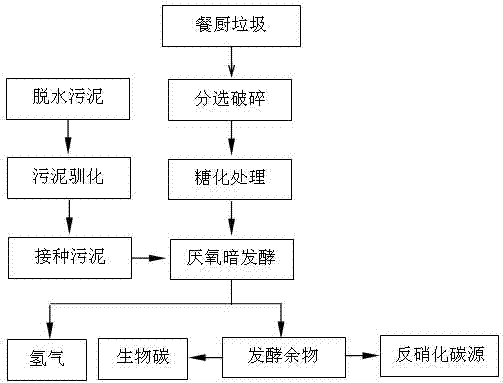
Method for producing hydrogen through kitchen waste enzymolysis and reinforced dark fermentation
The technology of kitchen waste and dark fermentation is applied in the field of hydrogen production through enzymatic hydrolysis of kitchen waste to strengthen dark fermentation, which can solve the problems of high cost, complicated process and high energy consumption, and achieves low cost, simple process and improved hydrogen production rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027]Fill the bucket with dewatered sludge from the sewage plant to remove impurities such as silt and grass, cover the bucket and leave it for 15-20 days to create an anaerobic environment, remove the aerobic bacteria in it, and then take 100g from the middle and lower part of the bucket Put the dehydrated sludge into a fermentation bottle, seal it, and heat it at 80°C for 0.5h, then add 1.2g of glucose and 1g of peptone, shake well, and seal it. The fermentation bottle is acclimated at 50-53°C, and the sludge is acclimated until no gas is produced, and the time is 20-30 hours. The acclimatized sludge is the inoculation sludge. Heat and gelatinize 100g of food waste, add α-amylase (40u / 100g of food waste) to react for 4 hours at 80°C, then cool down to 55-60°C and then add glucoamylase (40u / 100g of food waste) for heating reaction 4h, cool down. After saccharification, add food waste and inoculated sludge into the fermentation bottle and shake well, add water to adjust the ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Take 100g of the sludge left in the anaerobic state of Example 1 for 10-20 days, put it into a fermentation bottle, seal it, heat treat it at 85°C for 0.5h, then add 2g of glucose and 0.9g of peptone, shake it up, and seal it. The fermentation bottle is acclimatized at 50-53°C, and the sludge is acclimated until no gas is produced, and the time is 20-30 hours. The acclimatized sludge is recorded as inoculation sludge. Heat and gelatinize 100g of food waste, add α-amylase (20u / 100g of food waste) to react for 2 hours at 80°C, then cool down to 55-60°C and add glucoamylase (20u / 100g of food waste) for heating reaction 2h, cooling. After saccharification, add food waste and inoculated sludge into the fermentation bottle and shake well, add water to adjust the solid content between 5-10wt% (preferably 6-8%), seal it, control the dark fermentation reaction temperature at 50-53°C, hydrogen The yield is 73.07~94.36mLH 2 / gVS, after 14-20 hours of fermentation time, the proce...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Take 100g of the sludge left in the anaerobic state of Example 1 for 10-20 days, put it into a fermentation bottle, seal it, and heat-treat it at 83°C for 0.5h, then add 0.9g of glucose and 1.2g of peptone, shake well, and seal it. The fermentation bottle was acclimated at 53°C, and the sludge was acclimated until no gas was produced, and the time was 20-30 hours. The acclimated sludge was recorded as inoculation sludge. Heat and gelatinize 100g of food waste, add α-amylase (40u / 100g of food waste) to react for 6 hours at 80°C, then cool down to 55-60°C and add glucoamylase (40u / 100g of food waste) for heating reaction 6h, cooling. After saccharification, add food waste and inoculated sludge into the fermentation bottle and shake well, add water to adjust the solid content between 5-10wt% (preferably 6-8%), seal it, control the dark fermentation reaction temperature at 50-53°C, hydrogen The yield is 98.18~107.66mLH 2 / gVS, after 12-18 hours of fermentation time, the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com