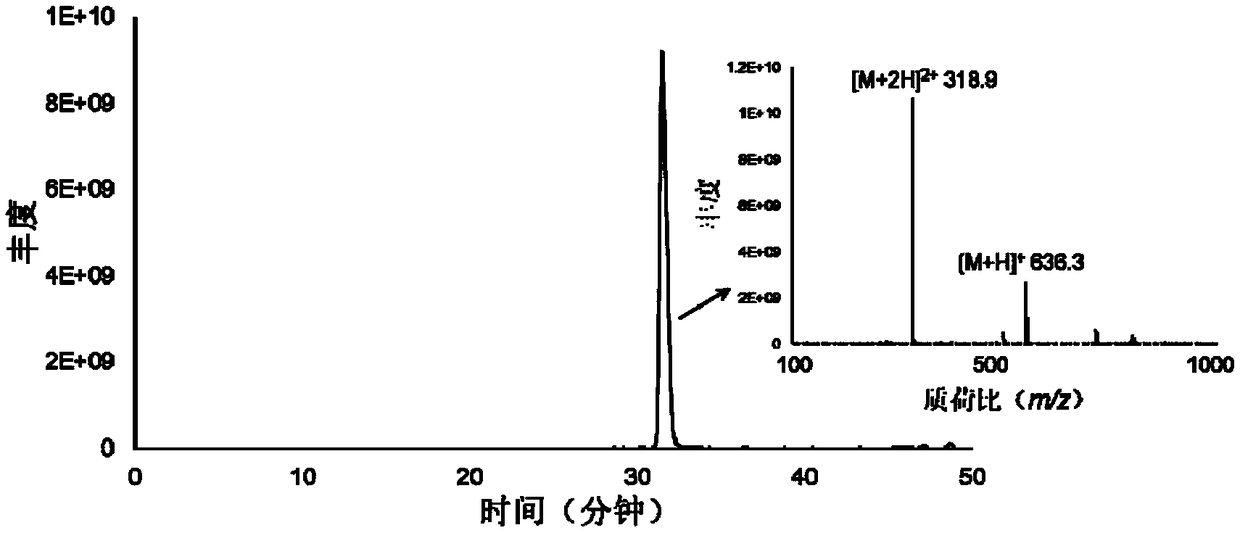
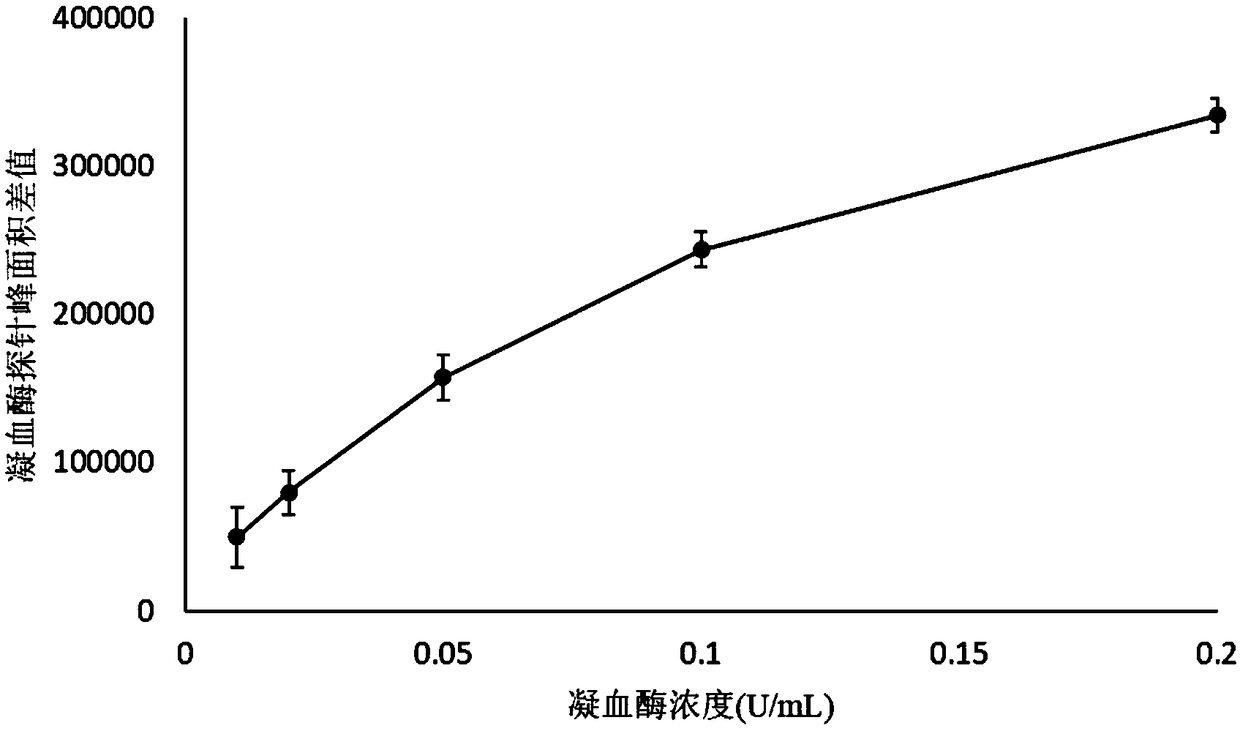
Mass spectrometry probe for thrombin activity detection, method for preparing mass spectrometry probe and application thereof
ActiveCN108707184AHigh mass responseHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEnzyme digestionAmino acid
The invention discloses a mass spectrometry probe for thrombin activity detection, a method for preparing the mass spectrometry probe and application thereof, and belongs to the field of medicine screening and evaluation. The mass spectrometry probe comprises polypeptides and piperazines compounds. Amino acid sequences of the polypeptides are Phe-Pro-Arg-beta-Ala, and the piperazines compounds aremodified on beta-alanine of the polypeptides. The mass spectrometry probe, the method and the application have the advantages that the polypeptides Phe-Pro-Arg-beta-Ala capable of being specificallyrecognized by thrombin are linked with the small-molecular piperazines compounds with high mass spectrometry response to obtain the mass spectrometry probe, accordingly, the mass spectrometry probe can be specifically recognized by the thrombin, enzyme digestion can be carried out on the mass spectrometry probe by the thrombin, the mass spectrometry probe is extremely high in mass spectrometry response and mass spectrometry detection accuracy, the activity of the thrombin or the inhibitory activity of thrombin inhibitors can be accurately reflected by the mass spectrometry probe, and the massspectrometry probe is quite applicable to screening compounds with thrombin inhibitory activity from complicated systems such as traditional Chinese medicines.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for producing beta-alanine as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for producing beta-alanine as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria. The construction method for the recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: knocking out fadR gene, fabF gene, fabH gene, iclR gene and sucA gene of recipient bacteria; introducing aspC gene or a gene cluster, panDgene, alkL gene and gdh gene into the recipient bacteria; enhancing expression of fadL gene, fadD gene, sthA gene, an atoSC gene cluster and an aceBA gene cluster in the recipient bacteria, wherein the recipient bacteria are bacteria or fungi containing the fadR gene, the fabF gene, the fabH gene, the iclR gene and the sucA gene. Experiments prove that the conversion rate of the beta-alanine produced by using the recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention with fatty acid as a raw material is 60.87 percent and shows that the recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the beta-alanine.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of preparing beta-alanine by means of microchannel reactor
ActiveCN108892621AShort reaction timeImprove reaction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSide reactionAmmonia
The invention discloses a method of preparing beta-alanine by means of a microchannel reactor. The method comprises the steps of (1) mixing well acrylic acid and ammonia water by a premixer of the microchannel reactor, allowing the mixture to enter a thermostatic reactor of the microchannel reactor and react to obtain discharge that includes beta-alanine; (2) decoloring the discharge of the step (1), filtering, concentrating, crystallizing, and drying to obtain refined beta-alanine. The microchannel reactor is used herein as a reaction device; adding additives to inhibit side reactions is notrequired; conversion rate of the acrylic acid is higher than 99%; product yield reaches 85% and above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +3
Method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by one-step method
ActiveCN109593805AAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesTransferasesNucleic acid vectorPhosphorylationL-Carnosine
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by a one-step method. The method comprises the steps of taking beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and polyphosphate as raw materials, and MgCl2 as an activator, adding L-amino acid ligase and polyphosphate kinase, and synthesizing L-carnosine through an enzymatic reaction and coupled coupleunder conditions of a pH of 6.5-8.5 and a temperature of 30-45 DEG C. According to the method, a sequence optimized L-amino acid ligase gene is successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and beta alanine and L-histidine can be catalyzed to synthesize L-carnosine at one step. A substrate is not required to be methylated or subjected to group protection; ATP required by a catalytic reaction is continuously regenerated by allowing polyphosphate kinase to catalyze phosphorylation of ADP (adenosine diphosphate); cyclic regeneration of ATP can be achieved only by consuming a small amount of ADP; and a renewable raw material, sodium hexametaphosphate, is wide in source, low in cost, simple to operate and easy in large-scale production.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
panD mutant gene, genetically engineered bacterium and application of genetically engineered bacterium in catalytic production of beta-alanine
ActiveCN107937422AIncrease productionImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a panD mutant gene with a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 or SEQ ID No.3. According to SEQ ID No.1 of the panD mutant gene, the 34th base of the panD gene is transformed from A into G; according to SEQ ID No.3 of the panD mutant gene, the 50th base of the panD gene is transformed from T into C. The invention also discloses a genetically engineered bacterium comprising the mutant gene and application of the genetically engineered bacterium in catalytic production of beta-alanine. The genetically engineered bacterium comprising the panD mutant gene can efficiently transform L-aspartic acid to prepare the beta-alanine through a biological method; the yields of the beta-alanine reach about 42.81 g / L and 19.46 g / L respectively, which are increased by almost 4.8times and 2.2 times when being compared with the yield of the beta-alanine of a parent strain.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Kit and method for determination of glycosylated hemoglobin in whole blood
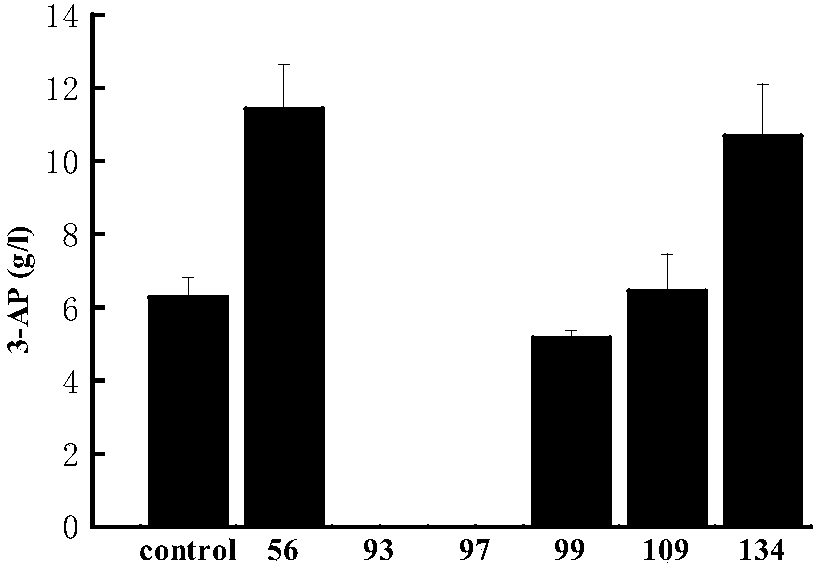
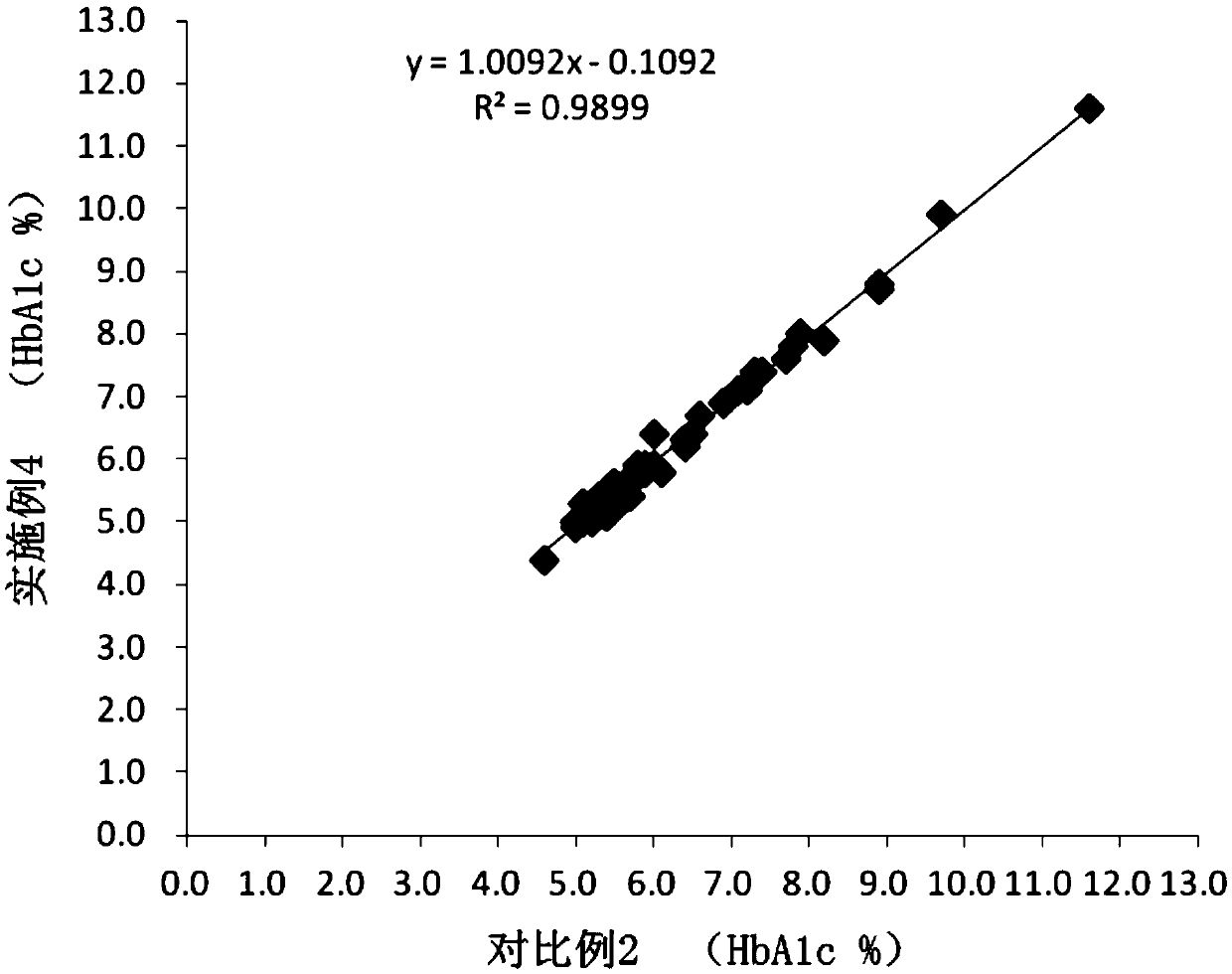
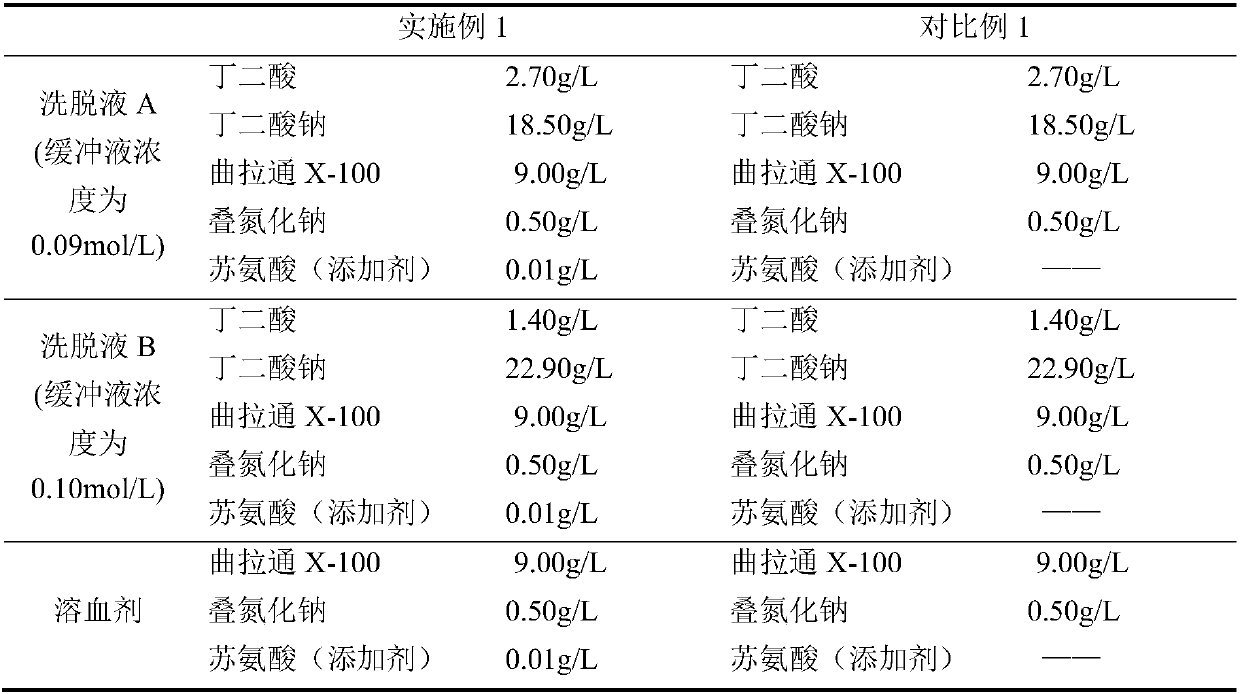
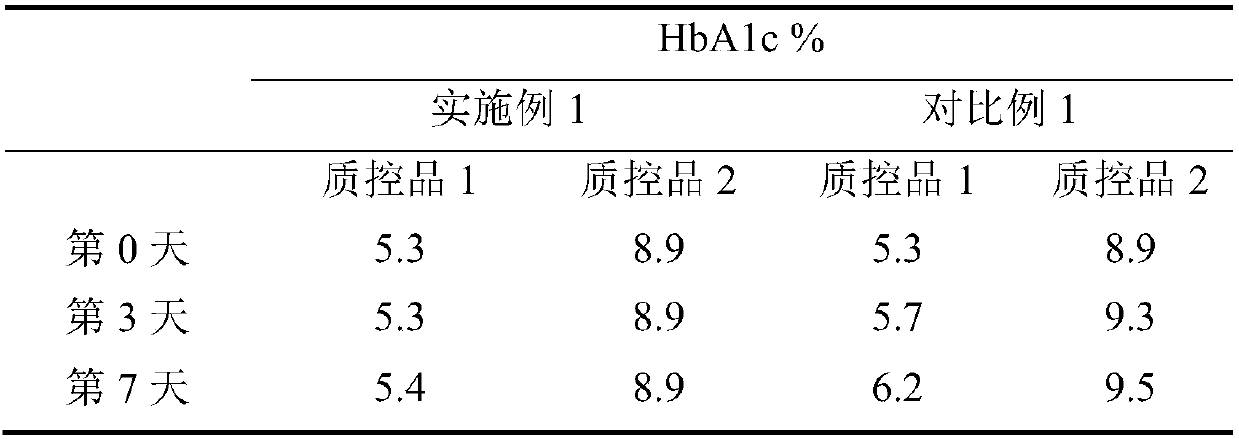
ActiveCN109633010AEfficient detectionAccurate detectionComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesGlycineHemolytic Agents
The invention relates to the field of clinical in vitro diagnosis and detection, and discloses a kit for the determination of glycosylated hemoglobin in whole blood. The kit comprises eluent A, eluentB and a hemolytic agent, wherein the eluent A and eluent B include buffer solutions, surfactants and additives respectively; the hemolytic agent includes a surfactant and an additive; and the additive is one or more of threonine, beta-alanine and glycine. A method for the determination of glycosylated hemoglobin in whole blood is also disclosed. The glycosylated hemoglobin kit provided by the invention can avoid the change of the measured value of a sample with the time of sample storage, and reduces the complex process of sample pretreatment, thereby realizing the efficient and accurate detection of glycosylated hemoglobin. In addition, the determination method provided by the invention can also realize fast and accurate detection of saved samples.
Owner:江山德瑞医疗科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com