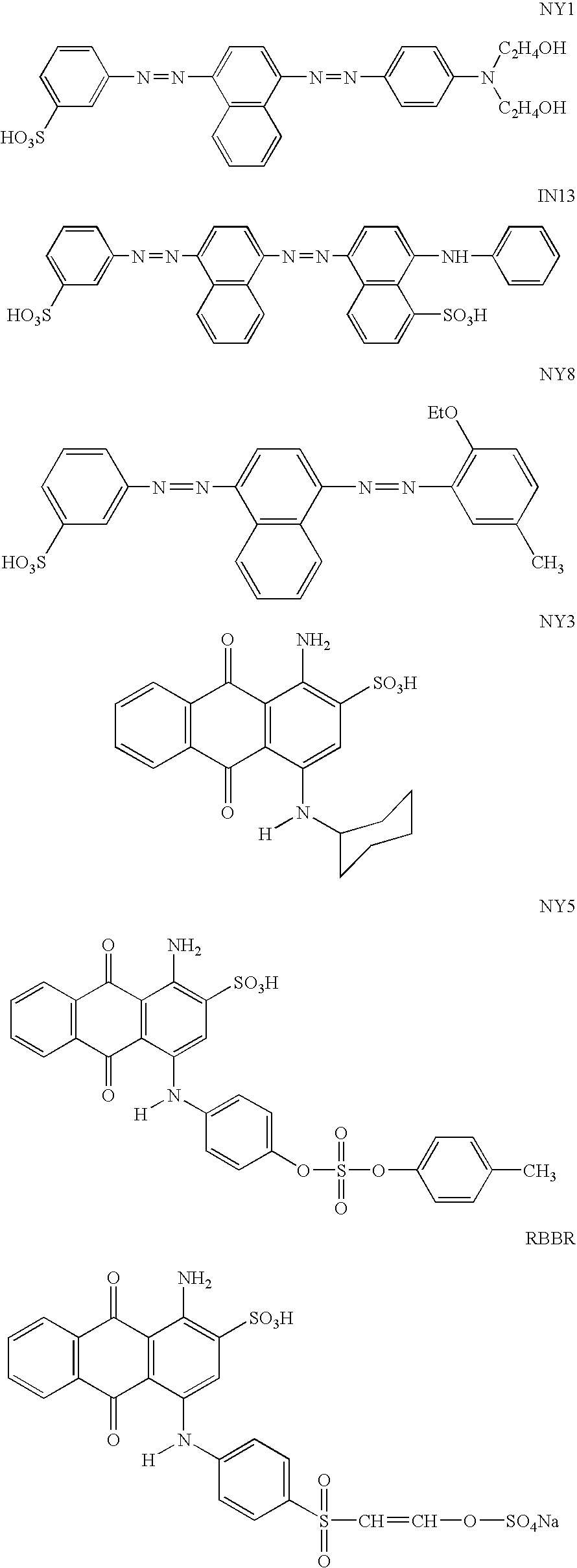
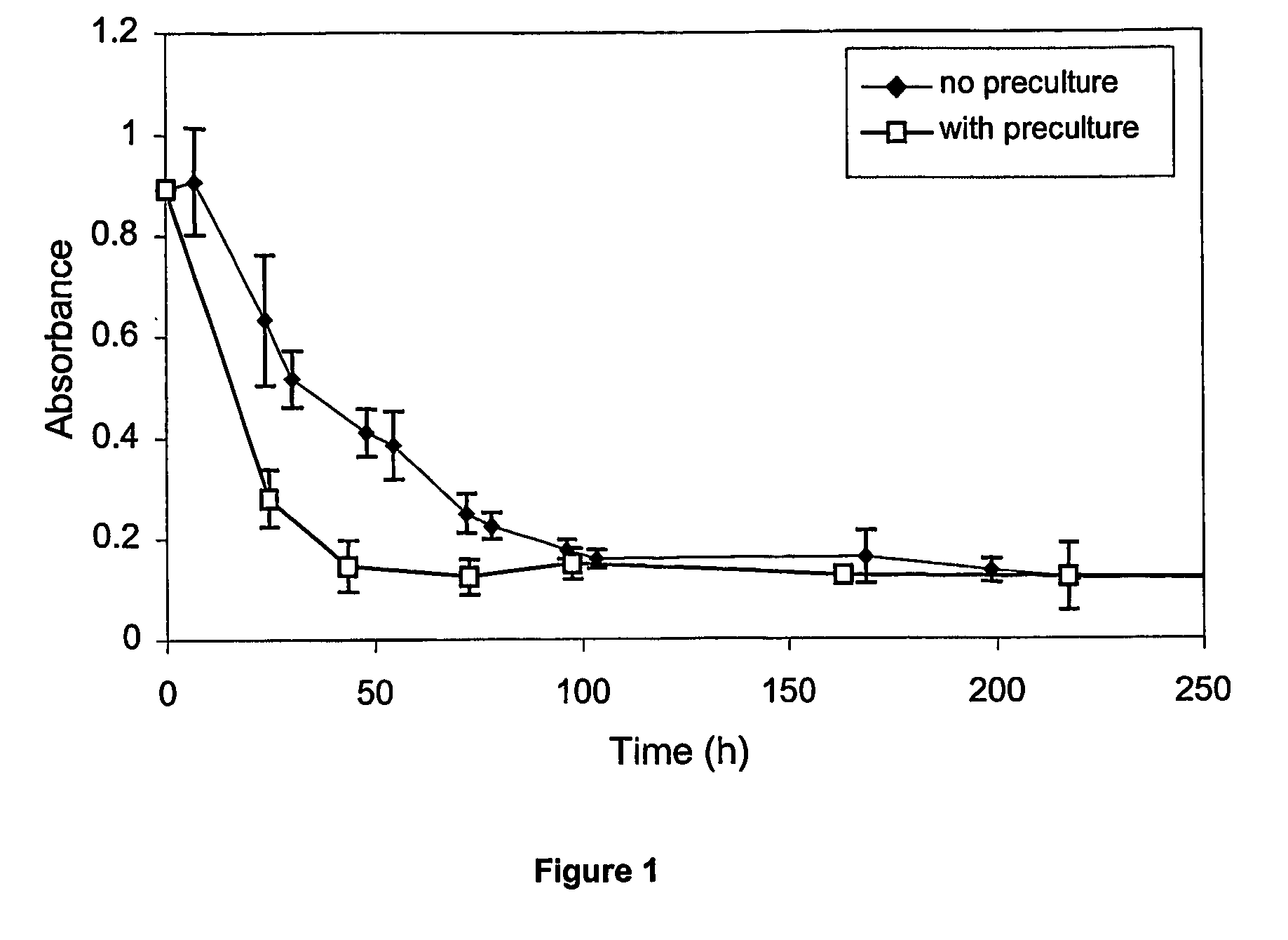
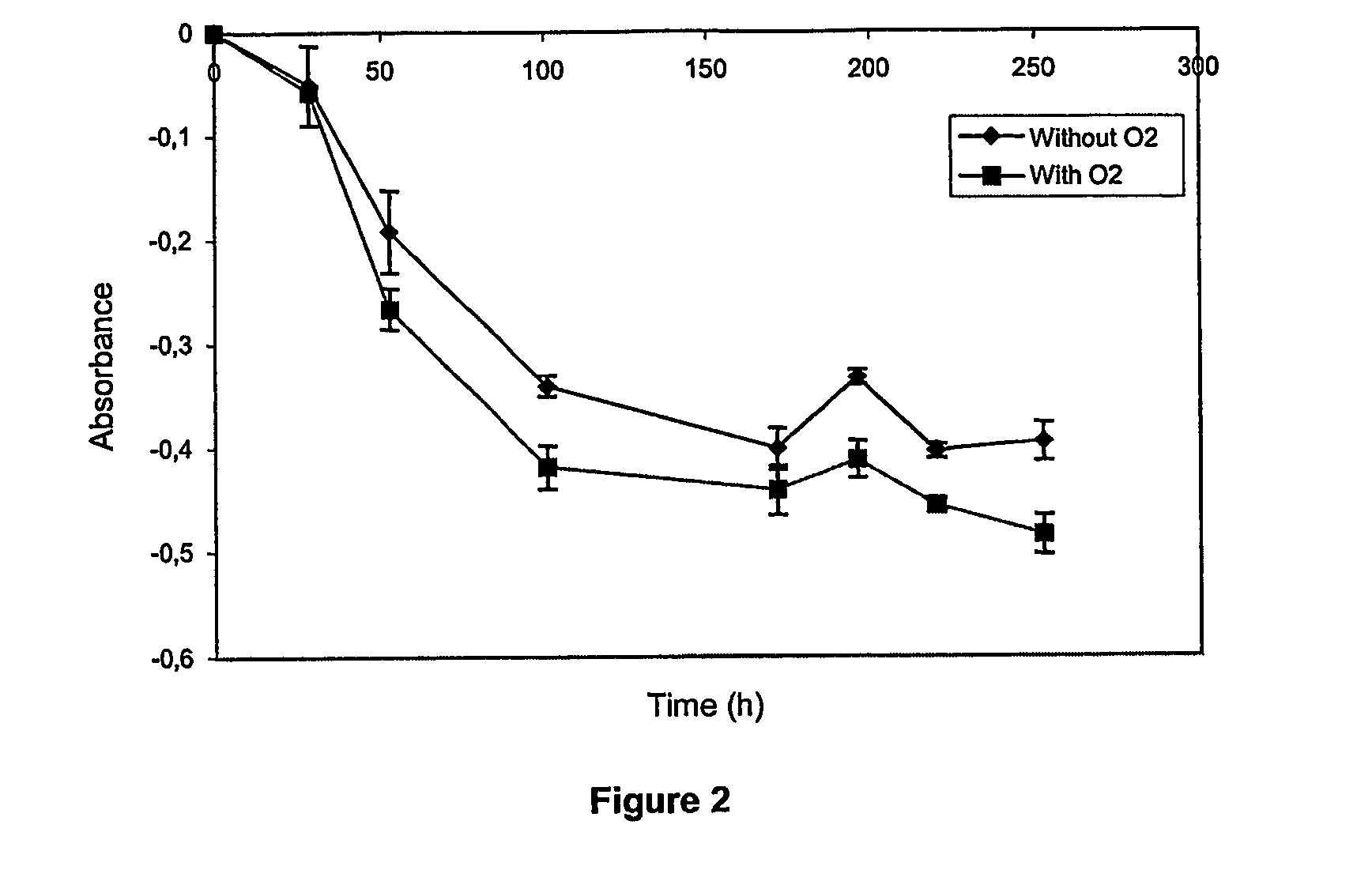
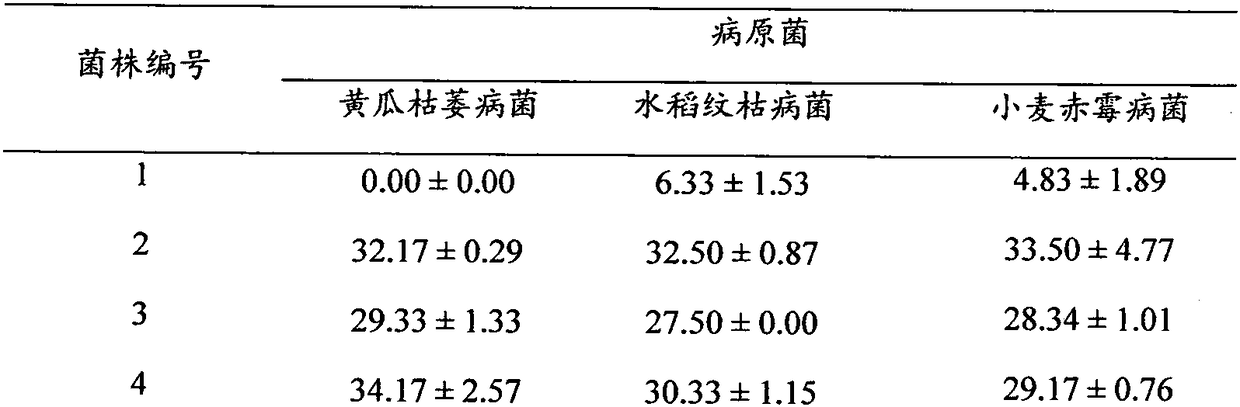
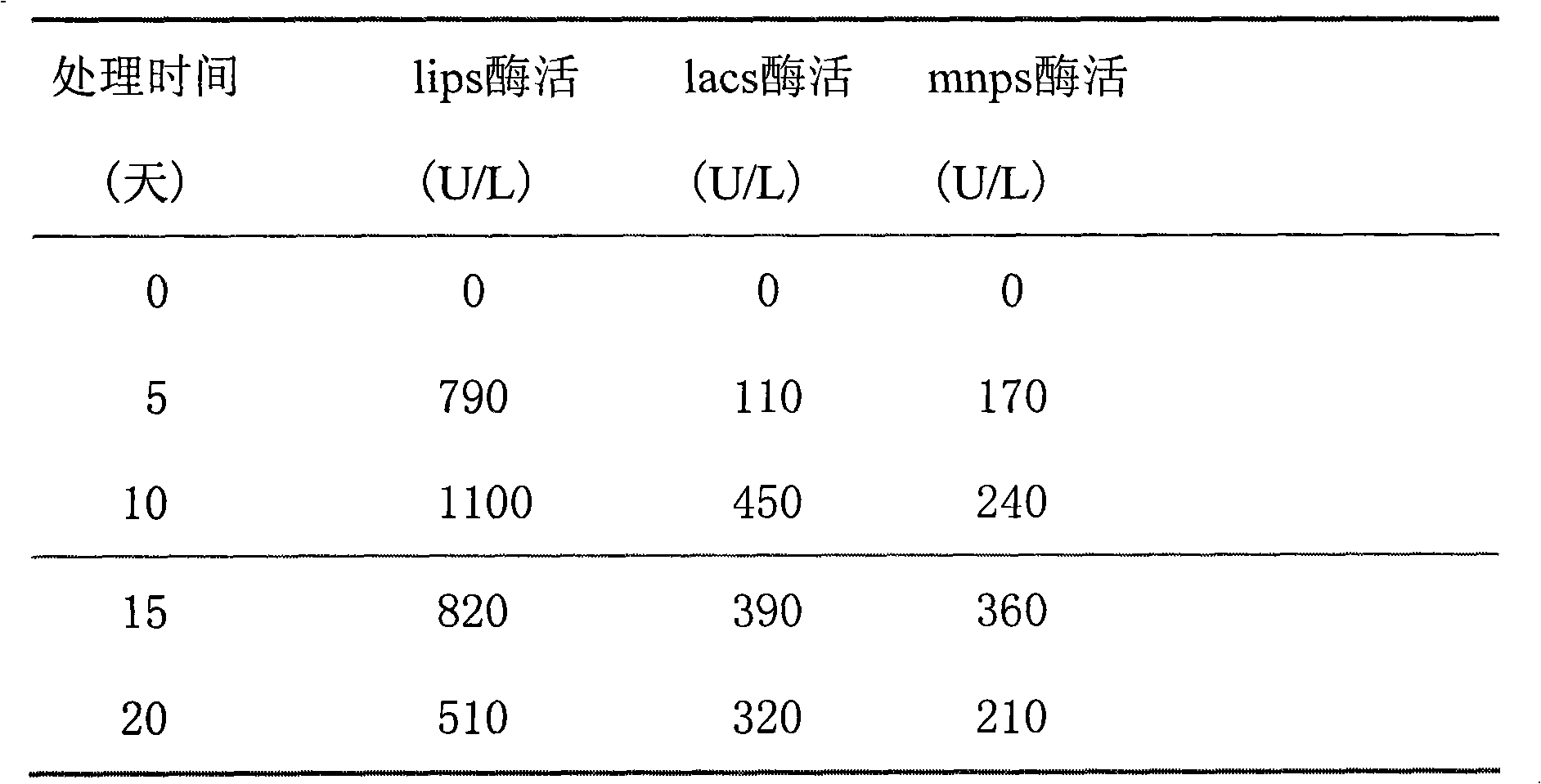
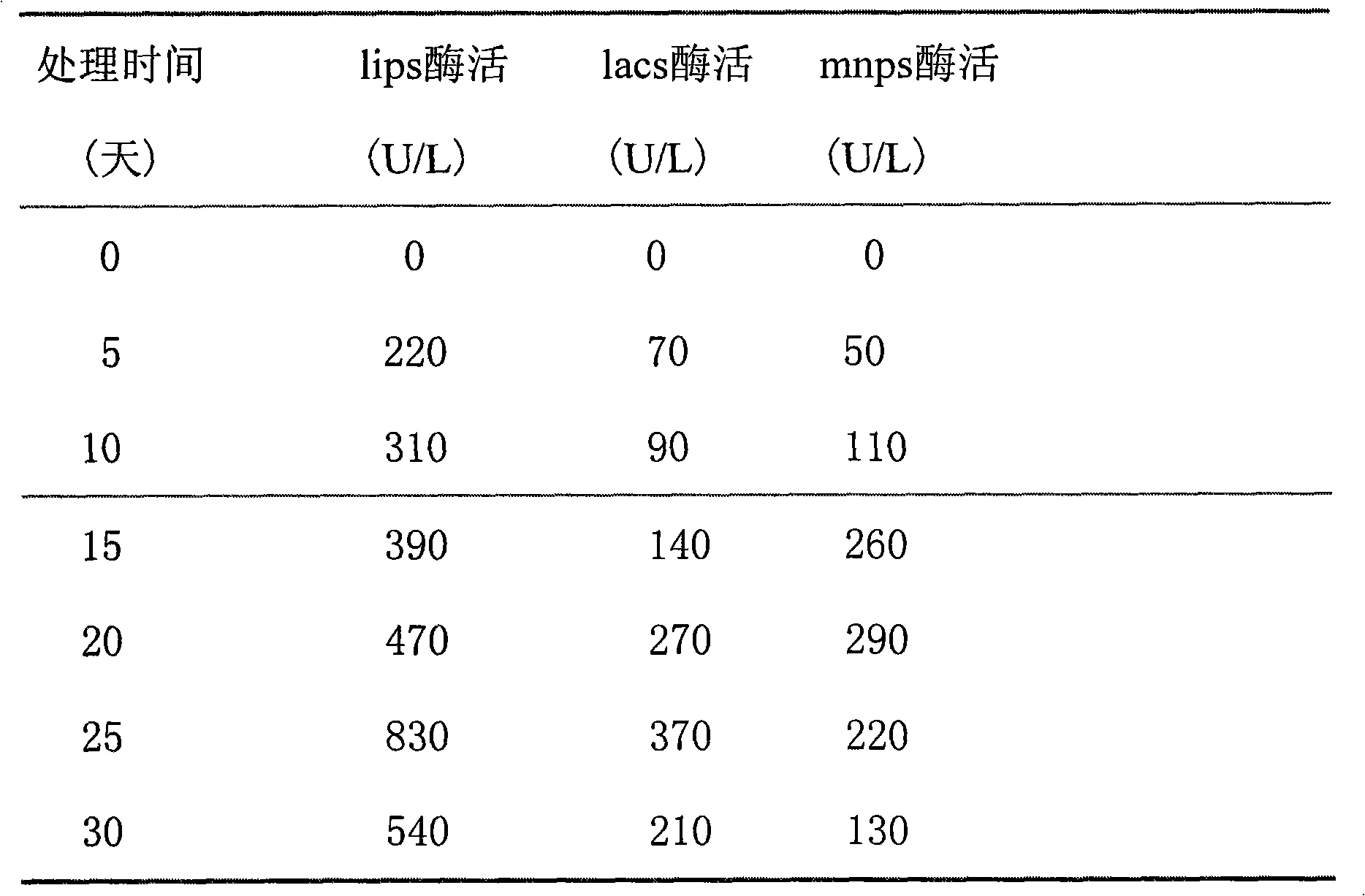
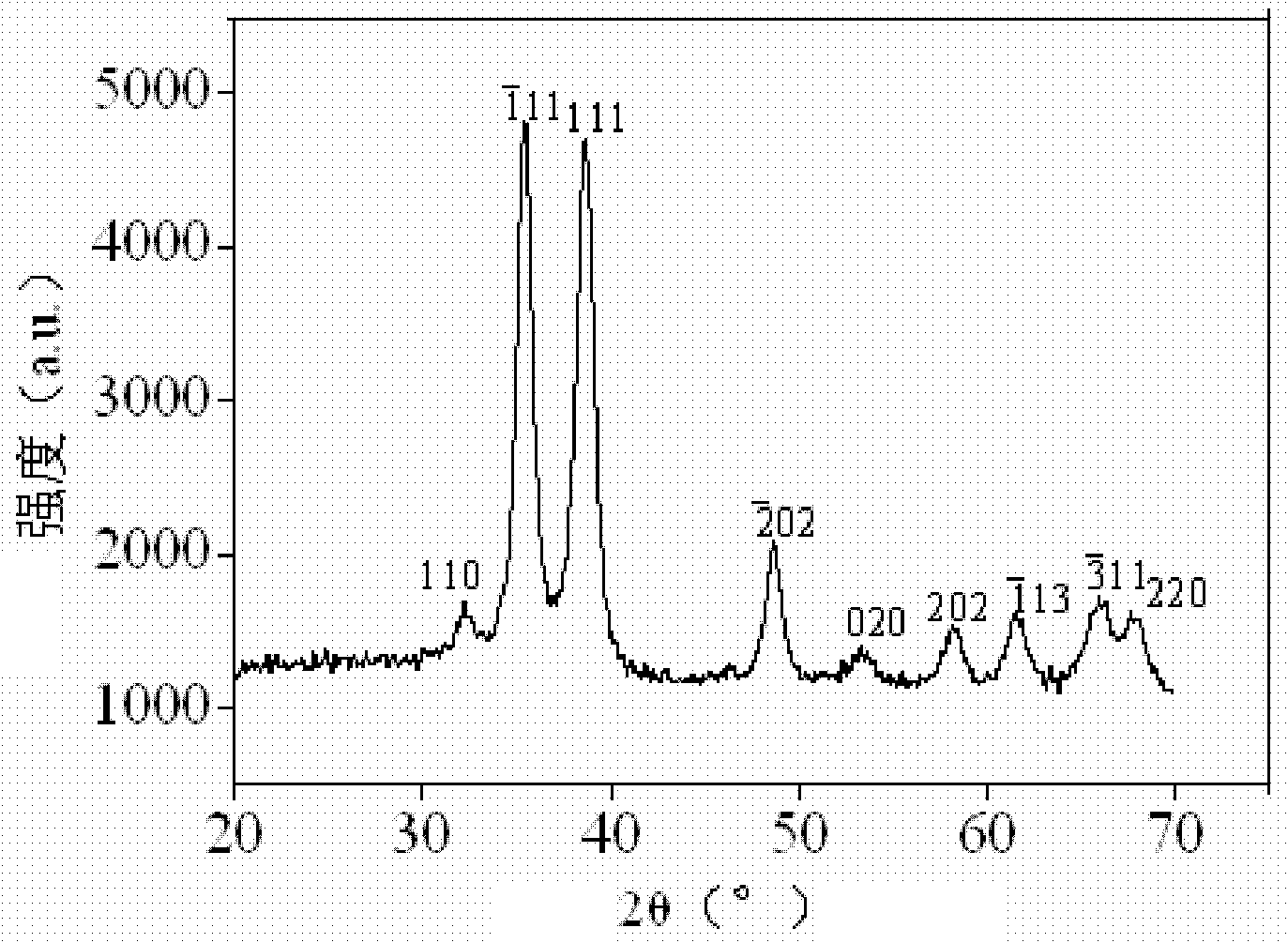
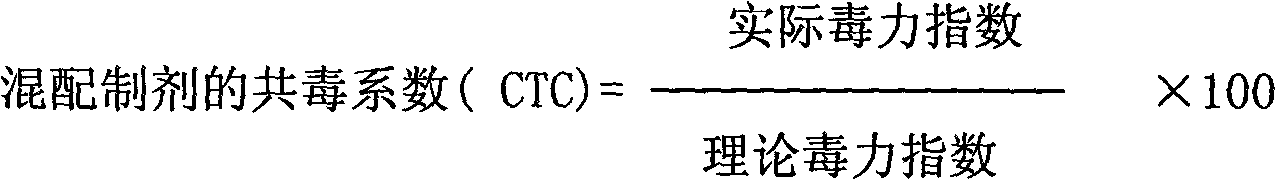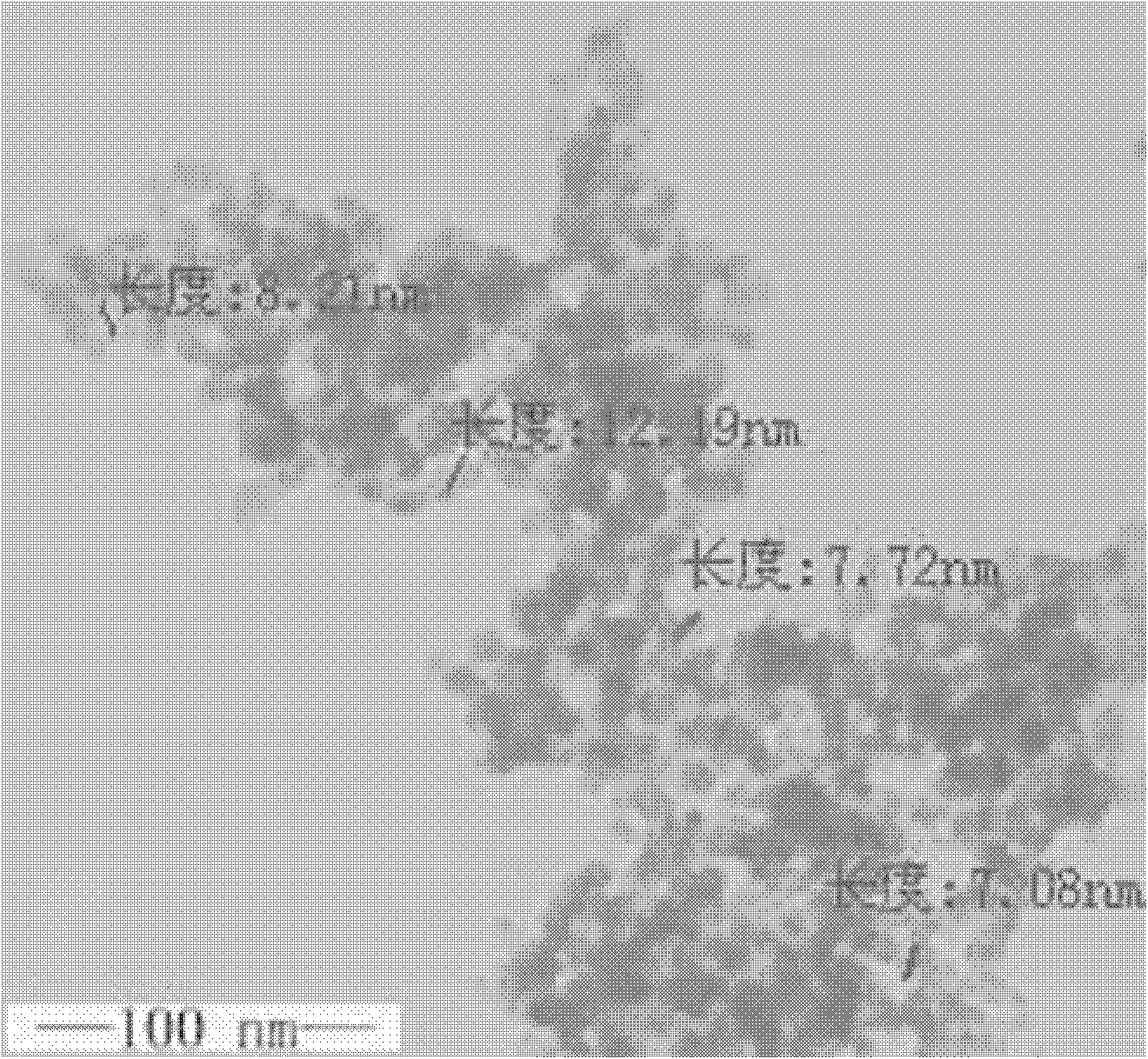Patents
Literature
611 results about "White rot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bio-protein feed prepared by adopting cellulose raw material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102232466ASimple preparation processShort fermentation cycleFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDecompositionRapeseed
The invention relates to a bio-protein feed prepared by adopting a cellulose raw material, and the bio-protein feed provided by the invention comprises an organic material and complex bacteria, wherein the weight of the complex bacteria is 1-10% of that of the organic material; and the organic material comprises the cellulose raw material, rapeseed meal and bran; the cellulose raw material is one or more of corn stalks, corn cobs, straw, manioc waste and fruit residue; and the complex bacteria comprises bacillus subtilis, microzyme, lactobacillus and cellulose decomposition bacteria, and the cellulose decomposition bacteria is one or more of trichoderma harzianum and white-rot fungi. In the bio-protein feed, the content of probiotics is more than 108cfu / g, the bio-protein feed contains a variety of prolease, cellulase, amylase and the like, the preparation process is simple, and the fermentation period is short. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the feed.
Owner:洋浦慷民高科生物有限公司
Sustainable process for the treatment and detoxification of liquid waste
InactiveUS20050067347A1Efficient decolorizationEfficiently detoxifyWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal processingLiquid wasteFungal microorganisms
A method for treatment of liquid waste is disclosed that includes the steps of (a) submitting the liquid waste to a pretreatment and (b) submitting the pretreated liquid waste to the action of fungi or active agents thereof. In particular, the described process is useful for the effective decoloration and detoxification of dye-containing liquid wastes using white rot fungi or active agents thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Bacillus belesei BMF 03 and use and fermentation method thereof
A marine-derived Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) BMF 03 having a deposit number of CCTCC NO: 2017374 is disclosed. BMF 03 strain and its aseptic fermentation broth have inhibitory effect onplant pathogenic fungi, including apple rot fungi, grape white rot fungi, mango anthracnose fungi and so on. The aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03 strain can be used as an active ingredient to prepare an antibacterial drug, and the bacteria is selected from the group consisting of Keratinobacteria, Bacillus subtilis and Ralstonia solanacearum. The invention also discloses a fermentation methodof aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03. The invention adopts a plate confrontation method and an Oxford cup method to screen a new marine bacterial strain BMF-03 with strong bacteriostatic effect andwide bacteriostatic spectrum, and adopts strain morphological observation, physiological and biochemical tests and 16S rDNA sequence analysis to determine the species relationship of excellent resistant strains. At that same time, the bacteriostatic substance produce by the strain, the sporulation fermentation medium and the shake flask fermentation conditions were also study, and the promoting effect of the strain fermentation broth and the solid fermentation product on the growth of the cucumber seedling was clarified, which laid a foundation for the application of the strain.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for expanding culture of microorganisms for wastewater treatment and microbial wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN102268394AEasy to handleImprove processing efficiencyFungiBacteriaWater treatmentWastewater disposal
A method of amplification culture of microorganism for waste water treatment. The waste water comprises heterocyclic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, cellulose and / or lignin. The method comprises the following steps: adding waste water containing heterocyclic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, cellulose and / or lignin into an acclimation reactor; adding a nutritional agent, acomplex bacterial agent, an enzyme preparation, a citric acid and riboflavin on a basis of concentrations in the waste water; performing aeration of the waste water, adjusting the liquid level and temperature of the acclimation reactor, holding for a period of time to allow the microorganism in the complex bacterial agent to reach a logarithmic growth phase, wherein on a basis of concentrations in the waste water, the complex bacterial agent comprises pseudomonas spp. microorganism, bacillus sp. microorganism, and white rot fungi, and the enzyme preparation comprises protease, amylase, cellulose and lipase. The invention also provides a method of waste water treatment by using the microorganism to be amplified and cultured.
Owner:北京赛富威环境工程技术有限公司
Method for preparing activated carbon by catalyzing and activating microorganism white-rot fungi or enzymes
InactiveCN102745689AReduce production safety hazardsShort manufacturing timeCarbon compoundsNicotiana tabacumBiological activation
The invention relates to a method for preparing activated carbon by catalyzing and activating microorganism white-rot fungi or enzymes, which belongs to the technical field of activated carbon preparation. According to the preparation method, tobacco solid waste is used as a raw material, and a product is obtained through simple processes of pretreating the raw material, preparing a tobacco activated base by microorganism white-rot fungi culture or enzyme catalysis and activation and preparing the activated carbon. The method has the characteristics of wide raw material source, low waste utilization cost, low energy consumption in the production process, no secondary pollution, benefit to environmental protection, good adsorptive property and wide application of the activated carbon production, and the like. The method can be widely applied to preparing the activated carbon by taking the tobacco solid waste as a raw material, and the activated carbon prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be widely applied to the fields of waste water treatment, removal of SO2 from smoke, adsorption of odors in food fresh keeping, and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
A method using white-rot fungus and carrier to process persistent wastewater
InactiveCN101549936ALow costWide range of vector sourcesImmobilised enzymesBio-organic fraction processingCelluloseNatural product
The invention is a method using white-rot fungus and carrier to process persistent wastewater which belongs to the field of water treatment technology. It first uses the carrier to absorb COD in wastewater, then uses the carrier to provide cellulose stimulating substrate to the white-rot fungus for its enzyme production, processes the persistent substance adsorbed on the carrier, selects different natural products as the core materials of the carrier, and produces the carrier coat after NaOH treatment. When handling the waste water, it adjusts the initial wastewater pH, adds the carrier and white-rot fungi, and takes the water sample into the conical flask; places the sample in the shaking table with the temperature of 35-60 DEG C and shaking speed of 170rpm for processing. The treatment process of the invention only needs to adjust the initial pH, has no operation during the middle process and does not need re-adjustment for subsequent treatment; the carrier used with a wide variety of sources can be treated directly as the fertilizer together with the bacteria after use, and has no secondary pollution; it has apparent decolorization effect after processing with the decolorization rate of above 90%.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting
ActiveCN103232944AWell mixedPromote the process of mixed aerobic compostingFungiBio-organic fraction processingFecesPseudomonas putida
The invention discloses a microorganism bacterium agent for straw and excrement mixed composting. The microorganism bacterium agent is composed of the following strains: (2-6)*10<10>cfu of hair mould per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of trichoderma virens per gram, (2-6)*10<10>cfu of geotrichum candidum per gram, (2-8)*10<9>cfu of saccharomyces cerevisiae per gram, (3-5)*10<11>cfu of bacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of lactobacillus thermophilus per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of white rot fungi per gram, (2-8)*10<10>cfu of monilinia fructicola per gram, (3-7)*10<8>cfu of pseudomonas putida per gram, (2-6)*10<11>cfu of nitrosococcus per gram, (1-4)*10<6>cfu of green algae per gram and (2-5)*10<7>cfu of blue-green algae per gram. The microorganism bacterium agent can promote a straw and excrement mixed aerobatic composting progress, shorten a composting period, improve a composting rotten degree, accelerate biodegradation of organic matters, alleviate ozone generation and diffusion during composting and reduce loss of nutrient substances such as nitrogen, can be applied to composting of different straw and excrement raw materials for composting enterprises and is used for producing bio-organic fertilizers.
Owner:山东土木启生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing biogas by degrading coal with microorganisms
InactiveCN102517368AEfficient degradationImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelBiogasWhite rot
The invention relates to technology for preparing biogas by degrading coal with microorganisms. The technology is suitable for any environment with oxygen or without oxygen. Under the condition of room temperature (15 to 35 DEG C), biologic methane can be ensured to be continuously generated without activating a strain in a way of raising temperature, so the development cost is effectively reduced; the adopted white-rot fungi is highly adaptive to the environment and is low in cost, so the technology has the feasibility of project development; and different types of colonies can be more effectively used and the effect of the colonies can be improved, so the degradation rate of a coal body is increased, and the yield of biological methane is improved.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
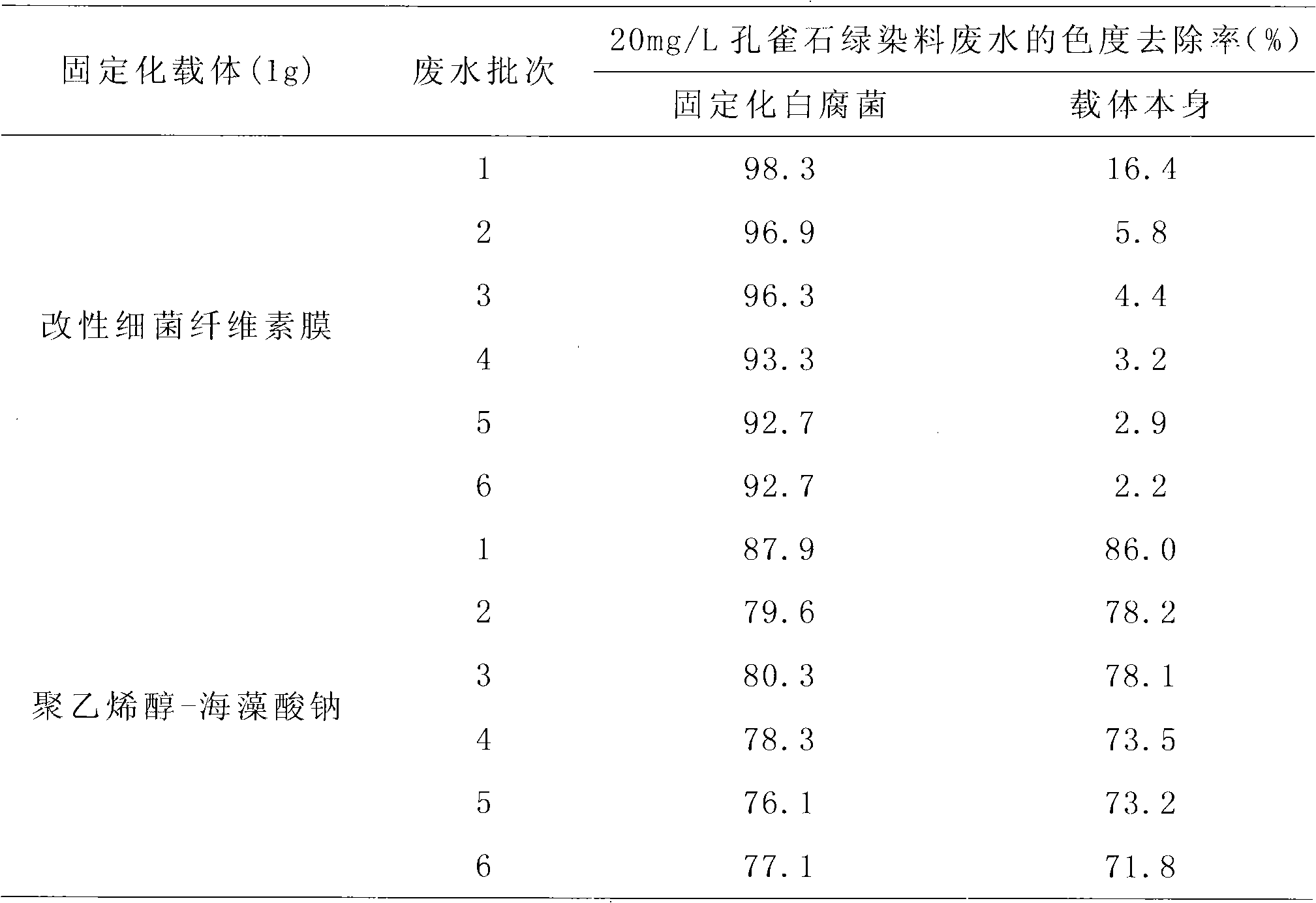
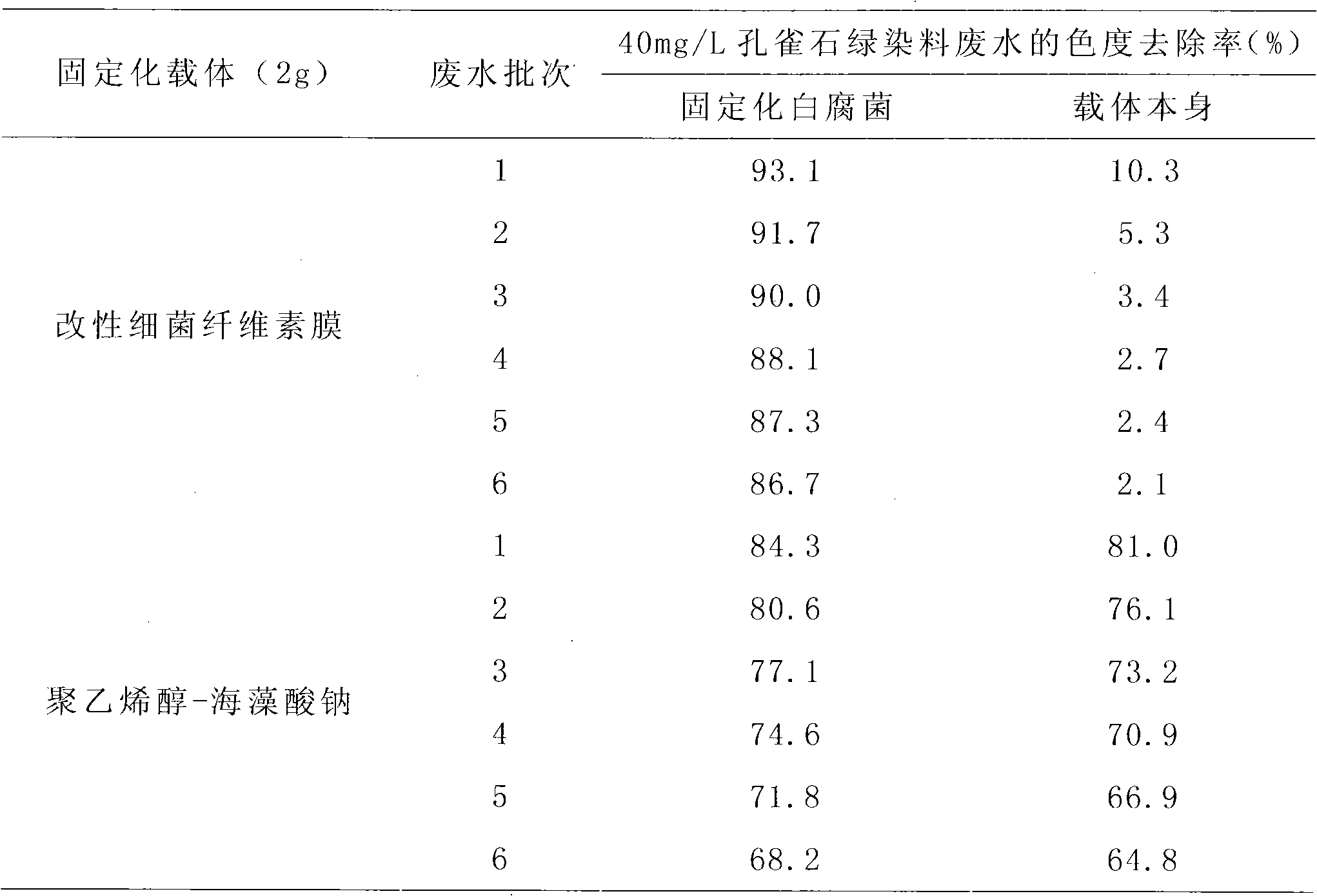
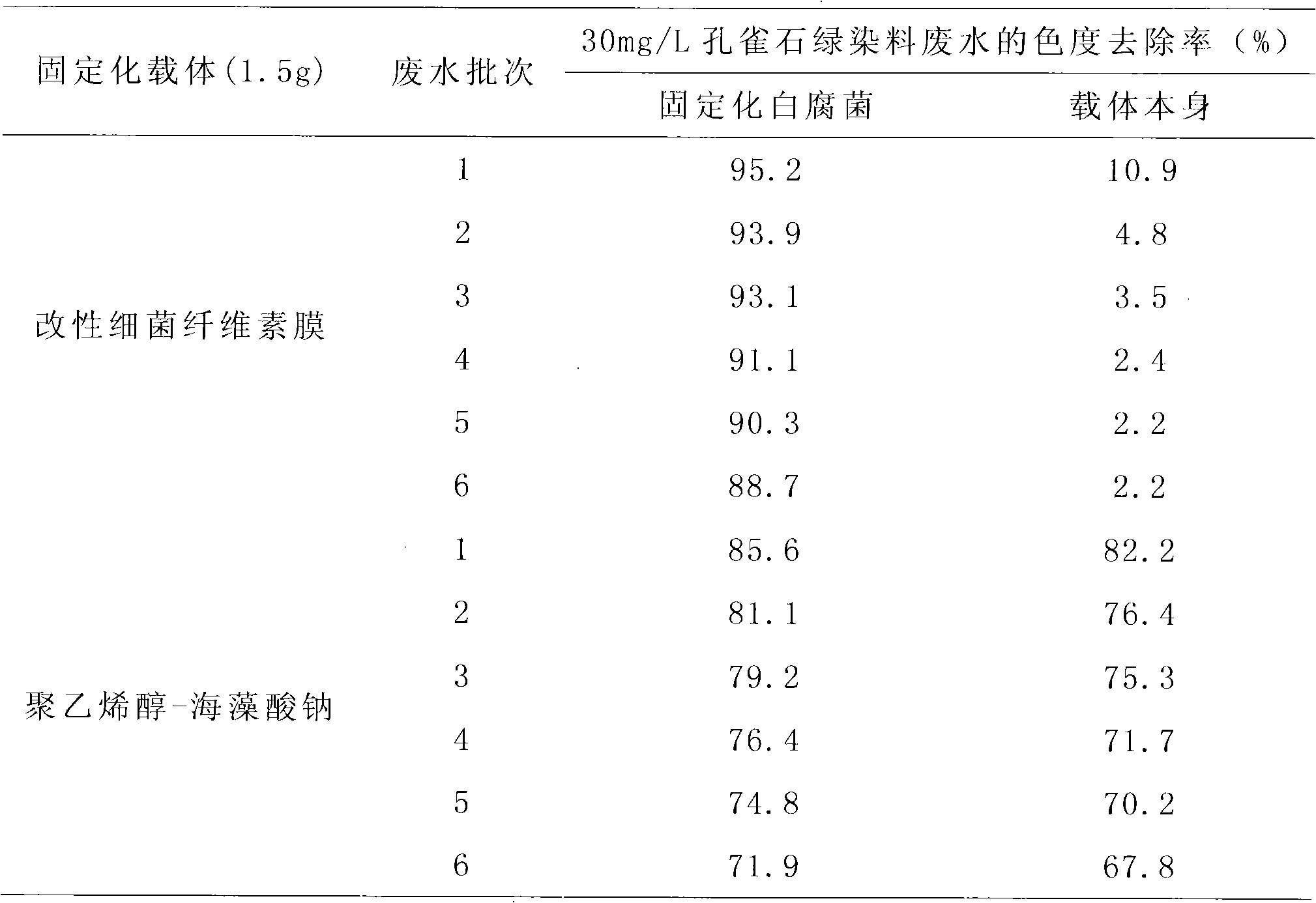
Method for treating malachite green dye waste water
InactiveCN101973640ASignificant progressSignificant positive effectNature of treatment waterBiological water/sewage treatmentMalachite greenMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for treating malachite green dye waste water, which comprises the following steps of: preparing a bacterial cellulose membrane; modifying the bacterial cellulose membrane; immobilizing white rot fungi by using the modified bacterial cellulose membrane; adding the obtained immobilized white rot fungi modified bacterial cellulose membrane into 50 mL of the malachite green dye waste water; dissolving 20 to 40 mg of malachite green into 1 L of white rot fungi liquid restrictive culture medium; treating the waste water on a gas bath constant-temperature shaking table at a speed of 120 rpm for 5 days at 28 DEG C, and measuring the chroma of the waste water at intervals of 24 hours; 5 days later, discarding the treated waste water, and retaining the immobilized fungi; adding 50 mL of newly-prepared dye waste water with the same concentration, treating the waste water under the same condition, and measuring the chroma of the waste water at intervals of 24 hours; and taking 5 days as a cycle, and repeating the steps for 5 times, wherein the removal rate of the chroma of the waste water is always over 86 percent. In the method, the referred bacillus xylinus and the white rot fungi are purchased from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +1
Straw feed fermented by white rot fungus and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101606579AReduce crude fiber contentImprove digestibilityFungiFood processingBiotechnologyRumen
The invention relates to a straw feed fermented by white rot fungus and a preparation method thereof, and strain is the combination of white rot fungus Tf1 (pleurotus sajor-caju) and JG1 (pleurotus cornucopiae) which are screened in an oriented way, so that solid fermentation fungicide is cultured and prepared by three-stage propagation. Straw is pretreated by quicklime instead of being processed by high temperature sterilization without being washed by water or neutralized by acid. The obtained straw is accessed with white rot fungus composite fungicide to be fermented for 15-20 days, thus being taken as a first step of fermentation for degrading lignin in the straw and improving the straw digestion utilization rate of ruminant. After that, the fermented straw is accessed with yeast to be fermented for 3-4 days, thus being taken as a second step of fermentation for improving the crude protein content of the straw and further enhancing the nutritional value of the straw feed. After the two steps of fermentation, the crude fiber content of the straw is reduced by over 25%, the dry matter rumen (nylon bag technique) digestion rate is improved by over 20%, the crude protein content is increased by more than 50%, and the straw feed has no safety risk when being fed for animals. The invention has the characteristics of no energy consumption, no pollution, low cost, easy operation, high feeding value of the straw, and being suitable for local production of villages in China.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
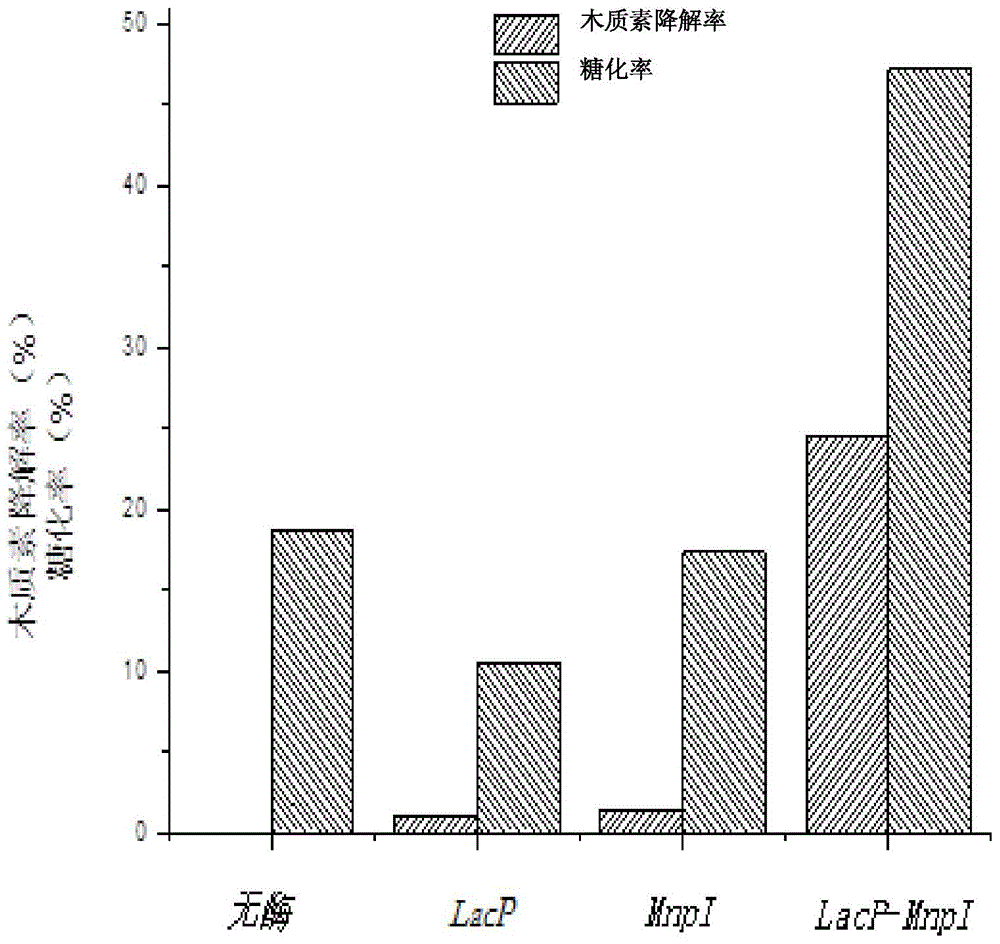
Lignin degradation solution and preparation method thereof as well as method for degrading lignin by using lignin degradation solution
InactiveCN104894079AEfficient degradationImprove degradation conversion efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationCelluloseSodium acetate
The invention discloses a lignin degradation solution and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for degrading lignin by using the lignin degradation solution, and belongs to biochemical and bio-refinery methods to solve the problem that the efficient biodegradation of lignin is difficult to realize by adopting single ligninase of laccase at present. The lignin degradation solution is prepared by the following steps: dissolving laccase and manganese peroxidase into an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution of which the pH value is 4-6 in an enzyme load ratio of (10:1)-(1:5) to ensure that the enzyme loads of the laccase and manganese peroxidase are respectively 1U / ml-50U / ml and 1U / ml-50U / ml; and then adding 1-10mM of MnSO4 and 0.1-1mM of H2O2, wherein the laccase and manganese peroxidase are obtained by fermenting white rot fungi to obtain extracellular crude enzyme liquid and then performing separation and purification respectively. According to the lignin degradation solution and the methods disclosed by the invention, the synergistic oxidative degradation of macromolecular lignin with rich structural diversity is realized, and compared with a degradation reaction system with single ligninase, the degradation rate of the macromolecules of the lignin can each 30-50%, the degradation conversion efficiency is significantly improved, and the degradation solution and the methods can be applied to the fields of bio-refinery of lignocelluloses, biological pulping or environmental treatment and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
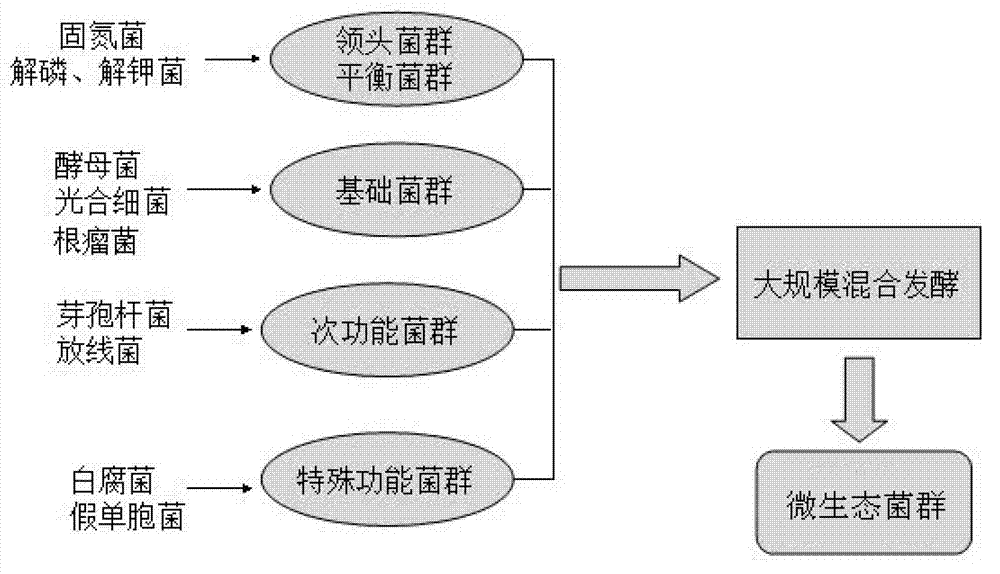
Micro-ecological flora of crop root system probiotics and application thereof
The invention discloses a micro-ecological flora of crop root system probiotics and an application thereof. The micro-ecological flora comprises a leading flora, a balance flora, a basic flora, a secondary-function flora and a special-function flora, wherein the leading flora comprises 25-35 parts of nitrogen-fixing bacteria by mass; the balance flora comprises 17-23 parts of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and 17-23 parts of potassium solubilizing bacteria by mass; the basic flora comprises 2-7 parts of yeast, 2-7 parts of rhizobia and 2-7 parts of photosynthetic bacteria by mass; the secondary-function flora comprises 2-7 parts of bacillus and 2-7 parts of actinomycetes by mass; the special-function flora comprises 2-4 parts of white rot fungi and 1-3 parts of pseudomonas. In the micro-ecological flora disclosed by the invention, the strain stability is good, functional microorganisms can be effectively planted in soil, and the functions of improving the crop yield and quality, improving the soil, detoxifying heavy metals and resisting diseases and pests can be realized.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Wheat straw decomposition agent and method for preparing same
InactiveCN105112343ARipe fastDecompose thoroughlyFungiBio-organic fraction processingYeastDecomposition
The invention discloses a wheat straw decomposition agent and a method for preparing the same. The wheat straw decomposition agent and the method have the advantage that bacillus subtilis, trichoderma viride, aspergillus niger, white rot fungi and candida are used as production strains, are free of antagonism and easy to cultivate and are nontoxic and harmless, and excellent wheat straw degradation effects can be realized; the method for preparing the wheat straw decomposition agent is simple, the strains are easily available and are convenient to store and low in cost, and obvious decomposition effects can be realized; the yield of crops can be greatly increased by decomposed wheat straw organic fertilizers, and the quality of the crops can be greatly improved by the decomposed wheat straw organic fertilizers.
Owner:安徽飞天农用生物科技有限公司
Grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation and application method thereof
The invention discloses a grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation and an application method thereof. The grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation comprises bacteria components and enzyme components, wherein the bacteria components comprise white rot fungi and zymogeneous bacteria, and the enzyme components comprise cellulose, xylanase, laccase, protease, thermostable amylase, ligninase and pectinase. According to the grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation, straw serving as the raw material is treated with a biological method, a biological cycle liquid and a waste cooking liquid produced in the treatment process can be recycled without drainage, and lignin can be extracted; and besides, according to the method, straw does not require cutting and dust removal, and the cooking does not require high temperature and high pressure, so that a large quantity of manpower and electric charges is omitted, and the preparation and the method are suitable for a plurality of raw materials such as wheat straw, straw, cotton stalks, reeds and the like, can be used for producing a paddle board, molded pulp, various types packaging paper, office paper and household paper and have the advantages of low cost and environment protection.
Owner:北京秸大环保科技有限公司
Compound bactericide for treating sewage and sewage treatment method thereof
ActiveCN106701633AGood removal effectFunction increaseFungiBacteriaOperabilityBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses compound bactericide for treating sewage and a sewage treatment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. The compound bactericide comprises the following active ingredients from following strains: rhodopseudomonas, anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, candida utilis, thiobacillus denitrificans, white-rot fungi, lactobacillus plantarum, bifidobacterium, lactobacillus acidophilus, green nonsulfur bacteria, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, aspergillus oryzae, nitrosomas, streptomyces, bacillus subtilis and propionibacterium acidipropionici. The invention also provides the method using the compound bactericide to treat the sewage. The compound bactericide and the sewage treatment method have the advantages that the effect of treating sewage is better, the technology is simple, the implementing is easy, the operability is strong, the pollution to environment is avoided, the industrial requirements are met, and the application prospect is better.
Owner:哈尔滨明慧生物技术开发有限公司
Ferment method of producing fuel ethanol using stalk material
The invention relates to a method for preparing fuel ethanol by taking straw as raw material. It comprises following steps: (1) selecting crop straw as raw material; (2) disintegrating: disintegrating straw by using hammer mill, sifting and getting straw powder of 20- 40 order; (3) pre- treating: lignin degrading raw material by way of culturing white-rot fungi in solid culture medium and liquid enzyme; (4) saccharifying two enzymes, saccharifying straw by using cellulase and xylanase at 45 Deg. C, pH 4.5, 150 rmp and ratio between liquid and solid 15, getting reduced sugar; (5) fermenting; (6) distilling. The fuel ethanol productivity is 16.7% in this invention, that is 16.7 ton waterless ethanol with every 100 ton straw, the production efficiency is high and economic benefit and social benefit is pretty good. Compared with current process, this invention is characterized in that the fermentation is thorough and the fuel ethanol production cost is low.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
ActiveCN103243044AEffective controlGood function and effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefaciens YJ01 which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection (CGMCC) center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms and the preservation number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is CGMCCNO.7328. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens is mainly used for preventing and treating a fungal disease of a wine-brewing grape. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens YJ01 can metabolize out antibacterial substances iturin A and surfactin, thereby playing an obvious role in inhibiting various pathogenic fungi of the wine-brewing grape. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has the advantages of being high in culture proliferation speed, capable of being cultured artificially, easy to operate, convenient to produce and apply, strong in adversity resisting capability, and the like; and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens has significance for preventing and treating diseases such as gray mold, white rot and anthracnose of wine-brewing grape caused by fungi, and is simple in culturing conditions, easy to preserve and easy to produce industrially, thereby having good development and application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Method for making active carbon fibers of cotton stalk skins by using microwave method
InactiveCN102191588AWell-developed poresImprove adsorption capacityFibre chemical featuresVegetable materialChemical treatmentFiber
The invention discloses a method for making active carbon fibers of cotton stalk skins by using the microwave method, comprising the following steps of: (1) a biological treatment: washing cotton stalk skins and removing impurities, cutting the cotton stalk skins into segments, inoculating with white rot fungi to ferment, washing and drying; (2) a chemical treatment: dipping cotton stalk skin fibers processed from the Step (1) into a KOH, NaOH or H3PO4 solution; (3) placing the cotton stalk skin fibers dipped in Step (2) into a microwave oven for carbonization and activation, taking the carbonized and activated cotton stalk skin fibers out of the microwave oven after cooling to room temperature, washing the cotton stalk skin fibers to pH 6-7, kiln drying or air drying to produce the active carbon fibers of cotton stalk skins. The method for making active carbon fibers by using cotton stalk skins as the raw material in the invention has advantages of simple preparation technology, fast preparation speed, low energy consumption, sufficient raw material and low price. The active carbon fibers prepared by using the method have a high carbon content rate, well-developed pores, strong sorption and excellent performance, can effectively remove harmful pollutants, and is good for environmental protection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bamboo wood preservative made from natural plant source and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103999885AImprove securityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungicidesMass ratioPlant Sources
The invention discloses a bamboo wood preservative made from a natural plant source and a preparation method of the bamboo wood preservative. The bamboo wood preservative comprises, by mass, 2.5%-10% of extract from roots of kudzu vines, 1%-5% of extract from smoke trees, 1%-5% of extract from onions, 30%- 60% of alcohol and the balance distilled water, wherein the sum of the mass percentages of the materials is 100%. The preparation method of the bamboo wood preservative comprises the steps that alcohol and distilled water are mixed according to a mass ratio into ethanol water with the mass percentage of 30%-60%, the extract from roots of kudzu vines, the extract from smoke trees and the extract from onions are added into the ethanol water according to the mass percentages, the mixture is stirred for 30 minutes to 60 minutes in a vacuum decompression sealed tank at the temperature of 50 DEG C to 60 DEG C, the mixture is cooled to the normal temperature, and then a bamboo wood preservative solution containing the extract from roots of kudzu vines, the extract from smoke trees and the extract from onions is obtained, wherein the mass percentage of the extract from roots of kudzu vines, the mass percentage of the extract from smoke trees and the mass percentage of the extract from onions are certain. The bamboo wood preservative made from the natural plant source has the antibacterial function and the insect prevention function and can well restrain bamboo wood rotting fungi, brown rot fungi (Gloeophyllum) and white rot fungi (Coriolus versicolor). The bamboo wood preservative is a totally environmentally friendly material, the preparation technology is simple, energy consumption can be reduced, and compared with a chemical preservative, the bamboo wood preservative is high in safety for the environment.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for removing 2, 4-dichlorophenol in water by using polyurethane sponge fixed white rot fungi
InactiveCN101734801AAvoid inactivationHigh removal rateWater contaminantsNature of treatment waterPorosityBiological reaction
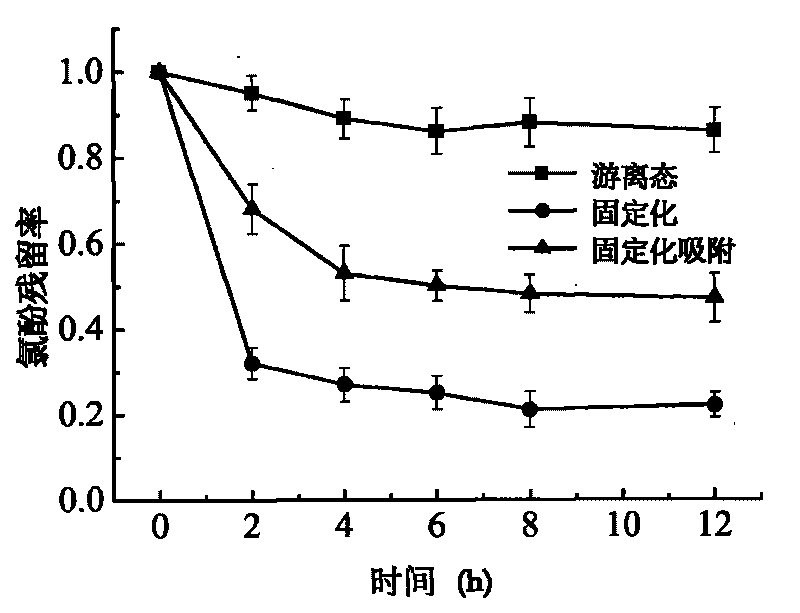
The invention discloses a method for removing 2,4-dichlorophenol in water by using polyurethane sponge fixed white rot fungi, belonging to the field of environmental microbiology. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a carrier, preparing fixed white rot fungi and removing 2, 4-dichlorophenol in water. The carrier has the characteristics of porosity, hydrophily and good adsorbability, enjoys stable chemical property and hydrolytic resistance, high organism bearing capacity and mass transfer rate and is not soluble in acid / alkaline water solution; while the fixed carrier can effectively absorb and fix white rot fungi, improve capacity of fixed white rot fungi in removing 2,4-dichlorophenol in water and leads the fixed white rot fungi to be easily separated from the product, thus being applicable to execute biological reaction processing on multiple sewages.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
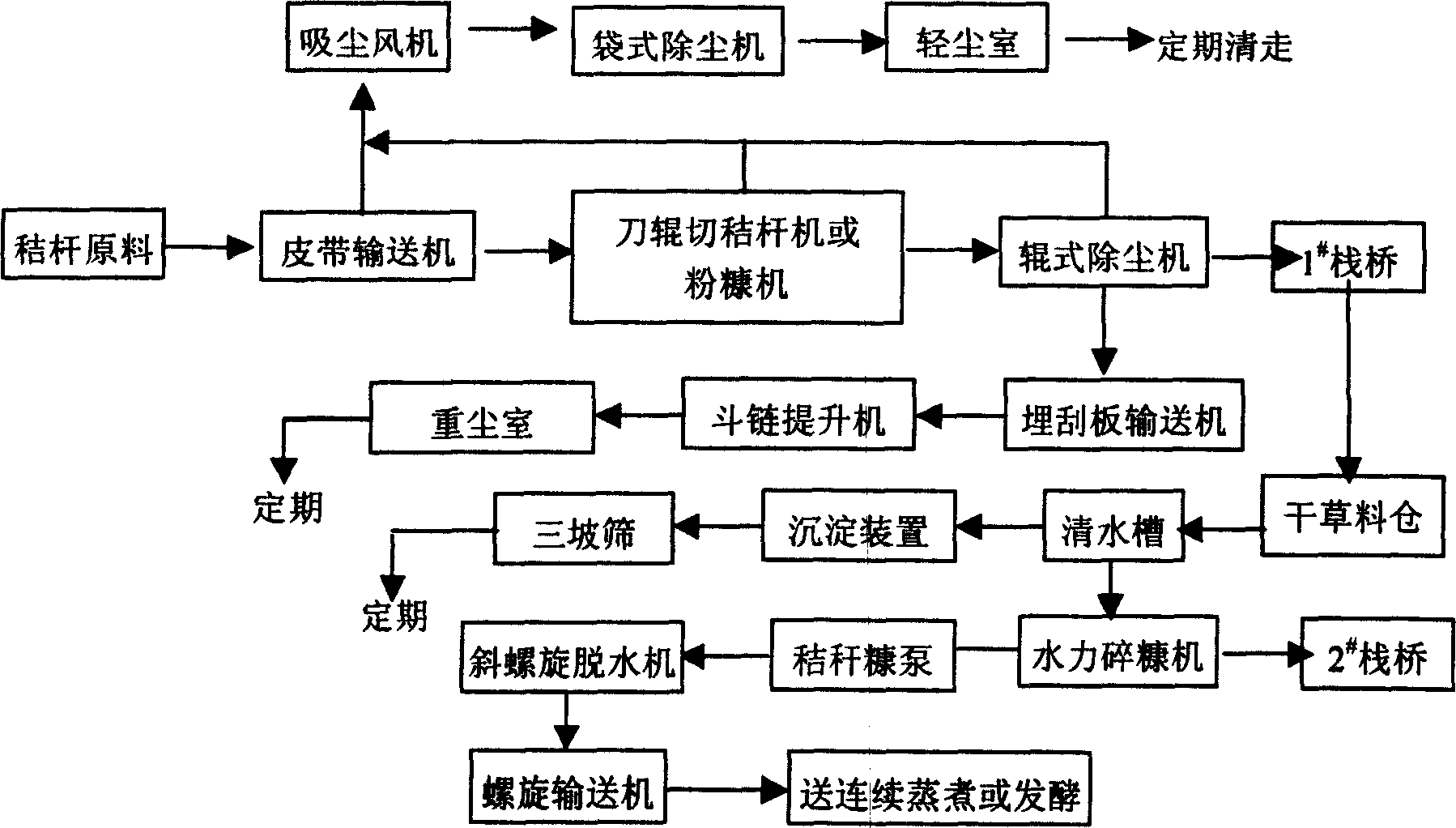
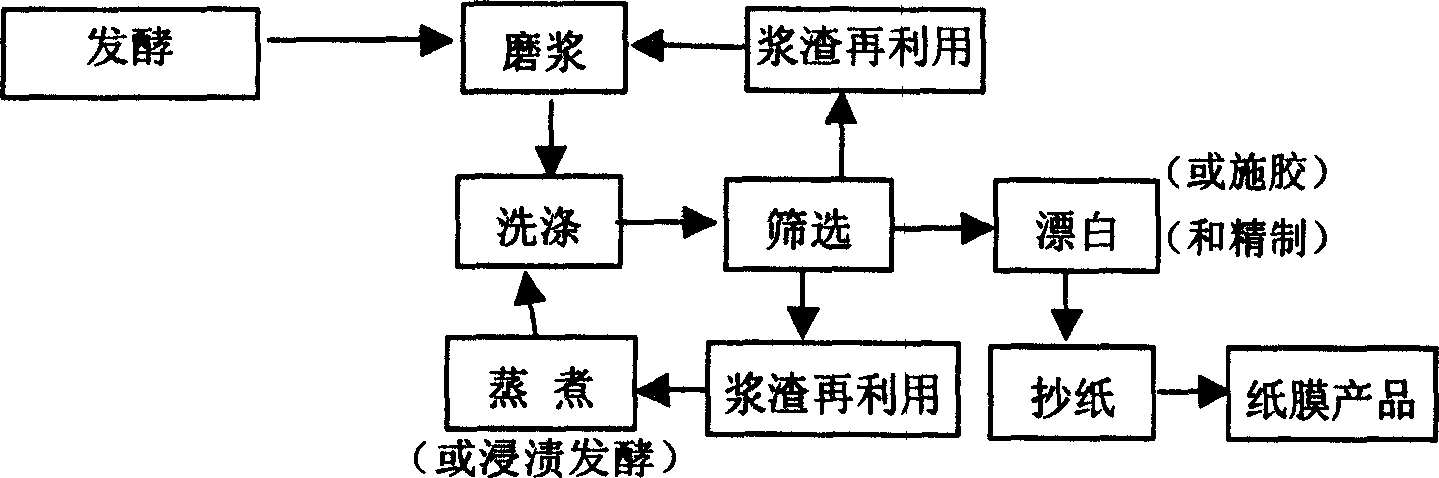
Pulp making process employing straw to make environment-friendly paper film
The invention discloses the pulping process with straw for producing environment protection paper film, comprising the following steps: using rice, wheat, paddy, corn, sorghum and cotton straw or waste straw or fruit tree waste branch as raw material, disintegrating them to 1mm-2mm, at the same time carrying out dust-absorbing; cleaning, putting them into fermenting tank or fermentation tank, adding 0.1% saccharomycete or white-rot fungi, stirring, keeping temperature, carrying out fermentation, then taking-up them and putting them into beating tank, direct pulping in beating tank, adding glue stock in slurry, the degree of applying glue amounting to 1.75mm, adding 1% talcum powder or calcium carbonate, and getting environment protection paper film slurry. The pulping process can prepare the environment protection paper film slurry, and has the advantages of good economic benefit, social benefit and ecological benefit.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Antibacterial packaging paper
The invention discloses antibacterial packaging paper. A preparation process comprises: preparation of packaging paper, preparation of a waterproof agent coating, and preparation of an antibacterial agent coating. According to the antibacterial packaging paper disclosed by the invention, the processing raw materials are bamboos and waste timbers. As bamboo fiber is naturally antibacterial, timbers are replaced by bamboos, so that cutting of trees is avoided, the environment is protected, the ecological balance is maintained, waste is turned into wealth as waste timbers are used, and the cost is saved; the bamboo fiber and wood fiber are matched in use, so that the strength and flexibility of paper are remarkably improved and the packaging paper is wide in using range; the waterproof layer and the antibacterial layer are natural materials which do not harm human body and environment and play natural roles of preventing water and resisting bacteria; in a delignification process, the raw materials are pre-treated by using white rot fungi first, so that the time and dosage for delignification by hydrogen peroxide are reduced; hydrogen peroxide further can disinfect and bleach the packaging paper, is safe and non-toxic, and does not cause the environmental pollution, thereby killing two birds with one stone and saving the cost.
Owner:HEFEI LONGFA PACKING CO LTD
Method for immobilizing white rot fungi by using bacteria cellulose film as vector
InactiveCN101392246AHigh purityGood biological stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesEpoxyTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a method for immobilizing white-rot fungi by utilizing a bacterial cellulose membrane as a carrier, which includes the following steps: the separation of the white-rot fungi and the preparation of spore solution of the white-rot fungi; the preparation of the bacterial cellulose membrane; the modification treatment of the bacterial cellulose membrane and the preparation of immobilized cells. After the bacterial cellulose membrane is processed by epoxy chloropropane, absolute ethyl alcohol, perchloric acid and the like, the modified bacterial cellulose membrane obtained is adopted as a carrier and reacts with a 25-percent glutaric dialdehyde solution and mixed with the spore solution of the white-rot fungi after the treatment of repetitive washing and the like, and then the solution is sealed and stays overnight at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and repetitively washed to obtain a bacterial cellulose membrane immobilized white-rot fungi. Three continuous batches of treatment tests for organics and chroma of xylitol production wastewater show that the treatment effects of immobilized white-rot fungi are not found to be obviously reduced and the immobilized white-rot fungi has obvious stability.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
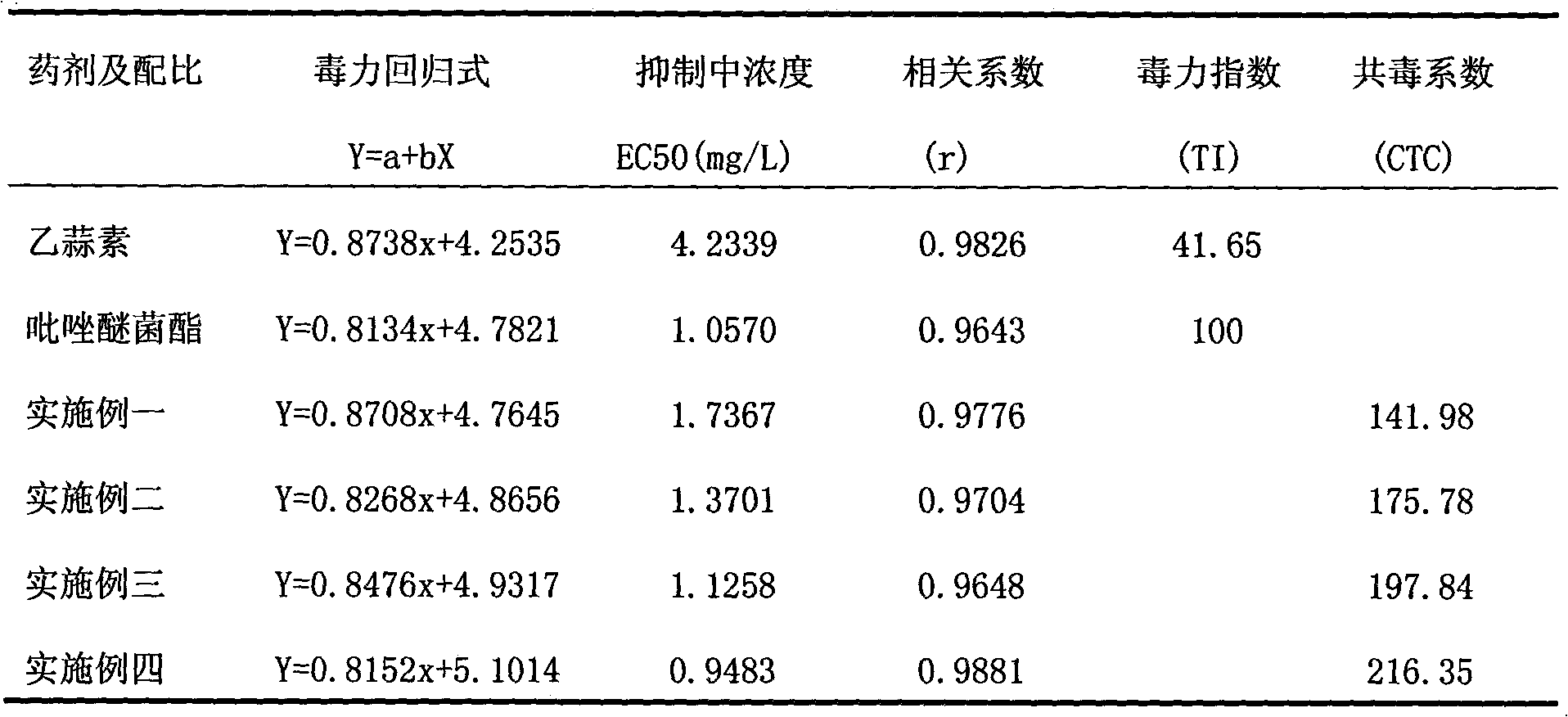
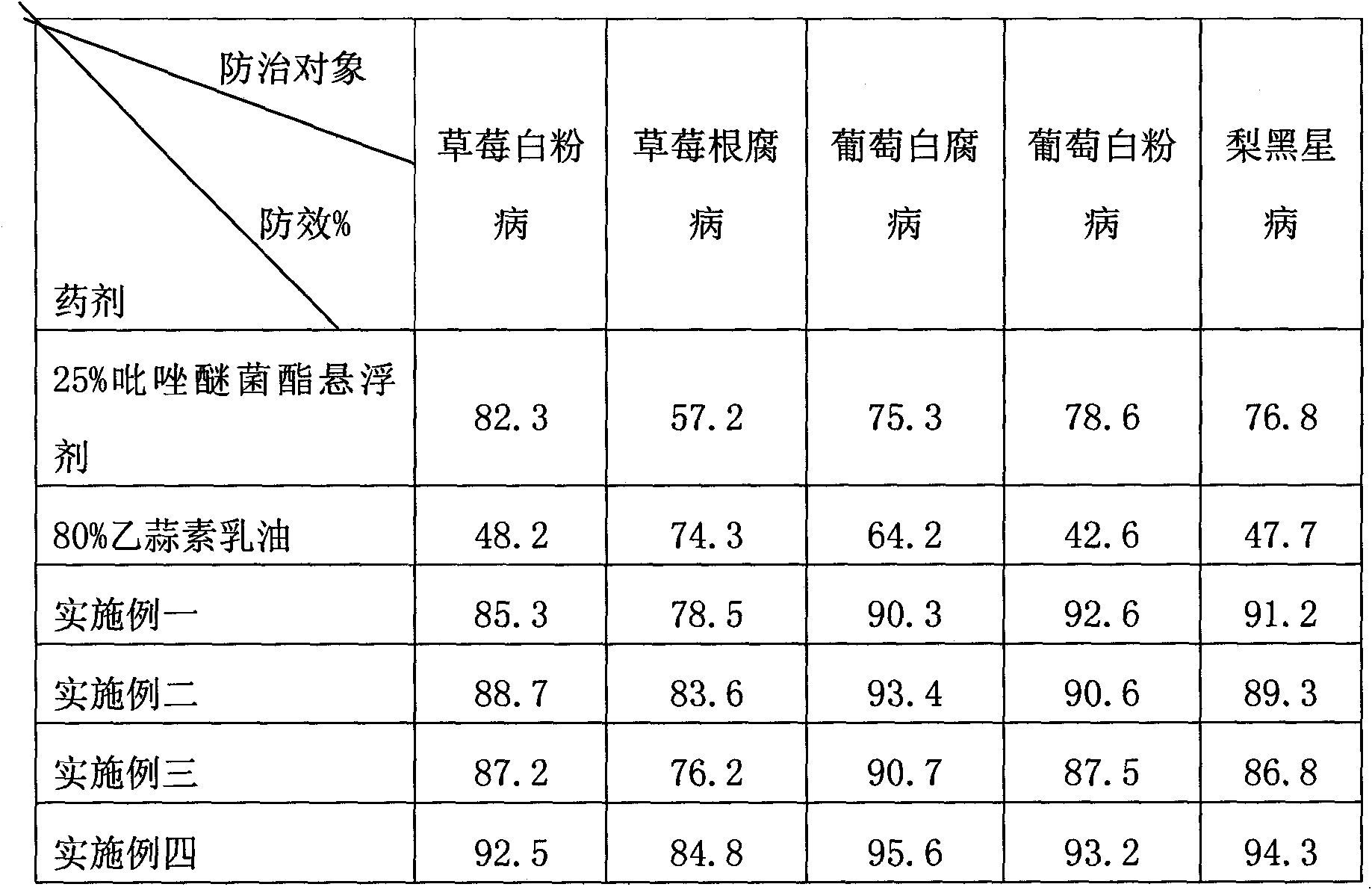
Bactericide for preventing and treating fruit diseases
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticide and relates to a pesticide for preventing and treating fruit diseases such as strawberry anthracnose, powdery mildew and root rot disease, grape white rot and powdery mildew, pear scab and the like. The pesticide comprises the active compositions of ethylicin and pyrachostrobin with the weight ratio of 1-50:1-20, and preferably 10-40:1-15. The invention has the advantages that firstly, the drug resistance caused by long-term use of single preparation is avoided, and the effective time of pesticide is prolonged; secondly, the combination of the ethylicin and the pyrachostrobin has a better synergistic effect, and the application amount and the cost are reduced; thirdly, the pesticide improves the treating effect, widens the anti-fungal spectrum, and has long effective duration and good effect on preventing and treating a plurality of diseases; and fourthly, the pesticide has low toxicity and non-pollution and is safe for environment.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
Control method of grape diseases and insect pests
A control method of grape diseases and insect pests comprises step 1, performing control before germination; step 2, controlling the anthrachose, the gray mold and gall mites during inflorescence phase separation in March; step 3, controlling the anthrachose, the gray mold, the anthracnose and the downy mildew during flowering period in April; step 4, controlling the anthrachose, the white rot, the gray mold, the anthracnose and spider mites during flower and fruit protection and expanding period in May; step 5, performing control during grape bagging in early June; step 6, controlling the anthracnose, the white rot and the downy mildew during fruit coloring and mature period in the middle of June to late June; step 7, giving priority to copper agents and spraying twice after the harvest. The control method of the grape diseases and insect pests is low in cost, free of pollution, high in fruit quality and high in yield.
Owner:江苏双昌肥业有限公司
Method for treating dye waste water by enzyme production through mixed biomass fermenting
InactiveCN102583769ASimple methodEasy to operateWaste water treatment from textile industryBiological water/sewage treatmentMalachite greenCongo red
The invention discloses a method for treating dye waste water by enzyme production through mixed biomass fermenting. In the method, white rot fungi which can generate a lignin degrading enzyme system are used as a fermenting enzyme-production strain; a solid and liquid culture method is adopted, a cottonseed hull and / or paddy straw are / is used as a fermentation substrate, and lignin degrading enzyme is induced to obtain an optimal lignin degrading enzyme system; and finally, crude enzyme liquid is extracted, separated and prepared and can be used for decoloring treatment of waste water of commonly-used synthetic dye, such as Congo red, phenol red, bromophenol blue, crystal violet, malachite green and the like so as to obtain the optimal decoloring effect of dye sewage. The method is simple and is easy to operate. The enzyme system induced by the method disclosed by the invention has high enzymolysis efficiency, and the optimal decoloring effect can be achieved by adopting the enzyme system to treat the dye waste water.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for biologic pretreatment of lignocellulose and hydrogen production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
ActiveCN102321671AReduce energy consumptionAvoid damageMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for biologic pretreatment of lignocellulose and hydrogen production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, relates to a method for pre-treating lignocellulose and producing hydrogen through fermentation, and solves the problems of high energy requirement, environmental pollution and production of a fermentation inhibitor existing in the pretreatment of the lignocellulose during the conventional fermentative hydrogen production. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, inoculating white rot fungi in lignocellulose liquid culture medium to culture, washing and drying to obtain pretreated cellulose; and 2, mixing hydrogenogens nutritive salt solution and environmentally-friendly trichoderma rough enzyme solution, and adding into the pretreated cellulose to obtain simultaneous saccharification and fermentation hydrogen production culture medium; then introducing nitrogen; and inoculating seed liquid of hydrogenogens to perform anaerobic fermentation to produce hydrogen. By adopting the method, the energy consumption during lignocellulose hydrogen production is reduced, equipment investment is reduced, the fermentation inhibitor is not produced, damage probably caused to environment during hydrogen production is reduced to the minimum; the relative removal rate of lignin reaches 55.7 percent; and the hydrogen production capacity is 72.6ml / g.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
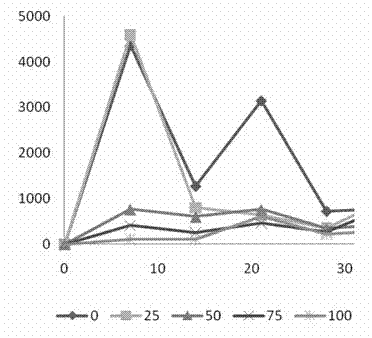
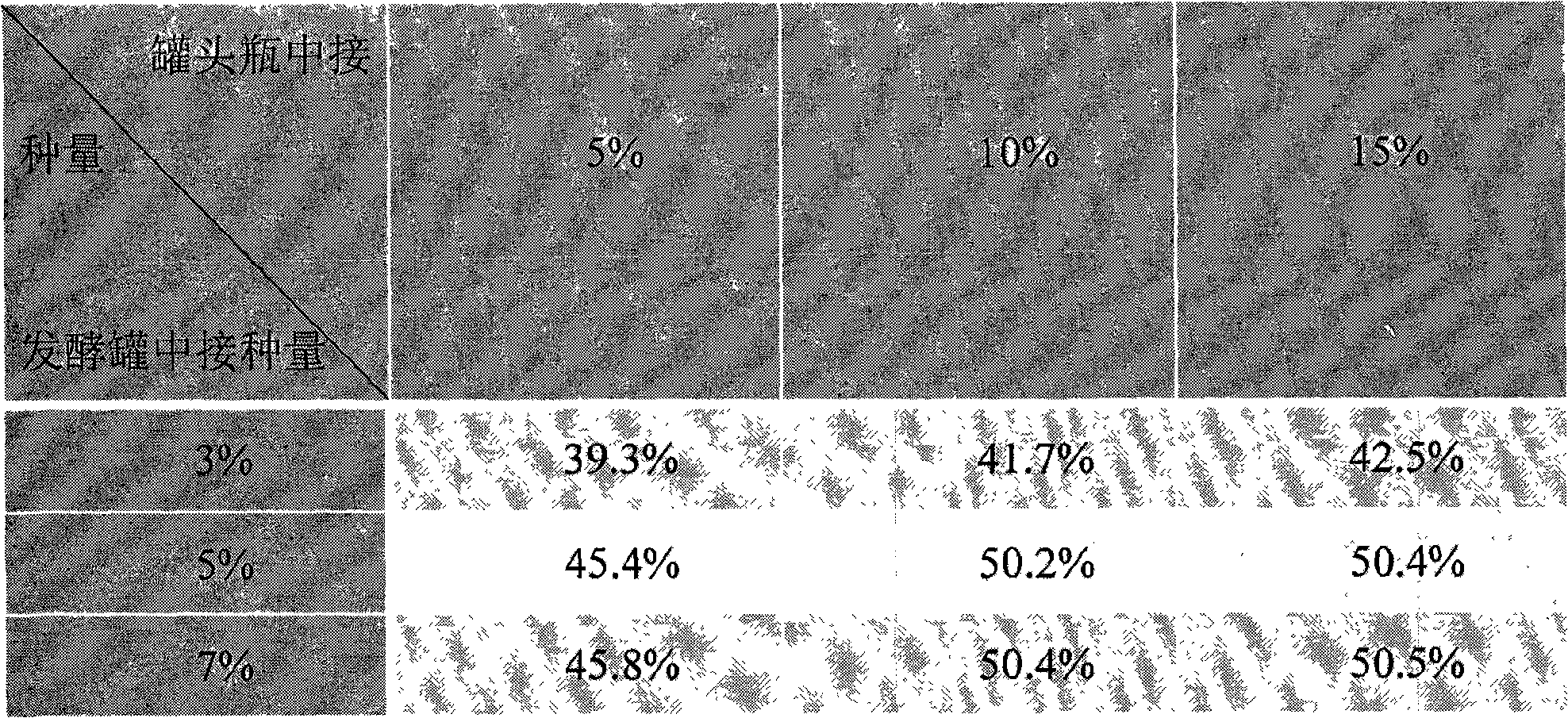
Method for propagation culture and solid fermentation of white-rot fungi
InactiveCN101591620ASimple processEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhacus
The invention relates to a method for propagation culture and solid fermentation of white-rot fungi, which belongs to a method for fungal solid fermentation and comprises the following steps: activation of strains; liquid propagation culture; fermentation tank liquid propagation culture; and solid culture and domestication in a canned bottle, and fermentation in a fermentation tank, wherein the inoculum sizes of the stage of the solid culture and domestication in the canned bottle and the stage of the fermentation in the fermentation tank are 10 percent and 5 percent respectively. The method has the following advantages: the method has simple technical process so as to be directly applied to large-scale fermentation tanks in factories, has strong the pertinence so as to be applied to sewage treatment and mixed white-rot fungi fermentation in the paper industry, and has high use value, high fermentation efficiency, low fermentation cost and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Wood preservative and preparation method thereof
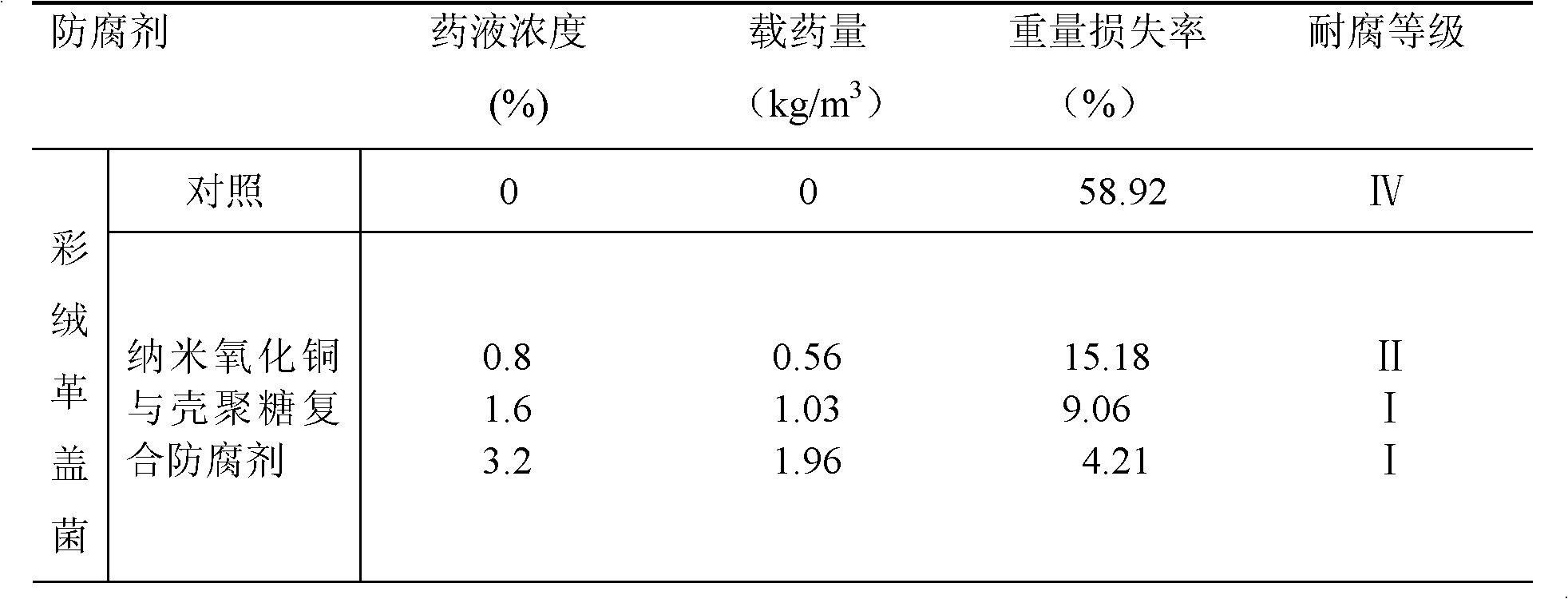
ActiveCN102275192AGood fixation rateImprove permeabilityWood impregnation detailsViscous liquidGloeophyllum trabeum
The invention discloses a wood preservative and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of preservatives. The invention aims to solve the technical problem that a wood preservative has severe environmental harm, low permeability and low erosion resistance in the prior art. The wood preservative is prepared from nano copper oxide, ammonium citrate, distilled water, chitosan and a solution of acetic acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1, mixing the nano copper oxide and the ammonium citrate, adding the distilled water, and stirring to obtain nano copper oxid dispersion; and 2, adding the chitosan into the solution of acetic acid, adding the nano copper oxid dispersion, and stirring to obtain the wood preservative. The wood preservative is black brown viscous liquid and has an obvious bacteriostatic effect on wood decomposing fungi, such as monilinia fructicola, namely Gloeophyllum trabeum, and white rot fungi, namely Coriolus versicolor.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Sandy soil modifier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104844357AAbundant resourcesNo pollution in the processFertilizer mixturesPhytasePotassium
The invention discloses a sandy soil modifier and a preparation method thereof. The sandy soil modifier is prepared from such raw materials in parts by weight as 100-300 parts of saw dust, 15-20 parts of horse (donkey) manure, 6-12 parts of mixed microbial liquid formed by mixing white rot fungi, sulfuric acid bacteria and pathogenic bacteria, 3-15 parts of humic acid, 1.2-3.6 parts of siliceous petrification powder, 5.8-9.2 parts of amino acid powder, 1.6-1.78 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 7.6-9.8 parts of acrylamide, 3.6-7.6 parts of boron-zinc-potassium-calcium, 7.3-11.6 parts of fulvic acid, 3.2-5.6 parts of urea peroxide, 0.4-0.6 parts of lysine, 0.2-0.6 parts of sulfur-containing amino acid, and 0.1-0.3 part of phytase. The sandy soil modifier has the advantages of abundant raw material resources, simple and easy-to-operate production process, relatively low production cost, and no pollution; the environment of the sandy soil and green plants are not contaminated by the sandy soil modifier, the soil is not hardened, and a remarkable soil modification effect can be achieved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF FORESTRY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com