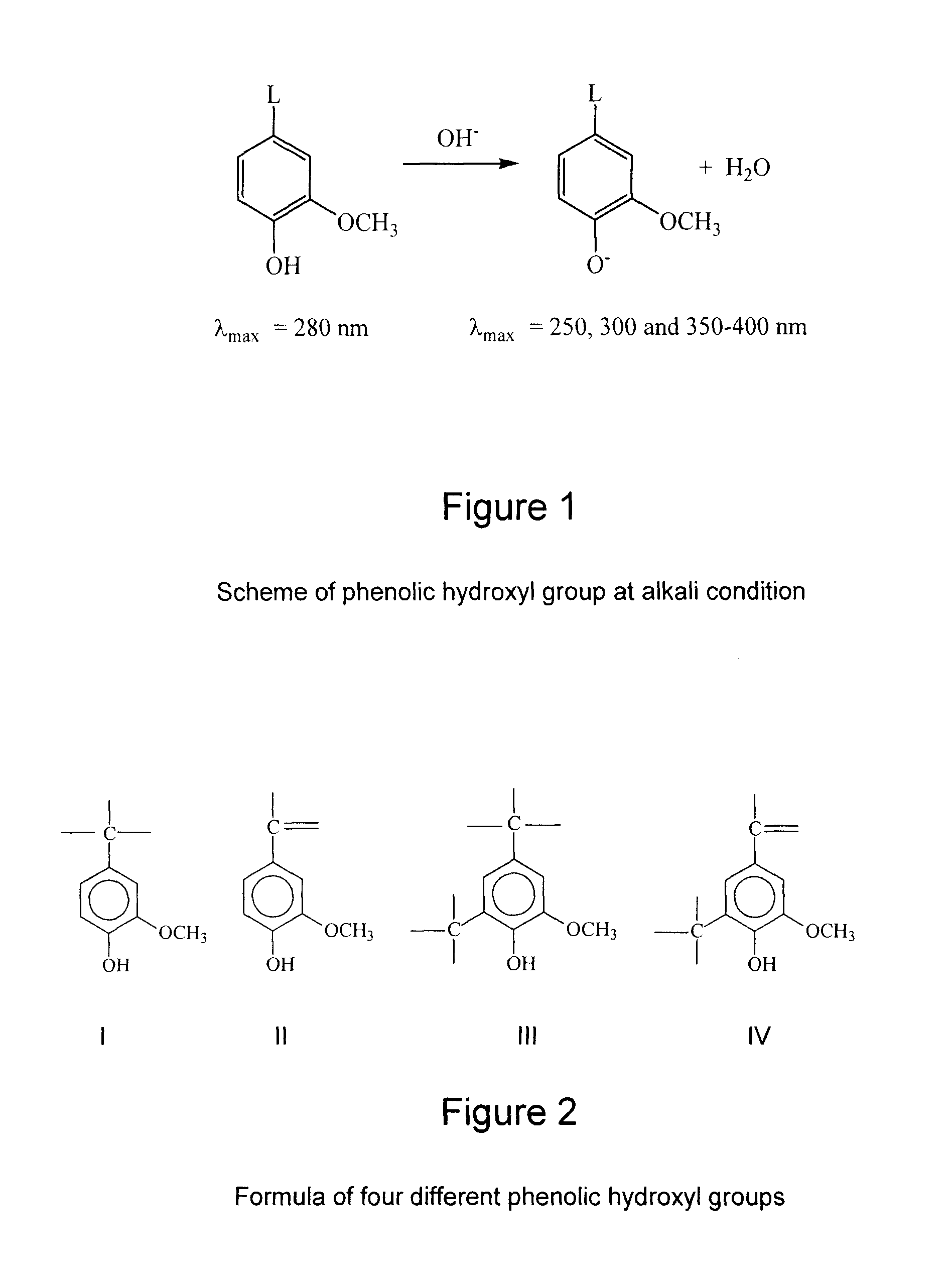
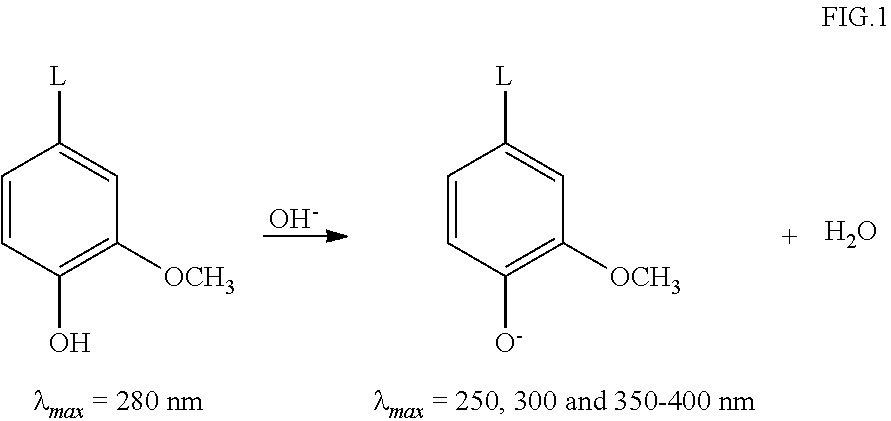
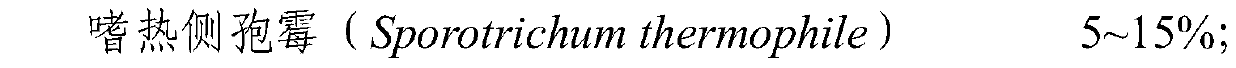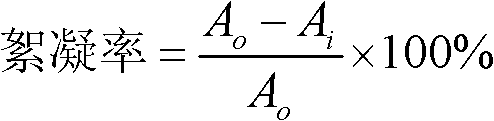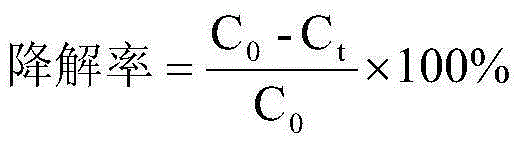Patents
Literature
57 results about "Phanerochaete" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phanerochaete is a genus of crust fungi in the family Phanerochaetaceae.
Preparation method for sludge aerobic composting composite inoculum
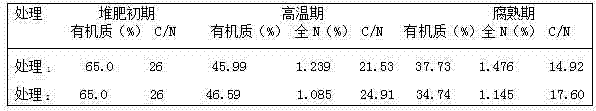
ActiveCN104293694APromote degradationPromote growth and reproductionFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisSludge
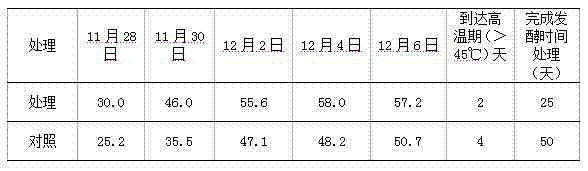
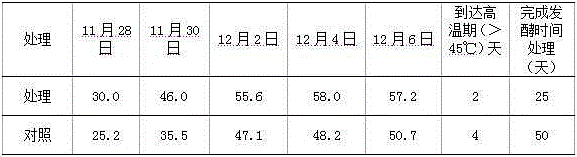
The invention discloses a preparation method for a sludge aerobic composting composite inoculums. According to the method, the Bacillus subtilis (No. 10066), the Bacillus licheniformis (No. 10103), the Lactobacillus acidophilus (No. 6075), the Candida utilis (No. 31272), and the Phanerochaete chrysosporium (No. 40719) that are preserved in China Center of Industrial Culture Collection (CICC) are subjected to individual culture, and are then mixed in proportion and inoculated into a fermentation culture to perform expanded culture, thus obtaining the composite inoculum. At the initial stage of inoculating the composite inoculums to sludge aerobic composting, the time for the compost body to reach a high temperature period is advanced by 4-6 days, the compositing period is shortened by 11-14 days, the stack moisture content is decreased by 18%-25%, and the total nitrogen content of the compost body is increased by 15%-20%, thus improving the composting effect.
Owner:GUANGXI BOSSCO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Crop straw decomposing inoculant and using method and effect thereof
ActiveCN103966150APromote repairImprove disease resistanceBio-organic fraction processingFungiBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
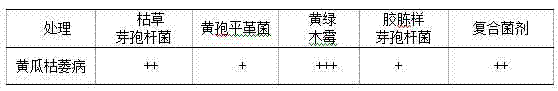
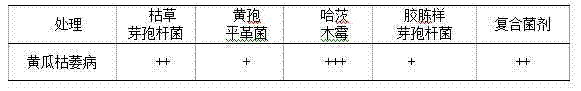
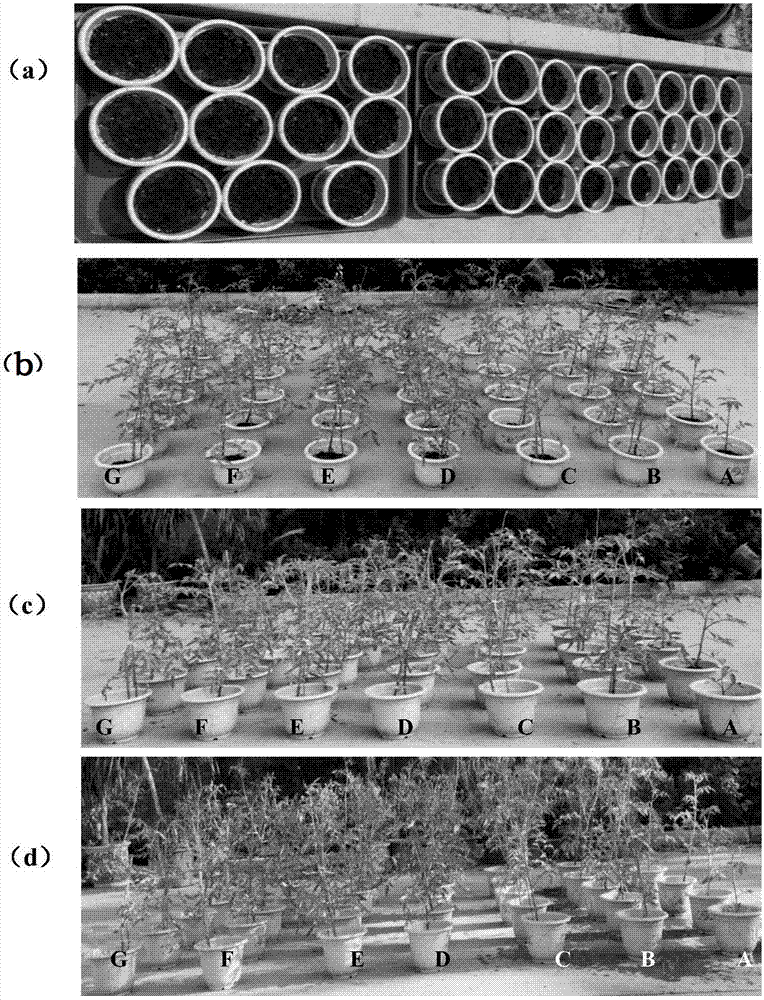
The invention discloses a crop straw decomposing inoculant and application in straw bioreactor and water-logged compost. The inoculant is compounded of 0.5-2 parts of phanerochaete chrysosporium, 0.5-2 parts of trichoderma aureoviride, 0.5-2 parts of bacillus subtilis and 0.5-2 parts of bacillus mucilagimosus krassilm, wherein the effective viable count is 6*10<8> per gram. The straw decomposing inoculant is applied to a tomato stalk bioreactor planting technology, and the average ground temperature is 18.3 DEG C and is increased by 2.2 DEG C as compared with that of contrast without use of the inoculant; the average greenhouse temperature is 14.3 DEG C and is increased by 2.0 DEG C as compared with the average greenhouse temperature of the contrast; the average CO2 concentration is 956ppm and is 2.17 times higher than that of the contrast; the harvest time is 15 days earlier than the harvest time of the contrast; the acre yield is 5881kg and is increased by 22.7 percent as compared with the acre yield of the contrast; the occurrence rate of plant diseases and insect pests is lower as compared with that of the contrast. The inoculant is applied to wheat straw retting and decomposing, is high in decomposition speed, high in compost flexibility, the straws are basically decomposed, and the fermentation time is shorter than that of an inoculant purchased in the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Vegetable waste composting bacterial agent, using method thereof and organic substrate prepared from vegetable waste composting bacterial agent
ActiveCN103966148AIncrease contentPromote repairPlant growth regulatorsBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a vegetable waste composting bacterial agent, a using method thereof and an organic substrate prepared from the vegetable waste composting bacterial agent. The vegetable waste composting bacterial agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1-3 parts of phanerochaete chrysosporium, 1-3 parts of trichoderma harzianum, 1-3 parts of bacillus subtilis and 1-3 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, wherein the effective viable count of the complex bacterial agent is up to 4*10<8> / g. The vegetable waste composting bacterial agent can be used for fermenting and composting vegetable wastes and resisting to cucumber fusarium wilt and has the fermentation period of 25 days for treating vegetable wastes and more than 50 days for treating uninoculated vegetable wastes. The organic substrate is prepared through fermenting by using a special process after adding 1kg of composting bacterial agent into every 5 cubic meters of vegetable wastes, wherein the vegetable wastes comprise the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of eggplant straw, 20-40 parts of cucumber vine, 5-15 parts of Chinese cabbage leaves and 5-15 parts of brown coal, wherein the organic substrate can be used as a seedling substrate of tomatoes, has the emergence rate of 92% and has the same effect as a seedling substrate sold on the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Straw decomposing inoculant
InactiveCN102146341AEasy to operateLow costMicroorganismsOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a straw decomposing inoculant which comprises the following components of 0.2-1.5 billion / g of bacillus subtilis, 0.2-1.5 billion / g of bacillus licheniformis, 20-150 million / g of thermophilic sporotrichosis, 20-150 million / g of Trichoderma Koningii and 20-150 million / g of Phanerochete chrysosporium. Therefore, the straw decomposing inoculant has the advantages of low cost and short decomposing time and is practical and easy to operate.
Owner:东莞市天盛生物科技有限公司
Composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste. The composite microbial agent is composed of composite bacterial liquid and a carrier, wherein the composite bacterial liquid comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus siamensis, Bacillus tequilensis and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. The bacterial strains of the composite microbial agent produce synergism, so the composite microbial agent can substantially degrade a variety of macro-molecular components in the garden waste, improve the decomposition degree of the waste, enhance the nutrient structure and microfloras of compost and reduce heavy metal pollution. The invention also relates to a preparation method for the composite microbial agent, a method for degrading and converting the garden waste by using the composite microbial agent and fertilizer prepared from products obtained after degradation and conversion of the garden waste with the composite microbial agent.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Compound microbial preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104313008AToxicAnti-bacteriaWater contaminantsOn/in organic carrierBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
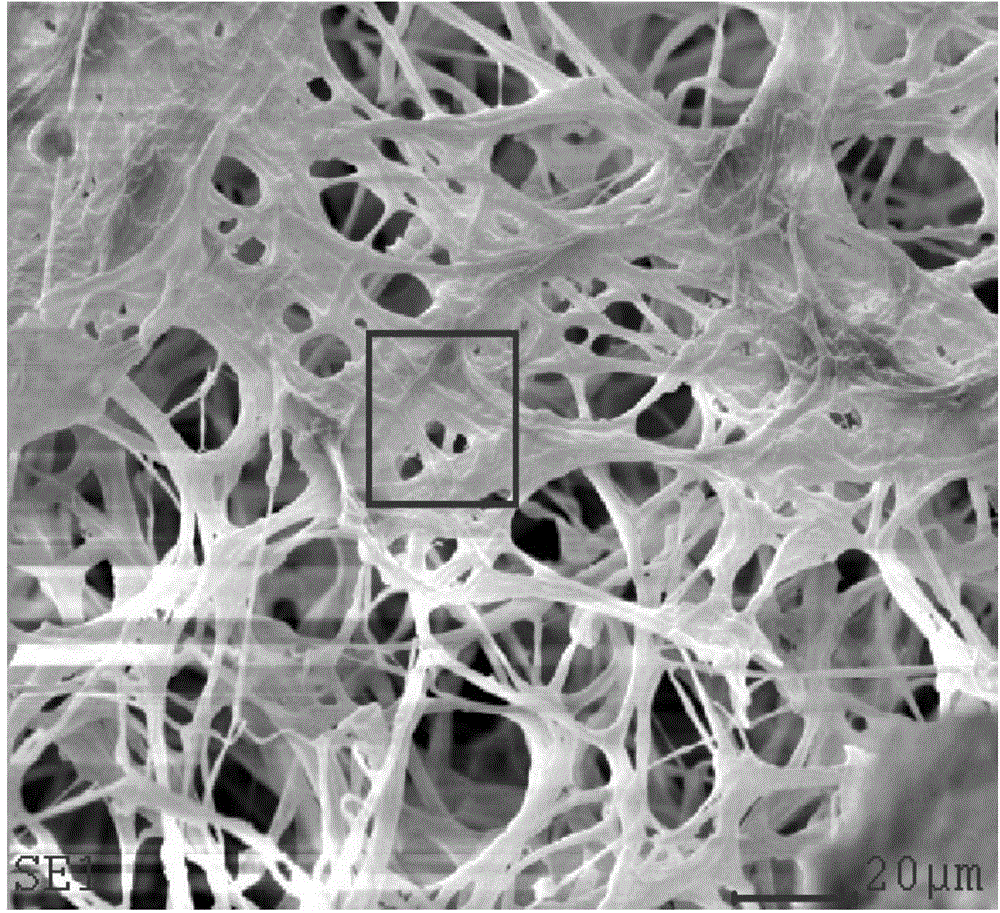
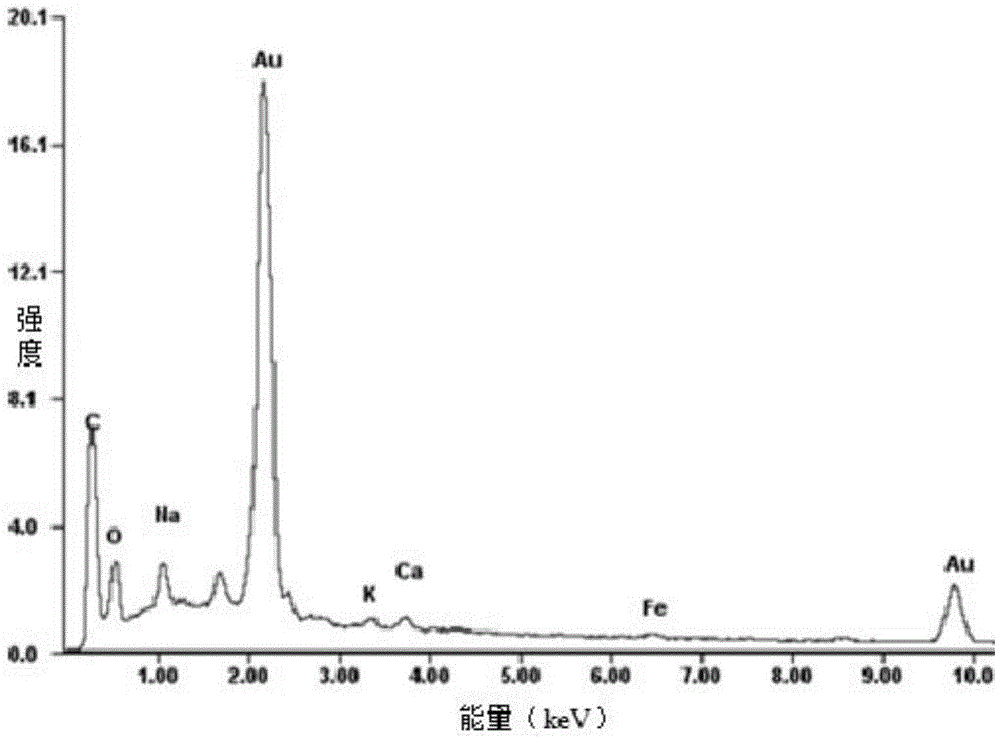
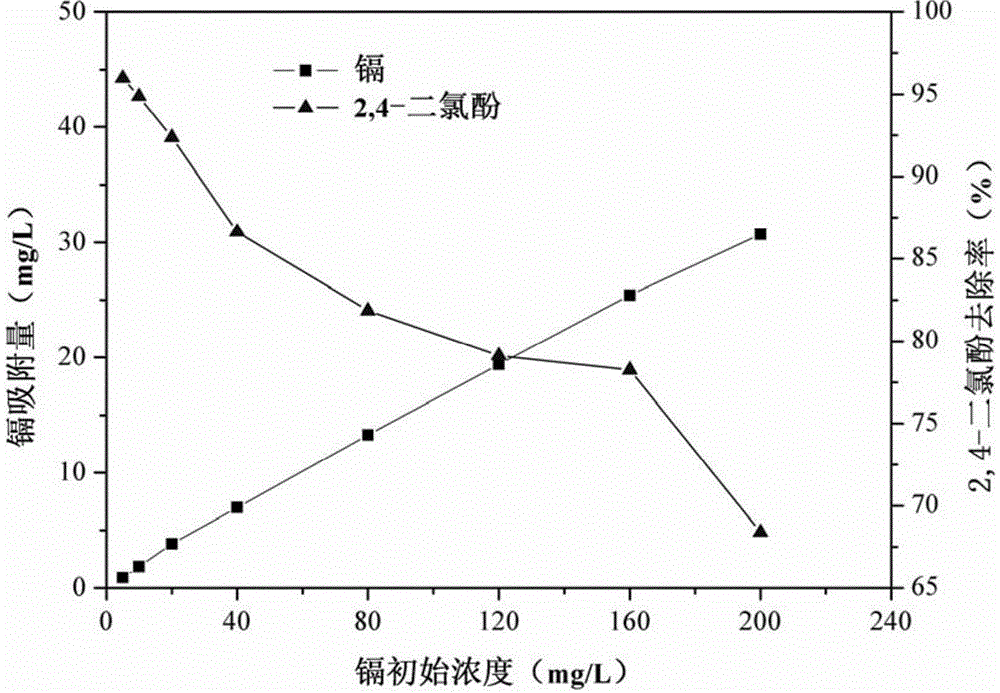
The invention discloses a compound microbial preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation comprises phanerochaete chrysosporium balls, polyvinyl alcohol, silicon dioxide, activated carbon, sodium alginate and zeolite powder, which form the compound microbial preparation through crosslinking by a solution with sodium dihydrogen phosphate. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing a gel liquid with the polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate, silicon dioxide and zeolite powder, mixing with a phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension with the activated carbon, then gradually dripping into the solution with the sodium dihydrogen phosphate so as to prepare embedded balls, and cultivating by a Kirk inorganic culture solution so as to prepare the compound microbial preparation. The compound microbial preparation has many gaps, high adsorption efficiency and good selectivity, the adsorbent has strong stability, the preparation method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, affordability and so on, and the compound microbial preparation can be used for eliminating cadmium and 2, 4-dichlorophen in waste water.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as preparation method and application of complex microbial agent
ActiveCN109852557APromote degradationAltered ion valence diseaseFungiBacteriaMicrobial agentPseudomonas putida
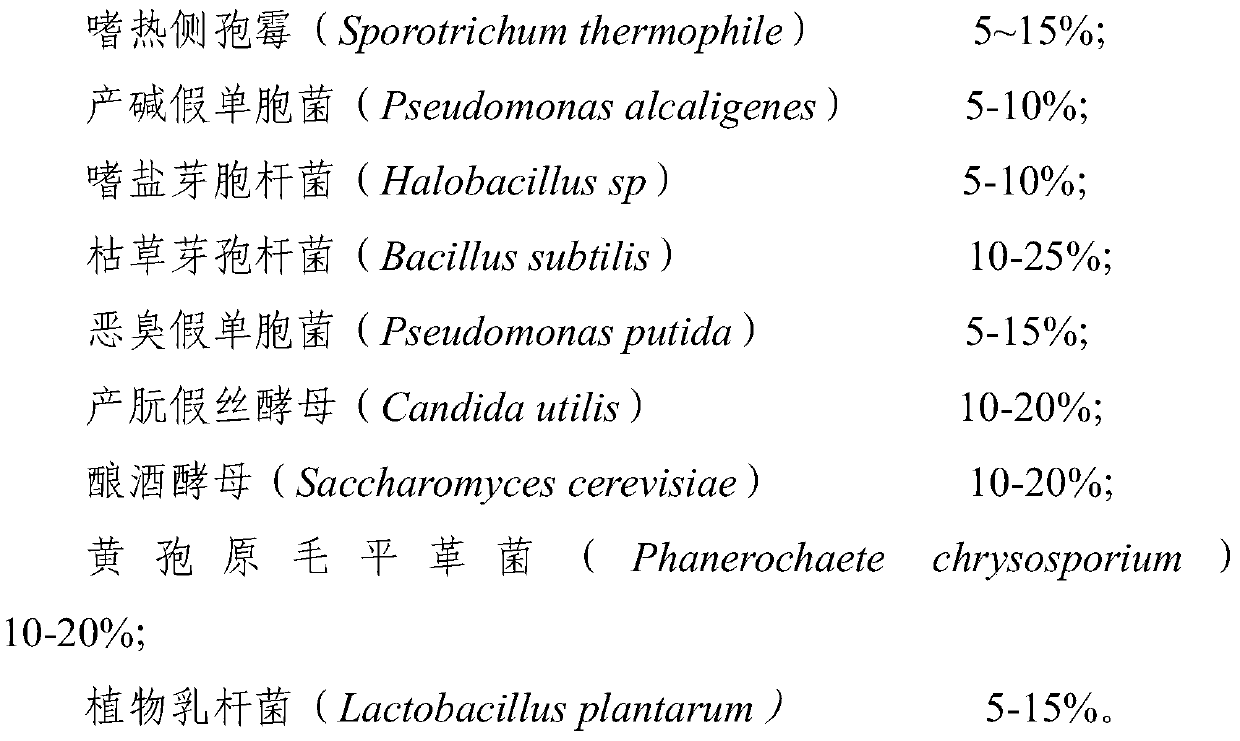
The invention provides a complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as a preparation method and an application of the complex microbial agent. The complex microbial agent contains sporotrichum thermophile, pseudomonas alcaligenes, halobacillus sp, bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, phanerochaete chrysosporium and lactobacillus plantarum. Growth metabolism, degradability and activity of all microbial strains in the complex microbial agent can effectively complement and cooperate with one another, the microbial strains can grow and propagate quickly in a landfill system to promote the temperature of a garbage treatment environment to increase quickly, meanwhile, organic matter, BDM and toxic andharmful substances in a landfill can be quickly and efficiently degraded, the stabilizing time of the garbage landfill is greatly shortened, stable harmless treatment of landfill is promoted, and thecomplex microbial agent can be applied to aerobic stabilizing treatment of garbage in cities and towns in practice.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
Biosynthesis method of cadmium sulfide quantum dot
InactiveCN102965406AGood biocompatibilityGood monochromaticityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhanerochaeteThio-
The invention discloses a Biosynthesis method of a cadmium sulfide quantum dot. The method comprises the following steps of: on the basis of taking thioacetamide as an S source, water soluble cadmium salt as a Cd source, a sulfhydryl compound as a stabilizer and a phanerochaete chrysosporium mycelium pellet as an adsorbent, adding the S source, the Cd source and the sulfhydryl compound into a culture solution which contains the phanerochaete chrysosporium mycelium pellet to carry out shake cultivation on a shaking table, and carrying out filtration, cleaning in deionized water, ultrasonication, centrifuging and purification after the cultivation to obtain the cadmium sulfide quantum dot. The method provided by the invention is simple in operation, low in cost and good in reproducibility; and the prepared cadmium sulfide quantum dot has the characteristics of low toxicity, good biocompatibility and excellent optical property.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Process for fungal modification of lignin and preparing wood adhesives with the modified lignin and wood composites made from such adhesives
Disclosed herein are method to modify the lignin with particular fungal species, and procedure to synthesize phenolic adhesives with the modified lignin as raw materials, and the adhesives compositions and methods for making adhesive compositions, and methods for making lingo-cellulosic composites from renewable materials. Four fungi in examples are Lenzites elegans (Spreng.) Pat. (FTK 329A), Phanerochaete cremea (Bres.) Parmasto (FTK 332A), Pycnoporellus alboluteus (Ellis & Everh.) Kotl. & Pouz. (FTK 76A) and Meruliopsis taxicola (Pers.) Bondartsev (FTK 122B). Lignin used in examples are organosolv lignin, Kraft lignin, and ammonium lignosulfonate. The present invention includes methods to (1) modify of lignin with fungi; (2) in-situ polymerize modified lignin-phenol-formaldehyde to generate bio-modified lignin-phenol-formaldehyde adhesive in liquid form, and (3) manufacture composite panels with bio-modified lignin-phenol-formaldehyde resins.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Composite bacterial coal biological flocculant and method for purifying slime water by same
ActiveCN102874912ALess restrictiveWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationPhanerochaete
The invention relates to a composite bacterial coal biological flocculant which has the advantages of high flocculation rate, reduction in the limit of various factors on a flocculation effect and wider application range. The composite bacterial coal biological flocculant comprises aspergillus niger bacterial solution and phanerochaete chrysosporium bacterial solution at a volume ratio of 1 : 1, wherein the aspergillus niger bacterial solution and the phanerochaete chrysosporium bacterial solution respectively refer to culture stock solution obtained by culturing aspergillus niger and phanerochaete chrysosporium, the centrifugal supernate of the culture stock solution obtained by centrifuging the culture stock solution, broken solution obtained by breaking the culture stock solution or broken centrifugal supernate obtained by centrifuging the broken solution. The culture stock solution of the aspergillus niger and the culture stock solution of the phanerochaete chrysosporium are obtained by the following steps respectively: a, enrichment culture, b, adaptability culture, c, further enrichment culture, and d, activity culture.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
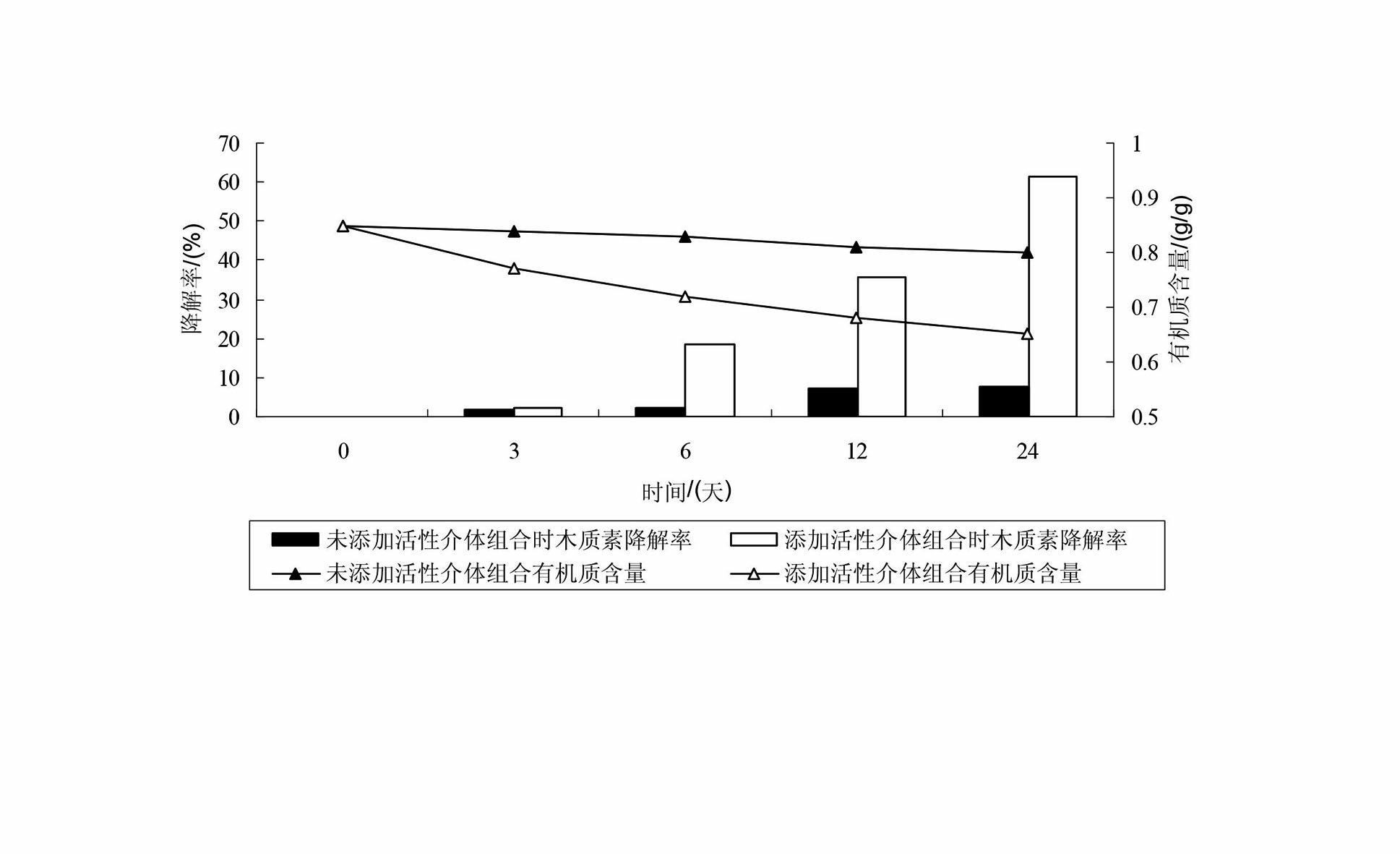
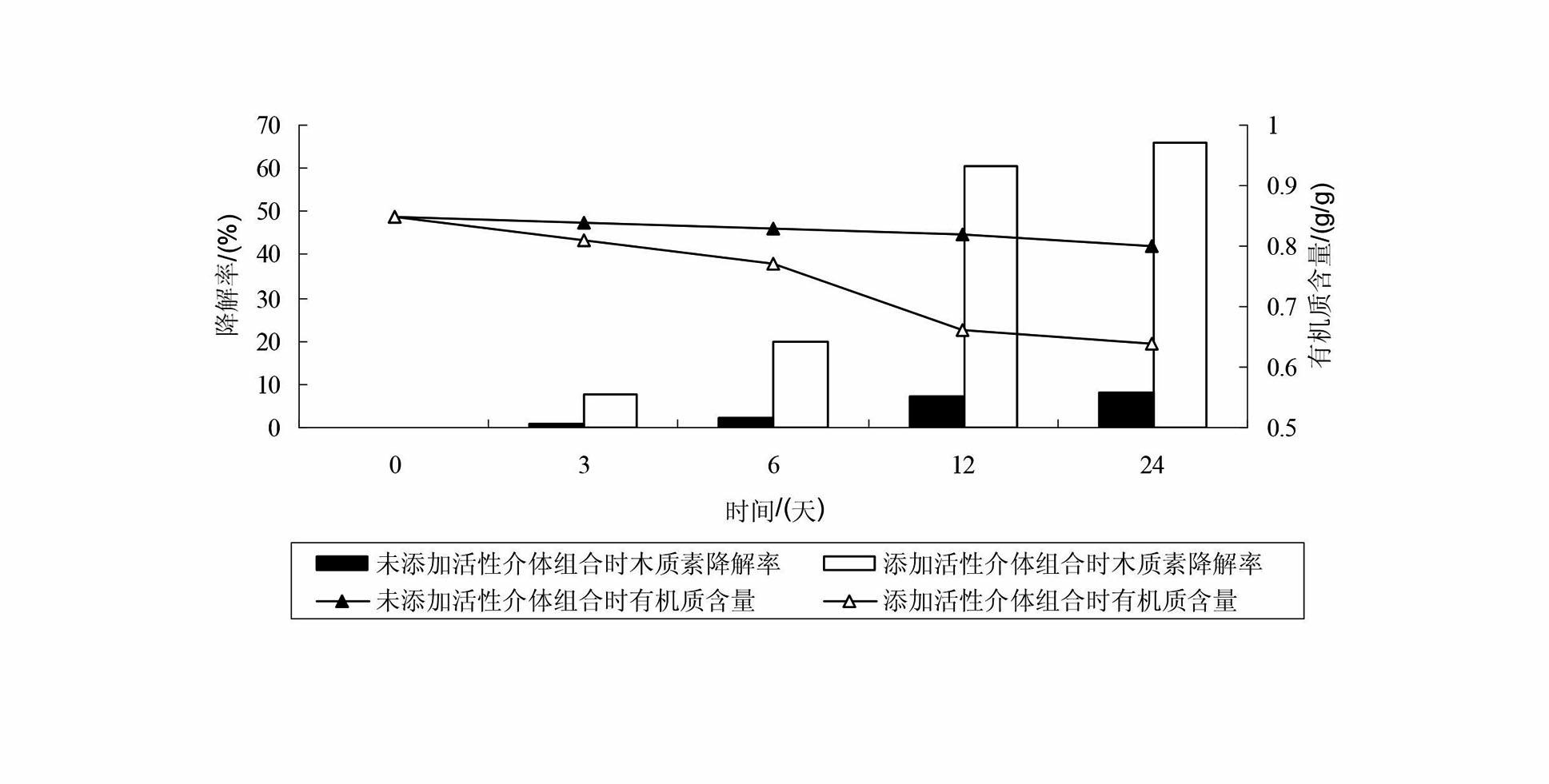
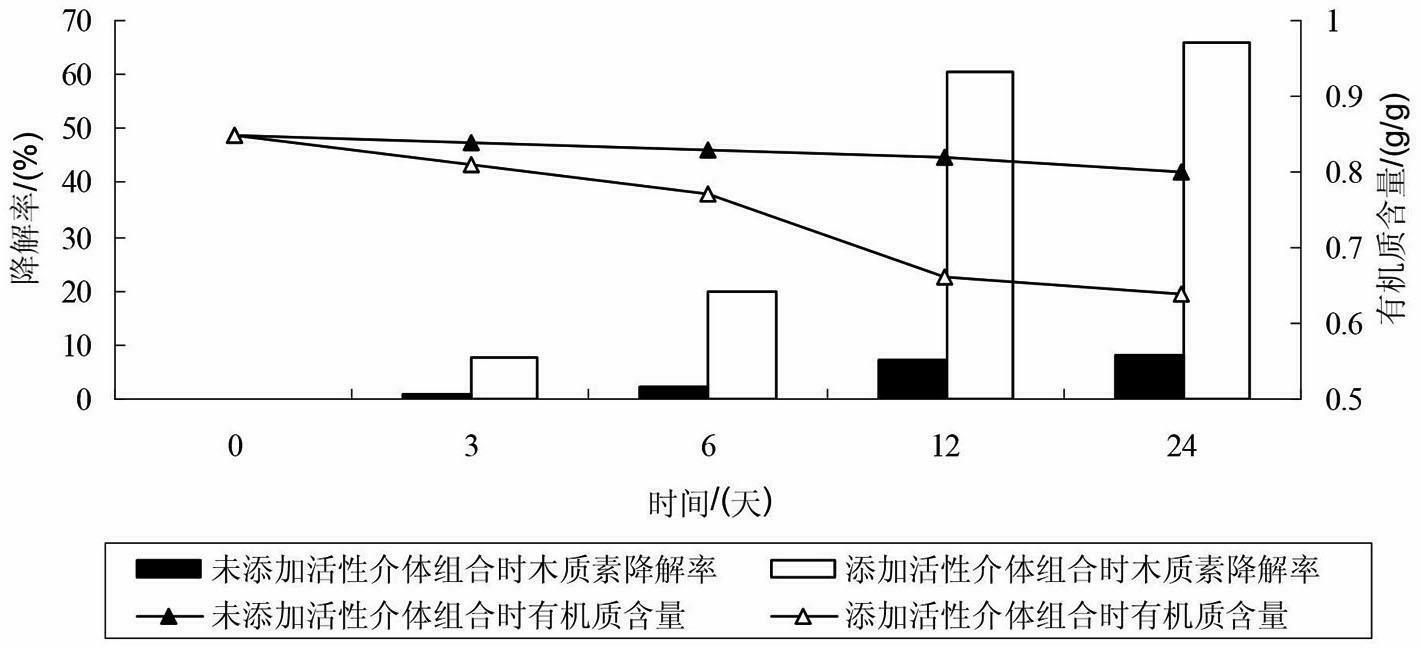
Method for promoting complex enzyme to catalyze degradation of straws by using active mediator combination
InactiveCN102559763AIncreased CorruptionPromote catalysisMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a method for promoting complex enzyme to catalyze degradation of straws by using active mediator combination, which includes the following steps: (1) preprocessing the straws: smashing the straws to obtain straw powder and sieving to be reserved; (2) preparing complex enzyme liquid: cultivating phanerochaete chrysosporium in liquid state to obtain the complex enzyme liquid; and (3) catalyzing degradation: adding the complex enzyme liquid into the straw powder, adding active mediator combination simultaneously, keeping warm, preserving moisture, and standing to finish degradation catalyzing. The method for degrading the straws improves enzymolysis rate of lignin in the straws, is favorable for decomposing and transforming and resource utilization of the straws, and is low in cost, simple in operation, low in operation cost, clean and free of pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
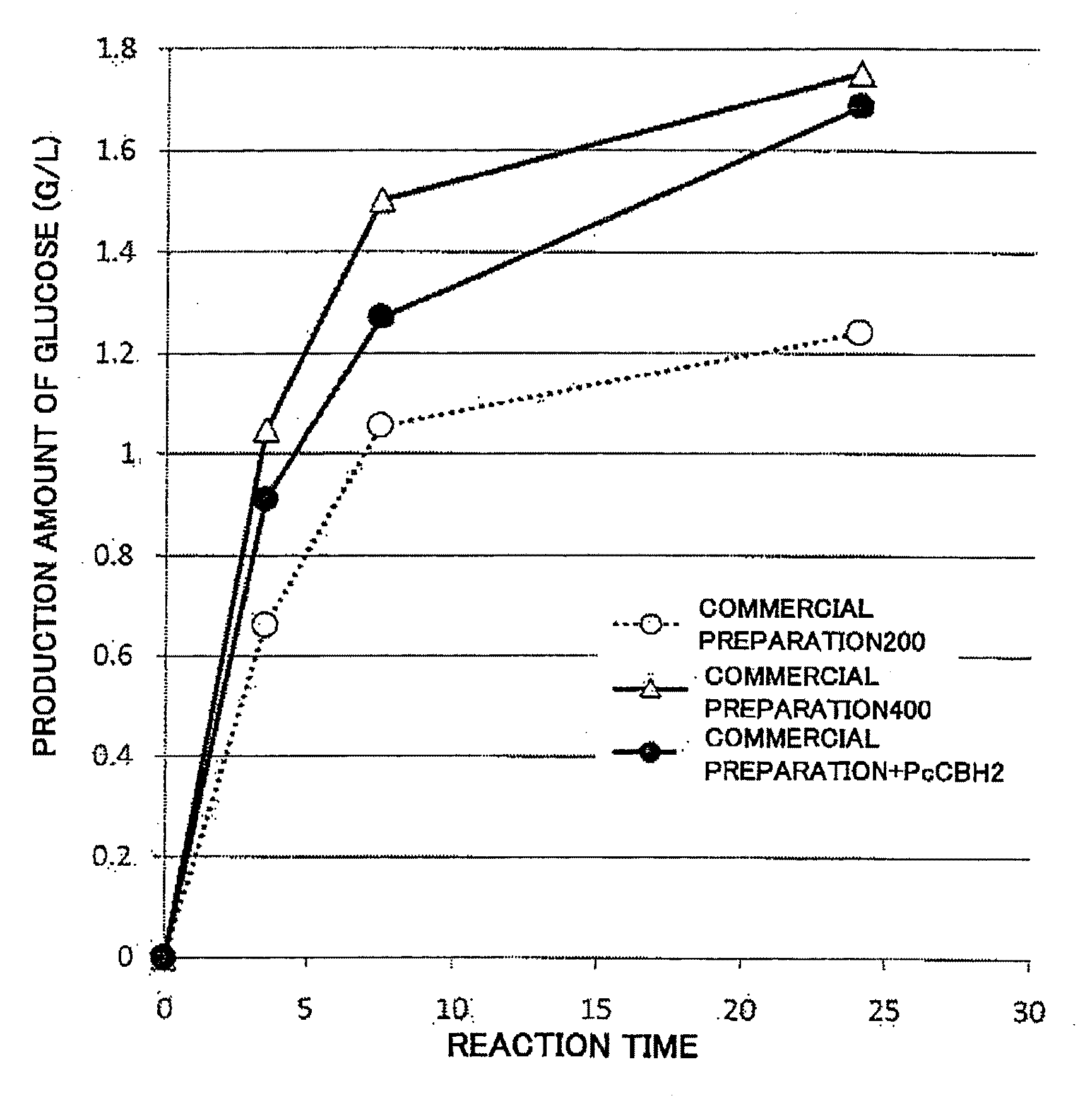
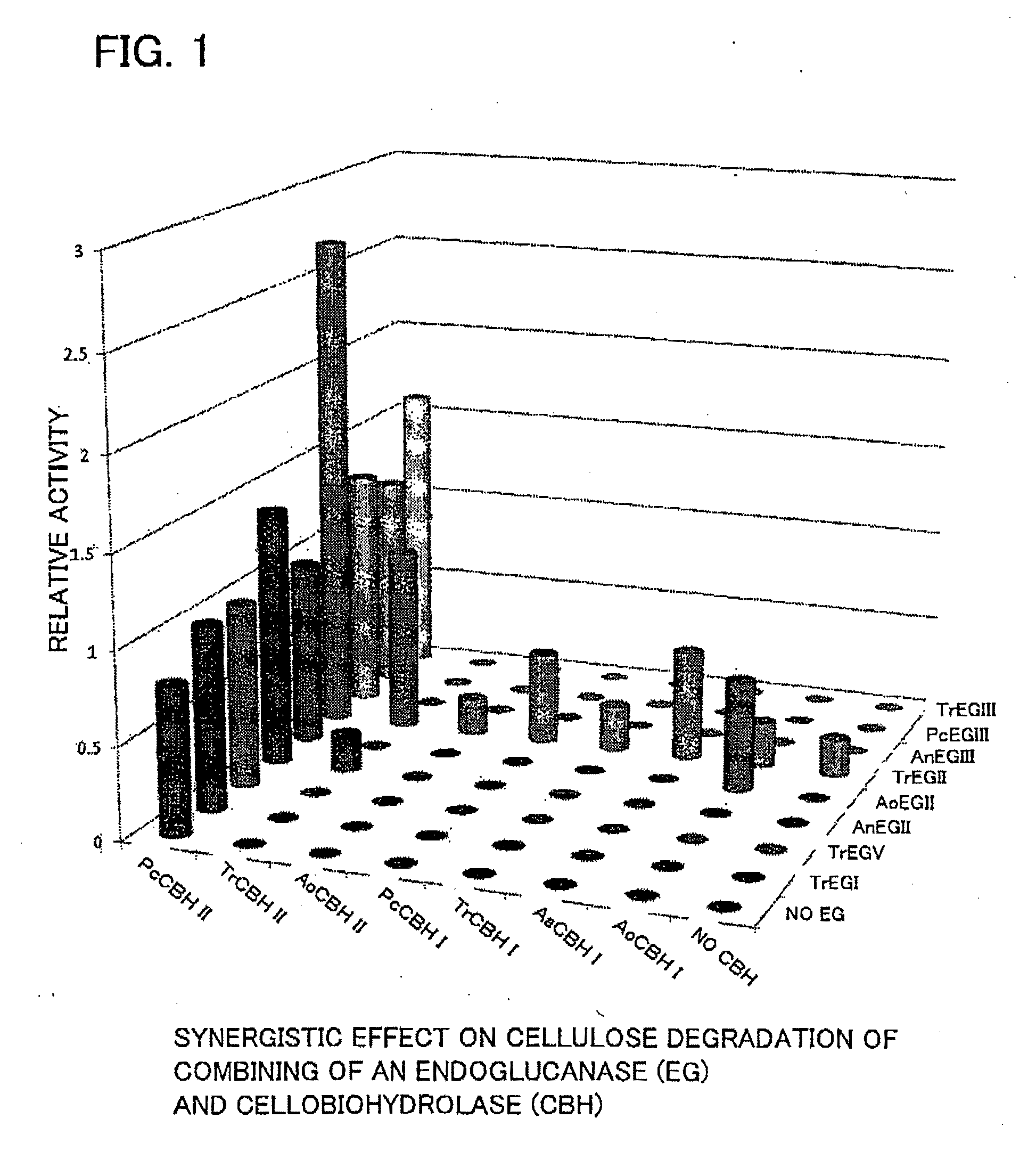
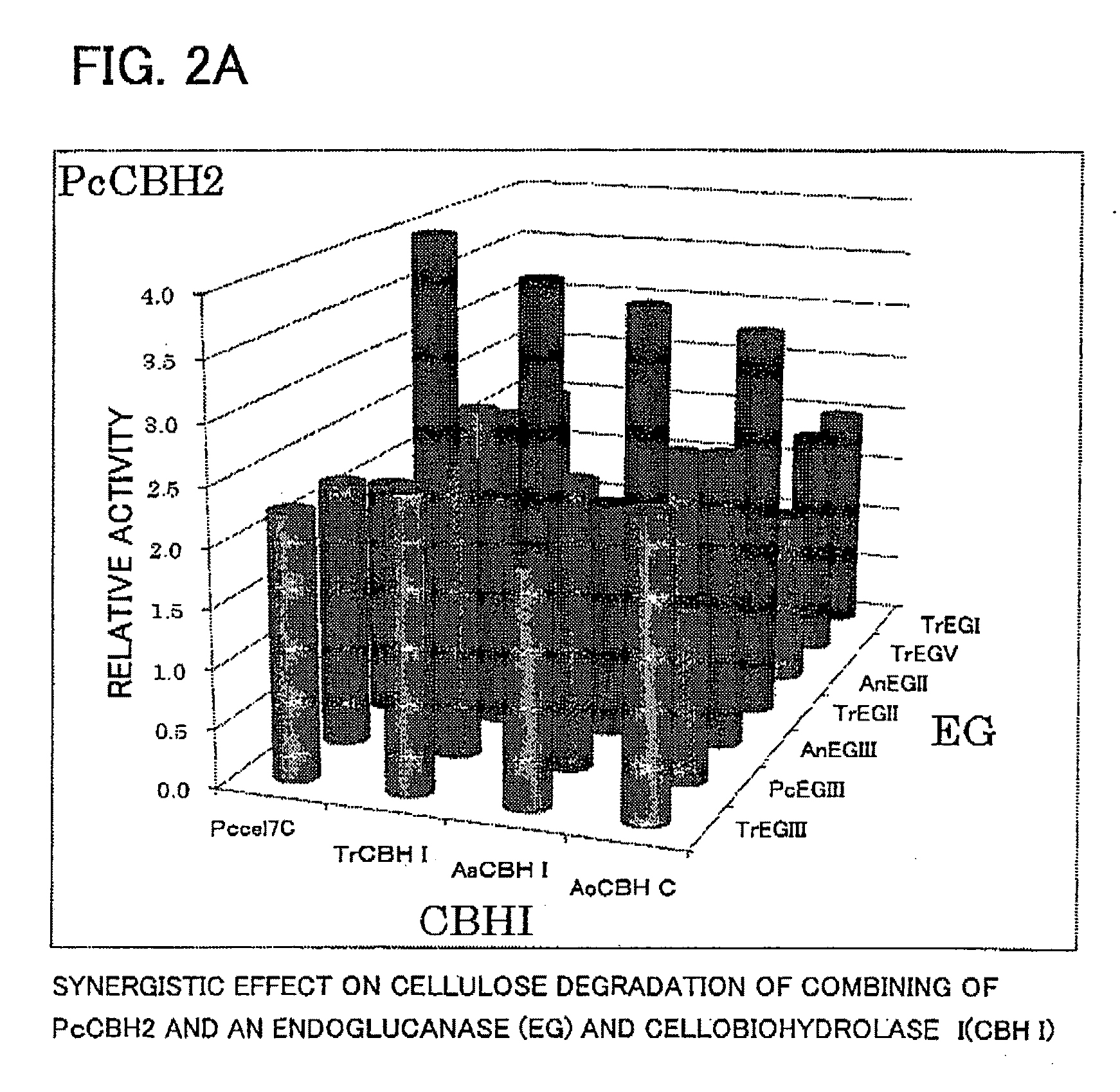
Use of cellobiohydrolase from phanerochaete
A cellobiohydrolase that can contribute to a synergistic effect on cellulose degradation and the use of such cellobiohydrolase in cellulose degradation are provided. The synergistic effect is achieved by an enzyme preparation for cellulose degradation containing a cellobiohydrolase originating in Phanerochaete chrysosporium and belonging to GHF6 or a variant thereof, and an endoglucanase originating in a different source other than Phanerochaete chrysosporium.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
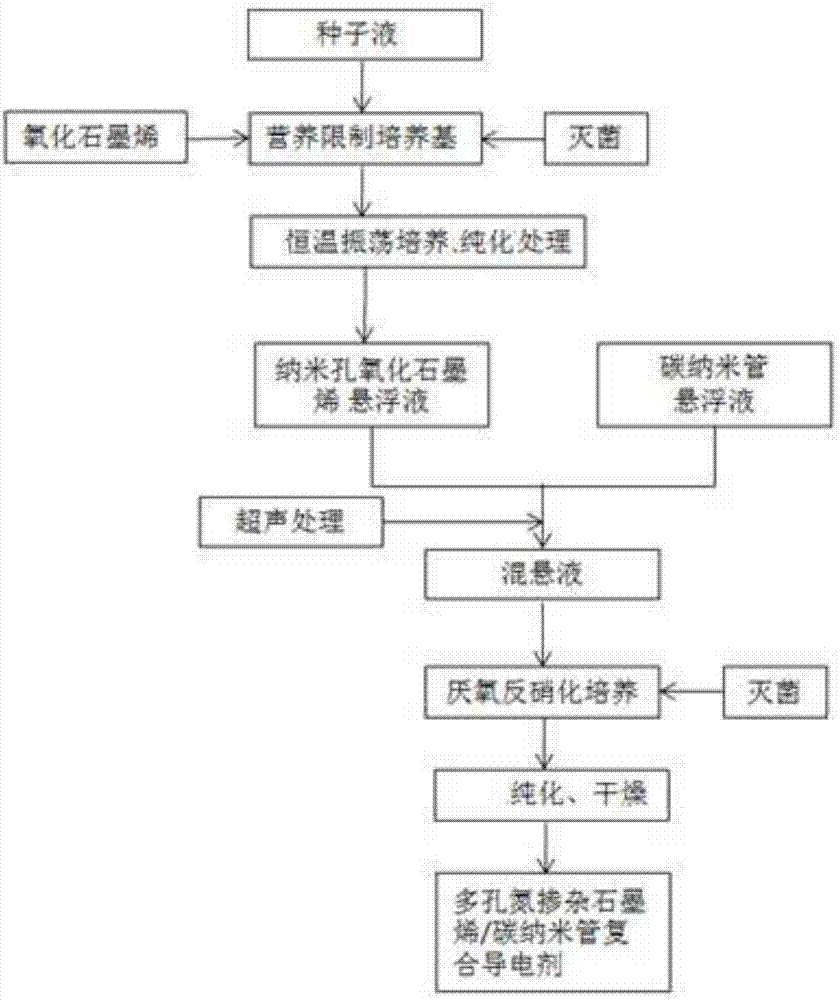
Preparation method of porous nitrogen-doped graphene/carbon nanotube composite conductive agent
InactiveCN107039656AMild reaction conditionsNo pollution in the processCell electrodesSecondary cellsDoped grapheneCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent. The preparation method comprises the steps of inoculating phanerochaete chrysosporium into a seed expansion culture solution for aerobic culture to obtain a seed liquid; adding the seed liquid and a graphene suspension liquid into a nutrition limitation culture solution, and dispersing the product subjected to constant-temperature shaking culture and processing in deionized water to obtain a nanopore graphene oxide suspension liquid; mixing the product and a carbon nanotube suspension liquid, performing ultrasonic processing, adding the mixed suspension liquid to an anaerobic denitrifying bacteria culture solution, and inoculating denitrifying bacteria seed liquid for anaerobic culture to obtain the porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent. A two-step green preparation method is employed, a toxic reagent is not used, the preparation method has the advantages of moderate and controllable reaction process and low cost, and is easy to promote, and the prepared porous nitrogen-doped graphene / carbon nanotube composite conductive agent can be widely applied into the fields of a lithium ion battery and the like.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Genetically engineered bacterium and applications thereof
InactiveCN104593279AHighly soluble polysaccharide monooxygenase 10320 secretion capacityFacilitated releaseFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityCellulose
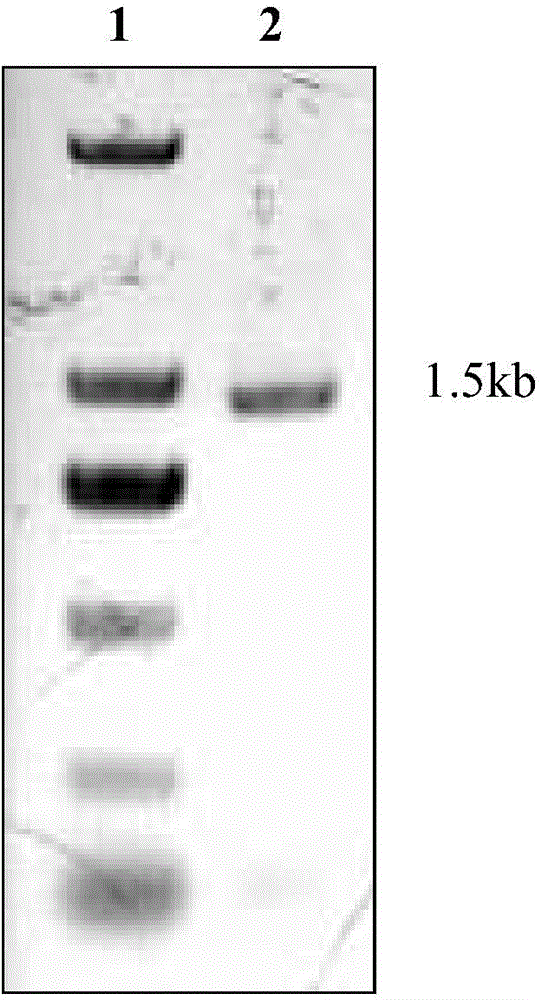
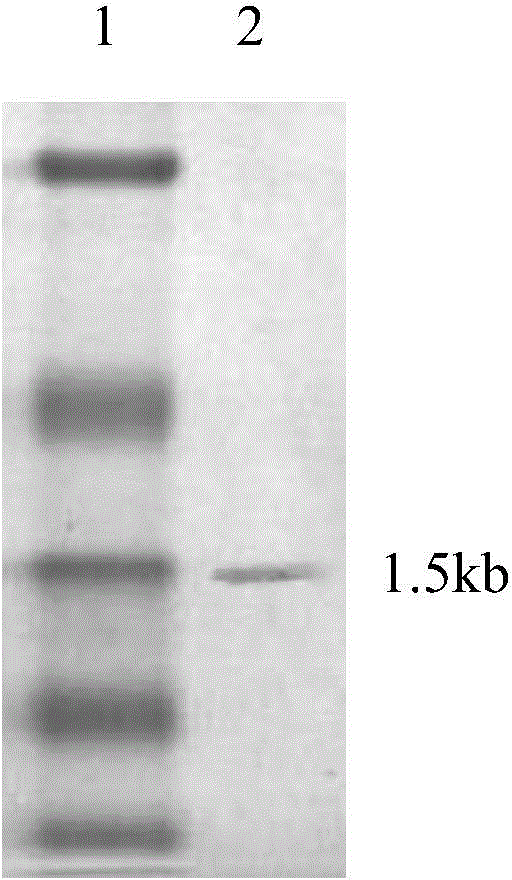
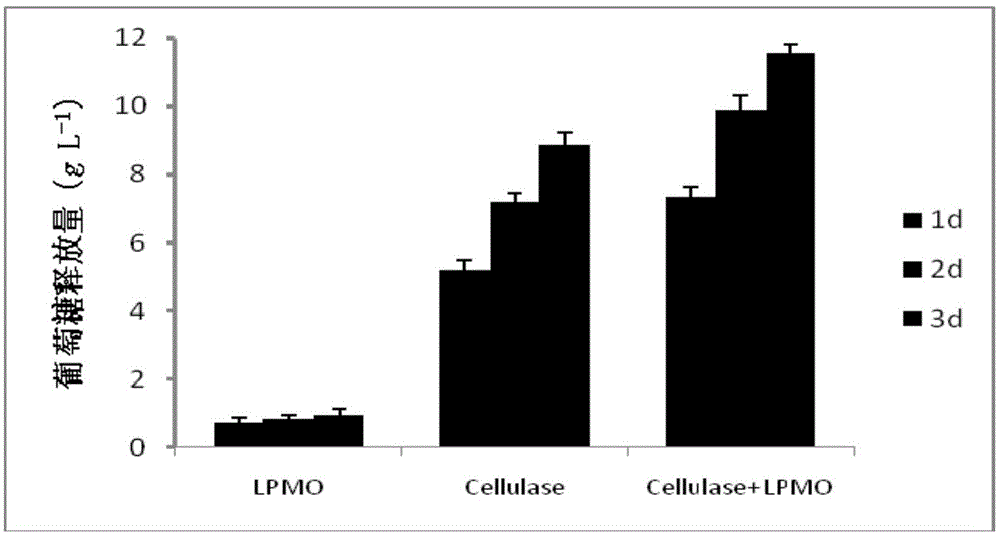
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium which comprises a host cell and a target gene transferred into the host cell, and the genetically engineered bacterium is characterized in that the target gene is an encoding gene of phanerochaete chrysosporium LPMO (lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases). The invention also discloses a construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium in degrading raw materials such as celluloses. The genetically engineered bacterium provided by the invention has a high CBM module containing LPMO (LPMO10320) secretion capacity, and the secretion capacity can reach 1.39mg / ml; and when the genetically engineered bacterium is applied to the degradation treatment of raw materials such as celluloses, the degradation velocity and degree of the celluloses can be improved, the generation amount of glucose can be increased, and compared with endogenously expressed phanerochaete chrysosporium, the generation amount is increased by nearly 100 times.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
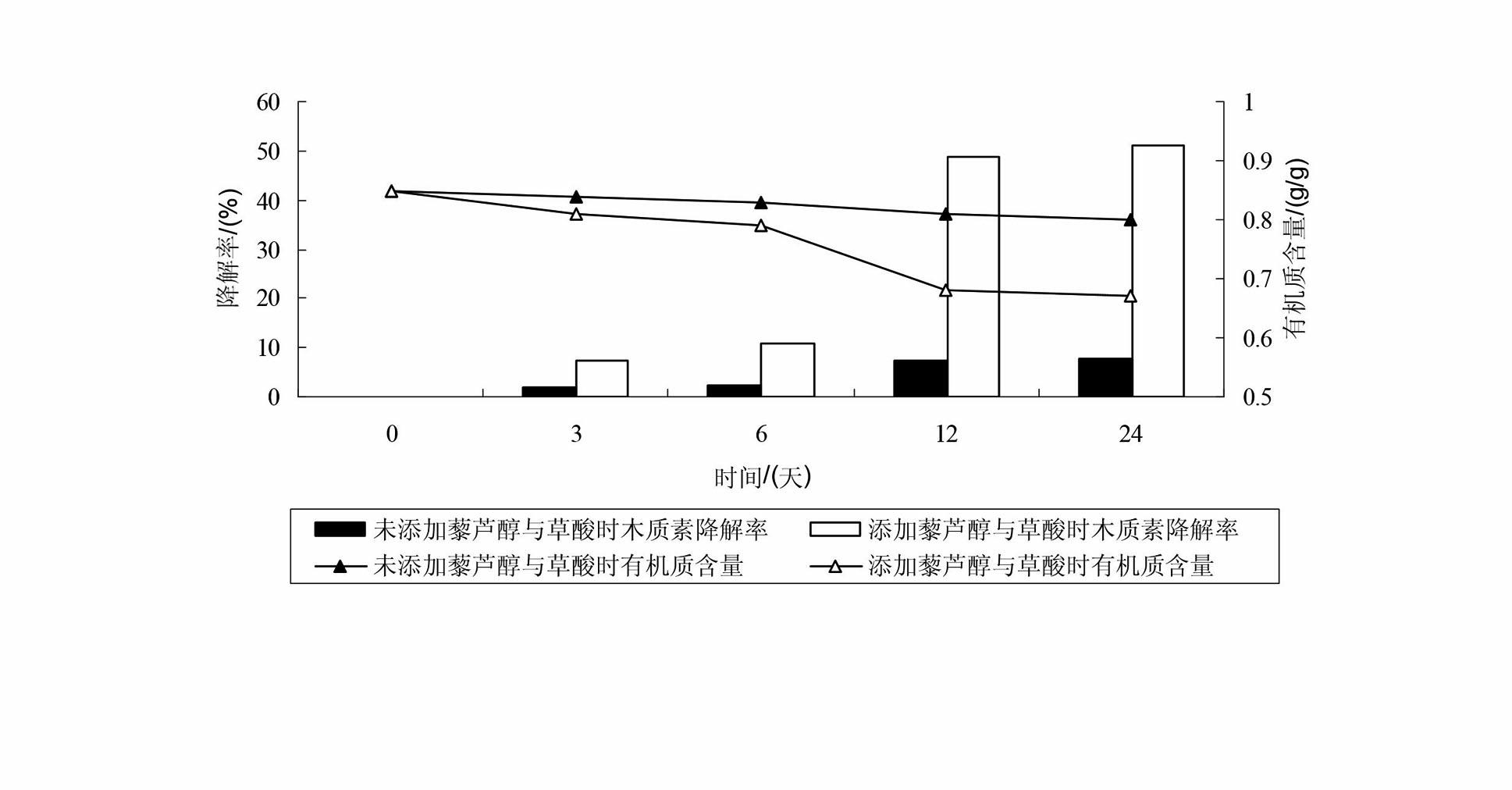
Method for promoting composite enzymes by utilizing resveratrol and oxalic acid to catalytically degrade rice straws
InactiveCN102559764AIncreased CorruptionImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
The invention discloses a method for promoting composite enzymes by utilizing resveratrol and oxalic acid to catalytically degrade rice straws, which comprises the following steps of: (1) straw pretreatment: crushing the rice straws to obtain straw powder and screening for standby; (2) composite enzyme liquid preparation: culturing phanerochaete chrysosporium in a liquid state to obtain composite enzyme liquid; and (3) catalytic degradation: adding the composite enzyme liquid in the straw powder, simultaneously adding resveratrol solution, oxalic acid solution and H2O2 solution, heat-insulating, moisturizing and standing to finish the catalytic degradation. The method for degrading the rice straws has the beneficial effects that the corruption speed of the rice straws is accelerated, the corruption degree of the rice straws is improved, the enzymolysis efficiency of lignin is improved, the usage amount of the composite enzymes can be effectively reduced, and the industrial production can be realized; and meanwhile, the method has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in operation, low running expense, cleanness and no pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Liquid preparation capable of degrading petroleum pollutants
InactiveCN105385645APromote degradationStrong complementarityFungiBacteriaPhanerochaeteBacterial strain
The invention discloses a liquid preparation capable of degrading petroleum pollutants. The liquid preparation consists of a fungus liquid cultural substance, a bacterial liquid cultural substance and a degradation accelerant, wherein the mixing ratio of the fungus liquid cultural substance and the bacterial liquid cultural substance is 1: (0.1 to 10); the fungus liquid cultural substance is a single plant liquid cultural substance of cunninghamella echinulata or white-rot fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium, or a mixture of the two fungus liquid cultural substances, the content of fungi in the fungus cultural substances is 10 to 80mg dry weight / ml; the bacterial liquid cultural substance is a liquid cultural substance of a bacterial strain with the capability of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation, and the bacterial content is 106 to 1012 pieces / ml; the degradation accelerant is barbaloin, and the concentration in the liquid preparation is 0.2 to 0.6mg / ml. The degradation accelerant provided by the invention can obviously improve the degradation ability of fungi and bacteria to the petroleum pollutants.
Owner:叶君芝
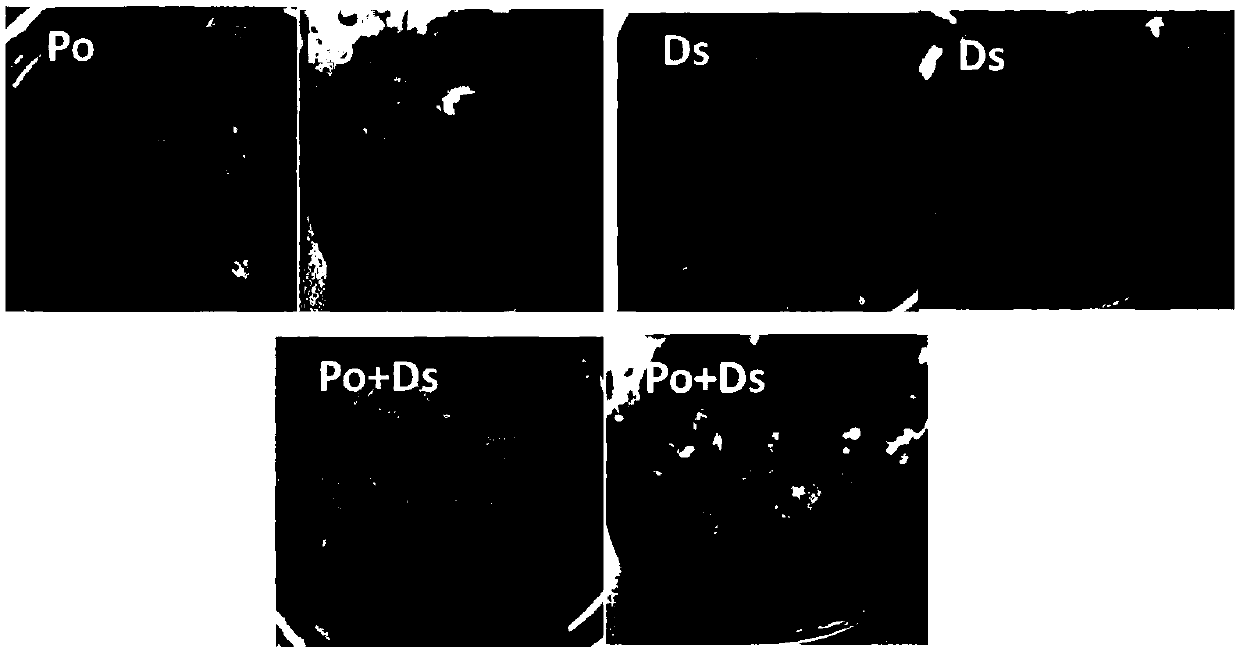
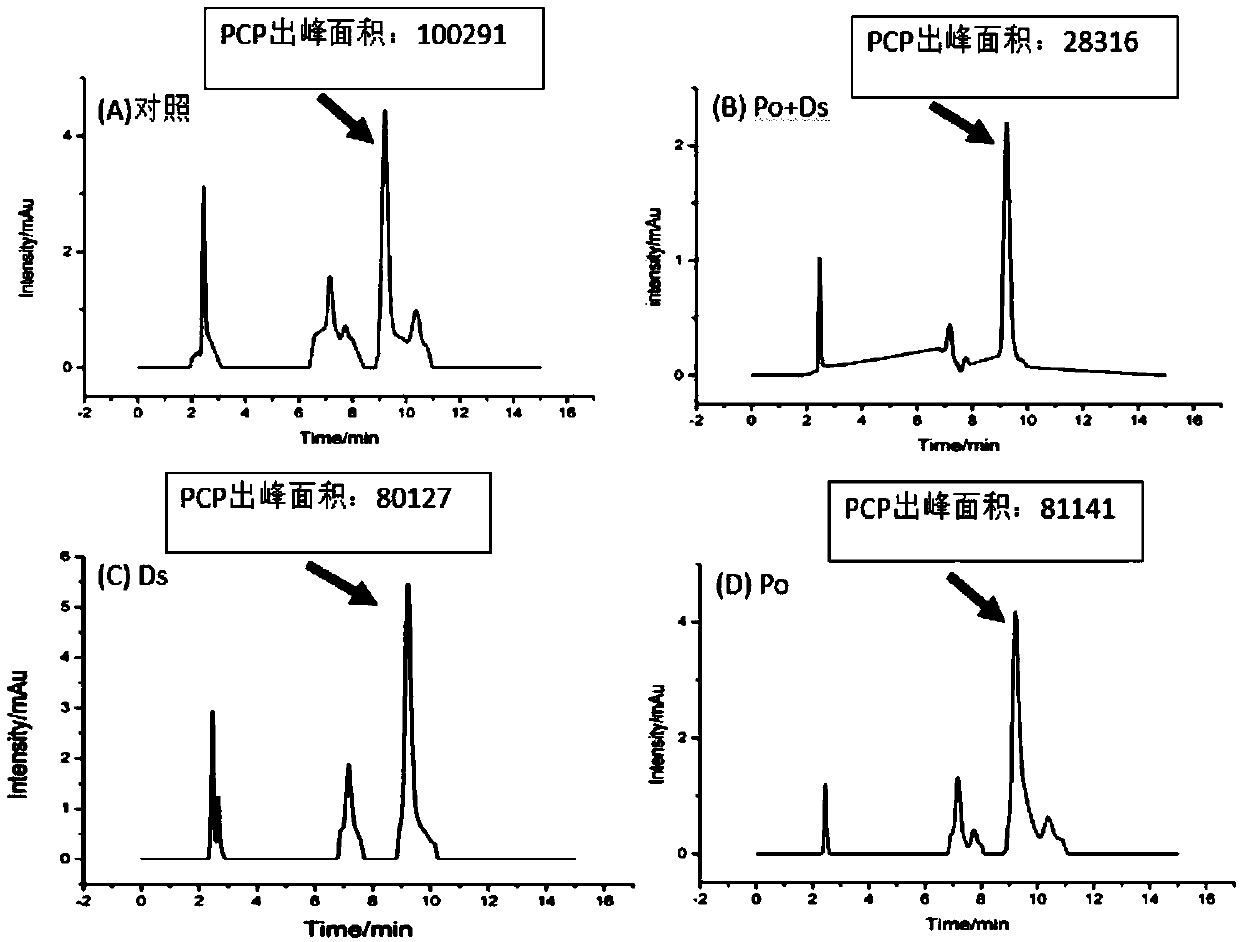
Soil remediation method based on pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium
InactiveCN110814018ANo secondary pollutionIncrease productionContaminated soil reclamationOxidoreductasesPentachlorophenolPhanerochaete
The invention belongs to the technical field of restoration of contaminated soil by a microbial method, and particularly relates to a soil remediation method based on pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium. In the soil remediation method, sterilized pine wood is used as a culture medium to cultivate pleurotus ostreatus and phanerochaete chrysosporium, and then a soil sample to be treated is added to continue the cultivation. The method cannot cause secondary pollution; the induction effect is good, and the laccase yield is significantly increased; and the content of pentachlorophenol in the soil can be significantly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A vegetable waste decomposing bacterial agent and its use method and prepared organic substrate
ActiveCN103966148BIncrease contentPromote repairPlant growth regulatorsBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a vegetable waste decomposing bacterial agent, a use method thereof and an organic matrix prepared therefrom. The decomposed bacterial agent is composed of 1-3 parts of Phaneroderma chrysosporium, 1-3 parts of Trichoderma harzianum, 1-3 parts of Bacillus subtilis and 1-3 parts of Bacillus peptone-like in parts by weight; The number of effective viable bacteria reached 4×108 / g. It can ferment decomposed vegetable waste and resist cucumber wilt bacteria. The fermentation cycle of vegetable waste treatment is 25 days, while the uninoculated one needs more than 50 days. The organic matrix is fermented by adding 1 kg of the decomposing bacteria agent to every 5 cubic meters of vegetable waste, and the parts by weight of the vegetable waste are as follows: 40-60 parts of eggplant stalks, 20-40 parts of cucumber seedlings , 5-15 parts of Chinese cabbage leaves and 5-15 parts of lignite, the organic substrate can be used as the seedling-raising substrate of tomato, and the emergence rate reaches 92%, reaching the effect of the seedling-raising substrate sold in the market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
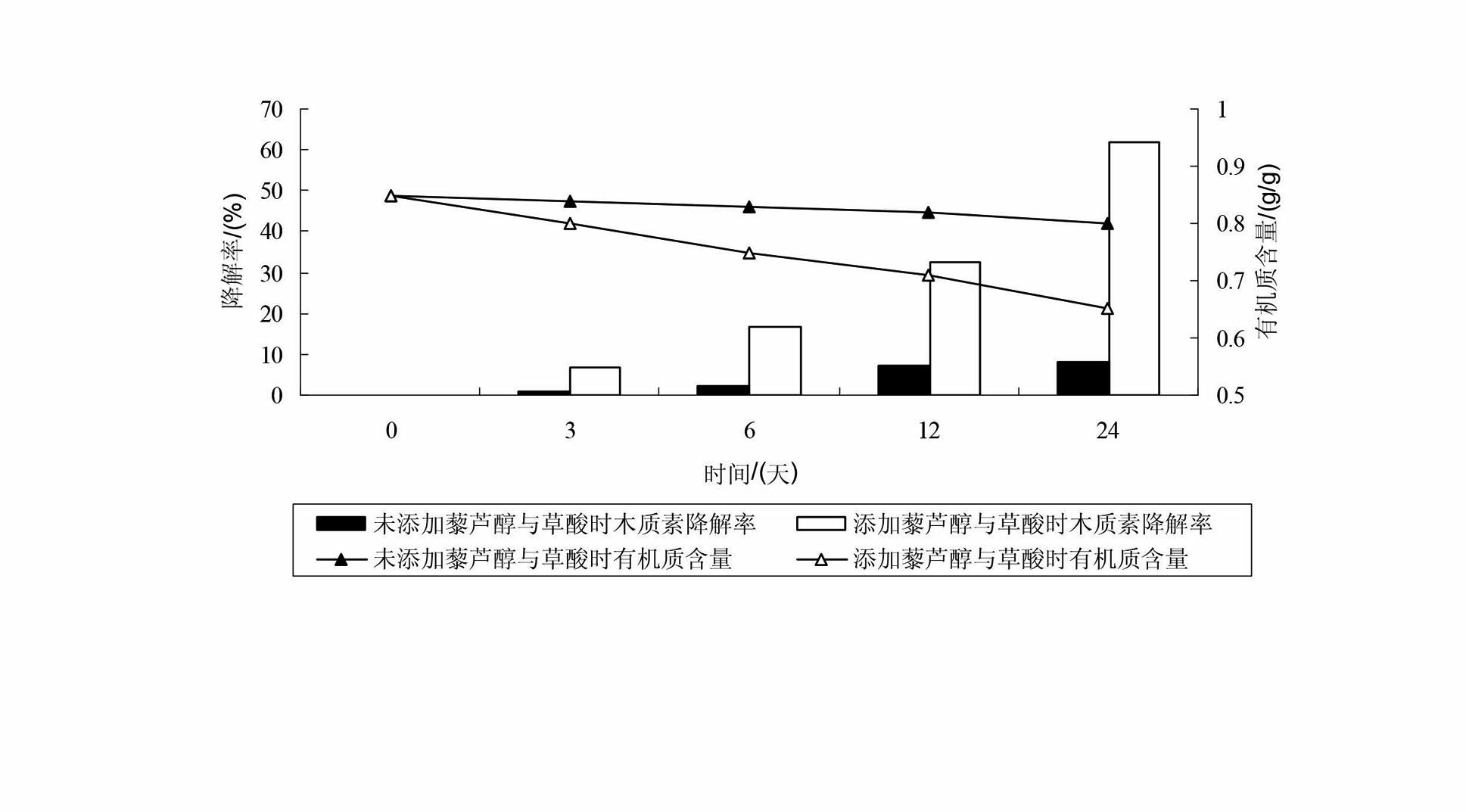
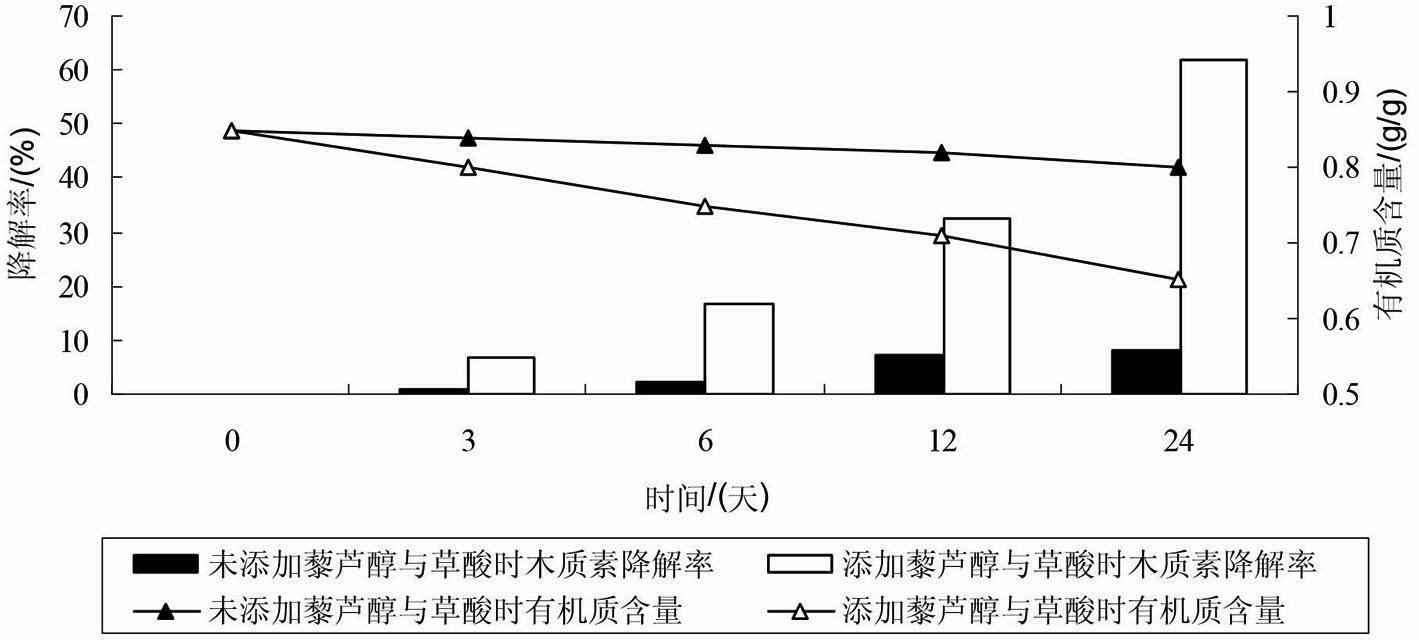
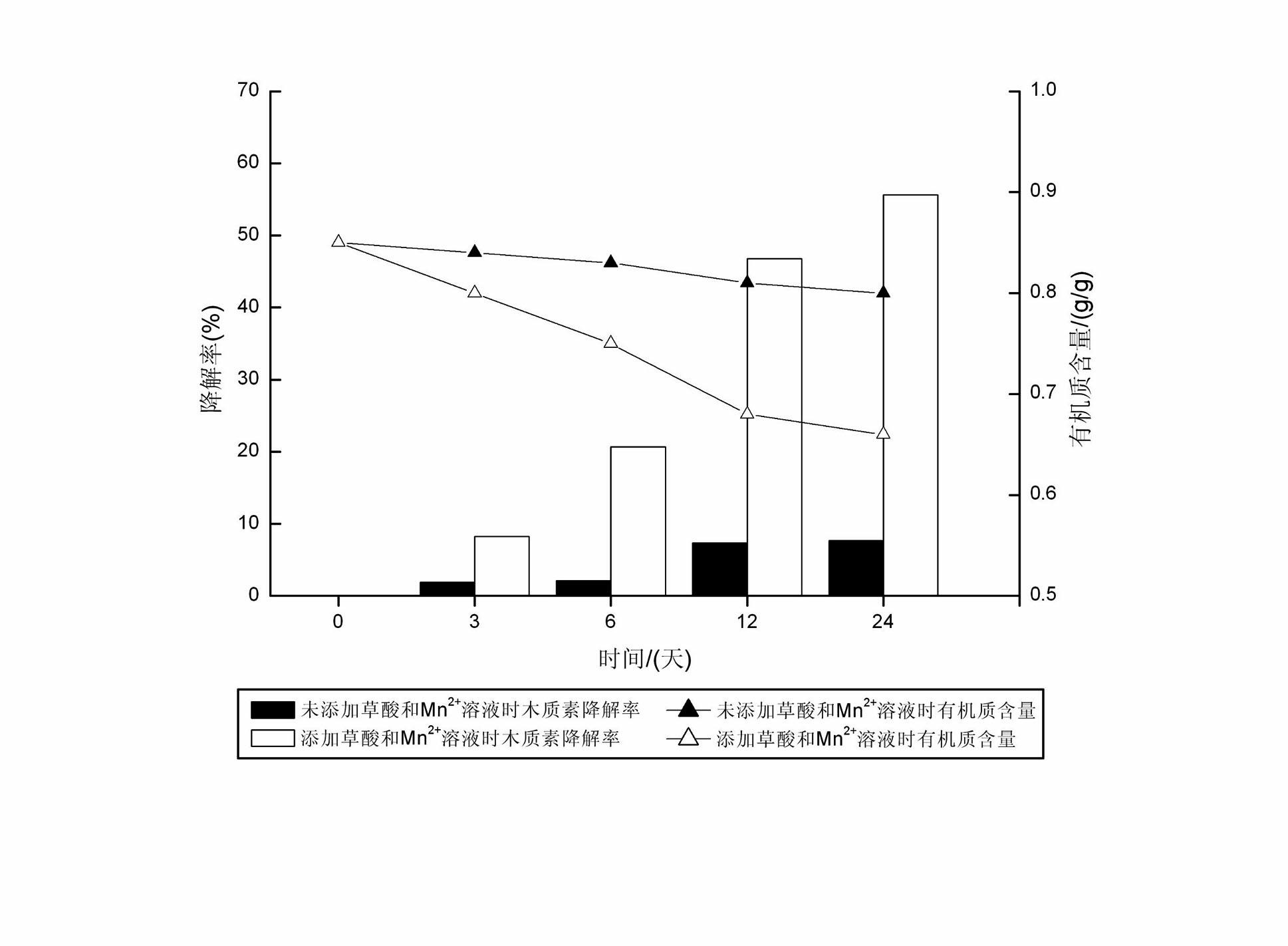
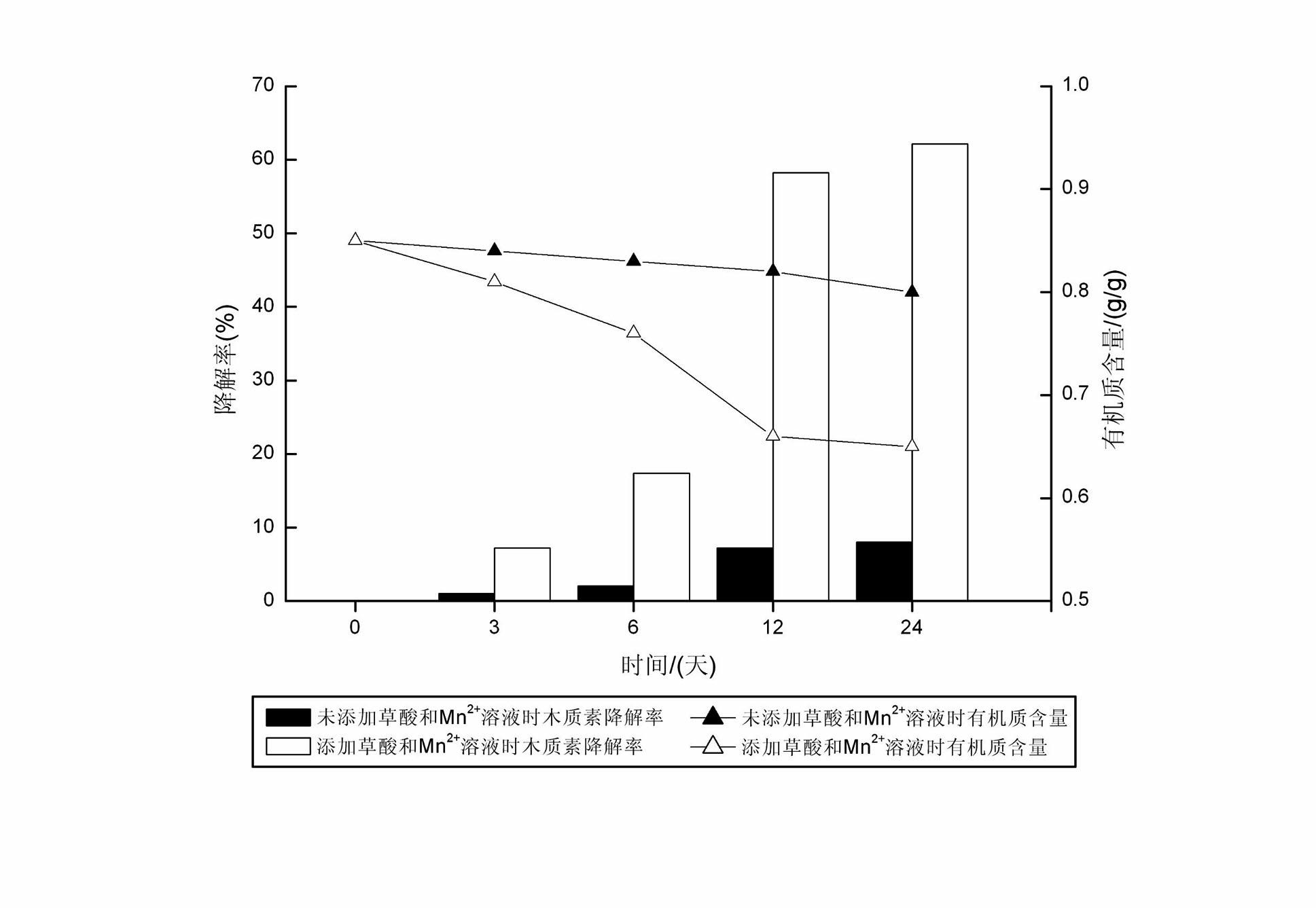
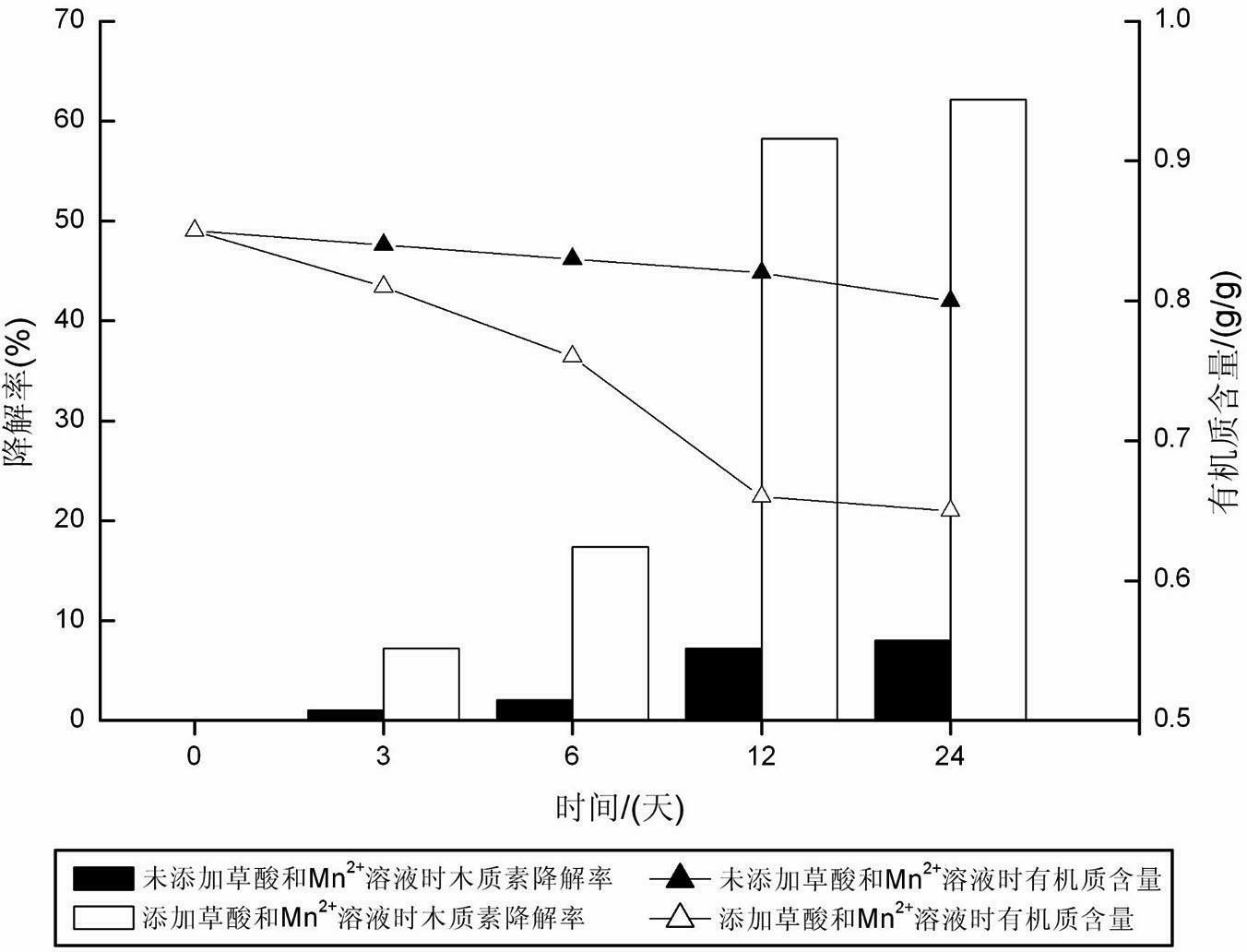
Method for degrading rice straws by using oxalic acid and Mn2+ for accelerating catalysis of compound enzyme
InactiveCN102535238AIncreased CorruptionImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyPulping with acid salts/anhydridesNon-woody plant/crop pulpOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a method for degrading rice straws by using oxalic acid and Mn2+ for accelerating the catalysis of a compound enzyme. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) perprocessing the straws: crushing the rice straws to obtain straw powder, and sifting for standby; (2) preparing a compound enzyme soltion:culturing phanerochaete chrysosporium in a liquid state to obtain the compound enzyme solution; and (3) carrying out catalytic degradation: adding the compound enzyme solution into the straw powder, meanwhile, adding an oxalic acid solution, a Mn2+ solution and a H2O2 solution, carrying out heat-preservation moisture-preservation standing, and finishing the catalytic degradation. The method for degrading the rice straws, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that: the degrading speed of the compound enzyme to lignin is increased, the thermal energy consumption is lowered, meanwhile, the cost is low, the operation is simple, the operating cost is low, the method is clean and pollution-free, and thus, the industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
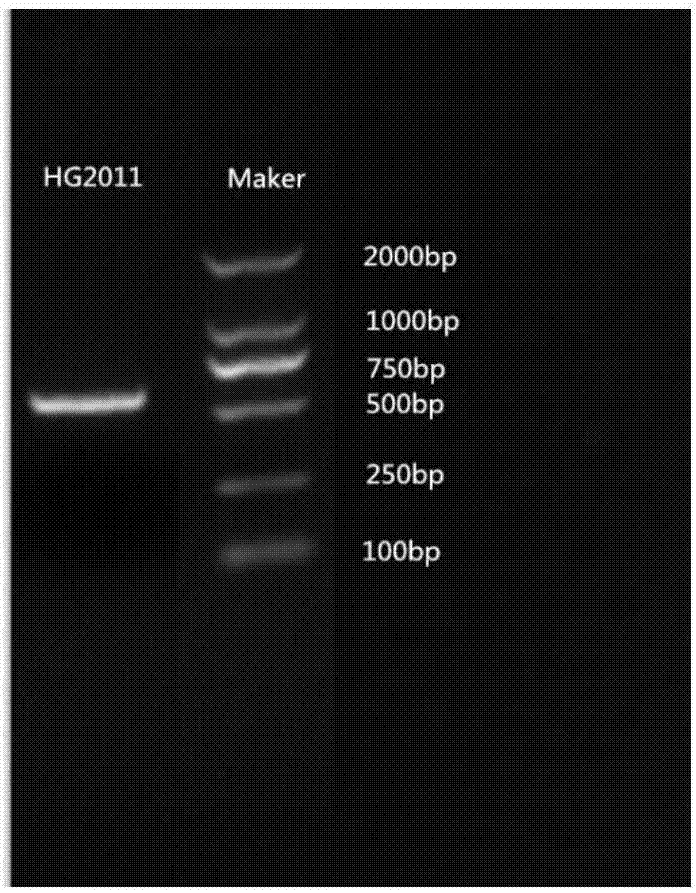
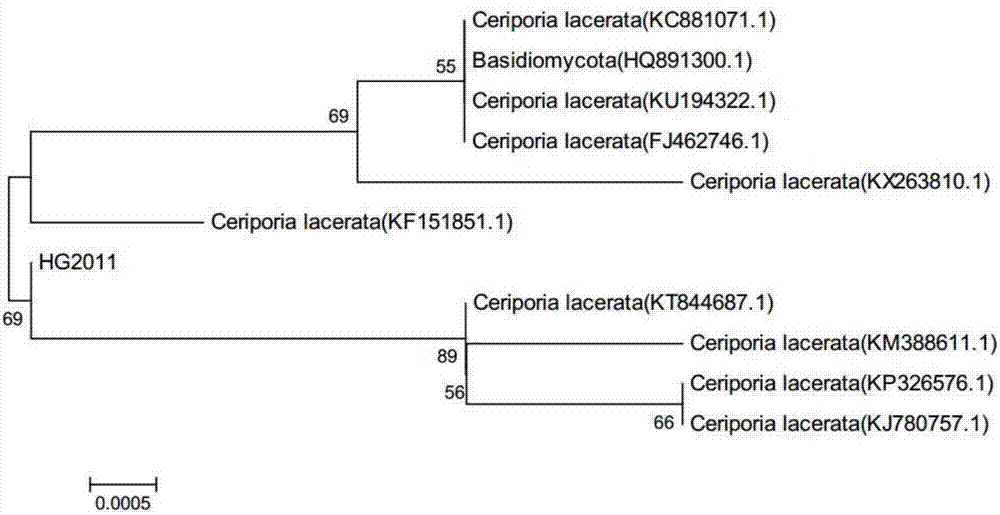
Ceriporialacerata and application thereof in preventing and treating crop fungus diseases
The invention relates to a novel ceriporialacerata species and application thereof in preventing and treating crop fungus diseases. A preservation number of the novel ceriporialacerata species is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.13899, the novel ceriporialacerata species is classified and named as Ceriporia lacerate HG2011, and the strain has a nucleotide sequence in a C. lacerate HG2011 18SrDNA sequence list and belongs to Ceriporia of Phanerochaetaceae. A bacterial colony is white and in villous and flocculent state, and an appropriate growth temperature is 25 to 28 DEG C. The strain can secrete varieties of extracellular enzymes of chitinase, cellulase, beta-1,3-glucanase, protease and the like; fermentation broth of the strain has a stronger antagonism effect on varieties of plant pathogenic fungi; the strain can be applied to preventing and treating flue-cured tobacco and phytophthora capsici diseases and has larger application potential in an aspect of preventing and treating the plant pathogenic fungi.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing modified soybean straw pig fodder and pig fodder prepared by means of method
The invention discloses a method for preparing modified soybean straw pig fodder and the pig fodder prepared by means of the method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, soybean straw, soybean hulls, soybean meal, soybean oil and soybean bran are placed in an ultrafine crusher to be crushed into fine powder with the particle size of 500-600 mesh; 2, a modifier is added to the fine powder in the step 1, wherein the modifier is prepared from, by weight, yeast, ceriporiopsis subvermispora, phanerochaete chrysosporium, variegated coriolus versicolor, pleurotus ostreatus, hirschioporuslacteus and coriolopsis gallica; a mixture is formed after the addition of the modifier and poured into a fermentation tank, water is added for stirring, and the moisture content of the mixture is controlled within 15%-30%; 3, after the water is added for stirring and the temperature rises to 30-40 DEG C, and fermentation is conducted for 12-20 hours; 4, the fermented material in the step 3 is taken out and placed in a granulation dryer for drying granulation, and the finished pig fodder is obtained after the granulation is completed.
Owner:张掖市金农源生物科技有限公司
A crop straw decomposing bacterial agent and its use method and effect
ActiveCN103966150BPromote repairImprove disease resistanceFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a crop straw rot rotten bacterium and its application in straw biological reactors and fertilizers.The fungus is made of 0.5 to 2 parts of the yellow spores, 0.5 to 2 parts of yellow and green wooden mold, 0.5 to 2 copus of Bacillus of Bacillus and 0.5 to 2 parts of gluebacteria.Number 6 × 108 / g.The straw rot cooked bacterium is used in tomato straw biological reactor planting technology, with an average ground temperature of 18.3 ° C, an increase of 2.2 ° C from the control of the non -bacterial agent; the average shed temperature is 14.3 ° C, an increase of 2.0 ° C.2.17 times; the harvest period is 15 days in advance; the perurone output is 5881kg, which is 22.7%more than the control of the control. Compared with the control, there is less pests.The bacteria are used in wheat straw stacks, rot, fast decomposition, good softness, and good softening, straw is basically decomposed, and the fermentation time is shorter than the bacteria purchased by the application market.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
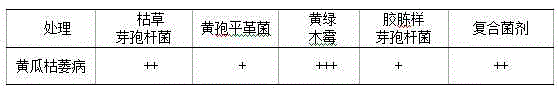
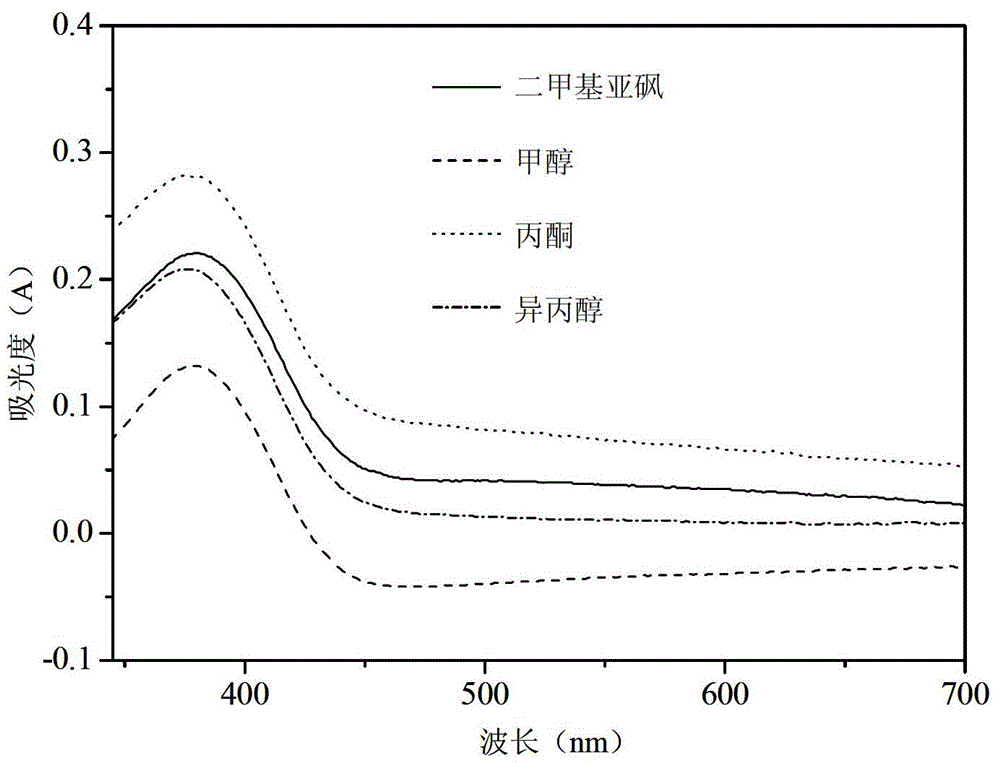
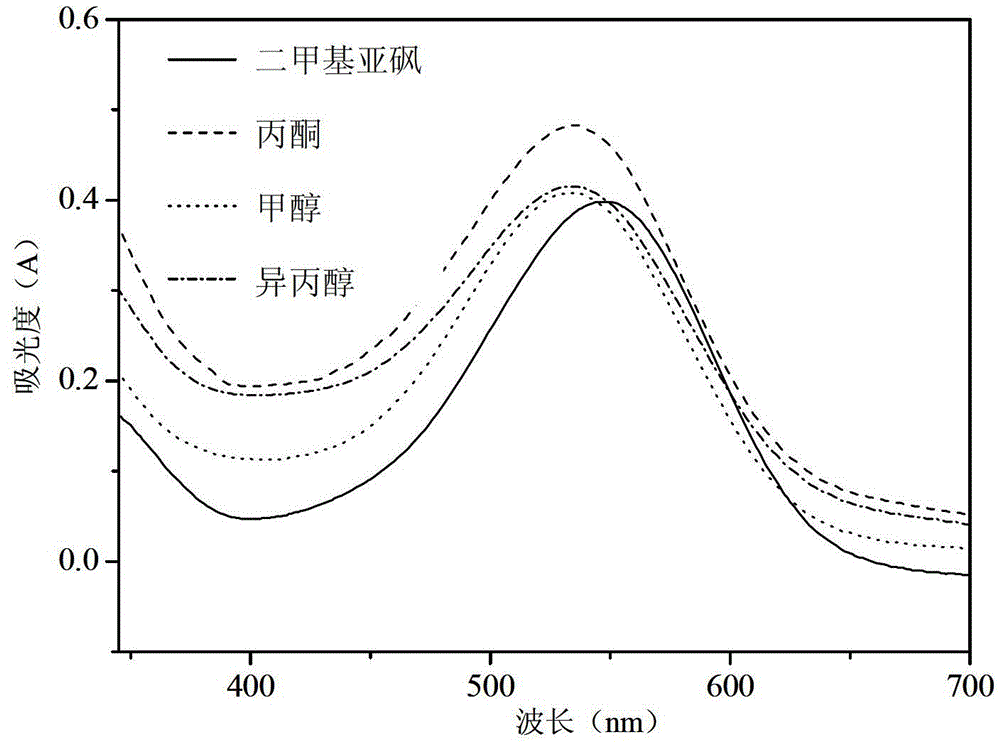
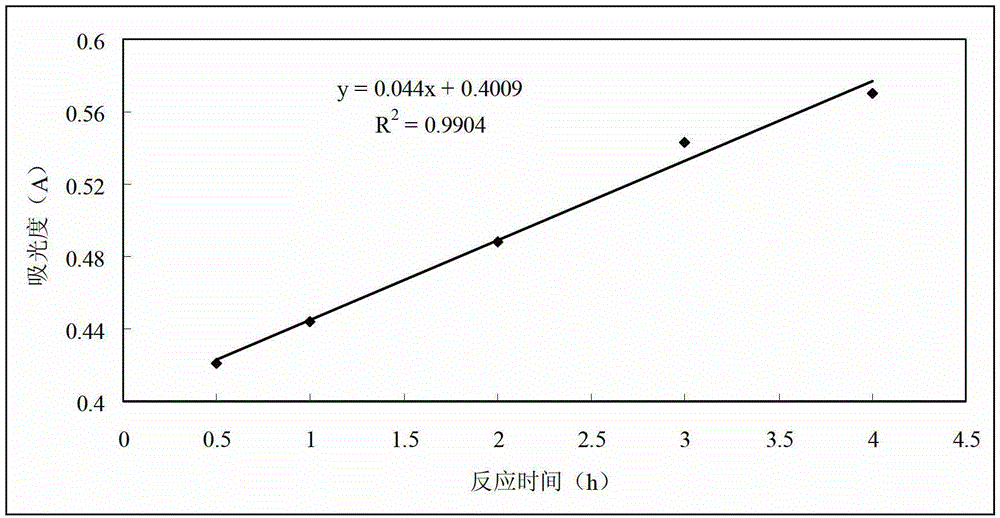
Detection method of living cell biomass of Phanerochaete chrysosporium under heavy metal stress
InactiveCN103424370BImprove processing efficiencyRegulating Processing EfficiencyColor/spectral properties measurementsPhanerochaeteMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for detection of the living cell biomass of phanerochaete chrysosporium under the heavy metal stress. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1, pellet culturing: adding the phanerochaete chrysosporium into a liquid culture medium for constant-temperature culturing, and adding heavy metal solution for stress treatment; 2, chromogenic reaction: adding the phanerochaete chrysosporium pellets obtained after heavy metal stress into sterile MTT solution and performing chromogenic reaction for 0.5-4 h at the temperature of 30-50 DEG C, and then quickly adding hydrochloric acid solution to stop the reaction, so as to obtain the mixed liquor after reaction; 3, centrifugal treatment: performing centrifugal treatment on the mixed liquor to remove the liquid supernatant and obtain the lower sediment; 4, extracting detection: adding an extracting agent into the sediment for extraction, determining the absorbance of the extract liquor, and calculating the living cell biomass of the phanerochaete chrysosporium under the heavy metal stress. According to the invention, the detection method is simple and convenient, wide in application and strong in practicability.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Biosynthesis method of cadmium sulfide quantum dot
InactiveCN102965406BGood biocompatibilityGood monochromaticityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhanerochaeteThio-
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Ecological special fertilizer of common yam rhizome and preparation and application method of ecological special fertilizer
InactiveCN105541518APromote absorptionGrowth inhibitionCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersDiseaseAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an ecological special fertilizer of common yam rhizome. The ecological special fertilizer is prepared from animal waste, coprinus comatus waste materials, cakes, straw, ETS compound bacteria, phanerochaete chrysosporium, JT compound bacteria, mountain soil, amino acid, urea, diammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, copper sulfate, ferrous sulfate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate and dolomite dust. The invention further discloses a preparation and application method of the ecological special fertilizer. The prepared ecological special fertilizer is reasonable in nutritional ingredient ratio, the nutrition requirements of common yam rhizome at all growth stages are met, the number of beneficial bacteria in common yam rhizome planting soil is increased, enzymatic activity in common yam rhizome planting soil is increased, ecological balance of the common yam rhizome plant rhizosphere soil environment is achieved, the soil structure is obviously improved, the stress resistance of common yam rhizome is enhanced, the morbidity and disease index of common yam rhizome are decreased, the aims of high yield and high quality are achieved, and the ecological virtuous circle of common yam rhizome production is achieved.
Owner:连云港市耕地质量保护站
Method for cultivating summer squashes in greenhouse in high-altitude area
PendingCN113331002AImprove yield per muAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSporelingPhanerochaete
The invention discloses a method for cultivating summer squashes in a greenhouse in a high-altitude area. The method specifically comprises the following steps: white spirit yellow water and an organic fertilizer are applied into soil, and rare earth and carbon-soluble organic fertilizer are added as a base fertilizer; during field planting, straws and wine-making waste distillers' grains are deeply buried between every two adjacent ridges, phanerochaete chrysosporium and bacillus amyloliquefaciens are added, and the mixture is covered with soil; in the seedling stage, gamma-PGA polyglutamic acid begins to be subjected to drip irrigation, meanwhile, bacillus mucilaginosus liquid is subjected to drip irrigation once, and amino acid selenium fertilizer is sprayed on leaf surfaces; calcium-boron fertilizer is subjected to drip irrigation in the early stage of flowering and pollination, organic silicon fertilizer is sprayed on leaf surfaces, and compound sodium nitrophenolate is applied along with water in the flowering stage; when the fruits begin to expand, trichoderma viride 3.2942 spore bacterial liquid and amino acid water-soluble nutrient fertilizer are subjected to drip irrigation and mixed with monopotassium phosphate for use at the same time, drip irrigation is conducted once every 15-20 days, and drip irrigation is conducted 2-4 times; after the first batch of summer squashes are picked, topdressing of bacillus mucilaginosus liquid is performed along with water; in addition, the monopotassium phosphate, the carbon-soluble organic fertilizer and the amino acid water-soluble nutrient fertilizer are subjected to drip irrigation along with water, and drip irrigation is performed once a month. The method effectively improves the acre yield of the summer squashes.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
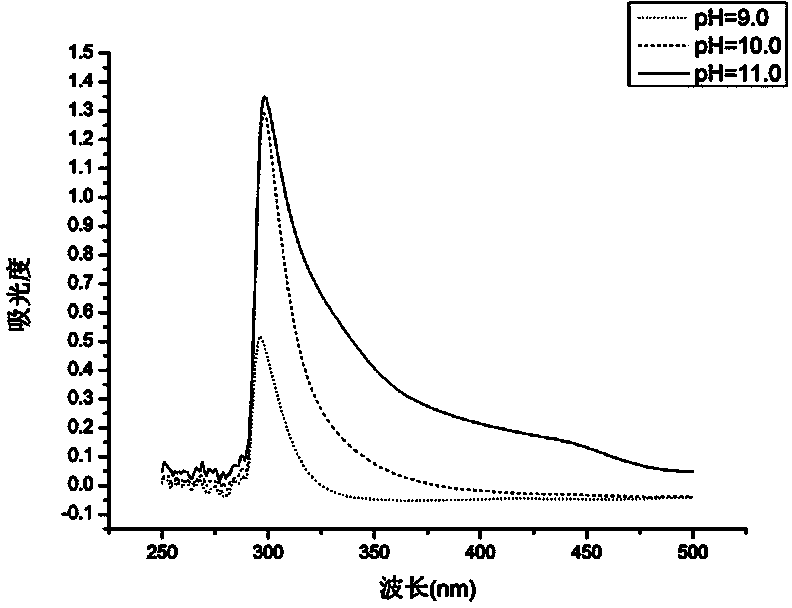
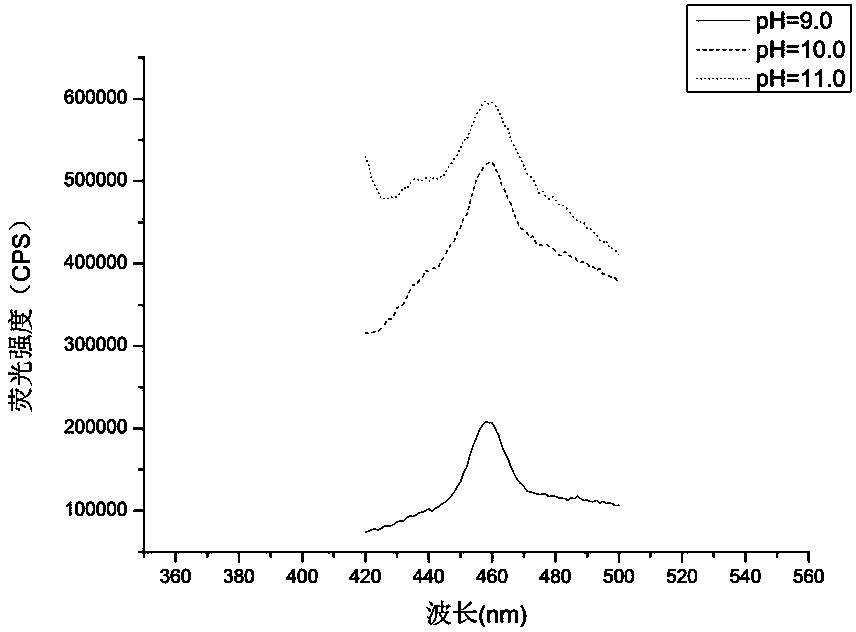
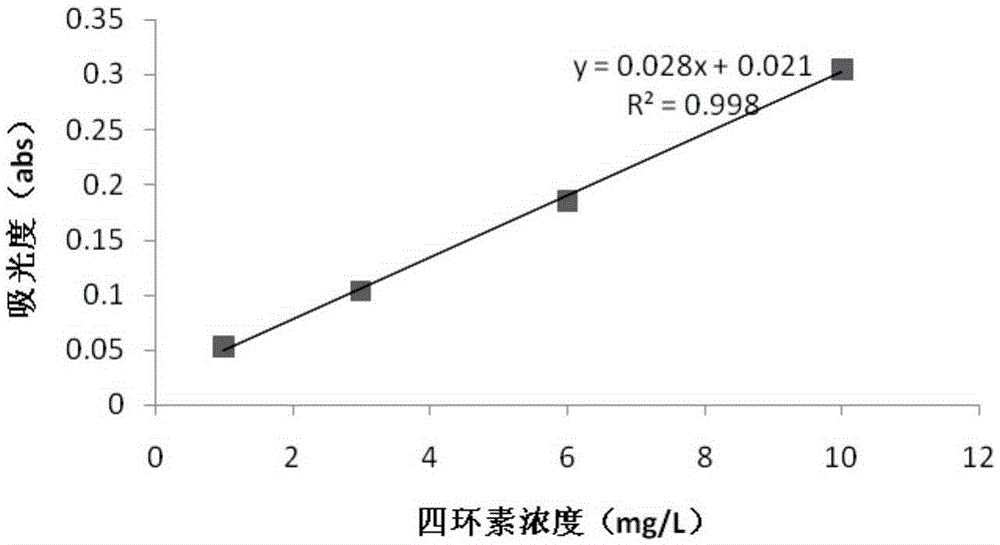
Application of phanerochaete chrysosporium in degradation of tetracycline
The invention relates to application of phanerochaete chrysosporium in degradation of tetracycline. According to the application, the microorganism species-phanerochaete chrysosporium which can degrade the tetracycline is discovered for the first time, and the content of the tetracycline in a water body can be easily, efficiently and quickly lowered through the action of biological metabolism and an enzyme system of the phanerochaete chrysosporium.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Bamboo stump decay promotion complexing agent
InactiveCN105802886AImprove darkeningAccelerated decayFungiBacteriaPhanerochaeteEcological environment
A bamboo stump decay promotion complexing agent comprises a chemical agent (the ratio of ammonium bicarbonate to urea is 11:2) and a microbial agent. The microbial agent is formed by compounding phanerochaete chrysosporium, bacillus subtilis, coriolus versicolor, bjerkandera adusta, gloeophyllum trabeum, poria vaporaria, gloeophyllum trabeum and an activator. According to the bamboo stump decay promotion complexing agent, the microbial agent, the chemical agent and other technologies are integrated, the decomposition period of bamboo stump is successfully shortened to 1-3 months, soil fertility is improved, the soil granular structure is improved, the micro-ecological environment of plant rhizosphere soil is activated, moso bamboo growth is promoted, and the yield of bamboos and bamboo shoots in a bamboo forest is increased.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
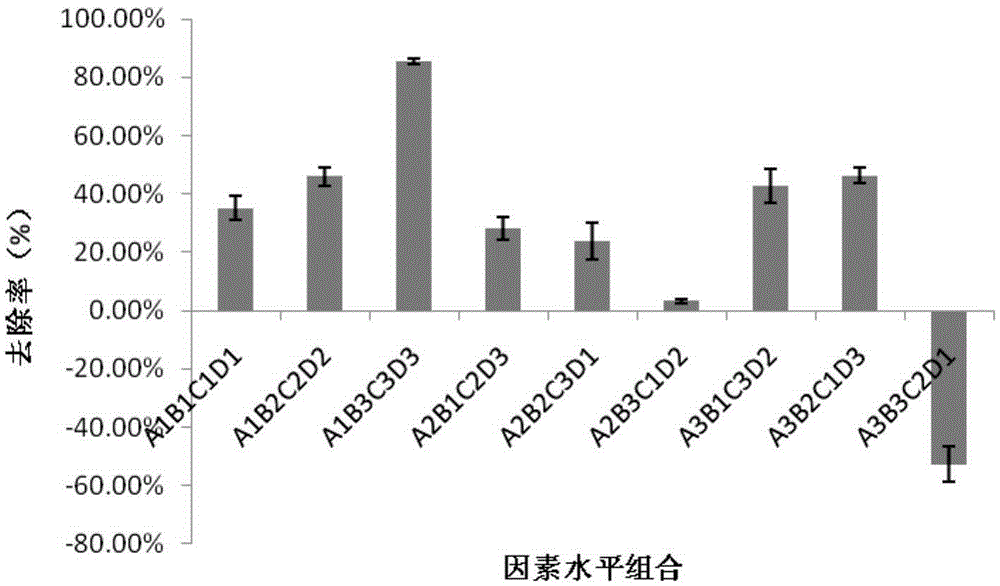
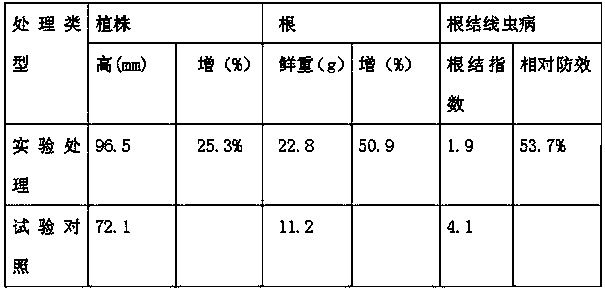
Bio-control agent for preventing and controlling root-knot nematodes, and application thereof
ActiveCN109169710AImprove developmentPromote growth and developmentBiocideNematocidesBacillus licheniformisDisease
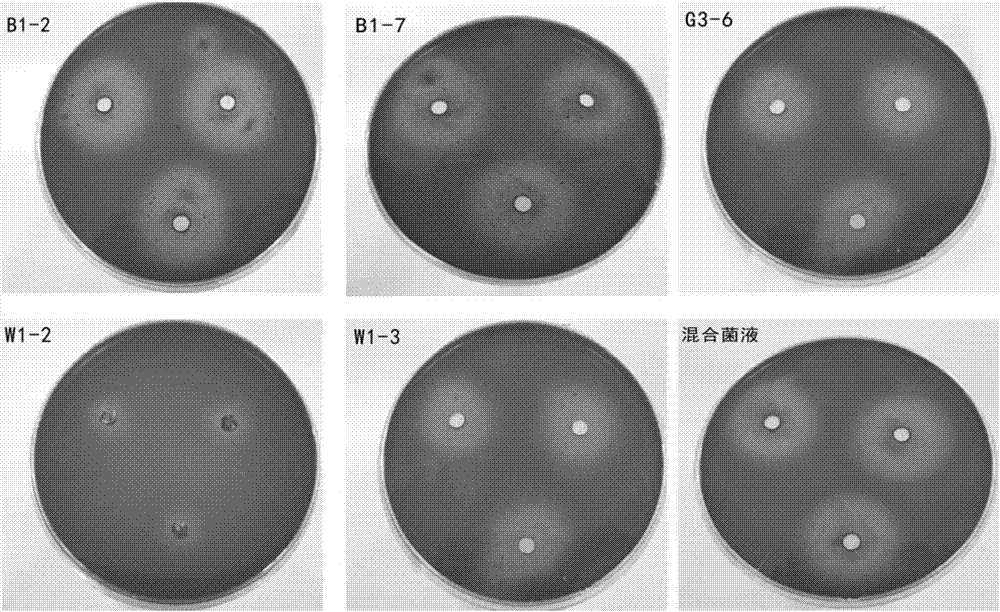
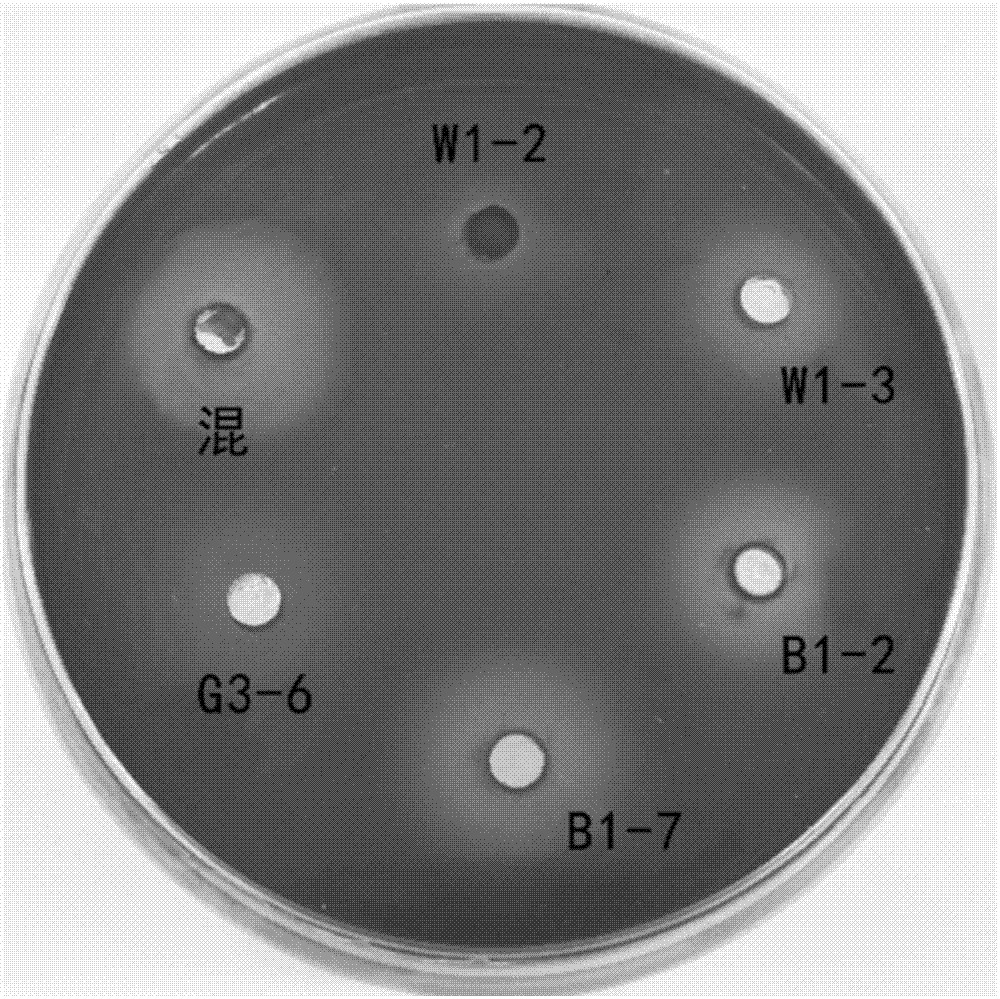
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides, and provides a bio-control agent for preventing and controlling root-knot nematodes, and an application thereof in order to solvethe problems of single disease prevention mechanism and low prevention and control effect of existing single strains for preventing and controlling root-knot nematodes. The bio-control agent is prepared by mixing a Bacillus licheniformis-Pseudomonas fluorescens mixed fermentation broth, a streptomyces fradiae fermentation broth and a Phanerochaete chrysosporium-Myrothecium verrucaria mixed fermentation broth according to a volume ratio of (2-5):(1-3):(1-7), and uniformly mixing the obtained mixed solution with quinoa bran according to a mass ratio of 1 kg:(6-8) kg. The above five strains do not antagonize each other and cooperate with each other to kill insects, and the preparation method is simple, so the bio-control agent has a broad application prospect. The bio-control agent can prevent and control root-knot nematodes, promote the growth and development of plants and improve the disease resistance of plants.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Compound photosynthetic bacteria agent for sewage treatment
The invention discloses a composite photosynthetic bacteria agent for sewage treatment, which is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 1-3 parts of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, 2-5 parts of Rhodopseudomonas swamp, and Rhodopseudomonas 4-6 parts of bacteria, 3-5 parts of Lactobacillus plantarum, 4-5 parts of phosphorus accumulating bacteria, 1-5 parts of Aspergillus oryzae, 4-6 parts of nitrous bacteria, 3-5 parts of Cellulomonas, Chrysosporium 1-3 parts of leather bacteria, 2-5 parts of white rot fungi and 3-6 parts of Bacillus subtilis. The present invention is favorable for popularization and application.
Owner:成都市新津胤春生物科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com