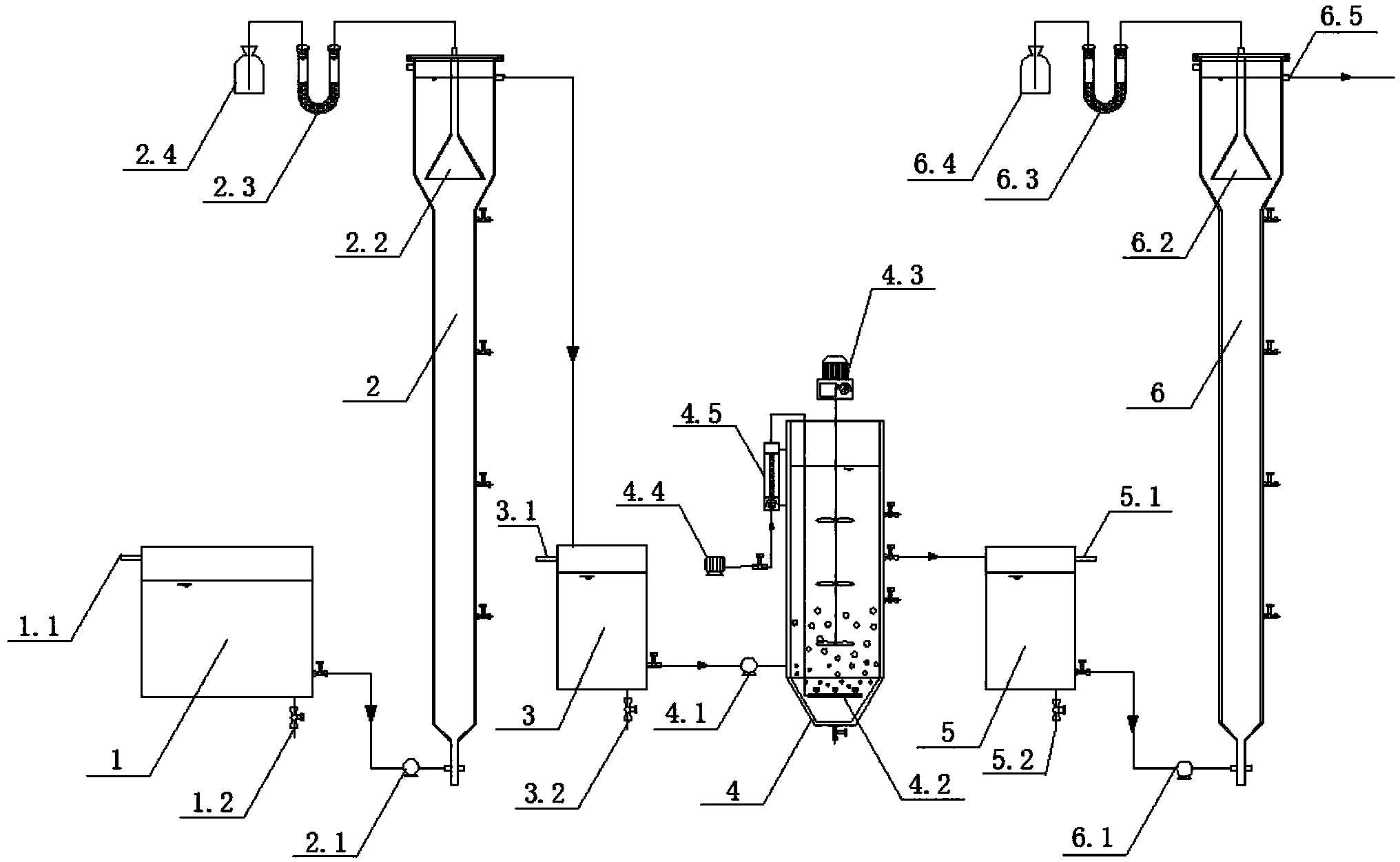
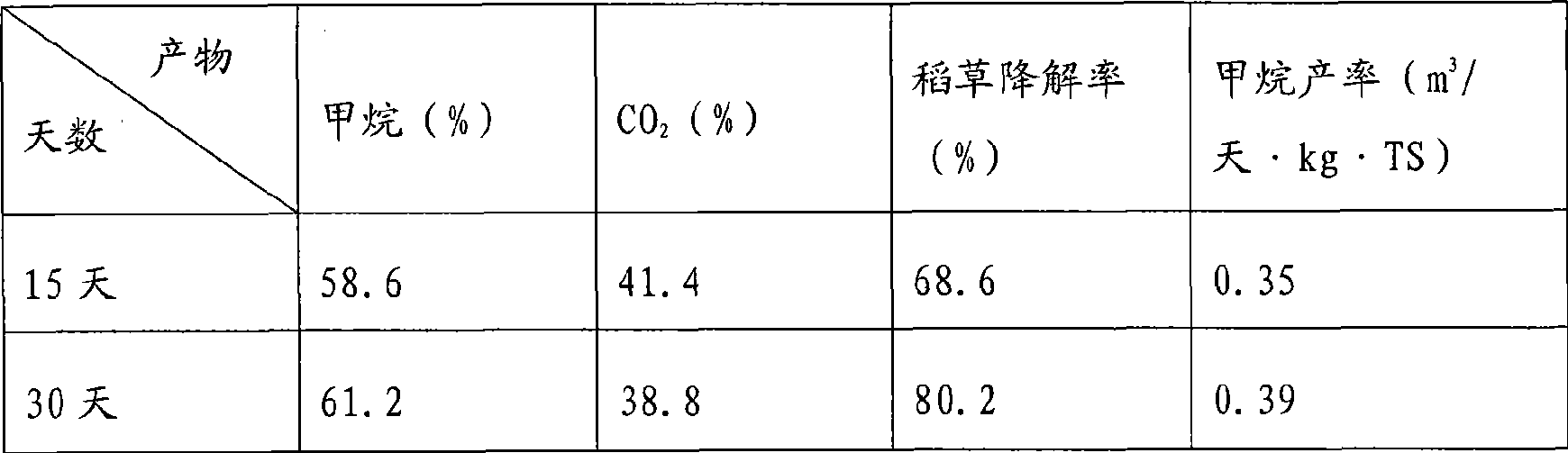
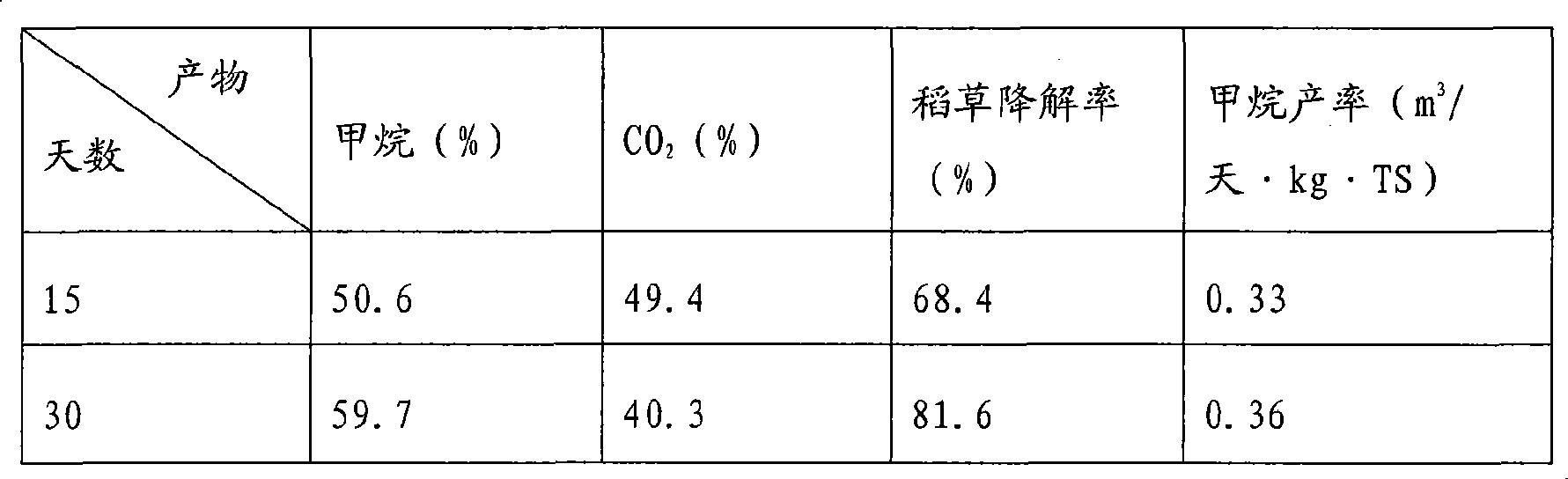
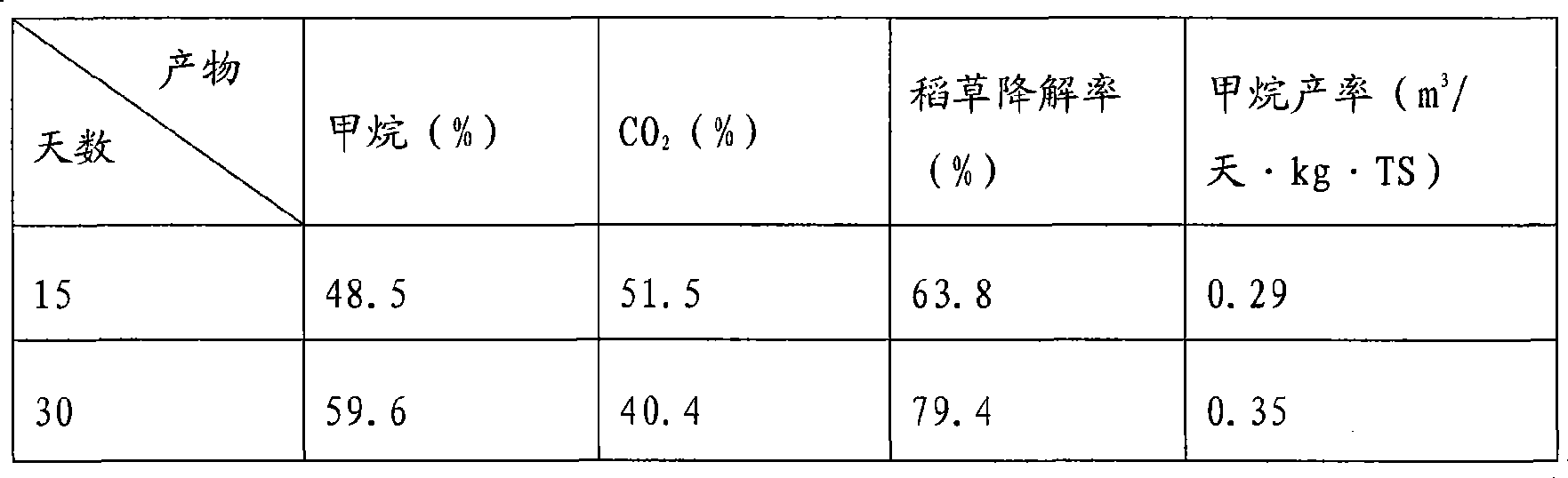
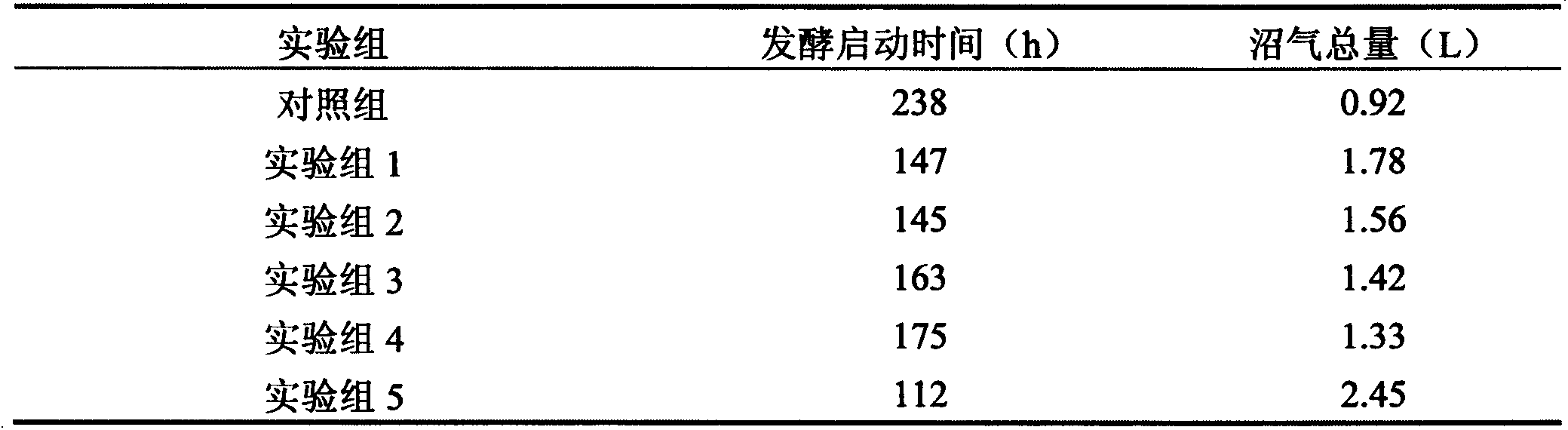
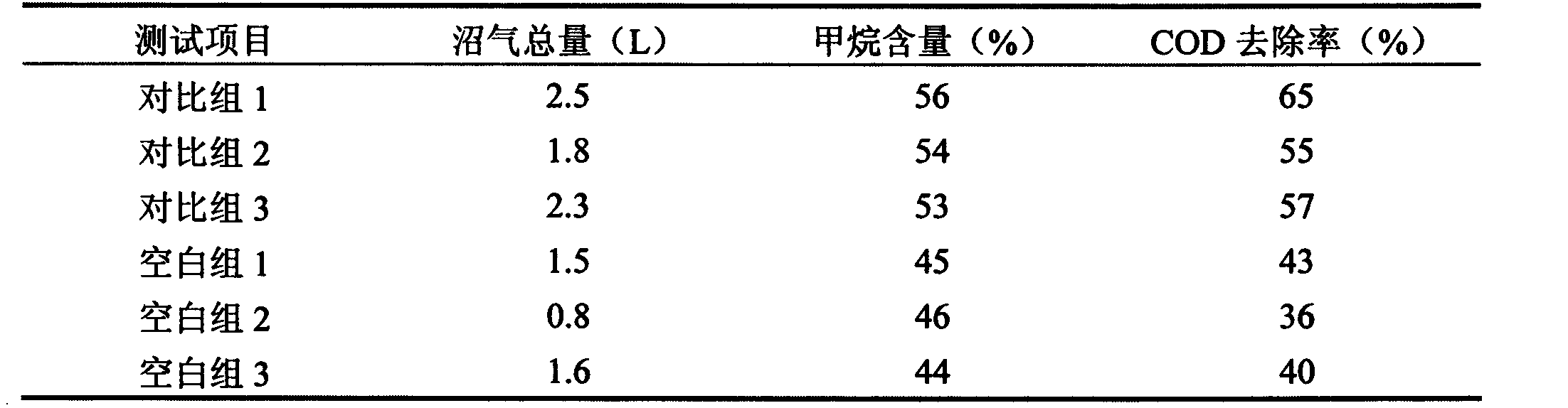
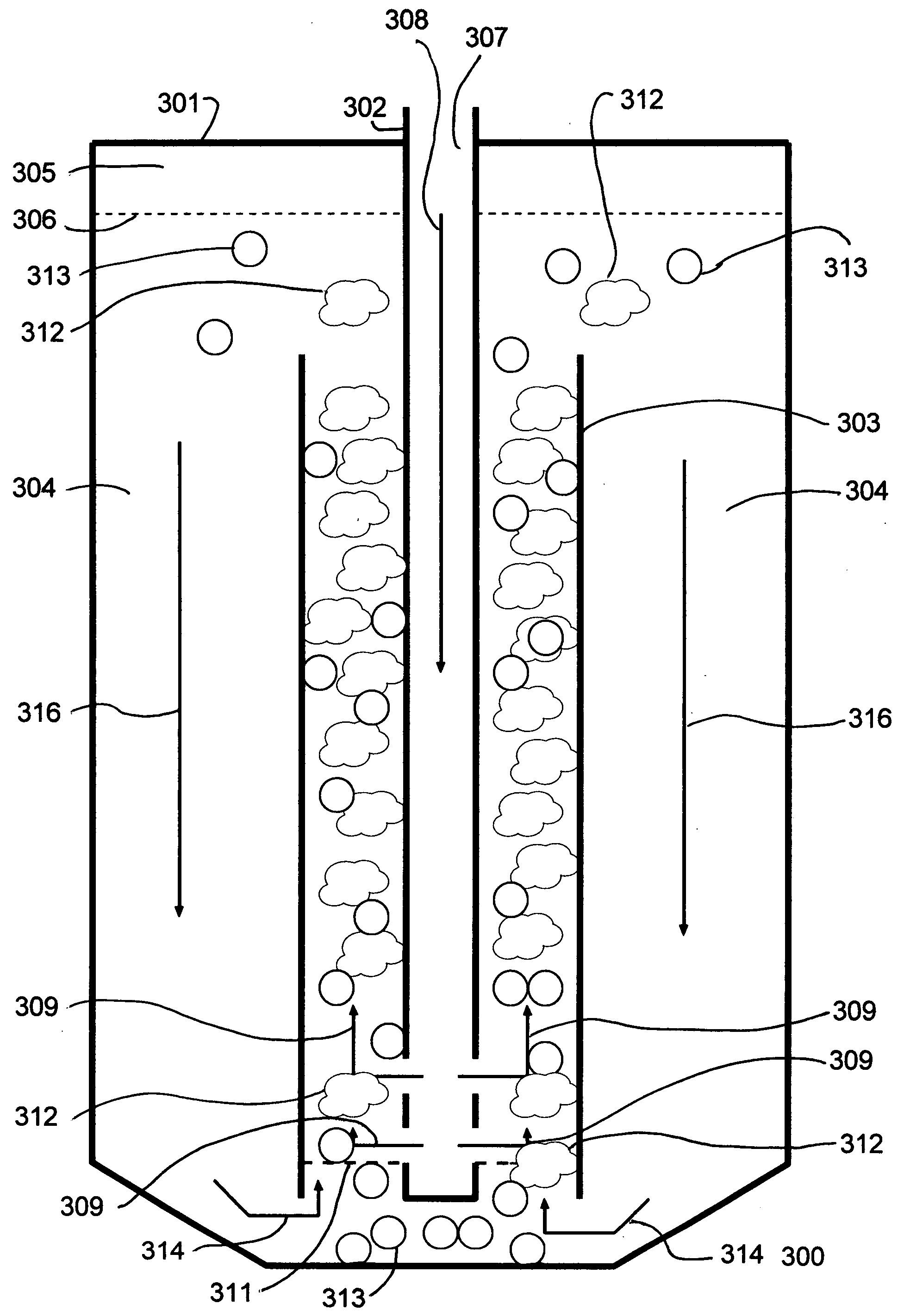
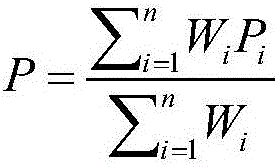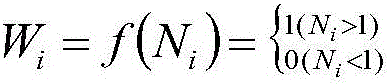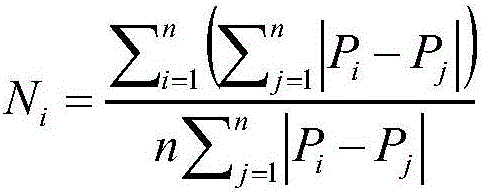Patents
Literature
270 results about "Methanogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain of archaea. They are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface.
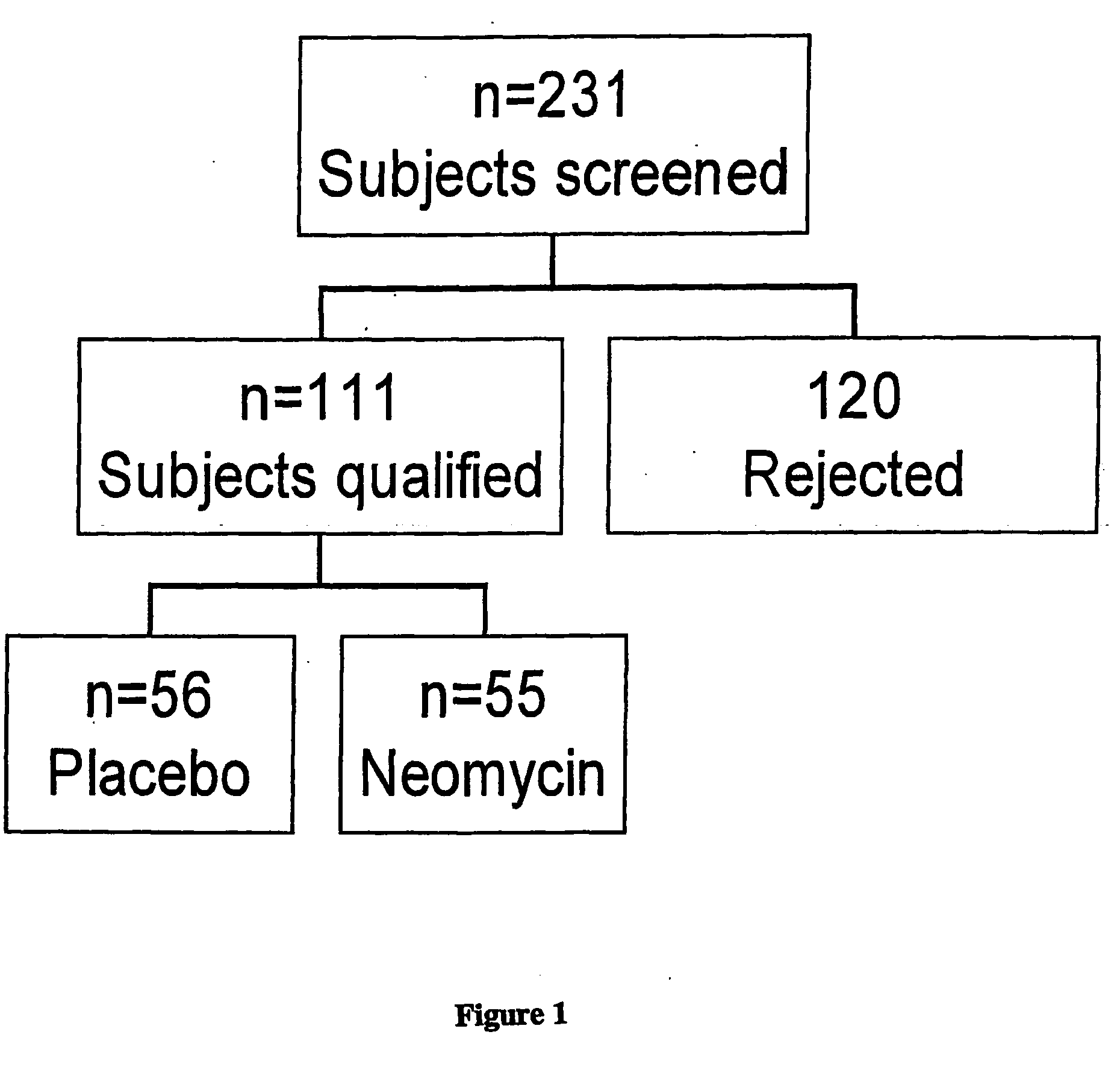
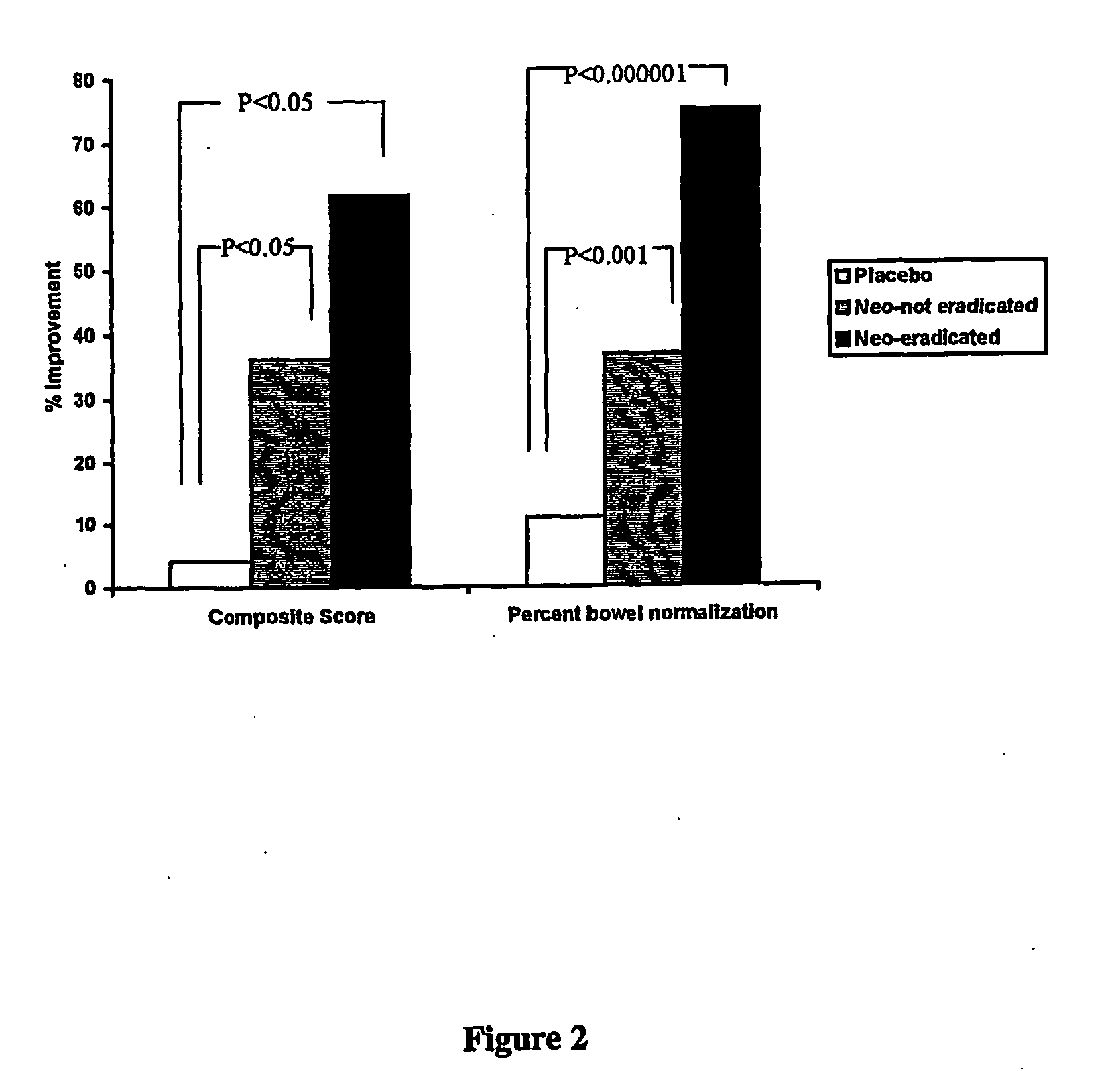
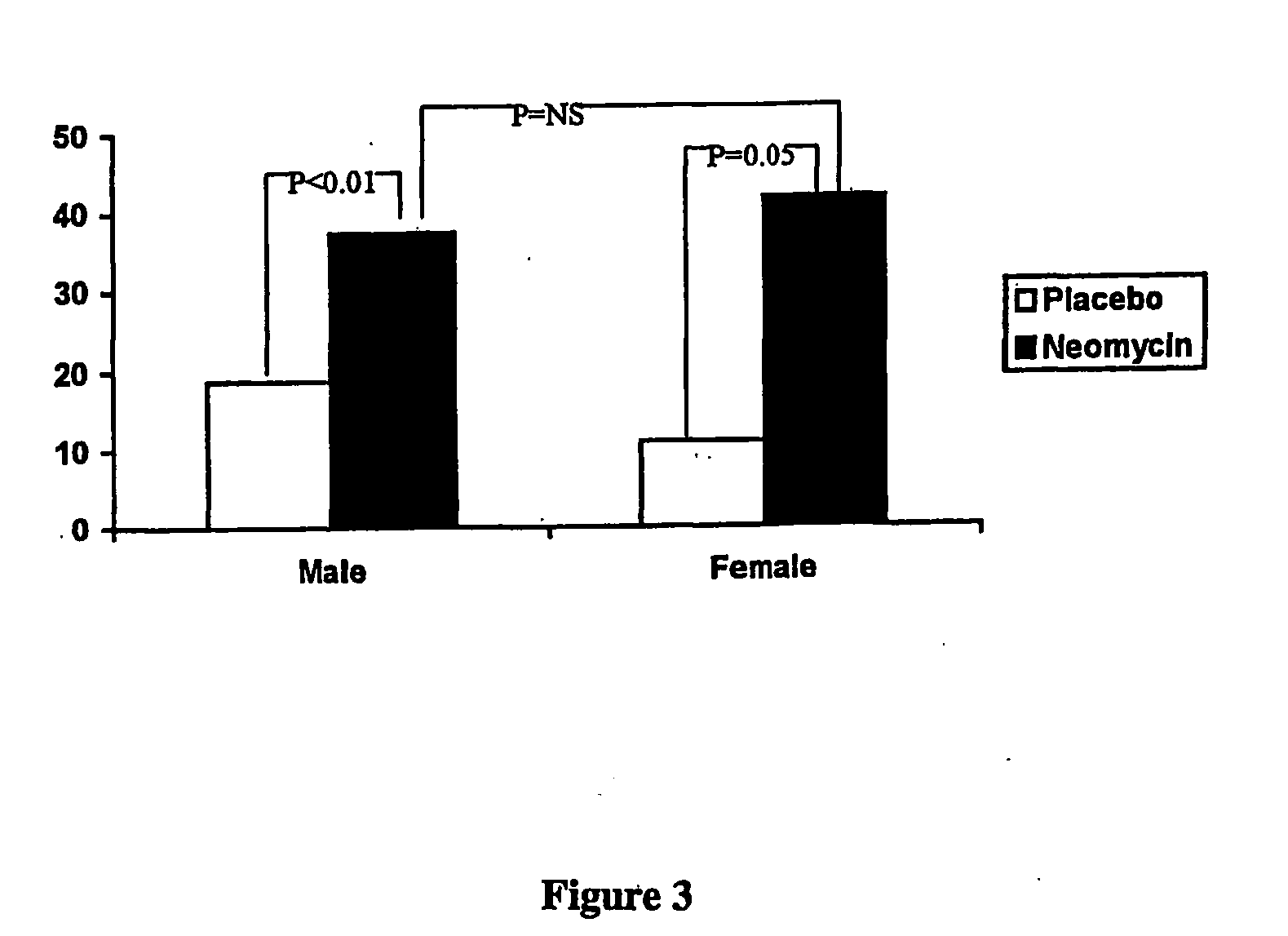
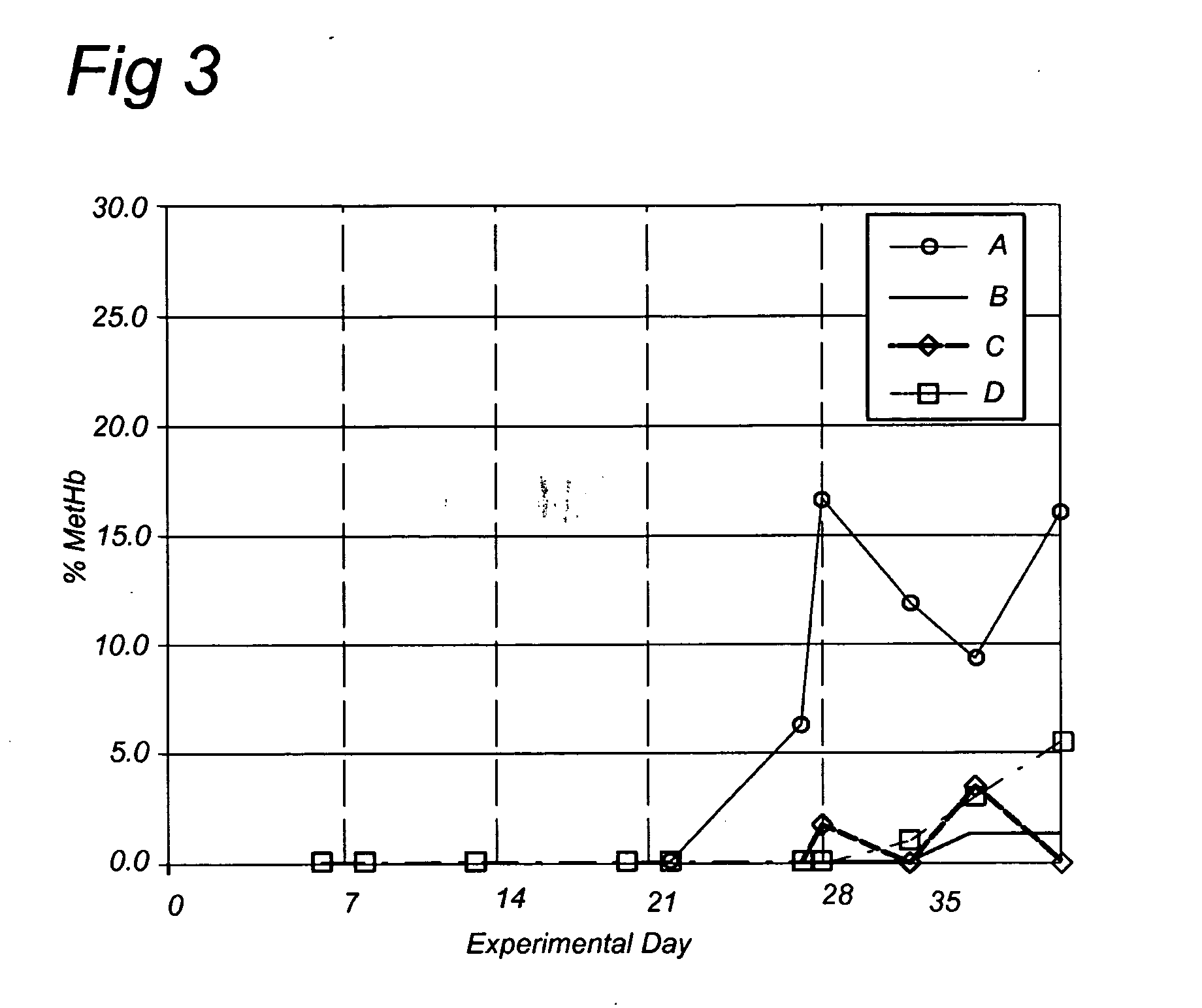
Methods of diagnosis, selection, and treatment of diseases and conditions caused by or associated with methanogens
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
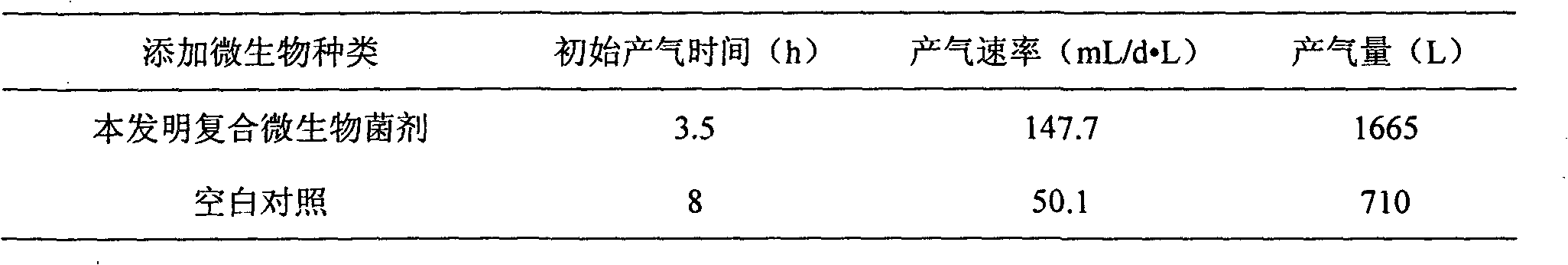
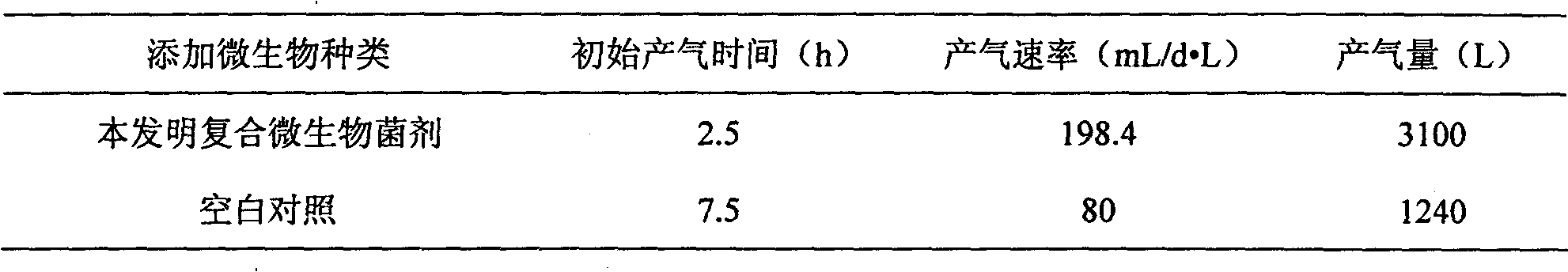
Compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101864362AOvercoming the problem of only targeting a single organic wastePromote enrichmentFungiBacteriaCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and discloses a compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof. The compound microbial bacterial preparation consists of fermentation liquor of four bacteria, i.e. Bacillus licheniformis, Pseudomonas putida, Enterobacter cloacae and Candida valida. The compound microbial bacterial preparation provided by the invention has strong digestion power for various types of cellulose, proteins and fat macromolecules. The addition of the compound microbial bacterial preparation into excess sludge and / or kitchen waste can quicken enrichment of methanogen, shorten anaerobic digestion time and improve methane yield. Moreover, the synergetic effect of the four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one, two or three strains of microorganisms.
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Method for utilizing nano ferroferric oxide for improving activity of anaerobic digestion methanogens and methanogenesis efficiency
InactiveCN104529116AMeet needsBreaking through thermodynamic barriersWater treatment compoundsWaste based fuelPhosphateElectron donor
The invention relates to a method for utilizing nano ferroferric oxide for improving the activity of anaerobic digestion methanogens and methanogenesis efficiency. The method aims at solving the problems that in the prior art, the addition concentration of Fe2+ / Fe3+ is hard to control, negative ion inhibition is caused, bioavailability is low, the chemical property is unstable, and cost is high. The method comprises the steps that short chain fatty acid salt is adopted as an electron donor, amine salt is adopted as a nitrogen source, phosphate is adopted as a phosphorus source, system basicity is maintained, and under the culture condition of continuous flow anaerobic fermentation, anaerobic mixed granule sludge is separated, and mixed seed sludge is obtained; the short chain fatty acid salt is adopted as the electron donor, the amine salt is adopted as the nitrogen source, the phosphate is adopted as the phosphorus source, the system basicity is maintained, the nano ferroferric oxide is adopted as an iron ion donor, the mixed seed sludge is adopted as inoculation sludge, and culturing is carried out under the static anaerobic fermentation condition. The method is used for improving the activity of the anaerobic digestion methanogens and the methanogenesis efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
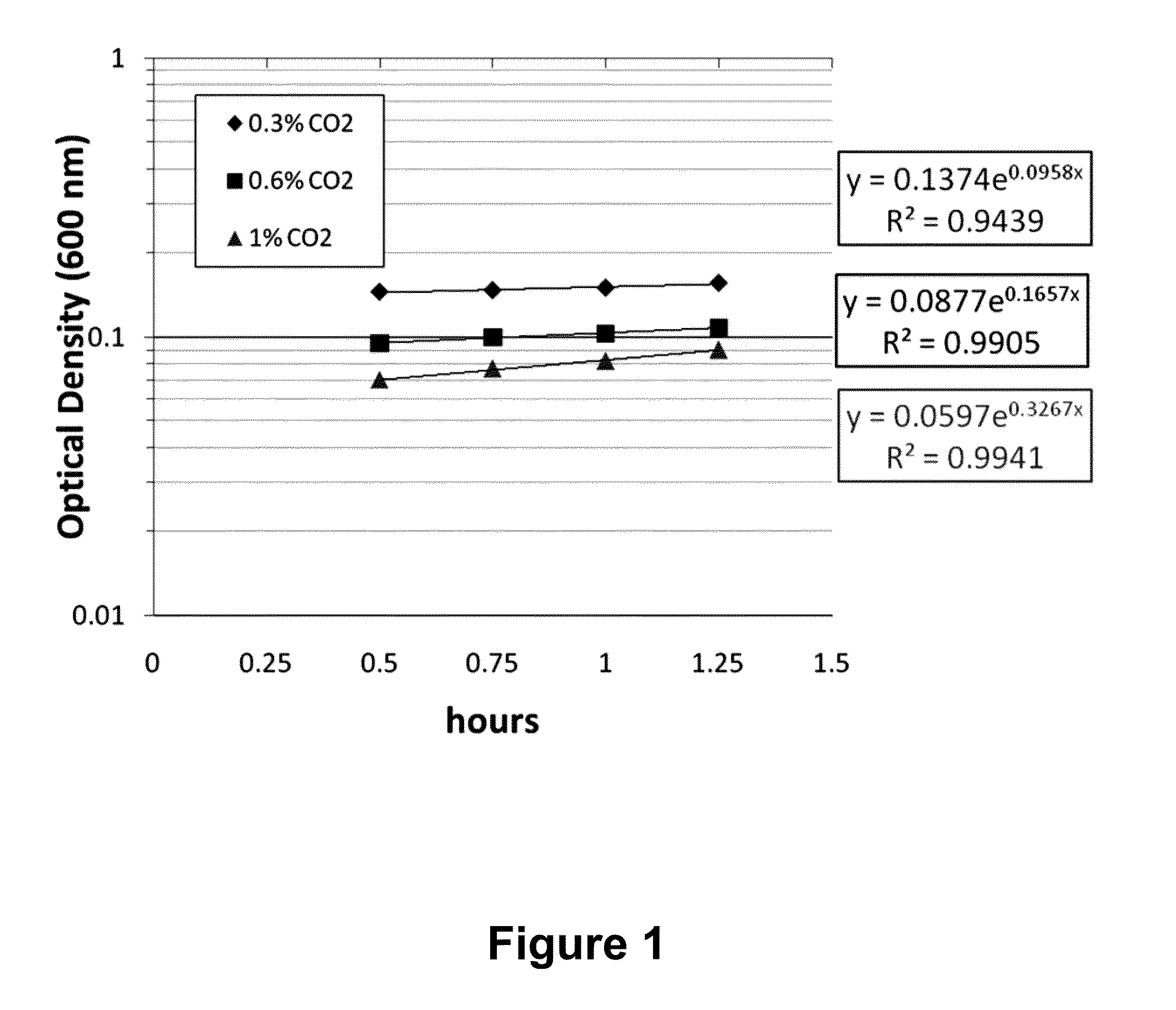
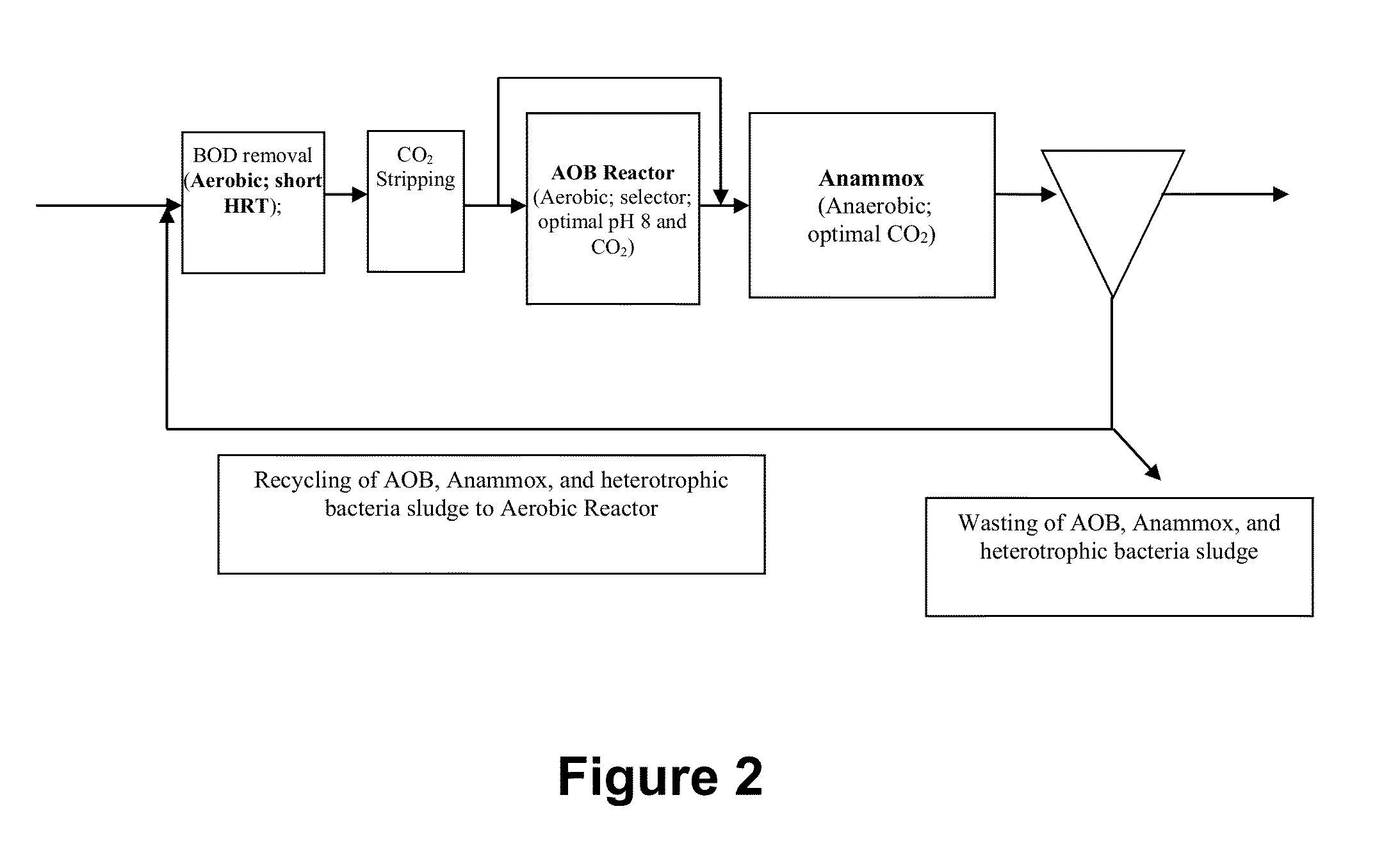
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR TREATING WASTEWATER AND SLUDGES BY OPTIMIZING sCO2 FOR ANAEROBIC AUTOTROPHIC MICROBES
InactiveUS20130327709A1Increase ratingsExcellent volatile solid destructionWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesNitrogen removalMicroorganism
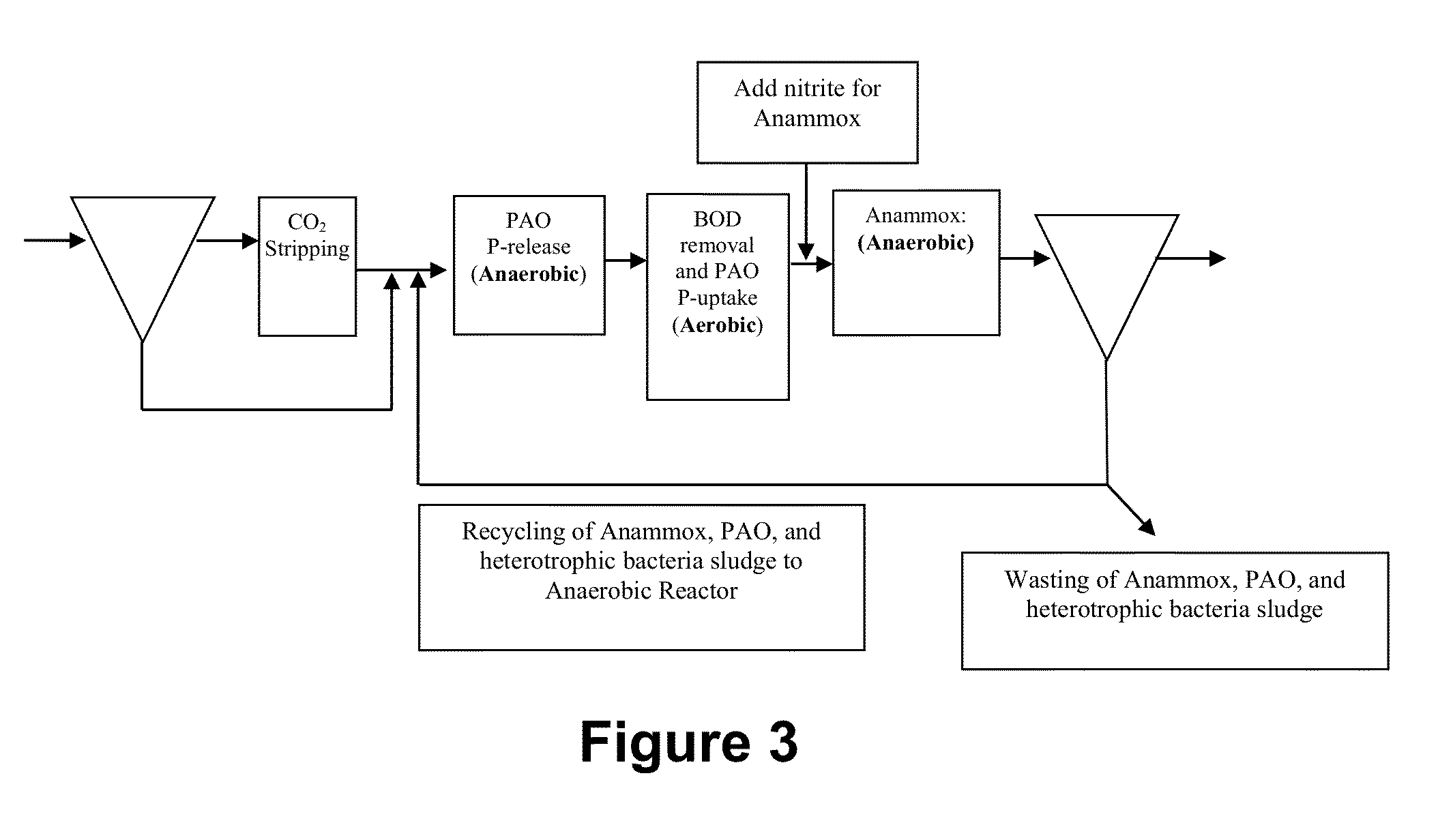
The present invention describes a method of optimizing CO2 concentration to increase the specific growth rate of Anammox bacteria and methanogens in wastewater and sludge treatment, as well as novel systems and methods of treating wastewater and sludge. The specific growth rate or doubling time of the Anammox bacteria and methanogens were determined to be sensitive to dissolved CO2 concentration. Optimizing dissolved CO2 concentration increases the specific growth rate of the Anammox bacteria, which may be used as an alternative biological nitrogen removal process for the treatment of domestic wastewater. In the method and system of treating sludge, the CO2 stripper returns biogas with low CO2 concentration to the headspace of an anaerobic digester in order to lower the headspace CO2 concentration and therefore, the soluble CO2 concentration. The lower soluble CO2 concentration increases the specific growth rate of the methanogens for a more efficient anaerobic digestion process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Manipulation of the rate of gastrointestinal transit by modulating intestinal methane concertration
InactiveUS20060246045A1Reduce probabilityReduce partial pressureBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsMethanogenesisGastrointestinal transit
Disclosed is a method of manipulating the rate of gastrointestinal transit in a mammalian subject Also disclosed is the use, in the manufacture of a medicamens for the treatment of constipation, of a selective inhibitor of methanogensis, a methanogen-displacing probiotic agent, or a prebiotic agent that inhibits the growth of methanogenic bacteria or promotes the growth of competing non-methanogenic intestinal flora. Alternatively, in accordance with the invention, is disclosed the use in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of diarrhea, of methane, or a methane precursor, a methanogenic or other methane-enhancing probiotic agent, or a methanogenesis-enhancing prebiotic agent.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Energy recovery-based landfill leachate autotrophic nitrogen removal method
ActiveCN103833185AAvoid active inhibitionReduce consumptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentEnergy recoveryLow oxygen
The invention discloses an energy recovery-based landfill leachate autotrophic nitrogen removal method belonging to the field of sewage treatment. A device mainly comprises three parts of respectively an anaerobic methane-generating reactor, a partial nitrification reactor and an anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, wherein landfill leachate firstly enters the anaerobic methane-generating reactor, anaerobic methanogens can convert organic matters in the landfill leachate into an energy gas methane and the energy gas methane is recovered, then the water quantity is adjusted through a middle water tank, the landfill leachate enters the partial nitrification reactor, and the partial nitrification reactor runs in a low-oxygen aeration manner, and a partial nitrification process is realized through controlling the aeration time; and finally, after the water quantity is adjusted through the middle water tank, the landfill leachate enters the anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, and an autotrophic nitrogen removal process of the landfill leachate is completed under the assistance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria. According to the energy recovery-based landfill leachate autotrophic nitrogen removal method, energy resources in the landfill leachate can be fully recovered, and the operation cost and the energy consumption of treating the landfill leachate are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Anaerobic cellulose-degrading methane producing composite bacterium
InactiveCN101475926AEfficient hydrolysisFermentation starts fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseFacultative
The invention discloses anaerobic degradation cellulose methane composite bacteria, which is composed of 13 strains that respectively belong to facultative anaerobic and strictly anaerobic fermentative bacteria, hydrogen-production and acetic acid-production bacteria and methane-producing bacteria. The composite bacteria can not only effectively perform anaerobic degradation to the cellulose, but also can use the degradation production of the cellulose to produce methane, which can be widely used in straw biogas fermentation, compost processing, and the like conversion processes.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
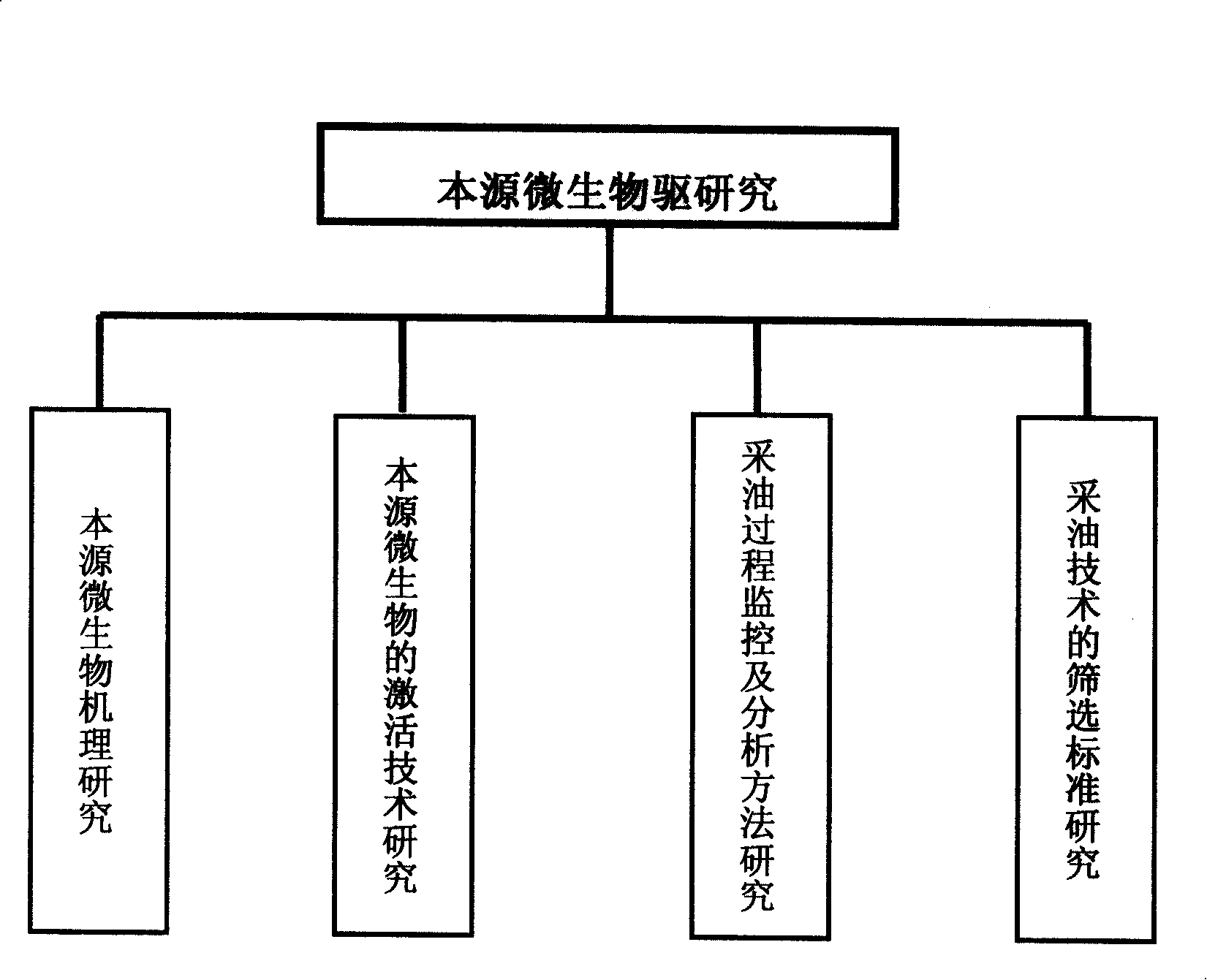
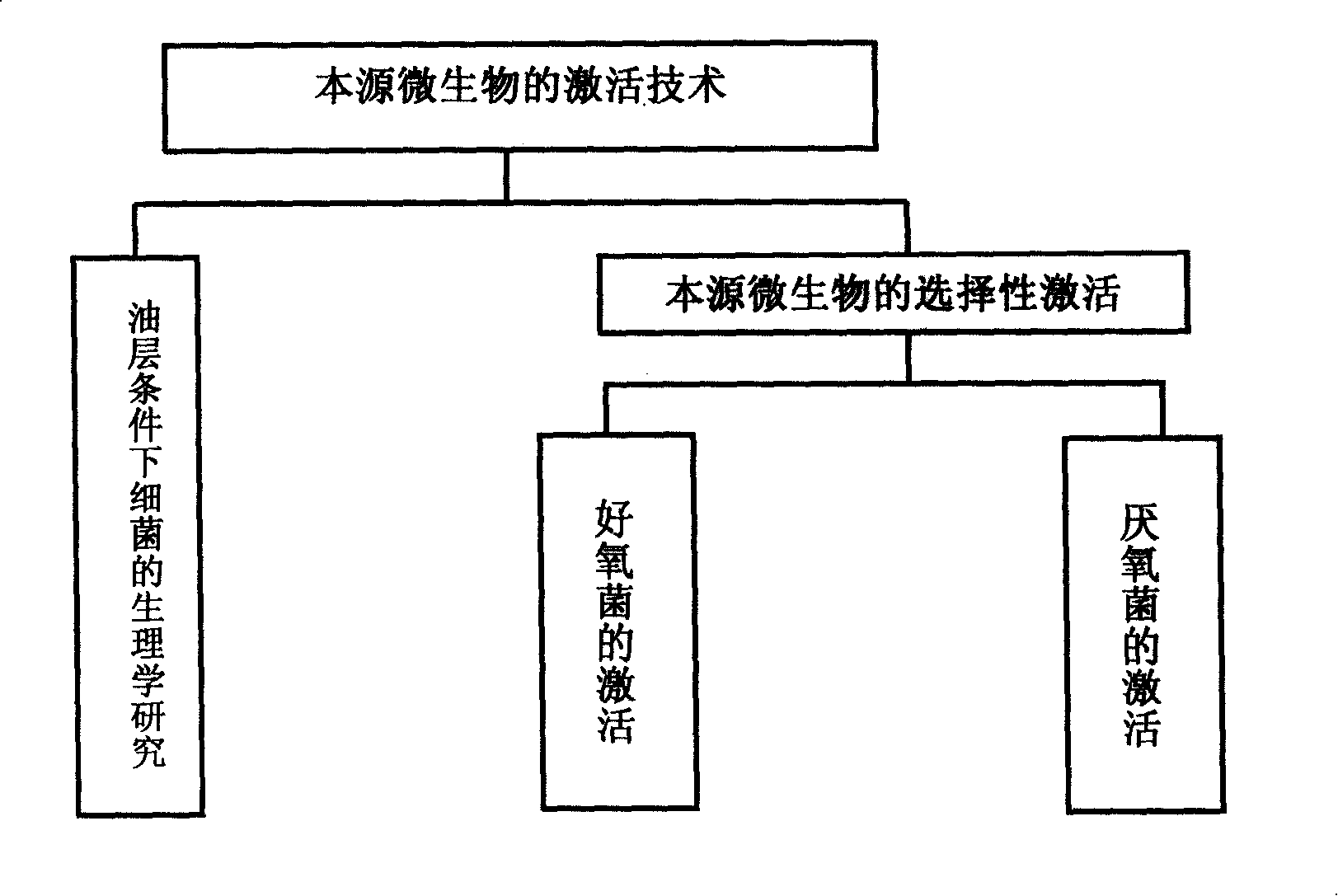
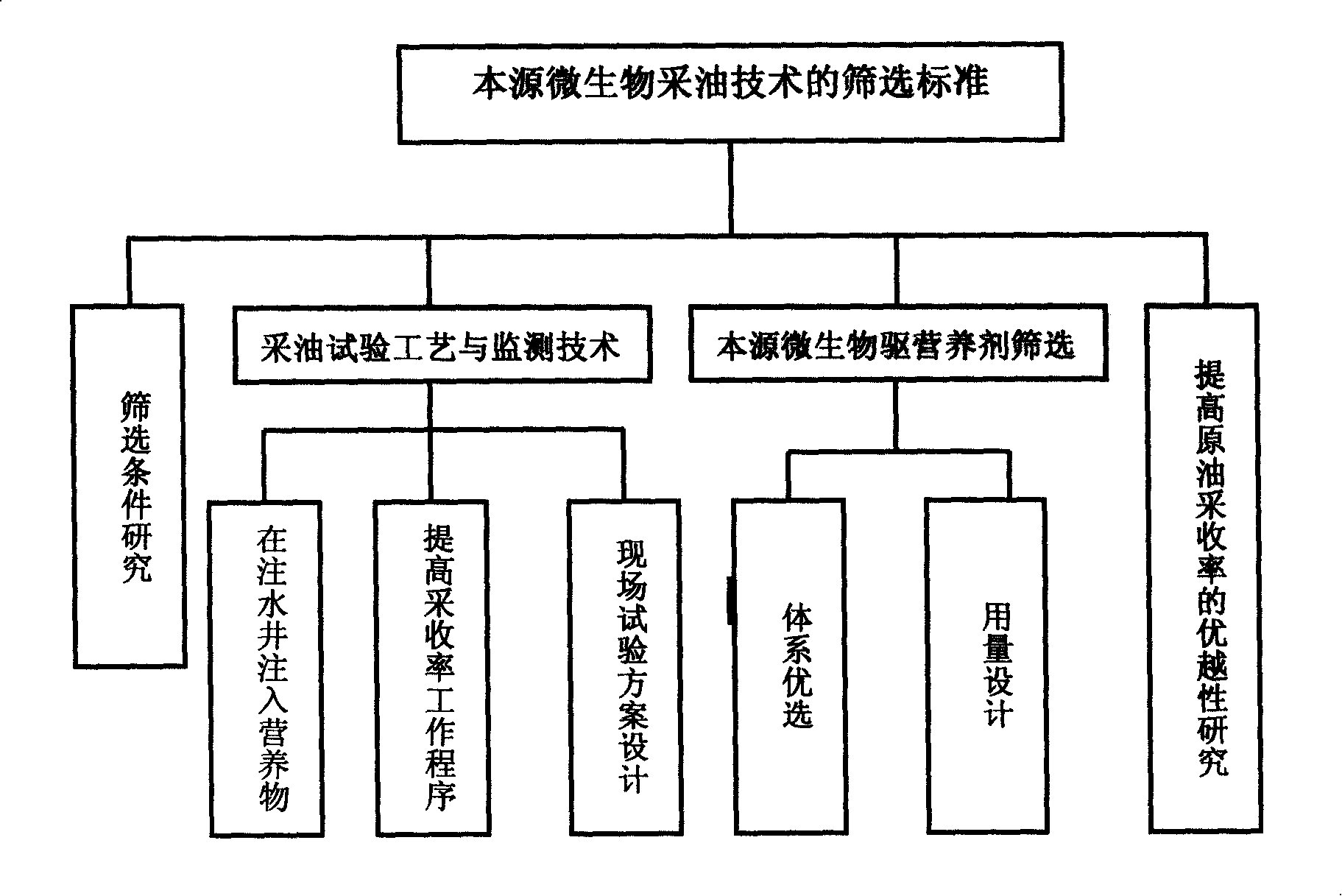
Indigenous microorganism oil flooding method
An oil extraction method driven by substrate microorganism, the first stage: aerobic fermentation stage, oxybiontic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacterium and facultative anaerobe of hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacterium are activated at the near zone of the water injection well. Because of being partial oxidation of hydrocarbons, it produces alcohol, fatty acid, surfactant, CO2, biological polysaccharide and other product; on one hand these substance is base oil releaser, on the other hand it is as nutrient source of anaerobe including methanogen; The second stage: anaerobic fermentation stage, methanogen is activated in the deep part of anoxic oil pool, producing CO4, CO2 and other matter which increases oil fluid and increases recovery after the matter dissolving in water; In the process, the proportion between isotope light methane produced by biology and general methane is increased.
Owner:TIANJIN JINDA GASOLINEEUM NEW TECH
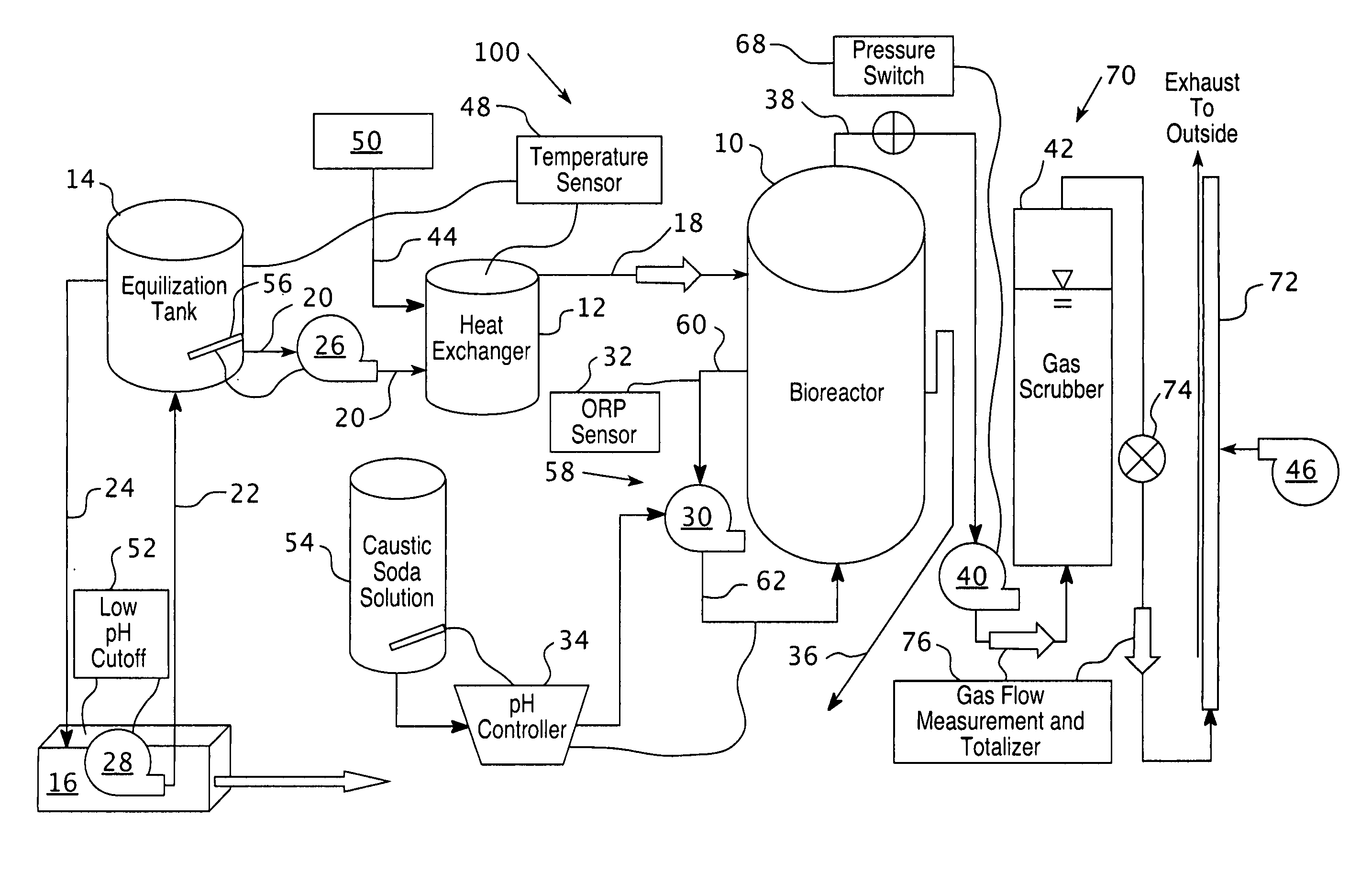
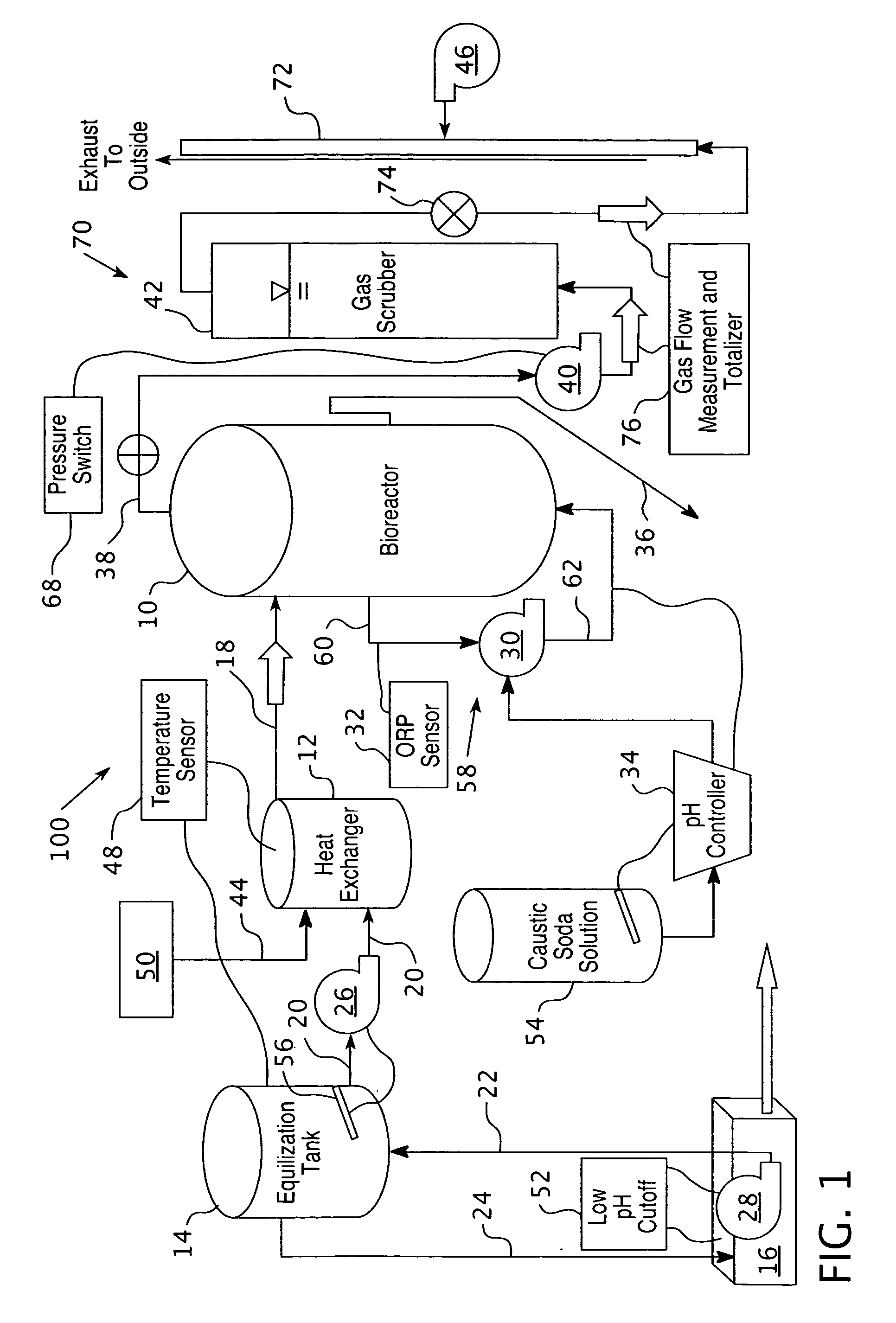
Reactor for producing acid phase with diphasic anaerobic digestion of urban biomass garbage
InactiveCN101402096AGood energy saving and environmental protection characteristicsLow consumption and efficient operationBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid waste disposalFermentationMaterials science
The invention discloses a two-phase anaerobic digestion acidogenic phase reactor for municipal biomass waste. The acidogenic phase reactor is provided with an enclosed vertical kettle formed with a thin corrosion resistant stainless steel inner barrel and a common carbon steel outer barrel. The kettle is welded with a dimple jacket outside, and is fixed with a hollow guiding barrel inside, and the insides of the dimple jacket and the hollow guiding barrel both have a heating medium so as to realize heating insulation operation under the combination control of a temperature sensing probe and a temperature controller. A multi-layer push type propeller blade with less flow resistance is used to perform mechanical stirring of the biomass waste entering the reactor, and meanwhile low consumption and high efficiency mixing of material and liquid can be realized with the forced current limit of the guiding barrel. The rotating inner stirring device and the resting kettle are mechanically sealed through a movable sealing element. The acidogenic phase reactor integrates the functions of stirring, mixture, reaction, fermentation, heating and insulation has good energy-saving and environmental-protection property, which can digest the high solid municipal biomass waste into small molecule organic acids that can be used by methanogens bacteria directly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
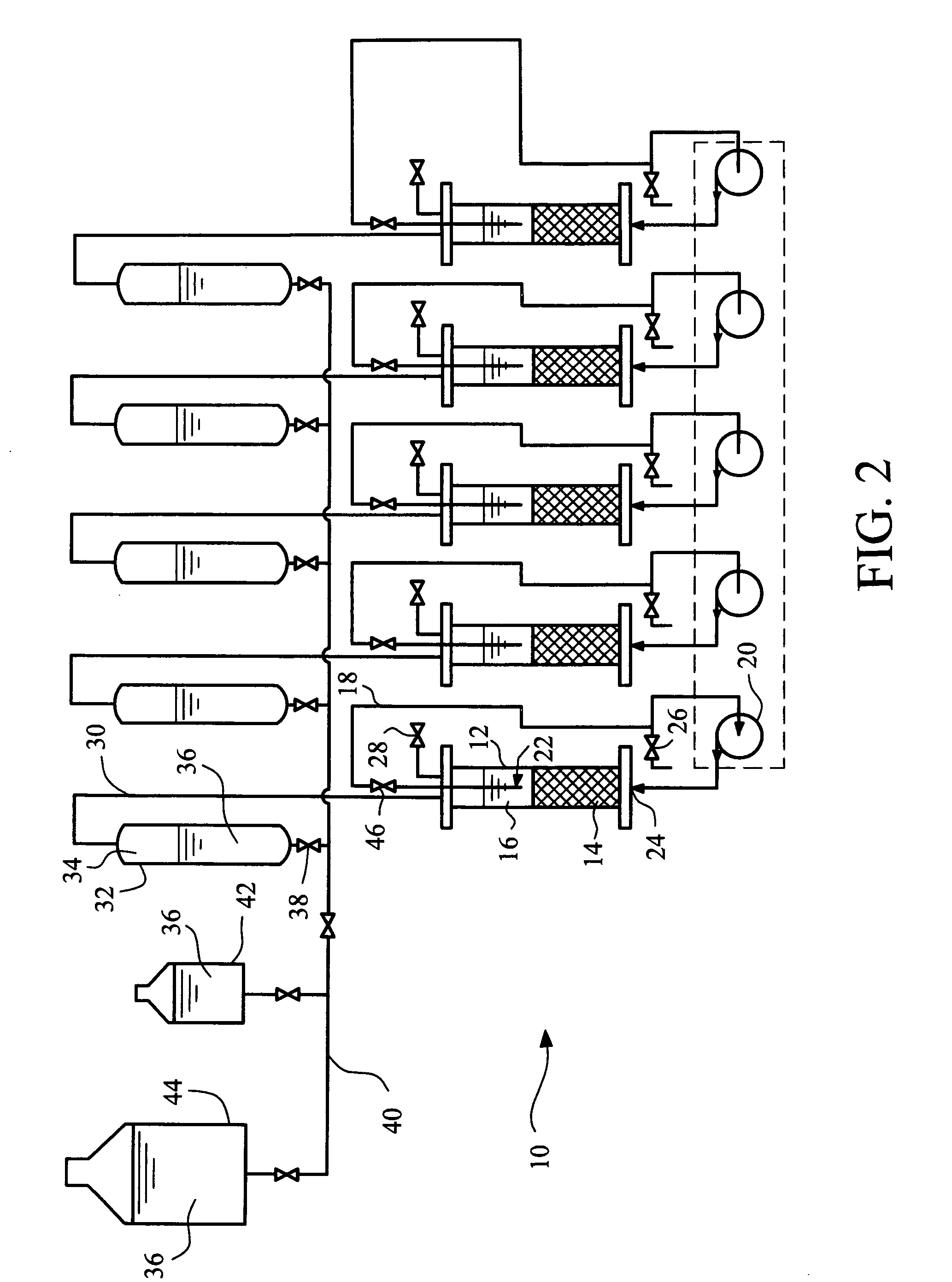
Dual hydrogen production apparatus
InactiveUS20060272956A1Readily combinableReadily proximateCellsBiological substance pretreatmentsBioreactorHydrogen production
The present invention provides an apparatus for the dual production of hydrogen, wherein organic feed material of a primary hydrogen production apparatus is heated with excess or diverted heat from a secondary hydrogen production apparatus, thereby substantially deactivating or killing methanogens within the organic feed material. Hydrogen producing microorganisms contained or added to the organic feed material metabolize the organic feed material in a bioreactor to produce hydrogen in a primary hydrogen production apparatus. As the methanogens are no longer substantially present to convert produced hydrogen to methane, a biogas that contains hydrogen without substantial methane can be produced.
Owner:FELDER MITCHELL S +2
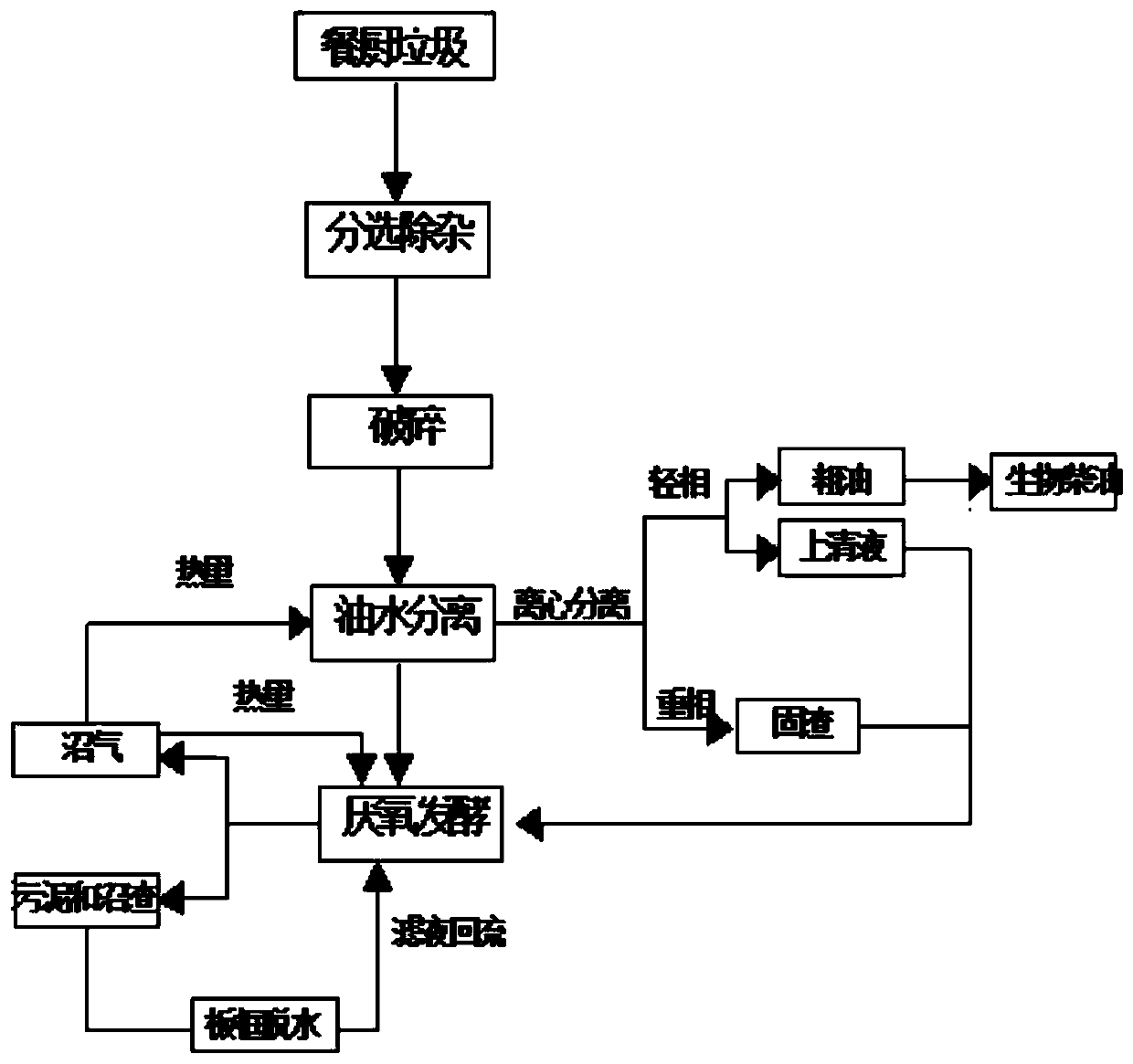
Kitchen waste harmless and resourceful processing method
InactiveCN110105095AEmission reductionReduce processing loadClimate change adaptationEnergy inputSewageOil water
The invention discloses a kitchen waste harmless and resourceful processing method. The method includes the steps of conducting sorting, impurity removing, smashing, oil-water separating and anaerobicfermentation, adding biogas slurry and sludge generated in anaerobic fermentation to PAM accounting for 1-3|%o of the absolute dry weight of the sludge, introducing the flocculated biogas slurry andsludge into a centrifugal machine to be dewatered, making one part of dewatered biogas slurry flow back into an adjusting pool, discharging the other part of dewatered biogas slurry to a sewage plant,and conditioning and modifying the centrifugally-dewatered sludge and biogas residues, adding the sludge and biogas residues into a plate-and-frame filter press to obtain filtrate and residues, making one part of filtrate flow back into the adjusting pool, discharging the rest of filtrate to the sewage plant, and conducting aerobic composting on the residues. The filtrate formed after the biogasresidues generated after anaerobic fermentation are dewatered and filter-pressed by a plate and frame flows back into an anaerobic fermentation tank, the activity of anaerobic methanogens can be improved, the gas yield is improved, meanwhile the generated filtrate can be recycled, the processing loads on the sewage plant are reduced, and the kitchen waste harmless and resourceful processing is realized to the maximum extent.
Owner:NANJING WONDUX ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Production of hydrogen gas and isolation of hydrogen producing microorganisms using replenishing coated substrates
InactiveUS20060281158A1Readily apparentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismHydrogen
The present invention provides a system of baiting and growing microorganisms on a gelatinous matrix. A bioreactor is provided wherein the bioreactor provides an environment conducive to the breakdown of organic aqueous material and the production of hydrogen from microorganisms and restrictive to the production of methane from methanogens. The bioreactor includes substrates coated with a gelatinous matrix, wherein the gelatinous matrix coating is replenished by additional coating material pumped into interior channels of the substrates wherein the substrates are permeable by the coating.
Owner:NANOLOGIX INC
Carbon source recycling based excess sludge treatment process
ActiveCN107265806AKeep aliveInhibitory activityWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludgeMethane production
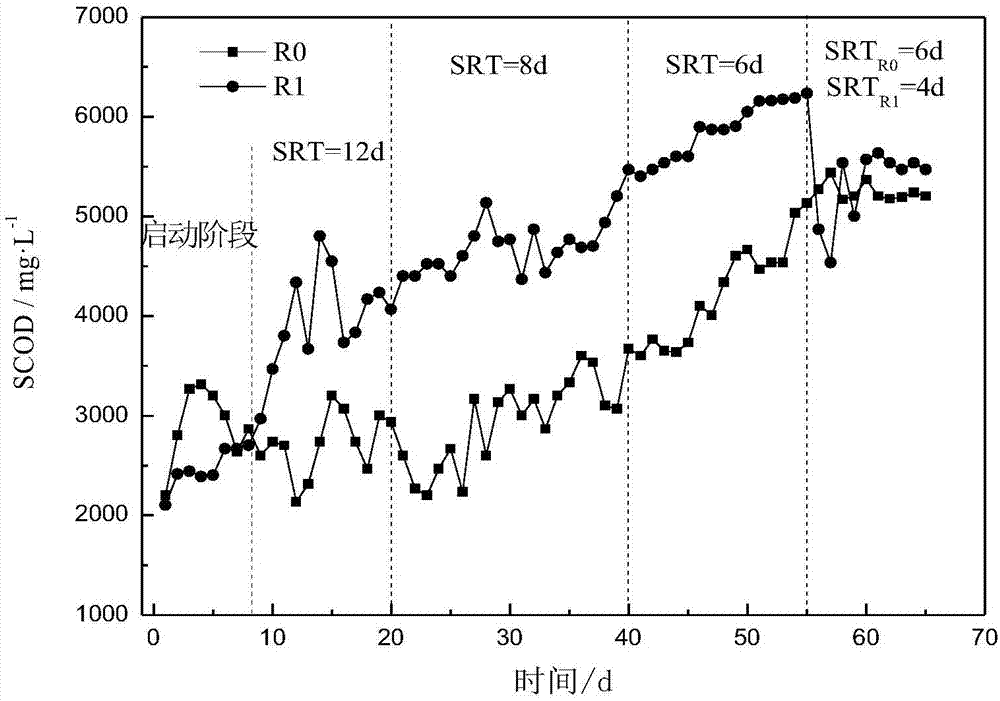
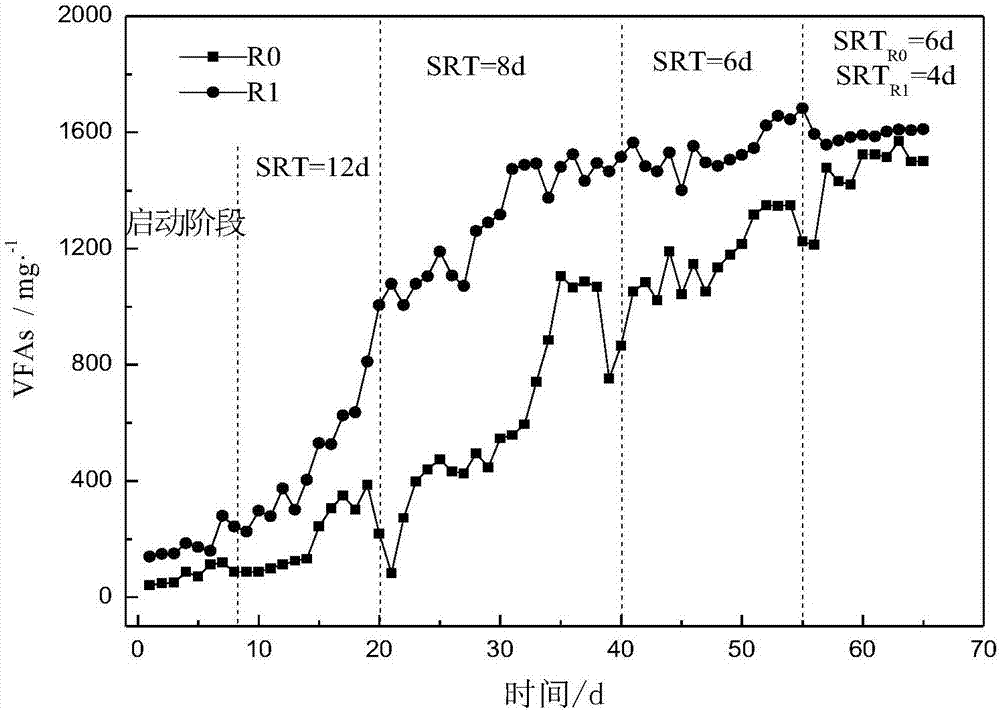
The invention relates to the technical field of excess sludge anaerobic fermentation in urban sewage treatment plants and discloses a carbon source recycling based excess sludge treatment process. By thermo-alkaline pretreatment of excess sludge, sludge cells are decomposed, macromolecules such as proteins and polysaccharides are released into supernatant; then sludge hydrolytic acidification is performed, activity of acid producing microorganisms is benefited while VFAs accumulation is promoted through an acidic starting (pH=6) stage, and through an alkaline fermentation (pH=10) stage, activity of methanogens can be inhibited to avoid VFAs consumption of methanogens in a methane producing process, and an acid production effect is kept stronger than a methane production effect, so that accumulation concentration of SCOD and VFAs in hydrolytic acidification liquid is greatly increased, and a high-quality regenerated carbon source is provided for upgrading of low C / N urban sewage.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAIYUAN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Method for increasing coal bed gas yield through indigenous bacteria
InactiveCN106285581AIncrease gas outputImprove porosity and permeabilityBacteriaPreparing sample for investigationFermentationCoal
The invention provides a method for increasing the coal bed gas yield through indigenous bacteria. The method comprises the steps of (1) a methanogens community is enriched and cultured, specifically, a coal sample and a water sample are collected from a target zone, enrichment culture and fermentation of the methanogens community are conducted, and fermentation liquor is obtained; (2) ultrasonic coupling supercritical CO2 treatment is conducted, specifically, a laboratory operation and maintenance management system is used, the optimal condition for ultrasonic coupling supercritical CO2 treatment on the coal seam sample is analyzed in a laboratory, and a target coal seam is treated under the optimal condition; and (3) coal degradation through microorganism is conducted, specifically, the fermentation liquor obtained in the step (1) is injected into the target coal seam, changes of injection wellhead gas components and the methane concentration are detected continuously, and methane is gathered in drainage, pressure lowering and recovering modes. The treatment time is effectively shortened through the ultrasonic coupling supercritical CO2 treatment, the coal bed gas generation speed is increased, and meanwhile the working efficiency is effectively improved through the laboratory operation and maintenance management system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Biogas fermentation accelerant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103255179AThe promotion effect is obviousWaste based fuelFermentationChemical oxygen demandTrace metal
The invention discloses a preparation method of a biogas fermentation accelerant. The fermentation accelerant comprises trace metal elements such as Fe, Co, Ni and Zn. The preparation method comprise the following steps of preparing a thick salt solution in a chloride form; adding quantified thick salt solution into a fermenting methane pool every day, then stirring for well mixing the metal elements in fermentation liquor. The accelerant has good effect for biogas fermentation taking cow dung, pig manure and sheep manure as raw materials, and has good immediate effect on methanogens in biogas fermentation; if the accelerant is added in biogas fermentation, the methane yield can be improved and the methane content of the methane can be improved, the removal rate of COD (chemical oxygen demand), TS (thymidylate synthase) and VS can be obviously improved, and the accelerant has good prospect for promotion and application of the biogas fermentation.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Method, composition and apparatus for high temperature production of methane from poultry waste
Compositions, methods and apparatus for the production of methane gas from poultry litter are provided. Particular features are selection of methanogens, well stirring of the digester, and control of critical parameters of digester temperature, pH, and solids content resulting in enhanced methane production and reduced nitrogen compositions. A benefit of the invention is the capability to maintain a closed system without waste by-products.
Owner:EAGLE GREEN ENERGY
Sustained microbial production of hydrogen gas from diluted fruit juice
InactiveUS20070178570A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismHydrogen
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for the production of hydrogen based on the capture of metabolic by-products of hydrogen-producing microbacteria, in which a bioreactor is maintained in an environment conducive to the growth of hydrogen-producing microbacteria and the production of hydrogen and at the same time is restrictive to the growth of undesirable microorganisms such as methanogens and the production of methane. The present invention utilizes concentrated growth of hydrogen-producing microbacteria such as Klebsiella oxytoca. The invention provides a simple and cost-effective way to produce hydrogen by selectively harnessing hydrogen-producing microbacteria utilizing glucose-based solutions while substantially eliminating methane-producing microbacteria.
Owner:NANOLOGIX INC
Preparation of composite bacteria
InactiveCN101481676APromote degradationPerformance unchangedMicroorganism based processesMicrobiology processesCelluloseMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for preparing composite bacterium, comprising the following steps: inoculating microorganism of zymogenous bacteria, hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and methanogen respectively belonging to facultative anaerobic bacteria and strict anaerobic bacteria which are mixed according to a certain proportion into a culture solution containing cellulose, sealing and keeping standing to culture at a temperature of between 30 to 50 DEG C and pH value of 3 to 10, wherein the culture solution containing cellulose contains CaCO3, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of NaCl, 0.5 to 1 percent of cellulose, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of urea, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of peptone and 0.05 to 0.15 percent of yeast powder, and water is used as a solvent. The composite bacterium having effective cellulose degrading property and capable of generating methane is prepared by the method.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Microbial fuel cell and power generation device with same
InactiveCN101800327AEasy to prepareLow costCell electrodesFinal product manufactureMicrobial fuel cellAdhesive
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell, a power generation device provided with the microbial fuel cell, and application of the power generation device provided with the microbial fuel cell in microbial power generation in a rice field. The microbial fuel cell comprises an anode, a cathode and a proton exchange membrane; the cathode comprises a catalyst, a conductive material and adhesive; the catalyst is manganese dioxide; and the proton exchange membrane is waterproof breathable cloth. The microbial fuel cell is used for manufacturing the power generation device, and the power generation device applied in the rice field can compete with methanogen in the rice field on organic substances so as to reduce the discharge amount of methane in the rice field, reduce the emission of greenhouse gas and contribute to the global climate.
Owner:刘忠毅 +4
Technology for methane production through aerobiotic acidification and anaerobic fermentation by means of straw
The invention relates to a technology for methane production through aerobiotic acidification and anaerobic fermentation by means of straw. According to the technology, a large amount of agricultural wasted straw is used as the main material, the aerobiotic acidification and anaerobic fermentation two-phase methane production process is conducted, solid-liquid separation is conducted on biogas slurry obtained after fermenting methane, the solid part can directly serve as organic fertilizer without dewatering, and the liquid part is recycled into an aerobiotic acidification tank for acidolysis; no waste water is discharged in the whole process. By adopting the aerobiotic acidification and anaerobic fermentation two-phase fermentation process, placing acid-forming bacteria and methanogens in two reactors respectively and conducting acidification through the aerobic reaction, biogas loss and propionic acid accumulation caused by methanogens during acidification are avoided, the time for anaerobic fermentation of biogas is shortened, and biogas producing efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU KAISHAN BIOCHEM ENG
Dual method of hydrogen production
InactiveUS20060272955A1Readily combinableReadily proximateCellsHydrogen separation using liquid contactBioreactorHydrogen production
The present invention provides a dual method of hydrogen production, wherein organic feed material is heated with excess or diverted heat from a secondary hydrogen production method, thereby substantially deactivating or killing methanogens within the organic feed material. Hydrogen producing microorganisms contained or added to the organic feed material metabolize the organic feed material in a bioreactor to produce hydrogen in a primary hydrogen production method. As the methanogens are no longer substantially present to convert produced hydrogen to methane, a biogas that contains hydrogen without substantial methane can be produced.
Owner:FELDER MITCHELL S +2
Power generation technology with biogas produced by mixed fermentation of excrement and straws of distributed swine breeder
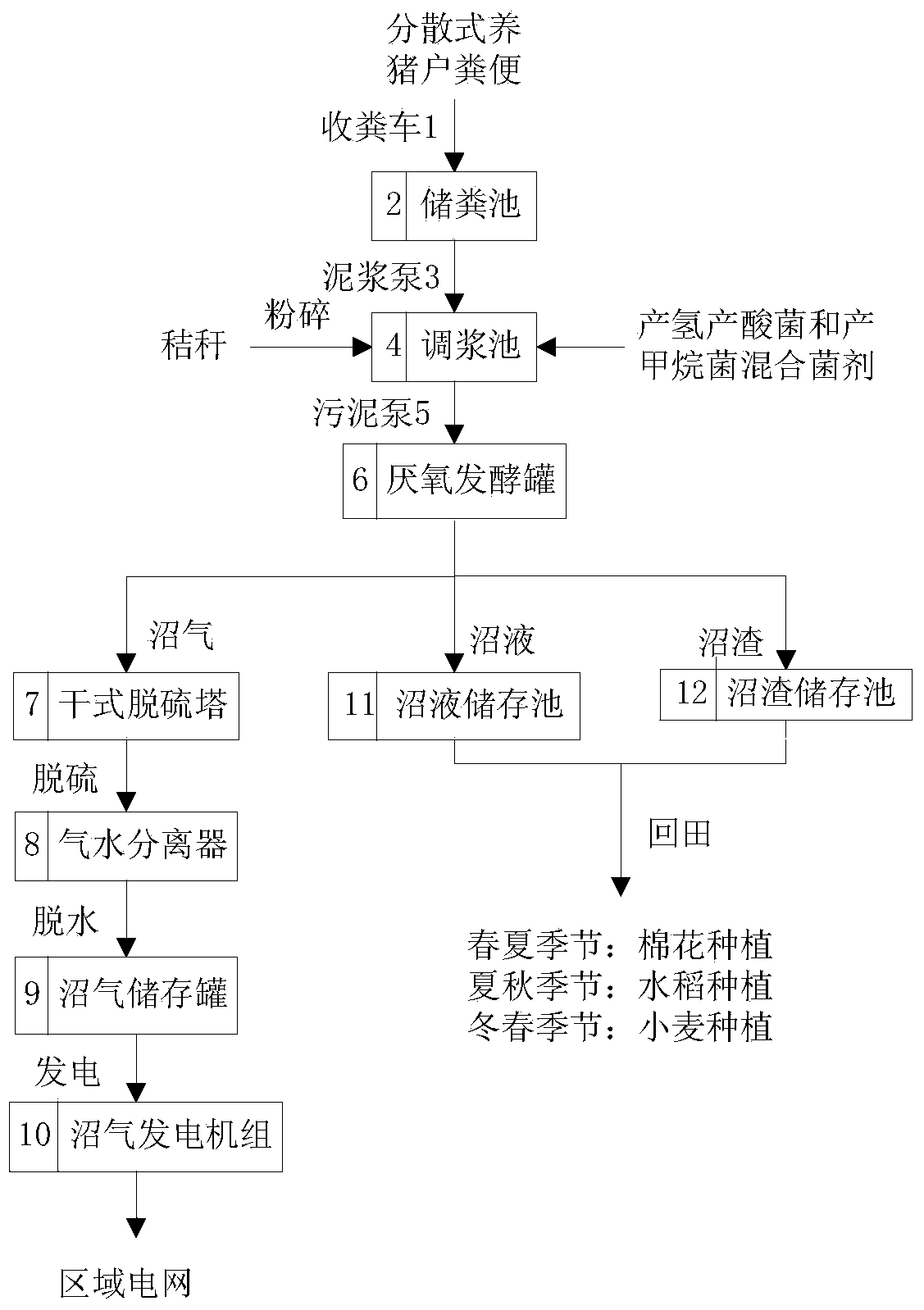
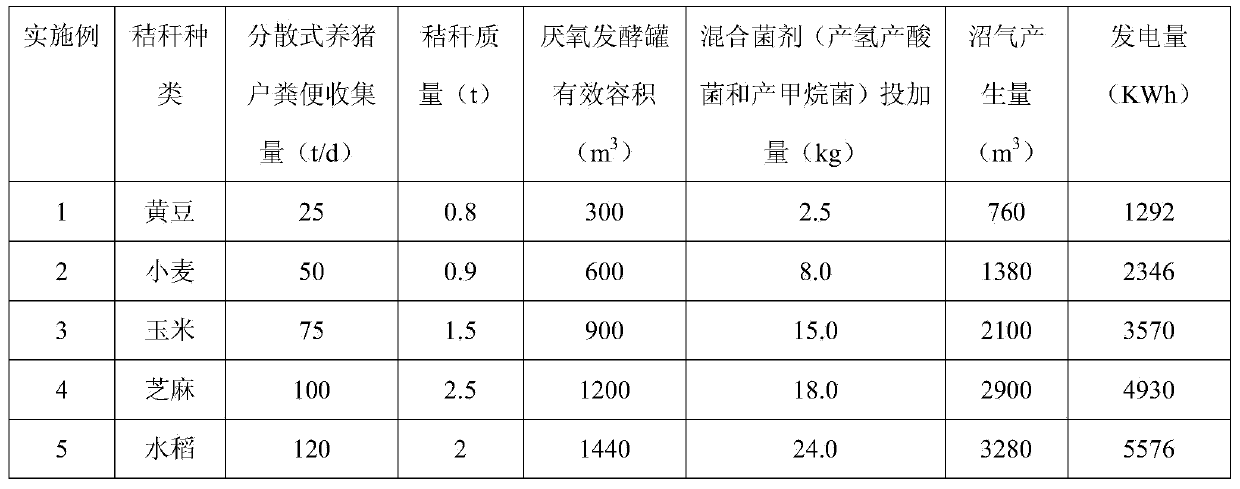
InactiveCN104004793AIncrease incidenceRealize resource utilizationWaste based fuelFermentationRural areaSocial benefits
The invention discloses a power generation technology with biogas produced by mixed fermentation of excrement and straws of distributed swine breeders. The power generation technology mainly solves the excrement processing problem and the processing problem of the abandoned crop straws of the distributed swine breeders in a rural area, after the excrement of the distributed swine breeders is collected, the smashed abandoned crop straws and mixed microbial inoculums (hydrogen and acid production bacteria and methane production bacteria) are added for conducting fermentation for producing the biogas, the generated biogas is used for power generation with a biogas power generation set, biogas residues and biogas slurry are returned to the field to be used for planting crops. By means of the processing technology, the excrement and the abandoned crop straws of the distributed swine breeders are processed, power generated by the biogas is connected into an area power grid, and certain economical benefits can be achieved; meanwhile, the biogas residues and the biogas slurry are absorbed by farmlands, the crop yield is improved, and the good environmental and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for accelerating anaerobic fermentation of organic waste water or organic castoff to prepare sludge gas
InactiveCN101319230AIncrease productionImprove bioavailabilityWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMethane yieldAnaerobic reactor
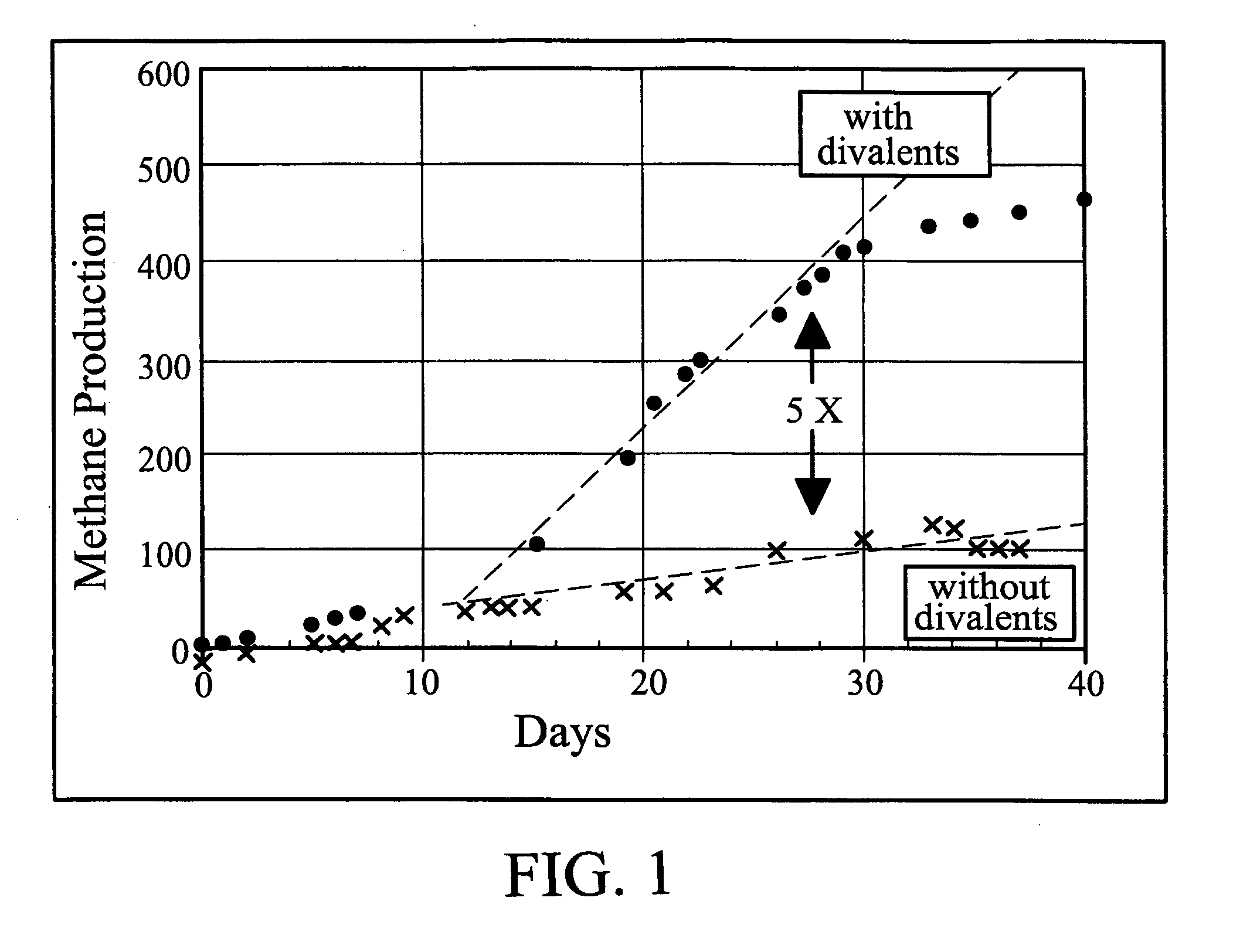
The invention relates to a method for promoting the anaerobic fermentation of organic waste water or organic wastes to produce biogas, belonging to the wastes biological treatment technical field. The method takes simulated organic waste water as a treatment object, and adds a trace metallic element sequestering agent into an anaerobic reactor to improve the bioavailability of the trace metallic element necessary for methanogens and to promote the growth and activity of the methanogens, thereby improving the methane yield and the contaminant conversion rate of a system. As the addition mount of the trace metallic element sequestering agent is very low, the method has not only simple and highly efficient operation, but also low cost, and can be expected to be widely applied to engineering practices.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving methane yield by organic waste water anaerobic fermentation
InactiveCN101157937AIncrease productionImprove bioavailabilityWaste based fuelFermentationChemical industryTransformation efficiency
The invention relates to a method used for raising the output of marsh gas by using anaerobic fermentation of organic effluent water, which pertains to the technical field of biological treatment of effluent water. The invention adopts simulated organic effluent water or practical wastewater from chemical industry as treatment objects, by adding trace metal element Co and metal ion chelating agent to an anaerobic reactor to improve the biological availability of trace metal elements which are essential for methanogen and promote the growth and activity of methanogen, thereby, methane output and transformation efficiency of contaminating material of the system is improved. The method needs only extreme micro-amount of trace metal element Co and metal ion chelating agent, therefore, the invention is not only convenient to be manipulated with high efficiency and but also low in cost which leads the invention to be extensively applicable in engineering practice.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions for reducing gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants
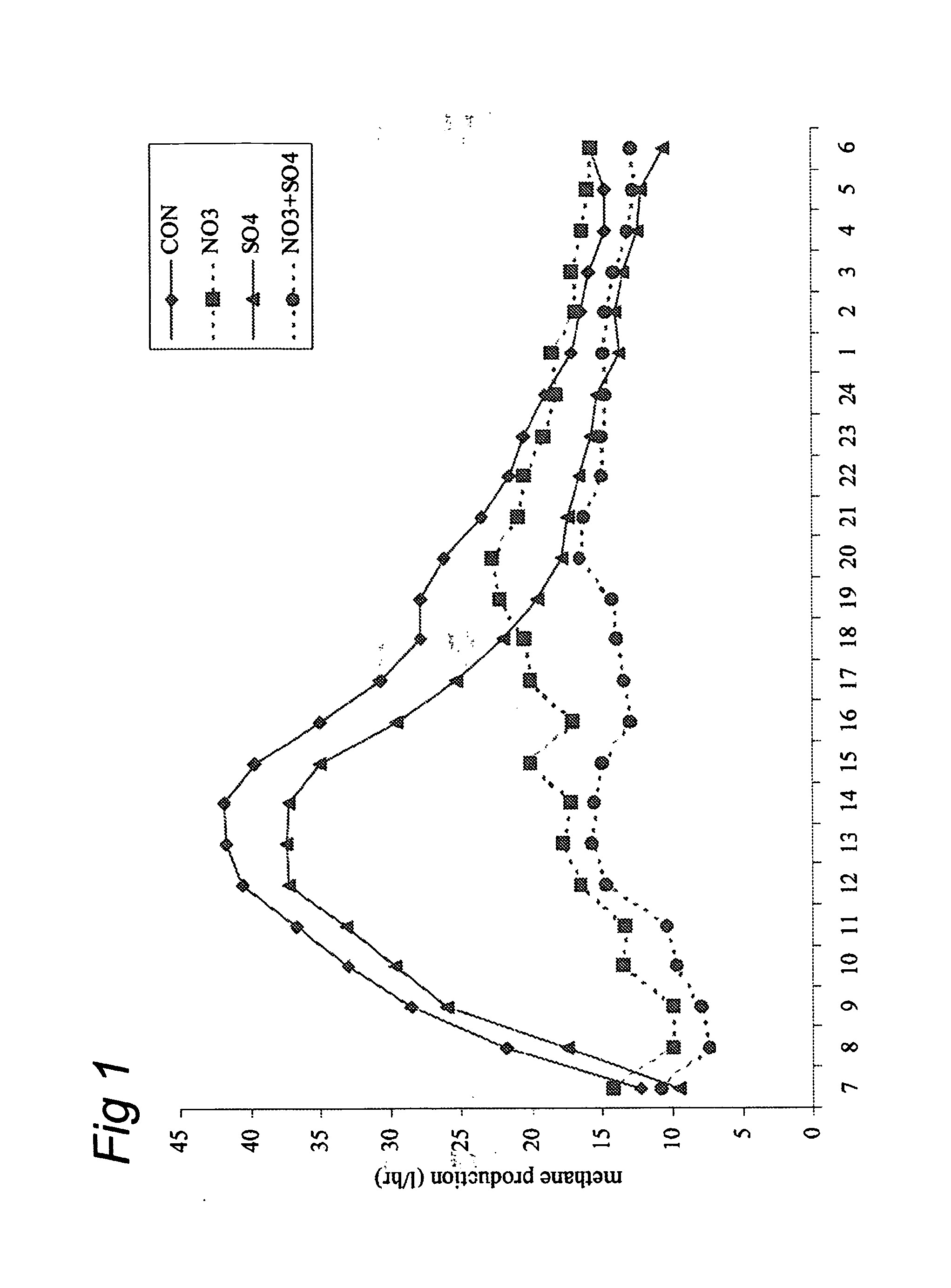
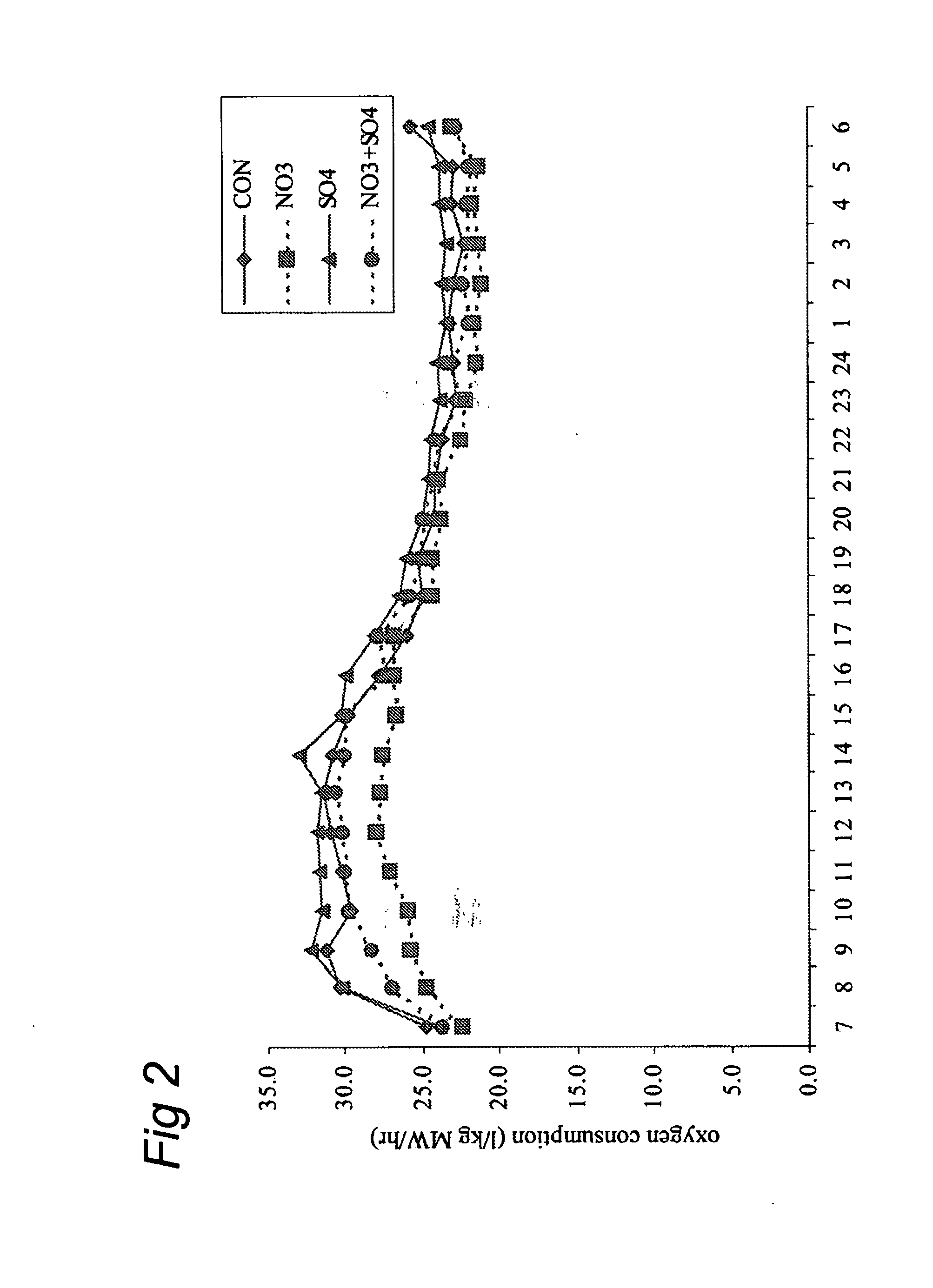
ActiveUS20120219527A1More energyEmission reductionBiocideMetabolism disorderNitrite poisoningFermentation
The present invention concerns the reduction of gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants with the aid of agents that compete for the hydrogen atoms required by methanogens during normal fermentation of ingested feed. The invention in one aspect resides in the findings that both nitrate reductive pathways as well as sulphate reductive pathways outcompete gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants and, that the methanogenesis reducing effects of nitrate and sulphate are completely additive. At the same time the combined administration of nitrate and sulphate was found to be fully effective to avoid or mitigate the potential problems of nitrite intoxication normally encountered when using nitrate alone, which effect is further enhanced, where necessary, by the addition of a nitrite reducing probiotic micoroorganism. Hence, products are provided comprising high amounts of a combination of a nitrate compound and a sulphate compound and optionally a nitrite reducing probiotic microorganism, as well as methods of reducing gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants using such compositions.
Owner:CARGILL THE NETHERLANDS HLDG
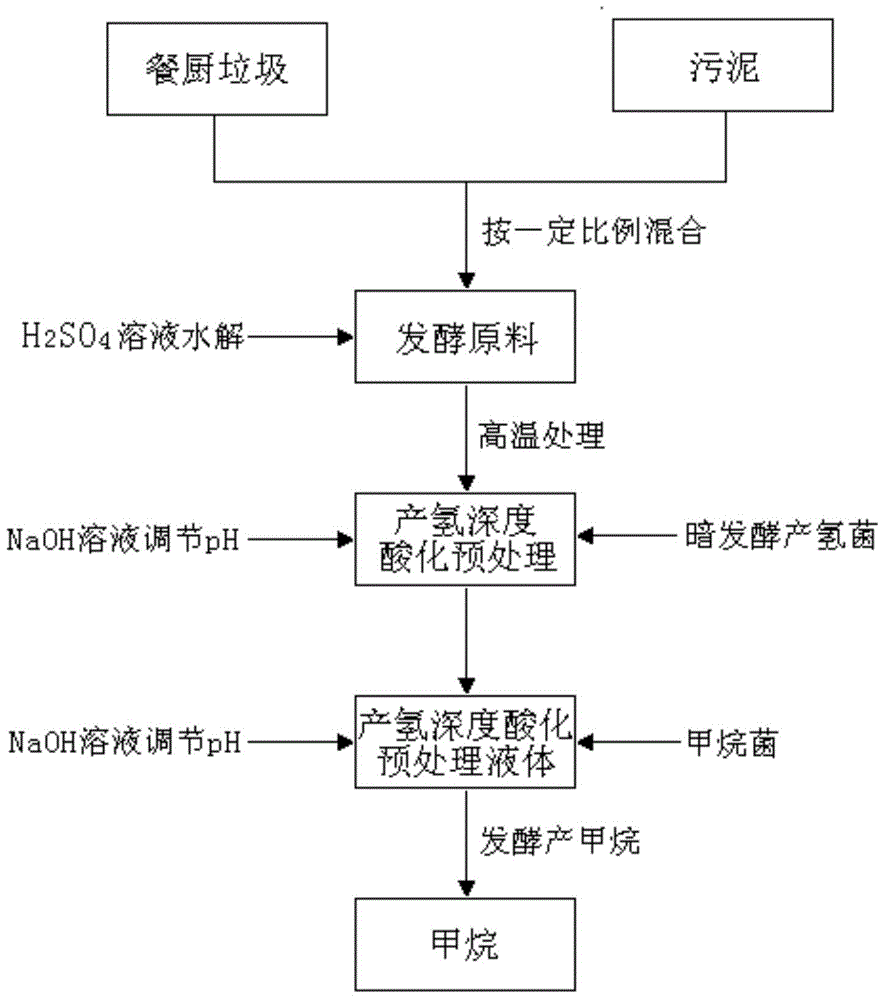
Kitchen waste and sludge hydrogen-producing acidification pretreatment method capable of increasing methane production rate
ActiveCN104561222AIncrease production rateIncrease throughputMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelPretreatment methodSludge
The invention relates to the technology of biomass energy utilization, and aims to provide a kitchen waste and sludge hydrogen-producing acidification pretreatment method capable of increasing the methane production rate. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the kitchen waste and the sludge after crushing pretreatment, using the mixture and a sulfuric acid solution to prepare a mixed liquid, performing hydrolysis on the mixed liquid at 135 DEG C to obtain a starting crude; adding yeast powder into the starting crude, inoculating dark-fermentation hydrogenogens, feeding high-purity nitrogen to build an anaerobic fermentation environment, then performing dark-fermentation hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment at the constant temperature of 37 DEG C, and obtaining a hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment liquid; adding methanogens into the liquid, keeping the anaerobic environment at 37 DEG C, and performing methane fermentation and coproduction. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the hydrogen-producing deep acidification pretreatment is utilized to obviously increase the methane production rate; the rate peak time of the produced methane is reduced by about 50%; the waste treatment and degradation time of the fermentation tank with a unit volume is reduced by about 50%; the waste treatment capacity of the single equipment in unit time is improved by about one time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biological methane production from coal, manure, sludge, wastes, or other carbonaceous feedstocks with simultaneous sequestration of co2
ActiveUS20100093049A1Reduce capacityReduce gas contentProductsGas treatmentParticulatesAlkaline earth metal
The present invention provides a method for generating methane from a carbonaceous fuel source with simultaneous sequestration of carbon dioxide, the method comprising anaerobically incubating a particulate alkaline earth metal salt in contact with a particulate and / or dissolved carbonaceous feedstock in a neutral or alkaline aqueous culture medium containing a culture of methanogenic bacteria consortia and collecting methane generated therefrom. At least a portion of carbon dioxide produced during the incubation reacts with the alkaline earth metal salt to form an alkaline earth metal carbonate, thereby sequestering the carbon dioxide.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Methane production from single-cell organisms
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing the growth of single-cell organisms, such as methanogens. The growth of the single cell organisms includes consuming carbon dioxide to produce methane. The method can include providing a porous solid having an internal surface with a surface charge density, adhering the single-cell organism to the internal surface of the porous solid, populating the internal surface with the single-celled organism at least to confluence, introducing to the single-cell organism essential macronutrients consumed in the production of methane, and controlling the temperature conditions and pH conditions to allow the single-cell organism to produce methane.
Owner:BROWN PAUL W +1
Method for co-producing hydrogen and methane by biomass and solid organic waste fermenting method
InactiveCN1858213APollution controlRealize joint productionWaste based fuelChemical recyclingPropanoic acidHigh energy
The present invention relates to hydrogen and methane producing method and especially method of co-producing hydrogen and methane with biomass and solid organic waste and through fermentation. The method includes hydrolyzing and acidifying biomass and solid organic waste to produce pyruvic acid, short chain fatty acid and small amount of H2 and CO2; fermenting the mixture of pyruvic acid and short chain fatty acid under the action of fermenting hydrogenogen to produce great amount of hydrogen as well as small molecular weight side products ethanol, acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid; and further fermenting to convert the small molecular weight side products into methane under the action of methanogen. The apparatus can treat waste effectively to produce clean energy source material, and has high energy source converting rate and high matrix utilizing rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
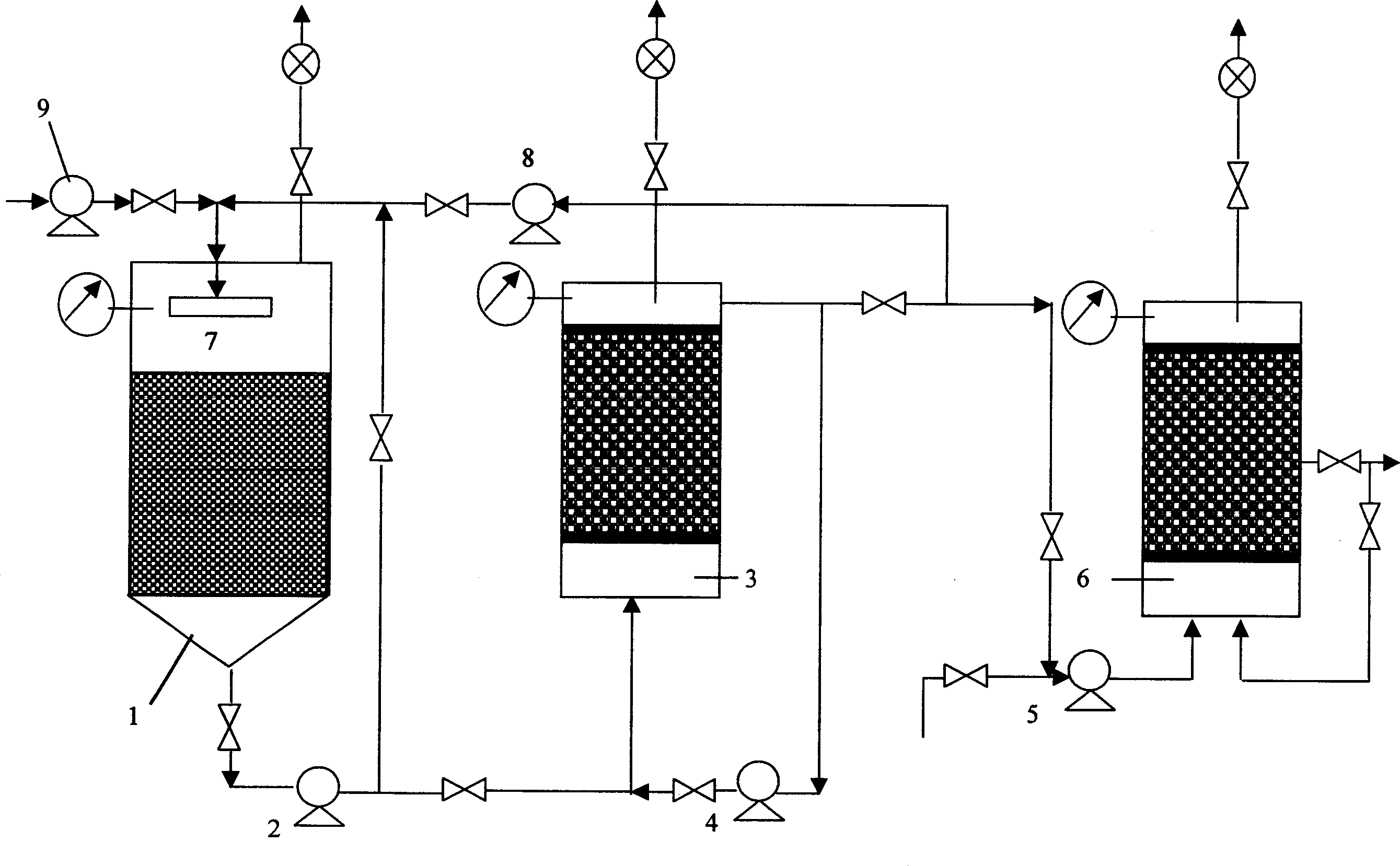
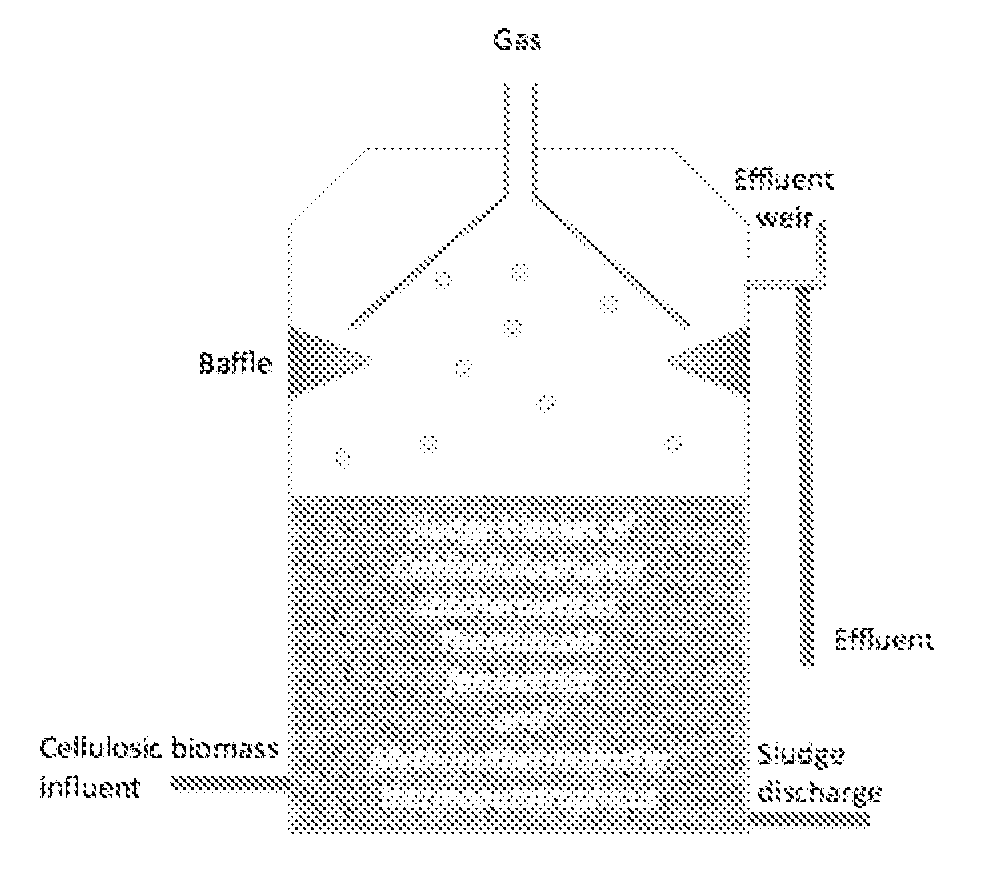
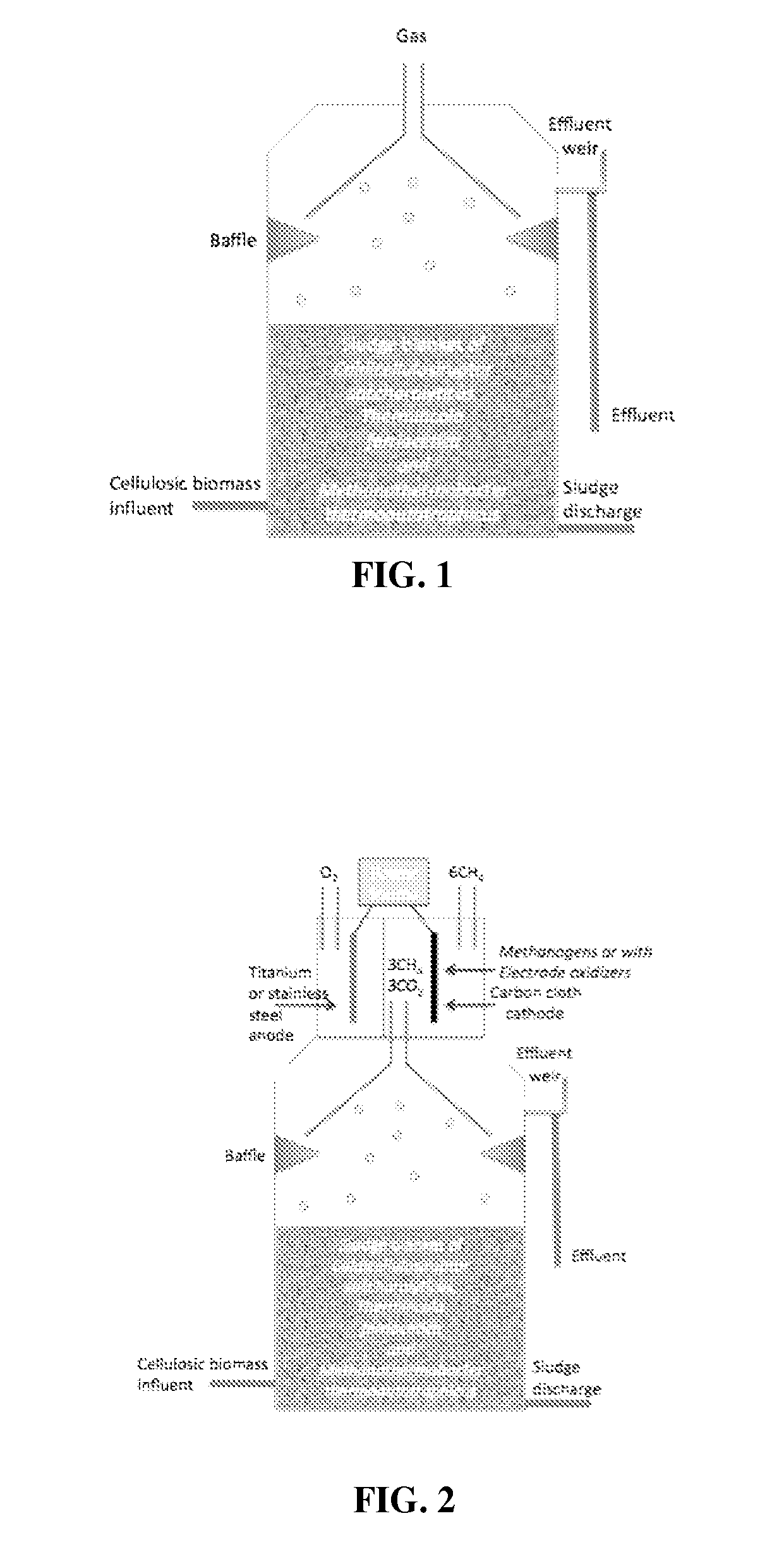
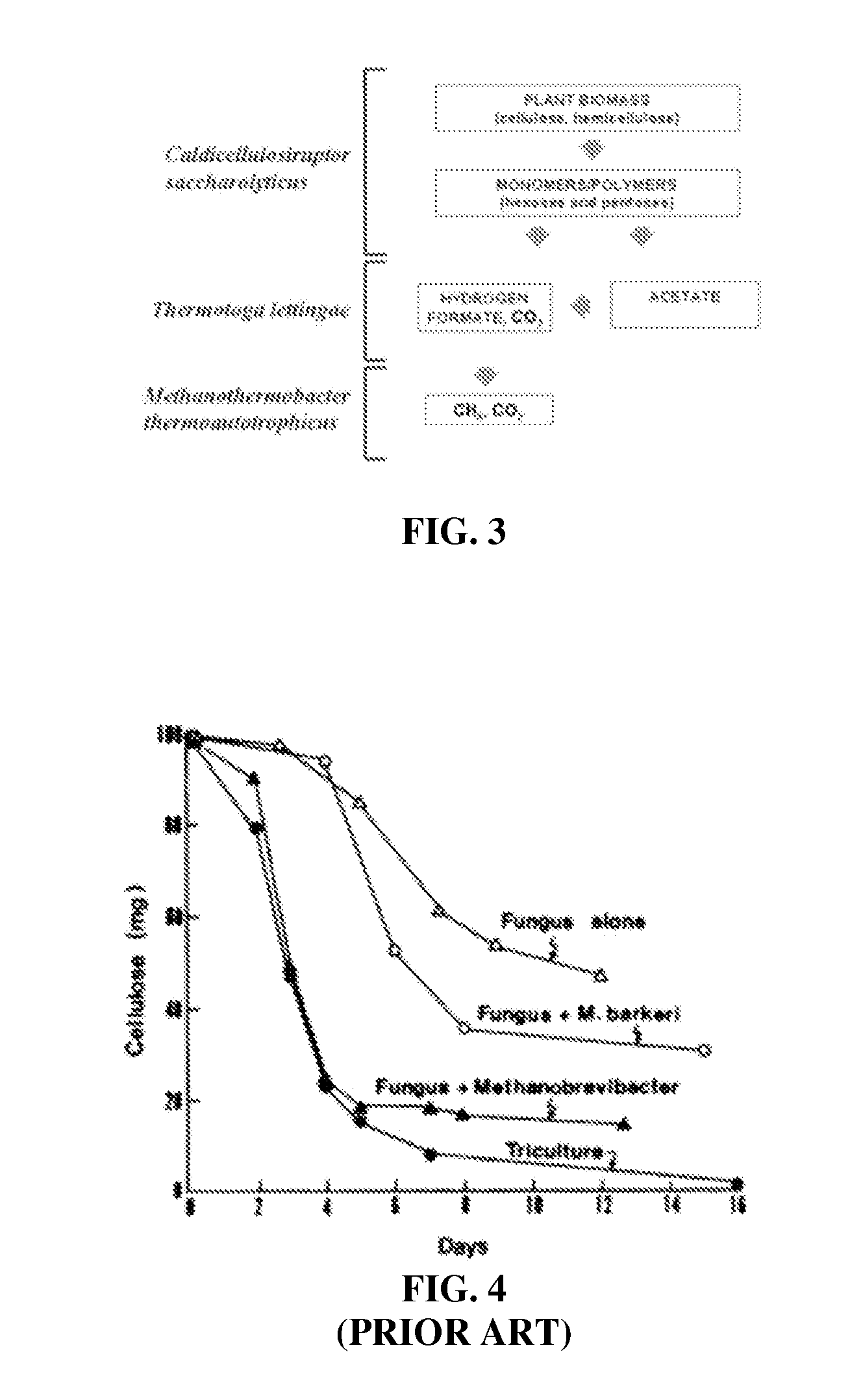
Thermophilic methanogenic consortium for conversion of cellulosic biomass to bioenergy
InactiveUS20110306089A1Efficient actionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseThermophile
A system for the efficient conversion of plant biomass to methane is provided, where the conversion includes use of a thermophilic methanogenic consortium containing a cellulolytic thermophile, an acetate-oxidizing thermophile and a thermophilic methanogen, the combination of which hydrolyzes hexoses and pentoses, oxidizes acetate and provides a hydrogen sink, to convert plant biomass to the theoretical limit of bioenergy.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com