Full-laser grooving and scribing method of large-area copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin-film solar cell assembly
一种太阳能电池、铜铟镓硒的技术,应用在电气元件、电路、光伏发电等方向,能够解决易发生翻边和崩边、加大组件制造成本、组件功率损失等问题,达到提高生产效率、降低生产和维护成本、提高组件功率的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
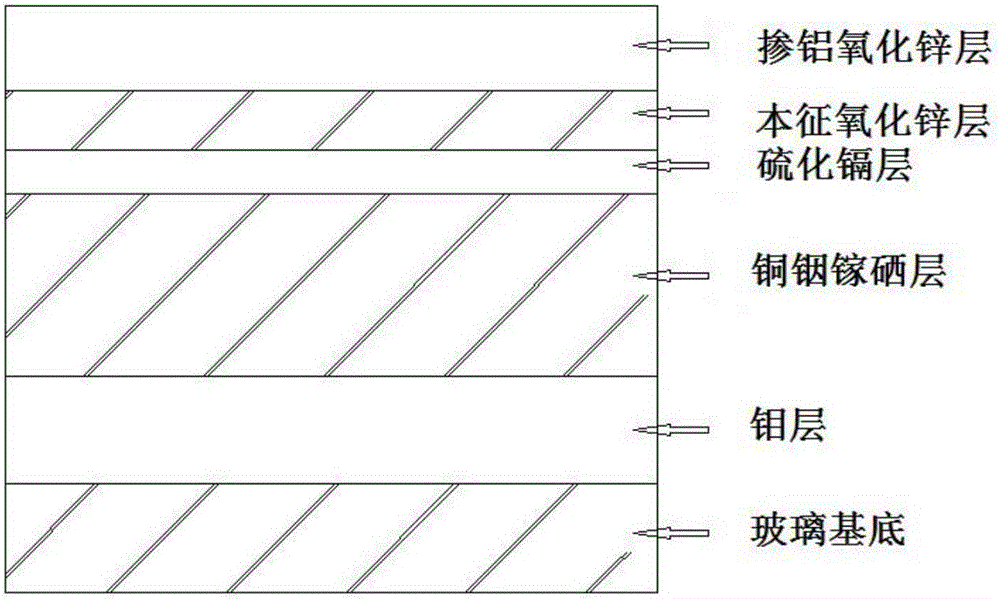
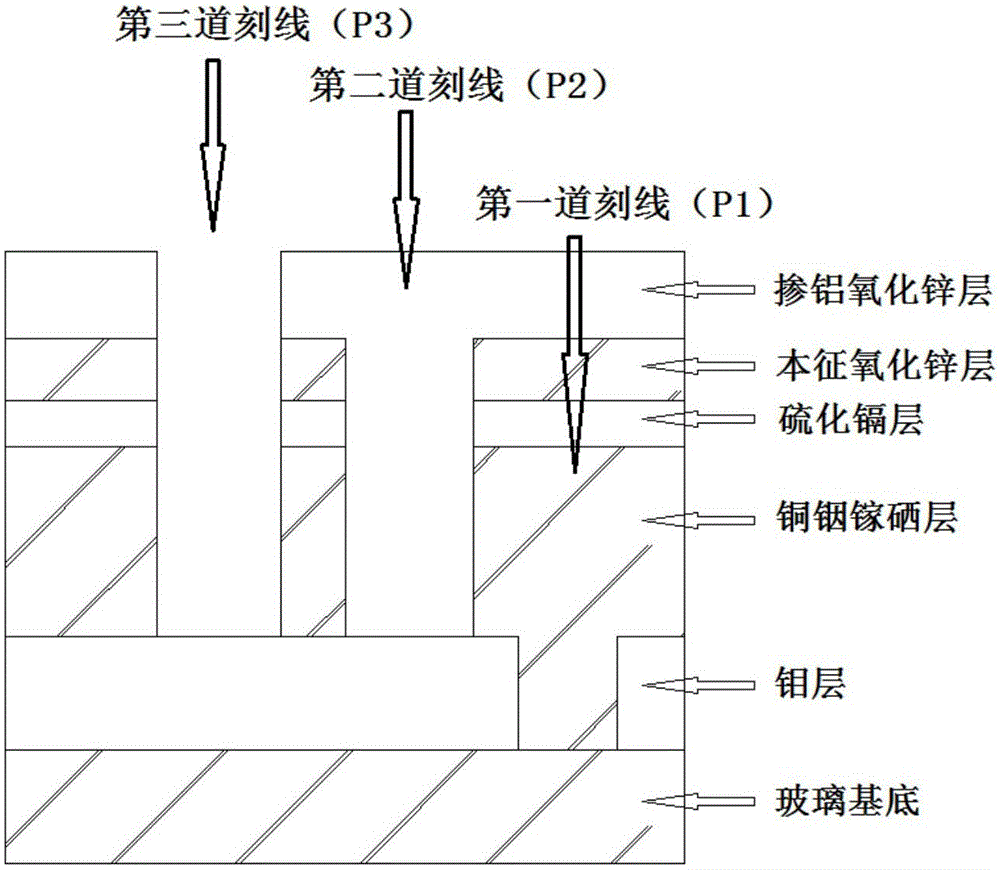
[0031] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a large-area copper indium gallium selenium thin film solar cell described in the present invention; as figure 1 As shown, the battery includes a glass substrate, a molybdenum layer, a copper indium gallium selenide layer, a cadmium sulfide layer, an intrinsic zinc oxide layer and an aluminum-doped zinc oxide layer; figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of full laser scribing of a large-area copper indium gallium selenium thin film solar cell according to the present invention; as figure 2 As shown, the all-laser scribing method includes three laser scribing. First, a molybdenum film is prepared on a glass substrate, and a laser is used to cut the prepared molybdenum film to form the first scribe line (P1); On the molybdenum layer scored by P1, the following film layers are prepared in sequence: copper indium gallium selenide film, cadmium sulfide film, and intrinsic zinc oxide film. Laser 2 is used to scribe t...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Step 1 is the same as in Example 1.
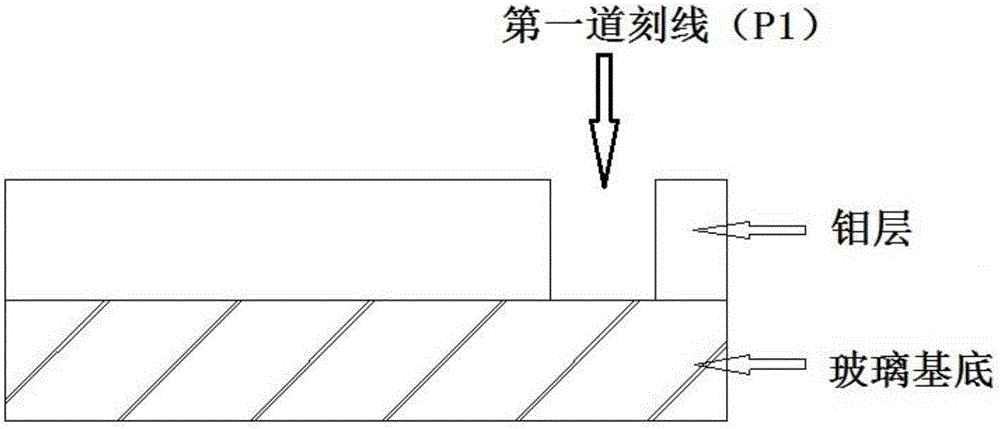
[0043] Step 2, P1 scribing: use a picosecond laser with a pulse width of 8 picoseconds, a wavelength of 532nm, a scribing power of 2.5W, a single pulse energy of 31.25μJ, and a repetition rate of 80kHz. The laser is incident from the back of the coating substrate, and the sample is Carry out P1 scribing, and the scribing speed is 2m / s. After scribing, the width of the scribed line is 35 μm, and the Mo layer in the scribed line is completely removed, exposing the surface of the soda-lime glass.
[0044] Step 3 to step 8 are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Step 1 is the same as in Example 1.
[0047] Step 2, P1 scoring: use a nanosecond laser with a pulse width of 10 nanoseconds, a wavelength of 1064nm, a scoring power of 3.2W, a single pulse energy of 40uJ, and a repetition rate of 80kHz. The laser is incident from the back of the coating substrate, and the sample is processed For P1 marking, the marking speed is 2m / s. After scribing, the width of the scribed line is 33 μm, and the Mo layer in the scribed line is completely removed, exposing the surface of the soda-lime glass.
[0048] Step 3 to step 8 are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com