Manipulation of the rate of gastrointestinal transit by modulating intestinal methane concertration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methane Excretion on Breath Test has a Positive Predictive Value of 100% for Constipation-Predominant IBS
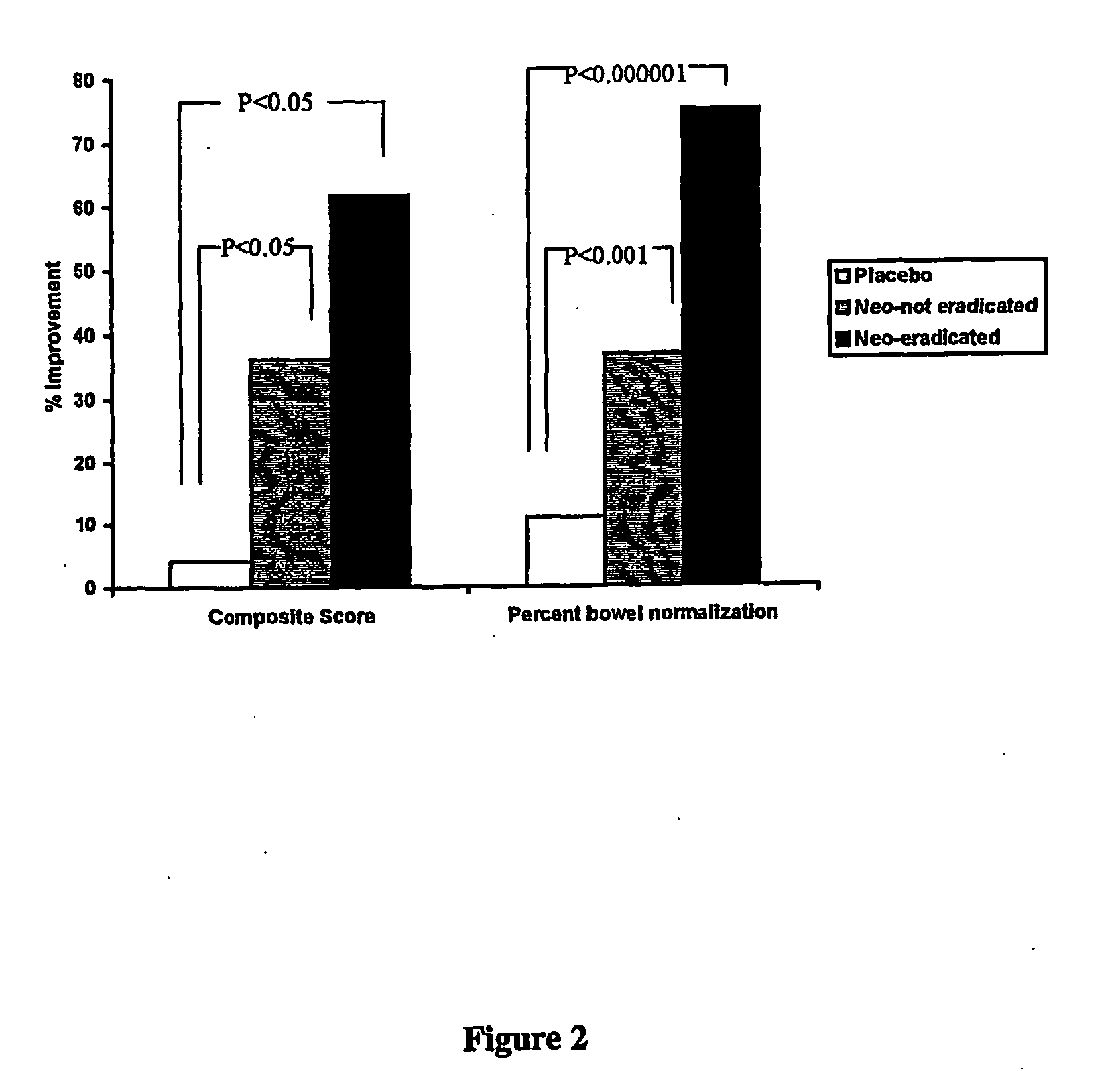
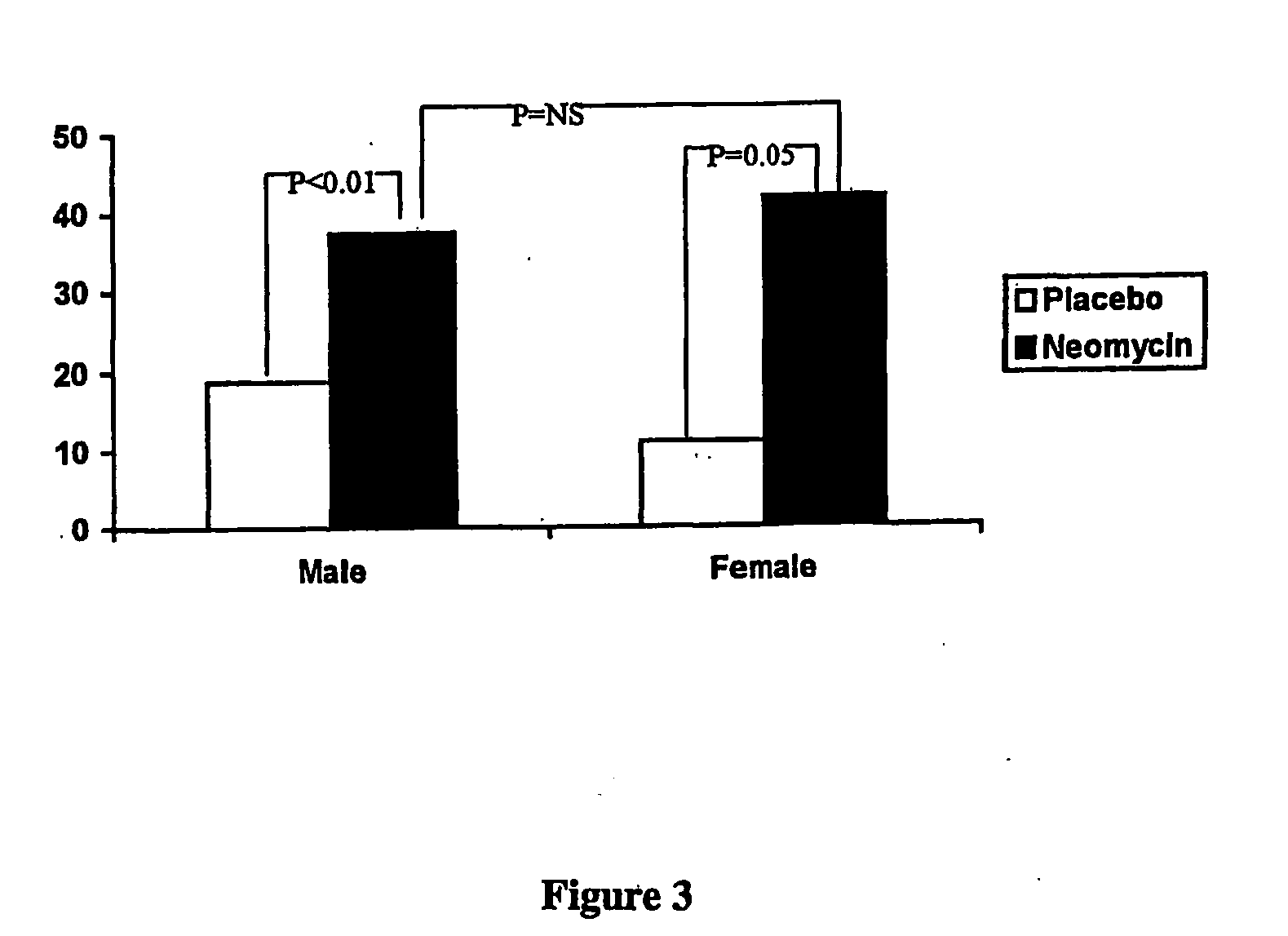
[0044] In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study, we confirm that an abnormal lactulose breath test is more prevalent in IBS than normal controls, and that antibiotic treatment in IBS leads to an improvement in symptoms and that this is based on antibiotic-induced normalization of breath test. Secondly, lactulose breath test profiles are evaluated to show that gaseous constituents vary among IBS subgroups. In this study, we show that methane excretion on breath test has a positive predictive value of 100% for constipation predominant IBS. This is another important step in linking SIBO and IBS.
A. Materials and Methods
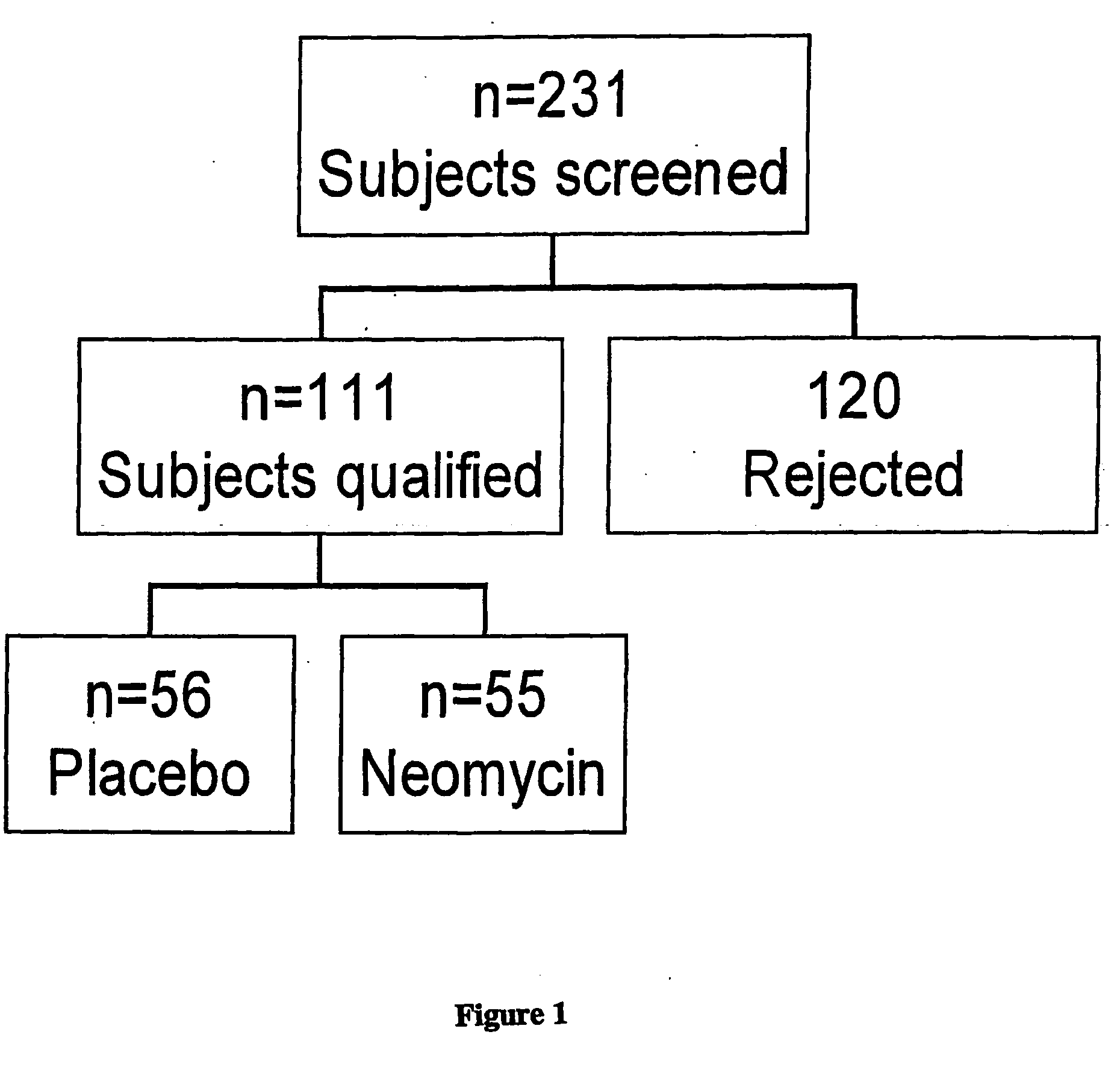
Study Population
[0045] Study subjects were recruited by advertising in local newspapers, radio and IBS support groups throughout the greater Los Angeles are& To avoid referral bias, subjects were not recruited through the GI motility clinic or any ...
example 2
Administration of Methane to the Distal Gut Slows Gastrointestinal Transit
[0075] We now show that methane administered directly to the distal gut produces a slowing of gastrointestinal transit. In dogs equipped with duodenal (10 cm from pylorus) and mid-gut (160 cm from pylorus) fistulas, intestinal transit was compared across an isolated 150 cm test segment (between fistulas) while the proximal segment of the gut was perfused with pH 7.0 phosphate buffer at 2 mL / min for 90 minutes. Room air (n=three dogs) or methane (n=three dogs) was delivered into the distal gut as a 180-ml bolus at time 0. Sixty minutes after the start of the perfusion, 20 μCi of 99 mTc-DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid) was delivered as a bolus into the proximal segment of the gut. Intestinal transit was then measured by counting the radioactivity of 1 ml samples collected every 5 minutes from the diverted output of the mid-gut fistula.
[0076] Intestinal transit was calculated by determining the area un...
example 3
[0078] The following study confirmed and further investigated the relationship between gastrointestinal complaints (specifically, diarrhea and constipation) in IBS-diagnosed subjects with SIBO and gas excretion on LBT in a large prospectively collected database. The prevalence of gas excretion patterns in IBS and the predominantly diarrheal conditions of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis were also compared.
A. Materials and Methods.
[0079] Consecutive patients referred for a lactulose breath test (LBT) to the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, GI Motility Program from 1998-2000 completed a questionnaire designed to assess bowel symptoms as previously described (12) after approval from the institutional review board. Subjects were requested to rate the severity of nine symptoms (diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, bloating, sense of incomplete evacuation, straining, urgency, mucus, and gas) on a scale of 0-5, 0 signifying the absence of the symptom. The questi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Partial pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com