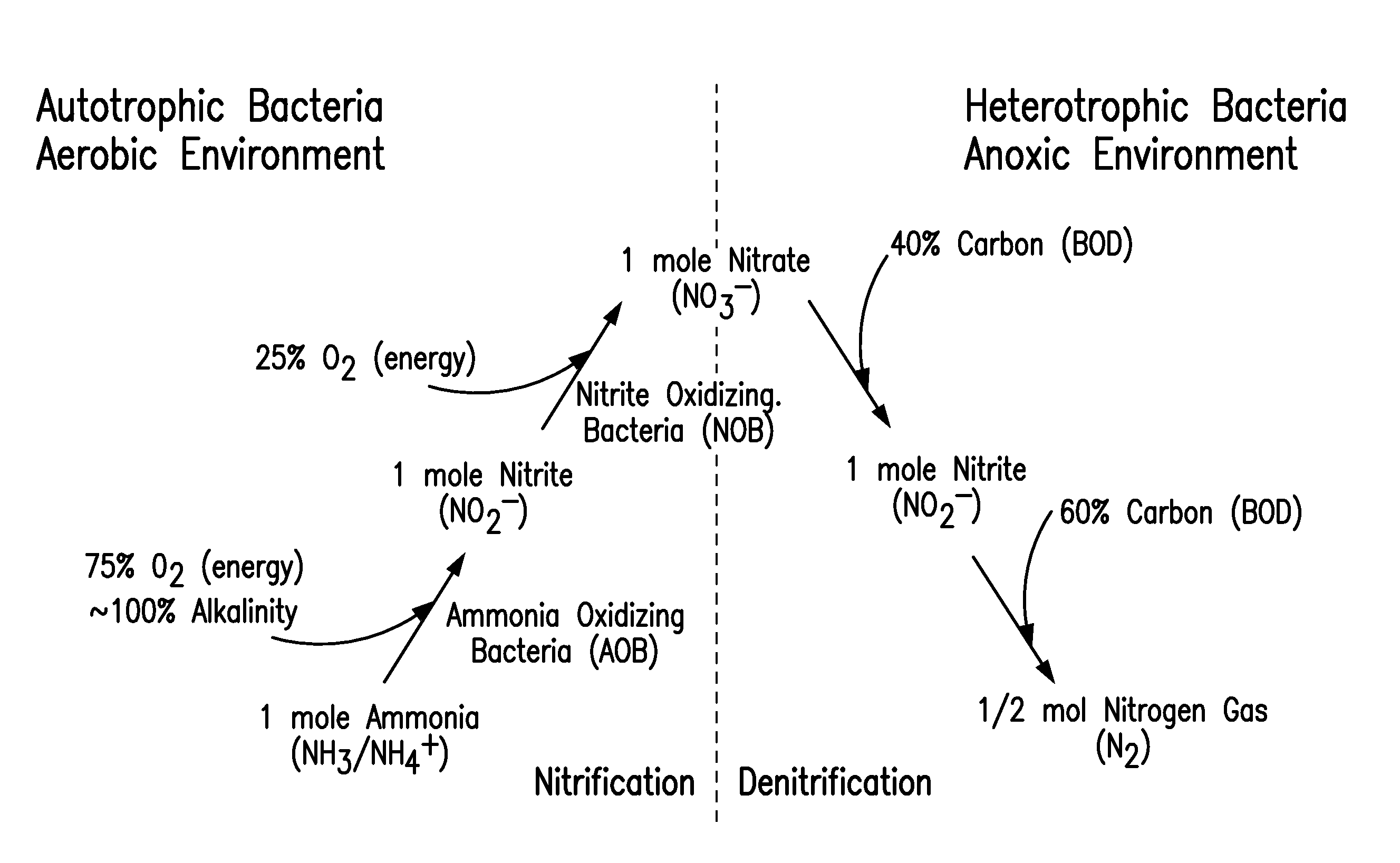
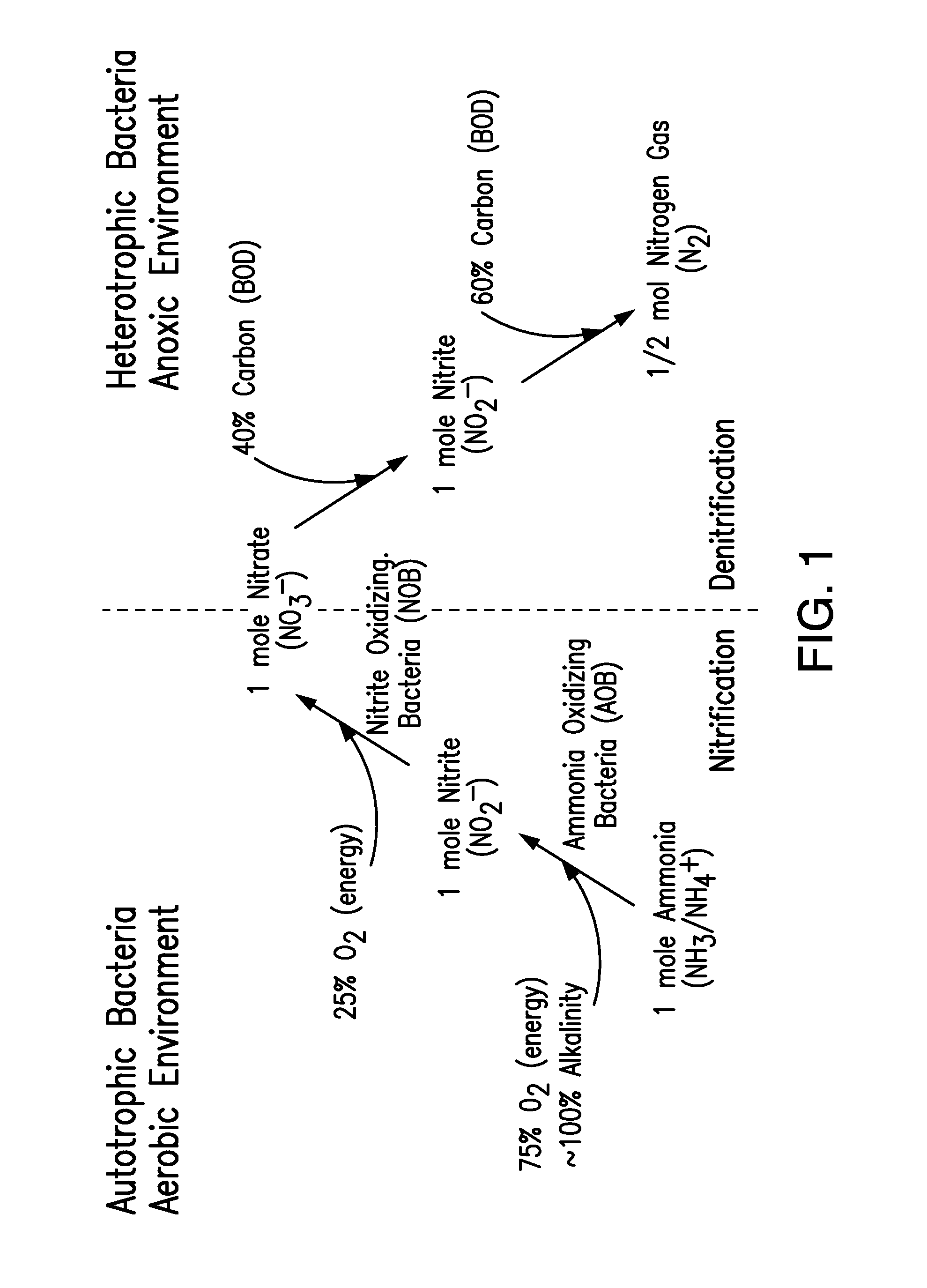
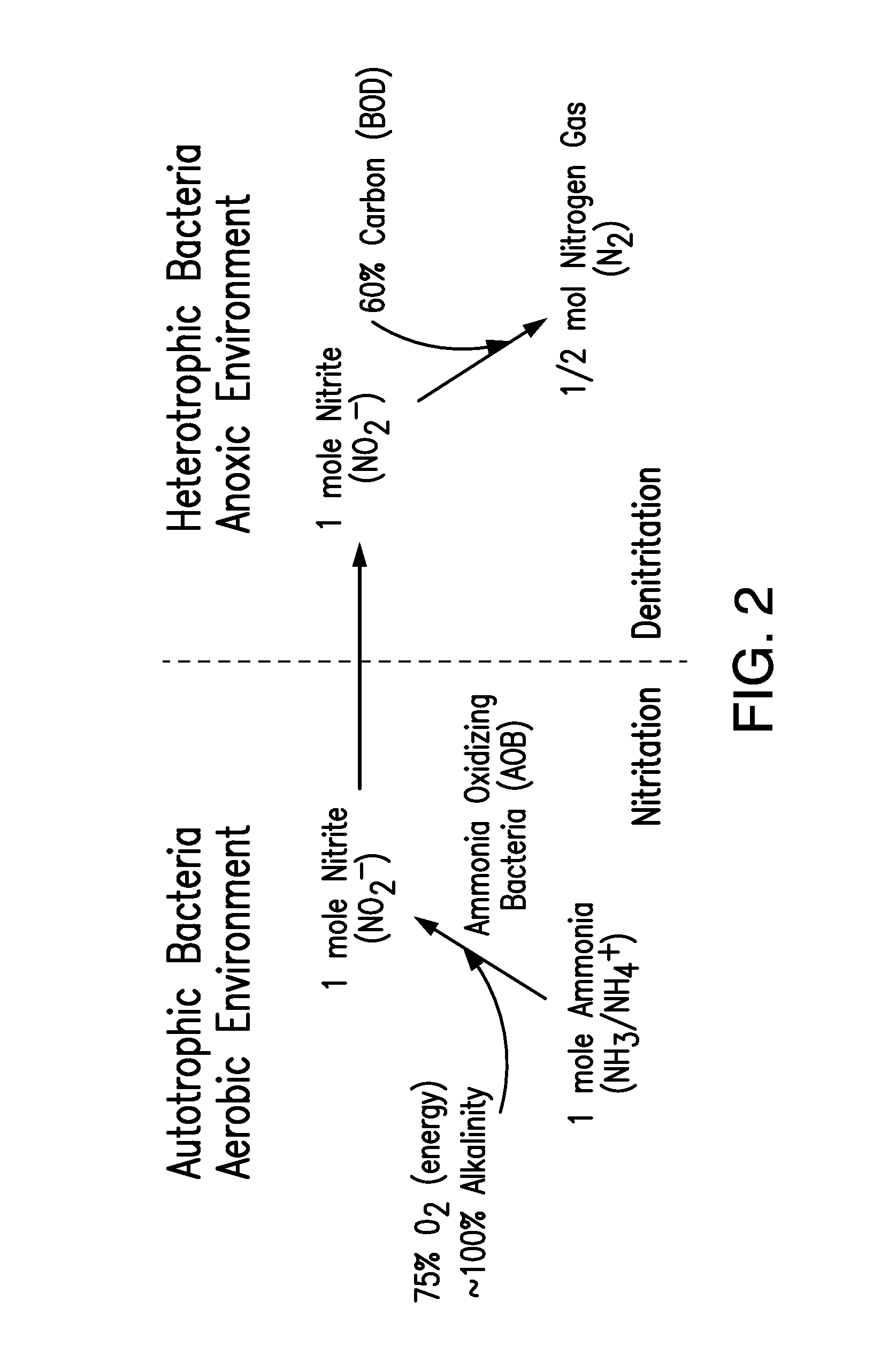
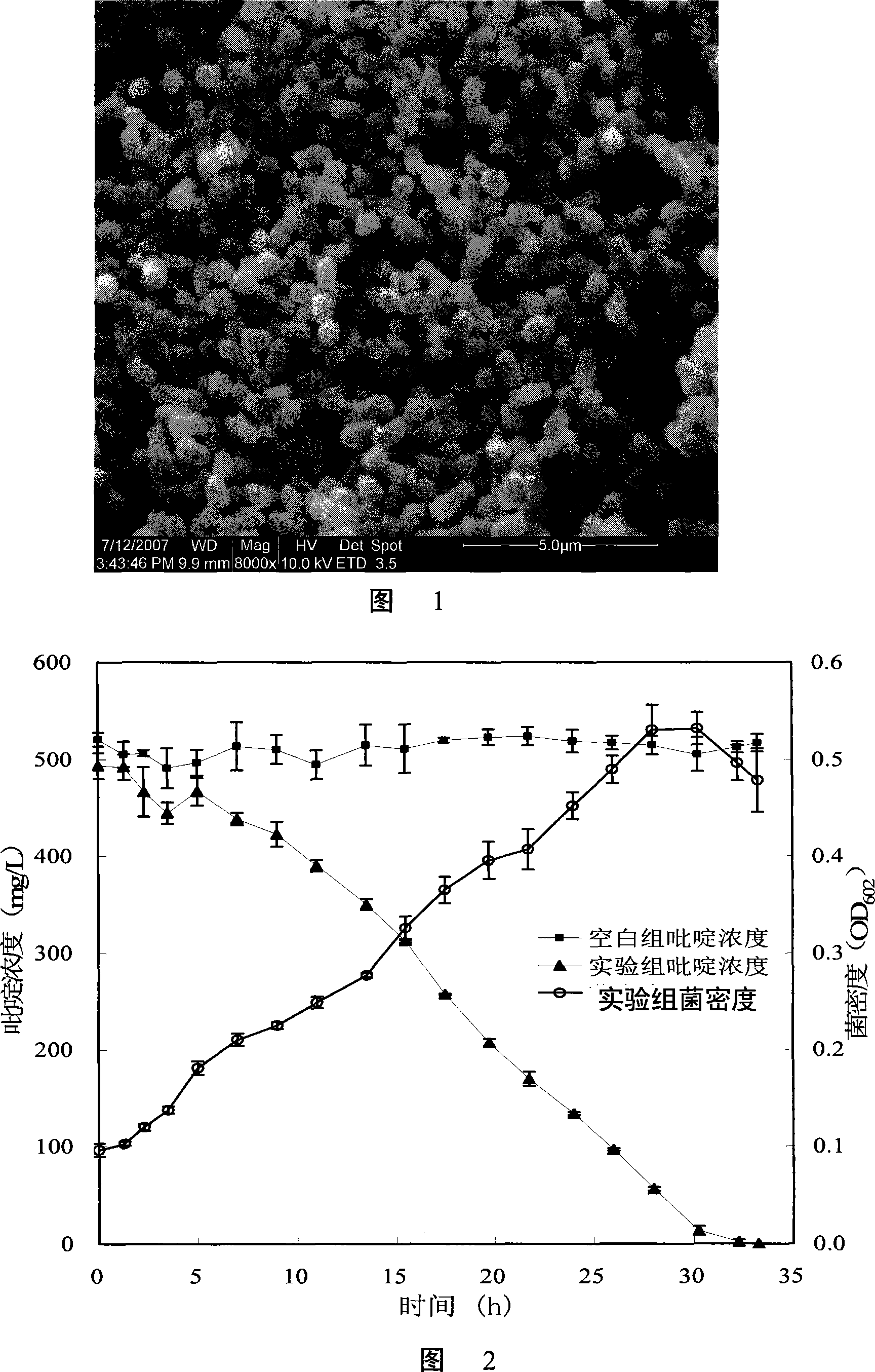
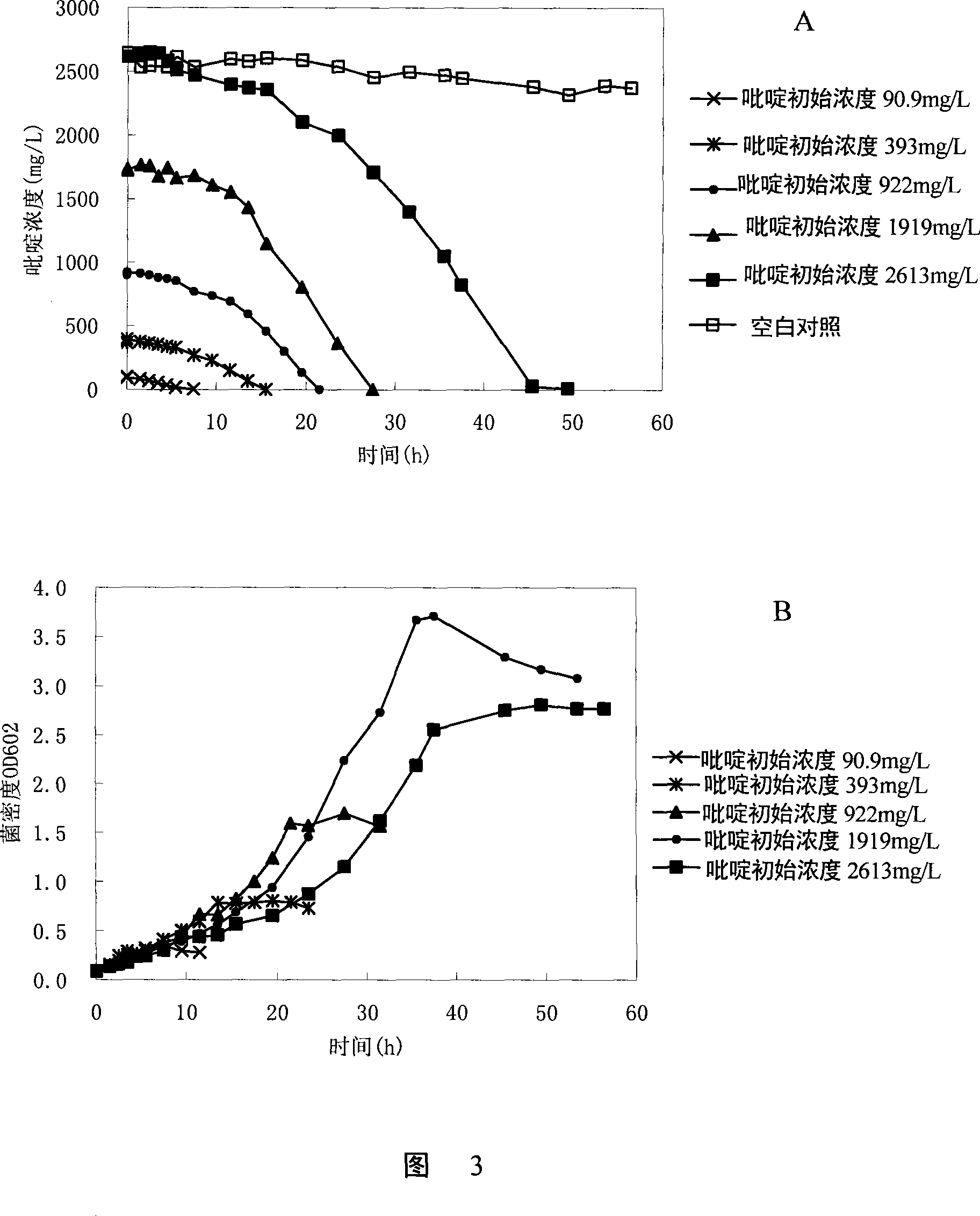
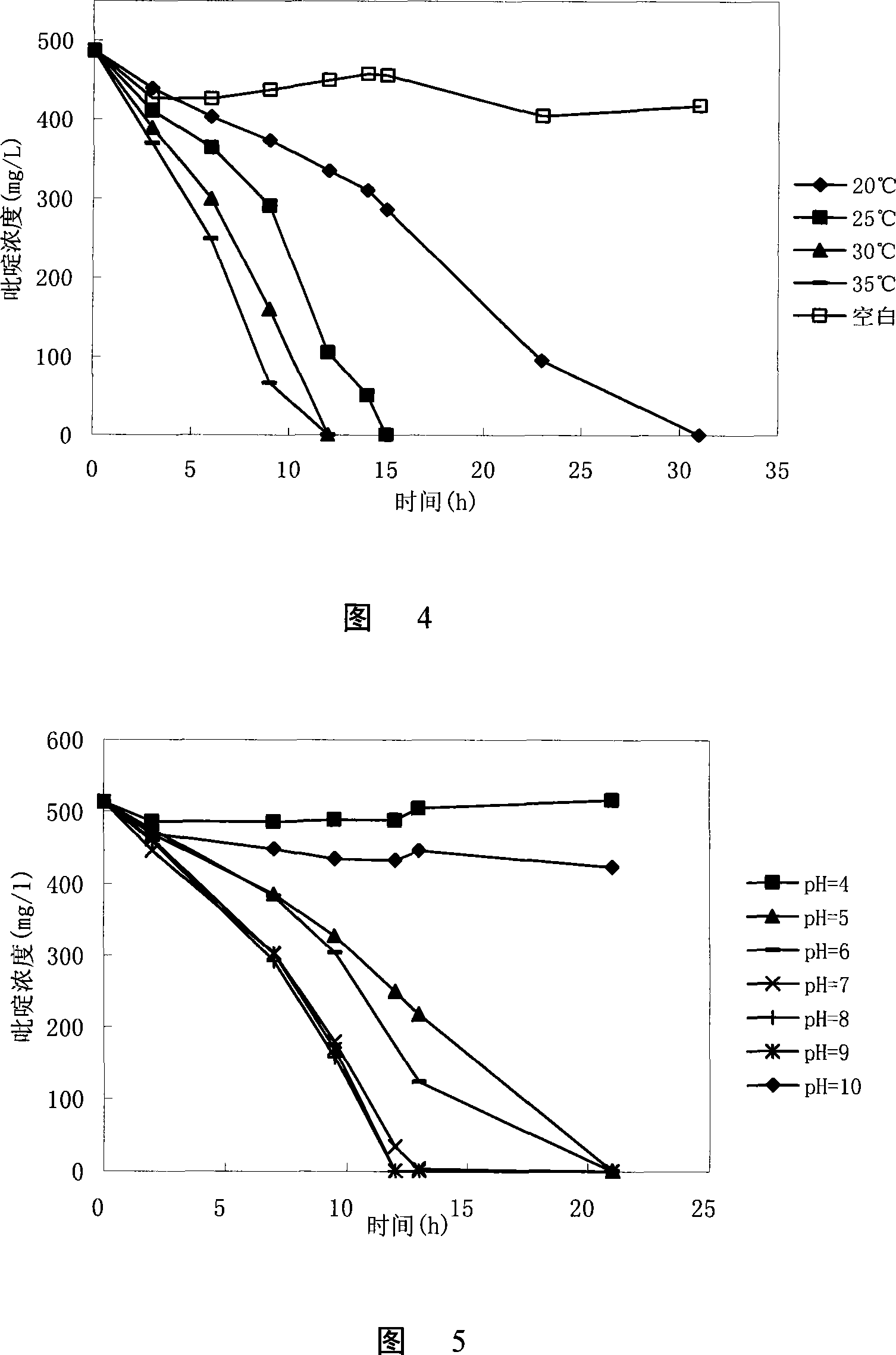
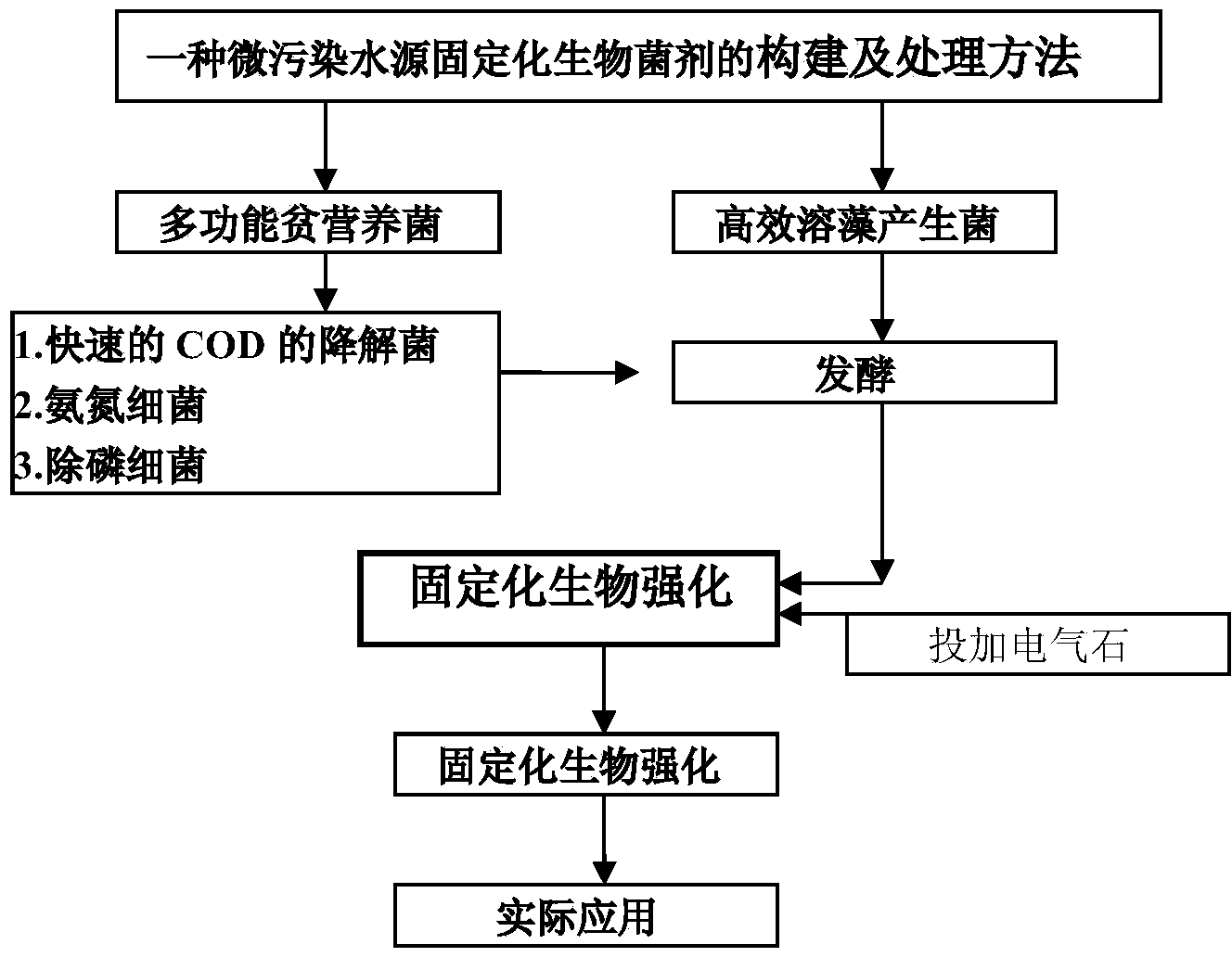
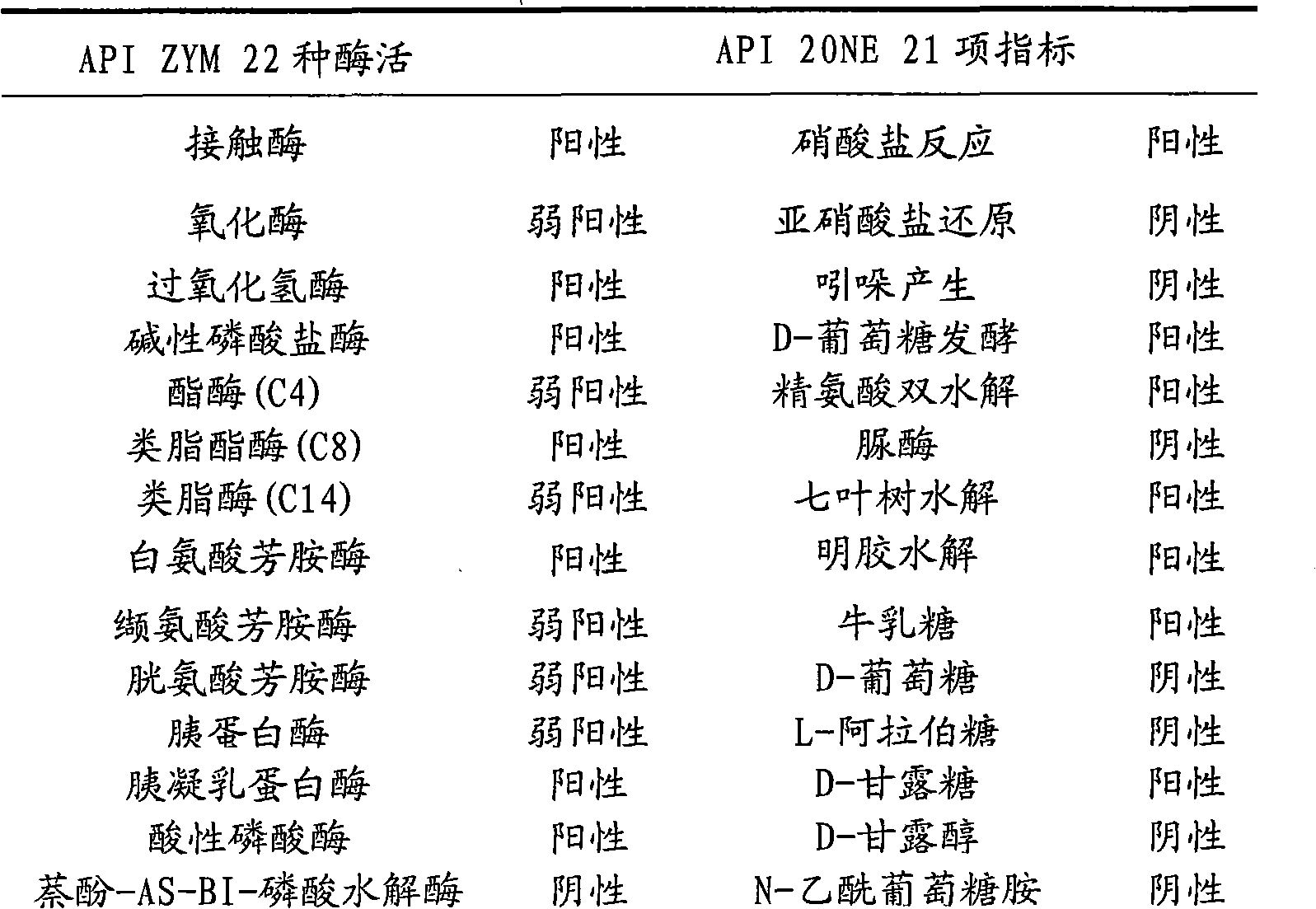
Patents
Literature
137 results about "Bioaugmentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
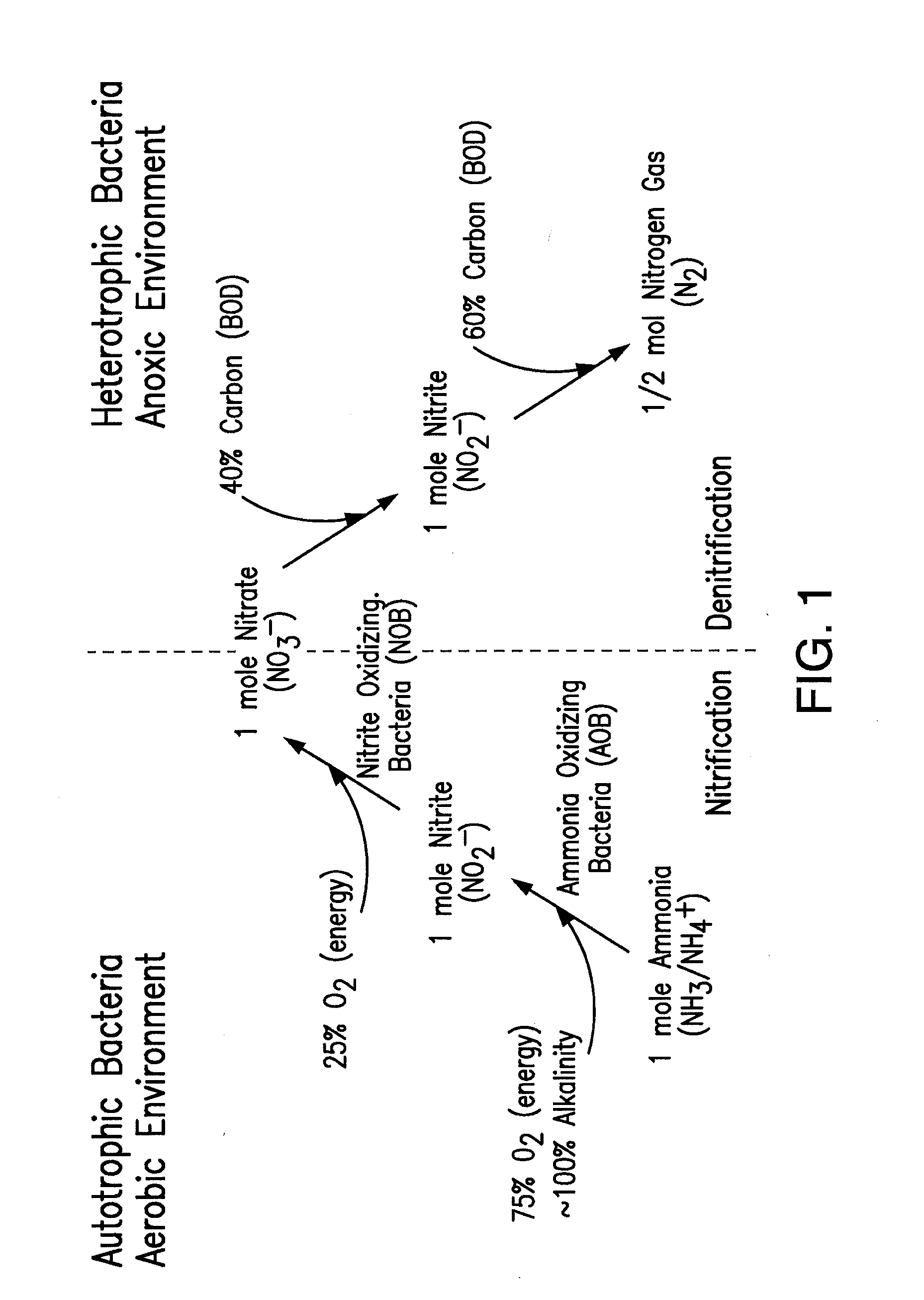
Biological augmentation is the addition of archaea or bacterial cultures required to speed up the rate of degradation of a contaminant. Organisms that originate from contaminated areas may already be able to break down waste, but perhaps inefficiently and slowly.
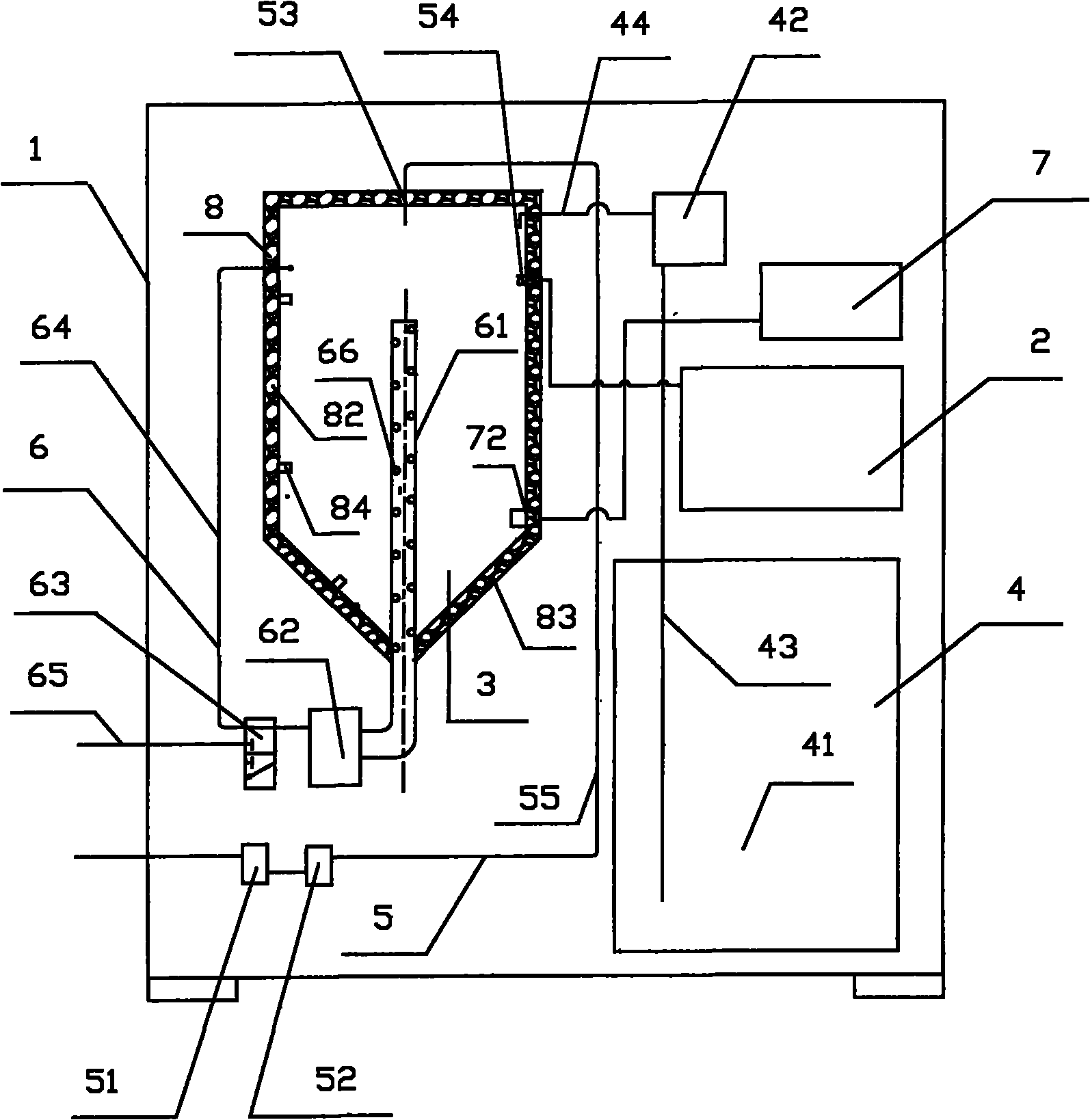
A method for the remediation of harmful organics and/or heavy metal contaminated matrix
ActiveCN105344709APlay a role in loosening and ventilatingRestoration concepts for green sustainabilityContaminated soil reclamationBiostimulationMicrobial agent
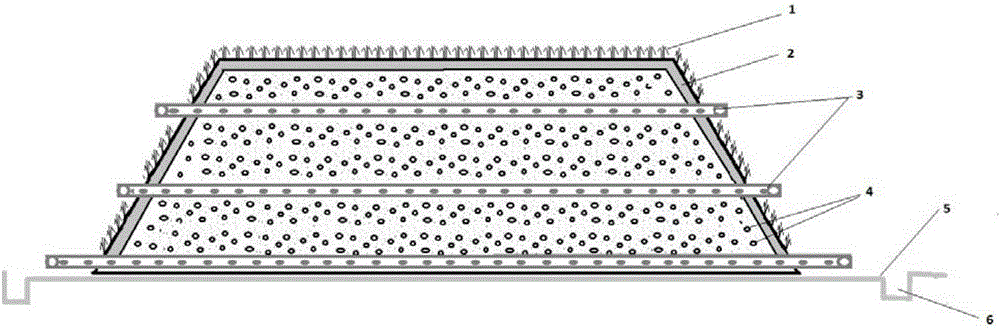
The present invention provides a method for the remediation of harmful organics and / or heavy metal contaminated matrix in order to remediate harmful organics and / or heavy metal contaminated soil, sediment and / or sludge. The method involves the processes of biostimulation, bioaugmentation, rhizoremediation, phytoremediation and a passive biopile. The method comprises steps of: a) designing a microbial agent comprising pollutant degrading bacteria, plant promoting bacteria and / or biosurfactant producing bacteria; b) preprocessing the matrix; c) constructing a passive biopile; and d) capping the biopile with plants for phytoremediation. The method achieves internationally-dominant green and persistent remediation while achieving bioremediation / phytoremediation degrading the organics and removing heavy metal.
Owner:山东迈科珍生物科技有限公司
Intensified biological treatment method for high strength ammonia wastewater
InactiveCN101229944AIncrease loadNot easy to loseTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBioaugmentationChemistry
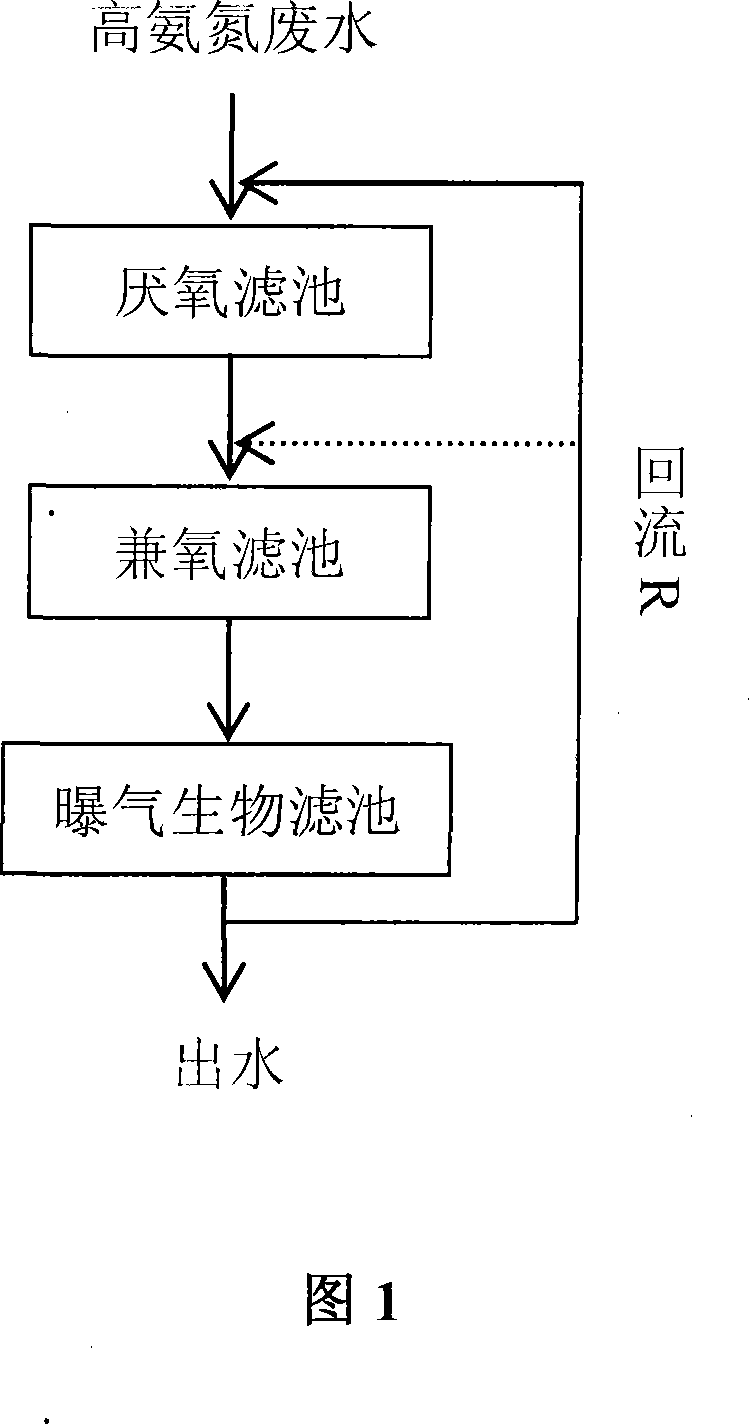
The invention relates to a bioaugmentation treatment method of high ammonia nitrogen, belonging to a sewage treatment technology field which adopts the combined process of anaerobic-hypoxia-aerobic. All the used reactors are biology filtering pool reactor and the inner of the reactor is filled with a macroporous poly urethano carrier. In the domestication and culture process of the biology filtering pool biology membrane, compound microorganism of a high efficiency is added. The high ammonia nitrogen water is processed by a strengthening immobilization technology. The detail functions of each unit are referred to the specification. The invention has the advantages that the two kinds of technologies of biology filtering and the bioaugmentation are combined with the strengthening immobilization technology; the carbon and nitrogen pollution in the leachate are removed. As an effective combined biology treatment method, the invention also has the advantages of high removal efficiency of nitrogen and non-need additional organic carbon source; the high efficiency of bacteria fixedly growing on the carrier, reducing the inhibition effect of the high ammonia nitrogen to the biology, avoiding the draining of the bacteria in the traditional method, having the strong ability of bearing the water inlet pollutants load changes and ability of resisting the system impact. Therefore, the invention is.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for high-efficiency combined treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater
InactiveCN101445311ASmall footprintGood effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentTreatment effectSludge
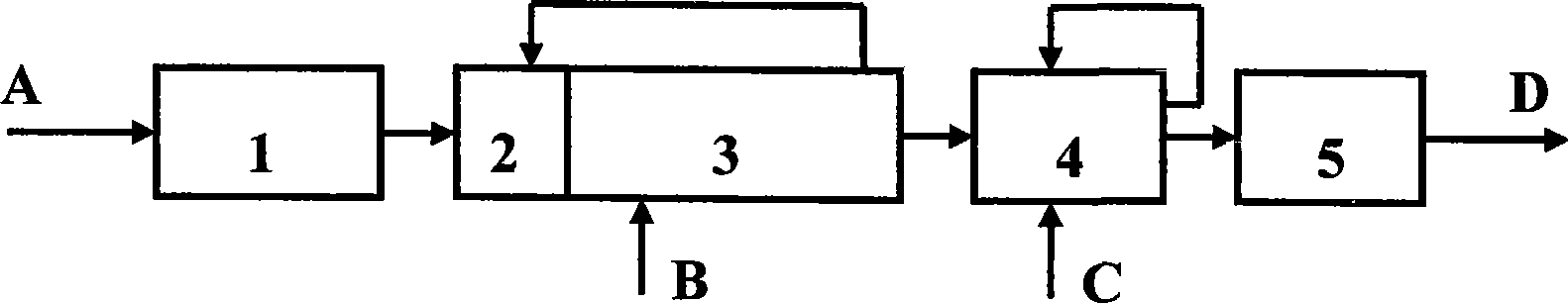
The invention discloses a method for high-efficiency combined treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, which belongs to the field of the organic wastewater treatment. The method comprises the following steps: pumping printing and dyeing wastewater to a hydrolysis pool for hydrolysis and acidification treatments; pumping the wastewater to an A / O (PACT) bioaugmentation reaction tank for biological treatment after hydrolysis and acidification treatments; subjecting the biologically-treated wastewater to the coagulation sedimentation; filtering after the coagulation sedimentation; and discharging. With the treatment method, the water quality of the effluent can meet the strictest effluent discharge standard of China, 'Discharge Standard of Main Water Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant and Key Industries of Taihu Area' (DB32 / T1072-2007). The method has the advantages of less occupied area, low sludge discharge, stable treatment effect and low running cost; achieves the effect of efficient treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, and overcomes the problem of high-efficiency treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater in the prior art.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI +1
Method and apparatus for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment
ActiveUS20140069863A1Easy to controlSemi-permeable membranesWater treatment parameter controlNitrogen removalAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
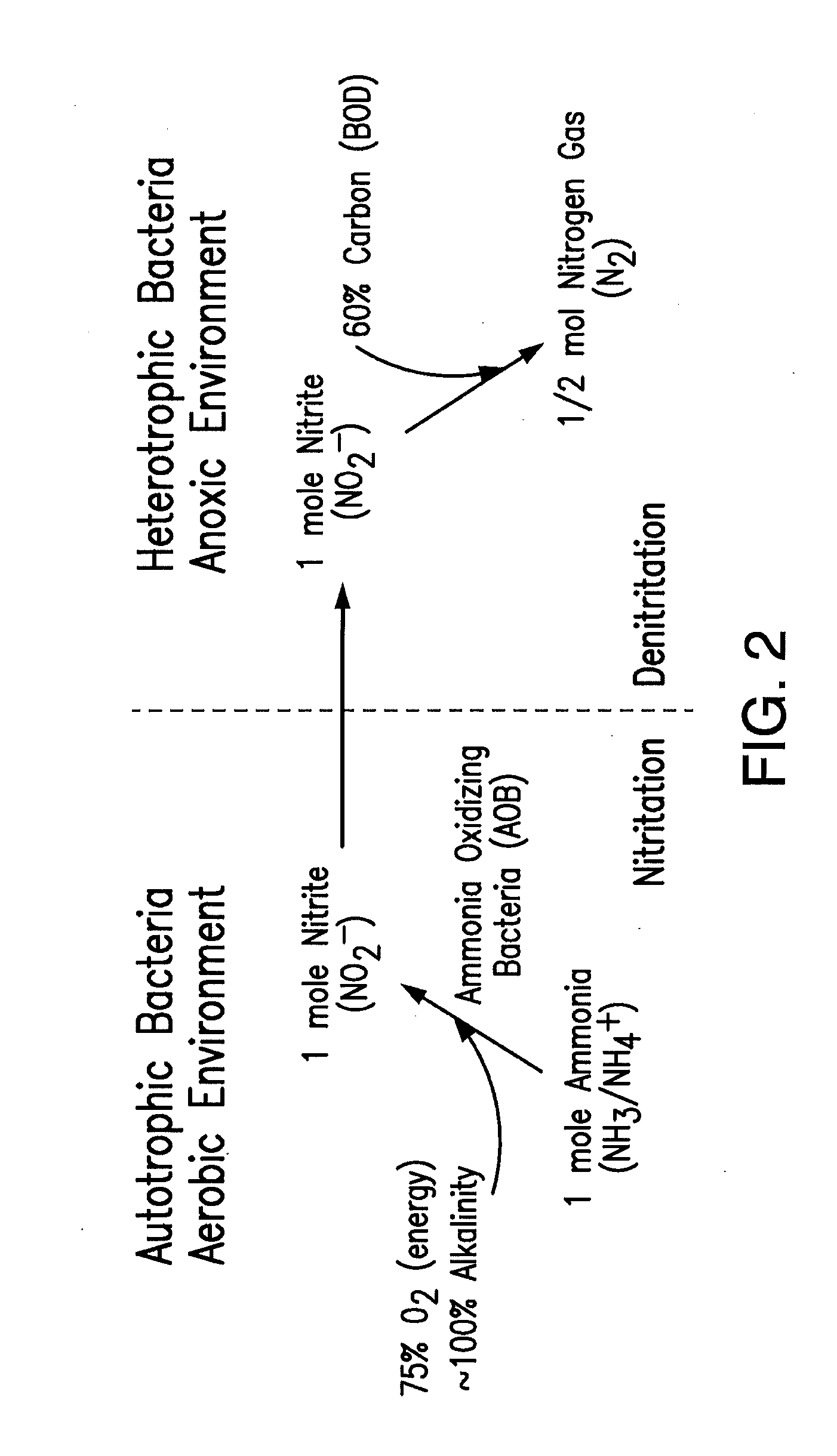
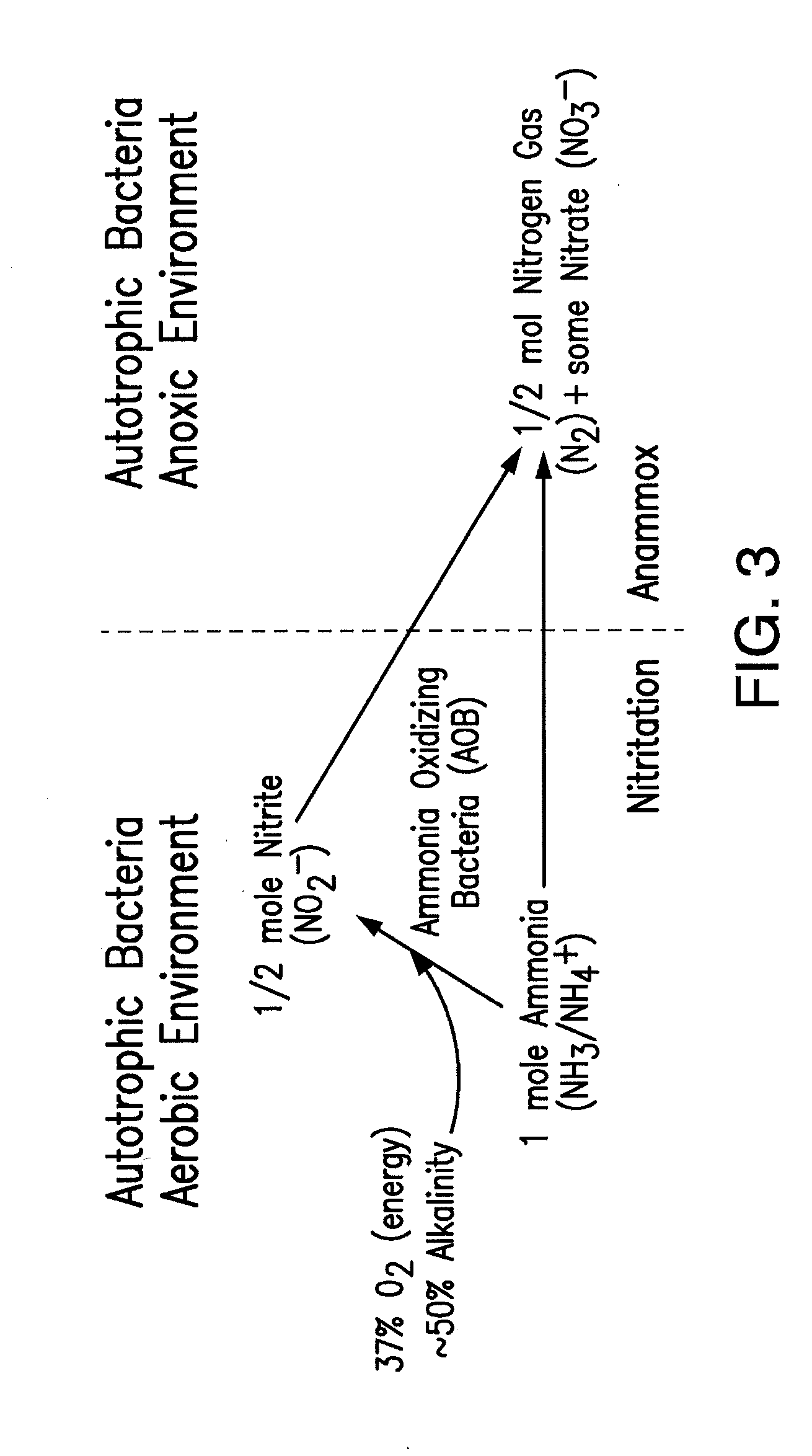
A reactor and control method thereof for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment achieves a measured control of maintaining high ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) oxidation rates while achieving nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) repression, using various control strategies, including: 1) ammonia and the use of ammonia setpoints, 2) operational DO and the proper use of DO setpoints, 3) bioaugmentation of a lighter flocculant AOB fraction, and 4) proper implementation of transient anoxia within a wide range of reactor configurations and operating conditions.
Owner:D C WATER & SEWER AUTHORITY +1
Biotechnological process for hydrocarbon recovery in low permeability porous media
ActiveUS20110146973A1Enhanced overall recoveryImprove mobilityFluid removalDrilling compositionMetaboliteAPI gravity
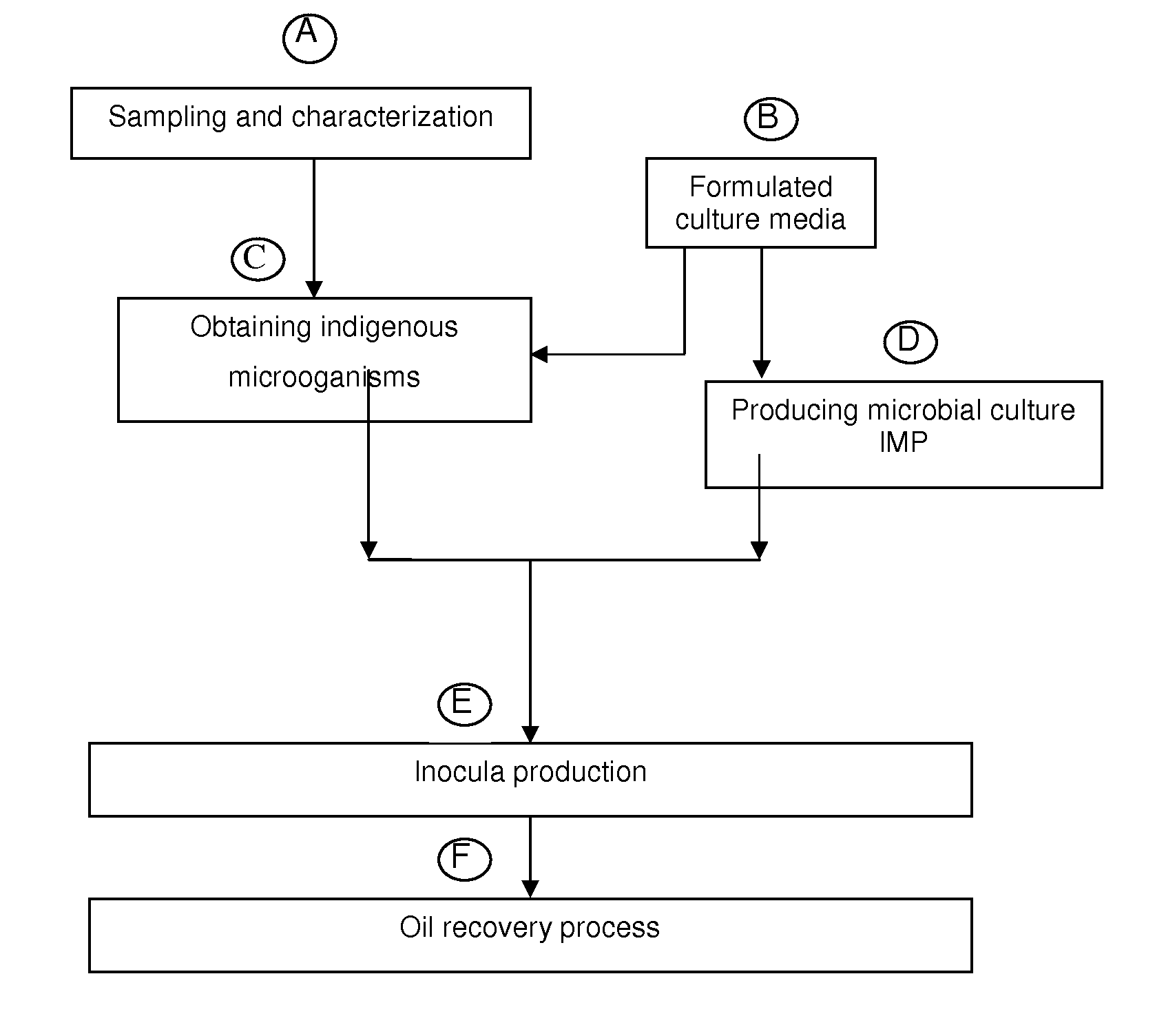
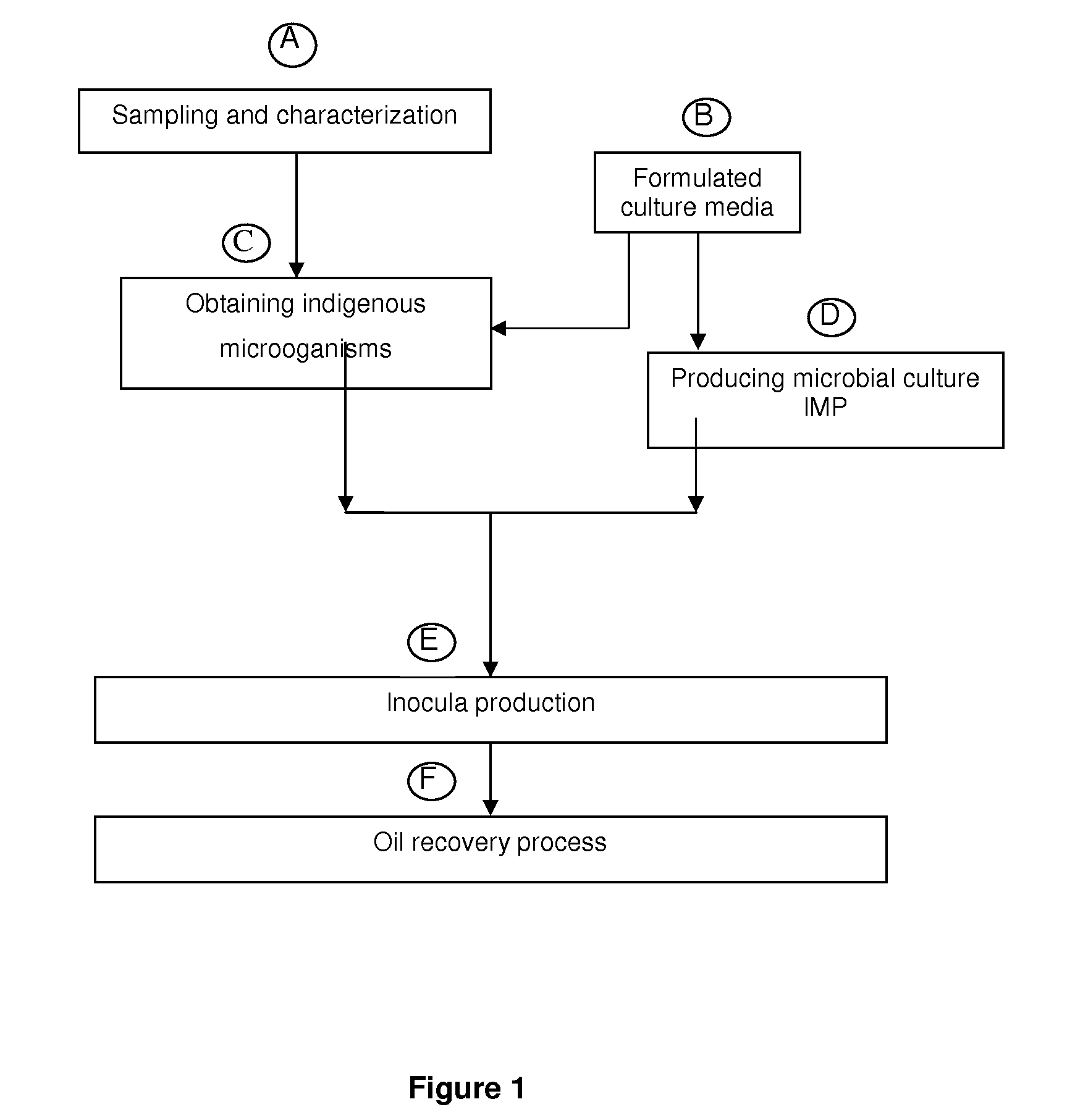
The present invention refers to a biotechnological process that enhances oil recovery of a 14 to 25 API Gravity oil contained in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous rock systems with low permeability (7 to 100 mD), thus focused to petroleum wells associated to zones with low recovery factor. The process utilizes the indigenous extremophile microorganisms activity from the oil reservoir and an IMP culture, as well as its metabolites (gases, acids, solvents and surfactants), which improve oil mobility and are able to develop at 60 to 95° C. temperatures, 7 to 154.6 Kg / cm2 (100 to 2,200 psi) pressures and NaCl content from 5,000 to 45,000 ppm, in anaerobic conditions. The biotechnological process of the present invention includes: indigenous microorganisms sampling, collecting and characterization from the reservoir; formulation of culture media; selection, enrichment, activation and preservation of such microorganisms, as well as biostimulation (indigenous microorganisms) and bioaugmentation (IMP culture) to increase the metabolite production, useful for oil recovery in a porous media impregnated with oil in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous systems, with one or several cycles and confinement periods from 5 to 10 days, to increase oil recovery. Experimental tests show that the biotechnological process of the present invention supplies an oil recovery increase up to 30%, additional to that obtained in secondary recovery processes.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Resourceful treatment process for alkali-minimization waste water
InactiveCN104926018AReduce processing costsSolve the problems that cannot be dealt with separatelyMultistage water/sewage treatmentResistant bacteriaWastewater
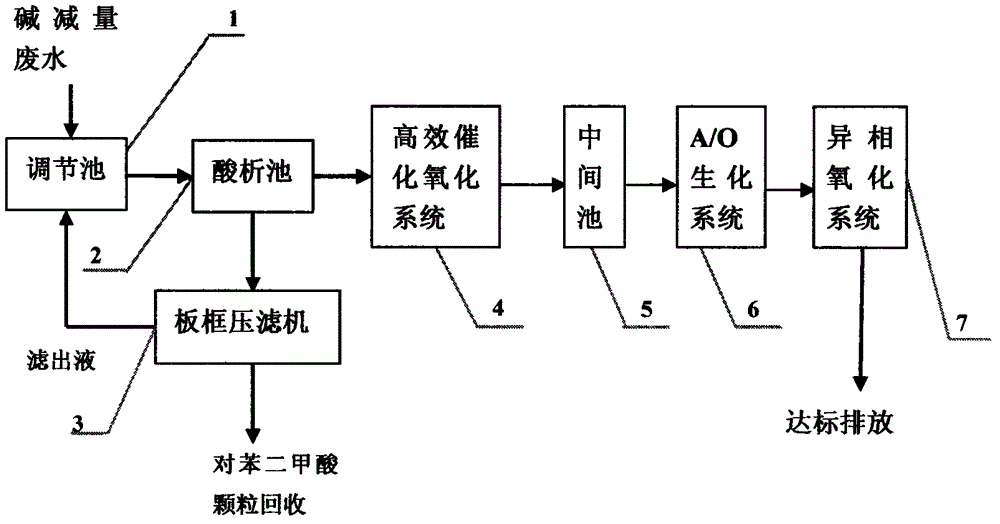
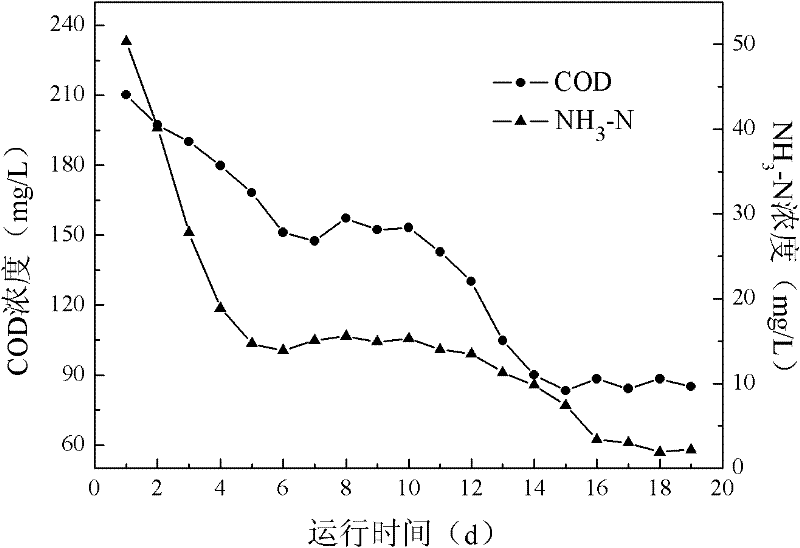
The invention discloses a resourceful treatment process for alkali-minimization waste water. The resourceful treatment process is used for recycling terephthalic acid which is difficult to be degraded, is capable of reducing treatment cost, and is combined with an efficient oxidation technology and a bioaugmentation technology for aerobic degradation of organic matters which cannot be degraded in a biochemistry manner; the possibility that waste water is degraded in the biochemistry manner is realized; high-salt resistant bacteria are introduced into the bioaugmentation technology, so that the problem that high-salt alkali-minimization waste water is difficult to be degraded in the biochemistry manner is solved; the process effluent CODcr is controlled to be less than 200 mg / L; the problem that single alkali-minimization waste water treatment cannot reach the standard is effectively solved.
Owner:宁波沐德环境科技有限公司
Bioaugmentation treatment technology of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater
InactiveCN101973678AIncrease the number ofSmall footprintMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationSludge
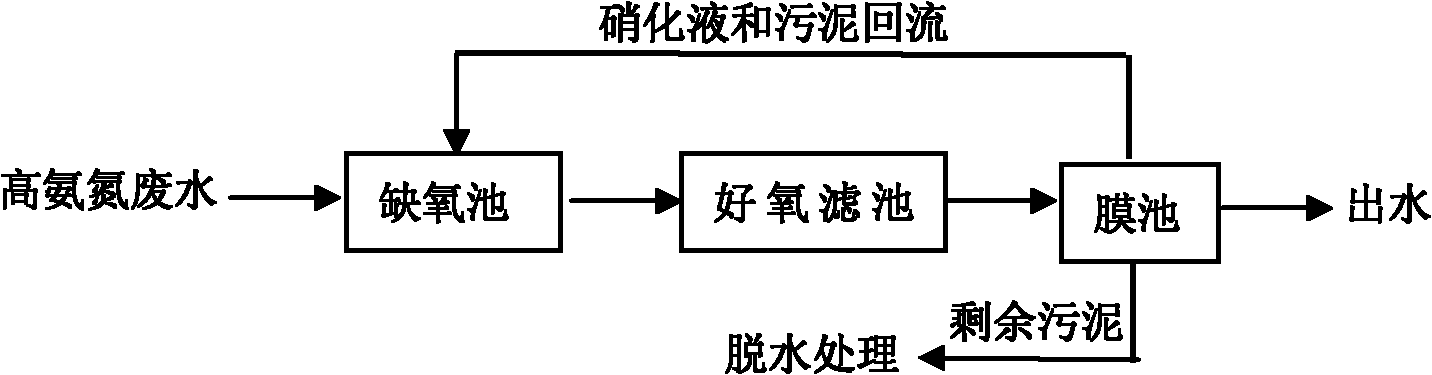
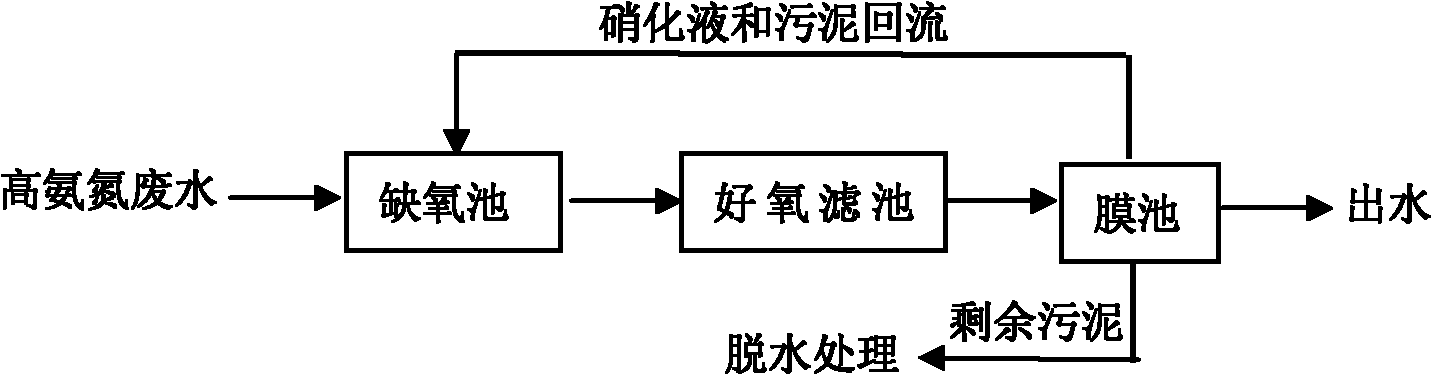
The invention relates to a bioaugmentation treatment technology of the high ammonia nitrogen wastewater. The treatment technology is characterized in that under the condition that dissolved oxygen exists in the high ammonia nitrogen wastewater, an aerobic pool, an aerobic filter and a membrane pool are established, wherein by utilizing the metabolism of the aerobic microorganism, high concentration of organic substances are degraded, the organic substances with high molecular weight and energy are converted to substances with low molecular weight and energy; the aerobic pool adopts internal circulation and large-scale external circulation hydraulic agitation; and the aerobic filter is filled with novel fixed enzyme-floating filler and immobilized microorganism and microporous aeration and jet aeration are combined for aeration, thus the flow pattern of the nitrification filter is improved. Compared with the prior art, the system of the invention has high sludge concentration and the corresponding volume loading is also high, thus the floor space is small and the capital cost is low; the conversion rate and utilization rate of atmospheric oxygen is high, the effect of mass transfer is good, the anti-shock loading capability of the system is high, the effluent quality is stable; the operating cost is low; the density is increased relatively, the solid-liquid separating effect is good and the yield of excess sludge is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI HONESS ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CORP
Paracoccus and application thereof in nitrogenous heterocyclic compound degradation
InactiveCN101186898AStrong degradative activityThe cultivation method is simpleBacteriaWater contaminantsSynechococcusNitrogenous heterocyclic compound
The invention discloses paracoccus and the application for degrading azotic heterocyclic compound. The paracoccus is paracoccus sp. BW001 CGMCC No. 2225. The paracoccus sp. BW001 CGMCC No. 2225 of the invention, on one hand, can grow into pyridine as the only carbon source and nitrogen source, which has a strong degradation activity (the degradation rate is 100%) for pyridine, is extremely suitable for biologic control of organic wastewater (such as coking wastewater) which contains pollutant of pyridine category, and can be used as biological hardening agent in the biological control technology of organic persistent wastewater, and corresponding environmental biological agent is exploited, thereby having relatively high value of study, application and marketing.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Construction method and application of immobilized biological bacterium agent for micro-polluted water source
InactiveCN104232546AImprove removal efficiencyExtended regeneration cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWater sourceManganese
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an immobilized biological bacterium agent for a micro-polluted water source and belongs to the field of ecological remediation of water environments. The method is a treating process for purifying a water body through construction of the biological bacterium agent, and ammonia nitrogen, iron, manganese, microcystis, algal toxins and the like in the water body can be removed effectively. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) rescreening and compounding of multifunctional oligotrophic ammonia nitrogen bacteria; (2) screening of efficient algicidal bacteria; (3) fermentation and construction of the bacterium agent; (4) bacterium agent immobilization and biological enhancement; (5) research on dosing methods of the bacterium agent, and treatment and biological enhancement of the micro-polluted drinking water source. The biological bacterium agent is constructed with an immobilization technology, after a system runs stably, the removal rate of the ammonia nitrogen is higher than 80%, removal rates of the microcystis and the algal toxins are higher than 40%, the removal rate of the iron in water is 50%, and the removal rate of manganese is 51%. The method can be combined with actual projects and is wider in application prospect.
Owner:松辽流域水资源保护局松辽流域水环境监测中心 +1
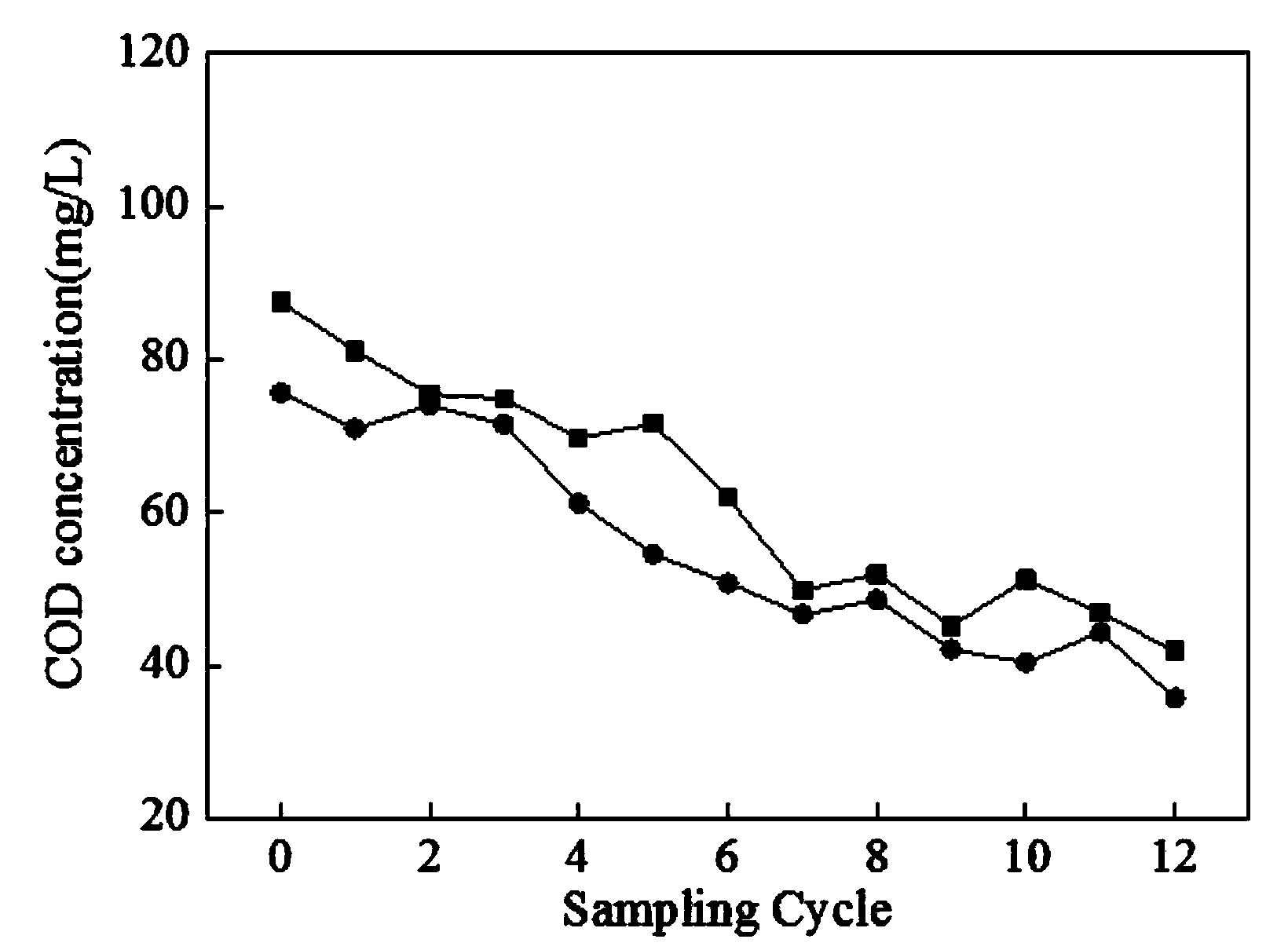
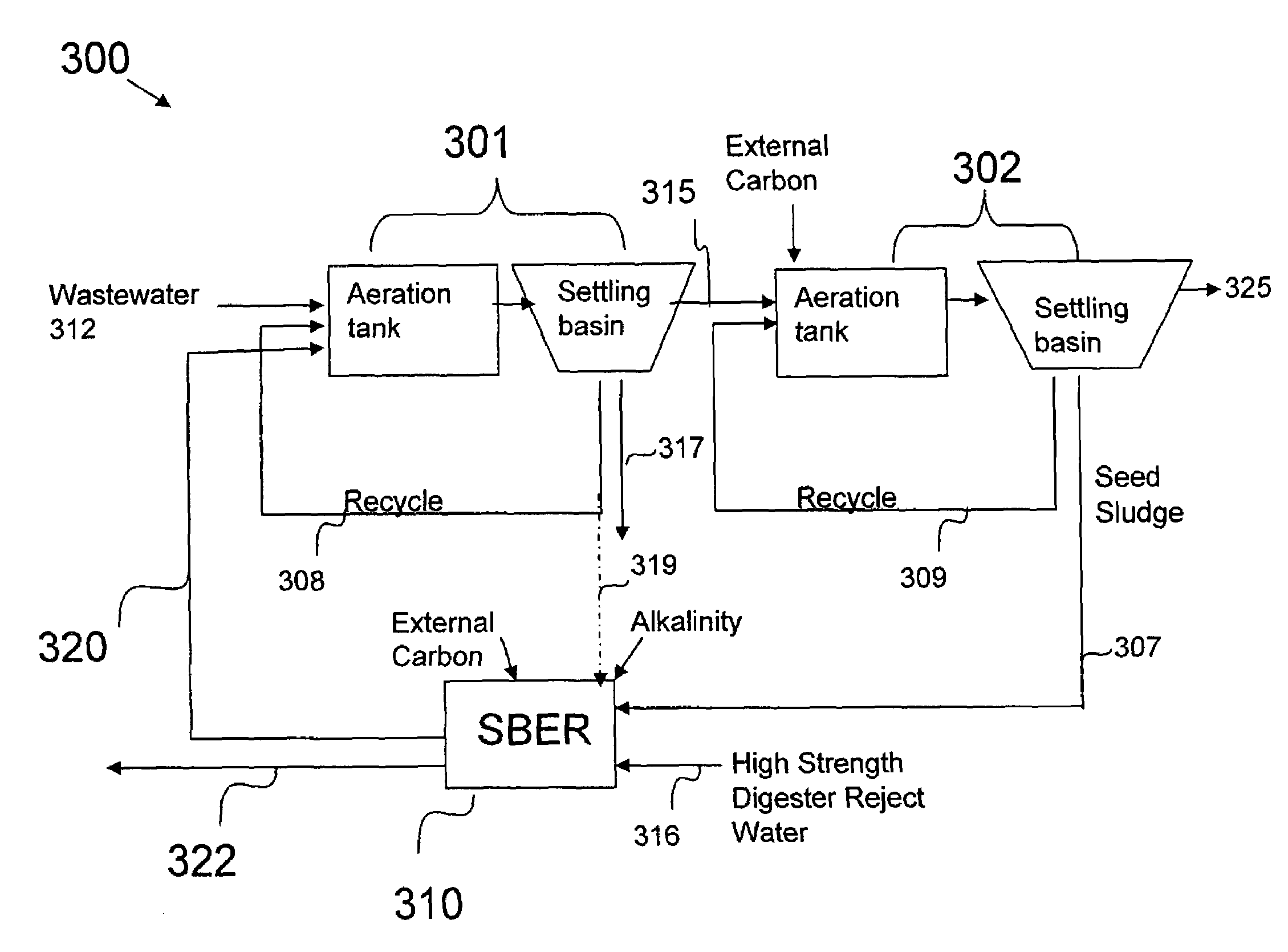
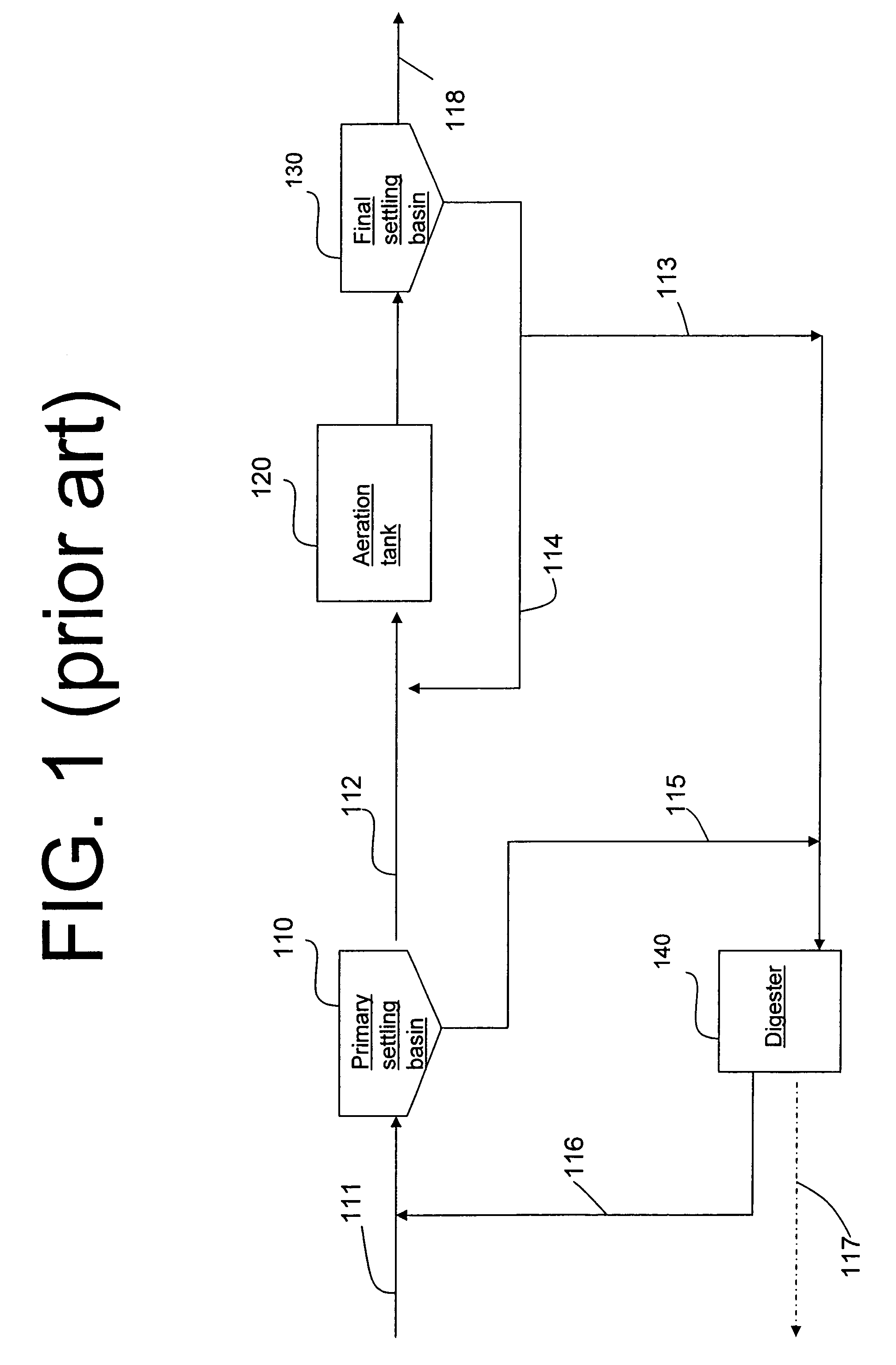
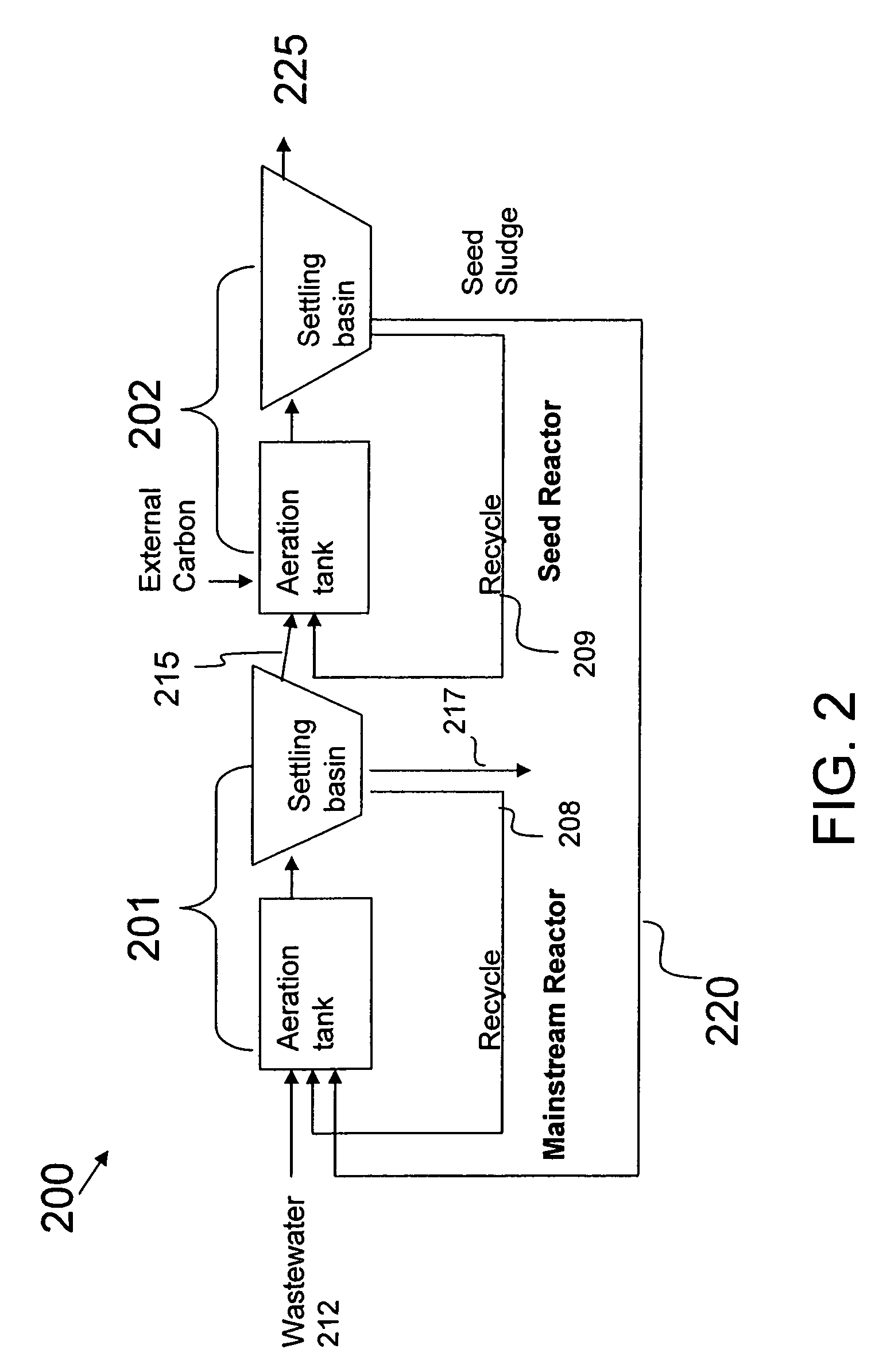
Method for nitrogen removal and treatment of digester reject water in wastewater using bioaugmentation
ActiveUS7404897B2Increase ratingsPromote nitrificationTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeNitrogen removal
An efficient system and process for removing nitrogen from wastewater while enriching seed sludge in the mainstream treatment process. Bioaugmentation of seed autotrophic organisms facilitate the nitrification reactions by enhancing the rates of reaction advantageously within a smaller volume or within a shorter activated sludge solids retention time. Likewise, bioaugmentation of seed denitrification organisms will also enhance rate of reaction within a smaller volume or shorter activated sludge solids retention time. Separate treatment of high ammonia digester reject water is an efficient method to treat nitrogen in recycle streams as well as to enrich the seed nitrifying and denitrifying cultures.
Owner:D C WATER & SEWER AUTHORITY
Method and apparatus for nitrogen removal in wastewater
InactiveUS20160257589A1Water treatment parameter controlBiological treatment regulationNitrogen removalAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
A reactor and control method thereof for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment achieves a measured control of maintaining high ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) oxidation rates while achieving nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) repression, using various control strategies, including: 1) ammonia and the use of ammonia setpoints, 2) operational DO and the proper use of DO setpoints, 3) bioaugmentation of a lighter flocculant AOB fraction, and 4) proper implementation of transient anoxia within a wide range of reactor configurations and operating conditions.
Owner:D C WATER & SEWER AUTHORITY +1
Method for remedying soil contaminated by DDT as pesticide residue through earthworm-based bioaugmentation and biodegradation
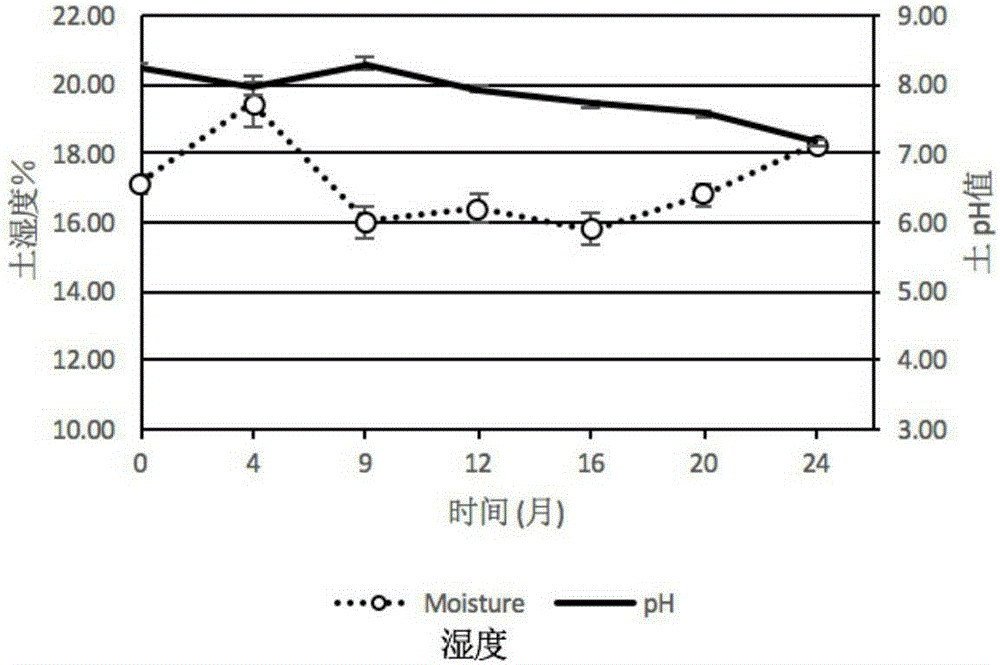
The invention discloses a method for remedying the soil contaminated by DDT (1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(pchlorophenyl)ethane) as a pesticide residue through earthworm-based bioaugmentation and biodegradation. The method comprises the following steps: feeding eiseniafoetida or amynthas rubusto in the contaminated soil; further feeding fermented chicken manure and / or cattle manure and fully and evenly mixing the chicken manure and / or cattle manure and the soil; and feeding the fermented chicken manure and / or cattle manure every three months, wherein the feeding density of the eiseniafoetida or amynthas robust is 5 to 30 earthworms per each kilogram of soil; the mass ratio between the chicken manure and / or cattle manure and the soil is 0.2-1:1; and the water content of the soil in the soil remediation is maintained at 55% to 65%. The invention has the advantage that the requirements for the external environment are low, so the invention is widely applicable to most of the soil contaminated by the DDT at current; and the method for remedying the soil contaminated by DDT as an organic chlorine pesticide is simple, effective and low-cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microbial composite functional bacterial agent for treating coking wastewater and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102337214AEfficient degradation abilityRemove inhibitionFungiBacteriaChemical oxygen demandEmission standard
The invention particularly relates to a microbial composite functional bacterial agent for treating coking wastewater and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, the microbial composite functional bacterial agent comprises the following microbes: 15-20wt% of n-hexadecane degrading bacteria, 20-30wt% of phenol degrading bacteria, 10-15wt% of pyridine degrading bacteria, 8-12wt% of chinoline degrading bacteria, 5-10wt% of carbazole degrading bacteria, 15-20wt% of naphthalene degrading bacteria and 8-12wt% of anthracene degrading bacteria. The microbial composite functional bacterial agent has the characteristics that: the composite functional bacterial agent prepared from artificially bred functional strains is added to an original biochemical treatment device, thus the removing capability of refractory organic matters in the coking wastewater is greatly improved and the contents of COD (chemical oxygen demand) and NH3-N in the coking biochemical effluent can both reach national first-level emission standard. The microbial composite functional bacterial agent has strong environment adaptability, good cooperativity, and broad application prospects in bioaugmentation of coking wastewater.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司 +1
DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)-degrading pseudomonad strain
InactiveCN102424806ANo secondary pollutionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPseudomonas tolaasii
The invention relates to a DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)-degrading pseudomonad strain, and specifically provides a pseudomonad strain capable of degrading DDT, which can be used for the biological intensified treatment of DDT pollutants and can help to degrade DDT organochlorine pesticides. The DDT-degrading pseudomonad strain is named pseudomonad No.12-3; the strain was preserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 8th, 2011; and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.5449. The pseudomonad No.12-3 has the characteristic of degrading DDT organochlorine pesticides; the DDT degradation rate can be up to 51.6%; and secondary pollution can not be caused to the environment. Thus, the DDT-degrading pseudomonad strain can help to solve the problems of DDT degradation, pollution remediation and the like, thereby having high application value.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Bioaugmentation Technology for Treatment of High Ammonia Nitrogen Wastewater at Low Temperature
ActiveCN102259975AReduce deliveryNo accumulationSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenMicroorganism
The invention discloses a bio-augmentation technique for treating high ammonia nitrogen waste water under a low temperature condition. The technique comprises the following stages: a, activating an efficient strain, and carrying out anaerobic culture, rejuvenation and propagation; b, carrying out membrane forming and acclimatisation by virtue of a biological aerated filter; and c, treating waste water in the biological aerated filter. By adopting the technique disclosed by the invention, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate in low-carbon source high-ammonia nitrogen waste water in a laboratory can reach more than 90%, the ammonia nitrogen waste water removal rate in the low-carbon source high-ammonia nitrogen waste water in an industrial experiment can reach more than 83% when the temperature is more than 10 DEG C, can reach more than 70% when the temperature is more than 4-10 DEG C and still can reach more than 61% when the temperature is 1-4 DEG C; the ammonia nitrogen concentration inthe low-carbon source high ammonia nitrogen waste water is effectively reduced, no nitrite is accumulated or few nitrite is accumulated, thus being beneficial to carrying out other subsequent biochemical reactions; and the technique disclosed by the invention can stably operate under the low temperature condition, thus having wide propagable region and being beneficial to popularization of microbiological treatment waste water.
Owner:GANSU GOLDEN BRIDGE GRP CO LTD +1
Dibutyl phthalate degrading bacteria and application of dibutyl phthalate degrading bacteria
InactiveCN102703347AGood bioaugmentation effectEfficient degradation abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a strain of dibutyl phthalate degrading bacteria and application of the dibutyl phthalate degrading bacteria. The strain of dibutyl phthalate degrading bacteria D8 provided by the invention belongs to Elizabethkingiasp and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, wherein the preservation date is March 23 2012; the preservation number is CCTCCNO:M2012088, and the GenBank accession number of a bacterial strain 16SrDNA is JQ673498. The bacterium is Gram-negative bacterium; the bacterial colony is yellow, round, smooth and humid; the brim is regular, and the centre protrudes. The bacterium utilizes dibutyl phthalate as sole carbon source and energy source to grow and breed. The bacterium can completely degrade 400mg / L of DBP (dibutyl phthalate) within 60 hours when being purely cultivated. The bacterial strain D8 can tolerate DBP of which the concentration can be up to 2000mg / L, and has excellent degradation effect on high-concentration DBP industrial wastewater. The bacterium is applied to bioaugmentation treatment of refinery waste water, pesticide wastewater, brewery wastewater and coking wastewater, and has excellent application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of microbial inoculant for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil
InactiveCN103333823ASimple preparation processLow costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationQuinoneHalohydrocarbon
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a microbial inoculant for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil, belonging to the technical field of soil remediation in environmental engineering. The invention is characterized in that the microbial inoculant containing the quinone-reducing facultative anaerobe Shewanella sp. and poly-halohydrocarbon dehalogenated product facultative aerobic degrading bacterium is prepared by surplus sludge lysis solution preparation and culture medium optimization, and is used for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil. The microbial inoculant has the advantages of wide raw material sources, simple preparation technique and no secondary pollution during soil remediation, can effectively overcome the defect that the high operating cost of the biologically reinforced remediation of poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil limits the large-scale application, and has wide application prospects in remediation of soil polluted by poly-chlorine organic substances, poly-bromine aromatic hydrocarbons and poly-fluorine organic substances.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Highly effective phosphorus removal bacteria and its produced bacteria formulation
InactiveCN1807585AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological propertyPseudomonas putida
The bacterium agent in this invention is used to biologically strenghen dephosphor- ization process in urban sewage treatment plant. It has mainly two uses: quickly start the biodephosphorization ability of new sewage treatment plant; resume the strong biodephosphorization ability of exasperate dephosphorization system. It is made from high efficient ployphospher bacterial strain GM6, and it is odor Pseudomonas putida from appraising result. Its main biocharacteristic is G-. Its thalli is rhabditiform with the size of 0. 7í‡2. 5ª–m, and it is facultative anaero-bic; it is positive in indole reaction, oxidase and sulfate reduction reaction; while negative in methyl red test, V-P reaction, citrate test and hydrogen sulfide reaction; the number of the strain 16S rDNA is DQ133506. The strain can be used to sewage dephosphorization.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for biological purification of waste
ActiveUS20090236282A1Low costSimple methodSolid waste disposalWater contaminantsMicroorganismBioaugmentation
A method for purifying a waste environment includes treating a portion of the waste environment to inactivate or diminish native microorganisms, adding augmenting microorganisms to the treated waste environment, simultaneously growing and acclimating a microbiological culture and discharging the microbiological culture to the waste environment. The method provides improved biological purification of waste and in-situ bioaugmentation.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Technical improvement method for biological sewage treatment process
InactiveCN102198976ALess prone to swellingAchieve deodorizationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeTreatment effect
The invention relates to a technical improvement method of an MUCT (Modified University of Cape Town) sewage treatment process, belonging to the technical field of biological sewage treatment in environmental engineering discipline. In order to further improve the comprehensive treatment efficiency of the MUCT process and improve the activity of sludge in an MUCT sewage treatment system, a bioaugmentation pool is respectively and additionally arranged in a sludge return section and a nitration liquid return section of the MUCT sewage treatment system, and a specially prepared biological active composite filler is filled in the pools as a culture medium and an adhesion carrier of microorganisms; and a part of returned sludge and nitration liquid in the sewage treatment system enter respective bioaugmentation pool, stay for a period and return to the original positions in the MUCT sewage treatment system according to different proportions after being full contact with the biological active composite filler. The invention has the advantages of simpleness and easiness in operation and obvious effect and can ensure that the performance of active sludge in the system can be improved, and the sewage treatment effect can be enhanced.
Owner:JILIN JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Online automatic microorganism dosing system
ActiveCN102079568AGuaranteed to lastAutomatically adjust dosageTreatment using aerobic processesBiochemistry apparatusTemperature controlChemical oxygen demand
The invention relates to an online automatic microorganism dosing system, which comprises a frame, a program controller, a culturing vat, a culture medium distribution unit, a water inlet unit, a self-circulation and water distribution unit, an aeration unit and a temperature control unit. Compared with the prior art, the online automatic microorganism dosing system has the advantages that: the culture medium distribution unit, the water inlet unit, the self-circulation and water distribution unit, the aeration unit and the temperature control unit provide various appropriate conditions for the activation of augmentation bacteria and necessary nutrition for growth and propagation to ensure that the dosing of the bioaugmentation bacteria is implemented, so as to ensure the continuous effectiveness of bioaugmentation on wastewater; meanwhile, the dosage of the bioaugmentation bacterial liquid can be automatically regulated according to the change of the chemical oxygen demand of effluent, and the production operation cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:宜态科水务技术(上海)有限公司
Method for biological strengthening of vinegar by using marine-derived bacillus licheniformis
ActiveCN107418909AAdd flavorImprove qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for biological strengthening of vinegar by using marine-derived bacillus licheniformis, and belongs to the technical field of food brewing. According to the method, bacillus licheniformis (B. licheniformis) with CCTCC NO: M 2017209 is selected from marine environment, and the B. licheniformis can grow at 65 DEG C and has a high amylase production capacity. According to the method, the B. licheniformis is made into B. licheniformis powder for enhancing fermentation of acetic acid of the vinegar, and the method has the advantages of improving the utilization ratio of raw materials, improving the product flavor of the vinegar and improving the quality of the vinegar.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
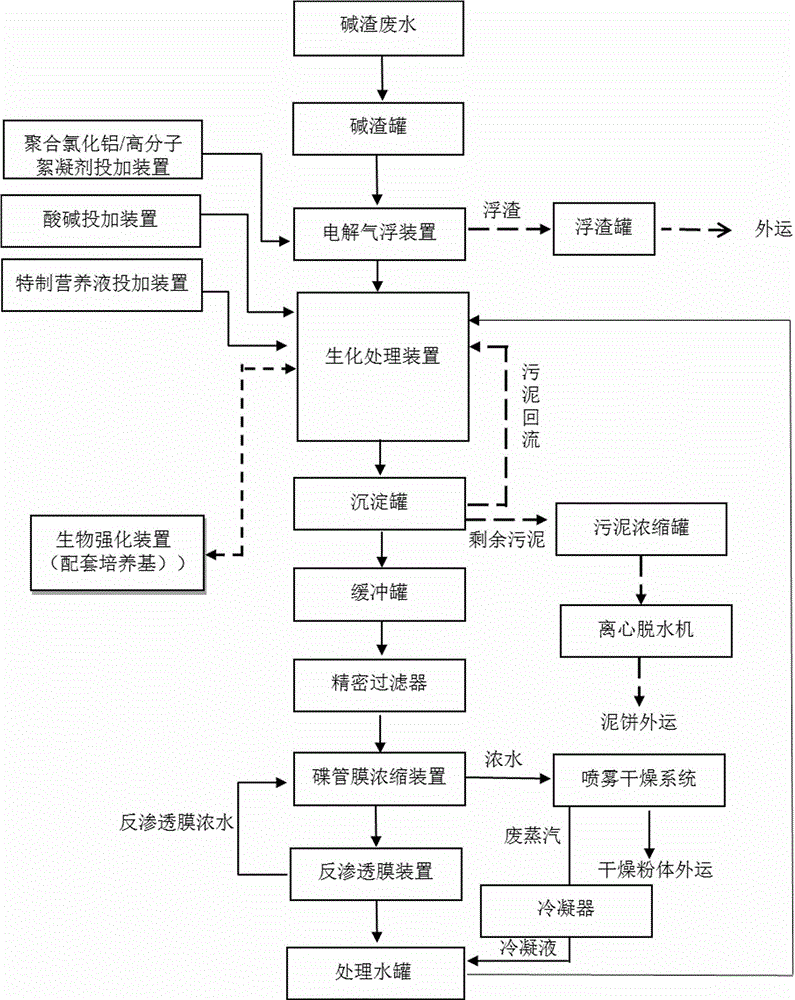
Alkali residue waste water treating method
InactiveCN106630377AAchieving processing powerAchieving zero emissionsSludge treatmentWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisHigh concentrationReverse osmosis
The invention relates to an alkali residue waste water treating method. An alkali residue tank, an electrolytic air-flotation device, a biochemical treatment device, a fine filter, a disc-tube membrane and reverse osmosis membrane concentrating device and a spray drying device are used in the method, and a bioaugmentation technology is used for the biochemical treatment device. The bioaugmentation technology comprises an efficient multiple microorganisms which are screened from raw water of alkali residue waste water through a modern biological means, a microbial intensified culture device, an assorted culture medium, a purpose-made nutrient and running parameters. Therefore, by effective combination of the electrolytic air-flotation pretreatment system, the bioaugmentation technology, the disc-tube membrane and reverse osmosis membrane concentrating device and the spray drying device, pollutants and salts in the alkali residue waste water are thoroughly removed and separated, the treated waste water can be reused, and thorough treatment and zero emission of the high-concentration and high-salinity alkali residue waste water are finished.
Owner:辽宁海润环保技术股份有限公司
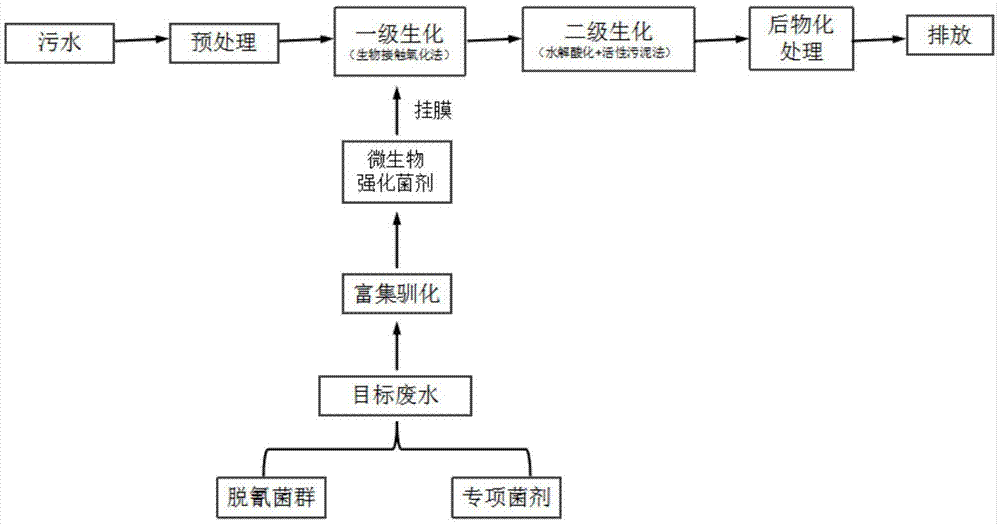
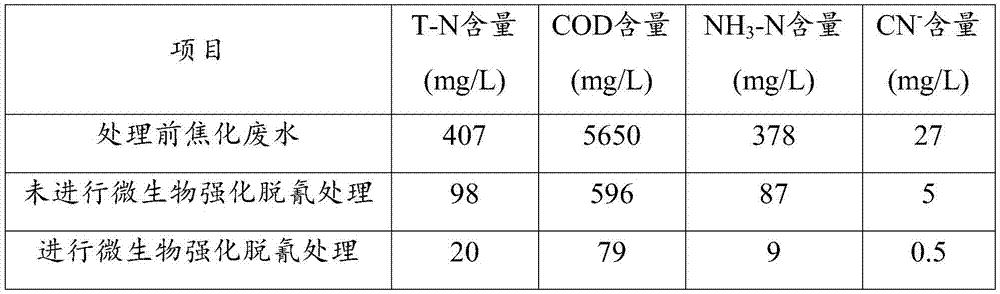
Biologically-enhanced treatment method for cyanide-containing chemical wastewater
ActiveCN105439391ANo secondary pollutionSolve the problem of poor adaptability and low removal rateWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeWater discharge
The invention discloses a biologically-enhanced treatment method for cyanide-containing chemical wastewater. The method comprises steps as follows: a pretreatment step: the cyanide-containing chemical wastewater is pretreated in an adjusting tank; a primary biochemical reaction step: the pretreated wastewater is sent into a primary biochemical reaction tank inoculated with a microorganism enhanced microbial agent for a reaction, and the microorganism enhanced microbial agent comprises cyanide removal flora and a special microbial agent; a secondary biochemical reaction step: the wastewater completing the primary biochemical reaction is sent into a hydrolyzation and acidification tank, passes by a sedimentation tank and then enters an aerobic reaction tank containing activated sludge to complete a secondary biochemical reaction; a follow-up treatment step: the wastewater completing the secondary biochemical reaction is subjected to follow-up treatment after passing by the sedimentation tank. By means of the treatment method, the concentration of cyanide in the chemical wastewater can be effectively reduced, the treatment cost is reduced, the activated sludge is prevented from being infected by cyanide, residual chlorine or other oxidants, the water discharge stability is guaranteed, and the treatment method has good environmental and economic benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN CARING TECH DEV
Low-temperature aniline-degrading strain
InactiveCN102093970AReduce processing costsNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismWastewater
The invention relates to an aniline-degrading strain, in particular relating to a low-temperature aniline-degrading strain. The low-temperature aniline-degrading strain A1 with the collection number CGMCC No. 5011) belongs to Pseudomonas and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection (CGMCC) on December 1st, 2010. The low-temperature aniline-degrading strain A1 provided by the invention is used for biological enhanced treatment of aniline-containing waste water in low-temperature conditions with 100% aniline degradation rate, no secondary environmental pollution and no need of addition of other chemicals, so that the waste water treatment cost is greatly reduced, and the application prospect is wide. The low-temperature aniline-degrading strain A1 is favorable for solving the problem of aniline-containing waste water biological treatment system in low-temperature conditions, and has high value of application.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Carbazole-degrading bacterium and its culture method
InactiveCN102367423AStrong degradative activityThe cultivation method is simpleBacteriaWater contaminantsCarbazolePseudomonas tolaasii
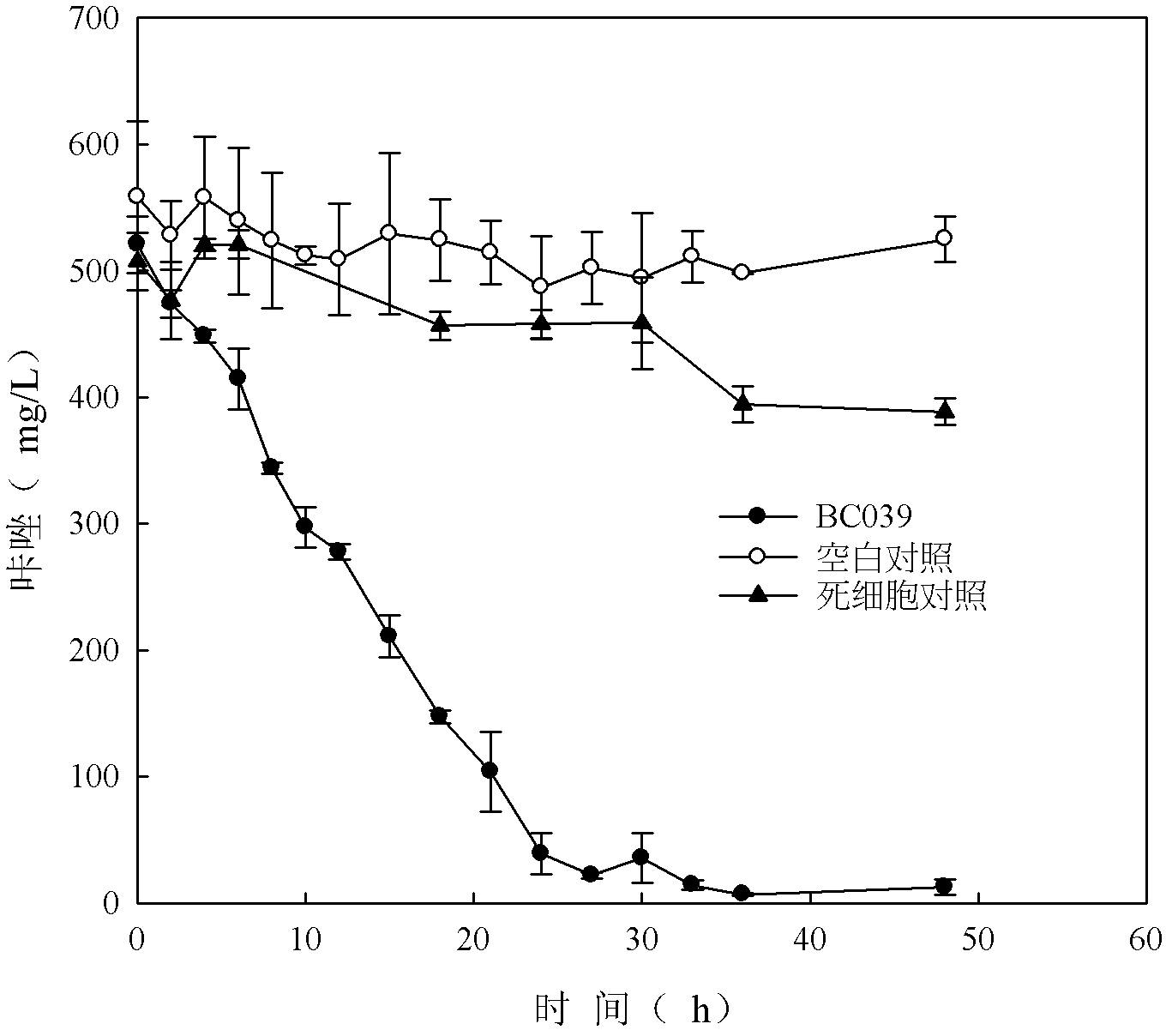
The invention discloses a strain of carbazole-degrading bacterium and its culture method. The collection number of the Pseudomonas sp. BC039 provided by the invention is CGMCC No.4222. The invention also provides an application of the Pseudomonas sp. BC039 CGMCC No.4222 in the degradation of carbazole. It is proved through an experiment that the Pseudomonas sp. BC039 provided by the invention canbe used as a bioaugmentation agent in the hardly-degraded organic wastewater biological treatment technology. In addition, corresponding environmental protection biological preparations developed from the Pseudomonas sp. BC039 has great research, application and market values.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparation method of halophilic decontamination bacterial agent and bacterial agent prepared by same
InactiveCN101811779AThe separation method is simpleWide variety of sourcesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismWastewater
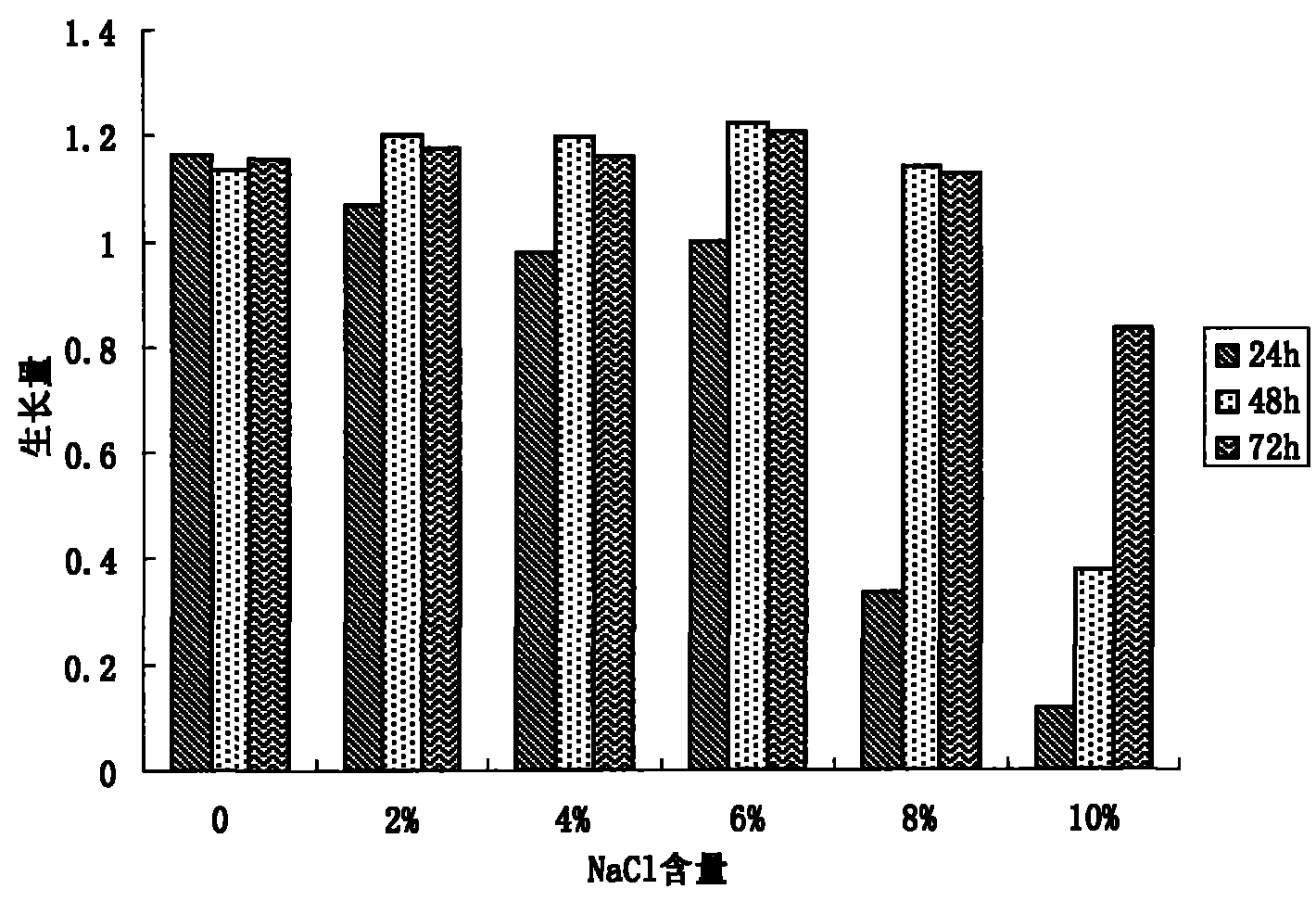
A preparation method of a halophilic decontamination bacterial agent and the bacterial agent prepared by the same belong to the technical field of biological treatment of salinity wastewater. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) inoculating the test tube strain of the halophilic decontamination bacterium into nutrient agar for culturing; 2) inoculating the cultured strain into a fermentor medium of preset volumetric quantity according to the inoculation quantity which is 1-2% of the medium weight to be cultured till logarithmic growth phase; and 3) in the fermentor production process, maintaining the ventilation volume of aseptic air to be 4.0-6.0L / min, the stirring rate to be 60-120r / min, the culture temperature to be 25-40 DEG C and the full-process culture time to be 24-48h, subpackaging the culture solution after fermentation or adopting aseptic attachments for adsorption and drying, thus preparing the solid bacterial agent. The strain of the bacterial agent was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number of CGMCC No.3314. The invention adopts the bioaugmentation technology, greatly improves the capability of treating salinity wastewater and has low cost and significant effects.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
Treating method for reverse osmosis (RO) concentrated water
ActiveCN108117221ASolve removal puzzlesReduce concentrationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentMicrobial agentReverse osmosis
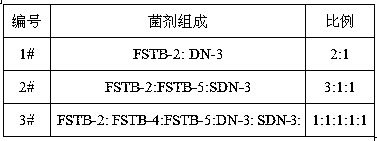
The invention relates to a treating method for RO concentrated water. The treating method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) treatment with an advanced oxidation unit: subjecting RO concentrated water to advanced oxidation to improve the biodegradability of the RO concentrated water; and (2) biologically strengthened treatment: allowing the RO concentrated water having undergone advanced oxidation to enter a biologically strengthened treatment unit, and adding a salt-tolerant COD-removing denitrifying microbial agent into a treatment system, wherein the microbial agent comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, Microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and further comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3. The treating method of the invention adopts a combination of an advanced oxidation treatment process and a biologically strengthened treatment process, and the salt-tolerant microbial agent is added into the biologically strengthened treatment unit, so COD and total nitrogen in the RO concentrated water are both removed efficiently, and effluent meets emission requirements.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Denitrification reinforcing agent for constructed wetland, and preparation method and application method thereof
InactiveCN106542638AImprove denitrification effectHigh activityBiological water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandNitrifying bacteria
The invention specifically discloses a denitrification reinforcing agent for a constructed wetland, and a preparation method and an application method thereof, belonging to the technical field of environmental engineering sewage treatment and biological reinforcement. According to the invention, the denitrification reinforcing agent without any bacterial strain is developed according to the demands of microbes in the constructed wetland for nutriments in growth; the denitrification reinforcing agent reinforces the activity of nitrobacteria and denitrifying bacteria in indigenous microorganisms in the constructed wetland and allows the nitrobacteria and denitrifying bacteria to propagate rapidly; and pollutants in sewage are removed through cometabolism of microbes, so the denitrification capability of the constructed wetland is substantially improved. The denitrification reinforcing agent mainly comprises beef extract, amino acid, biotin, cytokinin, humic acid, vitamin, trace elements, etc. The raw materials of the denitrification reinforcing agent are widely available and cheap; the preparation method is simple; and the denitrification reinforcing agent is applicable to a constructed wetland sewage treatment system in the North in winter and has good application prospects as an auxiliary process.
Owner:SHENYANG ALUMINIUM MAGNESIUM INSTITUTE
Biologically enhanced treatment method for medium-and-low concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater
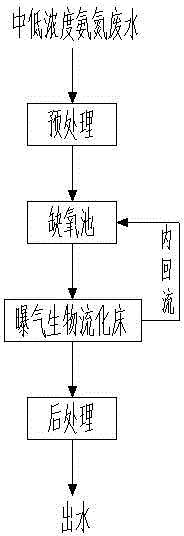
InactiveCN105084536AGood removal effectSmall pressure lossTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a biologically enhanced treatment method for medium-and-low concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. The method employs combined anoxic-aeration biological fluidized bed technology; an anoxic reaction tank is filled with a combined microbial filling material; and an embedding-process immobilized microbial carrier is added into an aeration biological fluidized bed. The method comprises the following successive steps: allowing pretreated medium-and-low concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater to enter the anoxic reaction tank, removing nitrogen oxide (mainly nitrite nitrogen) in back water by using denitrifying bacteria adhered on the combined filling material and removing a part of organic matters; allowing effluent of the anoxic reaction tank to enter the aeration biological fluidized bed, wherein since the immobilized microbial carrier is in a fluidized state under aeration conditions and uniformly distributed in the fluidized bed, full contact between the carrier and the wastewater is realized; and converting ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater into nitrite nitrogen by using ammoxidation bacteria growing in the carrier and on the surface of the carrier, removing a part of total nitrogen and rest organic matters at the same time and allowing effluent to flow back to the front anoxic reaction tank.
Owner:KESHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com