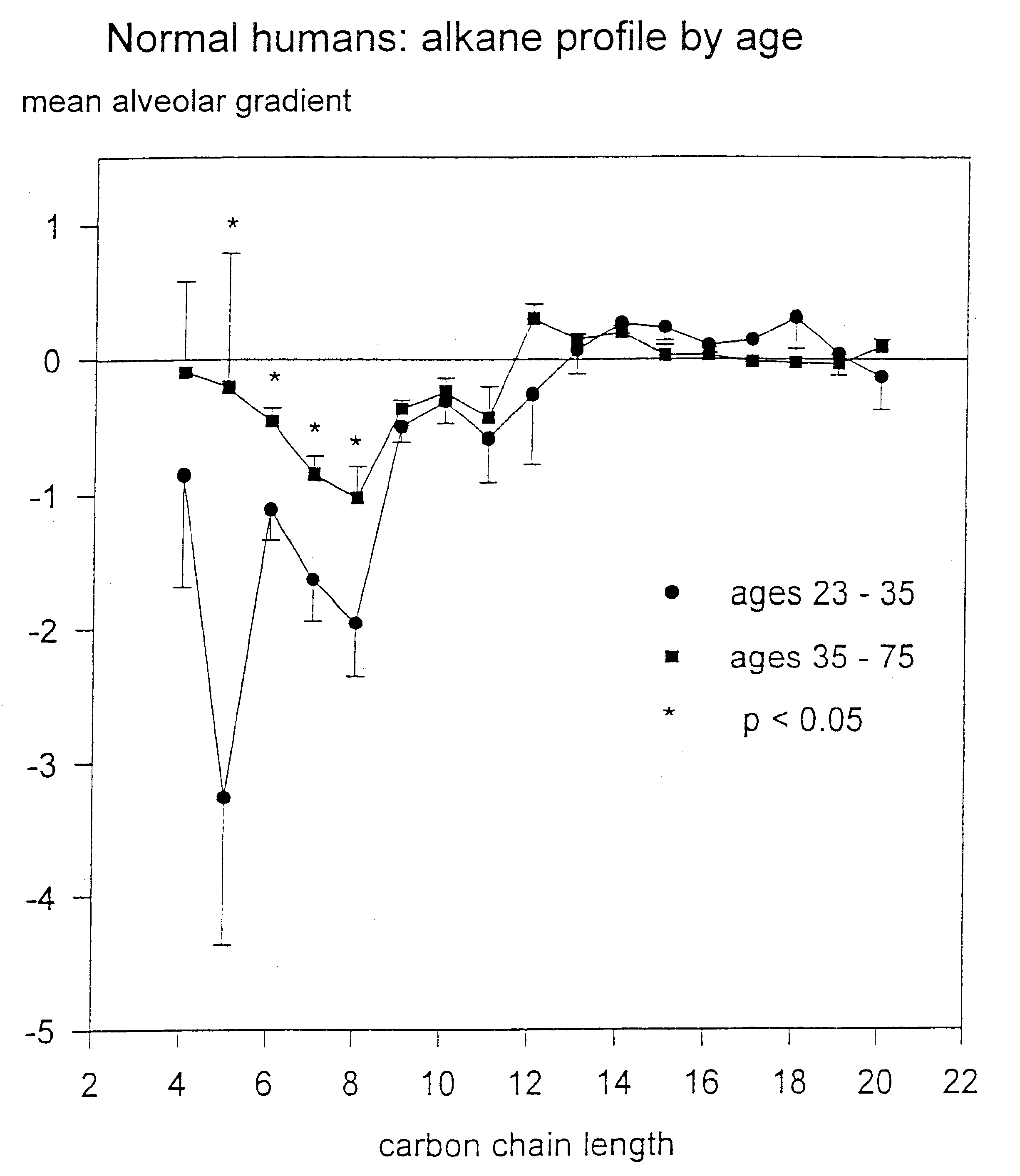
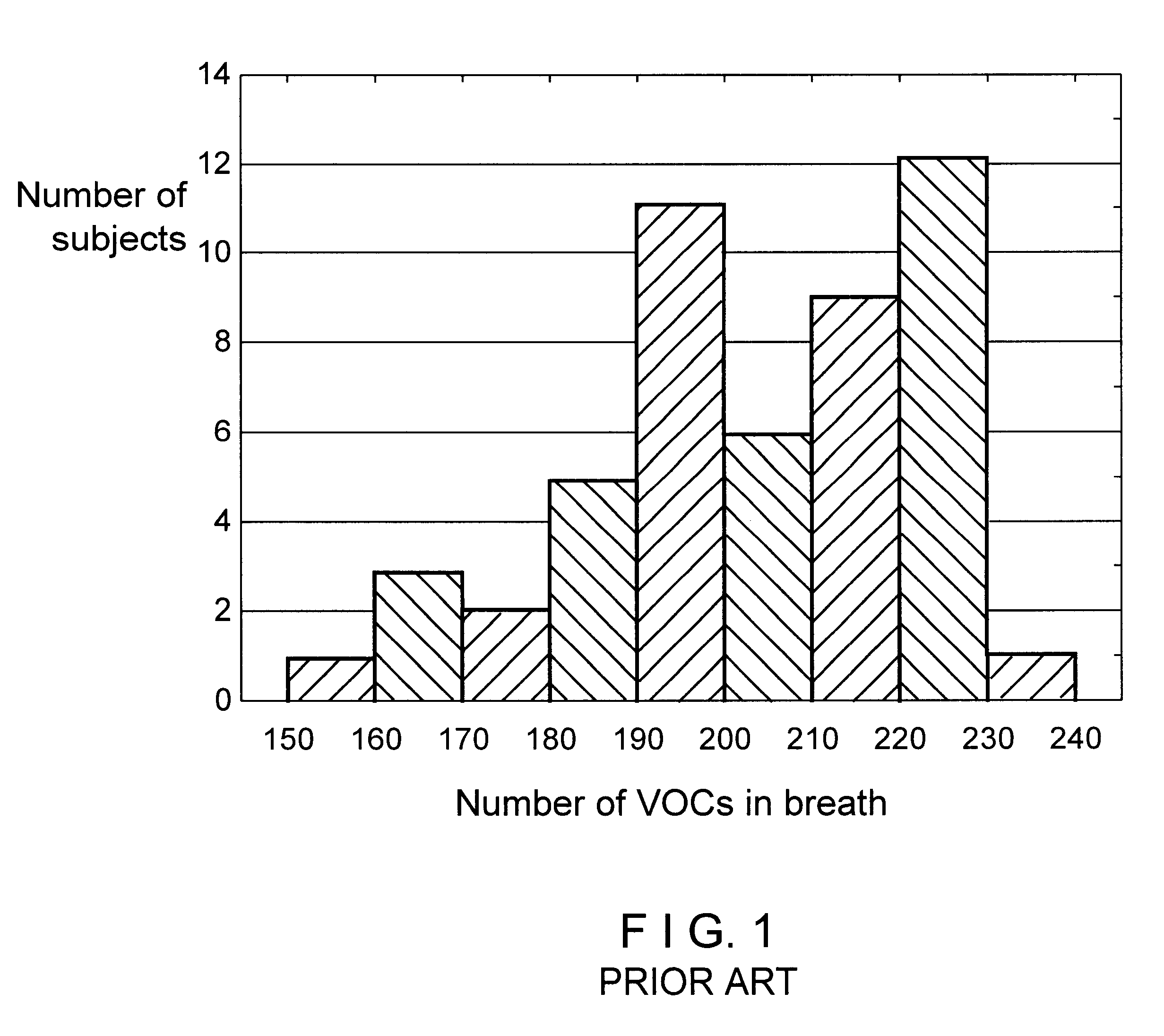
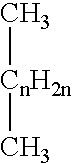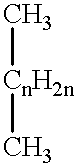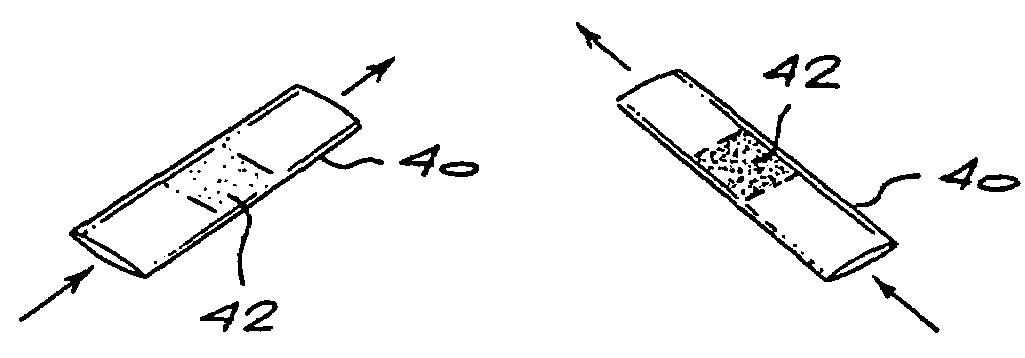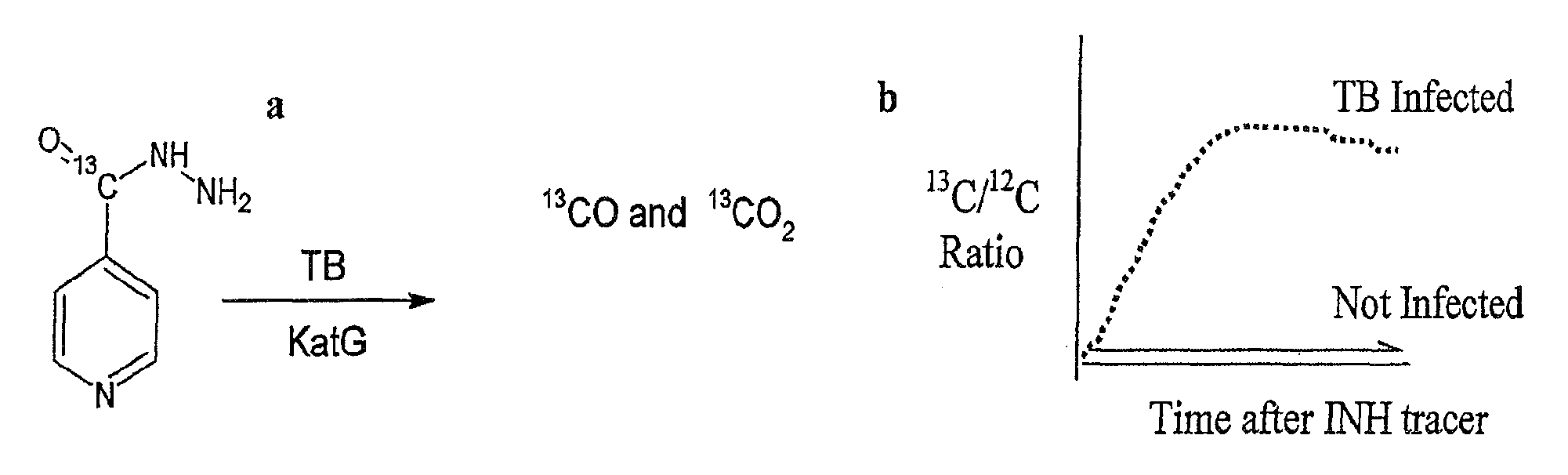Patents
Literature
71 results about "Breath test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
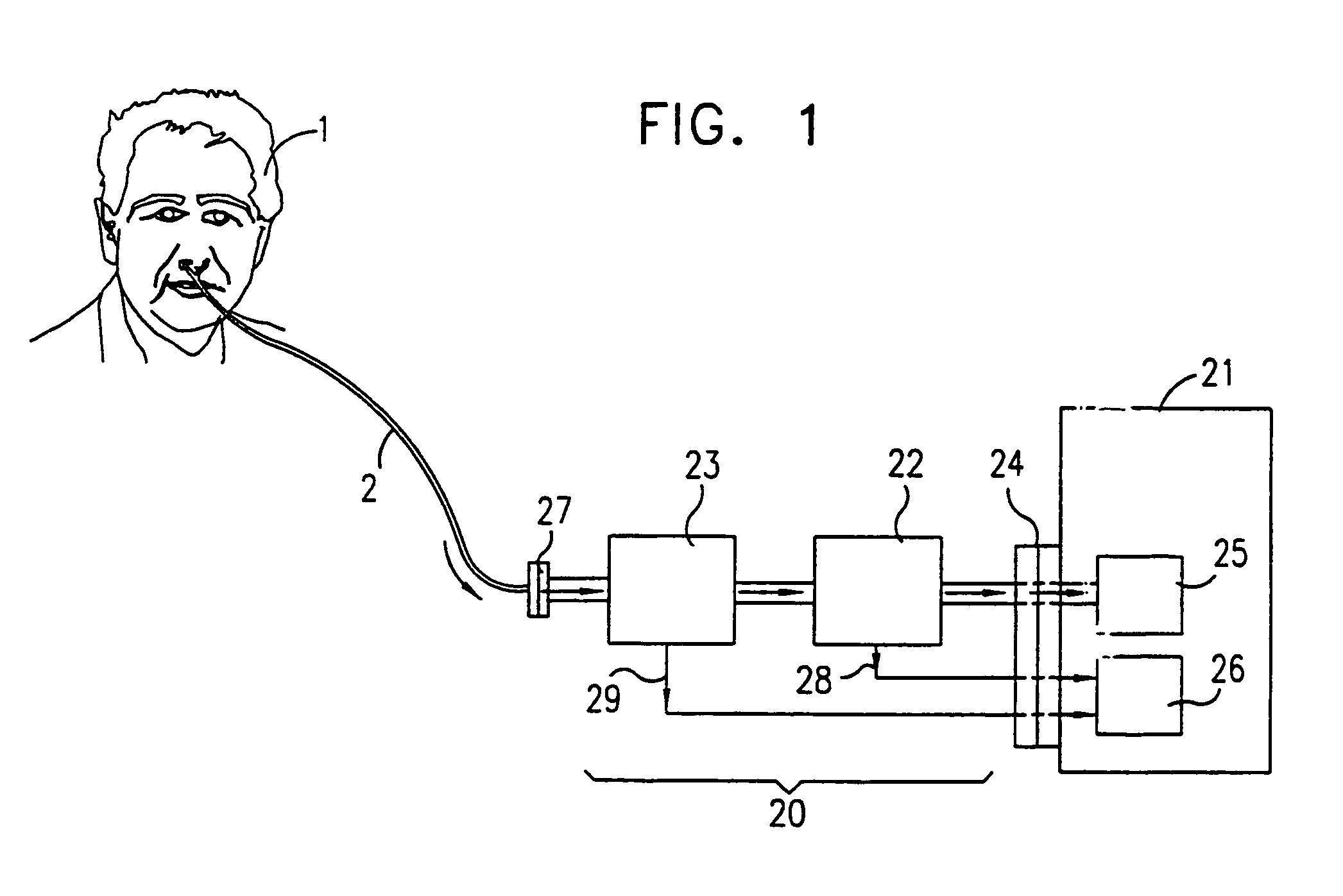
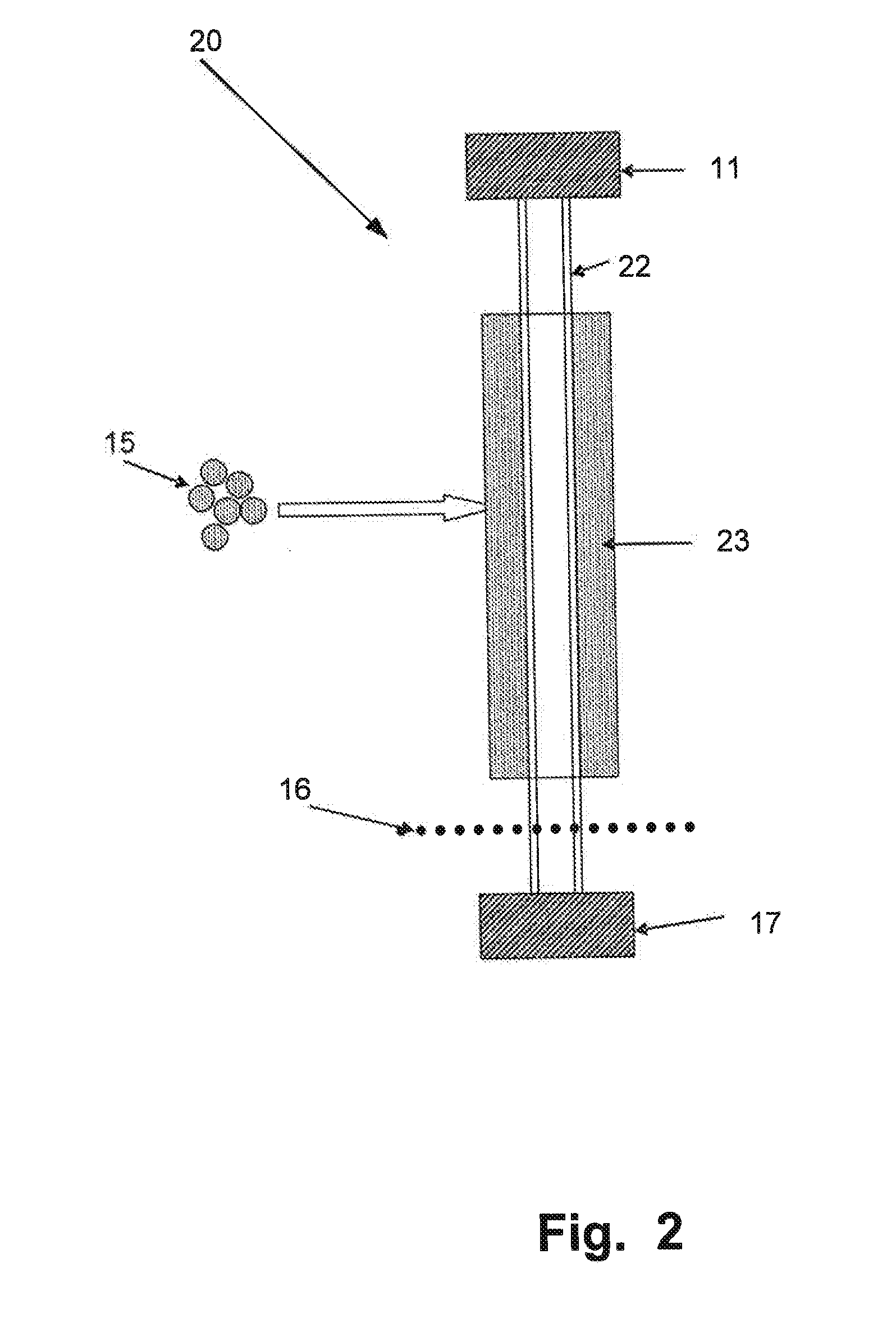
A breath test is a type of test performed on air generated from the act of exhalation.
Breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS6067989AMaximize accuracySpeed maximizationWithdrawing sample devicesSurgeryHp - Helicobacter pyloriUrease
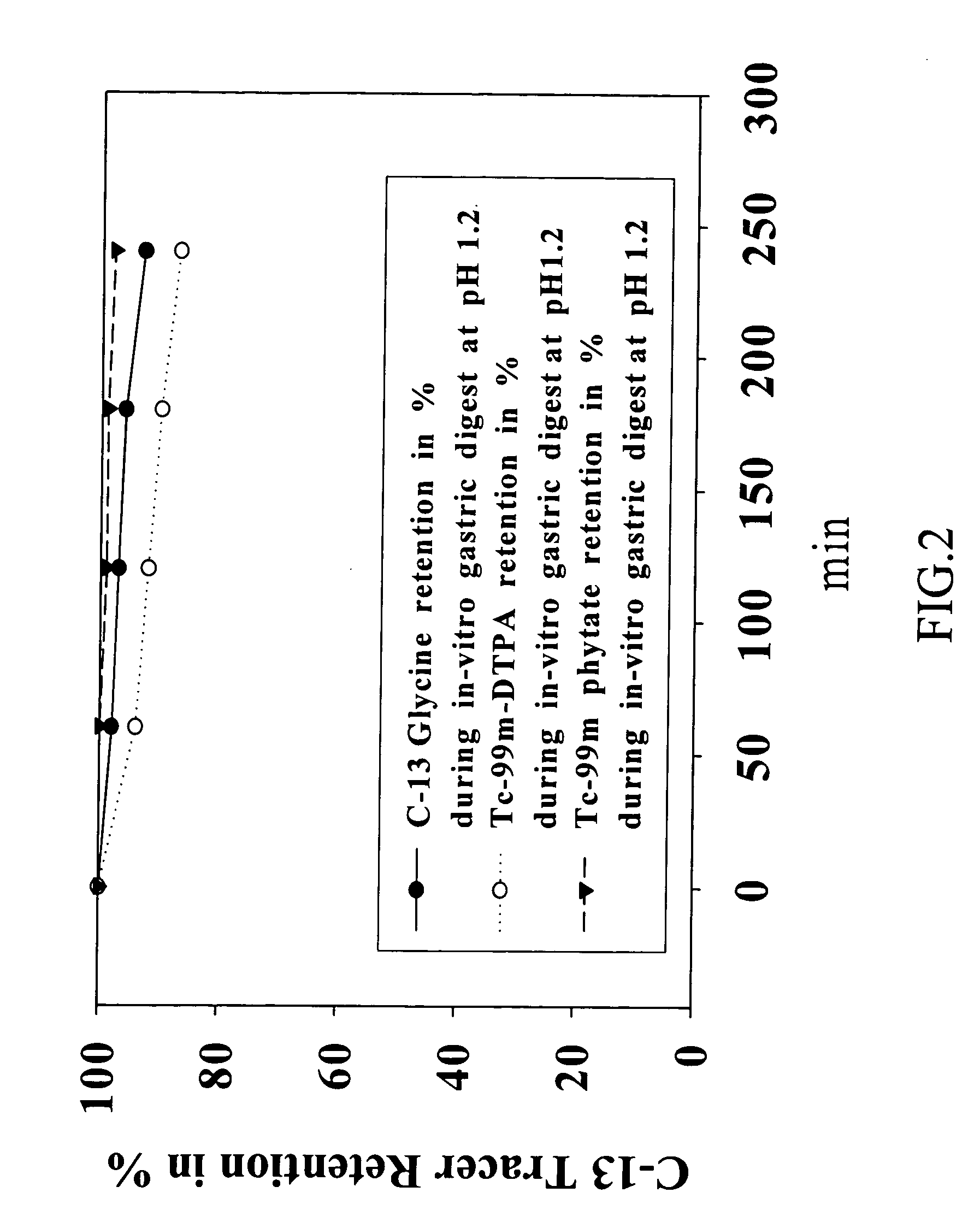
A breath test for diagnosing the presence of Helicobacter pylori in a subject is described. The method of diagnosing Helicobacter pylori is performed as follows. First, a safe and effective amount of urea, preferably appropriately labelled, is administered to the subject. Second, a plurality of the exhaled breaths of the subject is analyzed to detect the concentration of a cleavage product or products, produced when urease cleaves the substrate. The measured concentrations are then fitted to a curve, and the derivative is then calculated, to indicate the presence or absence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the subject.
Owner:EXALENZ BIOSCIENCE LTD +1
Breath test for detection of drug metabolism
InactiveUS6180414B1Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDrug metabolismMetabolite
A breath test for determining the rate of metabolism of a drug is described. First, a safe and effective amount of the drug, preferably appropriately labelled and most preferably isotopically-labelled, is administered to a subject. After a suitable time period, the exhaled breath of the subject is analyzed to determine the concentration of a metabolite. The concentration of the metabolite is then used to determine the rate of metabolism of the drug. A breath test kit is also described. Such a breath test kit would include an item or items necessary for performing at least one of the methods of determining the rate of metabolism of a drug in a subject. For example, such a breath test kit could include an isotopically-labelled drug to be administered to the subject.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL
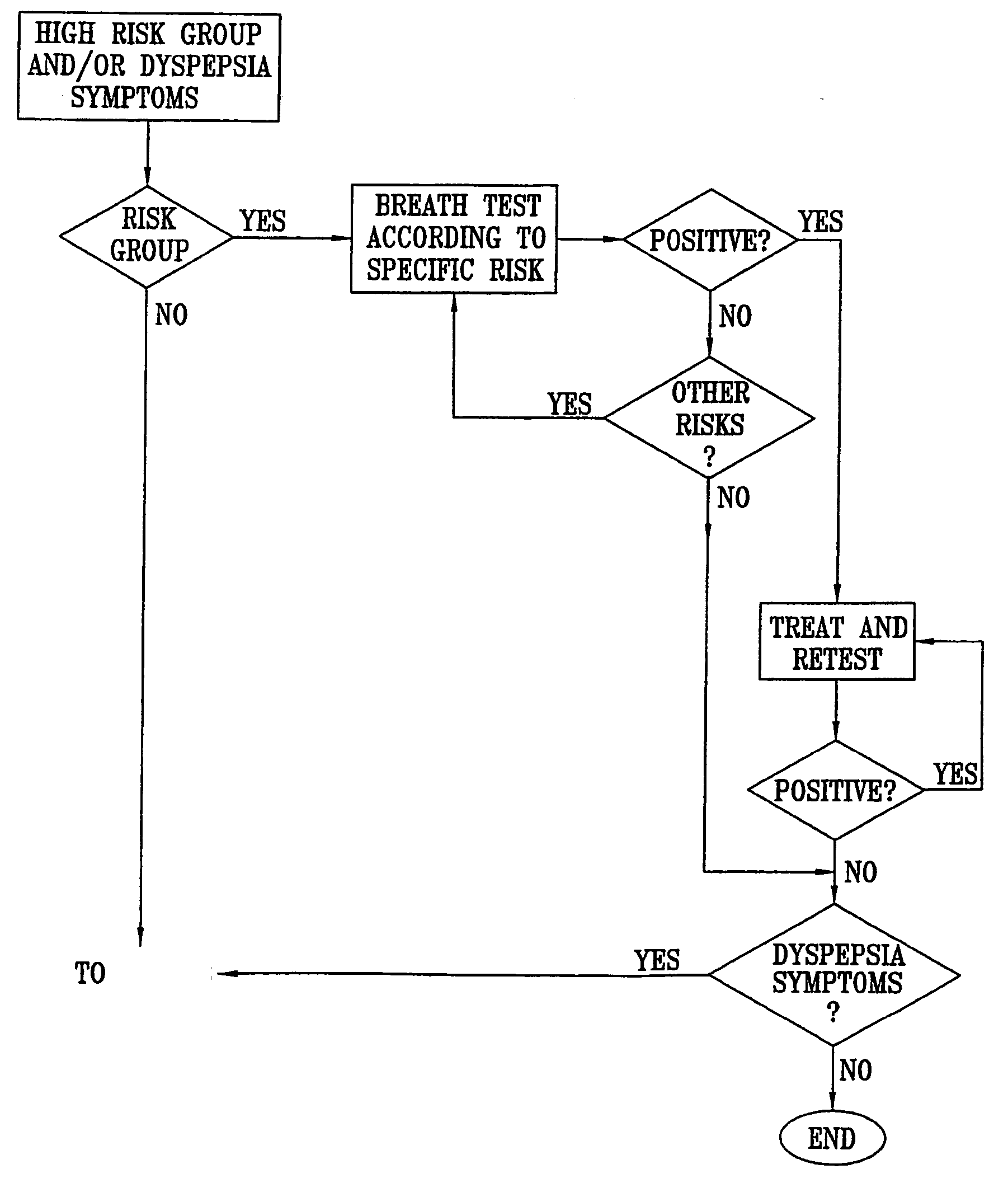
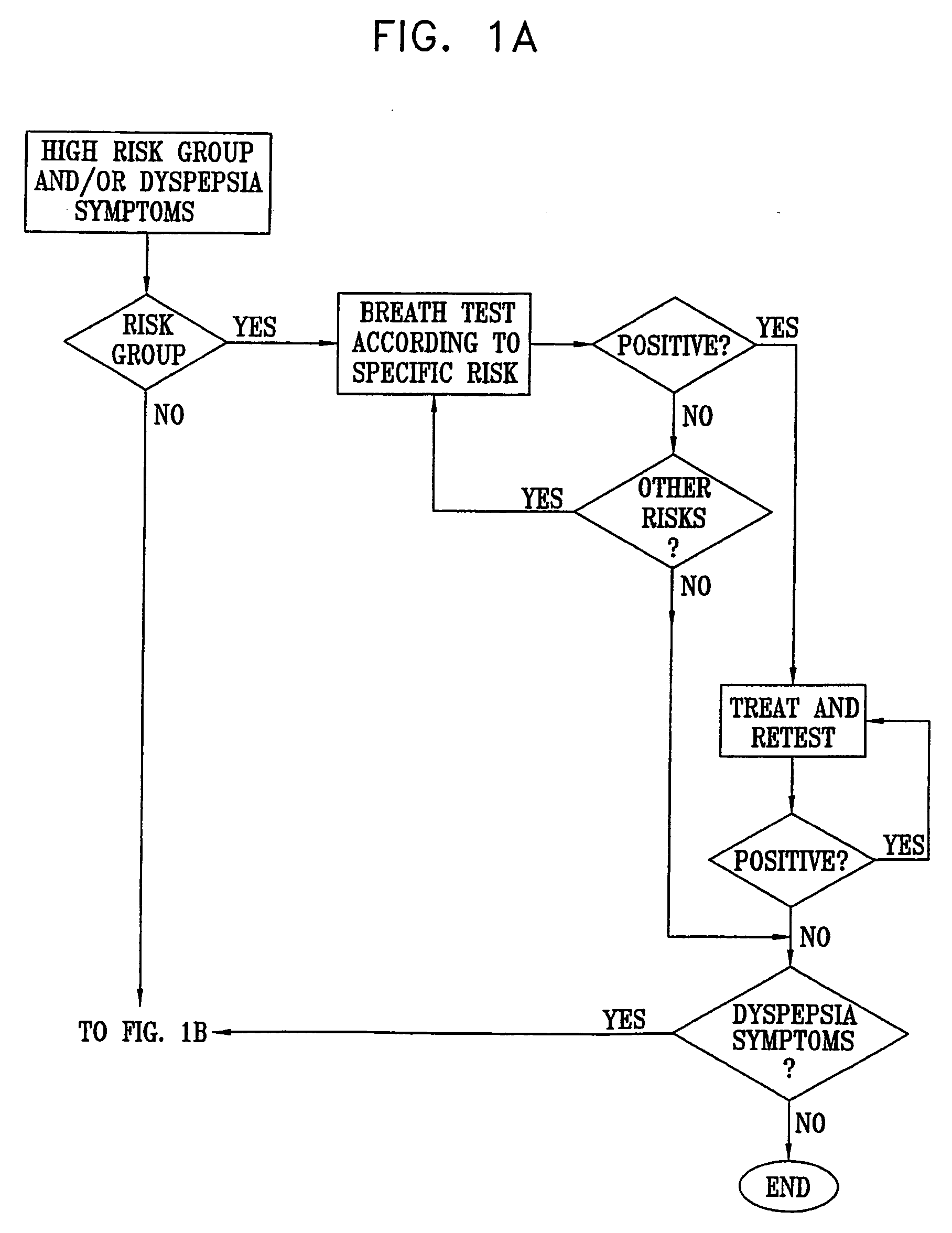
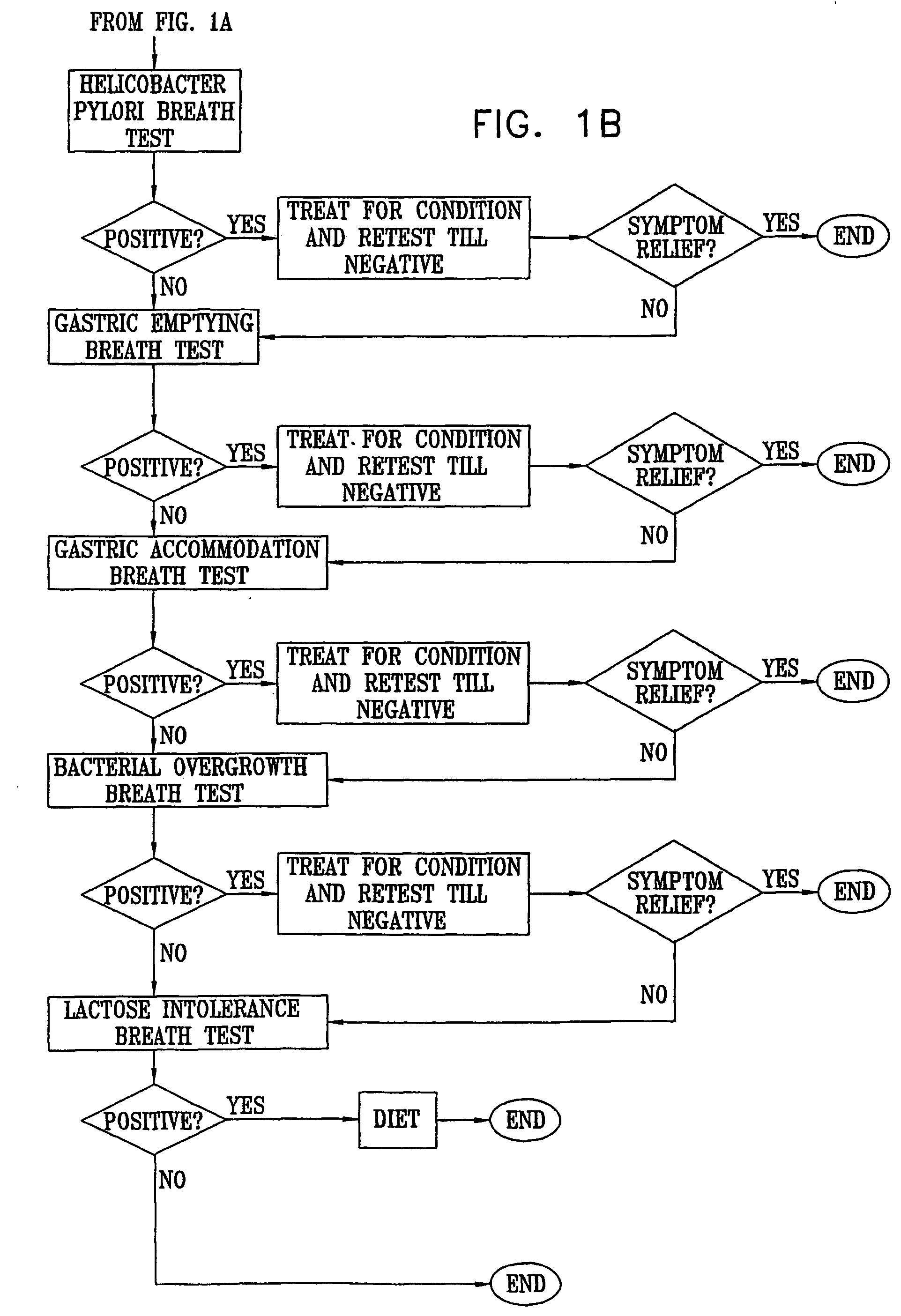
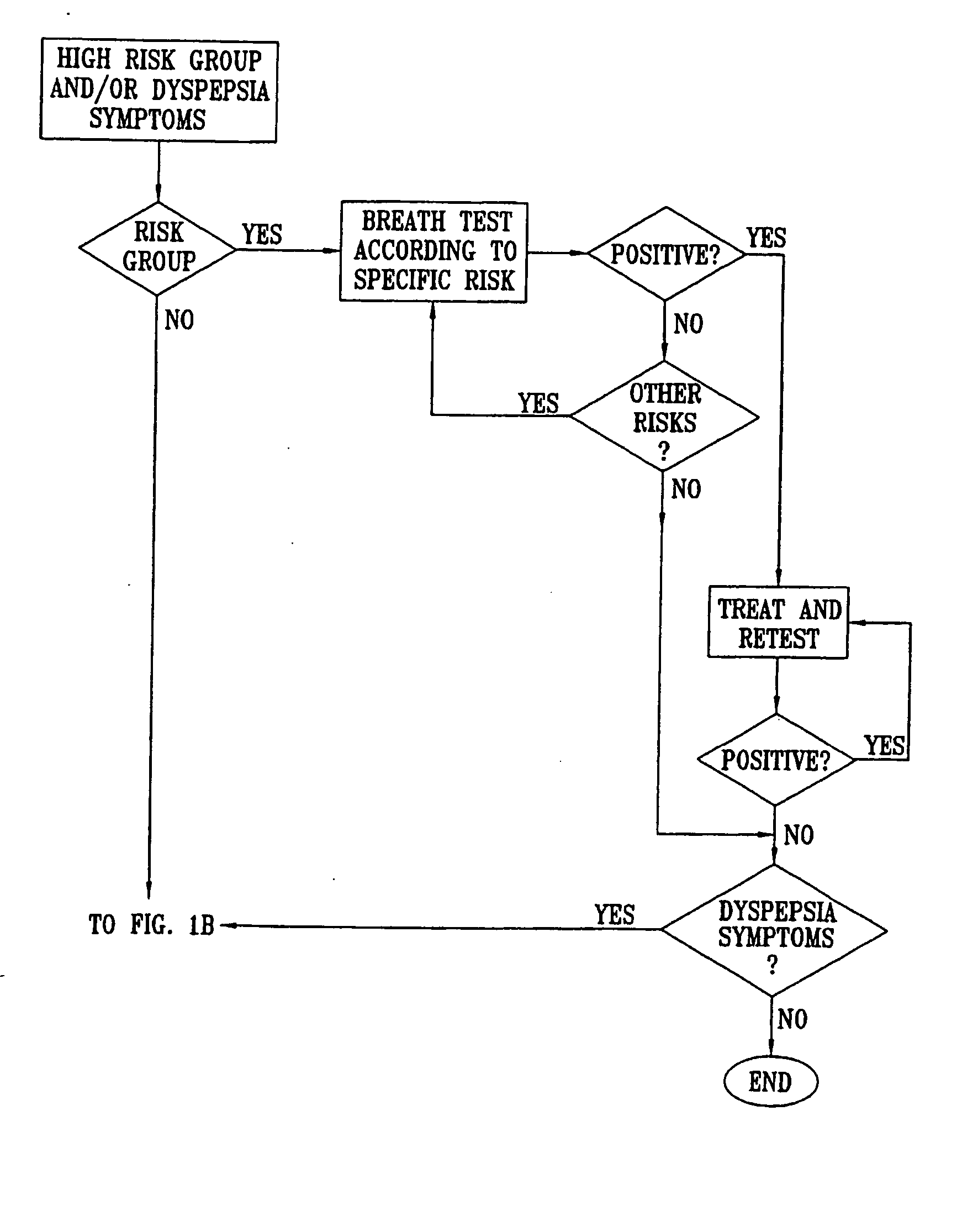
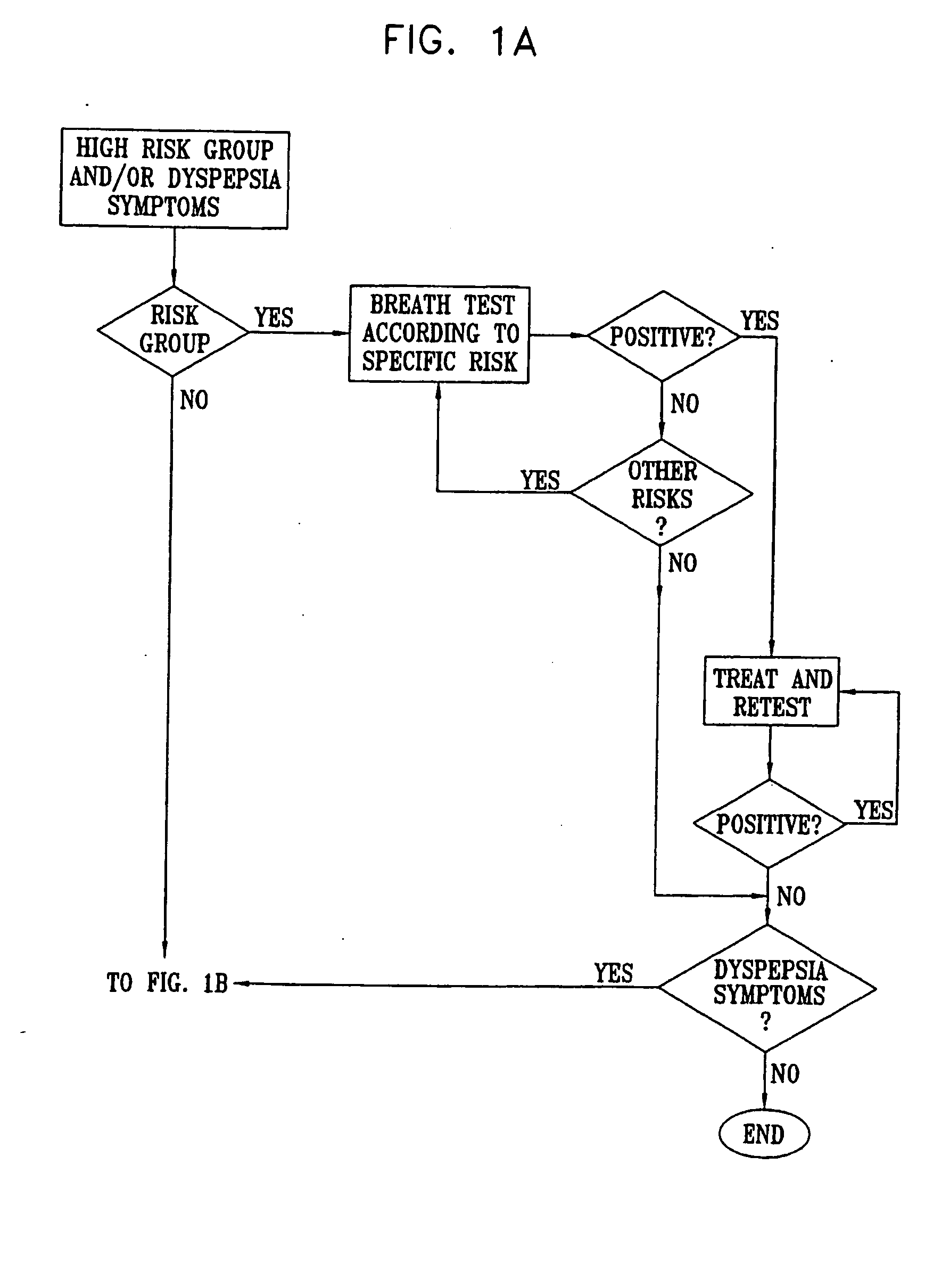
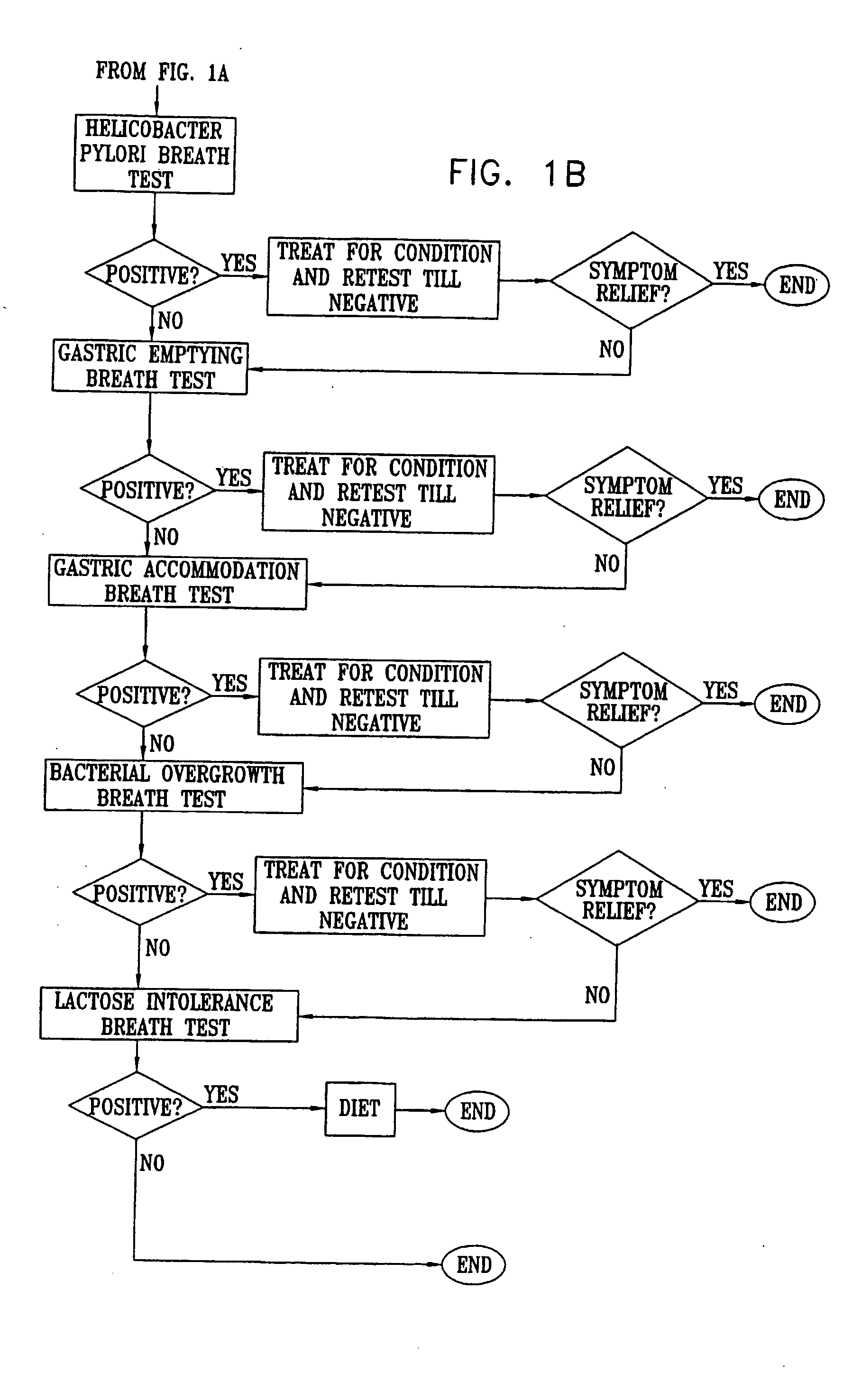
Management of gastro-intestinal disorders
InactiveUS20060074335A1Easily toleratedQuick testCompounds screening/testingPerson identificationDiseaseGastrointestinal dysfunction
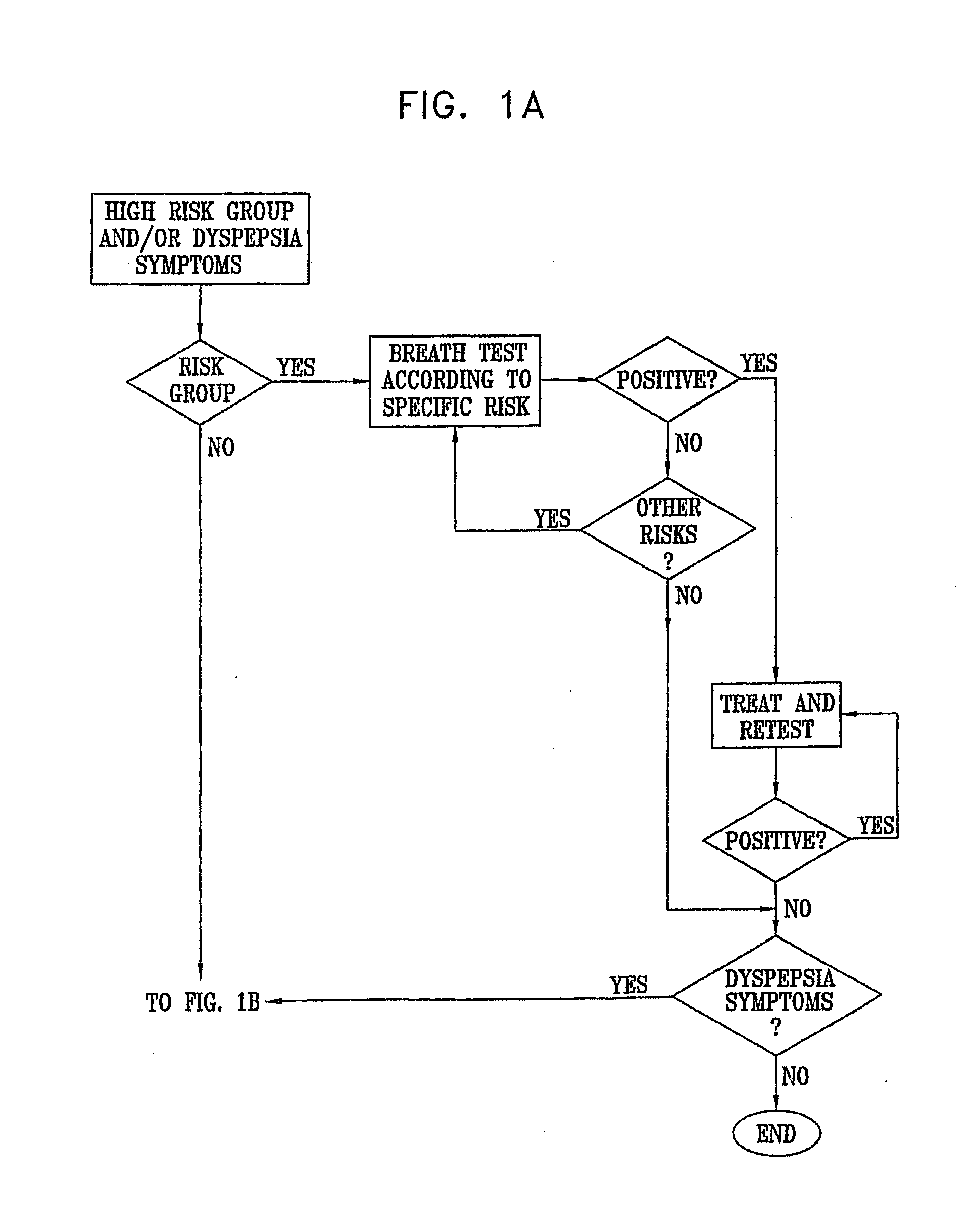
The present invention relates to the field of methods and apparatus for the determination of various conditions of gastric and gastro-intestinal malfunction, especially those performed by means of breath tests.
Owner:EXALENZ BIOSCIENCE LTD
Non-invasive test for assessing bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine
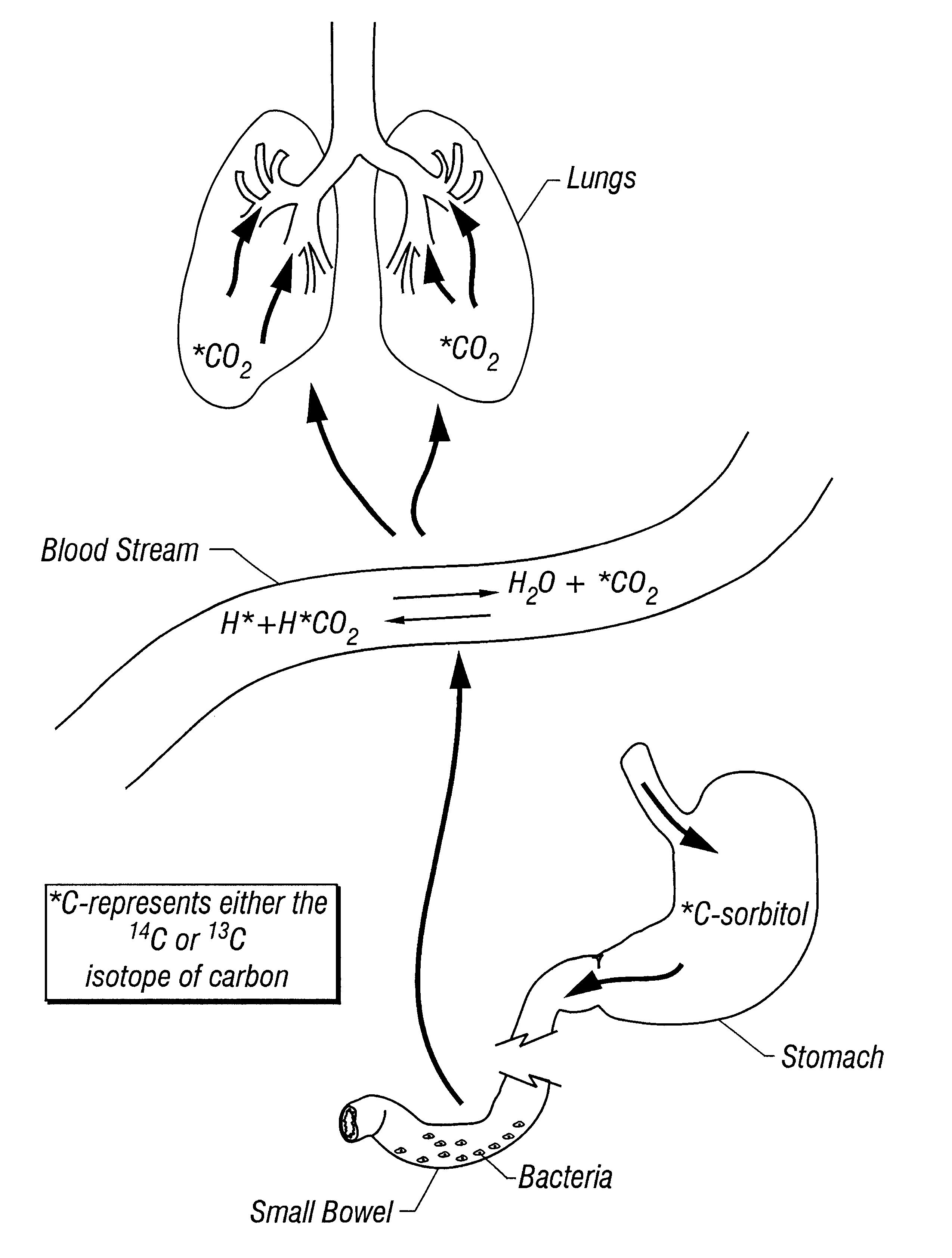
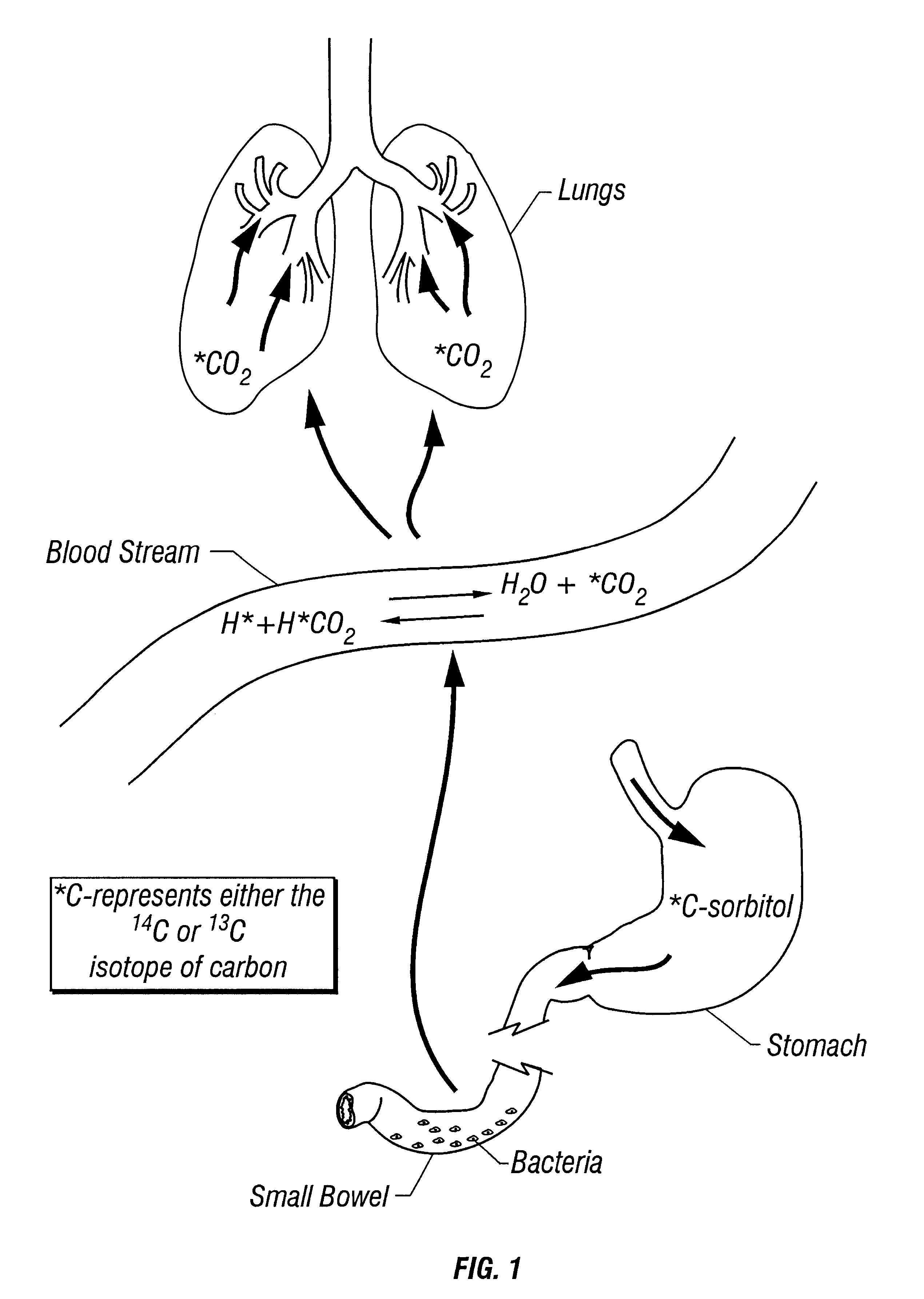
Provided herein is a novel breath test for assessing bacterial overgrowth. The test involves administration of a labeled sorbitol or sorbitol derivative to a subject and measurement of the label in breath and / or blood.
Owner:METABOLIC SOLUTIONS
Gas analyzer calibration checking device
InactiveUS20050273016A1Improve accuracyHigh selectivityWithdrawing sample devicesSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringMoisture
Owner:EXALENZ BIOSCIENCE LTD
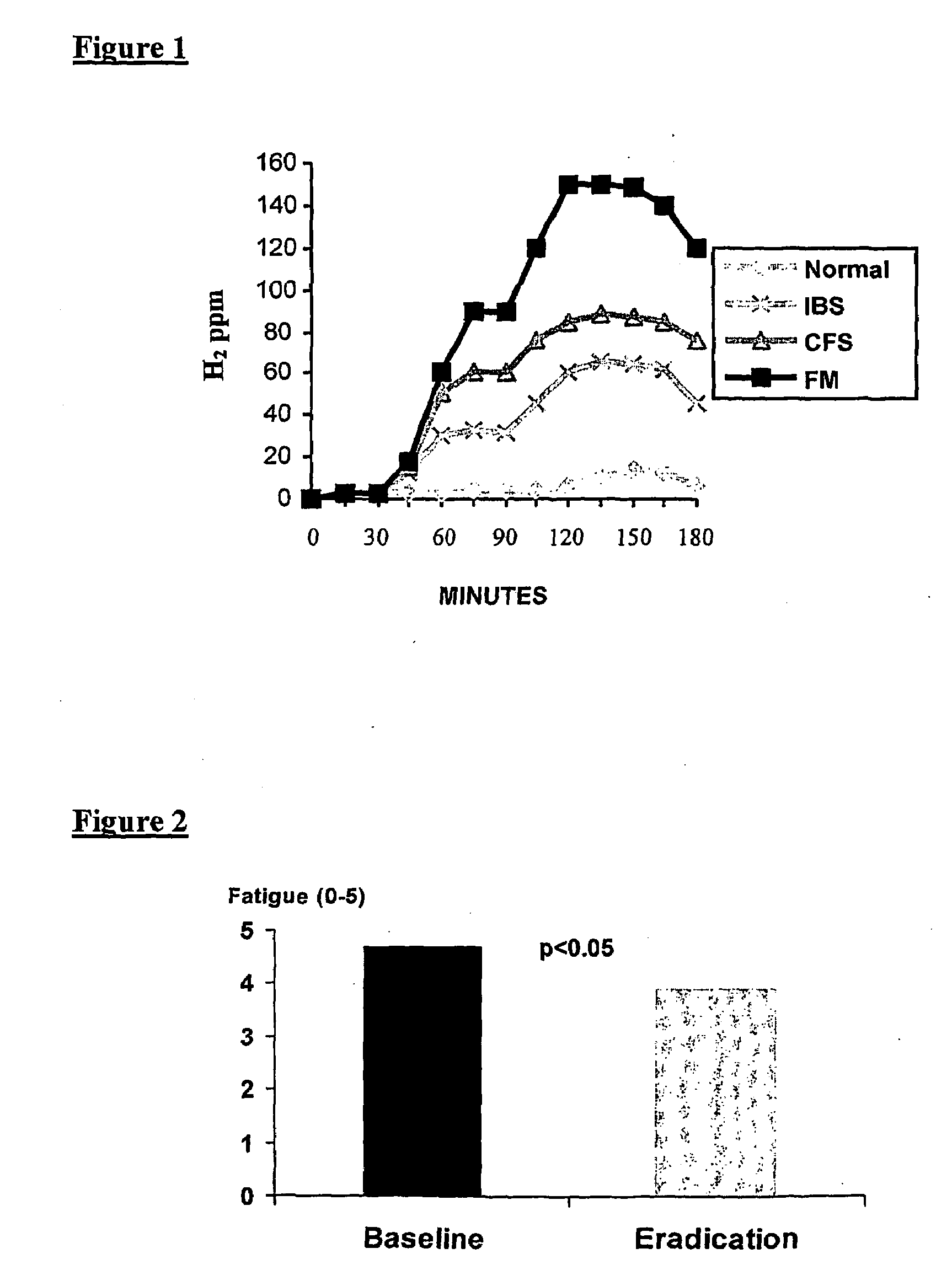
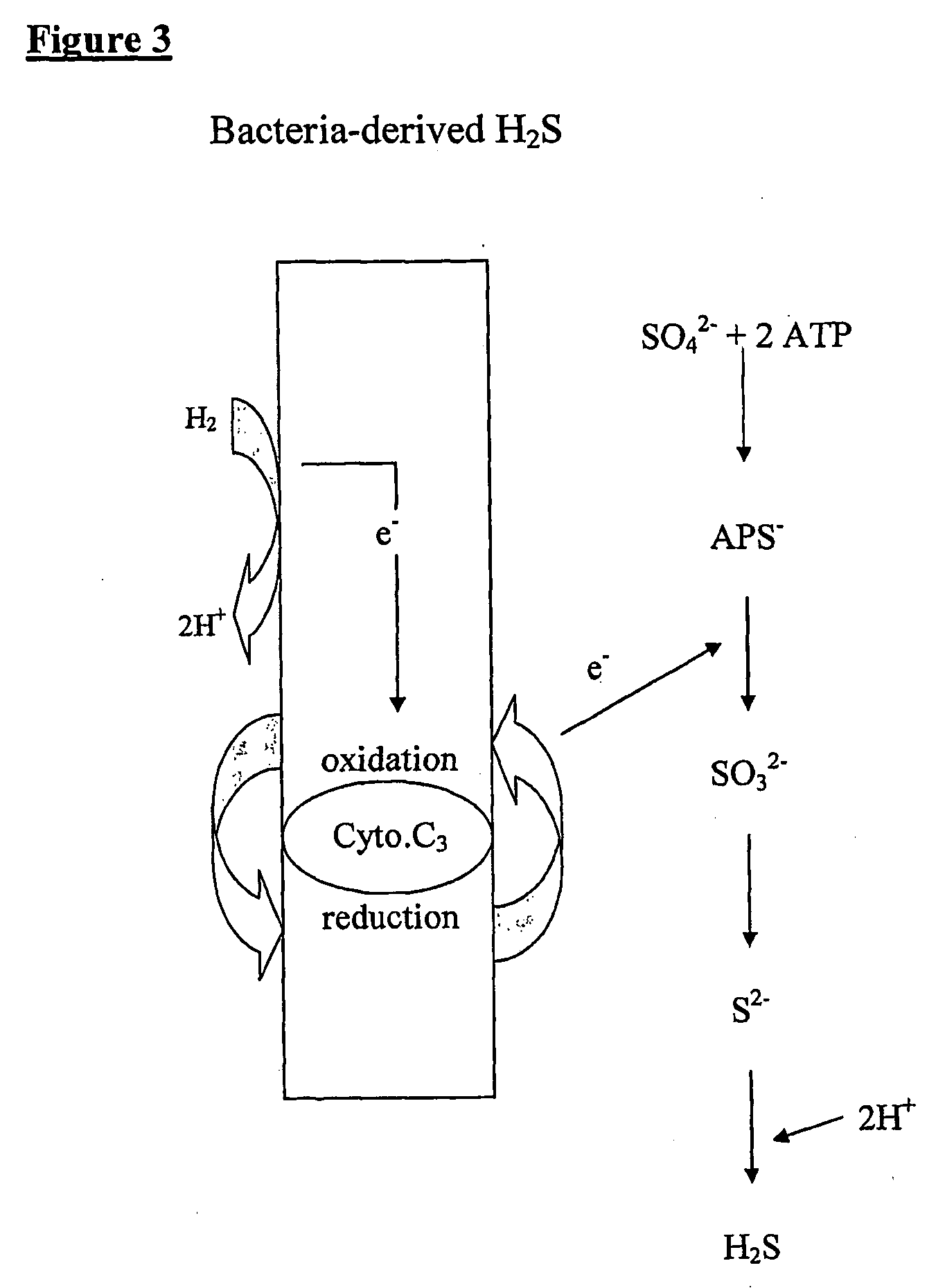
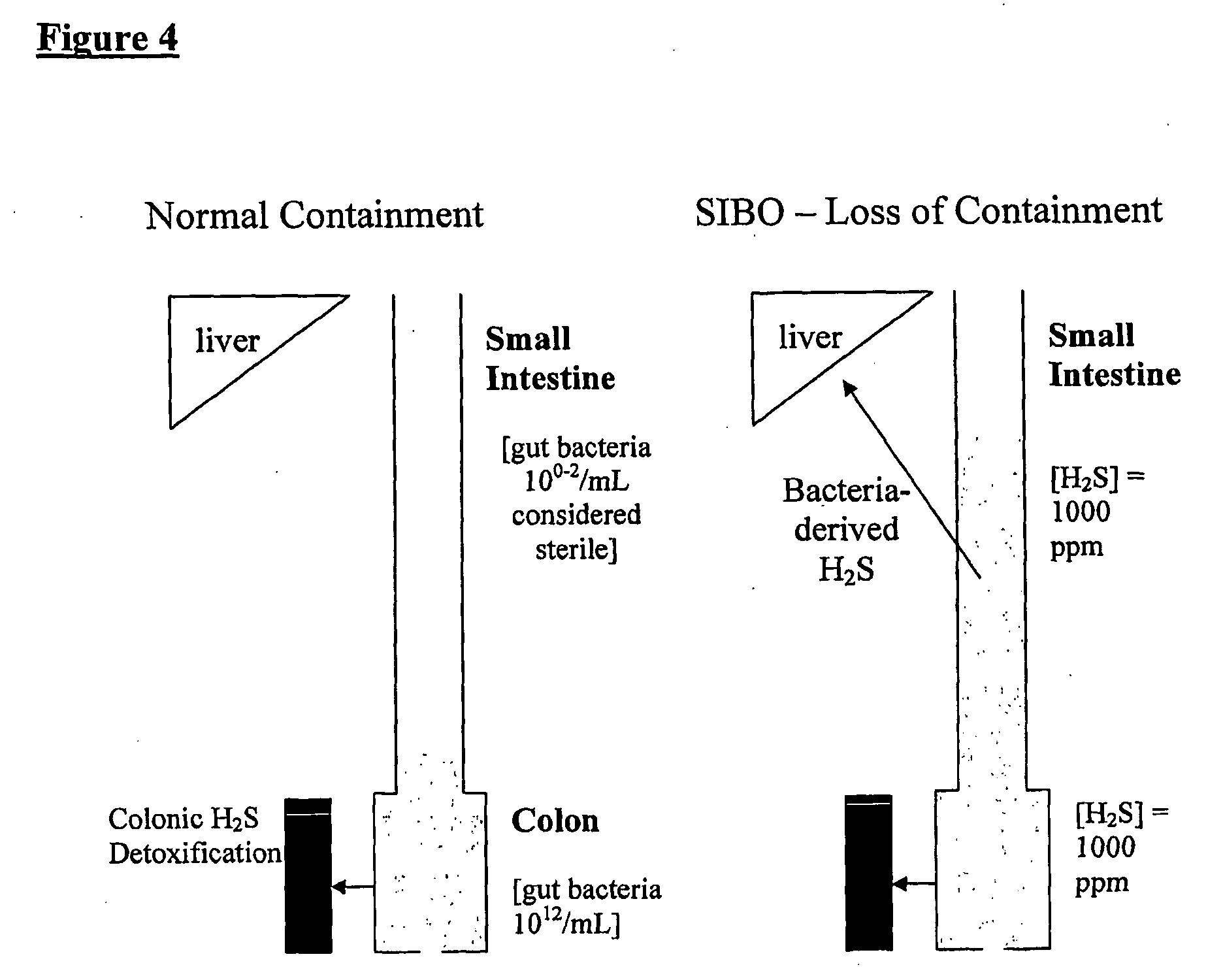
Treatment of disease conditions through modulation of hydrogen sulfide produced by small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
InactiveUS20090233888A1Lower Level RequirementsElevated level of H2SBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesHyperhomocysteinemia
The present invention relates to the treatment of a wide array of diseases and physiologic conditions based on modulating the level of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in the body by at least partially eradicating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in the gut. An H2S or lactulose breath test and / or detection of H2S or thiosulfate in the blood or urine may be used as a diagnostic and / or prognostic for assessing a systemic H2S load that exceeds a mammal's natural detoxification capacity. These tests may similarly be used to monitor the effectiveness of a therapeutic intervention for SIBO and / or the diseases or physiologic conditions whose pathology is linked thereto. Because SIBO is related to hyperhomocysteinemia, diseases and physiologic conditions that relate to hyperhomocysteinemia may further be monitored and treated in connection with the methods of the present invention.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection
InactiveUS7014612B2Accurate identificationWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationReflection spectroscopyIsotopic tracer
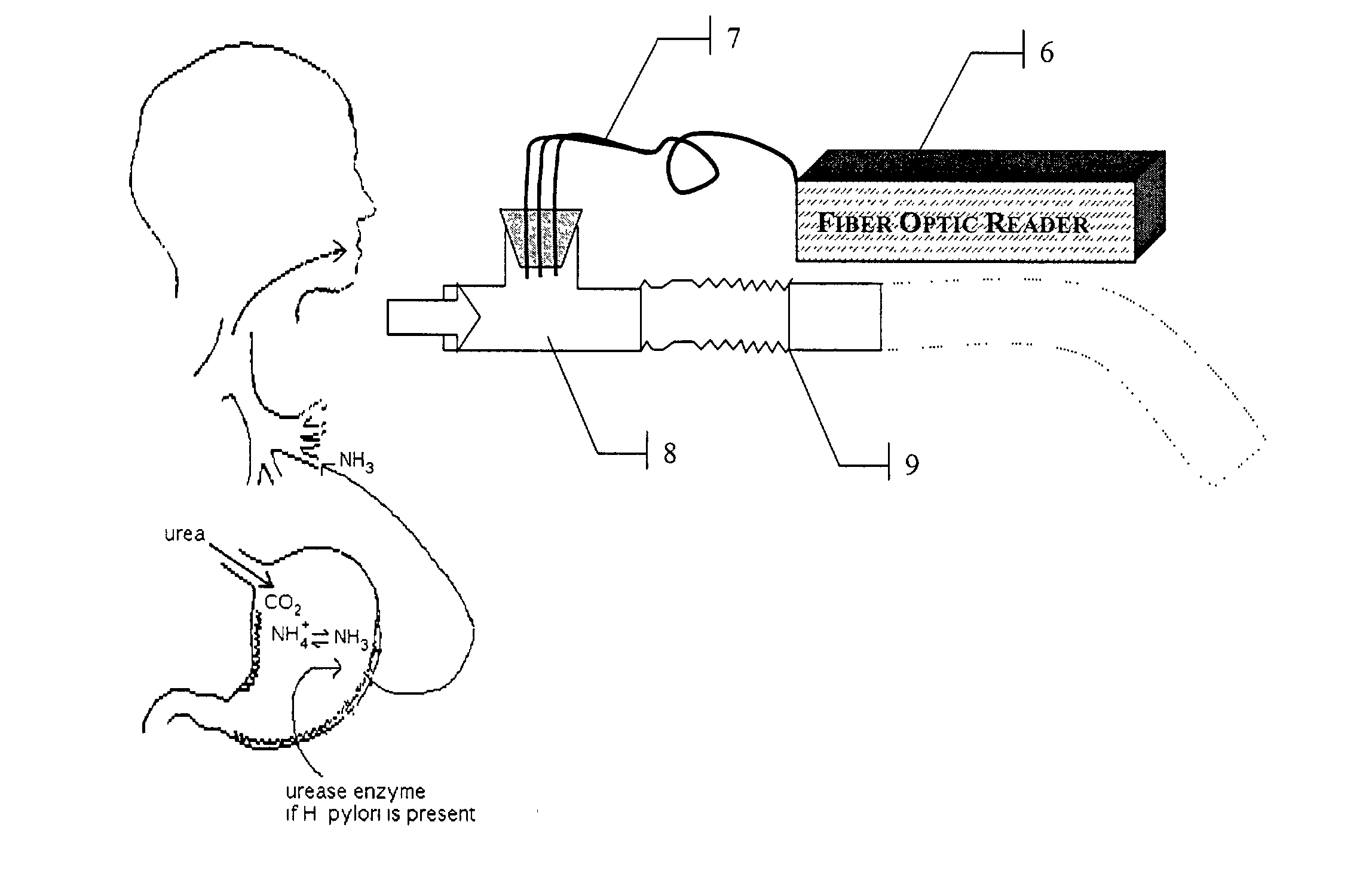
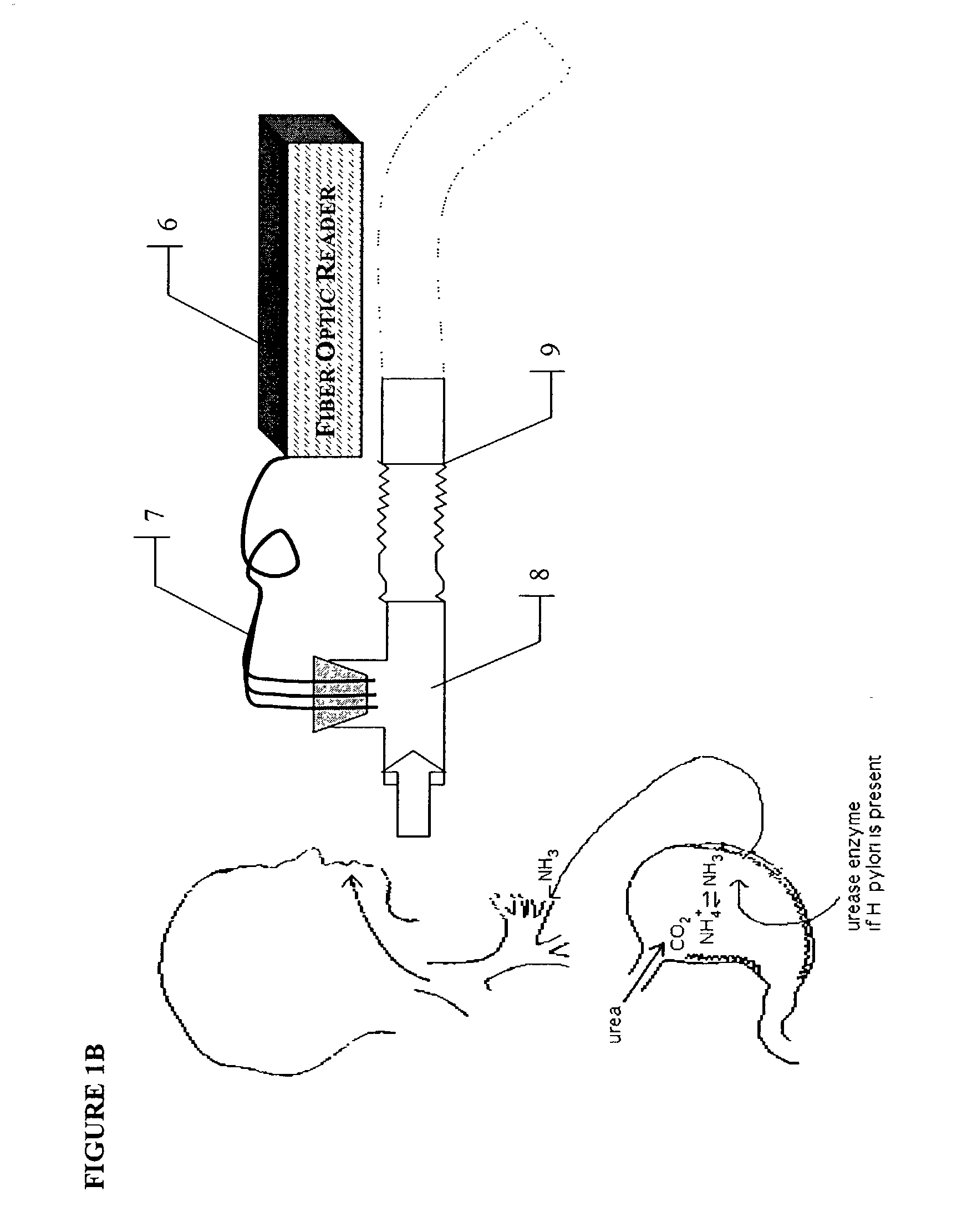
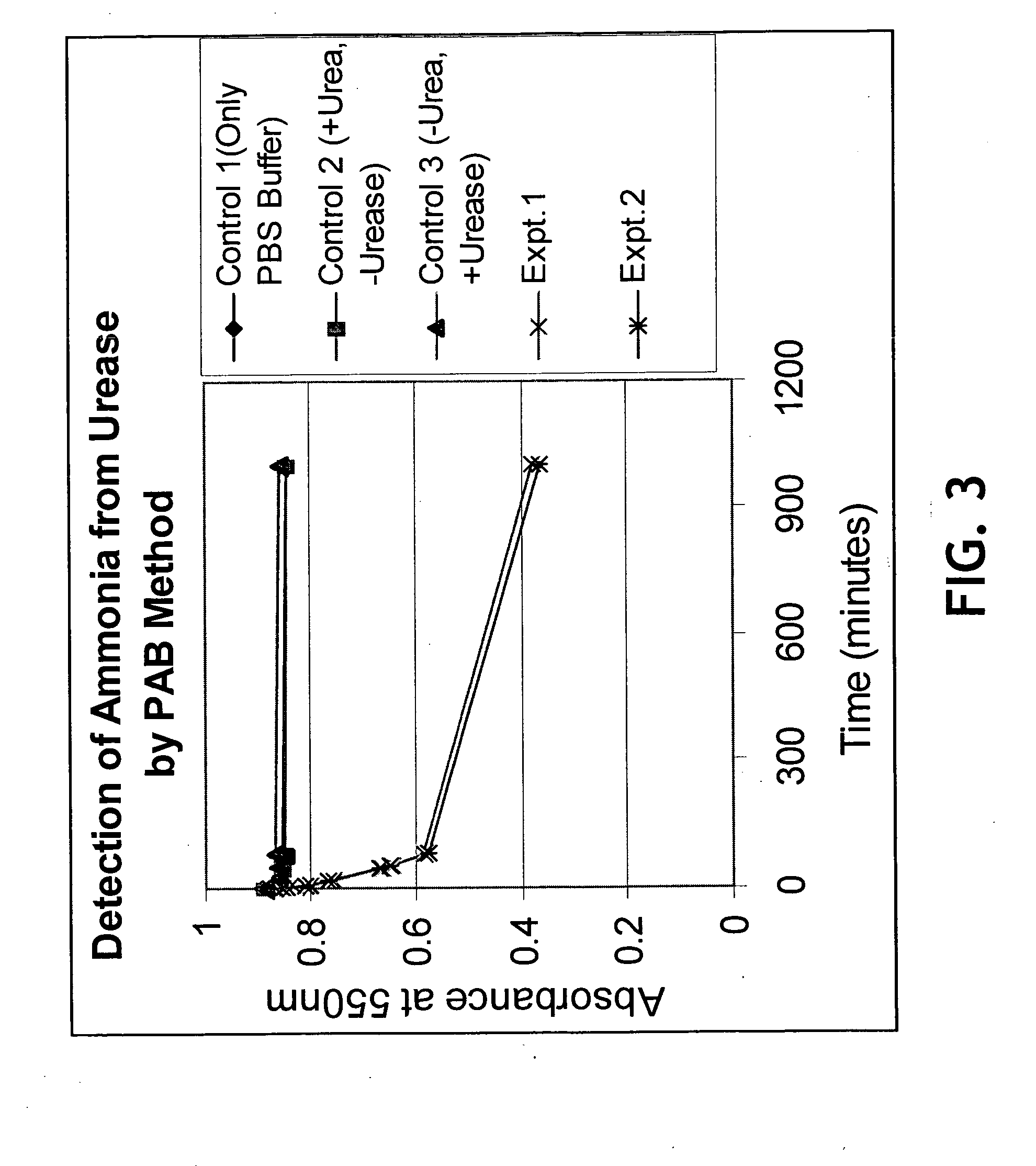
A rapid, non-invasive breath-test method and device for diagnosing the presence or absence of H. pylori in a subject without administration of isotopic tracers is described. The device consists of a highly sensitive colorimetric ammonia sensor placed in contact with sampled subject breath. The sensor is measured using appropriate reflection spectroscopy instrumentation. The breath-test method consists of measuring a basal ammonia level with the device, administering non-isotopic urea and continuing measurement of the ammonia content in a plurality of consecutive breaths. Diagnostic differences in breath ammonia are identified between H. pylori infected and uninfected individuals.
Owner:PHOTONIC BIOSYST
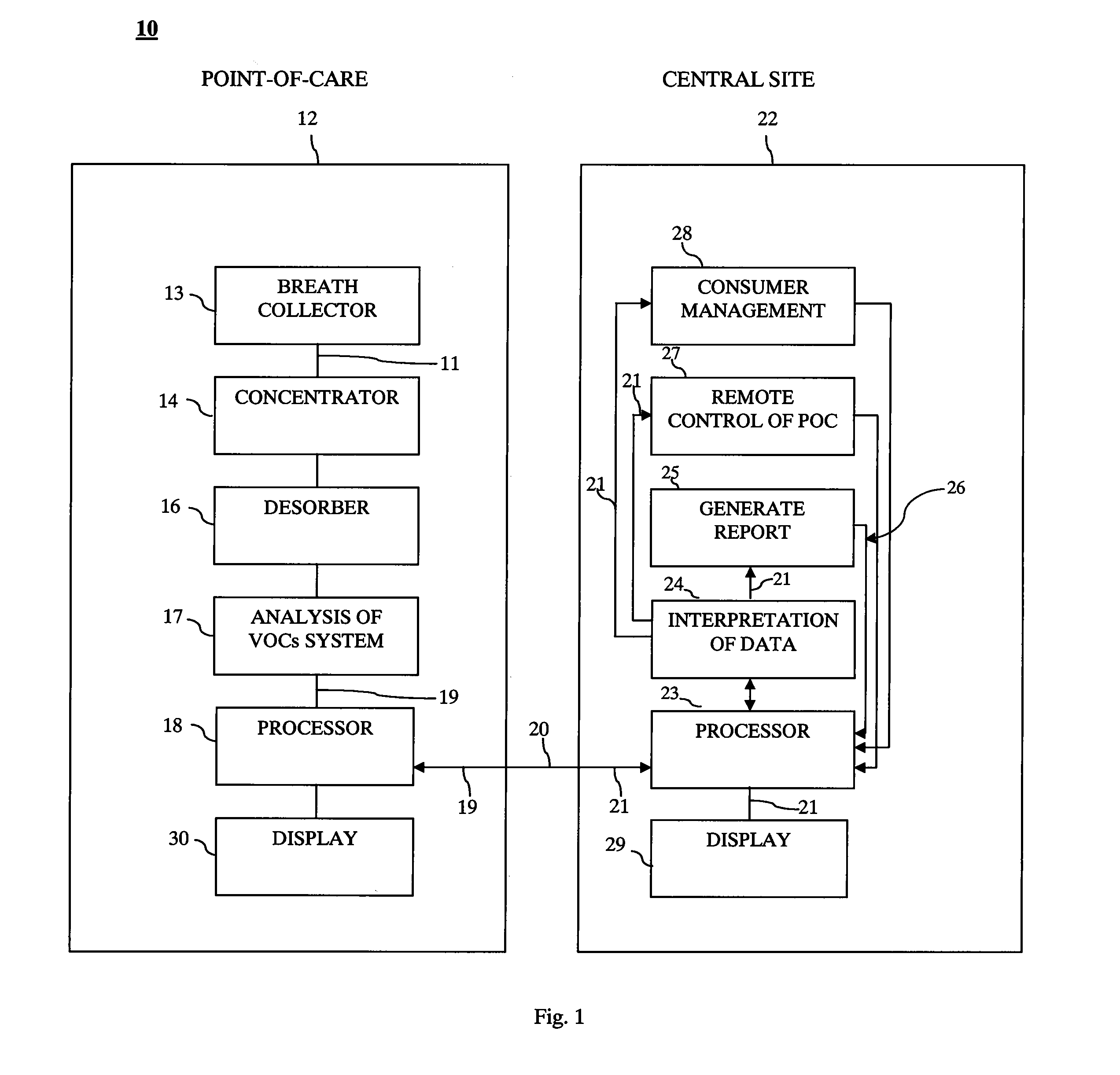
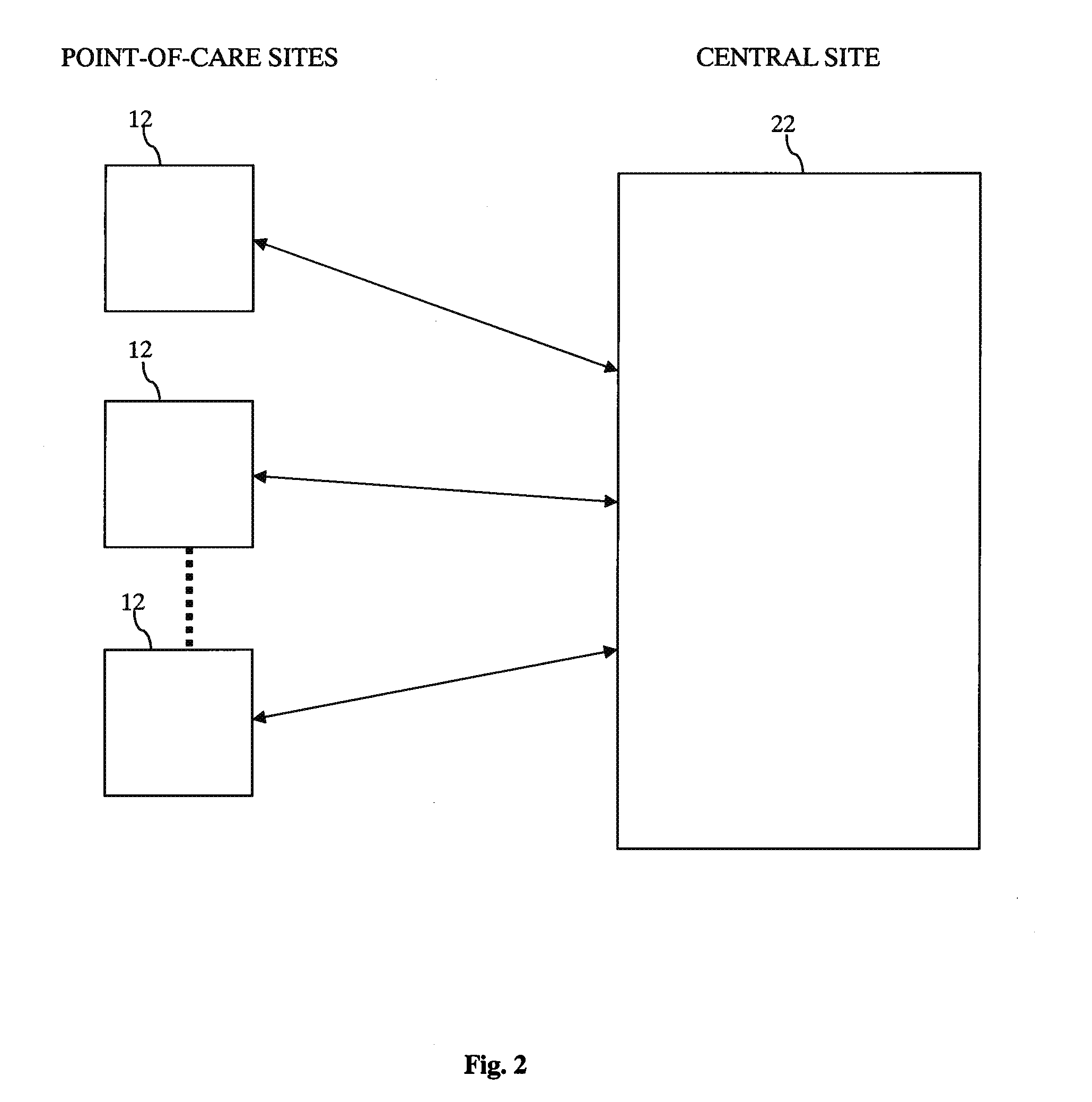
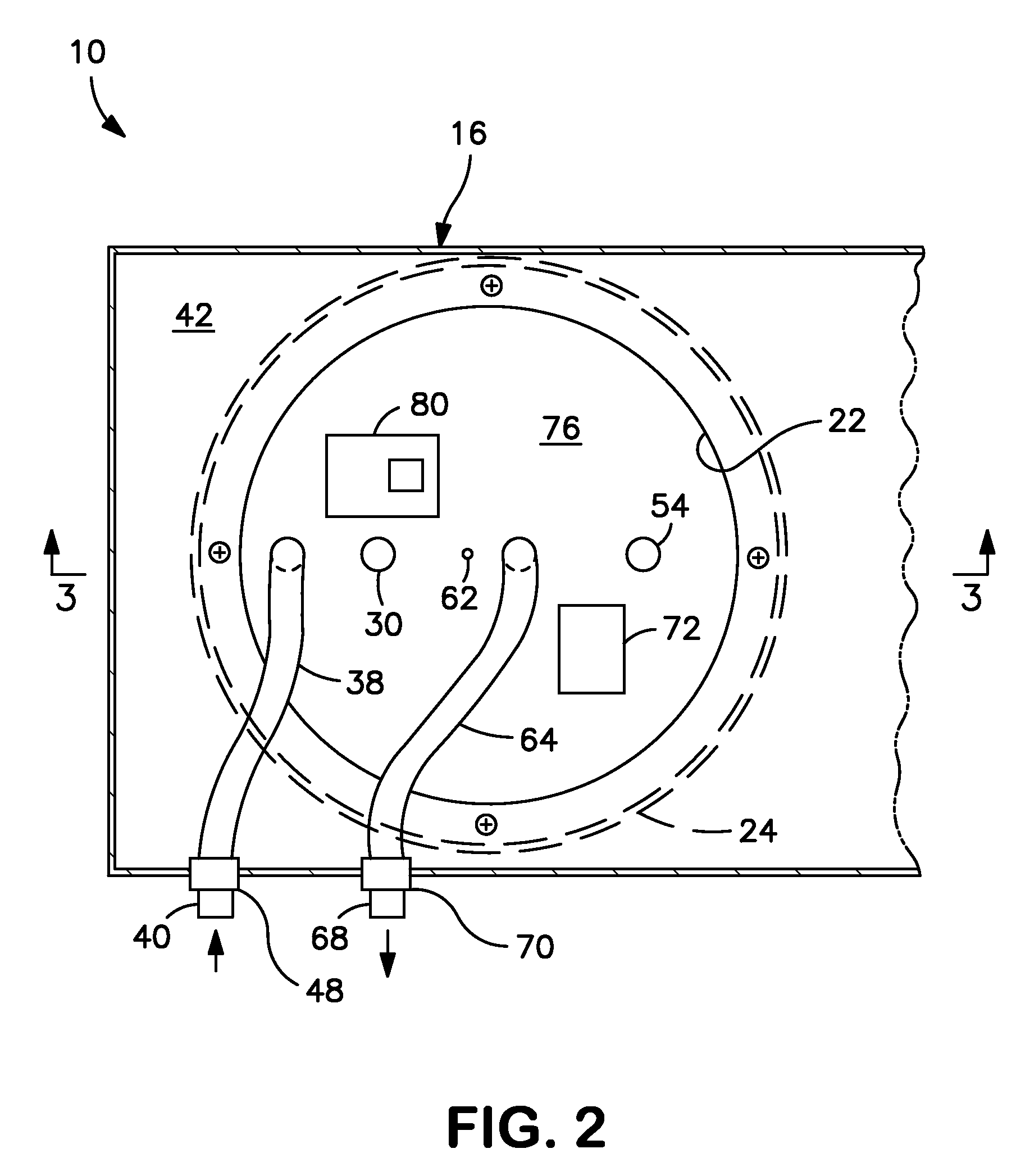
System and method for remote collection and analysis of volatile organic components in breath
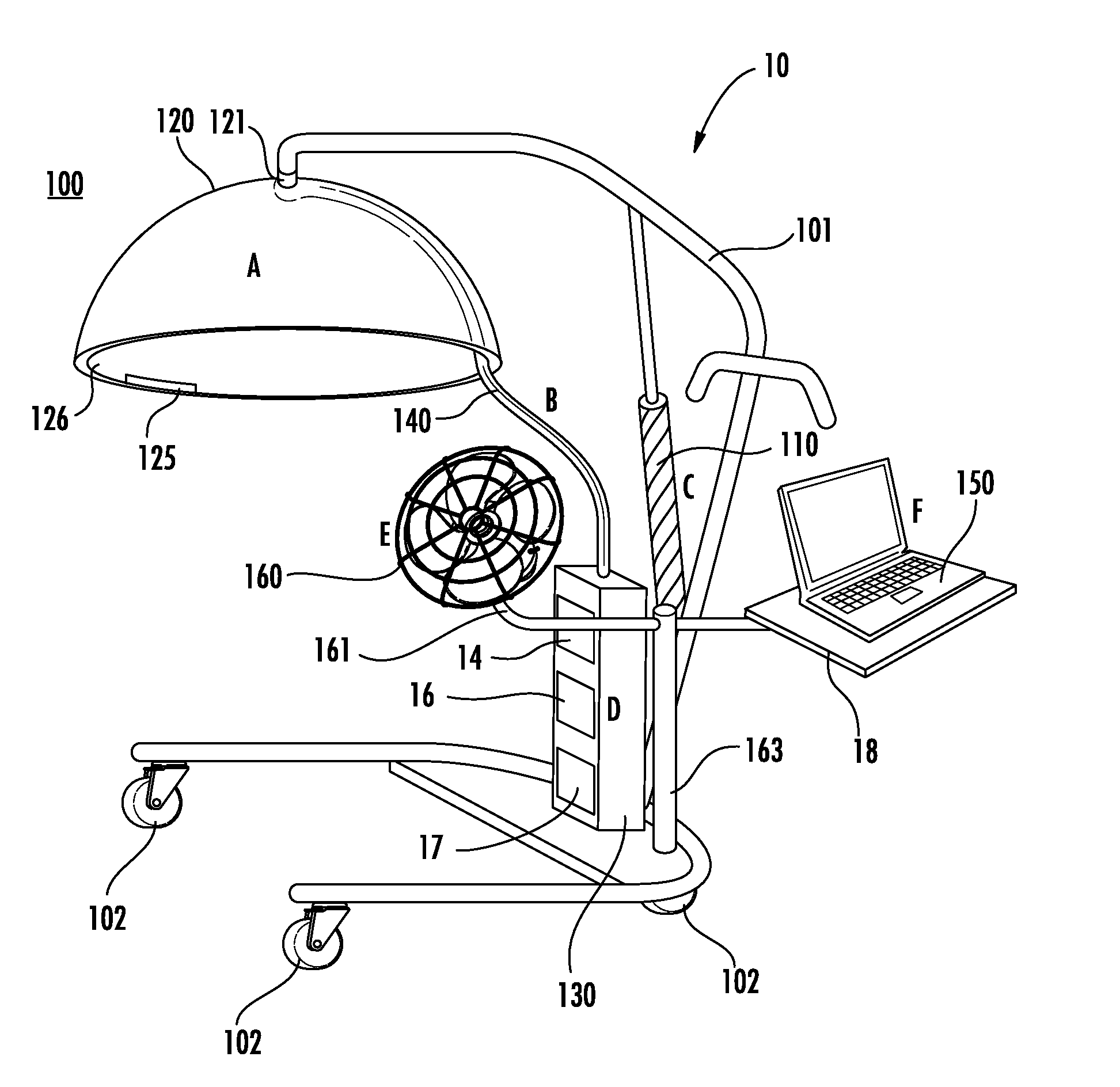
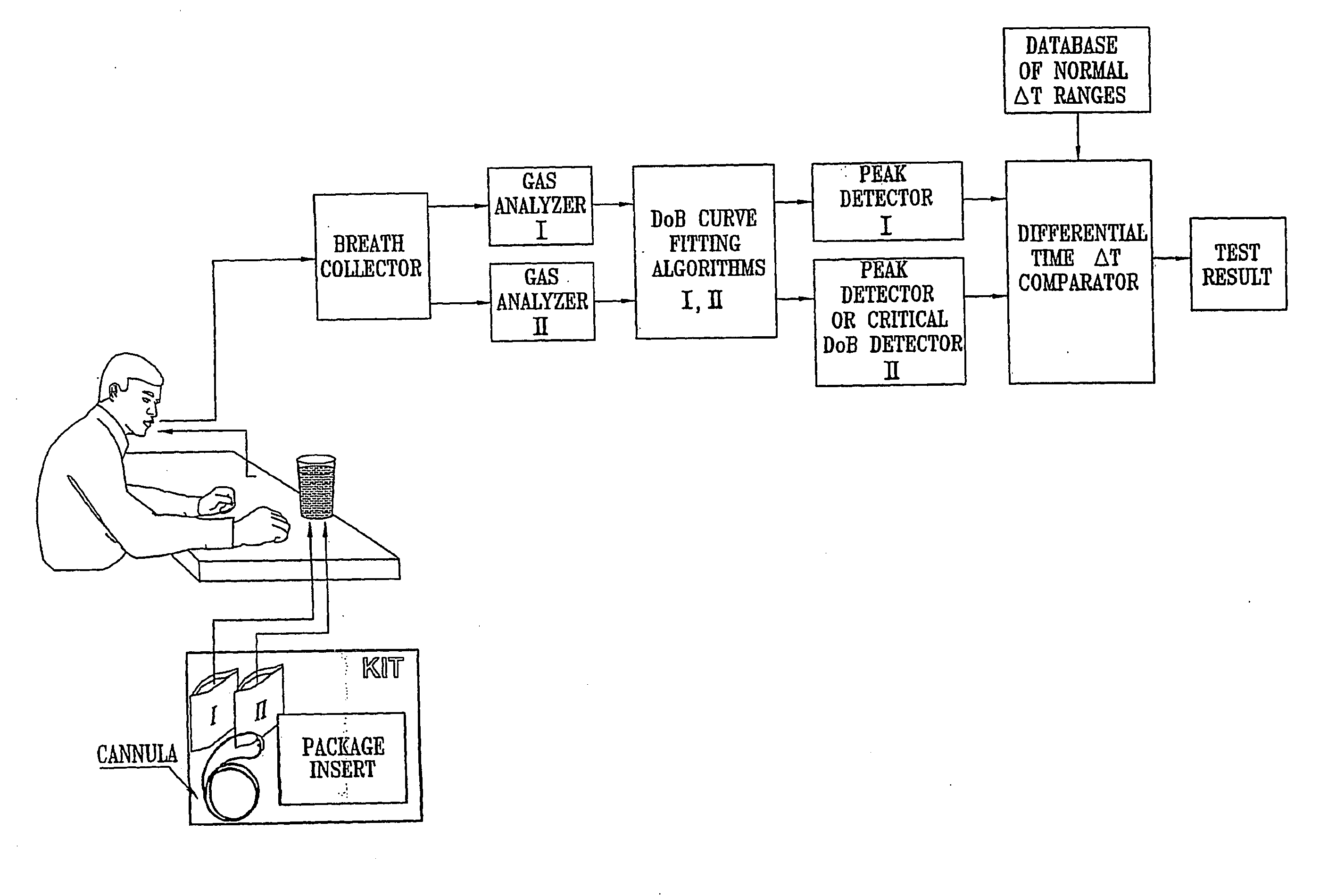
InactiveUS20130253358A1Reduce usageOvercome resistanceRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsCollection systemEngineering
A tool for telemedicine including an improved breath collection system of human breath to facilitate the analysis of volatile organic components (VOCs) contained in human breath in which breath tests can be performed at remote sites for rapid detection of different diseases. The system can include a standoff breath collection device including an arcuate structure for concentration and analysis of volatile organic components (VOCs) at the point-of-use that avoids the use of mouthpieces found in conventional breath collection apparatuses.
Owner:MENSSANA RES
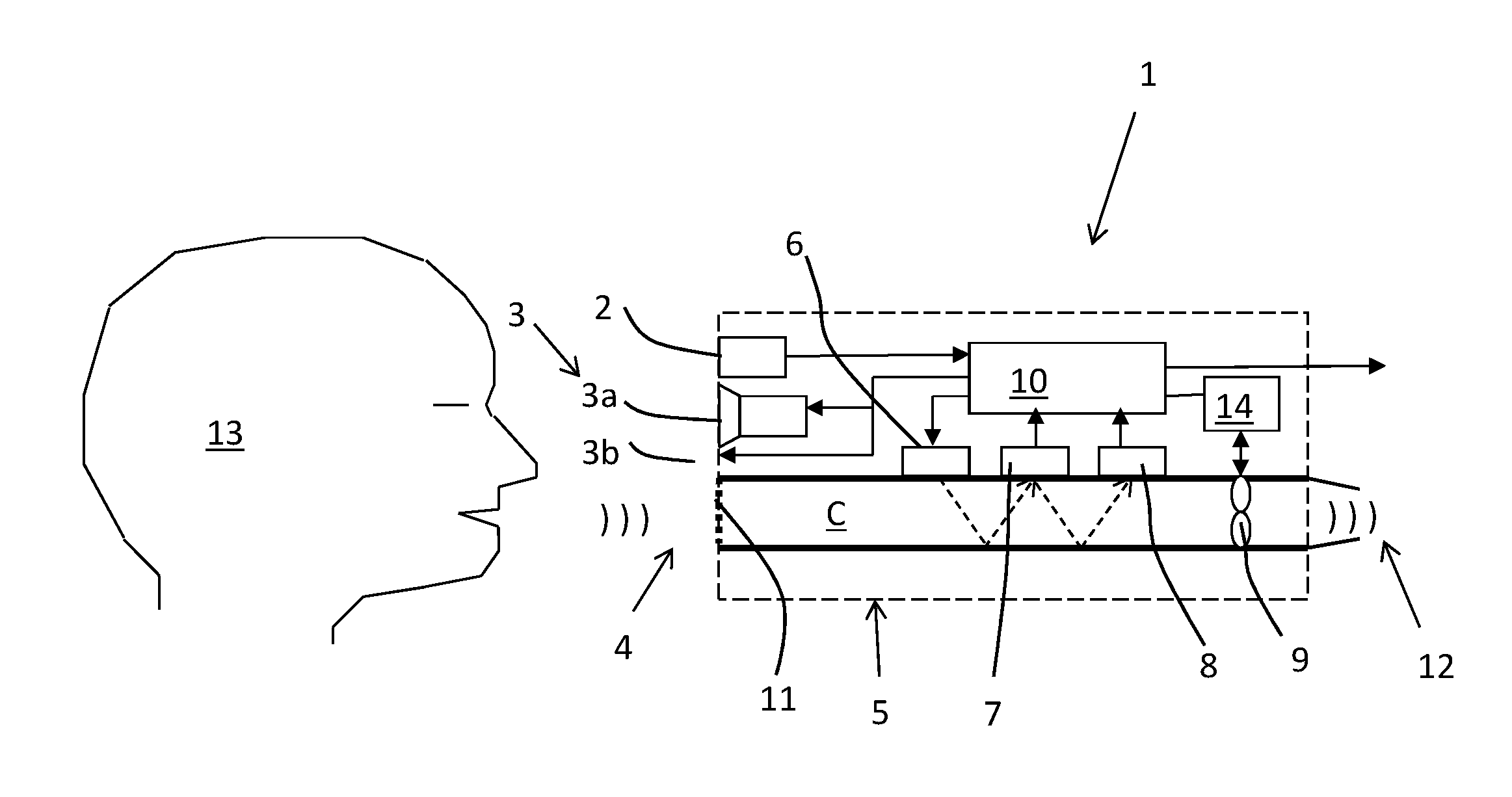
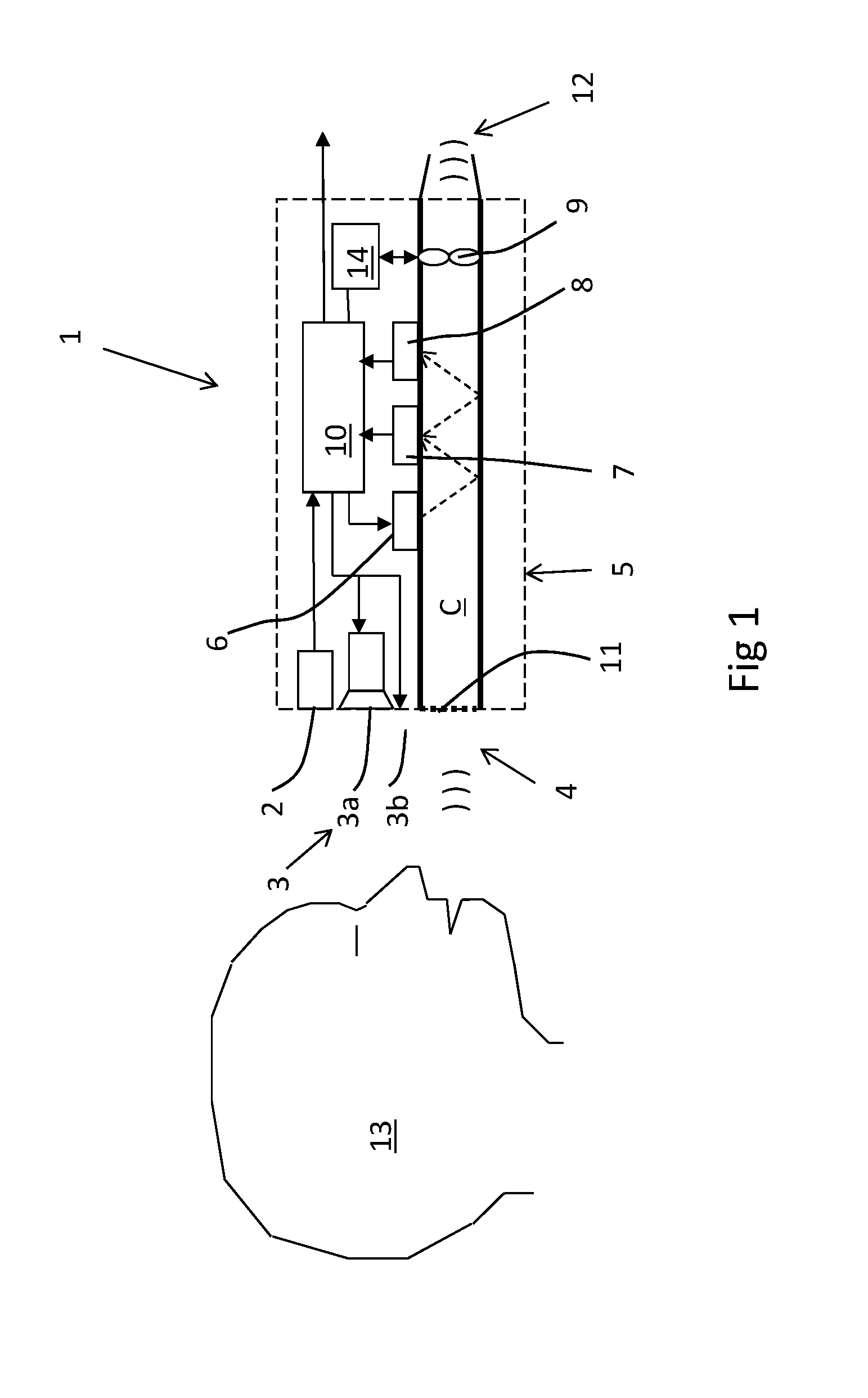
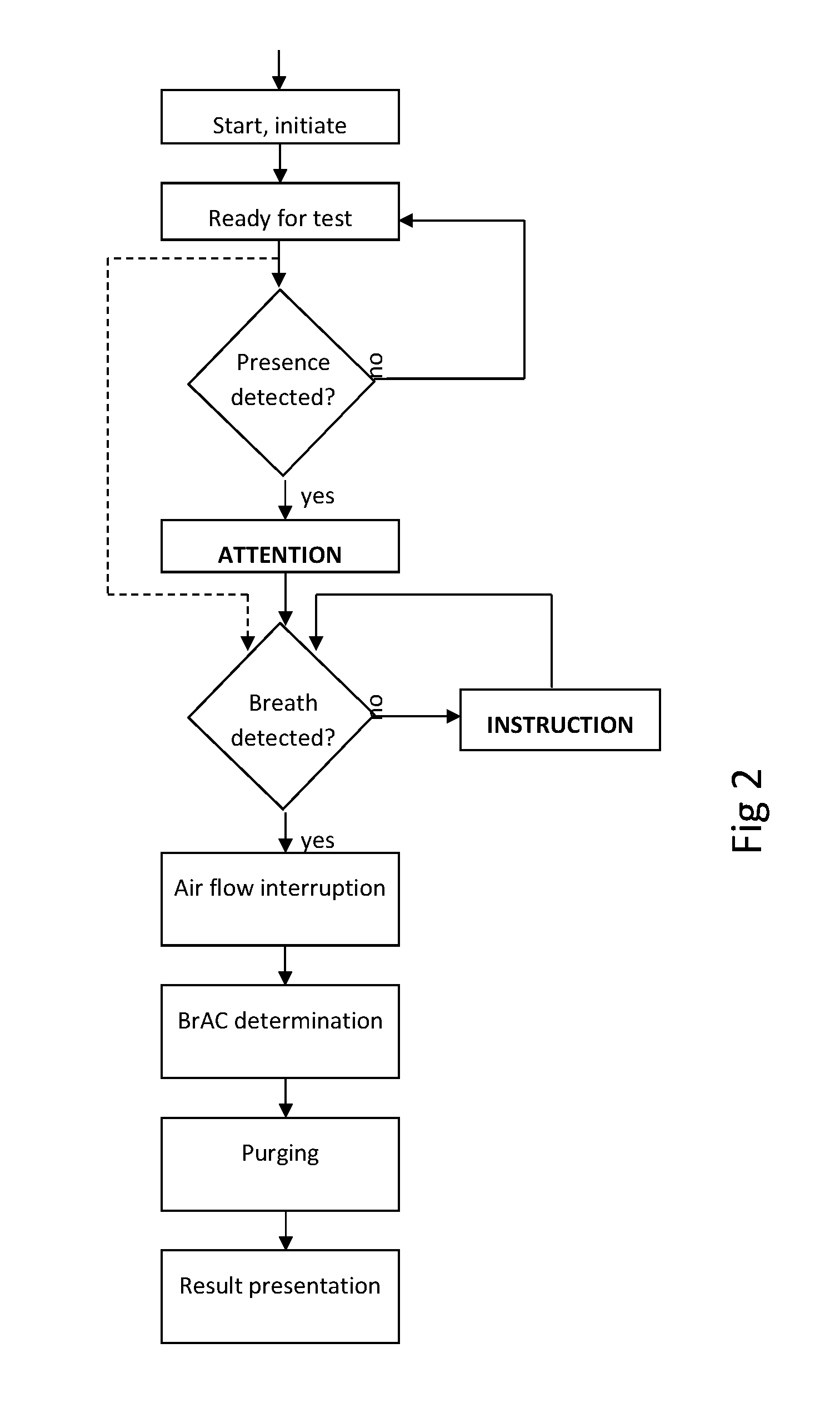
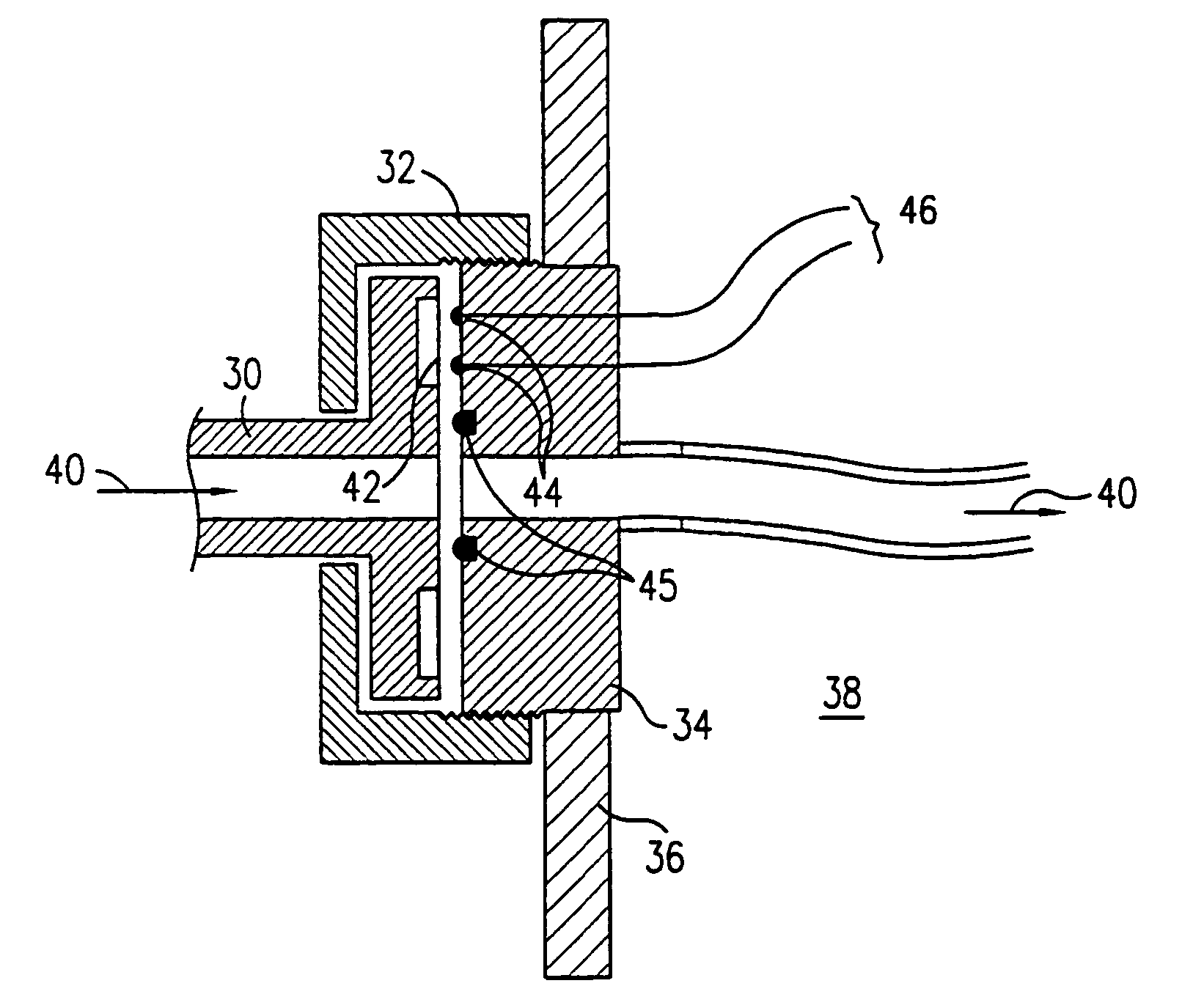
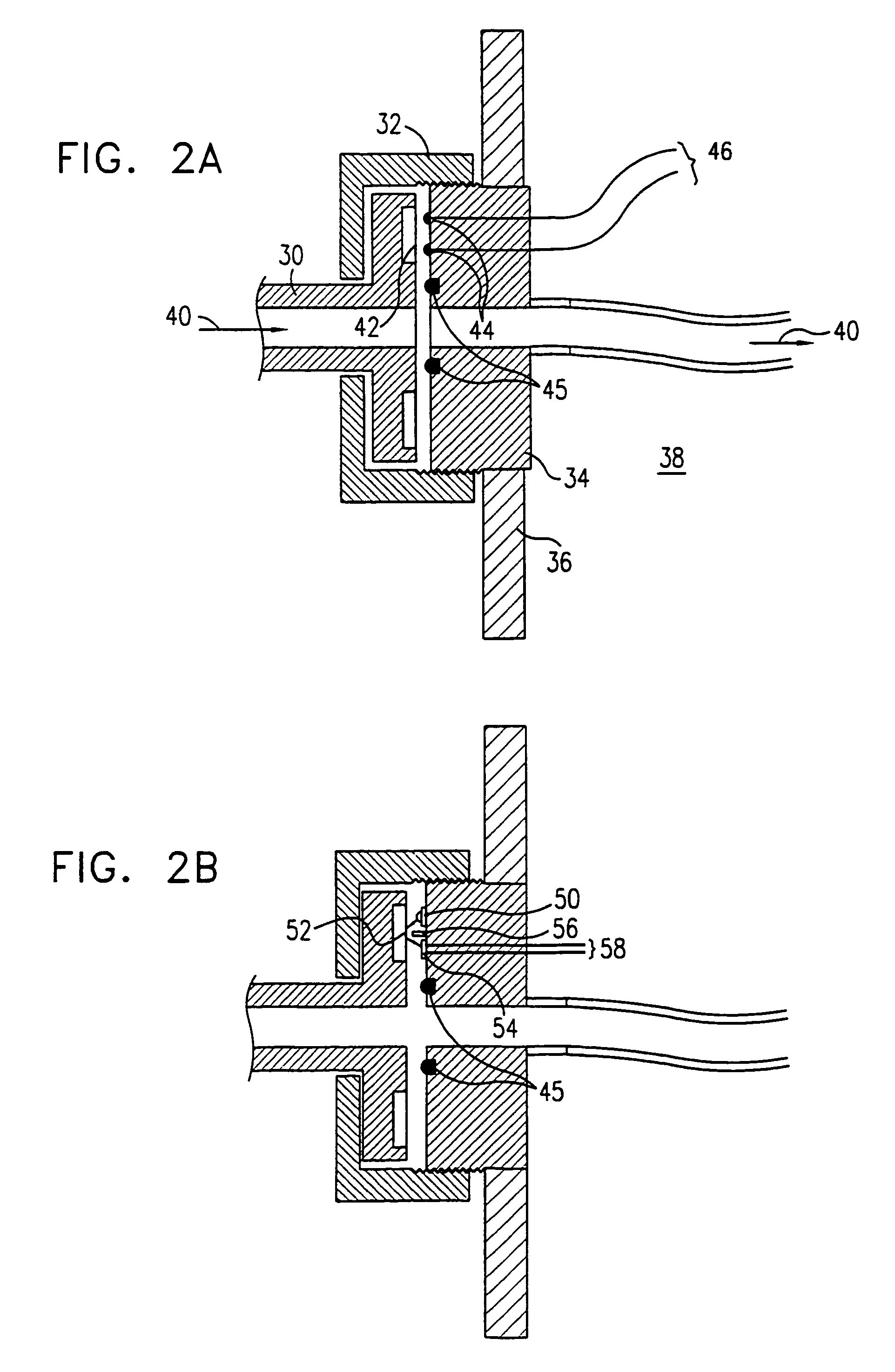
Highly accurate breath test system
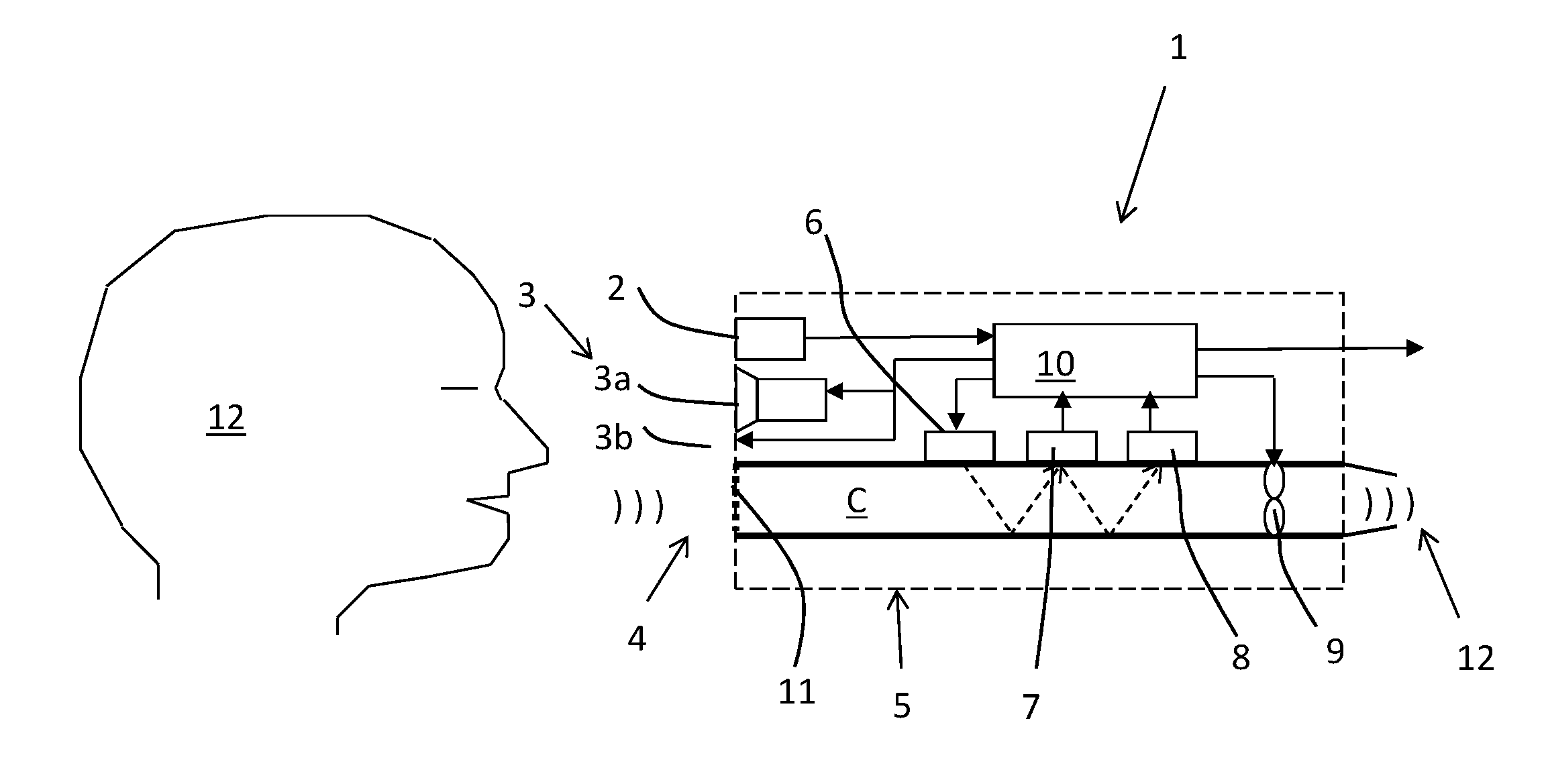
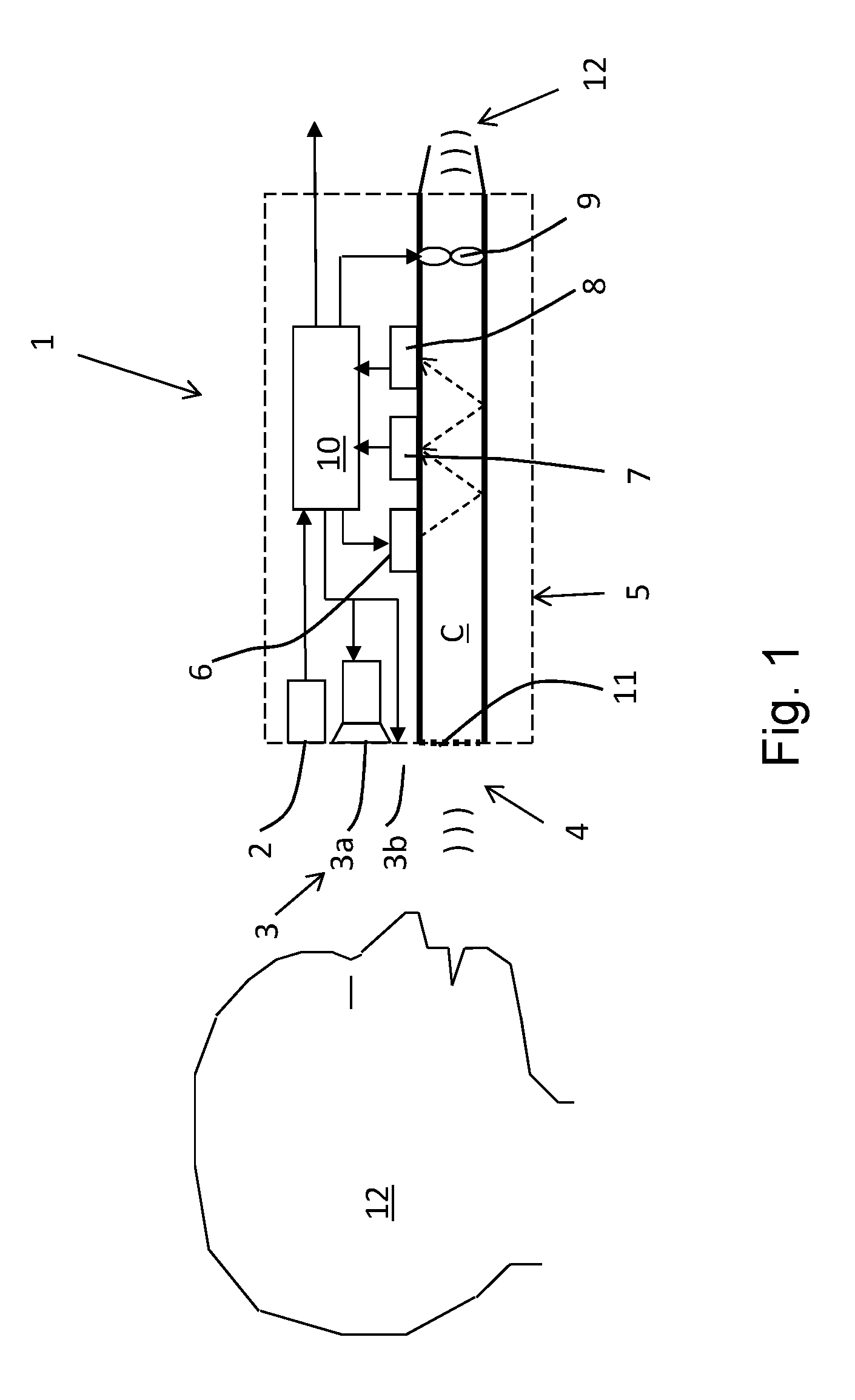
ActiveUS20150233897A1Improve accuracyIncreased mortalityWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAlcoholEngineering
The invention relates to a system for breath test of a person. It includes a sensor unit configured to sense the presence / concentration of a volatile substance, e.g. alcohol, present in air flowing through a predefined inlet area and generating a signal corresponding to the concentration of said substance. An analyzer determines the concentration of said substance in the breath of said person. It comprises means for the temporary interruption of said air flow at a point in time coinciding with the detection of a breath. It also relates to a method comprising interrupting the flow through said predefined area for a predetermined period of time, and detecting the concentration of said substance during said interruption.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE COALITION FOR TRAFFIC SAFETY
Gas analyzer calibration checking device
InactiveUS6969357B1Guaranteed accuracyEnsure reliabilityWithdrawing sample devicesSynthetic resin layered productsTester deviceEngineering
A calibration checking device, and methods of mandating its use at regular time intervals, to ensure maintenance of the accuracy of gas analyzers, especially for use with breath tests, Each calibration checking device is designed to be used for a predetermined number of tests. After first connection of a new calibration checking device, a volume of known calibration checking gas is released into the instrument, and a calibration checking measurement is initiated. A signal is sent to a counting mechanism which both enables the use of the instrument, and commences a count of the number of tests performed by the breath tester. When the number of tests is exceeded, the instrument is disenabled. The device can include a moisture filter having an interface with the instrument, which prevents its operation if the filter is used beyond the recommended number of times, or if excess moisture renders it saturated.
Owner:BREATHID 2006
Breath test system
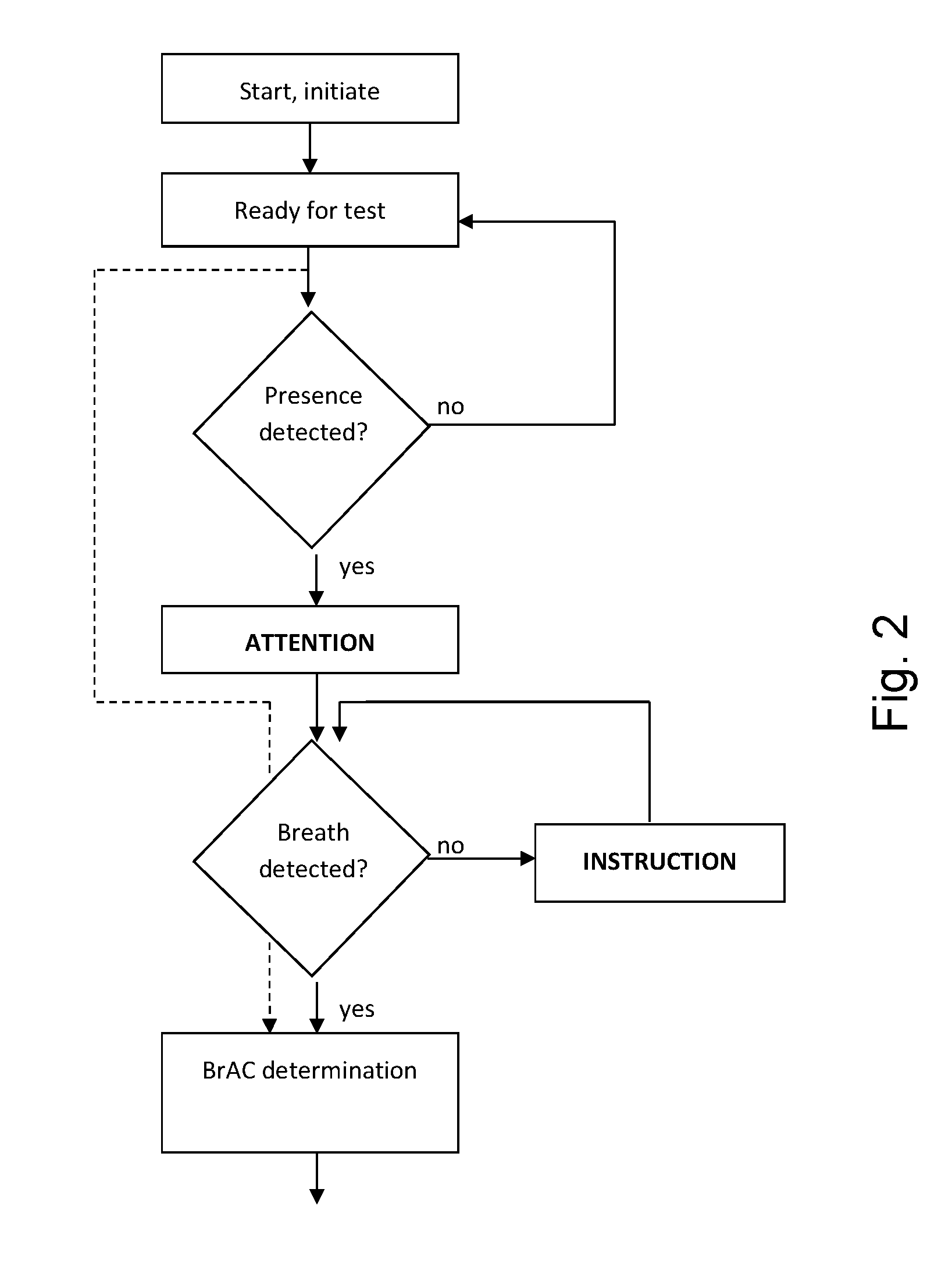
ActiveUS20150219620A1Shorten the timeReduce effortDiagnostics using lightWithdrawing sample devicesBiomedical engineeringAmount of substance
A breath test system is provided comprising a sensor unit configured to sense the presence or concentration of a volatile substance present in air flowing through a predefined inlet area, and generate a signal corresponding to the concentration of said substance. Also provided is an apparatus configured to detect the presence of a person in the vicinity of said input area, and registering said presence, and configured to respond by delivering an output. This apparatus includes a unit configured to call for immediate attention of said person, and upon registration of the presence of said person, provide instructions to said person to direct an expiratory air flow towards said inlet area. An analyzer to determine breath substance concentration of said person is also provided, the determination based on said signal corresponding to the substance concentration.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE COALITION FOR TRAFFIC SAFETY
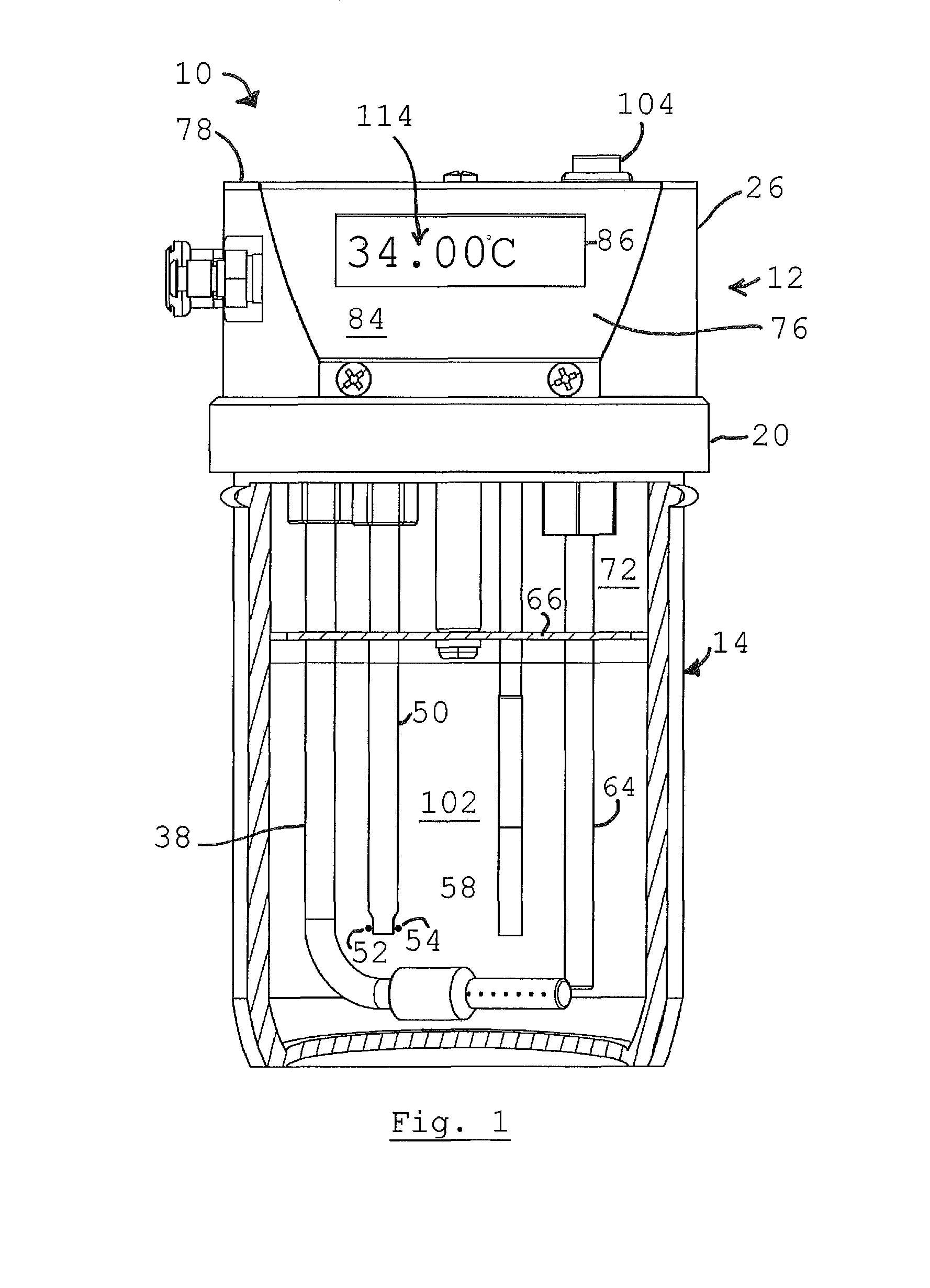
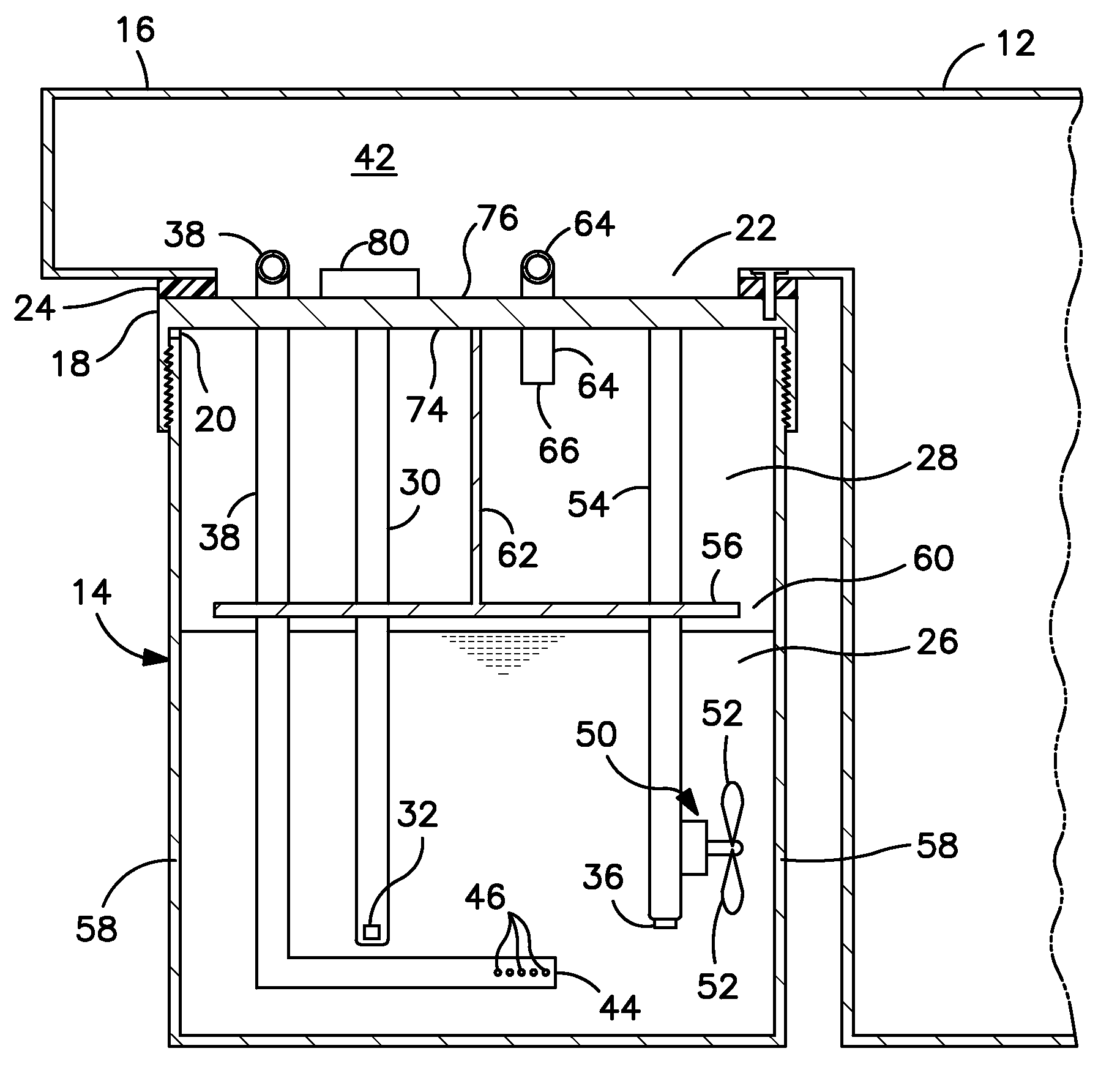
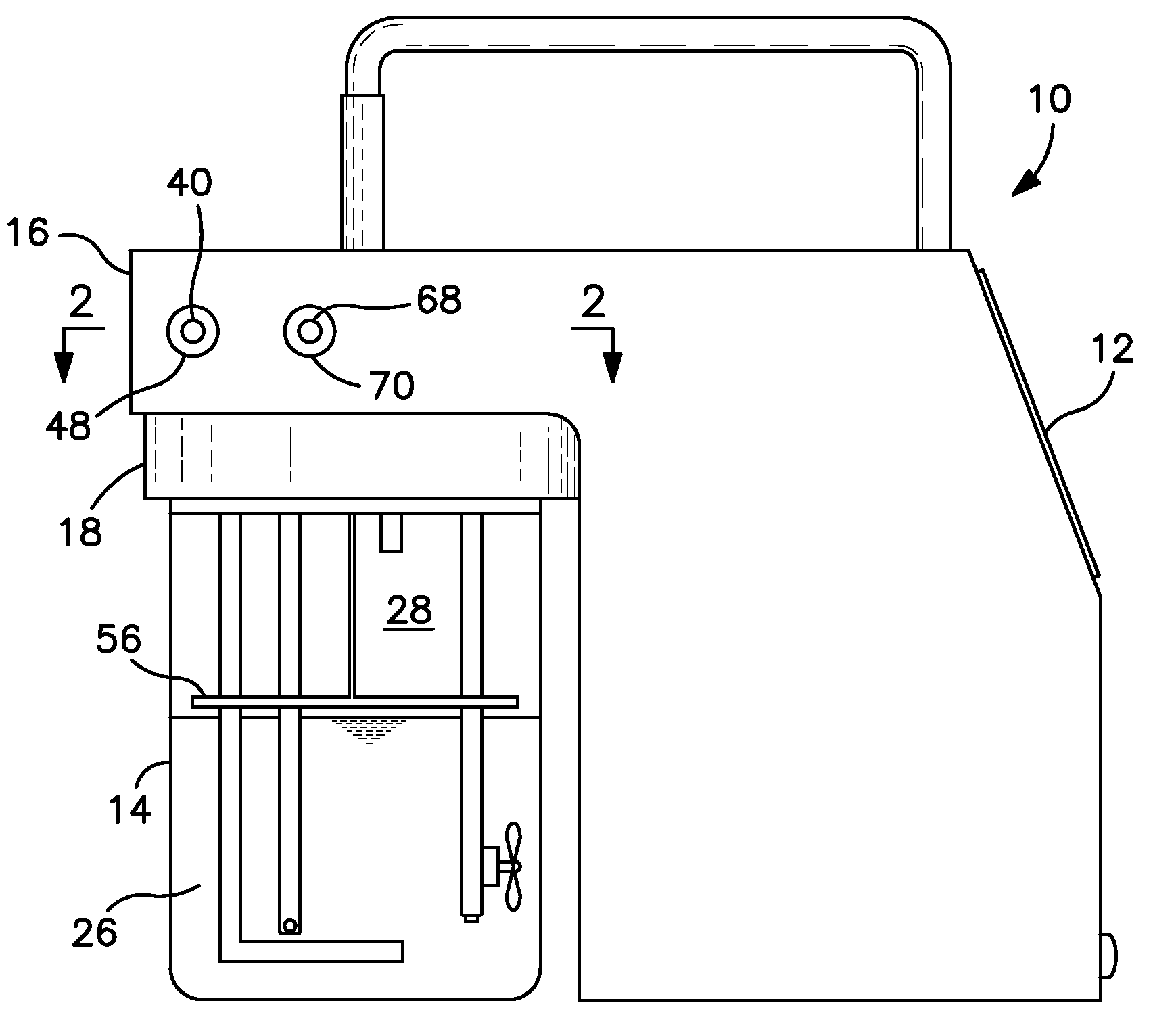
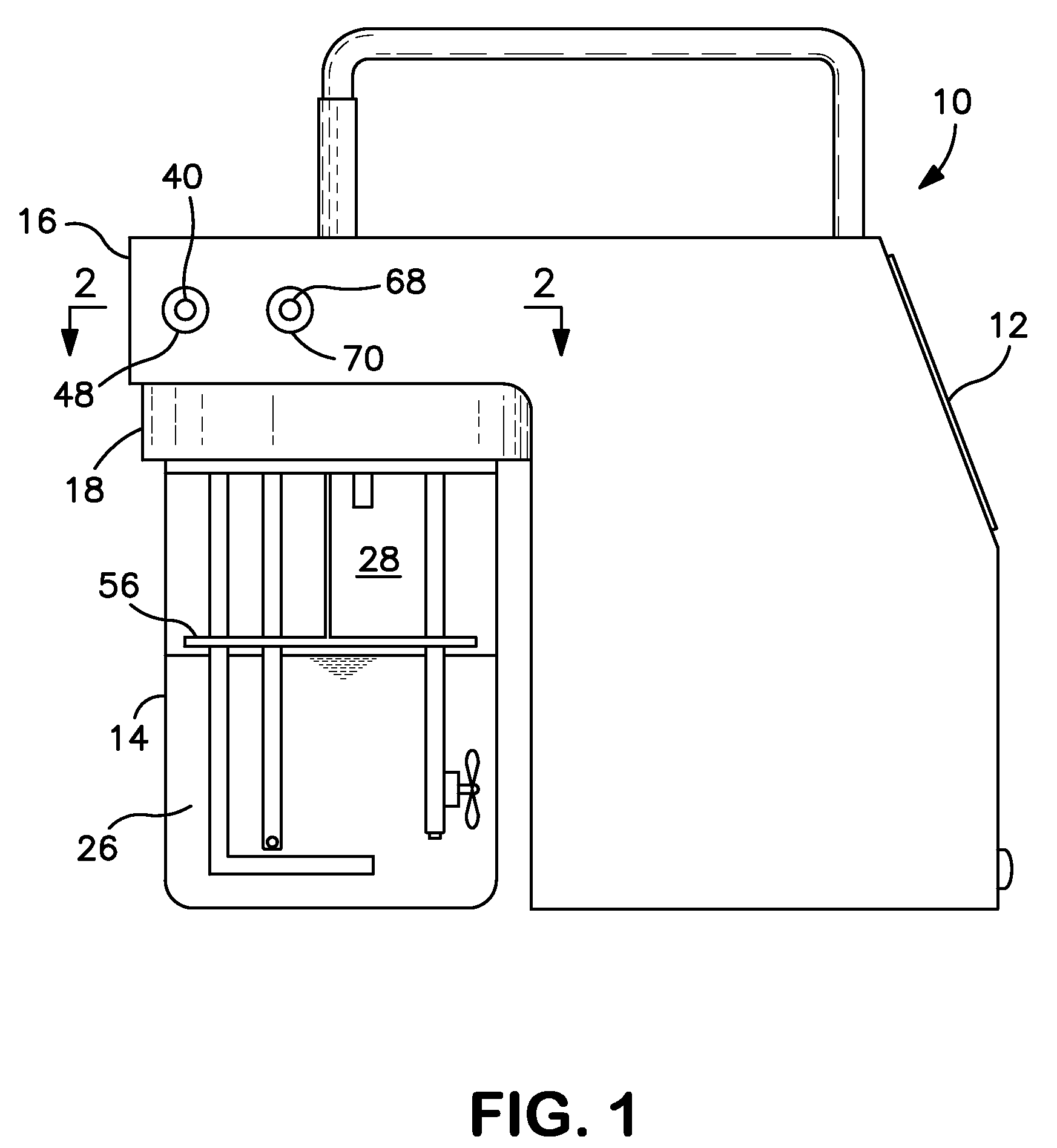
Breath test simulator and method
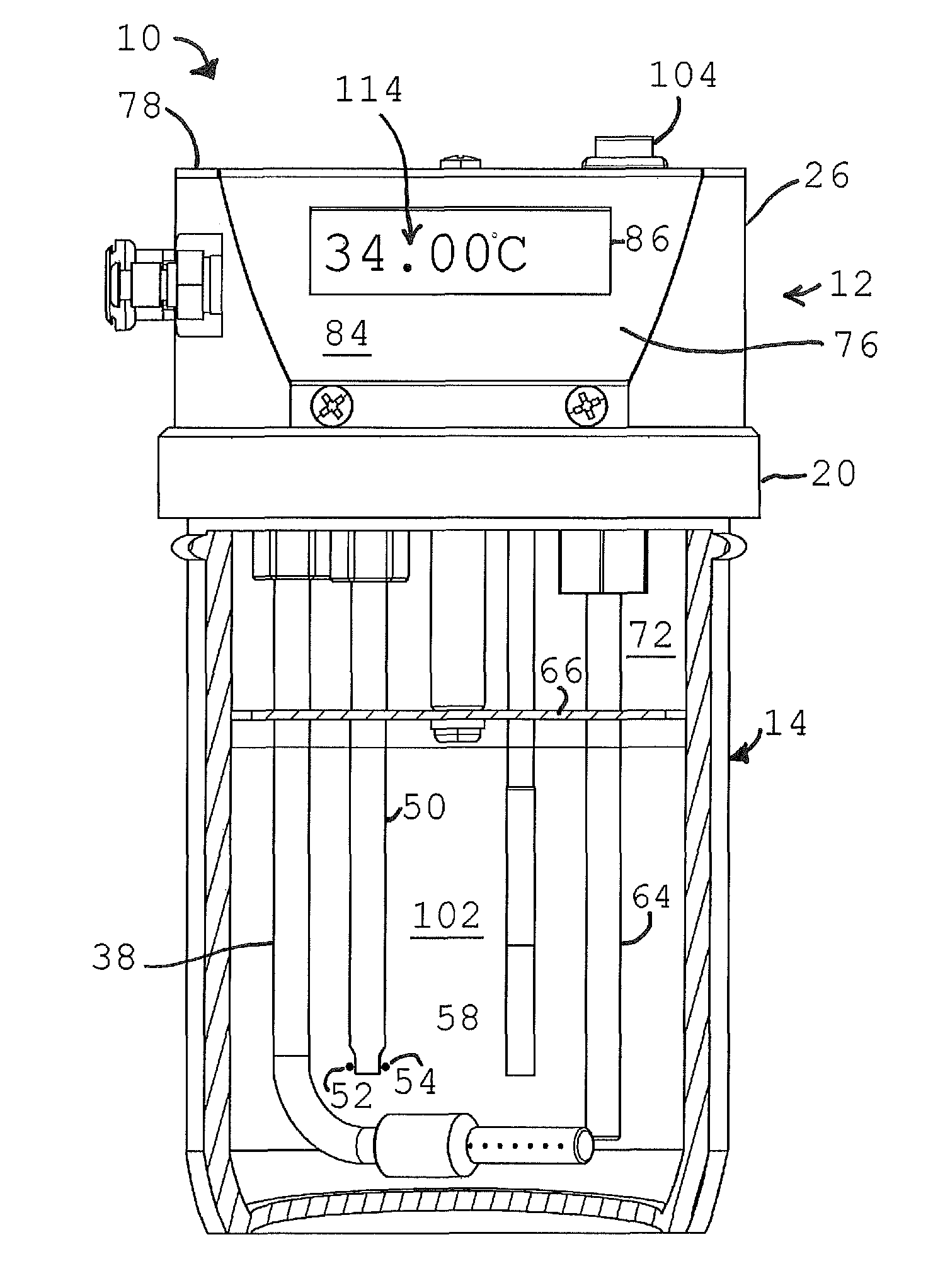
ActiveUS7895878B1Avoid coolingPrevents rapid fluctuation of temperatureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansAlcoholBreath test
A breath test simulator for supplying a breath test analyzer with a vapor including ethyl alcohol includes a heated thermal mass to heat an inlet passage.
Owner:GUTH LAB
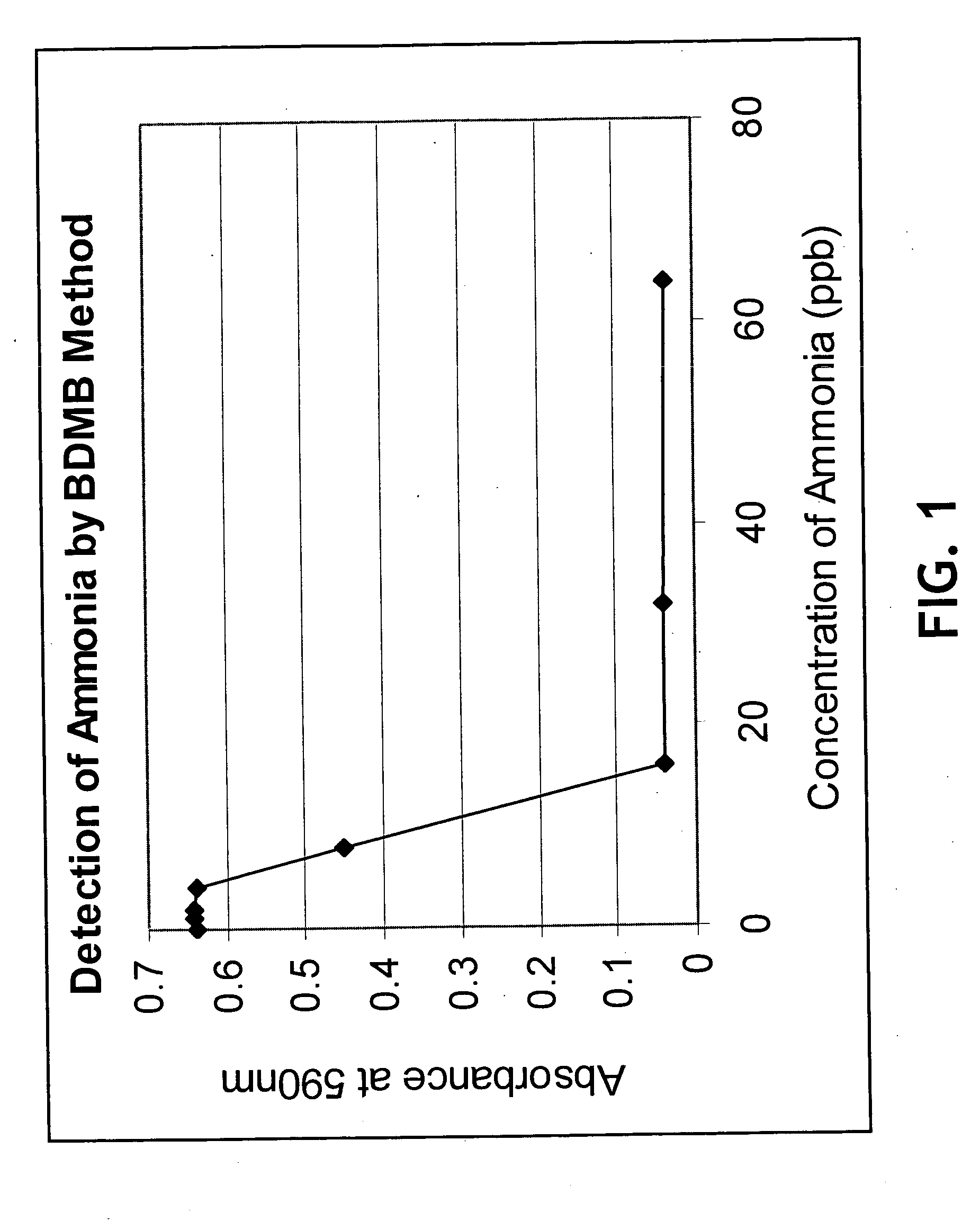
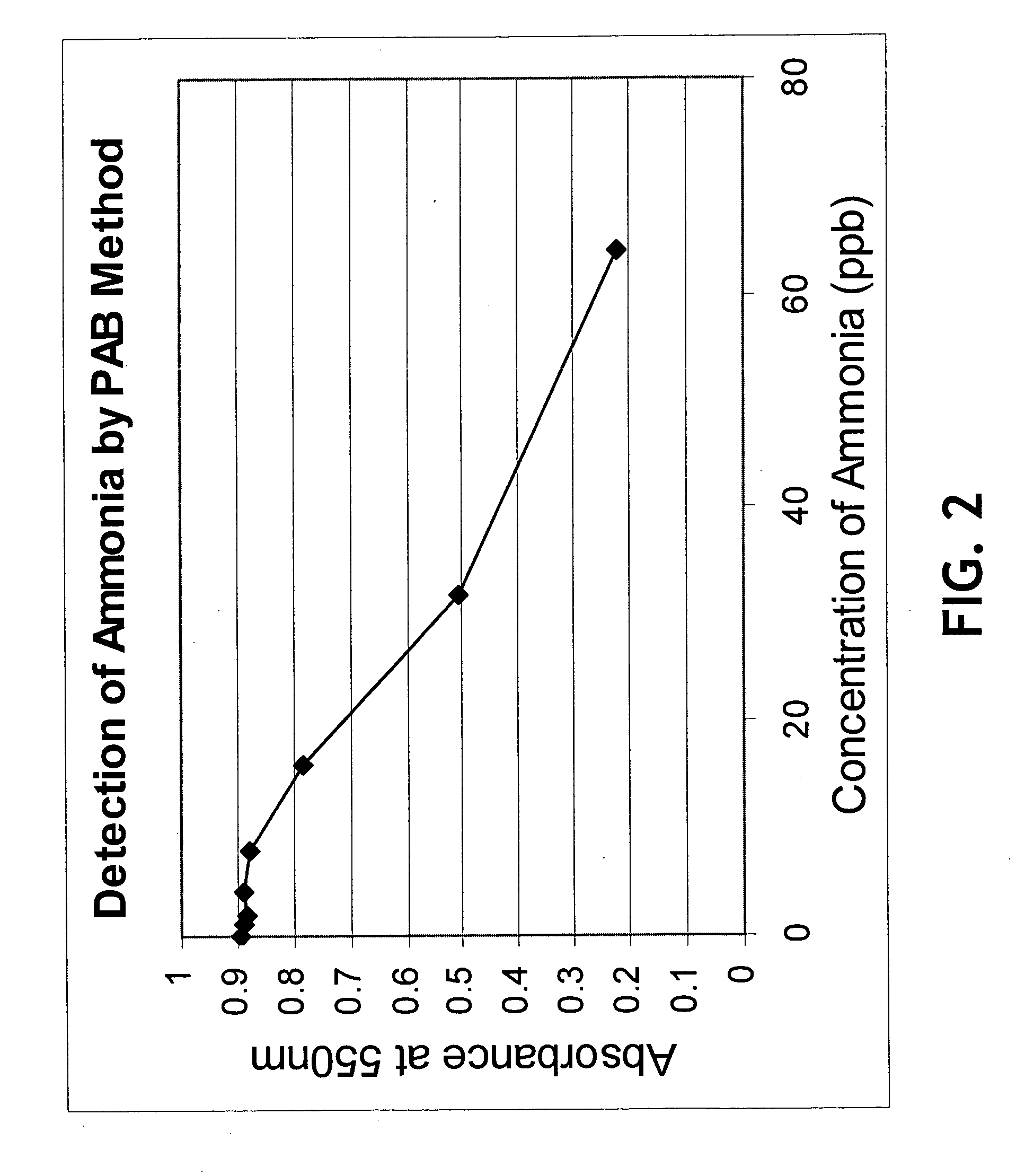
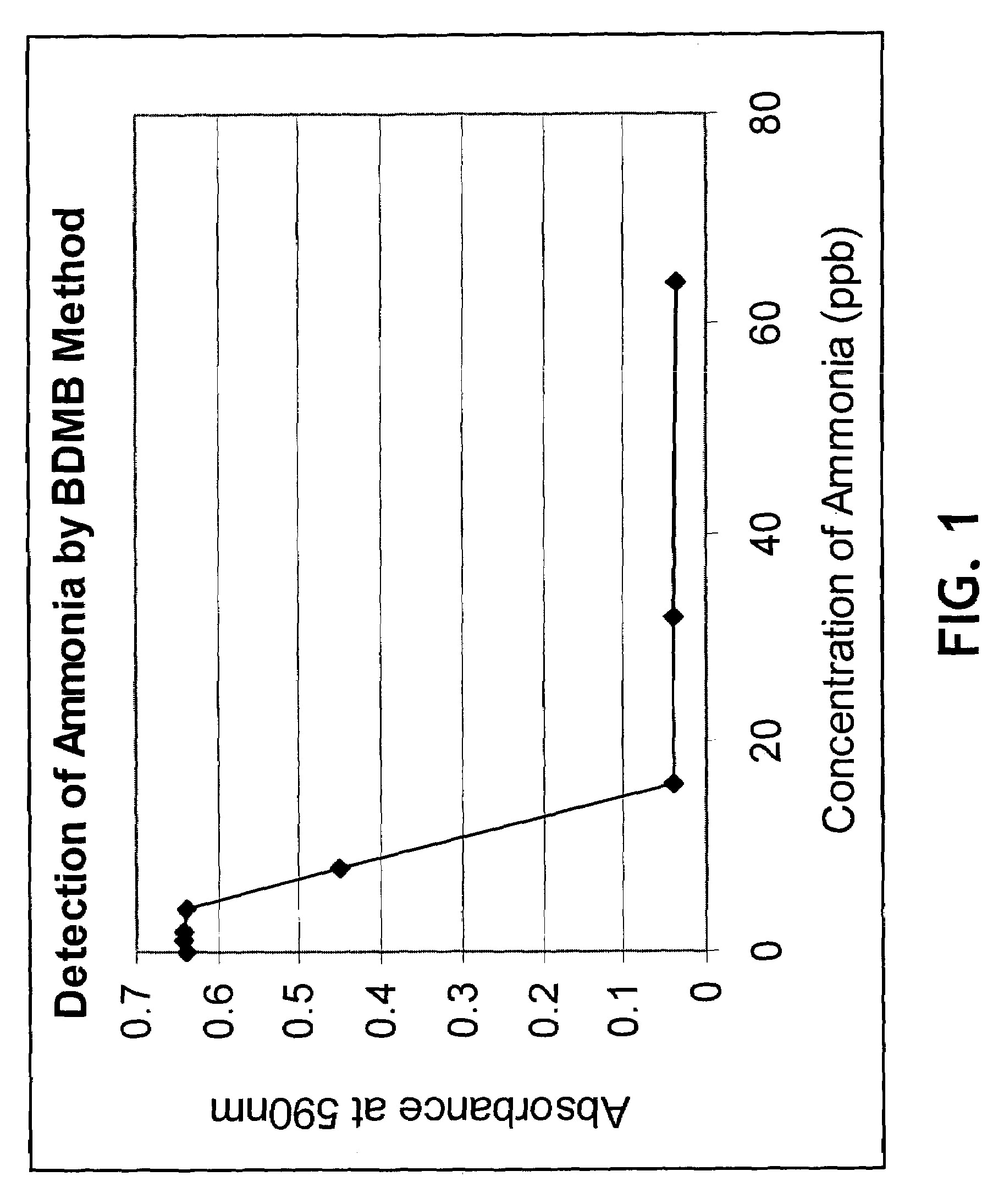
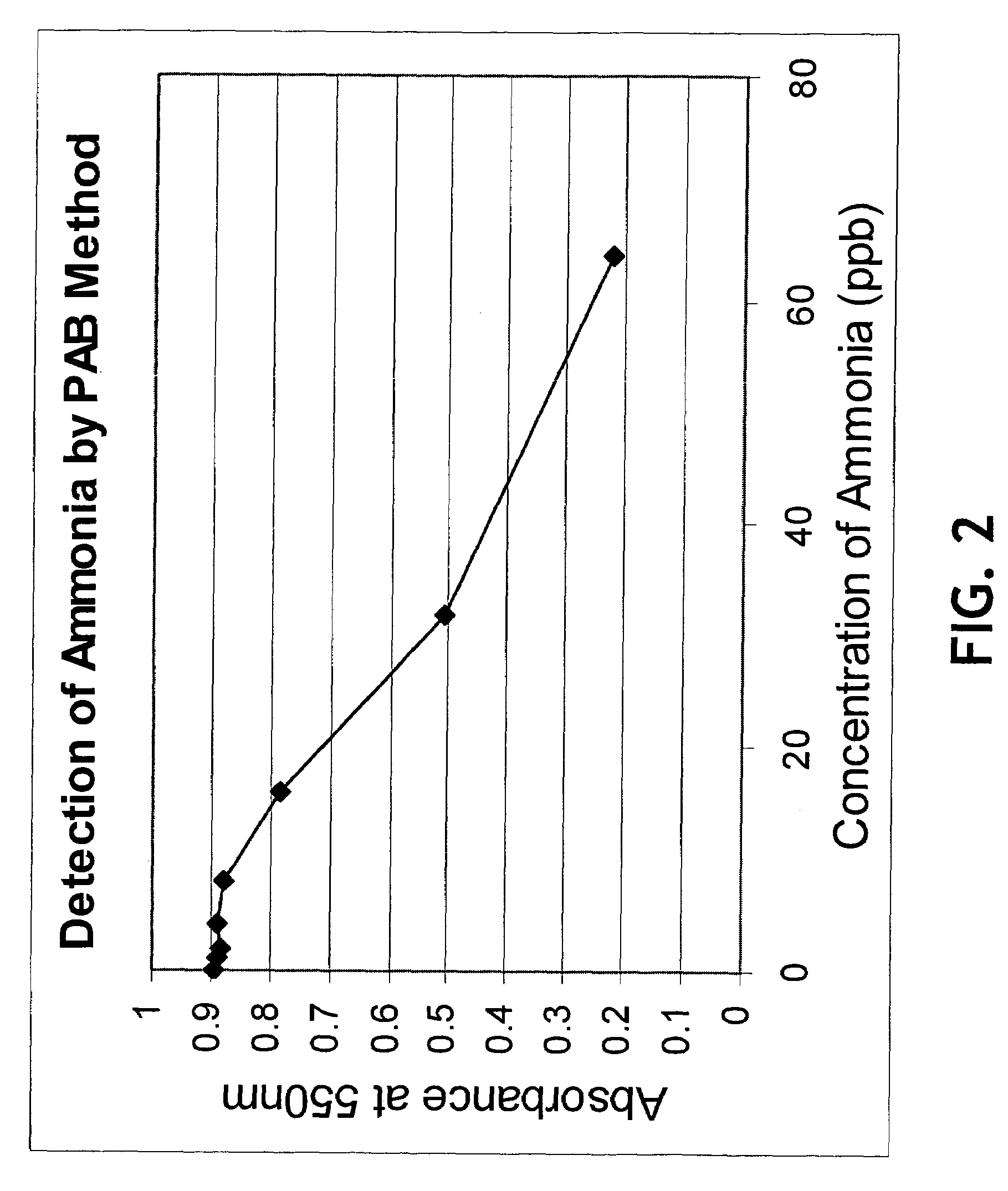
Method and device for detecting ammonia odors and helicobacter pylori urease infection
InactiveUS20050084977A1Easy to detectSure easyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionEnvironmental healthChange color
The invention provides a breath testing device which visually indicates the presence of ammonia in a patient's breath, in particular ammonia from helicobacter pylori urease infection. The breath testing device comprises a visual indicating agent which changes color in response to ammonia odors, such as 4,4′-bis(dimethylamino)-benzhydrol (Michler's hydrol or BDMB), pararosaniline base and alpha-naphtholbenzein. The indicating agent is applied to a substrate which is then inserted into a tube or straw, which can be attached to the inlet of a breath collection balloon. When the patient blows into the tube or straw, the indicating agent will change color if it detects levels of ammonia which are consistent with helicobacter pylori urease infection.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Breath test simulator
ActiveUS7404311B2Easy to controlImprove accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRespiratory simulatorAlcohol
Owner:GUTH LAB
Method and device for detecting ammonia odors and helicobacter pylori urease infection
InactiveUS7582485B2Sure easyEasy to storeMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionChange colorEnvironmental health
The invention provides a breath testing device which visually indicates the presence of ammonia in a patient's breath, in particular ammonia from helicobacter pylori urease infection. The breath testing device comprises a visual indicating agent which changes color in response to ammonia odors, such as 4,4′-bis(dimethylamino)-benzhydrol (Michler's hydrol or BDMB), pararosaniline base and alpha-naphtholbenzein. The indicating agent is applied to a substrate which is then inserted into a tube or straw, which can be attached to the inlet of a breath collection balloon. When the patient blows into the tube or straw, the indicating agent will change color if it detects levels of ammonia which are consistent with helicobacter pylori urease infection.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and composition to evaluate cytochrome P450 2D6 isoenzyme activity using a breath test
InactiveUS20070026480A1Organic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMetaboliteOral medication
The present invention relates, generally to a method of determining and assessing cytochrome P450 2D6 isoenzyme (CYP2D6)-related metabolic capacity in an individual mammalian subject via a breath assay, by determining the relative amount of 13CO2 exhaled by a the subject upon intravenous or oral administration of a 13C-labeled CYP2D6 substrate compound. The present invention is useful as an in vivo phenotype assay for evaluating CYP2D6-related activity using the metabolite 13CO2 in expired breath and to determine the optimal dosage and timing of administration of CYP2D6 substrate compound.
Owner:OTSUKA AMERICA PHARMA INC
Vehicle Interlocking System and Method Based on Detection of Analytes in Exhaled Breath
InactiveUS20130066223A1High resolutionLess wavelengthMaterial analysis by optical meansRespiratory organ evaluationAnalyteMedicine
A drug interlock for vehicles based on exhaled breath directed onto said SERS-active substrate, wherein a detected drug substance in exhaled breath of a subject locks said vehicle from use for at least a pre-determined time or a repeated exhaled breath test where no drugs are detected. A collecting surface has a Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS)-active layer that comprises at least one SERS-active material. The collecting surface is arranged as an outer surface of a waveguide for contact with exhaled breath, such that at least traces of said at least one drug substance in said exhaled breath can contact said SERS-active layer for read-out of a Raman shift spectrum that is detected in-situ for said detecting the presence or determining the quantitative amount of said at least one drug substance from said exhaled breath.
Owner:SENSA BUSB
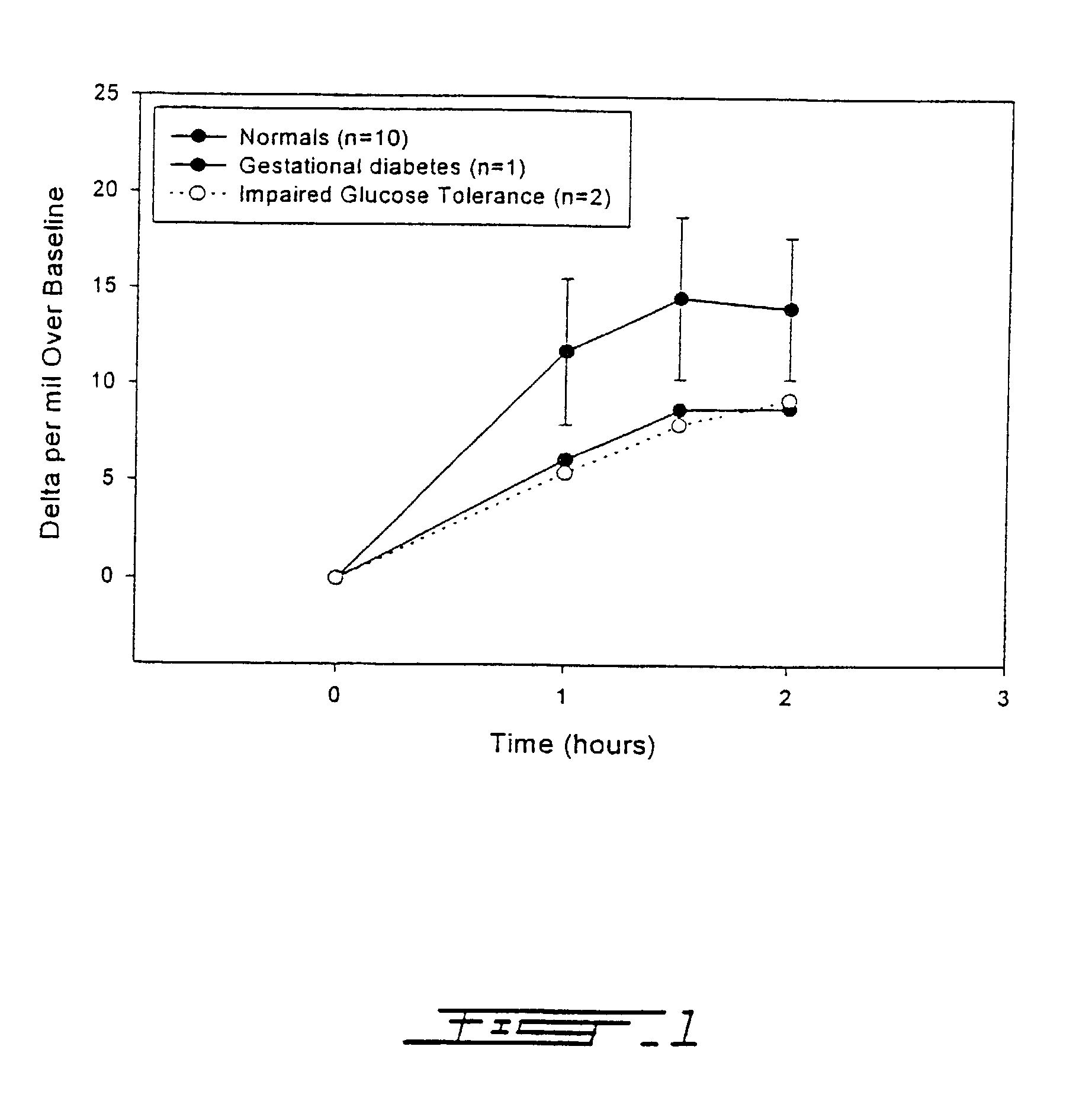
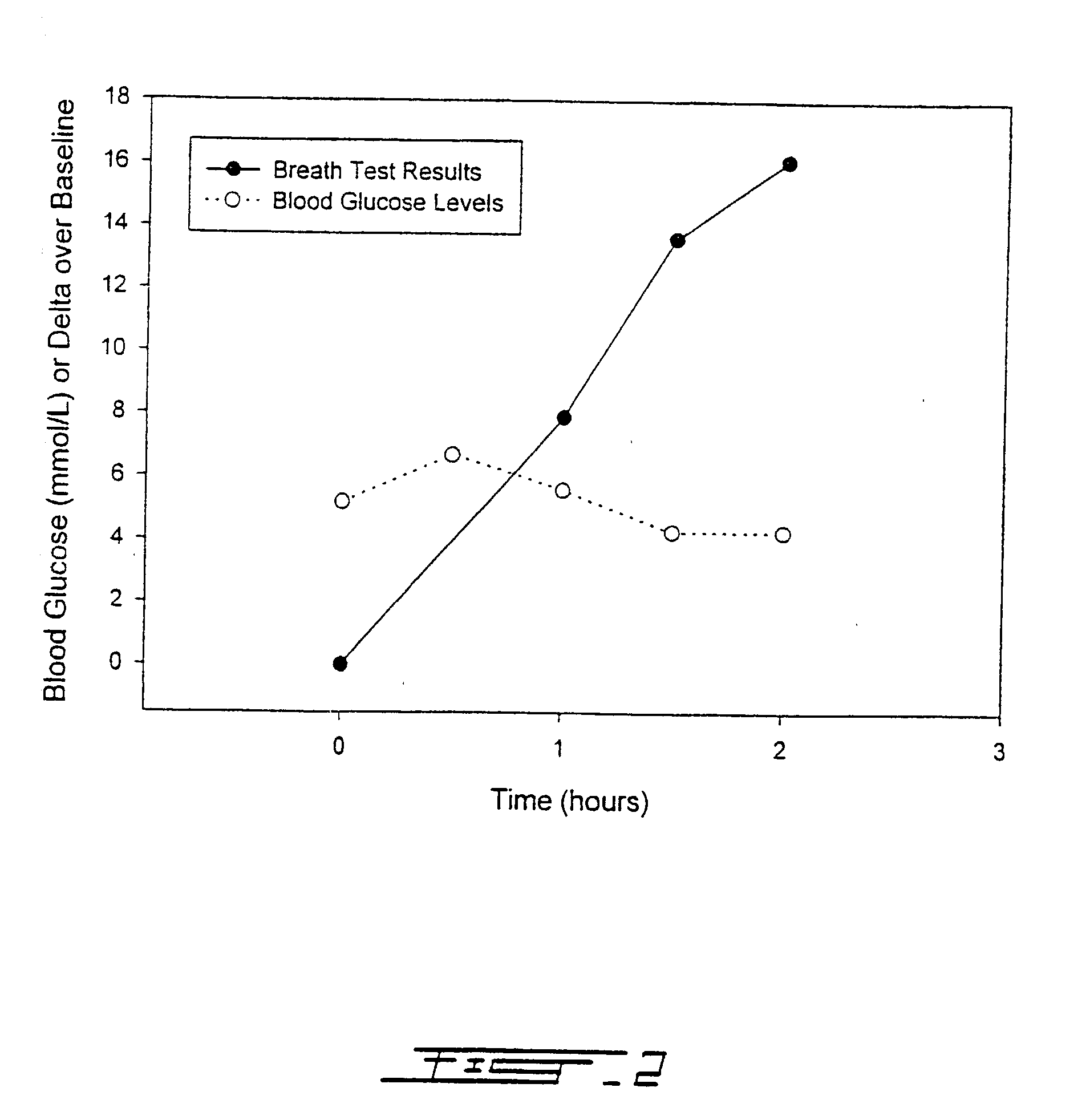
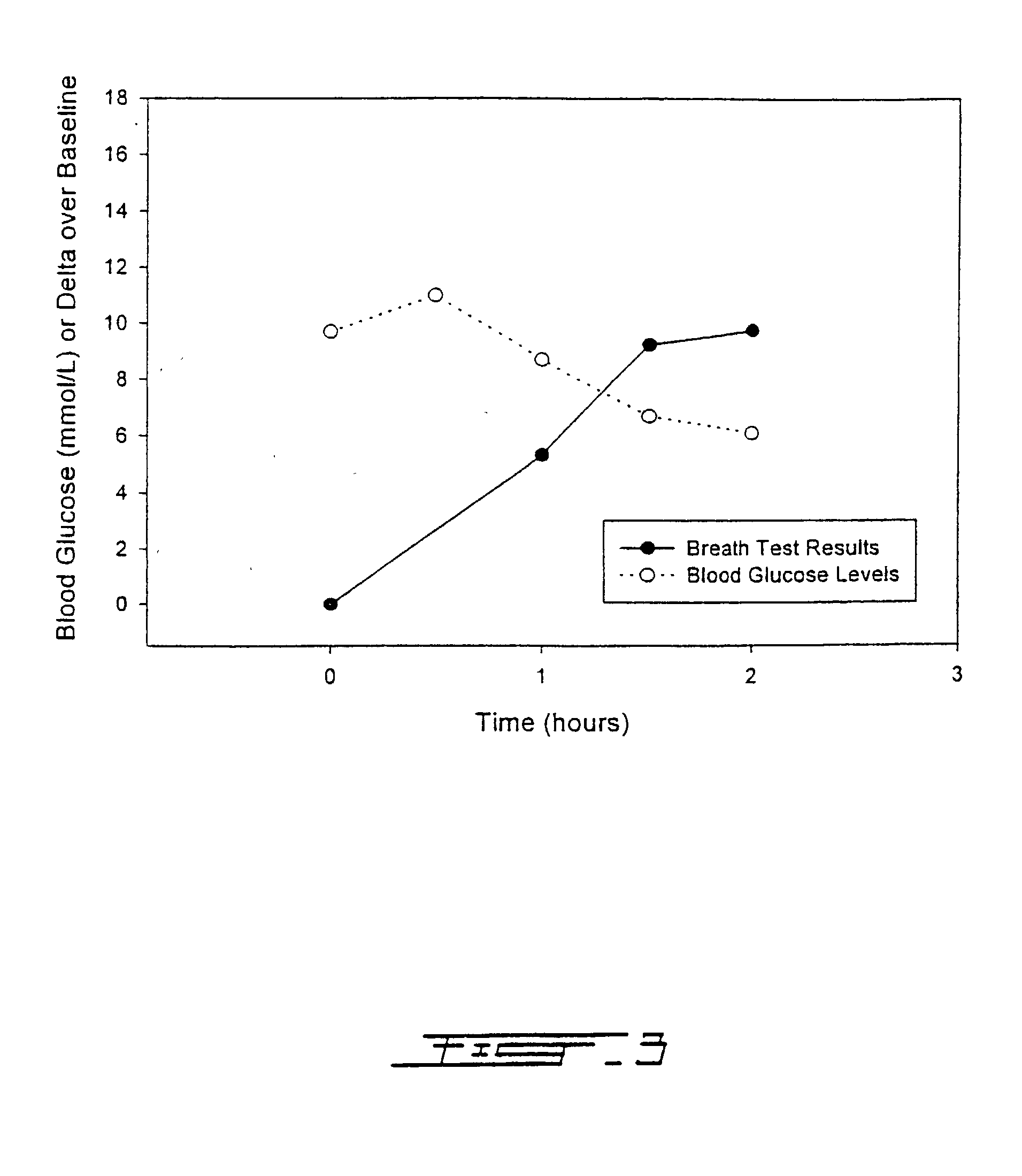
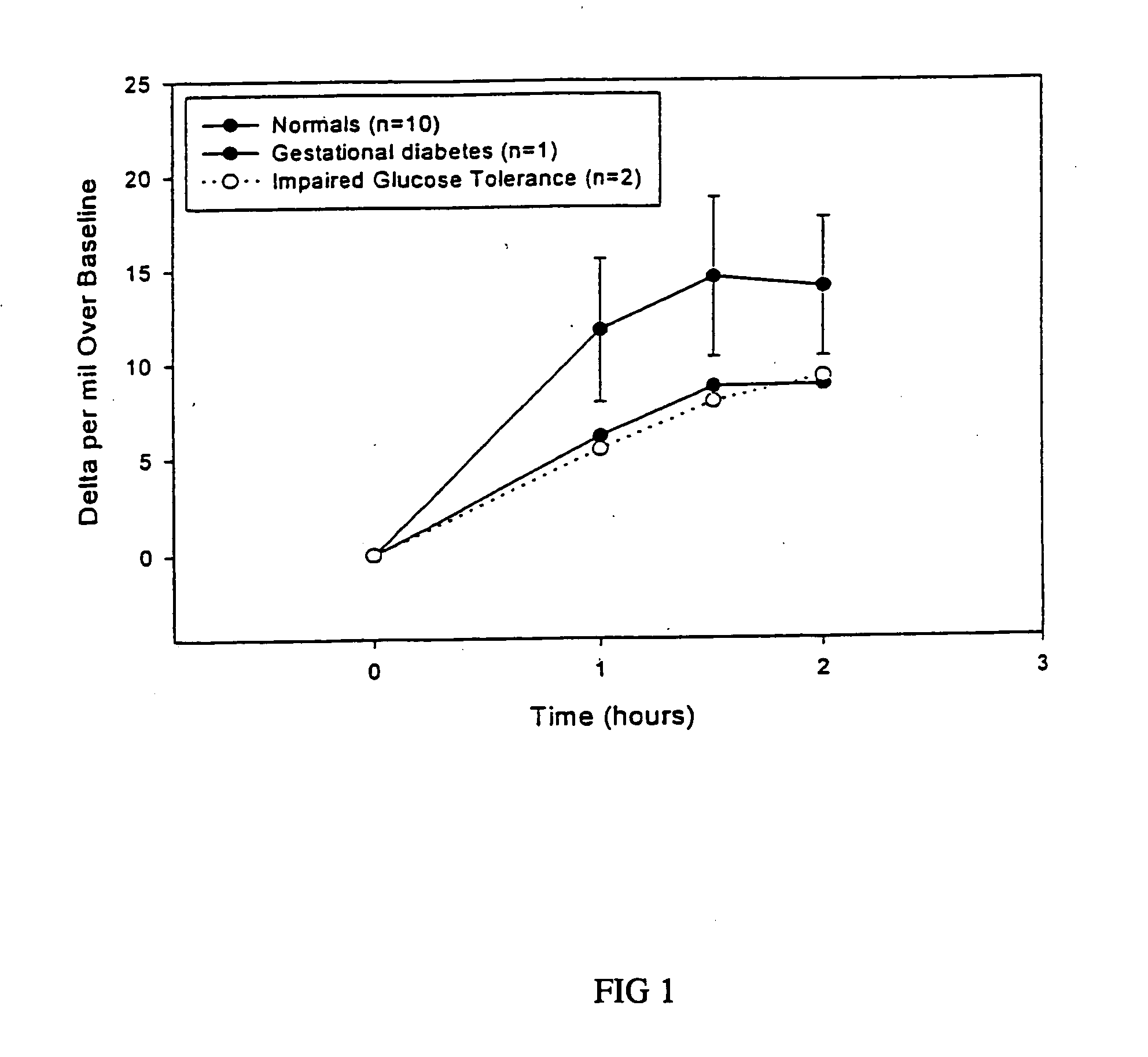
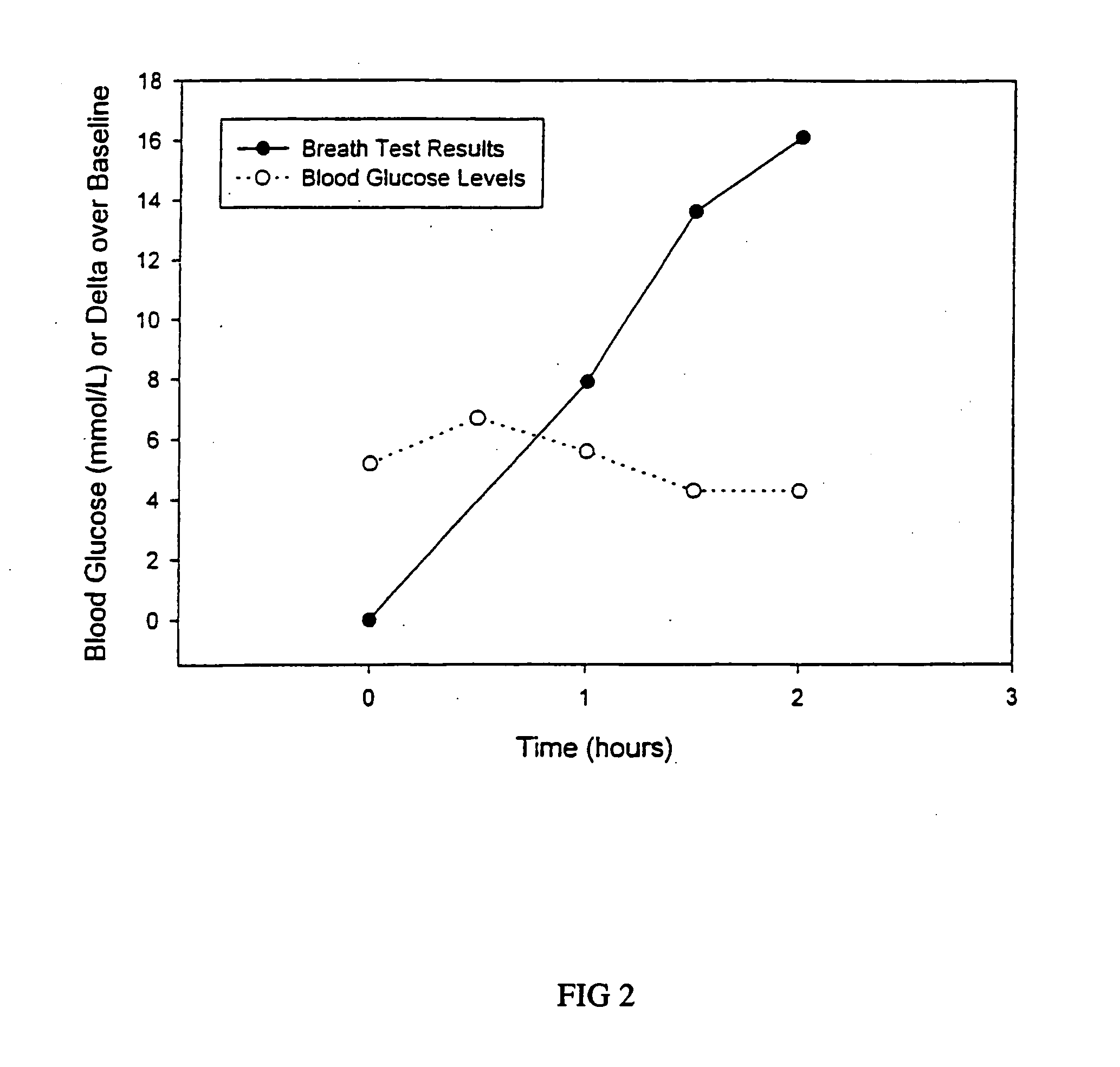
13C glucose breath test for the diagnosis of diabetic indications and monitoring glycemic control
InactiveUS20030044993A1Easy to operateEasy to useAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurement13c labelEnvironmental health
A breath test and kit for performing the breath test are described for the diagnosis of diabetic indications and monitoring of glycemic control. The breath test utilizes the measurement of expired 13C-labeled CO2 following the ingestion of a 13C-enriched glucose source.
Owner:ISOTECHNIKA INC
Management of gastro-intestinal disorders
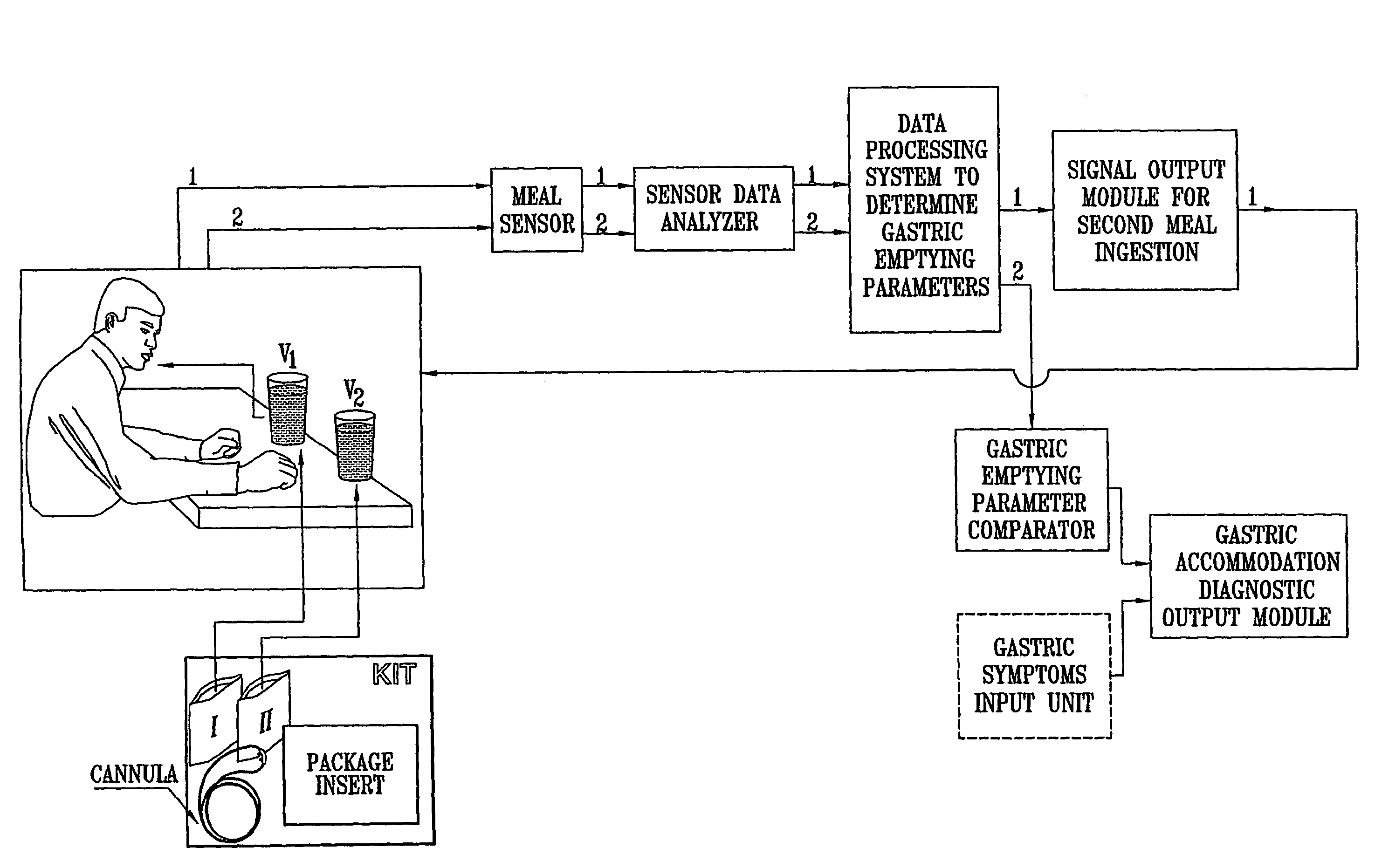
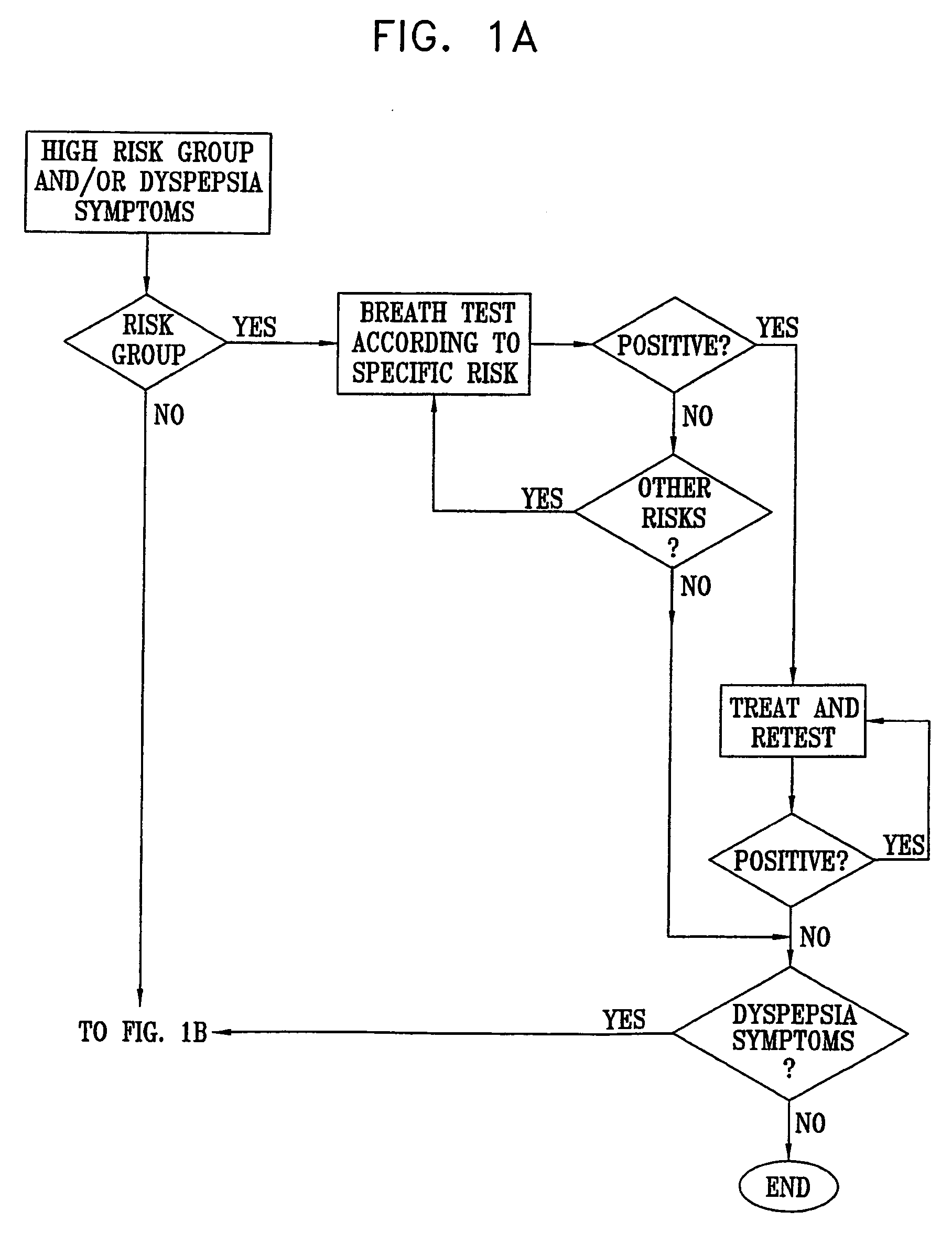
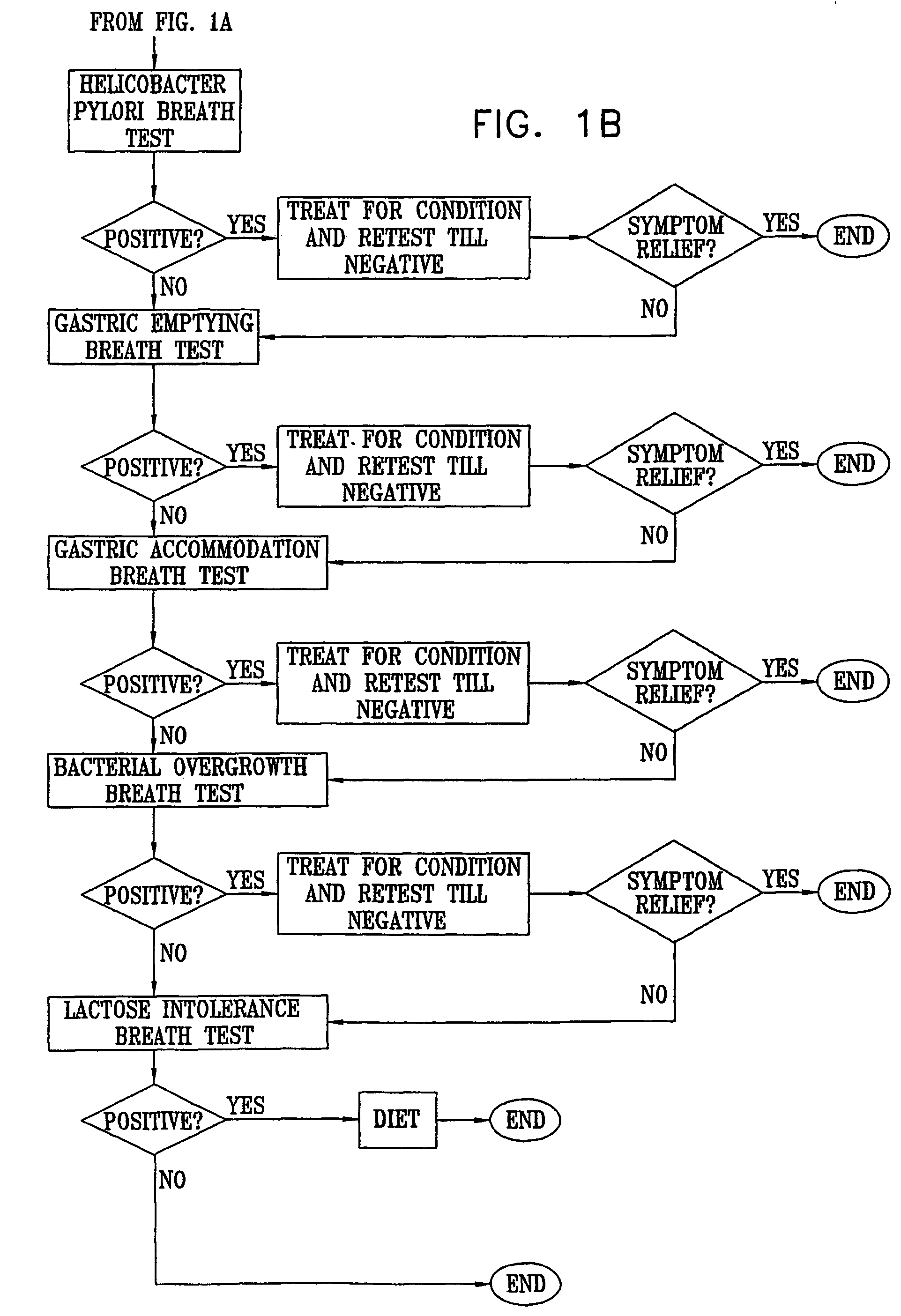
ActiveUS20050020931A1Easily toleratedQuick testCompounds screening/testingWithdrawing sample devicesDiseaseDisease irritable bowel
Methods of determining gastro-intestinal conditions by performing a succession of breath tests or others tests, particularly for determining the gastric emptying or gastric accomodation condition of a subject. Methods of performing successive gastric emptying tests with different test meals are also presented, enabling the gastric accommodation to be determined. The effects of different test means on the results is presented. Novel substrates for use in such tests are suggested, including the use of micro-encapsulation. Breath tests for the detection of bacterial overgrowth, lactose intolerance and combinations thereof are presented.
Owner:MERIDIAN BIOSCIENCE ISRAEL LTD
Breath test simulator
ActiveUS7493793B2Rapid warm up and controlled maintenanceImprove accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRespiratory simulatorAlcohol
A breath simulator for supplying a breath test analyzer with a sample effluent of ethyl alcohol that controls headspace and adjacent effluent passageway temperature.
Owner:GUTH LAB
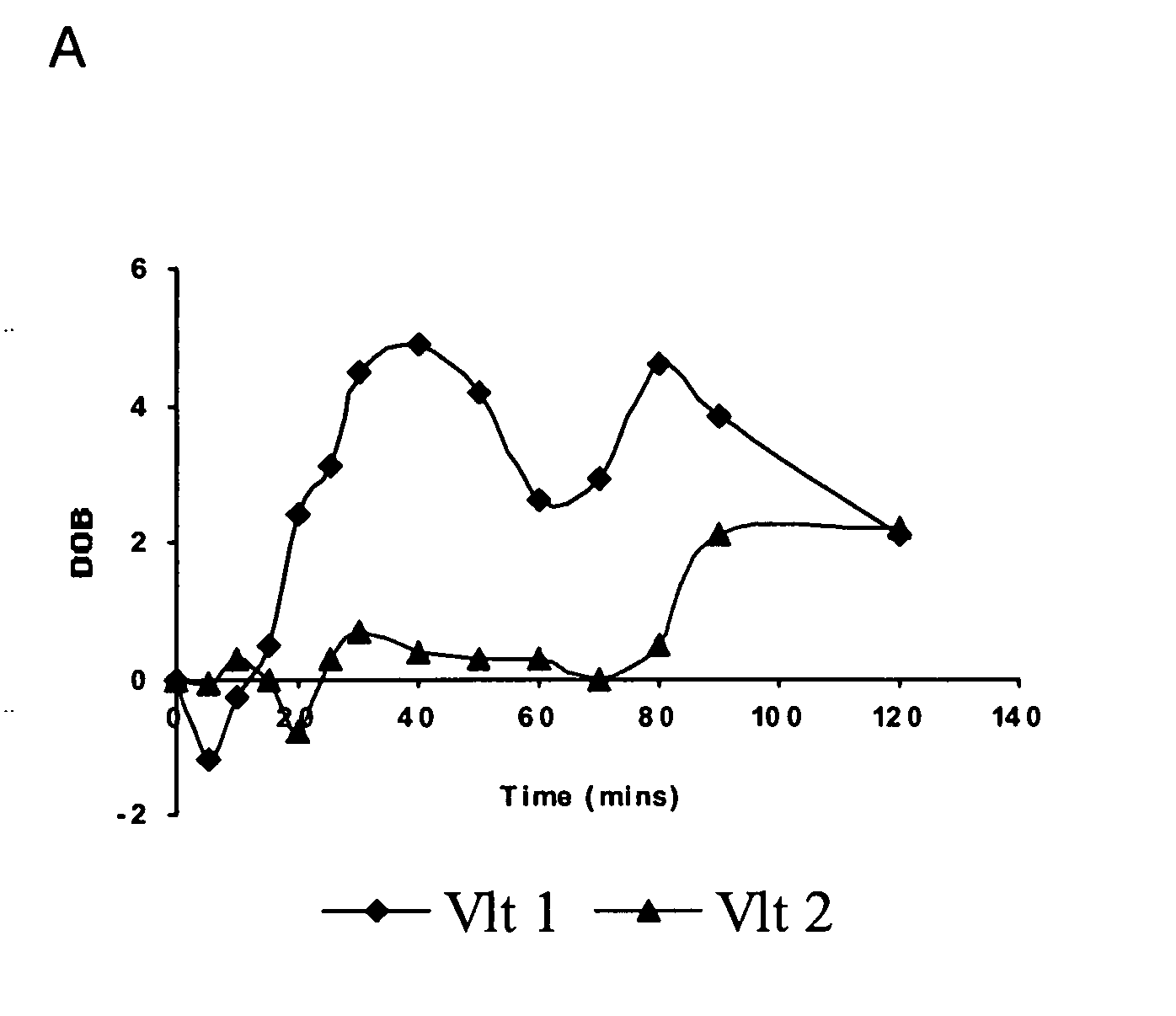
Methods of testing digestive functions using both a breath test and a scintigraphy test, and methods of using a breath test as an overall digestive health assessment
ActiveUS20080281194A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsPerson identificationLipid formationGastric emptying
Owner:ADVANCED BREATH DIAGNOSTICS
Non-invasive rapid diagnostic test for M. tuberculosis infection
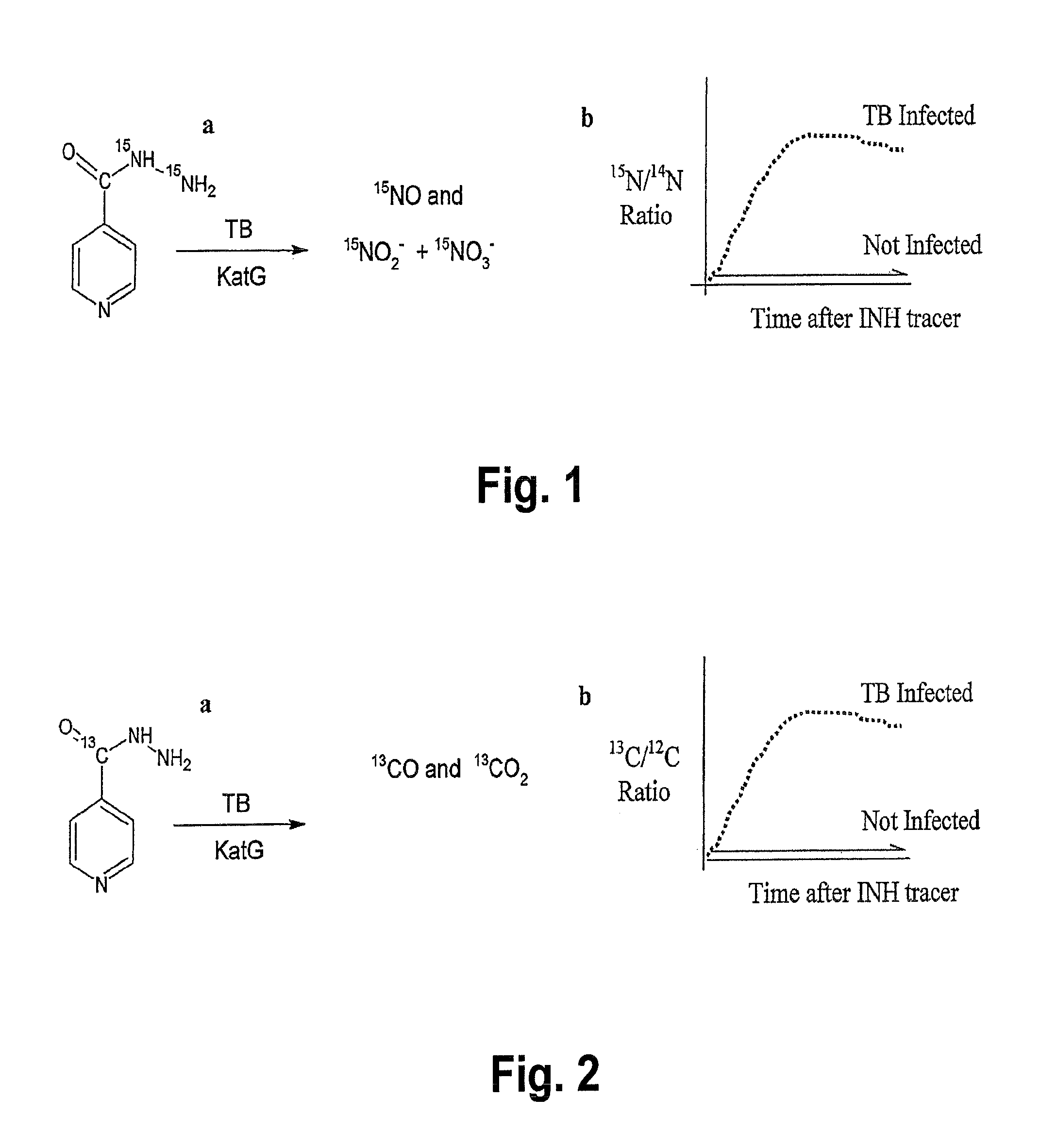
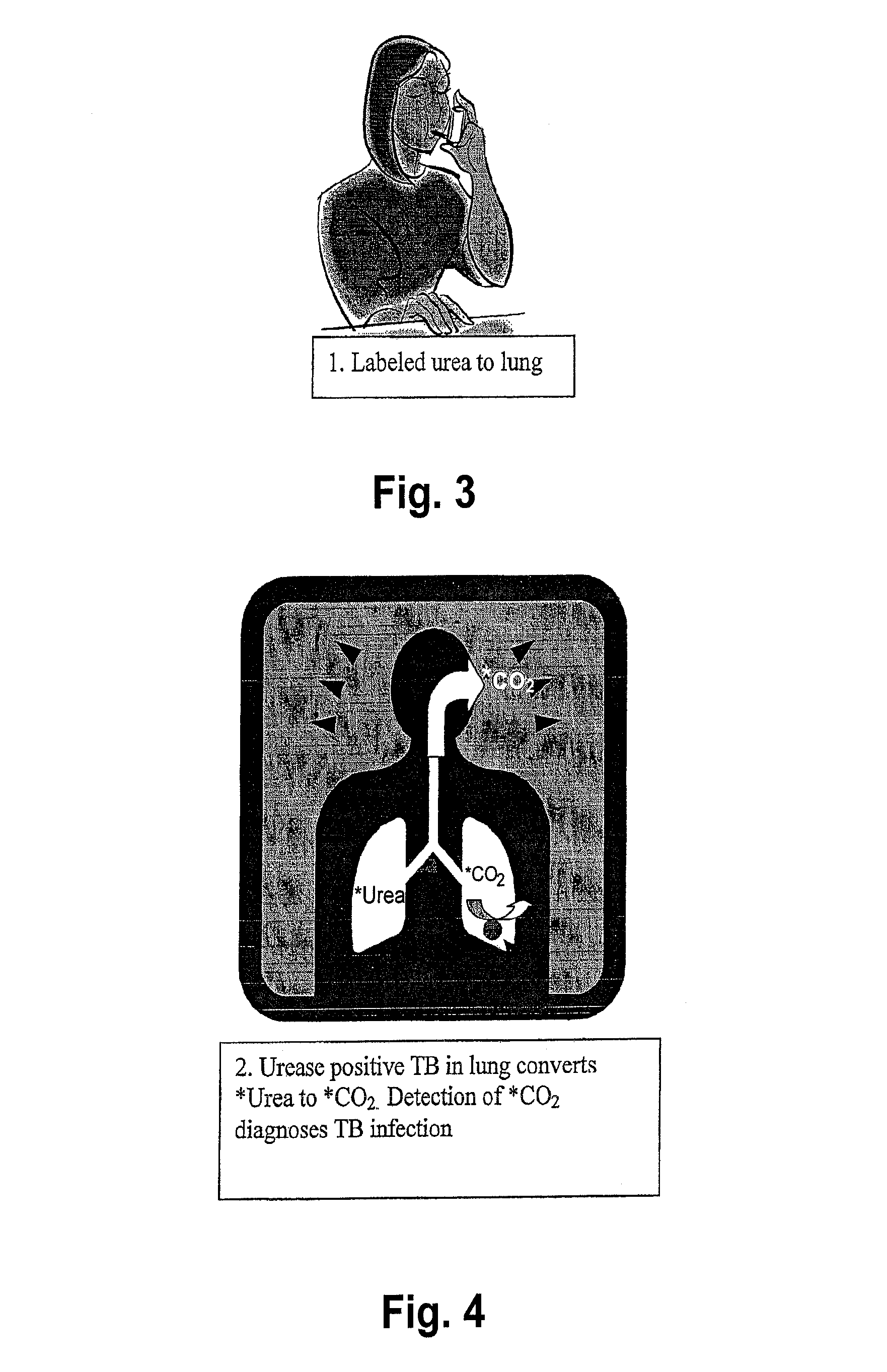
This invention relates to a test for detecting a Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis or TB) infection in a patient or subject, specifically a diagnostic test, including a breath test, whereby patients are provided a small dose of an isotopically labeled TB drug, Isoniazid (INH) orally or directly to the lungs of the patient or subject. If TB is present, a TB enzyme mycobacterial peroxidase KatG oxidizes the INH; and KatG specific metabolites, in particular, isotopically labeled nitric oxide (NO), nitrites, nitrates, carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide converted from carbon monoxide of INH cleavage are measured. Other embodiments relate to a diagnostic breath test for detecting TB utilizing isotopically labeled urea (preferably, carbon-13 labeled urea), alone or in combination with isotopically labeled isoniazid (preferably, nitrogen-15 labeled isoniazid), wherein M. tuberculosis organism, if present in the patient or subject's lungs (or other tissues), will metabolize the isotopically labeled urea to isotopically labeled carbon dioxide (CO2) such that a determination of the residence of M. tuberculosis, including residence of an isoniazid resistant strain of M. tuberculosis, may be made.
Owner:STC UNM
13C glucose breath test for the diagnosis of diabetic indications and monitoring glycemic control
InactiveUS20050147560A1Simple and sensitiveAvoid developmentBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementEnvironmental healthGlycemic
Use of 13C glucose in an analytical assay to monitor glucose metabolism by measurement of labeled exhaled CO2 is provided. A breath test and kit for performing the breath test are described for the diagnosis of diabetic indications and monitoring of glycemic control. The breath test utilizes the measurement of expired 13C-labeled CO2 following the ingestion of a 13C-enriched glucose source.
Owner:ISOTECHNIKA INC
Breath Test Simulator
ActiveUS20080060409A1Rapid warm up and controlled maintenanceImprove accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRespiratory simulatorAlcohol
A breath simulator for supplying a breath test analyzer with a sample effluent of ethyl alcohol that controls headspace and adjacent effluent passageway temperature.
Owner:GUTH LAB
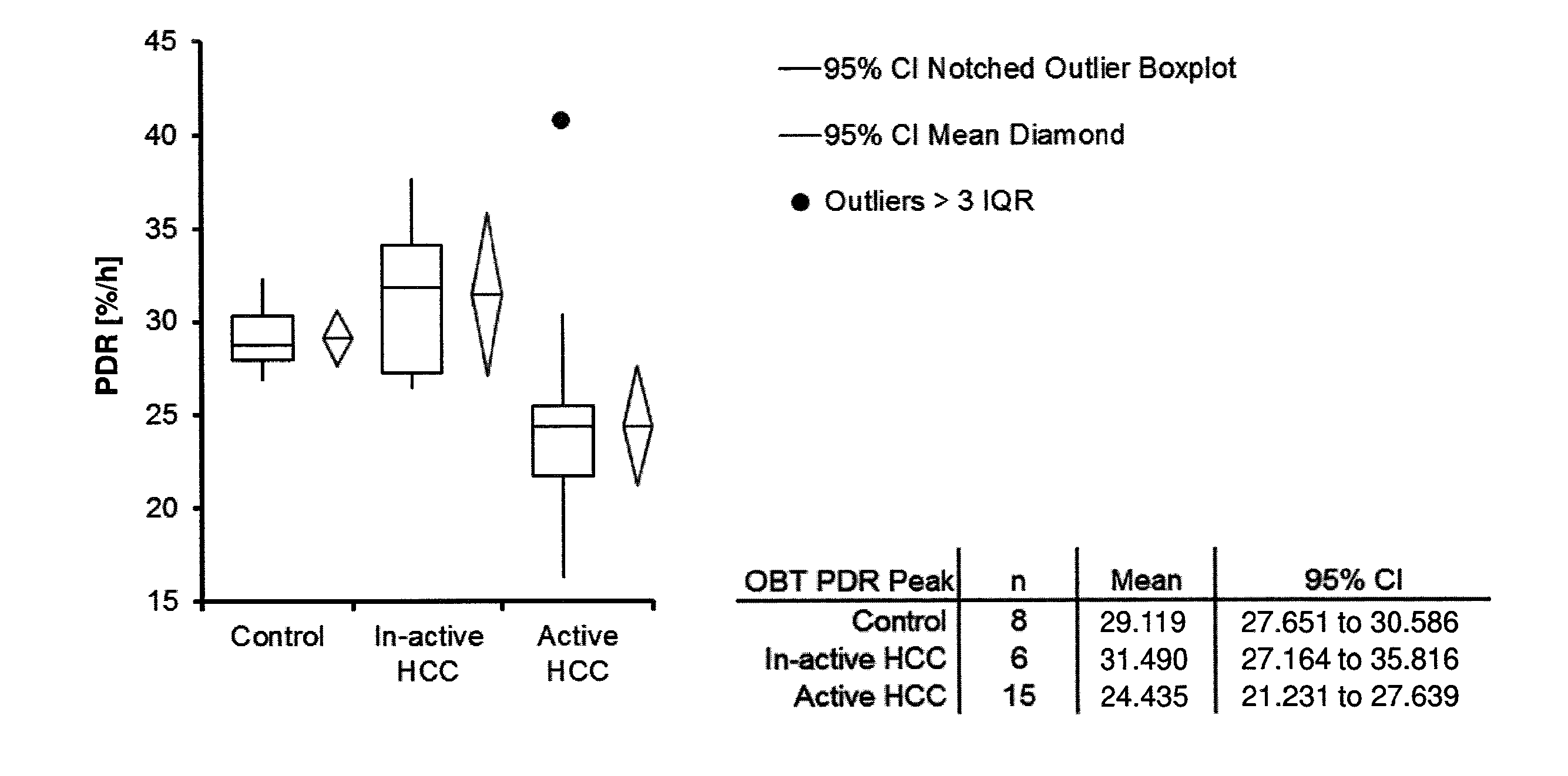
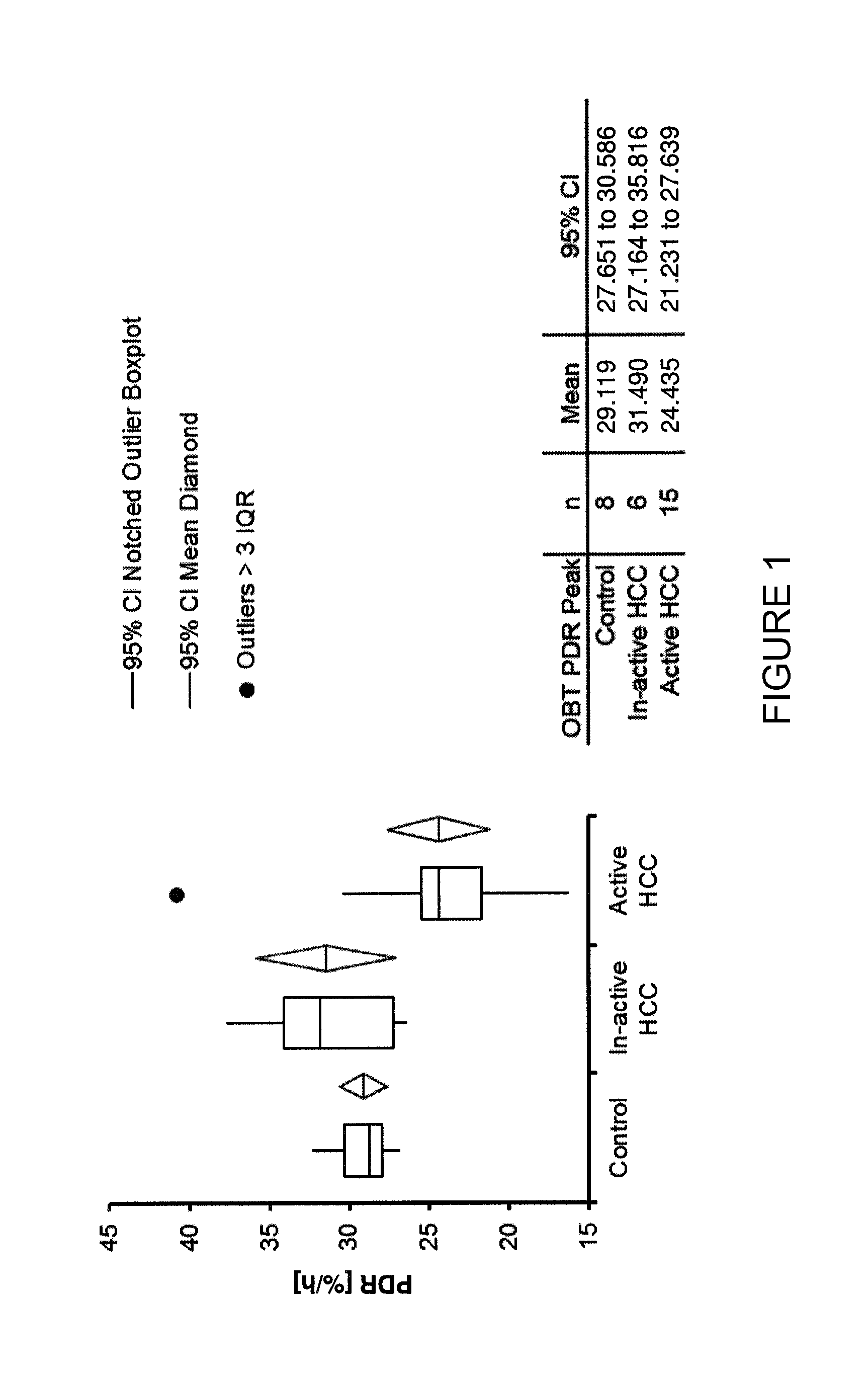
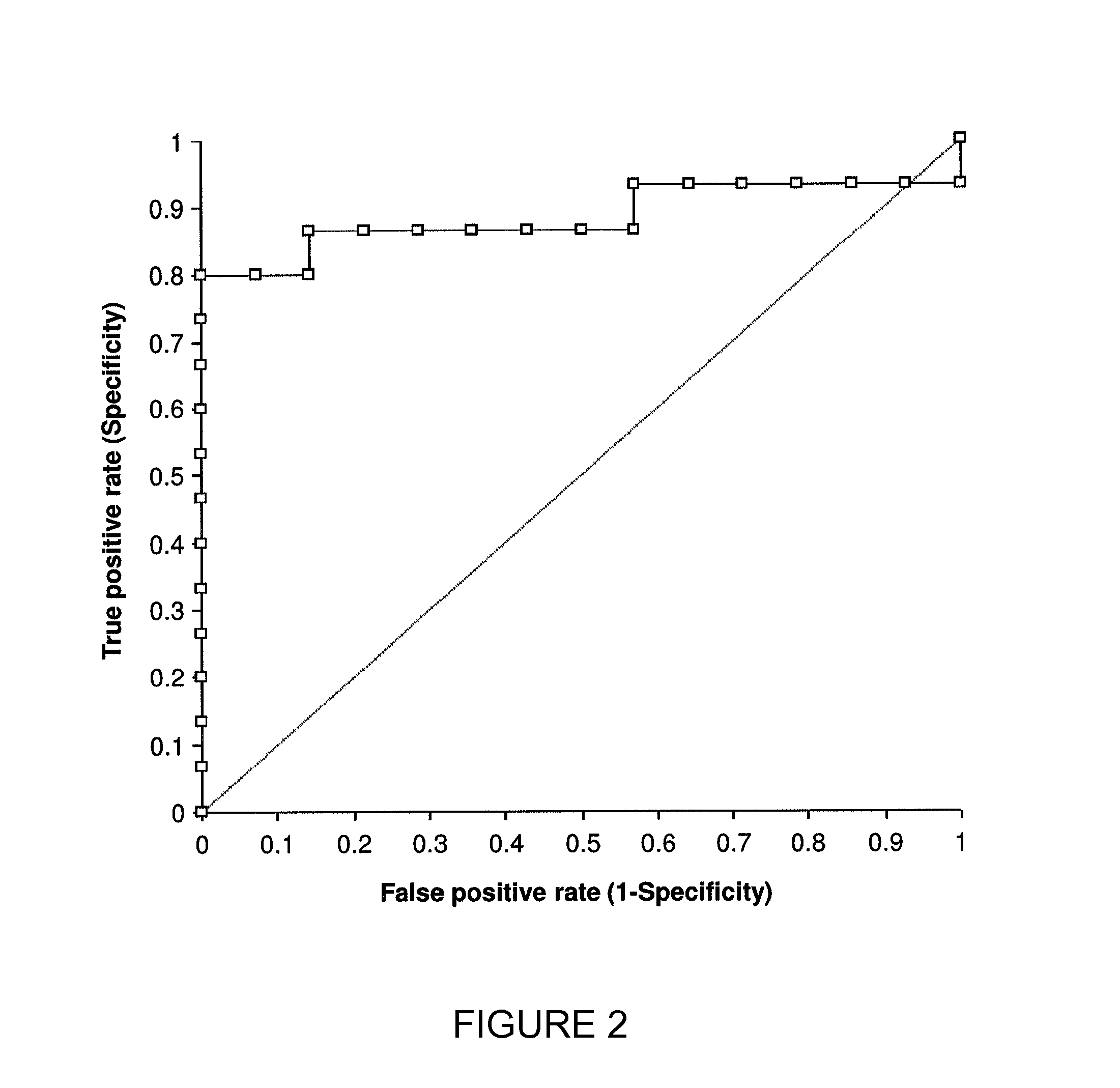
Methods For Diagnosis, Prognosis, Monitoring And Treatment Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
ActiveUS20140033795A1Decrease in OBTGood effectWithdrawing sample devicesSurgeryHepatocellular carcinomaCarcinoma Cell
Owner:MERIDIAN BIOSCIENCE ISRAEL LTD
Management of gastro-intestinal disorders
InactiveUS7338444B2Easily toleratedQuick testCompounds screening/testingPerson identificationDiseaseDisease irritable bowel
The present invention relates to the field of methods and apparatus for the determination of various conditions of gastric and gastro-intestinal malfunction, especially those performed by means of breath tests.
Owner:EXALENZ BIOSCIENCE LTD
Kits for gastric emptying measurement
InactiveUS20070014718A1Small molecular weightQuick measurementCompounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsTherapy monitoringDisease
The present invention provides a test meal kits that are used in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders characterized by changes in the rate of gastric emptying; and, with a breath test or a nuclear scintigraphy scan, are used to measure a half-gastric emptying time useful for therapy monitoring of gastrointestinal disorders in clinical.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Management of gastro-intestinal disorders
InactiveUS20080281193A1Easily toleratedQuick testCompounds screening/testingWithdrawing sample devicesDiseaseGastrointestinal dysfunction
The present invention relates to the field of methods and apparatus for the determination of various conditions of gastric and gastro-intestinal malfunction, especially those performed by means of breath tests.
Owner:MERIDIAN BIOSCIENCE ISRAEL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com