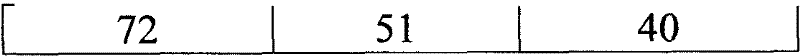Method for expanding culture of microorganisms for wastewater treatment and microbial wastewater treatment method
A technology for wastewater treatment and expanded cultivation, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve effects, death, and difficult domestication of strains, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and efficient degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
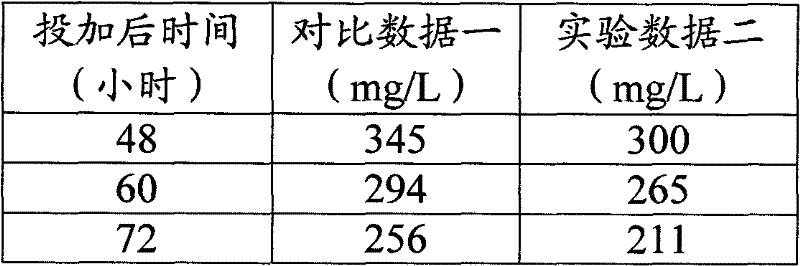
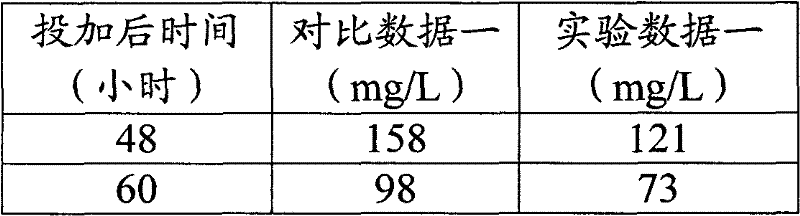
[0052] Embodiment 1 uses the method of the present invention to domesticate the effect of the microorganism of amplification to carry out wastewater treatment
[0053] 1.1 Experimental objects:
[0054] Wastewater from a coking plant. After testing, the wastewater that entered contained pollutants such as phenol, xylenol, quinoline, isoquinoline, indole, and pyridine.
[0055] 1.2 Experimental raw materials:
[0056] The compound microbial agent is 250ppm of Pseudomonas putida, 250ppm of Pseudomonas fluorescens, 250ppm of Bacillus subtilis, 250ppm of Bacillus thuringiensis and 500ppm of white rot fungus. The enzyme preparation is 500ppm of protease, 500ppm of amylase, 500ppm of cellulase and 500ppm of lipase. Citric acid is 250ppm. Riboflavin is 250ppm. The dosage unit of all additives is ppm, which refers to the corresponding concentration of the substance after it is added to the target wastewater biological treatment system.
[0057] 200L effective volume domesticat...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2 uses the microorganism of the inventive method domestication amplification to carry out the effect of wastewater treatment
[0069] 1.1 Experimental object: Antibiotic wastewater from a pharmaceutical factory. After testing, the wastewater entering the treatment station contains quinolines, pyridines, oxazoles, diazoles, triazoles, carbazoles, triazines and other pollutants.
[0070] 1.2 Experimental raw materials:
[0071] The compound bacterial agent is Pseudomonas fluorescens 5×10 4 ppm, Bacillus thuringiensis 5×10 4 ppm and white rot fungi 5×10 4 ppm. Enzyme preparation is protease 5×10 4 ppm, Amylase 5×10 4 ppm, Cellulase 5×10 4 ppm and lipase 5×10 4 ppm. Citric acid is 1 x 10 5 ppm. Riboflavin is 2.5 x 10 4 ppm. The dosage unit of all additives is ppm, which refers to the corresponding concentration of the substance after it is added to the target wastewater biological treatment system.
[0072] 200L effective volume domestication react...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3 uses the method of the present invention to domesticate the effect of the microorganism that amplifies carries out wastewater treatment
[0085] 1.1 Experimental object: Wastewater from printing and dyeing factories. After testing, the wastewater entering the treatment station contains quinone, anthracene, phenanthrene, perylene, azo, biphenyl, and naphthalene pollutants.
[0086] 1.2 Experimental raw materials:
[0087] The compound bacterial agent is Pseudomonas putida 2.5×10 4 ppm, Pseudomonas fluorescens 2.5×10 4 ppm, Bacillus subtilis 2.5×10 4 ppm, Bacillus thuringiensis 2.5×10 4 ppm and white rot fungus 2.5×10 4 ppm. Enzyme preparation is protease 5×10 4 ppm, Amylase 5×10 4 ppm, Cellulase 5×10 4 ppm and lipase 5×10 4 ppm. Citric acid is 1 x 10 5 ppm. Riboflavin is 2.5 x 10 4 ppm. The dosage unit of all additives is ppm, which refers to the corresponding concentration of the substance after it is added to the target wastewater biologica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com