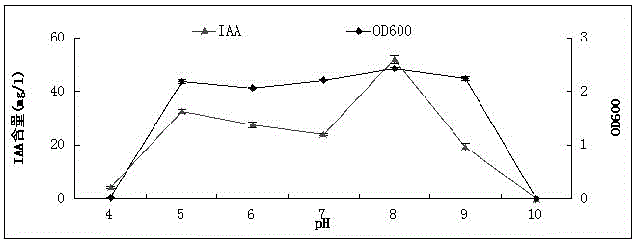
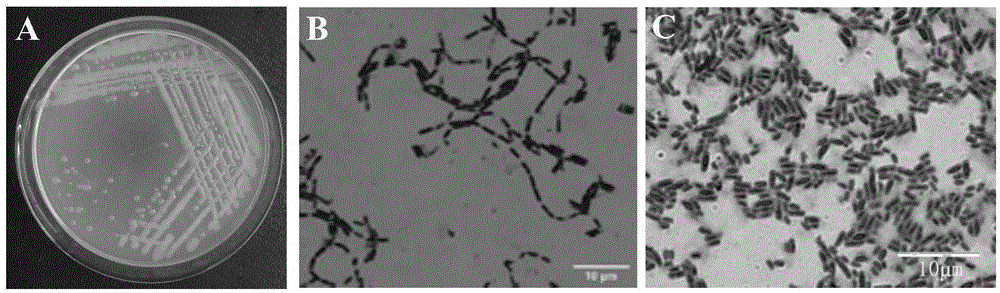
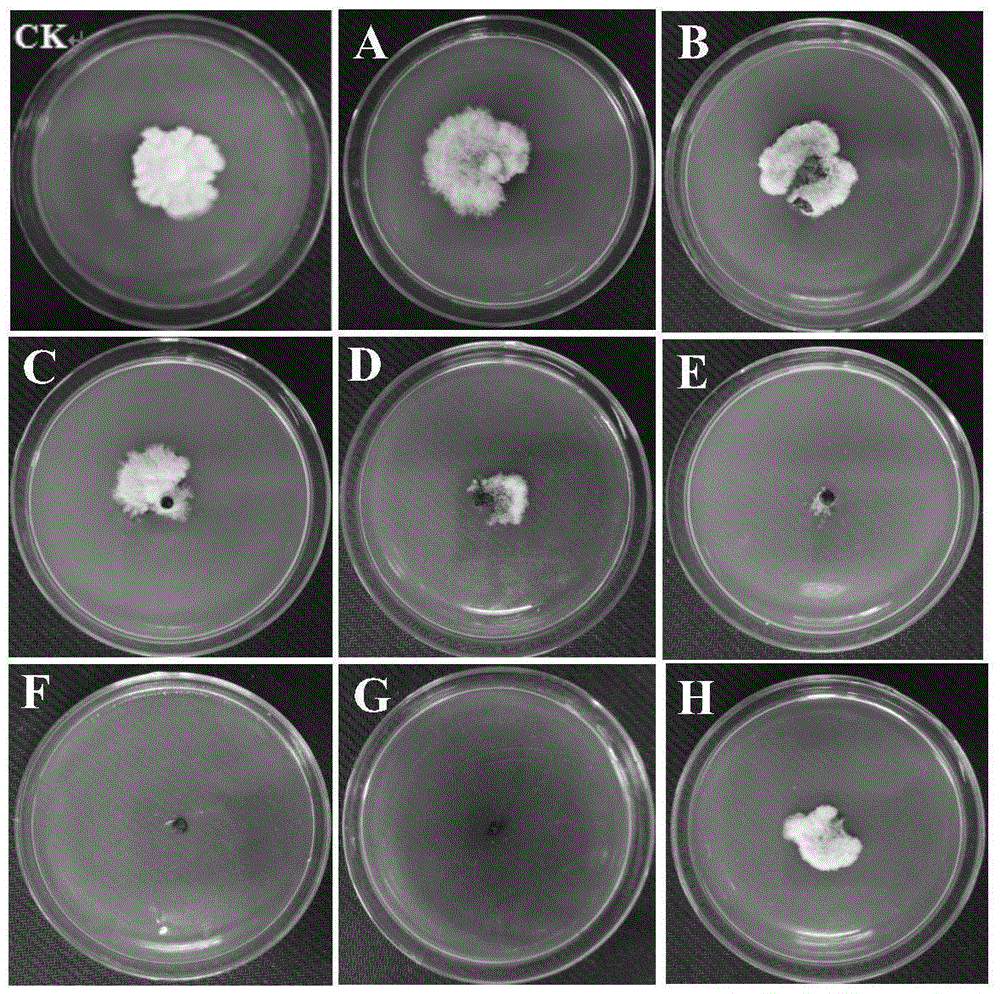
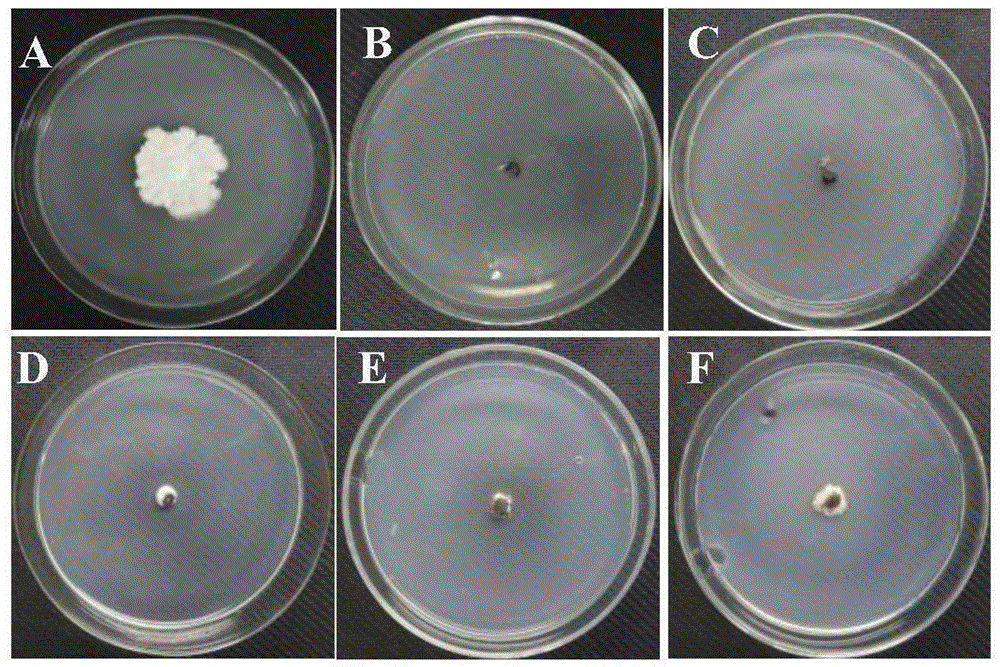
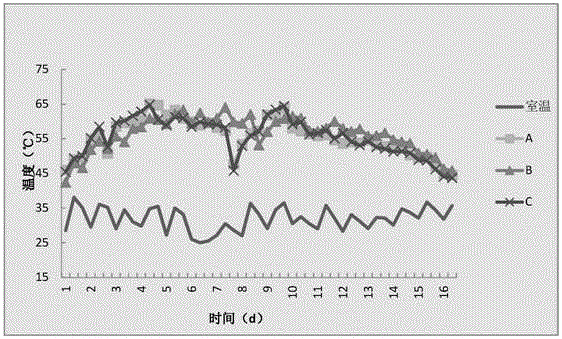
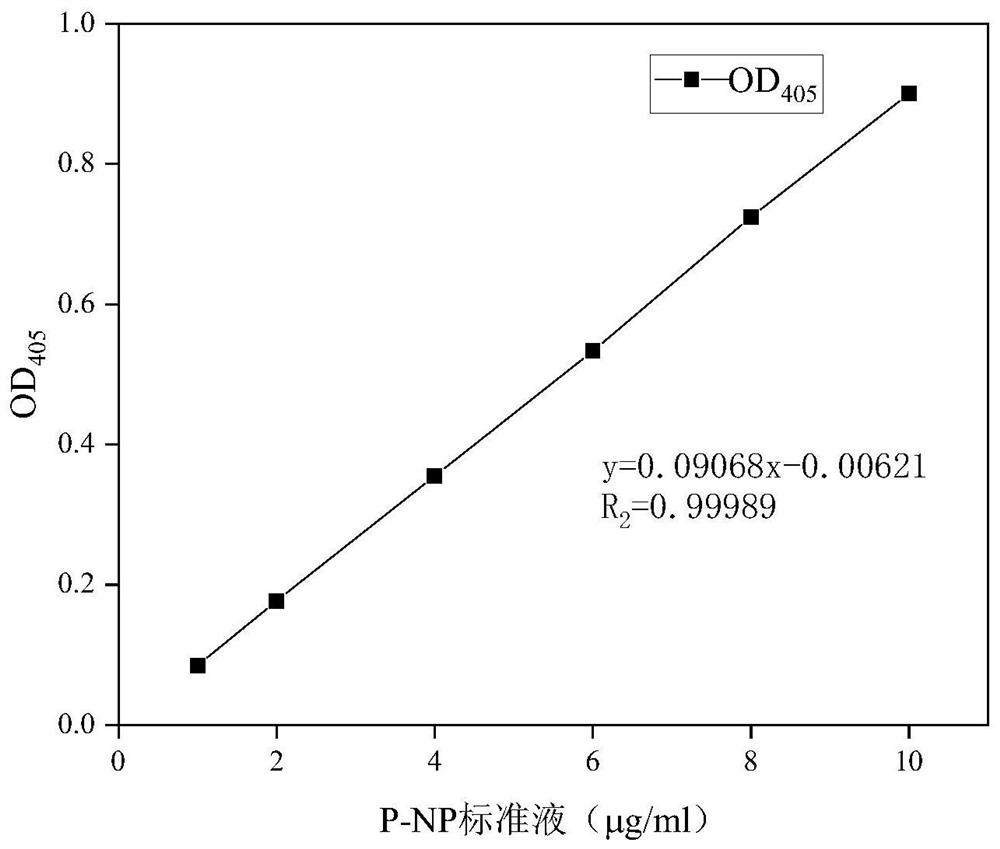
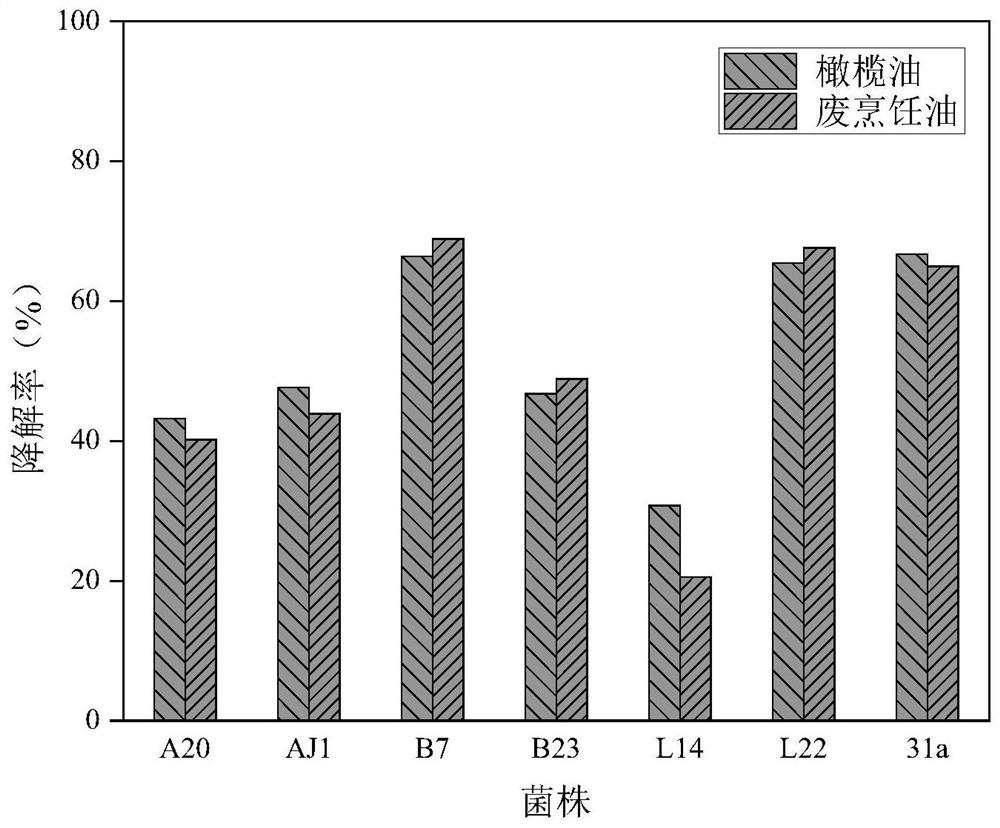
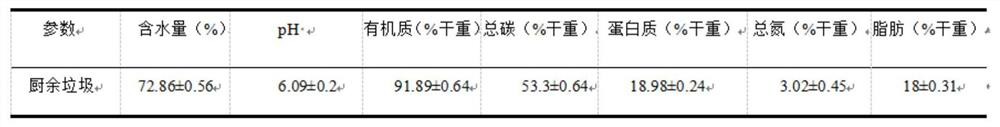
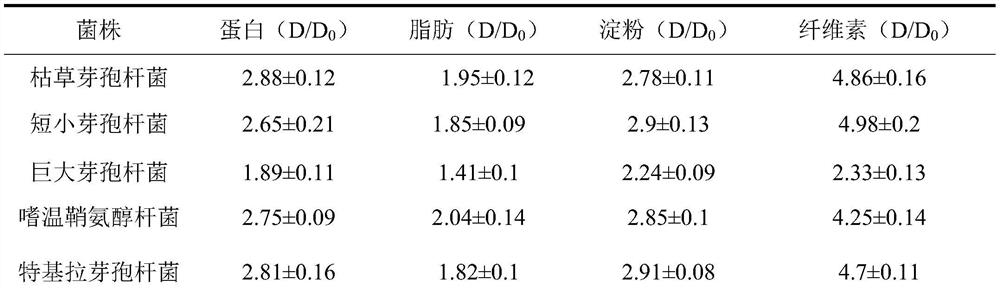
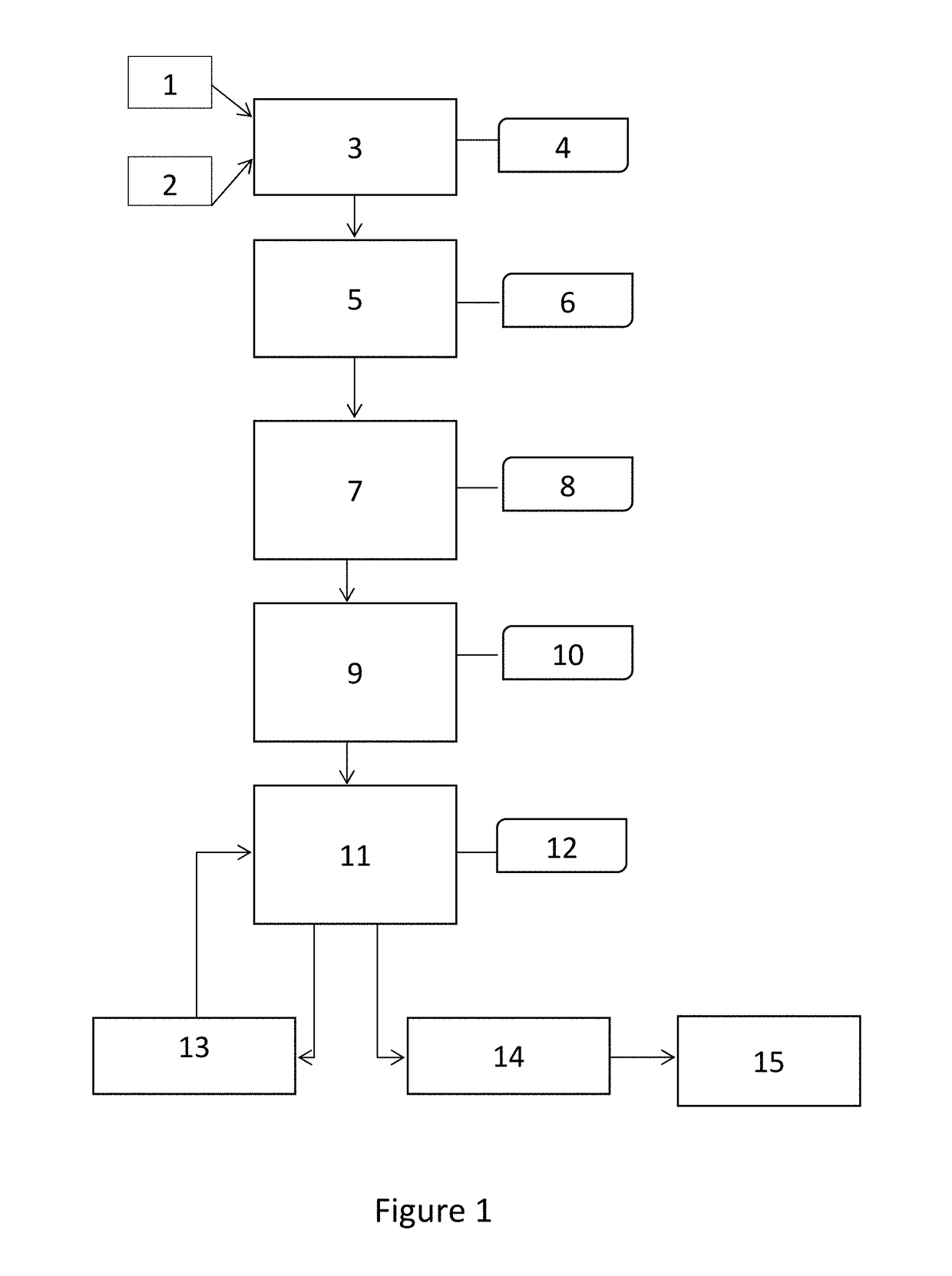
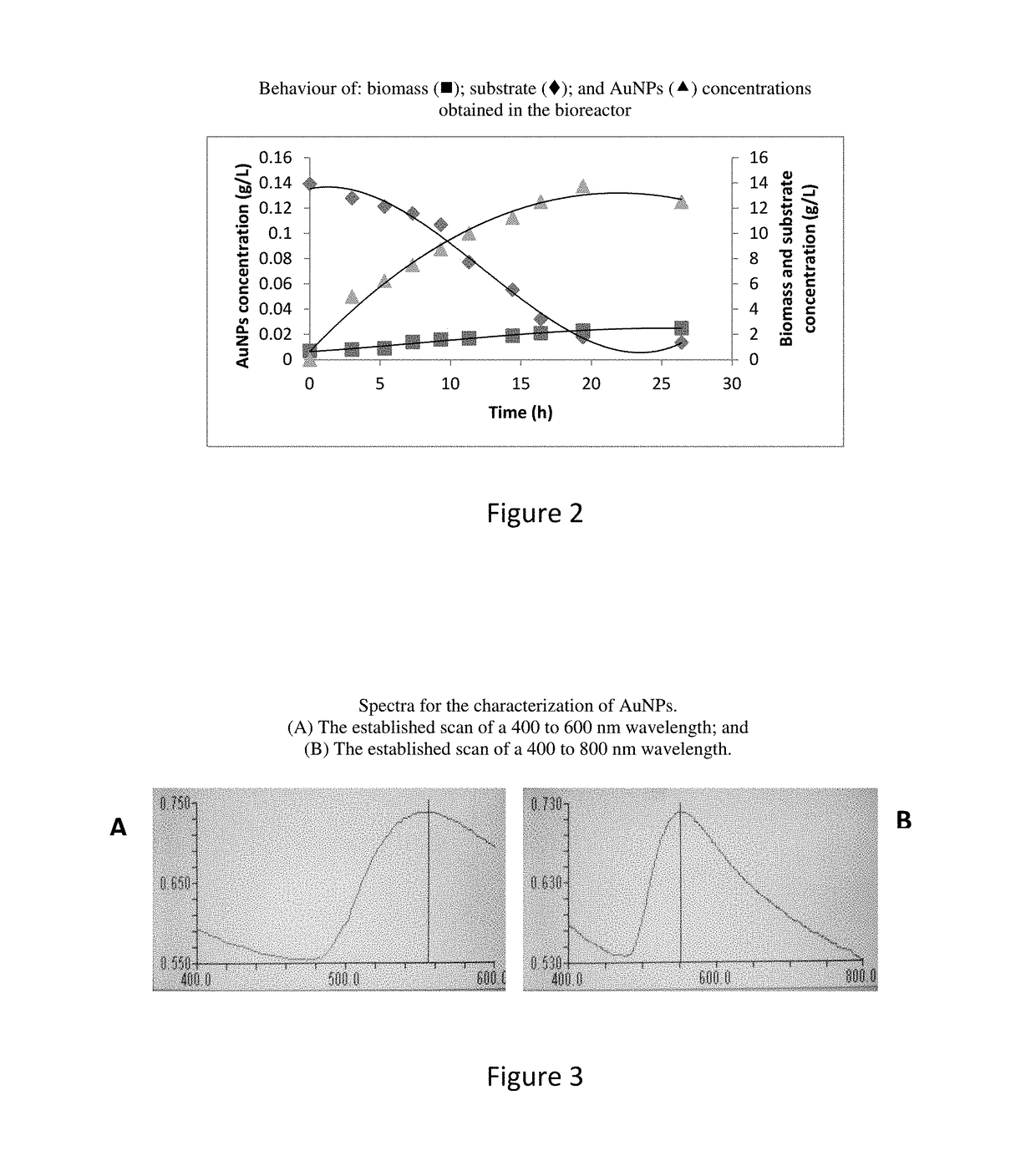
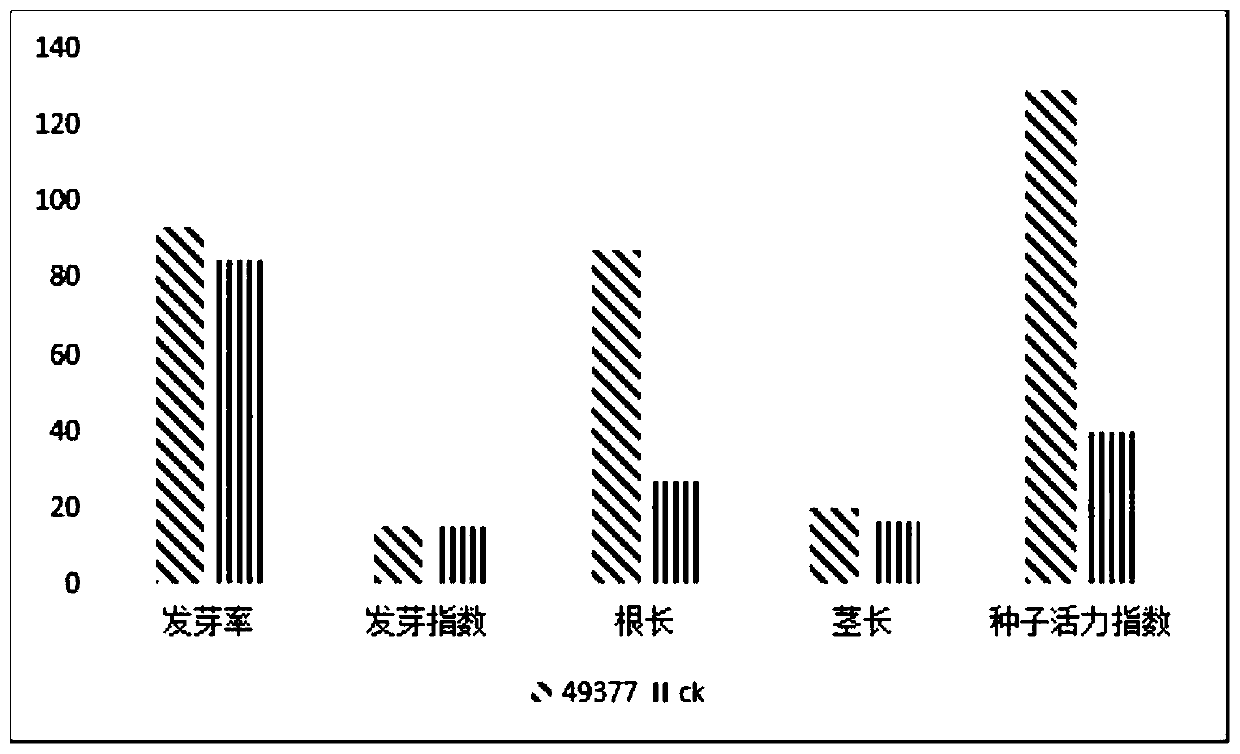
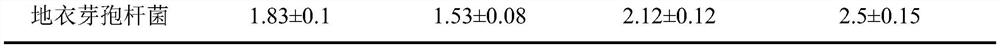Patents
Literature
69 results about "Bacillus tequilensis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
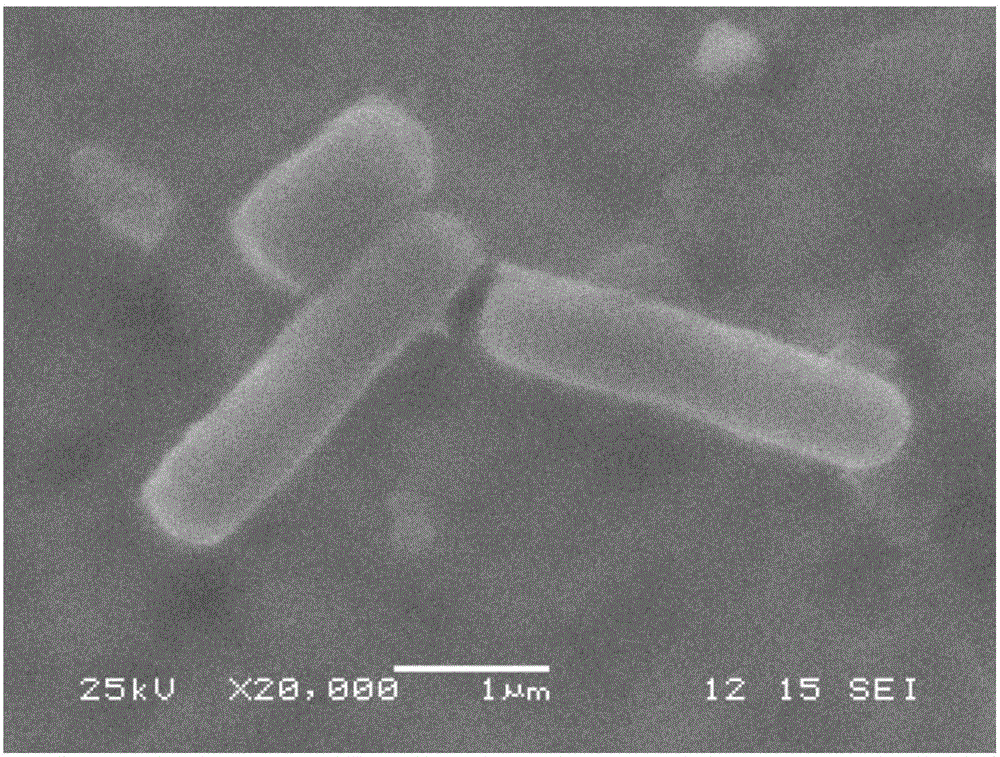
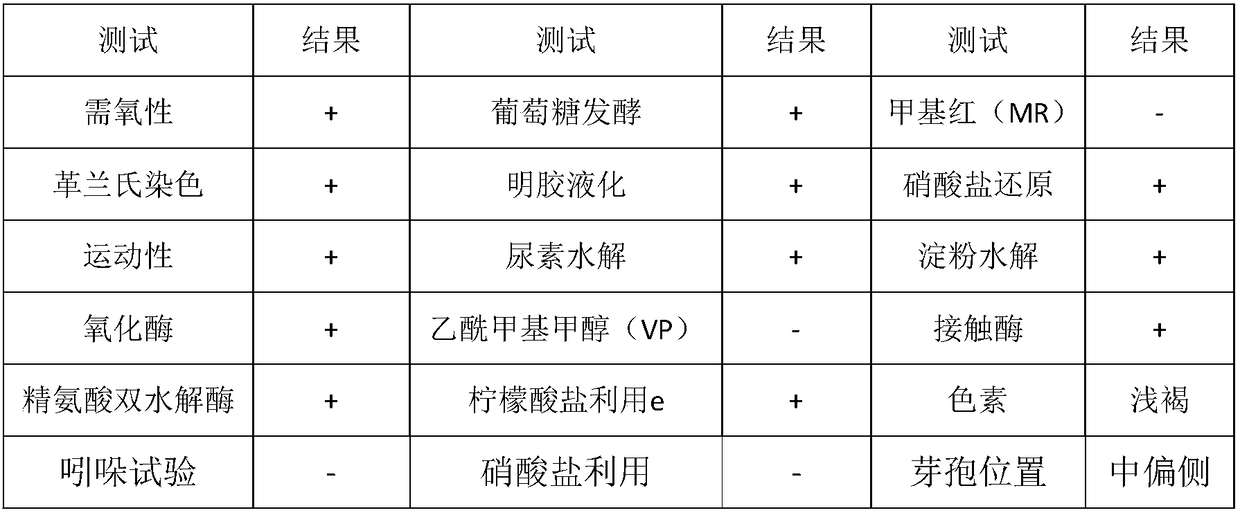
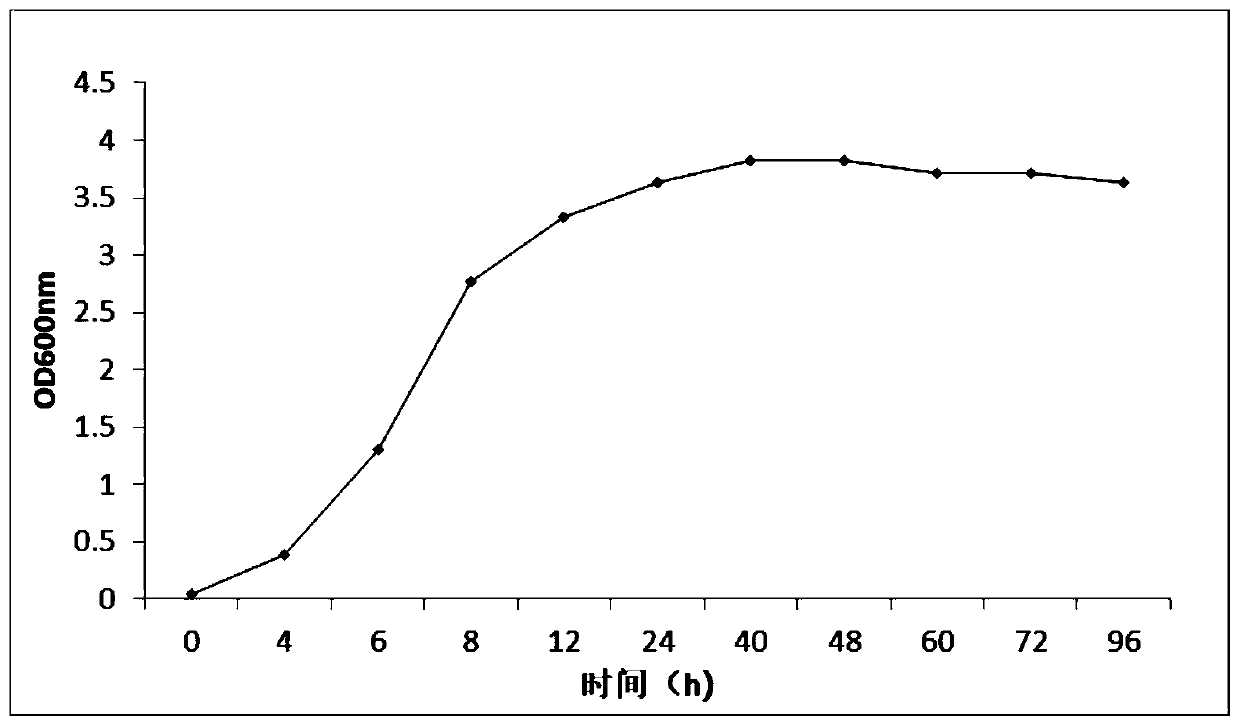
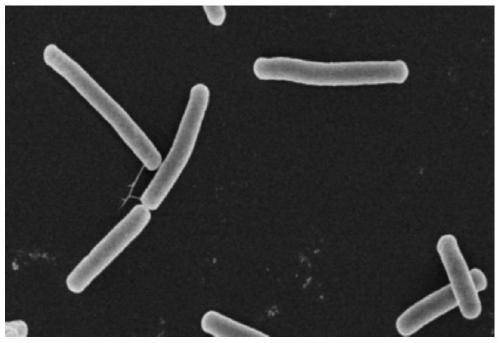
Bacillus tequilensis FJAT-14262a is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium. Here, we report the 4,038,551-bp genome sequence of B. tequilensis FJAT-14262a, which will provide useful information for genomic taxonomy and phylogenomics of Bacillus.
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus tequilensis CGX5-1 which is preserved with the number CGMCC No.5935 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 26, 2012. The bacillus tequilensis has high capability of producing beta-1, 3-1, 4-glucanase, and the bacillus tequilensis and good genes thereof are applied to the field of production of industrial enzyme preparations and have good prospects in reduction of cost for producing the beta-1, 3-1, 4-glucanase and improvement on enzyme preparation quality.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus tequilensis and its use in prevention and control of fusarium graminearum
The invention discloses Bacillus tequilensis and its use in prevention and control of fusarium graminearum. The Bacillus tequilensis has a preservation number of CGMCC No.9499. The Bacillus tequilensis can be used as a material for biological prevention and control of wheat scab and has good application prospect in development of both novel biopesticide and biological prevention and control inocula.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste. The composite microbial agent is composed of composite bacterial liquid and a carrier, wherein the composite bacterial liquid comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus siamensis, Bacillus tequilensis and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. The bacterial strains of the composite microbial agent produce synergism, so the composite microbial agent can substantially degrade a variety of macro-molecular components in the garden waste, improve the decomposition degree of the waste, enhance the nutrient structure and microfloras of compost and reduce heavy metal pollution. The invention also relates to a preparation method for the composite microbial agent, a method for degrading and converting the garden waste by using the composite microbial agent and fertilizer prepared from products obtained after degradation and conversion of the garden waste with the composite microbial agent.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107435032AHigh reduction rateImprove degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalBacillus oleroniusBacillus amyloliquefaciens
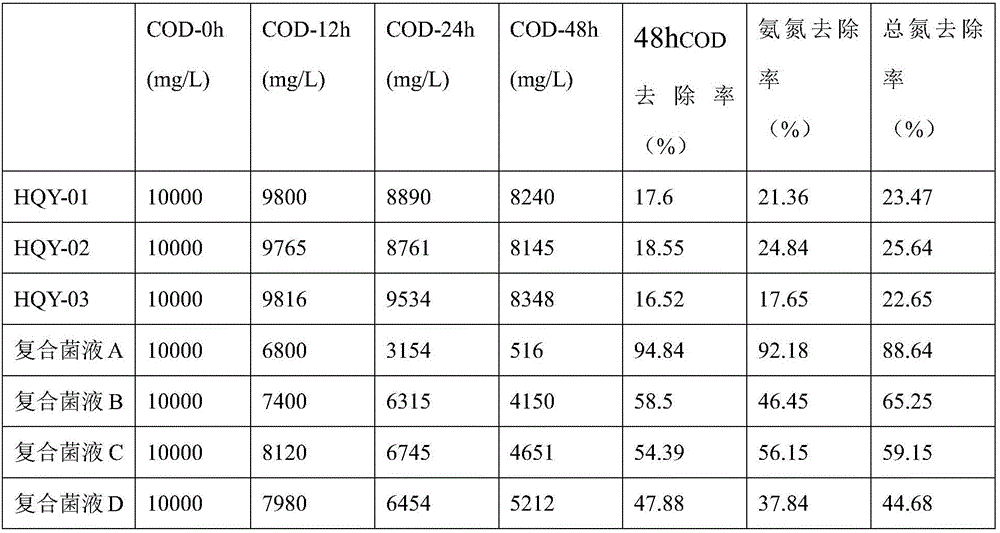
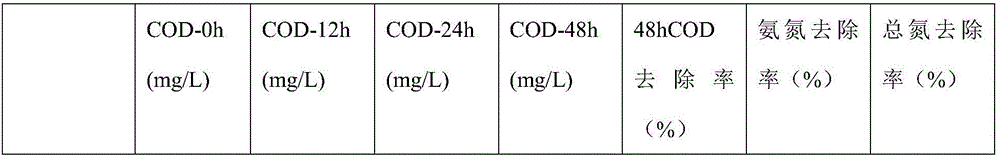
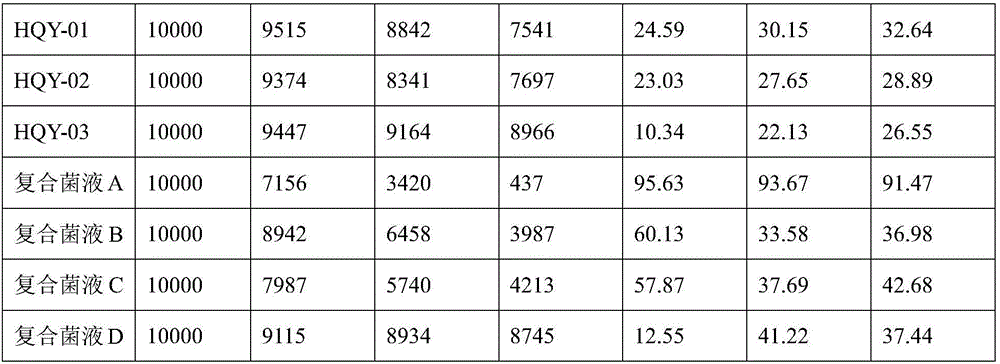
The invention discloses a kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium. The kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium is composed of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HQY-01, Bacillus oleronius HQY-02 and Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 which are preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, on February 16, 2017, the preservation number of the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HQY-01 is CCTCC NO:M2017040, the preservation number of the Bacillus oleronius HQY-02 is CCTCC NO:M2017039, and the preservation number of the Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 is CCTCC NO:M2017041. The kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium can be used for degrading kitchen wastes, and has the advantages of high waste weight loss rate, and high removal rate of CODs, ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAQINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Efficient Bottom-Improving Bacillus and Compound Bottom-Improving Microbial Agent Prepared From the Same and Applications Thereof
ActiveUS20170002310A1Function increaseImprove survivabilityBacteriaSpecific water treatment objectivesBacillus licheniformisBacillus megaterium
The applicant provides a strain of Bacillus tequilensis ZSGD5, with accession number of the deposit of CCTCC NO.: M 2014004, deposited at the China Center for Type Culture Collection, Wuhan University, Wuhan City, China on Jan. 6, 2014. The applicant also provides a compound microecological Bacillus agent. The compound microbial agent comprises the following bacterial species: Bacillus tequilensis, Type I Bacillus subtilis, Type II Bacillus subtilis, Type I Bacillus licheniformis, Type II Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus pumilus, and Bacillus megaterium. The Bacillus tequilensis provided in the present invention has an efficient water bottom cleaning capability, and can rapidly decompose and decrease the sludge at the bottom of a pond and effectively improve environmental waters for such phenomena as black water, and turbid water, so the Bacillus tequilensis can be used for water environment treatment in aquaculture and for urban wastewater treatment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fermentation method of chrysanthemum broad bean sauce
InactiveCN107751800AStrong flavorSpeed up the maturation processYeast food ingredientsBiotechnologySaccharomyces rouxii
The invention discloses a fermentation method of chrysanthemum broad bean sauce and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The fermentation method of the chrysanthemum broad bean sauce comprises thefollowing steps: (1) performing pretreatment on broad beans and performing pretreatment on chrysanthemum flowers; (2) making starters; (3) adding all the broad bean starters into a fermentation tank,adding saline water and chrysanthemum flower pulp, stirring uniformly and performing fermentation for 35 to 40 DEG C, wherein weissella confuse, saccharomyces rouxii, pediococcus pentosaceus LBST-L2 and bacillus tequilensis are added in the fermentation process and fermentation is conducted for 30 to 40 days. According to the fermentation method of the chrysanthemum broad bean sauce, the fermentation state of the broad bean sauce under the natural environment is simulated, the obtained broad bean sauce has strong flavor, different cultures are added at different stages, the maturation processof the broad bean sauce is accelerated, the fermentation cycle is shortened to 30 to 40 days, the beneficial active components are increased and the nutritional requirements of modern people are met.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of mixed microbial agent and application of same in high temperature composting
ActiveCN109022327AFacilitated DiffusionReduce processing timeBio-organic fraction processingFungiSporeMicroorganism
The invention provides a preparation method of a mixed microbial agent, the mixed microbial agent, and an application of same, and belongs to the technical field of environmental microorganisms. The preparation method includes: activating Mucor circinelloides, Bacillus tequilensis and Bacillus velezensis, mixing the spores of the Mucor circinelloides with the other two bacteria according to ratioof 1:3:3, and inoculating the mixed bacteria on a CPDA culture medium, culturing the mixed bacteria at 28 DEG C for 48 h in a constant temperature shaking table at 150 rpm to obtain a mixed microbialliquid. In the invention, by means of the character that the Mucor circinelloides is high in growth speed and can carry and diffuse bacteria, the Mucor circinelloides, applied to the aerobic composting of organic wastes, can enhance the diffusion of organic waste degrading bacteria in a heap, so that composting period is shortened and composting efficiency is increased effectively. Compared with simple microbial agent, the mixed microbial agent has great adaptability and stable performance, and has an extensive application prospect of quick composting reutilization of the organic wastes.
Owner:福建省致青生态环保有限公司
Microbial composition for promoting tobacco growth and use
ActiveCN106434471AImprove growth performanceAgronomic traits Plant heightBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCompound specificGenus Enterobacter
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and in particular provides a microbial composition for promoting tobacco growth. The microbial composition is formed by compounding specific Bacillus tequilensis, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella variicola and Enterobacter xiangfangensis strains at a ratio. The microbial composition can effectively improve agronomic characters of tobacco, adjust the proportion of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, and increase the yield of tobacco and the proportion of superior tobacco.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
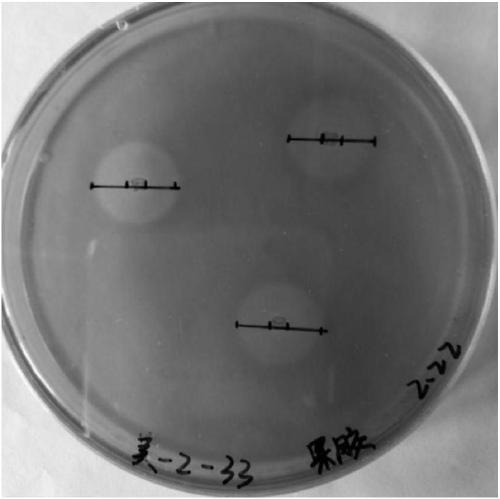
Bacillus tequilensis CAS-MEI-2-33 and application thereof
ActiveCN109957522APromote growthImprove utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPectinase
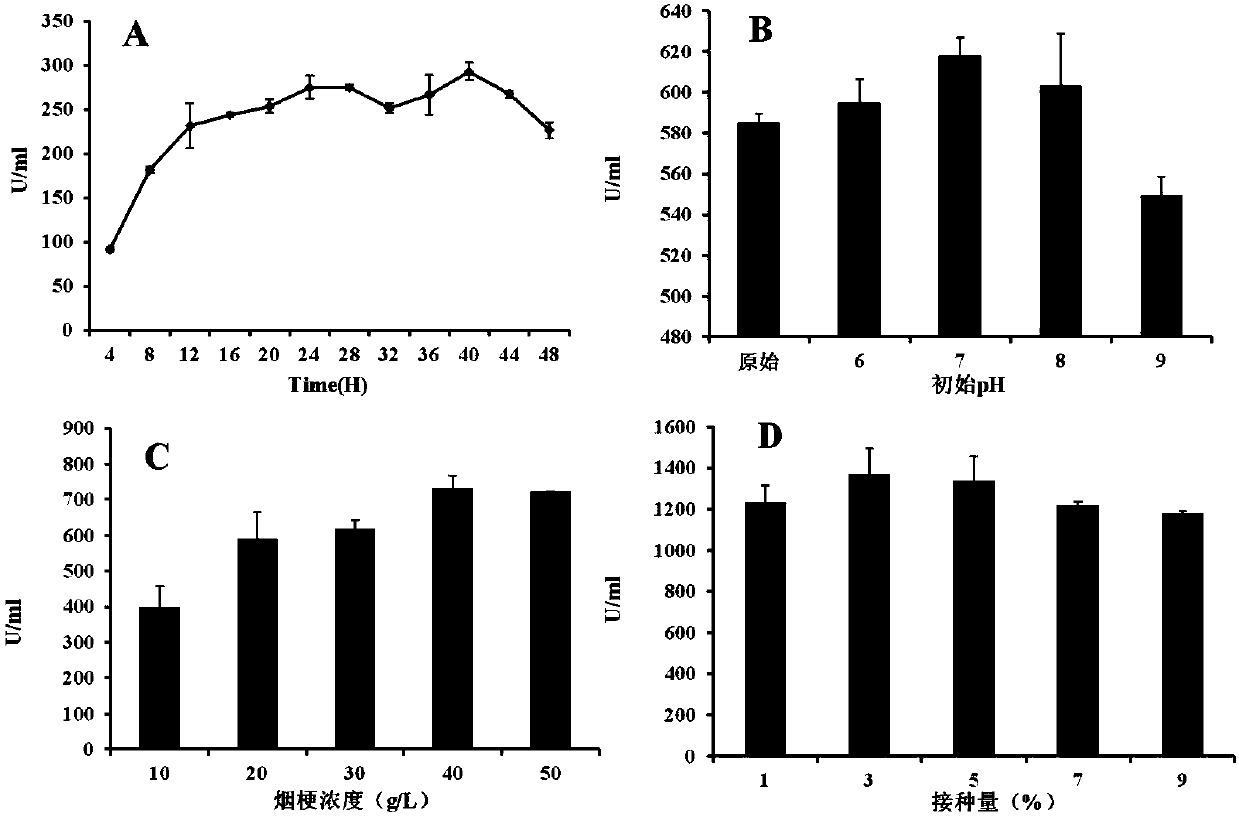
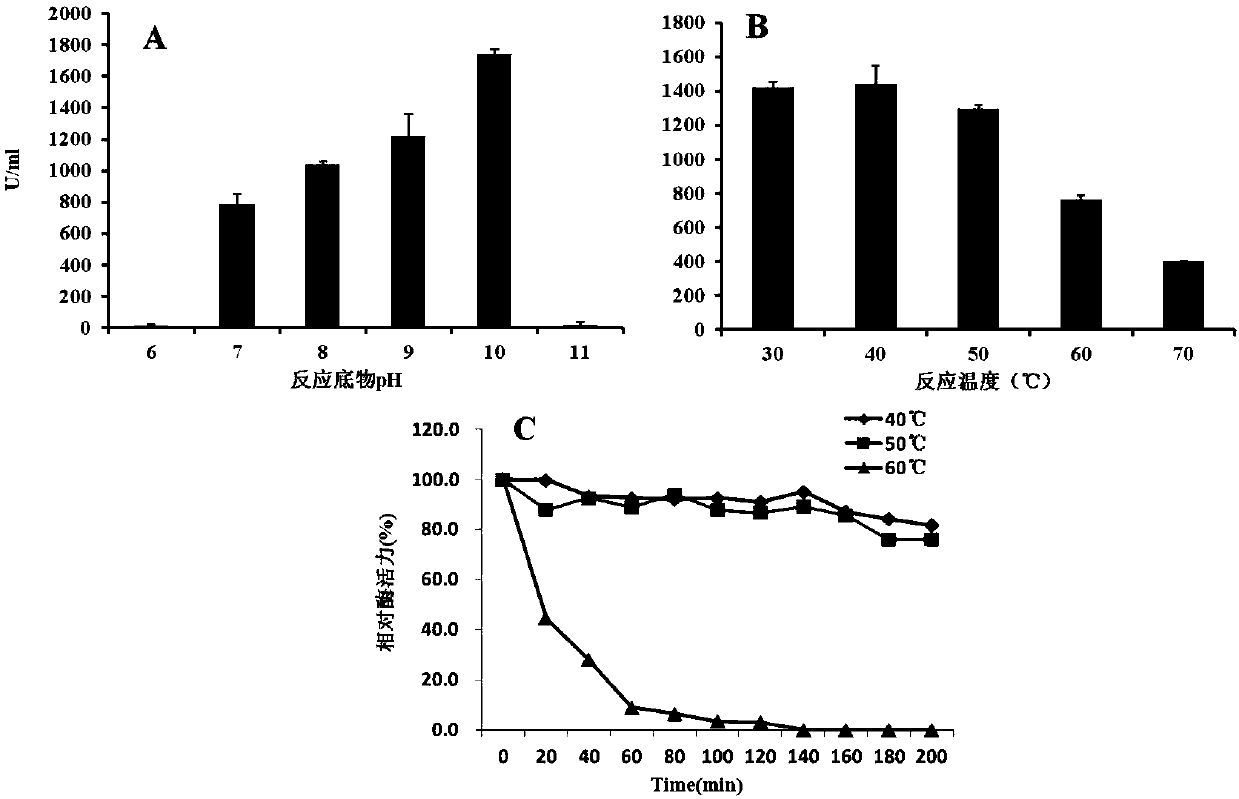
The invention discloses a strain of Bacillus tequilensis CAS-MEI-2-33 and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of tobacco waste recycling. The strain is deposited on October 17, 2017 at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 14826. The strain has the properties of rapid growth and pectin degradation, and the strain can beused to produce pectinase and obtain a crude pectinase liquid by taking tobacco waste as a raw material for fermentation. The strain can make tobacco waste turn waste into treasure, thereby not only solving the utilization problem of tobacco waste to a certain extent, but also expanding the source of alkaline pectinase. The strain of the invention is suitable for producing pectinase through fermentation.
Owner:中国烟草总公司海南省公司
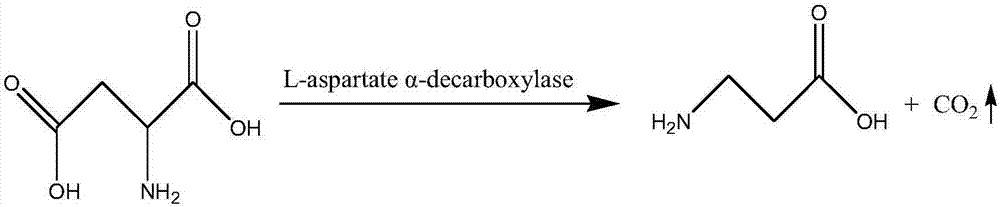
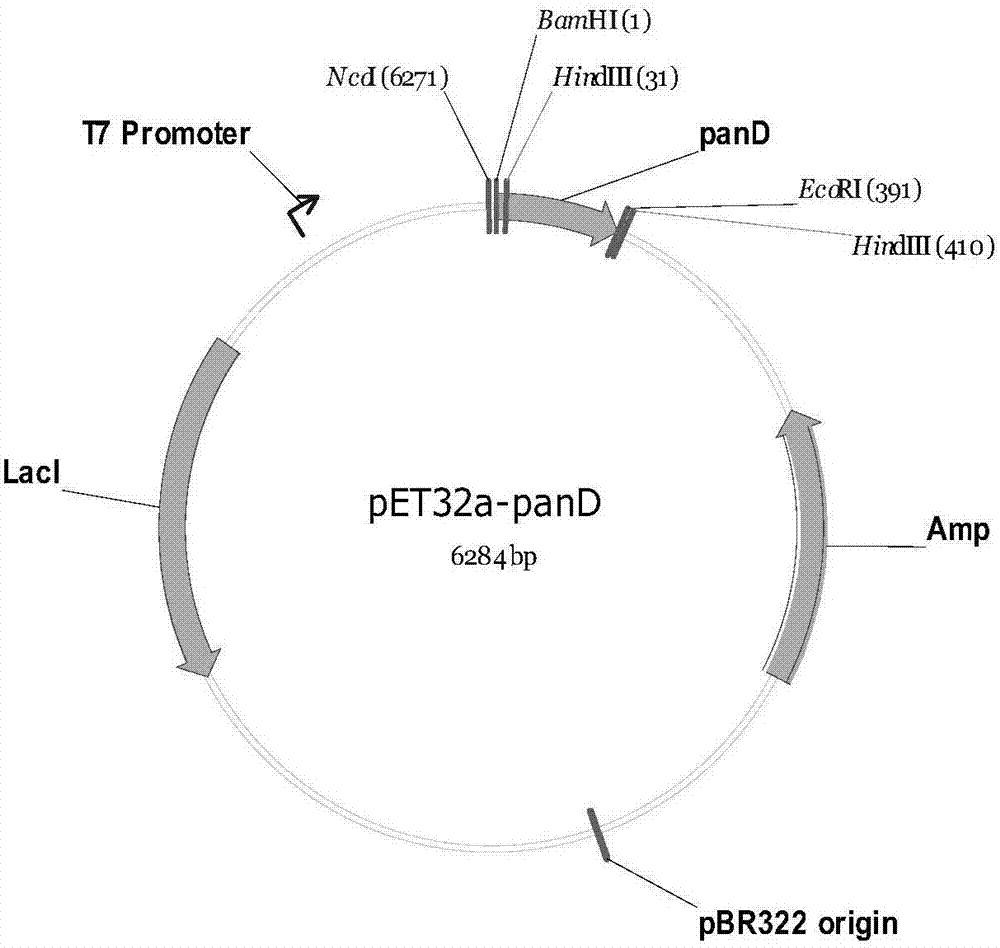
Method for constructing engineering bacterium capable of producing beta-alanine and method for producing beta-alanine by adopting engineering bacterium
InactiveCN107338258AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliL-Aspartate
The invention discloses a method for constructing an engineering bacterium capable of producing beta-alanine and a method for producing beta-alanine by adopting the engineering bacterium, belonging to the field of biotechnologies. The invention provides L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase gene of a bacillus tequilensis strain, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the engineering bacterium comprising the PanD gene. The invention further provides a constructing method of the engineering bacterium capable of producing the L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase, L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase obtained through expression and secretion is adopted for transforming L-aspartic acid, and thus beta-alanine is produced. According to the invention, L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase derived from bacillus tequilensis is adopted for transforming L-aspartic acid for producing beta-alanine for the first time at home and abroad, after the enzyme is expressed in escherichia coli, the generated L-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase has high enzyme activity, the thallus does not need to be crushed and can be directly used for carrying out transformation, L-aspartic acid of 180g / L can be transformed to the maximum, the yield of beta-alanine can achieve 119.8g / L, and the industrial application has the advantages.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
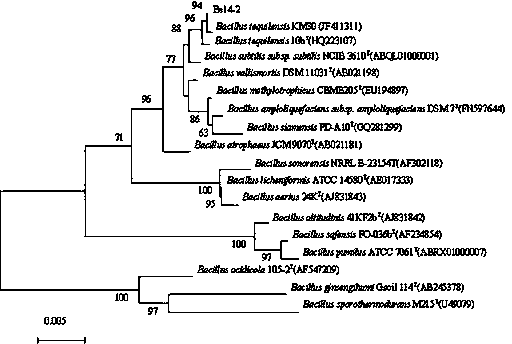
Bacillus and application of bacillus in exopolysaccharides preparation
ActiveCN103352017AImprove stabilityWith flocculationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPeroxyl radical
The invention discloses bacillus tequilensis Be14-2 CGMCC No. 7647 (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Number 7647), and an application of the bacillus tequilensis in polysaccharide metabolism. The bacillus tequilensis is inoculated in a czapek medium for inoculated cultivation, so that Pb<2+> tolerance is 2000mg / L, maximum Zn<2+> tolerance is 800mg / L, maximum Co<2+> tolerance is 400mg / L, and maximum Cu<2+> tolerance and maximum Hg<2+> tolerance are 100mg / L; a fermented culture can directly serve as an antioxidant; a concentration of polysaccharide with 50% hydroxyl radical (*OH) removed is 13.47mg / ml; the fermented culture can also be used for flocculating; and an activity range of the flocculating is 75.32-84.73%. The bacillus tequilensis is widely applied to the field of the polysaccharide metabolism, provides a new approach for industrially producing the natural polysaccharide, and has an important effect.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
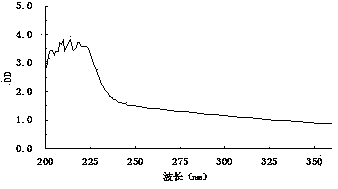
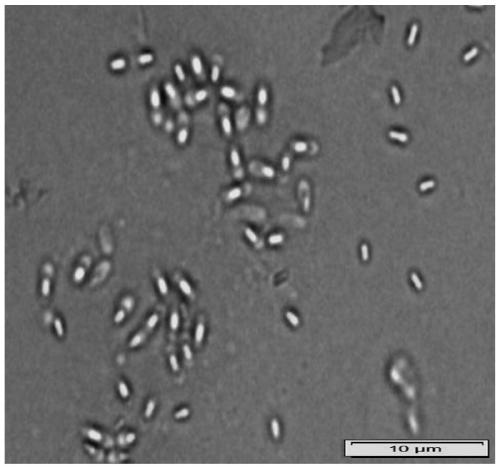
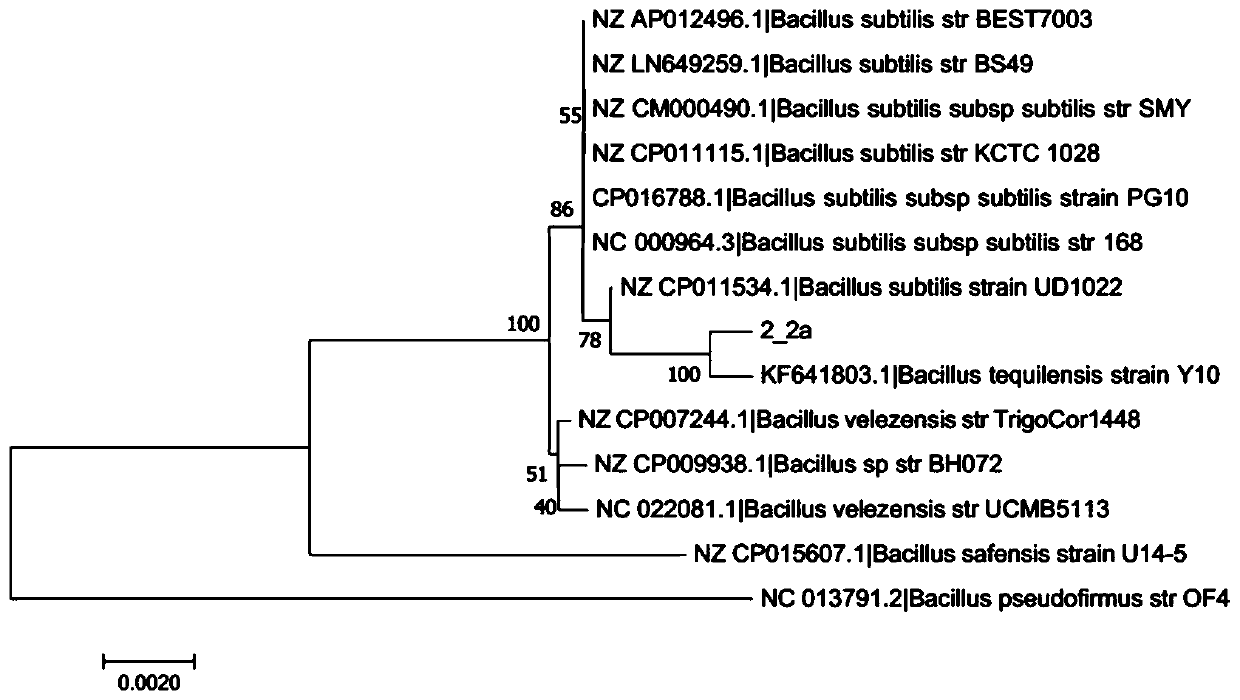
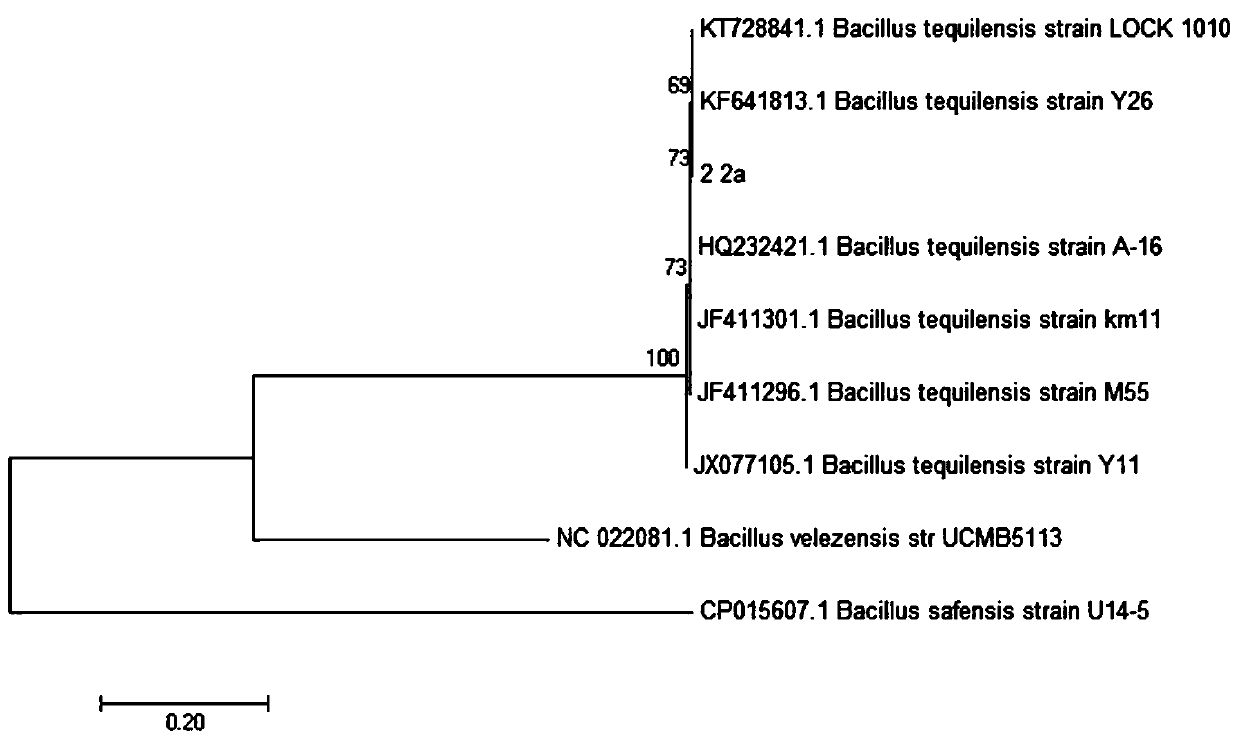
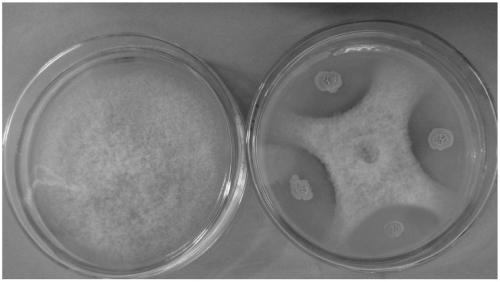
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to bacillus tequilensis and application thereof. The bacillus tequilensis 2_2a provided by the invention is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 19446. The bacillus tequilensis 2_2a is capable of being quickly and stably colonized in soybean plants, high in propagation speed and strong in multiplication capacity, has a high-efficiency and broad-spectrum plant pathogen resistance, and has a combined treatment effect on plant diseases of overground parts such as anthracnose, leaf spot disease, black spot disease, gray spot disease, etc. and underground soil-borne diseases such as root rot disease, wilt disease, stem rot disease, blight disease, etc., with a high prevention effect and a good application prospect in prevention and control of plant diseases, thus laying a foundation for developing high-efficiency and broad-spectrumbiocontrol agents.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus tequilensis and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fermenting.The bacillus tequilensis was stored in CGMCC on January 21, 2016 with the file No.12092.The storage address is Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, 1st Yard, Beichen West Rd, Chaoyang District, Beijing City.The bacillus tequilensis strain has high anti-bacteria performance, and is capable of effectively controlling growth of bacillus cereus in fermenting of broad-bean sauce, and bacillus cereus is a latent pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
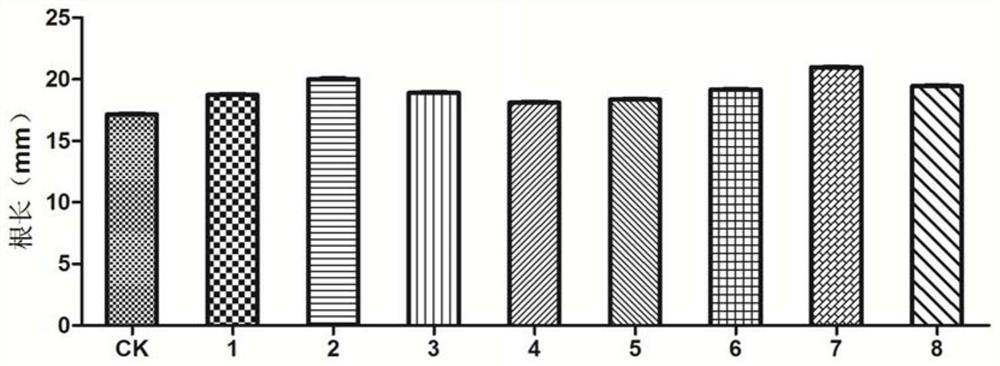
Growth-promoting bacteria combination for enhancing salt tolerance of crops in moderate-severe saline and alkaline lands
ActiveCN106635903AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought toleranceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAgricultural scienceRoot growth
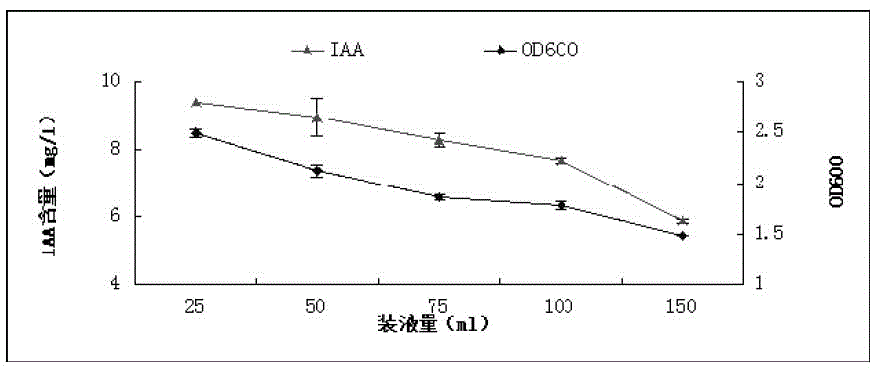
The invention discloses a growth-promoting bacteria combination for enhancing salt tolerance of crops in moderate-severe saline and alkaline lands. The growth-promoting bacteria combination comprises a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain ZCM18 and a bacillus tequilensis strain. Preservation numbers of the two strains are CGMCC No.1295 and CGMCC No.12960 respectively. The two strains are capable of tolerate the salinity of 5%, have high capabilities of phosphate solving, nitrogen fixing and producing IAA (indoleacetic acid), ACCD (acetyl-CoA carboxylase subunit D), siderophore and cytokinin, and can antagonize root pathogenic bacteria including fusarium, rhizoctonia, pythium and the like. The two stains after being combined are suitable for the moderate-severe saline and alkaline lands (with salt content ranging from 0.4% to 1.0%), and in the production field of biological fertilizer for salt tolerating and growth benefiting for the crops, the growth-promoting bacteria combination is promising in prospects of crop's salt tolerance enhancement, crop root growth benefiting, seedling existing rate increasing, fertilizer using amount decreasing and crop yield increasing.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
ActiveCN112646755APromote growthImprove performanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPlant growth
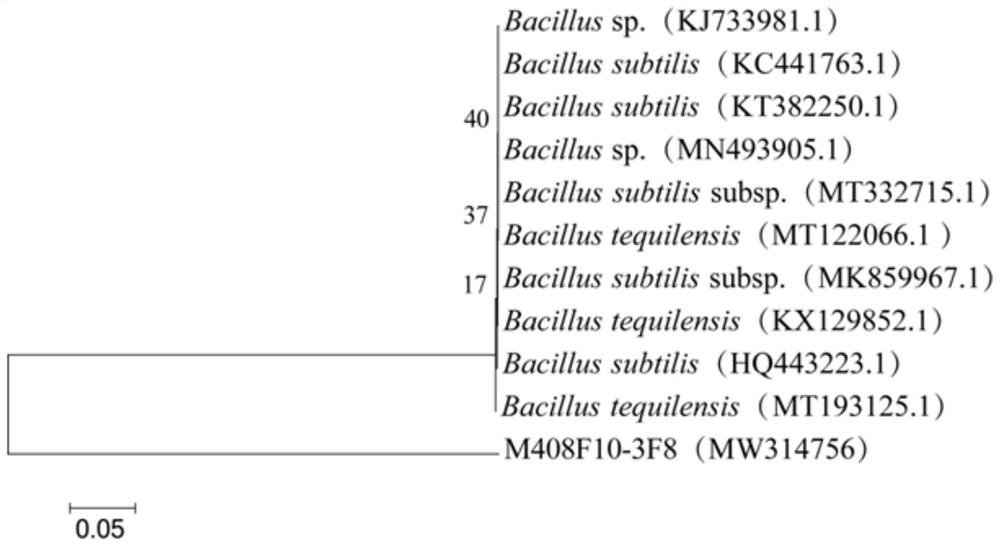
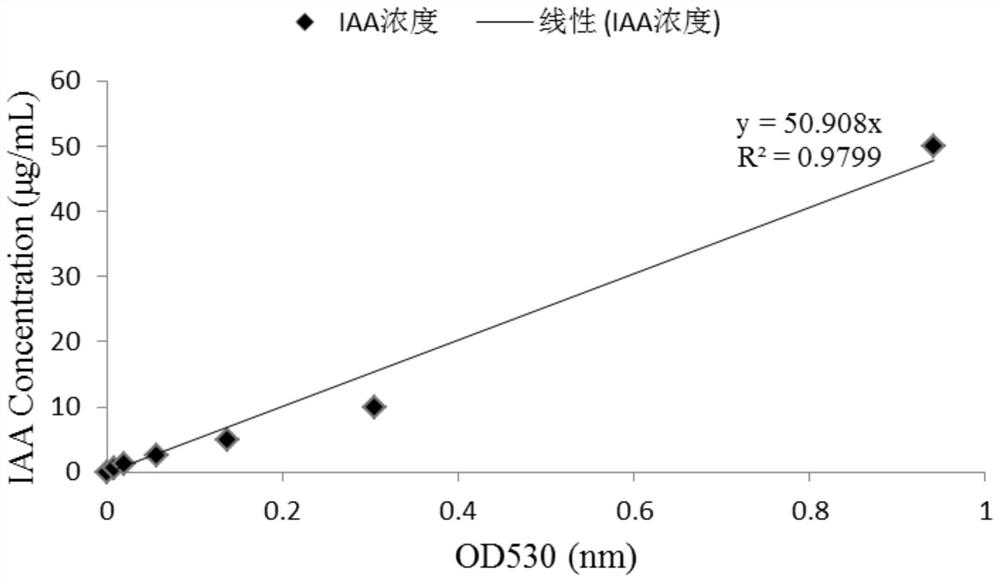
The invention discloses Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 7, 2020, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 21317, and the preservation name is Bacillus tequilensis M408F10-3F8. The strain is applied to the field of agricultural biological control, a biological membrane can be formed to be stably colonized at the plant rhizosphere, a high and broad-spectrum inhibition effect can be generated on 12 plant pathogenic fungi and oomycetes, and IAA can be generated to promote plant growth. The control effects of the Bacillus tequilensis bacterial suspension and fermentation liquor on cucumber fusarium wilt potted plants reach 50.00% and 58.00% respectively, the control effect is equivalent to that of a medicament control carbendazim, an obvious growth promoting effect is achieved on cucumbers, and the Bacillus tequilensis is a biocontrol strain with excellent performance and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Application of bacillus in promoting growth of plants
PendingCN109097302APromote growthReduce usagePlant growth regulatorsBiocideSalt resistanceGrowth plant
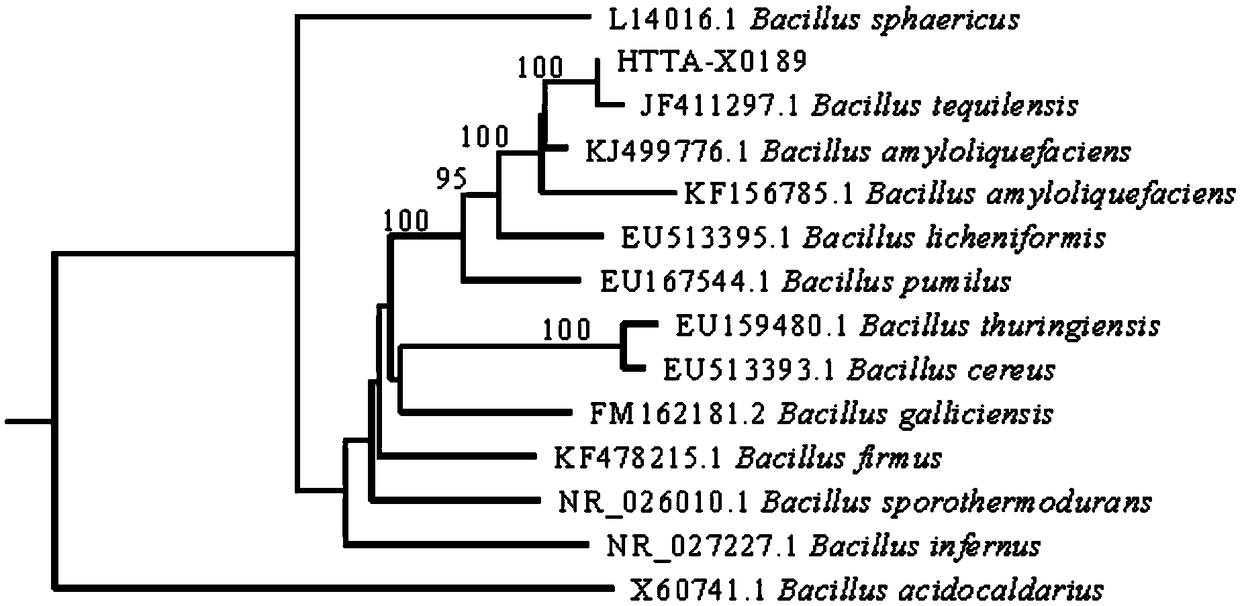
The invention discloses application of bacillus in promoting growth of plants. The bacillus is Bacillus tequilensis, the bacterial strain number of which is HTTA-X0189, and the preservation number ofwhich is CGMCC No.15770. The HTTA-X0189 bacterial strain is stable in biological characteristic and fertilizer action, simple and feasible in culture method, low in production cost and easy to realizeindustrialization. The HTTA-X0189 bacterial strain can promote growth of plants from multiple aspects, further can induce salt resistance of the plants, and is the bacterial strain which plays a multifunctional promoting role to the plants, and use of chemical fertilizers can be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Gossypol degradation strain coming from ruminant rumens and application thereof
InactiveCN104328063AAvoiding Toxicological UncertaintyAvoid uncertaintyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenus RathayibacterMicroorganism toxicology
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a gossypol degradation strain coming from ruminant rumens and application thereof. The gossypol degradation strain is collected in a common microorganism center of the microorganism culture preservation and management committee of Chinese on August 23, 2013; and the culture preservation number is CGMCC No.8069. According to the gossypol degradation strain coming from ruminant rumens and the application, gossypol serves as a unique carbon source, the new strain with higher degradation activity to the gossypol is separated, screened, purified and cultivated from the ruminant rumens; through morphology and molecular biological identification, the strain RBS is Bacillus subtilis; and the homology between the Bacillus subtilis and the Bacillus tequilensis strain KM34 is 98%. The strain comes from the ruminant rumens of a living body, the nondeterminacy of the microorganism toxicology coming from soil or other natural environments is avoided, and a mice toxicity test shows that bacteria do not have toxicity. The liquid state fermentative gossypol degradation rate reaches 94.74%; after the bacteria are used for fermenting cottonseed meal, it is determined that the degradation rate of the free gossypol in the fermented cottonseed meal approaches to 80% through liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus tequilensis, microcapsule microbial agent and preparation method
PendingCN112680379AStrong stress resistancePromoting effect is goodPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyPlant roots
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG +1
Peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN104630094AEffective growth and developmentPromote growth and developmentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismOrganic phosphorus
The invention relates to a peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium and the application thereof. The peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium is the peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium HS10 which is classified and named as bacillus tequilensis and collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 31, 2014, with the collection number CGMCC No. 9890; the peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium is capable of effectively transforming insoluble potassium-containing silicates into soluble potassium salts, decomposing organic phosphorus and increasing the fertilizer utilization rate and can be effectively applied to peanut planting to promote the growth of the peanut and increase the peanut yield; in short, the peanut growth-promoting rhizobacterium is a great innovation in microorganisms and peanut planting.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mulberry antergic endophyte Bacillus tequilensis
ActiveCN105274021AImprove thermal stabilityStrong antagonistic effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEndophyte
A strain of mulberry antergic endophyte Bacillus tequilensis ((i) Bacillus tequilensis( / i)) 7pj-16 (CCTCC No. M2015319) is separated and purified from stems of 'guosangchuan 7637'. The bacteria have a strong and stable antagonistic action to Scleromitrula shiraiana. The bacteria grows in a temperature ranging from 25 DEG C to 45 DEG C, the optimum temperature being 25DEG C; the bacteria has optimum fermentation time of 72 hours; a aseptic active fermentation filtering liquid is heat-stable; the bacteria suppressing effect of aseptic fermentation filtering liquid does not change obviously after treating the fermentation filtering liquid in a temperature of 100DEG C for 30 minutes. The bacterial body and the fermentation liquid have no lethal effect on the mulberry tissue culture plants but has growth-promoting actions, and have potential commercial development and application values.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Bacillus tequilensis JN369 and application thereof
ActiveCN106282049AGood prevention effectAvoid Potential Adverse EffectsBiocideBacteriaMetaboliteChemical control
The invention relates to the technical field of biological control, and in particular discloses bacillus tequilensis JN369 and an application thereof in preventing and controlling rice blast. The preservation number of the strain JN369 is CCTCC No:M2016340. With the application of the strain JN369 to prevent and control the rice blast, potential adverse impact of chemical control on environment and rice safety and disease infection risk of using disease-resistant varieties can be avoided. The living strain JN369 and metabolites thereof can take a relatively good effect on preventing the rice blast, and the strain JN369, which integrates both protecting and treating effects, can be processed and developed in the dosage forms of the living strain and the metabolites. In addition, the strain JN369 has an inhibitory effect on various pathogen indicating bacteria.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Bacillus subtilis for degrading edible mushroom dreg cellulose and application of bacillus subtilis
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis NFB7 for degrading edible mushroom dreg cellulose. The accession number of bacillus subtilis is CGMCC NO. 11927. The invention also provides a complex microbial inoculant, which comprises the following active ingredients: bacillus subtilis NFB7 with accession number of CGMCC NO. 11927, bacillus amyloliquefaciens BCB4 with accession number of CGMCC NO. 11141, and bacillus tequilensis BCB2 with accession number of CGMCC NO. 11140. After the complex microbial inoculants is added to compost, the contents of available nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in the compost are improved; by using the produced compost for planting, the yield and thousand seed weight are respectively increased by 8.14% and 5.57% compared with the conventional fertilizer way.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-temperature-resistant kitchen waste grease degradation compound microbial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN111849821ANormal growthEfficient degradationBacteriaSolid waste disposalOil and greaseMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant kitchen waste grease degradation compound microbial agent and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of kitchen waste treatment. The compound microbial agent comprises: the compound microbial agent comprises bacillus tequilensis ZJB19167 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2020177, a thermophilic bacillus ureaea ZJB20037 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 20279 and a bacillus sonora desert ZJB20038 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2020280. The microbial agent can survive by using grease as a unique carbon source, can normally grow under the conditions of high grease concentration and high environment temperature, has a grease degradation rate of 80% or above on olive oil, soybean oil, peanut oil andwaste cooking oil at 55 DEG C, is applied to rapid microbial decrement treatment of kitchen waste, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Microbial agent capable of degrading kitchen garbage and application thereof
ActiveCN112708586APromote degradationAdaptableBacteriaSolid waste disposalBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a microbial agent capable of degrading kitchen garbage and application of the microbial agent. The microbial agent is prepared from bacillus subtilis, bacillus pumilus, Sphingobacterium thalpophilum and bacillus tequilensis. The four strains are pre-cultured and activated by using a kitchen waste leachate and are prepared into the complex microbial inoculant, so that the degradation efficiency of the kitchen waste can be obviously improved, the degradation rate is improved by 15.5% compared with that of LB culture medium culture preparation, the COD of supernatant effluent after fermentation is completed is less than 200mg. L <-1 >, and the environmental pollution is small; the kitchen garbage leachate is used for pre-culturing and preparing the microbial inoculum, so that the production cost of the solid microbial inoculum can be greatly reduced, the wastewater treatment capacity is reduced, and the application prospect is higher.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
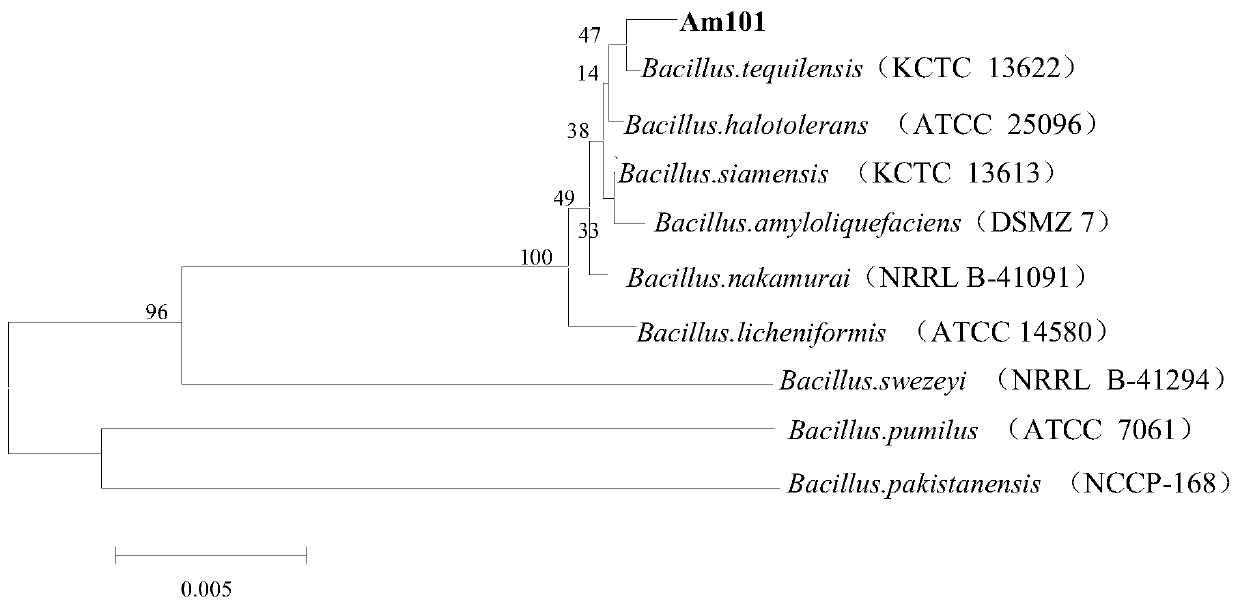
Strain Am101 capable of degrading various beta-lactam antibiotics and application of strain Am101
ActiveCN110791450ABroad degradation spectrumFast degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBenzylpenicillin potassium
The invention discloses bacillus tequilensis Am101 capable of degrading various beta-lactam antibiotics and an application of the bacillus tequilensis Am101. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 18, 2019, and a preservation number is CGMCC NO. 18965. The strain Am101 disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously degrading various beta-lactam antibiotics and can be used for efficiently degrading benzylpenicillin potassium, amoxicillin, cefuroxime sodium and ceftiofur sodium. The strain Am101 can be applied to degradation treatment of residual beta-lactam antibiotics in livestock and poultry manure, can also be applied to restoration of water and soil polluted by the beta-lactam antibiotics, and has the wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
ActiveCN109536425AEffective controlGood inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentPhytophthora sp.
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to Bacillus tequilensis and an application thereof. The Bacillus tequilensis is named Bacillus tequilensis QX13, and the Bacillus tequilensis is collected in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) with collection number of CGMCC No.16618 in Beijing China on October 24, 2018. The strain has a remarkable inhibition effect on Sclerotium rolfsii as a pathogenic fungus of peony southern blight, can effectively control peony southern blight and has a remarkable inhibition effect on other plant diseases such as peony brown spot, tomato early blight, Chinese rose shoot blight or pepper phytophthora blight, besides, the strain is harmless to the ecological environment, cannot cause drug resistance of pathogens, is easy to store, facilitates industrial production and has good development and application prospects, and the culture conditions are simple.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological process for producing magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveUS20170247720A1Efficient processingImprove thermal conductivityFermentationMagnetite NanoparticlesNanostructure
A process for obtaining gold magnetic nanoparticles or of other metallic elements by fermenting a culture medium in the presence of producer microorganisms such as Brevibacterium halotolerans, Bacillus mojavensis, Bacillus subtilis subsp. Inaquosorum, Bacillus subtilis subsp. Spizizenii, Bacillus tequilensis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. Amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus siamenensis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. Plantarum, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus subtilis subsp. Inaquosorum, Bacillus atrophaeus, or Bacillus vallismortis, inter alia. The process of the invention can be used to effectively control the size and shape of the nanostructure to be obtained, with production levels above those found at laboratory level.
Owner:LOPEZ NAVARRO CRISTHIAN RENE
Rooting-promoting Bacillus sporothermodurans and application of rooting-promoting Bacillus sporothermodurans
InactiveCN111560322AEfficient degradationPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyNutrition
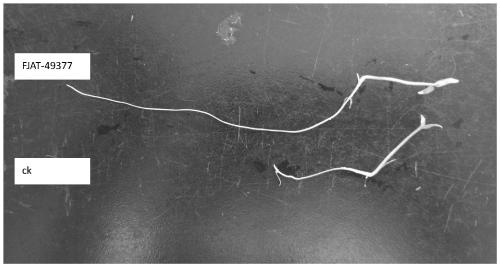
The invention provides rooting-promoting Bacillus sporothermodurans and application thereof, the strain is bacillus tequilensis FJAT-49377 which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.16330. The bacillus tequilensis FJAT-49377 can promote seed germination, can dissolve phosphorus and fix nitrogen, can improve soil fertility, provides sufficient nutrition for plant growth, has high temperature resistance, and is beneficial to composting treatment of agricultural wastes.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
InactiveCN111690566APrevent mildewGood effectBacteriaEdible seed preservationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention provides Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.15973, and provides an application of the Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 in the prevention of grain mildew. The specific step is as follows: evenly spraying a Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 bacterial solution on the surface of grains. The Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 provided by the invention is used for preventing grain mildew, the effect is good, and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Organic waste degrading compound bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107435033AHigh reduction rateImprove degradation rateFungiBacteriaBacillus oleroniusBacillus aryabhattai
The invention discloses an organic waste degrading compound bacterium. The organic waste degrading compound bacterium is composed of Bacillus oleronius HQY-02, Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 and Candida pseudolambica HQY-06 which are preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, on February 16, 2017, the preservation number of the Bacillus oleronius HQY-02 is CCTCC NO:M2017039, the preservation number of the Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 is CCTCC NO:M2017041, and the preservation number of the Candida pseudolambica HQY-06 is CCTCC NO:M2017043. The organic waste degrading compound bacterium can be used for degrading organic wastes, and has the advantages of high waste weight loss rate, and high removal rate of CODs, ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAQINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com