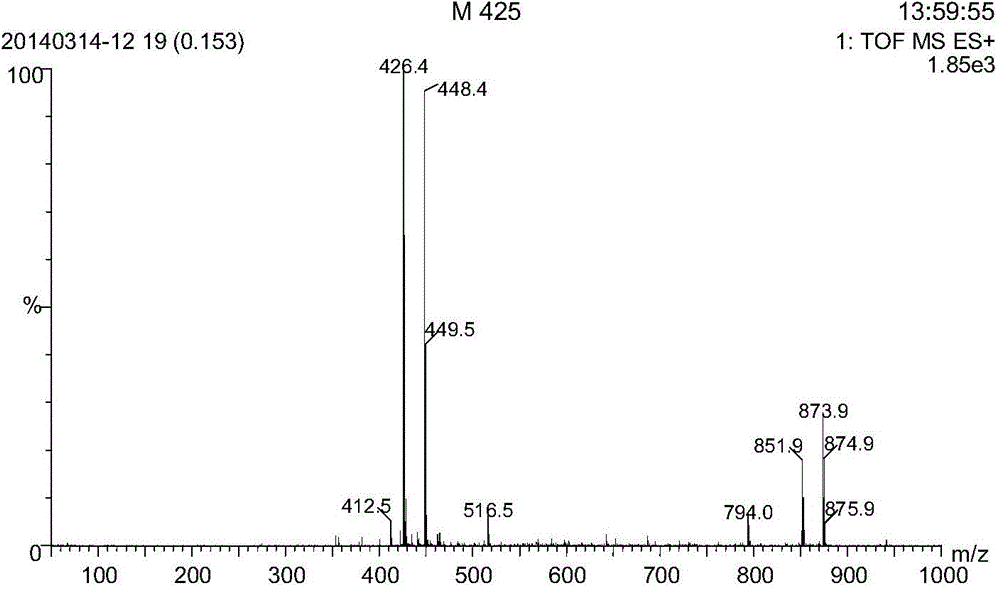
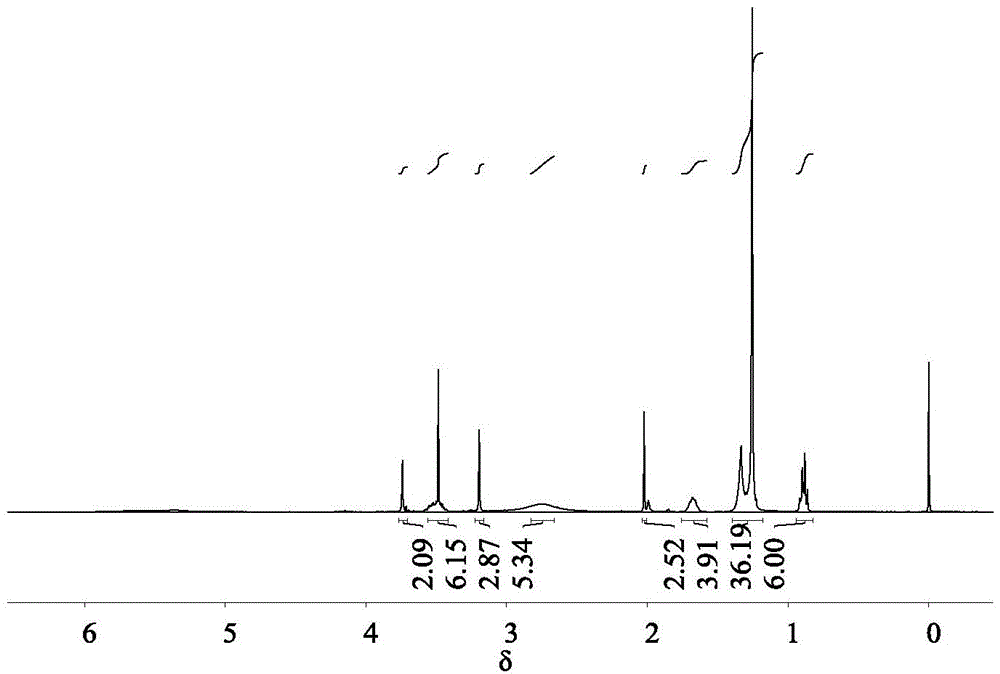
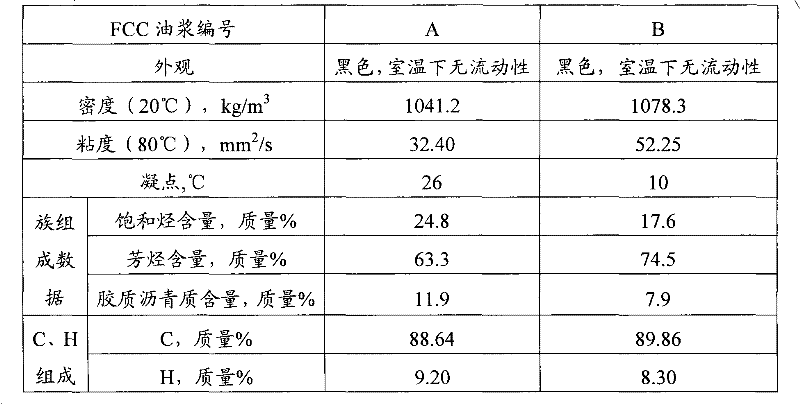
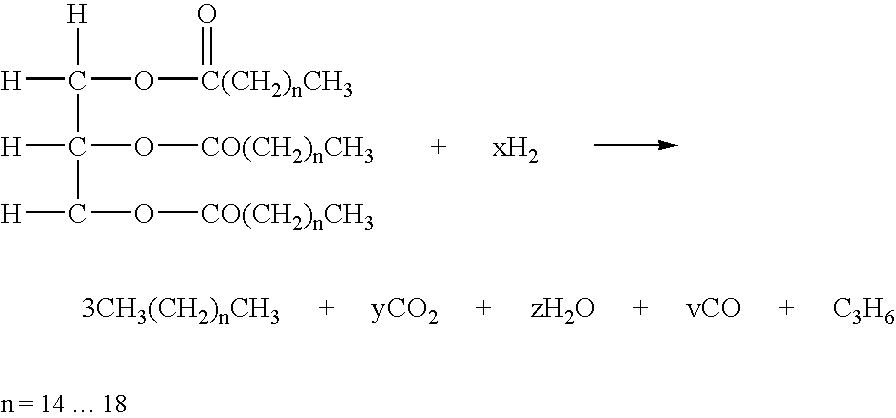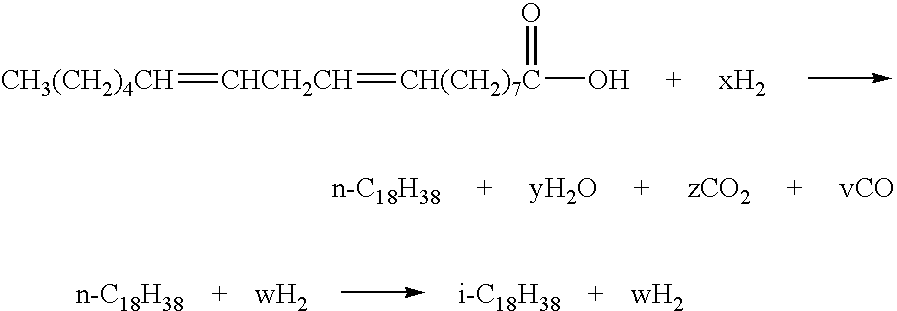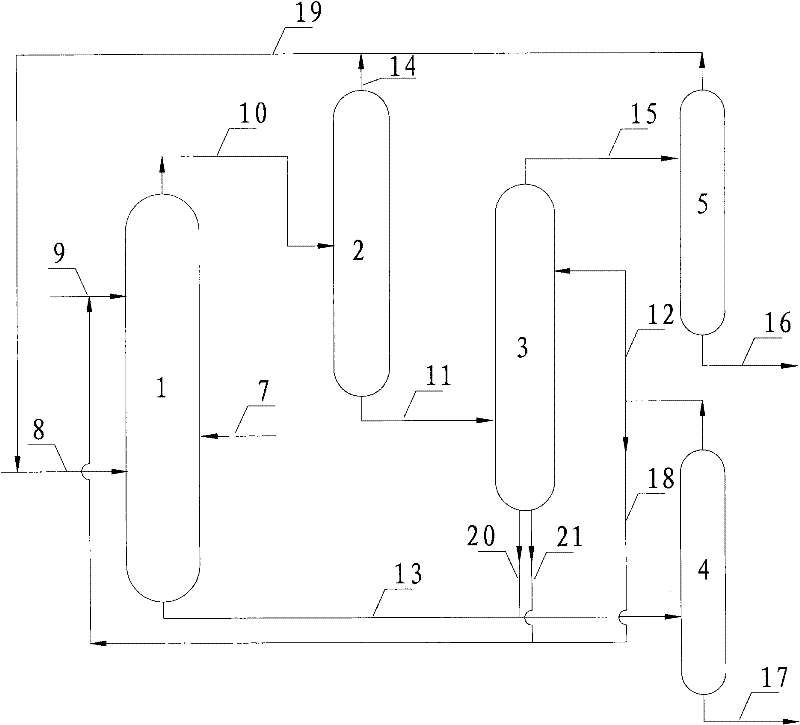Patents
Literature
297 results about "N alkanes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
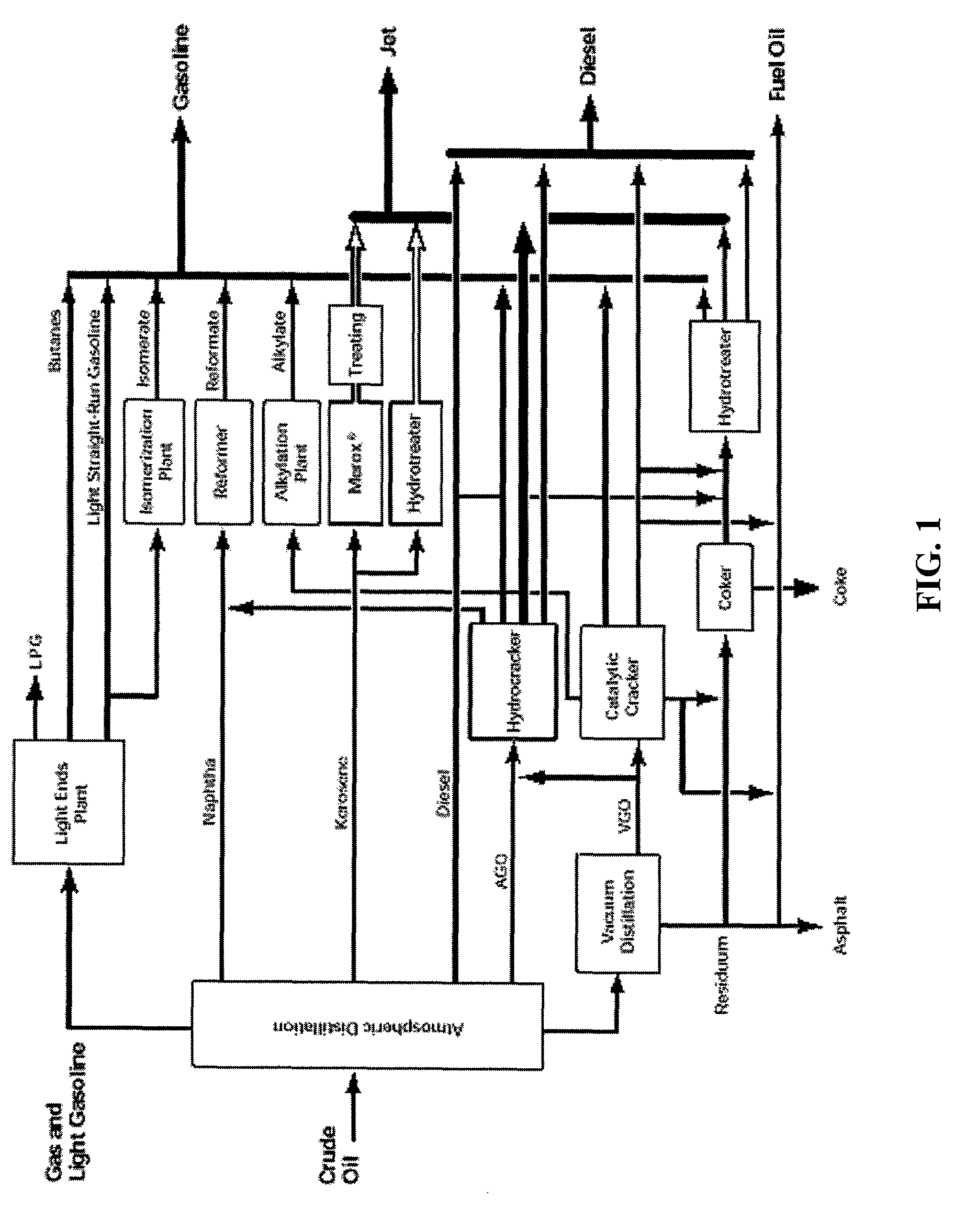
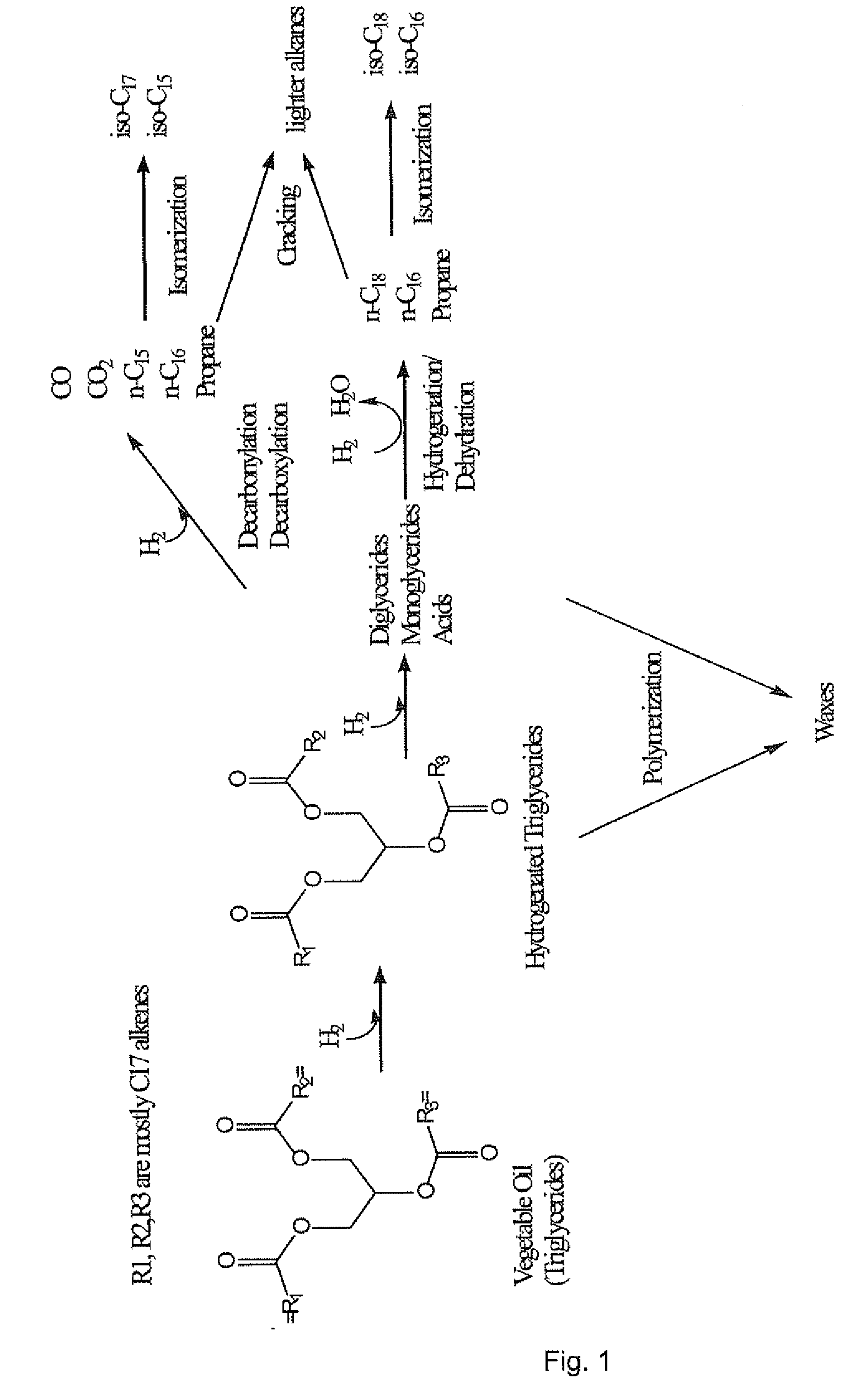
Gasoline is a mixture of alkanes from pentane up to about decane. Kerosene contains alkanes from about n=10 to n=16. Above n=17 they are solids at room temperature. Alkanes with higher values of n are found in diesel fuel, fuel oil, petroleum jelly, paraffin wax, motor oils, and for the highest values of n, asphalt.
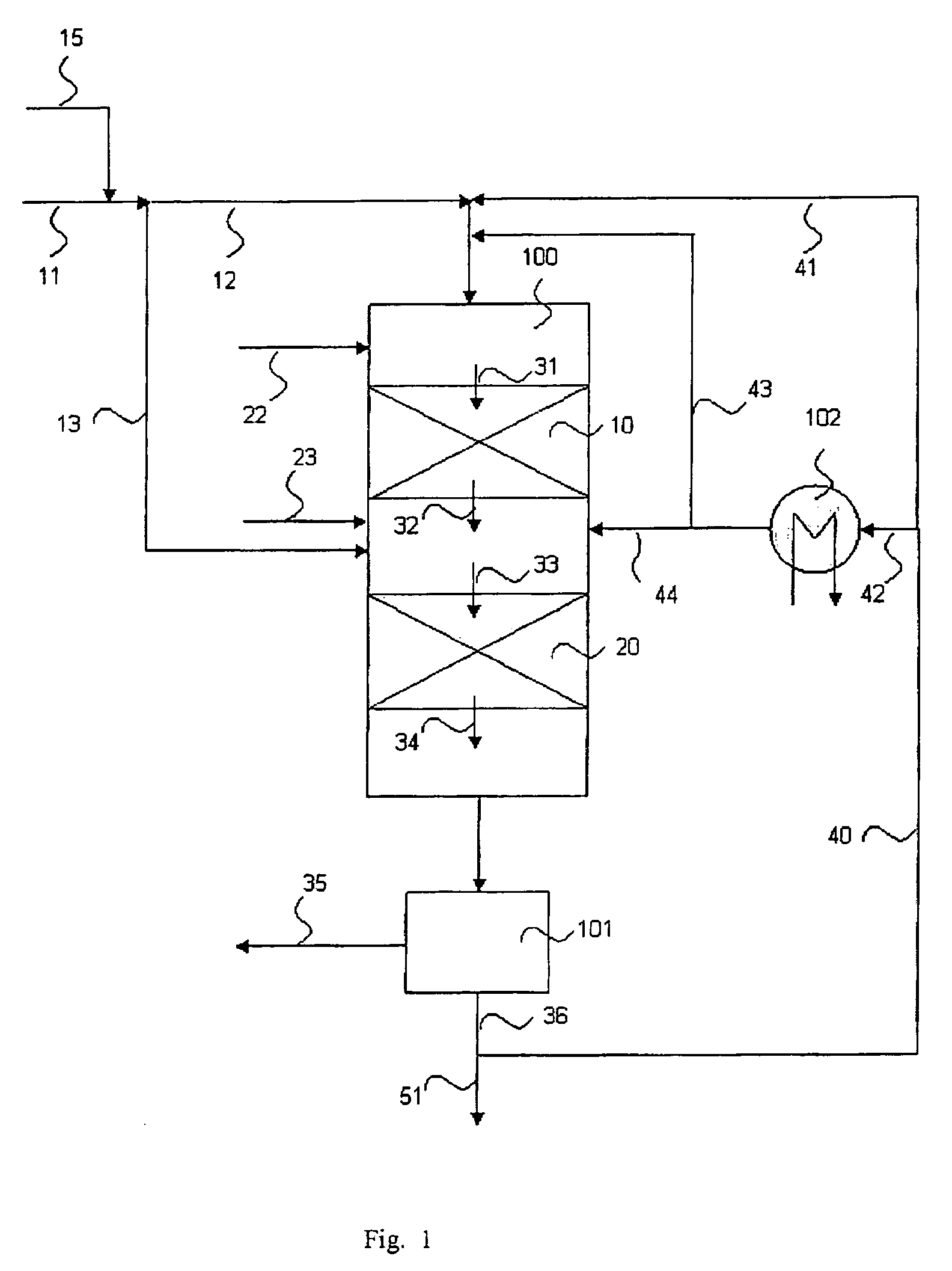
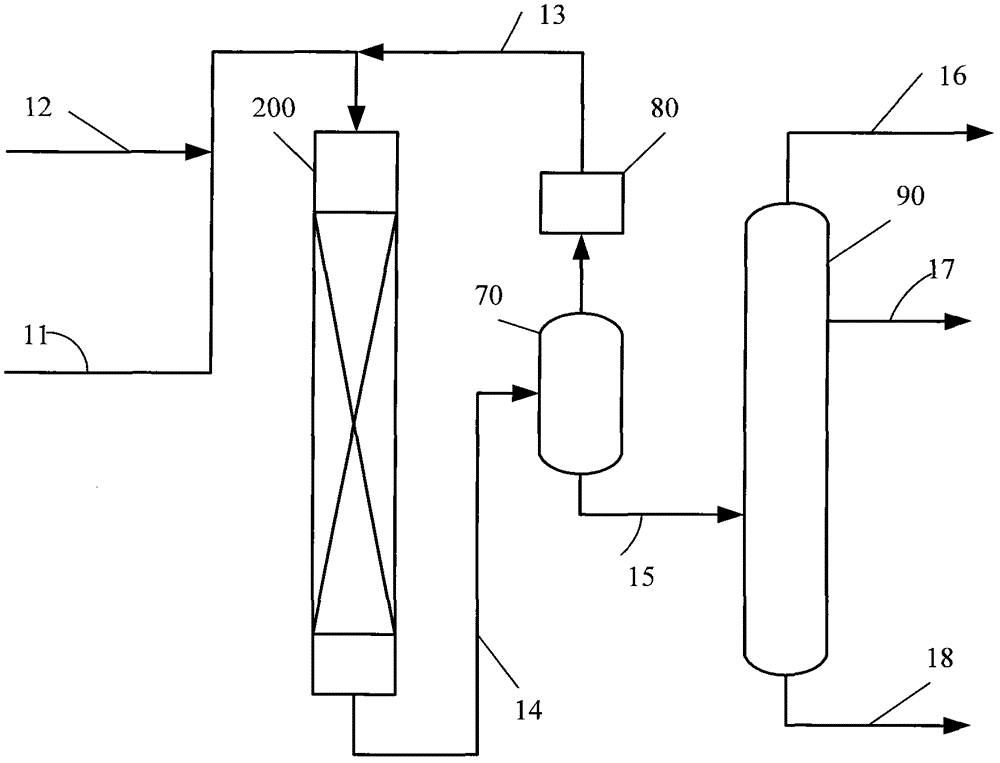
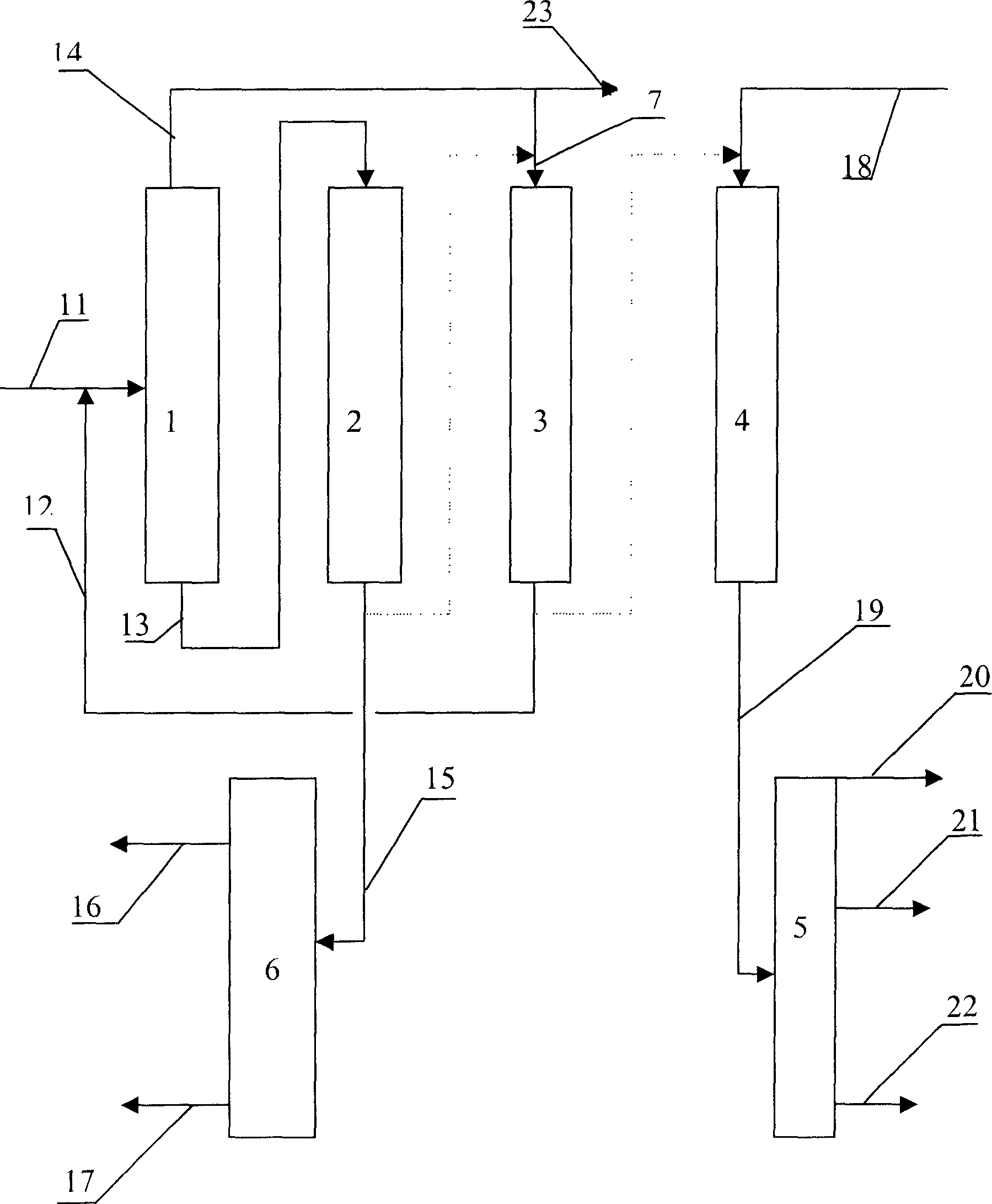
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydro-carbons
ActiveUS20070006523A1Improve low temperature performanceBig ratioBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsChemical industryAlkane
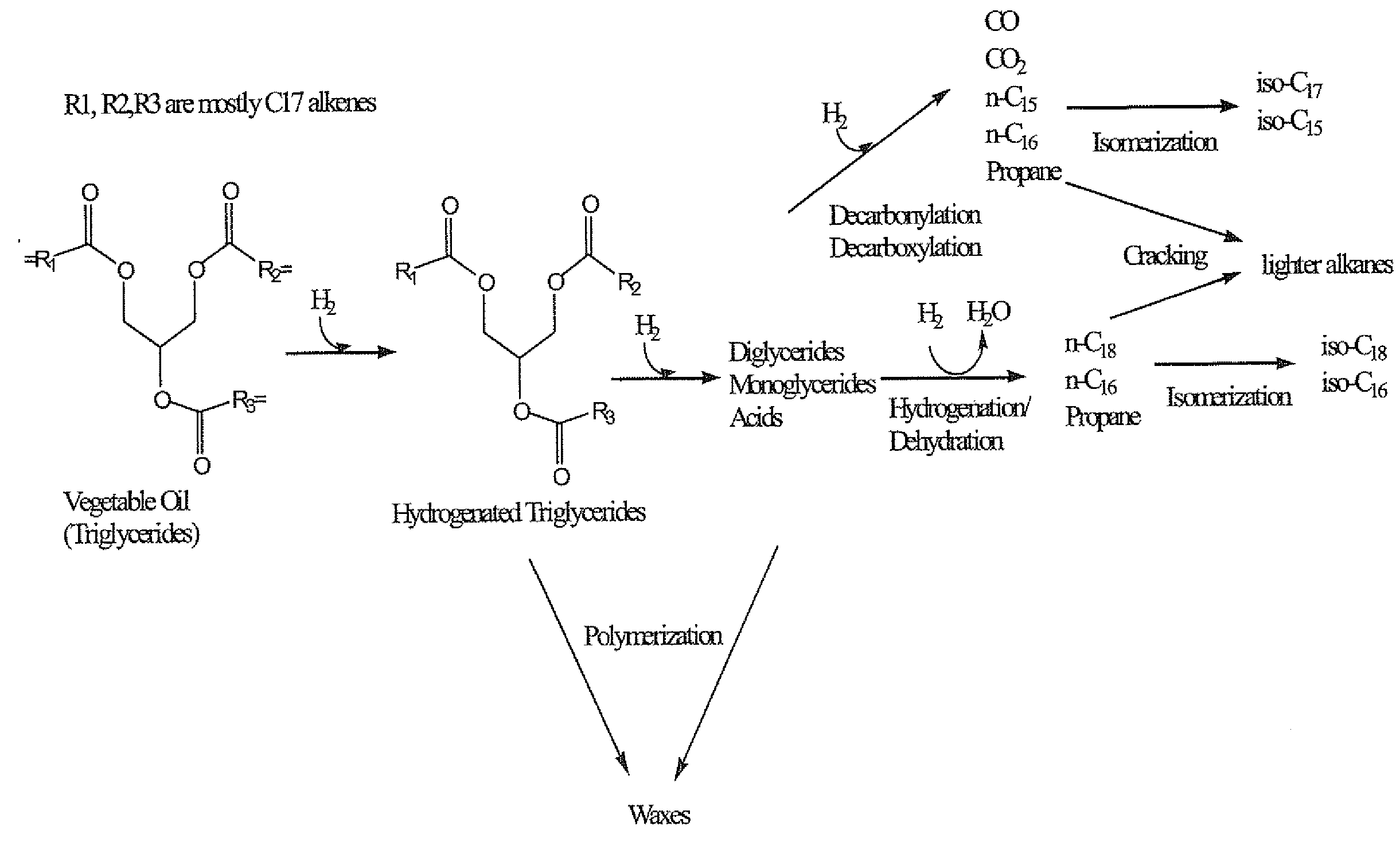
The invention relates to chemical industry and is directed to the production of middle distillate from vegetable oils. In the first step of the production method, the fatty acids or triglycerides of said vegetable oils are hydrogenated to give n-paraffins, and in the second step, the n-paraffins are catalytically converted to paraffins with branched chains. Using this process having two steps, a high-quality middle distillate useful as a component of diesel fuels without any particular specifications may be produced.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
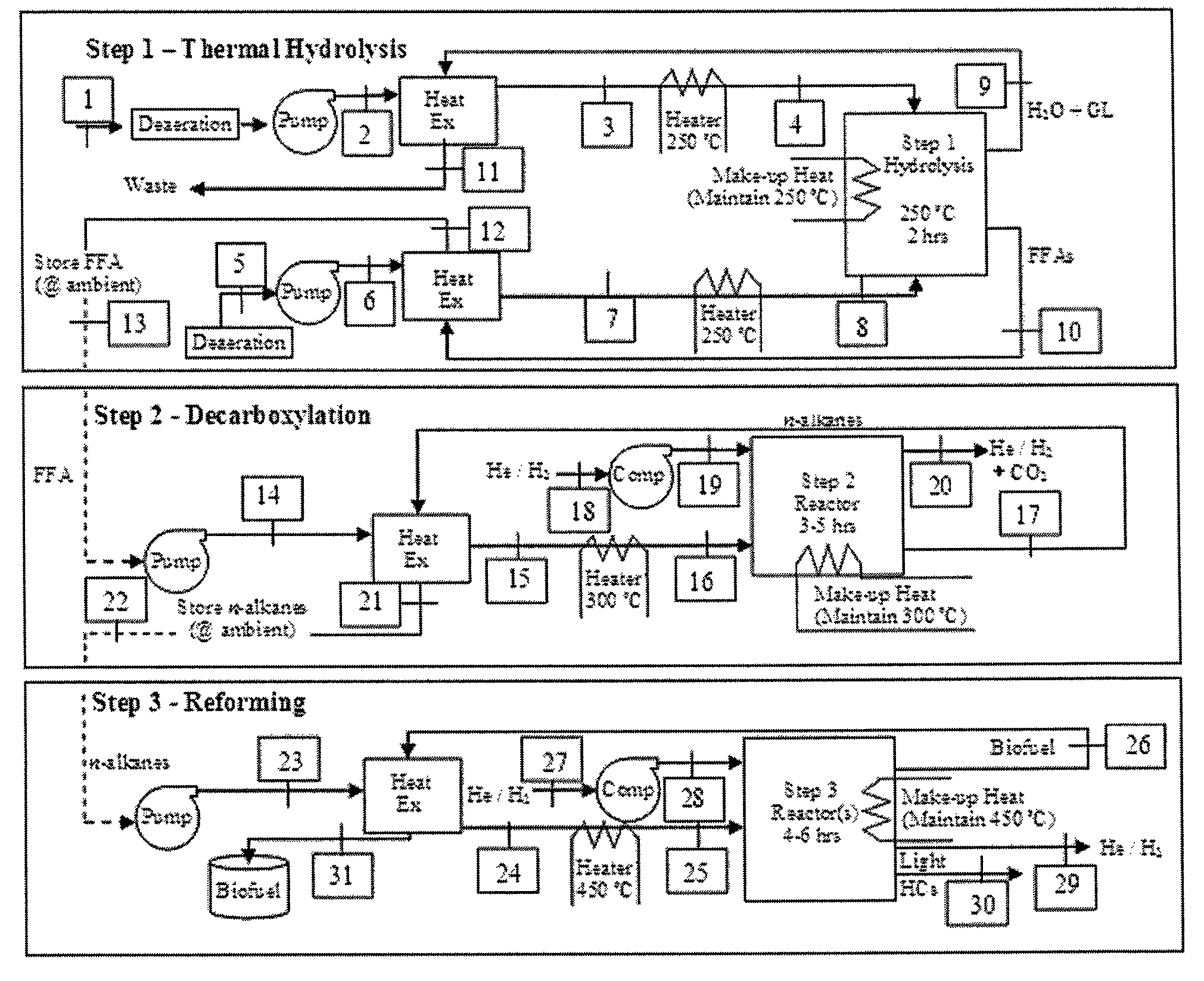
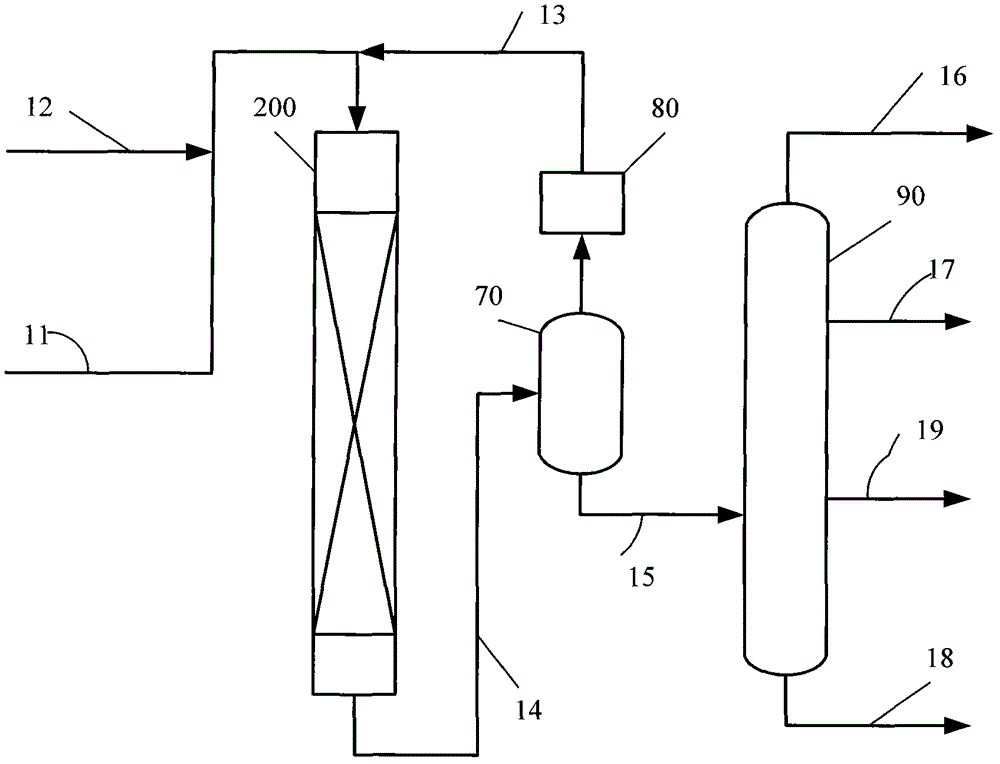
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS7816570B2Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS20090069610A1Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
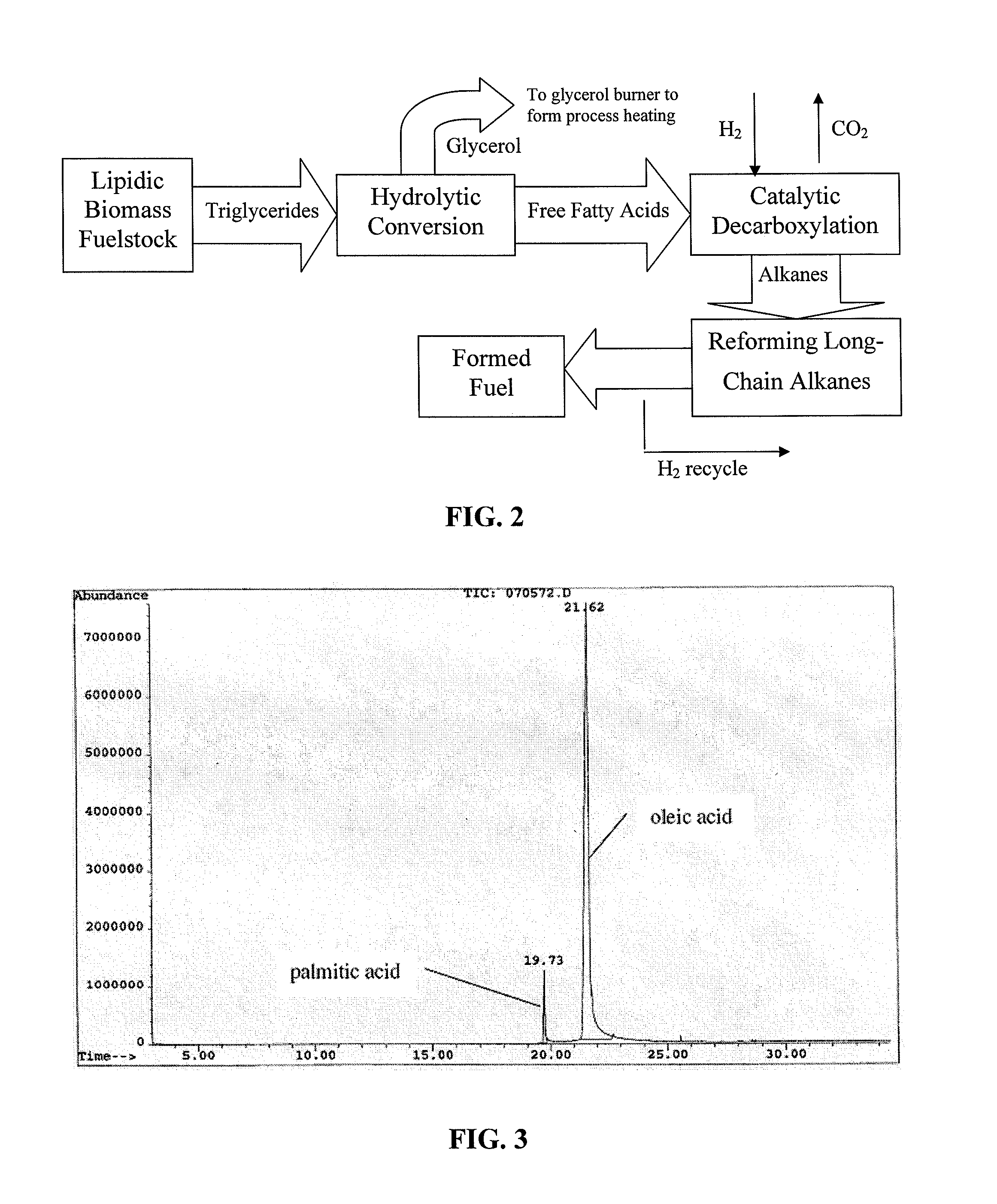
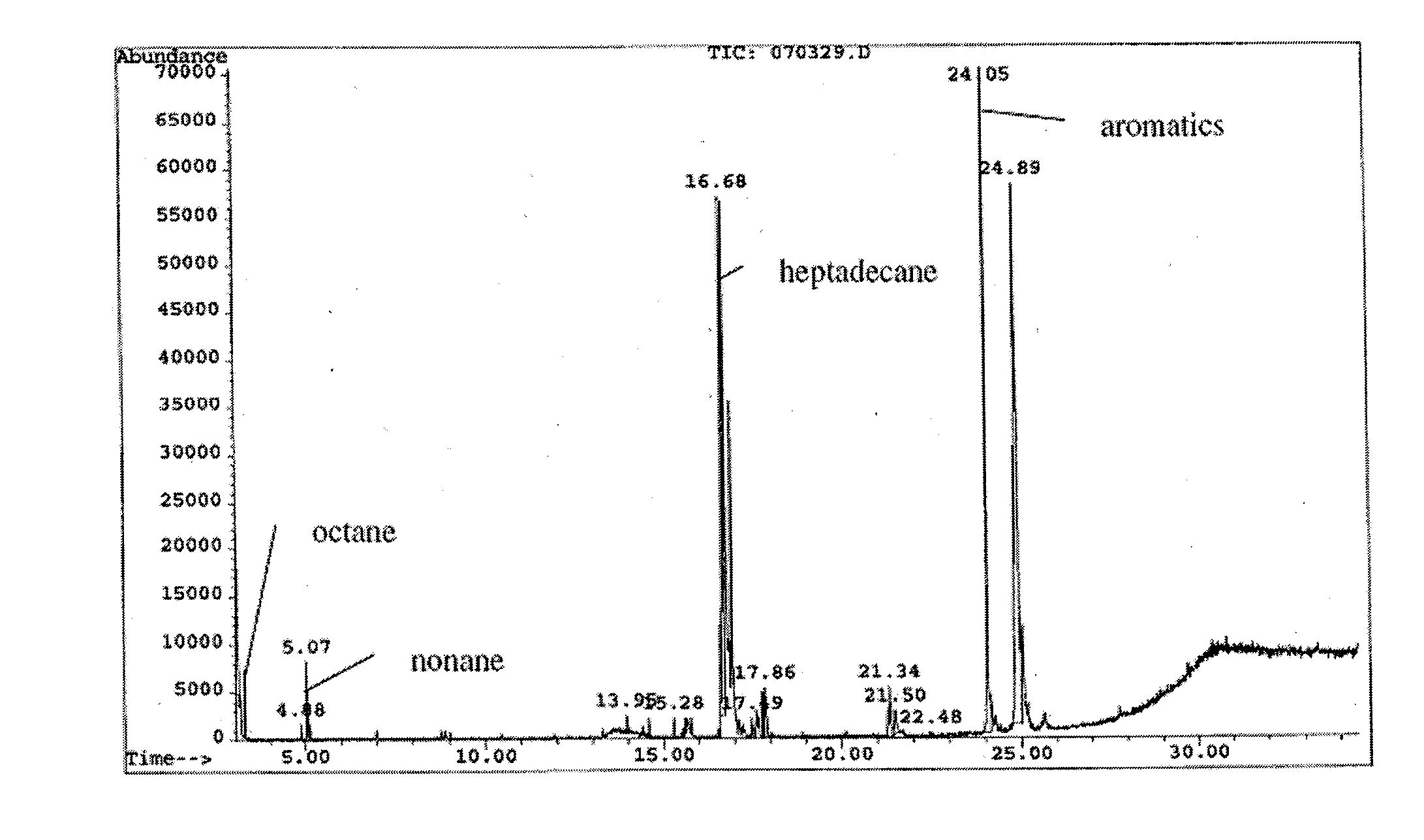
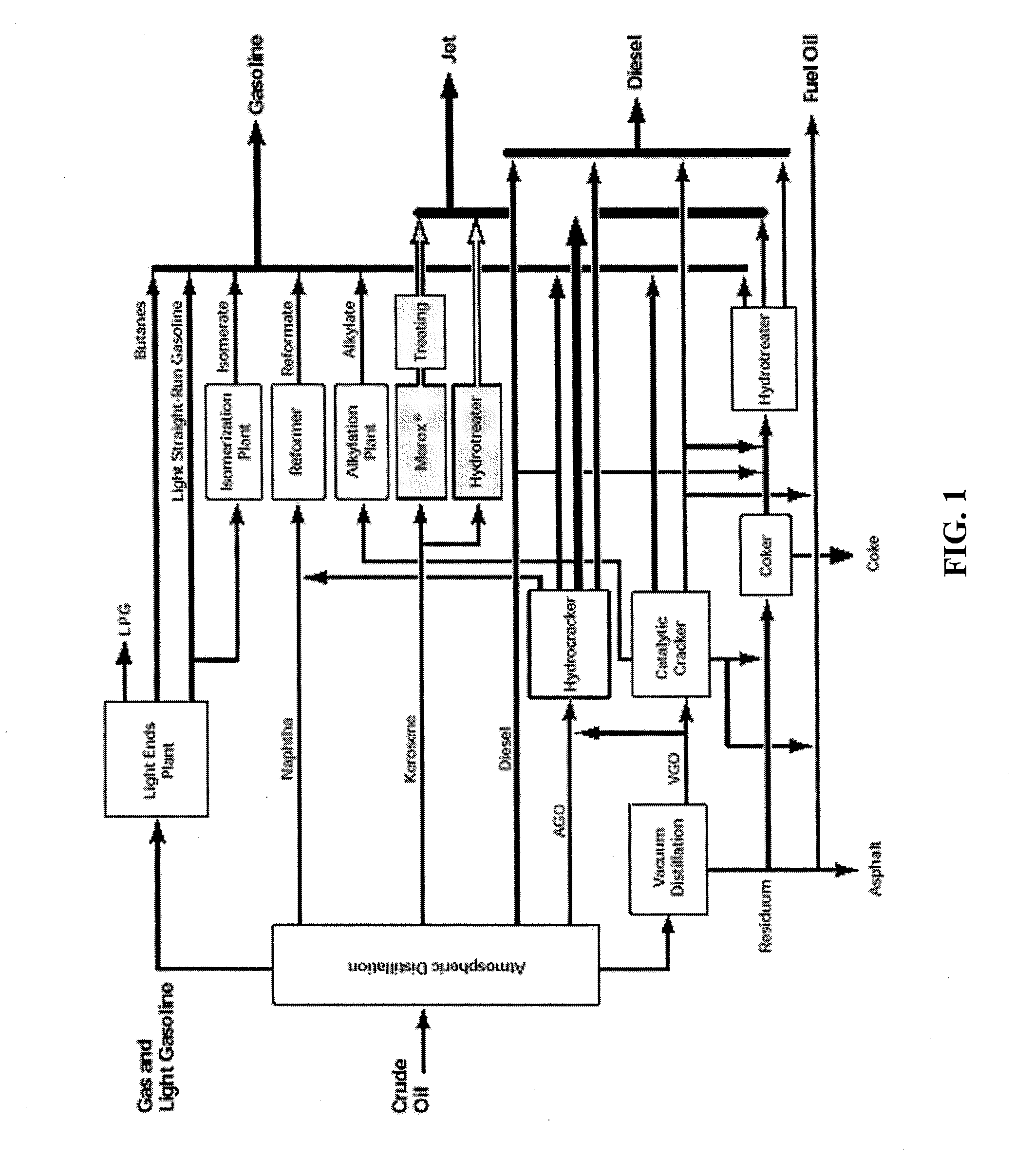
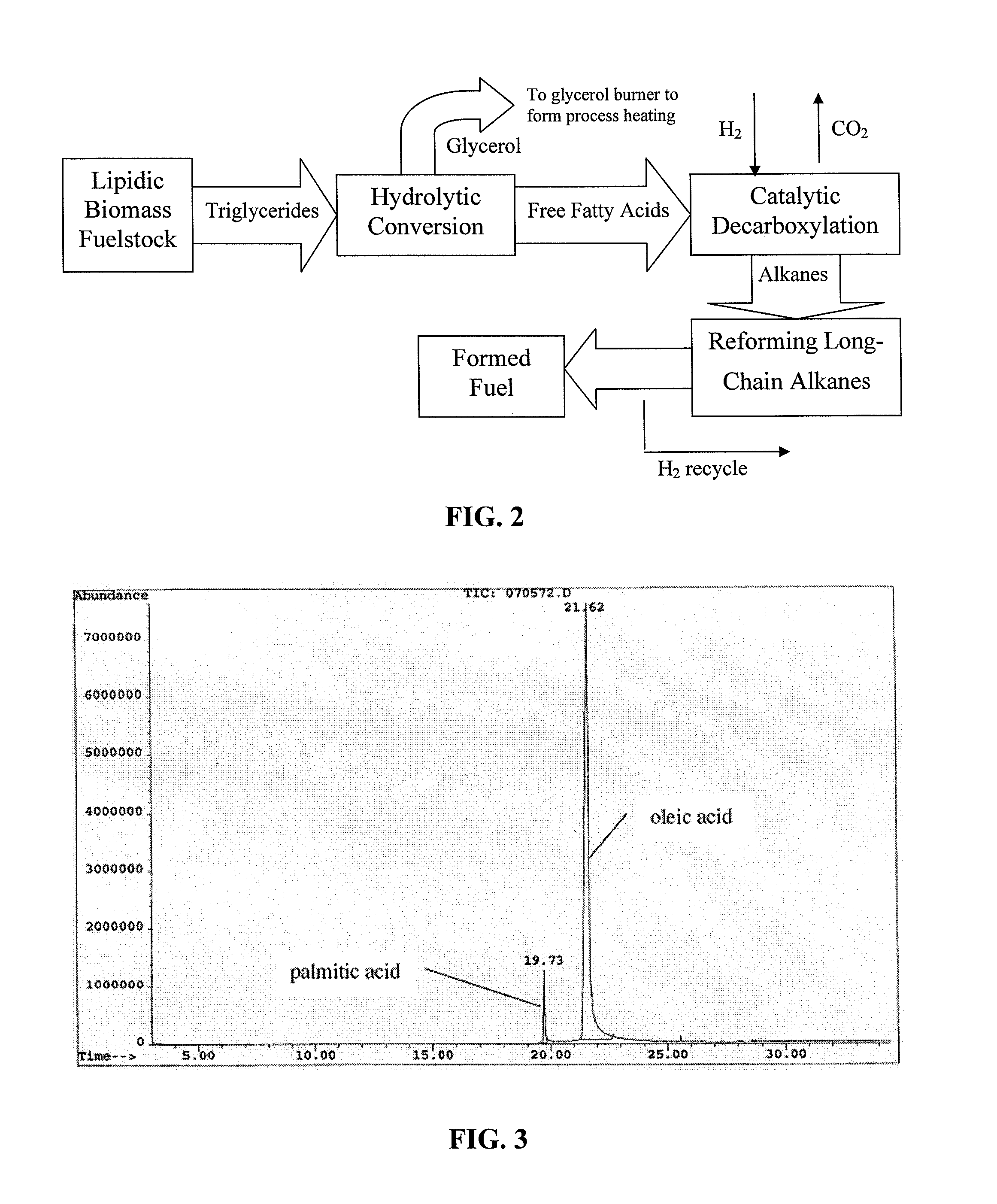
The present invention is directed to processes for the direct conversion of lipidic biomass fuelstock to combustible fuels. In particular, the invention provides a process for the direct conversion of animal fats to transportations fuels suitable as replacement for petroleum-derived transportation fuels. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of hydrolyzing a lipidic biomass to form free fatty acids, catalytically deoxygenating the free fatty acids to form n-alkanes, and reforming at least a portion of the n-alkanes into a mixture of compounds in the correct chain length, conformations, and ratio to be useful transportation fuels. Particularly, the product prepared according to the invention comprises mixtures of hydrocarbon compounds selected from the group consisting of n-alkanes, isoalkanes, aromatics, cycloalkanes, and combinations thereof.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Production of linear alkanes by hydrotreating mixtures of triglycerides with vacuum gasoil
A process is disclosed for mild hydro-conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbon compounds. The oxygenated hydrocarbon compounds are contacted with a hydro-conversion catalyst material at a reaction pressure below 100 bar.Preferred oxygenated hydrocarbon compounds are those obtained by the liquefaction of biomass.In a specific embodiment the process is used for production of normal alkanes by hydrotreating mixtures of triglycerides (or compounds derived-from triglycerides, including free fatty acids) and vacuum gasoil.
Owner:BIOECON INT HLDG NV
Method for separating normal alkane from full fraction naphtha
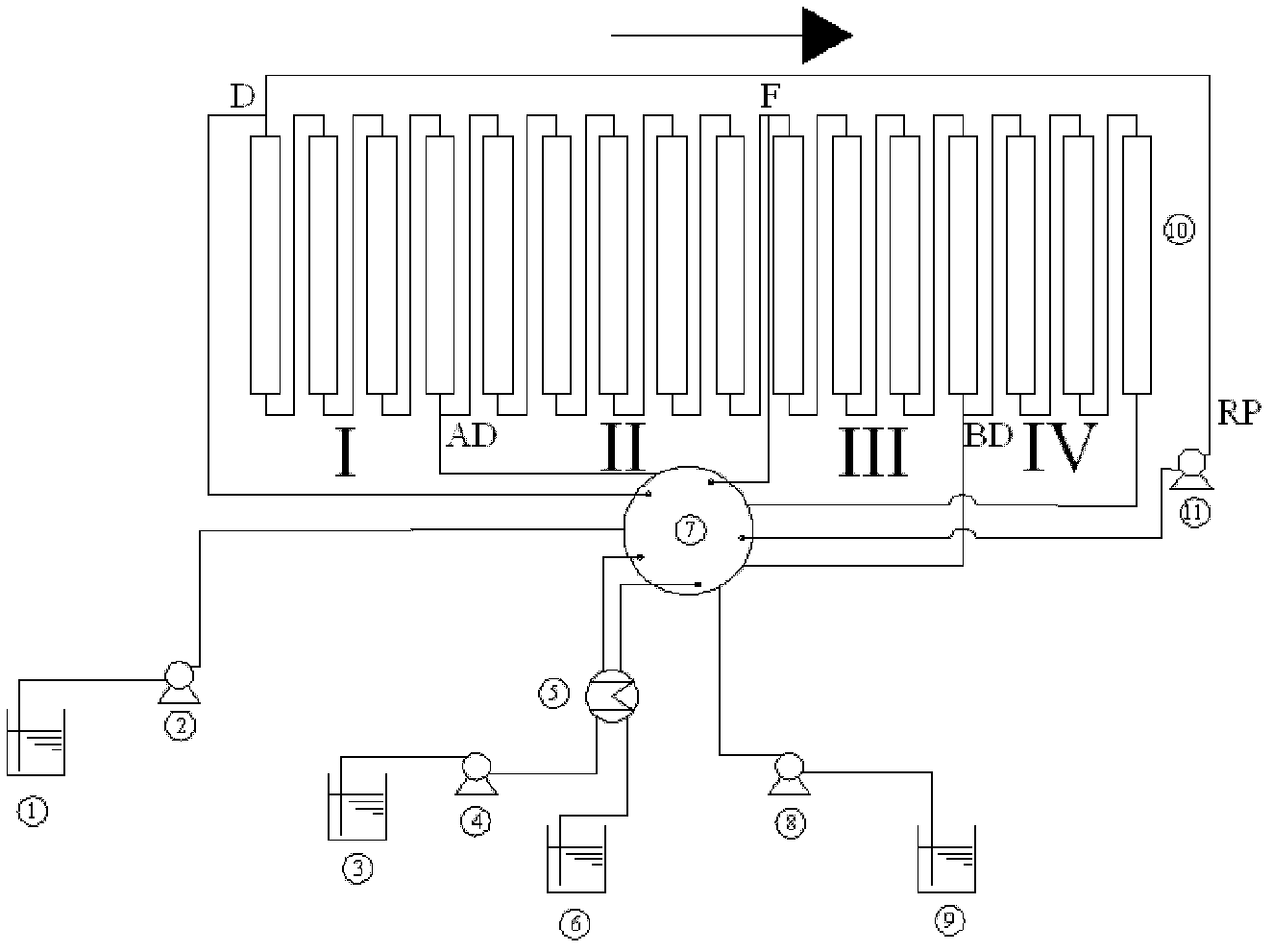
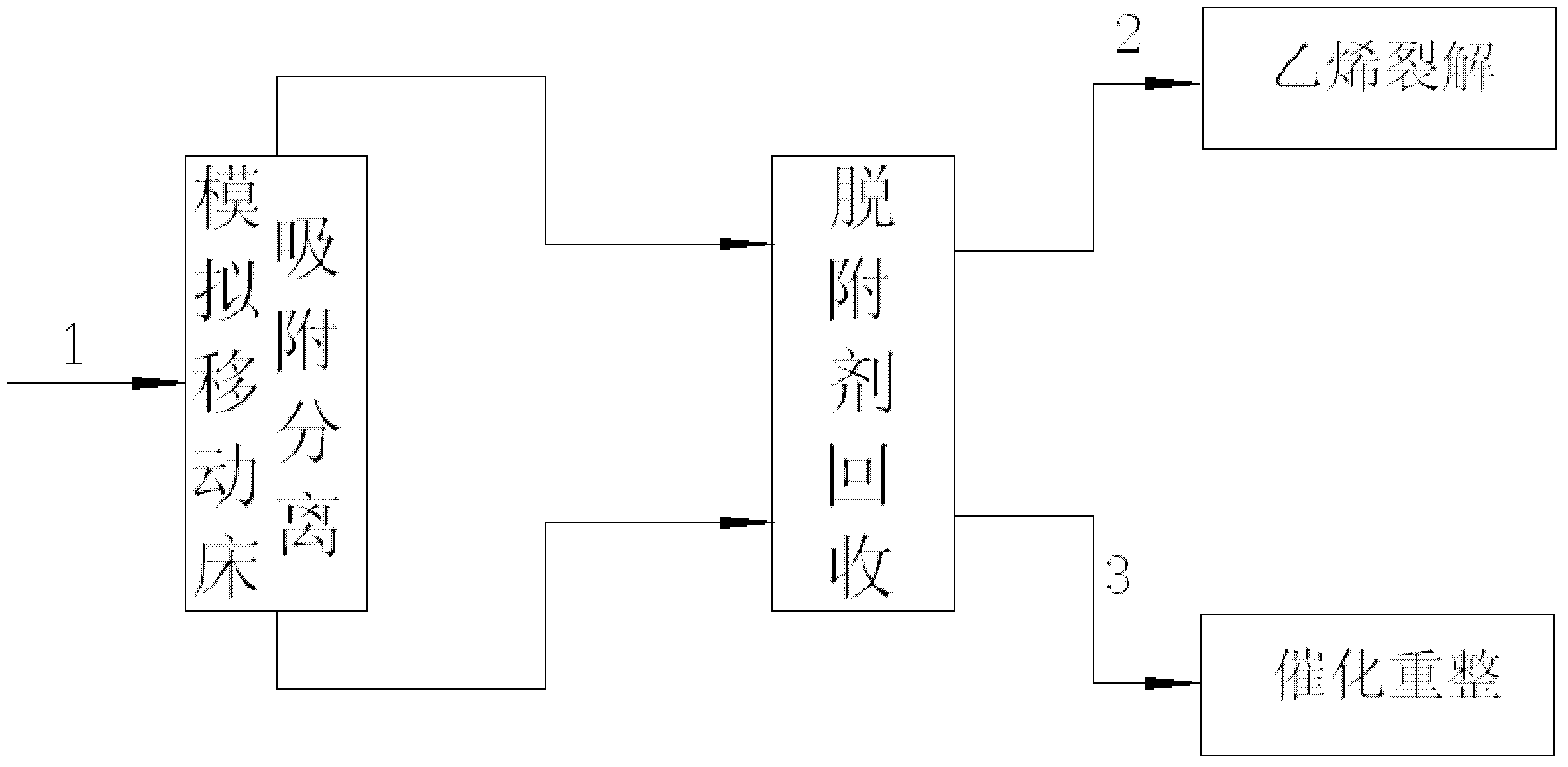
ActiveCN1715368AImprove ethylene yieldHigh yieldEthylene productionAdsorption purification/separationAlkaneNaphtha
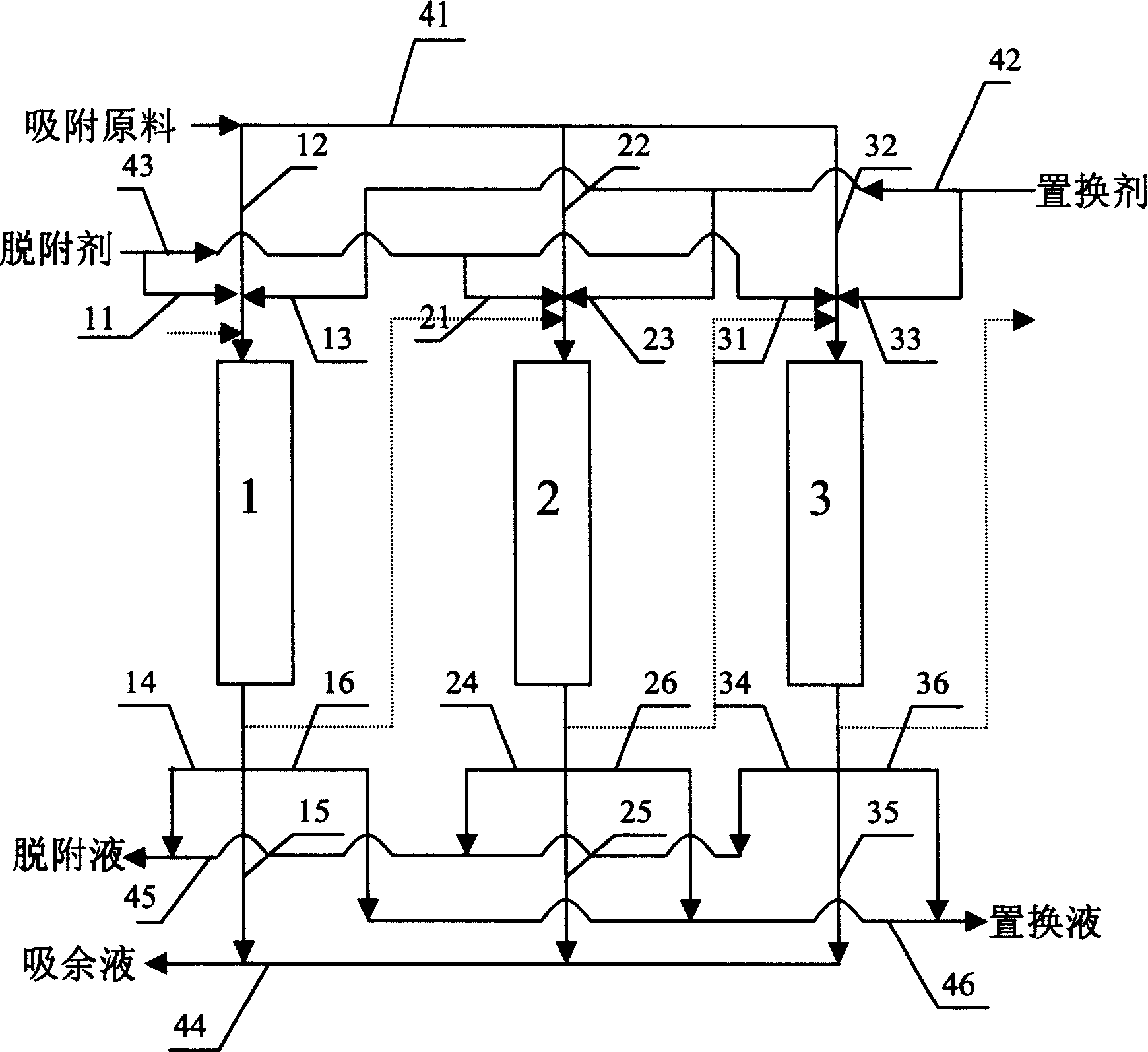
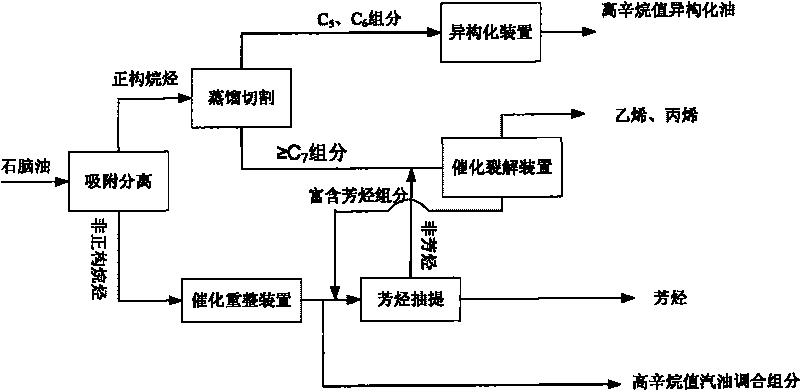
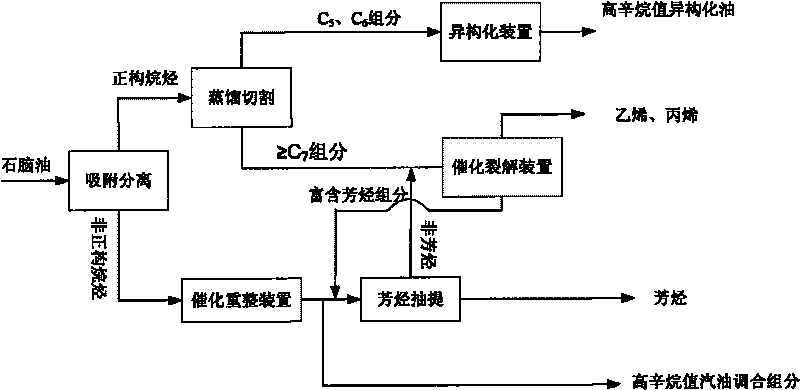
The full fraction naphtha is first treated via one adsorption and separation process to separate out arene, and then treated via one other adsorption and separation process to separate normal alkane from non-normal alkane. The naphtha component obtained through adsorption and separation process and with rich normal alkane is used as material for steam cracking equipment to raise the ethylene yield; the component with rich non-normal alkane is used as material for catalytic re-former to increase the yield of reformed gasoline or arene; and the component with rich arene is used as material for coking or reforming apparatus. The two adsorption and separation processes have efficient desorbing agent adopted for regenerating the adsorption saturated adsorbent for reuse.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
MoFs adsorbent and application thereof
ActiveCN105056896AHigh adsorption capacityGood adsorption and separation performanceOther chemical processesAdsorption purification/separationAlkaneSorbent
The invention relates to a MoFs adsorbent and application thereof. The adsorbent is prepared by the following steps: as the weight of metal organic framework material raw powder is used as the base, adding a binder accounting for 2-50% of the metal organic framework material raw powder in weight, an extrusion aid accounting for 3-60% of the metal organic framework material raw powder in weight, and water accounting for 1-30% of the metal organic framework material raw powder in weight into the metal organic framework material raw powder, stirring and kneading uniformly, and forming; and stoving, and roasting so as to obtain the formed MoFs adsorbent. A metal organic framework material is selected from one of ZIF-76, UiO-66, UiO-67 or MIL-125; the MoFs adsorbent is used for adsorbing isoparaffins from an alkane mixture in a back-shape-selective manner; the MoFs adsorbent has relatively high adsorption capacity or relatively high adsorption acting force on one or more kinds of isoparaffins, so that the isoparaffins are more preferentially adsorbed as compared with n-alkanes in an adsorption separation process; meanwhile, as the metal organic framework material has large specific surface area and pore volume, the adsorption capacity on alkanes is large, and the high-efficiency separation on n-alkanes and isoparaffins can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
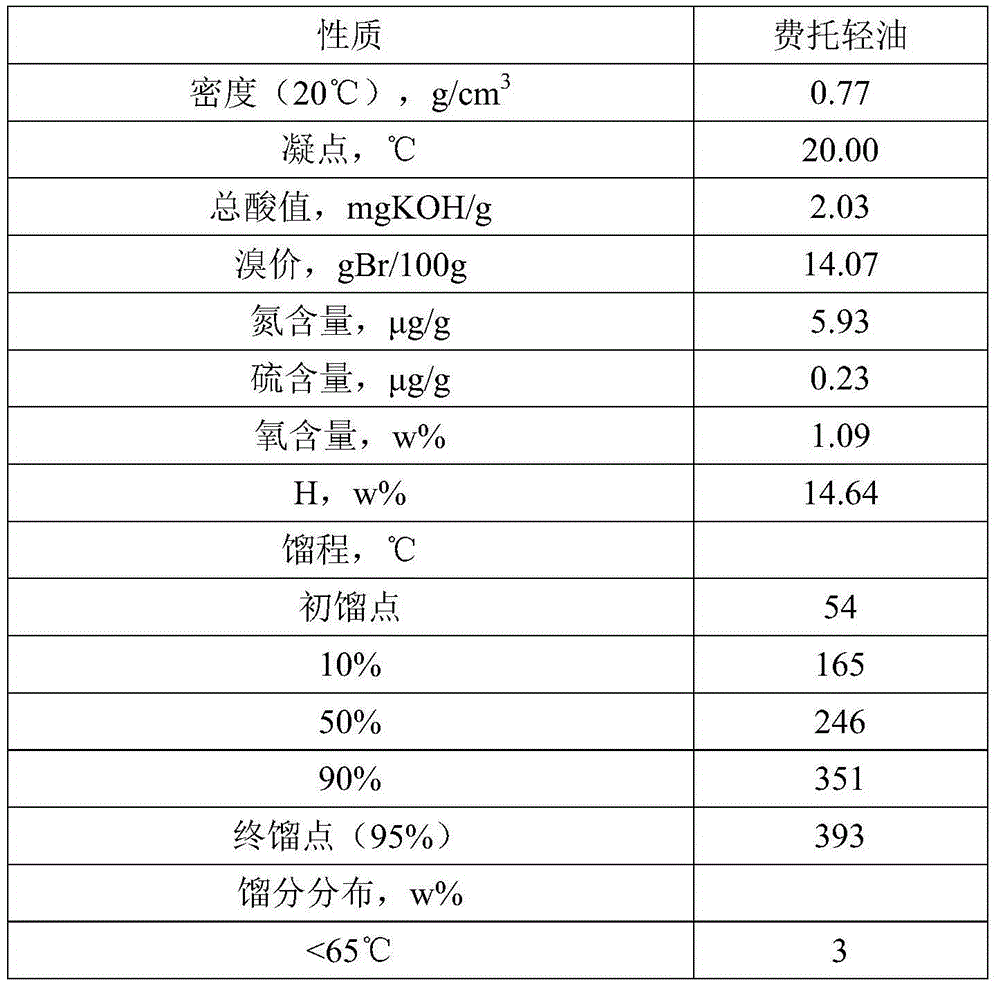
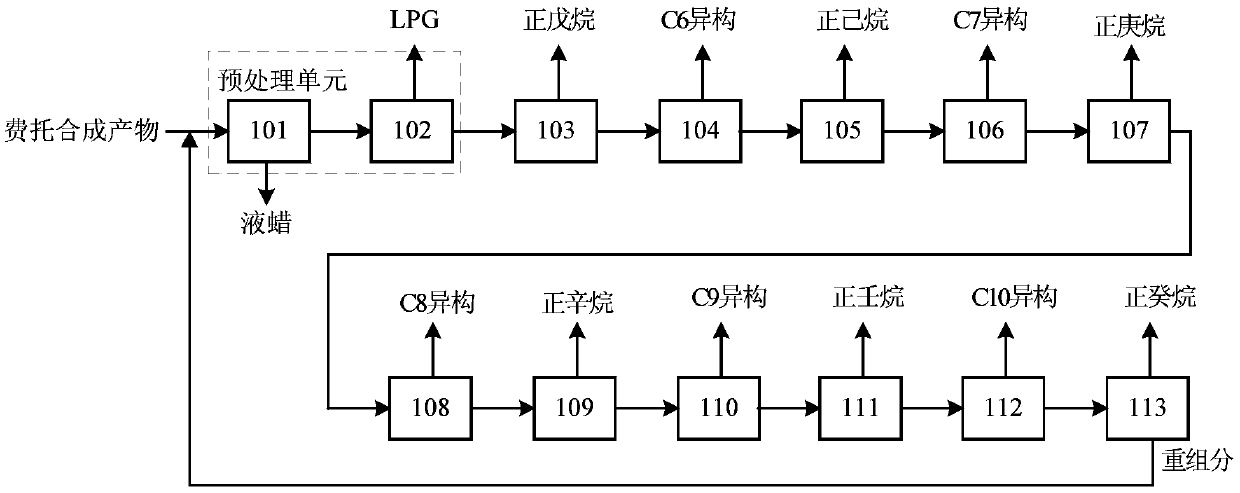
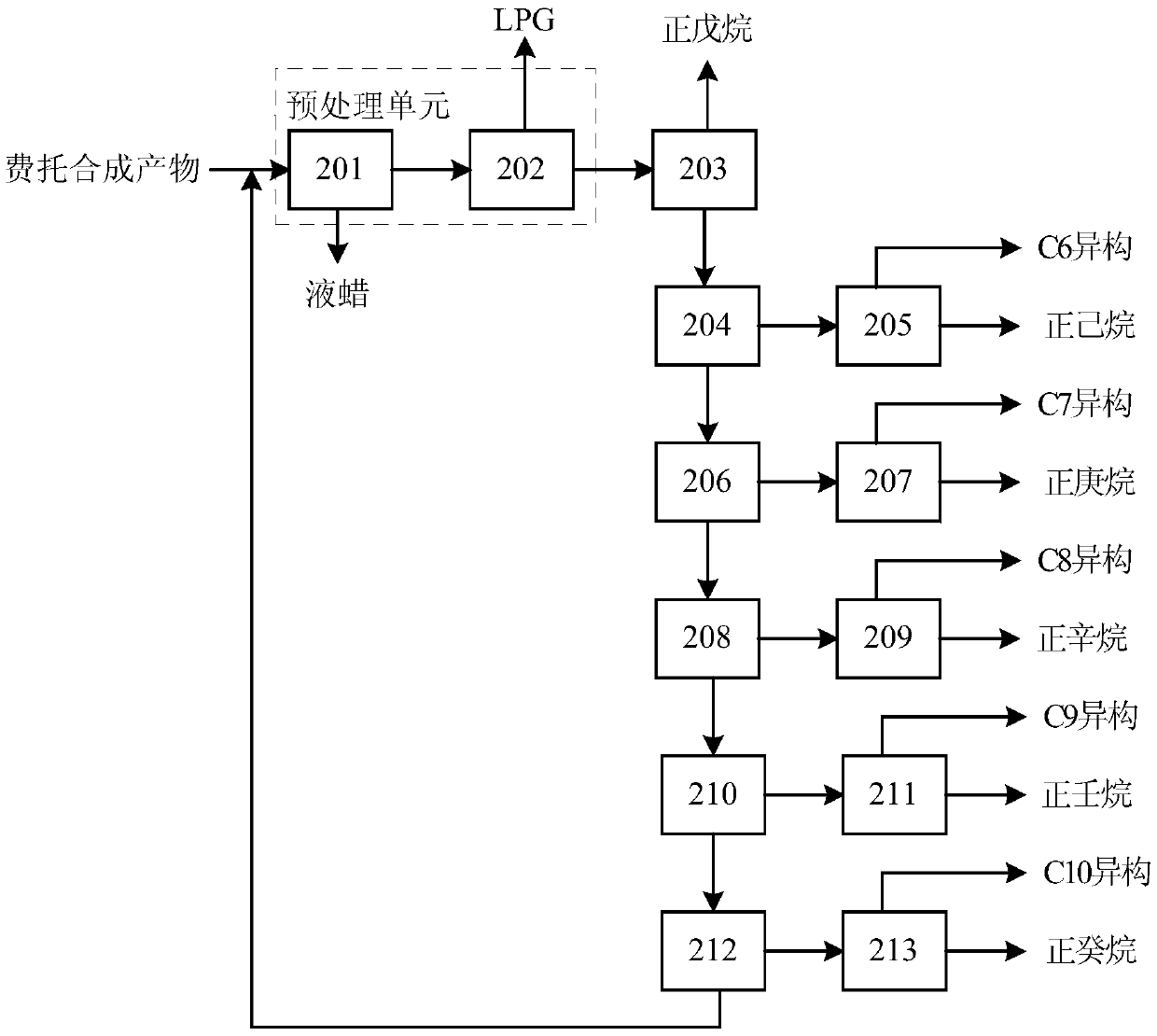
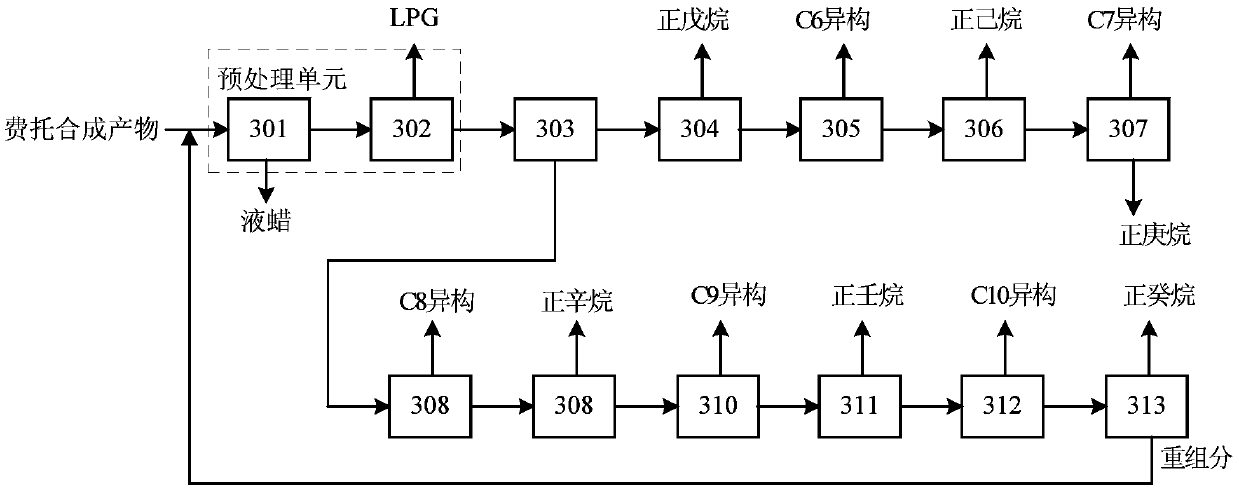
Method for producing n-alkane solvent oil from Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil
ActiveCN104910960AMany modelsImprove qualityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAlkaneDistillation
The invention relates to a method for producing n-alkane solvent oil from Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil. According to the method, low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthetic light oil is adopted as a raw material, and is processed through upgrading and distillation separation processes with a fractionation tower, hydro-finishing, a degassing tower, a C6 / C7 cutting tower, a C5 / C6 cut tower, a C10 / C11 cutting tower, a C8 / C9 cutting tower, a C7 / C8 cutting tower, a C9 / C10 cutting tower, a C13 / C14 cutting tower, and a C17 / C18 cutting tower; such that various types of solvent oils such as n-pentane-rich, #6, #120, #140, #200, #D30, #D40, #D65, #D100 and #D120 solvent oils can be obtained. Compared to prior arts, all products produced with the method are n-alkane solvent oils. The method has the advantages of simple process flow, more produced solvent oil types, high solvent oil quality, and the like.
Owner:YANKUANG ENERGY R&D CO LTD
Method for utilizing naphtha
ActiveCN101759513AImprove utilization efficiencyHigh yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic naphtha reformingAlkaneBenzene
The invention provides a method for utilizing naphtha. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dividing the naphtha to a normal alkane enriched component and an unnormal alkane enriched component; (2) cutting the normal alkane enriched component obtained by the step(1) into a C5 / C6 fraction and a C7 or above fraction; (3) isomerizing the C5 / C6 fraction obtained by the step(2) to obtain the C5 / C6 isoalkanes; (4) catalytically cracking the C7 or above fraction obtained by the step(2) to obtain ethylene and propylene; and (5) reforming the unnormal alkane enriched component obtained by the step (1) to obtain the arene or high-octane number blended component. The method can improve arene yield, gasoline yield, ethylene and propylene yields, and high-octane number gasoline blended component yield and lower the benzene content of gasoline.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Isomerization catalyst and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1488722AReduce concentrationReduce carbon depositionHydrocarbon oils refiningIsomerizationN alkanes
The present invention relates to a normal paraffin hydrocarbon hydrogenation isomerization catalyst using nano HBeta zeolite as carrier, and the grain size of nano HBeta is 30.0nm-180.0 nm. Said invented catalyst can shorten the dwell time of n-carbonionic intermediate in catalyst channel, raise selectivity of isomerization product and at the same time can inhibit the secondary reaction of polymeric coking, etc. Said invention also provides the preparation method of said catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing diesel oil component or jet fuel component by using animal and plant oil
ActiveCN103059901AHigh yieldHigh calorific valueLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockOil and greaseAlkane
The invention provides a method for preparing a diesel oil component or jet fuel component by using animal and plant oil. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dividing the animal and plant oil into at least two parts, introducing the at least two parts of animal and plant oil to a plurality of catalyst beds of a first hydrogenation reactor, and enabling the at least two parts of animal and plant oil and a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst to contact and react to obtain n-alkanes with the carbon number of 8-24; (2) filling an isomerization catalyst in a second hydrogenation reactor, introducing a reaction product obtained in the step (1) to the second hydrogenation reactor, and reducing a condensation point after isomerization reaction to obtain a diesel oil component; or, (3) filling a selective cracking catalyst in the second hydrogenation reactor, introducing the reaction product obtained in the step (1) to the second hydrogenation reactor, and then, carrying out selective hydrocracking and isomerization to obtain a jet fuel blending component. The method provided by the invention is high in jet fuel yield; and the prepared jet fuel blending component is good in quality and can be mixed with the traditional petroleum-based jet fuel according to any proportion so as to be an excellent blending component.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for hydroisomerizing normal alkane by using supported nickel phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN102887809AHigh activityGood choiceHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsAlkaneIsomerization
The invention discloses a method for hydroisomerizing normal alkane by using a supported nickel phosphide catalyst, which comprises the following steps: loading the supported nickel phosphide catalyst in a fixed bed type reactor, feeding hydrogen gas and the normal alkane according to a mol ratio of (1-20):1, and performing isomerization reaction under the reaction conditions that the reaction temperature is 250-400 DEG C, the hydrogen gas pressure is 0.1-5.0 MPa and the weight hourly space velocity of the normal alkane is 0.1-10 h<-1>, wherein the supported nickel phosphide catalyst takes SAPO-11 as a carrier; the active phase is nickel phosphide; and the mass of nickel accounts for 0.5-10% of the mass of the catalyst. The supported nickel phosphide catalyst used in the invention has the advantages of high activity, good selectivity, low cost, no need of vulcanizing agent and the like, and has favorable application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
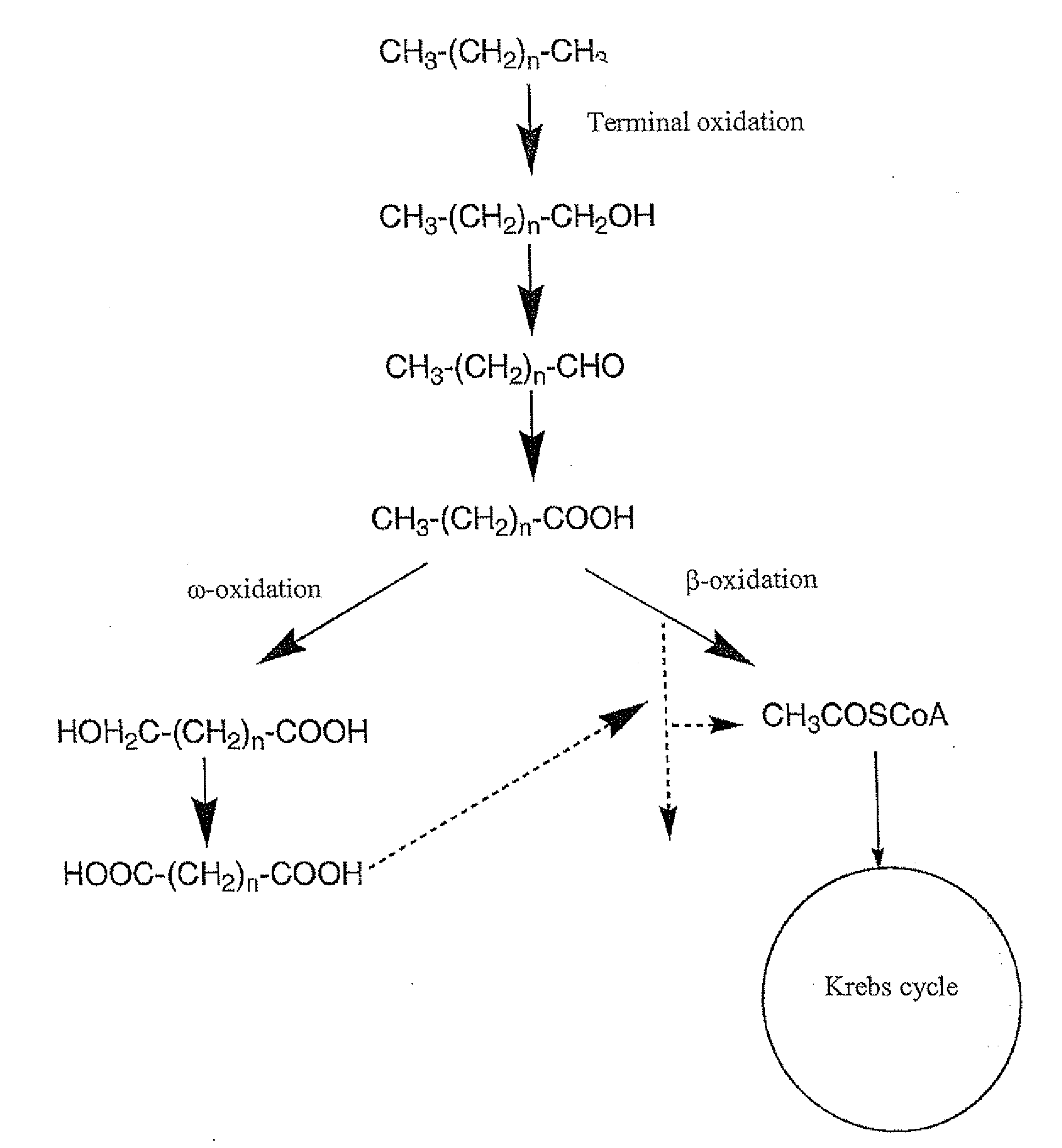
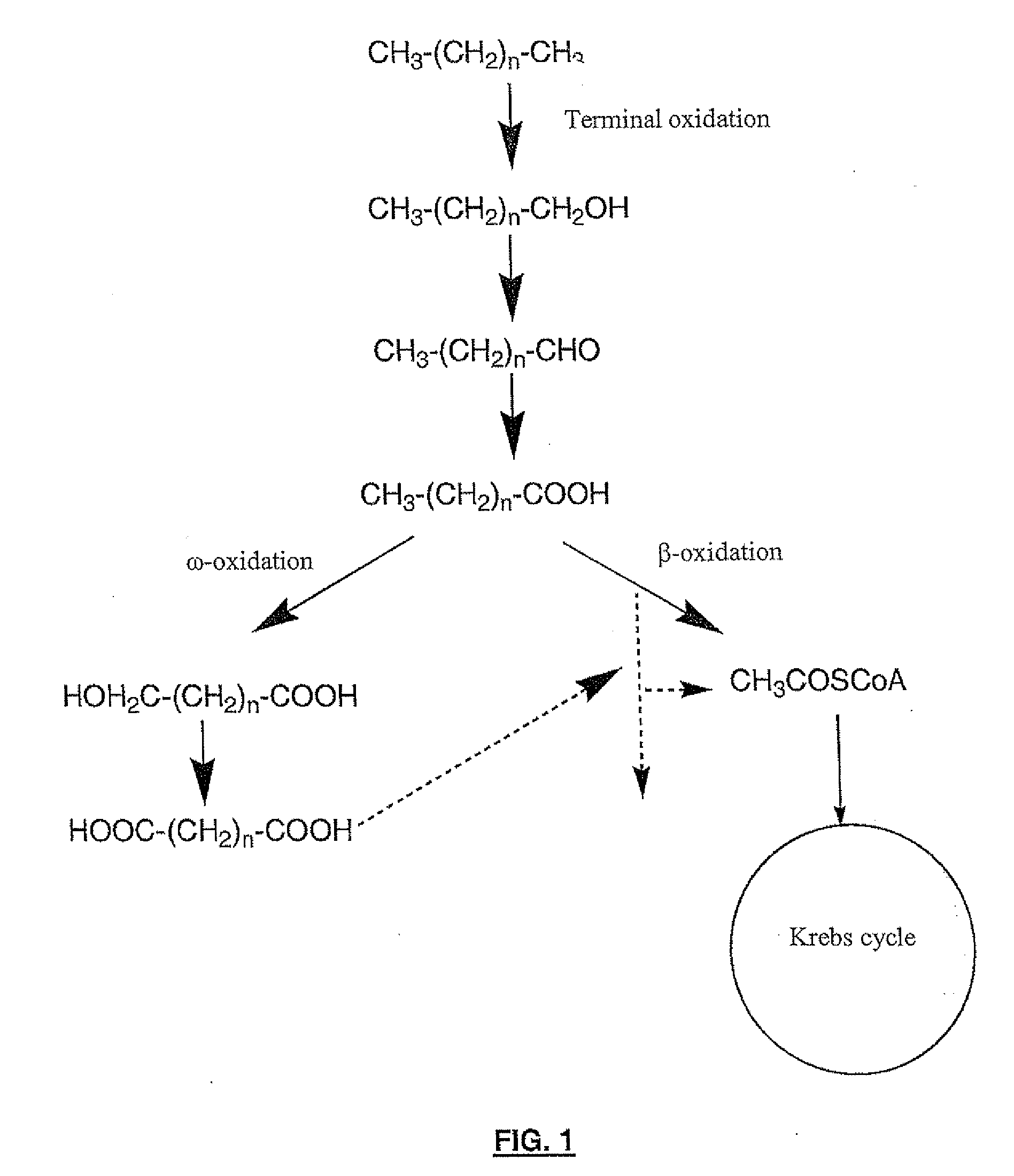
Production of dicarboxylic acids by improved mutant strains of yarrowia lipolytica
The invention concerns a method for producing dicarboxylic acids (DCA) with long hydrocarbon chains, also called diacids, which consists in culturing a mutant strain of Yarrowia lipolytica obtained by mutagenesis directed and more particularly disrupted at least for the POX2, POX3, POX4 and POX5 genes encoding acyl-CoA oxydase, in a medium consisting essentially of an energetic substrate including at least one carbon source and one nitrogen source and in subjecting said strain to a bioconversion substrate selected among n-alkanes of at least 10 carbon atoms, fatty acids of at least 10 carbon atoms, their alkyl esters and natural oils.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +2
Method for preparing phase-change materials from Fischer-Tropsch (F-T) synthesis product
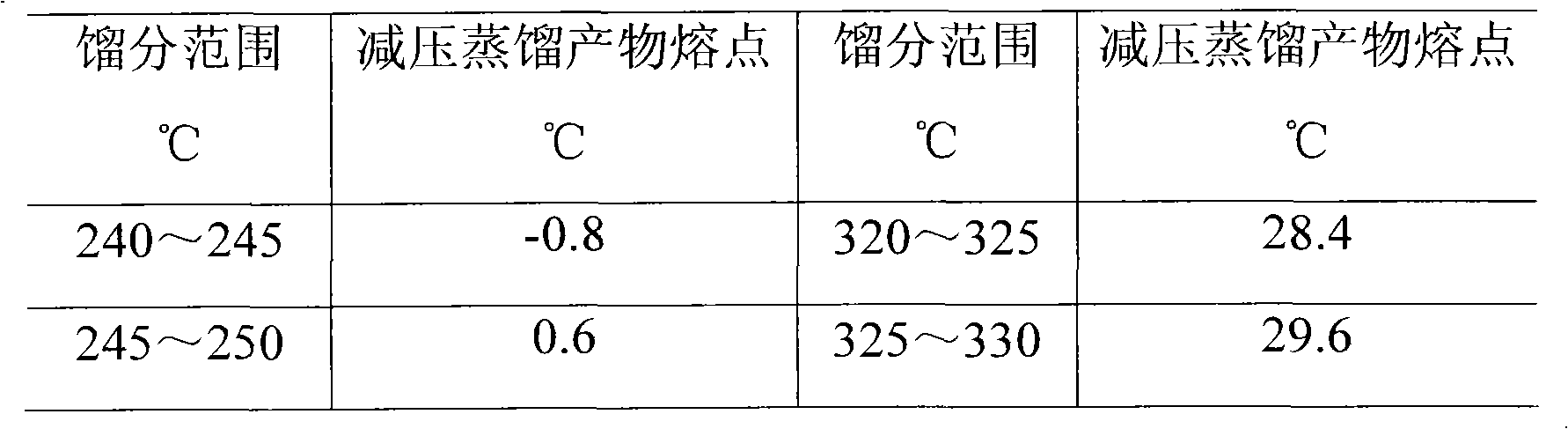
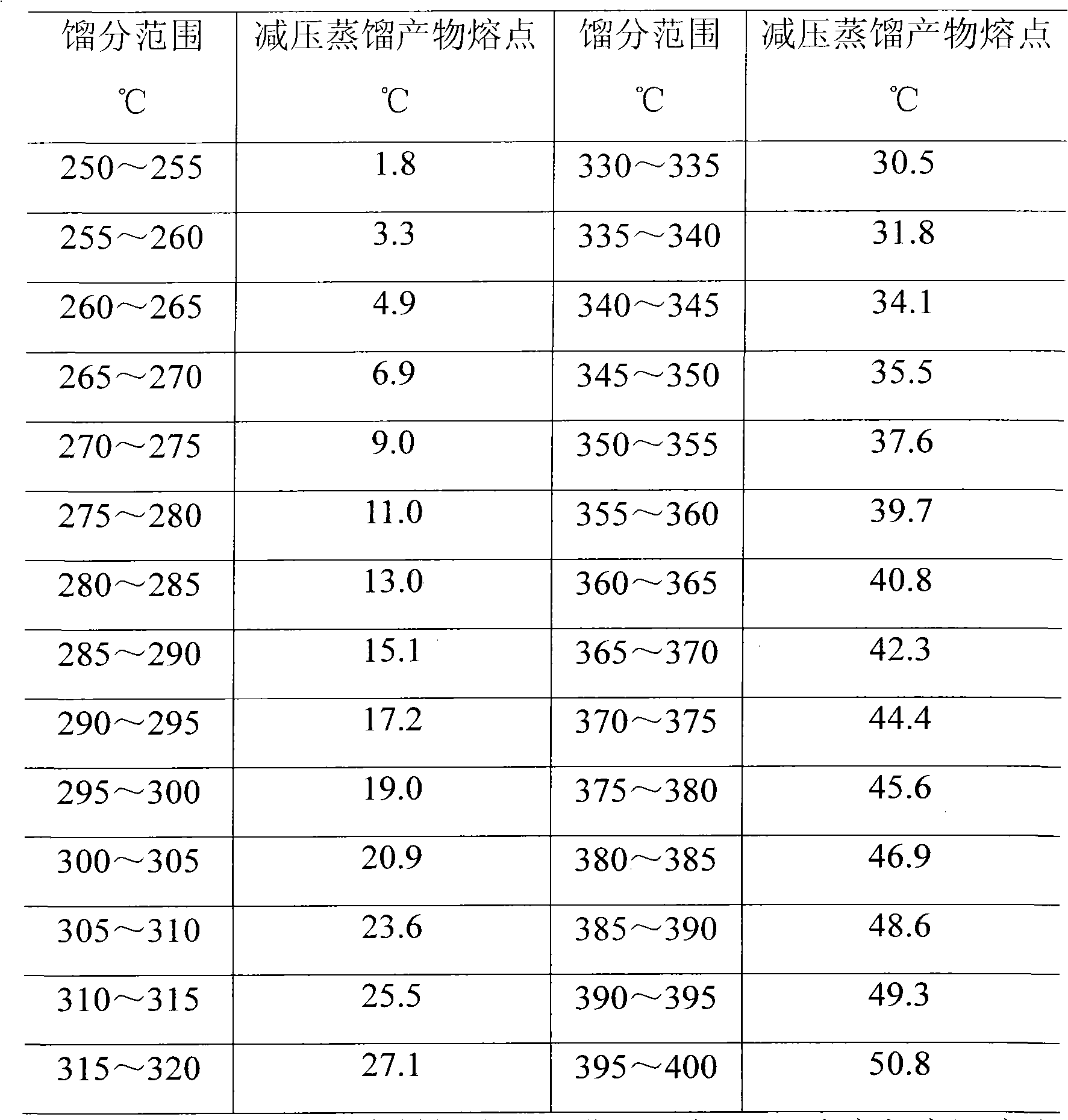
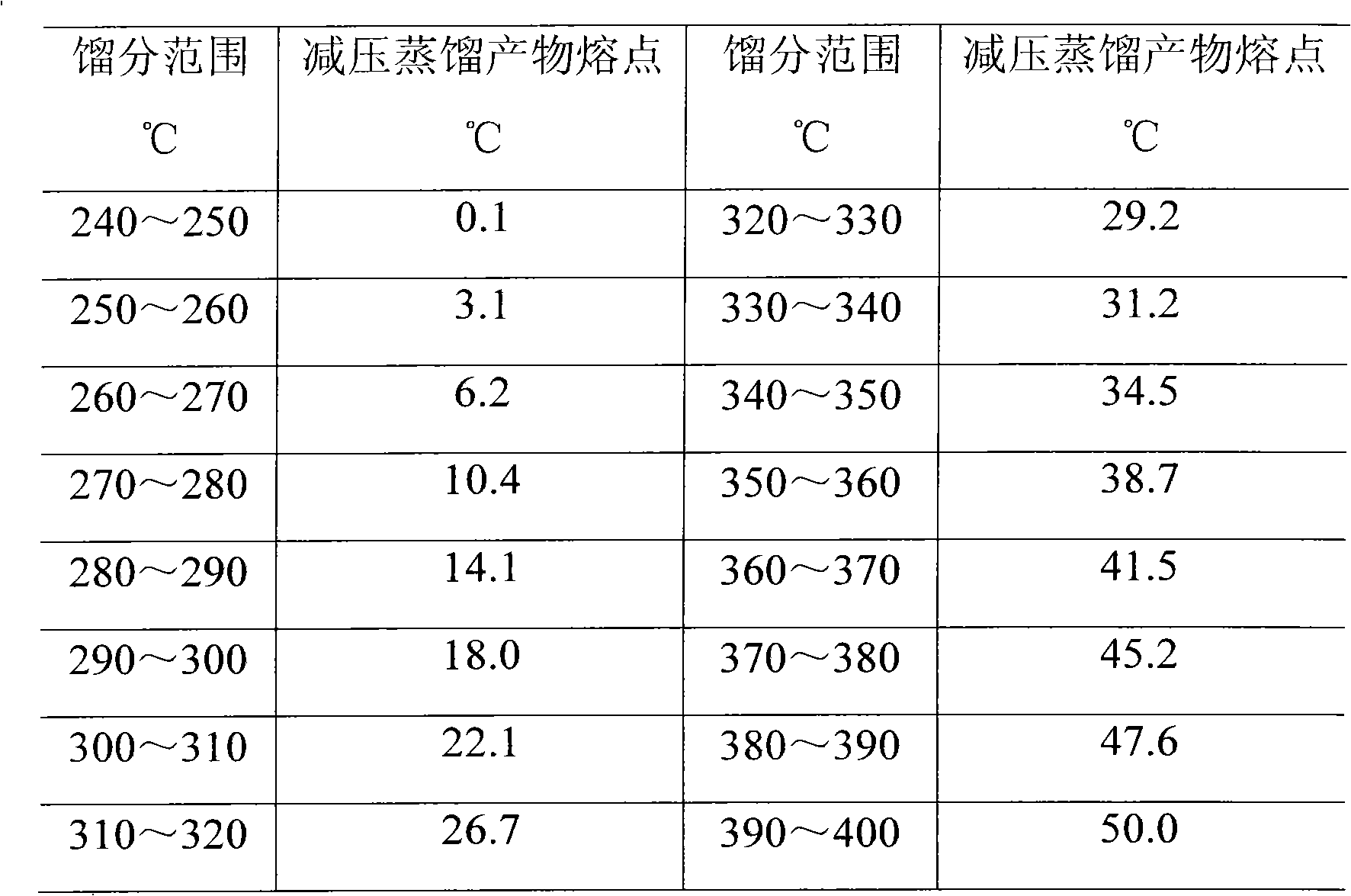
ActiveCN102041090AImprove performanceHigh latent heat of phase changeHydrocarbon distillationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesFiberOxygen
The invention relates to a method for preparing phase-change materials from a Fischer-Tropsch (F-T) synthesis product. The comprises the following steps: in the presence of catalyst, carrying out hydrogenation transformation on the F-T synthesis product in which the weight content of normal paraffin hydrocarbons is greater than 85%, thereby transforming olefins and oxygen-containing compounds in the F-T synthesis product into the proper components of the phase-change materials; and distilling the hydrogenated product, and preparing the fraction within the range of 240-400 DEG C according to the fraction width of 5-20 DEG C, wherein the mixture of all the fractions or any fraction is the phase-change material. The method has the advantages of simple process and low production cost, and is especially suitable for preparing serial phase-change materials; and the prepared phase-change materials have the characteristics of high phase-change latent heat, continuously adjustable phase-change temperature and the like. The phase-change materials can be used in the fields of fiber fabrics, architectural energy conservation, electric appliance protection and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for extracting C4-C6 normal paraffins and coproducing isopentane and heterogeneous hexane cooperatively produced from light naphtha
InactiveCN103254932AEasy to separateAdsorption and separation energy consumption is reducedDistillation purification/separationAdsorption purification/separation2-methylbutaneDesorption
The invention relates to a chemical separation process and in particular relates to a process for extracting C4-C6 normal paraffins and coproducing isopentane and heterogeneous hexane from light naphtha. A multi-tower variable pressure adsorption and distillation separation coupling process is adopted by the invention. The process comprises the following steps of: introducing mixed gaseous C4-C6 normal paraffins and isohydrocarbons serving as raw materials into an adsorption tower for adsorption and separation; desorbing a bed by taking gaseous C7-C9 normal paraffins as a desorption reagent after the adsorption ends; introducing the desorbed material into a rectifying tower to separate out the product C4-C6 normal paraffins and the desorption reagent C7-C9 normal paraffins; recycling the desorption reagent; then regenerating the adsorption tower which absorbs the C7-C9 normal paraffins by using the un-adsorbed C4-C6 isohydrocarbons; and rectifying and separating the regenerated material twice to obtain high-purity desorption reagent C7-C9 normal paraffins, high-purity isopentane and high-purity heterogeneous hexane. By adopting the process disclosed by the invention, normal paraffins and isohydrocarbons can be effectively separated; the adsorbent is easy to regenerate; the process flow is simple and economic benefit is high; and the energy consumption in the process disclosed by the invention is greatly reduced in comparison with the energy consumption in other desorption processes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel
InactiveCN103320153AStable sourceNo pollution in the processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockCyclic alkanePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel. According to the method, castor oil is selected as a raw material, an appropriate catalyst is prepared, and a hydrodeoxygenation reaction and a hydroisomerization reaction are carried out. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: hydrogen is blown into castor oil in the presence of a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst so as to generate n-alkanes; hydrogen is blown into n-alkanes in the presence of a hydroisomerization catalyst so as to isomerize to generate isoparaffin; and a fraction is subjected to fractionation so as to obtain the final product. The final product is the biological aircraft fuel which accords with usage requirements (such as American ASTMD7566 standard and the like). The obtained product castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel contains no alkene or napthene. By the adoption of the fuel, carbon formation of a motor is remarkably reduced. In addition, the fuel contains no sulfur compounds. When the fuel is in use, environmental pollution will not be caused. The castor-oil plant based biological aircraft fuel is an alternative for replacing a petrochemical aircraft fuel.
Owner:TIANJIN NANKAI UNIV CASTOR ENG SCI & TECH
Preparation method of jet fuel
ActiveCN103059900AStable in natureFulfil requirementsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAlkaneMolecular sieve
The invention provides a preparation method of jet fuel. The method comprises the following steps: (1) contacting vegetable oil, and / or animal fat and hydrogen with a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst under the hydrodeoxygenation conditions to obtain C8-C24 n-alkanes; (2) contacting the C8-C24 n-alkanes and hydrogen with a hydroisomerization catalyst under hydroisomerization conditions; and (3) under hydrofining conditions, contacting the contact products from the step (2) and hydrogen with a hydrofining catalyst, and fractioning to obtain the jet fuel. The hydroisomerization catalyst comprises a carrier and an active metal component; the carrier contains a silicon aluminophosphate molecular sieve; and the metal active component contains one or more from VIII metal elements. The jet fuel prepared by the method provided by the invention is almost entirely comprised of saturated alkanes, has stable quality, and can meet the requirements as a No. 3 jet fuel.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Naphtha adsorbing separation and optimized utilization method
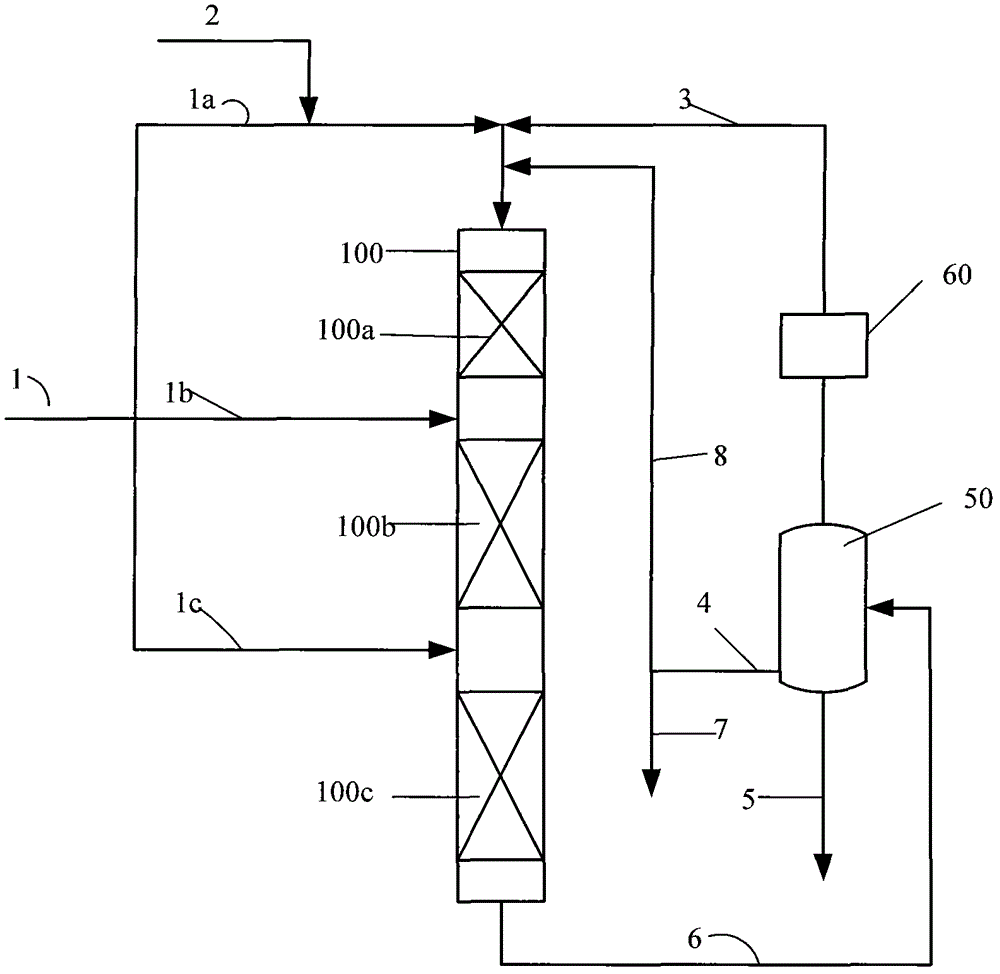
The invention provides a naphtha adsorbing separation and optimized utilization method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, filling naphtha into a simulation moving bed adsorbing separator filled with 5A molecular sieves under a liquid phase maintenance condition; 2, obtaining desorption effluents and raffinate effluents through a liquid-solid absorbing separation continuous technology; and 3, respectively recovering the desorption effluents and the raffinate effluents by a desorption agent to obtain desorption oil rich in n-alkanes and raffinate oil rich in non-normal alkanes, wherein the desorption oil contains 90-100wt% of the n-alkanes, and the raffinate oil contains 90-100wt% of the non-normal alkanes. The invention also provides a naphtha optimized utilization method. The adsorbing separation method provided in the invention, which has the advantages of low operation temperature, continuous operation, high yield, low desorption agent loss, and high molecular sieve utilization rate, couples a separating technology with subsequent processing technologies, and realizes the reasonable configuration of a resource.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for converting n-alkane into isoalkane by gold-loaded molecular sieve catalyst
InactiveCN102416341AEasy to prepareIncrease acidityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsAlkaneIsomerization
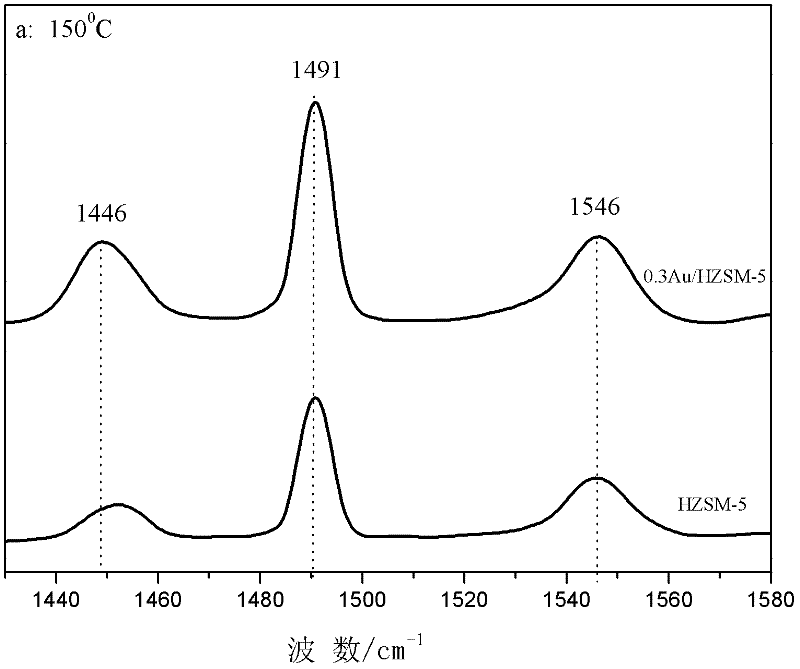
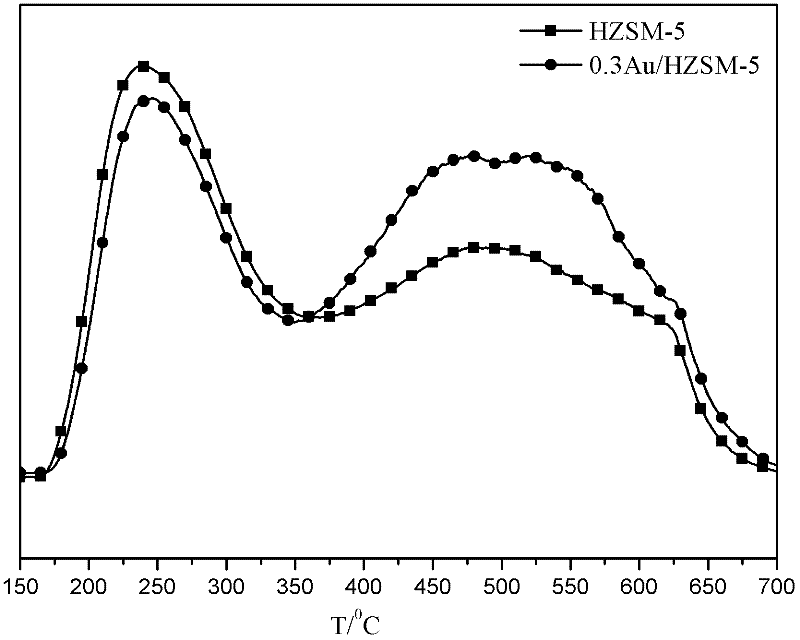
A method for converting n-alkane into isoalkane by a gold-loaded molecular sieve catalyst belongs to the technical field of catalysts. After a molecular sieve is treated by completely negative pressure degasification and purification, a gold precursor is loaded on the molecular sieve carrier by a negative pressure deposition precipitation method so as to form a Si-O(H)-Au structure. The molecular sieve is a high-silica zeolite molecular sieve; the preparation of gold-loaded catalyst under a negative pressure condition by the deposition precipitation method facilitates the purification of the internal and external surfaces and pore channels of the molecular sieve; and Au is easy to enter the pore channels of the molecular sieve to reach high dispersion, and can be combined with silicon hydroxyls on the internal and external surfaces to form the Si-O(H)-Au structure. The method can dehydrogenize n-alkanes to generate alkenes under the difunctional action of metal and the carrier; the alkenes obtain protons at the acid sites to form carbonium ions; and isoalkanes are generated by skeletal isomerization and hydrogenation desorption of the carbonium ions.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Isomerization catalyst, preparation and application
ActiveCN108126735AHigh selectivityHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningAlkaneMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of an isomerization catalyst. The method comprises the following specific steps: filling pore channels of a molecular sieve with hydrocarbon compounds firstly, then performing heating treatment to obtain a molecular sieve support with the blocked pore channels of the molecular sieve, supporting metal active components on the support,and performing drying and reduction to obtain the target catalyst. Part of organic matter is transformed into carbonaceous matter to block the pore channels of the molecular sieve by controlling treatment conditions, so that pore volume and pore channel depth of the molecular sieve are regulated. Compared with the prepared catalyst in the prior art, the catalyst prepared with the method has higherisomerization selectivity and isomerization yield in an isomerization reaction of n-alkanes.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
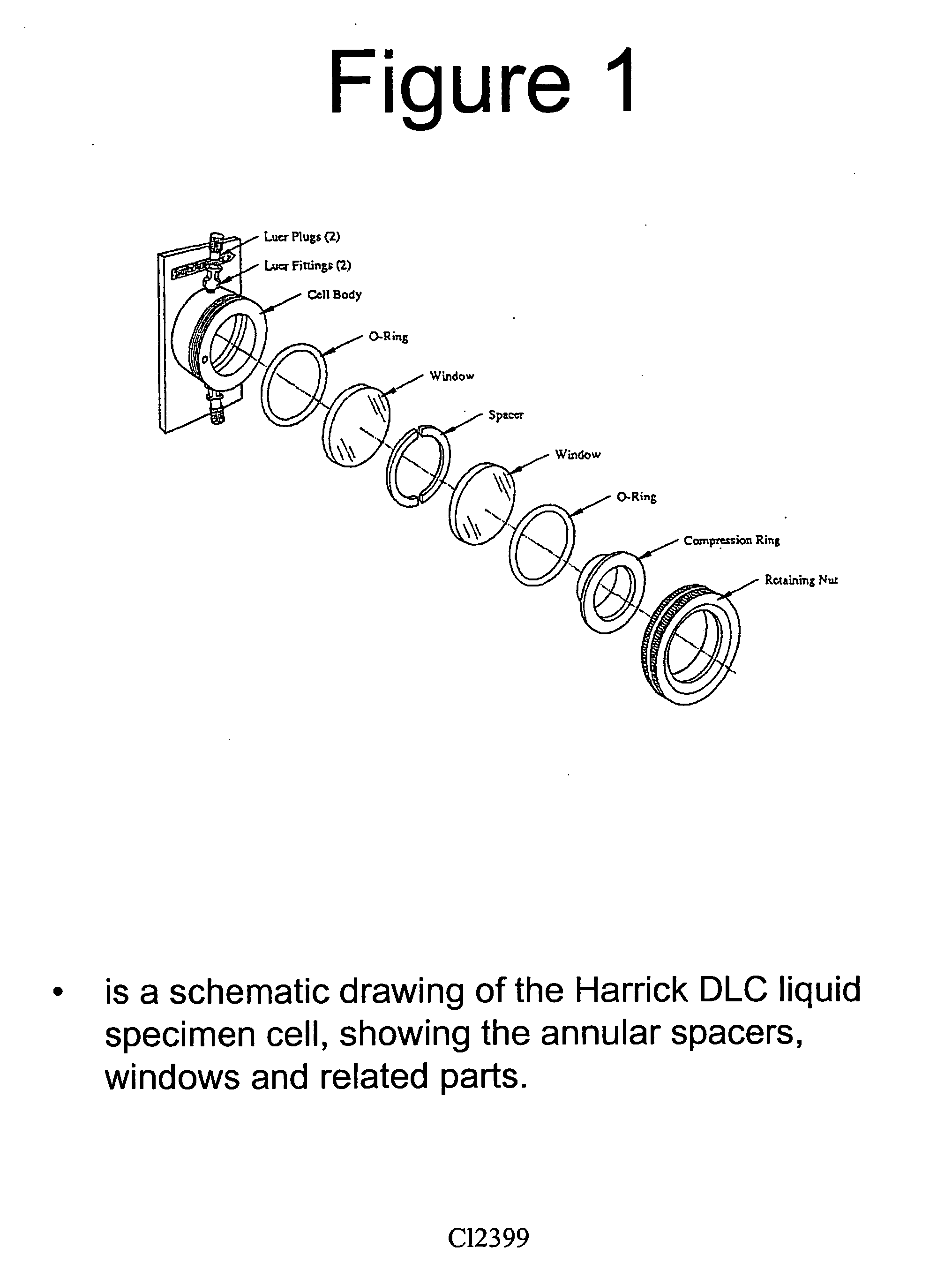
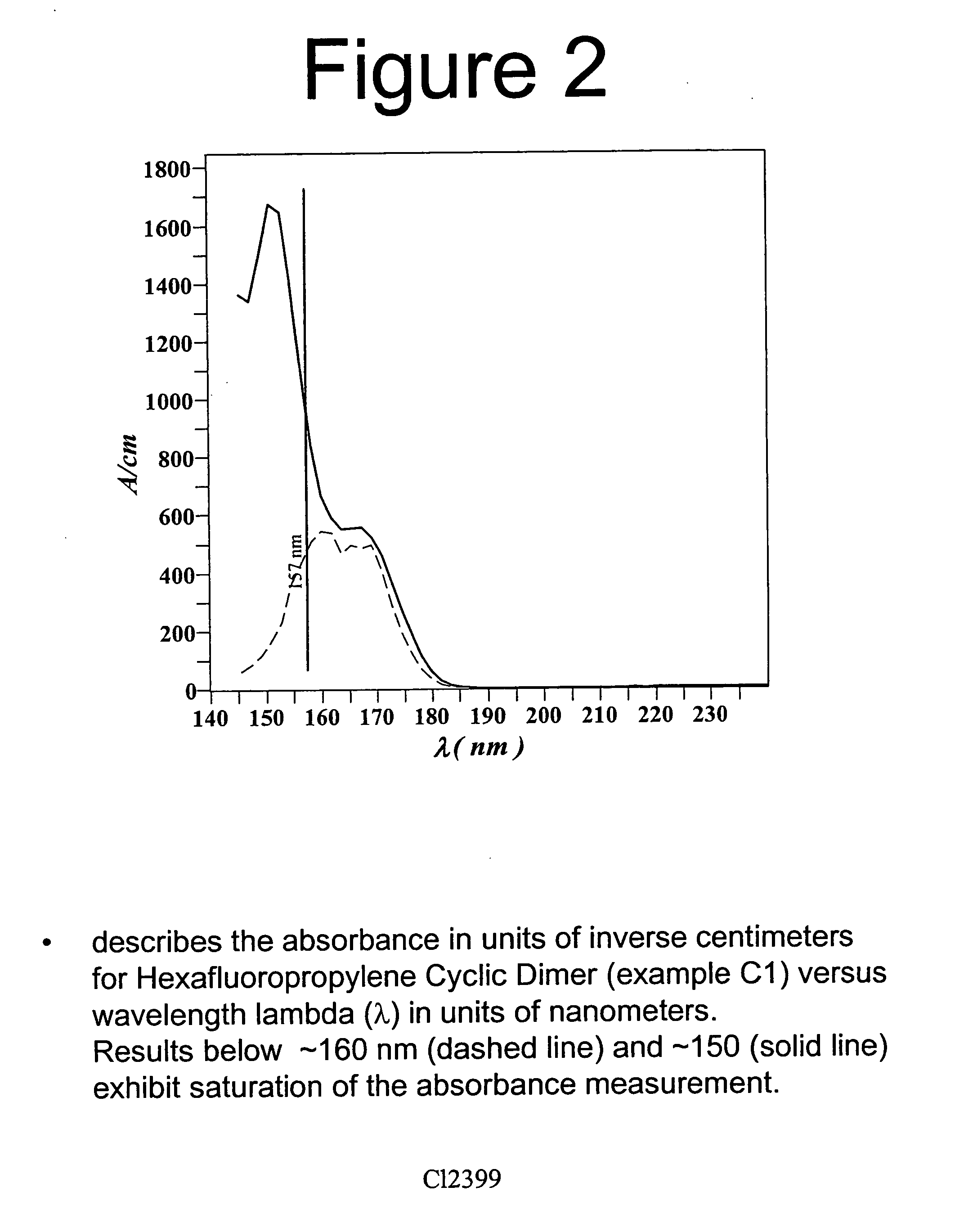
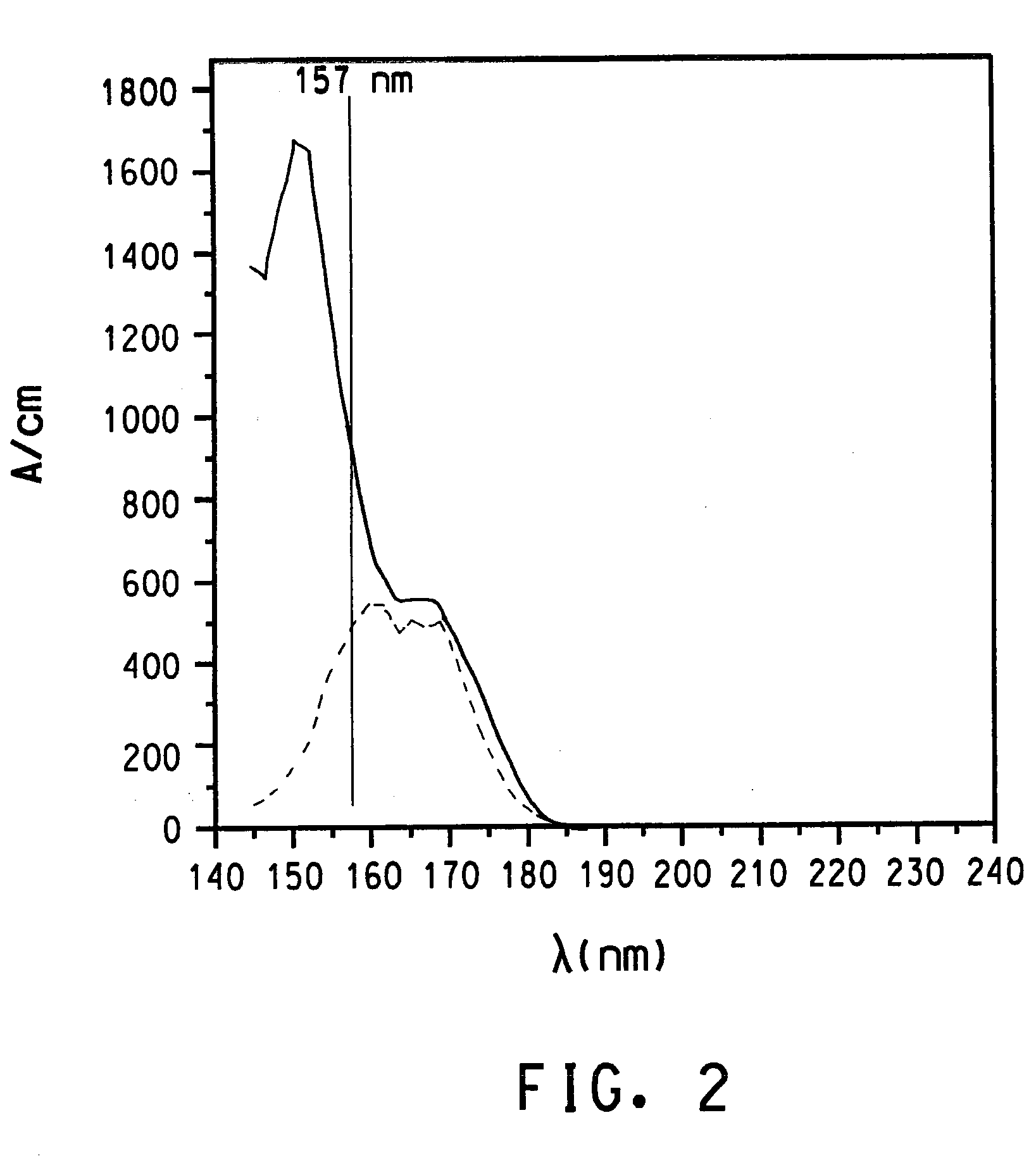
Use of Perfluoro-n-alkanes in vacuum ultraviolet applications
InactiveUS20050186514A1Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAlkaneUltraviolet
This invention concerns liquid perfluoro-n-alkanes for use in applications demanding high transparency at UV wavelengths ranging from about 150 to 165 nm, especially 157 nm. Uses include optical couplants, optical cements, optical elements, optical inspection media for semiconductor wafers and devices, and most especially immersion photolithography at 157 nm exposure wavelength.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for producing normal paraffin by hydrogenating fatty acid ester
InactiveCN104250558ACtiveSelectiveLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockVegetable oilFixed bed
The invention relates to a method for producing normal paraffin by hydrogenating fatty acid ester, mainly solves the problems of narrow application range, low added values and the like of first generation biodiesel (fatty acid methyl ester), and develops the application range of animal and vegetable oil (fatty glyceride). The method for producing normal paraffin by hydrogenating fatty acid ester comprises the following steps: mixing fatty acid ester with hydrogen, sequentially introducing the obtained mixture to enter a fixed bed prehydrogenation reactor and a hydrodeoxygenation reactor in order to remove most oxygen-containing groups in the above raw material, carrying out gas-liquid separation on crude products, fractioning, and introducing the fractioned product to an additional purifying unit to carry out deep hydrotreatment in order to produce highly pure normal paraffin with the oxygen content of below 0.5ppm. The method adopting the above technical scheme well solves the problems, can be used in the industrial production of normal paraffin through hydrogenating fatty acid ester, and has the advantages of low reaction pressure, low hydrogen / oil ratio, low hydrogen consumption, large apparatus load, high product purity and good product quality.
Owner:江苏佳誉信实业有限公司
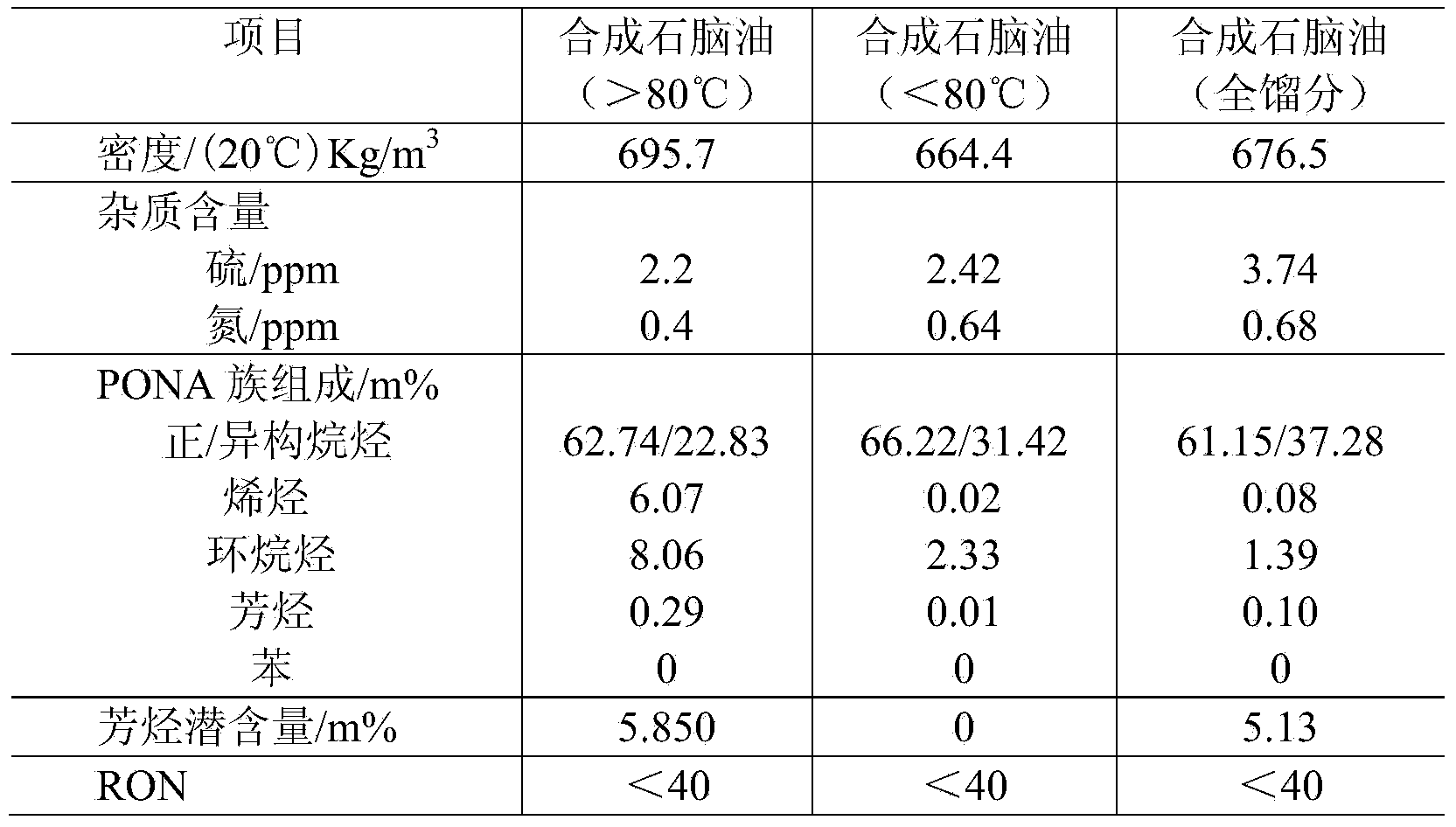
Method of producing gasoline for car from synthetic naphtha
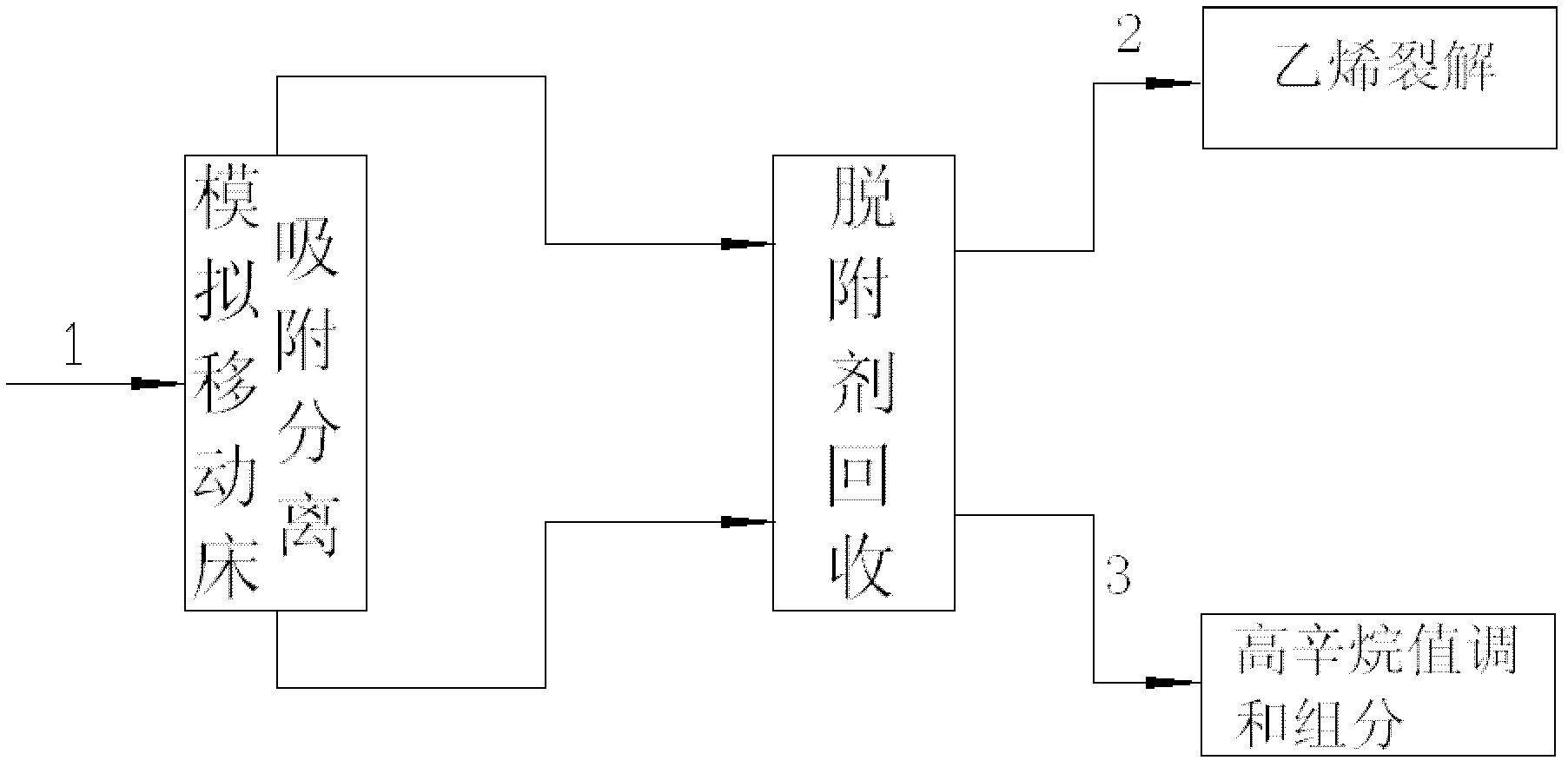
ActiveCN103396833ABoost octaneSolve the bottleneck problem of production technologyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesCatalytic reformingAlkane
The invention discloses a method of producing gasoline for a car from naphtha. The method comprises the following steps: feeding the naphtha which is synthesized by a coal indirect liquefaction process into a fractionating tower for fractioning, wherein C5-C6 which is fractioned out by a tower line I is fed to a normal paraffin hydro-isomerization process for being treated; and feeding fraction which is not lower than 80 DEG C and obtained at the tower bottom to a fixed-bed catalytic reforming process for being treated; and mixing and feeding the oil, which is obtained by the normal paraffin hydro-isomerization process and the fixed-bed catalytic reforming process, into a degassing tower for degassing to obtain a car gasoline component at the tower bottom. According to the method of producing gasoline for a car from naphtha disclosed by the invention, the fixed-bed catalytic reforming process is adopted for converting C7-C9 alkane not lower than 80 DEG C in the synthetic naphtha into aromatic hydrocarbon; and the normal paraffin hydro-isomerization process is adopted for realizing the hydrocarbon isomerization of the C5-C6 normal paraffin in the synthetic naphtha. And therefore, the octane value of the synthetic naphtha is effectively improved, and the car gasoline with indexes reaching National Gasoline Quality Standard-VI is produced.
Owner:中国寰球工程有限公司辽宁分公司
N-alkane low-temperature isomerization catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105080578AHigh activityImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationPhysical/chemical process catalystsAlkaneIsomerization
The invention discloses an n-alkane low-temperature isomerization catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application of the n-alkane low-temperature isomerization catalyst. The catalyst disclosed by the invention comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.1%-1.0% of loaded metal Pt, 5.0%-10.0% of an element Cl, and the balance of a carrier gamma-Al2O3. The preparation method of the catalyst disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: dipping chloroplatinic acid on the carrier gamma-Al2O3, and then drying and roasting to obtain Pt / gamma-Al2O3 catalyst containing 0.1%-1% of the Pt; and firstly reducing a platinum-containing catalyst, then uniformly dipping a chlorinating agent on the surface of the Pt / gamma-Al2O3 catalyst by adopting a chlorinating way of liquid-phase dipping, and then carrying out programmed warming for curing the chlorinating agent to obtain the Pt / gamma-Al2O3-Cl n-alkane isomerization catalyst with high chloride loading quantity (5%) and uniform distribution of the chlorine element. The catalyst provided by the invention has relatively high chlorine content, also has good chlorine distribution, and achieves high acidity loading quantity, high isomerization activity and high stability of the catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING SINO SPHERE PETROCHEM TECH CO LTD
Compound oil-displacing agent containing asymmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine and application thereof
The invention relates to a compound oil-displacing agent containing asymmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of chemical oil displacement. The asymmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine is prepared by adopting fatty acids with different chain lengths and monomethylamine as original raw materials by means of amide reduction and carboxymethylation, and a molecular formula of the asymmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine is abbreviated as Cm+nB, wherein m is not equal to n. Compared with the symmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine identical in main alkyl chain length, the asymmetric betaine basically maintains high surface activity of the symmetric betaine, but the water solubility of the product is remarkably improved, and the adsorption onto the surface of rock is obviously lowered. The interface tension between C7-C9 n-alkanes and Daqing formation water and between Daqing crude oil and Daqing formation water is respectively reduced to 10<-3>mN / m and 10<-2>mN / m by virtue of C18+6B single component; the asymmetric di-long chain alkylmethyl carboxyl betaine is compounded with a symmetric homologous series and a single-long-chain alkyl-dimethyl carboxyl betaine, the interface tension of Daqing crude oil / formation water is lowered to 10<-3>mN / m in a wide range of total concentration.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for extracting and separating aromatic hydrocarbon and saturated hydrocarbon in catalytic cracking slurry oil
ActiveCN102453503AReduce dosageEasy to handleTreatment with plural serial refining stagesAlkaneSlurry
A method for extracting and separating aromatic hydrocarbons and saturated hydrocarbons in catalytic cracking slurry oil comprises two-stage extraction and separation of aromatic hydrocarbons and saturated hydrocarbons in catalytic cracking slurry oil; the first-stage extraction adopts two solvents, wherein the first solvents are furfural, sulfolane, sulfoxide, N-methyl pyrrolidone or amide, and the second solvents are light oil, C6-C10 n-alkane or C6-C10 cycloalkane; before the second-stage extraction, the second solvents in raffinate oil obtained in the first-stage extraction are separated from the raffinate oil; the concentrated raffinate oil is treated by second-stage extraction by the first solvents, and the aromatic hydrocarbons and saturated hydrocarbons are further separated. The method can reduce the solvent using amount, and improve the extraction efficiency.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Synthetic base drilling fluid base oil
InactiveCN105505347ALow aromatic contentPromote degradationDrilling compositionCyclic alkanePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a base oil used during drilling operation, wherein the base oil is a synthetic base drilling fluid base oil with characteristics of environmental protection, low toxicity, high safety and low-temperature fluidity. According to the present invention, the synthetic base drilling fluid base oil is formed by mixing Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil and non-conventional petroleum-derived fine chemical base oil, and contains at least 35% by mass of a variety of C9-C20 n-alkanes, at least 60% by mass of a variety of C9-C20 branched or cyclic alkanes, and less than 0.5% by mass of aromatic hydrocarbon, the kinematic viscosity of the synthetic base drilling fluid base oil at the temperature of 40 DEG C is 2-3 mm<2> / s, the pour point is -10 to -30 DEG C, and the flash point is 50-80 DEG C.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Highly purified liquid perfluoro-n-alkanes and method for preparing
InactiveUS20050288535A1Photosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAlkaneLength wave
The present invention is drawn to liquid perfluoro-n-alkanes that are highly transparent to UV wavelengths ranging from about 150 nm to 165 nm, and to the method by which high transparency may be obtained. The liquid perfluoro-n-alkanes of the invention are useful in optical couplants, optical cements, optical elements, optical inspection media for semiconductor wafers and devices, and immersion photolithography at 157 nm exposure wavelength.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for producing elemental N-alkanes
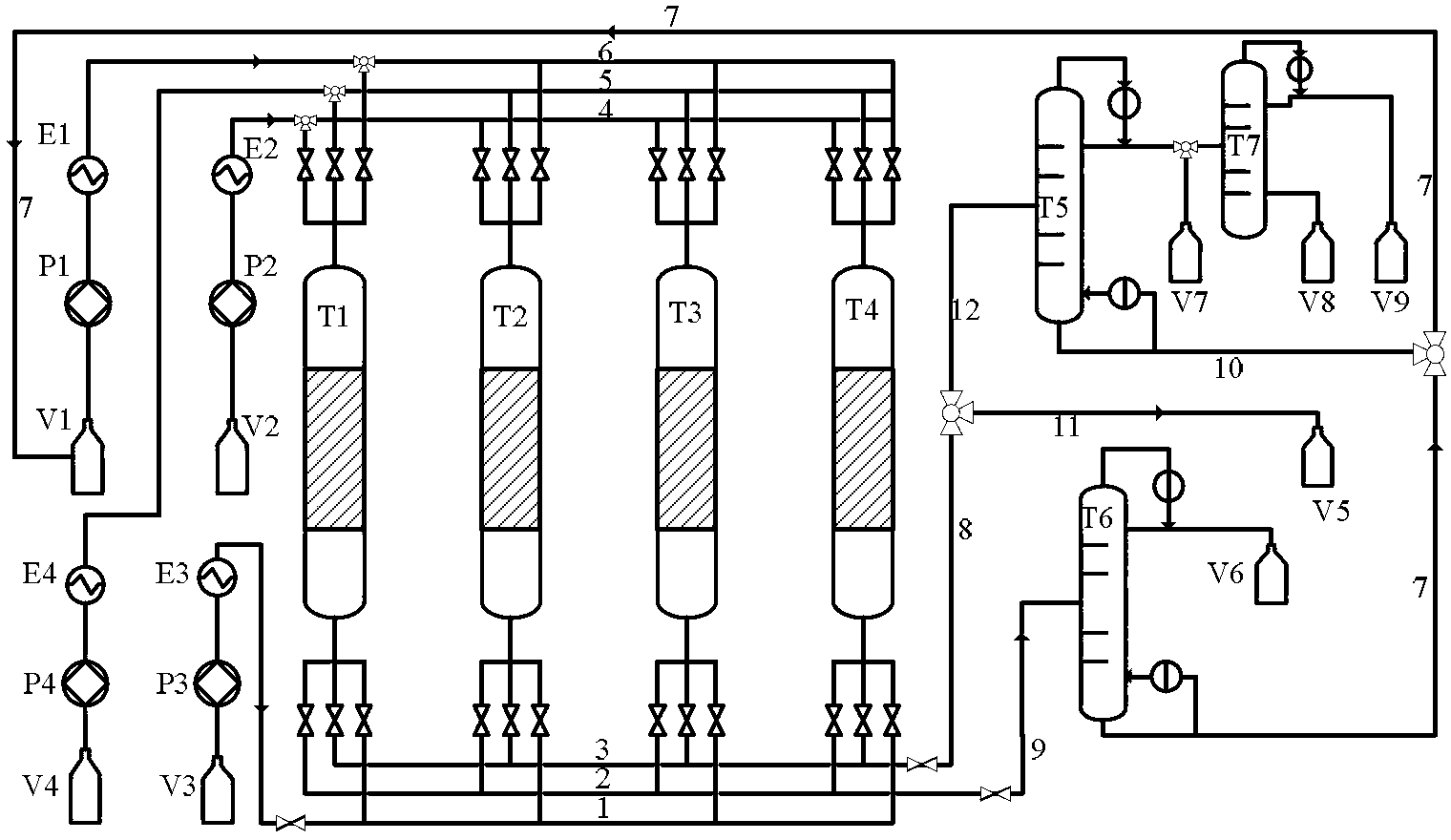
InactiveCN106699501ABenefit maximizationEasy to separateHydrocarbon distillationDistillation purification/separationAlkaneDistillation
The invention relates to the field of chemical engineering, and discloses a method for producing elemental N-alkanes. The method comprises the following steps of a pretreatment step, namely sequentially putting raw materials into a main fractionation tower and a stabilizer, and carrying out distillation under the effects of certain pressure and temperature to obtain stable distillate; and a distillation step, namely putting the stable distillate into fractionation towers, carrying out fractionation under the effects of certain pressure and temperature to obtain elemental N-alkanes, wherein the number of the fractionation towers is 2N-1; the variety number of the obtained elemental N-alkanes is N; and N is an integer of 1-6. The production technology of the elemental N-alkanes is simple and feasible, a product is convenient and fast to separate, the equipment investment is reduced and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:YASHENTECH CORP
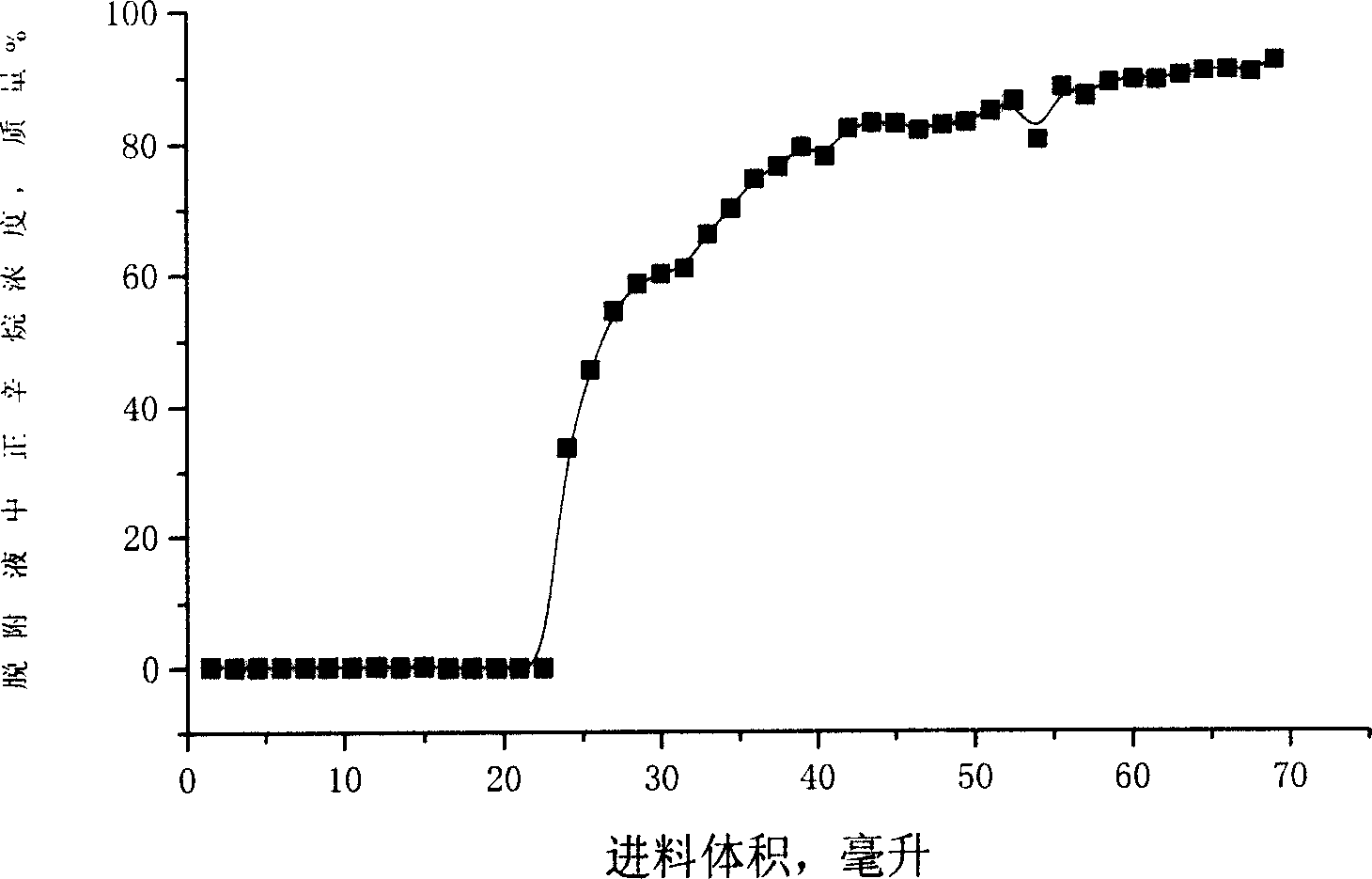
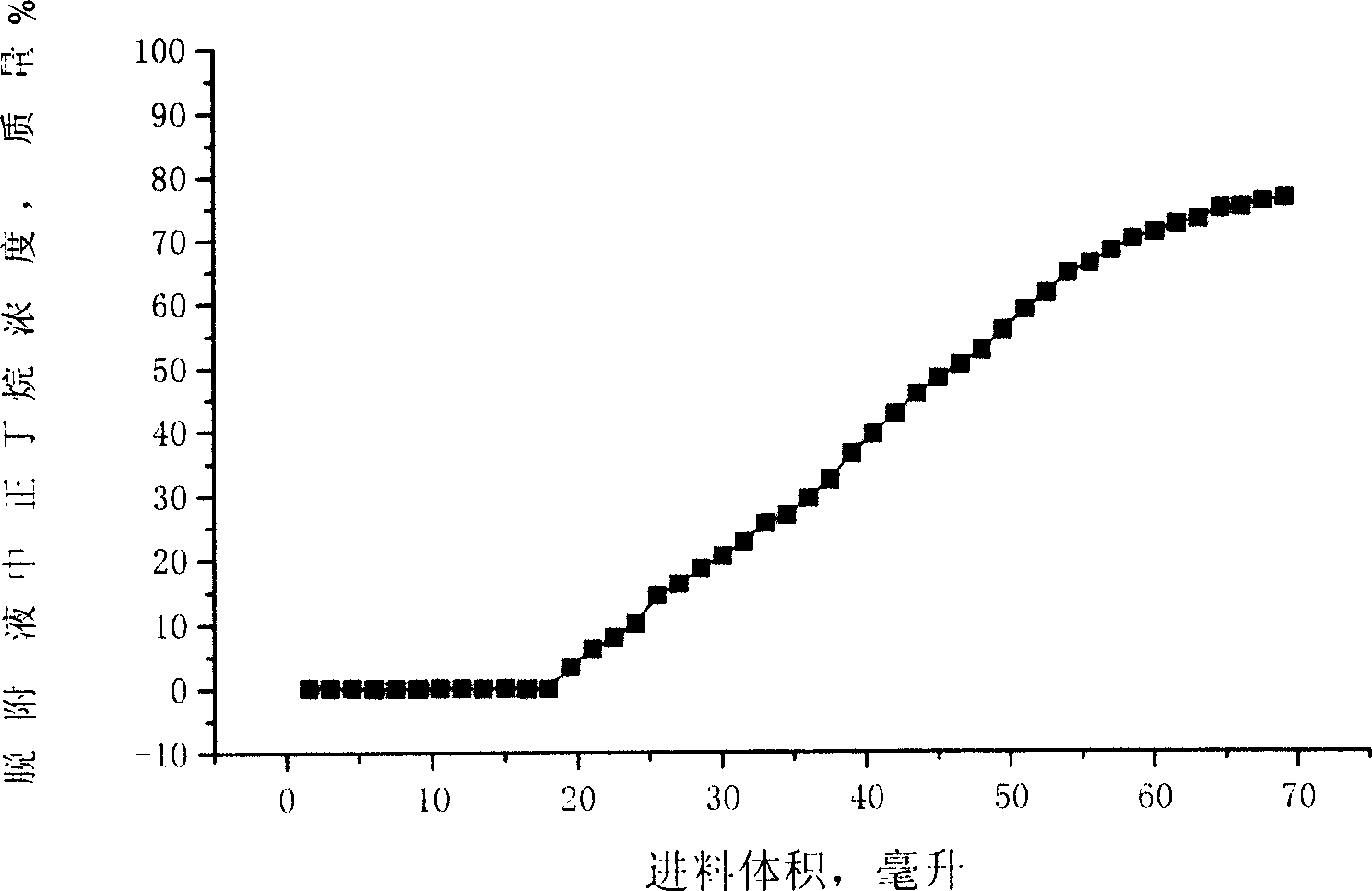
Method for separating n-alkane from C5 to C6 alkane isomerized products
Disclosed is a method for separating normal alkane from C5 to C6 alkane isomerized products. Isopentane is removed from raw materials, and the obtained materials are added into an adsorption separation post to adsorb normal alkane under 2.0-4.0 MPa, 100-150íµ and liquid phase condition, after saturation by adsorption, the adsorption separation post is flushed with flushing agent of isopentene, then desorbed by desorbing agent of C7 to C9 normal alkane. The method can separate normal alkane in light hydrocarbon isomerized products, and the used desorbing agent is less, the desorbing time is short.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com