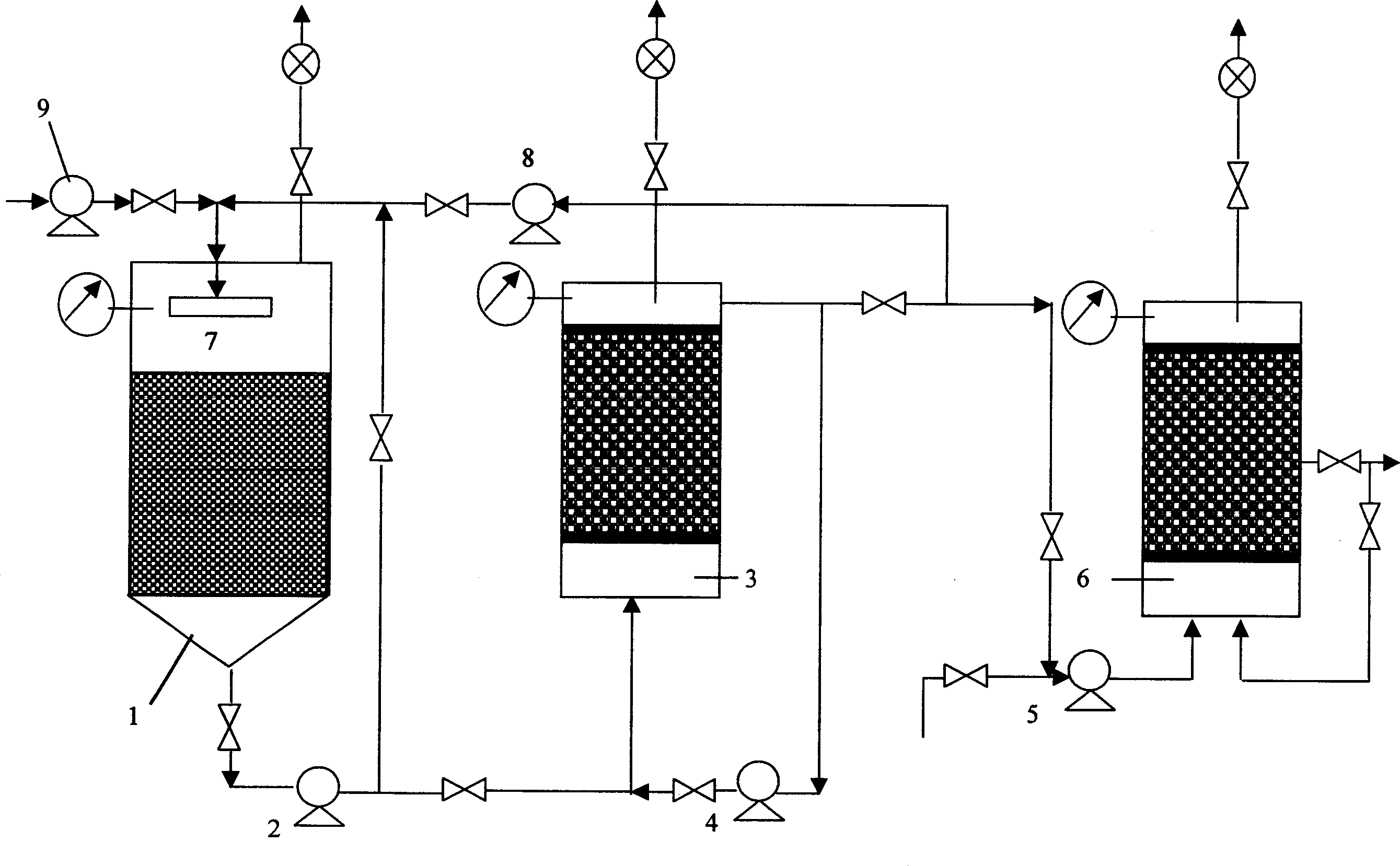
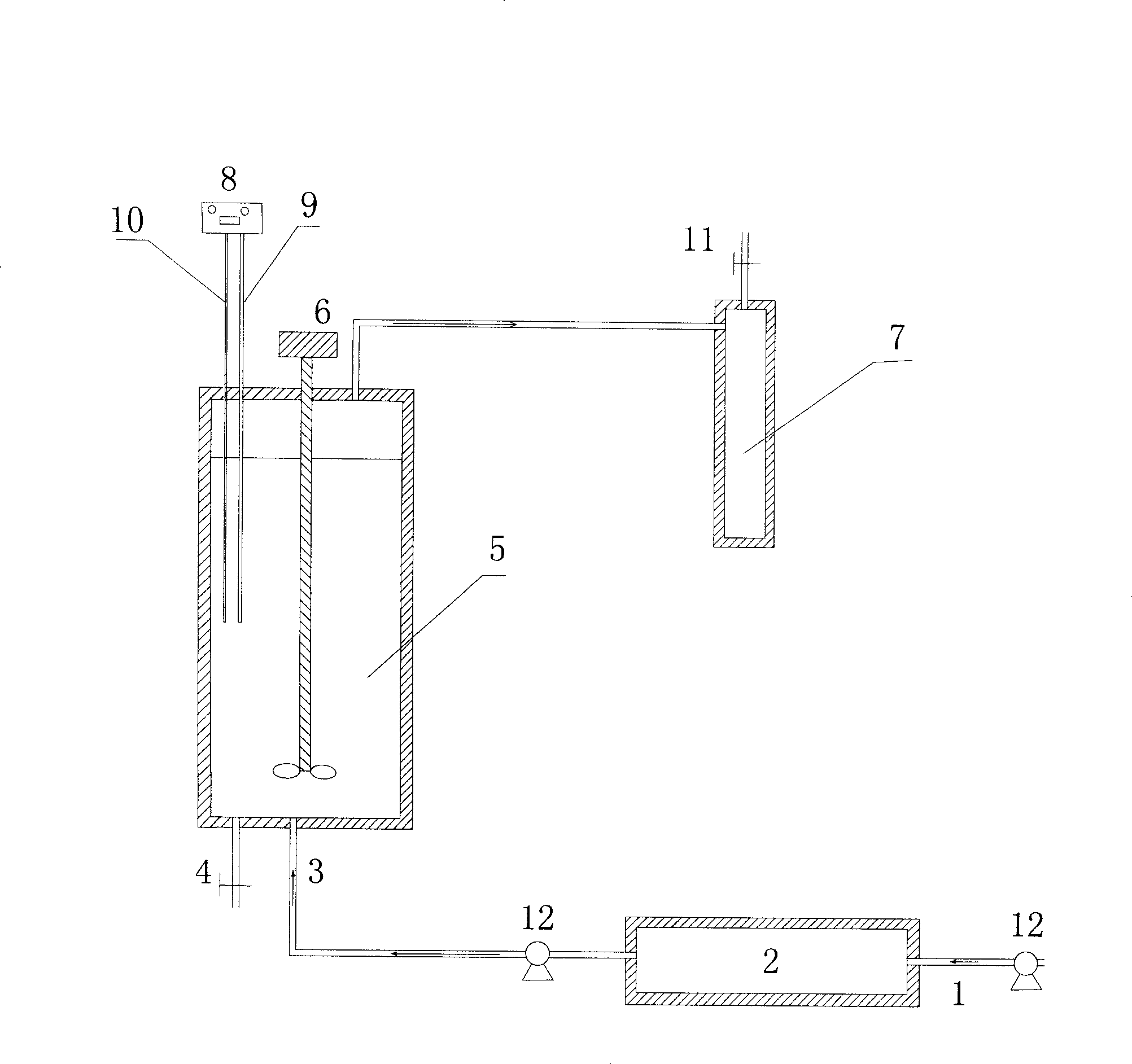
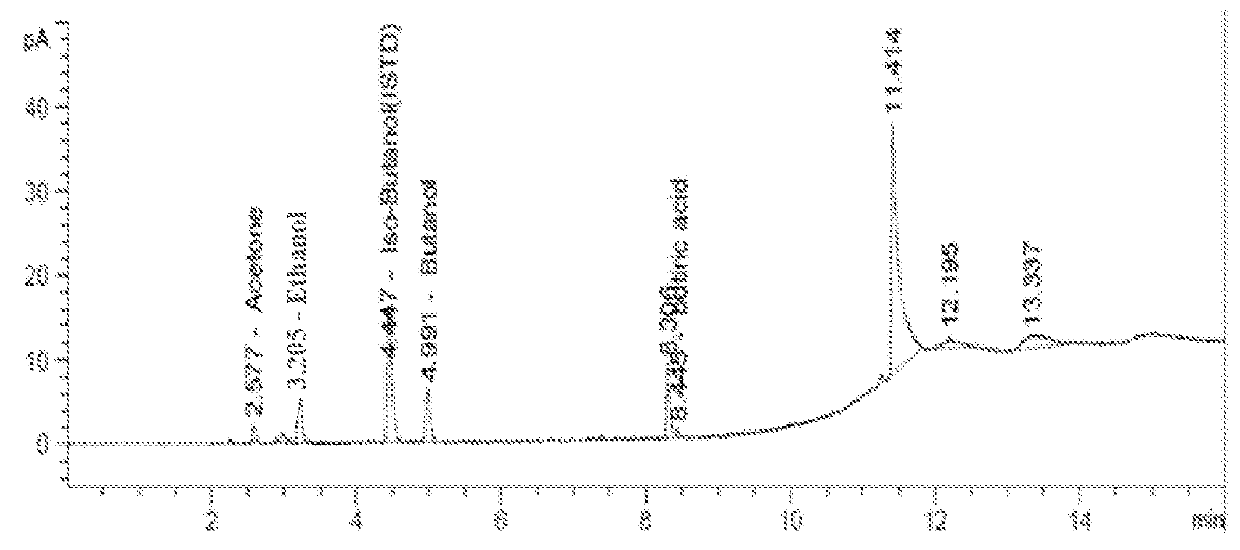
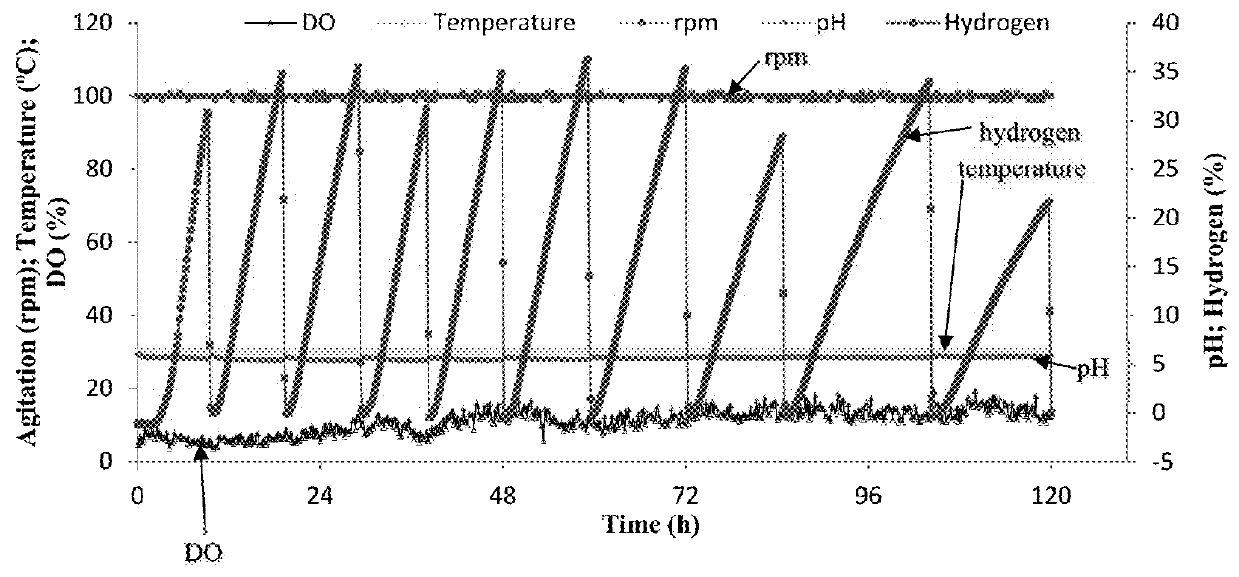
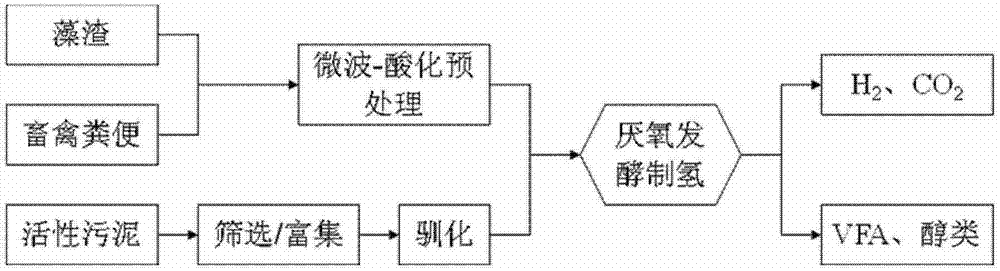
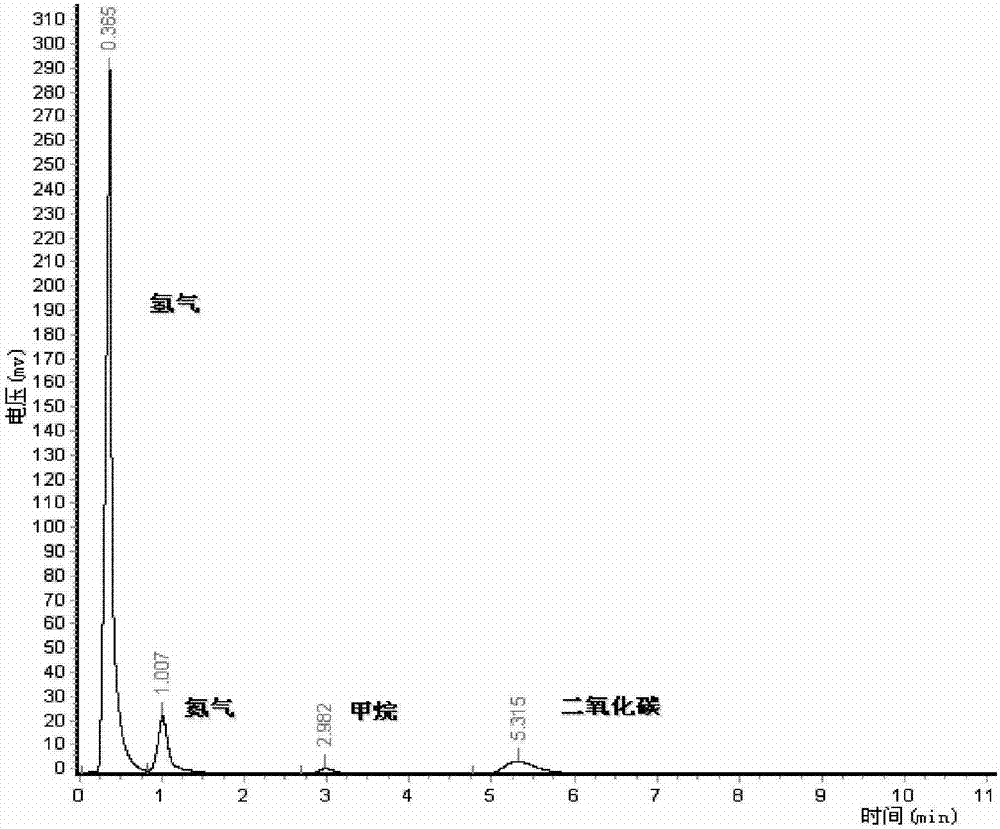
Patents
Literature
127 results about "Fermentative hydrogen production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fermentative hydrogen production is the fermentative conversion of organic substrates to H₂. Hydrogen produced in this manner is often called biohydrogen. The conversion is effected by bacteria and protozoa, which employ enzymes. Fermentative hydrogen production is one of several anaerobic conversions.
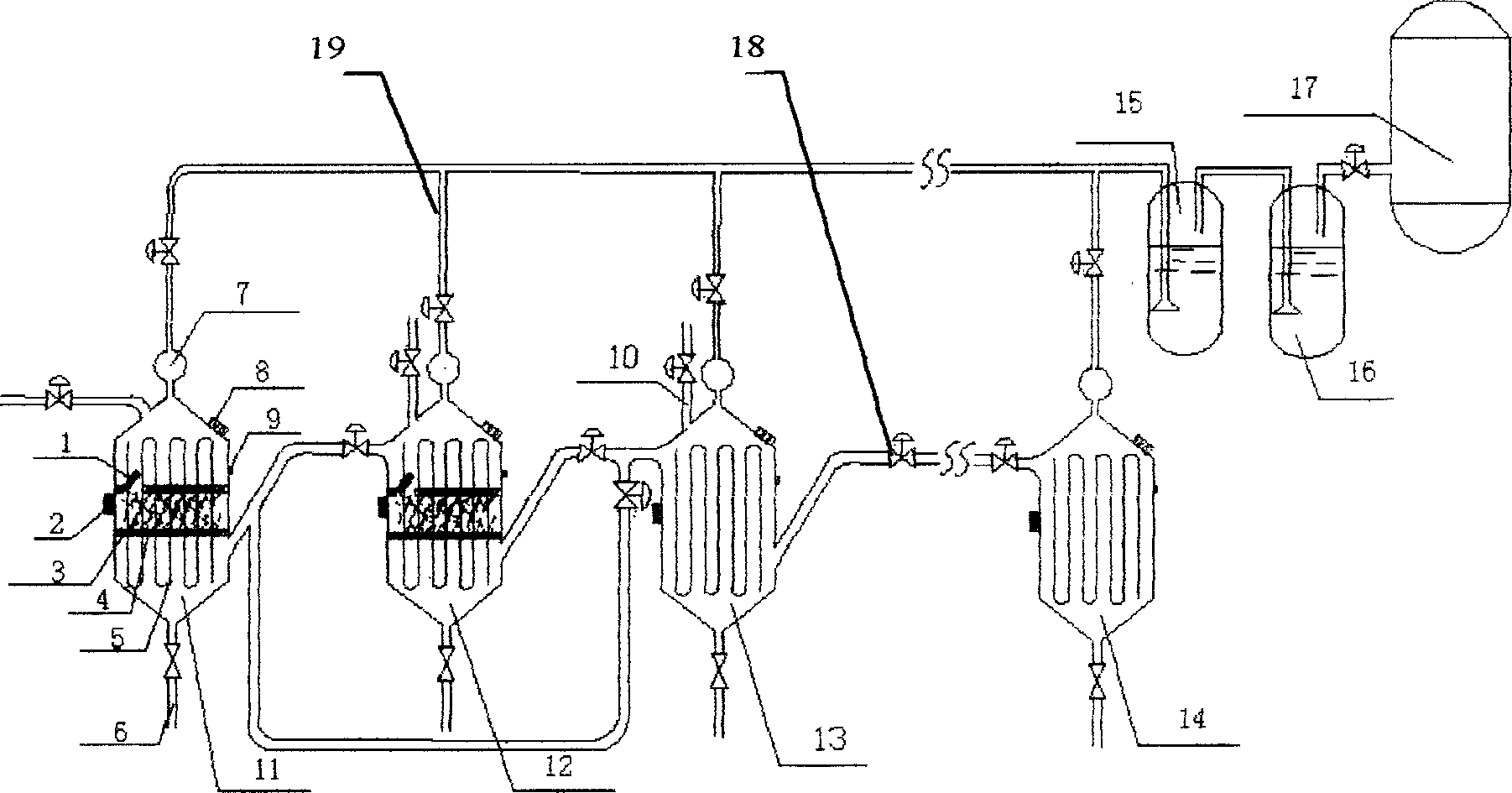
Method for co-producing hydrogen and methane by utilizing dry anaerobic fermentation of solid organic wastes
ActiveCN101638670ARealize continuous productionImprove energy efficiencyGaseous fuelsWaste based fuelMethane productionPre treatment
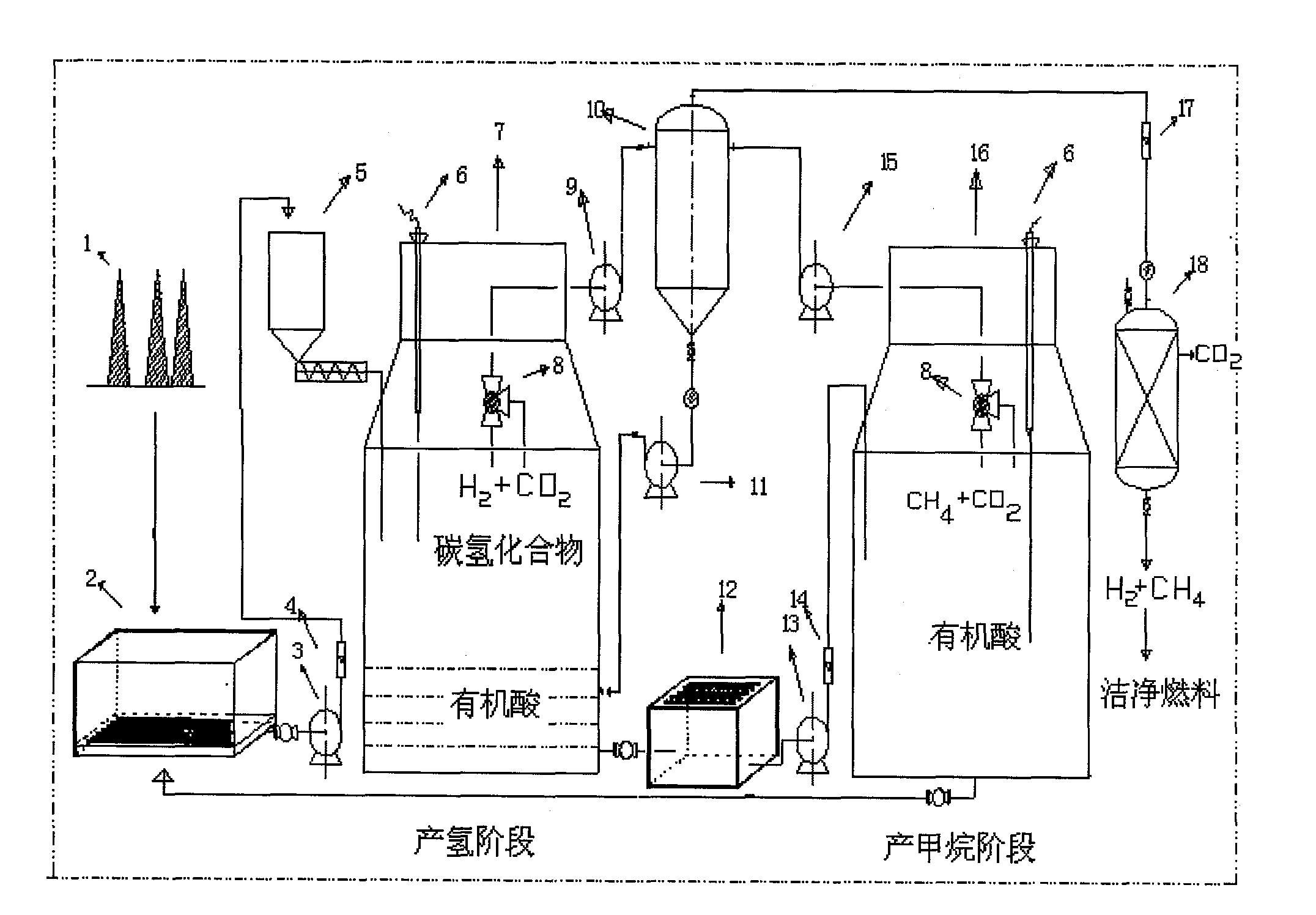
The invention discloses a method for continuously producing hydrogen and methane by utilizing the dry anaerobic fermentation of solid organic wastes, and relates to a method for the anaerobic digestion of urban garbage and agricultural wastes, in particular to a separation method in the stage of producing hydrogen and methane. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment process of dry anaerobic fermentation; (2) hydrogen production process of the dry anaerobic fermentation; (3) methane production process of the dry anaerobic fermentation; and (4) biogas purification. The methodavoids the problems of acid accumulation, inhibition of methanogenic activity, poor adaptability to raw materials and the like existing in the conventional methane-producing technology, and realizes the continuous production of the hydrogen and methane, thus effectively synthesizing the advantages of the pure hydrogen-producing technology and pure methane-producing technology, avoiding the respective shortcomings, improving the energy utilization efficiency of the organic wastes, and realizing the continuous production of biogases with methane as the key part simultaneously when solving environmental problems.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heat treatment-fermented hy drogen-generating method by preparing hydrogen from residual sludge for sewage treatment plant
InactiveCN1850582AImprove dehydration effectHuge marketChemical industryHydrogen productionMethanationSewage
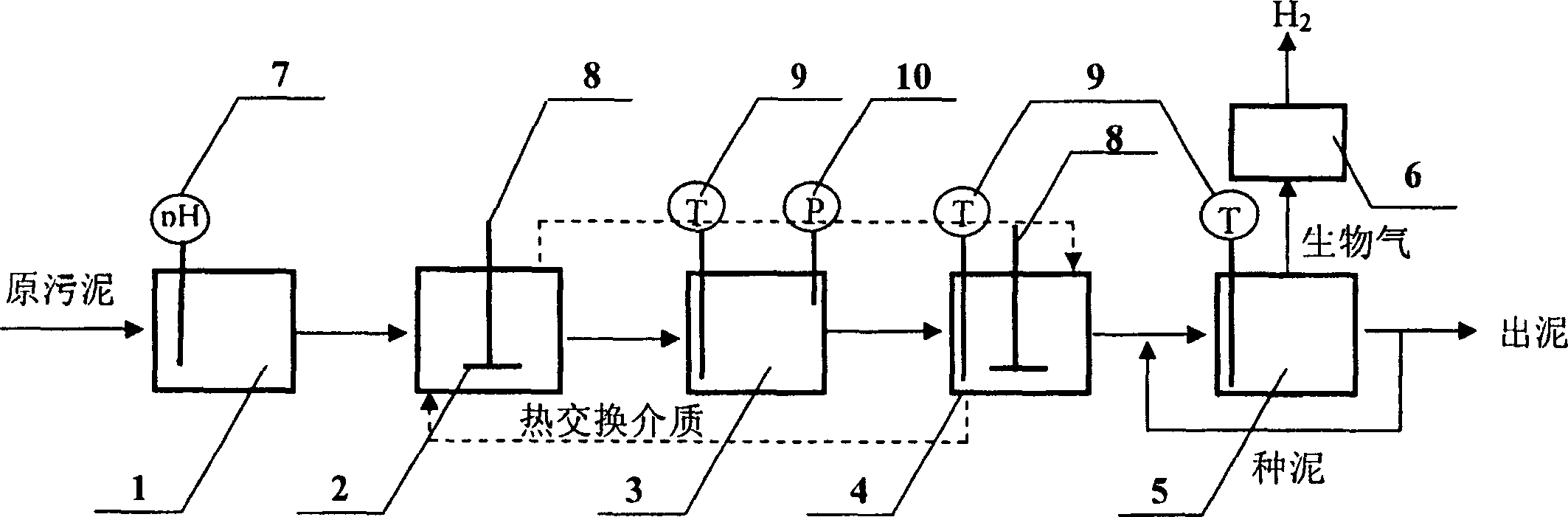
The invention is about a treatment-ferment integrated process and the operation method to produce hydrogen by the remaining sludge of the sewage treatment factory. The process includes the sewage adjustment, the preheating treatment and the anaerobic fermentation. The method is to adjust the density / pH firstly, then to heating pretreatment, last to anaerobic fermenting to produce the H2. The heating treatment can release the organic matter and prevent the methanation in the anaerobic digestion. The hydrogen production ratio can reach 19.42ml / gVS in the condition of temperature 121DEG C, pressure 1.5atm and time 0.5h. The consistency of the hydrogen in the biologic air can reach 47.0%. The sludge content has decreased and the dehydration has been improved. The invention can recovery the organic matter in the form of hydrogen energy.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for co-producing hydrogen and methane by biomass and solid organic waste fermenting method
InactiveCN1858197APollution controlLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh energySource material
The present invention relates to chemical production apparatus, and especially apparatus for co-producing hydrogen and methane with biomass and solid organic waste and through fermentation. The apparatus includes a hydrolysis and acidifying reactor, a hydrogen generating organic acid reactor, methane generating reactor and material pumps connected together. The apparatus can reduce environmental pollution while producing clean energy source material, and has high energy source converting rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Printing and dyeing wastewater pretreatment method based on anoxic zone phase separation technology
ActiveCN103274524AImprove biodegradabilityEfficient removalWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesChemical oxygen demandPretreatment method
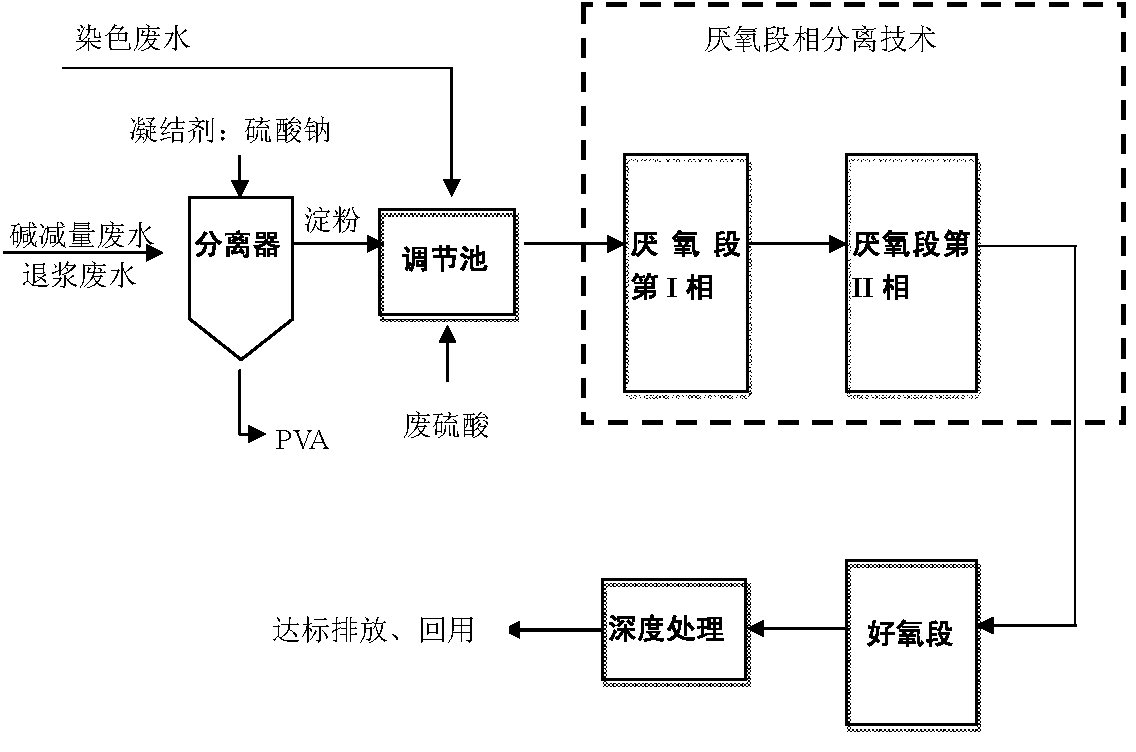
The invention relates to a printing and dyeing wastewater pretreatment method based on an anoxic zone phase separation technology. According to the printing and dyeing wastewater pretreatment method, an anoxic zone is divided into a phase I and a phase II, namely a phase for hydrogen production and acid production through fermentation and a methanogenesis phase; an electron donor is provided by organic matters in the wastewater, and dye is effectively decolored in the phase I by using a sulfate reducing process and the reducing capacity of reduzate, namely the sulfide, therefore the biodegradability of the wastewater is improved; and the organic matters can be efficiently removed in the phase II. As an anoxic phase transformation technology in the printing and dyeing wastewater treatment course, the printing and dyeing wastewater pretreatment method is used for providing a two-phase anoxic system and carrying out pretreatment on the printing and dyeing wastewater; the chromaticity and the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal rates can be effectively increased, the biodegradability of the wastewater can be greatly improved, and the defects that a traditional anoxic process is instable in treatment effect, large in sludge yield and the like are overcome. The printing and dyeing wastewater pretreatment method can be used for effectively removing chromaticity and COD in the printing and dyeing wastewater, the removal rates of the chromaticity and the COD respectively reach more than 95 percent and 60 percent, and the organic loading to subsequent procedures is greatly reduced.
Owner:浙江一清环保工程有限公司
Method for biologic pretreatment of lignocellulose and hydrogen production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
ActiveCN102321671AReduce energy consumptionAvoid damageMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for biologic pretreatment of lignocellulose and hydrogen production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, relates to a method for pre-treating lignocellulose and producing hydrogen through fermentation, and solves the problems of high energy requirement, environmental pollution and production of a fermentation inhibitor existing in the pretreatment of the lignocellulose during the conventional fermentative hydrogen production. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, inoculating white rot fungi in lignocellulose liquid culture medium to culture, washing and drying to obtain pretreated cellulose; and 2, mixing hydrogenogens nutritive salt solution and environmentally-friendly trichoderma rough enzyme solution, and adding into the pretreated cellulose to obtain simultaneous saccharification and fermentation hydrogen production culture medium; then introducing nitrogen; and inoculating seed liquid of hydrogenogens to perform anaerobic fermentation to produce hydrogen. By adopting the method, the energy consumption during lignocellulose hydrogen production is reduced, equipment investment is reduced, the fermentation inhibitor is not produced, damage probably caused to environment during hydrogen production is reduced to the minimum; the relative removal rate of lignin reaches 55.7 percent; and the hydrogen production capacity is 72.6ml / g.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Bacillus alcalophilus and application thereof to fermentative hydrogen production
InactiveCN102373238AIncrease productionHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPretreatment methodSludge
The invention relates to bacillus alcalophilus and an application thereof to fermentative hydrogen production. The steps of sludge and / or organic waste pretreatment and fermentative hydrogen production are adopted. The bacillus alcalophilus is characterized in that in the sludge and / or organic waste pretreatment step, bacillus alcalophilus liquid is inoculated in sludge and / or organic wastes, and bacillus alcalophilus hydrolysis pretreatment sludge and / or organic wastes are obtained after the treatment. In addition, the prepared bacillus alcalophilus hydrolysis pretreatment sludge can also be used as hydrogen production floras to be inoculated into the organic wastes for producing hydrogen through fermentation. A bacillus alcalophilus sludge pretreatment method can be effectively used for screening efficient hydrogen production floras in the sludge, inhabiting the growth of hydrogen consumption bacteria and killing pathogenic bacteria in the sludge and / or organic wastes. The sludge and / or organic wastes through all bacterial strain treatment has / have the large hydrogen generation quantity in the subsequent fermentative hydrogen production step, the purity of hydrogen gas is high, the delay time of the hydrogen production is short, and obvious economic values and development potential are realized.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for producing hydrogen and/or methane through fermentation of fiber wastes and device thereof
InactiveCN101760481ASolve pollutionWidely used valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingFiberLiquid storage tank
The invention provides a method for producing hydrogen and / or methane through fermentation of fiber wastes and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: smashing a straw into a certain grain diameter, placing into a hydrogen production reactor, adding a given amount of water and nutrient solution and then mixing with thermophile bacteria seed liquid together for fermentation to prepare the hydrogen; pumping hydrogen fermentation liquid into a liquid storage tank, continuously pumping into the hydrogen production reactor for fermentation to prepare the methane after pH is adjusted. Because of adopting fiber wastes, raw materials used by the invention have rich resource and low cost, effectively solve the resource problem of biological hydrogen production and overcome the problem that the fiber raw materials of the traditional straw are hard to effectively produce the hydrogen when being not subjected to pretreatment; and the semi-continuous hydrogen production is achieved through the fiber waste dynamic immobilization technology. The invention is easier to popularize and apply by adopting a coupled continuous methane production system and has the advantages of simple and highly-efficient method, energy conservation, low cost and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
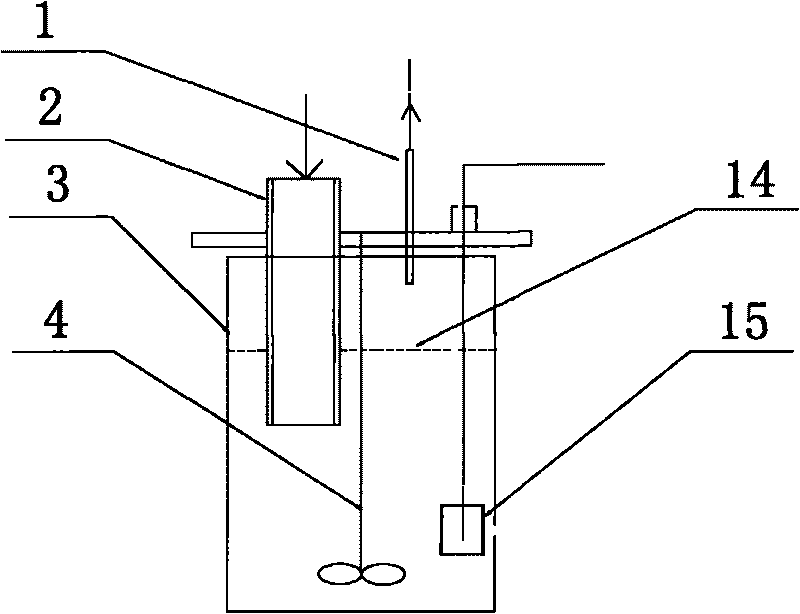
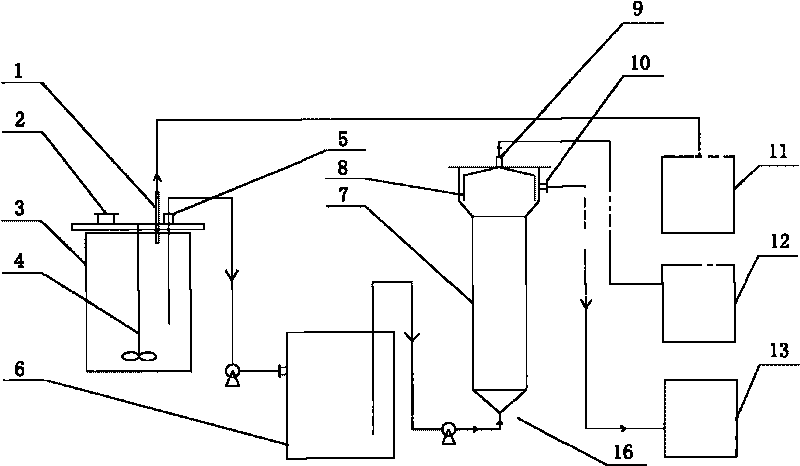
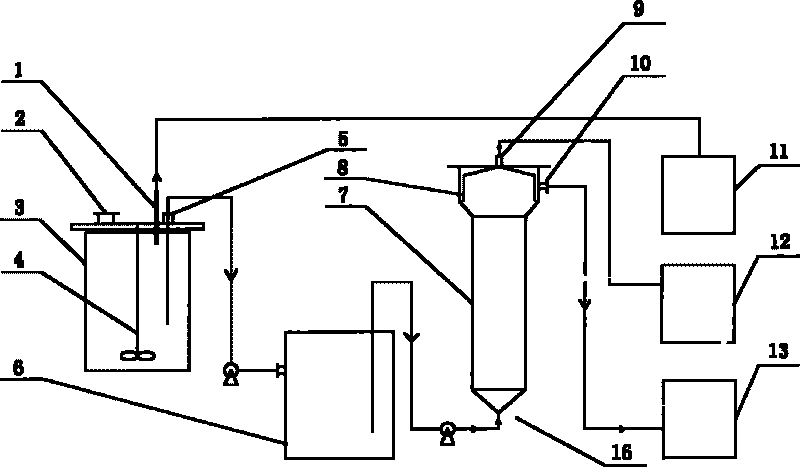
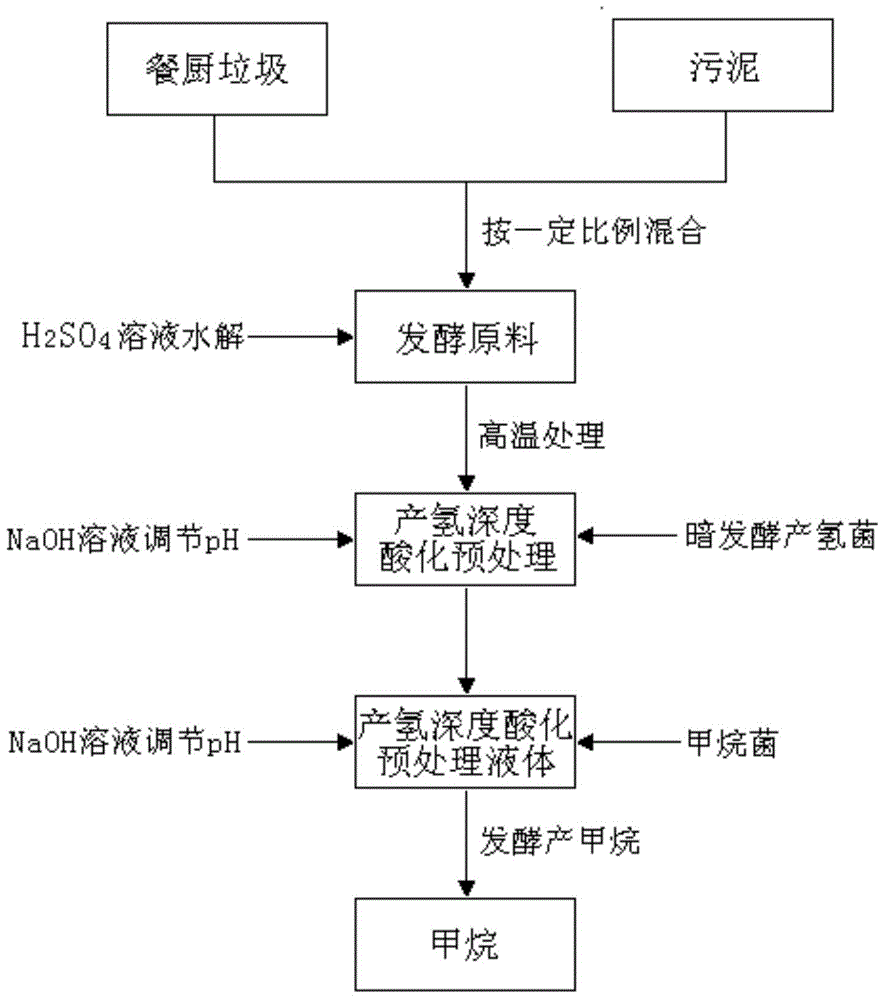
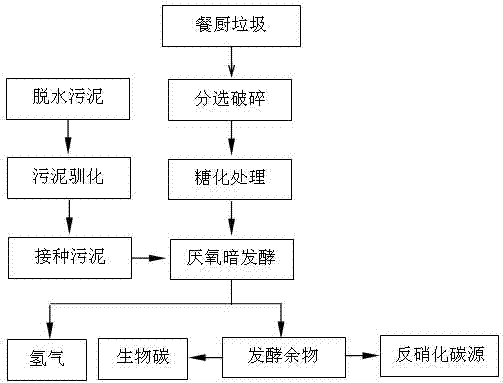
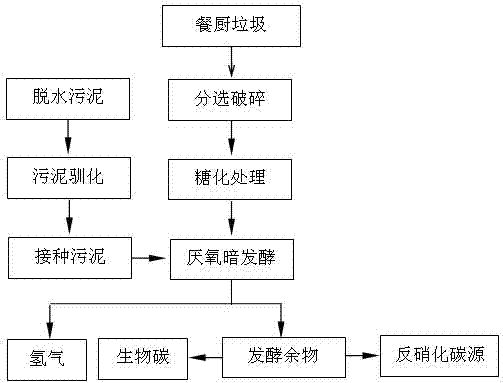
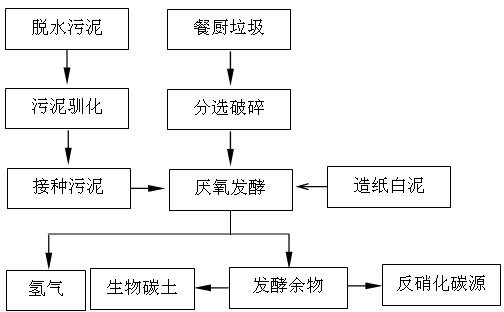
Kitchen waste and sludge hydrogen-producing acidification pretreatment method capable of increasing methane production rate
ActiveCN104561222AIncrease production rateIncrease throughputMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelPretreatment methodSludge
The invention relates to the technology of biomass energy utilization, and aims to provide a kitchen waste and sludge hydrogen-producing acidification pretreatment method capable of increasing the methane production rate. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the kitchen waste and the sludge after crushing pretreatment, using the mixture and a sulfuric acid solution to prepare a mixed liquid, performing hydrolysis on the mixed liquid at 135 DEG C to obtain a starting crude; adding yeast powder into the starting crude, inoculating dark-fermentation hydrogenogens, feeding high-purity nitrogen to build an anaerobic fermentation environment, then performing dark-fermentation hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment at the constant temperature of 37 DEG C, and obtaining a hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment liquid; adding methanogens into the liquid, keeping the anaerobic environment at 37 DEG C, and performing methane fermentation and coproduction. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment is utilized to obviously increase the methane production rate; the rate peak time of the produced methane is reduced by about 50%; the waste treatment and degradation time of the fermentation tank with a unit volume is reduced by about 50%; the waste treatment capacity of the single equipment in unit time is improved by about one time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for co-producing hydrogen and methane by biomass and solid organic waste fermenting method
InactiveCN1858213APollution controlRealize joint productionWaste based fuelChemical recyclingPropanoic acidHigh energy
The present invention relates to hydrogen and methane producing method and especially method of co-producing hydrogen and methane with biomass and solid organic waste and through fermentation. The method includes hydrolyzing and acidifying biomass and solid organic waste to produce pyruvic acid, short chain fatty acid and small amount of H2 and CO2; fermenting the mixture of pyruvic acid and short chain fatty acid under the action of fermenting hydrogenogen to produce great amount of hydrogen as well as small molecular weight side products ethanol, acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid; and further fermenting to convert the small molecular weight side products into methane under the action of methanogen. The apparatus can treat waste effectively to produce clean energy source material, and has high energy source converting rate and high matrix utilizing rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
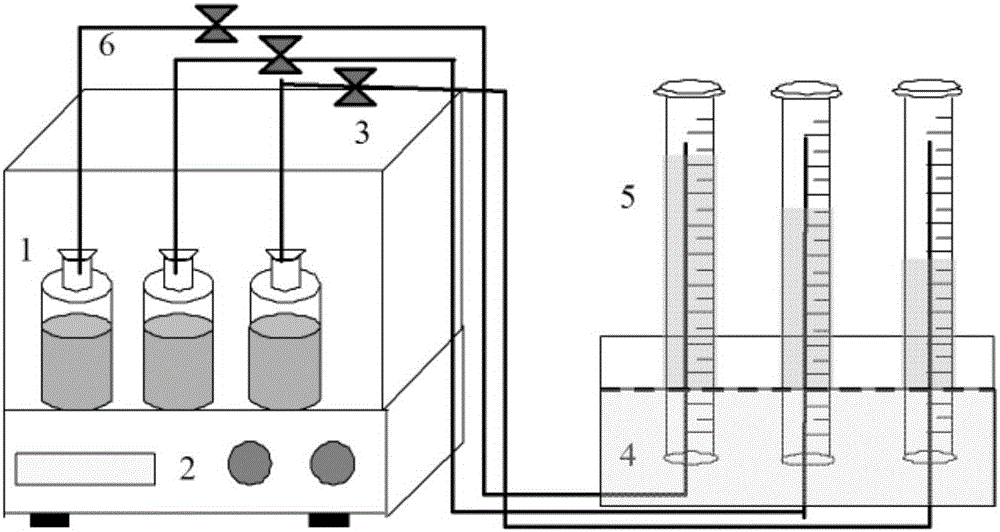
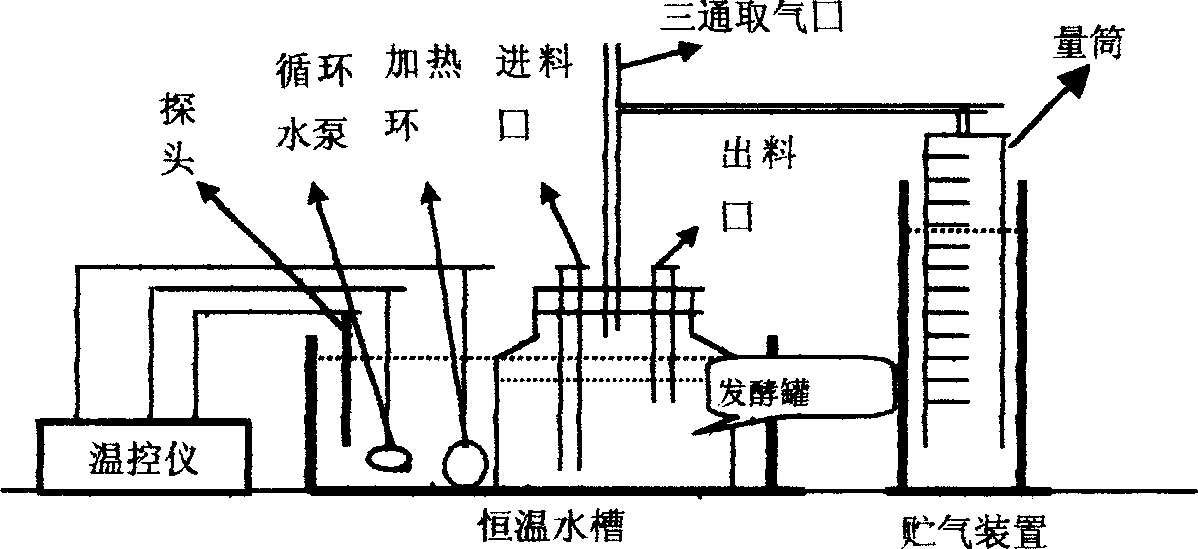
Method and apparatuses for pretreating sewage plant excess sludge by microwave method and producing hydrogen by fermentation
The invention discloses a method and a device for pretreating excess sludge of a sewage plant by a microwave method for fermentation to produce hydrogen. The method comprises the following steps: microwave is utilized to pretreat the excess sludge of the sewage plant for 2 to 20 minutes, then the sludge pretreated by the microwave is placed into a sealed fermentation hydrogen production reactor, hydrogen production seed sludge which accounts for 5 to 15 percent of the volume of the excess sludge is grafted, the temperature is controlled to between 25 and 45 DEG C for fermentation hydrogen production, and hydrogen is produced after 8 to 15 hours. The device comprises a microwave generator, the fermentation hydrogen production reactor and a hydrogen collection device, wherein the top of the fermentation hydrogen production reactor is provided with a hydrogen outlet, while the bottom is provided with a sludge inlet and a sludge discharge outlet; the microwave generator is connected with the sludge inlet of the fermentation hydrogen production reactor; the hydrogen collection device is connected with the hydrogen outlet of the fermentation hydrogen production reactor; and the fermentation hydrogen production reactor is provided with a stirrer and a heater. The method has the advantages that the method has large hydrogen yield and short delay time, can improve the biological redegradation capability of the sludge, can release heavy metals in the sludge, reduce the pollution of landfill treatment to soil, and has simple equipment, low cost and less energy consumption.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen by fermenting organism and alkali mat composite pretreated straw fiber raw erial at two steps
InactiveCN102031276ASolving environmental problems of incinerationSolve environmental problemsMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelFiberRenewable energy technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of renewable energy sources and particularly relates to a method for producing hydrogen by fermenting an organism and alkali composite pretreated straw fiber raw material at two steps. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing the straw fiber raw material and mixing the crushed raw material with a nutritive salt solution to obtain a mixture; (2) introducing a thermophile bacteria seed solution into the mixture and carrying out the first-step anaerobic fermentation to produce hydrogen gas; (3) mixing fermentation residue, water and sodium hydroxide according to the proportion for alkali pretreatment, pre-treating the residue and washing to be neutral to obtain a compound pretreated straw fiber; and (4) mixing the obtained compound pretreated straw fiber with the nutritive salt solution, introducing the thermophile bacteria seed solution into the mixture and carrying out the second-step anaerobic fermentation to produce hydrogen gas. Compared with the traditional method for producing the hydrogen by pre-treating the straw with alkali, the method for producing hydrogen by fermenting the composite pretreated straw fiber at two steps ensures that the hydrogen-producing level is improved by 75 percent, the utilization rate of the raw material is improved to 70 percent from 40 percent and the expense for the alkali pretreatment is reduced by 40 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
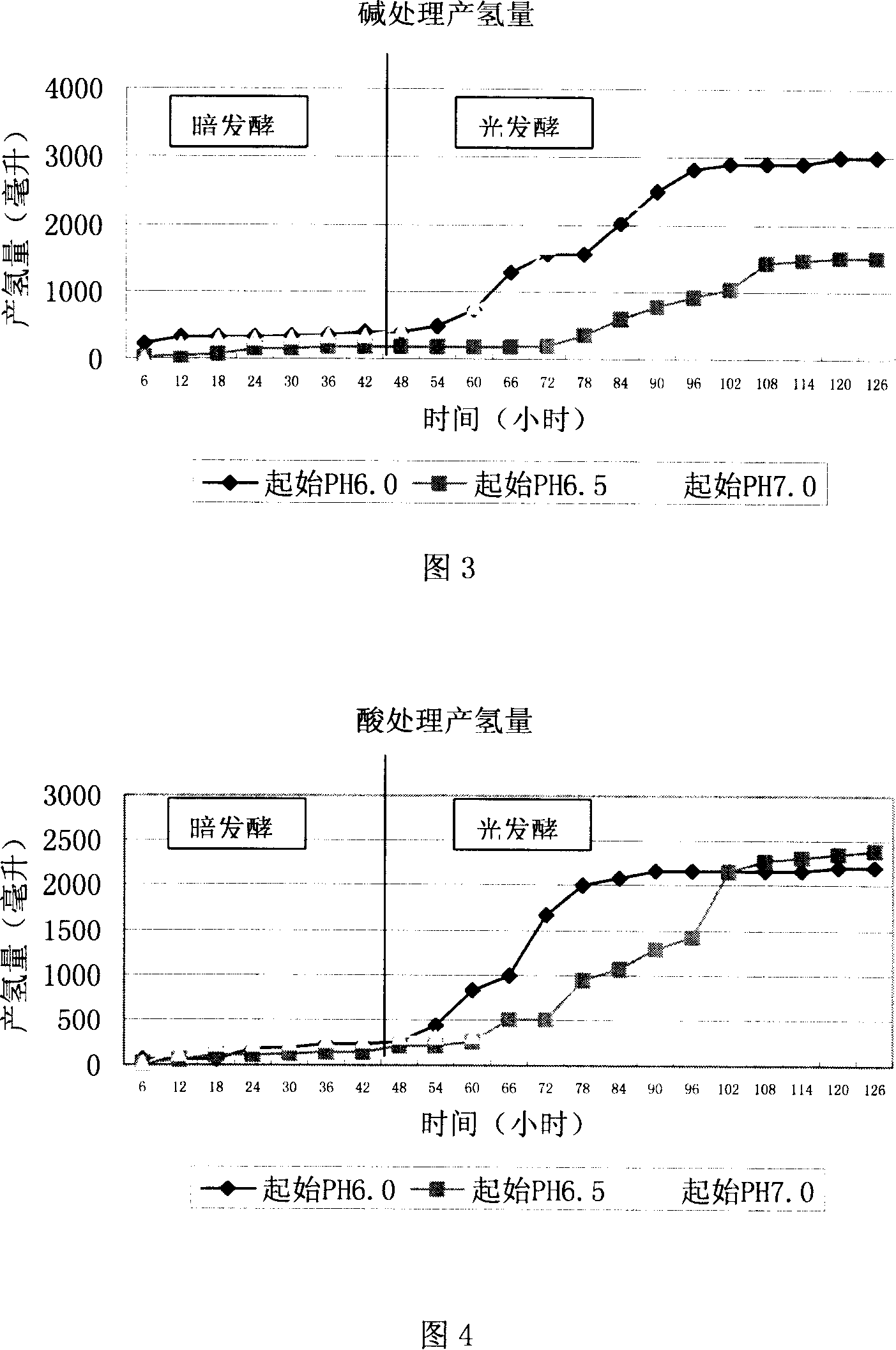
Disintegration method for excess sludge and application of disintegrated sludge in hydrogen production through fermentation
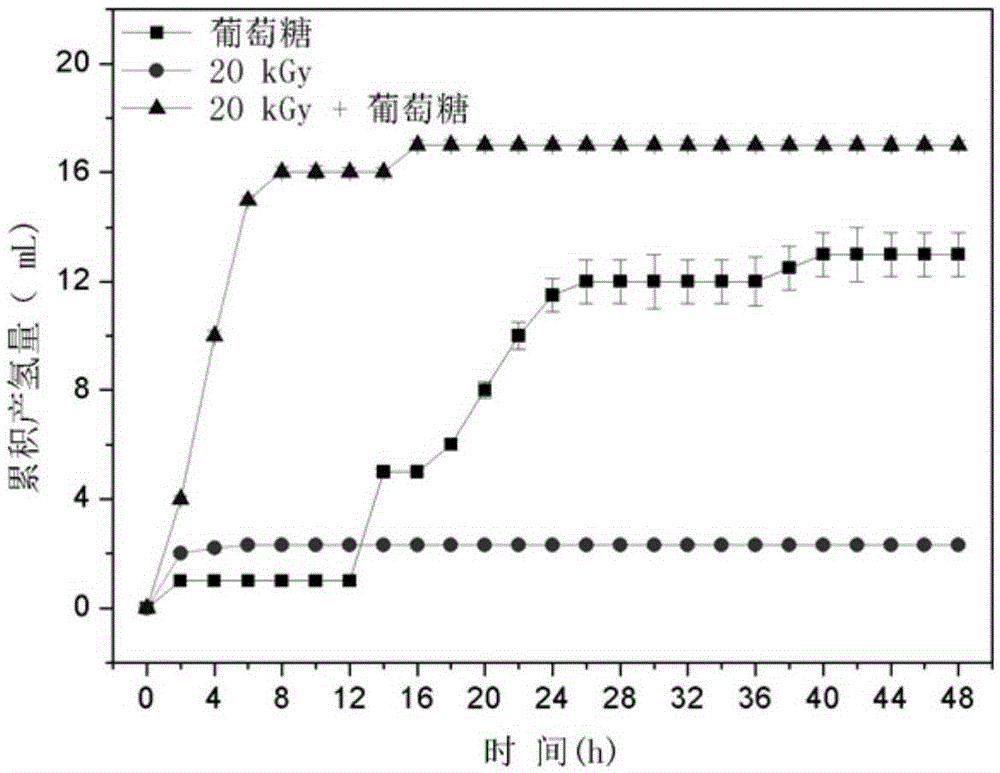
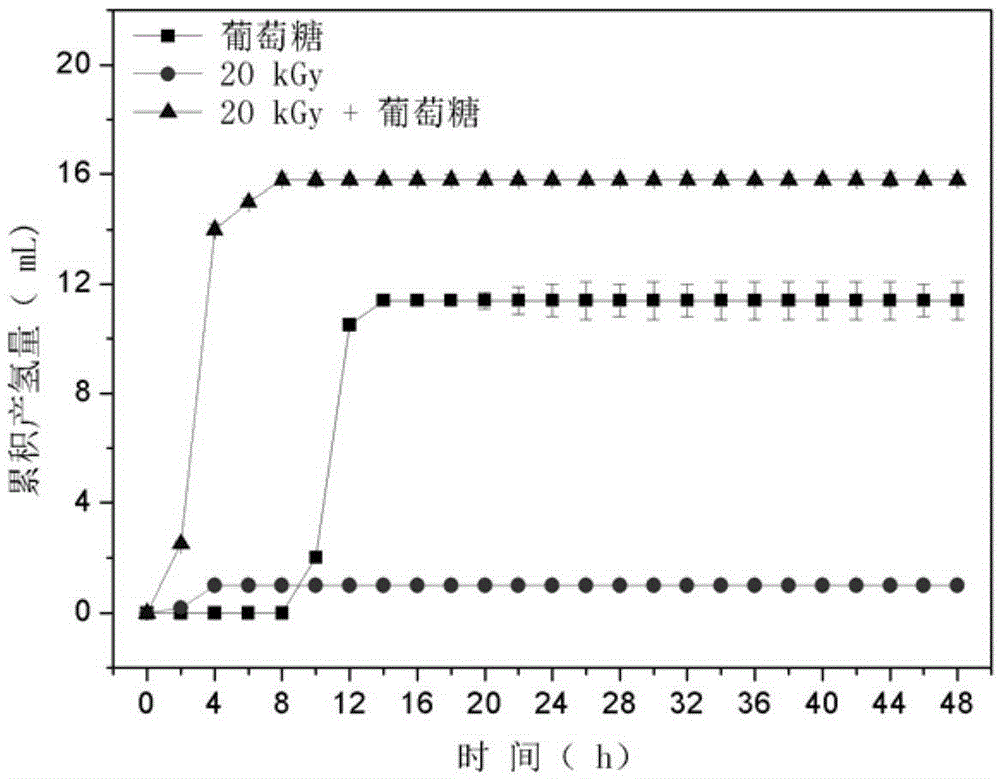
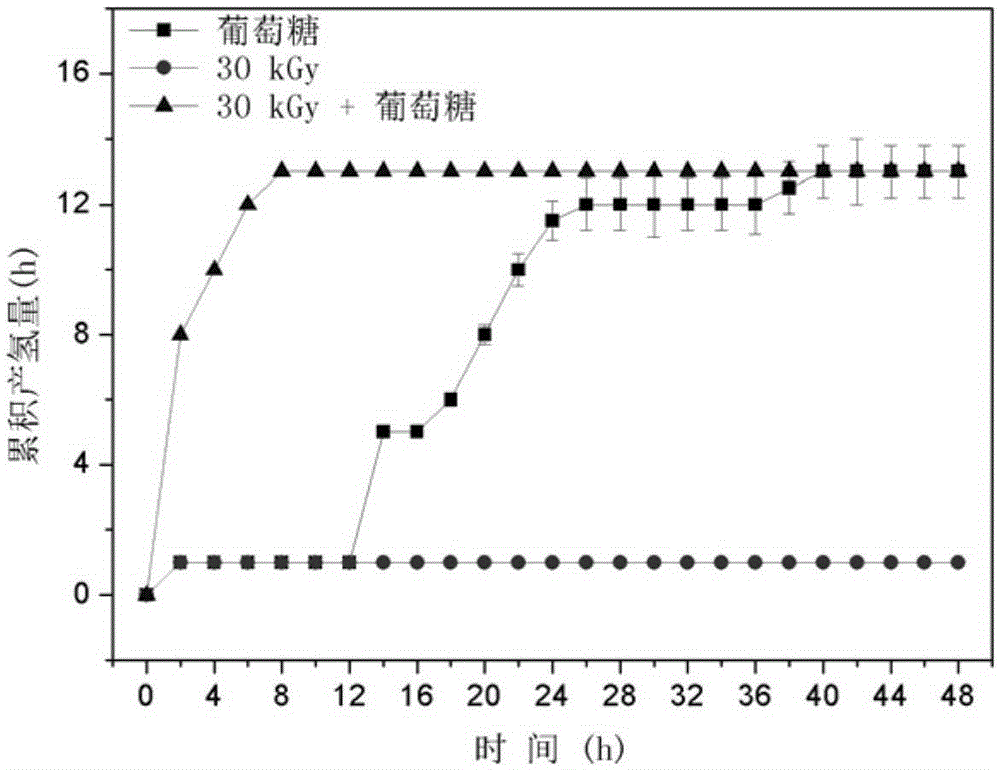
ActiveCN105399291ARelease fullyIncreased concentration of dissolved CODFermentationBiological sludge treatmentSludgeRoom temperature
The invention specifically relates to a disintegration method for excess sludge and application of disintegrated sludge in hydrogen production through fermentation, belonging to the technical field of hydrogen production through biological fermentation. The disintegration method disintegrates the excess sludge through irradiation and alkali coupled treatment and comprises the following concrete steps: adjusting the pH value of the excess sludge to 10 to 12 by using an alkaline solution and carrying out Gamma ray irradiation at room temperature, wherein irradiation dose is 10 to 30 kGy and a radioactive source is 60 Co; and after completion of irradiation, adjusting the pH value of the excess sludge to 7 so as to obtain the disintegrated sludge. According to the invention, through irradiation and alkali coupled treatment, full release of organic components in the excess sludge is promoted; high-efficiency hydrogen production with the disintegrated sludge as a substrate is realized; a cheap and easily available substrate source is provided for the process of biological hydrogen production; and cost for hydrogen production through fermentation is reduced. Compared with the raw sludge, the concentration of soluble COD in a sludge disintegration liquid is increased by 28 to 37 times, the concentration of polysaccharide is increased by 25 to 29 times, and the concentration of protein is increased by 32 to 37 times.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
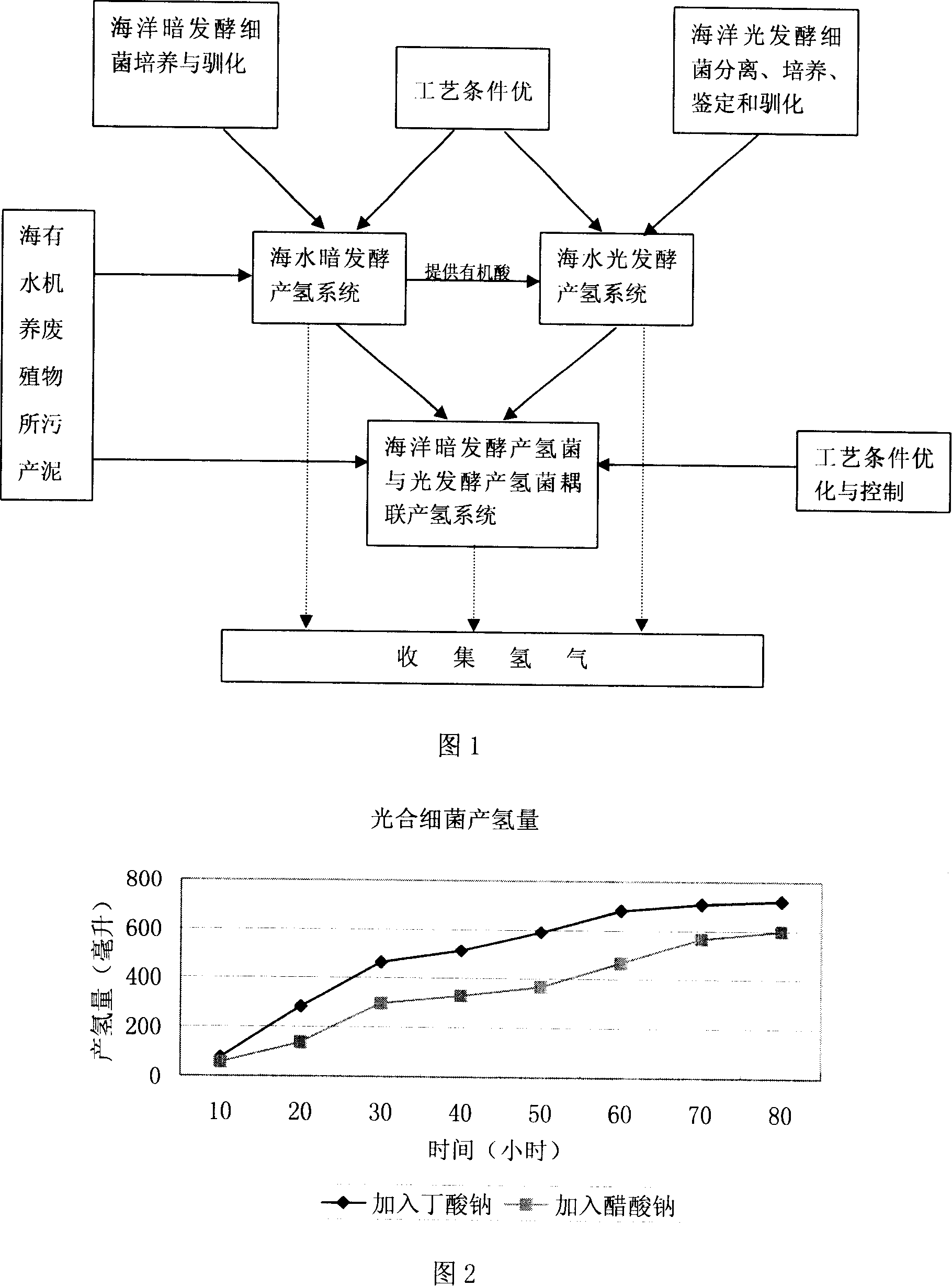
Method for culturing marine photosynthetic bacteria used for light-dark fermentation and coupling hydrogen production
InactiveCN101130786AHigh hydrogen production rateIncrease profitMicroorganism based processesFermentationSludgeSewage
The invention relates to a method for light-blind-fermentation-coupling-producing hydrogen by culturing sea photosynthetic bacterium with sludge and effluent of sea cultivation section, The method comprises the following steps: proceeding with culturing without light in order to produce hydrogen with sludge and effluent of sea cultivation as the culture medium; culturing with light; proceeding with coupling-production hydrogen by adding light fermenting bacteria in the culture medium in order to improve the releasing quantity of hydrogen and recover the production-hydrogen activity of the sea blind fermentation production-hydrogen bacterial. The method not only reduces the pollution of the environment, but also can release the present nervous energy crisis pressure.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium beijerinckii for hydrogen generation via fermentation as well as fermentation method and application of clostridium beijerinckii
ActiveCN104164395ALow costImprove competitivenessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWater bathsBiofuel
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii for hydrogen generation via fermentation as well as a fermentation method and an application of the clostridium beijerinckii. The clostridium beijerinckii is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM), and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.9411. The culture method of the clostridium beijerinckii comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out anaerobic culture on a freeze-stored liquid of the clostridium beijerinckii so as to obtain a cultured bacterial culture solution; centrifuging the bacterial culture solution and then resuspending thalli so as to obtain a resuspended bacterial solution taken as an inoculant source; inoculating the inoculant source into a hydrogen generation culture solution and carrying out photophobic culture on a constant-temperature shaking water bath for generating hydrogen until the hydrogen generation is finished. The clostridium beijerinckii can be fermented to generate hydrogen by utilizing a carbon source and a nitrogen source which are common in natural world and are difficultly utilized by the majority of microorganisms, and ethyl alcohol, butyl alcohol and other biofuels are generated while the hydrogen generation is carried out via the fermentation. The clostridium beijerinckii disclosed by the invention is the first novel multifunctional clostridium beijerinckii strain in the current report, and can be applied to the hydrogen generation of biomass via fermentation, the production of biofuels such as ethyl alcohol and butyl alcohol. Thus, the clostridium beijerinckii disclosed by the invention has a wide application prospect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen through kitchen waste enzymolysis and reinforced dark fermentation
InactiveCN102363794AKeep aliveGood hydrogen production capacityFermentationAmylaseFermentative hydrogen production
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen through kitchen waste enzymolysis and reinforced dark fermentation. The method comprises steps that: impurities are removed from dehydrated sludge discharged from a sewage factory; the sludge is settled for 10 to 20 days under anoxic stress, and is sealed and processed through heat treatment; glucose and peptone are added to the sludge, and the sludge is cultivated and acclimatized under a temperature of 50 to 53 DEG C, such that inoculated sludge is obtained; alpha-amylase and glucoamylase are added to kitchen waste for carrying out saccharification; the saccharified kitchen waste and the inoculated sludge are added into a fermentation bottle, and anaerobic fermentation is carried out under a temperature of 50 to 53 DEG C, such thathydrogen is produced; when the gas production is almost stopped, the reaction is stopped. According to the invention, alpha-amylase and glucoamylase are used for carrying out pre-treatment upon kitchen waste for a short time, such that a fermentation substrate micromolecular glycan which is rich and easy to utilize is provided for hydrogenogens. Therefore, fermentation time is shortened, and hydrogen yield is improved. The method provided by the invention has advantages of simple technology, fast starting, and low cost.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Biohydrogen production method and device adopting hydrophyte and animal manure light-dark cascade coupling
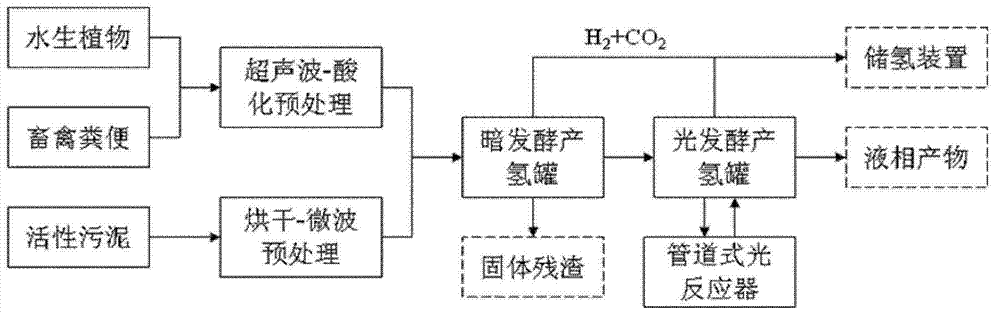
InactiveCN102766571AIncrease productionReduce startup timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActivated sludgeVaccination
A hydrogen preparation method adopting hydrophyte and animal manure light-dark coupling anerobic fermentation comprises the following steps: hydrophyte and animal manure which are subjected to composite ultrasonic-acidic treatment are mixed according to the proportion of 2:1-10:1 and then added into a dark fermenting hydrogen production tank, dried activated sludge (pH 5-7) subjected to microwave pretreatment is added as a bacterial source, the vaccination mass ratio of the bacterial source is 15-30 percent, nitrogen is pumped in to eliminate air a hydrogen production device, and continuous fermenting hydrogen production is carried out in the temperature of 30 DEG C-50 DEG C; and fermentation liquor of the dark fermenting hydrogen production tank enters into a light fermenting hydrogen production reactor, photosynthetic bacteria is vaccinated in a light fermenting hydrogen production tank, the vaccination mass ratio of the photosynthetic bacteria is 5-15 percent, the pH of the fermentation liquor is 7.0-8.0, a yellow-light lamp provides lighting, and light fermenting hydrogen production is carried out in the temperature of 30 DEG C-45 DEG C. The invention further provides a device for implementing the above method. The method provided by the invention effectively improves the hydrogen yield of organic wastes.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Kitchen garbage treatment and fermentation process
InactiveCN112620317AHigh purityReduce pollutionFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSolid waste disposalOil and greaseSludge
The invention belongs to the technical field of kitchen garbage treatment, and particularly relates to a kitchen garbage treatment and fermentation process. The process comprises the following steps of performing oil-residue separation on swill generated after dehydration in kitchen garbage, performing oil-water separation treatment on swill greases in an oil-water separation tank, and finally performing water purification treatment, so that the extracted swill greases are high in purity and free of impurity doping. Meanwhile, filtered wastewater can be recycled, the production cost is reduced, the environmental pollution is reduced, during sewage treatment, sludge precipitated from sewage can be mixed with the crushed and sieved kitchen garbage for heat treatment, a mixture after heat treatment is used as a source of hydrogen-producing bacteria and a hydrogen-producing matrix, the obtained mixed matrix is placed in a closed fermentation tank for room-temperature anaerobic fermentation hydrogen production, the fermentation process is carried out in a closed reactor, and fermentation residues can be used for producing biogas through methanation anaerobic fermentation or producing fertilizers through aerobic composting.
Owner:深圳茂元环保科技有限公司
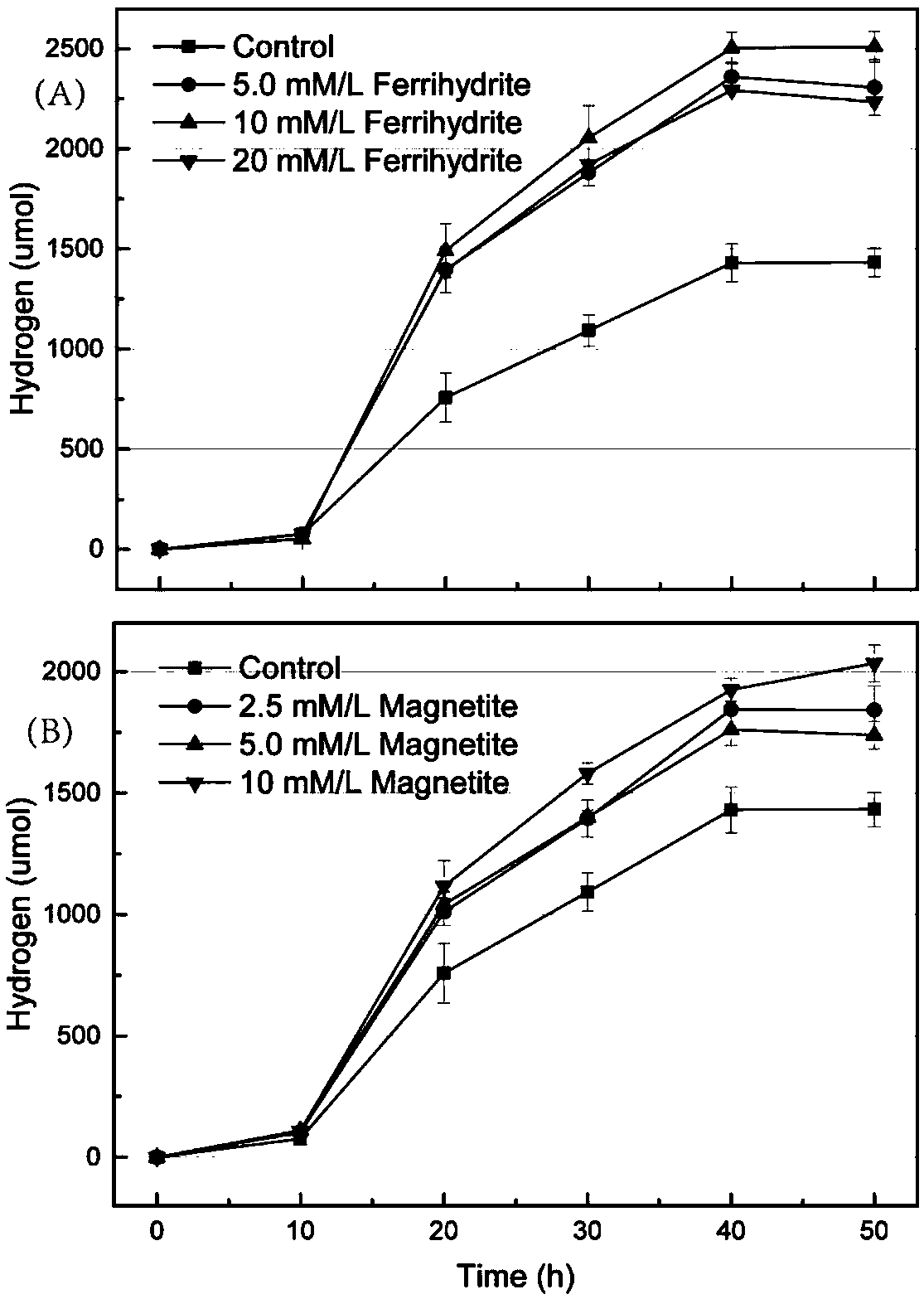
Method for improving hydrogen yield of hydrogenogens
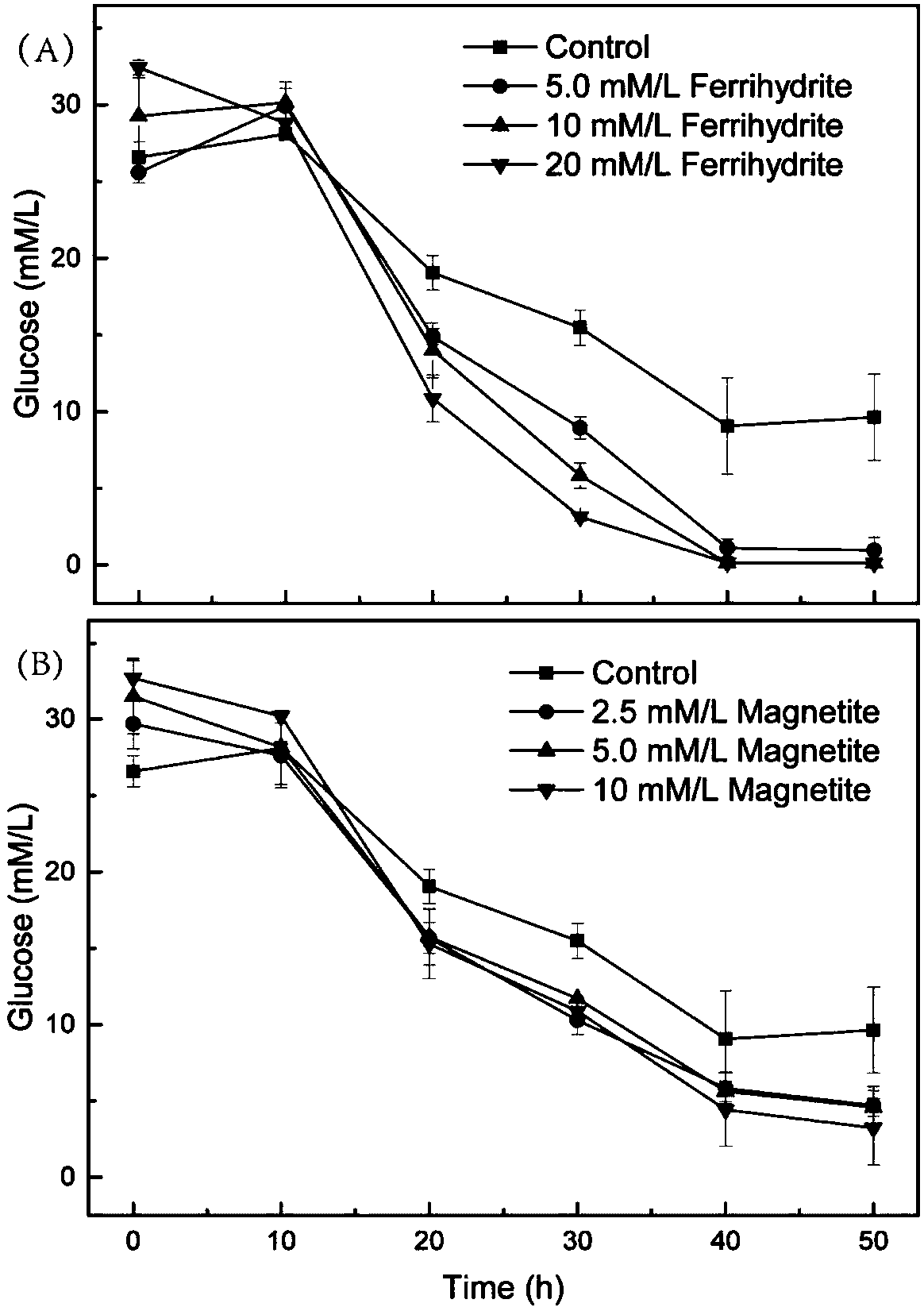
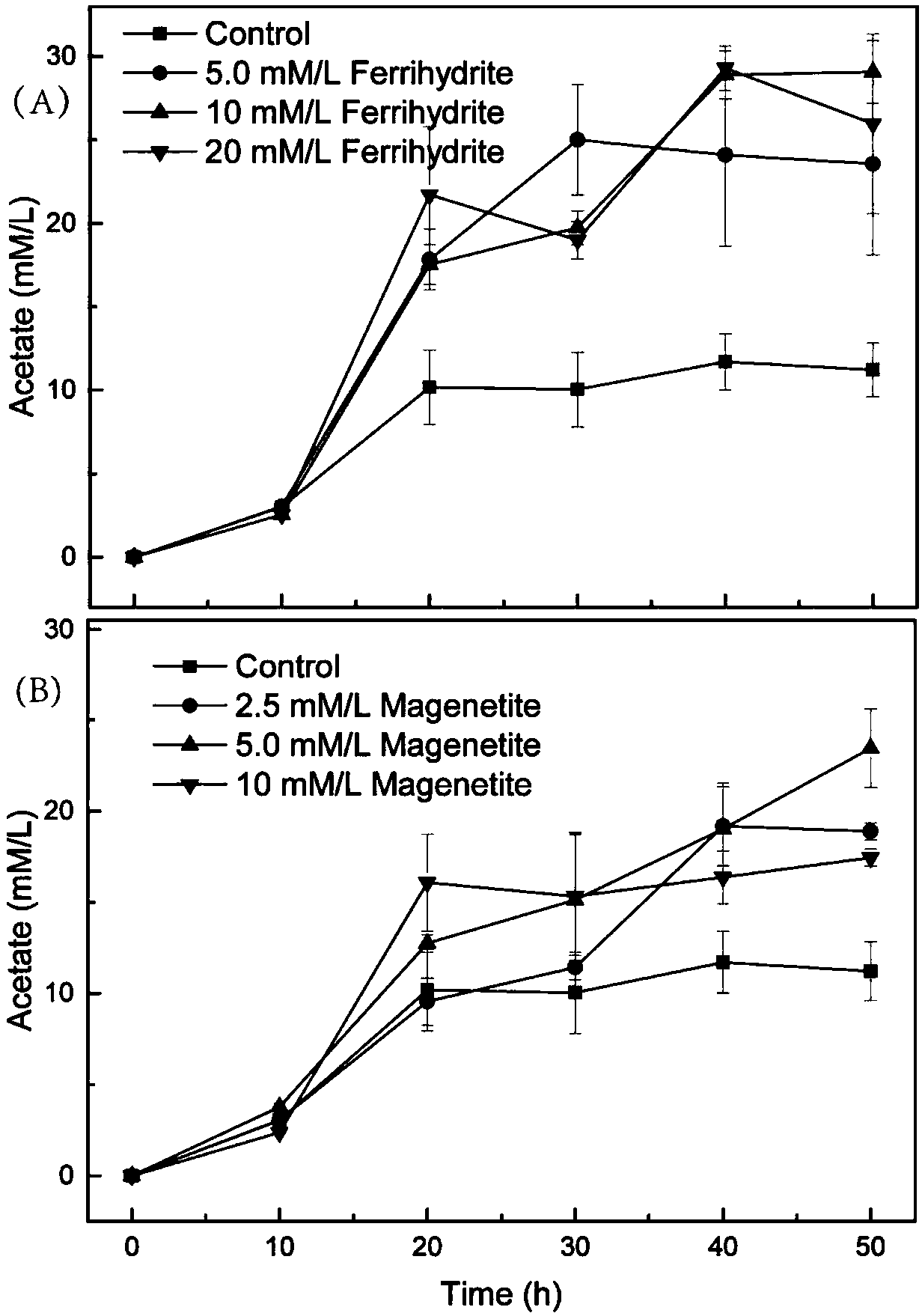
ActiveCN107904263ANo cost reductionLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationMetaboliteMagnetite
The invention belongs to the field of microbial technology application, and particularly relates to a method for improving the hydrogen yield of hydrogenogens. The hydrogenogens strains are inoculatedinto a culture medium containing 2.5 to 20 mmol / L ferriferous oxides; through dark fermentation culture, the great-quantity hydrogen generation of the hydrogenogens strains can be realized. Through the addition of ferrihydrite and magnetite, the growth of hydrogen production clostridium C.pasteurianum is promoted; the C.pasteurianum substrate conversion efficiency is accelerated; the yield of metabolite products of hydrogen gas, acetic acid and butyric acid is improved. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the hydrogen yield of the hydrogen production clostridium is greatly improved; the theoretical support is provided for the large-scale production of microbial dark fermentation hydrogen production.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
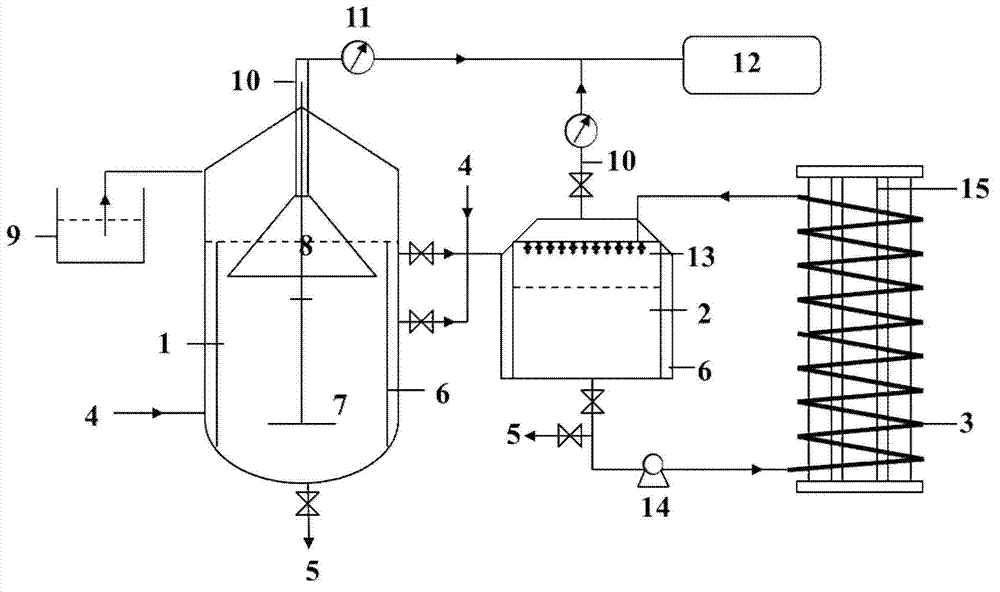
Device and method for temperature-controlled aerobic-anaerobic coupled biological hydrogen production
InactiveCN102827760AStart fastGuaranteed uptimeGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelTemperature controlBiochemical engineering
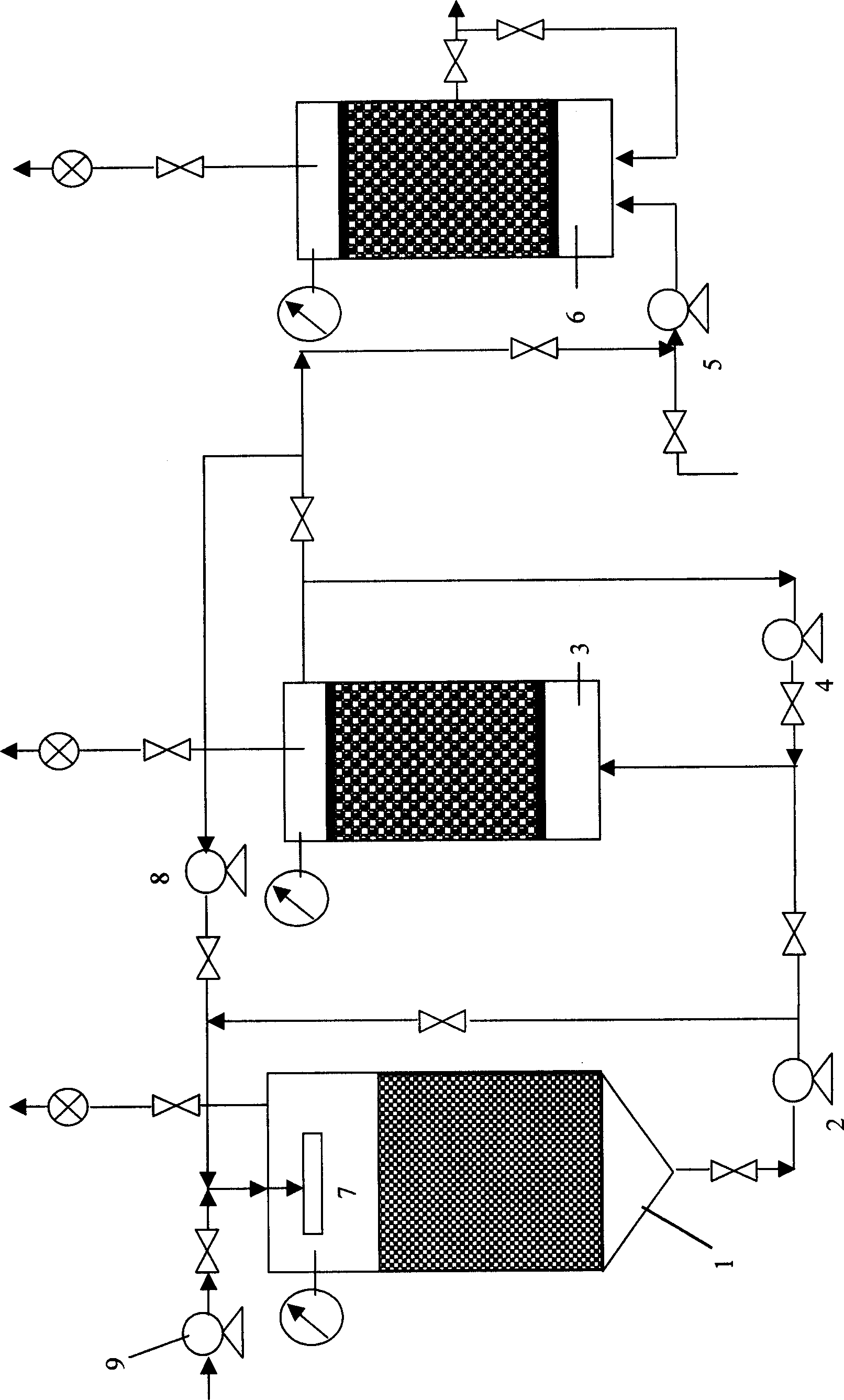
A device for temperature-controlled aerobic-anaerobic coupled biological hydrogen production comprises a fermentation tank which is installed on a base, wherein the base is provided with a universal wheel which can rotate for 36 degrees and a wheel lock; one side of a fermentation tank body is provided with a feed port, and the other side of the fermentation tank body is provided with a discharge port; the inner part of the fermentation tank is a double-reaction area structure which consists of an aerobic pretreatment chamber and a fermentation hydrogen production chamber, and valves which can be opened from one direction are respectively arranged in the middles of the aerobic pretreatment chamber and the fermentation hydrogen production chamber; a baffle is installed at the inner wall of the fermentation tank; the fermentation tank body is of a double-layer structure, namely two independent interlayers wrapping the aerobic pretreatment chamber and the fermentation hydrogen production chamber; heat transfer liquid is filled in interlayers; the two interlayers are respectively provided with a liquid inlet valve and a liquid discharge valve, and connected by pipelines to form a temperature control layer; and a nanophase ceramic membrane roller penetrates through the center of the tank body, and the gas outlet of the nanophase ceramic membrane roller is connected with a gas collection device. The invention further discloses a method for biological hydrogen production utilizing the device.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Combined pretreatment method for synergically degrading straw cellulose through compound florae and producing hydrogen through fermentation
InactiveCN106119289ARealize resourcesHigh hydrogen production rateFermentationCellulosePretreatment method
The invention relates to a combined pretreatment method for synergically degrading straw cellulose through compound florae and producing hydrogen through fermentation, belonging to the technical field of processing of solid waste. The combined pretreatment method for combining the compound florae with the combined pretreatment of sodium hydroxide and acidification steam explosion is utilized for carrying out efficient anaerobic fermentation biological hydrogen production for the first time. The method comprises the steps of firstly grinding straws into 30-60-mesh powder, carrying out sodium hydroxide pretreatment, finally carrying out acidification steam explosion pretreatment to obtain pretreated straw powder, adding the compound florae, culturing the mixture in an intermittent fermentation hydrogen production testing device, and carrying out the efficient anaerobic fermentation biological hydrogen production. According to the combined pretreatment method, by virtue of the combined pretreatment of sodium hydroxide and acidification steam explosion, the hydrogen production rate and the cellulose degradation rate of the straw fermentation hydrogen production are increased, and the recycling and the energy regeneration of lots of straws are realized.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
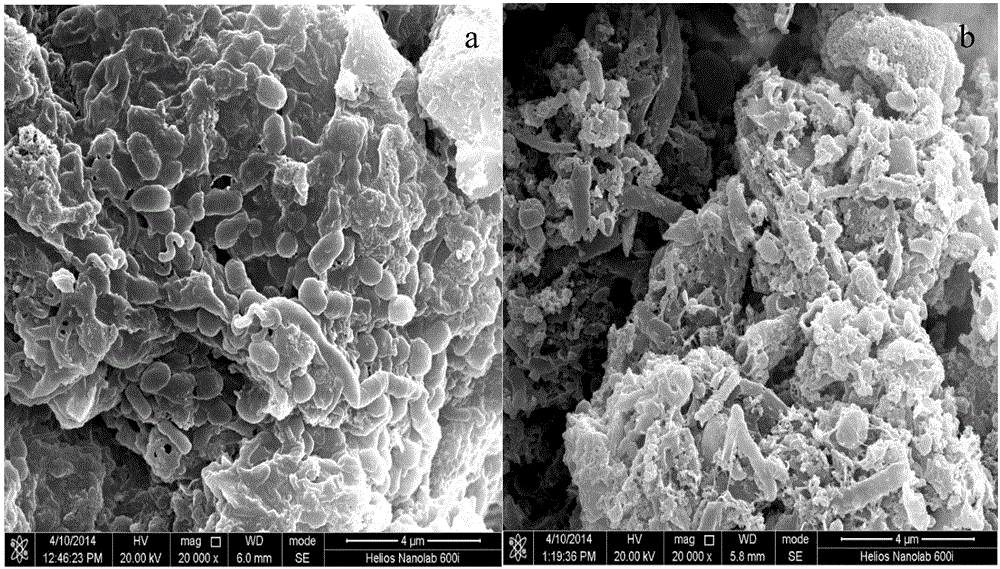
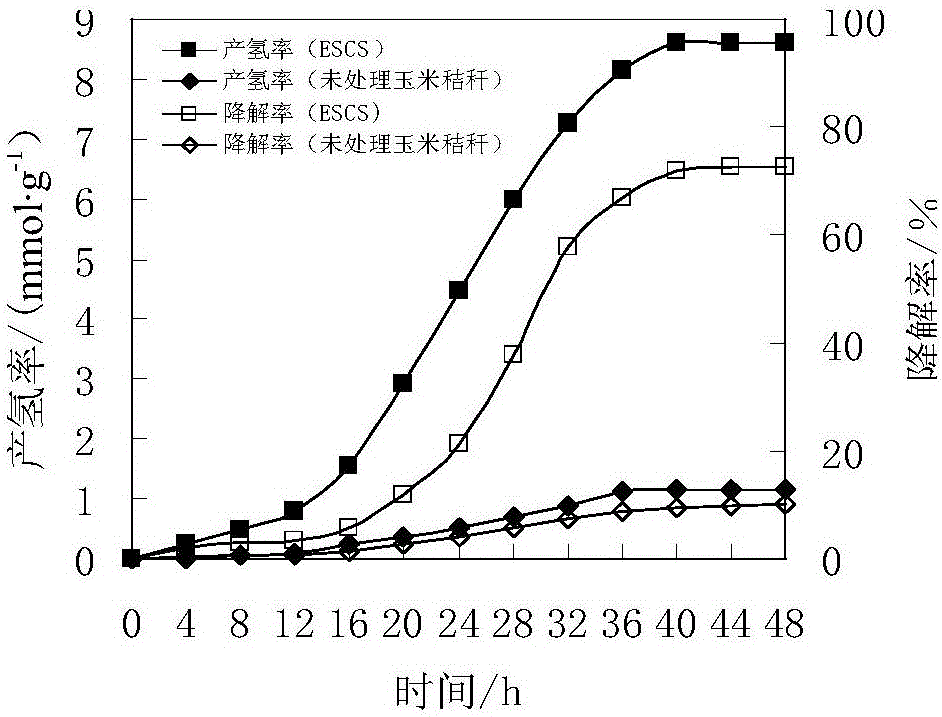
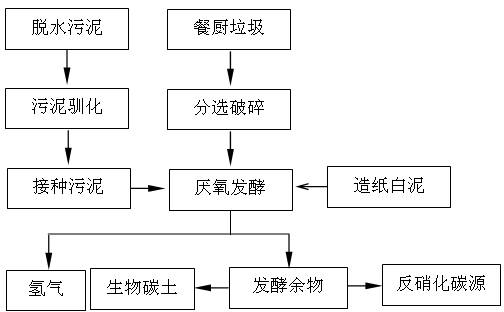
Application of papermaking white clay in biological fermentative hydrogen production
The present invention discloses an application of papermaking white clay in biological fermentative hydrogen production, which is characterized in that: the papermaking white clay is used as pH buffering agent and an inorganic nutrient of hydrogenogens; and the papermaking white clay is mixed with kitchen garbage and dewatered sludge of a sewage plant for performing biological fermentative hydrogen production. The application of papermaking white clay in biological fermentative hydrogen production has the advantages of simple operation and low cost. The papermaking white clay is adopted for performing reinforcement treatment for a kitchen garbage fermentation hydrogen production system. Not only is pollution of the papermaking white clay reduced, but also stability and gas production rateof the fermentation process are greatly improved. The activity of the hydrogenogen is improved. The hydrogen production rate can reach up to 112.39mL / gVS.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
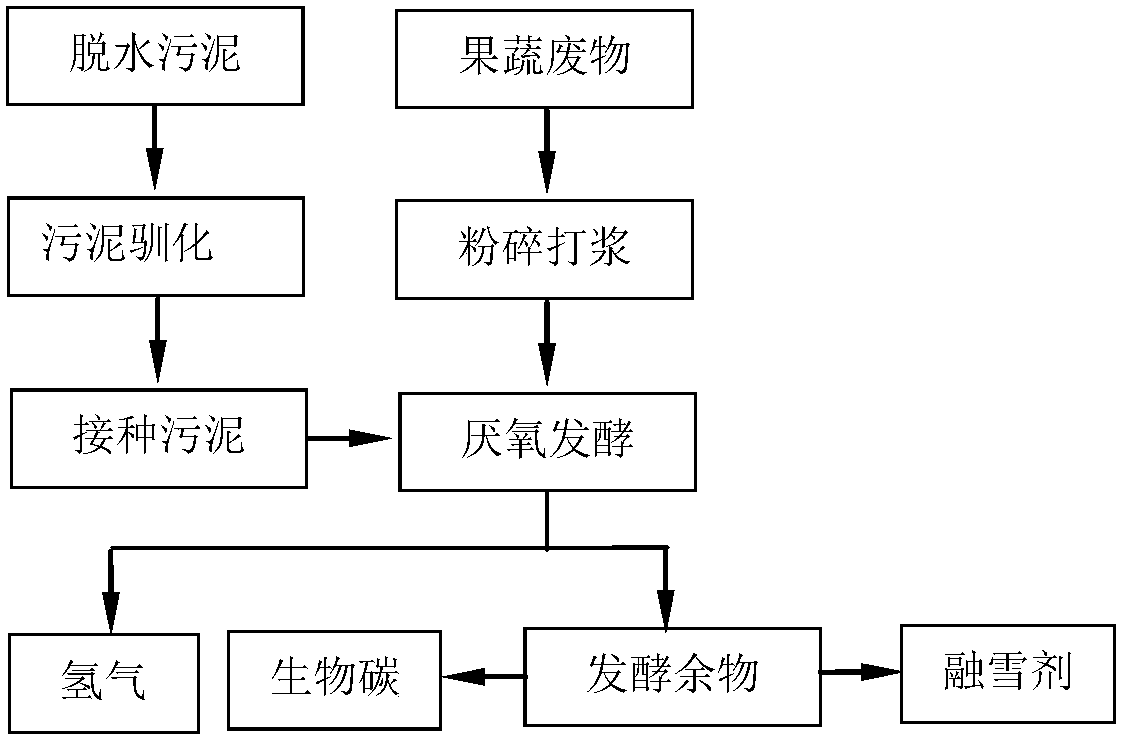
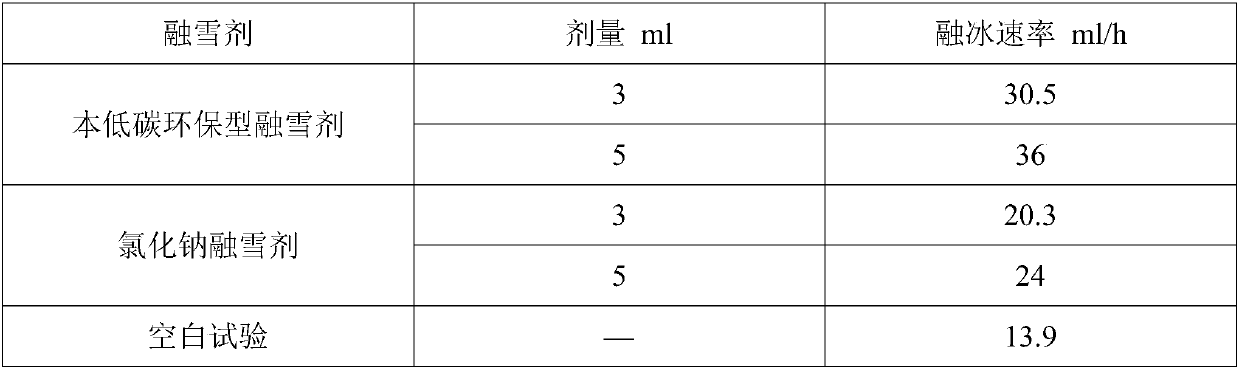
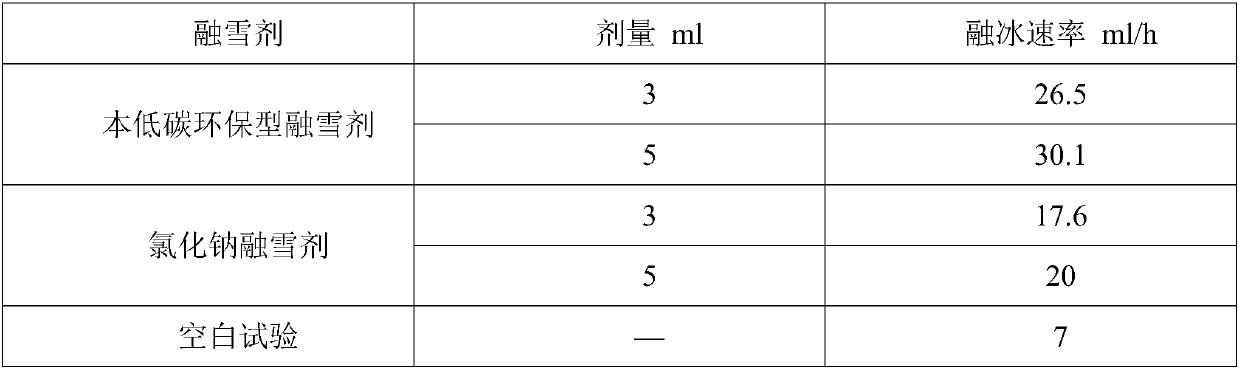
Preparation method of low-carbon environment-friendly snow melting agent
ActiveCN108018024ARealize high-value utilizationAvoid secondary pollutionOther chemical processesSolid componentLiquid product
The invention relates to a preparation method of a low-carbon environment-friendly snow melting agent, and relates to the field of fermentative hydrogen production and snow melting agents. The snow melting agent is generated through an acid-base neutralization reaction at suitable temperature with commercial calcium carbonate and metabolic products (organic mixed acid) generated when fruit and vegetable waste is subjected to anaerobic fermentative hydrogen production at medium temperature (35-38 DEG C) or high temperature (53-55 DEG C). The product is low in price, convenient to use, free of toxicity and corrosion and biodegradable, has no adverse effect on the growth of plants and is the efficient low-carbon environment-friendly snow melting agent. In addition, a liquid component generated after the operation of a solid-liquid separation unit is a liquid product of the low-carbon environment-friendly snow melting agent; a solid component is a substance containing cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin of calcium phosphate and other mineral fertilizer, serves as a raw material of biochar production and is used for soil improvement.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
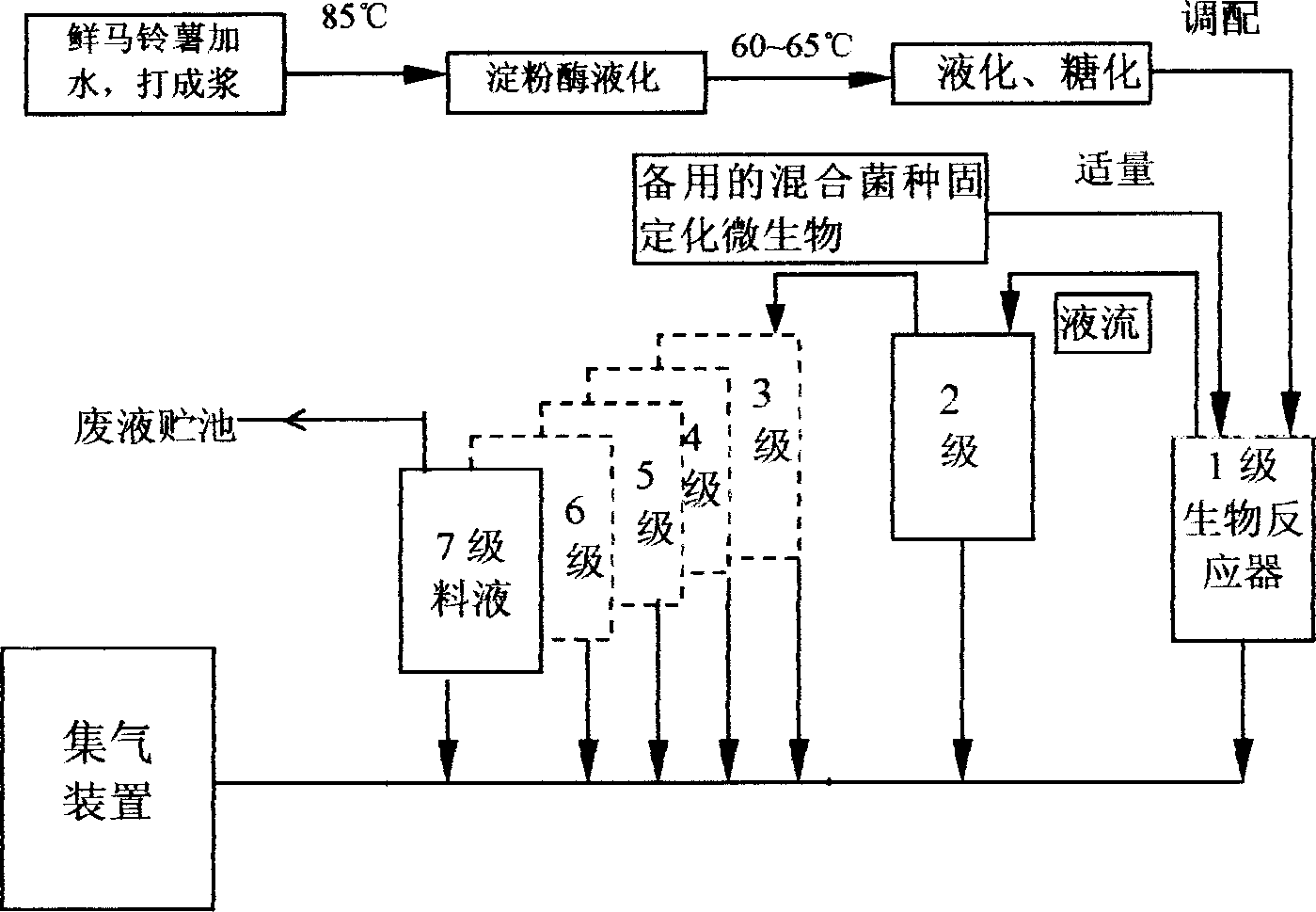
Series-parallel multi-stage compounding apparatus and method for producing hydrogen by biomass continceous fermentation
InactiveCN1814742AHigh gas productionHigh hydrogen contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrogenProduct gas
This invention relates to a serial and parallel multi-stage compound device and a method for continuously fermenting and generating hydrogen by biomass with immobilized animacules, in which, a first stage is a ferment tank for source cultivation and ferment, the second stage is an assistant ferment tank for assisting the cultivation and ferment and a third stage is a primary ferment tank and the latters are serial ferment tanks of n-stages(n>3), mixed immobilized bacteriums of 1-10% W / V of the tank are put into the 1and 2 stages and no immobilized blocks are set in other stages. The method includes: the 1 and 3 stages are for primary feeding, the first one is for putting up raw materials and the third is for producing raw material roughly, the fluid flowing to the next stage is natural without power supply and the collection or process of gas in concentration is realized by a tee.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
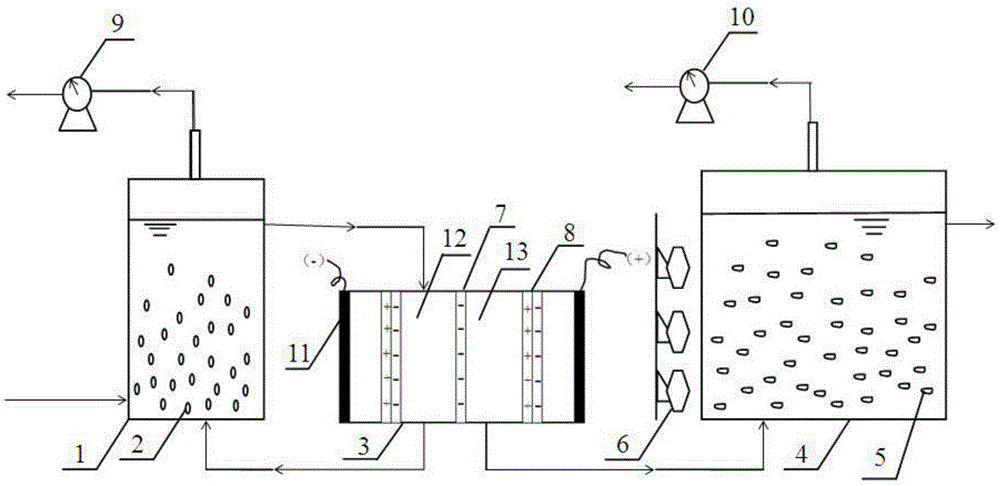
Dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process
InactiveCN106520842AIncrease profitImprove coupling hydrogen production efficiencyMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingAcetic acidPh regulation
The invention discloses a dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process. According to the dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process, a bipolar membrane electrodialysis unit is added behind a dark fermentation reactor, the components of the outgoing water obtained after dark fermentation are separated, thus the concentrated acetic acid is obtained, after pH regulation, the concentrated acetic acid is taken as incoming water of a light fermentation reactor, and meanwhile, the not utilized substrate is recycled and returns to the dark fermentation reactor to be reutilized. The product inhibition at the dark fermentation hydrogen production stage can be relieved, the pH of a fermentation system is controlled to be within the optimal range, the substrate is effectively recycled and reutilized, the total utilization ratio of the substrate is improved, the optimal substrate, namely, acetic acid is provided for the light fermentation hydrogen production stage, NH<4+> in the outgoing water obtained by dark fermentation is removed, then the inhibiting for the dinitrogenase of light fermentation bacteria is relieved, meanwhile, the interception and separation for the dark fermentation bacteria are completed, and the steps including centrifugalization, filtering and sterilization of the original process are replaced; the optimal hydrogen production conditions are provided for the dark fermentation and light fermentation stages, and the two-step coupled hydrogen production efficiency adopting the dark fermentation bacteria and the light fermentation bacteria is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Method for aerobically producing hydrogen by respiration interaction of aerobic hydrogen producing bacteria and aerobic bacteria
ActiveCN107119103AHigh purityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLiquid medium
The invention discloses a method for aerobically producing hydrogen by respiration interaction of aerobic hydrogen producing bacteria and aerobic bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of hydrogen production by fermentation. The method comprises co-culturing Ethanoligenens harbinense YUAN-3 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, specifically, inoculating Ethanoligenens harbinense YUAN-3 powder and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 powder into a sterilized liquid medium, performing sealed culture in a 35 DEG C constant temperature culture room for 1-50 h, and collecting the produced hydrogen. The invention provides a new route for culturing hydrogen producing bacteria, and the hydrogen gas prepared by the method of the invention has higher purity and yield. The method of the invention is simple in operation, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Process for hydrogen production from glycerol
The present document describes a process for production of hydrogen gas (H2) from fermentation of crude glycerol with a hydrogen producing microorganism in a bioreactor. The process comprises the step of introducing a volume of crude glycerol in a fermentation mixture which comprises a fermentation medium comprised of crude glycerol and hydrogen producing microorganisms under a fermentative hydrogen production condition, and then removing a volume of the fermentation mixture equal to the second volume of the crude glycerol, to maintain constant the total volume of the fermentation mixture.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA RECH SCI CENT EAU TERRE ENVIRONNEMENT INRS +1
Method for producing hydrogen through biomass fermentation and photosynthetic coupling
InactiveCN101760479AReduce the cost of hydrogen productionEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingCouplingFermentative hydrogen production
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for producing hydrogen by utilizing sweet potato, yam and other biomass fermentation and photosynthetic coupling. The method completes fermentative hydrogen production and photosynthetic hydrogen production in the same reactor, and comprises that: biomass is subjected to heat treatment first; a fermentation medium taking the biomass as a substrate is inoculated with fermentative bacteria; anaerobic fermentative hydrogen production is performed in an environment at the temperature of between 25 and 40 DEG C with a pH between 5.5 and 7.5; and after hydrogen production is completed, fermentation broth does not need to be added with any other nutrient substances or be diluted, and only needs to have pH regulated to be between 6.0 and 7.5 and then be directly inoculated with hybrid photosynthetic flora so as to continue anaerobic photosynthetic hydrogen production with the light intensity between 2,000 and 8, 000 lux. In the method, final fermentation broth after hydrogen production only needs to be added with sweet potatoes, yams and other biomass again and then can be used for coupling hydrogen production again, and the fermentation broth can be reused for 3 to 5 times. The method has the advantages of high hydrogen production efficiency, long duration of hydrogen production, high substrate conversion rate, easiness for industrialization, and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Algal residue and livestock/poultry feces coupled anaerobic fermentation method for producing hydrogen
The invention relates to an algal residue and livestock / poultry feces coupled anaerobic fermentation method for producing hydrogen. Algal residue and livestock / poultry feces as substrate are processed by microwaves, cooled and then added with inorganic acid, so that the pH value of the substrate is 2 to 5 and the substrate is acidified, and the acidified substrate is washed until the pH value is 6 or 7, and is then dried; the weight ratio of the algal residue to the livestock / poultry feces is 1:1 to 10:1, and the algal residue and the livestock / poultry feces are mixed, then added into 10 to 30 percent by weight of acclimated activated sludge and fermented in an anaerobic environment under the temperature being 30 DEG C to 50 DEG C and pH equal being 5 to 7 to produce hydrogen. According to the method, the advantages of the algal residue left over after the preparation of biodiesel and the livestock / poultry feces are complemented, the reaction conditions are mild, energy consumption is low, the output of hydrogen is great, the delay time is short, and the problems of anaerobic fermentation, such as low hydrogen production efficiency and unstable hydrogen production process are effectively solved, the goals of emission reduction and productivity are achieved while the organic wastes are utilized at high value, renewable resource utilization, pollution abatement and hydrogen production are combined together, and the method important environmental benefit and a broad application prospect.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for producing hydrogen by biomass cascade fermentation
InactiveCN101392269ASolve the problem of low hydrogen conversion rateImprove hydrogen conversionFermentationActivated sludgeSulfonate
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen by the step fermentation of biomass, which relates to a method for producing hydrogen and solves the problem that the transformation rate of the current fermentation method for biological hydrogen production is relatively low. The method comprises the steps: firstly, the shake culture of aerobic granular sludge is carried out, thus obtaining aerobic activated sludge; and then heat treatment is carried out; secondly, water of biological hydrogen production by the fermentation method and disodium bromoethane sulfonate are taken as the bottom materials of reaction equipment, and then the aerobic activated sludge after heat treatment is mutated; and thirdly, nitrogen gas is continuously pumped into the reaction equipment, thus obtaining hydrogen after running. The hydrogen transformation rate of a unit base material in the invention is improved to be more than 2.5molH 2 / mol of hexose.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
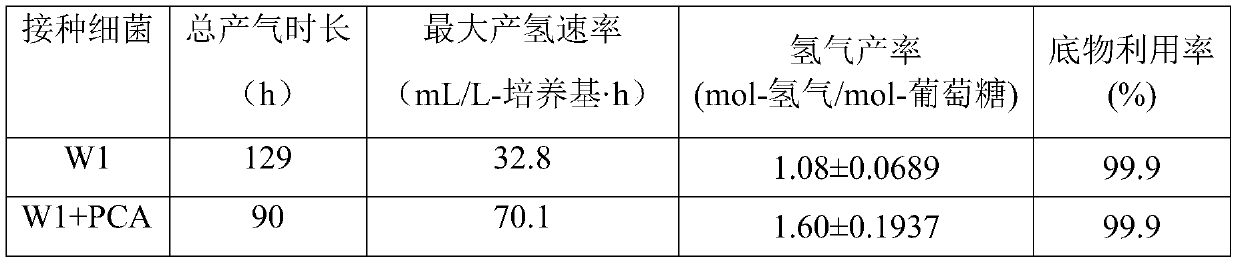
Method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria
ActiveCN110607337AReduce metabolic inhibitionReduce competitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteElectron transfer
The invention relates to a method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria, in particular to a method for realizinghigh-efficiency hydrogen production by utilizing syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria and inter-specific electron transfer, and belongs tothe technical field of hydrogen production by fermentation. The method aims to solve problems that the existing anaerobic biological hydrogen production process is inhibited by bacterial metabolism,substrate is not completely utilized, and then hydrogen production efficiency is influenced. According to the method, Ethanoligenens harbinense W1 and Geobacteria PCA are co-cultured, terminal metabolites such as acetic acid and ethanol produced by the hydrogen-producing bacteria in the fermentation system are consumed by the electroactive bacteria, so that metabolic inhibition among the bacteriain a closed fermentation system is reduced, and continuous and efficient hydrogen production is promoted. In addition, glucose can be used as a carbon source in the method, and the glucose only can beutilized only by the fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria, so that substrate competition is reduced, and the produced hydrogen has higher yield and higher purity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com