Bacillus subtilis for degrading edible mushroom dreg cellulose and application of bacillus subtilis
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and edible fungus, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and can solve the problems of slow degradation of cellulose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
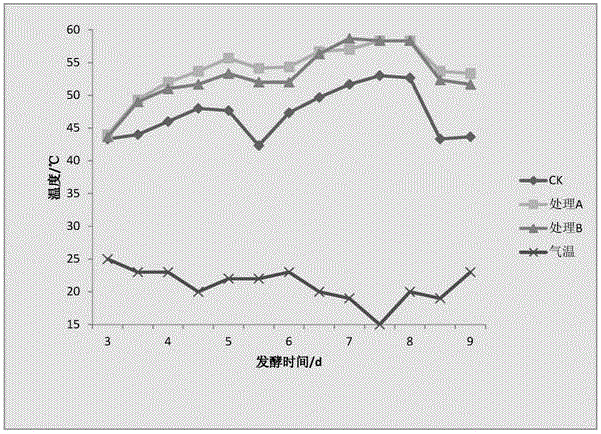
[0035] Embodiment 1: Isolation, cultivation, identification and degradation characteristics of Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) NFB7 (preservation number: CGMCCNO.11927)
[0036] 1. Materials and methods
[0037] 1.1 Test materials
[0038] Edible mushroom residues are collected from Pleurotus eryngii mushroom residues that are naturally stacked in Tongzhou Yongle Store, Beijing.
[0039] 1.2 Culture medium type
[0040] ① Enrichment medium formula: peptone 10.0g, K 2 HPO 4 1.0g, Na 2 CO 3 5.0g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.1g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.015g, MnSO 4 0.05g, yeast extract 10g, distilled water 1000mL, pH6.0.
[0041] ② LB solid medium formula: yeast extract 5g, NaCl 10g, peptone 10g, water 1000mL, agar 18g, pH 7.0.
[0042] ③Carboxymethylcellulose sodium medium (CMC-Na medium) formula: carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na) 15.0g, yeast 1.0g, NH 4 PO 3 1.0g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.5g, K 2 HPO 4 1.0g, 18g agar, 1000mL distilled water.
[0043] ④ Liquid seed medium formu...
Embodiment 2
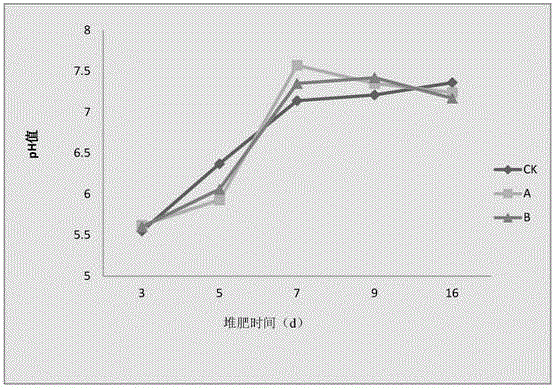
[0091] The composting effect of embodiment 2 bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) NFB7 bacterial strain to mushroom slag cultivation Agaricus bisporus
[0092] 1 Materials and methods
[0093] 1.1 Experimental materials
[0094] Bacterial agent: (NFB7+BCB4+BCB2) mixed bacterial agent, which is composed of NFB7 (preservation number: CGMCCNO.11927), BCB4 (preservation number: CGMCCNO.11141) and BCB2 (preservation number: CGMCCNO.11140).
[0095] The preservation number is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) BCB4 with the preservation number CGMCCNO.11141, which was preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microbial Cultures on July 21, 2015, address: Beichen West Road 1, Chaoyang District, Beijing No. 3 Courtyard, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zip Code 100101.
[0096] The preservation number is Bacillus tequilensis BCB2 with the preservation number CGMCCNO.11140, which was preserved in...
Embodiment 3
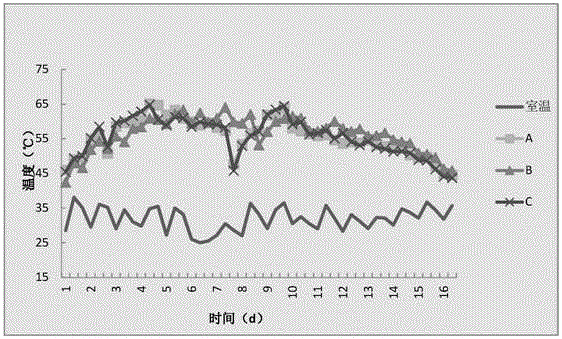
[0124] The fertility effect of embodiment 3 bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) NFB7 bacterial strain to slag compost
[0125] 1 Experimental materials and methods
[0126] 1.1 Experimental materials
[0127] Collect the discarded fungus bags after Bailing mushroom and Lentinus edodes are cultivated, and use the bag breaking machine to remove the bags and crush them for later use. Add 0.23 tons of dry cow dung and 5 L of (NFB7+BCB4+BCB2) mixed bacteria agent per ton of fungus residue (wet).
[0128] 1.2 Experimental method
[0129] The ratio of the slag of Bailing mushroom to that of shiitake mushroom is roughly 1:1, and the moisture content of the stock is preferably 65%-70%. When the temperature in the pile rises to 60°C and is maintained for 24 hours, the second turning is carried out. After that, turn over the pile every 2-3 days until the temperature no longer rises. Be sure to turn the pile evenly and thoroughly so that it can fully rot. If the material is found t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com