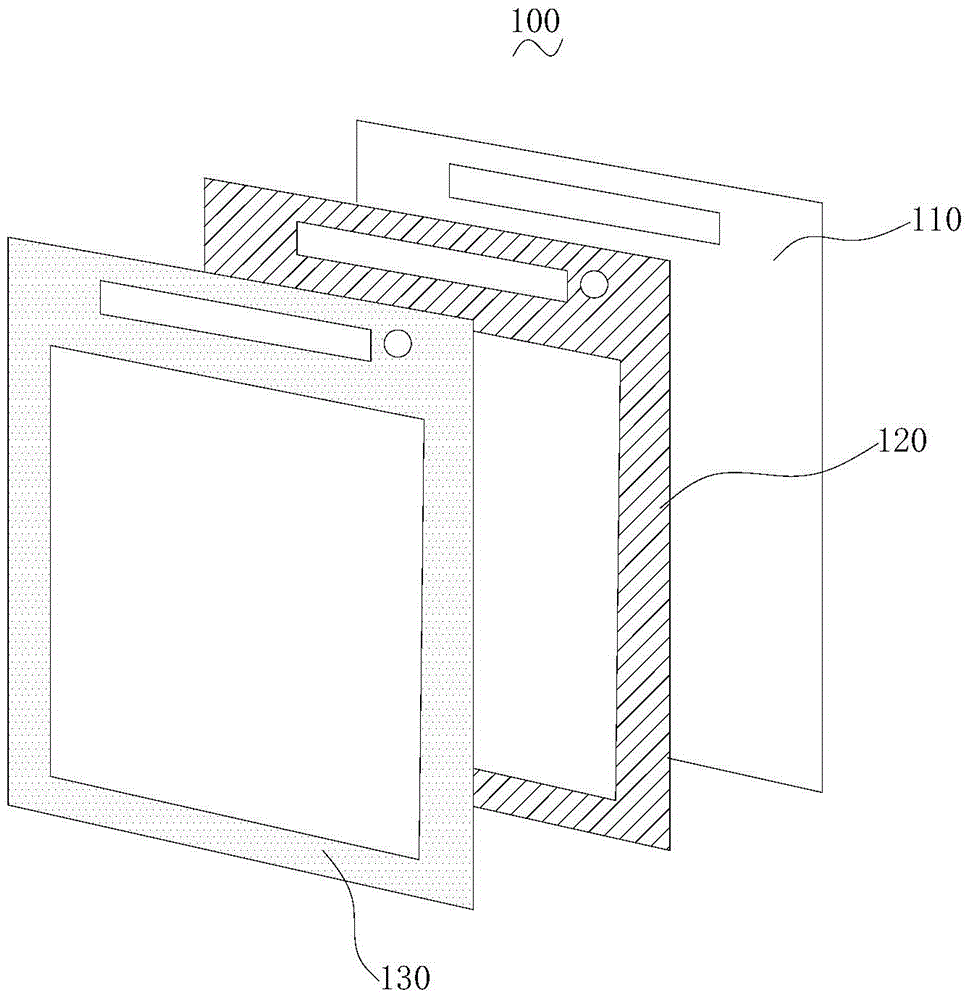
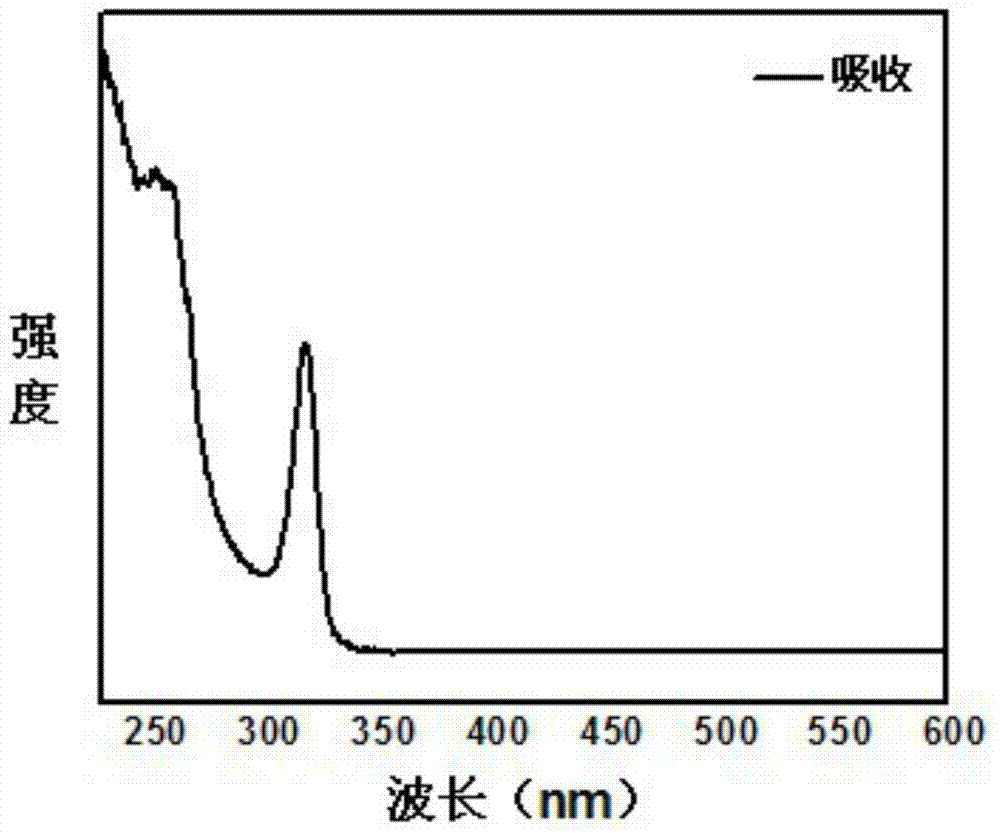
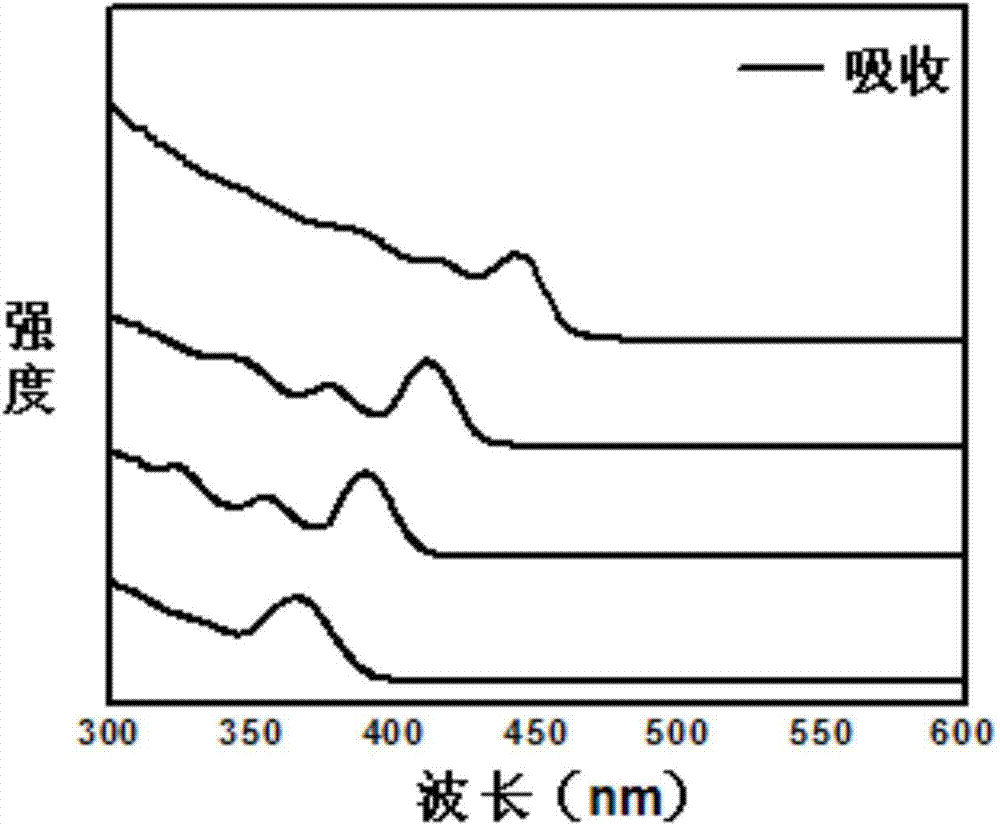
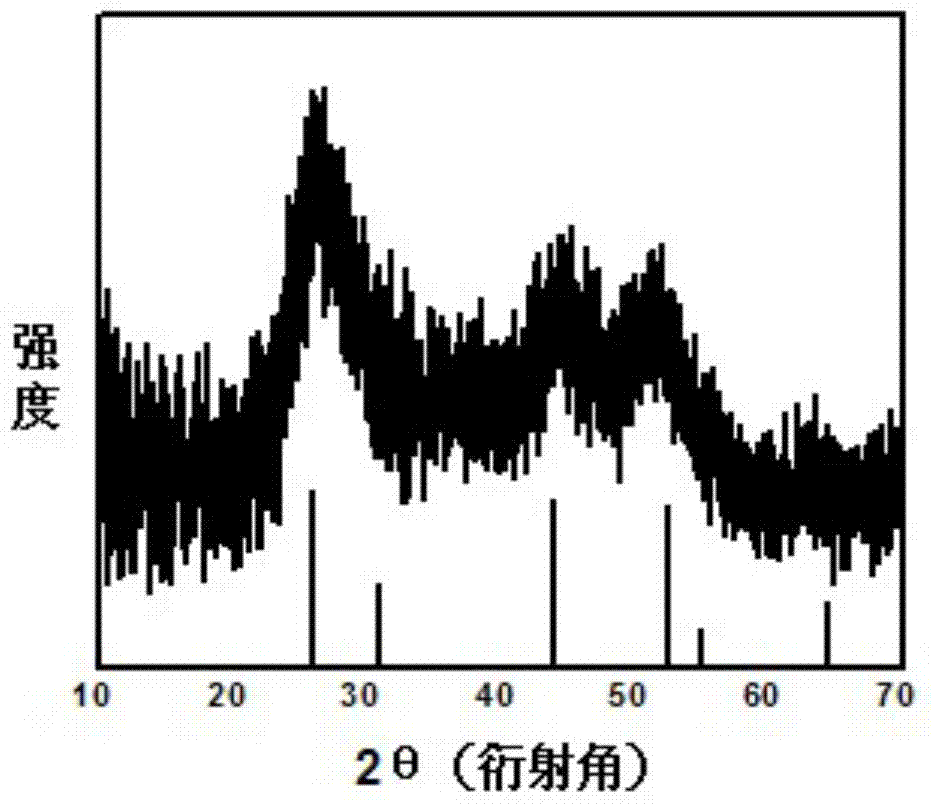
Patents
Literature
888 results about "Cadmium sulfide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cadmium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdS. Cadmium sulfide is a yellow solid. It occurs in nature with two different crystal structures as the rare minerals greenockite and hawleyite, but is more prevalent as an impurity substituent in the similarly structured zinc ores sphalerite and wurtzite, which are the major economic sources of cadmium. As a compound that is easy to isolate and purify, it is the principal source of cadmium for all commercial applications. Its vivid yellow color led to its adoption as a pigment for the yellow paint "cadmium yellow" in the 18th century.
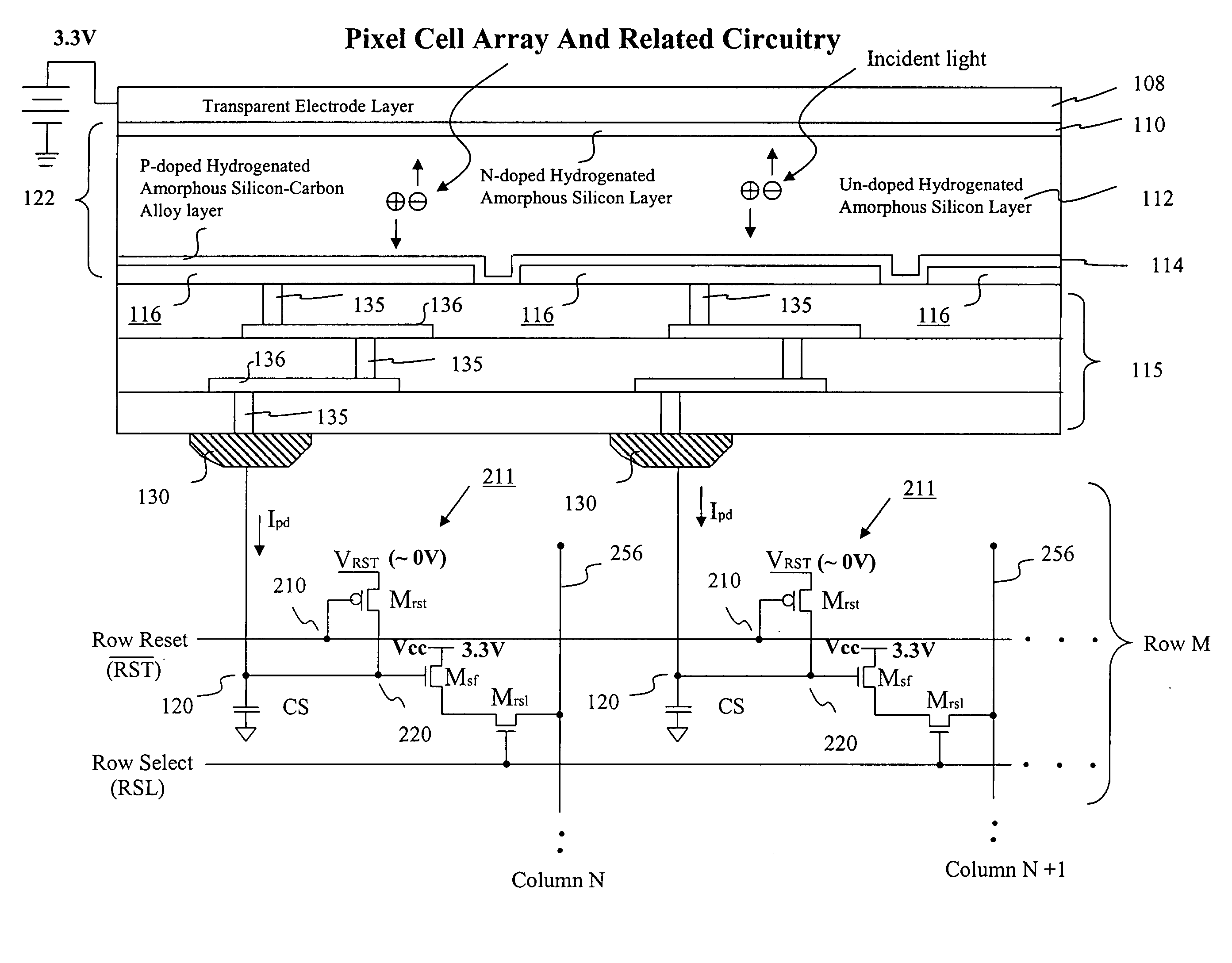
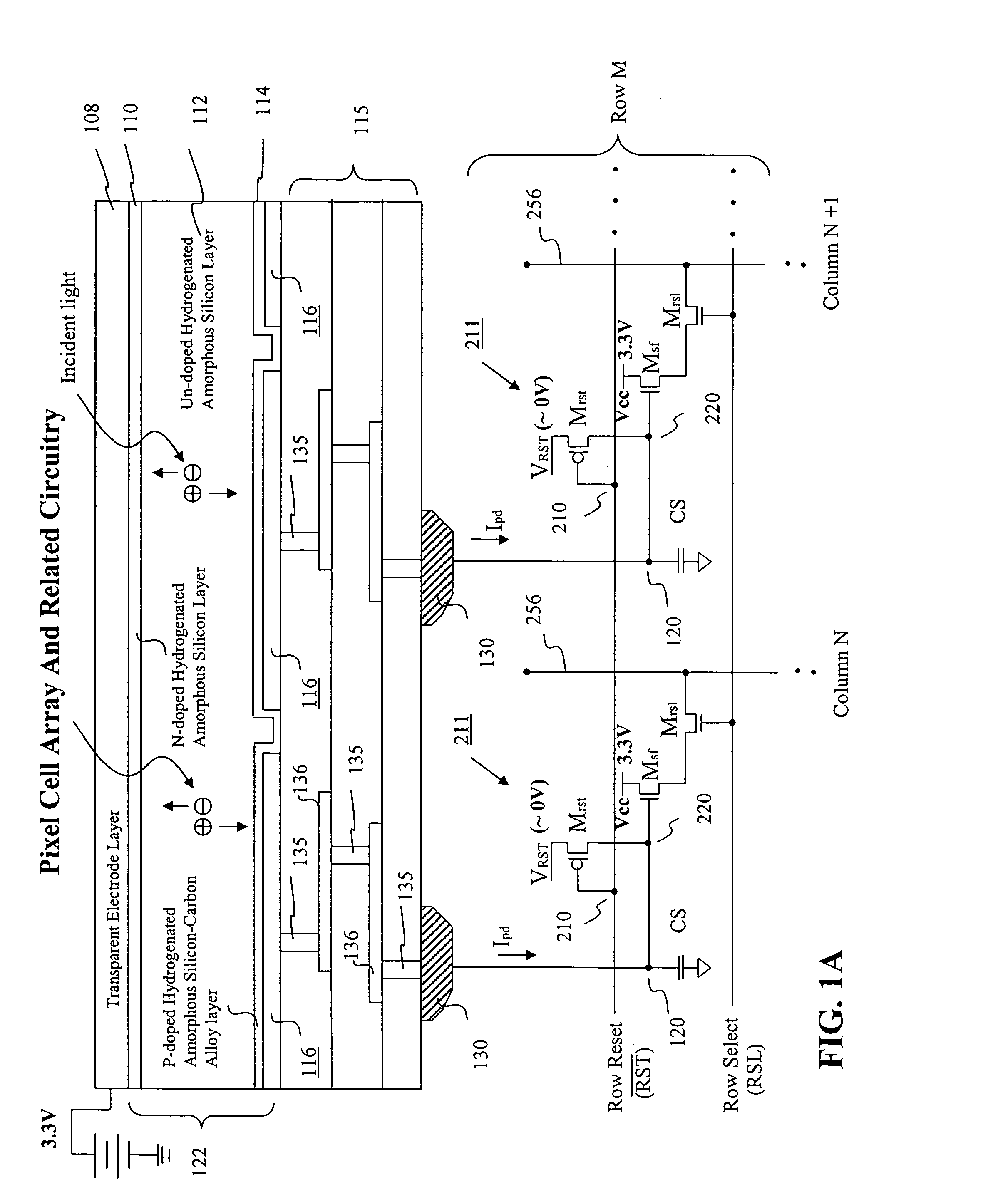
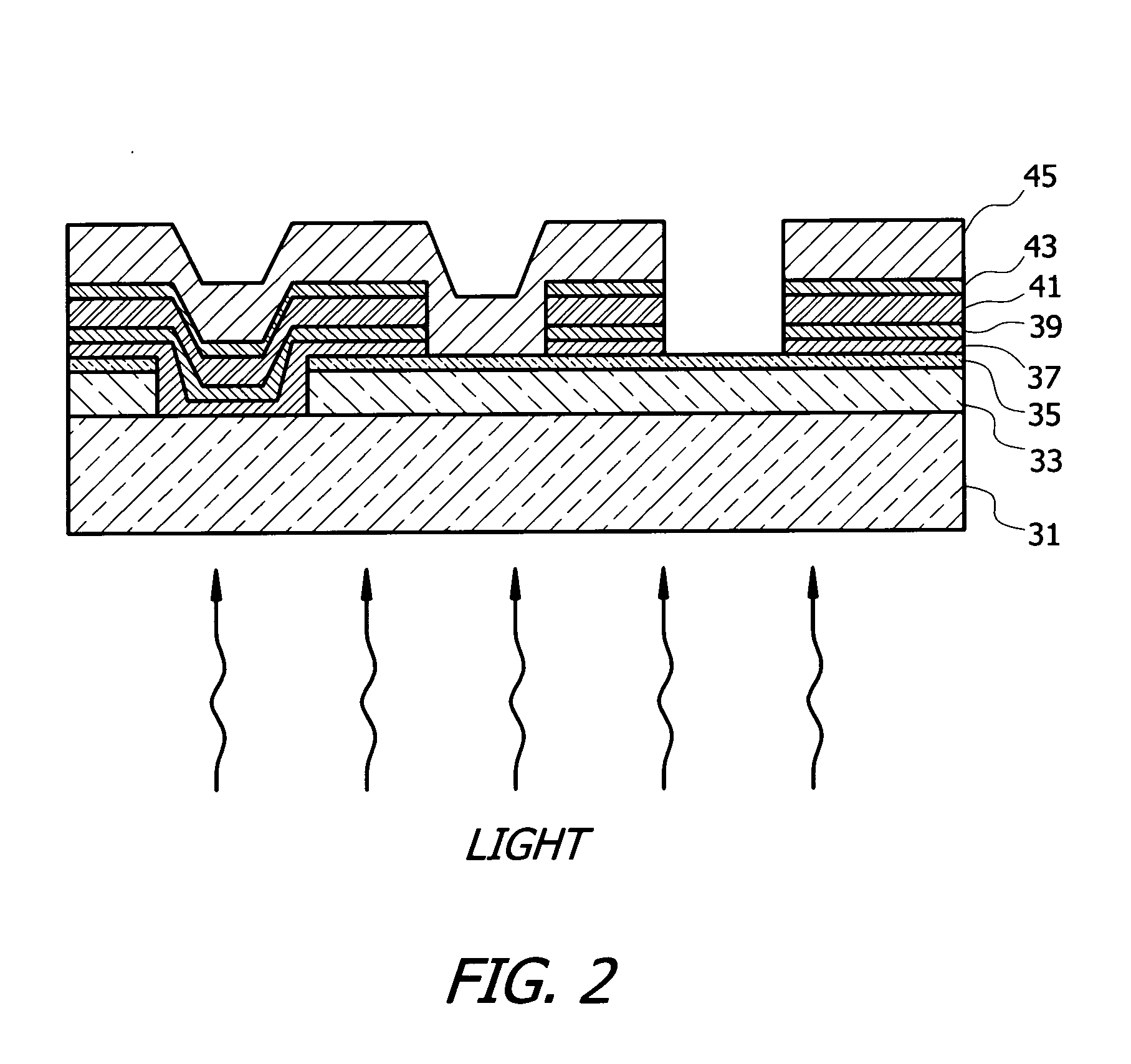
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
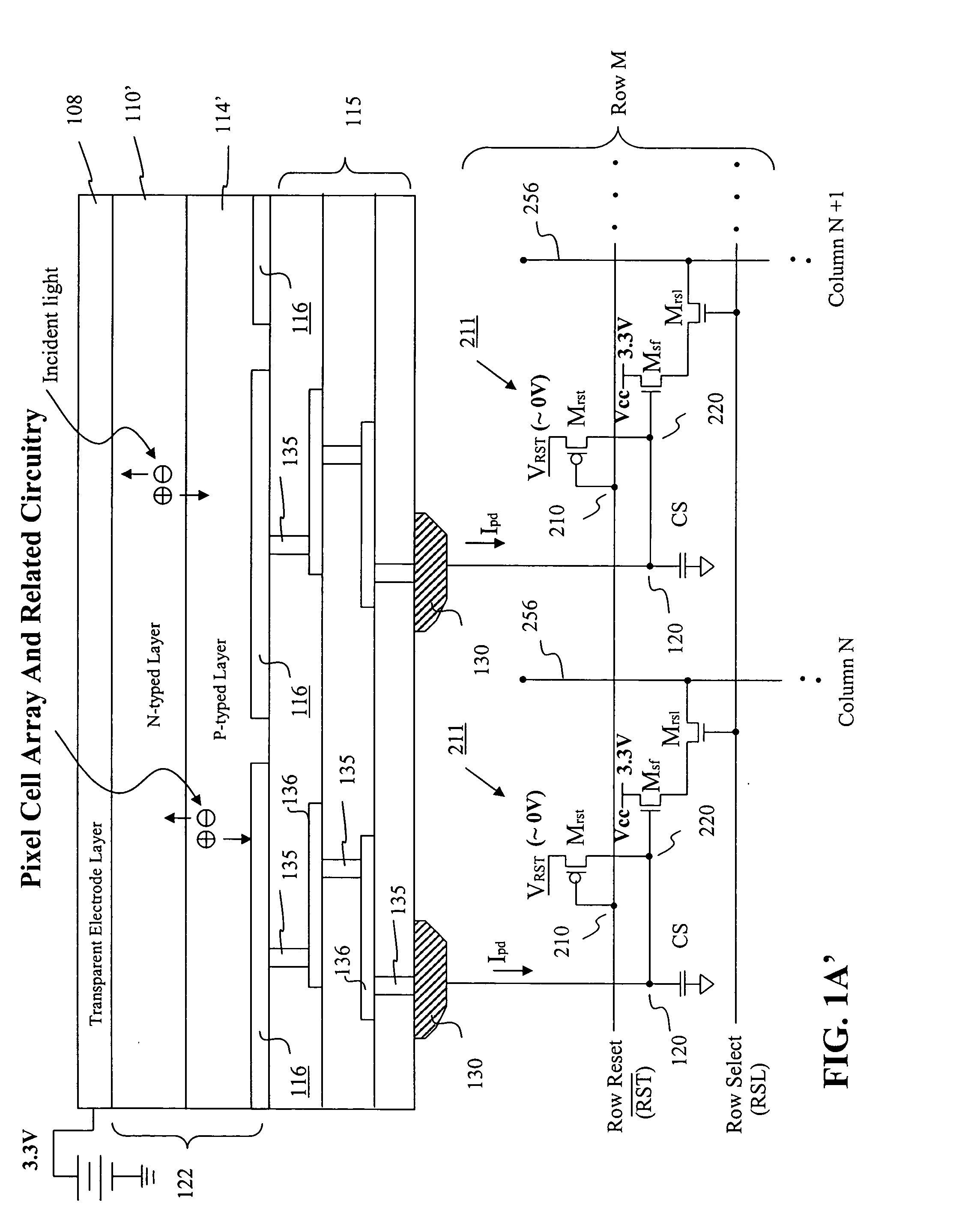
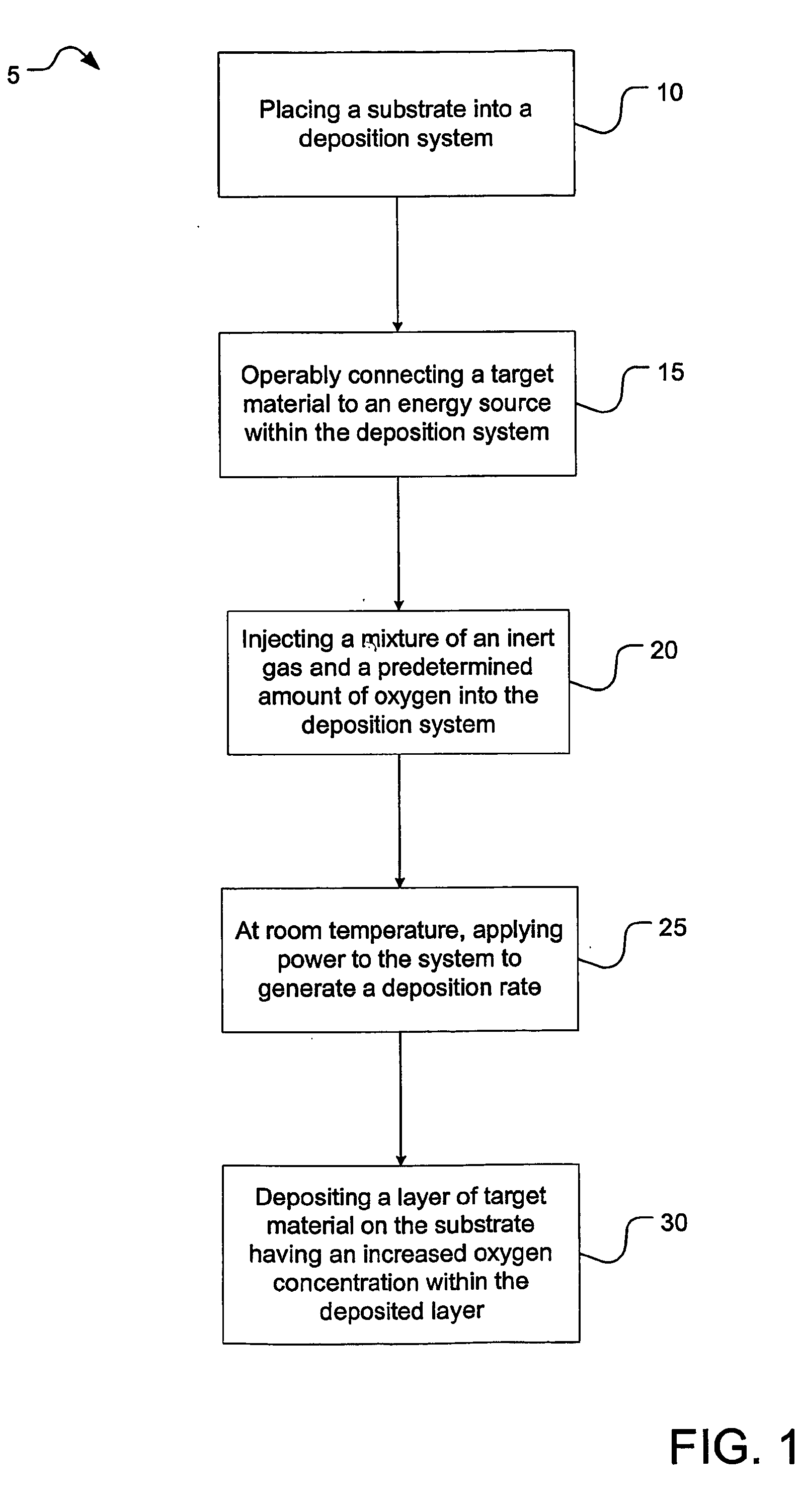
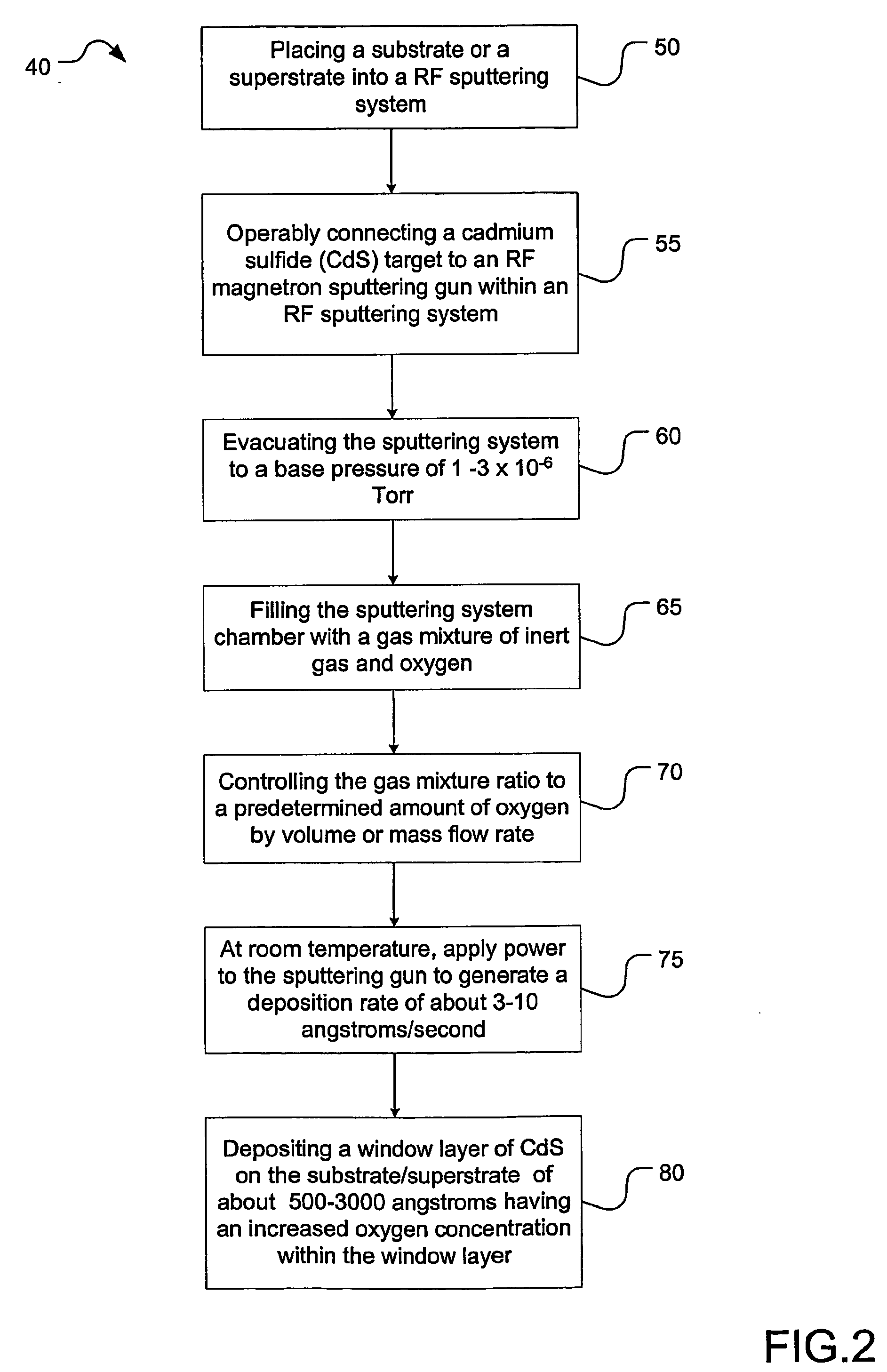
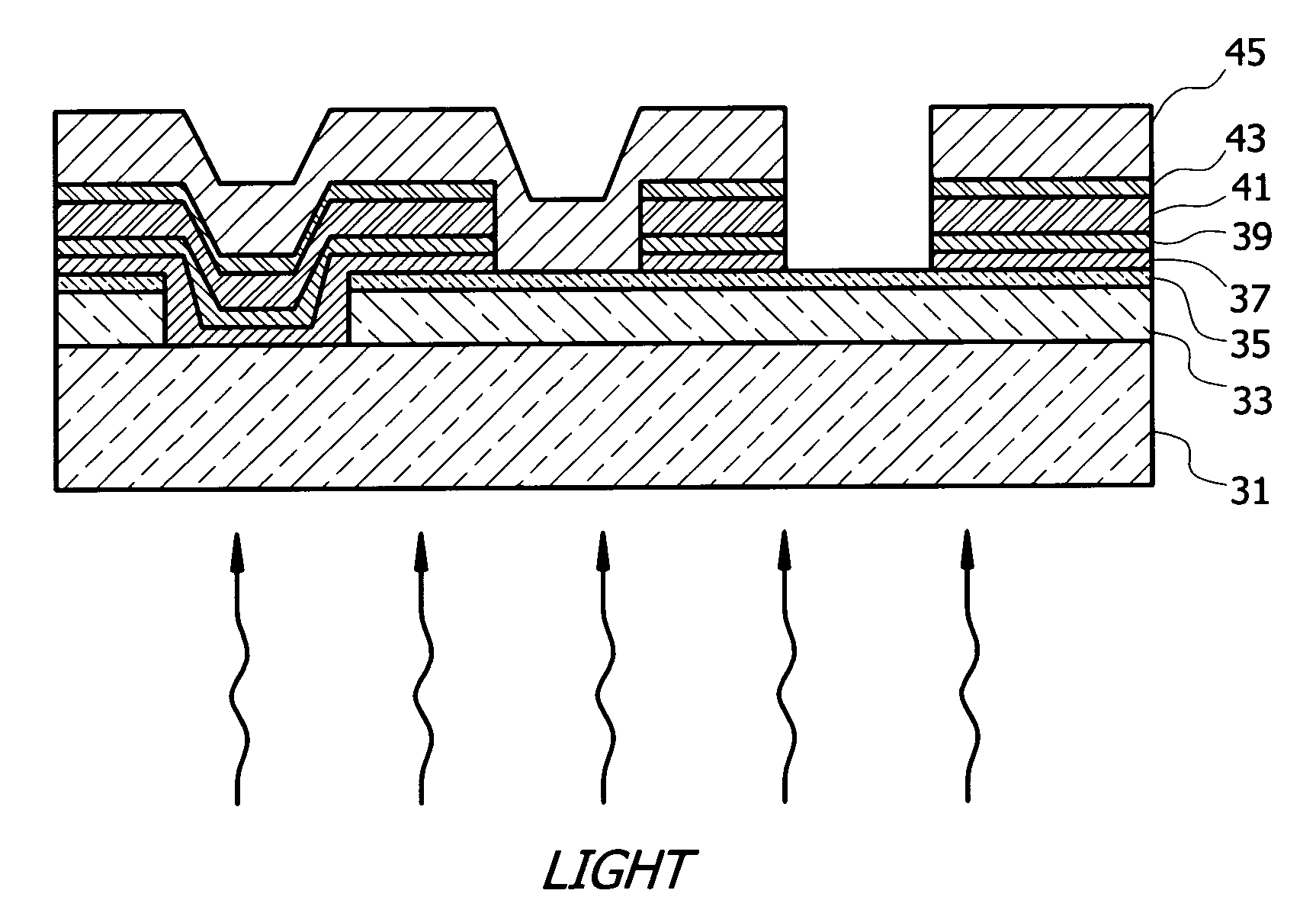
Semiconductor device with higher oxygen (02) concentration within window layers and method for making
InactiveUS20050009228A1Improve efficiencyIncrease oxygen concentrationVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionDevice material
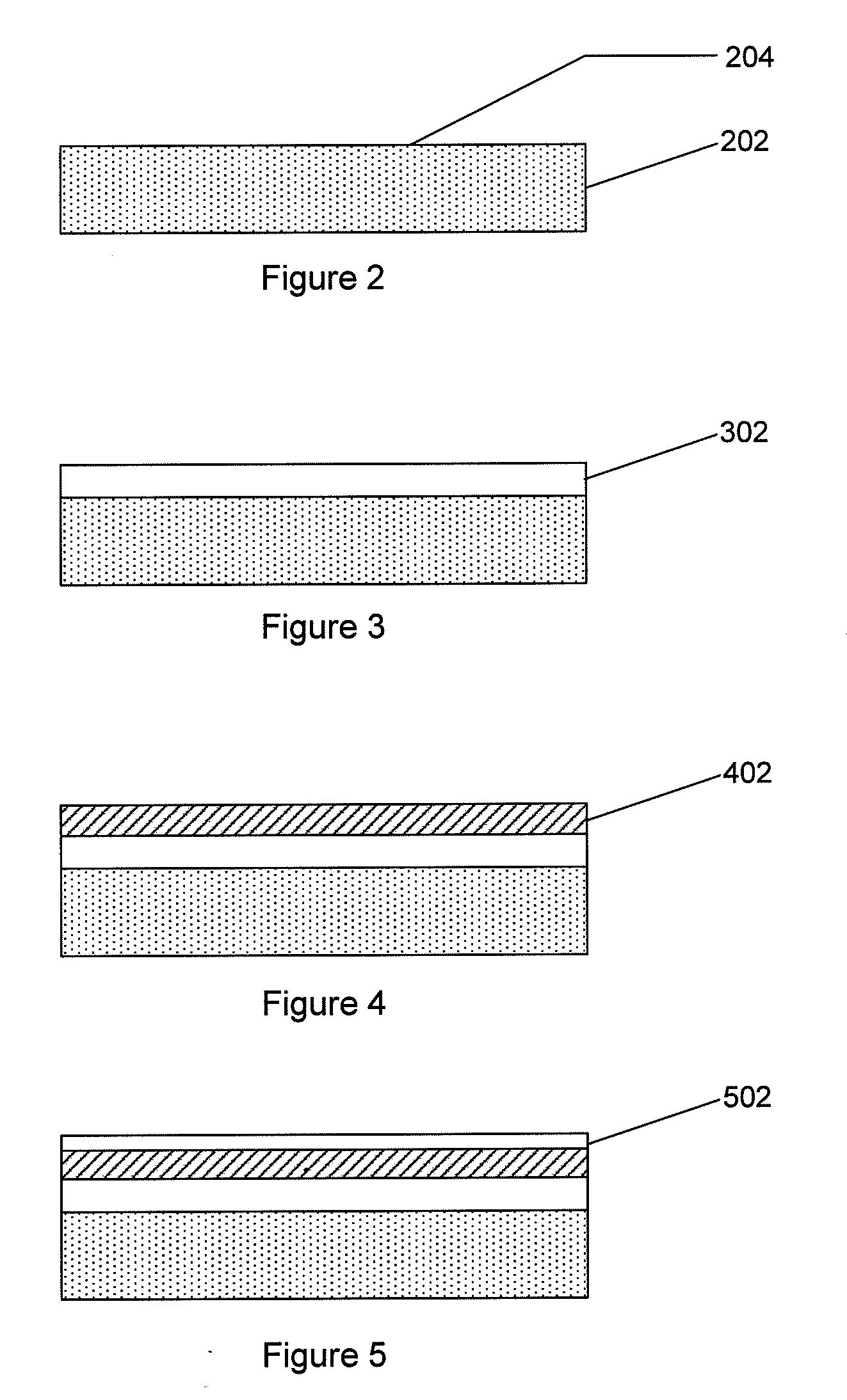
A method for making a heterojunction photovoltaic device (200) is provided for converting solar radiation to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The method and apparatus include an improved window layer (230) having an increased oxygen (140) concentration with higher optical bandgap and photo to dark conductivity ratio. The improved photovoltaic device (200) is made using a deposition method which incorporates the use of a gas mixture of an inert gas (115) and a predetermined amount of oxygen (140), deposited at or near room temperature. Window layers contemplated by the present invention include, but are not limited to, cadmium sulfide (CdS) and various alloys of zinc cadmium sulfide (ZnxCd1-xS). To further increase the efficiency of the resultant photovoltaic device (200), deposition parameters are controlled and monitored to improve the deposited window layer (230).
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
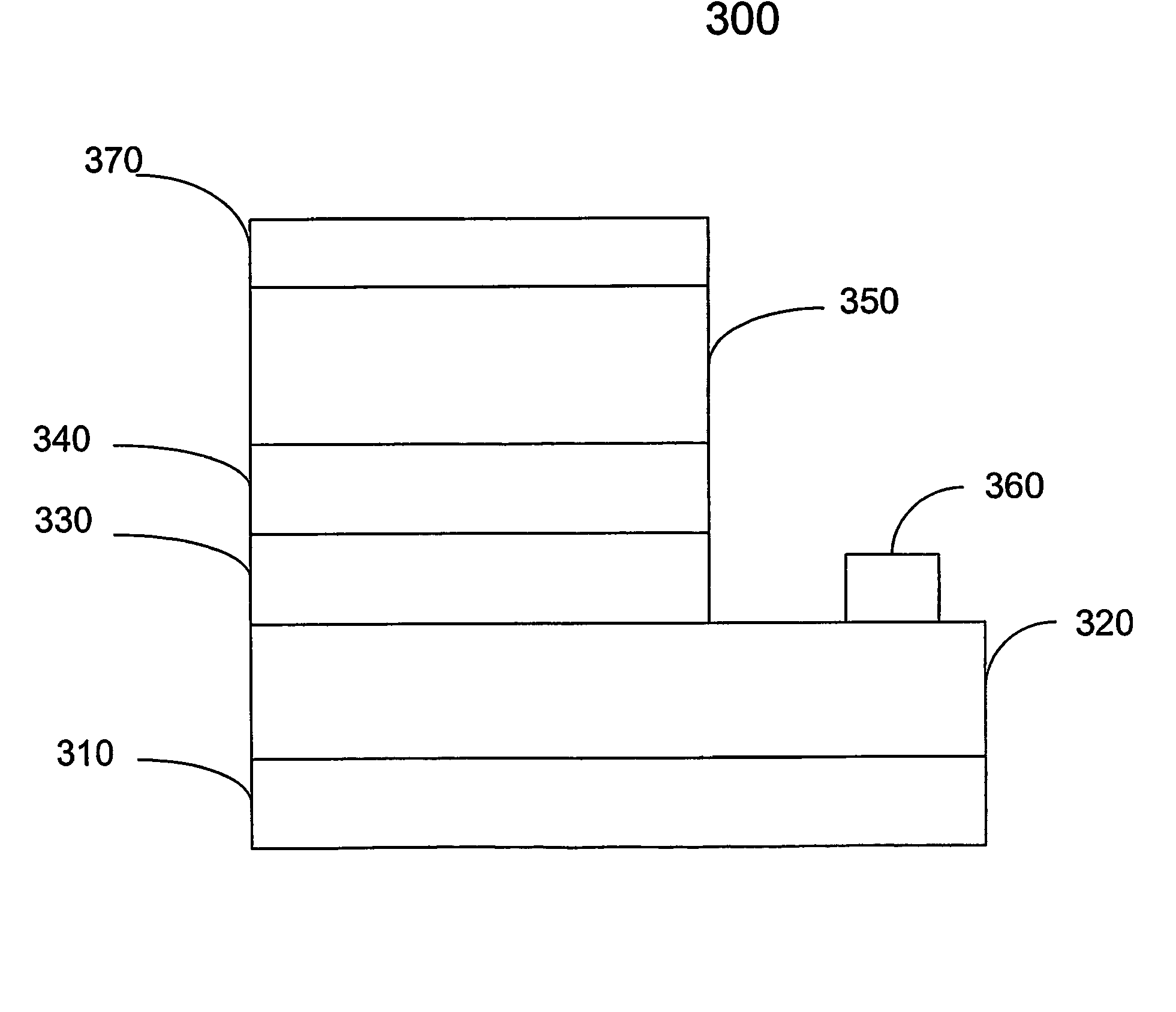
Multiple band gapped cadmium telluride photovoltaic devices and process for making the same
ActiveUS20100180935A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingHeterojunctionCharge carrier
A heterojunction photovoltaic device for the production of electrical energy in response to the incident light includes an optically transparent substrate, a front contact formed of an transparent conductive oxide for collecting light generated charge carriers, an n-type window layer formed of cadmium sulfide or zinc sulfide, a p-type absorber structure disposed on the window layer, thereby forming a rectification junction therebetween, and a back contact comprising at least one metal layer. The p-type absorber structure has a plurality of p-type absorber layers in contiguous contact. Each absorber layer contains cadmium as a principal constituent and has a different composition and a different band gap energy. The first absorber layer is in contiguous contact with the n-type window layer. The band gap energy progressively decreases from the first absorber layer to the last absorber layer in the p-type absorber structure.
Owner:AUCMOS TECH USA INC
Preparation method of active radical with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect
InactiveCN102759520AQuick checkIncrease surface areaRaman scatteringChemical vapor depositionCadmium Cation
The invention provides a preparation method of an active radical with a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect, belongs to the technical field of spectrum detection, and relates to the preparation technology of the SERS active radical, which is rapid, has high sensitivity and performs a low trace detection function. The preparation method is characterized in that firstly, a nano porous silicon columnar array with a large specific surface area is prepared by utilizing a hydrothermal etching technology; afterwards, a nanowire structure of an II-VI group compound semiconductor (such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, cadmium telluride, and the like) by utilizing a chemical vapor deposition method; and finally, nano particles of precious metal (such as gold, silver, copper and the like) are finally prepared on the nanowire structure by using a chemical reduction method, so as to obtain an active radical material. The preparation method has a wide application prospect in the aspects of clinical biomolecular fast recognition, trace chemical substance detection, biological sample analysis, and the like. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation process of each material is simple, the condition is mild and the repetition rate reaches 100 percent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
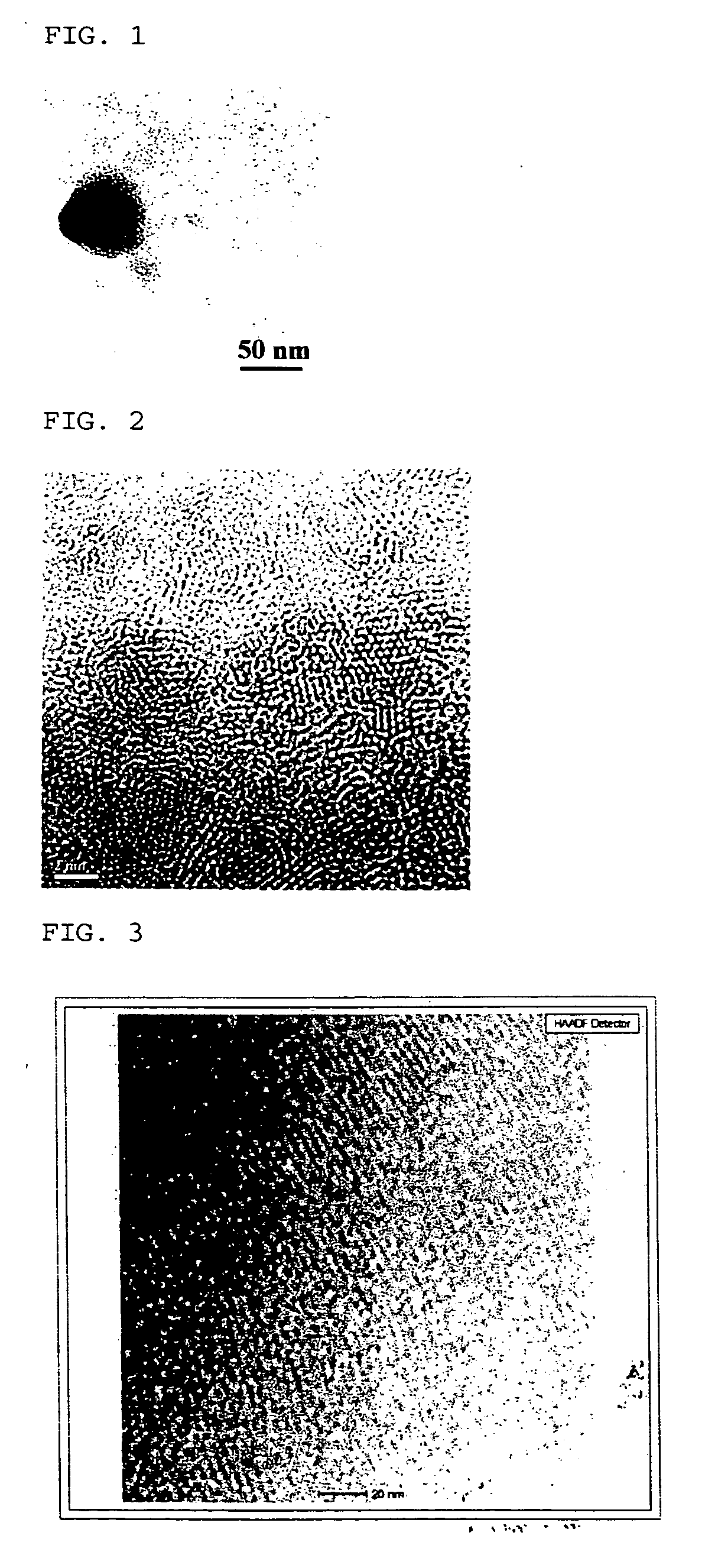
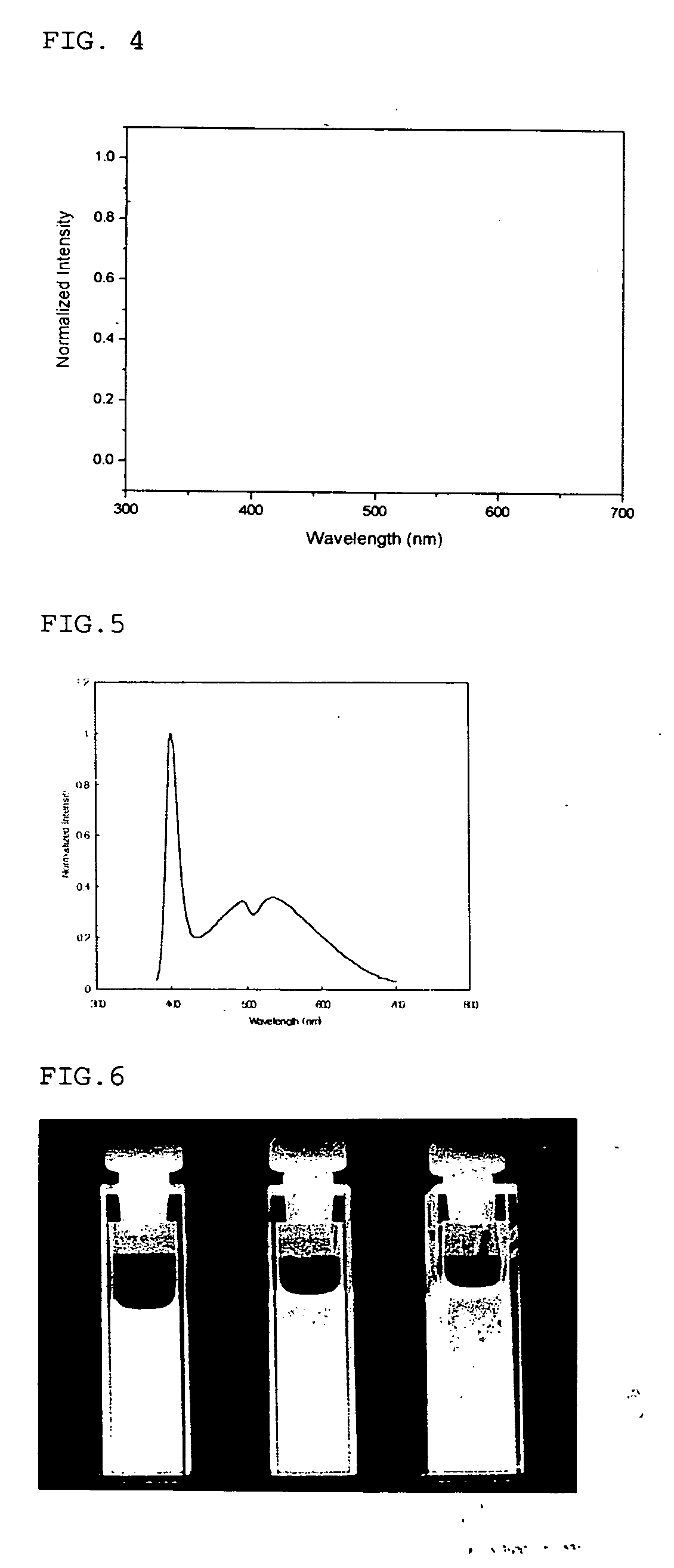
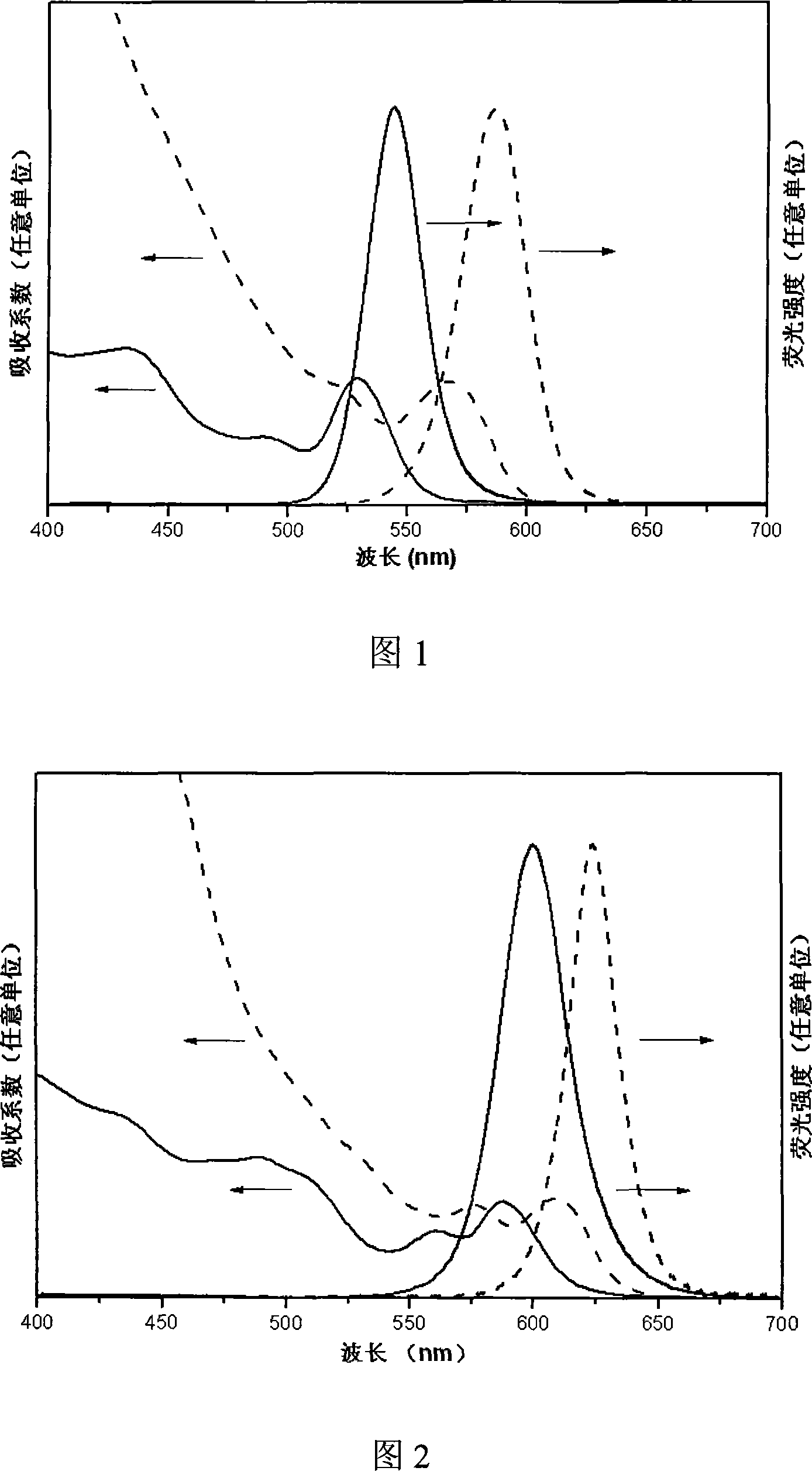
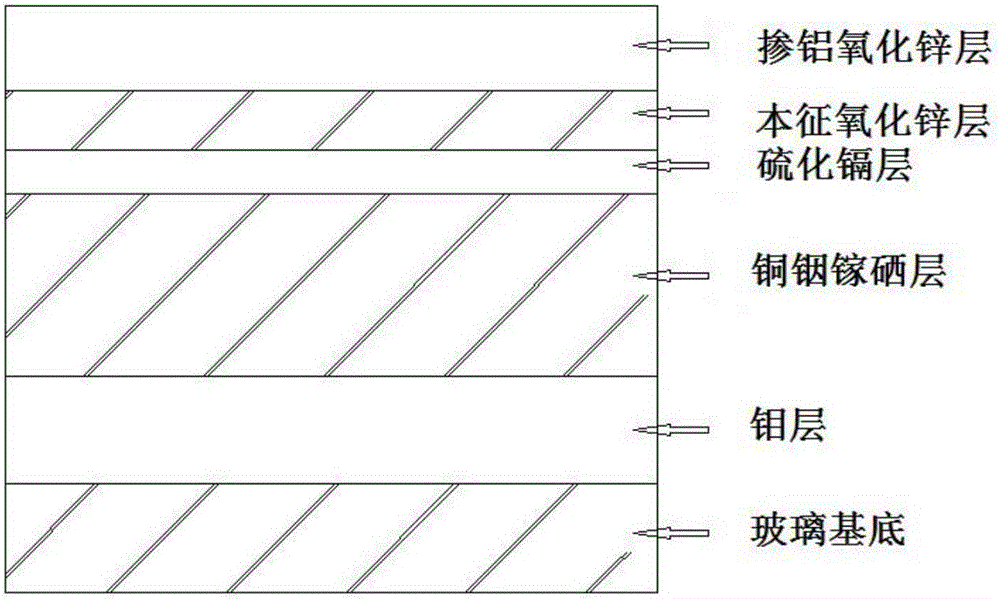
Method of preparing cadmium sulfide nanocrystals emitting light at multiple wavelengths, and cadmium sulfide nanocrystals prepared by the method
A method for preparing cadmium sulfide nanocrystals emitting light at multiple wavelengths. The method comprises the steps of (a) mixing a cadmium precursor and a dispersant in a solvent that weakly coordinates to the cadmium precursor, and heating the mixture to obtain a cadmium precursor solution, (b) dissolving a sulfur precursor in a solvent that weakly coordinates to the sulfur precursor to obtain a sulfur precursor solution, and (c) feeding the sulfur precursor solution to the heated cadmium precursor solution maintained at a high temperature to prepare cadmium sulfide crystals, and growing the cadmium sulfide crystals. Further, cadmium sulfide nanocrystals prepared by the method. The cadmium sulfide nanocrystals have uniform size and shape and can emit light close to white light simultaneously at different wavelengths upon excitation. Due to these characteristics, the cadmium sulfide nanocrystals can be applied to white light-emitting diode devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
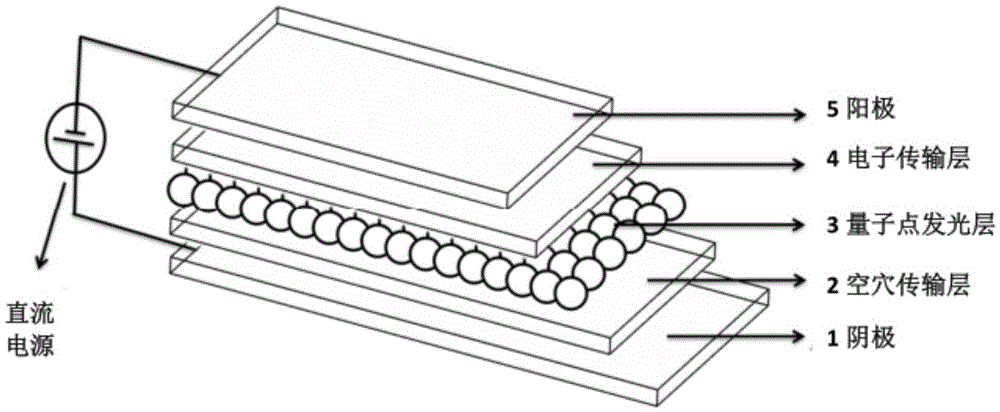
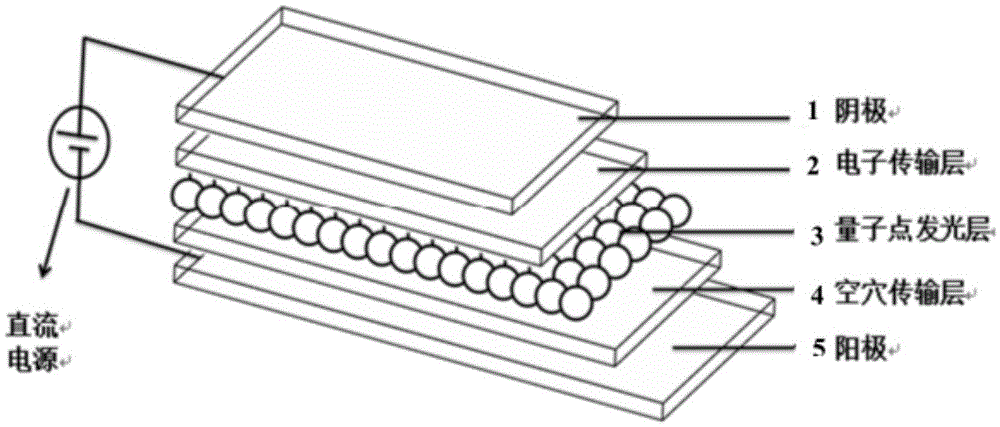
High-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure
InactiveCN105609651AIncrease transfer rateImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc selenidePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses and proposes a high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with a self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure. Except a positive electrode and a negative electrode, the high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode comprises a three-layer structure: a hole transmission layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer and an electron transmission layer, wherein one end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the hole transmission layer, the other end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the electron transmission layer, the electron transmission layer is organic nanoparticles after doped, the hole transmission layer is formed by doping a monomer, a polymer, small-molecule, inorganic oxidized metal nanoparticles or a two-dimensional nanometer material into poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene monomer), a quantum dot is quantum dots of zinc sulfide, zinc selenide, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, cadmium telluride, mercury sulfide, mercury selenide, mercury telluride or core-shell nanometer structured cadmium selenide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc selenide and graphene thereof and the like, and the negative electrode is glass or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with a layer of indium tin oxide (ITO) or fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) or graphene.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
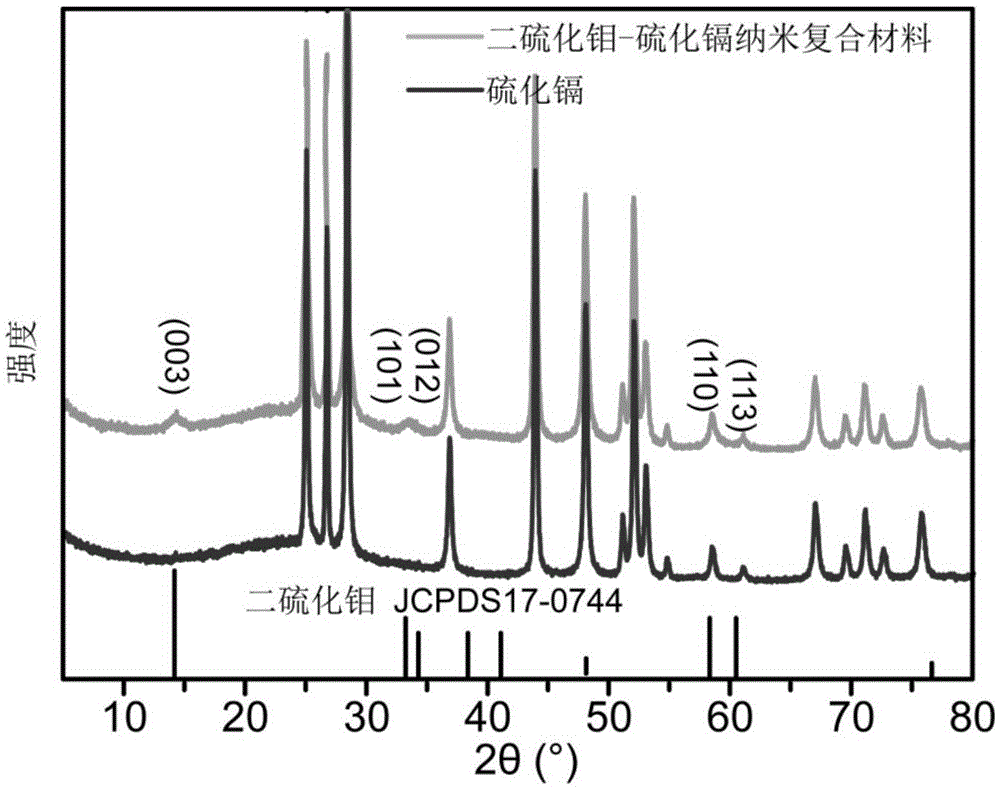
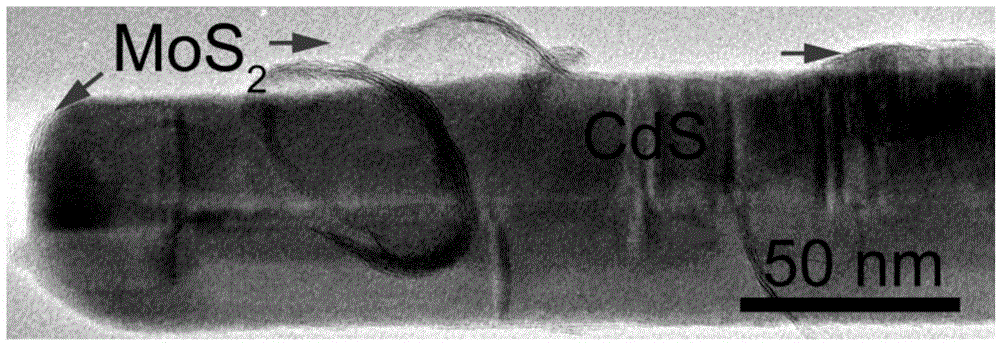
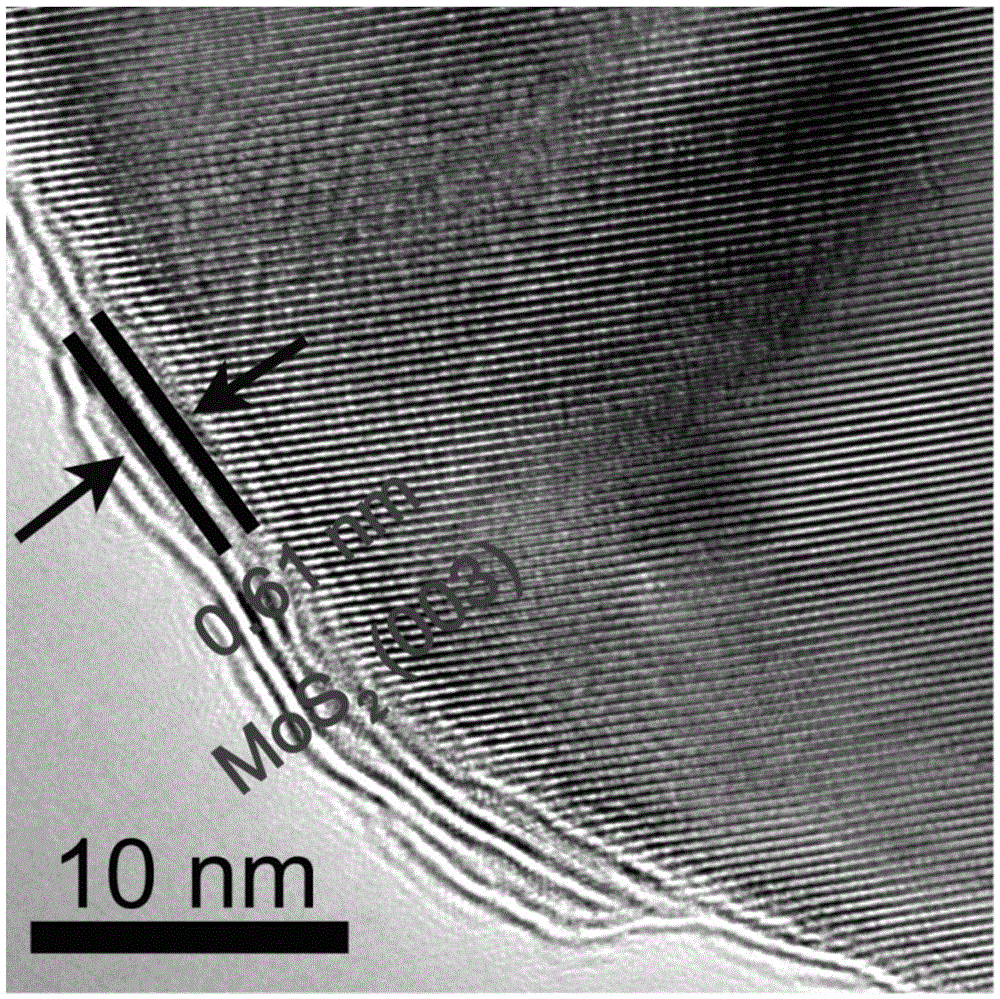
Molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105664977AThe load is easy to controlHigh catalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionElectron holeNano composites
The invention relates to a molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material and a preparing method thereof and an application of the molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material to water-photocatalytic-decomposition hydrogen production. The nanometer composite material comprises nanometer cadmium sulfide, and undefined-structure layered nanometer molybdenum disulfide growing on the nanometer cadmium sulfide in an in-situ mode. According to the nanometer composite material, the nanometer cadmium sulfide serves as a carrier; as the nanometer cadmium sulfide is of a nanometer structure, on one hand, the transmission path of electron holes can be shortened; on the other hand, as the specific surface area of the nanometer cadmium sulfide is large, the loading capacity of the molybdenum disulfide can be controlled. The molybdenum disulfide is in a layered shape and is of the undefined structure; when the molybdenum disulfide is used as a catalyst of water-photocatalytic-decomposition hydrogen production, a large number of active sites are provided for photoelectron and hydrogen ions in water reacting, and therefore the catalytic activity is improved. The molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material is used as the catalyst, and has the multiple advantages of being simple in method, low in cost, high in catalytic activity and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
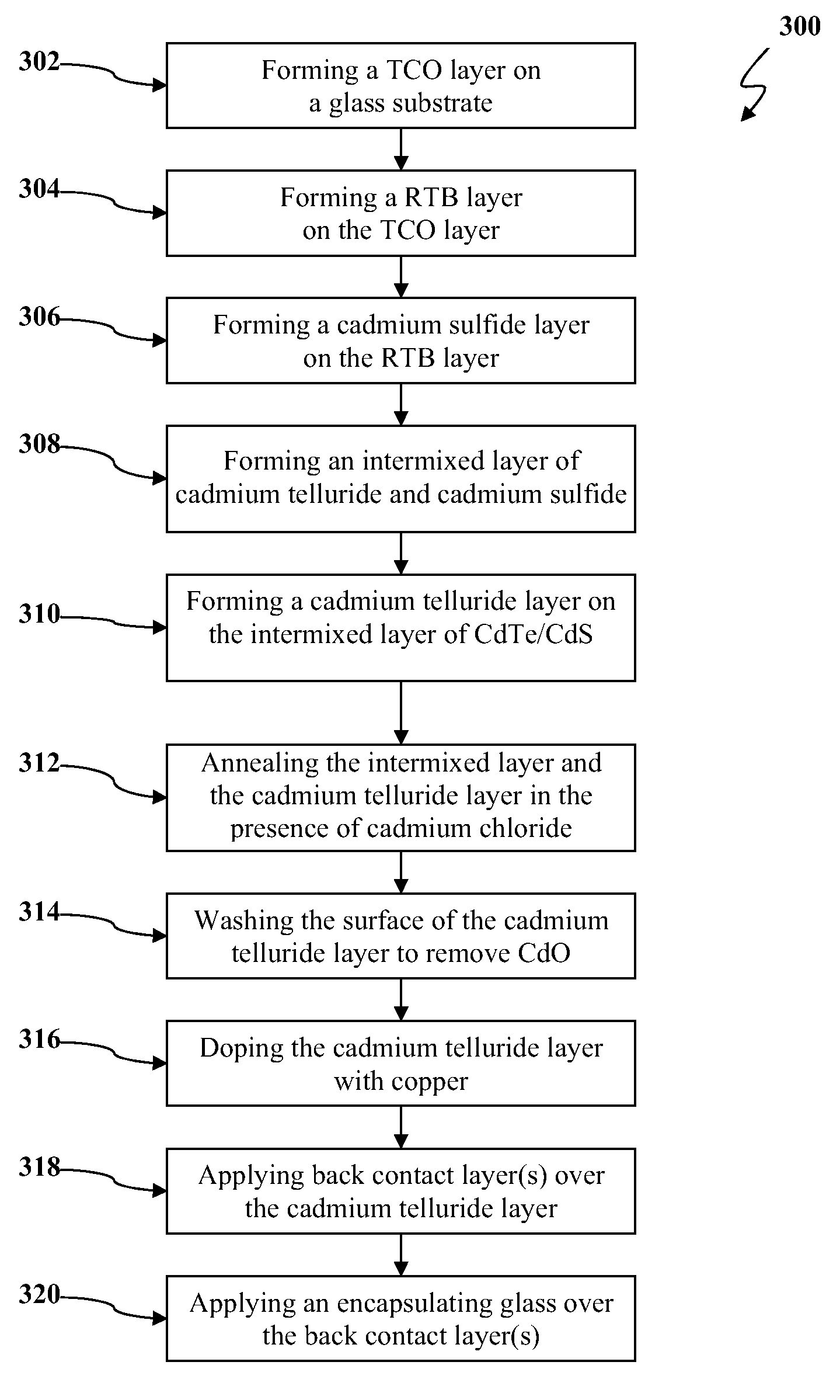
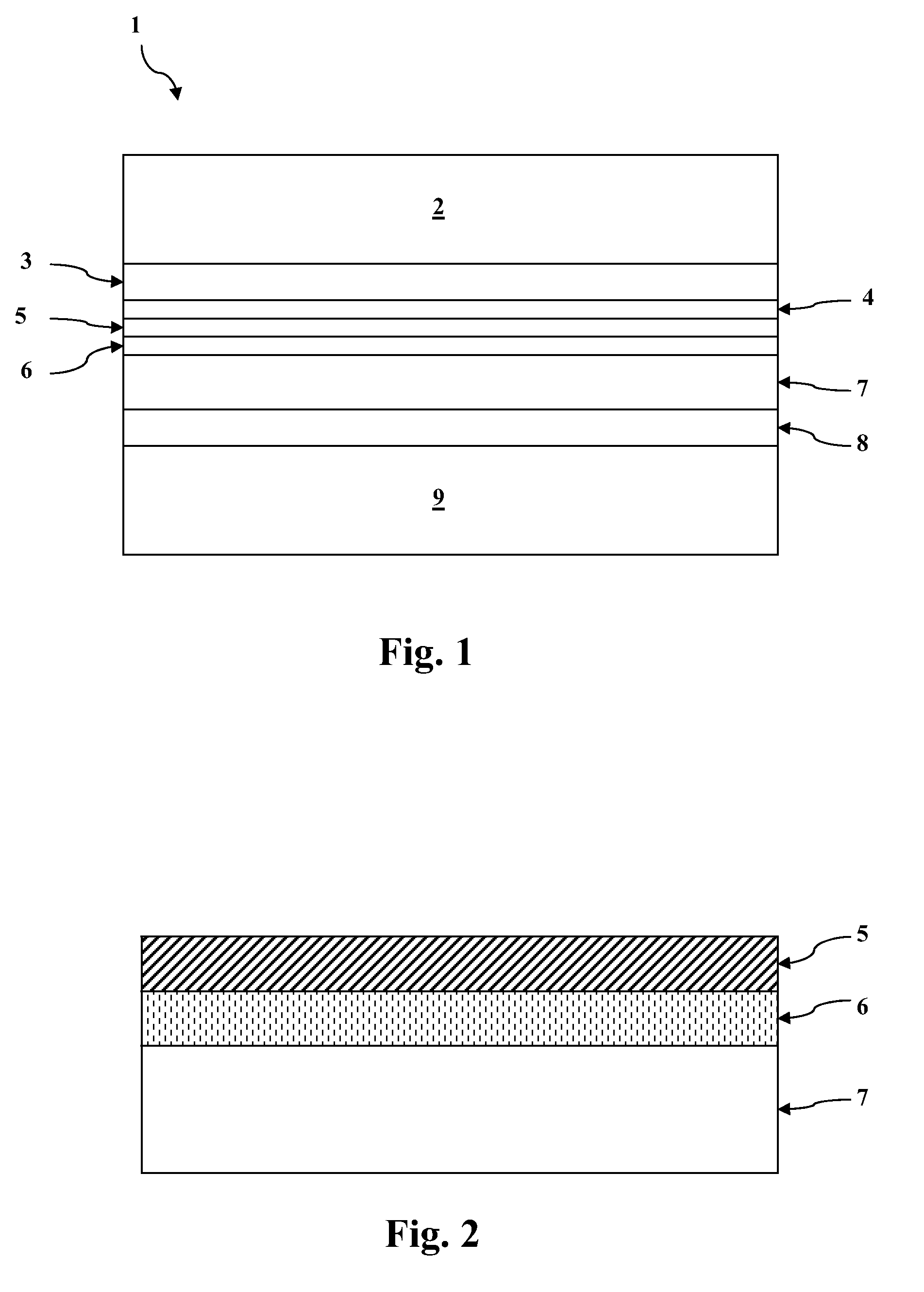
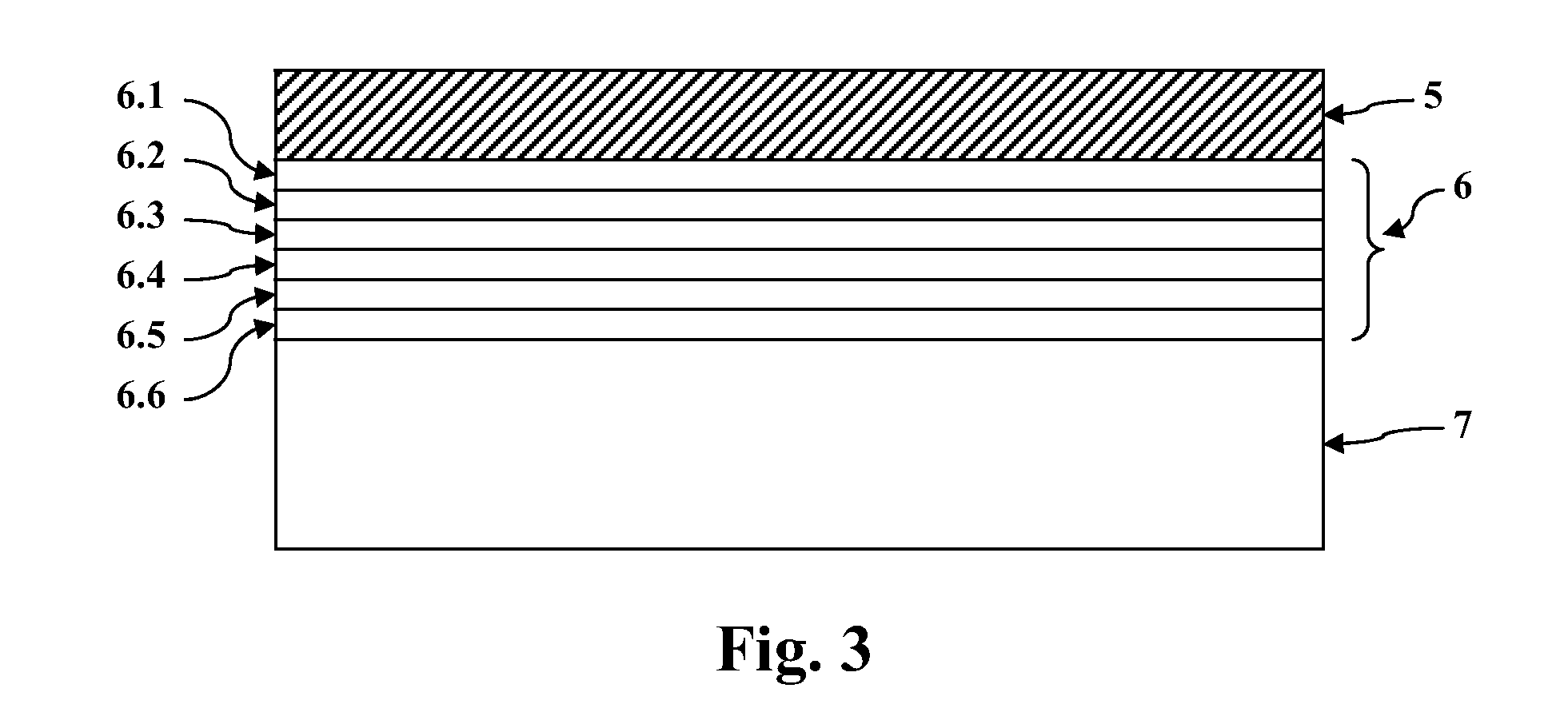
Systems and methods of intermixing cadmium sulfide layers and cadmium telluride layers for thin film photovoltaic devices
ActiveUS7939363B1Increasing tellurium concentrationReduce the concentration of sulfurFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSource materialTe element
A process for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device having an intermixed layer is provided. The process can include introducing a substrate into a deposition chamber, wherein a window layer (e.g., a cadmium sulfide layer) is on a surface of the substrate. A sulfur-containing gas can be supplied to the deposition chamber. In addition, a source vapor can be supplied to the deposition chamber, wherein the source material comprises cadmium telluride. The sulfur-containing gas and the source vapor can be present within the deposition chamber to form an intermixed layer on the window layer. In one particular embodiment, for example, the intermixed layer generally can have an increasing tellurium concentration and decreasing sulfur concentration extending away from the window layer.An apparatus for sequential deposition of an intermixed thin film layer and a sublimated source material on a photovoltaic (PV) module substrate is also provided.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Preparation method of cadmium selenide or cadmium sulfide two-dimensional monocrystal nanosheet
ActiveCN105463580AIncrease the areaHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSource materialSingle crystal
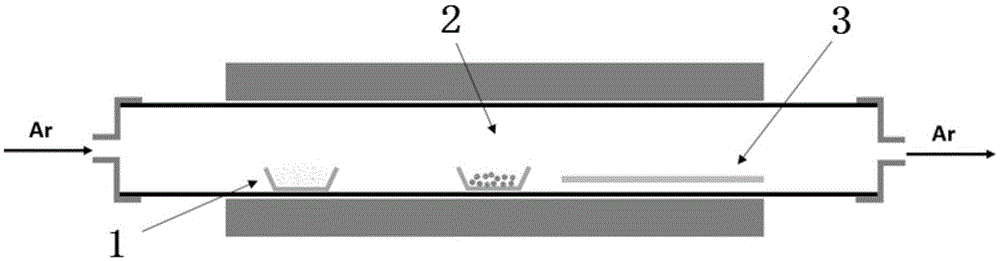
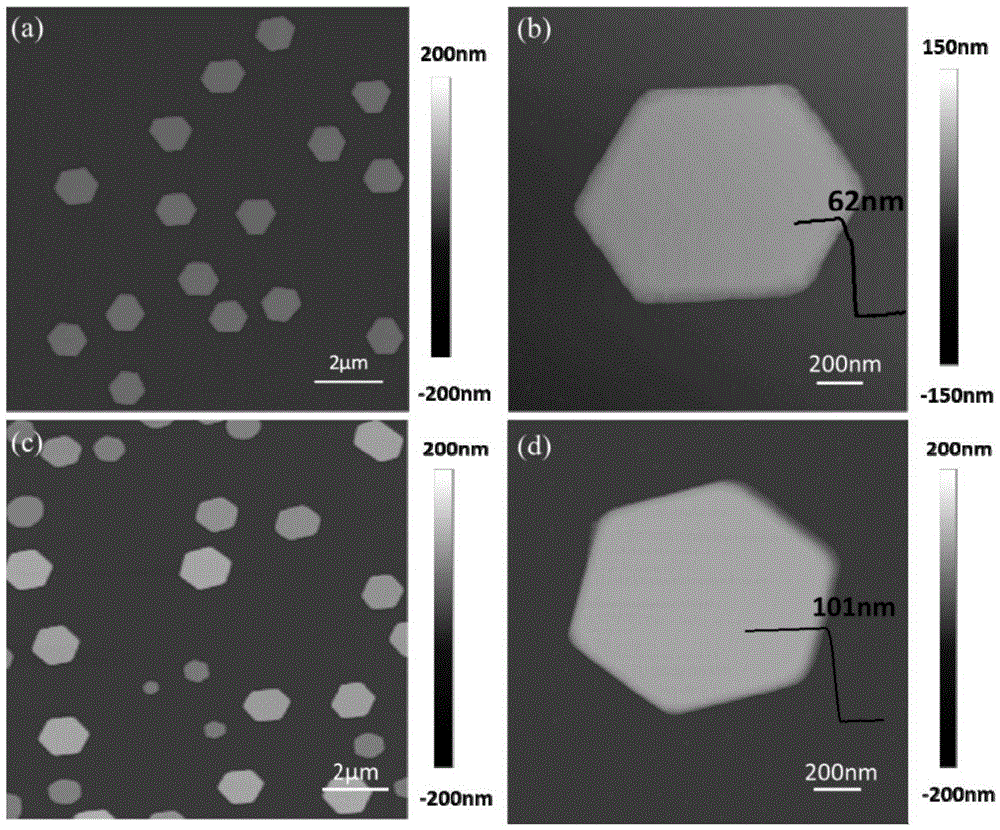
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cadmium selenide or cadmium sulfide two-dimensional monocrystal nanosheet. The method comprises the steps that the CdSe or CdS two-dimensional monocrystal nanosheet is prepared through a van der Waals epitaxial growth technology, the method is characterized in that a mica sheet which is smooth in surface and free of chemical dangling bond is adopted to serve as a substrate, CdCl2 powder or Se powder or S powder serves as a source material, argon serves as carrier gas, CdCl2 stream is reacted with Se or S steam to form CdSe or CdS steam at high temperature, and the steam is deposited on the mica sheet for nucleation and epitaxially grows into the CdSe or CdS two-dimensional monocrystal nanosheet. The preparation method of the cadmium selenide or cadmium sulfide two-dimensional monocrystal nanosheet is easy to operate, low in cost and strong in controllability, the obtained CdSe or CdS has the advantages of being good in size uniformity, high in degree of crystallinity and the like, and important research value and wide application prospect in the fields of solar cells, field effect transistors, photoelectric detectors, photocatalyses and the like are achieved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing cadmium selenide/cadmium sulfide /zinc sulfide core-shell quantum dots
InactiveCN101168663AEasy to operateRaw material safetyLuminescent compositionsCadmium selenideSolvent
The invention discloses the preparation method of low cost cadmium selenide (CdSe) / cadmium sulphide (CdS) / zinc sulphide (ZnS) quantum point. The invention is characterized in that ethide xanthic acid cadmium and ethide xanthic acid zinc are adopted to be respectively dissolved in the mixed solvent of oleic amine and oleic acid, as well as cadmium stearate and zinc stearate; as the front dirking liquid of clads CdS and ZnS of a SdSe quantum point, the invention is slowly dropped into the mixed liquor of octadecene and octadecylamine dissolved with CdSe quantum point, so as to obtain CdSe / CdS / ZnS quantum points. The invention has the advantages that the price of the raw material is cheap, the toxicity is low, the operation is simple, and the mass synthesis is proper.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
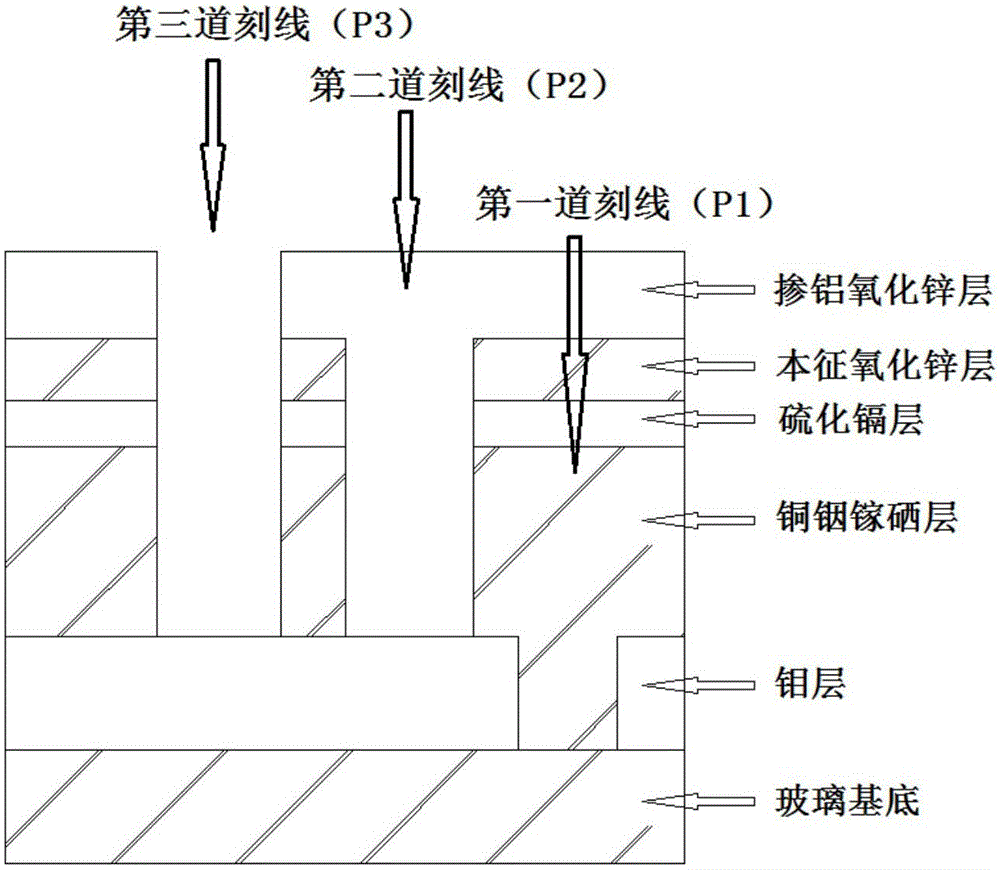
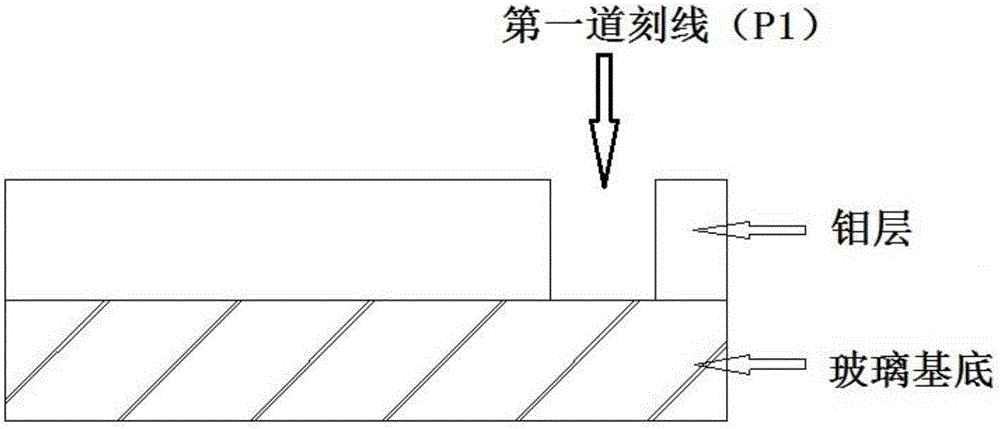
Full-laser grooving and scribing method of large-area copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin-film solar cell assembly
ActiveCN104993013AIncrease component powerReduce dead areaFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumAluminum doped zinc oxide
The invention provides a full-laser grooving and scribing method of a large-area copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin-film solar cell assembly. The method comprises steps of using a laser to groove and scribe a molybdenum thin film prepared on soda-lime glass so as to form a first scribed line (P1); successively preparing a CIGS layer, a cadmium sulfide layer and an intrinsic zinc oxide layer on the molybdenum layer where the P1 has been grooved and scribed; after finishing the above film layer preparation, using a laser to perform grooving and scribing so as to form a second scribed line (P2) which is parallel to the P1; and after preparing an aluminum-doped zinc oxide layer on the intrinsic zinc oxide layer where the P2 has been grooved and scribed, using a laser to perform grooving and scribing so as to form a third scribed line (P3) which is parallel to the P1. According to the invention, inner join is performed for the CIGS thin-film solar cell assembly by the laser grooving and scribing method, so defects of large area of dead zones and frequency change of machinery needles in traditional machinery grooving and scribing technology can be overcome, thereby increasing efficiency of the assembly, improving stability of the grooving and scribing device and achieving objectives to reduce production cost and improve production efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION
Large Scale Chemical Bath System and Method for Cadmium Sulfide Processing of Thin Film Photovoltaic Materials
InactiveUS20100087027A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumCelsius Degree
A method for forming a thin film photovoltaic material. The method includes providing a plurality of substrates. Each of the substrates has a surface region, an overlying first electrode material, an absorber material including at least a copper species, an indium species, and a selenium species. The method immerses the plurality of substrates in an aqueous solution including an ammonia species, a cadmium species, and a organosulfur (for example, thiourea) species in a bath to form a cadmium sulfide window material having a thickness of less than about 200 Angstroms overlying the absorber material. The aqueous solution is maintained at a temperature ranging from about 50 to about 60 Degrees Celsius. The plurality of substrates having at least the absorber material and the window layer are removed from the aqueous solution. The aqueous solution is further subjected to a filter process to substantially remove one or more particles greater than about 5 microns.
Owner:CM MFG
Method for preparing cadmium sulfide-titanium dioxide nano-tube composite catalyst
InactiveCN101786005AWide spectral responseImprove catalytic hydrogen production activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionTio2 nanotubeSpectral response
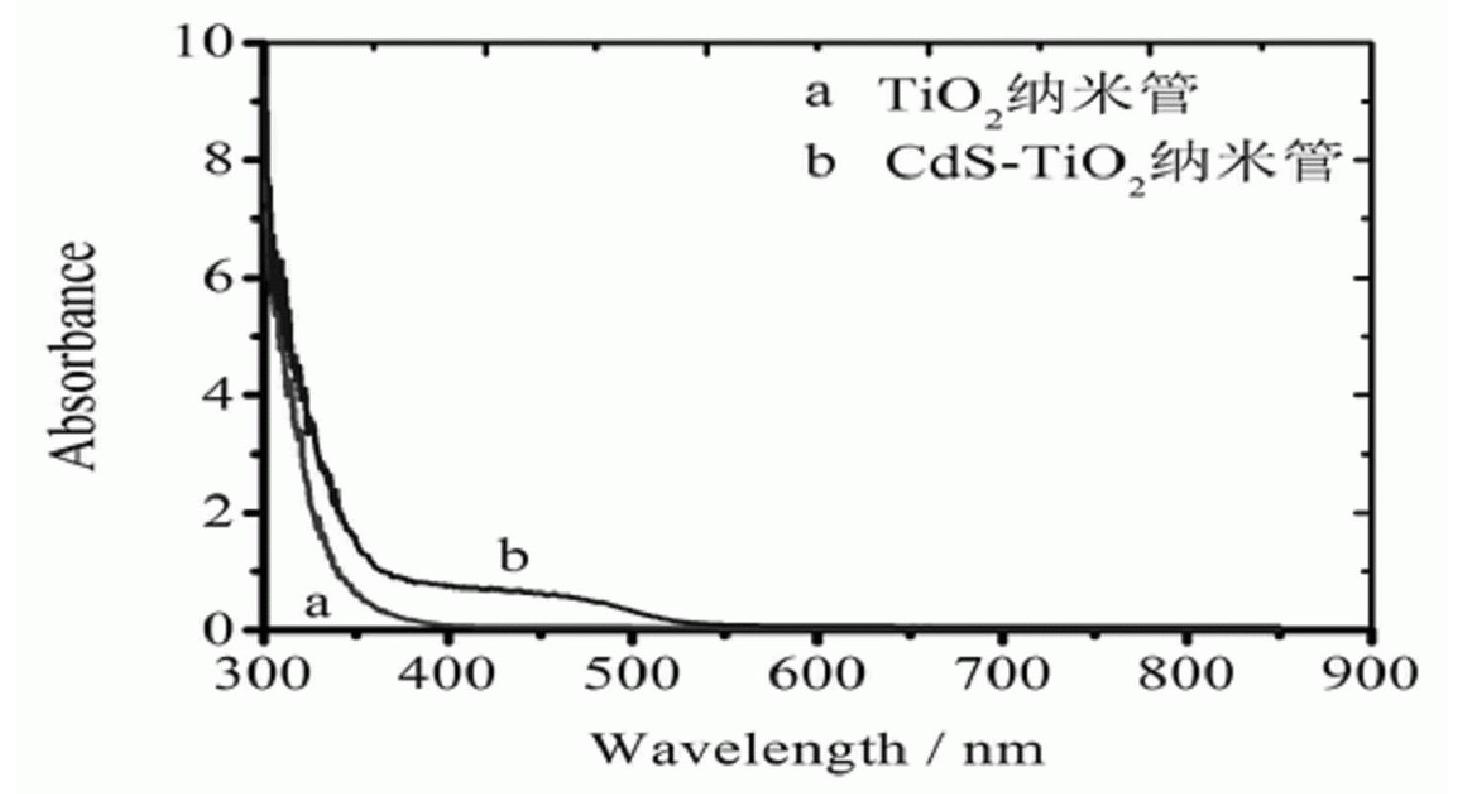
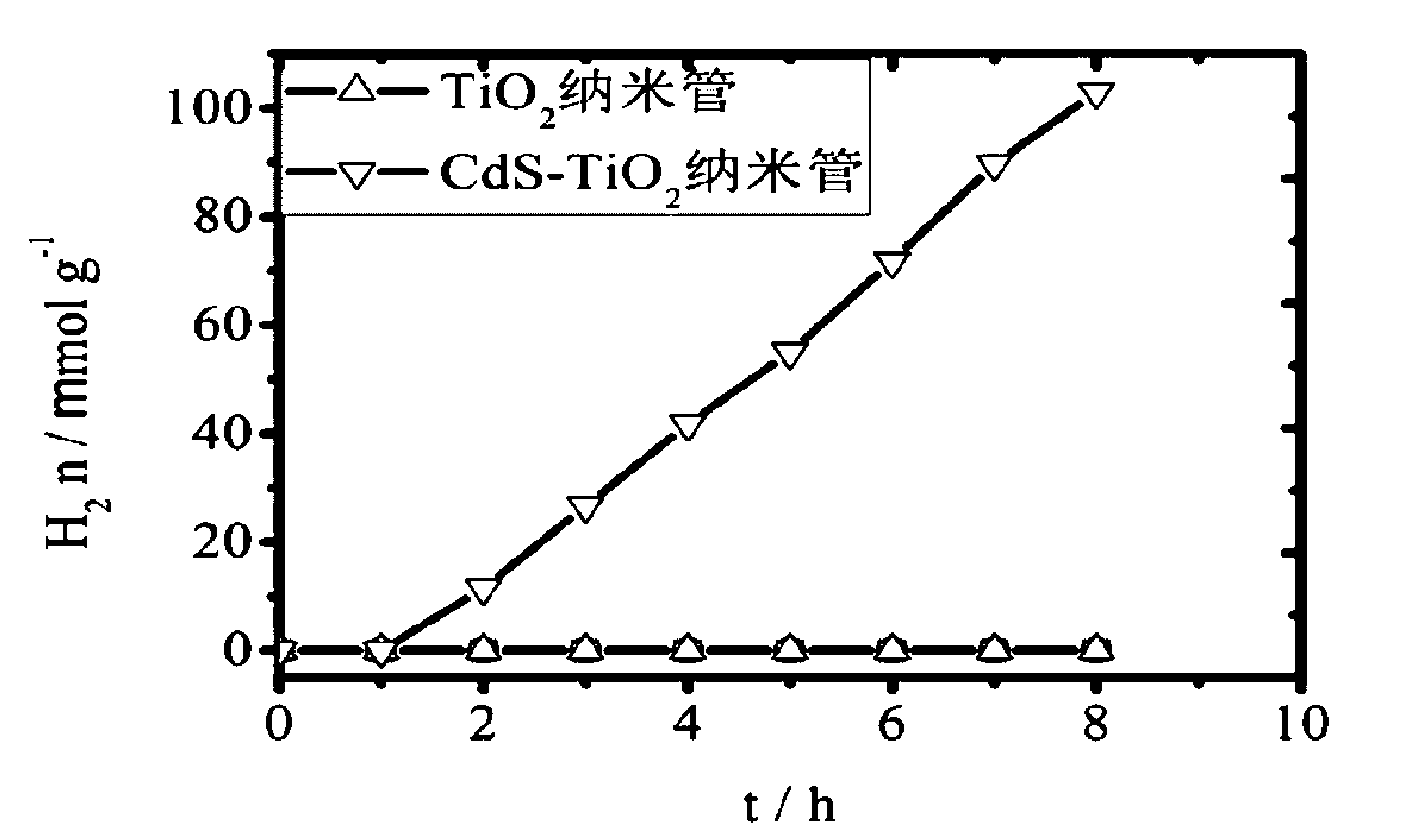
The invention provides a method for preparing a cadmium sulfide-titanium dioxide nano-tube composite catalyst in the technical field of photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: 1, putting anatase TiO2 nano-particles in a polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle, adding deionized water into the reaction kettle, and stirring the mixture; 2, adding aqueous solution of CdCl2.2.5H2O and aqueous solution of Na2S.9H2O into the polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle in sequence, mixing the mixture, adding NaOH into the mixture, and performing ultrasonic oscillation on the mixture; and 3, performing microwave heating on the polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle, standing the mixture, cleaning the mixture until the pH of the lotion is 7, pumping and filtering the lotion, and drying the filter cake in vacuum to obtain the CdS-TiO2 nano-tube composite catalyst. In the CdS-doped TiO2 nano-tube prepared by the method, spectral response of the titanium dioxide nano-tube is expanded to a visible light range to ensure that the catalyst can absorb the visible light, so that the catalytic hydrogen production activity of the catalyst is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
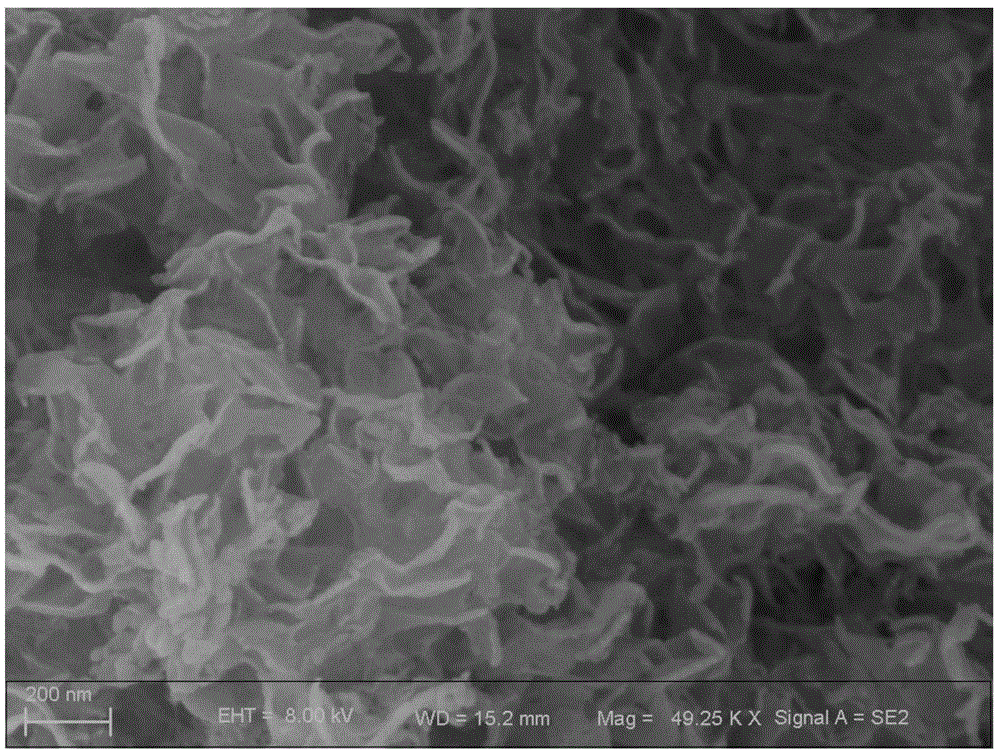
Complexing-agent-assisted preparation method of cadmium sulfide multi-level-structured nano-grade material
InactiveCN103073049AEasy to controlImprove protectionCadmium sulfidesNanotechnologyVacuum pumpingChemical reaction
The invention relates to a complexing-agent-assisted preparation method of a cadmium sulfide multi-level-structured nano-grade material. The method is characterized in comprising the steps that: a, a chemical reaction liquid is prepared, wherein 1 part of cadmium salt by weight and 0-50 parts of organic small-molecular compound by weight are dissolved in 100 parts of water or water / ethanol mixture by weight; under a temperature of 30-80 DEG C, stirring is sufficiently carried out, such that a reaction liquid is prepared; b, the cadmium sulfide multi-level-structured nano-grade material is synthesized, wherein the reaction liquid prepared in the step a is delivered into an autoclave with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner; a sulfur source is added, and a reaction is carried out; after the reaction, the autoclave is naturally cooled to 60 DEG C; methanol with a volume of 20-30% of that of the total volume of the reaction liquid is added; a product is filtered, and is washed multiple times by using anhydrous ethanol; and the product is dried by vacuum pumping, such that the cadmium sulfide nano-grade material with different crystal forms and morphologies is obtained. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost, and high operability. With the method, requirements of production and application can be satisfied by one step.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Method for manufacturing cadmium telluride thin film solar cell modules
InactiveCN101807622AThe consistency can be adjustedAvoid short circuitFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEtchingNew energy
The invention provides a method for manufacturing cadmium telluride thin film solar cell modules, belonging to the field of new energy materials and apparatuses. The method comprises the steps of: firstly depositing a cadmium sulfide thin film and a cadmium telluride thin film on a transparent conductive film glass which is not scribed by laser to obtain a 'glass / transparent conductive film glass / cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride' structure; heat treating the structure; performing laser grooving and scribing to elide 'transparent conductive film glass / cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride'; performing chemical etching; filling low-temperature solidified polyimide at a scratch place of the 'transparent conductive film glass / cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride'; depositing a back contact layer to perform postprocessing; performing the laser grooving and scribing to elide a 'cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride / back contact layer' near the score of the 'transparent conductive film glass / cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride'; depositing a metal back electrode layer;and performing the laser grooving and scribing to elide 'cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride / back contact layer / metal back electrode' near the scores of the 'transparent conductive film glass / cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride' and the 'cadmium sulfide / cadmium telluride / back contact layer' to obtain cadmium telluride thin film solar cell modules which are integrated in series. The method guarantees to be capable of obtaining the thin film with even and coincident quality when depositing the cadmium sulfide and the cadmium telluride thin film in the technology for manufacturing the cadmium telluride thin film solar cell modules by means of full drying, guarantees the uniformity of heat treating of subsequent cadmium chloride-containing atmosphere, can not influence formation of an element cell and realization of the in-series integration of the element cell.
Owner:SICHUAN SUNTECH POWER
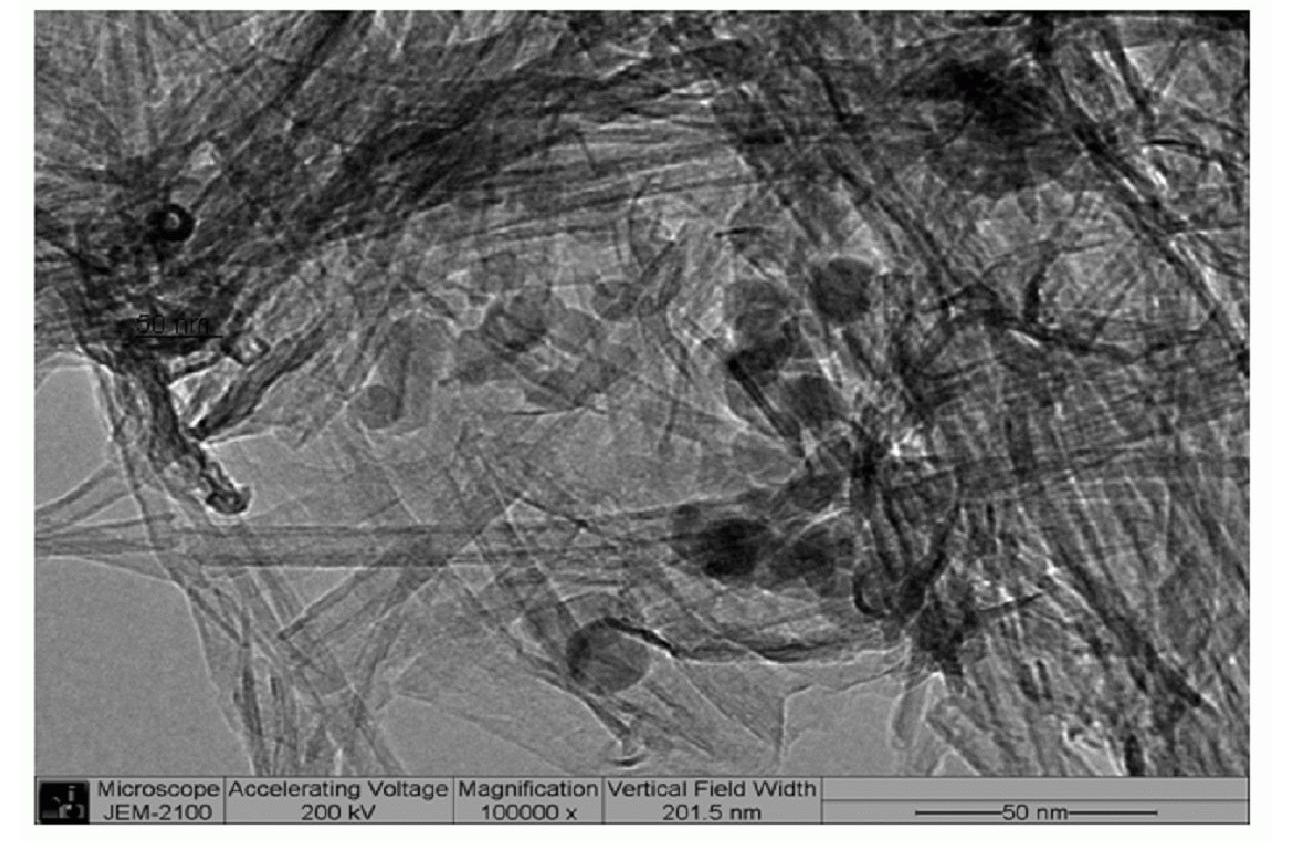
Synthesis method of cadmium sulfide nano rod
A process for synthesizing the cadmium sulfide nanorods which can emit blue light under irradiation of ultraviolet lamp includes sufficiently mixing cadmium chloride with thioacetamine in the aqueous solution of the micelles of amine trimethyl hexadecanebromide, dripping the solution of sodium hydroxide to make S ions released by thioacetamine and cadmium chloride take part in reaction to generate nuclei, and gradual growing to become nanorods.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Preparation of silver/cadmium sulfide-nanoparticle-comodified titanium dioxide nanotube array
InactiveCN102965710AEffective size controlEffective control of adhesionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingArray data structureSolar cell
The invention belongs to the field of nano material preparation, and relates to a method for comodifying a titanium dioxide nanotube array with silver and cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, which comprises the following steps: carrying out ultrasonic cleaning on a high-purity titanium sheet to remove oil, removing the natural oxide film, and carrying out secondary anodization to prepare an ordered titanium dioxide nanotube array; and treating the titanium dioxide nanotube array with a coupling agent, depositing Ag nanoparticles by an SILAR (successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction) process, and modifying the Ag-modified titanium dioxide nanotube array with CdS nanoparticles, thereby obtaining the Ag / CdS-nanoparticle-comodified titanium dioxide nanotube array. The invention is simple to operate and has the advantage of low cost; the noble metal and narrow-energy-gap semiconductor nanoparticles are utilized to comodify the titanium dioxide nanotube array, thereby effectively widening the absorption range of TiO2 in the visible light region and lowering the recombination rate of the electron-hole pair; and the invention has wide prospects in the aspects of solar cells, toxic or harmful pollutant degradation and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Heterogeneous p-n knot nano composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104549270AIncrease profitImprove photocatalytic efficiencyBiocideDisinfectantsSemiconductor materialsNano structuring
The invention discloses a p-n knot nano composite material in a special structure and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of inorganic non-metal nano materials, environmental protection and solar energy utilization. The p-n knot material is a surface-modified (partially wrapped) nanoscale large energy gap n type semiconductor material (titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, stannic oxide and the like) by taking a low energy gap p type semiconductor material (cuprous oxide, cuprous sulfide, cadmium sulfide and the like) in a low-dimensional nano structure (spherical, polyhedral, linear and the like) as the inner core. By adopting a method of controlling hydrolysis of a metal salt, a lot of heterogeneous p-n knots are constructed on the surface of low energy gap p type semiconductor material in the low-dimensional nano structure. The p-n knot nano composite material can be directly used for solving the problem of decomposition of organic matters under visible lights, deactivation of microbial pathogens and efficient utilization of solar energy, particular the problem of low electron-hole separation efficiency of a single-component photocatalyst material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanometer, composite semiconductor photocatalyst, and its prepn. method
InactiveCN1792445AImprove stabilityExtended Response Wavelength RangeCatalyst activation/preparationDispersityPhotocatalytic reaction
A nano-class semiconductor-type composite catalyst is a semiconductor nano-particle consisting of the sulfide or selenide as core and the coated TiO2 layer as shell. Its preparing process includes such steps as preparing high-dispersity cadmium sulfide (or selenide) nano-particles by wet chemical method and surfactant modifying, ultrasonic hydrolysis of the organic alkoxide of Ti to obtain TiO2, and physical combination between TiO2 and codmium sulfide (or selenide) nano-particles. It has high photocatalytic activity and stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing cadmium sulfide graphite-like carbon nitride compound photocatalyst
InactiveCN105562055AHigh activityEffective recoveryPhysical/chemical process catalystsMuffle furnaceCadmium sulfide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cadmium sulfide graphite-like carbon nitride compound photocatalyst. The photocatalyst is applied to the field of carbon dioxide reduction achieved through photocatalysis. Urea is placed in a quartz crucible drying box to be dried, and then a crucible is moved to a muffle furnace to be forged; after forging ends, the crucible is naturally cooled, and a g-C3N4 catalyst is obtained; the g-C3N4 catalyst is taken and placed in a round-bottom flask containing deionized water to be stirred to obtain suspension, and then a cadmium nitrate solution and a thioacetamide solution with the molar ratio being 1:1.5 are weighed and have a constant-temperature reaction in the suspension; after the reaction, the product is cooled to room temperature, centrifuged and washed with alcohol and deionized water for many times, the product is dried, ground and put into a bag, and the CdS / g-C3N4 compound photocatalyst is obtained. Raw materials used in the method are cheap and easy to obtain, operation is easy and convenient, activity evaluation is conducted on the prepared photocatalyst, results show that the photocatalyst can effectively reduce CO2, and the activity of the photocatalyst is greatly improved compared with a pure CdS catalyst and a pure g-C3N4 catalyst.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing nano bars of cadmiun sulfide
InactiveCN1519199ANo pollution in the processSimple operation processNanostructure manufactureCadmium sulfidesHigh volume manufacturingCadmium Cation
A process for preparing the cadmium sulfide nanorods includes proportionally adding mercaptoacetic acid to the solution containing cadmium ions, stirring, proportionally adding sodium sulfide, reaction at 100-500 deg.C for 1-200 hr, centrifugal treating, and drying. Its advantage is no environmental pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Establishing method of paper-based photoinduced electrochemical biological sensor with high flux
InactiveCN107064118AImprove conductivityHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFiberElectrochemical biosensor
The invention discloses a photoinduced electrochemical biological sensor with advantages of simple operation and high flux, which is successfully applied to simultaneously detect three types of cancer cells. The photoinduced electrochemical biological sensor is characterized in that a layer of gold nanoparticles is modified onto the surface of paper fiber through gold nanometer self-catalytic reduction; then, preparing cadmium sulfide-graphene-zinc oxide bar ternary composite materials at the surface of a paper working electrode which are modified by long gold, and using as photo-electrodes; using chemical light emitting to replace the traditional xenon lamp; by controlling the chemical light emitting reaction sequence, sequentially exciting photo-electrodes; sequentially detecting three photo-current peaks, so as to simultaneously detect the three types of cancer cells.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Monoatomic catalyst and preparation method thereof, and application of monoatomic catalyst in photolysis of water to produce hydrogen
InactiveCN108686680AImprove catalytic performanceHigh photocatalytic hydrogen production rateMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsMaterials preparationCadmium sulfide
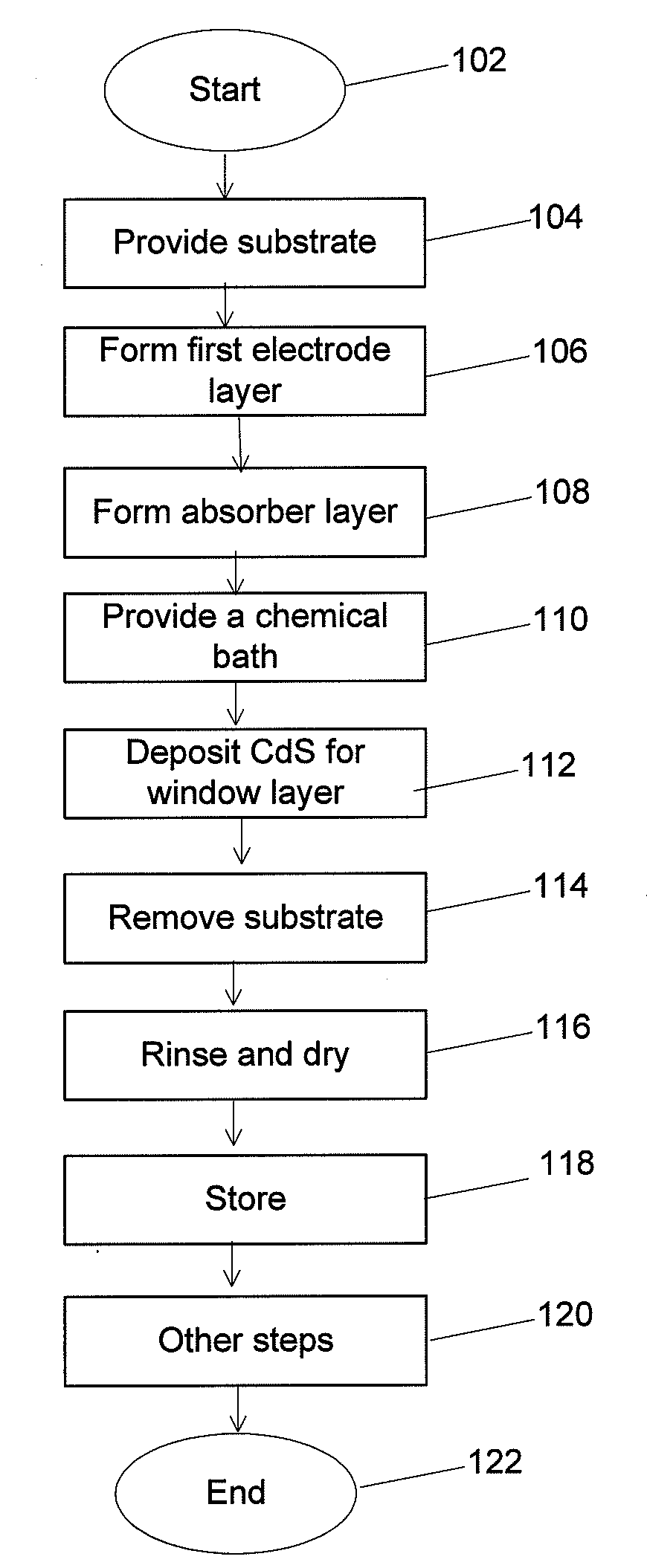
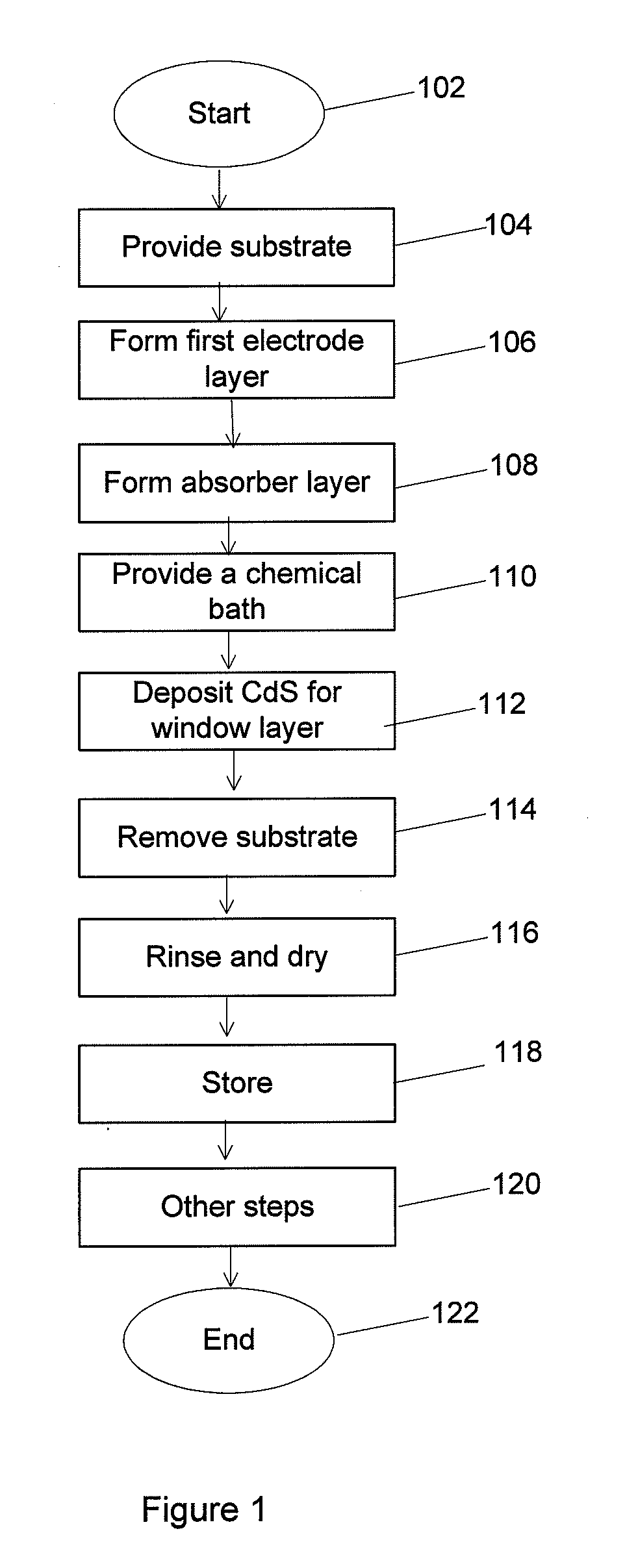
The invention specifically relates to a monoatomic catalyst and a preparation method thereof, and application of the monoatomic catalyst in photolysis of water to produce hydrogen, belonging to the technical field of nano-material preparation and hydrogen production catalysts. The catalyst is a composite material formed by loading the single atom of precious metal onto a cadmium sulfide nano-material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a cadmium sulfide nano-material; (2) introducing the cadmium sulfide nano-material prepared in the step (1) into a solution ofa precious metal source to obtain a reaction solution containing a precursor; and (3) separating the precursor from the reaction solution obtained in the step (2), and calcining the precursor so as toobtain the composite material. The monoatomic catalyst of the invention can be used for photolysis of water to produce hydrogen, and the photocatalytic hydrogen production rate of the catalyst can beas high as 47.41 mmol / h / g, which is nearly 50 times the catalytic efficiency of catalysts only using cadmium sulfide; so the photocatalytic hydrogen production effect of cadmium sulfide-based catalysts are remarkably improved.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
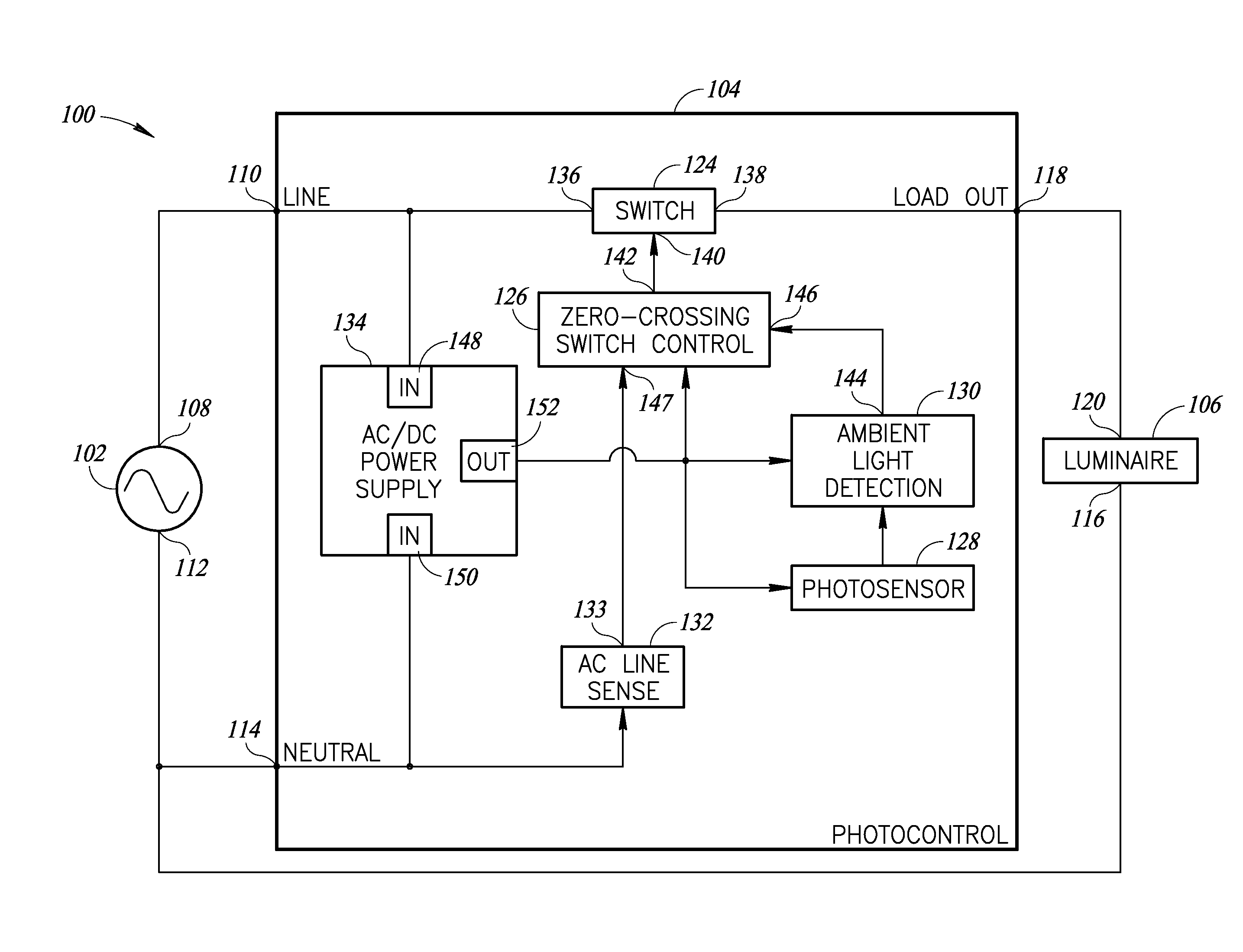
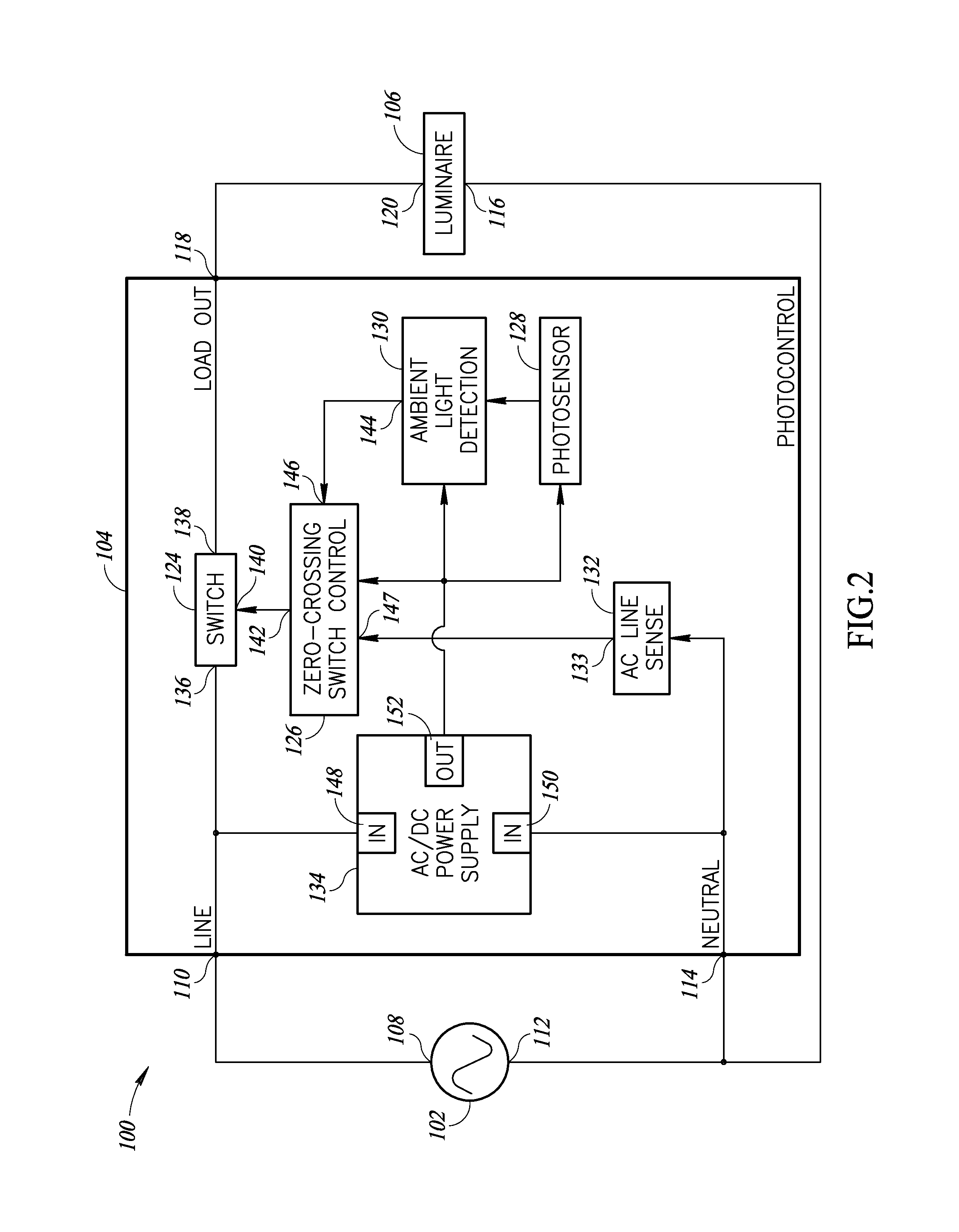
Low power photocontrol for luminaire
Photocontrol apparatus that controls a luminaire or other load such that the luminaire is switched on during nighttime hours and off during the daytime. The photocontrol consumes only microwatts of power in either the ON or the OFF state, unlike traditional relay- or triac-based photocontrols. The photocontrol does not require a voltage generating photo sensor to generate power for the photocontrol. A solar cell, semiconductor photo diode or photo diode string, cadmium sulfide cell, semiconductor ambient light sensor, etc., may be used as the sensor element. The photocontrol switches power to the load at the zero-crossing of an AC input voltage, which reduces inrush current and the switching currents caused by traditional photocontrols which may switch at any point on the AC input voltage waveform.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
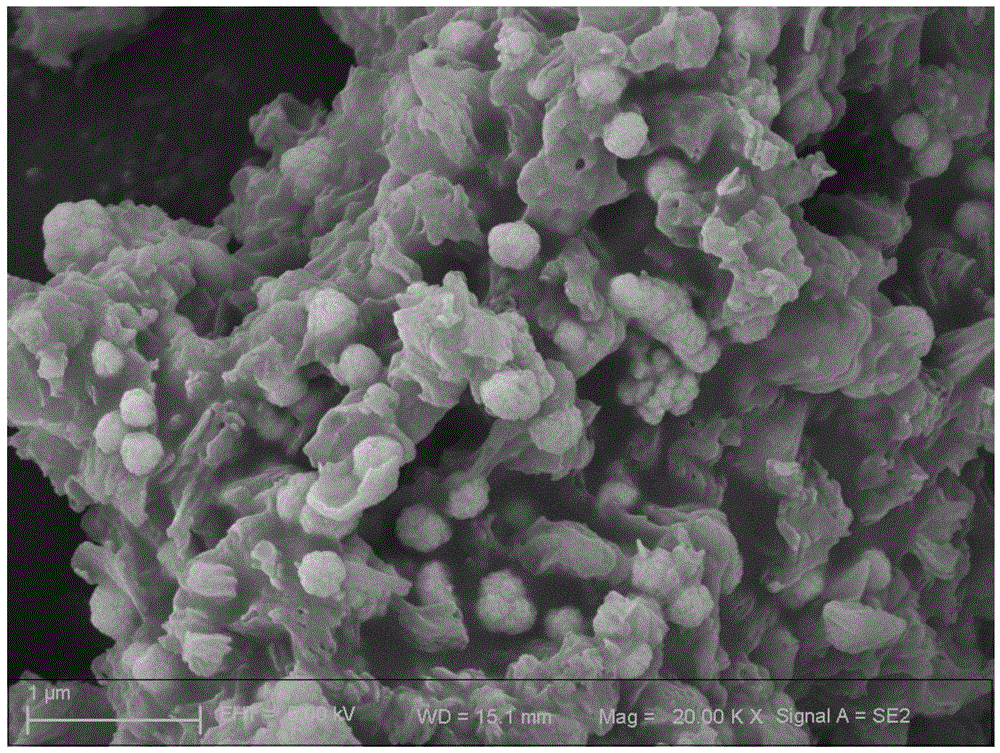
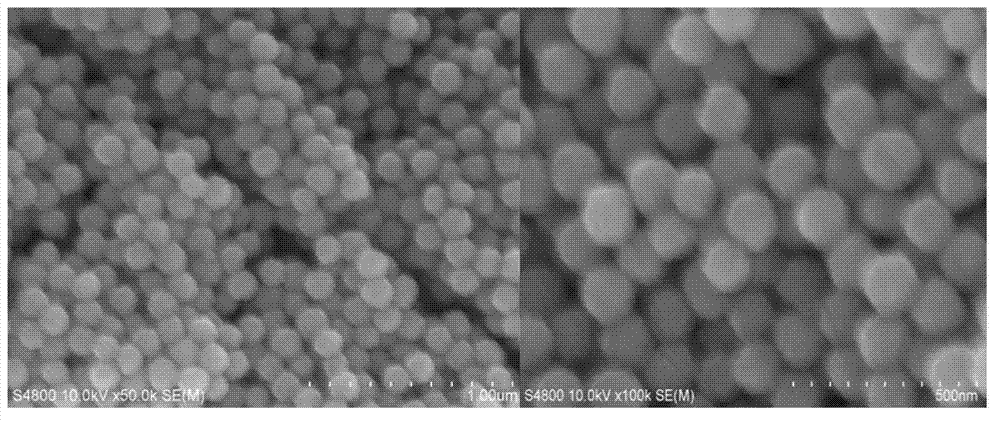
Method for preparing monodisperse cadmium sulfide nanospheres
InactiveCN102951675AGood repeatabilityShort preparation cycleMaterial nanotechnologyCadmium sulfidesMicrowave methodTemperature control mode
The invention provides a method for preparing monodisperse cadmium sulfide nanospheres, comprising steps of adding cadmium acetate dihydrate and sulfourea into deionized water respectively to obtain a solution A and a solution B, and adding the solution B into the solution A to obtain a solution C; uniformly mixing a PVP (Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone) solution D and the solution C to obtain a solution E; transferring the solution E into a hydrothermal reactor with Teflon as a lining, sealing the hydrothermal reactor, then putting the hydrothermal reactor into a temperature-pressure dual-control microwave hydrothermal reaction instrument for implementation of a preparation reaction in a temperature control mode, and naturally cooling after reaction completion; opening the hydrothermal reactor under the room temperature, washing with ethanol, then washing with the deionized water, performing centrifugal collection by taking absolute ethyl alcohol as a solvent, and drying at the temperature of 60 DEG C to obtain products CdS nanospheres. With the adoption of the method for preparing the monodisperse cadmium sulfide nanospheres, the high-temperature high-pressure environment of a hydrothermal method and the fast heating characteristic of a microwave method are combined; and with the adoption of a preparation technology of a microwave hydrothermal method, the monodisperse cadmium sulfide nanospheres with a regular spherical shape are prepared; and in addition, the method is short in preparation period, low in required temperature, small in pollution, low in energy consumption, simple to operate and high in repeatability, thereby being applicable for mass production.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mixed sputtering target of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride and methods of their use
Mixed targets are generally disclosed for sputtering an intermixed layer of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride. The mixed target can include cadmium sulfide, and cadmium telluride. Methods of forming the mixed target are also provided. For example, a powdered blend can be formed from powdered cadmium sulfide and powdered cadmium telluride, and pressed into a mixed target Methods are also generally disclosed for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device having an intermixed layer. For example, a mixed target of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride can be sputtered directly on a cadmium sulfide layer to form an intermixed layer, and a cadmium telluride layer can be formed on the intermixed layer.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Surfactant-Assisted Inorganic Nanoparticle Deposition on a Cellulose Nanocrystals
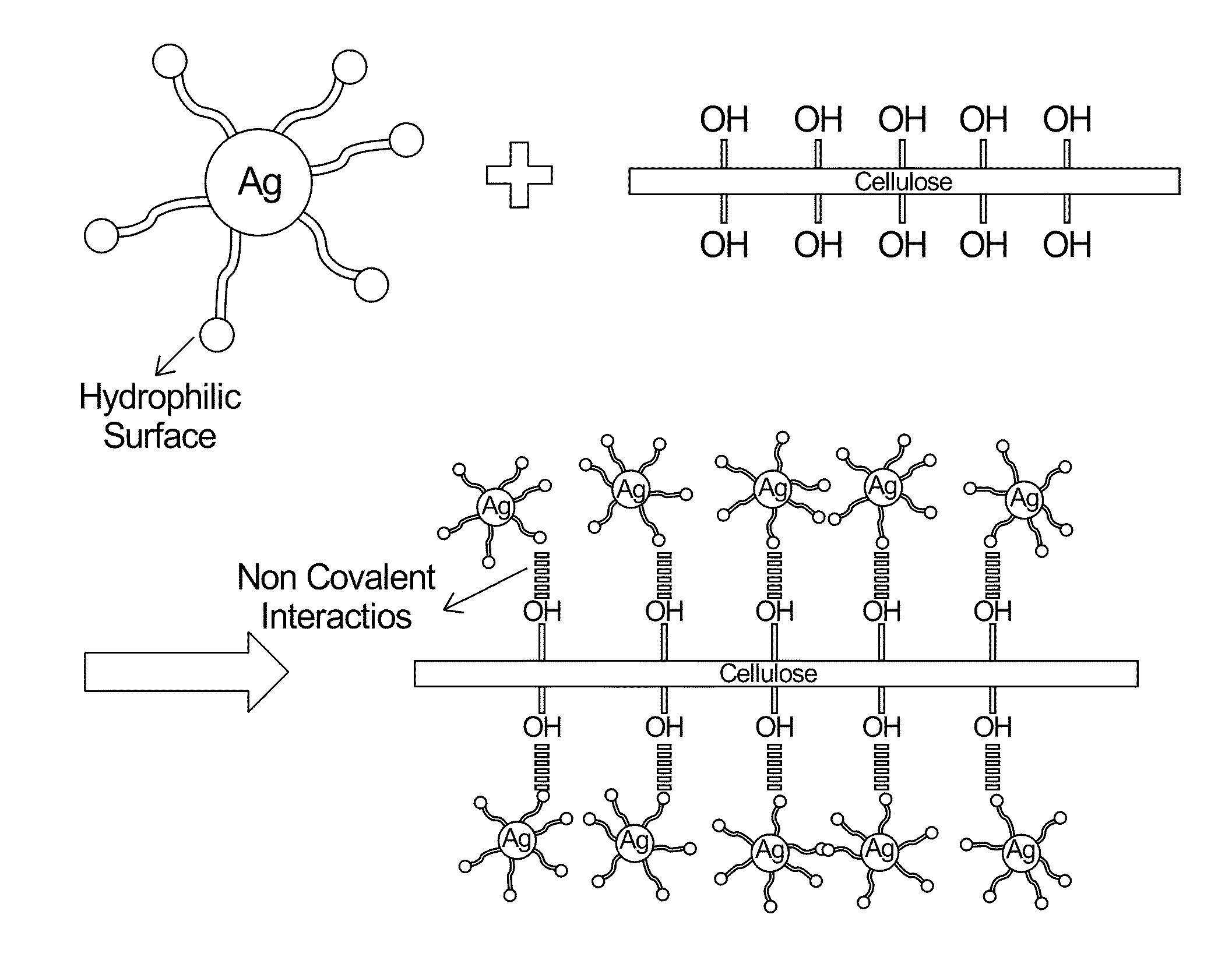
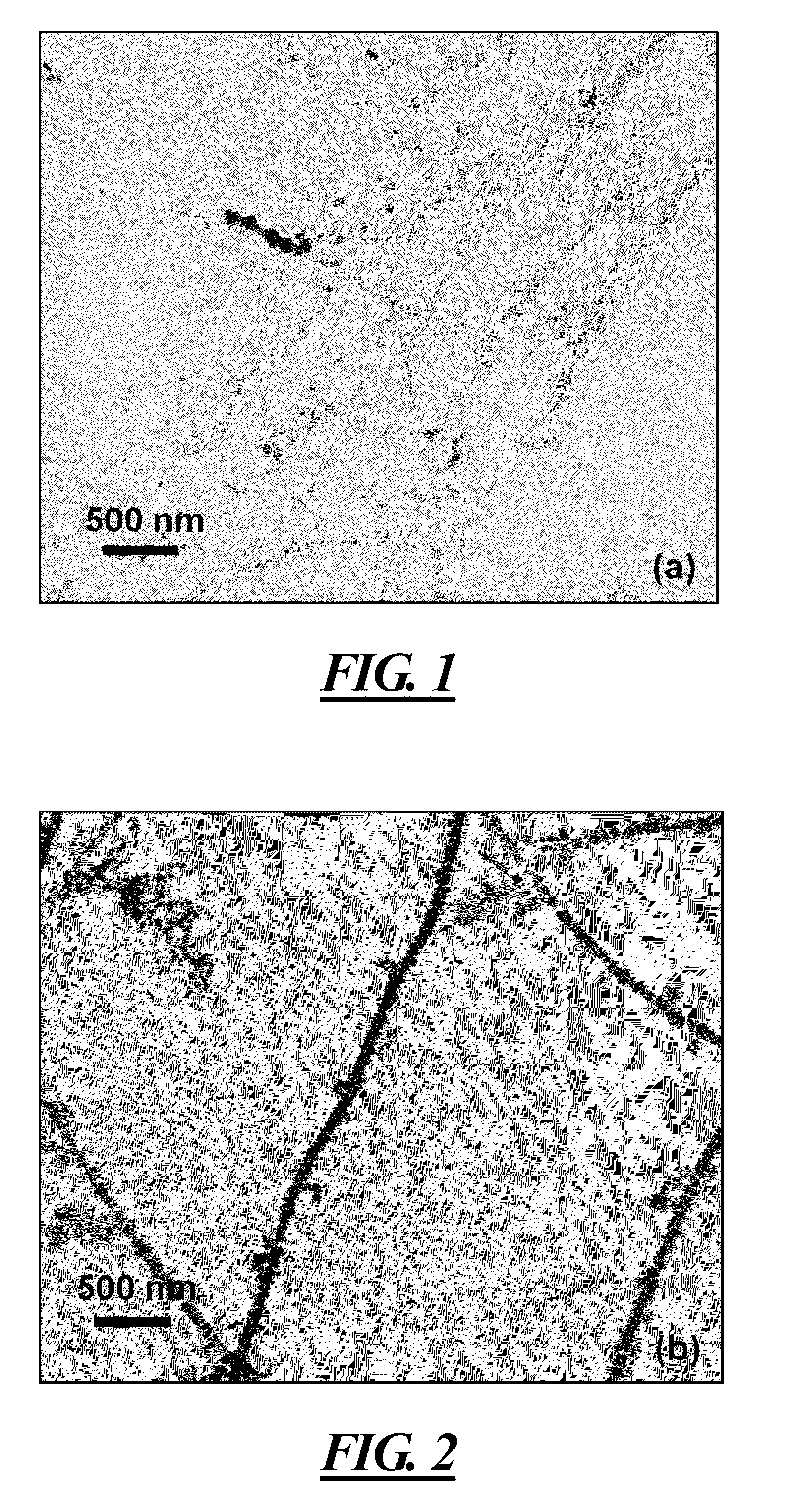
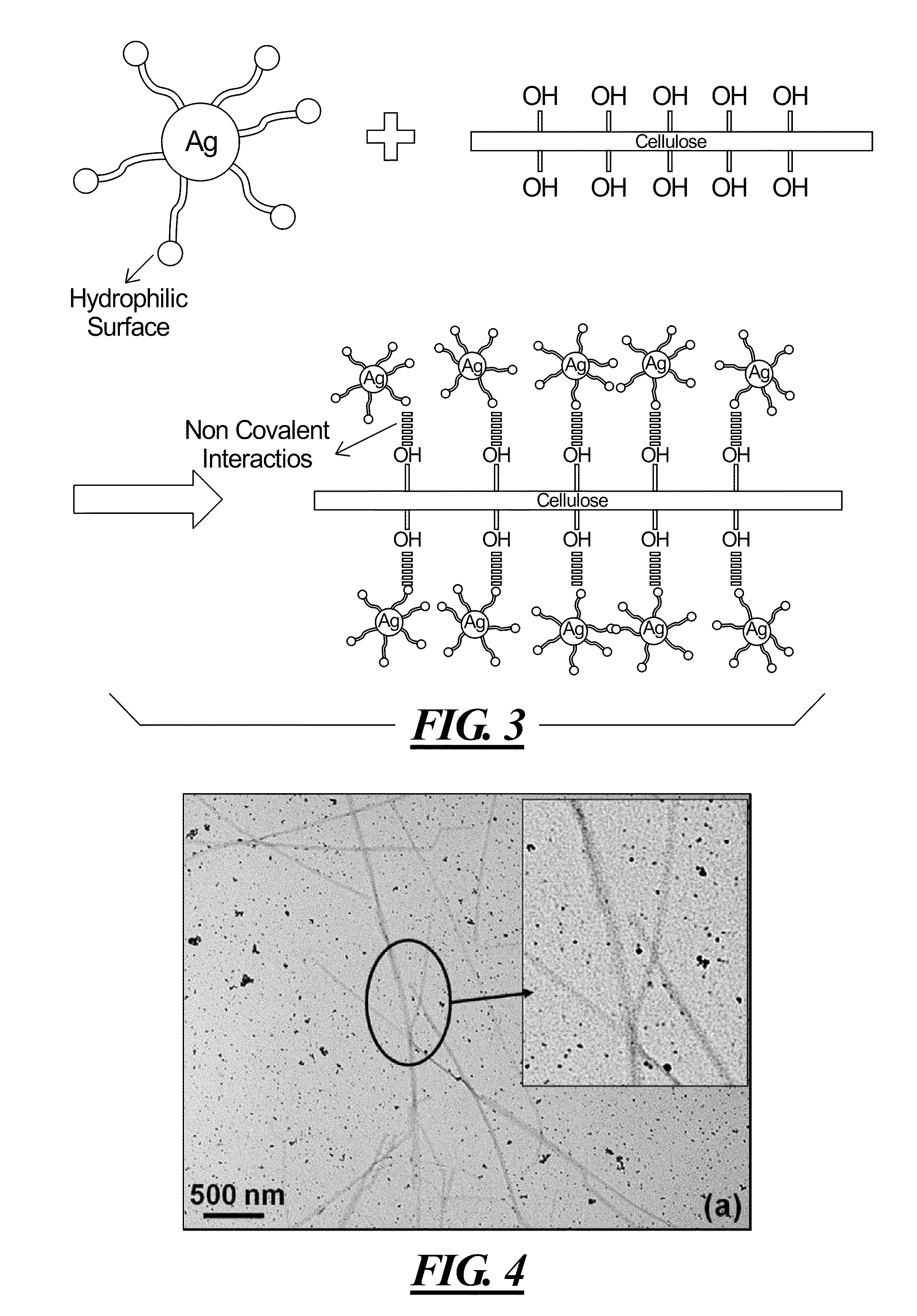
Natural biopolymers in the form of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) are shown to have the required characteristics to serve as chemically reactive biotemplates for metallic and semiconductor nanomaterial synthesis. Silver (Ag), gold (Au), copper (Cu) and platinum (Pt), cadmium sulfide (CdS), zinc sulfide (ZnS) and lead sulfide (PbS) nanoparticles, nanoparticle chains and nanowires may be synthesized on CNCs by exposing metallic precursor salts to a cationic surfactant, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and a reducing agent. The nanoparticle density and particle size may be controlled by varying the concentration of CTAB, pH of the salt solution, as well as the reduction time or reaction time between the reducing agent and the metal precursor.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Touch screen cover plate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106033288AHigh glossImprove reflectivityInput/output processes for data processingZinc selenideBarium titanate
The invention relates to a touch screen cover plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The touch screen cover plate comprises a substrate, a reflecting layer, and an ink layer. The reflecting layer is formed on one surface of the substrate. The reflecting layer is arranged on the periphery of the edge of the substrate. The reflecting layer is a metal elemental film or a compound film. The compound film is one selected from an oxide film, a fluoride film, a zinc sulfide film, a zinc selenide film, a titanium nitride film, a silicon carbide film, a lanthanum titanate film, a barium titanate film, a strontium titanate film, a praseodymium titanate film, and a cadmium sulfide film. The ink layer is on the reflecting layer, and the ink layer can reflect light which passes through the reflecting layer back to the reflecting layer. The touch screen cover plate has relatively high reflectivity, so glossiness of the touch screen cover plate is good.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL TECH +3
Method for preparing cadmium sulfide quantum dots
InactiveCN103936058AGood dispersionImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCadmium sulfidesSynthesis methodsCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing cadmium sulfide (CdS) quantum dots, belongs to the field of semiconductor nano-materials preparation and in particular relates to a method of preparing size-adjustable and monodispersity-excellent semiconductor quantum dots by a novel method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing carboxylic acid cadmium used as a cadmium source and (TMS)2S used as a sulfur source to form controlled-sized CdS semiconductor nanoclusters used as precursors for the synthetic reaction of CdS quantum dots, mixing the ligand with a non-coordinating solvent, heating and injecting the prepared CdS nanoclusters to obtain the CdS quantum dots. The synthesis method of the CdS quantum dots disclosed by the invention has inventive step and is convenient to operate and fast in reaction. The CdS quantum dots can be synthesized in large quantities and the synthesized quantum dot has adjustable sizes and excellent monodispersity and stability.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
One-step template-free method for preparing a great amount of monodisperse ZnS hollow nanospheres
The invention relates to a one-step template-free method for preparing a great amount of monodisperse ZnS hollow nanospheres. The method comprises the following steps: the zinc acetate is dissolved in distilled water; thiourea is added to the solution and stirred in the solution at the room temperature until the solution is clear; the obtained solution is transferred to a stainless steel reaction vessel with a polytetrafluoroethylene lining for sealing, then the reaction vessel is heated to the reaction temperature and kept at the reaction temperature for 1 to 48 hours, and the thiourea is decomposed and reacts with the zinc acetate to generate deposition; and after the reaction, the reaction vessel is cooled to the room temperature, then the clear solution on the upper layer is removed, and the obtained deposition is washed with the distilled water and dried in a vacuum drying oven at 30-100 DEG C to obtain the monodisperse ZnS hollow nanospheres. By adopting the method, the monodisperse ZnS hollow nanospheres with radius of 200 nm and with casing layers assembled by nano-particles can be prepared at a large scale. The method is simple and environment-friendly, needs lower temperature and no template and additive agent and takes the water as the solvent. The method can prepare other transition metal oxide hollow nanospheres, such as manganese sulfide, cadmium sulfide, and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com