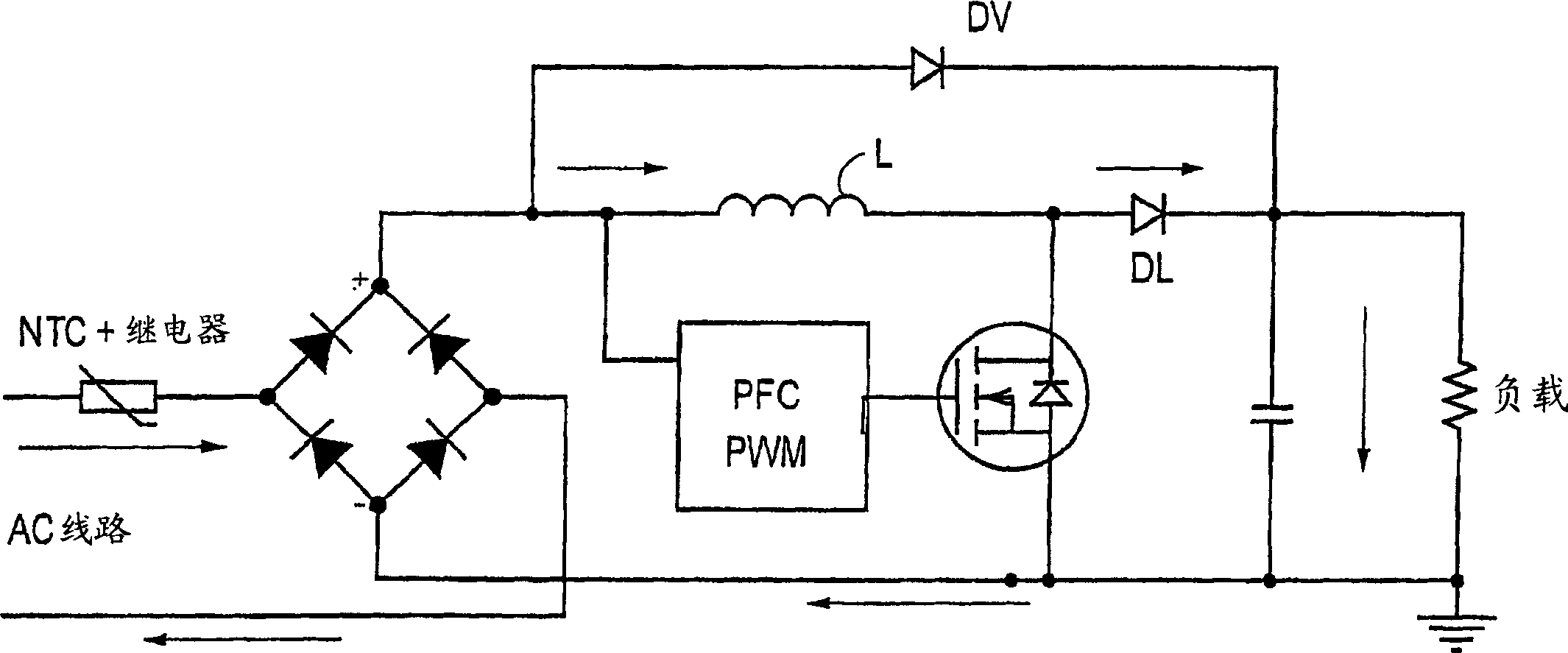
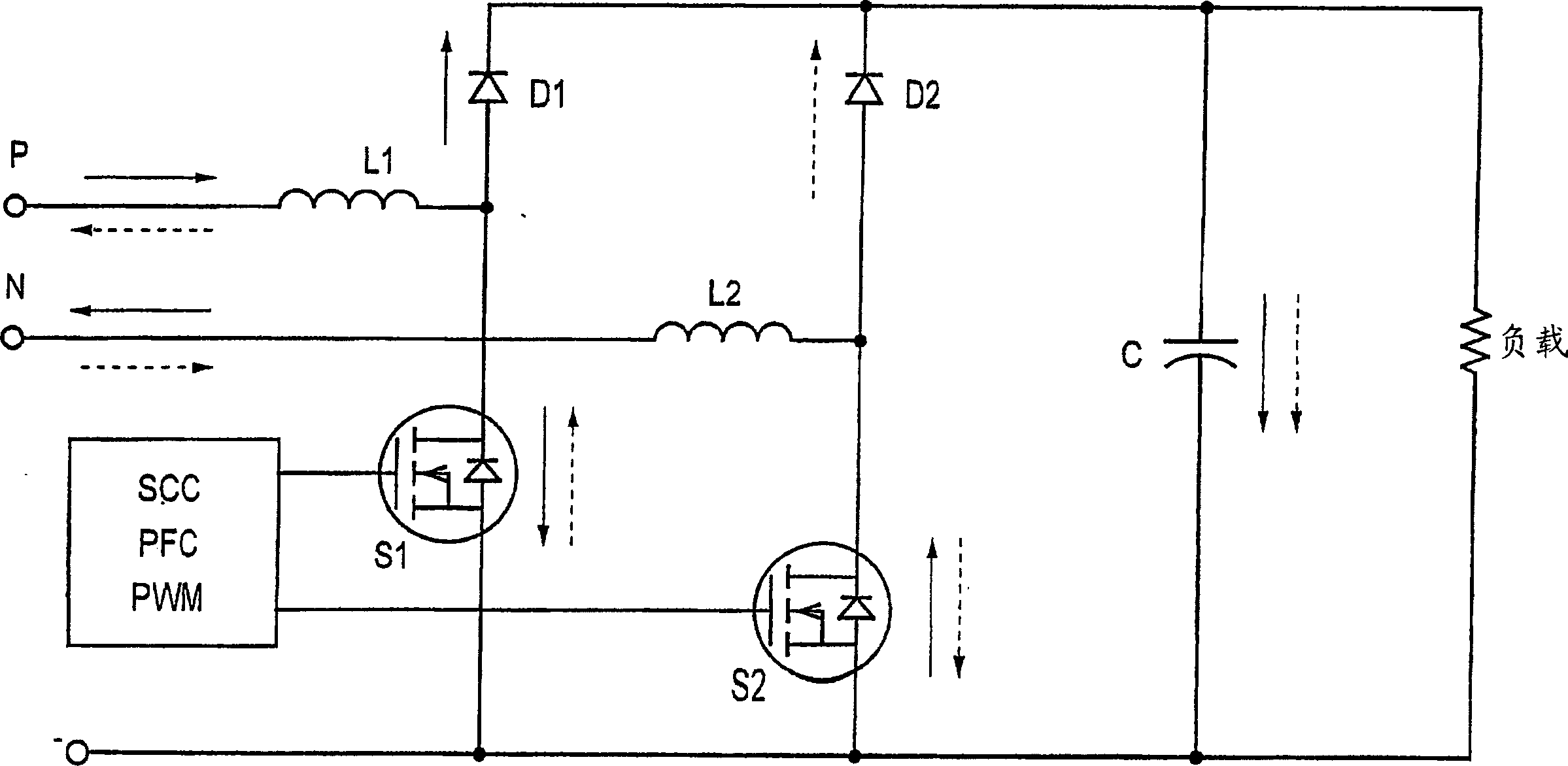
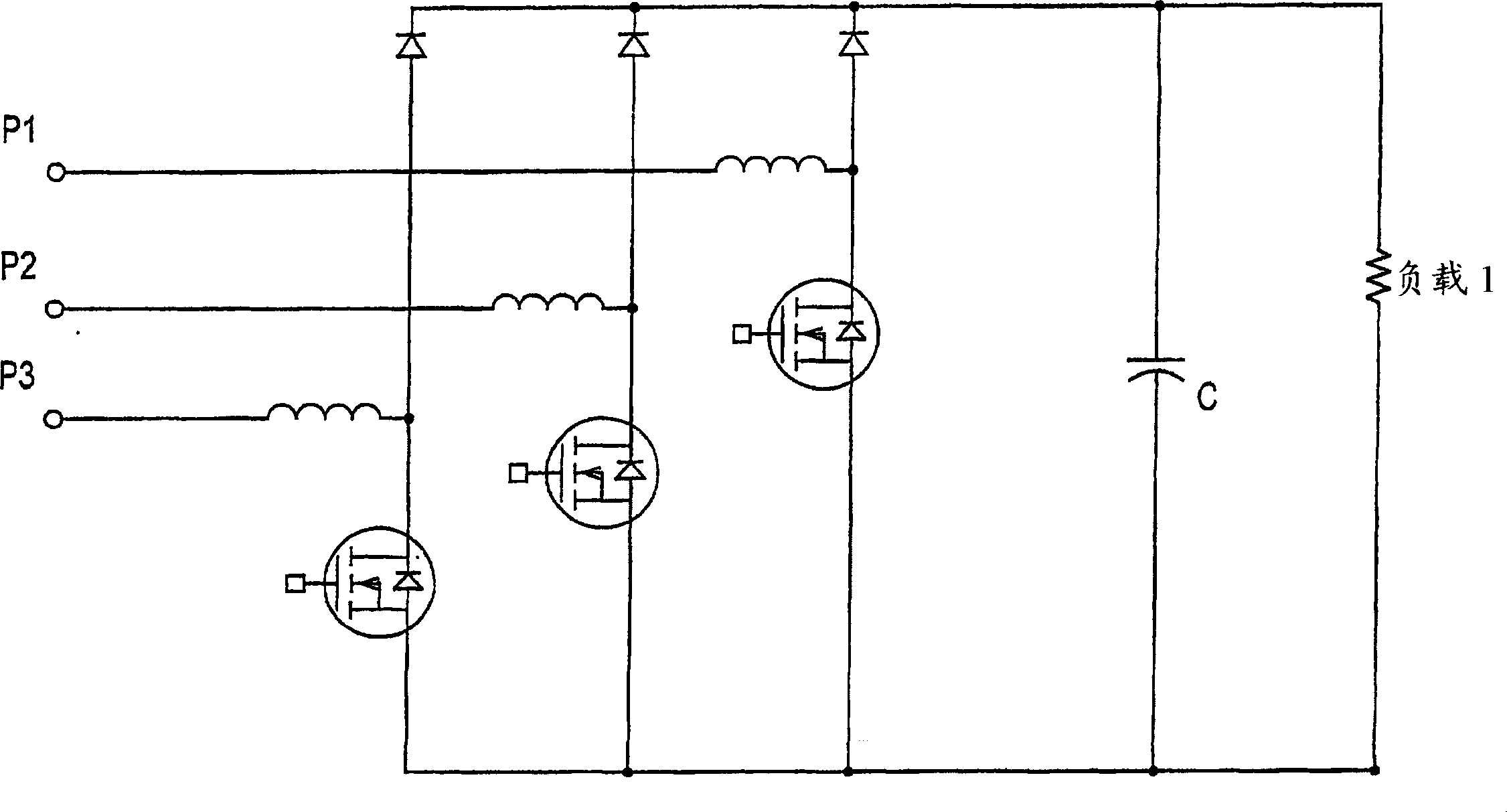
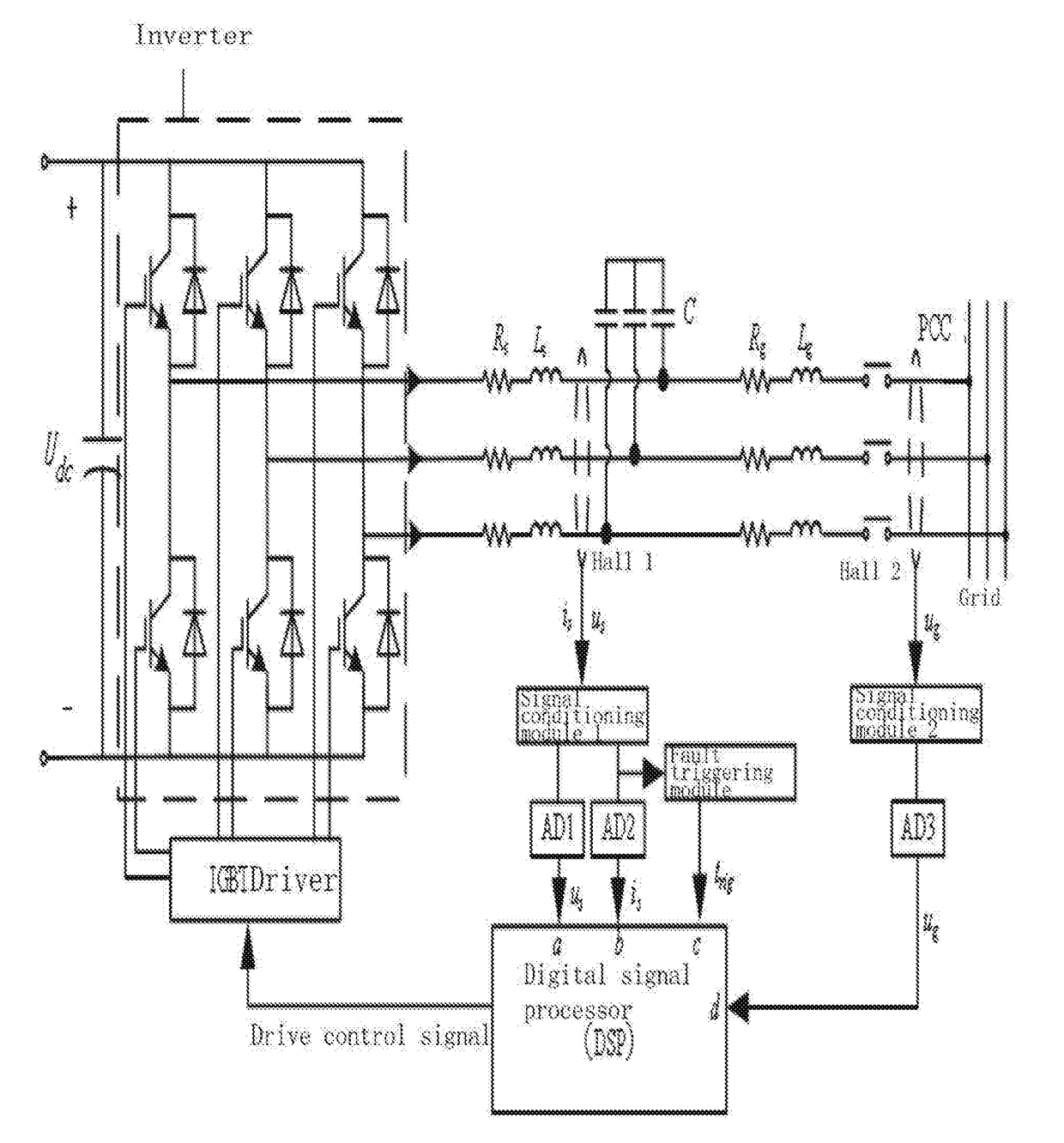
Patents
Literature
2008 results about "Inrush current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
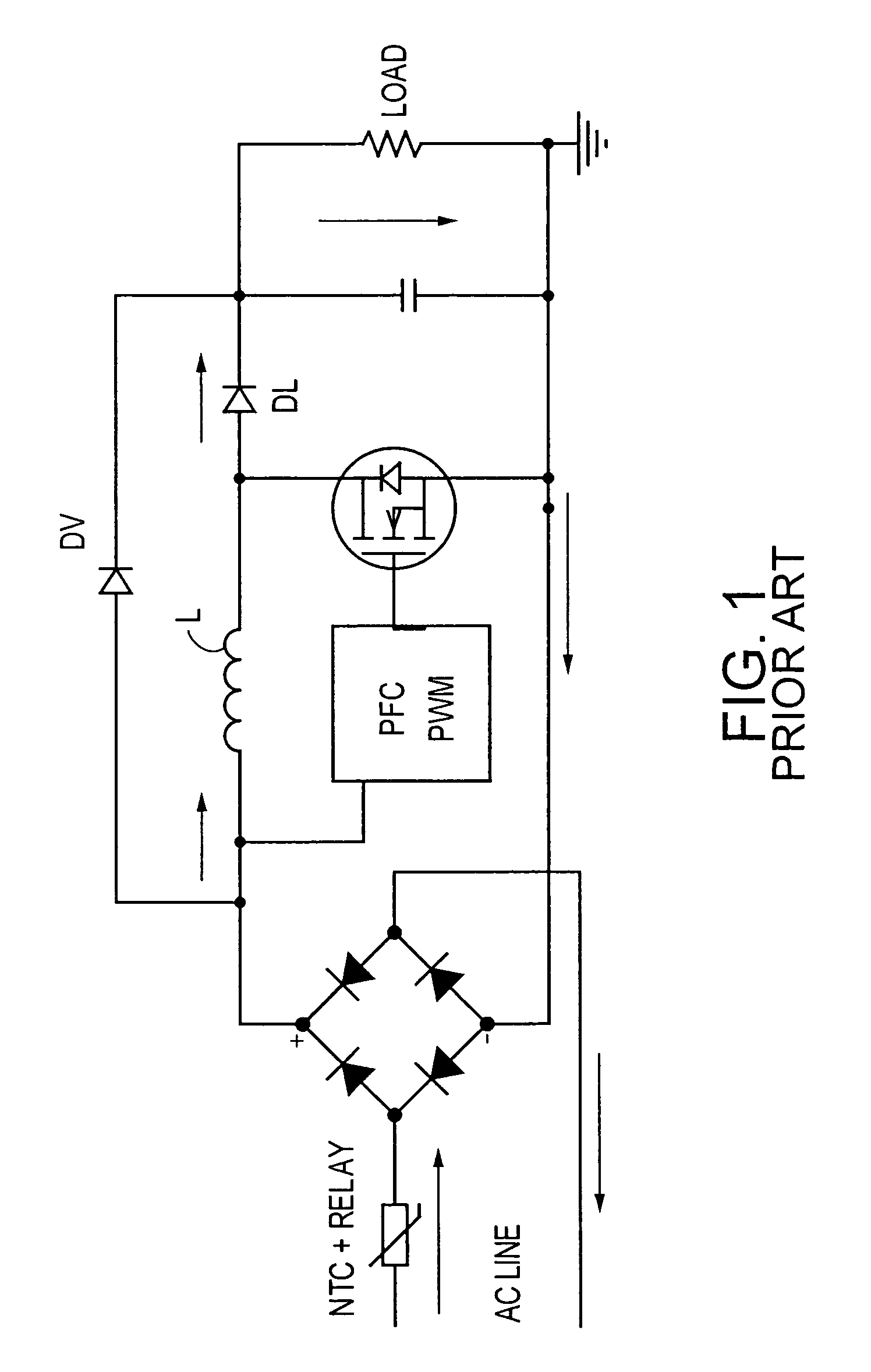
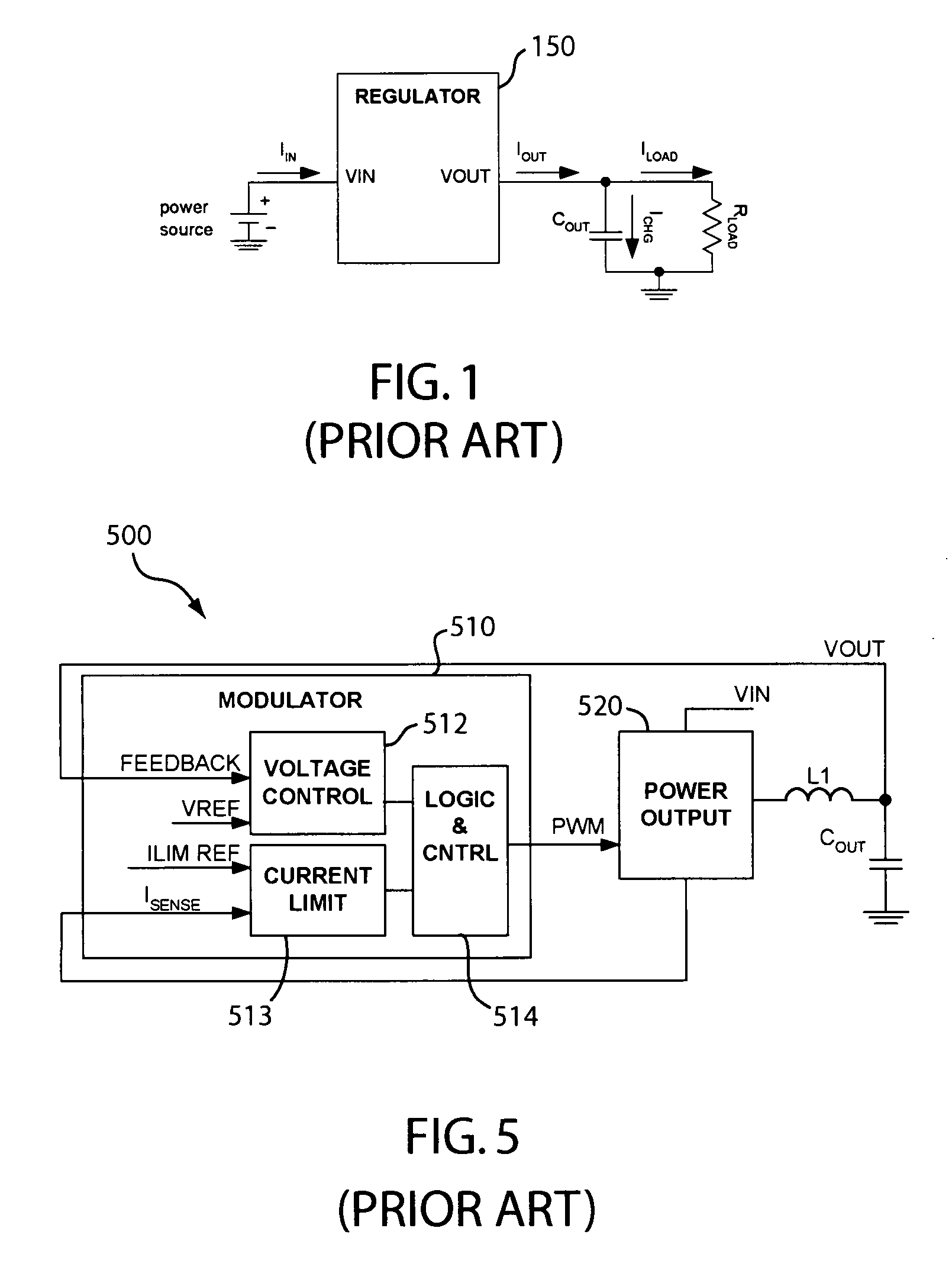
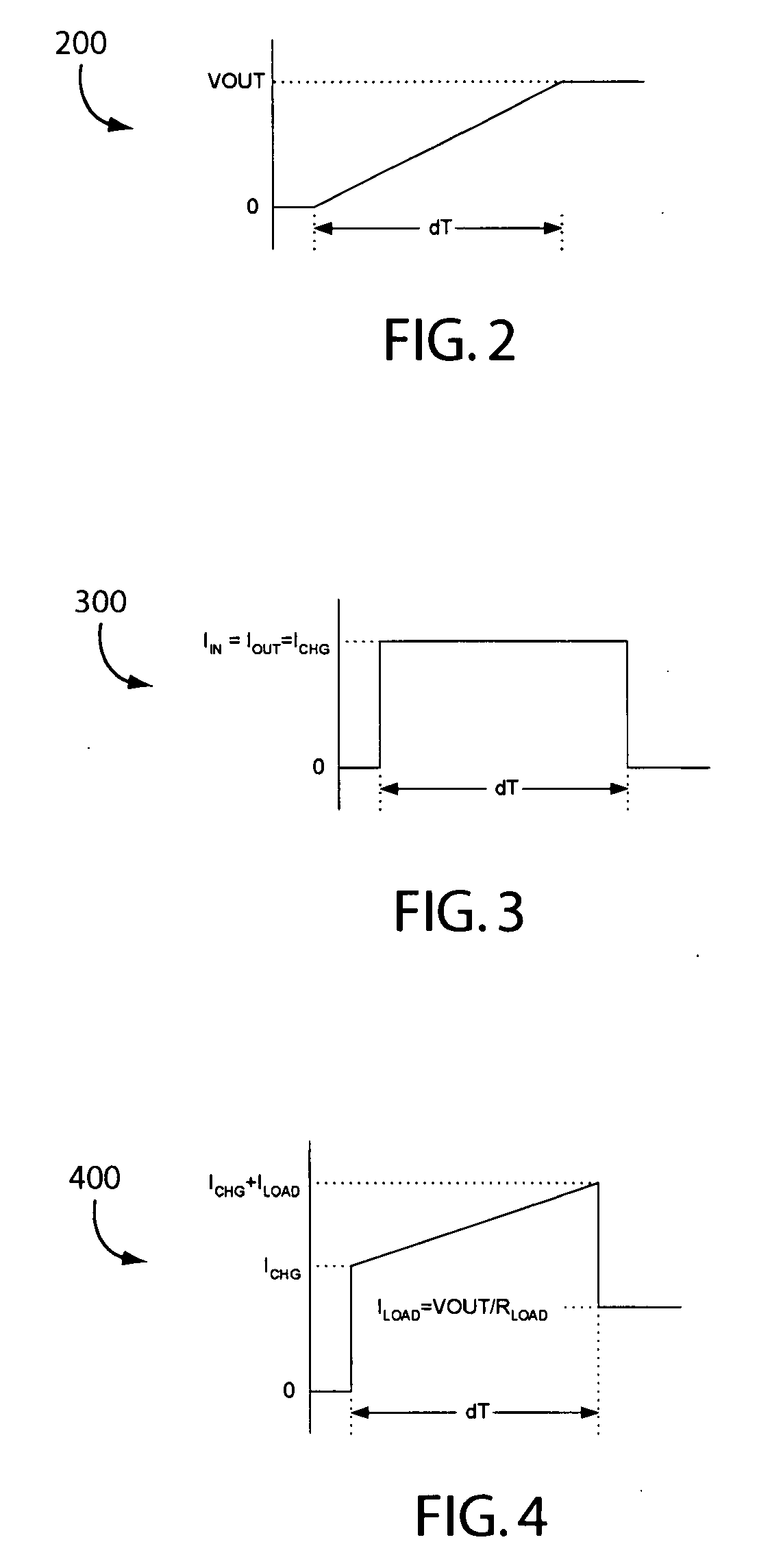
Inrush current, input surge current, or switch-on surge is the maximal instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when first turned on. Alternating-current electric motors and transformers may draw several times their normal full-load current when first energized, for a few cycles of the input waveform. Power converters also often have inrush currents much higher than their steady-state currents, due to the charging current of the input capacitance. The selection of over-current-protection devices such as fuses and circuit breakers is made more complicated when high inrush currents must be tolerated. The over-current protection must react quickly to overload or short-circuit faults but must not interrupt the circuit when the (usually harmless) inrush current flows.
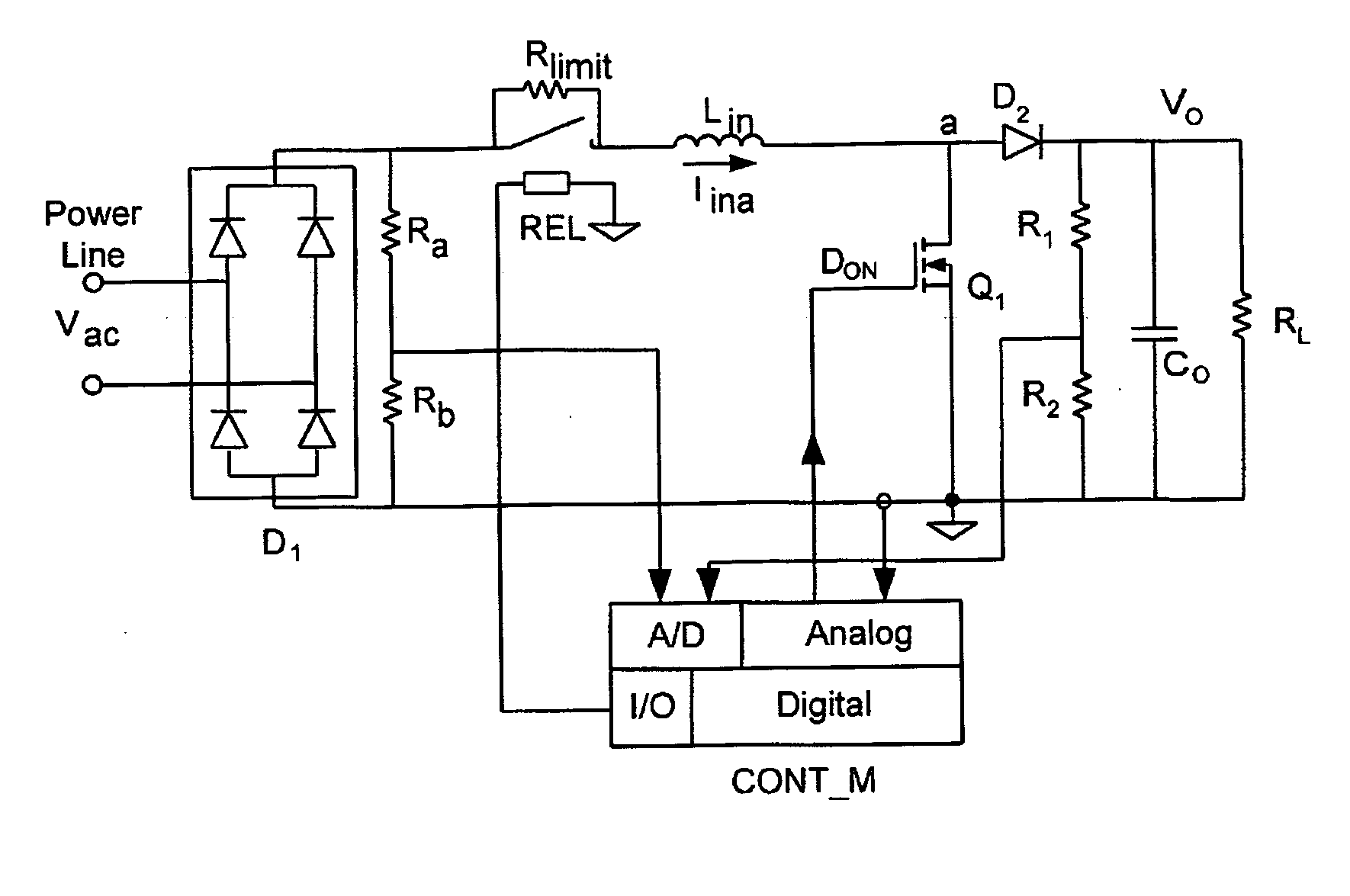
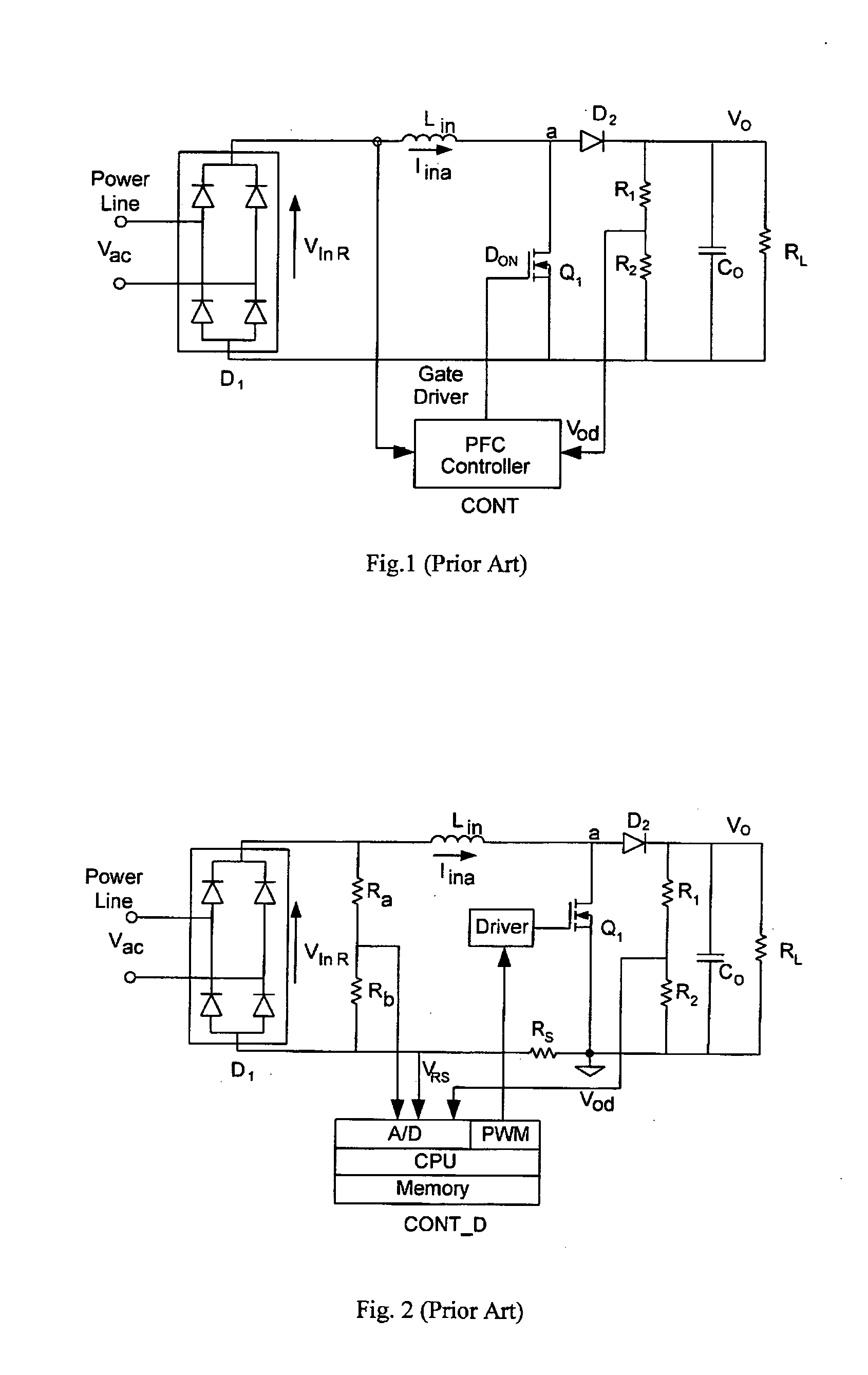
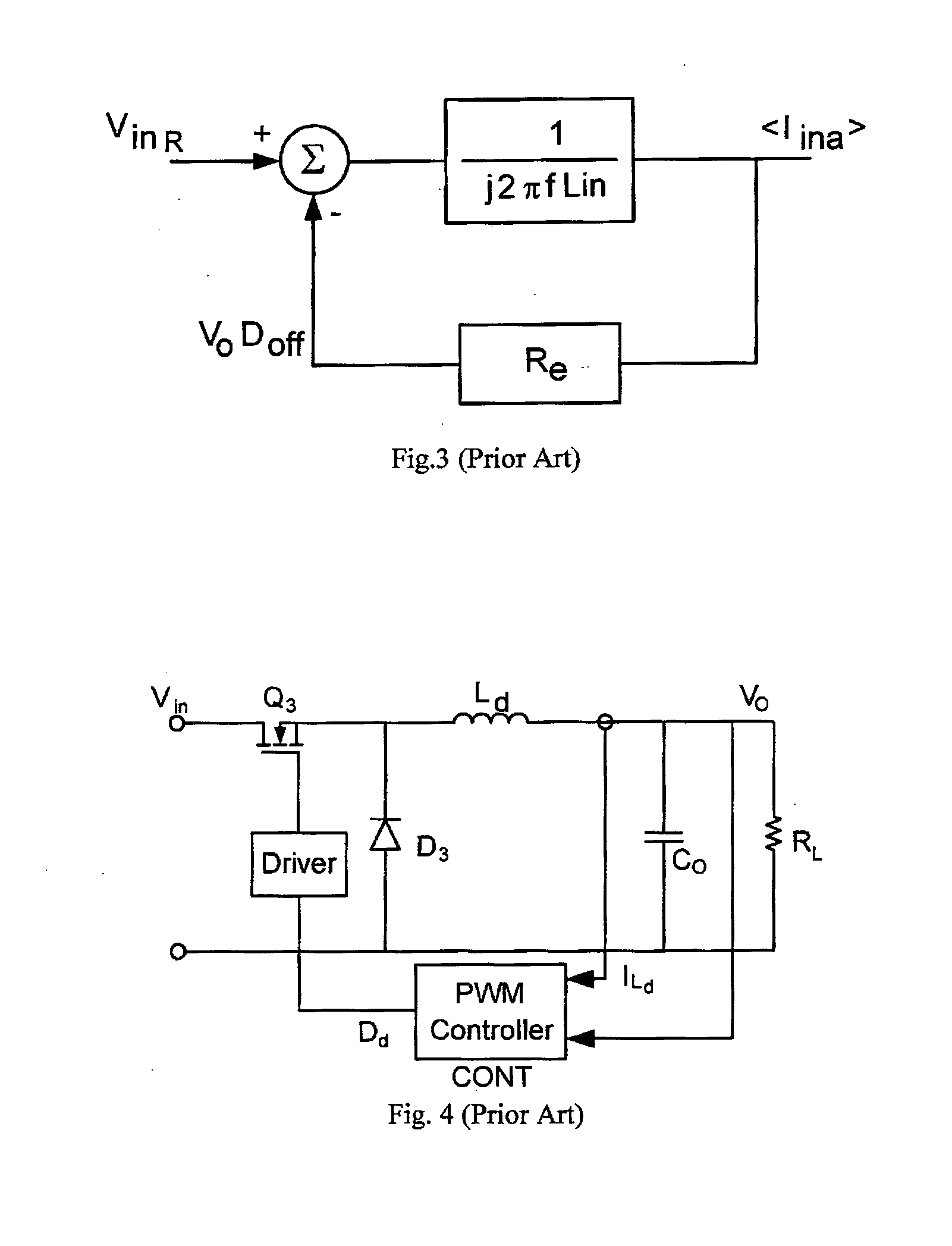
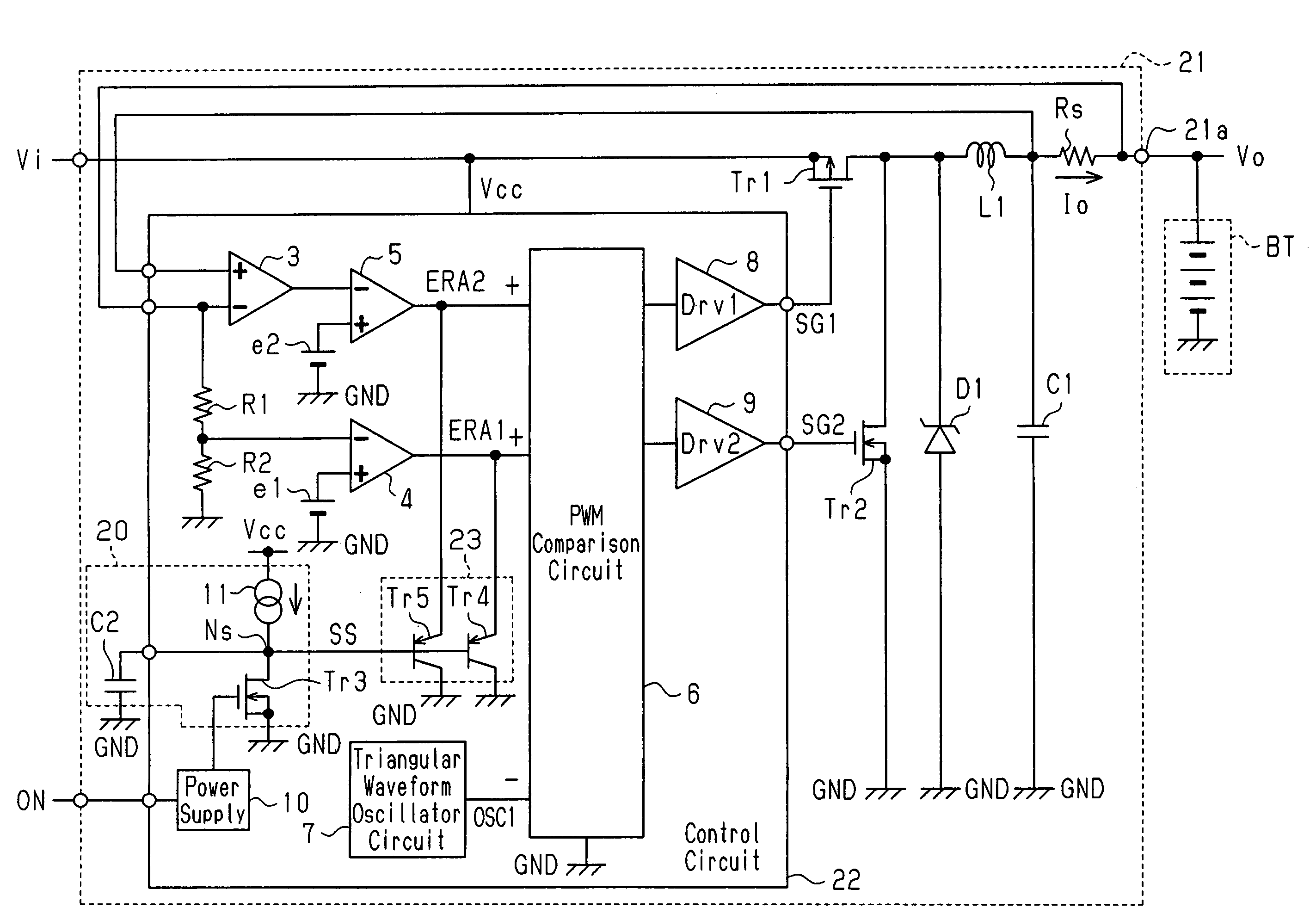
Method and control circuitry for improved-performance switch-mode converters
InactiveUS20060022648A1Relatively large bandwidthEasy constructionEfficient power electronics conversionElectric variable regulationElectricityPower factor
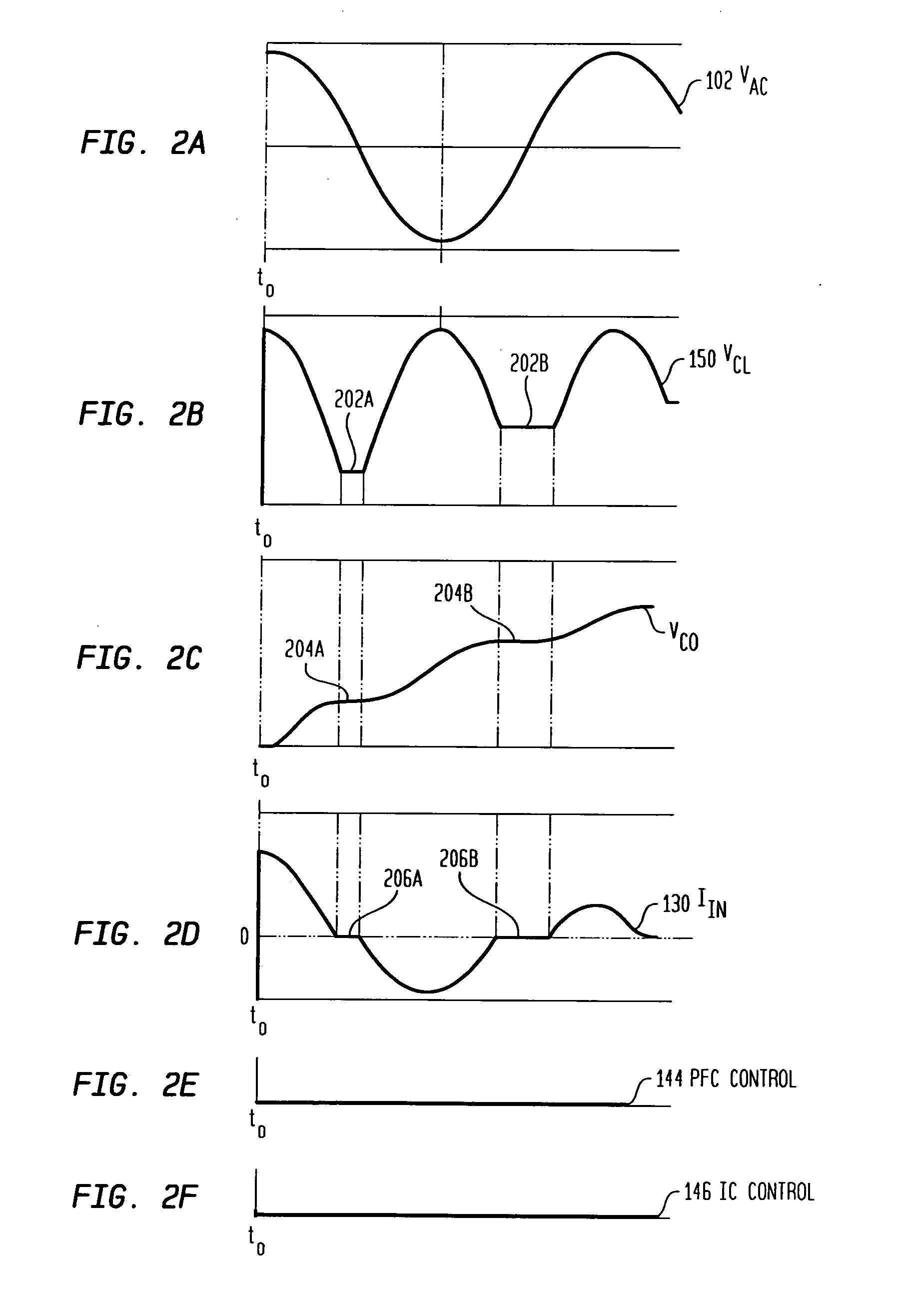
A system and method for supplying power to a load and for controlling the power factor presented to the power line. Output voltage is controlled by a digital, outer, control loop, and inner, analog, control loop causes the input current to be substantially proportional to the input voltage at any particular point in the power line cycle. Thus, the system presents a load to the power line that appears to be purely resistive. The use of an analog multiplier is not required, nor is sampling of input voltage. Limiting of inrush current provides for brown-out protection and soft-start.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
Smart Electronic Switch for Low-Power Loads
ActiveUS20100270982A1Small scaleElectronic switchingElectric light circuit arrangementElectricityElectronic switch
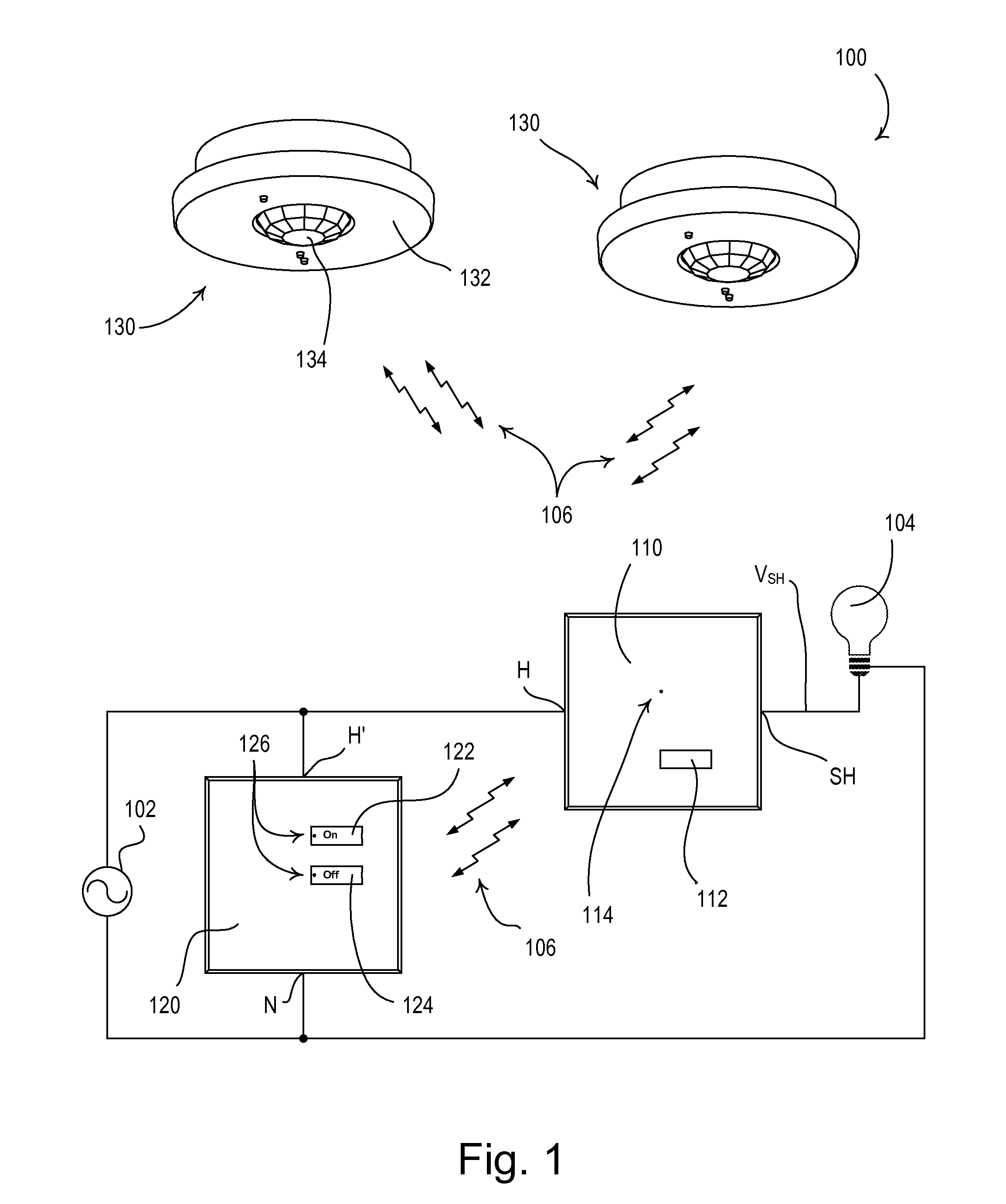
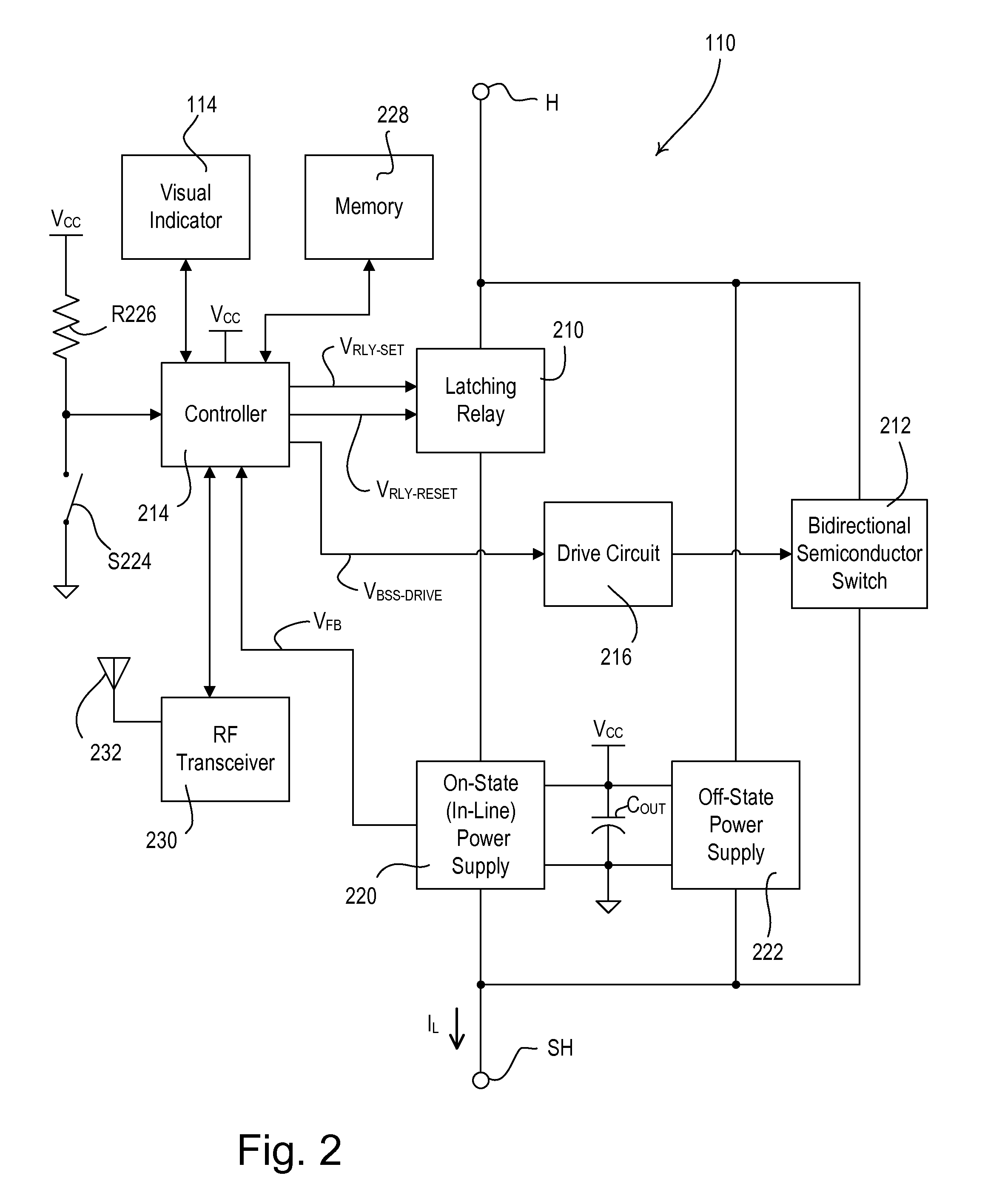
A two-wire smart load control device, such as an electronic switch, for controlling the power delivered from a power source to an electrical load comprises a relay for conducting a load current through the load and an in-line power supply coupled in series with the relay for generating a supply voltage across a capacitor when the relay is conductive. The power supply controls when the capacitor charges asynchronously with respect to the frequency of the source. The capacitor conducts the load current for at least a portion of a line cycle of the source when the relay is conductive. The load control device also comprises a bidirectional semiconductor switch, which is controlled to minimize the inrush current conducted through the relay. The bidirectional semiconductor switch is rendered conductive in response to an over-current condition in the capacitor of the power supply, and the relay is rendered non-conductive in response to an over-temperature condition in the power supply.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Motor controller incorporating an electronic circuit for protection against inrush currents
InactiveUS7050278B2Minimize the numberConveniently activatedSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlElectrical resistance and conductanceFiltration
Inrush currents in the dc intermediate circuit of a motor controller necessitate the incorporation of protection circuits. These circuits usually take the form of a resistor inserted in series with the intermediate circuit, and the resistor is short-circuited after completion of inrush by a switch positioned in parallel with the resistor. To reduce cable-transmitted electrical noise an earthed noise-decoupling capacitor is added to the intermediate circuit, but it also requires protection against inrush currents. To minimise the number of components, a protection circuit is described which combines noise filtration and inrush protection. According to the invention, the inrush resistor has the form of a resistor network and is connected to a switch which via a controller alters the resistance of the resistor network, so that when the switch is open, the resistance to a differential current is greater than the resistance to a common mode current, and when the switch is closed, there is greater resistance to a common mode current than to the differential current.
Owner:DANFOSS DRIVES
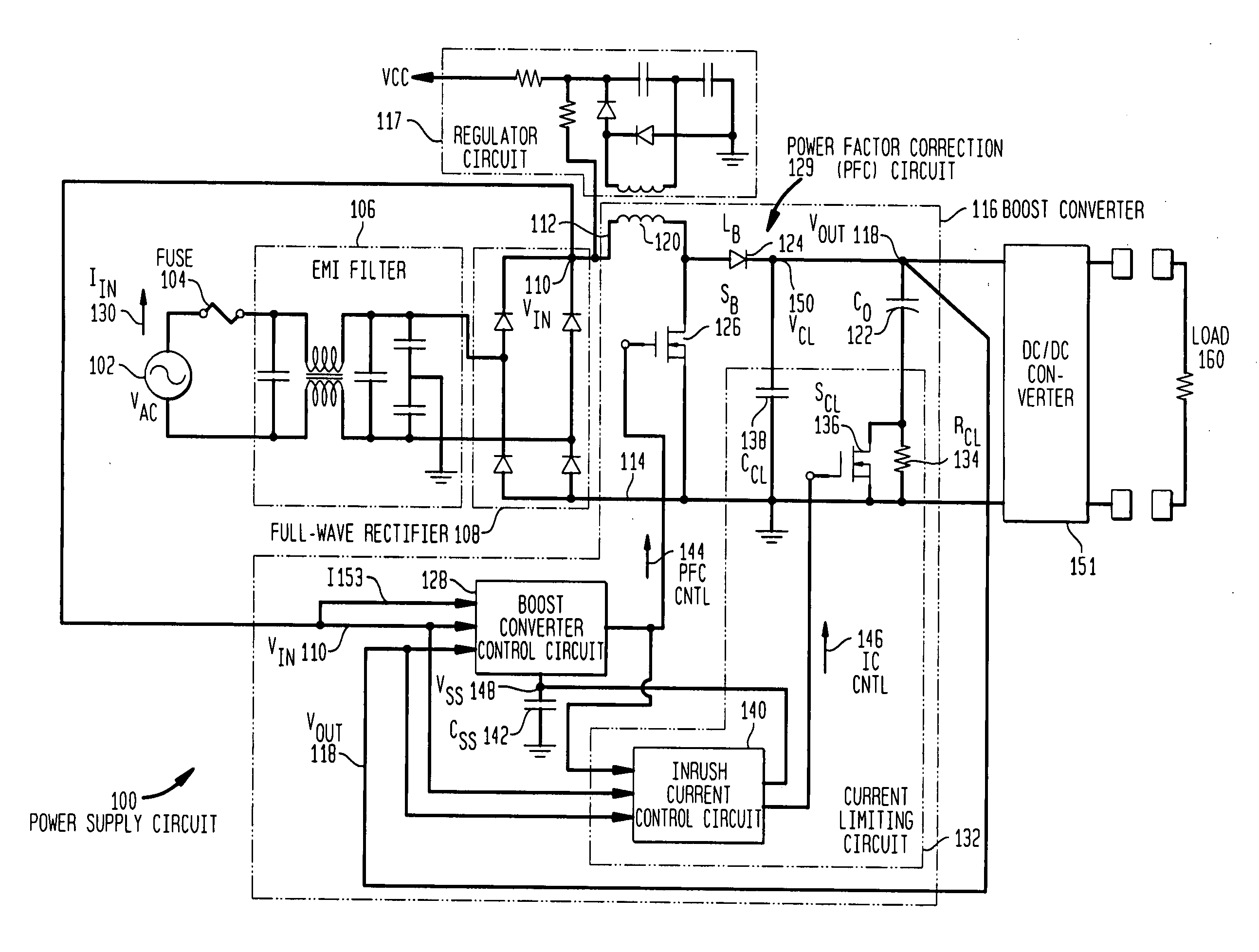
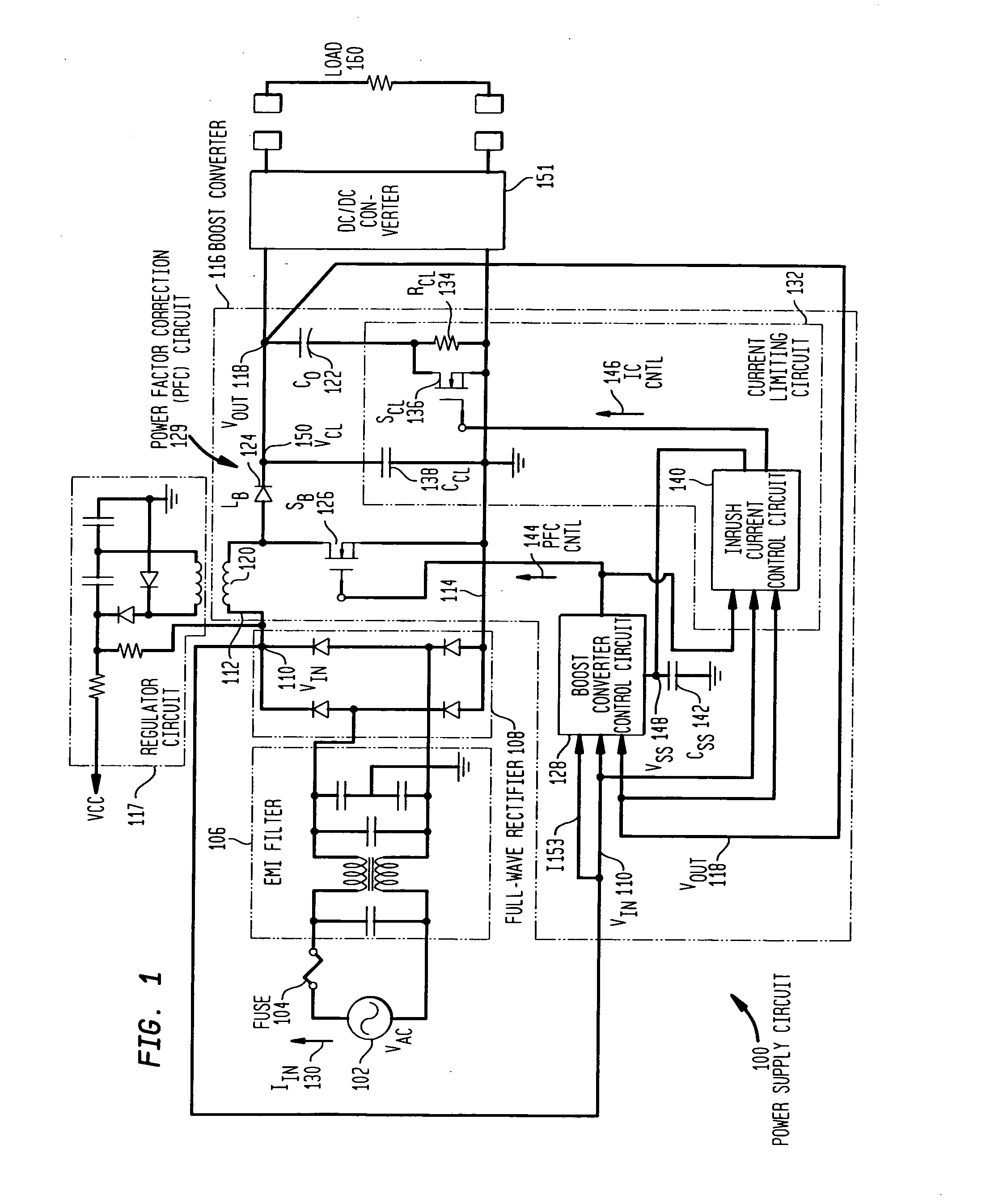
One cycle control PFC boost converter integrated circuit with inrush current limiting, fan motor speed control and housekeeping power supply controller
ActiveUS7068016B2Eliminating redundant switching circuitsSimplifies inclusionBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionMotor speedCycle control
A power factor corrected boost converter circuit includes a rectifier connectable to an ac input and having a rectified dc output provided across a dc bus, an inductor having first and second terminals connected in one leg of the dc bus, an integrated circuit comprising a control circuit for controlling a switch, the integrated circuit including a housing enclosing the control circuit, the integrated circuit having a power terminal, a ground terminal, a first control input terminal coupled to an output of the converter circuit, and a second control input terminal coupled to a sensor for sensing current in the dc bus and further having an output terminal connected to the switch, a boost rectifier diode having a first terminal, the diode coupled to the inductor, and a storage capacitor connected to the diode. The control circuit comprises a one cycle control circuit having an integrator reset by a clock signal for each cycle of the clock signal. The circuit further includes any or all of an inrush current limiting circuit for limiting the current through the inductor to a value below a predetermined level, a fan motor speed controller and a housekeeping power supply controller.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Bidirectional multimode power converter
ActiveUS20130039104A1Facilitates fault toleranceFacilitates load sharingEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionRemote controlTransverter
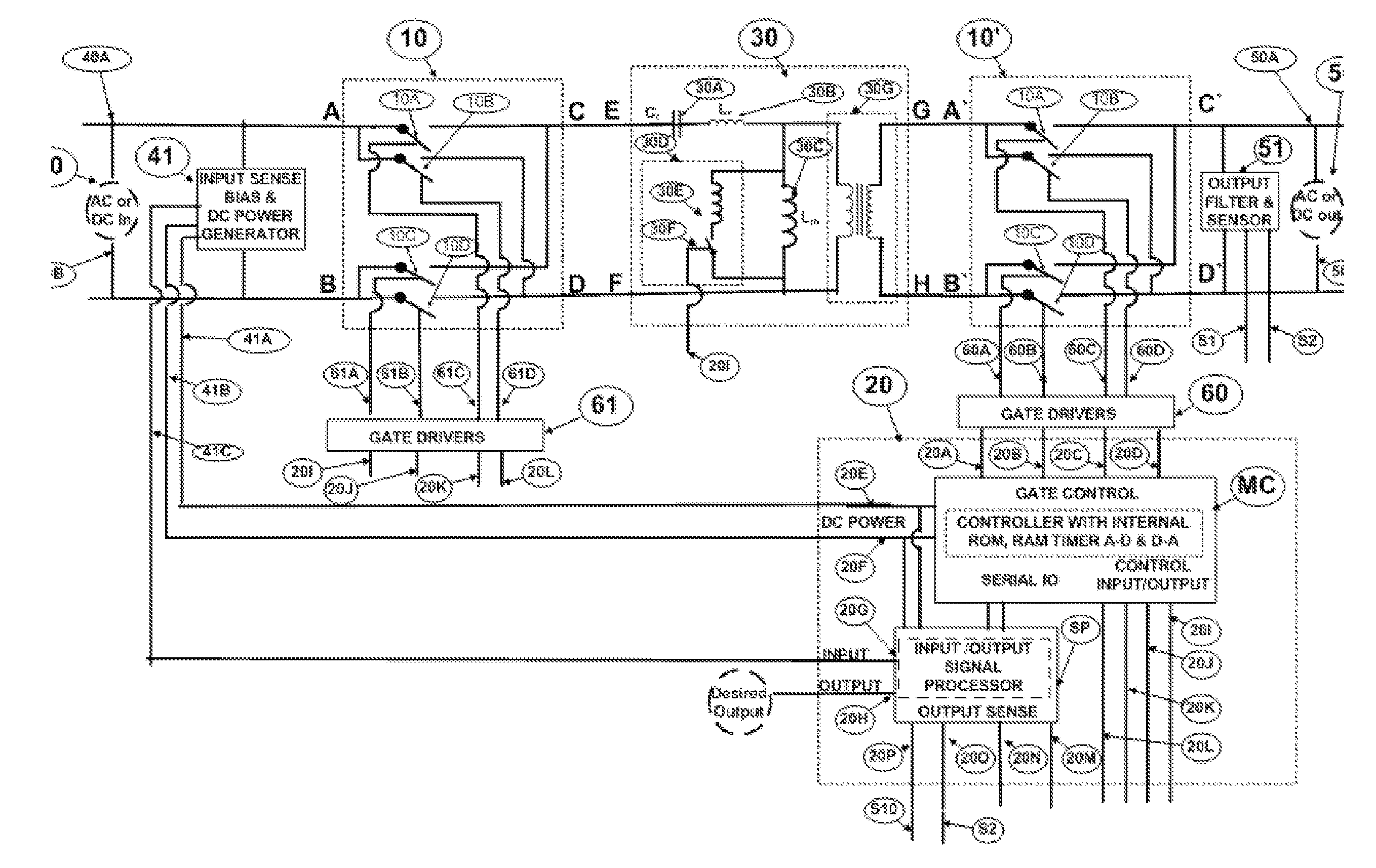
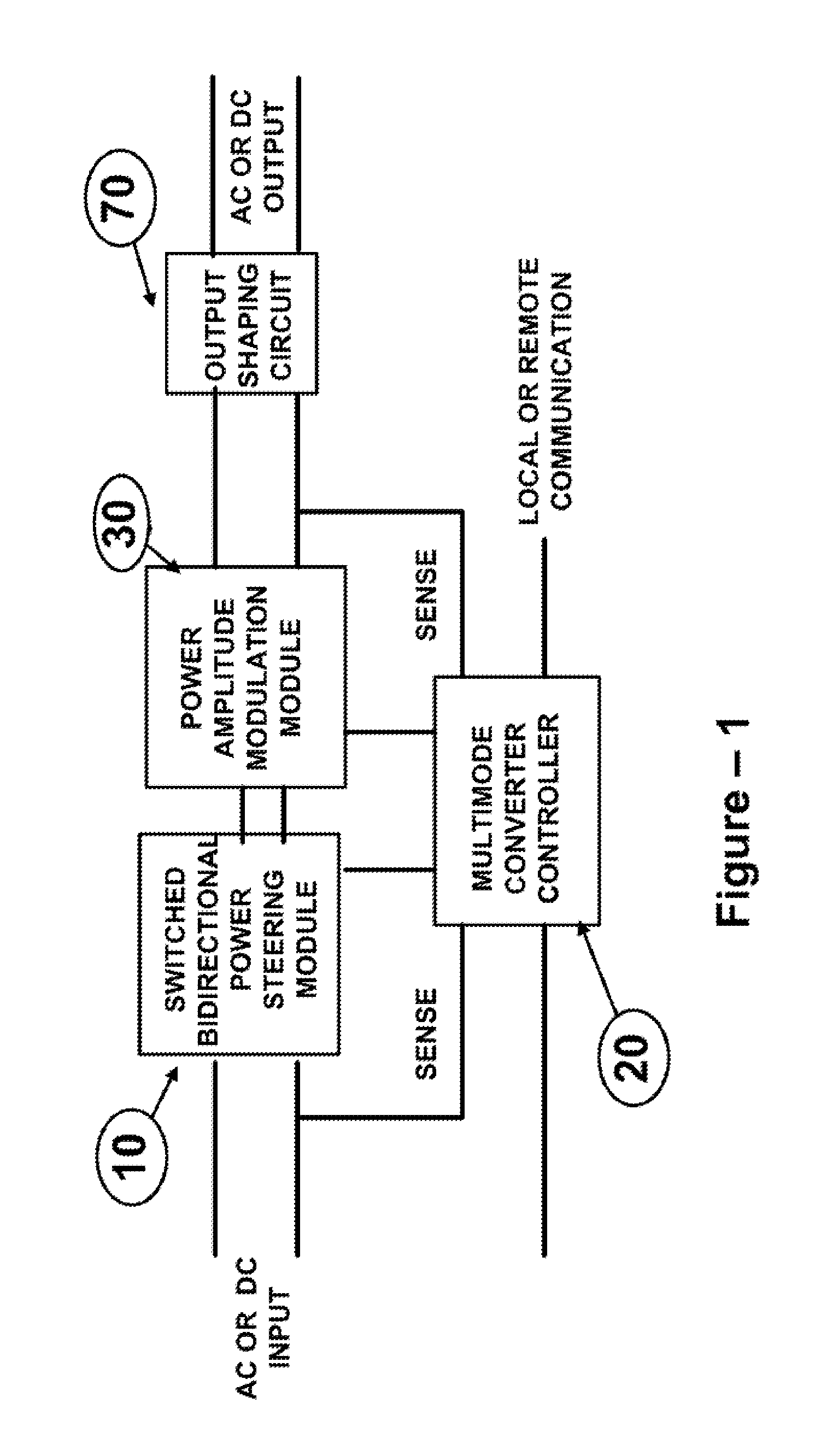
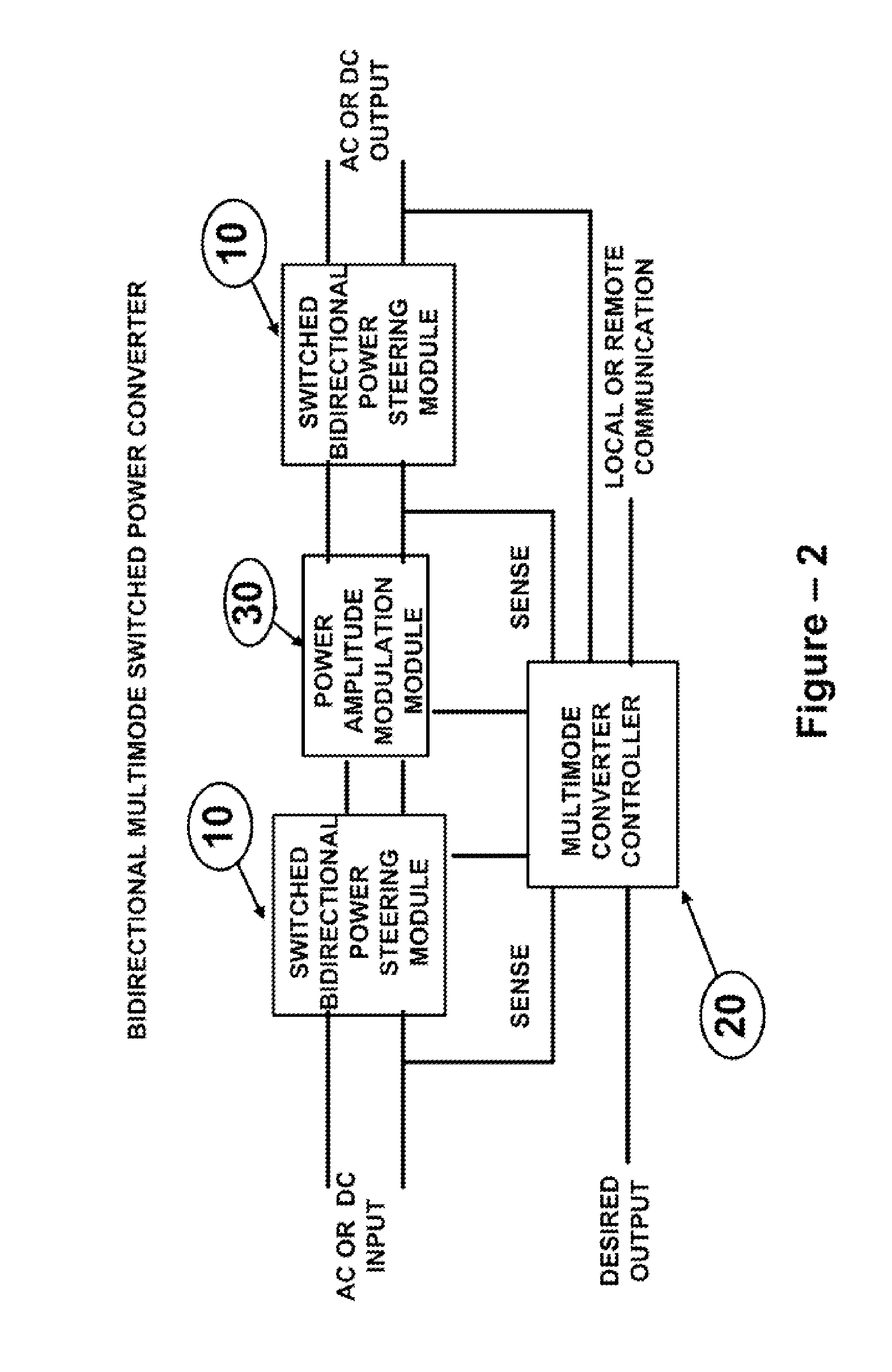
The present invention is directed to Bidirectional Multimode Power Converter which employs a high frequency dynamically varying amplitude modulation and voltage steering method to convert the source AC or DC voltages to output AC or DC voltages, with programmable output voltage levels, output voltage frequency and duration. The inrush current control, turning off the idle converter, line voltage brown out protection, soft start, high pre-charge voltage generation, soft shut down of converter, dimming operation modes are inherent characteristics of the Bidirectional Multimode power converter. The Bidirectional Multimode Power Converters of the present invention facilitates bidirectional conversion and coupling multiple bidirectional sources and or loads.The Bidirectional Multimode Power Converter of the present invention supports local and remote control for changing operational characteristics of the converter on demand or on a programmed time of the day for a specified duration of time.
Owner:SHARMA VISWA N
Bridge-less boost (BLB) power factor correction topology controlled with one cycle control
InactiveUS7164591B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCycle controlEngineering
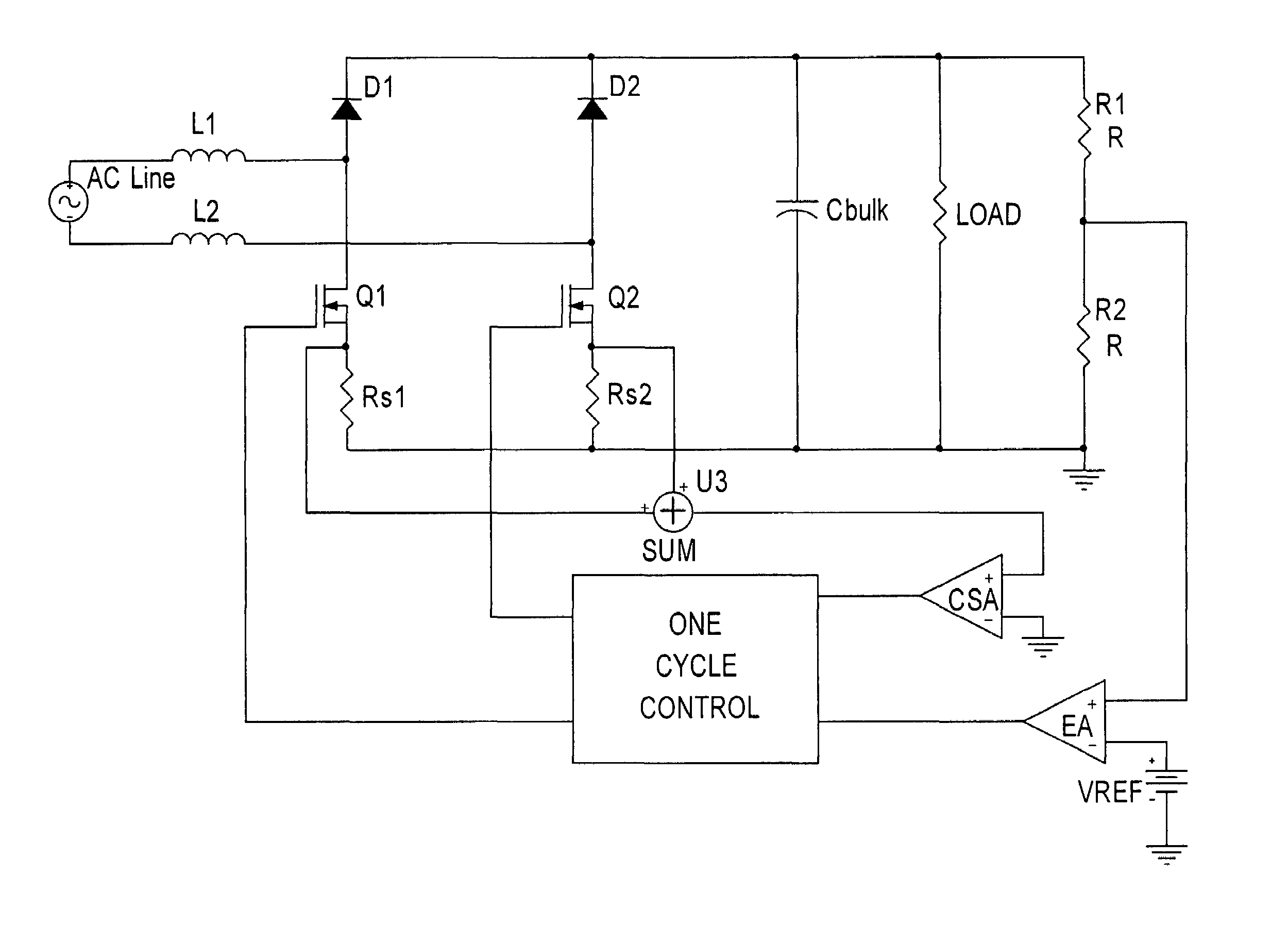
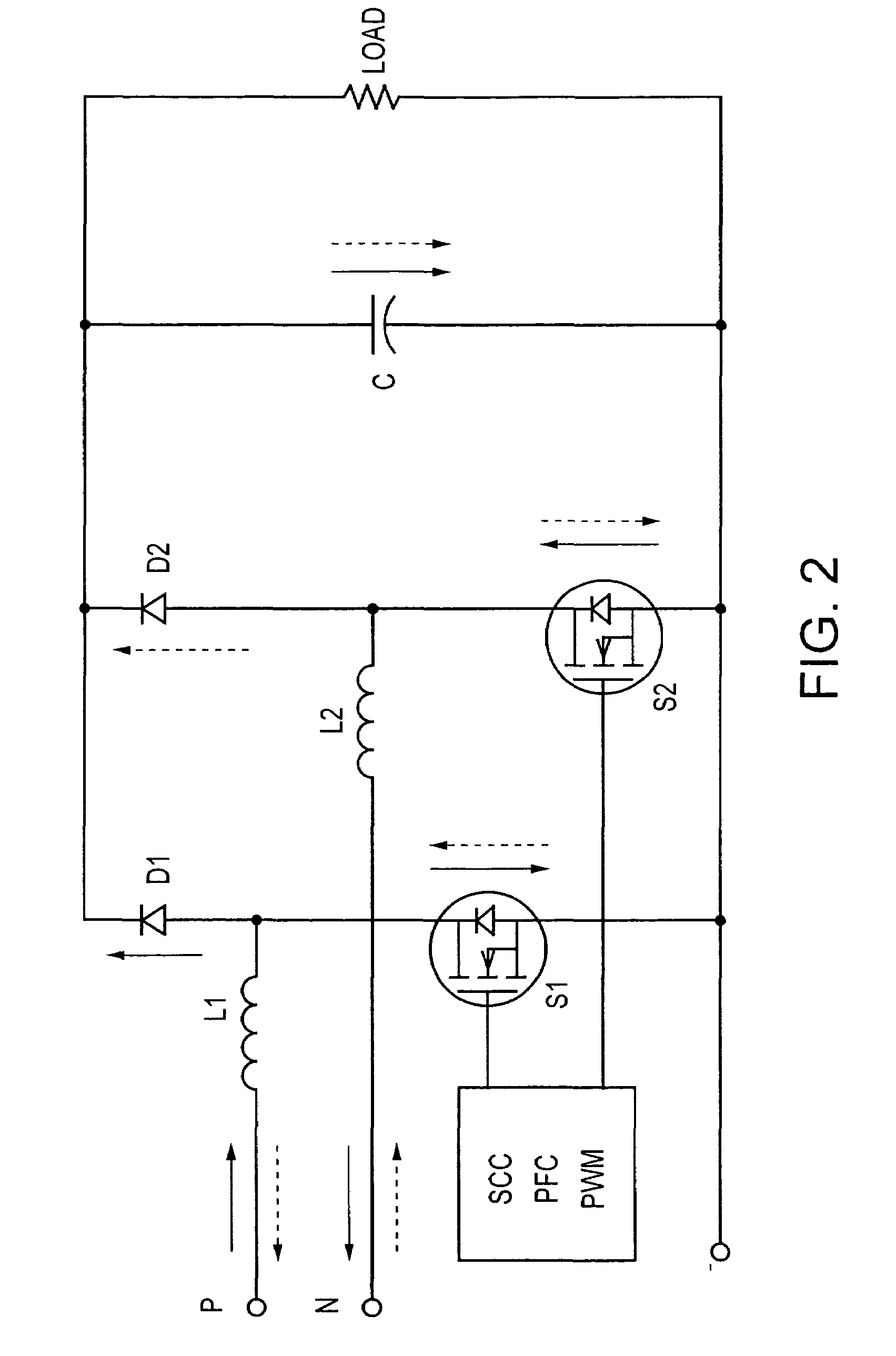
The bridgeless boost topology reduces the power dissipation, cost, and size of prior PFC systems by eliminating the intrinsic loss of the input rectifier bridge. Sensing of the input line voltage by the controller is unnecessary. The use of One Cycle Control (also known as Single Cycle Control) allows the Power Factor Correction function to be performed without complex rectification networks to obtain the AC line voltage reference. The use of bi-directional switches makes it possible to control inrush current (the startup over-current due to the charging of the output bulk capacitor), which allows elimination of over-current limiting devices and reduction of the diode surge capability requirements. Moving the boost inductor to the system input adds an additional filtering function, reducing the cost of input EMI filtering.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
Current control circuit and method thereof for a power converter
InactiveUS20140119076A1Improve responsivenessImprove system stabilityAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage referenceEngineering
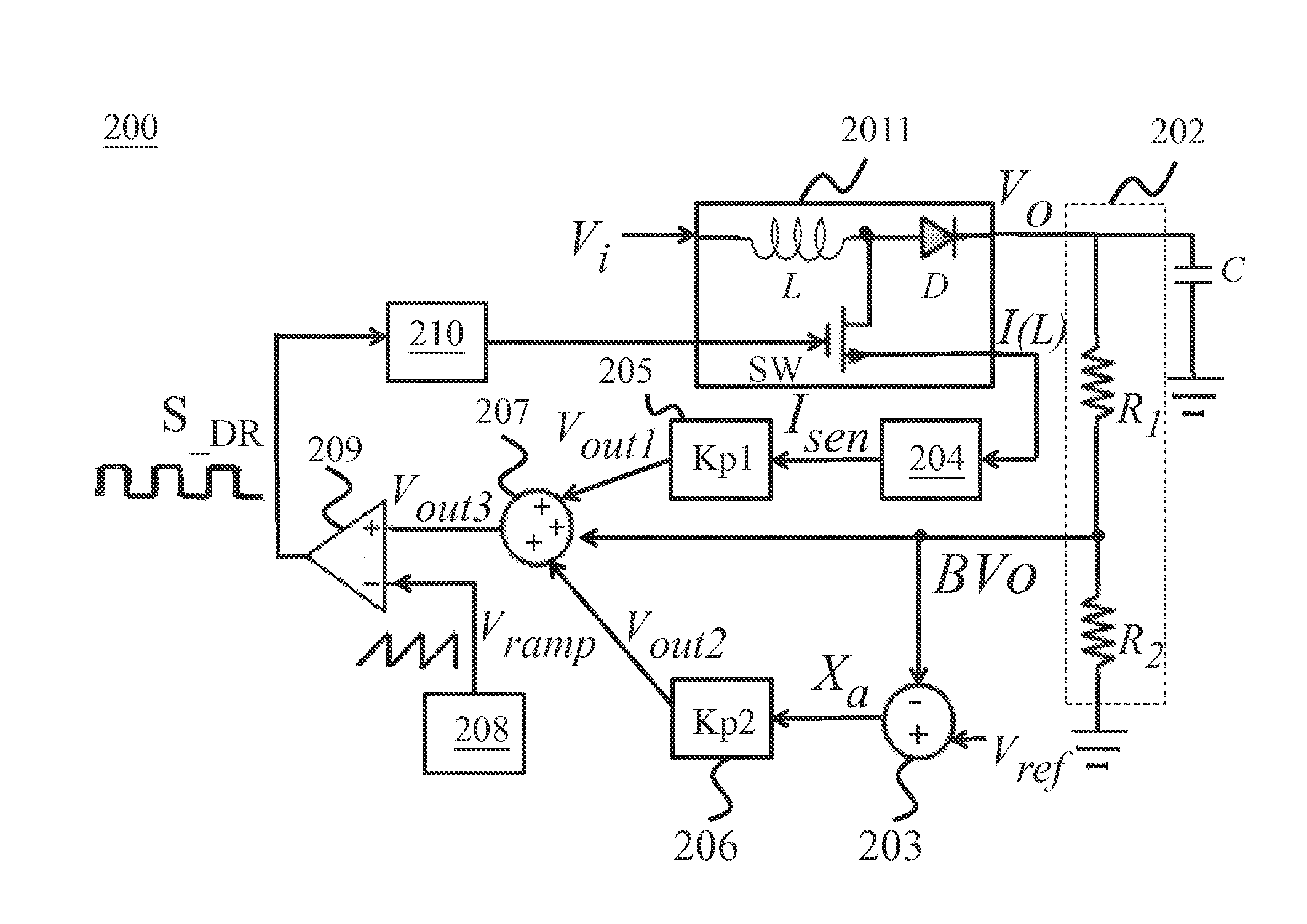
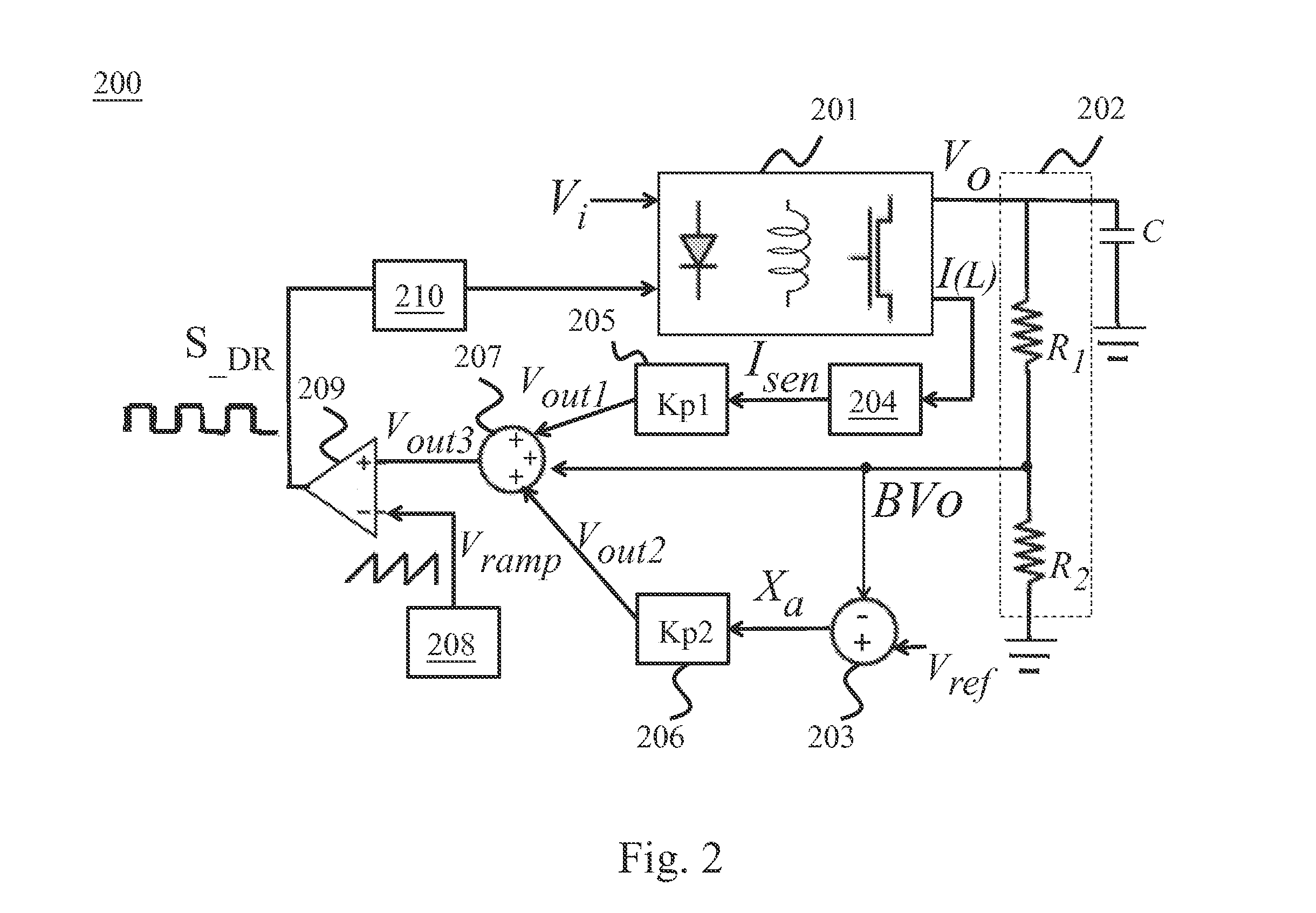
A power converter used in the current control circuit and control method, consisting of a converter, a voltage divider circuit, a current sampling circuit, a first gain circuit, a differential amplifier, a second gain circuit, a multiplier, a saw tooth wave generator, a modulation comparator, and a driver. The invention samples inductor current through the current sampling circuit and generates the current sense signal, then processes again. With the differential amplifier, it compares the feedback voltage from the voltage divider circuit with the reference voltage, and the results along a modulation comparator output a drive signal to control the duty cycle in order to avoid the generation of inrush current. The present invention avoids inrush current caused by the large drive signal and achieves a good response rate and better system stability.
Owner:LUXMILL ELECTRONICS
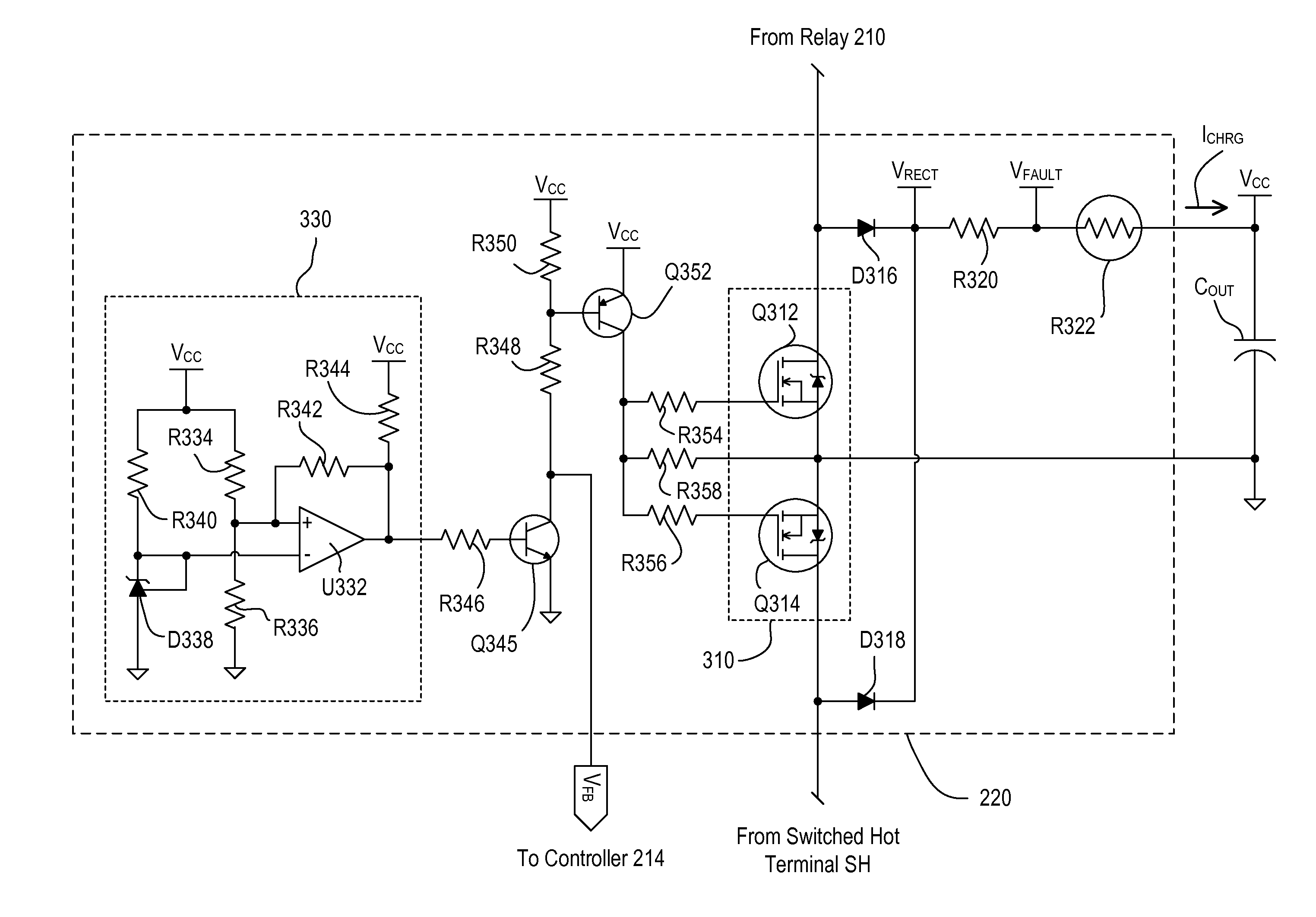
Active inrush current control using a relay for AC to DC converters
InactiveUS20060274468A1Improve efficiencyReduce power lossAc-dc conversionArrangements responsive to excess currentActive power factor correctionReduced size
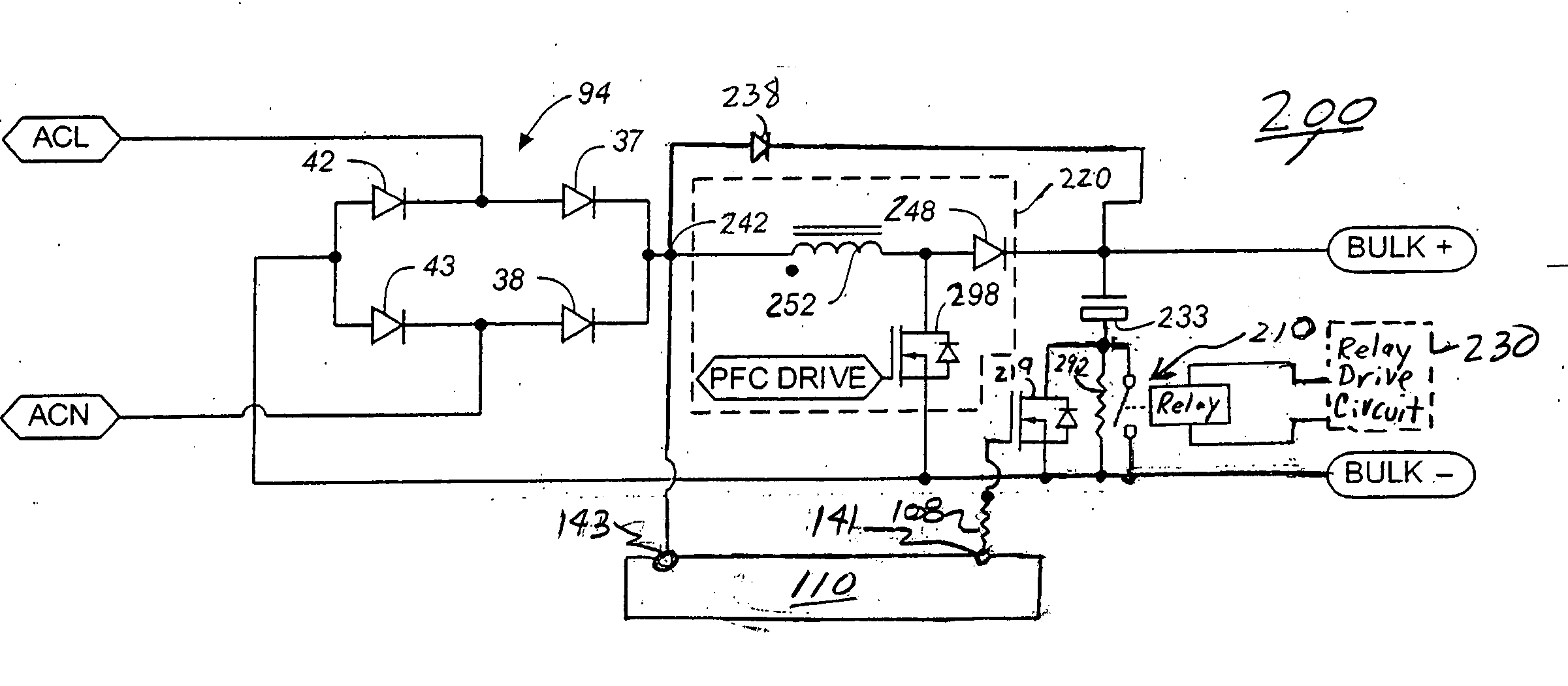
A circuit and corresponding method for controlling inrush current in an AC-DC power converter by providing a relay and a control circuit for limiting inrush current efficiently during cold startup, warm startup, and power line disturbance conditions. The relay is preferably connected in series with a bulk capacitor of the converter and in parallel with a limiting resistor and switch for shunting the resistor and switch so as to improve efficiency during operating conditions, at reduced size and cost. A preferred embodiment includes use of the circuit for AC-DC converters having active power factor correction.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Bridgeless boost converter with pfc circuit
InactiveCN1864319AAvoid restrictionsReduce overload capacity requirementsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceCycle control
The bridgeless boost topology reduces the power dissipation, cost, and size of prior PFC systems by eliminating the intrinsic loss of the input rectifier bridge. Sensing of the input line voltage by the controller is unnecessary. The use of One Cycle Control (also known as Single Cycle Control) allows the Power Factor Correction function to be performed without complex rectification networks to obtain the AC line voltage reference. The use of bi-directional switches makes it possible to control inrush current (the startup over-current due to the charging of the output bulk capacitor), which allows elimination of over-current limiting devices and reduction of the diode surge capability requirements. Moving the boost inductor to the system input adds an additional filtering function, reducing the cost of input EMI filtering.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
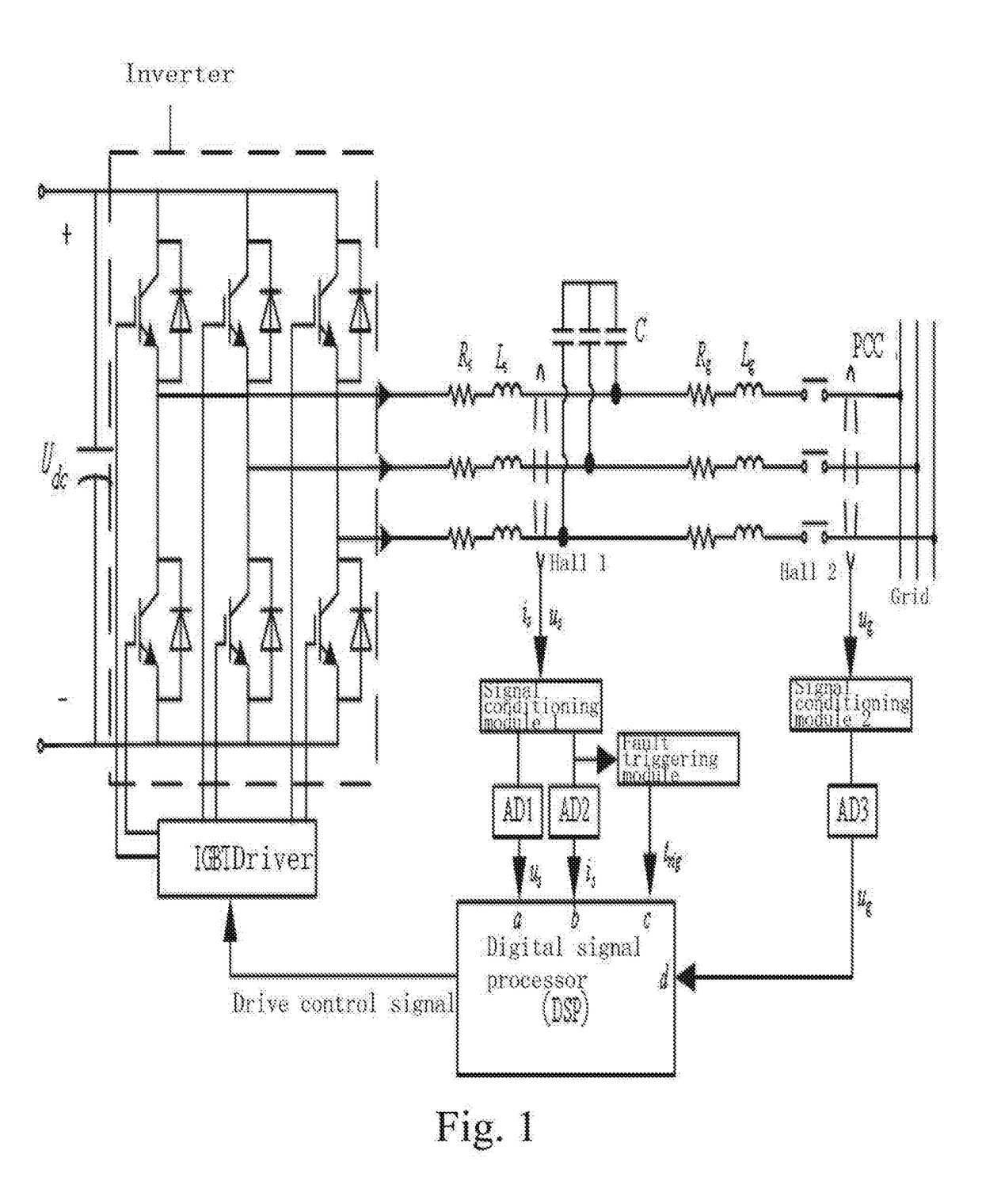
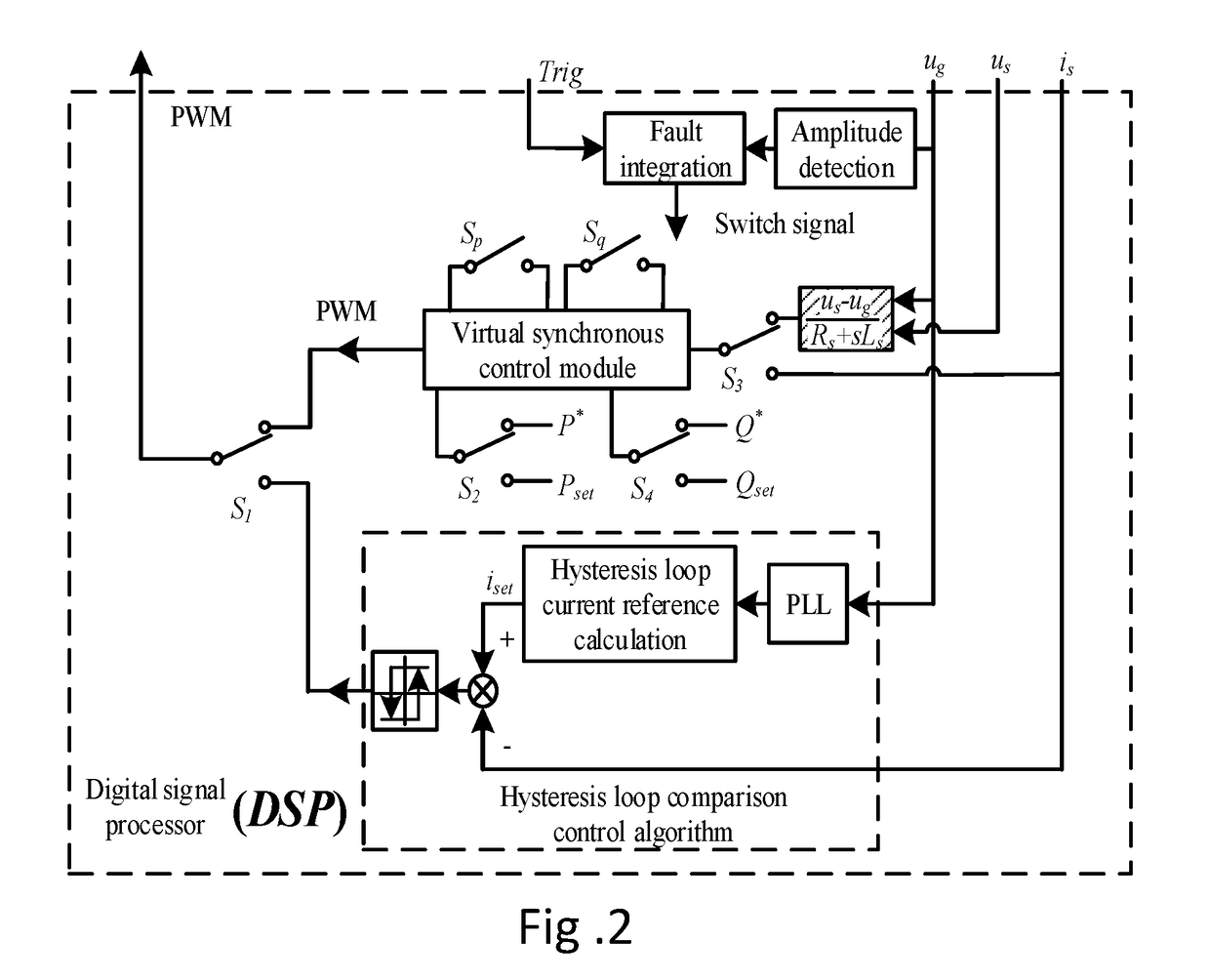
Virtual synchronous inverter with fast transient inrush fault currents restraining method thereof
ActiveUS20180145582A1Inhibit currentReduce voltageAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHysteresisVirtual synchrony
A fault inrush transient current restraining type virtual synchronous inverter and thereof is disclosed. The invention solves the problem that a virtual synchronous inverter will be burned due to inrush transient current in an extreme situation of a symmetrical fault occurring on the grid side by setting an information collection module for inverter output voltages and currents, a virtual synchronous inverting control module, a fault detection and synthesize module, a hysteresis comparison control module and a post fault clearing switch back grid-tie control module.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
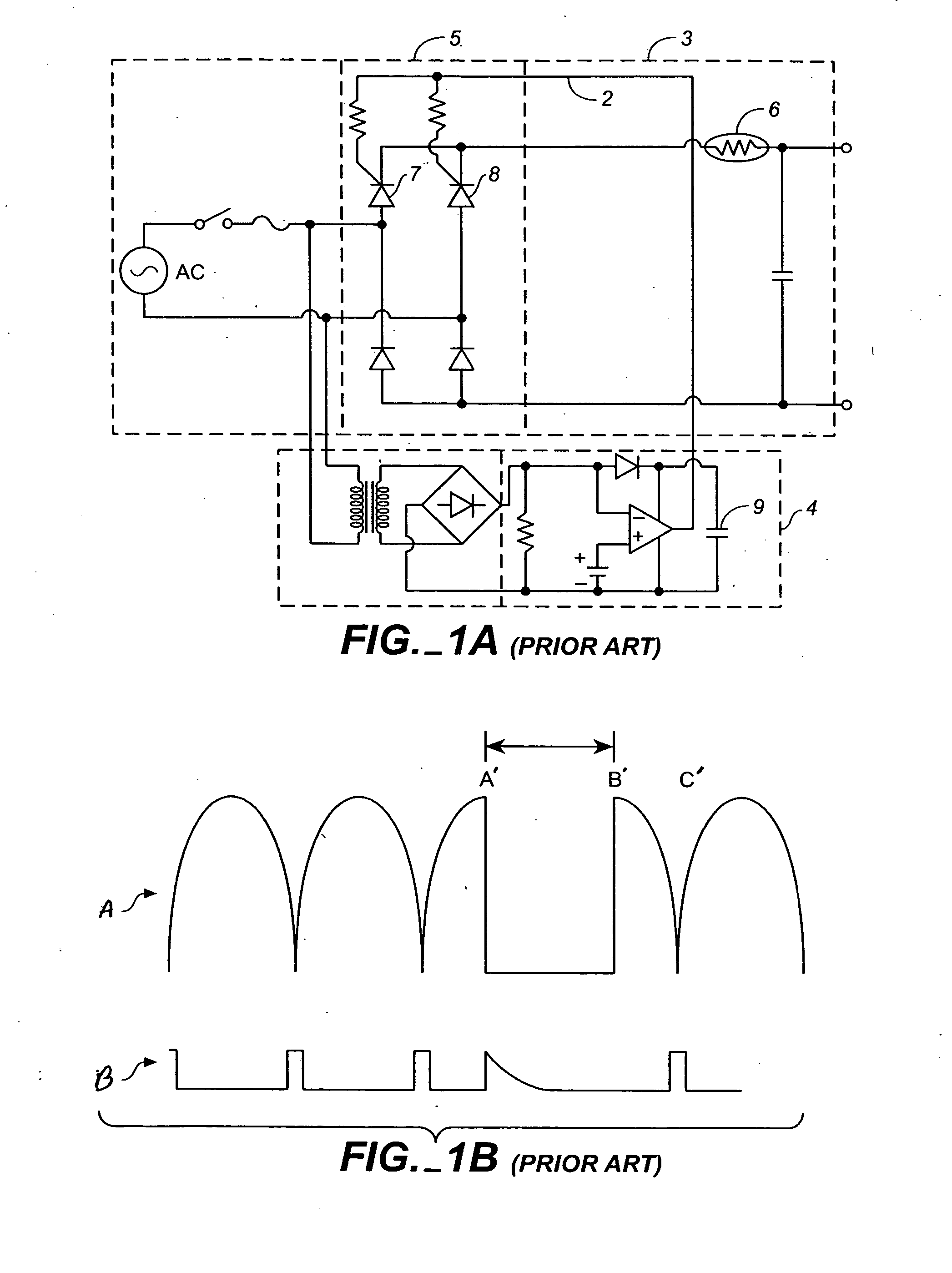
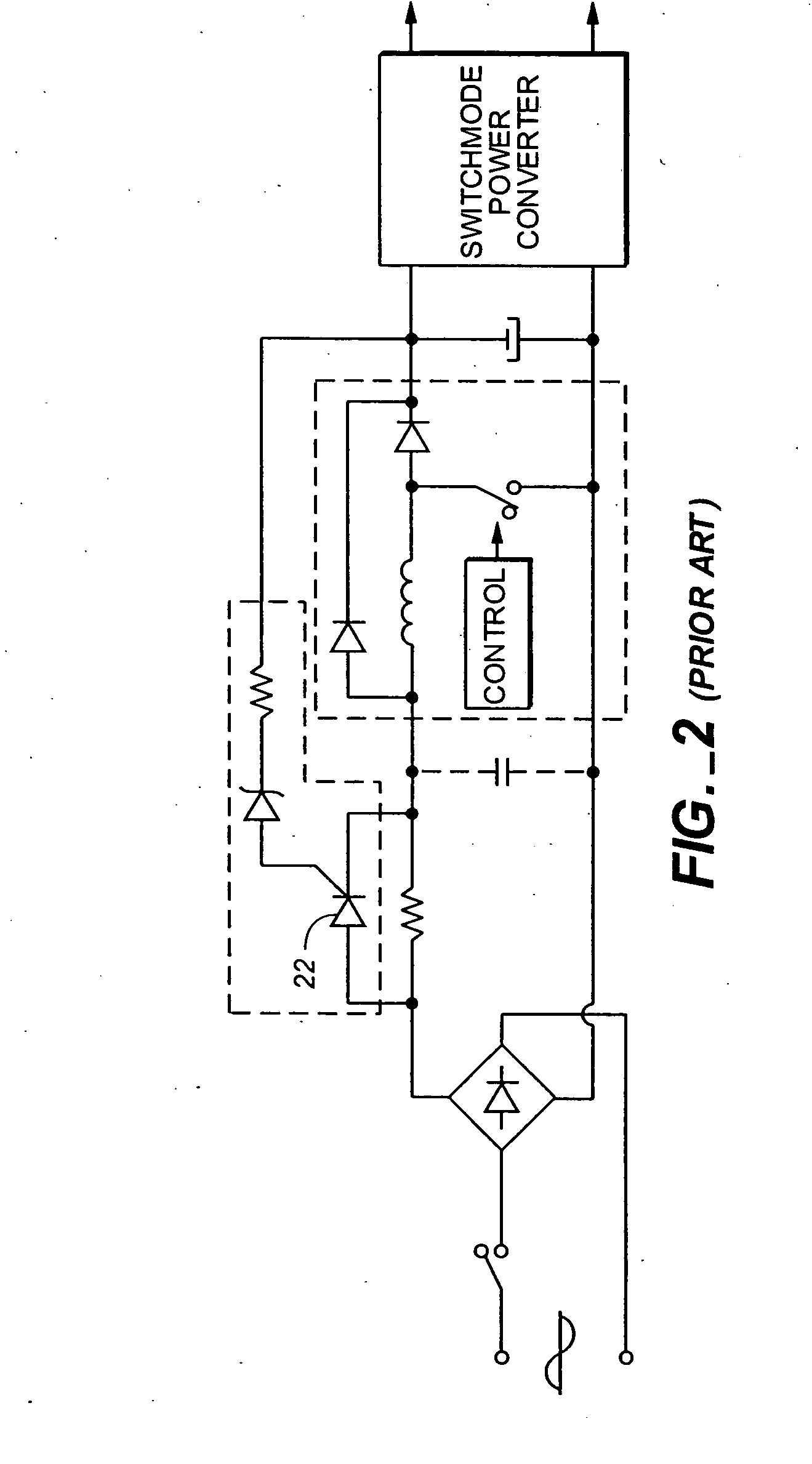
Controlling inrush current
InactiveUS20060132105A1Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentControl signalEngineering
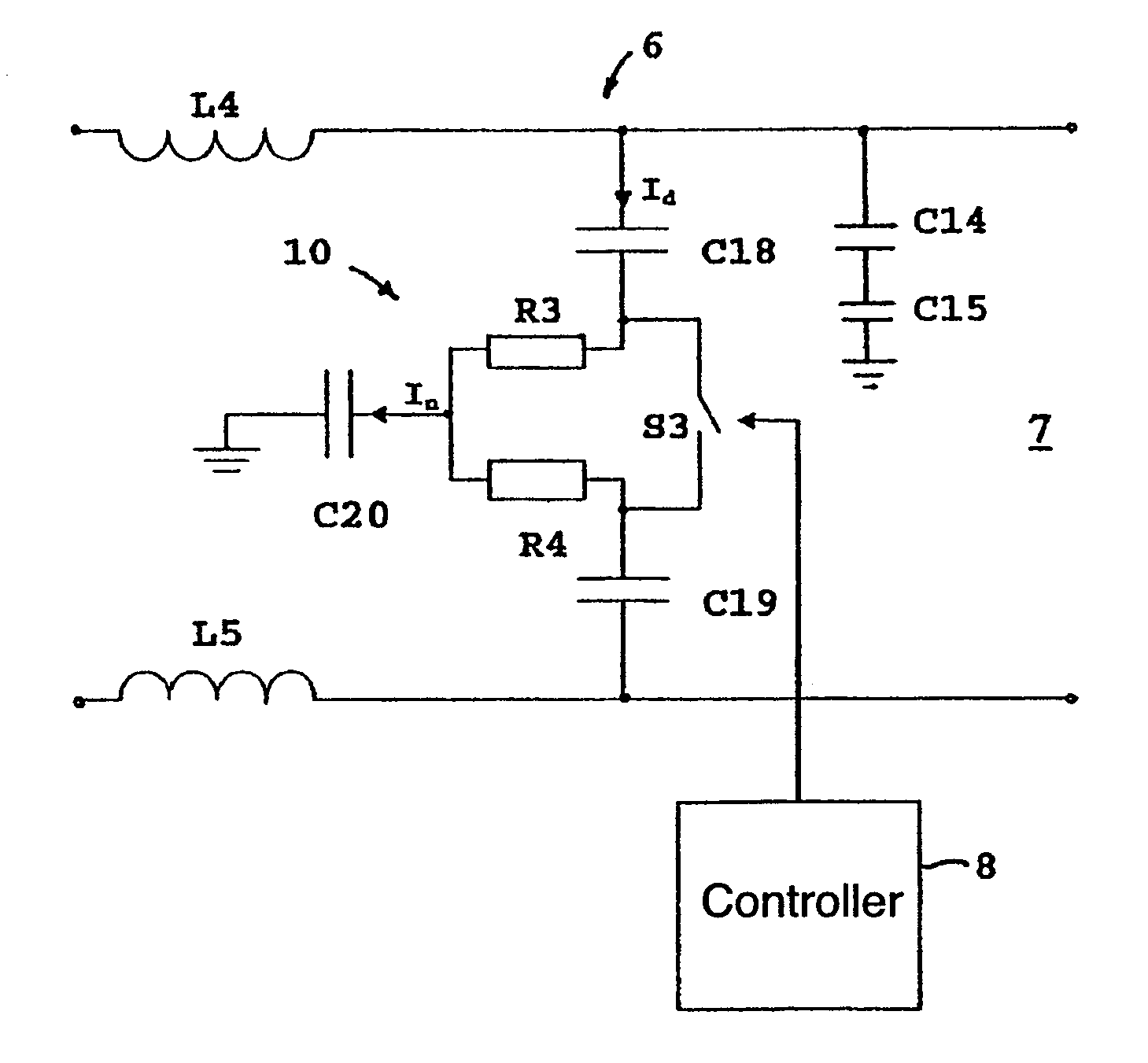
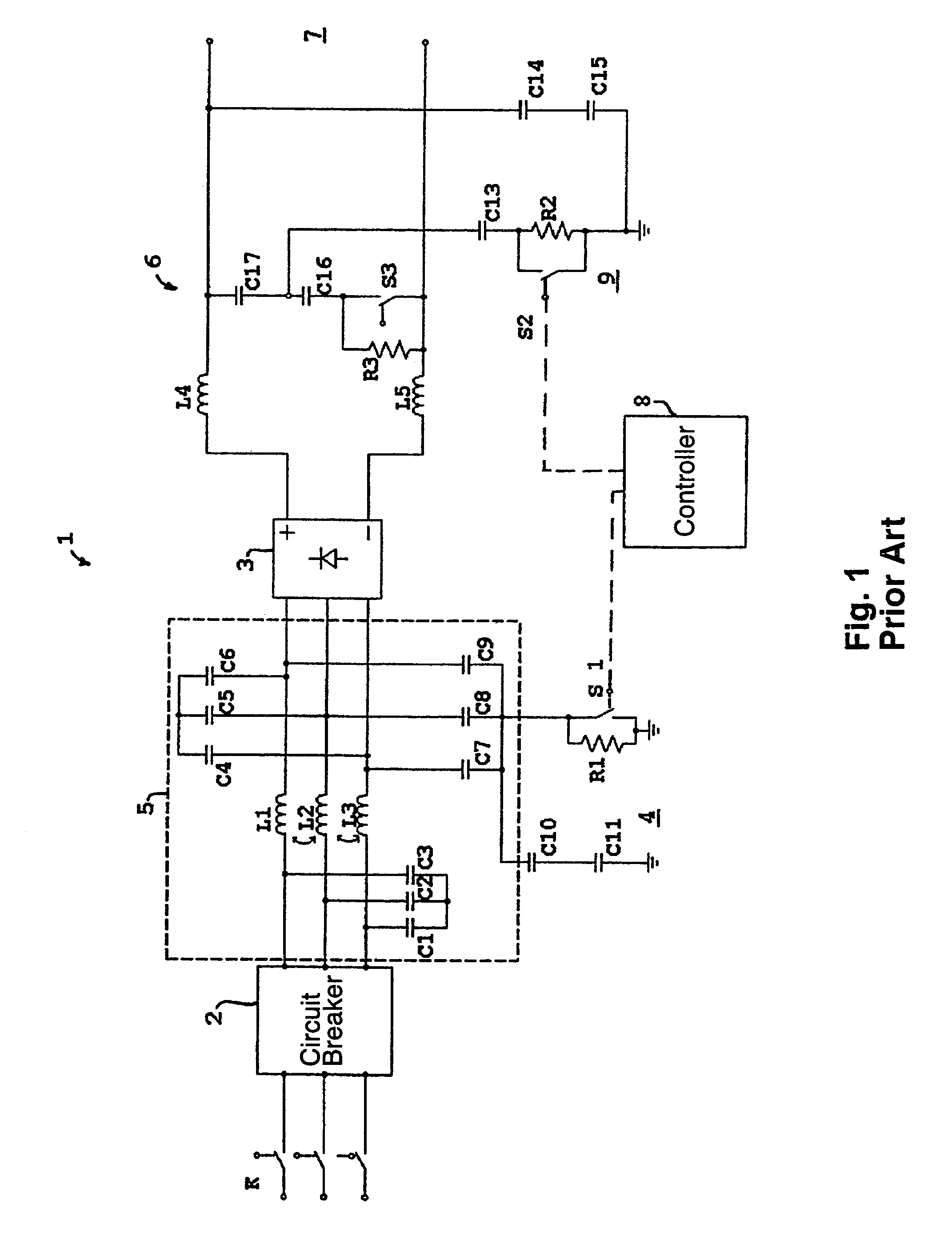
A control circuit and method for controlling a power factor correction circuit comprising: an inductor having an input terminal to receive an input voltage and an output terminal series connected to an anode of a diode; a first capacitor connected between a cathode of said diode and ground; a first switch connected between an anode of said diode and ground; a series arrangement of a second capacitor and a parallel arrangement of a resistor and a second switch series connected with said second capacitor. The control circuit is operable to generate synchronous first and second switch control signals to respectively control said first and second switches, wherein during inrush current conditions when said input voltage drops-in after an interruption, said control circuit is operable to cause said first and second switches to be synchronously switched at increasing duty cycles. The method comprises charging a first capacitor from an input voltage source; isolating the first capacitor from the input voltage source; transferring a portion of charge stored in said first capacitor to a second capacitor while said input voltage source is isolated from said first capacitor and from said second capacitor; and repeatedly said charging, isolating, and transferring until a voltage is formed on said second capacitor that is approximately equal to said input voltage source.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Fault indicator with auto-configuration for overhead or underground application
InactiveUS7106048B1Direction of current indicationVoltage polarity indicationFault indicatorMicrocontroller
A fault indicator for indicating the occurrence of a fault in an electrical conductor is automatically configured for an overhead application or for an underground application. The fault indicator has a housing, a battery, a display for indicating the occurrence of a fault, a current sensor for sensing the load current in a monitored conductor, and electromagnetic field sensor to sense the electromagnetic field about the conductor, and a microcontroller for determining whether a fault condition occurred, for determining the magnitude of the electromagnetic field, and for configuring the fault indicator in the overhead configuration if the electromagnetic field is above a predetermined magnitude or configuring the fault indicator for the underground mode if the field is below the predetermined magnitude. In the overhead configuration, voltage inrush restraint is enabled, the fault response time is set within a range of 1 to 50 ms, and the display is operated in bright or dims modes depending upon ambient lighting levels. In the underground configuration, inrush current restraint is enabled, the fault response time is set within a range of 1 to 24 ms, and the display is operated in only the dim mode. Related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Circuit and method for controlling DC-DC converter
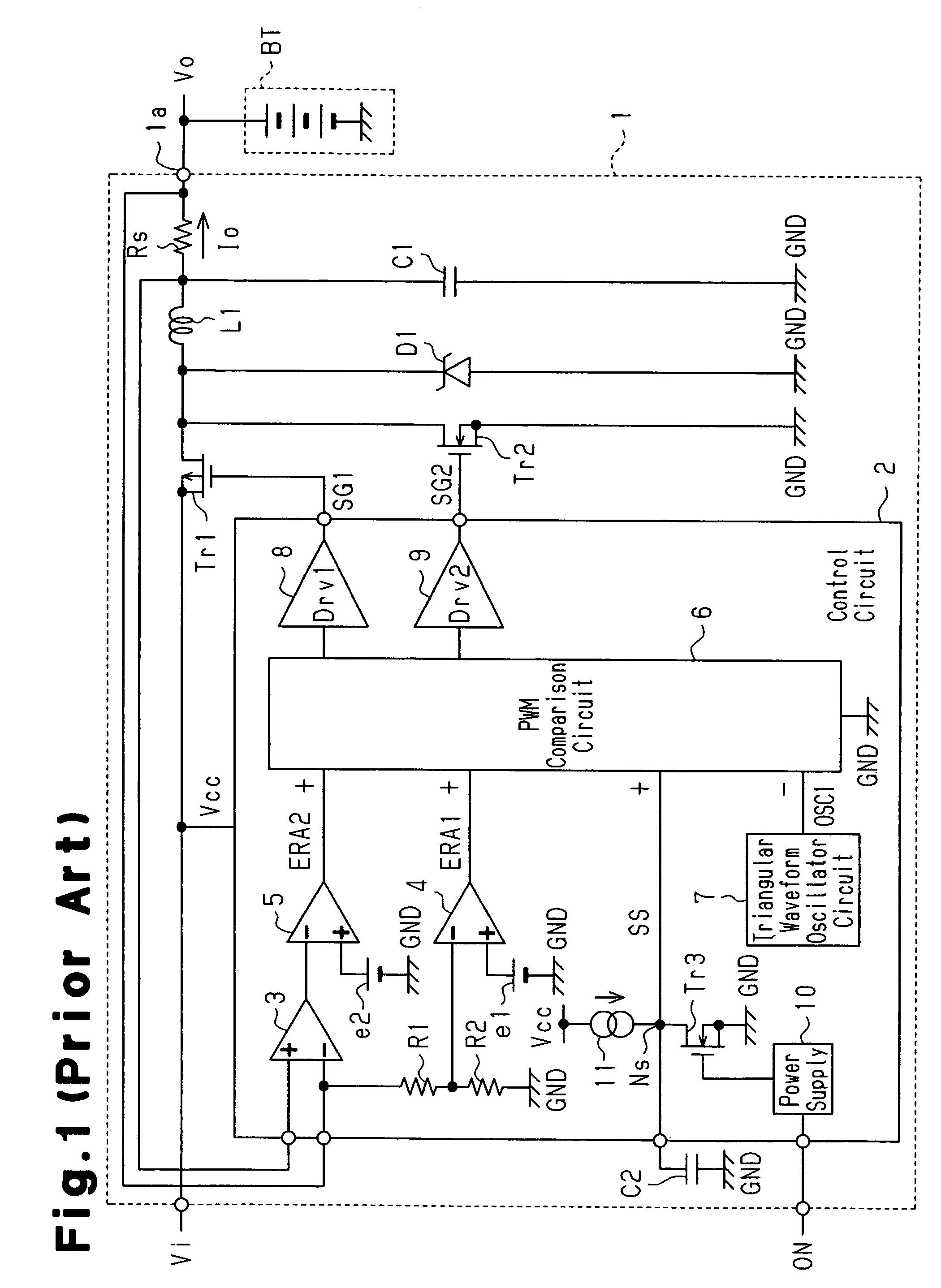
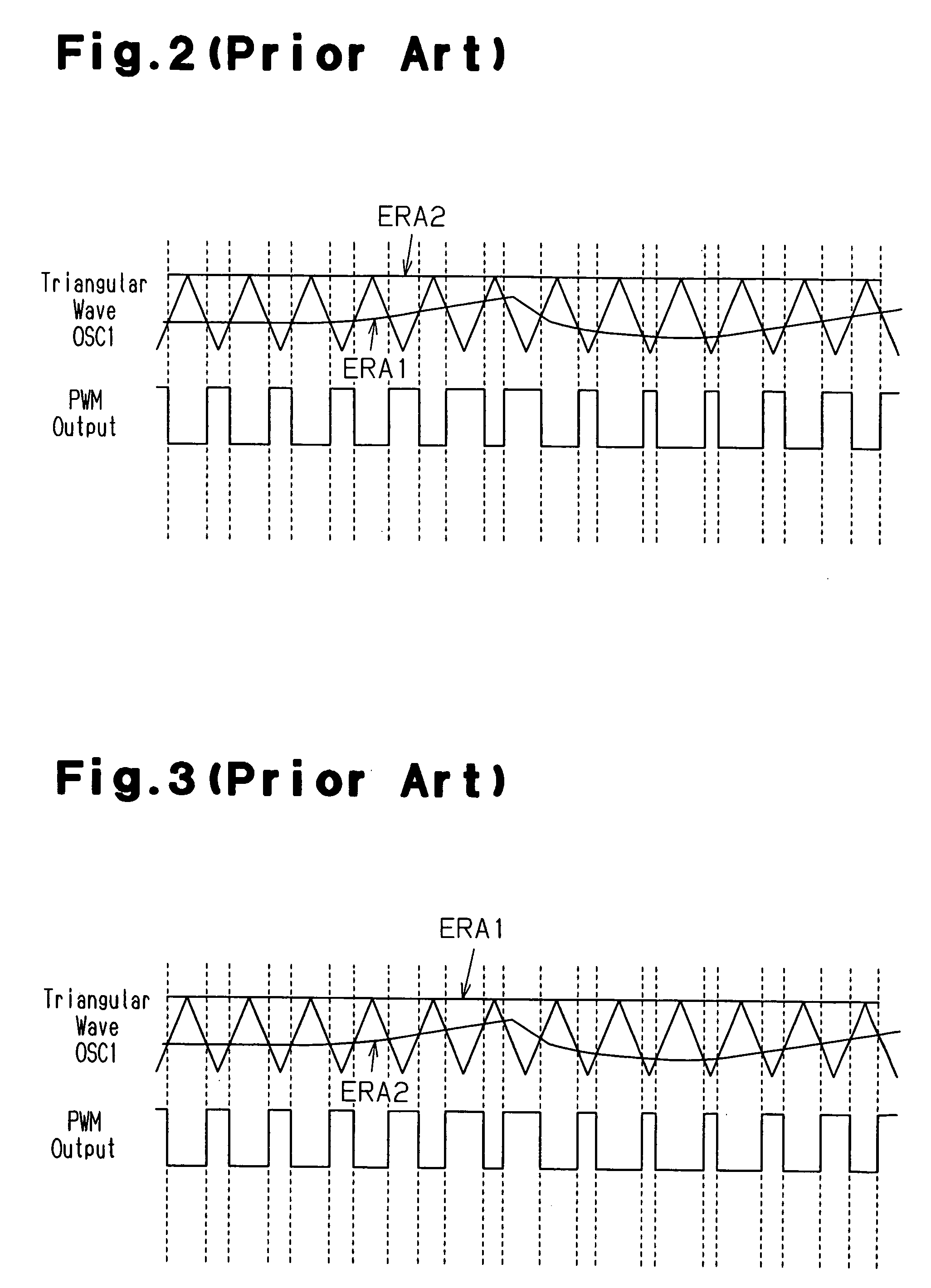
A control circuit for suppressing generation of inrush current during activation of a DC-DC converter, which controls output with control signals. The control circuit includes first and second error amplification circuits, each of which generates a control signal based on the difference between a reference voltage and voltage derived from an output voltage or an output current. During activation of the DC-DC converter, a soft start circuit generates a soft start signal having voltage lower than voltage of each control signal to control the output of the DC-DC converter. During activation of the DC-DC converter, a clamp circuit, which is connected to the first and second error amplification circuits, clamps the voltage of the first and second control signals to substantially the same voltage as the soft start signal.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
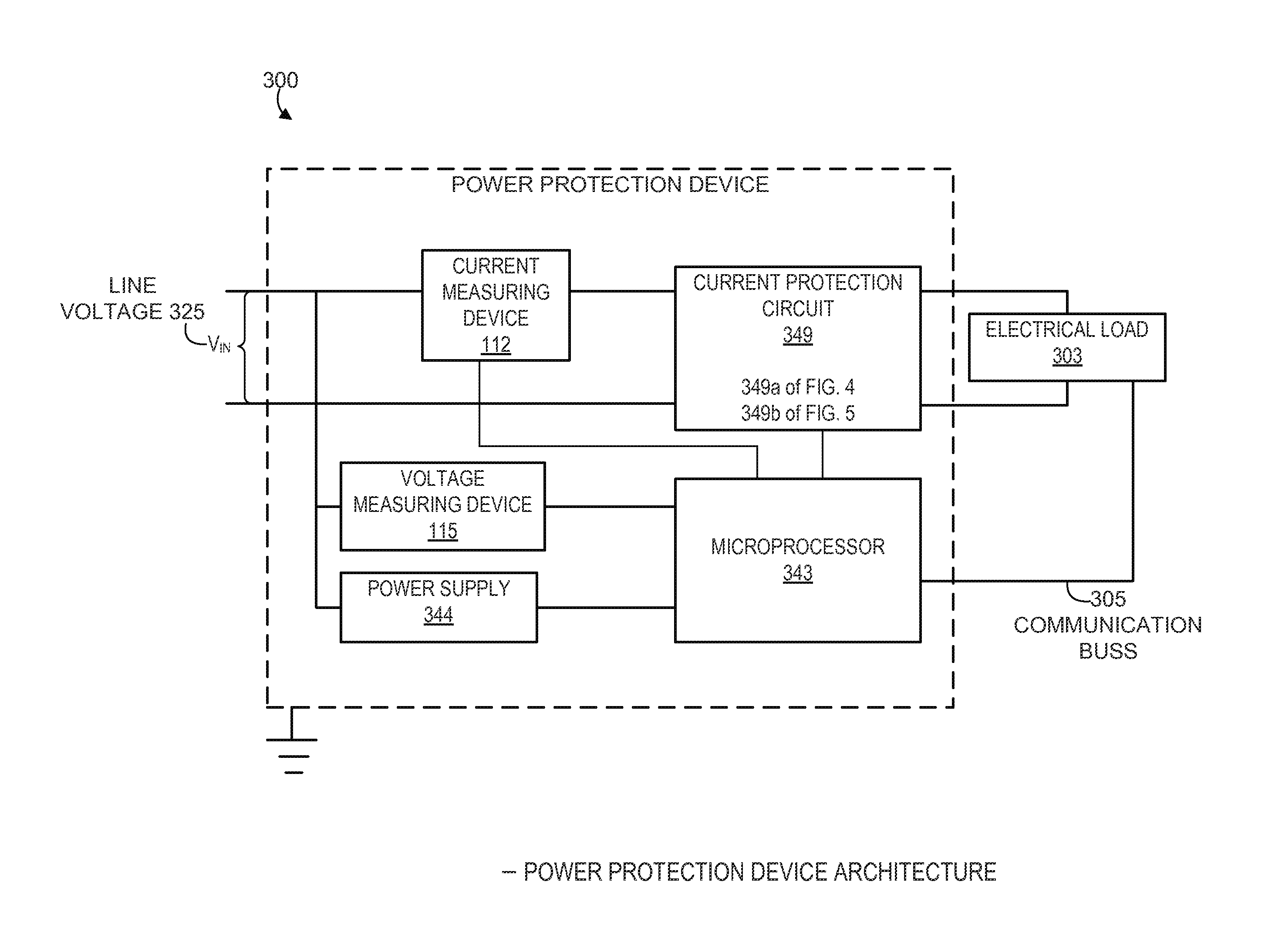
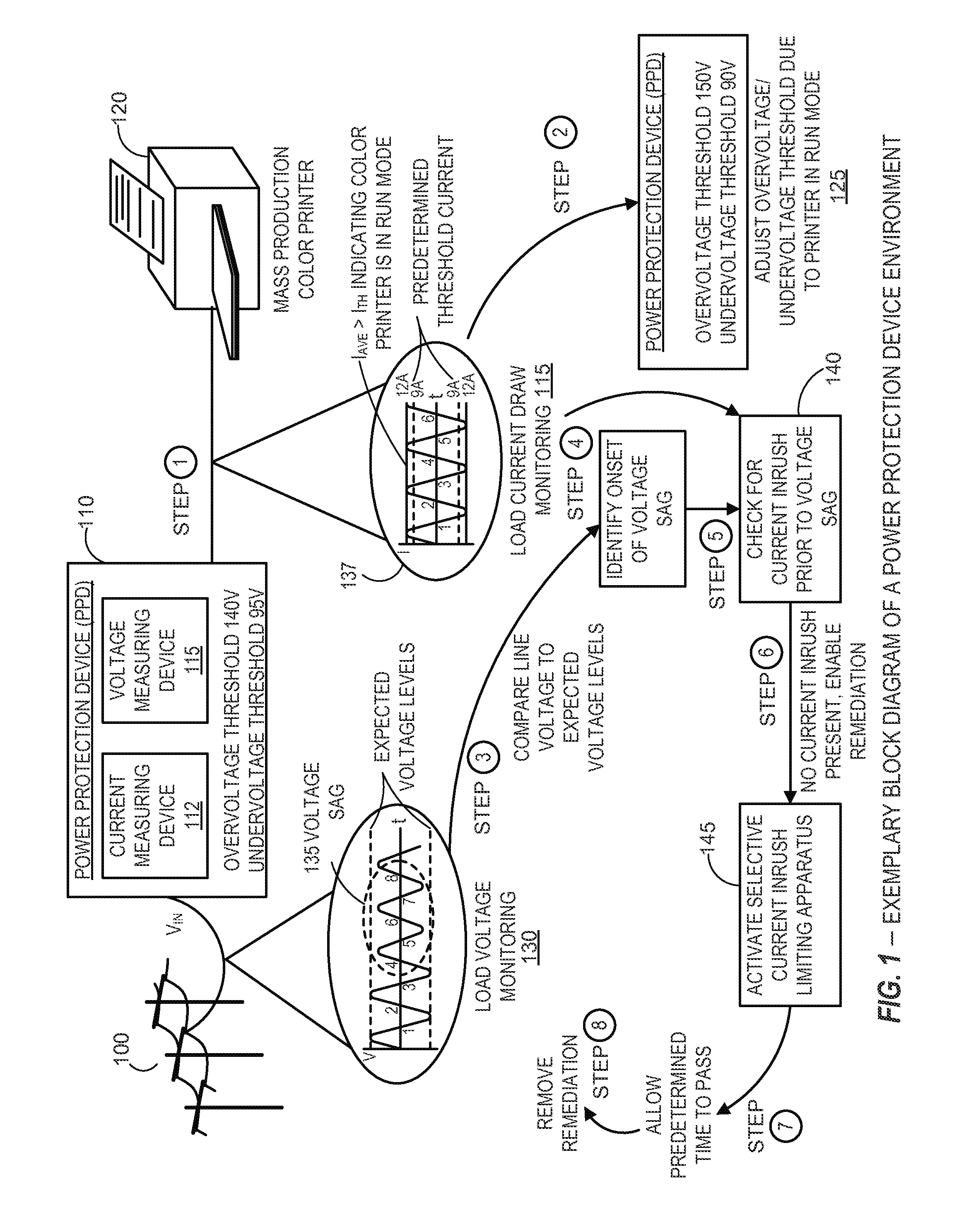
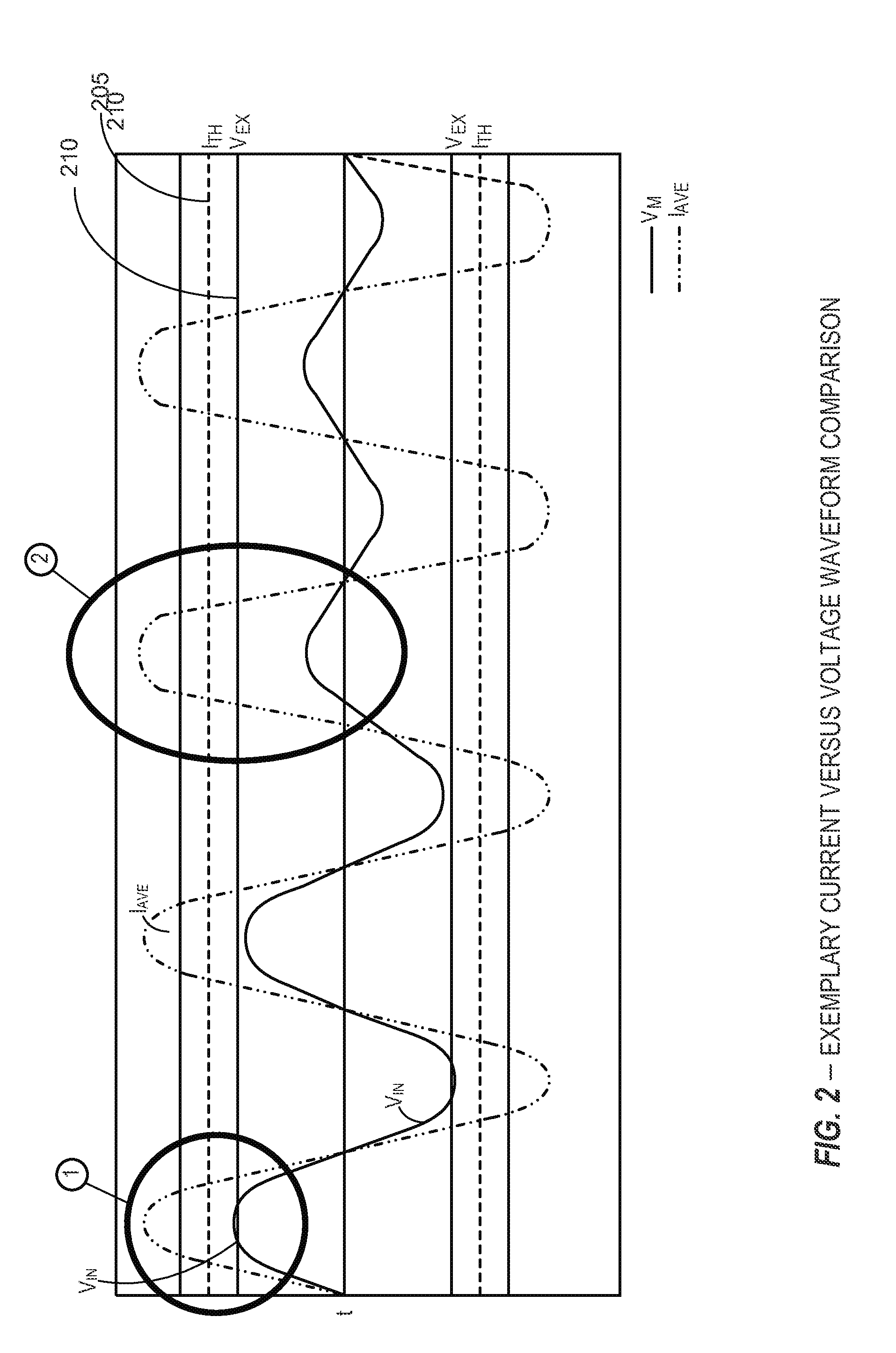
Systems and methods for detecting and determining sources of power disturbances in connection with effective remediation
ActiveUS20140268458A1Power disturbanceEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectricityCurrent limiting
Apparatus and methods for selective protection of an electrical load from disturbances on an input power line. A power protection circuit includes a selectively variable inrush current limiting circuit and a switch for disconnecting the input power line from the load. A control circuit determines that the electrical load is in a first operational state, such as a standby mode or normal operation, or a second operational state, such as full operation at rated current. The power protection circuit provides variable inrush current limiting to the electrical load in response to a first category of disturbances when the electrical load is in the first operational state. The power protection circuit inhibits disconnecting the electrical load in response to a second category of disturbances when the electrical load is in the second operational state. Species of selectively variable current limiting circuits are also described.
Owner:I EWM ACQUISITION LLC
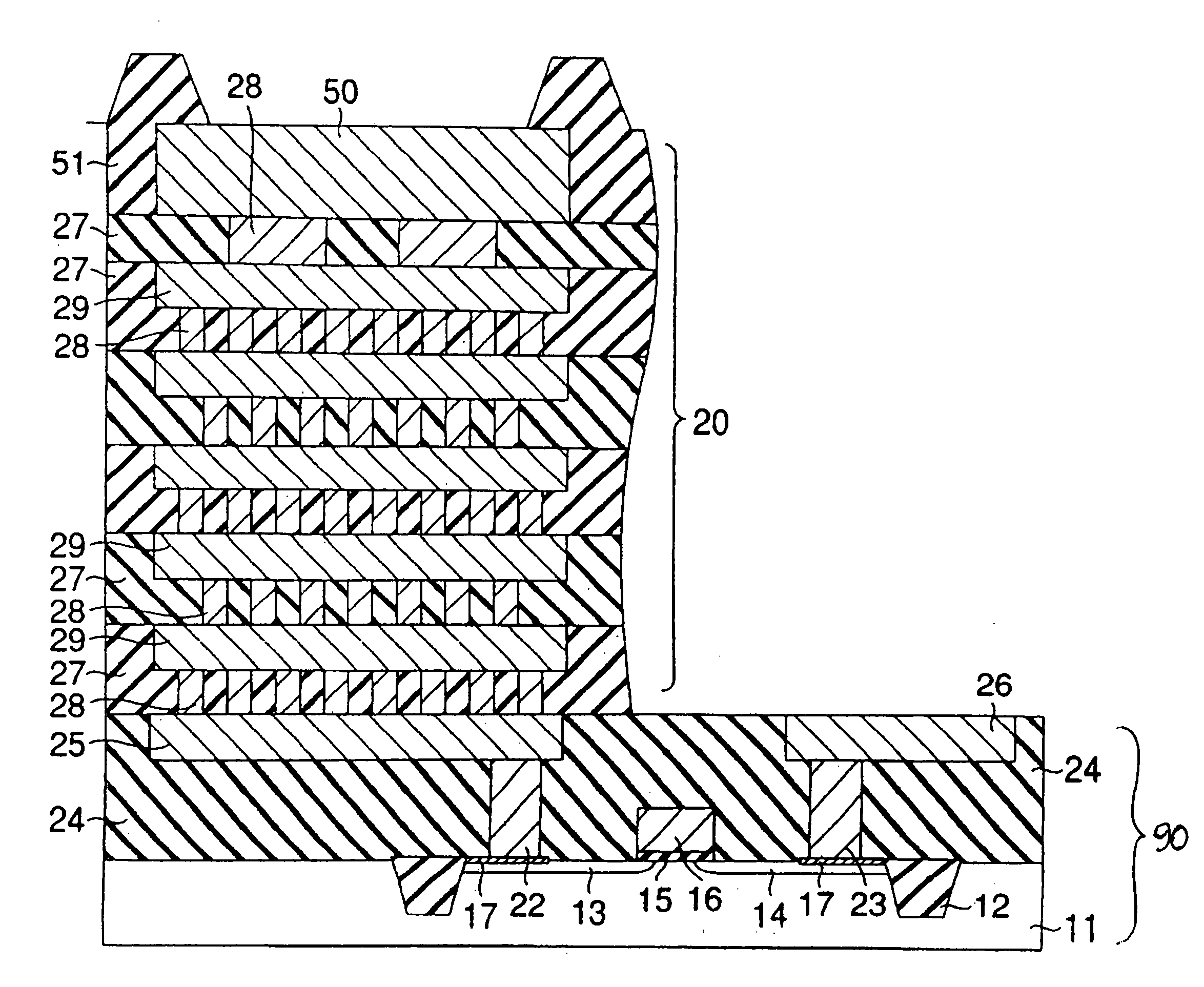
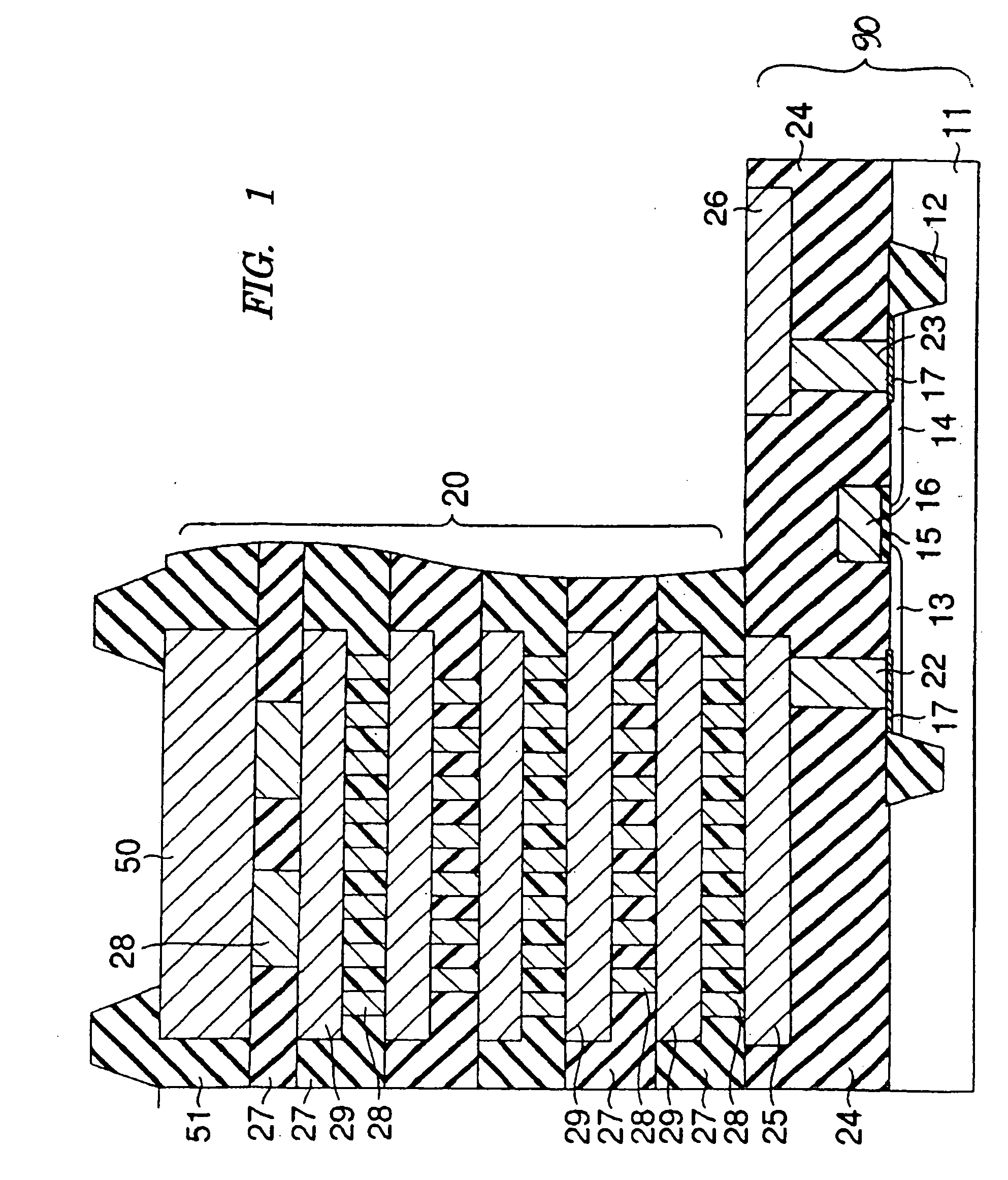
Semiconductor apparatus including a radiator for diffusing the heat generated therein
ActiveUS20050023692A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorInrush current
A semiconductor apparatus is provided that includes a radiator for efficiently radiating heat generated in a wiring layer used in a surge current path of an electrostatic discharge protection circuit, and also for protecting the wiring layer itself used as the surge current path. The semiconductor apparatus includes an input protection circuit coupled to a wiring provided between an external terminal and an internal circuit, the input protection circuit includes a protection element for protecting the internal circuit from an excessive electrostatic surge input supplied to the external terminal. The semiconductor apparatus further includes a first metal wiring layer coupled to the input protection circuit and included in a current path for the surge electrostatic surge input, and a radiator including a sufficient thermal conductivity material coupled to the first metal wiring layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Single stage isolated ac/dc power factor corrected converter
ActiveUS20170025962A1Improve efficiencyReduce the burden onEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorSingle stage
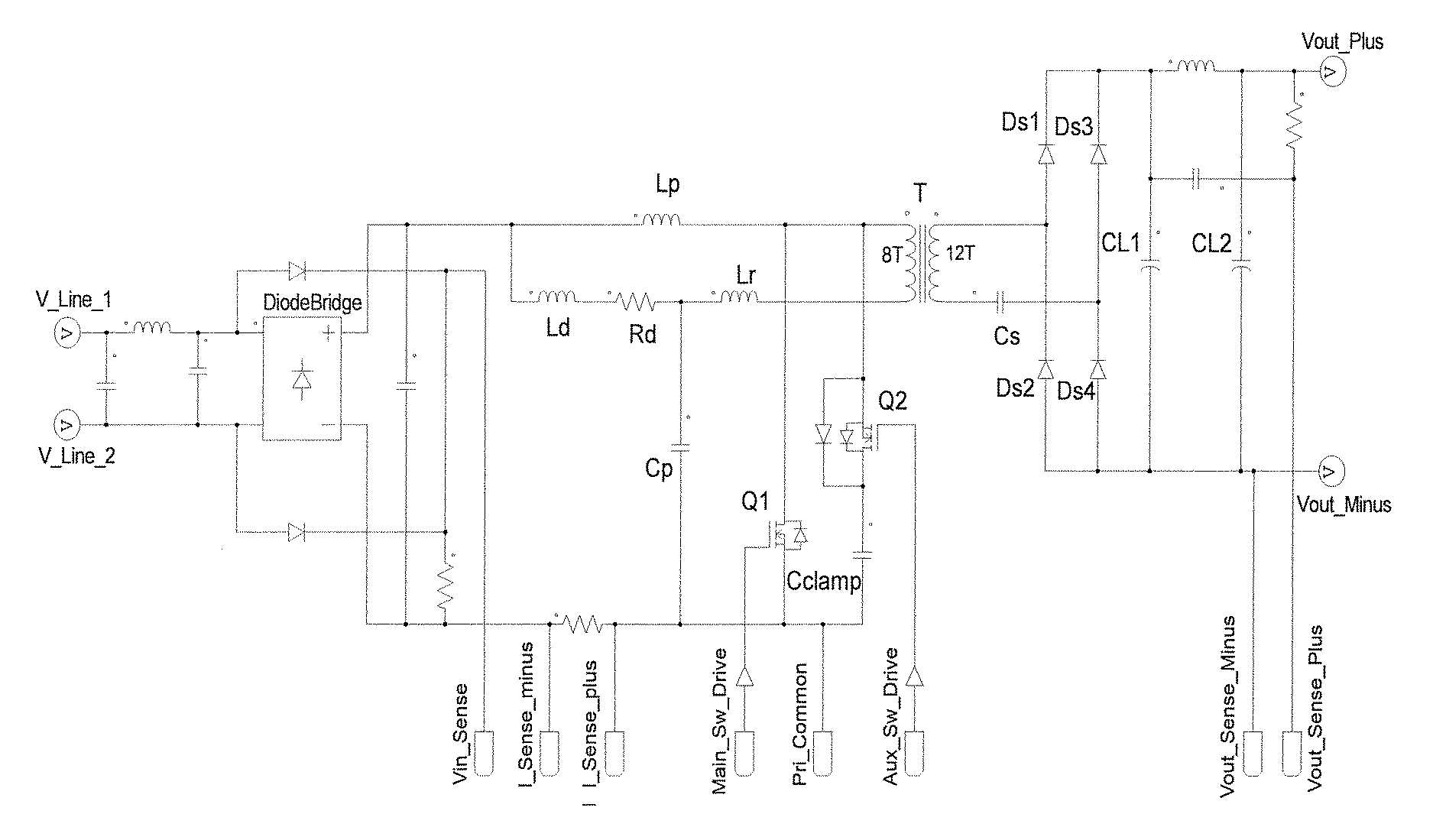
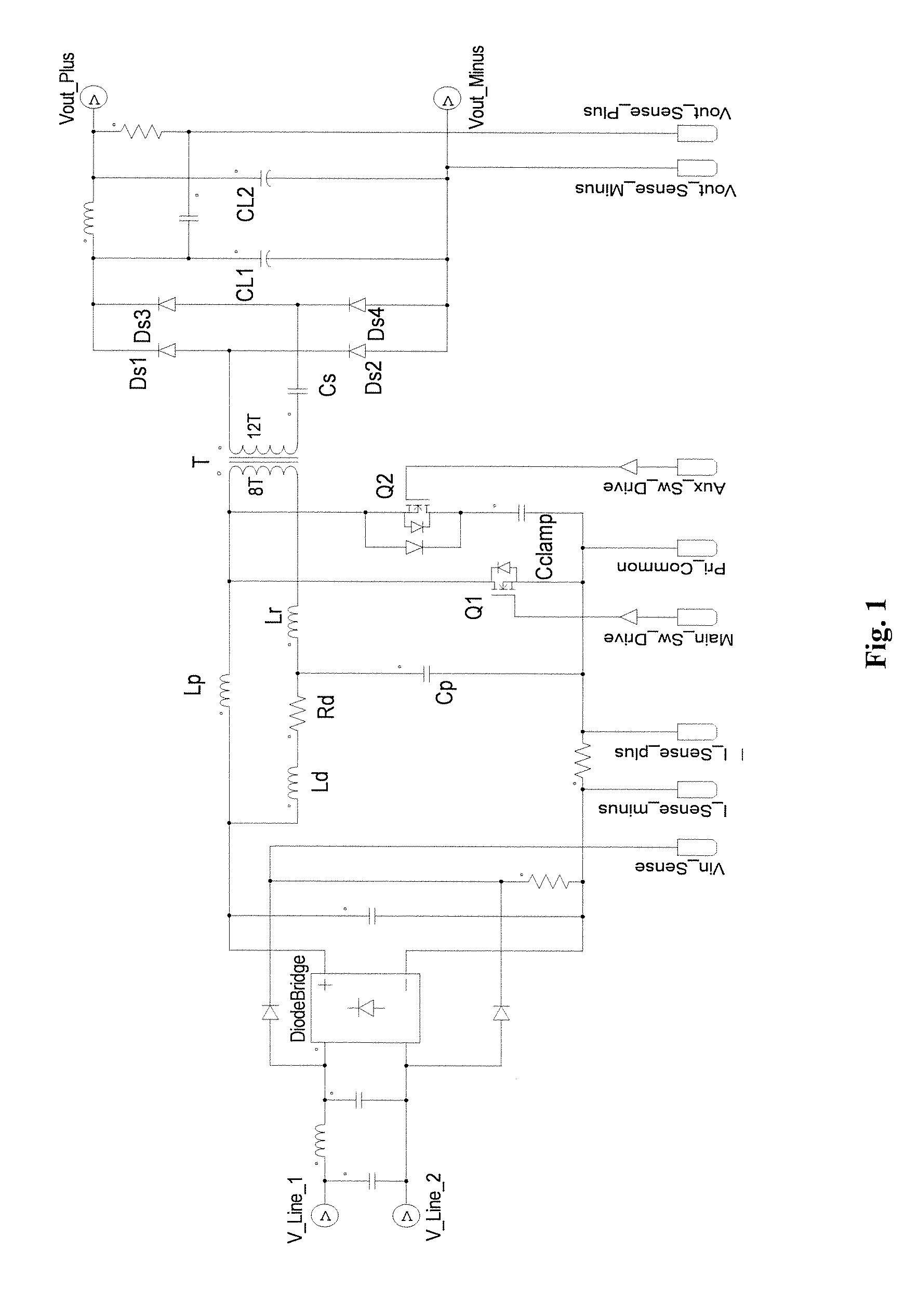
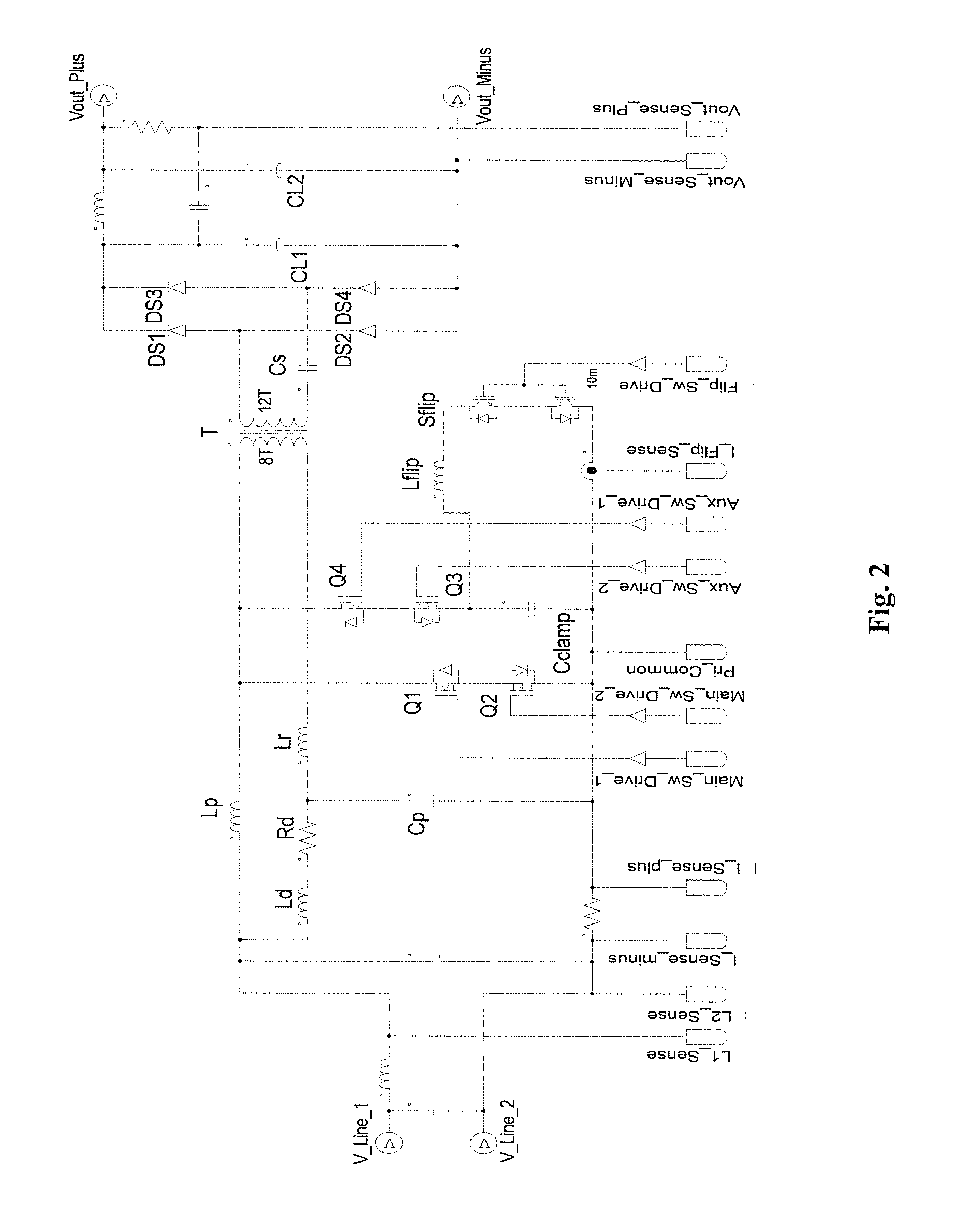
Two versions of an isolated single stage converter AC / DC Power Factor Corrected (PFC) converter topology have been invented. One is with a full bridge rectifier at its input and the other is a True Bridgeless version. The two versions of the topology feature new configurations and circuitry including a simplified damper circuit and a clamp capacitor flipping circuit and control methods that allow them to realize improved single stage isolated power factor converters which are suitable for high power operation, features Zero Voltage Switching to maximize conversion efficiency and to minimize Electro-Magnetic Interference generation, does not need an additional circuit to limit the inrush current, achieves reasonably low input current Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), and is easy to control. The second version provides a true bridgeless single stage isolated power factor converter with even higher efficiency and lower input current THD.
Owner:DAVIDSON CHRISTOPHER DONOVAN
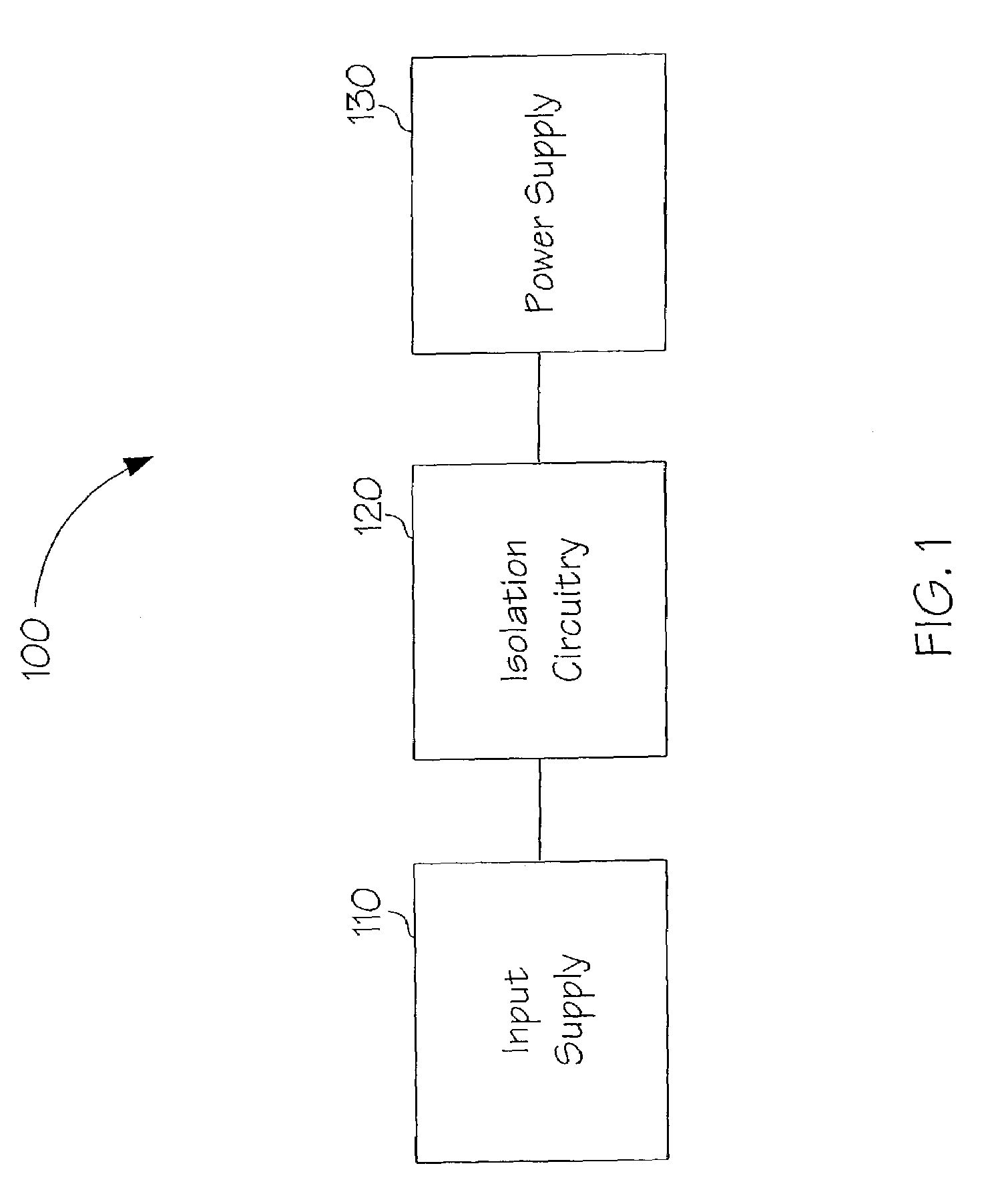
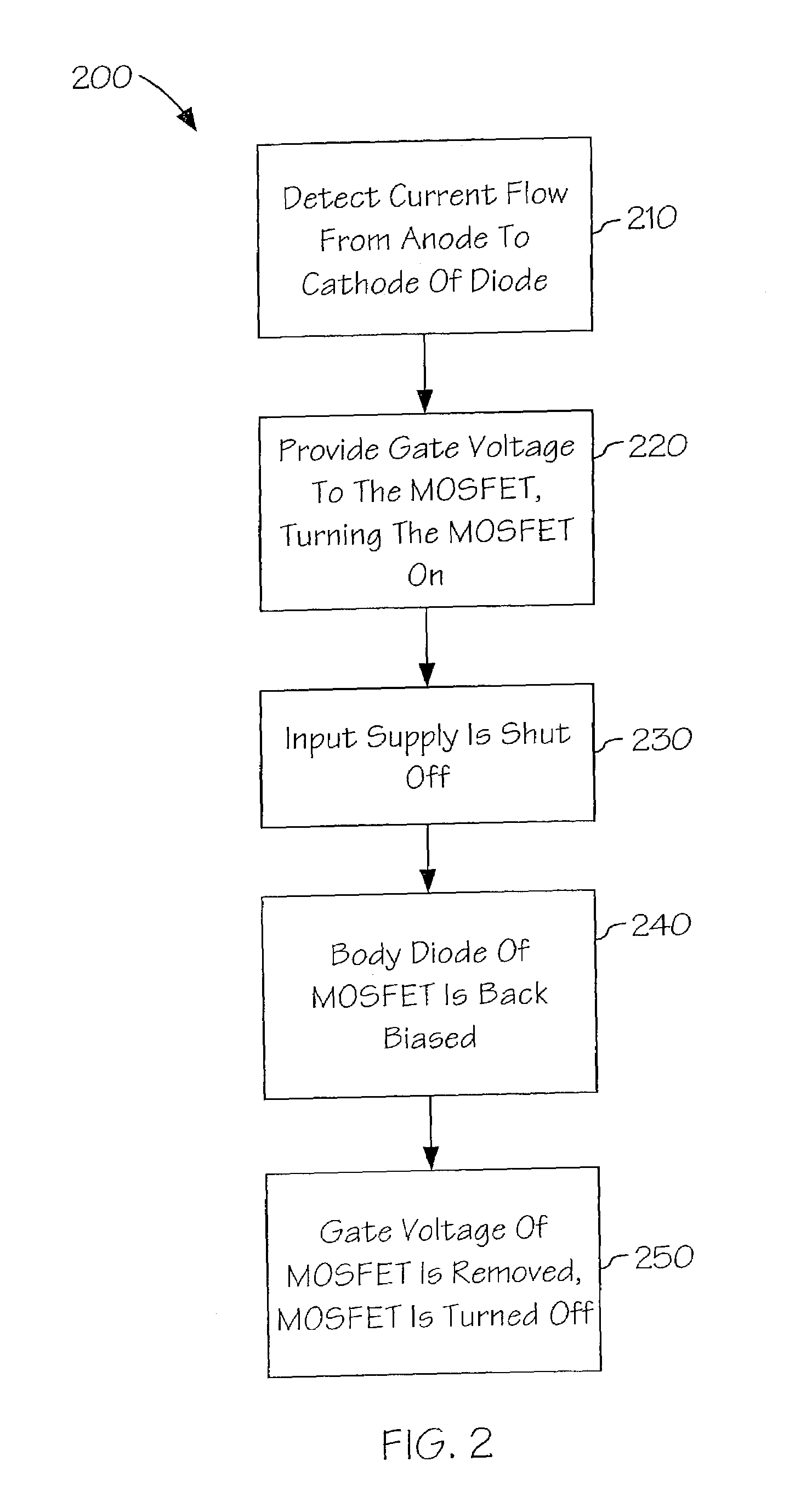
Input and output isolating diode for power dissipation reduction of power supplies
InactiveUS7379282B1Minimize power consumptionPower dissipationTransistorDc network circuit arrangementsMOSFETTime delays
The present invention is a method and system for providing improved isolation for power supplies while minimizing power dissipation. A body diode of a MOSFET may be utilized with a comparator circuit. The comparator circuit may detect current flow across the MOSFET and may turn the MOSFET on. This may shunt the diode with a low drain to source resistance limiting power dissipation across the diode to an amount of the drain to source current squared (Ids2) times the drain to source resistance of the MOSFET when on (RDSon). Use of the comparator circuitry may reduce the time delay associated with turning the MOSFET off to prevent a high reverse inrush current within a power supply.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
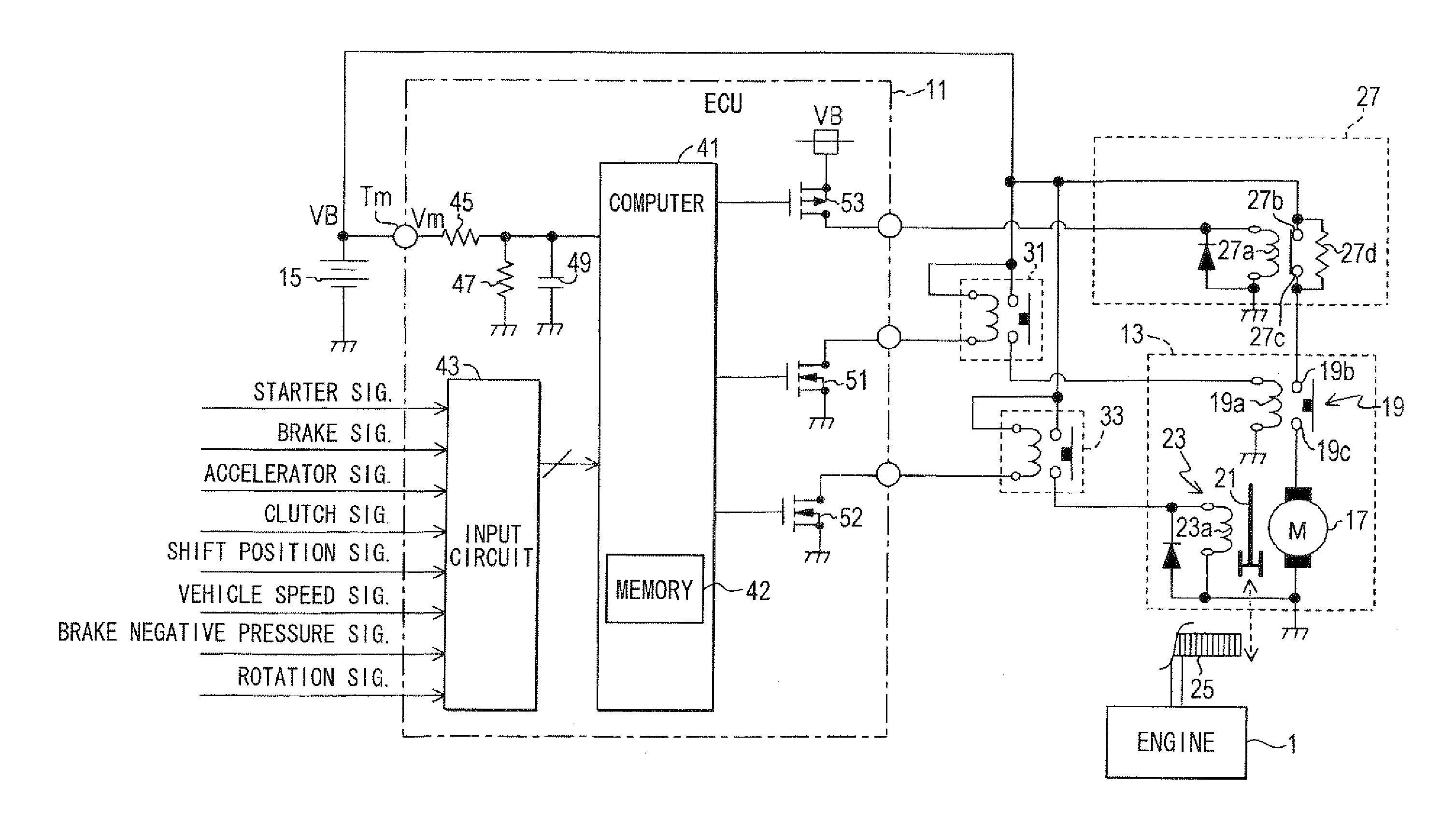
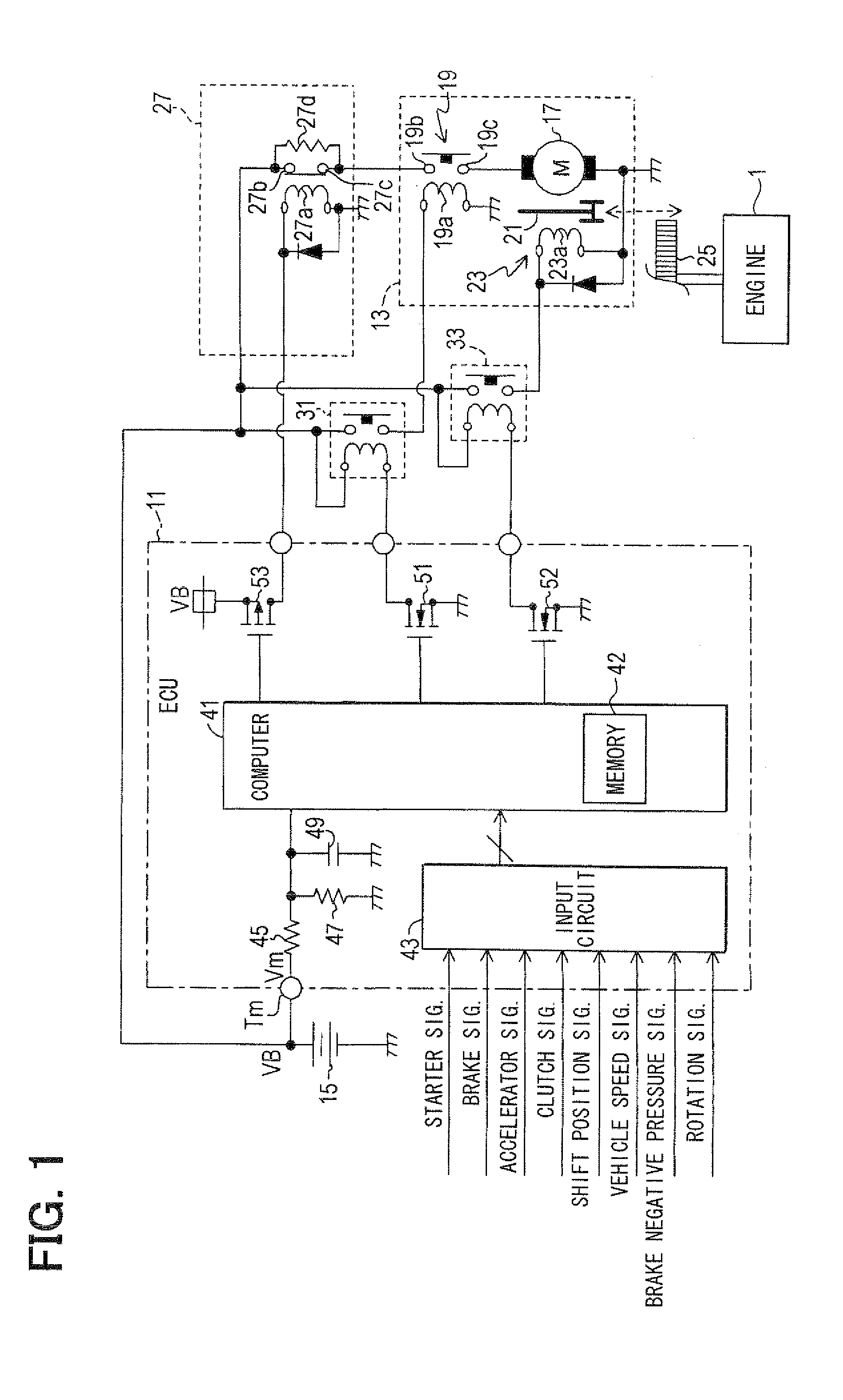
Starter controller
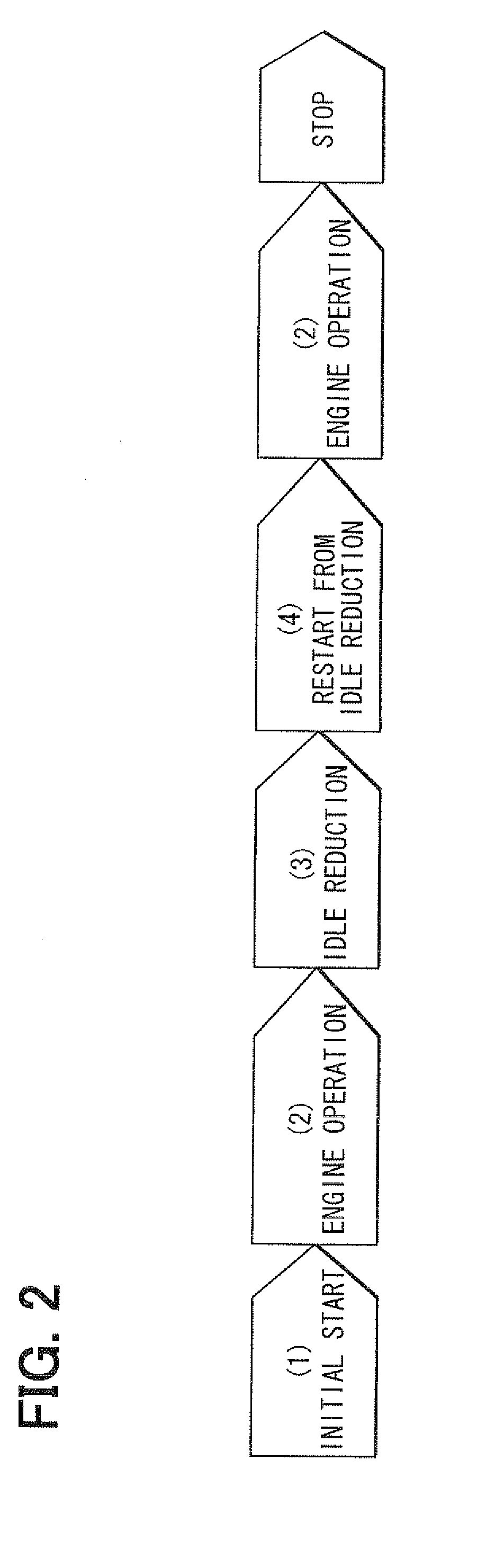
InactiveUS20110196570A1Increased amount of rotationReduce output voltageVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesIdle reductionIdle speed
An idle reduction vehicle has a relay in a power supply line from a battery to a starter motor. The relay is driven between a contact-side state, in which contacts short-circuit, and a resistor-side state, in which the contacts are opened and a resistor is serially inserted into the power supply line. At an engine restart from idle reduction, an ECU drives the relay to the resistor-side state and starts energization to the motor, thereby suppressing an inrush current. The ECU detects a contact-side state fixation abnormality of the relay based on a battery voltage at the time when the ECU drives the relay to the resistor-side state and energizes the motor. The ECU detects a resistor-side state fixation abnormality of the relay based on the battery voltage at the time when the ECU drives the relay to the contact-side state and energizes the motor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
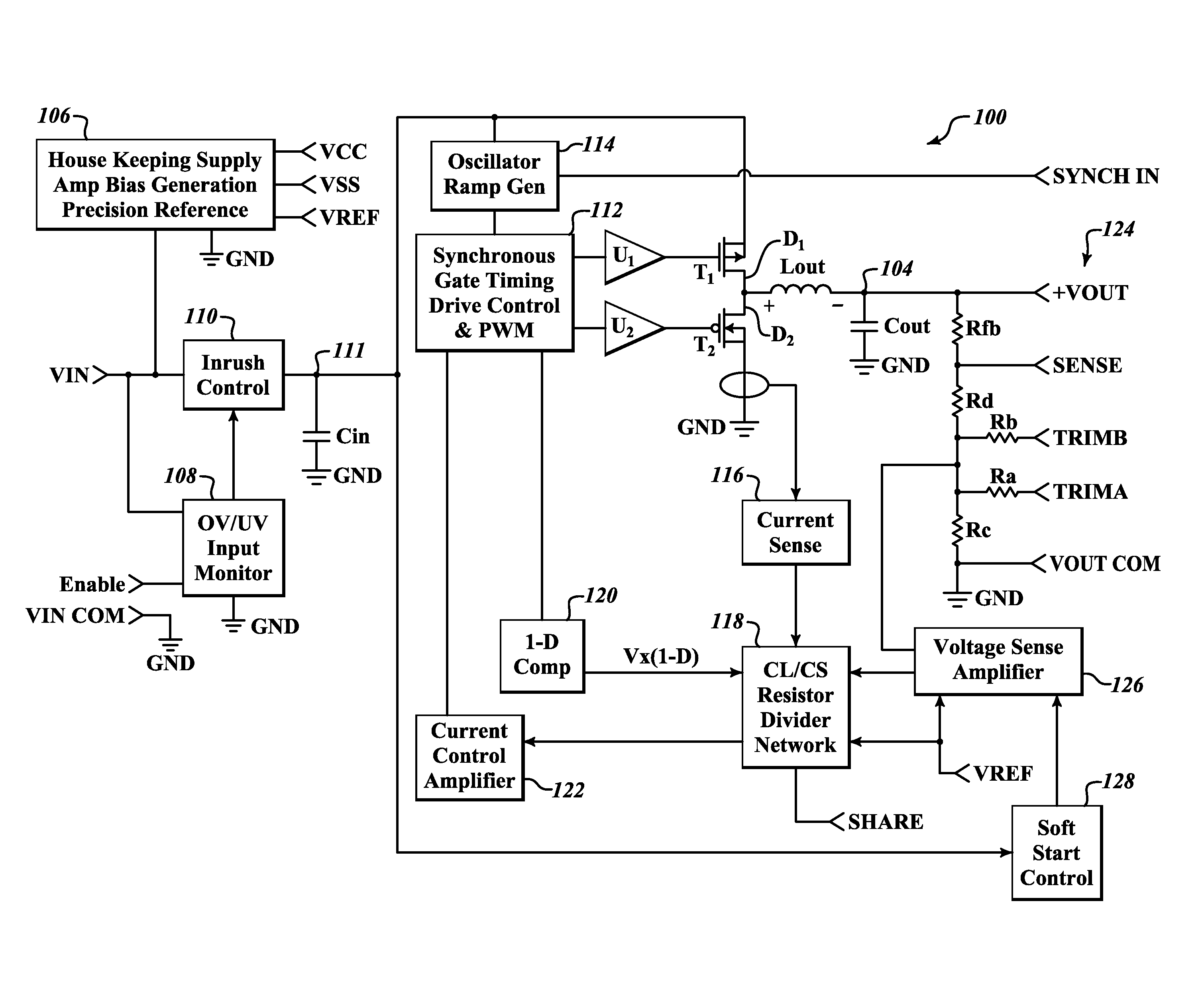
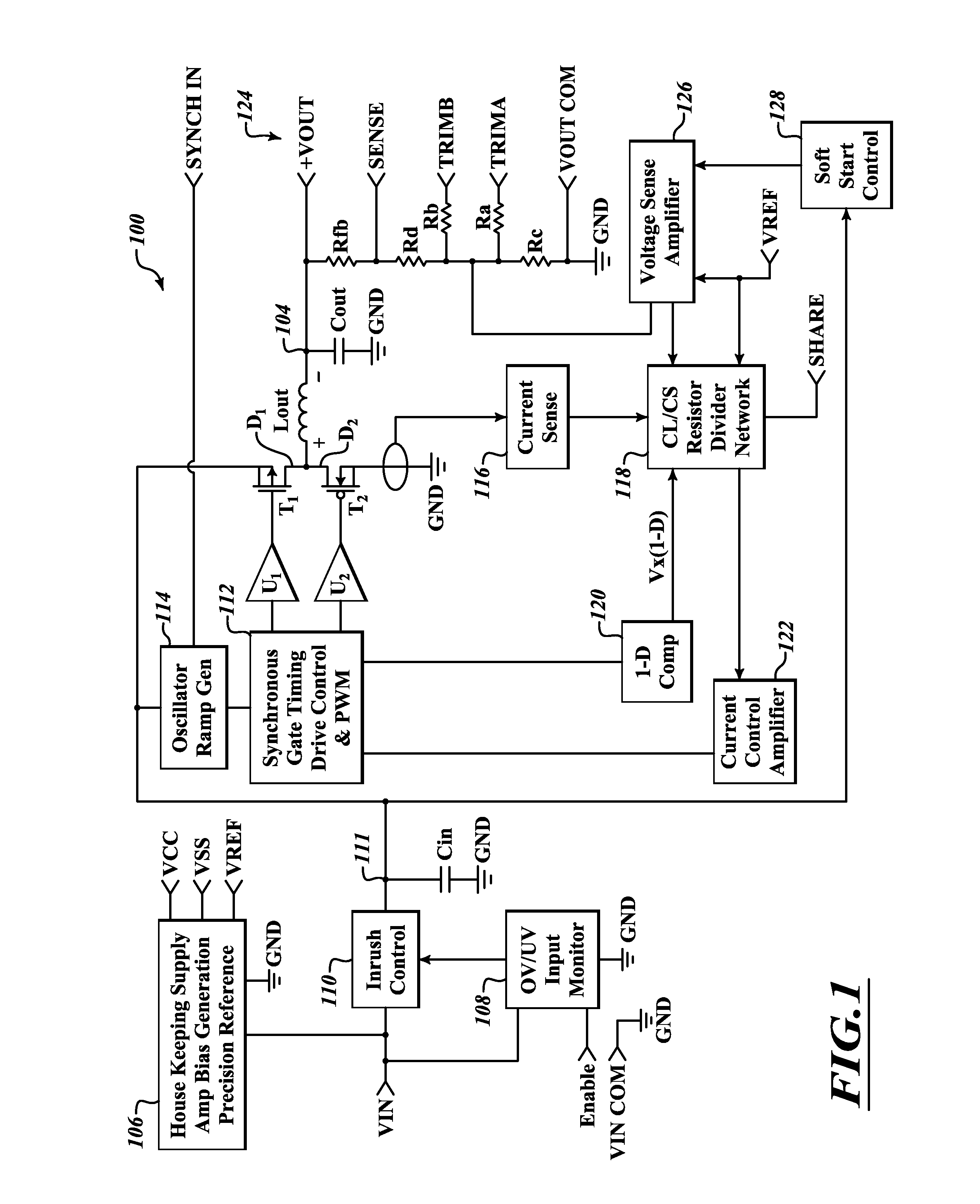
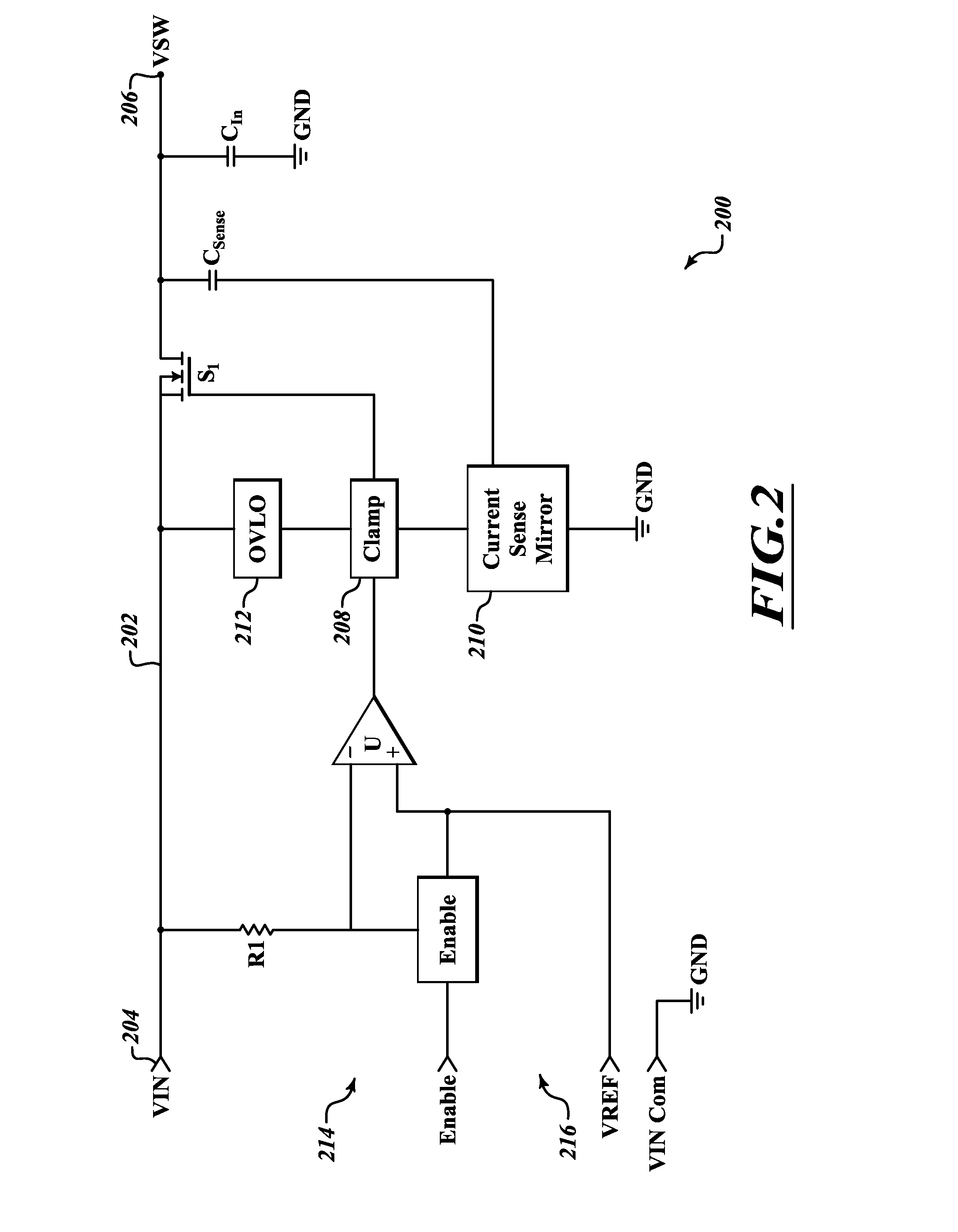
Input control apparatus and method with inrush current, under and over voltage handling
ActiveUS20130021702A1Improve reliabilityIncrease capacitance densityDc-dc conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentInput controlEngineering
Control circuitry handles inrush current, and may provide under voltage and / or over voltage monitoring and handling, as well as remote enable handling. The circuitry may advantageously employ a sense capacitor in parallel with an input capacitor (e.g., bulk input filter capacitor), and a current mirror to produce a signal proportional to input current. A clamp circuit may control a series pass device to regulate current in response to the proportional signal, or to interrupt current flow in response to an under voltage or over voltage condition or receipt of a signal indicative of a disable state. An enable signal may be summed into a comparator that handles under voltage condition determination.
Owner:CRANE ELECTRONICS INC
Boost circuit capable of step-up ratio control
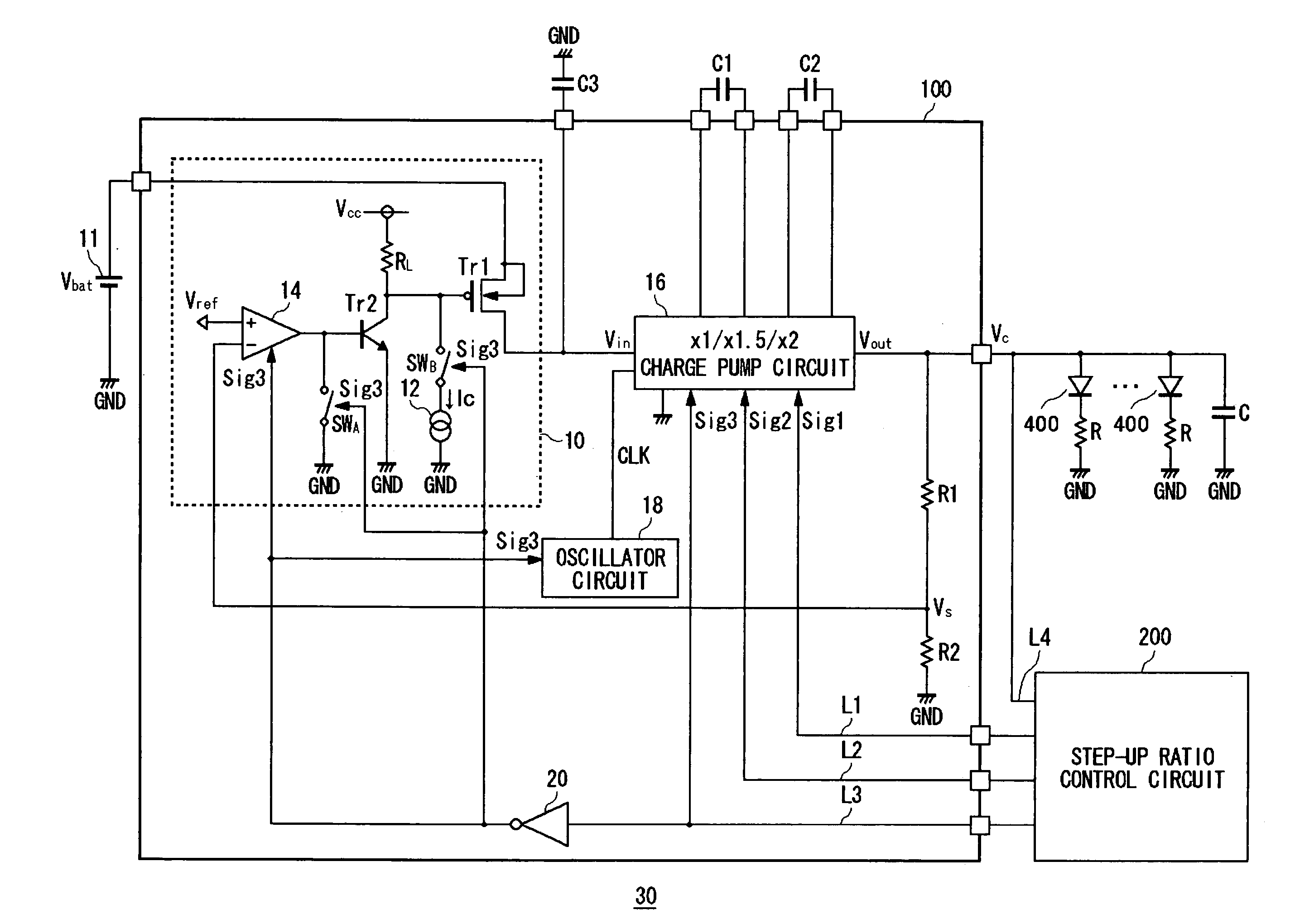
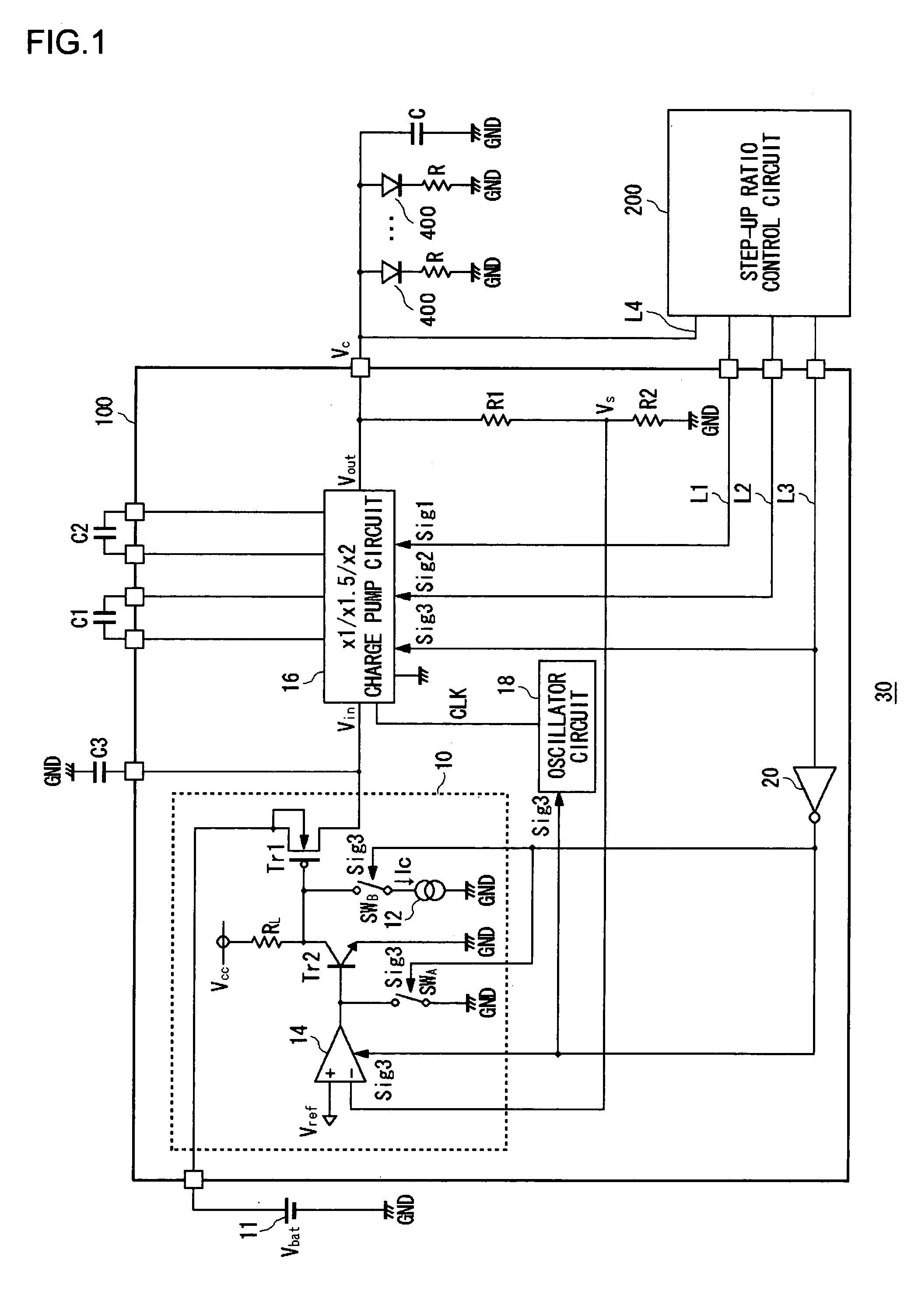
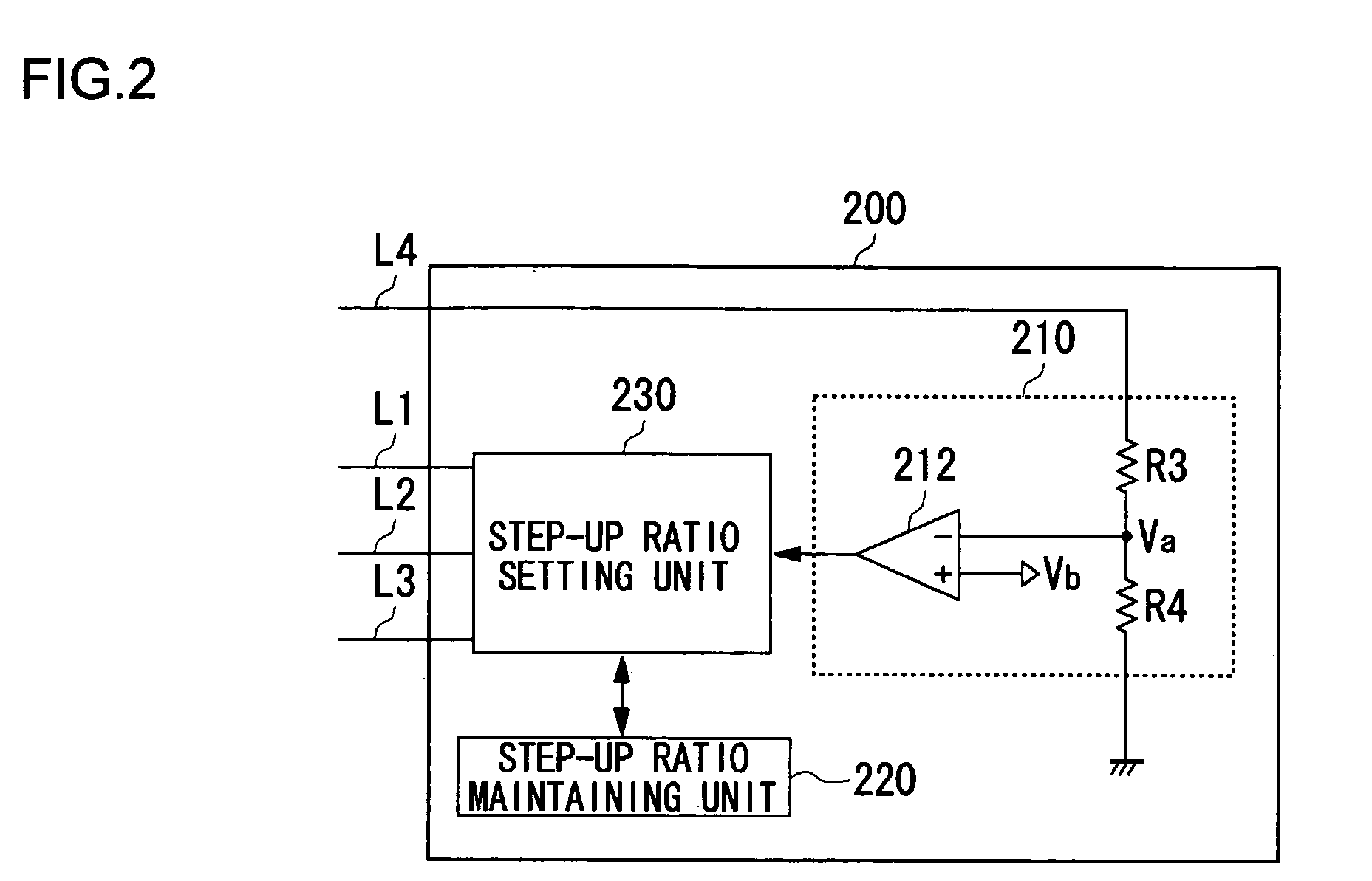
When a step-up ratio control circuit sets a step-up ratio of a charge pump circuit to 1.0 to enable a short mode, a path inside the charge pump circuit is short-circuited and a first transistor is completely turned on. This produces an inrush current derived from a battery voltage of a lithium ion battery flowing into the charge pump circuit. To address this, a constant current circuit is operated so that the first transistor is turned on slowly. Further, the operation of an oscillator and an operational amplifier is suspended when the short mode is enabled.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
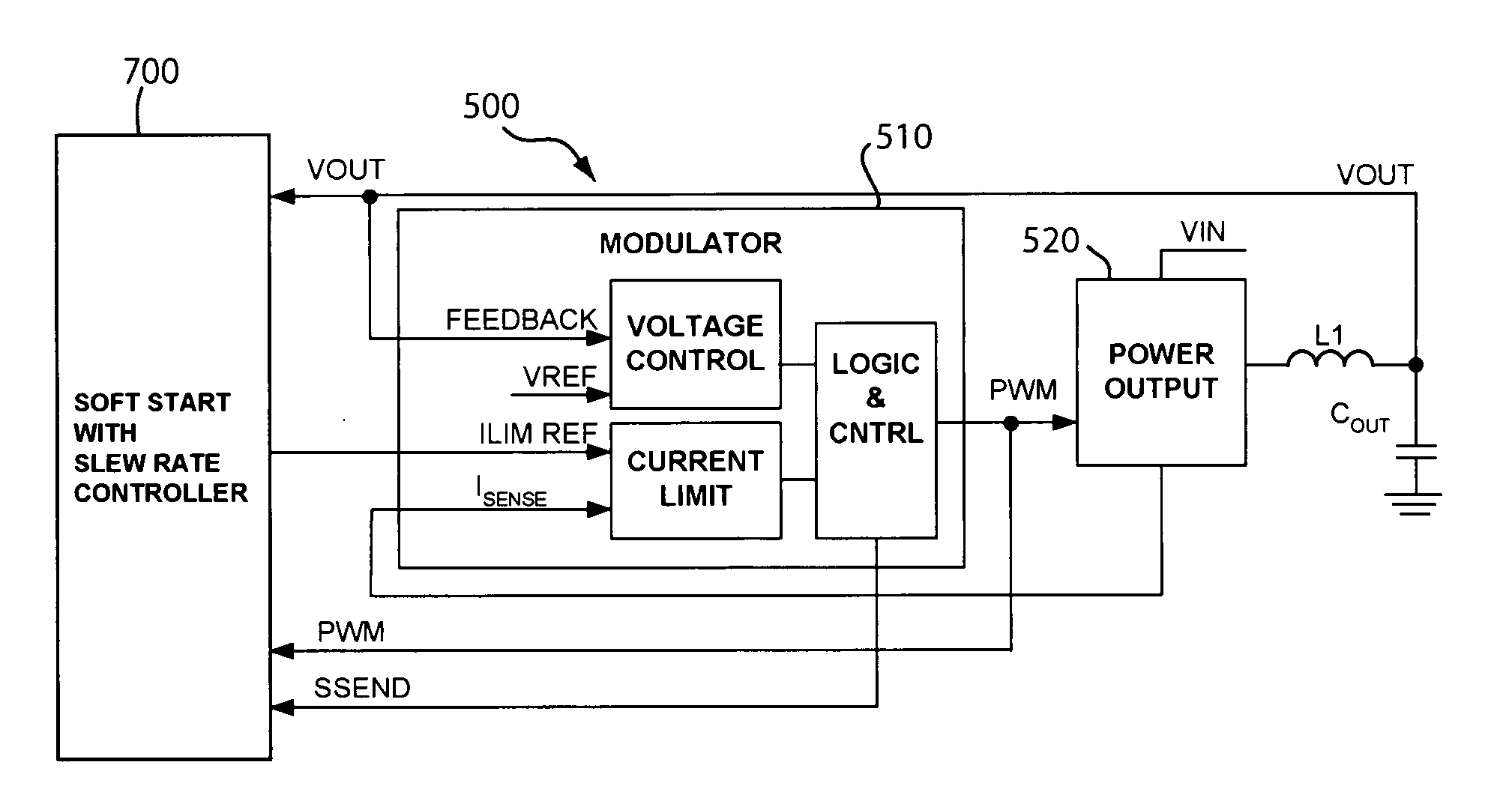
Soft start circuit with slew rate controller for voltage regulators
ActiveUS20080232144A1Power supply linesElectric variable regulationCurrent limitingDigital analog converter
In one embodiment, a soft start circuit includes a slew rate controller to limit inrush current to a voltage regulator during start up. The output voltage of the regulator may be compared to a previous sampled value to determine the slew rate of the output voltage. The slew rate of the output voltage may be controlled by adjusting the current limit of the regulator. The current limit of the regulator may be adjusted using digital circuits, such as a counter and a digital to analog converter, or analog circuits using a pulsed current source, for example. The slew rate may be controlled to exceed a target slew rate or to stay within a range of slew rate limits.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method for identifying transformer excitation surge current
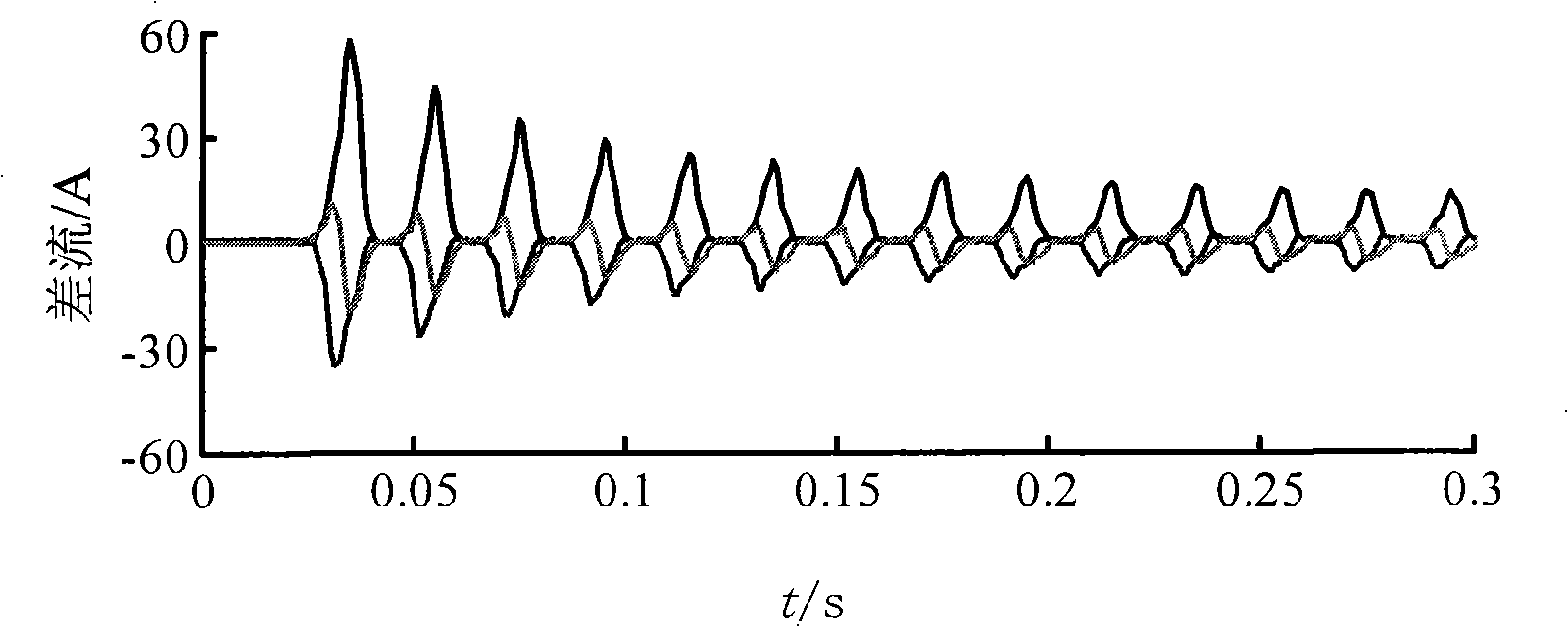
InactiveCN101257208ACurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCorrelation coefficientElectric power system
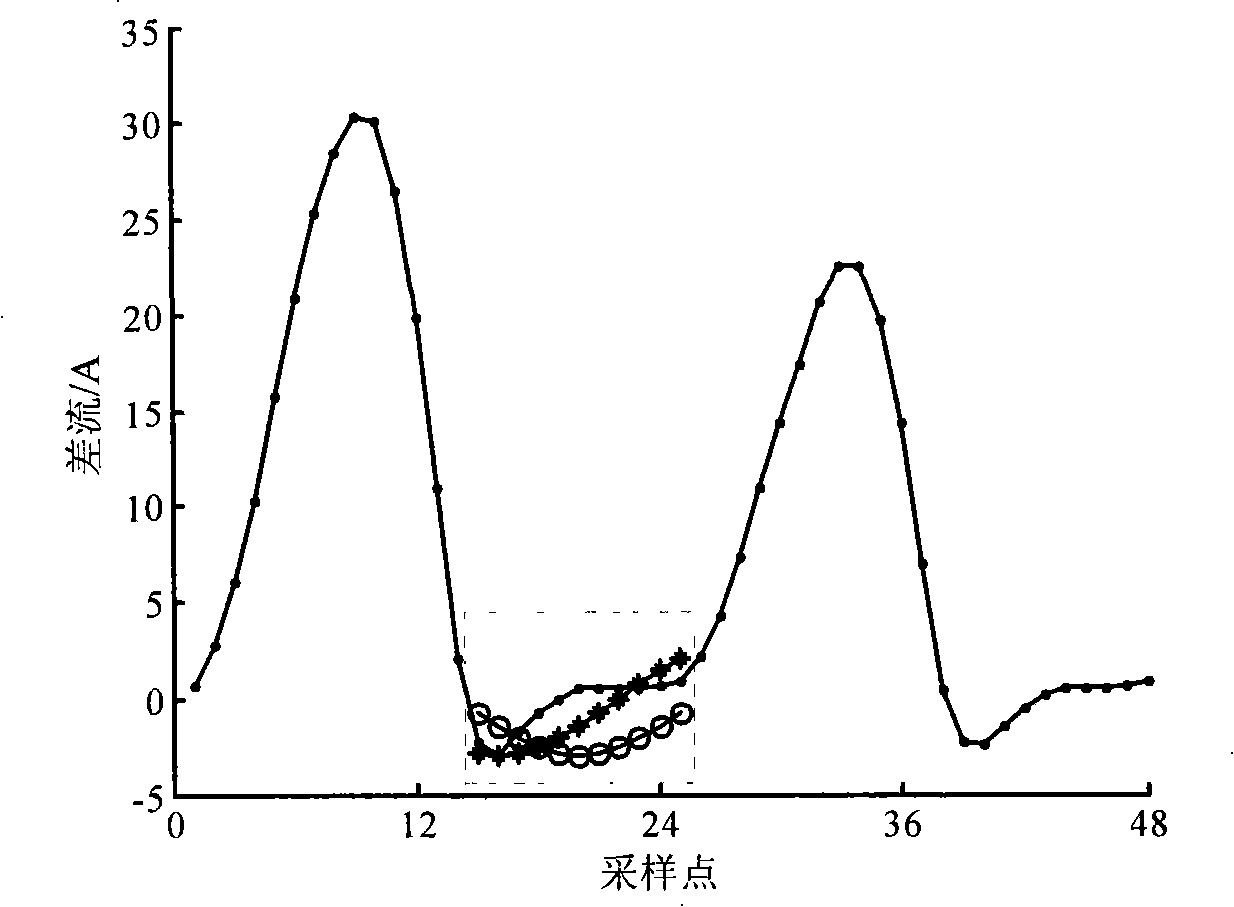
The invention provides an identification method for transformer inrush current which belongs to power system main equipment relay protection technology field. The method has characteristics in that the method identifies inrush current and fault current base on waveform correlation degree. By comparison with each sampling point algebraic sum in dynamic differential current short data window, non-saturation region of transformer under inrush current and fault current is searched, two form standard sine waves are constituted of max value and position of sampling data in non-saturation region, then differential current sampling waveform in non-saturation region and two form standard sine waves correlation degrees are calculated respectively, inrush current and fault current are differentiated according with correlation coefficient average. The method can open longitudinal differential protection rapidly when internal fault and no-load closing with fault occur in transformer operation; and can lock longitudinal differential protection reliably when on-load closing occurs inrush current.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
DC high power distribution assembly
InactiveUS20080174926A1Reduce amountEliminate needElectrical storage systemBatteries circuit arrangementsTransistor arrayDistribution system
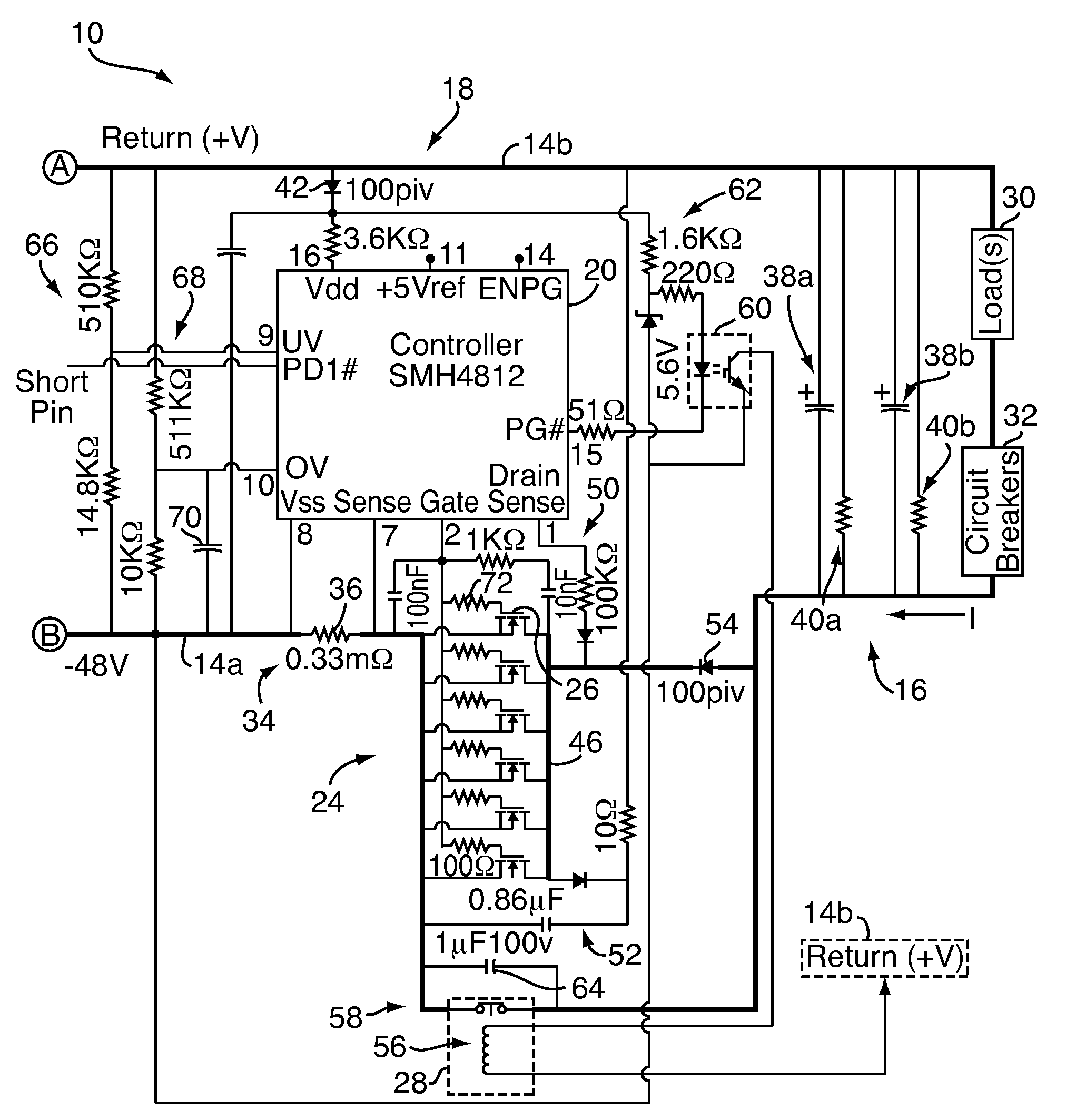
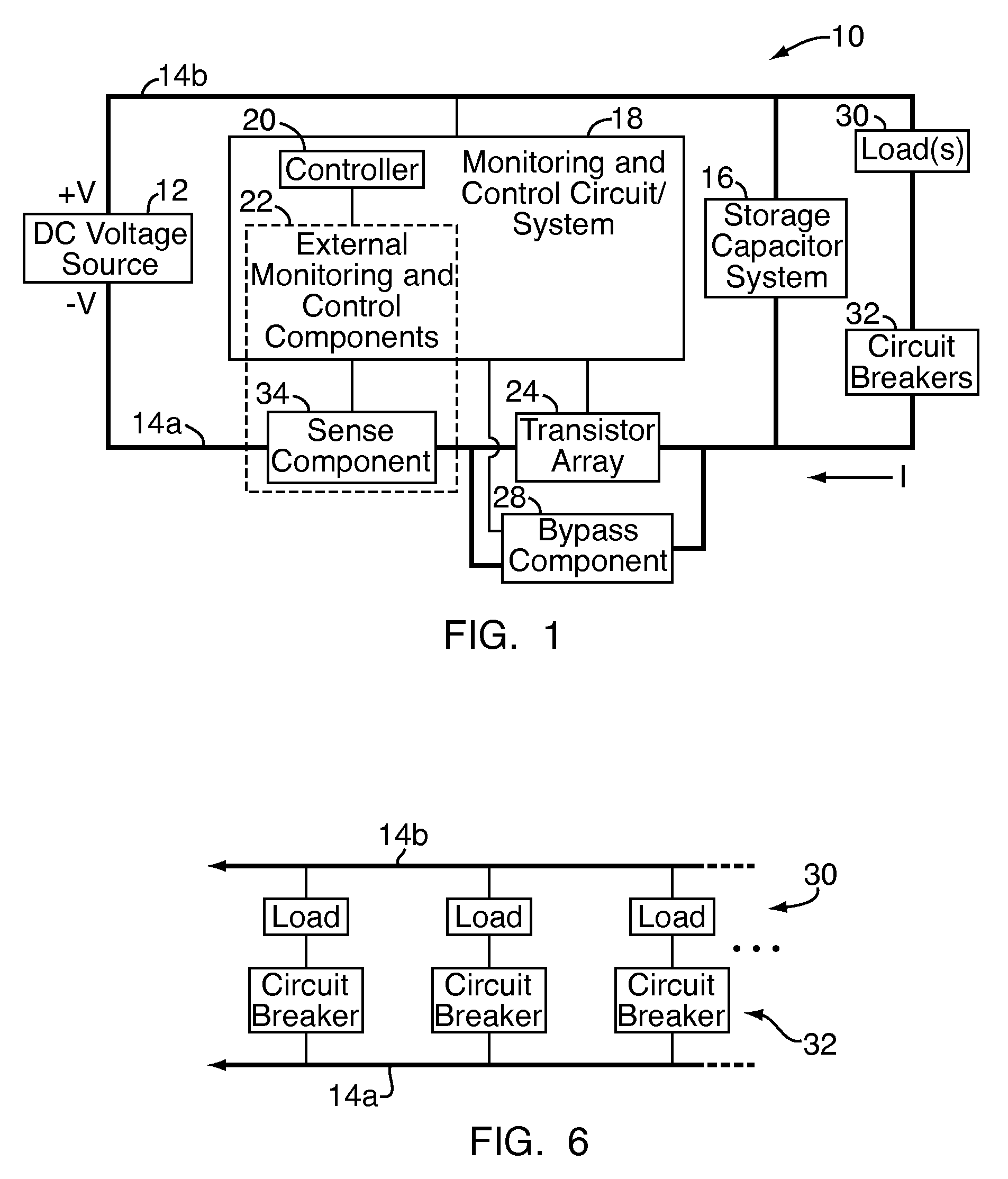
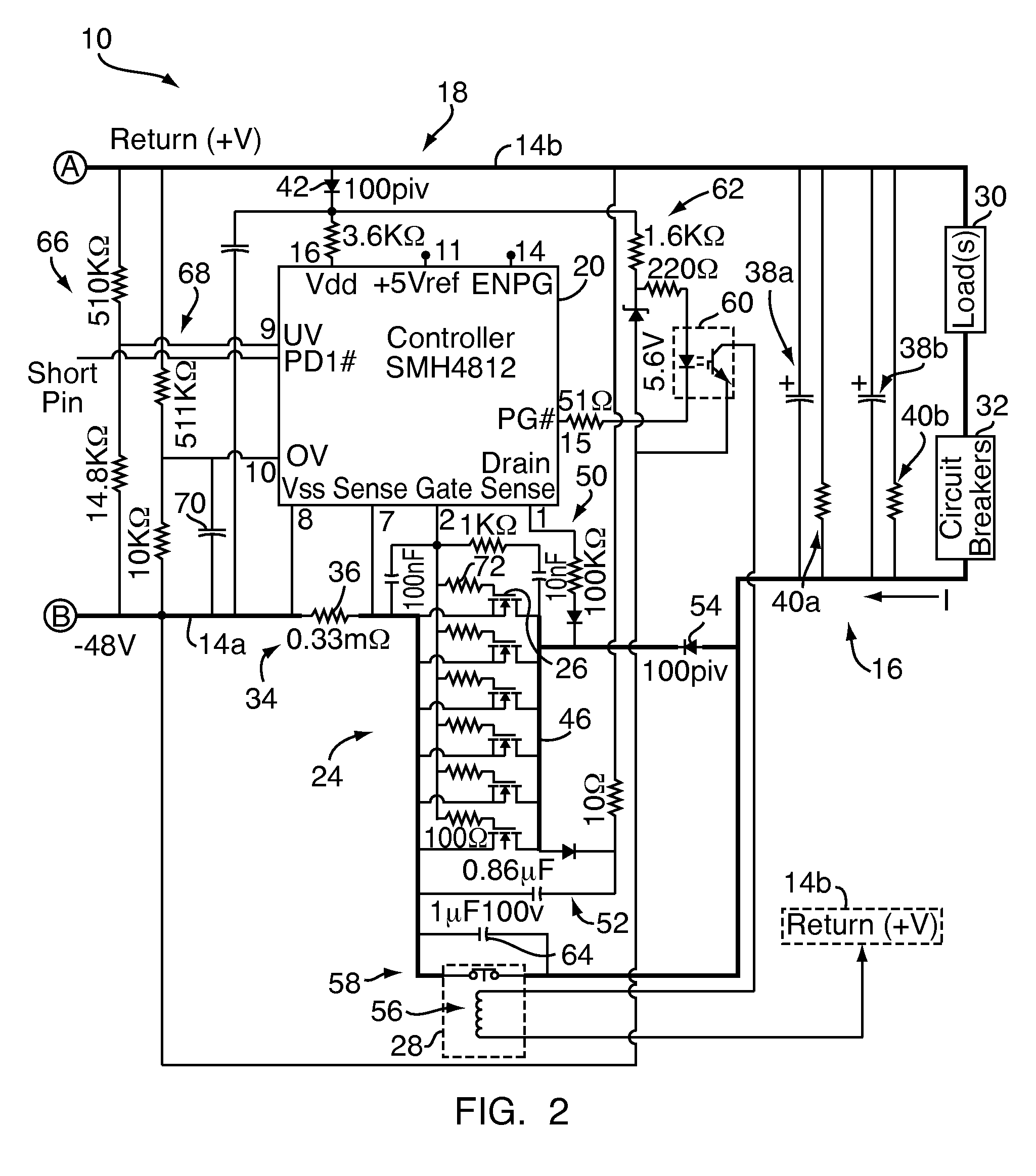
A DC high power distribution system provides power to a load in parallel with one or more storage capacitors. The system includes a hot-swap controller and an array of parallel-connected transistors connected in series between a DC source and the capacitors / load. A power contactor is connected in parallel to the transistor array, both of which are connected to control outputs of the controller. The controller monitors various circuit conditions of interest, such as input over-voltage, input under-voltage, and over-current. If the circuit conditions meet designated parameters, the controller activates the transistors for charging the capacitors, for limiting inrush current. After charging, the controller activates the power contactor for shunting the transistors and carrying the 150+ ampere current during ongoing operation. If any of the monitored circuit conditions fail to meet designated parameters, the controller halts operation of the circuit by deactivating the power contactor and / or transistors.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Power factor correction (PFC) circuit configured to control high pulse load current and inrush current
ActiveUS20130077362A1Avoid problemsEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPulse loadPower flow
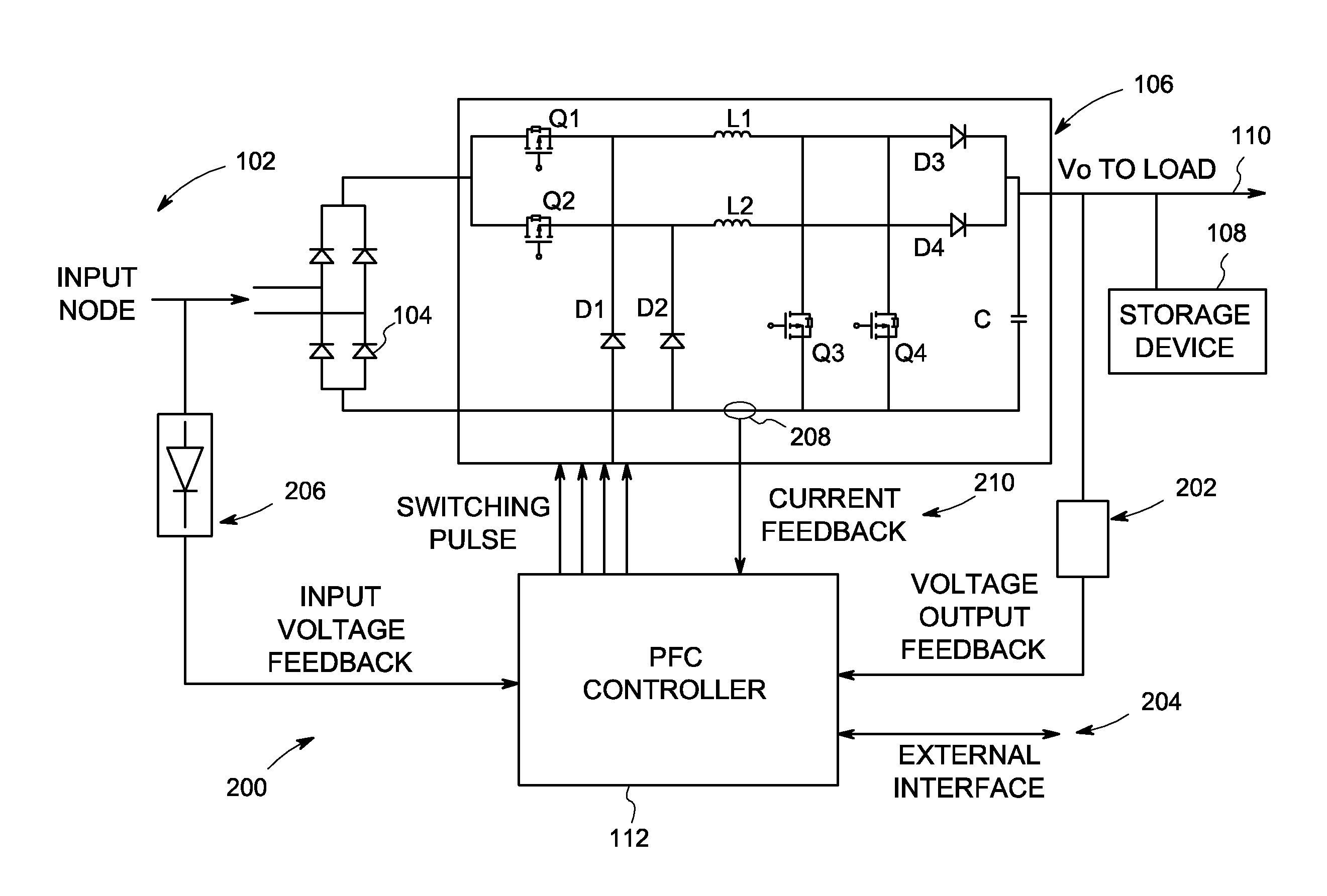
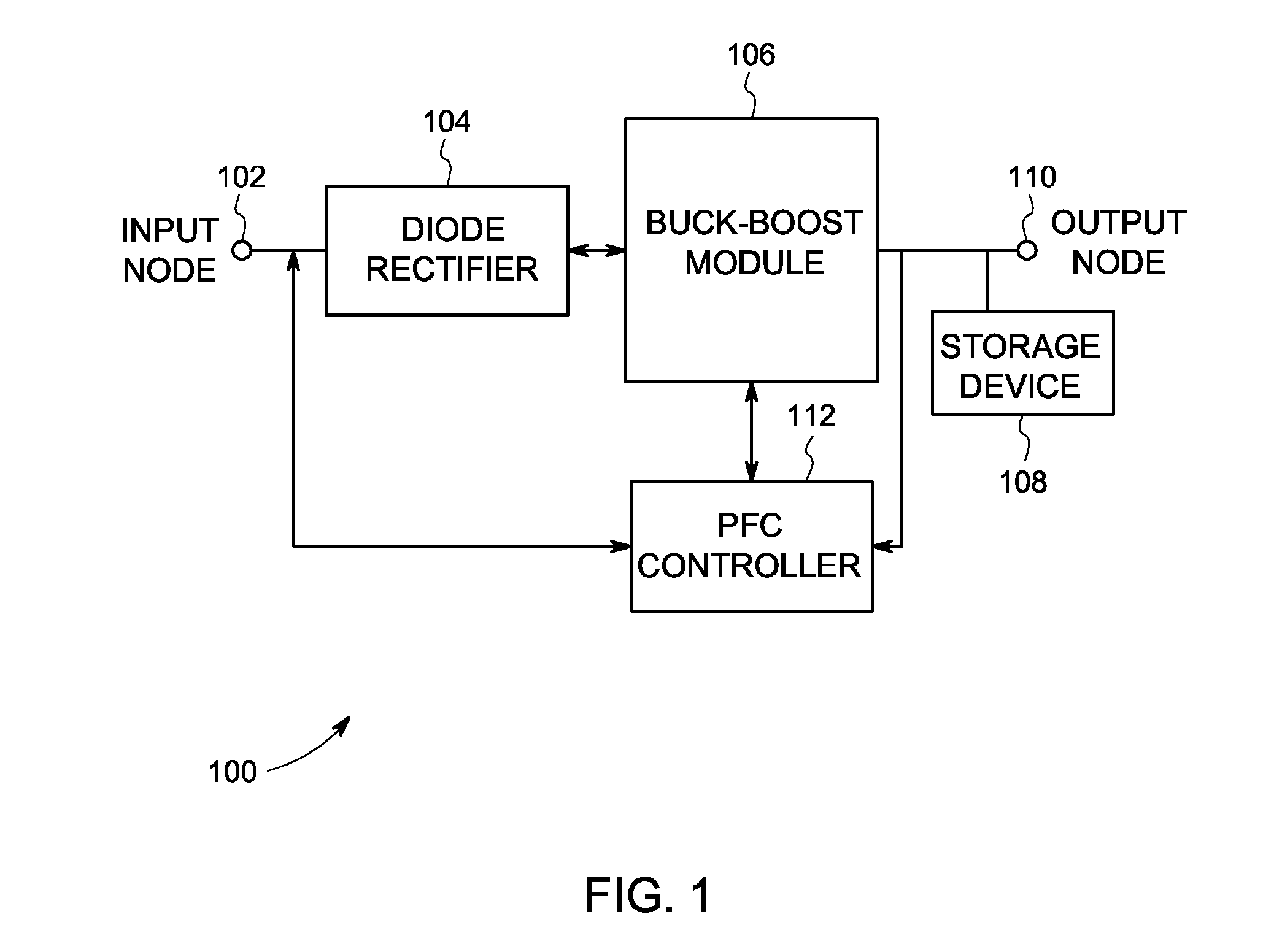
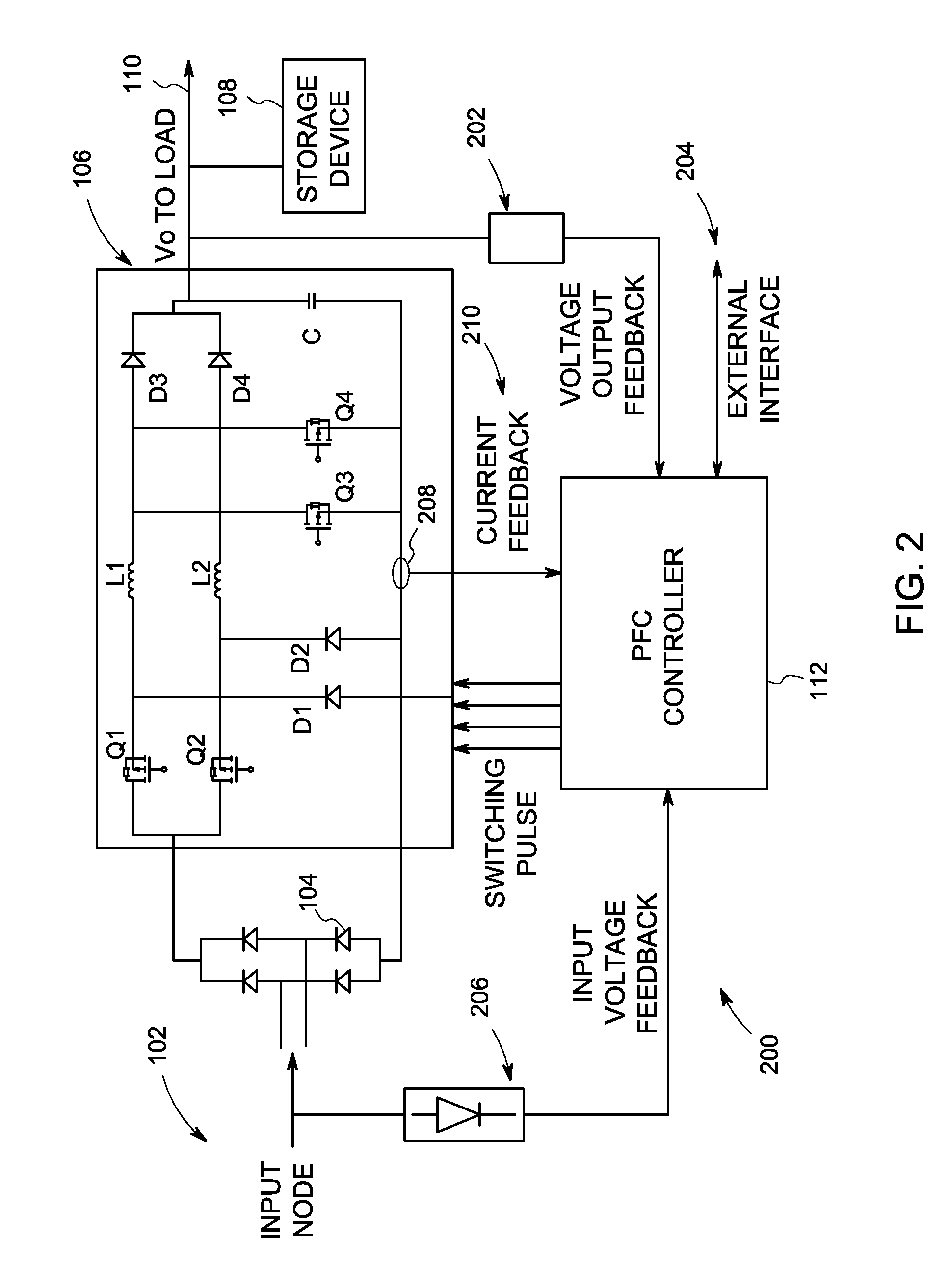
A power circuit for protecting against high pulse load current and inrush current is disclosed. The power circuit comprises a buck-boost module and a PFC controller operatively coupled with the buck-boost module. The PFC controller is configured to receive an input voltage feedback, an output voltage feedback, and a current feedback, and is configured to utilize one of an Integral Gain Compensation (IGC) and an Integral Value Compensation (IVC) to control the high pulse load current and inrush current in the power circuit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
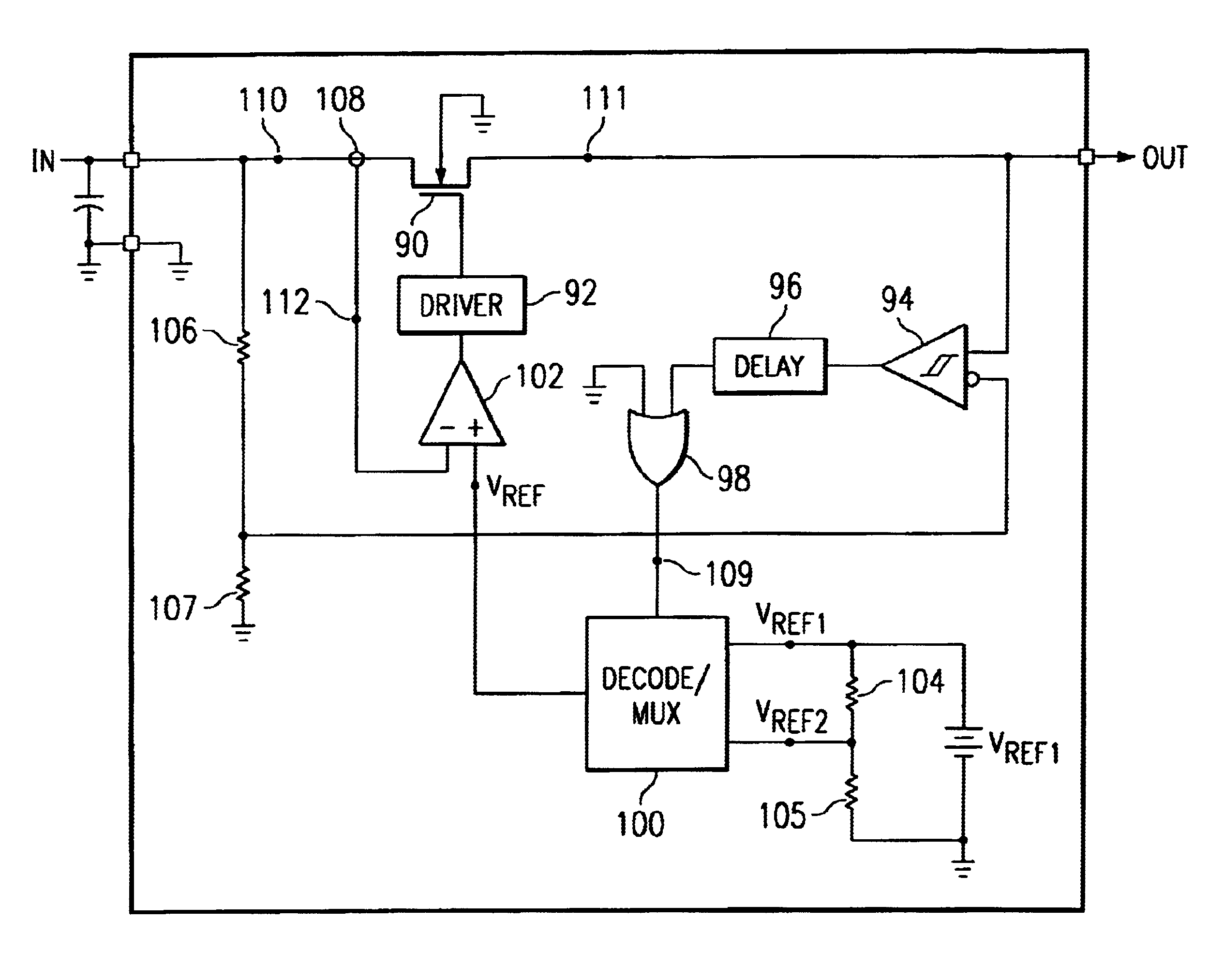
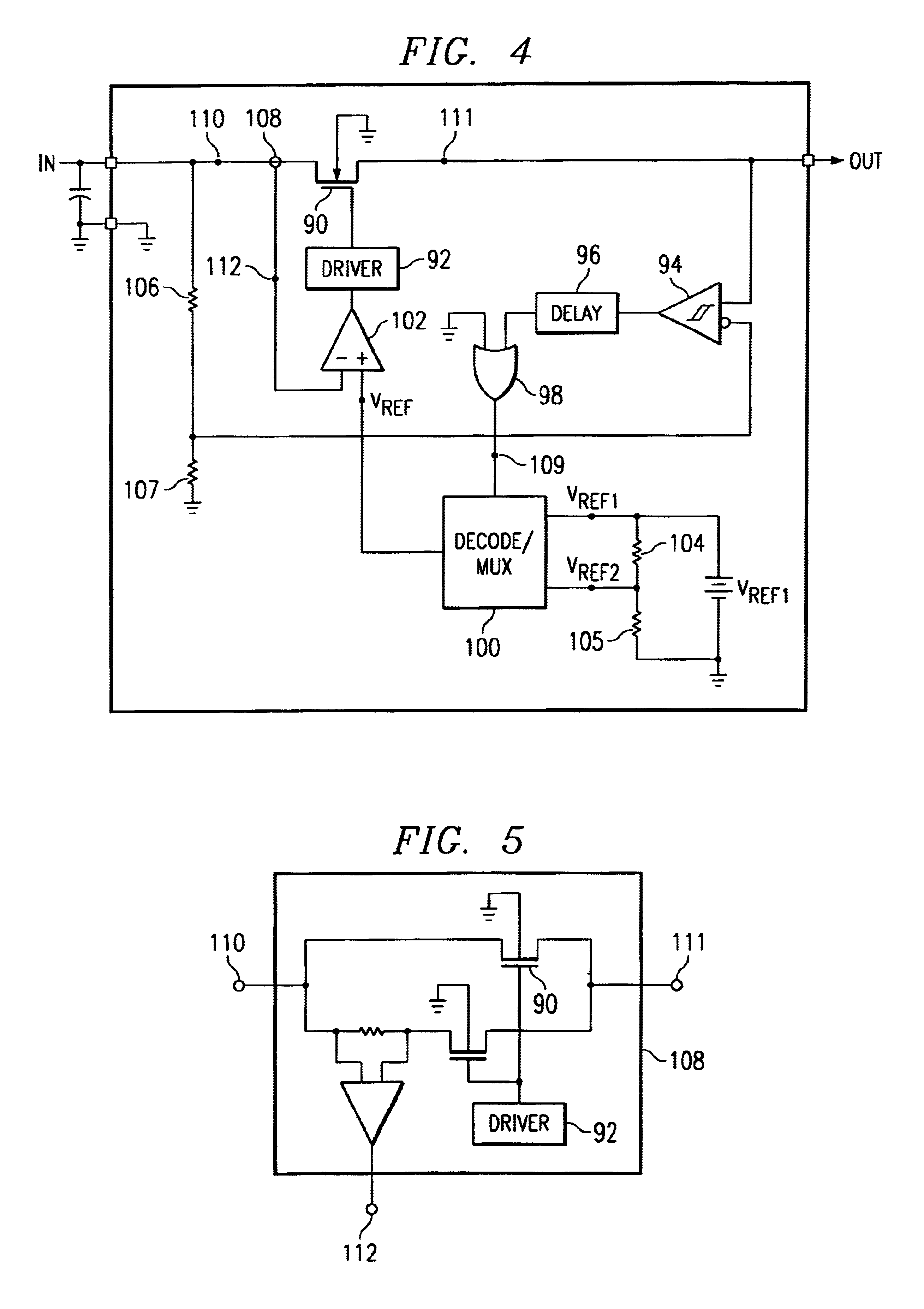
Inrush current control method using a dual current limit power switch
A current limit circuit regulates the current flow through a power switch 90 by measuring the current through the switch 90 and comparing it to a reference voltage VREF that represents the limit current. When the current through the power switch 90 is greater than the limit current, the current in the power switch 90 is pulled lower by a driver circuit 92 which controls the power switch 90. By using a current limit reference voltage that has two levels, the power switch 90 has two current limit thresholds. Using a comparator 94 to compare the input voltage of the power switch 90 to the output voltage of the power switch 90, an output signal is generated to control the current limit threshold. When the input voltage and output voltage has a large differential voltage, a lower current limit threshold voltage is selected. When the input voltage and output voltage has a small differential voltage, an upper limit threshold voltage is selected.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
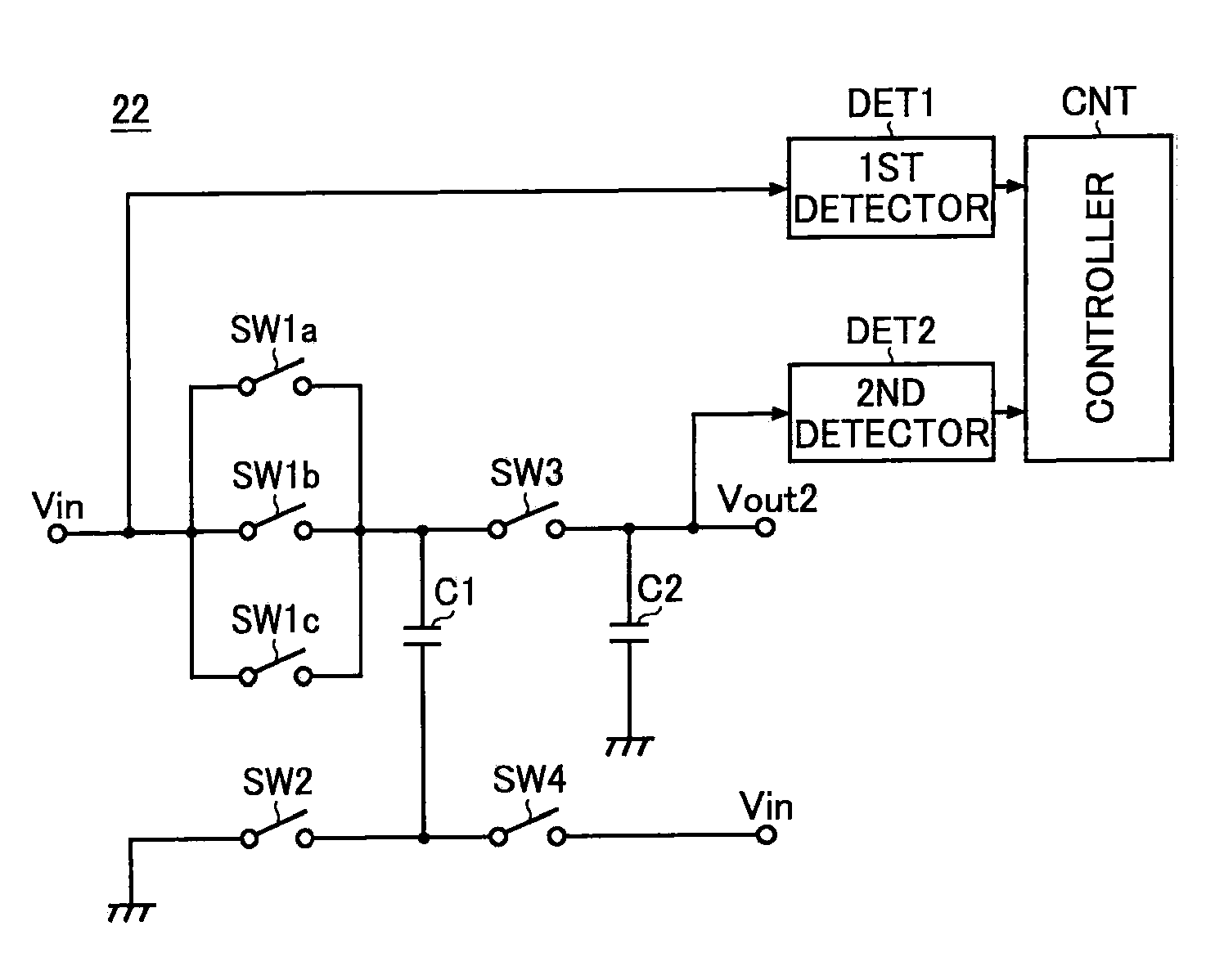
Power Supply Circuit, Charge Pump Circuit, and Portable Appliance Therewith
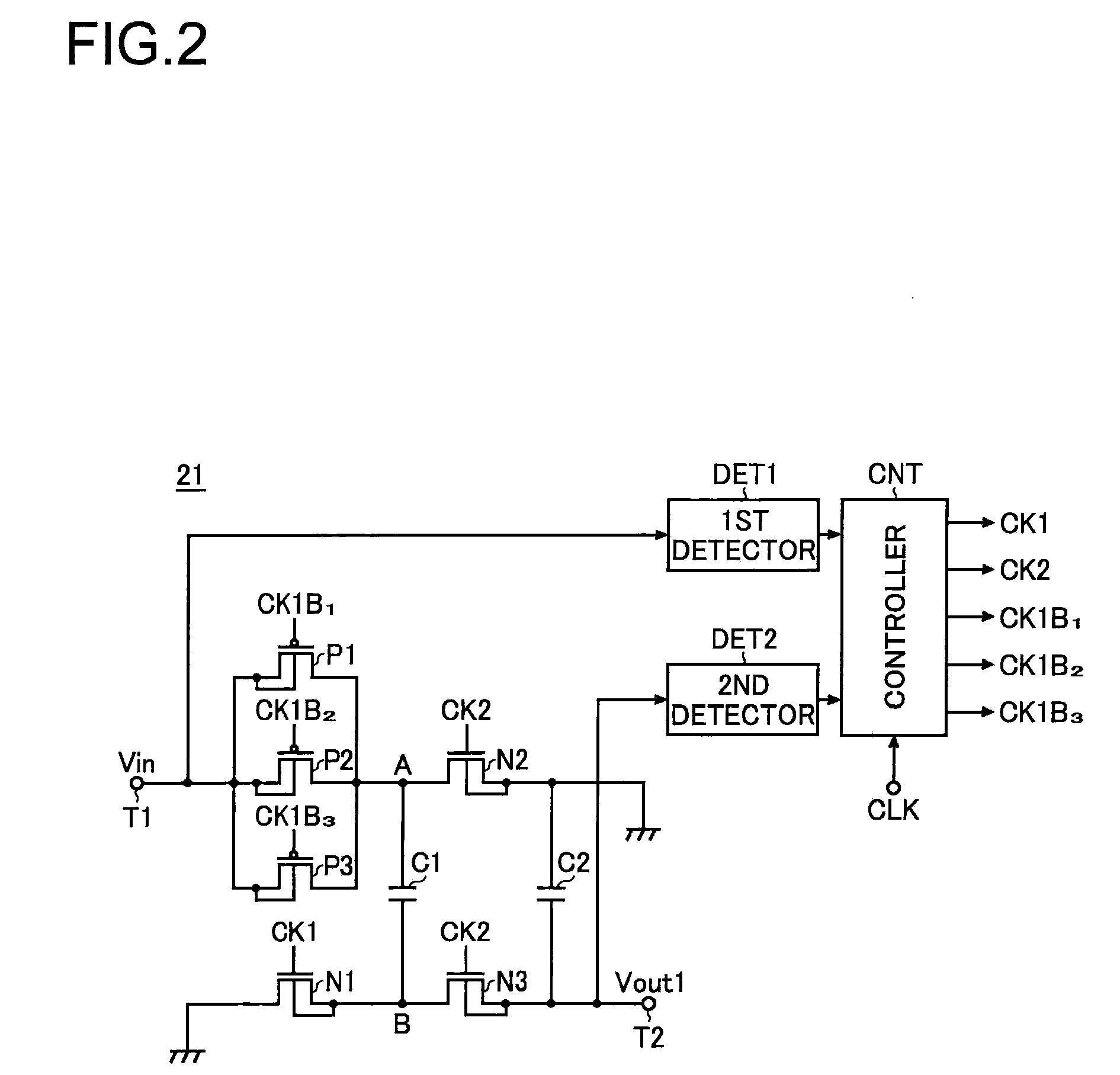
InactiveUS20070279021A1Reduce inrush currentLoss in efficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringPower circuits
According to the invention, a charge pump circuit (21) has, as switching means turned on when a capacitor (C1) is charged, transistors (P1 to P3) connected in parallel between one end of the capacitor (C1) and an input terminal (T1). When the capacitor (C1) is charged, a controller (CNT) determines which of the transistors (P1 to P3) to drive based on the results of monitoring of the input and output voltages by first and second detectors (DET1, DET2). Thus, even if the level of the input voltage varies, it is possible to reduce in-rush current at start-up without causing a drop in the output voltage or a loss in efficiency.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Transformer inrush current detector
ActiveUS20090147412A1Reduce inductanceImprove responseEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent sensorEngineering
A differential protection system for power transformers using Rogowski coils as current sensors can support an inrush current detection method based on sensing lows in the derivative of the sensed current. Effective detection of power transformer inrush conditions can enable blocking of a protection relay during inrush where the differential current may exceed a differential threshold value indicative of a fault without the presence of an actual fault. The outputs of the Rogowski coils, being proportional to the first time derivative of the sensed current, may be useful in the inrush detection method. Also, with reduced saturation concerns, the Rogowski coil protection system may employ a single slope response with increased sensitivity. A discrete time sampling technique for identifying low di / dt portions within the sensed current also may be useful in detecting power transformer inrush conditions.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Magnetizing inrush current suppression device and method for transformer
ActiveUS20100141235A1Accurate calculationBatteries circuit arrangementsVariable inductances/transformersEngineeringInrush current
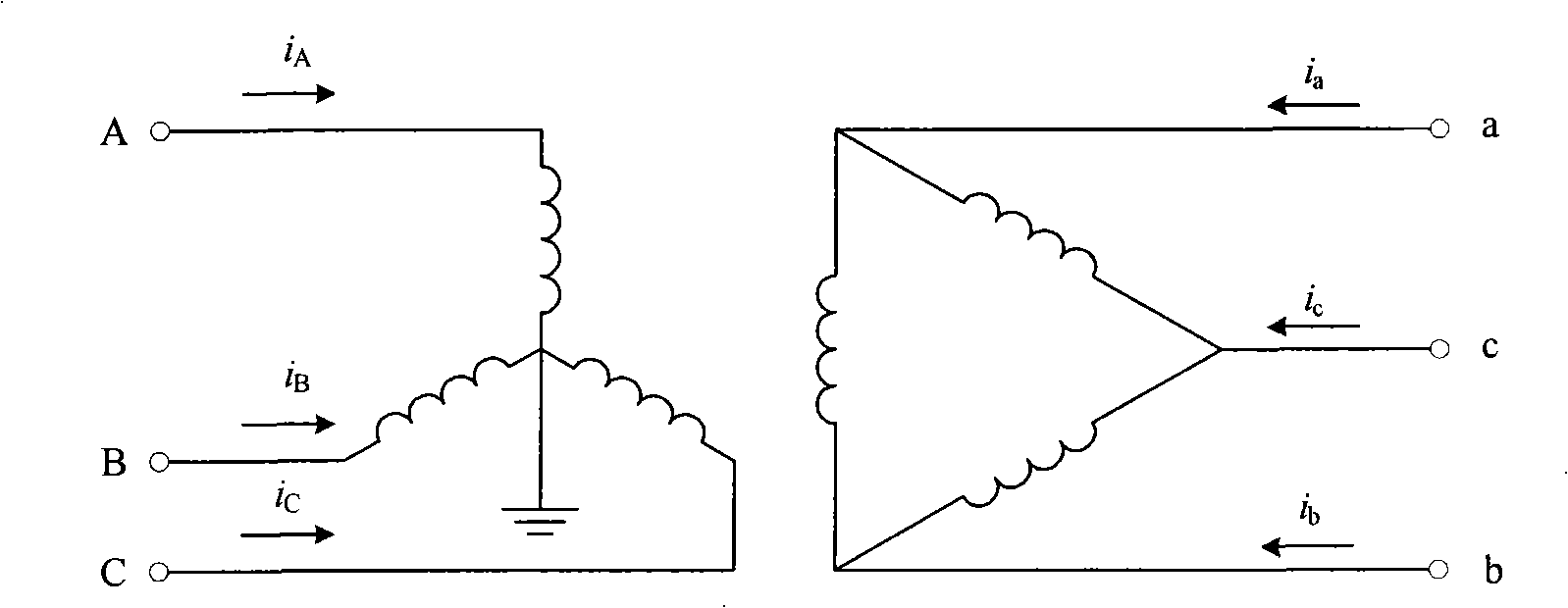
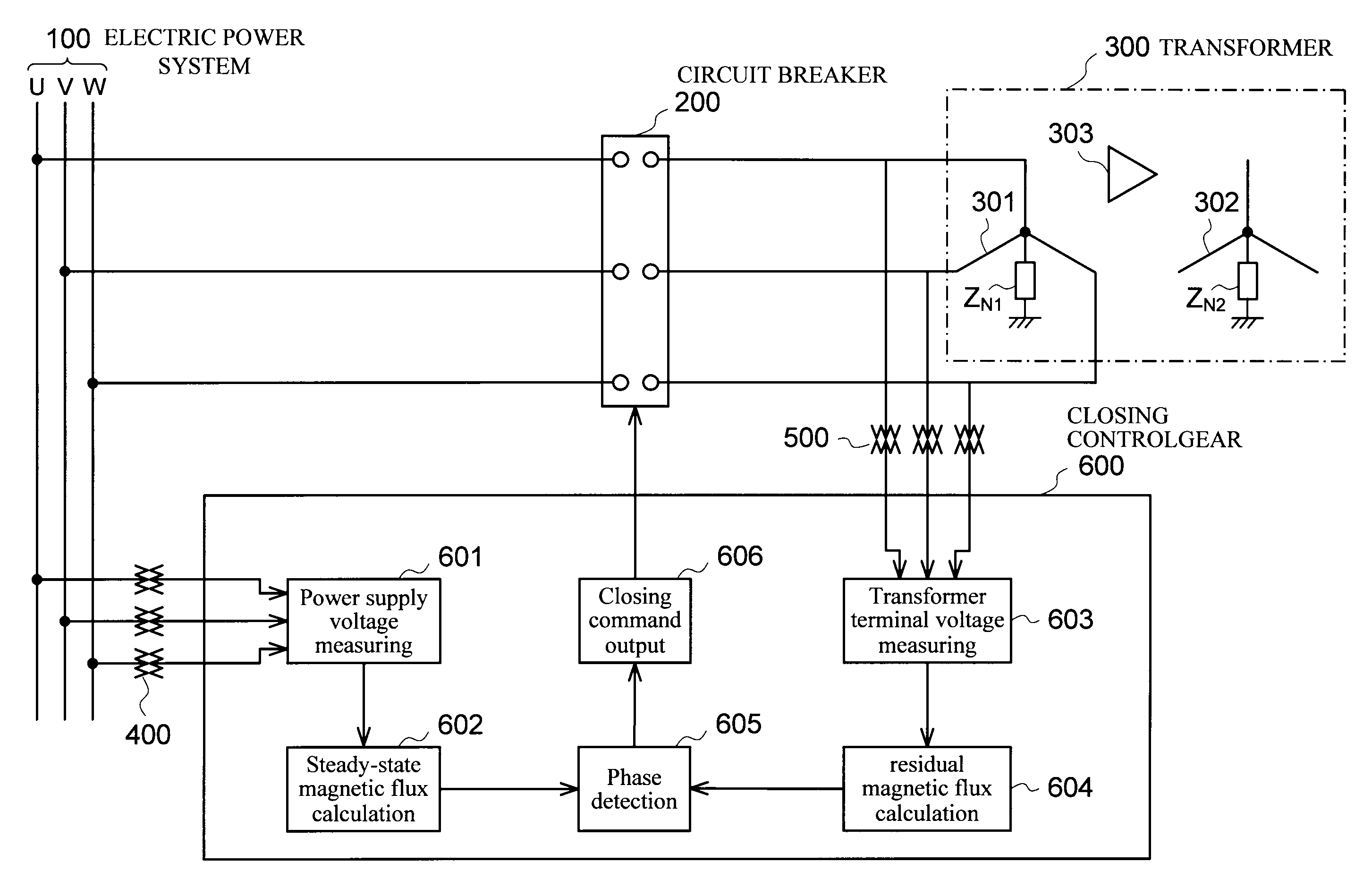
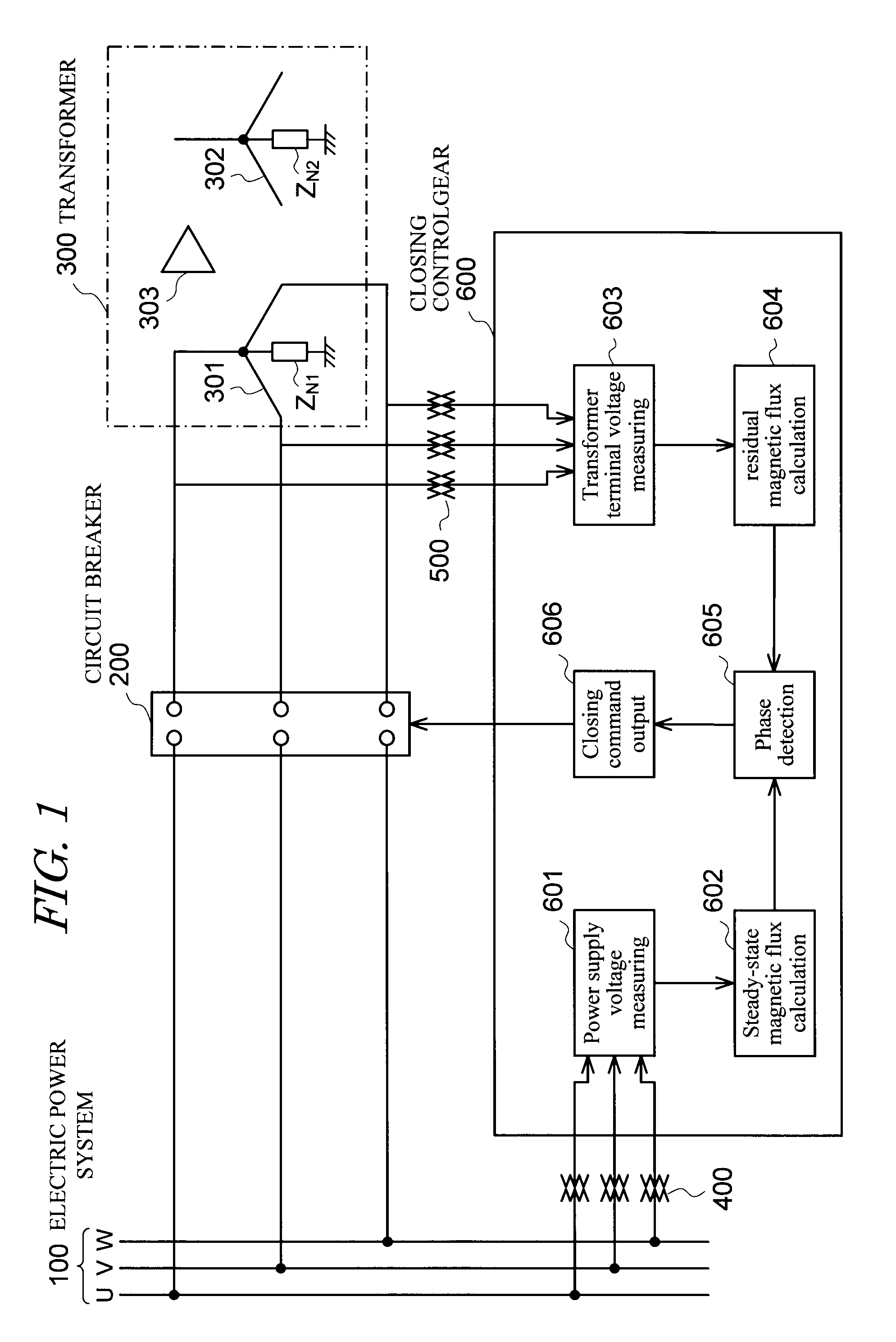
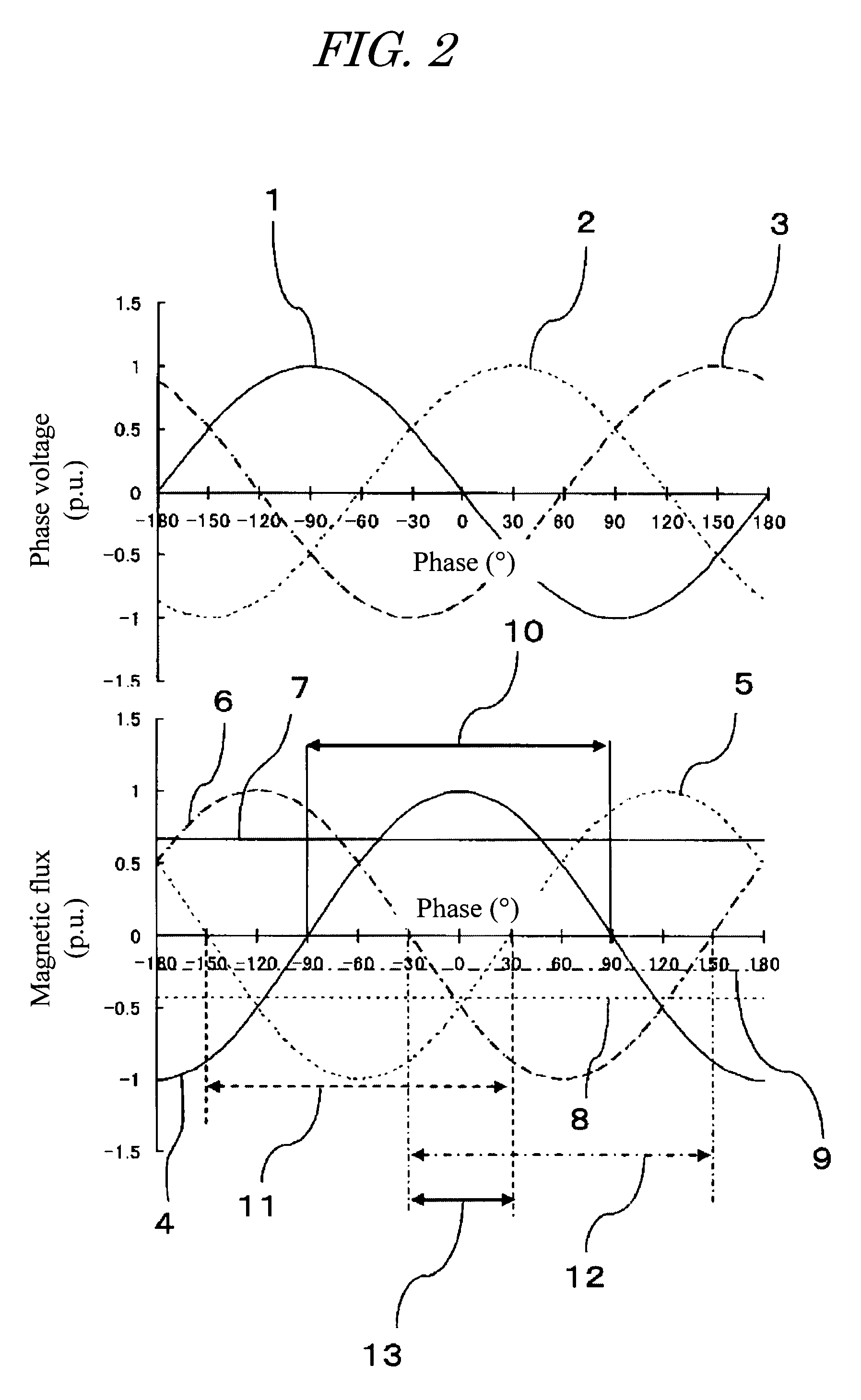
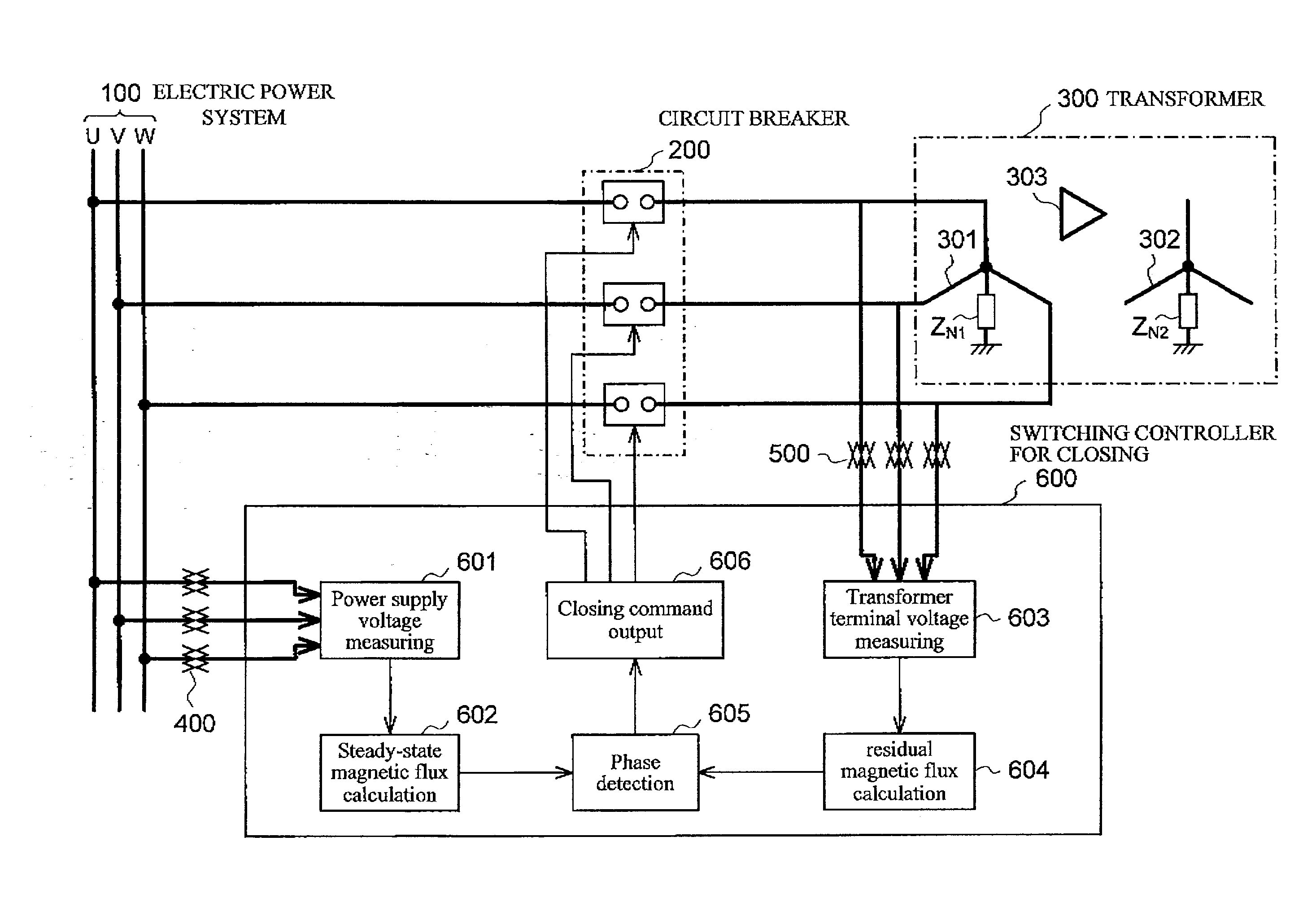
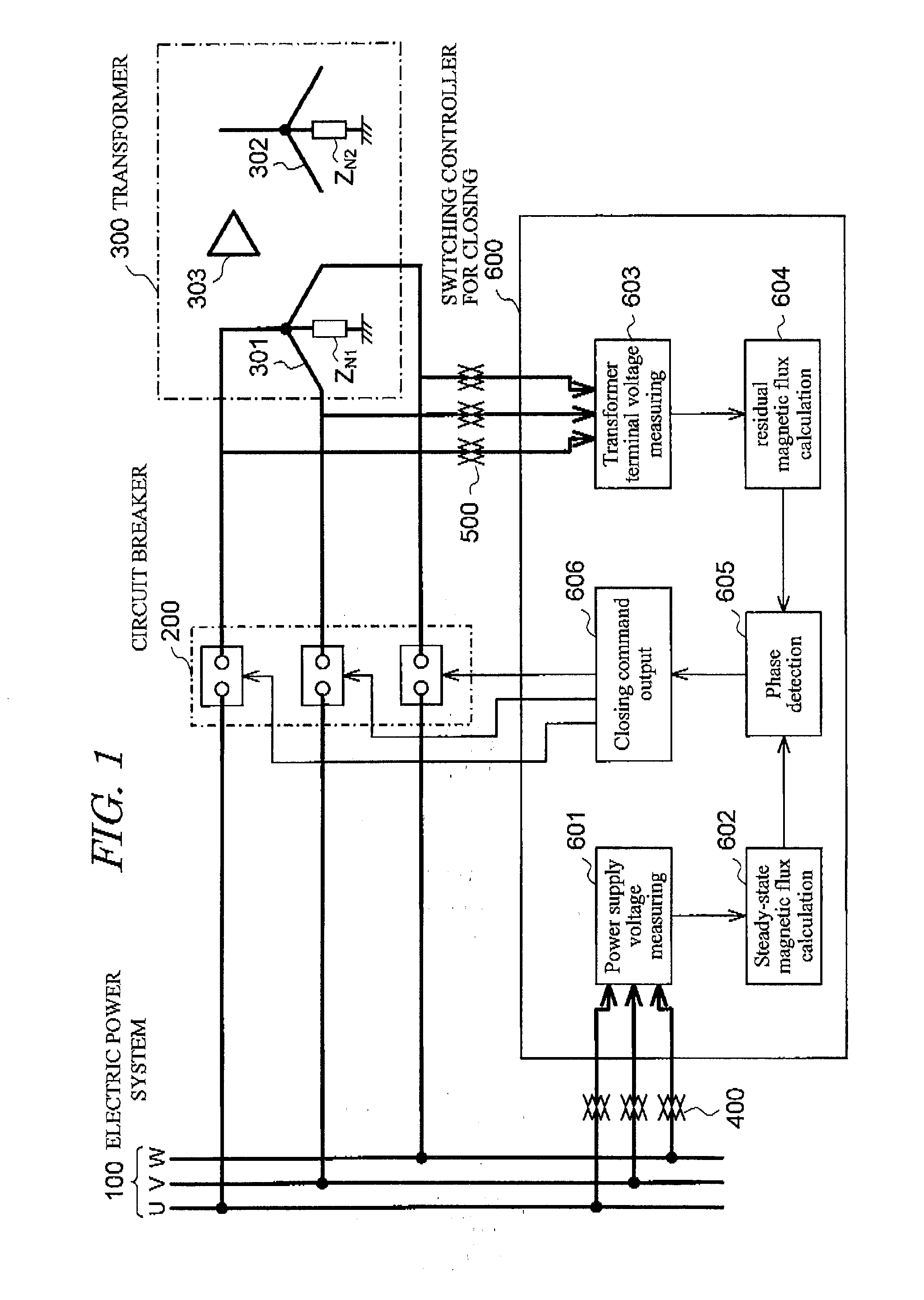
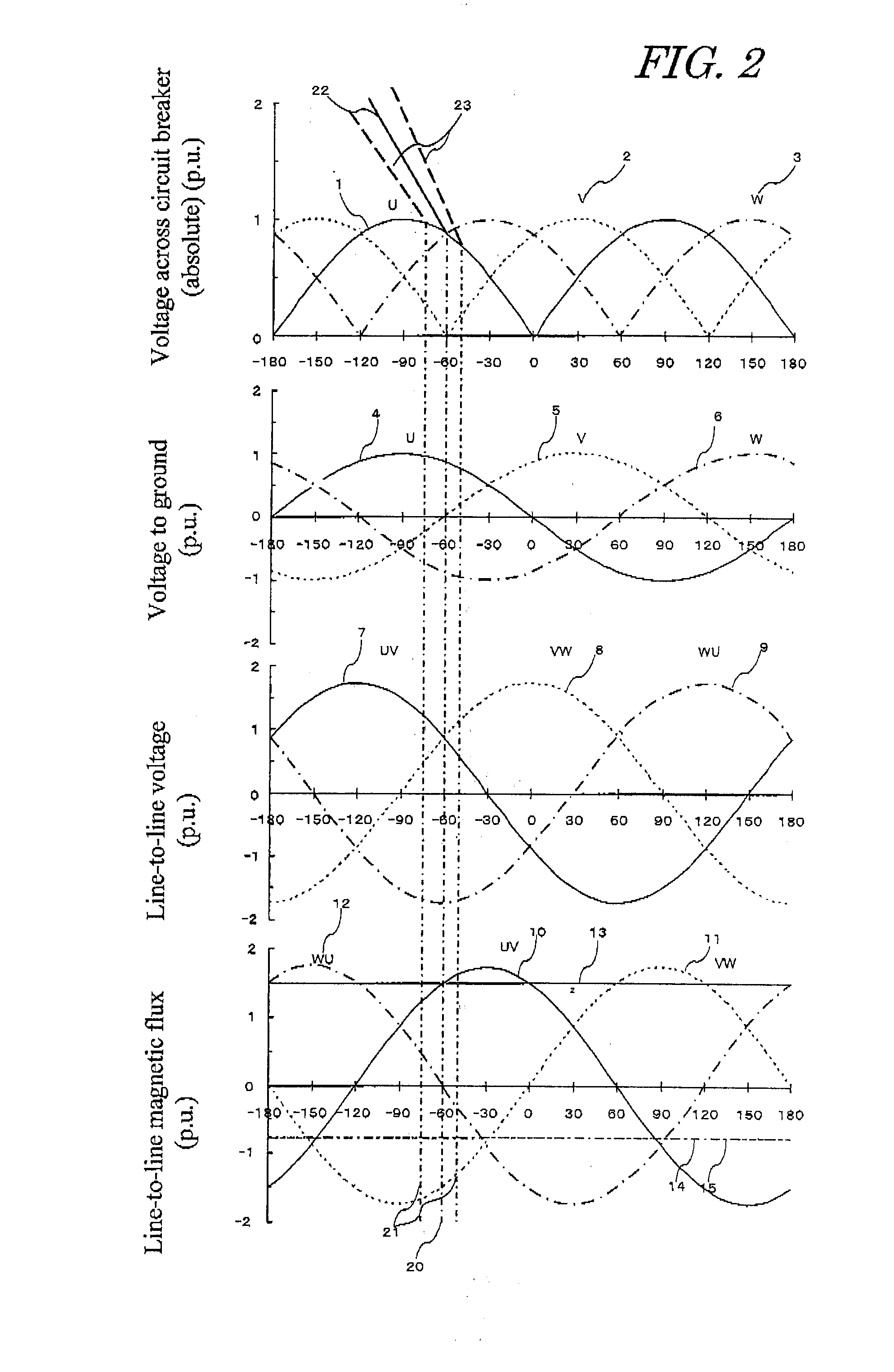
To suppress the magnetizing inrush current occurring when supplying power of three phases of the transformer are performed simultaneously using three single-phase circuit breakers or a non-phase segregated operation-type circuit breaker, without providing a circuit breaker with a resistor or other equipment. A magnetizing inrush current suppression method for transformer suppresses a magnetizing inrush current occurring at the start of energizing of a three-phase transformer 300, when a three-phase power supply 100 is input to a terminal of each phase by means of a three-phase circuit breaker 200. In the method, by integrating phase voltages or line-to-line voltages on the primary side or the secondary side or the tertiary side when three-phase AC voltages are applied in a steady state to the transformer 300, steady-state magnetic flux 4, 5, 6 for each phase of the transformer is calculated, and the polarity and magnitude of the residual magnetic flux 7, 8, 9 of each phase of the transformer after the circuit breaker 200 shuts off the transformer are calculated, and the three-phase circuit breaker is caused to close simultaneously in a region 13 in which three phases overlap, each of the three phases having the polarity of the steady-state magnetic flux 4, 5, 6 equal to the polarity of the residual magnetic flux 7, 8, 9 for each phase of the transformer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetizing inrush current suppression device for transformer and control method of same
ActiveUS20100039737A1Accurate calculationEnlarge the circuit breakerBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionResidual fluxElectrical polarity
To provide a magnetizing inrush current suppression device for transformer and control method of same, which accurately calculates the residual magnetic flux when a transformer installed in a non-solidly earthed system, is interrupted by circuit breakers, and which enables suppression of the magnetizing inrush current occurring when three single-phase circuit breakers or single-phase circuit breakers are used for simultaneously supplying power to three phases of the transformer, without providing a circuit breaker with a resistor or other equipment to enlarge the circuit breaker. The device has steady-state magnetic flux calculation means for calculating the line-to-line steady-state magnetic flux of three-phase power supplies, residual magnetic flux calculation means for calculating the primary line-to-line residual magnetic flux of the transformer when the circuit breakers interrupt the transformer, phase detection means for detecting a phase at which the polarity and magnitude of the calculated steady-state magnetic flux and residual magnetic flux coincide for each line-to-line. Closing control means firstly causes only two-phase of the circuit breakers, which are connected with the line-to-line, to close at the detected phase, and then causes the remaining one-phase circuit breaker to close.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com